
- Book Solutions
- State Boards

Case Study Questions Class 7 Science Weather, Climate and Adaptations of Animals to Climate
Case study questions class 7 science chapter 8 weather, climate and adaptations of animals to climate.
CBSE Class 7 Case Study Questions Science Weather, Climate and Adaptations of Animals to Climate. Important Case Study Questions for Class 7 Board Exam Students. Here we have arranged some Important Case Base Questions for students who are searching for Paragraph Based Questions Weather, Climate and Adaptations of Animals to Climate.
At Case Study Questions there will given a Paragraph. In where some Important Questions will made on that respective Case Based Study. There will various types of marks will given 1 marks, 2 marks, 3 marks, 4 marks.
CBSE Case Study Questions Class 7 Science Weather, Climate and Adaptations of Animals to Climate
Case study 1.
All changes in the weather are caused by the sun. The sun is a huge sphere of
hot gases at a very high temperature. The distance of the sun from us is very
large. Even then the energy sent out by the sun is so huge that it is the source of all heat and light on the earth. So, the sun is the primary source of energy that causes changes in the weather. Energy absorbed and reflected by the earth’s surface, oceans and the atmosphere play important roles in determining the weather at any place. If you live near the sea, you would have realized that the weather at your place is different from that of a place in a desert, or near a mountain.
The weather reports are prepared by the Meteorological Department of the Government. This department collects data on temperature, wind, etc., and makes the weather prediction
Que. 1) Changes in weather are caused by sun and the sun is a fireball of hot gases is it true or false.
(c) None of the above
Que. 2) The distance between sun and earth is ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… as compared to the distance between earth and moon.
(c) Maximum
(d) Minimum
Que. 3) Who prepares the weather report?
(a) Meteorological department
(b) Weather department
(c) Rain department
(d) All of the above
Que. 4) What is sun?
Que. 5) What determines the weather of any place?
Que. 1) (a) True
Que. 2) (b) Large
Que. 3) (a) Meteorological department
Que. 4) Answer: The sun is a huge fireball of hot gases at very high temperature of several thousands of degrees or even more.
Que. 5) Answer: The energy of sun absorbed and reflected by oceans, earth’s surface and atmosphere plays a role in determining weather of any place.
Case study 2
Meteorologists record the weather every day. The records of the weather have been preserved for the past several decades. These help us to determine the weather pattern at a place. The average weather pattern taken over a long time, say 25 years, is called the climate of the place. If we find that the temperature at a place is high most of the time, then we say that the climate of that place is hot.
If there is also heavyrainfall on most of the days in the same place, then we can say that the climateof that place is hot and wet. The mean temperature for a given month is found in two steps.First wefind the average of the temperatures recorded during the month. Second, wecalculate the average of such average temperatures over many years.
Que. 1) ………………………………………………………………………..……. records the weather everyday.
(a) Radiologists
(b) Scientist
(c) Meteorologist
Que. 2) The average pattern of weather is taken over …………………………………………………………..……………………. many years to see the pattern of weather and also to have prediction of how it will be in next few years in advance so that humans can prepare for any sort of calamity.
Que. 3) The mean temperature of a given months is found in how many steps?
Que. 4) How would you say that the climate is hot and wet?
Que. 5) When do we say that the climate of a particular place is hot?
Que. 1) (c) Meteorologist
Que. 2) (d) 25
Que. 3) (d) 2
Que. 4) Answer: if the climate of a place is hot and also there is a heavy rainfall in the same place for few days then we say that the climate of that place is hot and wet.
Que. 5) Answer: if the temperature of a particular geographical area is hot for most of the days than we say that the climate of that area is hot.
Case study 3
The polar-regions present an extreme climate. These regions are covered with snow and it is very cold for most part of the year. For six months the sun does not set at the poles while for the other six months the sun does not rise. In winters, the temperature can be as low as –37°C. Animals living there have adapted to these severe conditions. Let us see how they are adapted by considering the examples of polar bears and penguins. Polar bears have white fur so that they are not easily visible in the snowy white background. It protects them from their predators. It also helps them incatching their prey. To protect them from extreme cold, they have two thick layers of fur. They also have a layer of fat under their skin. In fact, they are so well-insulated that they have to move slowly and rest often to avoid getting overheated. Physical activities on warm days necessitate cooling. So, the polar bear goes for swimming.
It is a goodswimmer. Its paws are wide and large, which help it not only to swim well butalso walk with ease in the snow. While swimming under water, it can close itsnostrils and can remain under water for long durations. It has a strong sense ofsmell so that it can catch its prey for food.
Que. 1) The Polar Regions are covered with ………………………………………………………………………………………… .
Que. 2) Polar bears have …………………………………………………………………………………….. fur and this fur helps them to keep a warm body temperature than the outside cold temperature environment and this ensure better survivability even in very harsh weather conditions.
Que. 3) What is the temperature at Polar Regions?
(a) 37degrees
(b) -37 degrees
(c) 45 degrees
(d) -50 degrees
Que. 4) What makes polar bears a good swimmer?
Que. 5) what protects the polar bear from cold?
Que. 1) (a) Snow
Que. 2) (d) White
Que. 3) (b) -37 degrees
Que. 4) Answer: the wide and large paws of polar bears make them a good swimmer.
Que. 5) Answer: polar bears have two thick layer of fur which act as an insulating material against cold temperature.
Case study 4
Some migratory birds travel as much as 15000 km to escape the extreme climaticconditions at home. Generally they fly high where the wind flow is helpful andthe cold conditions allow them to disperse the heat generated by their flightmuscles. But how these birds travel to the same place year after year is still amystery. It seems that these birds have a built–in sense of direction and know inwhich direction to travel. Some birds probably use landmarks to guide them.
Manybirds may be guided by the sun during the day and stars at night. There is someevidence that birds may use the magnetic field of the earth to find direction. Andit is not only birds that migrate; mammals, many types of fish and insects arealso known to migrate seasonally in search of more hospitable climates.
Que. 1) The migratory birds travels ……………………………………………………………………………..….. Km of distance to escape the unfavorable weather to ensure better survivability and also to leave a less stressful life for several months and then they migrate again back to the place when the environment becomes good again.
Que. 2) Migratory birds uses ……………………………………………………..…………………………… to guide them.
(a) Landmarks
(c) Still a mystery
(d) None of the above
Que. 3) Many birds are guided by …………………………………………………….………… and ………………………………………………………………………….. .
(a) Sun and Stars
(b) Sun and Moon
(c) Sun and Sky
(d) Sun and Wind
Que. 4) Why does the birds migrate?
Que. 5) Other than birds which other organisms migrate?
Que. 1) (c) 15000
Que. 2) (a) Landmarks
Que. 3) (a) Sun and Stars
Que. 4) Answer: The birds migrate to avoid harsh weather conditions like low temperature.
Que. 5) Answer: other than birds many different types of insects and fishes are known to migrate to more favorable environmental place.
Case study 5
The tropical region has generally a hot climate because of its location around the equator. Even in the coldest month the temperature is generally higher thanabout 15°C. During hot summers, thetemperature may cross 40°C. Days andnights are almost equal in lengththroughout the year. These regions get
Plenty of rainfall. An important featureof this region is the tropical rainforests.Tropical rainforests are found inWestern Ghats and Assam in India,Southeast Asia, Central America andCentral Africa.
Because of continuouswarmth and rain, this region supportswide variety of plants and animals. Themajor types of animals living in therainforests are monkeys, apes, gorillas,tigers, elephants, leopards, lizards,snakes, birds and insects.
Que. 1) What is the location of the tropical region?
(a) North pole
(b) South pole
(c) Equator
Que. 2) ………………………………………………………………..……………. is the lowest temperature in a tropical region which is not as less as it is in polar regions like Antarctica where very less life forms can thrive in the environment.
(a) 40 degree Celsius
(b) 15 degree Celsius
(c) 20 degree Celsius
(d) 37 degree Celsius
Que. 3) …………………………………………………………………………………. is the summer temperature of tropical regions.
(a) 37 degree Celsius
(c) 40 degree Celsius
(d) 20 degree Celsius
Que. 4) Name the major types of animals living in the rain forest.
Que. 5) Why does the tropical regions have hot climate?
Que. 1) (c) Equator
Que. 2) (b) 15 degree Celsius
Que. 3) (c) 40 degree Celsius
Que. 4) Answer: The major types of animals that live in rainforest are: tiger, monkey, lizards, birds, insects, apes and gorillas.
Que. 5) Answer: tropical regions have hotter climate because they are present nearer to equator where the temperature is hotter on an average.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
We have a strong team of experienced Teachers who are here to solve all your exam preparation doubts
Rs aggarwal class 5 solutions chapter 11, 2025 solved icse specimen paper class 10 english paper 1, sikkim scert class 4 evs chapter 2 games we play solution, sikkim scert class 4 evs chapter 1 changing families solution.
Sign in to your account
Username or Email Address
Remember Me
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 7 Weather, Climate and Adaptations of Animals to Climate
NCERT Solutions for CBSE Class 7 Science Chapter 7 Weather, Climate and Adaptations of Animals to Climate are given below. These solutions help students to clear their doubts and to obtain good marks in final exam. Class 7 Science NCERT questions and answers provided in this article are strictly based on the CBSE syllabus and curriculum.
Class 7 Science Chapter Weather, Climate and Adaptations of Animals to Climate NCERT Solutions
Class 7 NCERT Solutions for Science Chapter 7 includes all the intext and exercise questions. All these questions are solved by experts with a detailed explanation that will help students complete their assignments and homework.
Question 1: Name the elements that determine the weather of a place.
Answer: Temperature, humidity, rainfall, wind speed, air pressure, etc. are the elements of the weather. Because the weather of a place can be determine using these elements.
Question 2: When are the maximum and minimum temperatures likely to occur during the day?
Answer: The maximum temperature of the day occurs generally in the afternoon while the minimum temperature occurs generally in the early morning.
Question 3: Fill in the blanks:
(i) The average weather taken over a long time is called ___________.
(ii) A place receives very little rainfall and the temperature is high throughout the year, the climate of that place will be ___________ and ___________ .
(iii) The two regions of the earth with extreme climatic conditions are ___________ and __________.
Answer: (i) The average weather taken over a long time is called climate .
(ii) A place receives very little rainfall, and the temperature is high throughout the year, the climate of that place will be hot and dry .
(iii) The two regions of the earth with extreme climatic conditions are polar region and tropical region .
Question 4: Indicate the type of climate of the following areas:
(a) Jammu and Kashmir: (b) Kerala:, (c) Rajasthan: (d) North-east India:
Answer: (a) Jammu and Kashmir: moderately hot and wet
(b) Kerala: hot and wet
(c) Rajasthan: hot and dry
(d) North-east India: wet
Question 5: Which of the two changes frequently, weather or climate?
Answer: Weather changes frequently.
Question 6: Following are some of the characteristics of animals:
(i) Diets heavy on fruits (ii) White fur (iii) Need to migrate (iv) Loud voice (v) Sticky pads on feet (vi) Layer of fat under skin (vii) Wide and large paws (viii) Bright colours (ix) Strong tails (x) Long and large beak
For each characteristic indicate whether it is adaptation for tropical rainforests or Polar Regions. Do you think that some of these characteristics can be adapted for both regions?
Answer: (i) Diets heavy on fruits- Tropical rain forests
(ii) White fur – Polar regions
(iii) Need to migrate- Polar regions
(iv) Loud voice-Tropical rain forests
(v) Sticky pads on feet – Tropical rain forests
(vi) The layer of fat under skin – Polar regions
(vii) Wide and large paws – Polar regions
(viii) Bright colours – Tropical rain forests
(ix) Strong tails – Tropical rain forests
(x) Long and large beak – Tropical rain forests
Question 7: The tropical rainforest has a large population of animals. Explain why it is so.
Answer: Hot and humid temperature and continuous rainfall in the tropical rainforest suit the survival of many animals; hence, the tropical rainforest has a large population of animals.
In tropical rainforest days and nights are almost equal in length throughout the year. The temperature of these region varies from 15°C to 40°C during the year. These regions get plenty of rainfall. Because of continuous warmth and rain, this region supports wide variety of plants and animals. The climatic conditions in rainforests are highly suitable for supporting an enormous number and a variety of animals. That is why the tropical rainforest has a large population of animals.
Question 8: Explain, with examples, why we find animals of certain kind living in particular climatic conditions.
Answer: Animals are adapted to the conditions in which they live. These adaptations are the just because of long process of evolution. It would be difficult for them to survive if they are moved to region having different climate conditions than from their habitat. Consider the following examples:
A polar bear has thick layer of fat under their skin which acts heat insulator. It protects the bear from extreme cold climate of polar region. The polar bear cannot survive if it is moved to hot and dry desert region.
Monkeys have long tails for grasping branches adapted to live in tropical rain forests. It cannot survive in Polar Regions.
Question 9: How do elephant living in the tropical rainforest adapt itself?
Answer: Following are the adaptation of elephants in rainforests
- It uses the trunk as nose to have strong sense of smell
- The trunk is also used to pick food
- It has modified teeth tear the bark of trees which are food for elephants
- Large ears of the elephant help it to hear even very soft sounds.
- Ears help the elephant to keep cool in the hot and humid climate of the rainforest.
Question 10: A carnivore with stripes on its body moves very fast while catching its prey. It is likely to be found in (i) polar regions (ii) deserts (iii) oceans (iv) tropical rainforests
Answer: (iv) tropical rainforests
Question 11: Which features adapt polar bears to live in extremely cold climate?
(i) A white fur, fat below skin, keen sense of smell. (ii) Thin skin, large eyes, a white fur. (iii) A long tail, strong claws, white large paws. (iv) White body, paws for swimming, gills for respiration.
Answer: (i) A white fur, fat below skin, keen sense of smell.
Question 12: Which option best describes a tropical region?
(i) hot and humid (ii) moderate temperature, heavy rainfall (iii) cold and humid (iv) hot and dry
Answer: (i) hot and humid
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
CBSE Class 7 Science Chapter 7 – Weather, Climate and Adaptations of Animals to Climate Class 7 Notes
Weather, climate and adaptations of animals to climate class 7 cbse revision notes.
Weather Climate and Adaptation Class 7 Notes is mainly about the weather, climate. Further, it is also about how different forms of living organisms adapt themselves to the climate of their own habitat. Moreover, people can know about day to day weather forecasting reports from the newspapers, news channels, the internet, etc. In addition, we predict the weather and meteorological departments prepares report after analyzing different aspects of our environment like temperature, wind, humidity, and many more of that particular place. Thus, it will become easier to study the chapter through weather climate and adaptation class 7 notes.
Download Toppr app for Android and iOS or signup for free.
Subtopics covered under Weather, Climate, and Adaptations of Animals to Climate:
- Weather : Weather is the state of the atmosphere for a particular area and for a particular time period, which could change any time. Further, temperature, humidity, air pressure amount of clouds, fog, and precipitation are some of the elements which make weather.
- Climate : Climate could be described as the average weather conditions in an area over a long period of time.
- Adaptation in Animals : From the day any living organisms were born on this planet the climate kept on changing. Thus, for survival, the animals of some particular area have adjusted to their adverse living environment which can be termed as adaptations in animals.
You can download CBSE Class 7 Science Chapter 7 Revision Notes by clicking on the download button below

Download Toppr – Best Learning App for Class 5 to 12
There is a step by step explanations of the NCERT solutions which will guide students during exams and in daily homework. The notes are in accordance with the latest editions of CBSE books by experienced faculties. Use Topprunlimited ad-free services, free online video lectures, online Mock tests, doubt solving sessions and free PDF downloads.
Download Toppr app for Android and iOS or signup for free.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

Class 7 Science Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 7 Science Chapter 17 – Forests: Our Lifeline Class 7 Notes
- CBSE Class 7 Science Chapter 18 – Wastewater Story Notes
- CBSE Class 7 Science Chapter 16 – Water Class 7 Notes
- CBSE Class 7 Science Chapter 15 – Light Class 7 Notes
- CBSE Class 7 Science Chapter 14 – Electric Current and Its Effects Class 7 Notes
- CBSE Class 7 Science Chapter 13 – Motion and Time Class 7 Notes
- CBSE Class 7 Science Chapter 12 – Reproduction in Plants Class 7 Notes
- CBSE Class 7 Science Chapter 11 – Transportation in Animals and Plants Class 7 Notes
- CBSE Class 7 Science Chapter 10 – Respiration in Organisms Class 7 Notes
- CBSE Class 7 Science Chapter 9 – Soil Class 7 Notes
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

- School Solutions
- Star Program
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Physics
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Chemistry
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Commerce
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Economics
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Accountancy
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Physics
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Chemistry
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Biology
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Commerce
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Accountancy
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Statistics
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 5 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 5 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 5 EVS
- NCERT Solutions Class 4 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 4 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 4 EVS
- NCERT Solutions Class 4 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 3 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 3 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 3 EVS
- NCERT Solutions Class 3 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 2 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 2 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 2 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 1 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 1 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 1 Hindi
- NCERT Books Class 12
- NCERT Books Class 11
- NCERT Books Class 10
- NCERT Books Class 9
- NCERT Books Class 8
- NCERT Books Class 7
- NCERT Books Class 6
- NCERT Books Class 5
- NCERT Books Class 4
- NCERT Books Class 3
- NCERT Books Class 2
- NCERT Books Class 1
- Important Questions Class 12
- Important Questions Class 11
- Important Questions Class 10
- Important Questions Class 9
- Important Questions Class 8
- Important Questions Class 7
- important questions class 6
- CBSE Class 12 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 11 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 10 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 9 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 8 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 7 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 6 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 12 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 11 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 10 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 9 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 8 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 7 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 6 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 5 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 4 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 3 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 2 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 1 Syllabus
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 12
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 11
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 10
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 9
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 8
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 7
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 6
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 5
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 4
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 3
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 2
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 1
- CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 12
- CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 10
- Extra Questions For Class 8 Maths
- Extra Questions For Class 8 Science
- Extra Questions For Class 9 Maths
- Extra Questions For Class 9 Science
- Extra Questions For Class 10 Maths
- Extra Questions For Class 10 Science
- NEET 2021 Question Paper
- NEET 2020 Question Paper
- NEET 2019 Question Paper
- NEET 2018 Question Paper
- NEET 2017 Question Paper
- NEET 2016 Question Paper
- NEET 2015 Question Paper
- NEET Physics Questions
- NEET Chemistry Questions
- NEET Biology Questions
- NEET Sample Papers
- NEET Physics Syllabus
- NEET Chemistry Syllabus
- NEET Biology Syllabus
- NEET Mock Test
- NEET Eligibility Criteria
- JEE Main 2021 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2020 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2019 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2018 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2017 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2016 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2015 Question Paper
- JEE Main Sample Papers
- JEE Main Physics Syllabus
- JEE Main Chemistry Syllabus
- JEE Main Maths Syllabus
- JEE Main Physics Questions
- JEE Main Chemistry Questions
- JEE Main Maths Questions
- JEE main revision notes
- JEE Main Mock Test
- JEE Advanced Physics Questions
- JEE Advanced Chemistry Questions
- JEE Advanced Maths Questions
- JEE Advanced 2021 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2020 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2019 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2018 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2017 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2016 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2015 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced Physics Syllabus
- JEE Advanced Chemistry Syllabus
- JEE Advanced Maths Syllabus
- JEE Advanced Mock Test
- ISC Class 12 Syllabus
- ISC Class 11 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 10 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 9 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 8 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 7 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 6 Syllabus
- ISC Sample Question Papers for Class 12
- ISC Sample Question Papers for Class 11
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 10
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 9
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 8
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 7
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 6
- ICSE Class 10 Revision Notes
- ICSE Class 9 Revision Notes
- ISC Important Questions for Class 12
- ISC Important Questions for Class 11
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 10
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 9
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 8
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 7
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 6
- ISC Class 12 Question Paper
- ICSE Class 10 Question Paper
- Maharashtra Board Syllabus
- Maharashtra Board Sample Question Paper
- Maharashtra Board Previous Year Question Paper
- AP Board Syllabus
- AP Board Sample Question Paper
- AP Board Previous Year Question Paper
- Tamilnadu Board Syllabus
- Tamilnadu Board Sample Question Paper
- Tamilnadu Board Previous Year Question Paper
- Telangana Board Syllabus
- Telangana Board Sample Question Paper
- Telangana Board Previous Year Question Paper
- Karnataka Board Syllabus
- Karnataka Board Sample Question Paper
- Karnataka Board Previous Year Question Paper
- Examination Full Forms
- Physics Full Forms
- Chemistry Full Forms
- Biology Full Forms
- Educational Full Form
- CUET Eligibility Criteria
- CUET Exam Pattern
- CUET Cutoff
- CUET Syllabus
- CUET Admit Card
- CUET Counselling
- CUET Previous Year Question Papers
- CUET Application Form
- CUET Sample Papers
- CUET Exam Centers
- CUET Exam Dates
- CUET Results
- Physics Formulas
- Chemistry Formulas
- Math Formulas
- Algebra Formulas
- Geometry Formulas
- Trigonometry Formulas
- Subscription
CBSE Class 7 Science Revision Notes Chapter 7
Home » CBSE » CBSE Class 7 Science Revision Notes Chapter 7

- CBSE Important Questions
- Important Questions Class 6
- CBSE Previous Year Question Papers
- CBSE Revision Notes
- CBSE Syllabus
- CBSE Extra Questions
- CBSE Sample Papers
- ISC & ICSE Syllabus
- ICSE Syllabus Class 9
- ICSE Syllabus Class 8
- ICSE Syllabus Class 7
- ICSE Syllabus Class 6
- ICSE Syllabus Class 10
- ICSE Question Paper
- ICSE Sample Question Papers
- ISC Sample Question Papers For Class 12
- ISC Sample Question Papers For Class 11
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 10
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 9
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 8
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 7
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 6
- ICSE Revision Notes
- ICSE Important Questions
- ISC Important Questions For Class 12
- ISC Important Questions For Class 11
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 10
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 9
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 8
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 7
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 6
- Maharashtra board
- Rajasthan-Board
- Andhrapradesh Board
- AP Board syllabus
- Telangana Board
- Tamilnadu Board
- Tamilnadu Sample Question Paper
- Tamilnadu Syllabus
- Tamilnadu Previous Year Question Paper
- NCERT Solutions Class 12
- NCERT Solutions Class 10
- NCERT Solutions Class 11
- NCERT Solutions Class 9
- NCERT Solutions Class 8
- NCERT Solutions Class 7
- NCERT Solutions Class 6
- NCERT Solutions Class 5
- NCERT Solutions Class 4
- NCERT Solutions Class 3
- NCERT Solutions Class 2
- NCERT Solutions Class 1
- JEE Main Question Papers
- JEE Main Syllabus
- JEE Main Questions
- JEE Main Revision Notes
- JEE Advanced Question Papers
- JEE Advanced Syllabus
- JEE Advanced Questions
- JEE Advanced Sample Papers
- NEET Question Papers
- Neet 2021 Question Paper
- Neet 2020 Question Paper
- Neet 2019 Question Paper
- Neet 2018 Question Paper
- Neet 2017 Question Paper
- Neet 2016 Question Paper
- Neet 2015 Question Paper
- NEET Syllabus

CBSE Class 7 Science Revision Notes Chapter 7 – Weather, Climate, and Adaptation of Animals to Climate
Extramarks provide quality materials to give an edge to exam preparations. Studying the chapters listed in the CBSE Syllabus becomes easy as students feel more confident in the clear explanations for each concept given in the notes.
Quick Links
Class 7 Science Chapter 7 Notes provided by Extramarks provide comprehensive study material to students preparing for the exams. In this chapter, students will learn the concepts of weather and climate, their differences, their effects on migration and adaptation of birds and animals, and finally the Important Questions at the end.
Class 7 Science Chapter 7 Notes notes are prepared by subject matter experts as per the CBSE Syllabus and its latest guidelines. These notes cover all of the key points mentioned in the chapter. Therefore, students can revise them all in a short time before the exam. Chapter 7 Science Class 7 Notes are easily accessible from the Extramarks website.
Revision Notes For CBSE Class 7 Science Chapter 7
Access class 7 science chapter 7 – weather, climate and adaptations to climate notes.
- Migration can be defined as a large-scale movement of birds and animals from one region to another to find a climate suitable for living, breeding, and getting sustenance.
- The seasonal migration of birds and animals happens from colder regions to warmer regions.
- During the daylight, birds are guided by the sun; but at night they follow the stars to carry on their journey.
- A Siberian crane migrates every year from the cold regions of Siberia to India.
Class 7 Chapter 7 Science Notes
Extramarks provides revision notes for the chapter Weather, Climate and Adaptations of Animals to Climate to help students enhance their exam preparation. They can easily access updated study materials from the Extramarks website at their convenience. Subject matter experts prepare these notes in pointers. This makes them concise and easy to understand. These notes explain the chapter in a structured manner, so students can understand the flow between two given concepts.
Weather and Climate Class 7 Revision Notes
The term “weather” refers to the state of atmospheric elements in a certain place at a certain period of time. The condition of the weather fluctuates depending on a change in the atmospheric elements like temperature, humidity, rainfall, wind pressure, etc. of that given place.
Conditions Affecting Weather
The weather of a region depends on multiple factors. These are:
- Temperature
- Humidity in atmosphere
- Wind or atmospheric pressure in that place
- Visibility of the horizon
- Separation of air masses
The climate of a place refers to the average weather pattern of that given place over a long period of time. If the average temperature of a place is usually hot then it is called a hot place. If scanty rainfall is also added to the prevailing weather conditions, the climate of that place is considered hot and arid as well.
Some of the determining factors of the climate of a place include the geographical location of that place, its height above sea level, and its overall topography.
Difference Between Weather And Climate – Table Will Be Updated Soon.
One of the key elements that affect the weather of a location is the presence of clouds. Clouds are made up of small droplets of water floating in the atmosphere freely. They are formed through convection.
The process of cloud formation is as follows:
- During the day, the air on the earth’s surface becomes hot and light. The warm and light air moves in the upward direction only to be transformed into water droplets after reaching a particular height, where the temperature of the atmosphere drops significantly.
- These water droplets take a more condensed form and merge to form a cloud.
- A cloud, therefore, is nothing but a collection of billions of water droplets floating in the air.
- The water that goes up to the higher sky comes back to the earth in the form of rainfall.
A rain gauge is an instrument used for measuring the amount of rainfall at a given place. It has a funnel-like structure at the mouth to collect the rainwater and a cylindrical body to store it. The measuring scale of a rain gauge is drawn on its body.
Tropical Rainforests
- Tropical rainforests are found in the regions around the equator, where the climate remains extremely hot throughout the year.
- In winters, the temperature goes down to 15⁰ C, whereas in summers, the temperature rises over 40⁰ C.
The climate of these regions is extremely hot and arid because of continuous exposure to sunlight and minimum rainfall.
Animal Adaptation
- The ability to adapt to hostile climatic conditions is the key to survival on earth.
- For example, polar bears have evolved to have long white fur to protect themselves from predators. The thick layer of fat under their skin helps them survive in the icy polar regions.
- All the species across the globe have developed certain features to survive in their environmental conditions.
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
1. what is meant by humidity.
Humidity is one of the factors that determine weather conditions. The humidity of a place refers to the amount of moisture present in the atmosphere of the given place. Humidity increases with the increasing amount of moisture in the atmosphere. It is measured in the form of a percentage. 100% humidity means the air of that given place cannot be further saturated with moisture.
2. What are the maximum and minimum temperatures of a place?
The maximum and minimum temperatures are measured on a daily basis. The highest temperature recorded in a day is called the maximum temperature, and the lowest recorded temperature is called the minimum temperature of the day. There is a specific thermometer to measure the highest and lowest temperature known as a maximum-and-minimum thermometer.
3. What is weather forecasting?
Weather forecasting is the act of predicting the state of atmospheric elements of a given place. Weather forecasting agencies analyse the rise and fall of temperature, the level of humidity, the clouds in the sky, and other factors to foretell where there will be bright sunshine or where there will be heavy rainfall.
4. What is a weather report?
A weather report is a record of several factors that influence the weather of a given place on a given day. Weather reports help understand the weather pattern of a place and record the temperature, precipitation, humidity, etc. daily.
5. What is the significance of adaptation?
Adaptation is the ability of organisms to adjust to the changing environment. A polar bear, for instance, has evolved to have long fur and developed a layer of fat beneath the skin to survive in the cold climate of the polar region.
CBSE Related Links

The Site is down as we are performing important server maintenance, during which time the server will be unavailable for approximately 24 hours. Please hold off on any critical actions until we are finished. As always your feedback is appreciated.

- Study Packages
- NCERT Solutions
- Sample Papers
- Online Test

- Questions Bank
- Weather, Climate and Adaptation of Animals to Climate
- Test Series
- Ncert Solutions
- Solved Papers
- Current Affairs
- General Knowledge
- Mathematics
- Mental Ability
- Social Science
- Computers Science
Question Bank for 7th Class Science Weather, Climate and Adaptation of Animals to Climate
Our environment, practice now, weather, climate and adaptations of animals to, weather climate and adaptations, weather, climate and adaptation of animals to.

Reset Password.
OTP has been sent to your mobile number and is valid for one hour
Mobile Number Verified
Your mobile number is verified.

- Andhra Pradesh
- Chhattisgarh
- West Bengal
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Jammu & Kashmir
- NCERT Books 2022-23
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Notes
- NCERT Exemplar Books
- NCERT Exemplar Solution
- States UT Book
- School Kits & Lab Manual
- NCERT Books 2021-22
- NCERT Books 2020-21
- NCERT Book 2019-2020
- NCERT Book 2015-2016
- RD Sharma Solution
- TS Grewal Solution
- TR Jain Solution
- Selina Solution
- Frank Solution
- ML Aggarwal Solution
- Lakhmir Singh and Manjit Kaur Solution
- I.E.Irodov solutions
- ICSE - Goyal Brothers Park
- ICSE - Dorothy M. Noronhe
- Sandeep Garg Textbook Solution
- Micheal Vaz Solution
- S.S. Krotov Solution
- Evergreen Science
- KC Sinha Solution
- ICSE - ISC Jayanti Sengupta, Oxford
- ICSE Focus on History
- ICSE GeoGraphy Voyage
- ICSE Hindi Solution
- ICSE Treasure Trove Solution
- Thomas & Finney Solution
- SL Loney Solution
- SB Mathur Solution
- P Bahadur Solution
- Narendra Awasthi Solution
- MS Chauhan Solution
- LA Sena Solution
- Integral Calculus Amit Agarwal Solution
- IA Maron Solution
- Hall & Knight Solution
- Errorless Solution
- Pradeep's KL Gogia Solution
- OP Tandon Solutions
- Sample Papers
- Previous Year Question Paper
- Value Based Questions
- CBSE Syllabus
- CBSE MCQs PDF
- Assertion & Reason
- New Revision Notes
- Revision Notes
- HOTS Question
- Marks Wise Question
- Toppers Answer Sheets
- Exam Paper Aalysis
- Concept Map
- CBSE Text Book
- Additional Practice Questions
- Vocational Book
- CBSE - Concept
- KVS NCERT CBSE Worksheets
- Formula Class Wise
- Formula Chapter Wise
- JEE Crash Course
- JEE Previous Year Paper
- Important Info
- JEE Mock Test
- JEE Sample Papers
- SRM-JEEE Mock Test
- VITEEE Mock Test
- BITSAT Mock Test
- Manipal Engineering Mock Test
- AP EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- COMEDK Previous Year Paper
- GUJCET Previous Year Paper
- KCET Previous Year Paper
- KEAM Previous Year Paper
- Manipal Previous Year Paper
- MHT CET Previous Year Paper
- WBJEE Previous Year Paper
- AMU Previous Year Paper
- TS EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- SRM-JEEE Previous Year Paper
- VITEEE Previous Year Paper
- BITSAT Previous Year Paper
- UPSEE Previous Year Paper
- CGPET Previous Year Paper
- CUSAT Previous Year Paper
- AEEE Previous Year Paper
- Crash Course
- Previous Year Paper
- NCERT Based Short Notes
- NCERT Based Tests
- NEET Sample Paper
- Previous Year Papers
- Quantitative Aptitude
- Numerical Aptitude Data Interpretation
- General Knowledge
- Mathematics
- Agriculture
- Accountancy
- Business Studies
- Political science
- Enviromental Studies
- Mass Media Communication
- Teaching Aptitude
- NAVODAYA VIDYALAYA
- SAINIK SCHOOL (AISSEE)
- Mechanical Engineering
- Electrical Engineering
- Electronics & Communication Engineering
- Civil Engineering
- Computer Science Engineering
- CBSE Board News
- Scholarship Olympiad
- School Admissions
- Entrance Exams
- All Board Updates
- Miscellaneous
- State Wise Books
- Engineering Exam
Weather Climate and Adaptations of Animals to Class 7 MCQ Test (Online Available)
Free mcq test, table of content, weather climate and adaptations of animals to climate test - 18.
Duration: 10 Mins
Maximum Marks: 10
Read the following instructions carefully.
1. The test contains 10 total questions.
2. Each question has 4 options out of which only one is correct .
3. You have to finish the test in 10 minutes.
4. You will be awarded 1 mark for each correct answer.
5. You can view your Score & Rank after submitting the test.
6. Check detailed Solution with explanation after submitting the test.
7. Rank is calculated on the basis of Marks Scored & Time
Weather Climate and Adaptations of Animals to Climate Test - 17
Weather climate and adaptations of animals to climate test - 16, weather climate and adaptations of animals to climate test - 15, weather climate and adaptations of animals to climate test - 14, weather climate and adaptations of animals to climate test - 13, weather climate and adaptations of animals to climate test - 12, weather climate and adaptations of animals to climate test - 11, weather climate and adaptations of animals to climate test - 10, weather climate and adaptations of animals to climate test - 9, weather climate and adaptations of animals to climate test - 8, weather climate and adaptations of animals to climate test - 7, weather climate and adaptations of animals to climate test - 6, weather climate and adaptations of animals to climate test - 5, weather climate and adaptations of animals to climate test - 4, weather climate and adaptations of animals to climate test - 3, weather climate and adaptations of animals to climate test - 2, weather climate and adaptations of animals to climate test - 1.
Objective questions have become the norm now, those students who are studying in class 7 must be well versed with all kinds of MCQ Questions; therefore, the link to access Weather Climate and Adaptations of Animals to Climate MCQ Class 7 is mentioned here on this page.
Weather Climate and Adaptations of Animals to Climate Class 7 MCQ questions are curated by subject experts referring to the prescribed NCERT Class 7 Science Book. Those students who have studied the lesson Weather Climate and Adaptations of Animals to Climate must practise the CBSE Class 7 MCQ Questions as it helps in deepening the understanding of the topics.
Class 7 Weather Climate and Adaptations of Animals to Climate MCQ with Answers Online
For the ease of students, the subject experts have simplified the practice process of the class 7 Weather Climate and Adaptations of Animals to Climate MCQ as they have solved each and every question given. The answers are detailed and easy to grasp. Students who want to practise the questions of Class 7 Weather Climate and Adaptations of Animals to Climate MCQ with Answers online can use the Selfstudys website.
The MCQ Questions of Weather Climate and Adaptations of Animals to Climate with answers are also given so that students can understand the methods of solving the concepts based questions. As well as, the solutions are helpful to understand where the students are making mistakes and need to improve.
How to Practise MCQ from NCERT Chapter Weather Climate and Adaptations of Animals to Climate?
There are several ways to practise the MCQ from NCERT Chapter Weather Climate and Adaptations of Animals to Climate; one is by solving questions from the chapter’s end and another is by using online medium. In this section, we have mentioned the steps to Practise MCQ from NCERT Chapter Weather Climate and Adaptations of Animals to Climate online.
- First of all open Selfstudys.com on your Smartphone, PC/Laptop
- Navigate to the CBSE by Tapping/clicking on the navigation bar or button
- It will open a new lists where you can find MCQ Test - Click on that
- Then, a new page will load containing the lists of classes; just Tap or click on Class 7. *In Smartphone, you may require to scroll the given classes name towards left.
- Now, after selecting the Class 7, the same page will reload, make sure you select the Science to access the MCQ Questions of Class 7 Weather Climate and Adaptations of Animals to Climate.
Note: The online MCQ Questions of Weather Climate and Adaptations of Animals to Climate can’t be downloaded, those who want to access the PDF of Weather Climate and Adaptations of Animals to Climate MCQ can refer to the CBSE Class 7 MCQ PDF section within the CBSE menu.
What is Weather Climate and Adaptations of Animals to Climate MCQ and How to Use it?
Since class 7 students are in their early stage of academics they may have questions regarding What is Weather Climate and Adaptations of Animals to Climate MCQ and How to Use it. So, the answer is MCQ Questions are objective questions which contain questions followed by 4 options where only one is considered the correct answer and remaining as a distraction. Why is it so, because MCQ questions are ideal to assess a student’s conceptual knowledge.
Those who want to use the Weather Climate and Adaptations of Animals to Climate MCQ can use this website to access the online MCQ questions to practise.
Top 5 Benefits of Weather Climate and Adaptations of Animals to Climate MCQ Class 7
Weather Climate and Adaptations of Animals to Climate MCQ Class 7 questions benefit students in several ways; however, here we have mentioned a total of 5 benefits that a student will get if they are using the MCQ from NCERT Chapter Weather Climate and Adaptations of Animals to Climate.
- Helps in Practising Questions: Sometimes, it's hard to get the questions to practise; therefore, the Selfstudys team has curated various sets of MCQ Questions of Class 7 Weather Climate and Adaptations of Animals to Climate. Having access to the objective questions of Class 7 Weather Climate and Adaptations of Animals to Climate helps students practising various questions for free of cost.
- Boosts the Critical Thinking Capability: The MCQs or objective questions must be answered in lesser time; therefore, those who will regularly solve Weather Climate and Adaptations of Animals to Climate MCQ Class 7 will benefit by having a great boost in the critical thinking capability as the questions are in the objective format which can be answered if one has a good command over the concepts of Weather Climate and Adaptations of Animals to Climate.
- Assists in Covering the Class 7 Science Syllabus: Weather Climate and Adaptations of Animals to Climate is a chapter of Class 7 Science and those who are going to solve the MCQs of Class 7 Weather Climate and Adaptations of Animals to Climate will be able to practise all the questions as per their Science Syllabus.
- Helps in Exam Preparation: If a student solves the objective questions from class 7 Weather Climate and Adaptations of Animals to Climate, they will be able to be prepared for the annual examination too. It is because the questions that are asked in the online MCQ of Weather Climate and Adaptations of Animals to Climate are asked in the final exam question papers too.
- A Deeper Understanding of Weather Climate and Adaptations of Animals to Climate: All the important points that are discussed in Weather Climate and Adaptations of Animals to Climate must be memorised by students as it helps in deepening the understanding of the Delhi Sultans. One of the great benefits of solving Weather Climate and Adaptations of Animals to Climate MCQ Class 7 is that one can be thorough with the topics and can develop a deeper understanding of Weather Climate and Adaptations of Animals to Climate chapter of class 7.
Apply These Techniques To Better Answer the MCQ Questions of Weather Climate and Adaptations of Animals to Climate
Although, there is no wrong or right method to answer the MCQ Questions, those who are interested in knowing the techniques to better answer the MCQ Questions of Weather Climate and Adaptations of Animals to Climate can follow the below given methods.
Read the Question Carefully: Questions in Weather Climate and Adaptations of Animals to Climate MCQ Class 7 can be asked from tricky to hard to understand. In this case, you must read the questions of Weather Climate and Adaptations of Animals to Climate MCQ carefully. By paying attention to the questions, it will help you connect the dots and assist you recall the studied concepts to answer the MCQs easily.
Eliminate Obviously Wrong Answers: Many questions of Weather Climate and Adaptations of Animals to Climate MCQ Class 7 will be so familiar that you can be certain for the wrong answer but uncertain for the right answer, in that situation obviously eliminate wrong answers first. By eliminating irrelevant or incorrect answers, it will help you find the one correct answer from all the given four options.
Look for Clues in the Question: As we have discussed the first technique is to read the questions carefully, it is vital for looking for the clues in the questions of Weather Climate and Adaptations of Animals to Climate MCQ Class 7. Every single question contains some kind of clues that help you answer them easily, but due to running out of time many don’t pay attention to it. In order to solve Weather Climate and Adaptations of Animals to Climate MCQ Class 7 by using this technique you may have to do a thorough practice of Class 7 MCQ Questions.
Use the Process of Elimination: There is not much difference in the elimination method and eliminating the wrong answer (discussed in point number 2) first, but one difference that makes the elimination process different is you can eliminate the right or wrong answer first.
This means that when you are confused between two options, you can separate them and then you try to focus on only those 2 options to find out the correct answer of Weather Climate and Adaptations of Animals to Climate MCQ Class 7. This elimination process works best in most of the scenarios.
Don't Spend too Much Time on One Question: It is never a good idea to be rigid on one question and spend most of your time answering them. When you are practising Weather Climate and Adaptations of Animals to Climate MCQ Class 7 questions, you have limited time and you have to make sure that you use your time smartly to attempt all the questions as asked in the Weather Climate and Adaptations of Animals to Climate Class 7 MCQ.
Double-check your Answer: Before submitting the Online test of Class 7 Weather Climate and Adaptations of Animals to Climate MCQ, you should double check your answer if the test time hasn't completed. When you do a double check of your answers, you may find some silly mistakes that you have made due to which you could have lost some marks. Therefore, be conscious and double check your answers before submitting Weather Climate and Adaptations of Animals to Climate MCQ Class 7.
*As per the Selfstudys Online MCQ Test instructions the time plays a crucial role in calculating your test rank so, be conscious when you use any single minute during your test.
Manage your Time: Having great time management skills doesn’t only help you quickly answer the questions, but gives you the ability to save time to review the questions or in doing a last minute cross-checking. Thus, when you start solving Weather Climate and Adaptations of Animals to Climate MCQ Class 7 questions, try to manage time and some of your test time to review the answers you have ticked throughout the test.
Apart from this, time management skills give you peace of mind and keep you calm.
Stay Calm to Recall Previously Studied Topics: When you struggle to come up with the correct answer of Weather Climate and Adaptations of Animals to Climate MCQ Class 7 Questions try to stay calm as it will help you recall previously studied topics. Research says, being calm and relaxed helps in saving energy. Thus, staying calm while solving the MCQ from NCERT Chapter Weather Climate and Adaptations of Animals to Climate helps you be more focused and answer the questions efficiently. The saved energy can be channelized to increase the focus and concentration to better recall the topics and subtopics of Weather Climate and Adaptations of Animals to Climate.
There is a high possibility of having more techniques of Weather Climate and Adaptations of Animals to Climate MCQ Class 7 as mentioned, but these given methods work well in most of the cases.

- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Maths
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths
- CBSE Syllabus 2023-24
- Social Media Channels
- Login Customize Your Notification Preferences

- Second click on the toggle icon

Provide prime members with unlimited access to all study materials in PDF format.
Allow prime members to attempt MCQ tests multiple times to enhance their learning and understanding.
Provide prime users with access to exclusive PDF study materials that are not available to regular users.

Weather Climate And Adaptation Of Animals To Climate
The World of Quizizz is the best tool for teachers who want to teach option based, real-world and stimulating science curriculum. Teachers can now create their own quizzes from a variety of topics including Pollution Control, Weather and Climate, Health Science, Geography and much more!

Explore our Quiz Library

Weather and Climate


Weather & Climate

Explore other chapters
Nutrition In Plants
Nutrition In Animals
Fibre To Fabric
Acids, Bases, And Salts
Physical Changes
- Winds, Storms, And Cyclones
- Respiration In Organisms
Transportation In Animals And Plants
Reproduction In Plants
Electric Current And Its Effects
Water: A Precious Resource
- Motion And Time
Waste Water Story
Any specific topic in mind?
Suggested topics, explore the subjects.
Mathematics
Other topics to explore
CBSE | Mathematics | 7th Grade | The Triangle and its Properties - Quizizz
CBSE | Mathematics | 7th Grade | Visualizing Solid Shape - Quizizz
CBSE | Mathematics | 7th Grade | Data Handling - Quizizz
CBSE | Mathematics | 7th Grade | Algebraic Expressions - Quizizz
CBSE | Mathematics | 7th Grade | Exponents and Powers - Quizizz
CBSE | Science | 7th Grade | Electric Current And Its Effects - Quizizz
CBSE | Science | 7th Grade | Weather Climate And Adaptation Of Animals To Climate - Quizizz
CBSE | Science | 7th Grade | Reproduction In Plants - Quizizz
CBSE | Science | 7th Grade | Respiration In Organisms - Quizizz
CBSE | Science | 7th Grade | Transportation In Animals And Plants - Quizizz
Everything you need for mastery and engagement
Explore our powerful tools.
- Open access
- Published: 24 May 2024
The association between gender equality and climate adaptation across the globe
- Ana-Catarina Pinho-Gomes 1 , 2 &
- Mark Woodward 1 , 3
BMC Public Health volume 24 , Article number: 1394 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
Metrics details
Introduction
Climate change has a disproportionate impact on women in comparison to men, and women have a key role to play in climate adaptation. However, evidence is lacking on how gender inequalities may be associated with climate vulnerability and ability to respond at country level.
This ecological study investigated the association between climate adaptation, measured by the Notre Dame Global Adaptation Initiative Country Index (ND-GAIN), and gender equality, measured by the Global Gender Gap Index (GGGI) developed by the World Economic Forum and the Gender Inequality Index (GII) developed by the United Nations. Simple linear regression was used to estimate the associations between the indices and their subdomains for 146 countries.
There was an approximately linear association between the GGGI and climate adaptation. Each 1% increase in gender equality was associated with a 0.6% increase in the ND-GAIN score (the slope was 0.59, with a 95% confidence interval [0.33 to 0.84]). This was driven by a negative association between gender equality and vulnerability (-0.41 [-0.62 to -0.20]), and a positive association between gender equality and readiness (0.77 [0.44 to 1.10]). The strongest associations between gender equality and climate adaptation were observed for the education domain of the GGGI. There was a strong negative linear association between the GII and climate adaptation, which explained most (86%) of the between-country variation in climate adaptation. Each 1% increase in gender inequality was associated with a 0.5% decrease in the ND-GAIN score (-0.54 [-0.57 to -0.50]). The association between gender inequality and readiness was stronger than the association with vulnerability (0.41 [0.37 to 0.44] for vulnerability versus − 0.67 [-0.72 to -0.61] for readiness).
Conclusions
Gender inequality, measured broadly across different domains of life, is associated with climate adaptation at country level, both in terms of vulnerability to impact and readiness to respond.
Peer Review reports
The climate crisis, as with many other crises including the COVID-19 pandemic, is not gender neutral. On the one hand, women and girls across the globe experience the greatest impact of climate change and have the least capacity to respond to climate-related hazards, such as heatwaves, floods, volcanic eruptions, and hurricanes [ 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 ]. On the other hand, women’s unequal participation in policy, decision making and labour markets prevents them from fully contributing to climate change mitigation [ 5 ]. Barriers to women’s participation include time constraints due to other responsibilities, such as childcare, and lack of experience, awareness, support within institutional frameworks, and access to finance [ 6 ]. This has been acknowledged by the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC), which established a dedicated agenda item on gender and climate change under the Convention and included overarching text in the Paris Agreement [ 7 ].
Climate change has a disproportionate impact on women, in comparison to men, particularly in low- and middle-income countries (LMIC). Worldwide, populations that rely on natural resources for their livelihoods, as well as those experiencing poverty, are the most vulnerable to climate change. Women are over-represented in both groups [ 5 ]. Furthermore, climate-induced extreme weather events are forcing migration and causing conflicts, with the UN estimating that 80% of people displaced by climate change are women [ 5 ]. Climate migration and extreme events expose women to increased risk of gender-based violence and trafficking due to economic instability, food insecurity, mental stress, disrupted infrastructure, increased exposure to men [ 8 , 9 ]. Climate change is, thus, a threat multiplier for women’s health and wellbeing.
Women have a huge potential to mitigate, adapt, and respond to climate change [ 10 ]. Particularly in LMICs, women’s local knowledge and leadership has been critical for implementation of sustainable practices at household and community level. For instance, in South Africa, local women farmers are trained on agroecology and permaculture farming to overcome challenges posed by erratic weather conditions and climate change impacts [ 11 ]. This provides them with unique knowledge and skills that can help make the response to climate change more effective and sustainable. It also helps them to be more respected and given an opportunity in the current male-dominated positions. Globally, companies with a greater share of women in boards are more likely to adopt climate and eco-friendly policies [ 12 ]. Likewise, countries with a larger representation of women in Parliament are more prone to ratify environmental treaties and adopt policies that address climate change [ 13 ]. However, women still experience barriers in ascending to positions of leadership in government and private companies, and hence remain underrepresented in both settings [ 14 , 15 ].
Considering both women’s disproportionate vulnerability and their role in the response to climate change, it is germane to ask to what extent gender inequality may exacerbate the impact and undermine collective efforts to adapt to climate change. Therefore, this study aimed to investigate the association between gender inequality in several societal domains and vulnerability and readiness to adapt to climate change across the globe. This evidence may reinforce the importance of gender equality for successful climate adaptation. Conversely, it could support the argument that failure to adapt to climate change may further exacerbate gender inequality.
We conducted an ecological study to investigate the association between gender equality and climate adaptation across the globe.
Gender equality
We used the Global Gender Gap Index (GGGI), developed by the World Economic Forum, and the United Nations Gender Inequality Index (GII), to assess gender equality. The GGGI was first introduced in 2006 to benchmark progress towards gender parity and compare countries’ gender gaps across four dimensions: economic opportunities, education, health, and political leadership. There are three basic concepts underlying the GGGI, forming the basis of how indicators were chosen, how the data are treated and how the scale can be used. First, the index focuses on measuring gaps, rather than levels. Second, it captures gaps in outcome variables, rather than gaps in input variables. Third, it ranks countries according to gender equality, rather than women’s empowerment. The GGGI includes four subindexes, each of which is calculated from several indicators (Table S 1 ). The overall GGGI score is a simple average of each subindex score and, similarly to subindex scores, ranges between one (parity) and zero (imparity). Detailed information about the GGGI is available elsewhere [ 16 ].
The GII is a composite metric that reflects gender-based disadvantage in three dimensions: reproductive health, empowerment, and the labour market. It shows the loss in potential human development due to inequality between women and men’s achievements in these dimensions. It ranges from zero (parity) to 1 (imparity). The GII values are computed using several indicators (Table S2) [ 17 ]. A detailed description of the GII is available elsewhere [ 18 ]. Note that, contrary to the GGGI, higher values of GII denote greater gender equality.
Climate vulnerability and readiness
We used the Notre Dame Global Adaptation Initiative (ND-GAIN) Country Index to assess climate adaptation worldwide. The ND-GAIN Country Index is composed of two key dimensions of adaptation: vulnerability and readiness (Table 1 ). Vulnerability reflects the exposure, sensitivity, and capacity of each country to adapt to the negative effects of climate change. The index considers overall vulnerability across six life-supporting sectors: food, water, health, ecosystem service, human habitat and infrastructure. Readiness reflects the ability of each country to leverage investments and convert them into adaptation actions. The index considers overall readiness across three components: economic readiness, governance readiness, and social readiness. Both vulnerability and readiness vary between zero and one, but whilst lower is better for vulnerability, higher is better for readiness. Thirty-six indicators are used to assess vulnerability and nine indicators measure aspects of readiness. The overall ND-GAIN Score is calculated as the average of the vulnerability and readiness scores for each country and varies between zero and one (higher is better adaption). An explanation of each indicator and their data sources is available elsewhere [ 19 ].
Data analysis
To ensure that all data used are contemporaneous we used data from 2022 for all three indices, this being determined by the GII index, which had the least recent data available. For ease of interpretation, both the GGGI, the GII, and the ND-GAIN indices, and respective subindices, were converted into percentages by multiplying the scores by 100. Whilst maintaining the relationship between the indices, conversion of proportions into percentages made the indices easier to understand. Countries were grouped into regions according to the World Bank classification [ 20 ]. Simple linear regression was used to estimate the association between the GGGI, and its subindices, and the ND-GAIN index and the vulnerability and readiness dimensions. Scatterplots were used to display the associations with loess (i.e., local polynomial regression) curves fitted to explore the inherent assumption of linearity. We also estimated the correlation between the GGGI and GII using Spearman’s correlation coefficient (r). All analyses were carried out using R version 4.3.0.
Worldwide distribution of the ND-GAIN, GGGI and GII
A total of 146 countries were included in this study (details are available in Table S 3 ). The median GGGI was 71% with a range from 43% for Afghanistan to 91% for Iceland. The median GII was 33% and it ranged from 1% Denmark to 82% for Yemen. The median of the ND-GAIN score was 50% and it varied between 27% for Chad and 75% for Norway. There was more variation in readiness than vulnerability (median of vulnerability 41%, range 25% for Switzerland to 67% for Niger, and median of readiness 43%, range 19% for Central African Republic to 80% for Singapore). In these data there was a modest correlation between the GII and GGGI ( r = -0.31). In general, countries in Europe and North America tended to cluster at the lower end of the vulnerability and gender inequality, whilst countries in Africa and South Asia clustered at the higher end of the vulnerability and gender inequality (Fig. 1 and Figure S 1 ).
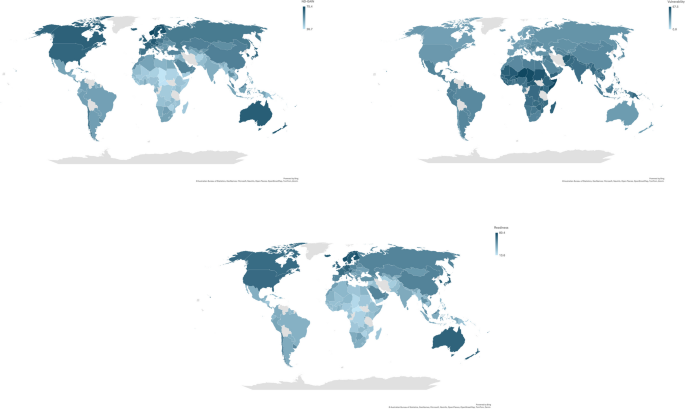
World map illustrating the distribution of the Notre Dame Global Adaptation Index (ND-GAIN), Global Gender Gap Index (GGGI) and Gender Inequality Index (GII)
Association between the GGGI and the ND-GAIN
There was an approximately linear association between gender equality measured by GGGI and climate adaptation (Fig. 2 ; Table 2 ). Overall, each 1% increase in gender equality was associated with a 0.6% increase in the ND-GAIN score (the slope was 0.59, with a 95% confidence interval [0.33 to 0.84]). This was driven by a negative association between gender equality and vulnerability, with each 1% increase in gender equality associated with a 0.4% decrease in vulnerability (-0.41 [-0.62 to -0.20]), and a positive association between gender equality and readiness, with each 1% increase in gender equality associated with a 0.8% increase in readiness (0.77 [0.44 to 1.10]). Overall, the strongest associations between gender equality and climate adaptation were observed for the education domain of the GGGI. Each 1% increase in gender equality in the education domain was associated with a 0.4% increase in climate adaptation (0.39 [0.19 to 0.60]). There was a weaker association with gender equality in the economic and political domains (0.21 [0.06 to 0.36] for the economic domain and 0.18 [0.07 to 0.28] for the political domain). There was no evidence of an association between health equality and climate adaptation. The education domain had the strongest association with both vulnerability and readiness (-0.32 [-0.48 to -0.15] for vulnerability and 0.47 [0.20 to 0.74] for readiness).
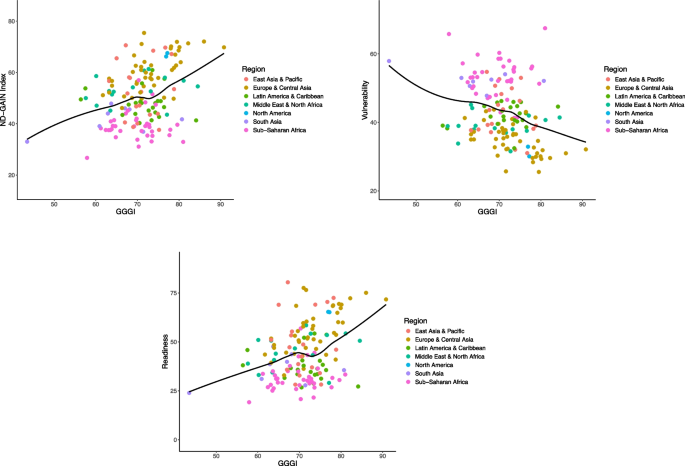
Association between gender equality based on the GGGI and climate adaptation based on the ND-GAIN country index
Association between the GII and the ND-GAIN
When gender inequality was measured by the GII, there was a strong negative linear association between gender inequality and climate adaptation, which explained most (86%) of the between-country variation in climate adaptation (Fig. 3 ; Table 2 ). Each 1% increase in gender inequality was associated with a 0.5% decrease in the ND-GAIN score (-0.54 [-0.57 to -0.50]). The association between gender inequality and readiness was stronger than the association with vulnerability (0.41 [0.37 to 0.44] for vulnerability versus − 0.67 [-0.72 to -0.61] for readiness).
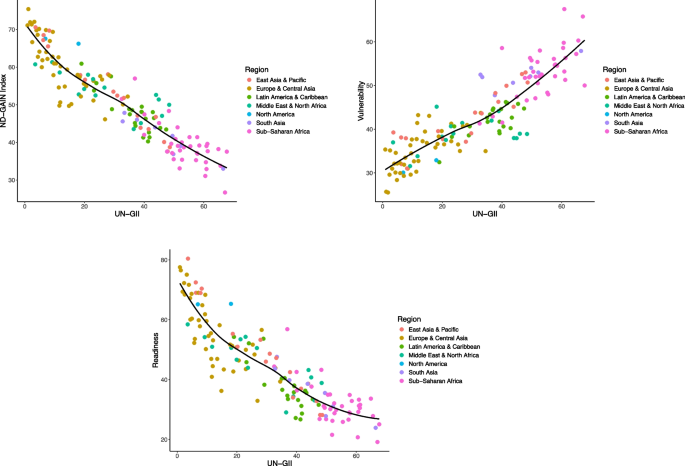
Association between gender equality based on the UN-GII and climate adaptation based on the ND-GAIN country index
This study found an approximately linear association between gender equality, measured using two different indices, and climate adaptation across 146 countries. The unexplained country-to-country variation was considerably less for the GII index than the GGGI. The association was underpinned by a positive association between gender equality and readiness and a negative association between gender equality and vulnerability, irrespective of the index used to assess gender equality. The association with readiness appeared to be stronger than the association with vulnerability.
Interpretation in light of previous evidence
The underlying reasons for the association between gender inequality and climate adaptation are likely manifold. First, countries with the greatest gender inequality tend to have low socioeconomic development [ 21 ]. Therefore, these countries are likely to rely on sectors that are particularly susceptible to the impact of climate change, such as agriculture [ 22 ]. In LMICs, about 70% of the estimated 1.3 billion people living below the poverty line are women and most depend on subsistence agriculture to survive [ 5 ]. These sectors are also where women are disproportionately employed due to a complex interplay between gendered societal roles and norms and lack of access to education, which then compromises their employment opportunities. This means that gender inequality in education, labour, and economic domains results in women being the most vulnerable population in the most vulnerable countries [ 23 ]. Second, the impact of climate change-induced extreme weather events tends to be more severe for women than men [ 24 ]. This results from a complex interaction of biological and socioeconomic factors. The increasingly frequent extreme weather events of the past two decades, such as floods, storms, volcanic eruptions, heatwaves, and droughts, have resulted in socioeconomic instability, breakdowns in safety and law enforcement, and political unrest or even armed conflicts. These, in turn, have increase gender-based violence and sexual exploitation, particularly in the context of forced migration [ 23 ]. In addition, women are more likely to skip meals as they are often last in household food hierarchies, thus being more exposed to the impact of food scarcity. Gender inequality thus compounds the impact of extreme weather events by further increasing women’s vulnerability and disadvantage.
Implications for climate policy
Women account for about 50% of the world’s population and hence, from a purely numerical perspective, by excluding women from the workforce and participation in society, politics, and the labour market countries lose substantial human resources. This curtails their ability to respond to the challenges posed by climate change and protect lives and livelihoods, especially in resource-poor settings. Furthermore, women’s contribution to society as well as political and economic systems has wide benefits. For instance, women in positions of authority tend to resolve crises without resorting to violence [ 25 ]. Women’s involvement in politics is crucial to assuage tensions that may be precipitated, for instance, by food and water scarcity and vector-borne diseases. Women leaders are also more likely than men to consider and address social injustice and inequalities, which are exacerbated by climate change [ 10 ]. Greater representation of women in parliaments and governments increases commitment to sustainability and climate change action [ 13 ]. Therefore, fair involvement of women at all levels of societal life, including particularly in leadership positions, is crucial to ensure that countries successfully and equitably adapt to climate change.
Notwithstanding the evidence supporting the importance of involving women in climate adaptation worldwide, women still experience barriers to engaging with climate adaptation, such as gender bias and discrimination, lack of access to financing and education, or gendered roles and responsibilities in the household, community and labour markets [ 15 , 26 ]. For instance, the relocation of communities affected by raising sea levels in the Fiji islands compelling illustrates how failure to involve women in decision making can compromise climate adaptation [ 27 ]. Women reported that men decided they had to relocate and the women had to agree without even being consulted. Their testimonies demonstrated how climate change is exacerbating gender inequalities by perpetuating gendered cultural and societal norms, which often exclude women from decision making [ 28 ]. This precludes their full engagement in the response to climate change at local and international levels.
In general, gender equality in leadership enhances the diversity of perspectives, which then leads to more fact-based and, therefore, higher-quality decision-making. There is also compelling evidence that gender equality drives economic prosperity [ 29 ]. For instance, the losses to an economy from economic disempowerment of women are estimated to range from 10% of gross domestic product in advanced economies to more than 30% in South Asia and in the Middle East and North Africa [ 30 ]. Our study lends further support to the importance of women’s empowerment in politics and economy as these domains of the GGGI were strongly associated with climate adaptation, particularly readiness. However, education was the domain with the strongest association with climate adaptation, perhaps because it is a quintessential condition for women’s empowerment. Gender equality in the economic and political domains will never happen until women have fair access to education. Although in 2020 more than two-thirds of countries worldwide had reached gender parity (defined as having a gender parity index value between 0.97 and 1.03) in enrolment in primary education, gender disparities disadvantaging girls in primary education persisted in Africa, the Middle East and South Asia [ 31 ]. For instance, 78 girls in Chad and 84 girls in Pakistan were enrolled in primary school for every 100 boys in 2020 [ 31 ]. Unless women’s rights are respected and gender inequalities eliminated, our ability to adapt to climate change will be in jeopardy and, sadly, the worst consequences will be faced by women [ 1 ].
For the past years of international climate change negotiations, governments worldwide have agreed that promoting gender equality and protecting women’s rights are crucial to meet global climate and development goals. This was formally recognised in the Gender Action Plan, which was approved at COP25 and subsequently reviewed in more recent COP meetings. The plan sets out objectives and activities that aim to “advance knowledge and understanding of gender-responsive climate action and promote women’s full, equal, and meaningful participation” in the UNFCCC process. Notwithstanding some initiatives to enhance women’s participation, from travel funds to mentorship networks, progress remains uneven and unacceptably slow [ 32 ]. After reaching a peak of almost 40% at the Conference of the Parties (COP) 24, women’s representation in country delegations has been in decline [ 32 ]. For instance, at COP27, women delegates accounted for 36% of all national Party delegates, which is better than the 35% at the previous year but lower than pre-pandemic COPs. Likewise, at COP27 women only encompassed 20% of Heads of Delegation, revealing an increase from COP26 (13%) but a decrease from previous COPs. In some countries, men accounted for 90% of the delegations. This means that the voices of women are not being heard commensurately with the impact of climate change on their lives at the most visible global arena. The dire representation of women at the negotiating table raises questions about the true commitment of the parties to address the gendered impact of climate change. In addition, lack of gender-disaggregated data prevents a comprehensive evaluation of the gendered consequences of climate change and the development of gender specific policy and interventions [ 23 ]. Without fair representation of women, and evidence on the gender-specific impact of climate change, the commitments of the Gender Action Plan will continue to be unmet. Unless longstanding gender inequalities across several domains of society are uprooted, effective climate mitigation and adaptation targets will not be achieved, hence threatening the lives and livelihoods of women and men alike.
Limitations
The robustness of the conclusions when using two different indices of gender equality, and the inclusion of the majority of the countries in the world, attest confidence to our findings. However, these findings need to be interpreted in light of methodological limitations. First, as an aetiological study, it is possible that the associations observed at country level do not reflect associations at a local level. Second, it is an observational, cross-sectional study and hence cannot prove causality. Third, data were not available for all countries in the world and including all countries could have changed some of the results. However, data were available for the majority of the countries, and it is unlikely that the overall associations would be changed substantially by adding a few countries. Fourth, although we used two differences indices, only moderately correlated, to measure gender equality, neither is exhaustive in its assessment of gender equality, for which there is no gold standard metric or index. It is possible, if unlikely, that including other dimensions would have changed the overall associations. To complement our research and address its limitations, further research is warranted to understand to what extent gender-sensitive policies and interventions contribute to climate adaptation in high- and low- and middle-income countries.
Gender inequality, measured broadly across different domains of life, is associated with lack of climate adaptation at country level, both in terms of vulnerability to impact and readiness to respond. Therefore, promoting gender equality and empowering women is critical for countries to adapt to the increasing threats posed by poorly mitigated climate change, which will fall disproportionately on women.
Availability of data and materials
All data are available on the GitHub repository https://github.com/Ana-Catarina/Climate-and-gender.git .
Sidun NM, Gibbons JL. Women, girls, and climate change: human rights, vulnerabilities, and opportunities. Int J Psychol. 2024;59(2):257–66.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Nnadi OI, Liwenga ET, Lyimo JG, Madukwe MC. Impacts of variability and change in rainfall on gender of farmers in Anambra, Southeast Nigeria. Heliyon. 2019;5(7):e02085.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Chersich MF, Wright CY, Venter F, Rees H, Scorgie F, Erasmus B. Impacts of Climate Change on Health and Wellbeing in South Africa. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2018; 15(9).
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Ballester J, Quijal-Zamorano M, Méndez Turrubiates RF, et al. Heat-related mortality in Europe during the summer of 2022. Nat Med. 2023;29(7):1857–66.
UN Women. Explainer: How gender inequality and climate change are interconnected. 2022. https://www.unwomen.org/en/news-stories/explainer/2022/02/explainer-how-gender-inequality-and-climate-change-are-interconnected . Accessed 25 June 2023.
Alcobé F, Harty E. Understanding the gender imbalance at the international climate negotiations. International Institute for Environment and Development. 2023. https://www.iied.org/understanding-gender-imbalance-international-climate-negotiations#:~:text=Barriers%20to%20women's%20participation%20include,frameworks%20and%20access%20to%20finance . Accessed 5 May 2024.
United Nations Climate Change. Introduction to Gender and Climate Change. 2023. https://unfccc.int/gender . Accessed 25 June 2023.
van Daalen KR, Kallesøe SS, Davey F, et al. Extreme events and gender-based violence: a mixed-methods systematic review. Lancet Planet Health. 2022;6(6):e504–23.
van Daalen KR, Dada S, Issa R, et al. A scoping review to assess sexual and Reproductive Health outcomes, challenges and recommendations in the Context of Climate Migration. Front Glob Womens Health. 2021;2:757153.
United Nations Climate Change. Five Reasons Why Climate Action Needs Women. 2023. https://unfccc.int/news/five-reasons-why-climate-action-needs-women . Accessed 25 June 2023.
GenderCC Southern Africa. Our Work: Women for Climate Justice Southern Africa. 2022. https://gendercc.org.za/our-work/ .
Nadeem M, Bahadar S, Gull AA, Iqbal U. Are women eco-friendly? Board gender diversity and environmental innovation. Bus Strategy Environ. 2020;29(8):3146–61.
Article Google Scholar
Wedeman N, Petruney T. Invest in girls and women to tackle climate change and conserve the environment. Deliver for Good, New York 2018.
Google Scholar
Alqahtani T. Barriers to women’s leadership. Granite Journal: Postgrad Interdisciplinary J. 2019;3(2):34–41.
Schwanke D-A. Barriers for women to positions of power: how societal and corporate structures, perceptions of leadership and discrimination restrict women’s advancement to authority. Earth Common J. 2013; 3(2). https://journals.macewan.ca/earthcommon/article/view/125 .
Global Gender Gap Report2021. https://www3.weforum.org/docs/WEF_GGGR_2021.pdf . Accessed 17 Apr 2022.
Seth S. A class of association sensitive multidimensional welfare indices: Oxford Poverty & Human Development Initiative (OPHI); 2009. UK: University of Oxford. https://ophi.org.uk/publications/WP-27 .
United Nations Development Programme. Gender inequality index. https://hdr.undp.org/data-center/thematic-composite-indices/gender-inequality-index#/indicies/GII . Accessed 11 June 2023.
Notre Dame University. Notre Dame Global Adaptation Initiative - Indicators. https://gain.nd.edu/our-work/country-index/methodology/indicators/ . Accessed 4 June 2023.
The World Bank. The world by region. 2017. https://datatopics.worldbank.org/sdgatlas/archive/2017/the-world-by-region.html . Accessed 11 June 2023.
Santos Silva M, Klasen S. Gender inequality as a barrier to economic growth: a review of the theoretical literature. Rev Econ Househ. 2021;19(3):581–614.
Wade K, Jennings M. The impact of climate change on the global economy. London: Schroders Talk Point; 2016.
United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change. Dimensions and examples of the gender-differentiated impacts of climate change, the role of women as agents of change and opportunities for women. 2022. https://unfccc.int/sites/default/files/resource/sbi2022_07.pdf . Accessed 25 June 2023.
Sorensen C, Murray V, Lemery J, Balbus J. Climate change and women’s health: impacts and policy directions. PLoS Med. 2018;15(7):e1002603.
Council on Foreign Relations. Women’s participation in peace processes. 2023. https://www.cfr.org/womens-participation-in-peace-processes/ . Accessed 25 June 2023.
Women U. Women, gender equality and climate change. UN WOMEN; 2009. https://www.un.org/womenwatch/feature/climate_change/downloads/Women_and_Climate_Change_Factsheet.pdf .
Piggott-McKellar AE, McNamara KE, Nunn PD, Sekinini ST. Moving people in a changing climate: lessons from two Case studies in Fiji. Social Sci. 2019;8(5):133.
Singh-Peterson L, Iranacolaivalu M. Barriers to market for subsistence farmers in Fiji – A gendered perspective. J Rural Stud. 2018;60:11–20.
Gopinath G. Gender Equality Boosts Economic Growth and Stability. International Monetary Fund, 2022. https://www.imf.org/en/News/Articles/2022/09/27/sp092722-ggopinath-kgef-gender-korea#:~:text=Gender%20equality%20goes%20hand%2Din,performance%2C%20and%20reduce%20income%20inequality . Accessed 25 June 2023.
Kochhar MK, Jain-Chandra MS, Newiak MM. Women, work, and economic growth: leveling the playing field. Washington: International Monetary Fund; 2017.
Gender and education. United Nations Children's Fund. 2020. https://data.unicef.org/topic/gender/gender-disparities-in-education/ . Accessed 28 May 2022.
Women’s Environment and Development Organization (WEDO). Women’s Participation in the UNFCCC: 2022 Report2022. https://wedo.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/06/WEDO_ParticipationNumbersBrief_2022.pdf . Accessed 24 June 2023.
Download references
Acknowledgements
ACPG is funded by an Academic Clinical Lectureship by the National Institute for Health Research. MW is supported by the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia grant APP1174120. The funders had no influence in this study.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
The George Institute for Global Health, Imperial College London, Scale Space, 58 Wood Lane, London, W12 7RZ, UK
Ana-Catarina Pinho-Gomes & Mark Woodward
Institute for Global Health, University College London, London, UK
Ana-Catarina Pinho-Gomes
The George Institute for Global Health, University of New South Wales, Sydney, Australia
Mark Woodward
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
ACPG and MW designed this study. ACPG extracted and analysed the data and drafted the manuscript. MW critically reviewed and edited the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Ana-Catarina Pinho-Gomes .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
This study did not require ethics approval, as it does not involve human or animal participants and all the data are publicly available.
Consent for publication
All the authors consent for publication of this manuscript.
Competing interests
MW has been a consultant for Amgen and Freeline. ACPG has no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Supplementary material 1., rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Pinho-Gomes, AC., Woodward, M. The association between gender equality and climate adaptation across the globe. BMC Public Health 24 , 1394 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-024-18880-5
Download citation
Received : 14 July 2023
Accepted : 17 May 2024
Published : 24 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-024-18880-5
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Gender inequalities
- Climate change
- Climate adaptation
BMC Public Health
ISSN: 1471-2458
- General enquiries: [email protected]
- CBSE Notes For Class 7
- CBSE Class 7 Science Notes
- Chapter 7: Weather Climate And Adaptations Of Animals To Climate
Weather, Climate and Adaptations of Animals to Climate Class 7 Science Notes - Chapter 7
According to the CBSE Syllabus 2023-24, this chapter has been removed from NCERT Class 7 Science textbook .
The atmospheric condition of a place on a daily basis with regards to aspects such as – humidity, the temperature, wind-temperature, rainfall, wind speed, etc., is referred to as the weather of that place.
- The place’s humidity, temperature, and other factors are known as the elements of the weather.
To know more about Weather, visit here .
Fronts and Weather Conditions
Weather is produced by the interaction of several factors that, include:
- temperature or heat
- humidity or amount of water vapour in the air
- wind and atmospheric pressure.
- precipitation or the amount of rain
- cloudiness or the amount of cloud cover
- visibility that is how far you can look into the horizon
- Wind and an atmospheric pressure
A weather front is a boundary separating two masses of air of different densities.
- The air masses separated by a front usually differ in temperature and humidity.
- The weather analysis usually includes information about the weather fronts also.
- The average pattern of the weather recorded over a long time, say 25 years, is known as the climate of the place.
- If the temperature at a place is high mostly, then we affirm that the climate of that place is hot.
- If, on most days, there is heavy rainfall in the same place, then we affirm that the climate of that place is wet and hot.
Factors Affecting Climate
- Different factors affect climates, such as altitude, latitude, geography and topography.
To know more about “Factors Affecting Climate”, visit here .
Weather vs Climate
- Meteorologists record the weather every day.
- The records of the weather have been preserved for the past several decades.
- These help us to determine the weather pattern at a place.
- The average of the weather pattern over a time period is determined by the climate.
To know more about the “Difference Between Weather and Climate”, visit here .
Meteorology and Climatology
- The major focus in meteorology is weather forecasting.
- The daily weather reports are prepared by the Meteorological Department of the Government.
- This department collects data on temperature, wind, etc., and makes the weather prediction.
- Climatology is the study of climate, defined as weather conditions averaged over a period of time.
Formation and Types of Clouds
- Clouds form occurs via a phenomenon known as convection.
- As sun rays heat the ground and the immediate air over it, the warm air tends to become lighter, which is carried away along with the warm air upwards. As the air rises higher, the temperature falls, causing the amount of water vapour that the air can hold to decrease.
- This vapour condenses rapidly, and soon clouds — made up of billions of minuscule water droplets or ice crystals — result.
- Air that blows over mountains or hills is expelled upwards, leading to the development of clouds. Precipitation and clouds are often found on the windward side of a mountain.
To know more about Cloud Formation, visit here .
- Rainfall is measured by an instrument called the rain gauge.
- It is basically a measuring cylinder with a funnel on top to collect rainwater.
To know more about Rain Gauge, visit here .
Thunderstorm

To know more about Thunderstorms and Lightning, visit here .
The Polar Regions
- The polar regions manifest an extremely cold climate.
- For most of the year, these areas are extremely cold, covered in snow
- Sun does not set for six months, and once it is set, it does not rise for six months.
- The temperature in winter can go as low as −37∘C.
- The north polar region is the Arctic region, while the south polar region is the Antarctic region.
- Animals living at both these poles have adjusted to these harsh conditions.
The Tropical Rainforests
- The tropical region generally has a hot climate because of its location around the equator.
- In winter, the temperatures are above 15∘C and during summers, it may cross even 40∘C.
- The climatic conditions in rainforests are highly suitable for supporting an enormous number and variety of animals and plants.
The Temperate Grasslands
- Temperate grasslands are located north of the Tropic of Cancer (23.5 degrees North) and south of the Tropic of Capricorn (23.5 degrees South).
- The major temperate grasslands include the veldts of Africa, the pampas of South America, the steppes of Eurasia, and the plains of North America.
Animal Adaptation
- Based on different climatic conditions, animals adapt or evolve to survive in these conditions.
- For example, Polar regions – Polar bears have white fur and hence are not visible easily in the snowy white background.
- It safeguards them from their predators.
- Also beneficial for them to catch their prey.
- They are naturally provided with two thick layers of fur to shield them from extreme cold.
- Also, they possess a layer of fat under their skin.
For more information on Adaptation and Habitats for Animals, watch the below video

To know more about Adaptation and Habitats, visit here .
Frequently Asked Questions on CBSE Class 7 Science Notes Chapter 7 Weather Climate and Adaptation of Animals to Climate
What are the animals found in the polar regions.
1. Polar Bear.2. Whale.3. Arctic Fox.4. Arctic Wolf.5. Pacific Salmon.6. Brown Bear.
How can we save this climate change situation?
1. Avoid over usage of natural resources 2. Do not use or buy items made from animals 3. Avoid plastic usage and pollution
Are there any natural causes for climate change?
Yes, some of the natural causes of climate change are: 1. Solar variations 2. Volcanic eruption and tsunamis 3. Earth’s orbital changes
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

COMMENTS
CBSE Case Study Questions Class 7 Science Weather, Climate and Adaptations of Animals to Climate Case study 1. All changes in the weather are caused by the sun. The sun is a huge sphere of. hot gases at a very high temperature. The distance of the sun from us is very. large.
Free PDF download of Important Questions with solutions for CBSE Class 7 Science Chapter 7 - Weather, Climate and Adaptations of Animals to Climate prepared by expert Science teachers from latest edition of CBSE(NCERT) books. Register online for Science tuition on Vedantu.com to score more marks in your examination.
Weather, Climate and Adaptations of Animals to Climate Class 7 Science Extra Questions Short Answer Type Questions. Question 1. The polar bear are white in colour. Explain why. Answer: Polar bear have white fur. This is an adaptation of polar bear to blend it with the white background of ice or snow.
Extra questions for Class 7 Science Chapter 7 Weather, Climate And Adaptations of Animals To Climate with answers is given below. Our subject expert prepared these solutions as per the latest NCERT textbook. These questions will be helpful to revise the all topics and concepts. CBSE Class 7 extra questions are the most simple and conceptual ...
It helps you understand the importance of weather, climate and adaptation to different climates in our day-to-day life. Topics Covered in NCERT Exemplar Solution for Chapter 7 Weather, Climate and Adaptation of Animals to Climate. 7.1 - Weather. 7.2 - Climate. 7.3 - Climate and Adaptation
Free PDF download of NCERT Exemplar for Class 7 Science Chapter 7 Weather, Climate and Adaptation of Animals to Climate solved by Expert Teachers as per NCERT CBSE Book guidelines. All Chapter wise Questions with Solutions of Class 7 to help you to revise complete Syllabus and Score More marks in your examinations.
Chapter 7 "Weather, Climate and Adaptations of Animals to climate" of Class 7 Science has a total of 12 questions. These 12 questions are divided into four short questions and eight long questions. Also, this chapter includes the topic "Projects and Activities " which has two questions.
Class VI science book the definition of adaptation. Features and habits that help animals to adapt to their surroundings are a result of the process of evolution. In Chapter 9 you will learn about the effect of weather and climate on soil. Here we will study the effect of climate on animals only. In Class VI, you have read about adaptations of ...
There are 12 questions in Chapter 7 of Class 7 Science, "Weather, Climate, and Animal Adaptations.". There are a total of 12 questions, in total, from which there are four short questions and eight long questions. This chapter also contains two questions on "Projects and Activities.".
Class 7 NCERT Solutions for Science Chapter 7 includes all the intext and exercise questions. All these questions are solved by experts with a detailed explanation that will help students complete their assignments and homework. Question 1: Name the elements that determine the weather of a place. Answer: Temperature, humidity, rainfall, wind ...
Using NCERT Science Class 7 solutions Weather, Climate and Adaptations of Animals to Climate exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in NCERT Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam.
Q.1.Name the elements that determine the weather of a place. Ans.The temperature, humidity, rainfall, wind-speed, etc. are called the elements that determine the weather of a place.
Free Question Bank for 7th Class Science Weather, Climate and Adaptation of Animals to Climate Weather, Climate and Adaptation of Animals to Climate. Customer Care : 6267349244. Toggle navigation 0 . 0 ... Study Packages Question Bank Online Test Solved Papers Clat;
Weather Climate and Adaptation Class 7 Notes is mainly about the weather, climate. Further, it is also about how different forms of living organisms adapt themselves to the climate of their own habitat. Moreover, people can know about day to day weather forecasting reports from the newspapers, news channels, the internet, etc.
Class 7 Science Chapter 7 Notes provided by Extramarks provide comprehensive study material to students preparing for the exams. In this chapter, students will learn the concepts of weather and climate, their differences, their effects on migration and adaptation of birds and animals, and finally the Important Questions at the end.. Class 7 Science Chapter 7 Notes notes are prepared by subject ...
Free Question Bank for 7th Class Science Weather, Climate and Adaptation of Animals to Climate. Customer Care : 6267349244. Toggle navigation 0 . 0 . Railways; UPSC; CET; Banking; CUET; SSC; ... Study Packages Question Bank Online Test Rajasthan State Exams ; Videos Sample Papers Study Packages Question Bank Online Test
Students should also practice a lot of questions from CBSE Class 7 Science Question Papers and score good marks in the examinations. CBSE Class 7 Science Weather, Climate and Adaptations of Animals to Climate worksheets are very helpful for students who want to score good marks in their CBSE Board Examination.
All Exercises are Covered: In the NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 7 Weather, Climate and Adaptations of Animals of Climate theory, all the exercises are covered so that students can find different ways to attempt different questions. Diagrams are Included: Diagrams are considered to be graphical representation of the Chapter 7 ...
Access answers to NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 7 - Weather, Climate and Adaptations of Animals to Climate. Class 7 Science Chapter 7 Exercise Questions . 1. Name the elements that determine the weather of a place. Solution: Temperature, humidity, rainfall and wind are the elements that determine the weather of a place. 2.
Class 7 Weather Climate and Adaptations of Animals to Climate MCQ with Answers Online. For the ease of students, the subject experts have simplified the practice process of the class 7 Weather Climate and Adaptations of Animals to Climate MCQ as they have solved each and every question given. The answers are detailed and easy to grasp.
Weather Climate And Adaptation Of Animals To Climate The World of Quizizz is the best tool for teachers who want to teach option based, real-world and stimulating science curriculum. Teachers can now create their own quizzes from a variety of topics including Pollution Control, Weather and Climate, Health Science, Geography and much more!
Climate change has a disproportionate impact on women in comparison to men, and women have a key role to play in climate adaptation. However, evidence is lacking on how gender inequalities may be associated with climate vulnerability and ability to respond at country level. This ecological study investigated the association between climate adaptation, measured by the Notre Dame Global ...
Chapter - 7 - Weather, Climate and Adaptations to Climate Weather is the day-to-day state of the atmosphere at a location, which is influenced by factors such as humidity, temperature, wind speed, and so on. Humidity: A hygrometer is used to measure the amount of water vapour present in the atmosphere. Climate refers to the average weather ...
Weather of a place is defined as the daily condition of the atmosphere of a particular place concerning humidity, wind-speed, temperature, rainfall, etc. Download PDF of Weather, Climate and Adaptations of Animals to Climate Class 7 Science Notes on BYJU'S.