- Open access
- Published: 20 June 2023

A qualitative quantitative mixed methods study of domestic violence against women
- Mina Shayestefar 1 ,
- Mohadese Saffari 1 ,
- Razieh Gholamhosseinzadeh 2 ,
- Monir Nobahar 3 , 4 ,
- Majid Mirmohammadkhani 4 ,
- Seyed Hossein Shahcheragh 5 &
- Zahra Khosravi 6
BMC Women's Health volume 23 , Article number: 322 ( 2023 ) Cite this article
8906 Accesses
1 Altmetric
Metrics details
Violence against women is one of the most widespread, persistent and detrimental violations of human rights in today’s world, which has not been reported in most cases due to impunity, silence, stigma and shame, even in the age of social communication. Domestic violence against women harms individuals, families, and society. The objective of this study was to investigate the prevalence and experiences of domestic violence against women in Semnan.
This study was conducted as mixed research (cross-sectional descriptive and phenomenological qualitative methods) to investigate domestic violence against women, and some related factors (quantitative) and experiences of such violence (qualitative) simultaneously in Semnan. In quantitative study, cluster sampling was conducted based on the areas covered by health centers from married women living in Semnan since March 2021 to March 2022 using Domestic Violence Questionnaire. Then, the obtained data were analyzed by descriptive and inferential statistics. In qualitative study by phenomenological approach and purposive sampling until data saturation, 9 women were selected who had referred to the counseling units of Semnan health centers due to domestic violence, since March 2021 to March 2022 and in-depth and semi-structured interviews were conducted. The conducted interviews were analyzed using Colaizzi’s 7-step method.
In qualitative study, seven themes were found including “Facilitators”, “Role failure”, “Repressors”, “Efforts to preserve the family”, “Inappropriate solving of family conflicts”, “Consequences”, and “Inefficient supportive systems”. In quantitative study, the variables of age, age difference and number of years of marriage had a positive and significant relationship, and the variable of the number of children had a negative and significant relationship with the total score and all fields of the questionnaire (p < 0.05). Also, increasing the level of female education and income both independently showed a significant relationship with increasing the score of violence.
Conclusions
Some of the variables of violence against women are known and the need for prevention and plans to take action before their occurrence is well felt. Also, supportive mechanisms with objective and taboo-breaking results should be implemented to minimize harm to women, and their children and families seriously.
Peer Review reports
Violence against women by husbands (physical, sexual and psychological violence) is one of the basic problems of public health and violation of women’s human rights. It is estimated that 35% of women and almost one out of every three women aged 15–49 experience physical or sexual violence by their spouse or non-spouse sexual violence in their lifetime [ 1 ]. This is a nationwide public health issue, and nearly every healthcare worker will encounter a patient who has suffered from some type of domestic or family violence. Unfortunately, different forms of family violence are often interconnected. The “cycle of abuse” frequently persists from children who witness it to their adult relationships, and ultimately to the care of the elderly [ 2 ]. This violence includes a range of physical, sexual and psychological actions, control, threats, aggression, abuse, and rape [ 3 ].
Violence against women is one of the most widespread, persistent, and detrimental violations of human rights in today’s world, which has not been reported in most cases due to impunity, silence, stigma and shame, even in the age of social communication [ 3 ]. In the United States of America, more than one in three women (35.6%) experience rape, physical violence, and intimate partner violence (IPV) during their lifetime. Compared to men, women are nearly twice as likely (13.8% vs. 24.3%) to experience severe physical violence such as choking, burns, and threats with knives or guns [ 4 ]. The higher prevalence of violence against women can be due to the situational deprivation of women in patriarchal societies [ 5 ]. The prevalence of domestic violence in Iran reported 22.9%. The maximum of prevalence estimated in Tehran and Zahedan, respectively [ 6 ]. Currently, Iran has high levels of violence against women, and the provinces with the highest rates of unemployment and poverty also have the highest levels of violence against women [ 7 ].
Domestic violence against women harms individuals, families, and society [ 8 ]. Violence against women leads to physical, sexual, psychological harm or suffering, including threats, coercion and arbitrary deprivation of their freedom in public and private life. Also, such violence is associated with harmful effects on women’s sexual reproductive health, including sexually transmitted infection such as Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV), abortion, unsafe childbirth, and risky sexual behaviors [ 9 ]. There are high levels of psychological, sexual and physical domestic abuse among pregnant women [ 10 ]. Also, women with postpartum depression are significantly more likely to experience domestic violence during pregnancy [ 11 ].
Prompt attention to women’s health and rights at all levels is necessary, which reduces this problem and its risk factors [ 12 ]. Because women prefer to remain silent about domestic violence and there is a need to introduce immediate prevention programs to end domestic violence [ 13 ]. violence against women, which is an important public health problem, and concerns about human rights require careful study and the application of appropriate policies [ 14 ]. Also, the efforts to change the circumstances in which women face domestic violence remain significantly insufficient [ 15 ]. Given that few clear studies on violence against women and at the same time interviews with these people regarding their life experiences are available, the authors attempted to planning this research aims to investigate the prevalence and experiences of domestic violence against women in Semnan with the research question of “What is the prevalence of domestic violence against women in Semnan, and what are their experiences of such violence?”, so that their results can be used in part of the future planning in the health system of the society.
This study is a combination of cross-sectional and phenomenology studies in order to investigate the amount of domestic violence against women and some related factors (quantitative) and their experience of this violence (qualitative) simultaneously in the Semnan city. This study has been approved by the ethics committee of Semnan University of Medical Sciences with ethic code of IR.SEMUMS.REC.1397.182. The researcher introduced herself to the research participants, explained the purpose of the study, and then obtained informed written consent. It was assured to the research units that the collected information will be anonymous and kept confidential. The participants were informed that participation in the study was entirely voluntary, so they can withdraw from the study at any time with confidence. The participants were notified that more than one interview session may be necessary. To increase the trustworthiness of the study, Guba and Lincoln’s criteria for rigor, including credibility, transferability, dependability, and confirmability [ 16 ], were applied throughout the research process. The COREQ checklist was used to assess the present study quality. The researchers used observational notes for reflexivity and it preserved in all phases of this qualitative research process.
Qualitative method
Based on the phenomenological approach and with the purposeful sampling method, nine women who had referred to the counseling units of healthcare centers in Semnan city due to domestic violence in February 2021 to March 2022 were participated in the present study. The inclusion criteria for the study included marriage, a history of visiting a health center consultant due to domestic violence, and consent to participate in the study and unwillingness to participate in the study was the exclusion criteria. Each participant invited to the study by a telephone conversation about study aims and researcher information. The interviews place selected through agreement of the participant and the researcher and a place with the least environmental disturbance. Before starting each interview, the informed consent and all of the ethical considerations, including the purpose of the research, voluntary participation, confidentiality of the information were completely explained and they were asked to sign the written consent form. The participants were interviewed by depth, semi-structured and face-to-face interviews based on the main research question. Interviews were conducted by a female health services researcher with a background in nursing (M.Sh.). Data collection was continued until the data saturation and no new data appeared. Only the participants and the researcher were present during the interviews. All interviews were recorded by a MP3 Player by permission of the participants before starting. Interviews were not repeated. No additional field notes were taken during or after the interview.
The age range of the participants was from 38 to 55 years and their average age was 40 years. The sociodemographic characteristics of the participants are summarized in table below (Table 1 ).
Five interviews in the courtyards of healthcare centers, 2 interviews in the park, and 2 interviews at the participants’ homes were conducted. The duration of the interviews varied from 45 min to one hour. The main research question was “What is your experience about domestic violence?“. According to the research progress some other questions were asked in line with the main question of the research.
The conducted interviews were analyzed by using the 7 steps Colizzi’s method [ 17 ]. In order to empathize with the participants, each interview was read several times and transcribed. Then two researchers (M.Sh. and M.N.) extracted the phrases that were directly related to the phenomenon of domestic violence against women independently and distinguished from other sentences by underlining them. Then these codes were organized into thematic clusters and the formulated concepts were sorted into specific thematic categories.
In the final stage, in order to make the data reliable, the researcher again referred to 2 participants and checked their agreement with their perceptions of the content. Also, possible important contents were discussed and clarified, and in this way, agreement and approval of the samples was obtained.
Quantitative method
The cross-sectional study was implemented from February 2021 to March 2022 with cluster sampling of married women in areas of 3 healthcare centers in Semnan city. Those participants who were married and agreed with the written and verbal informed consent about the ethical considerations were included to the study. The questionnaire was completed by the participants in paper and online form.
The instrument was the standard questionnaire of domestic violence against women by Mohseni Tabrizi et al. [ 18 ]. In the questionnaire, questions 1–10, 11–36, 37–65 and 66–71 related to sociodemographic information, types of spousal abuse (psychological, economical, physical and sexual violence), patriarchal beliefs and traditions and family upbringing and learning violence, respectively. In total, this questionnaire has 71 items.
The scoring of the questionnaire has two parts and the answers to them are based on the Likert scale. Questions 11–36 and 66–71 are answered with always [ 4 ] to never (0) and questions 37–65 with completely agree [ 4 ] to completely disagree (0). The minimum and maximum score is 0 and 300, respectively. The total score of 0–60, 61–120 and higher than 121 demonstrates low, moderate and severe domestic violence against women, respectively [ 18 ].
In the study by Tabrizi et al., to evaluate the validity and reliability of this questionnaire, researchers tried to measure the face validity of the scale by the previous research. Those items and questions which their accuracies were confirmed by social science professors and experts used in the research, finally. The total Cronbach’s alpha coefficient was 0.183, which confirmed that the reliability of the questions and items of the questionnaire is sufficient [ 18 ].
Descriptive data were reported using mean, standard deviation, frequency and percentage. Then, to measure the relationship between the variables, χ2 and Pearson tests also variance and regression analysis were performed. All analysis were performed by using SPSS version 26 and the significance level was considered as p < 0.05.
Qualitative results
According to the third step of Colaizzi’s 7-step method, the researcher attempted to conceptualize and formulate the extracted meanings. In this step, the primary codes were extracted from the important sentences related to the phenomenon of violence against women, which were marked by underlining, which are shown below as examples of this stage and coding.
The primary code of indifference to the father’s role was extracted from the following sentences. This is indifference in the role of the father in front of the children.
“Some time ago, I told him that our daughter is single-sided deaf. She has a doctor’s appointment; I have to take her to the doctor. He said that I don’t have money to give you. He doesn’t force himself to make money anyway” (p 2, 33 yrs).
“He didn’t value his own children. He didn’t think about his older children” (p 4, 54 yrs).
The primary code extracted here included lack of commitment in the role of head of the household. This is irresponsibility towards the family and meeting their needs.
“My husband was fired from work after 10 years due to disorder and laziness. Since then, he has not found a suitable job. Every time he went to work, he was fired after a month because of laziness” (p 7, 55 yrs).
“In the evening, he used to get dressed and go out, and he didn’t come back until late. Some nights, I was so afraid of being alone that I put a knife under my pillow when I slept” (p 2, 33 yrs).
A total of 246 primary codes were extracted from the interviews in the third step. In the fourth step, the researchers put the formulated concepts (primary codes) into 85 specific sub-categories.
Twenty-three categories were extracted from 85 sub-categories. In the sixth step, the concepts of the fifth step were integrated and formed seven themes (Table 2 ).
These themes included “Facilitators”, “Role failure”, “Repressors”, “Efforts to preserve the family”, “Inappropriate solving of family conflicts”, “Consequences”, and “Inefficient supportive systems” (Fig. 1 ).
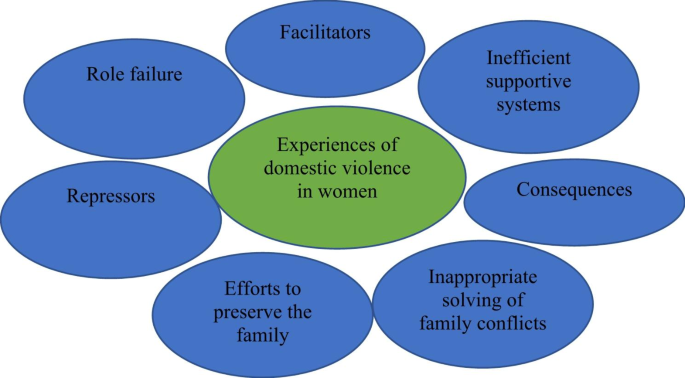
Themes of domestic violence against women
Some of the statements of the participants on the theme of “ Facilitators” are listed below:
Husband’s criminal record
“He got his death sentence for drugs. But, at last it was ended for 10 years” (p 4, 54 yrs).
Inappropriate age for marriage
“At the age of thirteen, I married a boy who was 25 years old” (p 8, 25 yrs).
“My first husband obeyed her parents. I was 12–13 years old” (p 3, 32 yrs).
“I couldn’t do anything. I was humiliated” (p 1, 38 yrs).
“A bridegroom came. The mother was against. She said, I am young. My older sister is not married yet, but I was eager to get married. I don’t know, maybe my father’s house was boring for me” (p 2, 33 yrs).
“My parents used to argue badly. They blamed each other and I always wanted to run away from these arguments. I didn’t have the patience to talk to mom or dad and calm them down” (p 5, 39 yrs).
Overdependence
“My husband’s parents don’t stop interfering, but my husband doesn’t say anything because he is a student of his father. My husband is self-employed and works with his father on a truck” (p 8, 25 yrs).
“Every time I argue with my husband because of lack of money, my mother-in-law supported her son and brought him up very spoiled and lazy” (p 7, 55 yrs).
Bitter memories
“After three years, my mother married her friend with my uncle’s insistence and went to Shiraz. But, his condition was that she did not have the right to bring his daughter with her. In fact, my mother also got married out of necessity” (p 8, 25 yrs).
Some of their other statements related to “ Role failure” are mentioned below:
Lack of commitment to different roles
“I got angry several times and went to my father’s house because of my husband’s bad financial status and the fact that he doesn’t feel responsible to work and always says that he cannot find a job” (p 6, 48 yrs).
“I saw that he does not want to change in any way” (p 4, 54 yrs).
“No matter how kind I am, it does not work” (p 1, 38 yrs).
Some of their other statements regarding “ Repressors” are listed below:
Fear and silence
“My mother always forced me to continue living with my husband. Finally, my father had been poor. She all said that you didn’t listen to me when you wanted to get married, so you don’t have the right to get angry and come to me, I’m miserable enough” (p 2, 33 yrs).
“Because I suffered a lot in my first marital life. I was very humiliated. I said I would be fine with that. To be kind” (p1, 38 yrs).
“Well, I tell myself that he gets angry sometimes” (p 3, 32 yrs).
Shame from society
“I don’t want my daughter-in-law to know. She is not a relative” (p 4, 54 yrs).
Some of the statements of the participants regarding the theme of “ Efforts to preserve the family” are listed below:
Hope and trust
“I always hope in God and I am patient” (p 2, 33 yrs).
Efforts for children
“My divorce took a month. We got a divorce. I forgave my dowry and took my children instead” (p 2, 33 yrs).
Some of their other statements regarding the “ Inappropriate solving of family conflicts” are listed below:
Child-bearing thoughts
“My husband wanted to take me to a doctor to treat me. But my father-in-law refused and said that instead of doing this and spending money, marry again. Marriage in the clans was much easier than any other work” (p 8, 25 yrs).
Lack of effective communication
“I was nervous about him, but I didn’t say anything” (p 5, 39 yrs).
“Now I am satisfied with my life and thank God it is better to listen to people’s words. Now there is someone above me so that people don’t talk behind me” (p 2, 33 yrs).
Some of their other statements regarding the “ Consequences” are listed below:
Harm to children
“My eldest daughter, who was about 7–8 years old, behaved differently. Oh, I was angry. My children are mentally depressed and argue” (p 5, 39 yrs).
After divorce
“Even though I got a divorce, my mother and I came to a remote area due to the fear of what my family would say” (p 2, 33 yrs).
Social harm
“I work at a retirement center for living expenses” (p 2, 33 yrs).
“I had to go to clean the houses” (p 5, 39 yrs).
Non-acceptance in the family
“The children’s relationship with their father became bad. Because every time they saw their father sitting at home smoking, they got angry” (p 7, 55 yrs).
Emotional harm
“When I look back, I regret why I was not careful in my choice” (p 7, 55 yrs).
“I felt very bad. For being married to a man who is not bound by the family and is capricious” (p 9, 36 yrs).
Some of their other statements regarding “ Inefficient supportive systems” are listed below:
Inappropriate family support
“We didn’t have children. I was at my father’s house for about a month. After a month, when I came home, I saw that my husband had married again. I cried a lot that day. He said, God, I had to. I love you. My heart is broken, I have no one to share my words” (p 8, 25 yrs).
“My brother-in-law was like himself. His parents had also died. His sister did not listen at all” (p 4, 54 yrs).
“I didn’t have anyone and I was alone” (p 1, 38 yrs).
Inefficiency of social systems
“That day he argued with me, picked me up and threw me down some stairs in the middle of the yard. He came closer, sat on my stomach, grabbed my neck with both of his hands and wanted to strangle me. Until a long time later, I had kidney problems and my neck was bruised by her hand. Given that my aunt and her family were with us in a building, but she had no desire to testify and was afraid” (p 3, 32 yrs).
Undesired training and advice
“I told my mother, you just said no, how old I was? You never insisted on me and you didn’t listen to me that this man is not good for you” (p 9, 36 yrs).
Quantitative results
In the present study, 376 married women living in Semnan city participated in this study. The mean age of participants was 38.52 ± 10.38 years. The youngest participant was 18 and the oldest was 73 years old. The maximum age difference was 16 years. The years of marriage varied from one year to 40 years. Also, the number of children varied from no children to 7. The majority of them had 2 children (109, 29%). The sociodemographic characteristics of the participants are summarized in the table below (Table 3 ).
The frequency distribution (number and percentage) of the participants in terms of the level of violence was as follows. 89 participants (23.7%) had experienced low violence, 59 participants (15.7%) had experienced moderate violence, and 228 participants (60.6%) had experienced severe violence.
Cronbach’s alpha for the reliability of the questionnaire was 0.988. The mean and standard deviation of the total score of the questionnaire was 143.60 ± 74.70 with a range of 3-244. The relationship between the total score of the questionnaire and its fields, and some demographic variables is summarized in the table below (Table 4 ).
As shown in the table above, the variables of age, age difference and number of years of marriage have a positive and significant relationship, and the variable of number of children has a negative and significant relationship with the total score and all fields of the questionnaire (p < 0.05). However, the variable of education level difference showed no significant relationship with the total score and any of the fields. Also, the highest average score is related to patriarchal beliefs compared to other fields.
The comparison of the average total scores separately according to each variable showed the significant average difference in the variables of the previous marriage history of the woman, the result of the previous marriage of the woman, the education of the woman, the education of the man, the income of the woman, the income of the man, and the physical disease of the man (p < 0.05).
In the regression model, two variables remained in the final model, indicating the relationship between the variables and violence score and the importance of these two variables. An increase in women’s education and income level both independently show a significant relationship with an increase in violence score (Table 5 ).
The results of analysis of variance to compare the scores of each field of violence in the subgroups of the participants also showed that the experience and result of the woman’s previous marriage has a significant relationship with physical violence and tradition and family upbringing, the experience of the man’s previous marriage has a significant relationship with patriarchal belief, the education level of the woman has a significant relationship with all fields and the level of education of the man has a significant relationship with all fields except tradition and family upbringing (p < 0.05).
According to the results of both quantitative and qualitative studies, variables such as the young age of the woman and a large age difference are very important factors leading to an increase in violence. At a younger age, girls are afraid of the stigma of society and family, and being forced to remain silent can lead to an increase in domestic violence. As Gandhi et al. (2021) stated in their study in the same field, a lower marriage age leads to many vulnerabilities in women. Early marriage is a global problem associated with a wide range of health and social consequences, including violence for adolescent girls and women [ 12 ]. Also, Ahmadi et al. (2017) found similar findings, reporting a significant association among IPV and women age ≤ 40 years [ 19 ].
Two others categories of “Facilitators” in the present study were “Husband’s criminal record” and “Overdependence” which had a sub-category of “Forced cohabitation”. Ahmadi et al. (2017) reported in their population-based study in Iran that husband’s addiction and rented-householders have a significant association with IPV [ 19 ].
The patriarchal beliefs, which are rooted in the tradition and culture of society and family upbringing, scored the highest in relation to domestic violence in this study. On the other hand, in qualitative study, “Normalcy” of men’s anger and harassment of women in society is one of the “Repressors” of women to express violence. In the quantitative study, the increase in the women’s education and income level were predictors of the increase in violence. Although domestic violence is more common in some sections of society, women with a wide range of ages, different levels of education, and at different levels of society face this problem, most of which are not reported. Bukuluki et al. (2021) showed that women who agreed that it is good for a man to control his partner were more likely to experience physical violence [ 20 ].
Domestic violence leads to “Consequences” such as “Harm to children”, “Emotional harm”, “Social harm” to women and even “Non-acceptance in their own family”. Because divorce is a taboo in Iranian culture and the fear of humiliating women forces them to remain silent against domestic violence. Balsarkar (2021) stated that the fear of violence can prevent women from continuing their studies, working or exercising their political rights [ 8 ]. Also, Walker-Descarte et al. (2021) recognized domestic violence as a type of child maltreatment, and these abusive behaviors are associated with mental and physical health consequences [ 21 ].
On the other hand and based on the “Lack of effective communication” category, ignoring the role of the counselor in solving family conflicts and challenges in the life of couples in the present study was expressed by women with reasons such as lack of knowledge and family resistance to counseling. Several pathologies are needed to investigate increased domestic violence in situations such as during women’s pregnancy or infertility. Because the use of counseling for couples as a suitable solution should be considered along with their life challenges. Lin et al. (2022) stated that pregnant women were exposed to domestic violence for low birth weight in full term delivery. Spouse violence screening in the perinatal health care system should be considered important, especially for women who have had full-term low birth weight infants [ 22 ].
Also, lack of knowledge and low level of education have been found as other factors of violence in this study, which is very prominent in both qualitative and quantitative studies. Because the social systems and information about the existing laws should be followed properly in society to act as a deterrent. Psychological training and especially anger control and resilience skills during education at a younger age for girls and boys should be included in educational materials to determine the positive results in society in the long term. Manouchehri et al. (2022) stated that it seems necessary to train men about the negative impact of domestic violence on the current and future status of the family [ 23 ]. Balsarkar (2021) also stated that men and women who have not had the opportunity to question gender roles, attitudes and beliefs cannot change such things. Women who are unaware of their rights cannot claim. Governments and organizations cannot adequately address these issues without access to standards, guidelines and tools [ 8 ]. Machado et al. (2021) also stated that gender socialization reinforces gender inequalities and affects the behavior of men and women. So, highlighting this problem in different fields, especially in primary health care services, is a way to prevent IPV against women [ 24 ].
There was a sub-category of “Inefficiency of social systems” in the participants experiences. Perhaps the reason for this is due to insufficient education and knowledge, or fear of seeking help. Holmes et al. (2022) suggested the importance of ascertaining strategies to improve victims’ experiences with the court, especially when victims’ requests are not met, to increase future engagement with the system [ 25 ]. Sigurdsson (2019) revealed that despite high prevalence numbers, IPV is still a hidden and underdiagnosed problem and neither general practitioner nor our communities are as well prepared as they should be [ 26 ]. Moreira and Pinto da Costa (2021) found that while victims of domestic violence often agree with mandatory reporting, various concerns are still expressed by both victims and healthcare professionals that require further attention and resolution [ 27 ]. It appears that legal and ethical issues in this regard require comprehensive evaluation from the perspectives of victims, their families, healthcare workers, and legal experts. By doing so, better practical solutions can be found to address domestic violence, leading to a downward trend in its occurrence.
Some of the variables of violence against women have been identified and emphasized in many studies, highlighting the necessity of policymaking and social pathology in society to prevent and use operational plans to take action before their occurrence. Breaking the taboo of domestic violence and promoting divorce as a viable solution after counseling to receive objective results should be implemented seriously to minimize harm to women, children, and their families.
Limitations
Domestic violence against women is an important issue in Iranian society that women resist showing and expressing, making researchers take a long-term process of sampling in both qualitative and quantitative studies. The location of the interview and the women’s fear of their husbands finding out about their participation in this study have been other challenges of the researchers, which, of course, they attempted to minimize by fully respecting ethical considerations. Despite the researchers’ efforts, their personal and professional experiences, as well as the studies reviewed in the literature review section, may have influenced the study results.

Data Availability
Data and materials will be available upon email to the corresponding author.
Abbreviations
Intimate Partner Violence
Human Immunodeficiency Virus
Organization WH. Violence against women prevalence estimates, 2018: global, regional and national prevalence estimates for intimate partner violence against women and global and regional prevalence estimates for non-partner sexual violence against women. World Health Organization; 2021.
Huecker MR, Malik A, King KC, Smock W. Kentucky Domestic Violence. StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL) ineligible companies. Disclosure: Ahmad Malik declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies. Disclosure: Kevin King declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies. Disclosure: William Smock declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies.: StatPearls Publishing Copyright © 2023, StatPearls Publishing LLC.; 2023.
Gandhi A, Bhojani P, Balkawade N, Goswami S, Kotecha Munde B, Chugh A. Analysis of survey on violence against women and early marriage: Gyneaecologists’ perspective. J Obstet Gynecol India. 2021;71(Suppl 2):76–83.
Article Google Scholar
Sugg N. Intimate partner violence: prevalence, health consequences, and intervention. Med Clin. 2015;99(3):629–49.
Google Scholar
Abebe Abate B, Admassu Wossen B, Tilahun Degfie T. Determinants of intimate partner violence during pregnancy among married women in Abay Chomen district, western Ethiopia: a community based cross sectional study. BMC Womens Health. 2016;16(1):1–8.
Adineh H, Almasi Z, Rad M, Zareban I, Moghaddam A. Prevalence of domestic violence against women in Iran: a systematic review. Epidemiol (Sunnyvale). 2016;6(276):2161–11651000276.
Pirnia B, Pirnia F, Pirnia K. Honour killings and violence against women in Iran during the COVID-19 pandemic. The Lancet Psychiatry. 2020;7(10):e60.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Balsarkar G. Summary of four recent studies on violence against women which obstetrician and gynaecologists should know. J Obstet Gynecol India. 2021;71:64–7.
Ellsberg M, Jansen HA, Heise L, Watts CH, Garcia-Moreno C. Intimate partner violence and women’s physical and mental health in the WHO multi-country study on women’s health and domestic violence: an observational study. The lancet. 2008;371(9619):1165–72.
Chasweka R, Chimwaza A, Maluwa A. Isn’t pregnancy supposed to be a joyful time? A cross-sectional study on the types of domestic violence women experience during pregnancy in Malawi. Malawi Med journal: J Med Association Malawi. 2018;30(3):191–6.
Afshari P, Tadayon M, Abedi P, Yazdizadeh S. Prevalence and related factors of postpartum depression among reproductive aged women in Ahvaz. Iran Health care women Int. 2020;41(3):255–65.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Gebrezgi BH, Badi MB, Cherkose EA, Weldehaweria NB. Factors associated with intimate partner physical violence among women attending antenatal care in Shire Endaselassie town, Tigray, northern Ethiopia: a cross-sectional study, July 2015. Reproductive health. 2017;14:1–10.
Duran S, Eraslan ST. Violence against women: affecting factors and coping methods for women. J Pak Med Assoc. 2019;69(1):53–7.
PubMed Google Scholar
Devries KM, Mak JY, Garcia-Moreno C, Petzold M, Child JC, Falder G, et al. The global prevalence of intimate partner violence against women. Science. 2013;340(6140):1527–8.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Mahapatro M, Kumar A. Domestic violence, women’s health, and the sustainable development goals: integrating global targets, India’s national policies, and local responses. J Public Health Policy. 2021;42(2):298–309.
Lincoln YS, Guba EG. Naturalistic inquiry: sage; 1985.
Colaizzi PF. Psychological research as the phenomenologist views it. 1978.
Mohseni Tabrizi A, Kaldi A, Javadianzadeh M. The study of domestic violence in Marrid Women Addmitted to Yazd Legal Medicine Organization and Welfare Organization. Tolooebehdasht. 2013;11(3):11–24.
Ahmadi R, Soleimani R, Jalali MM, Yousefnezhad A, Roshandel Rad M, Eskandari A. Association of intimate partner violence with sociodemographic factors in married women: a population-based study in Iran. Psychol Health Med. 2017;22(7):834–44.
Bukuluki P, Kisaakye P, Wandiembe SP, Musuya T, Letiyo E, Bazira D. An examination of physical violence against women and its justification in development settings in Uganda. PLoS ONE. 2021;16(9):e0255281.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Walker-Descartes I, Mineo M, Condado LV, Agrawal N. Domestic violence and its Effects on Women, Children, and families. Pediatr Clin North Am. 2021;68(2):455–64.
Lin C-H, Lin W-S, Chang H-Y, Wu S-I. Domestic violence against pregnant women is a potential risk factor for low birthweight in full-term neonates: a population-based retrospective cohort study. PLoS ONE. 2022;17(12):e0279469.
Manouchehri E, Ghavami V, Larki M, Saeidi M, Latifnejad Roudsari R. Domestic violence experienced by women with multiple sclerosis: a study from the North-East of Iran. BMC Womens Health. 2022;22(1):1–14.
Machado DF, Castanheira ERL, Almeida MASd. Intersections between gender socialization and violence against women by the intimate partner. Ciência & Saúde Coletiva. 2021;26:5003–12.
Holmes SC, Maxwell CD, Cattaneo LB, Bellucci BA, Sullivan TP. Criminal Protection orders among women victims of intimate Partner violence: Women’s Experiences of Court decisions, processes, and their willingness to Engage with the system in the future. J interpers Violence. 2022;37(17–18):Np16253–np76.
Sigurdsson EL. Domestic violence-are we up to the task? Scand J Prim Health Care. 2019;37(2):143–4.
Moreira DN, Pinto da Costa M. Should domestic violence be or not a public crime? J Public Health. 2021;43(4):833–8.
Download references
Acknowledgements
The authors of this study appreciate the Deputy for Research and Technology of Semnan University of Medical Sciences, Social Determinants of Health Research Center of Semnan University of Medical Sciences and all the participants in this study.
Research deputy of Semnan University of Medical Sciences financially supported this project.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Allied Medical Sciences, Semnan University of Medical Sciences, Semnan, Iran
Mina Shayestefar & Mohadese Saffari
Amir Al Momenin Hospital, Social Security Organization, Ahvaz, Iran
Razieh Gholamhosseinzadeh
Department of Nursing, Faculty of Nursing and Midwifery, Semnan University of Medical Sciences, Semnan, Iran
Monir Nobahar
Social Determinants of Health Research Center, Semnan University of Medical Sciences, Semnan, Iran
Monir Nobahar & Majid Mirmohammadkhani
Clinical Research Development Unit, Kowsar Educational, Research and Therapeutic Hospital, Semnan University of Medical Sciences, Semnan, Iran
Seyed Hossein Shahcheragh
Student Research Committee, School of Allied Medical Sciences, Semnan University of Medical Sciences, Semnan, Iran
Zahra Khosravi
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
M.Sh. contributed to the first conception and design of this research; M.Sh., Z.Kh., M.S., R.Gh. and S.H.Sh. contributed to collect data; M.N. and M.Sh. contributed to the analysis of the qualitative data; M.M. and M.Sh. contributed to the analysis of the quantitative data; M.SH., M.N. and M.M. contributed to the interpretation of the data; M.Sh., M.S. and S.H.Sh. wrote the manuscript. M.Sh. prepared the final version of manuscript for submission. All authors reviewed the manuscript meticulously and approved it. All names of the authors were listed in the title page.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Mina Shayestefar .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
This article is resulted from a research approved by the Vice Chancellor for Research of Semnan University of Medical Sciences with ethics code of IR.SEMUMS.REC.1397.182 in the Social Determinants of Health Research Center. The authors confirmed that all methods were performed in accordance with the relevant guidelines and regulations. All participants accepted the participation in the present study. The researchers introduced themselves to the research units, explained the purpose of the research to them and then all participants signed the written informed consent. The research units were assured that the collected information was anonymous. The participant was informed that participating in the study was completely voluntary so that they can safely withdraw from the study at any time and also the availability of results upon their request.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
All authors declare that there are no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Shayestefar, M., Saffari, M., Gholamhosseinzadeh, R. et al. A qualitative quantitative mixed methods study of domestic violence against women. BMC Women's Health 23 , 322 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12905-023-02483-0
Download citation
Received : 28 April 2023
Accepted : 14 June 2023
Published : 20 June 2023
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12905-023-02483-0
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Domestic violence
- Cross-sectional studies
- Qualitative research
BMC Women's Health
ISSN: 1472-6874
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
- General enquiries: [email protected]
- Utility Menu
Violence Against Women Research Database
- Domestic Violence
The Multicultural Community Liaison Officer (MCLO) Program is designed to combat domestic violence in the Australia. This presentation briefly discusses the challenges and achievements of MCLO.
http://digitalcommons.law.yale.edu/ylsd/3/
This thesis is born of the question: why do women suffer domestic violence disproportionately to any other group? Why does it continue, in the same form, with the same degree of pain, without rebate? And, if the same harm occurs over and over again, consistent through generations and uniform across borders, why then has the international community not yet developed effective means to address it? This thesis attempts to find a legal answer. This is prefaced, however, by the acknowledgement that the law is only one tool in an array of mechanisms, such as health, economics, and politics, which, if properly combined, could alleviate the pain and difficulties experienced by many victims of domestic violence. The area of law to which I look is international human rights law. My initial motivation for considering public international law arose from the repetition of similar forms of domestic violence around the globe. All over the world women suffer the same type of violence at the hands of their intimate partners and they endure the same feelings of helplessness and isolation when looking to the state for protection. If such violence is universal, it seems then, so too should be the solution. I propose in this thesis that international law, if properly fashioned, can be used effectively as part of this solution. In particular, I maintain that the authoritative enunciation of a norm against domestic violence in international law can improve the way states address domestic violence. I do not propose that individual abusers should be tried by international law. My focus instead is on the extent to which states fail consistently to alleviate domestic violence. This is important because many legal systems appreciate neither the exigency of extreme forms of domestic violence, nor the extent to which women as a group are disproportionately victims of this violence. The result of this lack of appreciation is an almost universal failure to police, prevent and punish domestic violence effectively.3 Due to the socialized normalcy of domestic violence, very few cases are reported or actually prosecuted. Where prosecutions do proceed, victims will often drop their complaints either because they have reconciled with, or because they fear recrimination from, their abuser. Given the disjuncture between the reality of domestic violence and the inefficacy of many legal systems to address it, a revision of the law vis-à-vis domestic violence is needed. Both national and international legal systems are in need of change. This thesis proposes that the international community should adopt a clear and authoritative articulation of a legal right against extreme and systemic forms of domestic violence and a corresponding duty of states to help remedy such violence. This proposition is made on the basis that international law currently does not contain an effective articulation of this right, and that adopting effective global standards in international law for addressing such violence would help improve state enforcement of this right. Under the current state of international law, it is difficult to convince states to prioritize its resources and infrastructures to protect abused women. Articulating clear and effective global standards in international law for addressing extreme forms of domestic violence would provide an important and practical benchmark against which domestic state legislation could be evaluated and re-shaped. Formulating such global standards could place pressure on states to take basic remedial steps against such violence, such as enacting legislation that allows for restraining orders to be made at the same time as a maintenance order, or creating accessible shelters, which will accommodate the divergent needs of women, including their children.
http://odhikar.org/fairness-creams-skin-colour-based-discrimination-and-violence-against-women-time-to-stop/
Ruma (not her real name), a school teacher by profession and a mother of two, living in Dhaka, married Mainul eight years ago. Soon after, Mainul started harassing her, calling her an ‘ugly’ woman – because of her dark complexion. Her mother-in-law and other members of her husband’s family used to verbally abuse her almost every day, saying that her skin is ‘moyla’ (dirty); and expressed their anger and frustration, and thought that Mainul had bad luck as he was not able to marry a ‘beautiful’ woman–meaning a fair-complexioned woman. Ruma tried very hard to be seen as beautiful in the eyes of her husband and in-laws and experimented to see how she could look fairer. She started buying brand name fairness creams, hoping to make her skin lighter as she started to believe that fair meant lovely, as the advertisements say. She regularly watched fairness cream advertisements on television, read about them on bill boards and newspapers and wanted to be as fair as the models in the advertisements. Unfortunately, nothing really worked or showed much of a result. Her husband and in laws demanded a huge amount of dowry repeatedly – apparently as a retaliation for her darker skin.
http://www.civicresearchinstitute.com/online/issue.php?pid=18
*The full article is available through this link. This article may be available free of charge to those with university credentials.
The leading professional report devoted exclusively to innovative programs, legal developments, and current services and research in domestic violence law and prevention.
Domestic Violence Report keeps you up-to-date on...
- Successful programs for prevention, protection, enforcement, prosecution, aftercare and corrections
- New legislation, court decisions, regulatory and policy developments
- Practical intervention strategies
- Criminal and civil litigation
- Medical and psychological treatment of victims, abusers and their children
http://odhikar.org/are-you-a-silent-observer-of-dowry-and-related-violence/
Every year many women in Bangladesh are killed and physically abused and many commit suicide because of the the vicious dowry practice and related violence. According to the rights organisation Odhikar, at least 2,800 women were killed, 1,833 were physically abused and 204 committed suicide because of dowry-related violence between 2001 and July 2014.
By analysing the overall dowry situation, reported statistics indicate that it is only the tip of the iceberg. Majority of the victims continue to tolerate abuse, if they are not killed, all through their married life and never report it. The main reasons behind tolerating or not reporting such abuse is that they are either financially incapable of going away and protecting themselves from their abusive husbands or they are not welcome by their poverty-stricken or stigmatised parental families.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24777256
Exposure to intimate partner violence (IPV) has negative consequences for children's well-being and behavior. Much of the research on parenting in the context of IPV has focused on whether and how IPV victimization may negatively shape maternal parenting, and how parenting may in turn negatively influence child behavior, resulting in a deficit model of mothering in the context of IPV. However, extant research has yet to untangle the interrelationships among the constructs and test whether the negative effects of IPV on child behavior are indeed attributable to IPV affecting mothers' parenting. The current study employed path analysis to examine the relationships among IPV, mothers' parenting practices, and their children's externalizing behaviors over three waves of data collection among a sample of 160 women with physically abusive partners. Findings indicate that women who reported higher levels of IPV also reported higher levels of behavior problems in their children at the next time point. When parenting practices were examined individually as mediators of the relationship between IPV and child behavior over time, one type of parenting was significant, such that higher IPV led to higher authoritative parenting and lower child behavior problems [corrected]. On the other hand, there was no evidence that higher levels of IPV contributed to more child behavior problems due to maternal parenting. Instead, IPV had a significant cumulative indirect effect on child behavior via the stability of both IPV and behavior over time. Implications for promoting women's and children's well-being in the context of IPV are discussed.
http://www.pearsonhighered.com/educator/product/Heavy-Hands-An-Introduct...
Heavy Hands, Fifth Edition, provides an authentic introduction to the crimes of family violence, covering offenders and offenses, impact on victims, and responses of the criminal justice system. This established text is essential reading for those considering careers in criminal justice, victim advocacy, social work, and counseling. Gosselin draws on extensive field experience and uses real-life examples to provide sharp insight into how and why abuse occurs and its effects on abuse survivors. The text’s accessible language and effective learning tools keep students engaged and motivated, while its practical, real-world focus helps students connect text material to the world around them.
http://dhsprogram.com/publications/publication-DHSQMP-DHS-Questionnaires...
**Go to the publication " DHS6_Module_Domestic_Violence_6Aug2014_DHSQMP"
This document is part of the Demographic and Health Survey’s DHS Toolkit of methodology for the MEASURE DHS Phase III project, implemented from 2008-2013.
This publication was produced for review by the United States Agency for International Development (USAID). It was prepared by MEASURE DHS/ICF International.
http://www.pulp.up.ac.za/edited-collections/strengthening-the-protection...
Strengthening the protection of sexual and reproductive health and rights in the African region through human rights uses rights-based frameworks to address some of the serious sexual and reproductive health challenges that the African region is currently facing. More importantly, the book provides insightful human rights approaches on how these challenges can be overcome. The book is the first of its kind. It is an important addition to the resources available to researchers, academics, policymakers, civil society organisations, human rights defenders, learners and other persons interested in the subject of sexual and reproductive health and rights as they apply to the African region. Human rights issues addressed by the book include: access to safe abortion and emergency obstetric care; HIV/AIDS; adolescent sexual health and rights; early marriage; and gender-based sexual violence.
Myanmar Activists Demand Law to Ban Violence Against Women
This article from The New York Times explores Myanmar's lack of infrastructure to combat violence against women and children.
http://euromedrights.org/publication/violence-against-women-in-the-conte...
On the occasion of International Women’s Day (8th of March), the Euro Mediterranean Human Rights Network (EMHRN) published today its regional report “Violence against women in the context of political transformations and economic crisis in the Euro-Mediterranean region; trends and recommendations towards equality and justice”.
This report alerts that violence against women has dramatically increased in the Euro-Mediterranean region during the recent years, showcasing key patterns of violence against women, through case studies from Egypt, Syria, Tunisia, Libya, France, Cyprus and Spain.
The report also underlines the alarming increase and severity of sexual violence in countries such as Libya, Syria and Egypt mounting to sexual terrorism. In Egypt, women protestors were subjected to systematic and seemingly planned harassment and gang rapes in Tahrir Square. In Syria, women and are subjected to trafficking and sexual exploitation girls in refugee camps.
Subject : This research memorandum presents key findings from desk research conducted in January and February 2014, on the barriers to instituting appropriate VAW laws against domestic violence (DV), and to effectively implementing them in three countries in Asia (China, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka).
Background and Cross-Cutting Findings: China, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka have all ratified CEDAW; however, both China and Pakistan have not passed the Optional Protocol to CEDAW. Research found four cross-cutting barriers impeding the institutionalization of appropriate VAW laws against DV in these three countries:
1) The predominant public discourse on DV is fragmented. As a result, an overall sense of urgency and severity of the problem is not felt among key stakeholders in all 3 countries.
2) Other national policies regarding housing, marriage, fertility, migration, etc. undermine both the international (CEDAW) legal framework, and the national policies set up for service provision and protection across all three countries.
3) There is an overall lack of appropriate resource allocation among all 3 countries for comprehensively implementing appropriate VAW laws against DV. A large body of evidence suggests multiple root causes for VAW-DV, and States disagree on where and how to allocate resources to VAW-DV (prevention, intervention, prosecution, and protection).
4) Incomparable and unreliable data is the 4 th major barrier to instituting appropriate VAW laws against DV both internationally through CEDAW, and nationally within all 3 countries. Transparency of data collection methodologies is also a noted concern.
Violence against Women (VAW) is a pervasive, global human rights violation. This research memo discusses the current state of VAW in Australia, and the Australian Governments proposed National Action Plan (NAP) addressing VAW across Australia’s diverse community. Noting that women’s rights are not fully protected by the Commonwealth and revealing the current appalling statistics around domestic and sexual violence against Australian women, the memo then provides insight on Indigenous women and VAW, followed by a deeper look at NAP. Finally, after a brief look at the recent study tour of Australia by the Special Rapporteur on Violence against Women, Australia’s commitment to addressing VAW is discussed with reference to reporting for CEDAW and UPR. The memo then considers the Special Rapporteur’s study tour in light of the election of a new federal government. It then concludes that if the state shows genuine commitment to its people, and to its obligations under human rights treaties, the onus ultimately rests on it to work with civil society to make use of the human rights mechanisms and seek to honestly and with purpose examine their human rights status and develop and adopt sustainable positive change.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24164531
Intimate partner violence (IPV) has detrimental consequences for women's mental health. To effectively intervene, it is essential to understand the process through which IPV influences women's mental health. The current study used data from 5 waves of the Women's Employment Study, a prospective study of single mothers receiving Temporary Assistance for Needy Families (TANF), to empirically investigate the extent to which job stability mediates the relationship between IPV and adverse mental health outcomes. The findings indicate that IPV significantly negatively affects women's job stability and mental health. Further, job stability is at least partly responsible for the damaging mental health consequences of abuse, and the effects can last up to 3 years after the IPV ends. This study demonstrates the need for interventions that effectively address barriers to employment as a means of enhancing the mental health of low-income women with abusive partners.
http://jbp.sagepub.com/content/40/6/563
Racial microaggressions are often unintentional and subtle forms of racism that manifest in interpersonal communications, behaviors, or environments. The purpose of this study was to explore the presence of racial microaggressions within domestic violence shelters and to understand how women respond to them. Using a phenomenological approach to data collection and analysis, 14 Black women from 3 different shelters were interviewed. Twelve women reported experiencing at least one racial microaggression, although few identified the experience as racist. Additional themes were also examined to understand why women did not identify their experiences of racial microaggressions as racist. Implications for research and practice are discussed.
http://www.unwomen.org/en/digital-library/publications/2010/1/ending-vio...
Can be found under the 'View Online' portion of the site
Ending violence against women is at the heart of the mandate of the United Nations Development Fund for Women (UNIFEM). The international community has an unprecedented opportunity to make meaningful progress in tackling this universal human rights violation. Within this context, UNIFEM has developed its Strategy 2008-2013 to end violence against women and girls, an overview of which is presented here.
http://www.larepublica.ec/blog/internacional/2013/02/15/bolivia-enfrenta...
La Paz, 15 feb (EFE).- Bolivia ha asumido el reto de frenar la hasta ahora reinante impunidad en los crímenes contra las mujeres con una ley que castigará con dureza la violencia machista, tras el asesinato esta semana de una periodista a manos de su esposo policía.
http://www.echr.coe.int/sites/search_eng/pages/search.aspx#{"fulltext":["factsheet: Violence against women"],"subcategory":["factsheets"]}
Document summaries the court’s case law in relation to domestic violence, genital mutilations, rape, violence and social exclusion, violence at the hands of state authorities and violence in public places.
12 cases dealing with domestic violence refer to the violation of different articles of the European Convention of human rights, namely of the article 2 on the right to life, article 13 on the right to an effective remedy, article 8 on the right to respect for family life, prohibition of inhuman or degrading treatment and article 14 on prohibition of discrimination. Both cases relating genital mutilation against Austria and Ireland were declared inadmissible for the reasons of insufficient protection of the young Nigerian girls that should be provided by their parents. 5 cases dealing with rape reaffirmed the violation of articles 3 on the prohibition of inhuman or degrading treatment or punishment, article 8 and artcile 13 mentioned above. The case of violence and social exclusion confirmed violation of the article 3 whereas the violence at the hands of state authorities brought forward violation of the article 3, artcile 14 and article 11 on freedom of assembly. The last case presented in the factsheet deals with the violence in public places giving declaring the violation of the article 3 and article 8.
http://www.statcan.gc.ca/pub/85-002-x/2013001/article/11766-eng.htm
For the past three decades, Federal-Provincial-Territorial (FPT) Ministers responsible for the Status of Women have shared a common vision to end violence against women in all its forms. Violence against women inCanada is a serious, pervasive problem that crosses every social boundary and affects communities across the country. It remains a significant barrier to women's equality and has devastating impacts on the lives of women, children, families and Canadian society as a whole.
This report marks the third time that the FPT Status of Women Forum has worked with Statistics Canada to add to the body of evidence on gender-based violence. Assessing Violence Against Women: A Statistical Profile was released in 2002 and was followed by Measuring Violence Against Women: Statistical Trends 2006. The 2006 report expanded the analysis into new areas, presenting information on Aboriginal women and women living in Canada's territories. The current report maintains this important focus and also includes information on dating violence, violence against girls and violence that occurs outside of the intimate partner/family context. It also shows trends over time and provides data at national, provincial/territorial, and census metropolitan area levels. A study on the economic impacts of one form of violence against women, spousal violence, is also presented.
http://mptf.undp.org/document/search?fund=WAV00&document_areas=fund,proj...
Please enter "Consolidated Report China" into the search engine in order to find this document.
The United Nations Trust Fund in Support of Actions to Eliminate Violence against Women (UN Trust Fund to EVAW) is a leading multilateral grant-making mechanism devoted to supporting national and local efforts to end violence against women and girls. Established in 1996 by a UN General Assembly Resolution, the UN Trust Fund to EVAW is now administered by UN WOMEN. In 2008, the UN Trust Fund to EVAW began awarding grants on a competitive basis for Joint Programmes submitted by UN Country Teams.
Filter by Type of Publication
- Book Chapter
- Conference Paper
- Government Report
- Journal Article
- Legal Ruling
Filter by Year
- Working Paper
- Latin America
- North America
By Type of Violence
- Access to Water/Sanitation/Hygiene
- Court System
- Early/Child Marriage
- Family Violence
- Forced Marriage
- Forced Prostitution / Prostitution
- Forcible Sterilization
- Gender Based Violence
- Governmental/Police Violence
- Help seeking
- Honor Killings
- Indigenous Women
- Intimate Partner Violence
- Peace and Security
- Race/Racism
- Refuge/Shelter
- Reproductive Rights
- Trafficking
- VAW in Conflict
- Widows (of all ages)
- Workplace Violence
Filter by Country
- Afghanistan
- Sign up for Email Updates
Wednesday, March 27, 2024
Russian offensive campaign assessment, march 27, 2024.
Christina Harward, Karolina Hird, Riley Bailey, Nicole Wolkov, and Frederick W. Kagan
March 27, 2024, 5:10pm ET
Click here to see ISW’s interactive map of the Russian invasion of Ukraine. This map is updated daily alongside the static maps present in this report.
Click here to see ISW’s 3D control of terrain topographic map of Ukraine. Use of a computer (not a mobile device) is strongly recommended for using this data-heavy tool.
Click here to access ISW’s archive of interactive time-lapse maps of the Russian invasion of Ukraine. These maps complement the static control-of-terrain map that ISW produces daily by showing a dynamic frontline. ISW will update this time-lapse map archive monthly.
Note: The data cut-off for this product was 2:15pm ET on March 27. ISW will cover subsequent reports in the March 28 Russian Offensive Campaign Assessment.
The UN Human Rights Monitoring Mission in Ukraine (HRMMU) released its 38th report on the human rights situation in Ukraine on March 26, confirming several of ISW’s longstanding assessments about Russia’s systematic violations of international human rights and humanitarian law in occupied territories and towards Ukrainian prisoners of war (POWs). [1] The HRMMU report details activities between December 1, 2023 and February 29 2024, and includes new findings about Russia’s abuse of Ukrainian POWs during this timeframe, based on interviews with 60 recently released male POWs. [2] Nearly all of the POWs that HRMMU interviewed detailed how they were tortured by Russian forces with beatings and electric shocks and threatened with execution, and over half of the interviewees experienced sexual violence. HRMMU also reported that it has evidence of Russian forces executing at least 32 POWs in 12 different incidents during the reporting period and independently verified three of the executions. ISW observed open-source evidence of several POW executions during this reporting period: the execution of three Ukrainian POWs near Robotyne, Zaporizhia Oblast on December 27, 2023; the execution of one Ukrainian POW near Klishchiivka, Donetsk Oblast on February 9, 2024; the executions of three Ukrainian POWs near Robotyne, the execution of six Ukrainian POWs near Avdiivka, Donetsk Oblast, and the executions of two Ukrainian POWs near Vesele, Donetsk Oblast on or around February 18, 2024; and the execution of nine Ukrainian POWs near Ivanivske, Donetsk Oblast, on February 25. [3] The summary execution and mistreatment of POWs is a violation of Article 3 of the Geneva Convention relative to the Treatment of Prisoners of War. [4] The HRMMU report also details the forced Russification of Ukrainian populations in occupied areas, including the imposition of Russian political, legal, and administrative systems onto occupied Ukraine in violation of Russia’s international legal obligations as an occupying power. [5] ISW has reported at length on the specifics of Russia’s illegal occupation of Ukraine, consistent with the findings of the UN HRMMU report. [6]
Russian officials are tying the US and the West to a broader set of “terrorist” attacks against Russia following the Crocus City Hall attack, likely to intensify rhetoric about alleged Western and Ukrainian threats to generate greater domestic support for the war in Ukraine. The Russian Investigative Committee and Prosecutor General’s Office stated on March 27 that they will consider an appeal from the Russian State Duma to investigate American and Western financing and organization of terrorist attacks against Russia. [7] The Russian Investigative Committee, Prosecutor General’s Office, and the Duma Deputies that made the appeal did not explicitly reference the Crocus City Hall attack. [8] Kremlin officials have previously tied Ukraine and the West to the Crocus City Hall attack but have yet to make a formal accusation, and the Kremlin may refrain from issuing an official accusation as all available evidence continues to show that the Islamic State (IS) is very likely responsible for the attack. [9] Russian officials routinely describe Ukrainian military strikes against legitimate military targets in occupied Ukraine and Russia as terrorism and consistently claim that Western actors help organize these strikes. [10] The Kremlin likely aims to seize on wider Russian social fears and anger following the Crocus City Hall attack by portraying Ukraine, the US, and the West as immediate terrorist threats. The Kremlin likely hopes that perceptions of Ukrainian and Western involvement in the Crocus City Hall attack will increase domestic support for the war in Ukraine, and Russian officials will likely invoke a broader view of what they consider terrorism to further cast Ukrainians as terrorists and the West as a sponsor of terrorism. [11] The Kremlin may still formally accuse Ukraine of conducting the Crocus City Hall attack if it believes that these other informational efforts are insufficient to generate the domestic response it likely desires. [12]
Russian authorities are increasing legal pressure against migrants in Russia following recent Russian officials’ proposals for harsher, measures against migrant communities in response to the March 22 Crocus City Hall attack. BBC News Russian Service stated that there has been a significant increase in the number of cases related to violations of the rules of entry for foreign citizens into Russia following the Crocus City Hall attack. [13] BBC News Russian Service reported on March 27 that 784 such cases have been registered since the morning of March 25, as compared with 1,106 during the entire previous week. A Russian lawyer who often works with Tajik citizens reportedly told BBC News Russian Service that over 100 people waited for a Moscow district court to hear their cases on March 25 alone and that Russian authorities are especially targeting migrants from Tajikistan during searches. BBC News Russian Service reported that representatives of the Tajik diaspora in Russia are expecting Russian authorities to conduct a large wave of deportations following the Crocus City Hall attack. A Russian insider source claimed on March 27 that unspecified actors gave the Moscow Ministry of Internal Affairs (MVD) an “unspoken” order to “not spare” migrants and for MVD employees to use their own judgement in the field. [14] The insider source claimed that a source suggested that Russian authorities are not preparing to conduct raids on migrant communities but will apply the “strictest measures” to migrants in “controversial situations.” Kremlin newswire TASS stated on March 27 that Russian police and Rosgvardia conducted a raid at the Wildberries warehouse in Elektrostal, Moscow Oblast to check the documents of migrant workers, and Russian opposition outlet Baza reported that Russian authorities detained 21 people during the raid. [15] Several Russian ultranationalist milbloggers complained that the way Russian-language schools in Tajikistan are teaching about Russia’s historical imperial occupation of Tajikistan is discouraging Tajik migrants from integrating into Russian society, essentially blaming migrants for the alienation that Russian society subjects them to. [16] Select Russian officials recently called for the introduction of several anti-migrant policies, which Russian authorities are unlikely to enact given Russia’s reliance on migrants for its force generation and labor needs. [17] Russian authorities may continue the practice of raiding migrant workplaces and increase crackdowns at border crossings to temporarily placate emotional cries for retribution following the March 22 attack as the Kremlin continues to develop a cogent and practical response.
Key Takeaways:
- The UN Human Rights Monitoring Mission in Ukraine (HRMMU) released its 38th report on the human rights situation in Ukraine on March 26, confirming several of ISW’s longstanding assessments about Russia’s systematic violations of international human rights and humanitarian law in occupied territories and towards Ukrainian prisoners of war (POWs).
- Russian officials are tying the US and the West to a broader set of “terrorist” attacks against Russia following the Crocus City Hall attack, likely to intensify rhetoric about alleged Western and Ukrainian threats to generate greater domestic support for the war in Ukraine.
- Russian authorities are increasing legal pressure against migrants in Russia following recent Russian officials’ proposals for harsher, measures against migrant communities in response to the March 22 Crocus City Hall attack.
- Russian forces recently made confirmed advances near Avdiivka and southwest of Donetsk City on March 27.
- Russian Storm-Z personnel continue to complain about their poor treatment by the Russian Ministry of Defense (MoD) as the MoD tries to posture efficacy in its force generation and social benefit allocation system.
We do not report in detail on Russian war crimes because these activities are well-covered in Western media and do not directly affect the military operations we are assessing and forecasting. We will continue to evaluate and report on the effects of these criminal activities on the Ukrainian military and the Ukrainian population and specifically on combat in Ukrainian urban areas. We utterly condemn Russian violations of the laws of armed conflict and the Geneva Conventions and crimes against humanity even though we do not describe them in these reports.
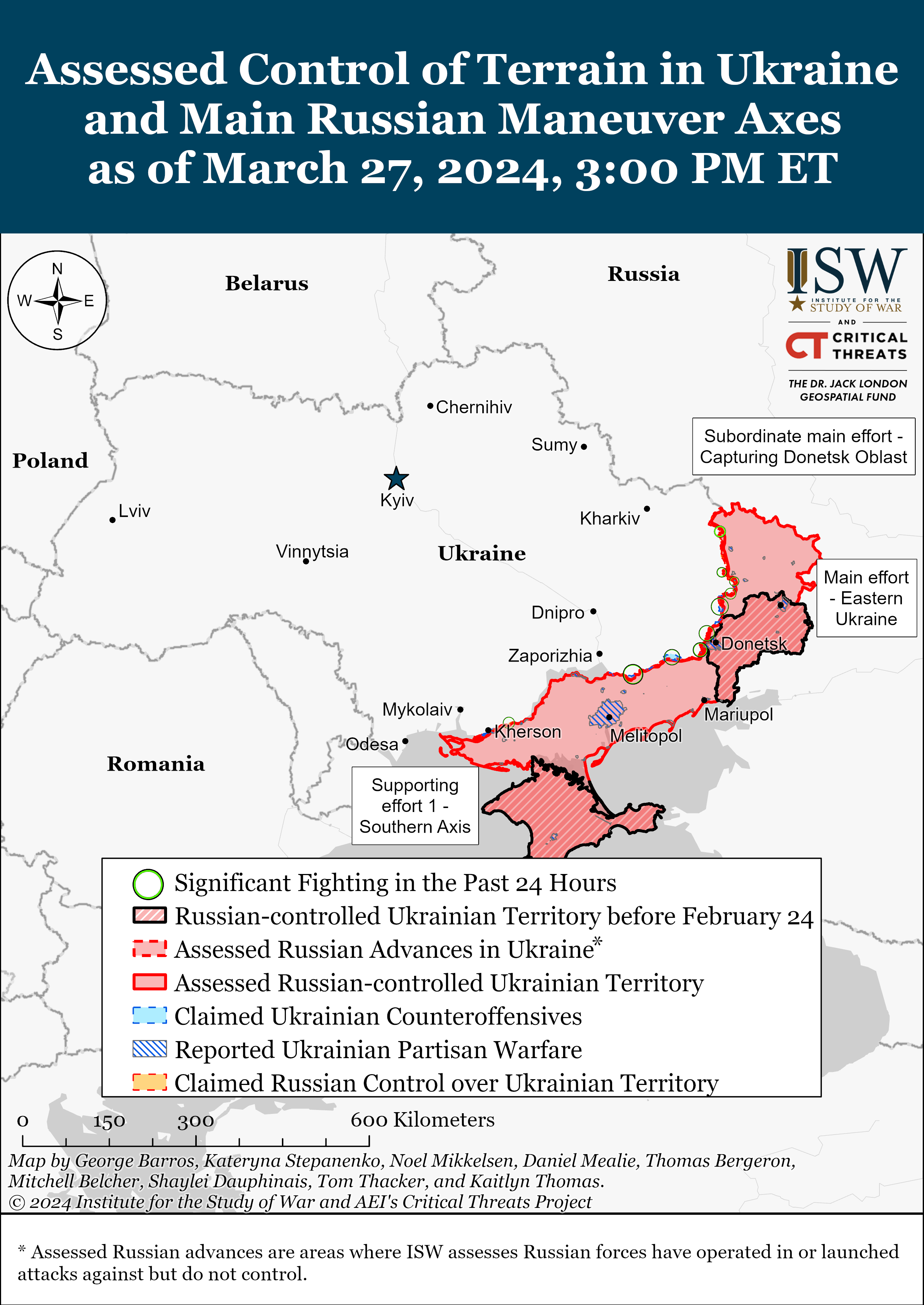
- Russian Main Effort – Eastern Ukraine (comprised of two subordinate main efforts)
- Russian Subordinate Main Effort #1 – Capture the remainder of Luhansk Oblast and push westward into eastern Kharkiv Oblast and encircle northern Donetsk Oblast
- Russian Subordinate Main Effort #2 – Capture the entirety of Donetsk Oblast
- Russian Supporting Effort – Southern Axis
- Russian Air, Missile, and Drone Campaign
- Russian Mobilization and Force Generation Efforts
- Russian Technological Adaptations
- Activities in Russian-occupied areas
- Ukrainian Defense Industrial Base Efforts
Russian Information Operations and Narratives
- Significant Activity in Belarus
Russian Main Effort – Eastern Ukraine
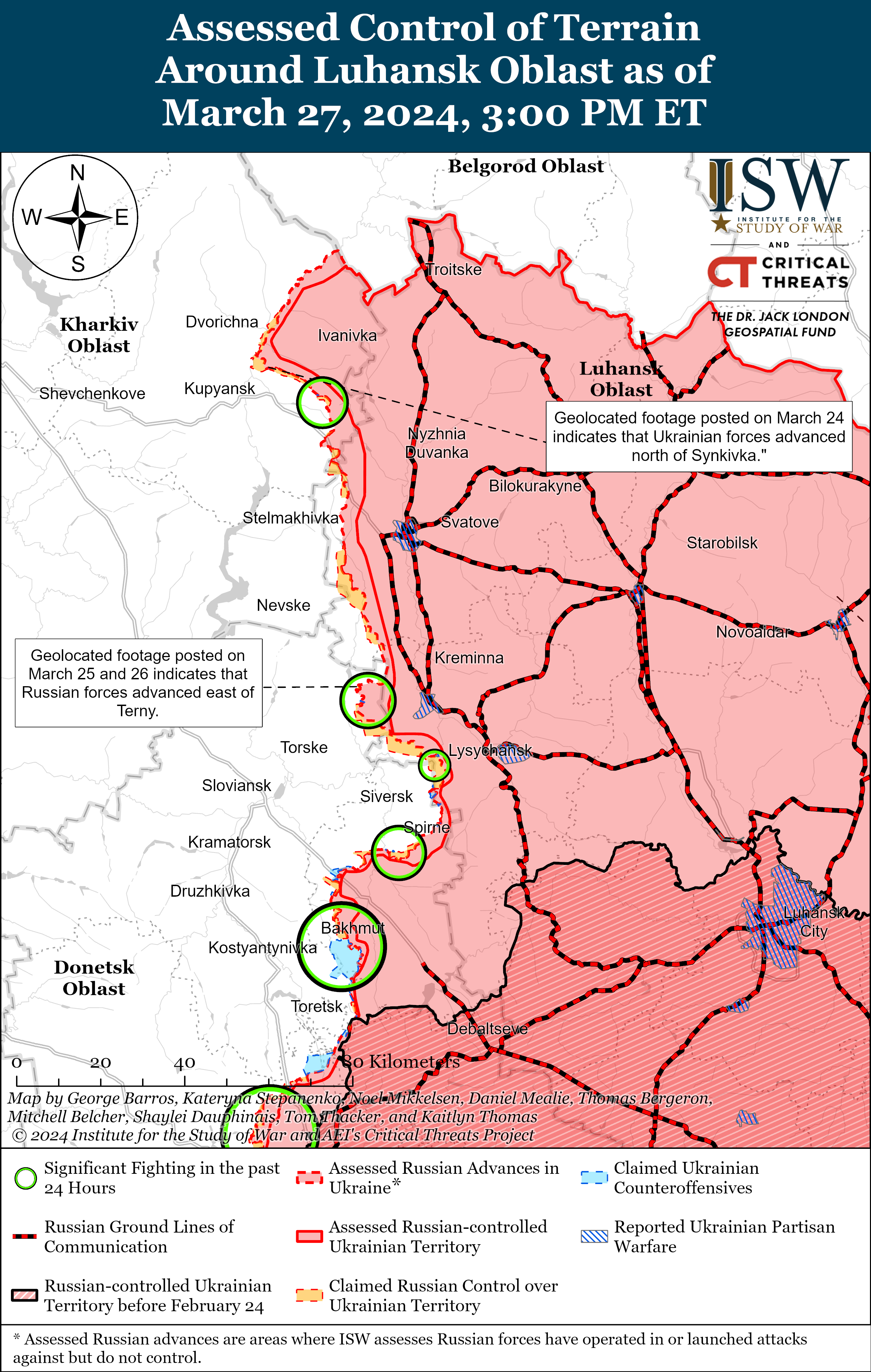
Russian Subordinate Main Effort #1 – Luhansk Oblast (Russian objective: Capture the remainder of Luhansk Oblast and push westward into eastern Kharkiv Oblast and northern Donetsk Oblast)
Positional engagements continued along the Kupyansk-Svatove-Kreminna line on March 27, but there were no confirmed changes to the frontline in this area. Ukrainian and Russian sources stated that positional engagements continued northeast of Kupyansk near Synkivka and Lake Lyman; southeast of Kupyansk near Ivanivka; west of Kreminna near Terny and Yampolivka; and south of Kreminna near Bilohorivka. [18] Russian milbloggers claimed that Russian forces advanced near Terny, but ISW has not observed visual confirmation of this claim. [19] Chechen Republic Head Ramzan Kadyrov stated that elements of the Chechen Akhmat Spetsnaz “Aida” detachment are operating near Bilohorivka. [20]
Ukrainian officials reported that Russian forces struck Kharkiv City with a D-30 universal joint glide munition (UMPB), a guided glide bomb, on March 27. [21] Ukrainian officials noted that the strike was the first Russian glide bomb strike against Kharkiv City since the beginning of the full-scale invasion in 2022. [22] Ukrainian Kharkiv Oblast Military Administration Head Oleh Synehubov stated that the UMPB D-30 has a range of up to 90 kilometers and that Russian forces can launch the bomb from aircraft or ground-based Smerch multiple rocket launch systems (MLRS). [23] Russian forces struck Myrnohrad, Donetsk Oblast with three UMPB D-30SN guided glide bombs on March 10. [24]
Russian Subordinate Main Effort #2 – Donetsk Oblast (Russian objective: Capture the entirety of Donetsk Oblast, the claimed territory of Russia’s proxies in Donbas)
Russian forces reportedly advanced west of Bakhmut, although there were no confirmed changes to the frontline in the area on March 27. Russian milbloggers claimed that Russian forces advanced west of Bakhmut along a railway line and a section of the O0506 (Khromove-Chasiv Yar) highway by 1.15 kilometers in depth and 1.85 kilometers in width. [25] A Russian milblogger claimed that elements of the 98th Airborne (VDV) Division are advancing near Ivanivske and are within 500 meters of the city limits of Chasiv Yar (west of Bakhmut). [26] Russian Defense Minister Sergei Shoigu credited elements of the Russian 102nd Motorized Rifle Regiment (150th Motorized Rifle Division, 8th Combined Arms Army [CAA], Southern Military District [SMD]) with seizing Ivanivske on March 24, although ISW has yet to observe visual evidence confirming that Russian forces have seized Ivanivske. [27] Positional fighting continued northeast of Bakhmut near Vesele; northwest of Bakhmut near Bohdanivka; west of Bakhmut near Ivanivske; southwest of Bakhmut near Klishchiivka and Andriivka; and south of Bakhmut near Shumy and Pivdenne. [28] A Ukrainian military observer reported that Russian forces have intensified transfers of equipment and personnel along ground lines of communication (GLOCs) through Kadiivka, Pervomaisk, and Popasna (all east of Bakhmut), but did not specify the destination of these transfers. [29] Kadiivka, Pervomaisk, and Popasna all lie along the T0504 Luhansk City-Bakhmut highway that runs directly from the Russian rear in occupied Luhansk Oblast into Bakhmut, however.
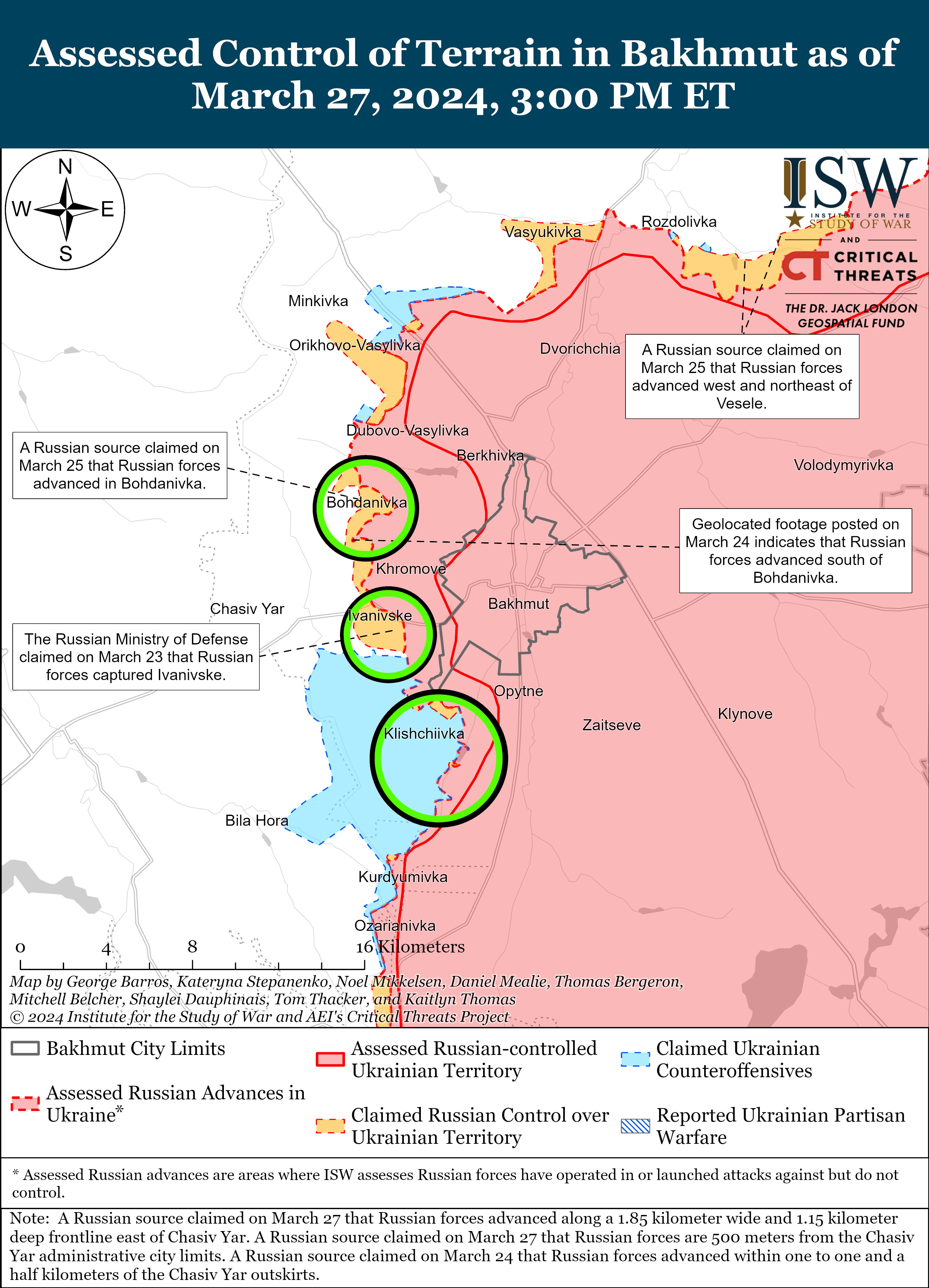
Russian forces recently advanced west of Avdiivka amid continued positional fighting in the area on March 27. Geolocated footage published on March 27 indicates that Russian forces recently advanced within Berdychi (northwest of Avdiivka) and in Orlivka (west of Avdiivka). [30] Russian milbloggers claimed that Russian forces entered Semenivka (northwest of Avdiivka) and are attacking Ukrainian positions within the settlement but that Ukrainian forces are actively counterattacking in the area. [31] A Russian milblogger claimed that Russian forces advanced 200 meters west of Orlivka on the western bank of the Durna River, 200 meters west of Tonenke (west of Avdiivka), 200 meters in the direction of Umanske (west of Avdiivka), 300 meters south of Tonenke towards Pervomaiske (southwest of Avdiivka), and 100 meters south of Nevelske (southwest of Avdiivka). [32] ISW has not observed visual confirmation of these claims. Positional fighting continued northwest of Avdiivka near Berdychi and Semenivka; west of Avdiivka near Orlivka, Tonenke, and Umanske; and southwest of Avdiivka near Vodyane, Nevelske, and Pervomaiske. [33]
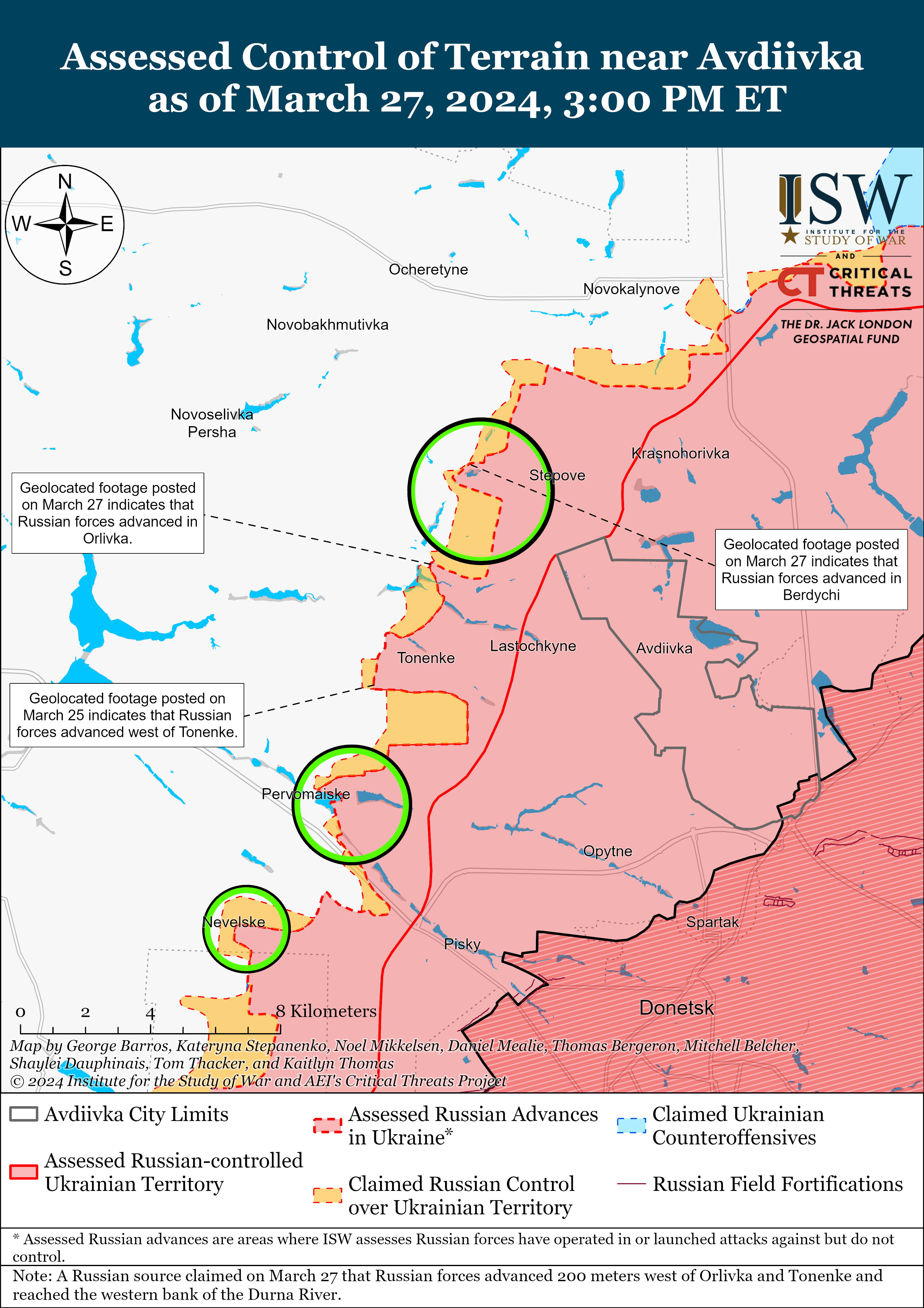
Russian forces recently advanced southwest of Donetsk City amid continued positional fighting west and southwest of Donetsk City on March 27. Geolocated footage published on March 27 indicates that Russian forces recently advanced within central Novomykhailivka (southwest of Donetsk City). [34] Positional fighting continued west of Donetsk City near Heorhiivka and Krasnohorivka and southwest of Donetsk City near Novomykhailivka and Pobieda. [35] Elements of the Russian 5th Motorized Rifle Brigade (1st Donetsk People’s Republic [DNR] Army Corps [AC]) are reportedly operating near Krasnohorivka. [36]
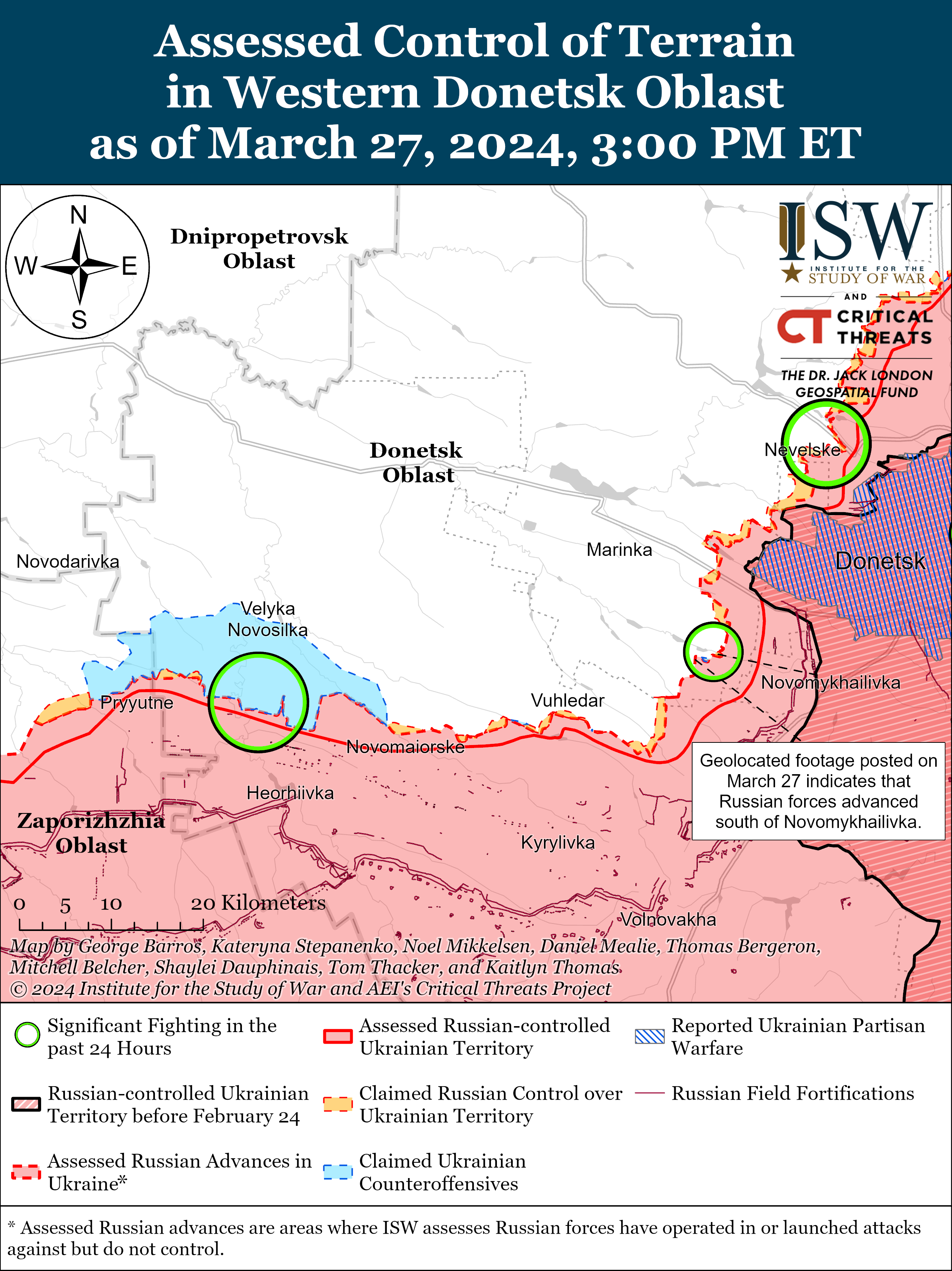
Positional engagements continued south of Velyka Novosilka near Staromayorske and Urozhaine in the Donetsk-Zaporizhia Oblast border area on March 27. [37]
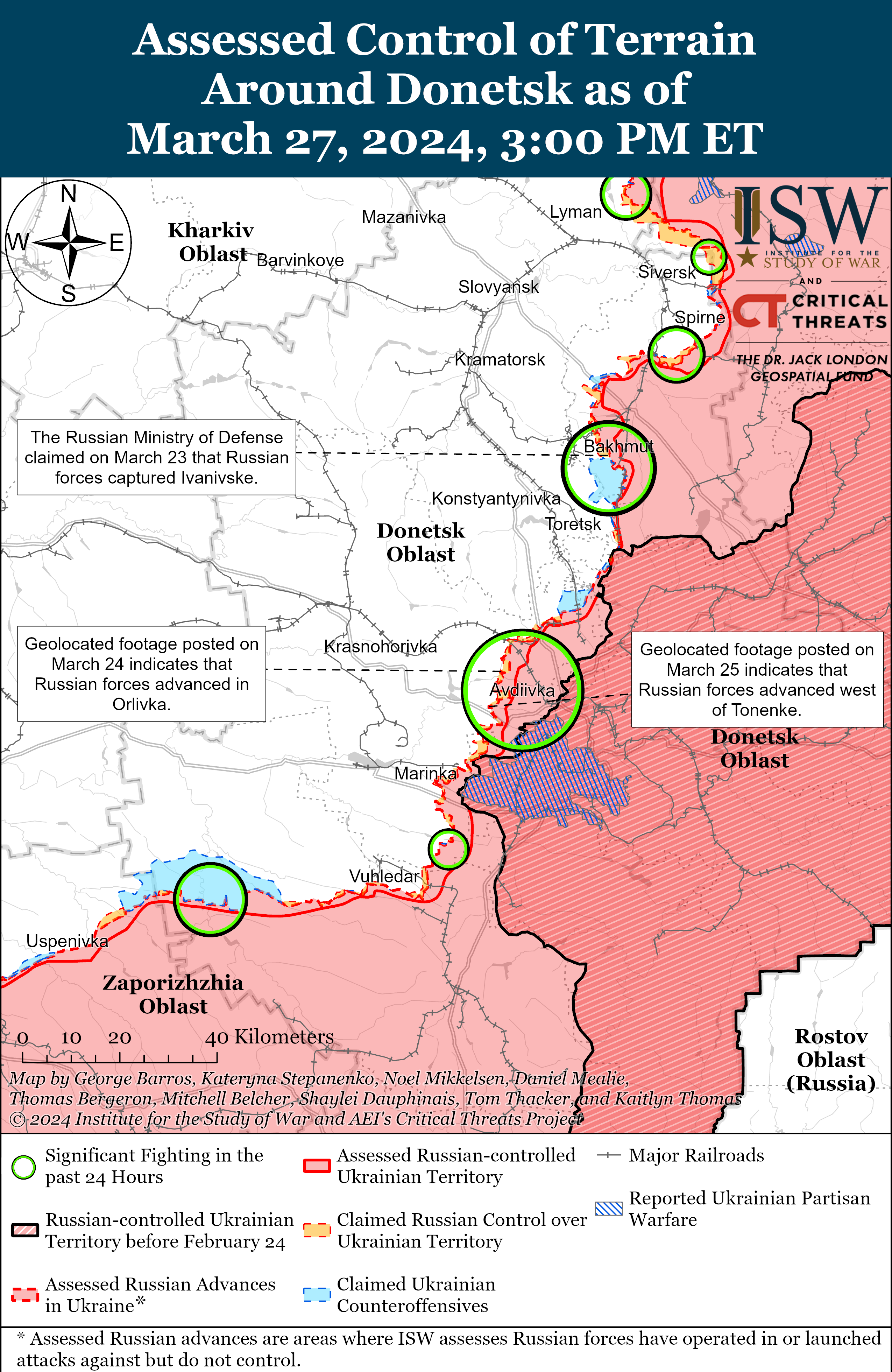
Russian Supporting Effort – Southern Axis (Russian objective: Maintain frontline positions and secure rear areas against Ukrainian strikes)
Positional engagements continued in western Zaporizhia Oblast on March 27, but there were no confirmed changes to the frontline. Positional engagements continued near Robotyne, near Mala Tokmachka (northeast of Robotyne), northeast of Novoprokopivka (south of Robotyne), and northwest of Verbove (east of Robotyne). [38] Elements of the Russian 71st Motorized Rifle Regiment (42nd Motorized Rifle Division, 58th Combined Arms Army [CAA], Southern Military District [SMD]) reportedly continue operating within Robotyne. [39]
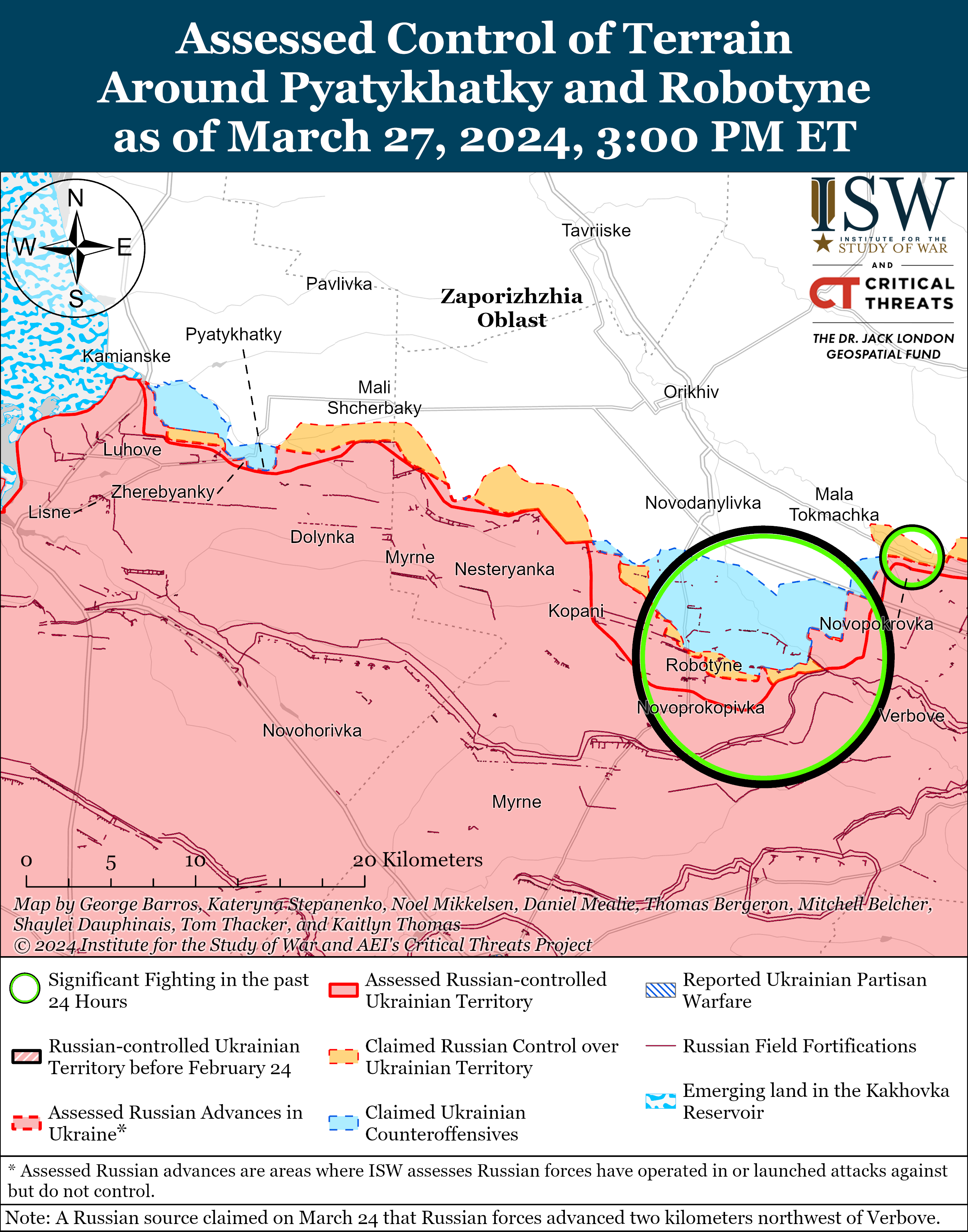
Positional engagements continued in east (left) bank Kherson Oblast, including near Krynky, on March 27. [40]
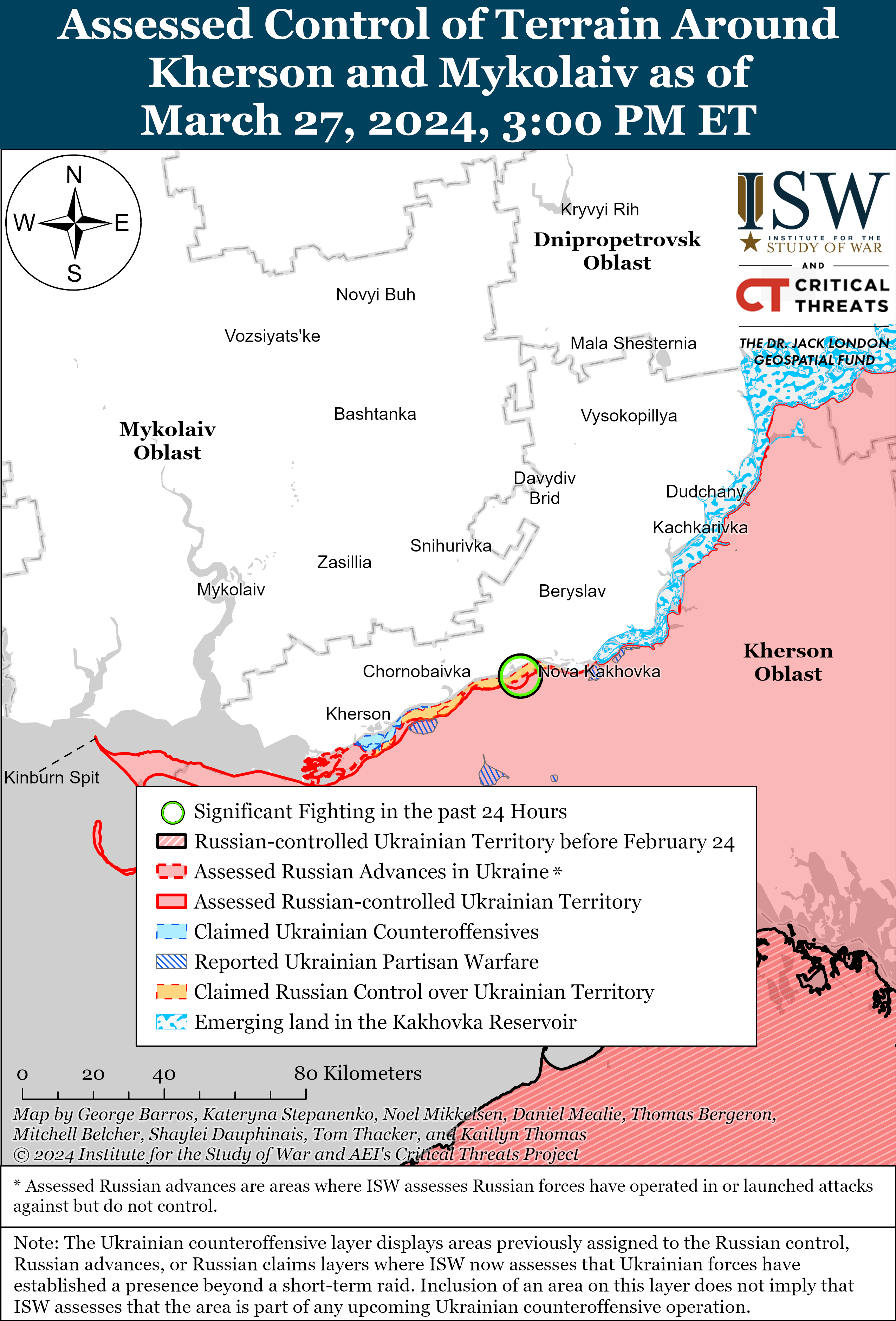
Russian Air, Missile, and Drone Campaign (Russian Objective: Target Ukrainian military and civilian infrastructure in the rear and on the frontline)
Russian forces conducted a series of drone and missile strikes against Ukraine on the night of March 26 to 27 and on March 27. The Ukrainian Air Force reported that Russian forces launched 13 Shahed-136/131 drones from Kursk Oblast and that Ukrainian forces shot down 10 drones over Kharkiv, Sumy, and Kyiv oblasts on the night of March 26 to 27. [41] Ukrainian officials reported that Russian drones struck civilian infrastructure in Izyum, Kharkiv Oblast. [42] Ukrainian Kharkiv Oblast Head Oleh Synehubov stated that a Russian Kh-35U subsonic anti-ship cruise missile struck Kharkiv City on the morning of March 27. [43] Ukraine’s Eastern Air Command reported that Ukrainian forces shot down an unspecified Russian cruise missile over Dnipropetrovsk Oblast on March 27. [44] Ukrainian officials stated that Russian forces struck an industrial enterprise in Mykolaiv City with an Iskander-M ballistic missile on the afternoon of March 27. [45]
Ukraine’s Southern Operational Command Spokesperson Colonel Nataliya Humenyuk stated that Russian forces have stored “several dozen” Zircon missiles in military facilities in occupied Crimea. [46] Ukrainian Air Force Spokesperson Major Ilya Yevlash stated that Ukrainian air defense systems, such as Patriot and SAMP/T systems, can intercept Zircon missiles when they slow down to about 3,700 kilometers per hour on approach to a target. [47]
Russian Mobilization and Force Generation Efforts (Russian objective: Expand combat power without conducting general mobilization)
Russian Storm-Z personnel continue to complain about their poor treatment by the Russian Ministry of Defense (MoD) as the MoD tries to present the efficacy of its force generation and social benefit allocation system. Russian opposition outlet Mobilization News posted a video appeal from Storm-Z fighters from Kaluga Oblast on March 27 wherein one fighter claimed that after signing contracts with the Russian MoD, Russian command sent a Storm-Z unit of 230 people to the frontline, of whom only 38 survived combat. [48] The Storm-Z fighter complained that he has been unable to receive combat veteran status or promised payments from the Russian authorities for his service. [49] Mobilization News released another video on March 27 wherein relatives of killed and wounded Storm-Z fighters complain to Russian President Vladimir Putin that Russian authorities have not issued the Storm-Z fighters combat status or granted payments in the event of their death or injury in Ukraine. [50] The relatives of the Storm-Z fighters blamed the Russian MoD and Defense Minister Sergei Shoigu for the poor treatment and lack of benefits for Storm-Z fighters. The Russian MoD relies heavily on Storm-Z recruits from penal colonies to carry out costly infantry-led frontal assaults against Ukrainian positions and is very unlikely to address complaints concerning their poor treatment. The Russian MoD claimed on March 27 that it is issuing electronic combat veteran certificates and streamlining and digitizing the process for veterans to obtain payments and social benefits — but these privileges evidently do not apply evenly to all personnel who have signed contracts with the Russian MoD. [51]
Russian news outlet Vedemosti reported that US-sanctioned Russian company Baikal Electronics is struggling to domestically package semiconductor chips to produce processors and that over half of its domestically produced processors are defective. [52] Vedemosti reported that Baikal Electronics began to experiment with domestically packaging chips in Russia at the end of 2021 and that outdated equipment and a lack of experienced employees caused the large amount of processor defects.
Russian Technological Adaptations (Russian objective: Introduce technological innovations to optimize systems for use in Ukraine)
Russian drone developer Albatross LLC told Kremlin newswire TASS that Russian forces used the Albatross M5 long-range reconnaissance drones to guide aviation and artillery strikes while repelling recent pro-Ukrainian Russian raids into Belgorod Oblast. [53] Albatross LLC noted that the modernized Albatross M5 drone has a maximum range of 60-80 kilometers.
Russian state news outlet RIA Novosti reported that Russian T-72B3, T-72B3M, T-80BVM, and T-90M tanks operating in Ukraine use Reflex-M guided weapon systems with the Invar-M/M1 anti-tank guided missiles to strike Ukrainian and Western-made vehicles. [54]
Ukrainian Defense Industrial Efforts (Ukrainian objective: Develop its defense industrial base to become more self-sufficient in cooperation with US, European, and international partners)
ISW is not publishing coverage of Ukrainian defense industrial efforts today.
Activities in Russian-occupied areas (Russian objective: Consolidate administrative control of annexed areas; forcibly integrate Ukrainian citizens into Russian sociocultural, economic, military, and governance systems)
ISW is not publishing coverage of activities in Russian-occupied areas of Ukraine today.
Russian officials are weaponizing international responses to the Crocus City Hall attack to accuse the West of espousing Russophobic policies and to baselessly blame Ukraine of involvement in the attack. Russian Ambassador to Austria Dmitry Lyubinsky claimed on March 27 that while the Austrian government reacted to the Crocus City Hall attack, it did not use the words “terrorist attack” or condemn the attack. [55] Lyubinsky accused Austria of having “taken a very special position in its hypocrisy” and a “daze of permissiveness” towards Ukraine and reiterated the Kremlin narrative baselessly connecting Ukraine to the attack. Russian Foreign Ministry Spokesperson Maria Zakharova reported that Russia has received 24-hour non-stop words of support from around the globe following the attack, but immediately pivoted to accuse Ukraine of involvement in the attack and blame NATO members of monopolizing the global fight against terror. [56]
Significant activity in Belarus (Russian efforts to increase its military presence in Belarus and further integrate Belarus into Russian-favorable frameworks and Wagner Group activity in Belarus)
Nothing significant to report.
Note: ISW does not receive any classified material from any source, uses only publicly available information, and draws extensively on Russian, Ukrainian, and Western reporting and social media as well as commercially available satellite imagery and other geospatial data as the basis for these reports. References to all sources used are provided in the endnotes of each update.

[1] https://ukraine.un.org/sites/default/files/2024-03/2024-03-26%20OHCHR%2038th%20Periodic%20Report.pdf
[2] https://ukraine.un.org/en/264368-un-says-russia-continues-torture-execute-ukrainian-pows
[3] https://www.understandingwar.org/backgrounder/russian-offensive-campaign-assessment-february-20-2024 ; https://www.understandingwar.org/backgrounder/russian-offensive-campaign-assessment-february-18-2024 ; https://www.understandingwar.org/backgrounder/russian-offensive-campaign-assessment-february-10-2024 ; https://www.understandingwar.org/backgrounder/russian-offensive-campaign-assessment-january-3-2024 ; https://www.understandingwar.org/backgrounder/russian-offensive-campaign-assessment-february-20-2024 ; https://www.understandingwar.org/backgrounder/russian-offensive-campaign-assessment-december-27-2023
[4] https://www.ohchr.org/en/instruments-mechanisms/instruments/geneva-convention-relative-treatment-prisoners-war
[5] https://ukraine.un.org/sites/default/files/2024-03/2024-03-26%20OHCHR%2038th%20Periodic%20Report.pdf
[6] https://www.understandingwar.org/sites/default/files/24-210-01%20ISW%20Occupation%20playbook.pdf
[7] https://t.me/tass_agency/240300 ; https://t.me/astrapress/52521 ; https://t.me/tass_agency/240322
[8] https://ria dot ru/20240327/rassledovanie-1936142056.html ; https://meduza dot io/news/2024/03/27/deputaty-gosdumy-potrebovali-ot-sk-rassledovat-akty-terrorizma-kotorye-ssha-sovmestno-so-stranami-nato-i-spetssluzhbami-ukrainy-osuschestvlyayut-v-rossii
[9] https://isw.pub/UkrWar032324 ; https://isw.pub/UkrWar032424 ; https://isw.pub/UkrWar032524 ; https://isw.pub/UkrWar032624
[10] https://t.me/tass_agency/239253%C2%A0;%C2%A0https://isw.pub/UkrWar020624%C2%A0;%C2%A0https://isw.pub/UkrWar031824%C2%A0 ; https://www.reuters.com/world/europe/putin-calls-ukrainian-attack-belgorod-terrorism-promises-more-strikes-2024-01-01/ ; https://www.understandingwar.org/backgrounder/russian-offensive-campaign-assessment-march-23-2024 ; https://isw.pub/RusCampaignOct10
[11] https://isw.pub/UkrWar032324
[12] https://isw.pub/UkrWar032324
[13] https://t.me/bbcrussian/62850
[14] https://t.me/vchkogpu/47045
[15] https://t.me/bazabazon/26432 ; https://t.me/bazabazon/26440 ; https://meduza dot io/news/2024/03/27/politsiya-i-rosgvardiya-priehali-s-reydom-na-sklad-wildberries-v-podmoskovnoy-elektrostali-u-rabotnikov-proveryayut-dokumenty-nekotoryh-uvozyat-v-voenkomat ; https://t.me/tass_agency/240303 ; https://t.me/tass_agency/240290
[16] https://t.me/rybar/58588 ; https://t.me/notes_veterans/16295 ; https://t.me/historiographe/12011 ; https://t.me/voenacher/63252
[17] https://www.understandingwar.org/backgrounder/russian-offensive-campaign-assessment-march-26-2024 ; https://understandingwar.org/backgrounder/russian-offensive-campaign-assessment-march-24-2024
[18] https://www.facebook.com/GeneralStaff.ua/posts/pfbid02rxTJAPqhSGh5mqY7C4XDTQiRjiVX25K4Tmx6tT6GCypPhjw8tmKBZAmRa5jaETbGl ; https://www.facebook.com/GeneralStaff.ua/posts/pfbid02ReTBwNLG8czu42xB89ixKbv1WzZE2LqsgMcXwngSeHHpRjAXoaR3esPk1eCxZiZ8l ; https://t.me/mod_russia/37036 ; https://t.me/wargonzo/19025 ; https://t.me/luhanskaVTSA/17835 ; https://t.me/wargonzo/19025
[19] https://t.me/dva_majors/38313 ; https://t.me/DnevnikDesantnika/8702
[20] https://t.me/RKadyrov_95/4620
[21] https://suspilne dot media/714544-zelenskij-zminiv-sekretara-rnbo-zvit-oon-sodo-stracenih-ukrainskih-polonenih-763-den-vijni-onlajn/?anchor=live_1711553688&utm_source=copylink&utm_medium=ps ; https://armyinform dot com.ua/2024/03/27/boyeprypas-yakym-rosiyany-vdaryly-po-harkovu-mozhe-letity-na-vidstan-do-90-km-oleg-synyegubov/
[22] https://suspilne dot media/714544-zelenskij-zminiv-sekretara-rnbo-zvit-oon-sodo-stracenih-ukrainskih-polonenih-763-den-vijni-onlajn/?anchor=live_1711553688&utm_source=copylink&utm_medium=ps; https://armyinform dot com.ua/2024/03/27/boyeprypas-yakym-rosiyany-vdaryly-po-harkovu-mozhe-letity-na-vidstan-do-90-km-oleg-synyegubov/
[23] https://armyinform dot com.ua/2024/03/27/boyeprypas-yakym-rosiyany-vdaryly-po-harkovu-mozhe-letity-na-vidstan-do-90-km-oleg-synyegubov/
[24] https://isw.pub/UkrWar031024
[25] https://t.me/RVvoenkor/64758; https://t.me/basurin_e/10068 ; https://t.me/rusich_army/13845
[26] https://t.me/rusich_army/13845
[27] https://t.me/mod_russia/37029 ; https://www.understandingwar.org/backgrounder/russian-offensive-campaign-assessment-march-23-2024
[28] https://t.me/mod_russia/37044 ; https://t.me/mod_russia/37051 ; https://www.facebook.com/GeneralStaff.ua/posts/pfbid02Lh7wn9dDbMDZcCSUP4kHDoHuABYPPUB5vnfakuyQw21x2MKXQ1fcsLqAgYeuSQVWl ; https://www.facebook.com/GeneralStaff.ua/posts/pfbid02rxTJAPqhSGh5mqY7C4XDTQiRjiVX25K4Tmx6tT6GCypPhjw8tmKBZAmRa5jaETbGl; https://www.facebook.com/GeneralStaff.ua/posts/pfbid02ReTBwNLG8czu42xB89ixKbv1WzZE2LqsgMcXwngSeHHpRjAXoaR3esPk1eCxZiZ8l ; https://t.me/DnevnikDesantnika/8702 ; https://t.me/negumanitarnaya_pomosch_Z/16170 ; https://t.me/wargonzo/19025 ; https://t.me/rusich_army/13845 ;
[29] https://t.me/samotniyskhid/4868
[30] https://t.me/creamy_caprice/4888; https://t.me/kultshturmovika_ukraine/1773 ; https://t.me/creamy_caprice/4889; https://t.me/c/1595839251/3625; https://x.com/GeoConfirmed/status/1772981767139430744?s=20
[31] https://t.me/DnevnikDesantnika/8702 ; https://t.me/dva_majors/38373 ; https://t.me/negumanitarnaya_pomosch_Z/16183 ; https://t.me/DnevnikDesantnika/8724 ; https://t.me/rybar/58575
[32] https://t.me/DnevnikDesantnika/8720
[33] https://www.facebook.com/GeneralStaff.ua/posts/pfbid02rxTJAPqhSGh5mqY7C4XDTQiRjiVX25K4Tmx6tT6GCypPhjw8tmKBZAmRa5jaETbGl; https://www.facebook.com/GeneralStaff.ua/posts/pfbid02ReTBwNLG8czu42xB89ixKbv1WzZE2LqsgMcXwngSeHHpRjAXoaR3esPk1eCxZiZ8l ; https://www.facebook.com/GeneralStaff.ua/posts/pfbid02Lh7wn9dDbMDZcCSUP4kHDoHuABYPPUB5vnfakuyQw21x2MKXQ1fcsLqAgYeuSQVWl ; https://t.me/mod_russia/37044 ; https://t.me/mod_russia/37051 ; https://t.me/dva_majors/38313 ; https://t.me/DnevnikDesantnika/8720 ; https://t.me/DnevnikDesantnika/8702 ; https://t.me/wargonzo/19025 ; https://t.me/voenkorKotenok/55225
[34] https://t.me/tivaz_artillery/3650; https://t.me/creamy_caprice/4893
[35] https://www.facebook.com/GeneralStaff.ua/posts/pfbid02Lh7wn9dDbMDZcCSUP4kHDoHuABYPPUB5vnfakuyQw21x2MKXQ1fcsLqAgYeuSQVWl ; https://www.facebook.com/GeneralStaff.ua/posts/pfbid02rxTJAPqhSGh5mqY7C4XDTQiRjiVX25K4Tmx6tT6GCypPhjw8tmKBZAmRa5jaETbGl; https://www.facebook.com/GeneralStaff.ua/posts/pfbid02ReTBwNLG8czu42xB89ixKbv1WzZE2LqsgMcXwngSeHHpRjAXoaR3esPk1eCxZiZ8l ; https://t.me/dva_majors/38313 ; https://t.me/wargonzo/19025 ; https://t.me/boris_rozhin/118101 ; https://t.me/voenkorKotenok/55225
[36] https://t.me/boris_rozhin/118105
[37] https://www.facebook.com/GeneralStaff.ua/posts/pfbid02rxTJAPqhSGh5mqY7C4XDTQiRjiVX25K4Tmx6tT6GCypPhjw8tmKBZAmRa5jaETbGl; https://www.facebook.com/GeneralStaff.ua/posts/pfbid02ReTBwNLG8czu42xB89ixKbv1WzZE2LqsgMcXwngSeHHpRjAXoaR3esPk1eCxZiZ8l ; https://t.me/mod_russia/37044 ; https://t.me/mod_russia/37052 ; https://www.facebook.com/GeneralStaff.ua/posts/pfbid02Lh7wn9dDbMDZcCSUP4kHDoHuABYPPUB5vnfakuyQw21x2MKXQ1fcsLqAgYeuSQVWl
[38] https://www.facebook.com/GeneralStaff.ua/posts/pfbid02Lh7wn9dDbMDZcCSUP4kHDoHuABYPPUB5vnfakuyQw21x2MKXQ1fcsLqAgYeuSQVWl ; https://www.facebook.com/GeneralStaff.ua/posts/pfbid02rxTJAPqhSGh5mqY7C4XDTQiRjiVX25K4Tmx6tT6GCypPhjw8tmKBZAmRa5jaETbGl; https://www.facebook.com/GeneralStaff.ua/posts/pfbid02ReTBwNLG8czu42xB89ixKbv1WzZE2LqsgMcXwngSeHHpRjAXoaR3esPk1eCxZiZ8l ; https://t.me/SJTF_Odes/7591 ; https://t.me/rybar/58575 ; https://t.me/dva_majors/38313 ; https://t.me/DnevnikDesantnika/8715 ; https://t.me/DnevnikDesantnika/8692 ; https://t.me/wargonzo/19025
[39] https://t.me/batalyon15/4045
[40] https://www.facebook.com/GeneralStaff.ua/posts/pfbid02rxTJAPqhSGh5mqY7C4XDTQiRjiVX25K4Tmx6tT6GCypPhjw8tmKBZAmRa5jaETbGl; https://www.facebook.com/GeneralStaff.ua/posts/pfbid02ReTBwNLG8czu42xB89ixKbv1WzZE2LqsgMcXwngSeHHpRjAXoaR3esPk1eCxZiZ8l ; https://t.me/dva_majors/38313
[41] https://t.me/kpszsu/12330
[42] https://t.me/pgo_gov_ua/22717 ; https://armyinform.com dot ua/2024/03/27/vijska-rf-atakuvaly-izyum-shahedamy-poshkodzheno-gimnaziyu-poraneno-ohoronczya/ ; https://t.me/synegubov/8827?single
[43] https://t.me/synegubov/8827
[44] https://www.facebook.com/pvkshid/posts/pfbid0LGmUtBDdzmxud8zZ23FDoN8eKarYJkLS6YrsSUzB62HVo7uSrXWhxPxnnzAhuSUyl
[45] https://t.me/mykolaivskaODA/8840 ; https://t.me/dsns_mykolaiv/4948 ; https://t.me/SJTF_Odes/7600
[46] https://armyinform.com dot ua/2024/03/27/u-sylah-oborony-povidomyly-pro-kilkist-rosijskyh-czyrkoniv-u-krymu/
[47] https://armyinform.com dot ua/2024/03/27/u-povitryanyh-sylah-povidomyly-pro-sposoby-zbyttya-rosijskyh-czyrkoniv/
[48] https://t.me/mobilizationnews/18111
[49] https://t.me/mobilizationnews/18111
[50] https://t.me/mobilizationnews/18114
[51] https://t.me/mod_russia/37031
[52] https://www.severreal.org/a/bolshe-poloviny-rossiyskih-protsessorov-baykal-okazalis-brakovannymi/32879476.html ; https://www.vedomosti dot ru/technology/articles/2024/03/26/1027924-razrabotchik-protsessorov-baikal-lokalizuet-odin-iz-etapov-proizvodstva
[53] https://t.me/tass_agency/240240 ; https://t.me/tass_agency/240241 ; https://t.me/tass_agency/240268
[54] https://ria dot ru/20240327/rakety-1936068479.html
[55] https://t.me/RusBotWien_RU/4869
[56] https://t.me/MID_Russia/38112
- Yekaterinburg
- Novosibirsk
- Vladivostok
- Tours to Russia
- Practicalities
- Russia in Lists
Rusmania • Deep into Russia
Out of the Centre
Savvino-storozhevsky monastery and museum.

Zvenigorod's most famous sight is the Savvino-Storozhevsky Monastery, which was founded in 1398 by the monk Savva from the Troitse-Sergieva Lavra, at the invitation and with the support of Prince Yury Dmitrievich of Zvenigorod. Savva was later canonised as St Sabbas (Savva) of Storozhev. The monastery late flourished under the reign of Tsar Alexis, who chose the monastery as his family church and often went on pilgrimage there and made lots of donations to it. Most of the monastery’s buildings date from this time. The monastery is heavily fortified with thick walls and six towers, the most impressive of which is the Krasny Tower which also serves as the eastern entrance. The monastery was closed in 1918 and only reopened in 1995. In 1998 Patriarch Alexius II took part in a service to return the relics of St Sabbas to the monastery. Today the monastery has the status of a stauropegic monastery, which is second in status to a lavra. In addition to being a working monastery, it also holds the Zvenigorod Historical, Architectural and Art Museum.
Belfry and Neighbouring Churches

Located near the main entrance is the monastery's belfry which is perhaps the calling card of the monastery due to its uniqueness. It was built in the 1650s and the St Sergius of Radonezh’s Church was opened on the middle tier in the mid-17th century, although it was originally dedicated to the Trinity. The belfry's 35-tonne Great Bladgovestny Bell fell in 1941 and was only restored and returned in 2003. Attached to the belfry is a large refectory and the Transfiguration Church, both of which were built on the orders of Tsar Alexis in the 1650s.

To the left of the belfry is another, smaller, refectory which is attached to the Trinity Gate-Church, which was also constructed in the 1650s on the orders of Tsar Alexis who made it his own family church. The church is elaborately decorated with colourful trims and underneath the archway is a beautiful 19th century fresco.
Nativity of Virgin Mary Cathedral

The Nativity of Virgin Mary Cathedral is the oldest building in the monastery and among the oldest buildings in the Moscow Region. It was built between 1404 and 1405 during the lifetime of St Sabbas and using the funds of Prince Yury of Zvenigorod. The white-stone cathedral is a standard four-pillar design with a single golden dome. After the death of St Sabbas he was interred in the cathedral and a new altar dedicated to him was added.

Under the reign of Tsar Alexis the cathedral was decorated with frescoes by Stepan Ryazanets, some of which remain today. Tsar Alexis also presented the cathedral with a five-tier iconostasis, the top row of icons have been preserved.
Tsaritsa's Chambers

The Nativity of Virgin Mary Cathedral is located between the Tsaritsa's Chambers of the left and the Palace of Tsar Alexis on the right. The Tsaritsa's Chambers were built in the mid-17th century for the wife of Tsar Alexey - Tsaritsa Maria Ilinichna Miloskavskaya. The design of the building is influenced by the ancient Russian architectural style. Is prettier than the Tsar's chambers opposite, being red in colour with elaborately decorated window frames and entrance.

At present the Tsaritsa's Chambers houses the Zvenigorod Historical, Architectural and Art Museum. Among its displays is an accurate recreation of the interior of a noble lady's chambers including furniture, decorations and a decorated tiled oven, and an exhibition on the history of Zvenigorod and the monastery.
Palace of Tsar Alexis

The Palace of Tsar Alexis was built in the 1650s and is now one of the best surviving examples of non-religious architecture of that era. It was built especially for Tsar Alexis who often visited the monastery on religious pilgrimages. Its most striking feature is its pretty row of nine chimney spouts which resemble towers.

Plan your next trip to Russia
Ready-to-book tours.
Your holiday in Russia starts here. Choose and book your tour to Russia.
REQUEST A CUSTOMISED TRIP
Looking for something unique? Create the trip of your dreams with the help of our experts.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
perpetrated domestic violence against an intimate partner is the concentration of this dissertation. The official statistics indicate that the scope of the problem of intimate partner violence in the United States is overwhelming. Further, domestic violence constitutes a public health
Violence against women is one of the most widespread, persistent and detrimental violations of human rights in today's world, which has not been reported in most cases due to impunity, silence, stigma and shame, even in the age of social communication. Domestic violence against women harms individuals, families, and society. The objective of this study was to investigate the prevalence and ...
exposure to domestic violence in childhood was the second highest predictor for experiencing domestic violence as an adult (Kimber et al., 2018). By gaining insight into the problem, this research can educate adolescents and adults on the impacts of domestic violence and identify methods to decrease or prevent violence in future relationships.
This Dissertation is brought to you for free and open access by the Walden Dissertations and Doctoral Studies Collection at ScholarWorks. It has been accepted for inclusion in Walden Dissertations and Doctoral Studies by an ... domestic violence victims every year, while domestic violence against women, overall, is on the rise. 5 . Problem ...
The U.S. Department of Justice (2018) has defined domestic violence (DV) as a pattern of abusive behavior in any relationship that is used by one partner to gain or maintain power and control over another intimate partner. Domestic violence can be physical, sexual, emotional, economic, or threats of actions that influence another person. (p. 1)
School of Professional Psychology Theses, Dissertations and Capstone Projects 7-25-2008 Domestic Violence Against Women: A Literature Review Amanda J. Grovert Pacific University This Thesis is brought to you for free and open access by the Theses, Dissertations and Capstone Projects at CommonKnowledge. It has been accepted
As domestic violence continues to pose a significant social and public health burden, all avenues pursued at an interagency, interstate, and federal level collaborative effort will adequately mitigate the risk proponents of domestic violence, especially during adverse
Domestic Violence Definitions and Power in Relationships For the purpose of this thesis the author will be relying on many definitions of terms regarding domestic violence against women. The United States Department of Justice defines domestic violence as a pattern of abusive behavior in any relationship that
Abstract. This empirical literature review examines and synthesizes inter-national domestic violence literature related to prevalence, types of violence, honor and dowry killings, health=pregnancy ...
The first part of this article considers this thesis as it is articulated in present policy responses to domestic violence. The Criminalisation Thesis: Strengths and Weaknesses. Goodmark's analysis points to the different ways in which criminal justice responses have reaped benefits for women living in violent relationships. For example ...
This thesis foregrounds data from a survivor-led, qualitative study on domestic violence and abuse (DVA) prevention and intervention, set against the backdrop of UK austerity and the increasingly prominent political endorsement of a gender-neutral conceptualisation of DVA. The study charts how DVA prevention, victimhood and perpetration discourses might be productively reworked to shift the ...
My dissertation will contribute to the larger political science field by showcasing how public policy decisions are affected by political culture, resources, and information. ... Domestic violence encompasses any "physical, visual, verbal, or sexual acts that are experienced by a woman or girl as a threat, invasion, or assault and that have ...
Publisher's Version Abstract. Jemia MB, Sedou L, Scott M, Thill M, Pavlou S, Brié F, Alqurah L. Violence against Women in the context of Political Transformations and Economic Crisis in the Euro-Mediterranean Region: Trends and Recommendations towards Equality and Justice. EuroMed Rights - Euro-Mediterranean Human Rights Network; 2014.
officers' responses at the scene of incidents of domestic violence? The thesis is structured around four published journal papers. Paper 1 uses national population survey data to show that coercive control is experienced primarily by women, and is more harmful than other forms of domestic violence. Paper 2 uses data from risk
of abuse and perpetrators exploit this avenue to continue abuse against victims. Some of the adverse effects that abuse of technology has on women who are. victims of domestic violence include changes in sleep and eating, anxiety, safety. concerns, and feelings of helplessness (Winkelman, Early, Walker, Chu & Yick-.
Domestic Violence Sofia Amaral* Gordon B. Dahl† Victoria Endl-Geyer ‡ Timo Hener§ Helmut Rainer¶ January 2023 Abstract There is a vigorous debate on whether arrests for domestic violence (DV) will deter future abuse or create a retaliatory backlash. We study how arrests affect the dynamics of DV using
Welcome to White Rose eTheses Online - White Rose eTheses Online
This dissertation will focus specifically on the violence aspect of domestic violence. Marianne Hester et al (2007) states that there is no official definition of domestic violence and because of this there are significant difficulties in getting a conviction through the courts. The Government on the other hand have a different
Dmitriy V. Mikheev, Karina A. Telyants, Elena N. Klochkova, Olga V. Ledneva; Affiliations Dmitriy V. Mikheev
Russian forces recently made confirmed advances near Avdiivka and southwest of Donetsk City on March 27. Russian Storm-Z personnel continue to complain about their poor treatment by the Russian Ministry of Defense (MoD) as the MoD tries to posture efficacy in its force generation and social benefit allocation system.
shocks and threatened with execution, and over half of the interviewees experienced sexual violence. ... efforts are insufficient to generate the domestic response it likely desires.[12] Russian authorities are increasing legal pressure against migrants in Russia following recent Russian officials' proposals for harsher, measures against ...
White, Nadine, "Women, Domestic Violence Service Providers, and Knowledge of Technology-Related Abuse" (2019). Walden Dissertations and Doctoral Studies. 6703. Many victims of domestic violence face continued exposure to abuse through technology because intimate partners may use technology as weapon against them.
Zvenigorod's most famous sight is the Savvino-Storozhevsky Monastery, which was founded in 1398 by the monk Savva from the Troitse-Sergieva Lavra, at the invitation and with the support of Prince Yury Dmitrievich of Zvenigorod. Savva was later canonised as St Sabbas (Savva) of Storozhev. The monastery late flourished under the reign of Tsar ...