Dissertation Information
Dissertation Requirements : Given the breadth of types of work conducted in the Psychology Department, there is no one-size fits all fully quantitative description of what is required of a PhD dissertation. However, there are broad principles that should be met by every dissertation regardless of things like exact format, number of studies, methods employed, length of the final document, etc.
These include:
- The final product should demonstrate original and independent thought and investigation. In short, it should be clear that the student played the primary role in all aspects of the dissertation – from selecting an important topic, to generating hypotheses, to designing studies/methods/analytic procedures, to interpreting the outcomes, to writing up/disseminating the results. Output where, for instance, an advisor or labmate played a major role (e.g., wrote most of the text, designed the experiment or conducted the analyses, etc.) will likely not meet this principle.
- The final product should represent a coherent and significant advancement in knowledge. The dissertation should clearly lay out the initial state of scientific knowledge, the new ideas and/or lines of inquiry proposed by the student, and why those new ideas/lines of inquiry are important. The full dissertation should also be coherent and address some well-defined topic and sections should flow logically together. As an example, three different studies each on very different topics with no easily apparent logical flow or link will likely not meet this principle.
The best arbiter of whether these principles are adhered to will always be the student’s mentor and Mentoring Committee (as they are best suited to evaluate whether, for instance, the work is coherent and significant). Upon hitting dissertator status, students, in concert with their mentor should begin mapping out the path toward a final dissertation together with one *required* step being the dissertation proposal meeting (see below) . In short, when students leave that meeting if the proposal is approved (and the associated form is filled out: Dissertation Proposal Form ) the student should have confidence that the planned research, if conducted and presented in an appropriate manner, will meet the general dissertation principles outlined above.
Dissertation Proposal : You should meet with your full Mentoring Committee as early as you can to propose your thesis. You should realize your proposal is not a contract that commits you to conducting only what is proposed. Instead, the dissertation proposal provides you the opportunity to think deeply about your research and formulate a research plan with the expert advice from your committee. Early completion of the proposal is key to a timely degree completion. You can change experimental plans as your research unfolds. The Dissertation Proposal Form should be completed and turned in to the Graduate Coordinator’s office.
Dissertation Committee Composition : Dissertation committees must have at least four members. At least three members of the committee must be in Psychology or be Psychology-affiliated, and at least one member must be from outside Psychology. Further, at least three members of the dissertation committee must be UW-Madison graduate faculty or former UW-Madison graduate faculty up to one year after resignation or retirement. The chair of the committee must be in Psychology or be Psychology-affiliated at UW-Madison.
Additional notes : (1) The Graduate Coordinator in Psychology can help you determine whether particular individuals are “graduate faculty”. (2) Students who feel a different committee composition (e.g., two in Psychology and two outside) would be more appropriate for their dissertation may petition the Graduate Committee for an exception. (3) The “outside Psychology” member must be UW-Madison graduate faculty or former UW-Madison graduate faculty up to one year after resignation or retirement. (4) More details about the Graduate School’s requirements for dissertation committees can be found here: https://grad.wisc.edu/documents/committees/
Dissertation Defense : As part of the thesis planning, you should consult the Graduate School’s “Guide to Preparing Your Doctoral Dissertation” http://grad.wisc.edu/currentstudents/doctoralguide . These publications contain important information concerning formatting your thesis, submission of your thesis, and deadlines for completion of degree requirements. You and your Committee will set a date for theIn-Person Defense of the thesis.
Timeline : The date chosen for the defense must allow sufficient time prior to your departure from the University for revisions suggested by the Committee to be incorporated into the final version of the Dissertation.
Final Warrant & Defense : At least 4 weeks before the final Public Presentation and Dissertation Examination, please contact the Graduate Coordinator so your Final Ph.D. warrant can be ordered. No later than 2 weeks before the defense and after the details have been approved by your major professor, you should provide the Graduate Coordinator with the date, time, and place of the Public Presentation. An announcement will be e-mailed to faculty, graduate students, and affiliated faculty.
The completed Dissertation should be delivered to your Committee at least 2 weeks before the defense. If the Dissertation is submitted later than this, the date for the defense will be rescheduled automatically by your major professor to allow at least 2 weeks for review. Any change in this schedule must receive prior approval by all members of your Committee.
The thesis defense normally consists of a public presentation of the thesis followed by a closed meeting with the Committee. At the conclusion of the defense you will be asked to leave the room and the Committee will discuss whether to accept the thesis. This decision will be based on the quality of the public presentation and of the written Dissertation. The Committee will not approve the Dissertation until it is judged to be a satisfactory final version acceptable for the Ph.D. degree and for submission to the Graduate School. Thesis: While the details of your Dissertation will be determined by you and your Committee, all Dissertations are expected to be of publishable quality and to conform to a general standard. The Dissertation should be written in a style that is compatible with that commonly used for manuscripts published in major scientific journals.
*INTERIM AI-USE POLICY* When going through the dissertation process, keep in mind that the Interim AI-Use Policy comes into play at both the proposal and final paper stage for any written work. The policy and associated forms are below.
Interim AI-Use Policy
If students utilize generative-AI in any fashion while preparing written work that is part of a major department milestone (specifically: FYP paper, preliminary exams, dissertation), they must include an AI-use statement fully describing the ways AI was used in the preparation of the written work. The statement will consist of a checklist (e.g., use of AI for developing analysis code, data-visualization code, creating bullet points or paper skeleton/structure, editing grammar, editing style, coming up with new research ideas, making suggestions regarding possible research designs or methods, reviewing literature), and a more open-ended short narrative section describing in more detail how generative AI was used for these purposes.
Students should discuss their planned use of generative-AI with their respective committees and fill out the associated AI-Use form prior to beginning any written work to ensure that the student and committee members are on the same page with regard to the planned use(s) of generative-AI and if any deviations from that plan occur during the process of producing the written work, to inform the committee prior to implementation (in essence, the committee members should not be surprised by any uses when they receive the final document(s)).
Students should have this discussion and fill out the associated AI-Use Form for BOTH the proposal and final paper stages.
- Technical Support
- Find My Rep

You are here
Your Psychology Dissertation
- Emily Harrison - Birmingham City University, UK
- Panagiotis Rentzelas
- Description
Your Psychology Dissertation has been specifically created to guide your students through their dissertation helping them to feel confident at every stage of their independent psychology research projects.
This book will take them through the entire process of designing, conducting and then writing up their research, providing invaluable tips and support along the way, as well as answering all those frequently asked questions. Whether they need to know more about quantitative or qualitative research methodology, need help in choosing a topic, and/or are struggling to review and understand the literature, this book covers it all. Your Psychology Dissertation is suitable for all psychology students looking for dissertation success.
Take a look at the online resources to get lots of useful templates and guidance to help with every step of the way.
See what’s new to this edition by selecting the Features tab on this page. Should you need additional information or have questions regarding the HEOA information provided for this title, including what is new to this edition, please email [email protected] . Please include your name, contact information, and the name of the title for which you would like more information. For information on the HEOA, please go to http://ed.gov/policy/highered/leg/hea08/index.html .
For assistance with your order: Please email us at [email protected] or connect with your SAGE representative.
SAGE 2455 Teller Road Thousand Oaks, CA 91320 www.sagepub.com
Supplements
Preview this book, for instructors.
Please select a format:
Select a Purchasing Option
Related products.

notifications_active To return to the old version of the website Click here
How to Write a Psychology Dissertation?

How to Write a Psychology Dissertation: A Comprehensive Guide to Thriving in Your Academic Journey
Embarking on the journey of writing a psychology dissertation can feel like setting out to conquer an uncharted wilderness. You’ve taken countless courses, poured over numerous books, and spent long nights researching theories and experiments. Now, the culmination of years of study lies ahead, and the challenge feels both exciting and daunting.
What is a psychology dissertation, exactly? At its core, it’s a systematic and comprehensive exploration of a chosen topic in the realm of psychology. It’s a formal, written work that presents your original research and findings, acting as a testament to your scholarly competence and your contribution to the field.
Crafting a psychology dissertation indeed feels like moving mountains—an undertaking that requires a firm grasp of the subject matter, meticulous research, and adept academic writing. Understanding the “how to write a psychology dissertation” process begins with demystifying the task itself, breaking it down into manageable pieces, and realizing its nature within the field of psychology. It’s a mountain that can be moved. With the right knowledge, tools, and strategies, you can navigate this journey successfully, transforming your psychology dissertation from a looming mountain into a manageable and rewarding endeavor.
In this article, we’ll be your experienced guide, helping you understand the nature and structure of a psychology dissertation. We’ll outline the step-by-step process involved in writing your dissertation, provide a treasure trove of innovative dissertation topics in psychology for inspiration, and offer top tips to survive—and even thrive—during this process. So, lace up your academic boots and get ready for a journey that will not only shape your psychology career but will also hone your skills as a researcher and a scholar.
Laying the Foundations: Psychology Dissertation Structure
Structuring your psychology dissertation involves more than simply organizing chapters. It’s about creating a logical sequence of arguments, evidence, and conclusions that guide your reader through your research journey. To come up with the perfect structure for your psychology dissertation, you first need to understand the dissertation definition psychology uses—it’s a formal, extensive piece of original research on a specific topic in the field of psychology. Here’s how you can shape each of its key components:
- The Abstract of your dissertation should be a microcosm of your research. It’s a short yet comprehensive snapshot of your dissertation, serving as a trailer that entices readers to delve into the main feature.
- Your Introduction sets the stage, presenting your research question and clarifying its significance. The key here is to captivate your readers, piquing their interest and illustrating what lies ahead. It’s important to clearly set out your objectives, painting a picture of the destination at the end of the research journey.
- In your Literature Review , you wear the hat of a detective, sifting through previous studies related to your topic and identifying the research gap your study intends to fill. This section is your opportunity to show your comprehensive understanding of the research landscape.
- The Methodology section is where you share the blueprint of your research design. It’s important to detail your approach, including the participants, materials, and procedures used, ensuring that your study could be replicated based on this information.
- Next, the Results section presents your findings. The spotlight here is on the data, presented clearly and objectively, often supported with visual aids for easier understanding. Your analysis should be transparent, making it easy for your readers to connect the dots themselves.
- The Discussion allows you to wear the hat of a storyteller. Here, you interpret your results, draw comparisons with previous research, and create a narrative that links back to your research question.
- Finally, the Conclusion is your reflective moment, summarizing the research journey, the insights gained, and the implications of your study. It’s also here that you propose future research directions inspired by the strengths and limitations of your study.
Remember, a dissertation is akin to a carefully crafted story—your research story. Building it with a solid and clearly outlined structure not only helps you, the author, but also your readers, helping them understand your thought process, follow your research journey, and appreciate your scholarly contribution.
You might also be interested in How to Do an Appendix for Your Dissertation or Thesis
Climbing the Ladder: Sequential Steps in Writing a Psychology Dissertation
Understanding the structure of a psychology dissertation is the first stepping stone. The journey towards completing it in full may initially seem daunting, but breaking the task into digestible steps can substantially lighten the load.
- Picking a Relevant and Original Topic
The first step towards writing your psychology dissertation is selecting a suitable topic. It should be something you are passionate about, as it will keep your interest during the long research and writing process. It should also be original, meaning it either hasn’t been researched before or offers a new perspective on an existing topic.
- Conducting an Extensive Literature Review
Having pinpointed your subject of interest, it’s time to dive deep into the existing scholarly work. Knowing what’s already been explored and identifying the uncharted territories not only frames the context of your research but also highlights its significance by filling an identified gap in the current body of knowledge.
- Crafting a Strong Hypothesis
Based on your topic and literature review, you’ll develop a hypothesis or research question. This statement should be clear, focused, and answerable within the scope of your study. It will guide the rest of your research.
- Detailing Your Methodology
Next, you need to decide how you’ll answer your research question. This involves picking a research method, identifying participants or data sources, choosing measurement instruments, and planning your data analysis. Detailing your methodology with precision is crucial for the validity of your study.
- Collecting and Analyzing Data
With your methodology in place, you’re ready to collect your data. This step can vary greatly depending on your research method but often involves running experiments, conducting surveys, or gathering existing data. Once collected, you’ll analyze your data using appropriate statistical techniques.
- Discussing Your Findings
After analyzing your data, it’s time to interpret your results. Discuss your findings in relation to your research question and the existing literature. It’s also important to acknowledge any limitations in your study and suggest areas for future research.
- Referencing Properly: APA Style in Psychology
Throughout this process, you’ll be drawing on the work of others to inform your study and support your claims. Always be diligent in crediting these sources to maintain academic integrity. Within psychological academia, referencing and bibliographies adhere to the stylistic prescriptions of the American Psychological Association (APA).
Crafting a psychology dissertation is indeed a demanding endeavor, but breaking the process into manageable tasks prepares you to confront upcoming challenges and ultimately, to contribute a substantial piece of work to your field.
Inspiration Awaits: 50 Innovative Psychology Dissertation Topics
Before you gear up for the rigorous task of crafting a psychology dissertation, choosing a captivating topic that intrigues you and has the potential to add something new to your field is crucial. The joy of your dissertation journey is enhanced manifold when the topic strikes a chord with you. Given the wide range of psychology subfields, you have an abundance of choices. Below, we offer fifty innovative topics spanning diverse areas of psychology to stimulate your creative thought process. Our aim here is to spark your imagination and provide you with a collection of innovative psychology dissertation ideas, which will serve as a springboard for your unique research, or you can just go ahead and pick the topic that speaks to you from our list.
Broadening Perspectives: Clinical Psychology
- The Impact of Mindfulness-Based Cognitive Therapy on Anxiety Disorders
- The Effectiveness of Teletherapy in Treating Depression
- The Role of Resilience in Coping with Chronic Illness
- The Impact of Sleep Disorders on Mental Health
- Psychotherapy Approaches for PTSD in Military Veterans
The Enigma of the Mind: Cognitive Psychology
- The Influence of Multitasking on Cognitive Load
- Memory Retention Strategies for Alzheimer’s Patients
- Decision-Making Processes in High-Pressure Situations
- The Role of Attention in Learning and Retention
- Cognitive Biases in Financial Decisions
Delving Deeper: Developmental Psychology
- The Influence of Parenting Styles on Child Self-Esteem
- Effects of Bullying on Adolescent Mental Health
- The Impact of Screen Time on Child Development
- How Does Gender Identity Unfold in a Child’s Developmental Journey?
- The Role of Play in Cognitive Development
Bridging the Gap: Social Psychology
- The Impact of Social Media on Body Image Perceptions
- Prejudice and Discrimination: Factors and Mitigation Strategies
- The Psychology of Altruism: Why Do We Help Others?
- The Role of Empathy in Conflict Resolution
- The Effect of Stereotypes on Interpersonal Relationships
Inside the Workplace: Organizational Psychology
- The Influence of Leadership Styles on Employee Satisfaction
- Emotional Intelligence: A Key Ingredient for Success in the Workplace?
- Impacts of Remote Work on Employee Productivity
- Strategies for Reducing Job Burnout
- The Effect of Organizational Culture on Employee Loyalty
The Mysterious Unconscious: Psychoanalytic Psychology
- The Influence of Childhood Trauma on Adult Relationships
- Understanding Defense Mechanisms: A Modern Perspective
- The Role of Dreams in Psychoanalysis
- Freud’s Theory of Personality: Modern Applications
- Transference and Countertransference in Therapeutic Settings
The Mind-Body Connection: Health Psychology
- The Psychological Impacts of Chronic Pain
- The Role of Self-Efficacy in Managing Diabetes
- Coping Mechanisms for Patients with Terminal Illnesses
- The Influence of Stress on Immune Response
- Mental Health Outcomes of Weight Loss Surgery
Life’s Final Chapter: Geriatric Psychology
- Mental Health Challenges in Aging Populations
- The Influence of Social Networks in Promoting Healthy Aging
- Cognitive Stimulation Therapies for Dementia Patients
- The Psychological Impact of Retirement
- Depression and Anxiety in Elderly: Intervention Strategies
Bridging Species: Comparative Psychology
- The Study of Animal Emotion: Can Animals Feel Joy or Sadness?
- Comparing Problem-Solving Abilities in Different Species
- The Influence of Environment on Animal Behavior
- Inter-species Communication: Myth or Reality?
- Studying Animal Behavior to Understand Human Psychology
Into the Unknown: Parapsychology
- Exploring Reports of Near-Death Experiences
- The Psychology Behind Belief in Paranormal Activities
- The Impact of Extra-sensory Perception (ESP) Beliefs on Anxiety Levels
- A Study on the Popularity and Psychological Impact of Astrology
- Analyzing the Effects of Hypnosis on Pain Management
Whether you’re captivated by cognitive processes, intrigued by interpersonal dynamics, or fascinated by the underpinnings of abnormal behavior, these topics offer a launching pad for your exploration. Remember, the best dissertation topic is one that excites your intellectual curiosity and aligns with your career aspirations.
You might also be interested in Dissertation Acknowledgements: Say Thank You with Dignity
Surviving and Thriving: Top Tips for Navigating Your Psychology Dissertation Journey
Embarking on your psychology dissertation is a substantial endeavor that requires not only intellectual effort but also strategic planning, emotional resilience, and diligent self-care. Here are ten tips to help you navigate this journey smoothly:
- Start early. The sooner you begin, the better. Start thinking about your dissertation topic well before it’s due. Early planning gives you plenty of time for thorough research, careful writing, and thoughtful revision.
- Choose a topic you love. Passion for your topic will fuel your research and keep you motivated during the lengthy writing process. Choose a topic that excites your intellectual curiosity and aligns with your career aspirations.
- Develop a work plan. Create a realistic timeline for your dissertation, breaking down the process into manageable tasks. Regularly update and refine your plan as you progress.
- Assemble a support team. Your supervisor is an invaluable guide, but don’t forget to build a broader support network. Seek out peers, mentors, and even professional support like writing consultants or tutors.
- Embrace the research process. Be prepared for unexpected findings and potential roadblocks. They are part of the research journey. Embrace them as learning opportunities that refine your problem-solving skills.
- Write regularly. Make writing a daily habit. Even if you only write a few sentences a day, this regular practice will keep your project moving forward and reduce the chance of writer’s block.
- Practice self-care. Burnout is a real risk during the dissertation process. Remember to prioritize self-care. Regular exercise, a healthy diet, adequate sleep, and mindfulness practices can all help maintain your mental and physical well-being.
- Seek constructive feedback. Regularly share your work with your supervisor and trusted peers. They can provide fresh perspectives and constructive criticism that help improve your dissertation.
- Cherish minor milestones. Each stride you make, irrespective of its size, is a step in the right direction. Recognizing these small achievements can lift your spirits and keep you fueled with determination.
- Keep the end goal in sight. Always remember why you’re undertaking this journey. Whether it’s to further your career, contribute to the field, or simply for the love of psychology, let your end goal be your guiding light.
Remember, the dissertation journey is not a sprint but a marathon. Embrace the process, nurture your resilience, and know that every challenge faced is an opportunity for growth.
Embracing the Journey: Making Your Psychology Dissertation an Achievable Endeavor
We completely understand that plunging into a psychology dissertation can seem like embarking on a voyage across an endless sea. It can be strenuous and, at times, tediously repetitive, but don’t lose your bearing. Your destination is there, even if it’s not immediately apparent.
This colossal endeavor, while daunting, is a remarkable landmark in your academic journey and a testament to your resolve, grit, and intellect. Granted, the journey is lengthy, strenuous, and at times, it will stretch your endurance. However, bear in mind that the most formidable journeys often end with the most gratifying outcomes.
When the dissertation journey seems too steep, remember why you chose this path in the first place – your passion for psychology, your quest for knowledge, and your desire to make a meaningful contribution to the field. Hold onto these motivations when the going gets tough.
If you find yourself cornered at times, don’t be hard on yourself. It’s an inherent part of the journey. Esteemed scholars have also experienced hurdles and unexpected shifts in their plans. When that happens, as it probably will, don’t hesitate to ask for assistance. Your advisors, peers, and a myriad of online platforms can serve as your navigational guide, leading you through these challenges. Additionally, maintain vigilance over your physical and mental health during this daunting yet exciting academic journey.
Regular respites, physical exercise, balanced nutrition, and sufficient rest can immensely contribute to sustaining your drive and concentration. Remember, every single step you take, regardless of its size, nudges you closer to your objective.
With tenacity, resilience, and the right network of support, this formidable project will progressively morph into an attainable goal. As you progress, your expertise in your chosen topic will broaden, and you will glean precious revelations about your own capacities and fortitude.
Embarking on the task of writing a psychology dissertation is utterly demanding, but it’s a task well worth tackling. So, inhale deeply, keep your eyes fixated on your goal, and march forward with bravery and resolve. You are capable of this!
You might also be interested in Effective Political Science Dissertation Topics to Choose
Do you have
Guidelines For Writing A Psychology Dissertation
Writing a psychology dissertation is difficult. Adhering to guidelines will help you finish this writing project. This article will provide clear instructions on how to write a psychology dissertation in order to achieve the highest quality end product possible. It will also explain why students must follow these guidelines to get the most out of their dissertations. Students can ensure that their psychological research papers are compelling and comprehensive by following these steps.
Definition Of A Psychology Dissertation
A psychology dissertation presents original research conducted by the author and submitted in partial fulfilment of doctoral degree requirements in psychology. To study a field topic, it usually requires extensive primary or secondary research. Neuropsychology, psychopharmacology, clinical, social, economic, developmental, and educational psychology are research topics.
The process of writing a dissertation requires careful planning and execution over a period of several months. This includes selecting suitable dissertation topics, developing hypotheses, designing experiments, collecting data through surveys, interviews, questionnaires, observations, etc., analysing results using statistical software programmes, drawing conclusions based on findings, synthesising information into a cohesive argument/theory proposal, and submitting the completed work to one’s university or college for assessment.
Choosing A Research Question
Choosing a psychology dissertation topic can be intimidating. A successful project requires careful consideration of the type of research needed, the resources available, and the nature of data collection. Here are some suggestions:
- Review previous literature: Before starting your own research, read existing literature to learn about current trends and topics. This will also help you identify knowledge gaps or areas that need more research.
- Consider practical considerations: When choosing a potential dissertation research question, consider whether it is feasible given time and resource constraints, e.g. Consider how much data your study needs to collect and analyse so you can schedule enough time for it.
- Brainstorm with peers: Discussing potential research questions with peers or faculty can be helpful. Collaborating with others may give you new perspectives and valuable feedback on the feasibility and scope of your project idea.
- Take inspiration from everyday life: If feeling stuck on coming up with new ideas, try reflecting upon issues faced in daily life or conversations overheard between family/friends which could potentially lead to interesting research question related to psychology.
Finding Sources And Data
Finding reliable sources and data for psychology research is crucial. According to a recent survey of over 200 dissertation writers in the field of psychology, 45% reported that they found their sources through online databases such as PsycINFO or Google Scholar. It’s crucial for aspiring psychologist researchers to know how to find reliable information.
Identifying what information you need from different sources is the first step. Depending on your topic, you may want to use interviews, surveys, quantitative or qualitative data, or existing studies and statistics. After determining the type of data collection techniques required for your project, you can begin looking for pertinent sources and materials.
Peer-reviewed journals, magazines, newspapers, and other publications are in online databases, making them great resources for psychology research. Searching these databases with keywords will narrow results to relevant items. Look at government websites for public access documents on psychosocial phenomena like mental health services utilisation rates or incarcerated population trends over time. Finally, interview professionals in the field who can provide insights and anecdotes about specific issues being studied.
Writing The Proposal
Writing a psychology dissertation proposal is an essential part of the process that must be done carefully in order to get approval. The structure and content of your proposal will depend on your institution’s requirements and any other guidance provided by your supervisor or department. However, there are some e g general elements you should include in a psychology dissertation proposal.
Consider possible topics before starting your proposal. Brainstorm ideas with colleagues or brainstorming alone can provide useful insights into possible dissertation topics. Consider recent developments in the field and think broadly about areas that may benefit from further exploration. Create detailed outlines after narrowing topics to ensure that every element in the final document has been considered during planning. By addressing all necessary components early on, this step can save time later.
Setting Objectives And Aims
When writing a psychology dissertation, it is essential for students to set objectives and aims. This guides the student’s research and provides a roadmap for their project. The objective of a psychology dissertation should be made clear from the onset so as to ensure that all subsequent research conducted aligns with this ultimate aim.
The overall aims of a psychology dissertation typically revolve around answering a specific question or solving some kind of problem within the field of psychology. These goals must be measurable; a successful dissertation must show progress towards them. As such, when setting objectives and goals for your psychology dissertation, make sure you have thoroughly considered what needs to be done to answer or solve the relevant issue. This will help you stay on track and track your project’s progress.
Structuring The Dissertation
To succeed, plan ahead and build a solid structure. Therefore, this section will explore how to effectively structure a psychology dissertation while providing helpful guidance throughout the process.
When structuring a paper, it’s important to remember that formats vary by context and topic. An introduction, literature review, methodology, results, and discussion should be included in most dissertations. If needed, students may add appendices or glossaries. Nevertheless, regardless of any extra formatting elements added – the standard format must remain consistent throughout.
The content of each section depends on your institution/requirements. tutor’s However, many universities provide templates outlining what is expected from each section or part (e.g., headings and sub-headings). This can help ensure that all information is relevant and presented clearly so readers can better understand your work’s main points. It also ensures logical flow between sections so readers don’t get confused when switching topics. Finally, examples can help clarify concepts and improve comprehension, improving readability!
Seeking Feedback And Advice
Receiving input on one’s work can provide valuable insight into the strengths and weaknesses of a written piece. Seeking feedback doesn’t mean giving up control; it’s an opportunity to learn and improve. Questions about research design and methods can help identify issues before they become major problems. Additionally, conversations with knowledgeable people often lead to new ideas or perspectives which can be used to improve the overall quality of a dissertation.
To maximise this process, ask psychology-related questions. Seeking general advice may seem helpful, but it will likely leave many gaps in understanding how to approach the task. It’s also important to listen and take notes when asking for feedback. Finally, while taking criticism personally can be difficult, it should be remembered that critics are doing so out of respect for one’s work and dedication to improving it.
Using Referencing Styles Correctly
To ensure that your psychology dissertation is of the highest academic standard, properly cite all sources. Referencing styles vary by discipline; in psychology, there are three main systems: APA, Harvard, and Chicago.
While researching your paper, record all relevant bibliographic information, cite each source in the text and at the end of your work, list all sources.
Also check your university’s style guide, as different departments have different reference formatting preferences (e.g. Follow the publisher’s guidelines if you want to be published!
Editing And Proofreading The Final Draft
It is essential that students take the time to edit and proofread their psychology dissertation draughts before submitting them as final. Restructuring sentences, eliminating redundancies, ensuring style and formatting consistency, and correcting spelling improves readability. Proofreading involves checking the draught for typos, misspellings, incorrect punctuation, subject-verb agreement issues, etc.
A psychology dissertation draught should be read aloud before proofreading to catch any mistakes or areas for improvement. It’s also helpful to have someone else proofread your work, as they may catch errors you missed. Finally, grammar checkers and other online tools can help spot minor errors in the text.
Preparing For Submission
It’s time to submit after all the edits. To meet deadlines, start early. First, make a checklist of items needed for submission. These may include required formatting standards and document length guidelines, as well as specific instructions for title page layout or table of contents. This list will help you meet all requirements before submitting your work. Make sure to include copies of primary sources in your dissertation and any additional materials requested by faculty reviewers.
In this stage of preparation for submission, it’s helpful to read over your entire dissertation again before mailing out documents so there are no surprises and you can determine whether further revisions are necessary. Finally, fill out all forms correctly with accurate contact and other personal data so universities or colleges can process submissions quickly and efficiently.
Defending The Work
The dissertation defence is the last step in finishing your psychology dissertation. It’s a chance to present and defend your research to a committee of experts, including university and outside faculty. During this process, you must explain the context of your work, provide evidence for its validity, discuss potential implications, and answer committee questions.
To defend your thesis or dissertation, you must understand the committee’s expectations and how to communicate with them. You should study their fields of expertise so you can quote them in your presentation. On exam day, practise presenting your material and make sure all materials are ready. When defending your project, you must understand every aspect because committees may ask difficult or unexpected questions. Finally, remember that these professors want what’s best for you and only want to help you finish your dissertation!
Publishing Outcomes
Disseminating research requires publishing the results of a psychology dissertation. It allows others to access and analyse findings that can influence future research, knowledge, and public policy.
Research findings can be published in academic journal articles. Academic journals have peer-review policies to ensure quality and accuracy. For timely information dissemination, many academic journals prioritise publication speed. Thus, these publications often require authors to format manuscripts and submit supplemental material according to specific guidelines (e.g., data sets). Therefore, review an academic journal’s requirements before publishing. This process requires researchers to consider copyright laws and ethics.
Online forums or self-publishing options like blogs or research websites are alternatives to academic journals. These options offer faster access but lack the oversight of more formalised outlets, which must meet strict standards before publishing.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long does it take to complete a psychology dissertation.
The student’s organisation, focus, commitment, and resources determine the answer. Here are some dissertation duration estimation tips:
- Time Frame: Generally speaking, writing a psychology dissertation will typically take anywhere between 12 months up to two years or more depending on the complexity of the subject matter you research and write about. It is important that you familiarise yourself with your university’s guidelines regarding length and format requirements in order to plan accordingly.
- Finish Psychology Dissertation: It takes time and effort to complete the dissertation. So you know what’s coming, think through every step. Make sure you set realistic goals for researching topics, collecting data, analysing results, writing draughts, and revising them until you reach a final version.
- Dissertation Duration: How much time you spend on your dissertation each day, week, month, etc. will determine how long it takes to complete. Setting aside regular chunks of time each week to work on your project can speed things up compared to working on it when free time allows. Small deadlines within larger ones help motivate by breaking down large tasks into smaller manageable ones.
- Psychology Dissertation Process: Creating plans like Gantt charts or mind maps can help visualise progress and provide structure and clarity at every stage of the dissertation process. Seeking feedback from peers or professors early on helps identify potential issues before too much time is spent on something that may be irrelevant or problematic for meeting the goals set out in advance, saving time!
Are There Any Resources Available To Help With The Writing Process?
Luckily, there are several resources available to help you write the dissertation. These resources offer assistance with all aspects of dissertation writing from start to finish, including research methods and materials, professional advice, and editing and revising draughts.
Many universities have dissertation writing centres to help students. For instance, these centres may have experienced tutors who can review draughts or answer questions about paper formatting. Some universities also offer online tutorials on dissertation writing, such as how to develop an argumentative thesis statement or use primary sources effectively.
Researchers can also access subject matter experts’ published work in psychology dissertation databases at online libraries. When writing a dissertation, it’s important to stay organised and use resources like those above.
How Do I Make Sure I’m Citing Sources Correctly?
Any psychology dissertation must accurately cite sources. This avoids plagiarism and adds credibility and validity to the research being conducted. To properly cite, there are several guidelines, referencing methods, and writing methods.
Citation rules may vary depending on the format or style used for the psychology dissertation. APA (American Psychological Association), for instance, requires authors to include a “in-text” reference and a full bibliographic reference at the end of each section or chapter. Therefore, you must know the citation format before starting your project. The Modern Language Association (MLA) and Harvard Referencing Systems have many online resources that can help you cite references.
When citing someone else’s work, include author name(s), year of publication, and page numbers if applicable. Finally, make sure all cited sources appear in the reference list at the end of your paper/chapter; these should be listed alphabetically by author surname and contain complete bibliographical information so that readers can access them easily if needed.
Online Dissertations Psychology Tuition
Recommended articles for Dissertations Psychology
How To Choose The Best Dissertation Topic For Psychology?
How To Create An Effective Outline For Psychology Dissertations
Writing A Psychology Dissertation Tips And Tricks
Mastering Psychology Advice For Writing A Dissertation
A service you can depend on
The quickest way to talk with us
Email us at [email protected]
Our partners
We are proud partners of TheProfs and BitPaper

- USF Research
- USF Libraries
Digital Commons @ USF > College of Arts and Sciences > Psychology > Theses and Dissertations
Psychology Theses and Dissertations
Theses/dissertations from 2023 2023.
Improving the Subjective Well-Being of Autistic Youth Utilizing a Positive Psychology Intervention , Nicolette Bauermeister
An Experimental Study of Negative Performance Feedback: Consideration of a Cognitive Pathway and Individual Difference Factors , Ansley M. Bender
A Critical Analysis of the Graduate Socialization of Racially Minoritized School Psychology Students , Tatiana J. Broughton
The Influence of COVID-19 on Tobacco Racial Health Disparities: Testing the Differential Effects of COVID-19 on Smoking Motivation Variables across Black and White Smokers , Patricia F. Calixte-Civil
An Evaluation of Measurement Invariance of DSM-5 Borderline Personality Disorder Criteria Across Heterosexual, Lesbian, Gay, and Bisexual Adults , E. Elisa Carsten
The Development of a Behaviorally Based Mentoring Workplace Scale , Christina N. Falcon
Examining the Role of Executive Functions on the Intention-Behavior Gap of Alcohol Harm Reduction Strategy Use , Becky K. Gius
The Effect of Psychopathy Trait Descriptions on Mock Juror Decision-Making , Bailey A. Hall
Context matters: Profiles of emotion regulation at work and home , Roxanne C. Lawrence
Planning to Behave Impulsively to Feel Better: An EMA Study of College Students' Nonsuicidal Self-Injury, Binge Eating, and Exercise Behaviors , Rose H. Miller
One Year Impact of the Advancing Coping and Engagement (ACE) Program on Advanced Placement and International Baccalaureate Student Success , Amanda C. Moseley
The Effects of Divided Attention in Free Recall: Affecting Trace Accumulation by Dividing Attention , Anne Olsen
Investigating Risk Factors of the Development of Compulsive Exercise and Eating Disorder Symptoms in College Students , Madeline Palermo
Invisible Families, Clear Consequences: Work-Family Integration Among Employees in Same Gender Presenting Romantic Relationships , Joseph Regina
Threats to School Safety: Examining Levels of Community Violence and Its Relation to School-Related Threats , Dorie Ross
The Social Anxiety Stigma Scale (SASS): Development, Factor Structure, and Validation , Ruba Rum
Socio-emotional effects of rejection: An experience-sampling examination , Gabriella Silva
Observed Error Monitoring as an Index of Theory of Mind , Kipras Varkala
I'll Make a Man Out of You: Precarious Manhood Beliefs among Heterosexual-Cisgender Men and Queer Men , Serena L. Wasilewski
From Other and From World: Expanding the Current Model of Existential Isolation , Roger Young Jr.
Temporal and Spatial Properties of Orientation Summary Statistic Representations , Jacob S. Zepp
Theses/Dissertations from 2022 2022
Boredom, Interoceptive Ability, and Emotional Eating , Erica Ahlich
Environmental Transmission of Career Interests Through a Genetic Lens: Understanding the Confounding Around Parental Occupation , Tyler Allan
Do Suicide Attempt Survivors Have Reduced Long-Term Well-Being? A Study of Veterans Across Three Nationally Representative Cohorts , Bradley A. Brown
Depersonalized, Dysregulated, and Demanded: The Impact of Burnout on Appraisal and Emotional Events , Katrina M. Conen
Breast Health Esteem to Motivate Breast Health Behavioral Intentions: An Application of the Terror Management Health Model , Emily P. Courtney
Gender Differences in College Drinkers: The Role of Masculine Norms , Jared A. Davis
Prevalence and Predictors of Careless Responding in Experience Sampling Research , Alexander J. Denison
Perceptions of Workplace Discrimination: A Closer Look , Jeremiah Doaty
The Impact of Cannabis on Motivational Processes for Smoked Tobacco and Cigarettes , Claire M. Gorey
Outcomes of a Telehealth Adaptation of a Trauma-Based Parent Training Program , Holland Hayford
Why Don’t They Just Ask?: Barriers to Directly Requesting Affirmative Sexual Consent by Gender and Sexual Orientation , Jessica A. Jordan
Examining the Social Validity of Parent Training: Post-Participation Parent Perceptions and Reflections of Group Triple P , Nycole C. Kauk
Individual Differences in Response to Hostile and Benevolent Sexism in a STEM Interview Context: The Moderating Role of Behavioral Activation , Elizabeth Kiebel
Do Sociability Expectancies Moderate Social Anxiety Predicting Alcohol Consumption Following a Social Stressor Speech Task , Jacob A. Levine
An Object for Sexual Pleasure: Does Viewing Sexualized Media Predict Increases in Self and Partner Objectification Impacting Feelings of Sexual and Romantic Closeness? , Kaitlyn Ligman
Influences of Sentence Context and Individual Differences in Lexical Quality on Early Phonological Processing during Silent Reading , Sara Milligan
Testing the Effects of Social Exclusion on Emotional Arousal: An Examination of the Effects of Psychological Pain and Rumination , Amanda L. Peterson
Creating a Short, Public-Domain Version of the CPAI-2: Using an Algorithmic Approach to Develop Public-Domain Measures of Indigenous Personality Traits , Mukhunth Raghavan
Equitable Implementation of the Good Behavior Game , Faith D. Reynolds
Ethnic-Racial Minoritized Adolescents’ Perceptions of Cyberhate, School Connectedness, Ethnic-Racial Identity, and Life Satisfaction , Alexis Taylor
Predicting Future Well-Being Among United States Youth Who Attempted Suicide and Survived , Bingjie Tong
Approach and Avoidance Food Craving: A Dual Cue Reactivity Investigation , Christina Lee Verzijl
Theses/Dissertations from 2021 2021
School Professional Coaching on Facilitation of Prevent-Teach-Reinforce (PTR) Model for Students with Persistent Problem Behavior , Rachel Ayres
Influencing Motivation for Alcohol through Social Bonding , Bryan Benitez
Case Studies in Applied Behavior Analysis: Using a Desensitization Procedure to Decrease Problem Behavior Towards Peers and Using a Treatment Package to Increase Time Spent in a Small Group , Mallamy I. Camargo Pena
Testing the Congruence of Espousals and Enactments Predicting Team Innovation , Rylan M. Charlton
The General Psychopathology Factor ( p ) From Adolescence to Adulthood: Disentangling the Developmental Trajectories of p Using a Multi-Method Approach , Alexandria M. Choate
An Ecological Momentary Assessment of Disordered Eating Behaviors within Alcohol Use Episodes: Determining Temporal Sequencing in Food and Alcohol Disturbance , Emily M. Choquette
The Influence of Maternal Body-Shaming Comments and Bodily Shame on Portion Size , Savannah R. Flak
Mental Health Problems, Traumatic Brain Injury, and Offending Behavior Among Persons Incarcerated in a County Jail , Lauren F. Fournier
The Adaptive, Social, Communication, and Cognitive Skills of Monolingual and Bilingual Toddlers with Autism , Marcela A. Galicia
Good Intentions Go Awry: Investigation of Unhelpful Supportive Leadership , Cheryl E. Gray
Hello Traitor: An Examination of Individual Differences in Perceptions of Technology-Related Incivility , David J. Howard
Measuring State Empathy: Exploring the Efficacy of a Film Clip Task and Examining Individual Differences in Empathic Responding , Stephanie R. Hruza
The Relationship of Hope to Goals and Psychological Outcomes in Patients with Advanced Lung Cancer: A Test of Hope Theory , Kelly A. Hyland
Decisions and How Doctors Make Them: Modeling Multilevel Decision-Making within Diagnostic Medicine , Michelle S. Kaplan
Cultural Values as a Moderator of the Emotion Suppression to Strain Relationship: A Comparison of Two Dominant Theoretical Mechanisms , Roxanne C. Lawrence
How Enduring is Global Precedence? , Jong Lee
Cool Under Fire: Psychopathic Traits and Decision-Making in Law Enforcement-Oriented Populations , Sean J. McKinley
Cognitive Ability and Ambivalence toward Alcohol: An Examination of Working Memory Capacity’s Influence on Drinking Behavior , Emily T. Noyes
The Relationship Between Parenting Stress, Attendance, and Attrition in a Group-Based Parent Management Training Program , David Rubio Jr.
Unintended Consequences? Testing the Effects of Adolescent-Targeted Anti-Vaping Media upon Adult Smokers , Leslie E. Sawyer
“Just Joking”: Women’s Cardiovascular Responses to Sexist Humor , Samantha Shepard
Negative Performance Feedback and the Self-Regulatory Benefits of Mindfulness , Jeremiah Slutsky
Examining the Potential Interactions of Expectancies and Disordered Eating Behavior , Cody B. Staples
The nature of resilience: A person-centered approach using latent profile analysis , Yuejia Teng
Evaluation of Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) Fit Indices in Distinguishing between Circumplex and Other Factor Models , Andrew J. Thurston
Comparison of Parameter Estimation Approaches for Multi-Unidimensional Pairwise Preference Tests , Naidan Tu
Theses/Dissertations from 2020 2020
The Impact of Cues on Autobiographical Memory Recall in Depression , Ena Begovic
Perfectionism, Negative Life Events, and Cognitive Appraisal: A Contextual Model of Perfectionism’s Maladaptive Nature , Ansley M. Bender
The Effect of Acute Interpersonal Racial Discrimination on Smoking Motivation and Behavior among Black Smokers , Patricia F. Calixte-Civil
Parent Coping and Sibling Relationship Quality in Pediatric Cancer: The Moderating Effects of Parental Emotion Socialization Beliefs , Esther Davila
Higher Sense of Control Predicts Long-term Well-being After Depression , Andrew R. Devendorf
Villains or Vermin? The Differential Effects of Discrimination and Dehumanization on Immigrant Cardiovascular Responses , Mona El-Hout
Alcohol Expectancy Associates as a Probe of the Motivational Processes that Lead to Drinking , Daniel C. Faraci
Features of borderline personality and related psychopathologies as a contemporaneously and temporally connected network , Haya Fatimah
Editing the Self Away: The Effects of Photo Manipulation on Perceptions of the Self , Roxanne N. Felig
Motivation Matters: The Interaction of Approach and Avoidance Alcohol Motivation and Self-Control Demands in College Drinkers , Becky K. Gius
Facilitators and Barriers to Treatment Engagement in a Behavioral Parent Training Program , Holland Hayford
Effects of Inter-Male Status Challenge and Psychopathic Traits on Sexual Aggression , Amy M. Hoffmann
If at First You Don’t Succeed...Your Coworkers Just Might Be Pleased: A Story of Workplace Schadenfreude , Kim Johnson
Motivation to Volunteer , Lendi N. Joy
Exploration of Drive for Leanness in Relation to Drives for Thinness and Muscularity, as well as their Concurrent Associations with Health-Related Outcomes , Brittany Lang
Affect and Craving: Examining the Differential Influences of Positive and Negative Affect on Inclinations to Approach and Avoid Alcohol Use , Jacob A. Levine
Threat-Induced Alterations in Cognition and Associations with Disinhibited Behavior , Julia B. McDonald
A Prospective Examination of Psychosocial Outcomes Following Gynecomastia Surgery , D. Luis Ordaz
Assessing the Impacts of Sensorimotor Stimuli and Nicotine Content on Cravings and Other Outcomes of E-Cigarette Use , Amanda M. Palmer
The Threat of Virality: Digital Outrage Combats the Spread of Opposing Ideas , Curtis Puryear
Why Are Women Leaving STEM? An Examination of Workplace Rivalry , Joseph Regina
A Fidelity-based Integration Model for Explicit and Implicit Ensemble Coding , Ke Tong
Care in Context: Constructing a Theory of Care in One Fifth Grade Classroom , Emily J. Wingate
Depression, Music Choice, and Affective Outcomes in Daily Life , Sunkyung Yoon
The Immediate Effect of a Brief Mindfulness Intervention on Attention and Acceptance , Xiaoqian Yu
Theses/Dissertations from 2019 2019
Understanding the Mechanisms Between Job Stress and Employee Sleep: A Daily Diary Study , Marijana L. Arvan
The Effects of Mortality Salience on Interest in Death (and Life) Among High Openness Individuals , Patrick Boyd
Linking Sleep and Aggression: The Role of Response Inhibition and Emotional Processing , Melanie L. Bozzay
Advanced Search
- Email Notifications and RSS
- All Collections
- USF Faculty Publications
- Open Access Journals
- Conferences and Events
- Theses and Dissertations
- Textbooks Collection
Subject Guide: Psychology: Theses and Dissertations
- Subject Databases
Theses and Dissertations
- Archives and Special Collections
- Develop Your Skills
- Researcher Support This link opens in a new window
Theses banner

You can get in touch through our live chat service or by email, and search our FAQs for answers to your questions.

Faculty Librarian - Science

Accessing Theses and Dissertations
- Durham Theses and Dissertations
- Other UK Theses and Dissertations
- Non-UK Theses and Dissertations
Durham e-Theses contains the full-text of Durham University Higher Degree theses .
All theses passed after 1 October 2009 (with a small number of exceptins) are available, or will be available following an embargo determined by the author. Durham University Library has also digitised its extensive collection of PhD, MPhil and Research Masters dissertations from 1899 onwards.
EThOS - The UK’s national thesis service which aims to maximise the visibility and availability of the UK’s doctoral research theses. EThOS aims to provide a national aggregated record of all doctoral theses awarded by UK Higher Education institutions, and free access to the full text of as many theses as possible for use by all researchers to further their own research.
ProQuest Dissertations and Theses - ProQuest Dissertations & Theses (PQDT) Global is the world's most comprehensive collection of dissertations and theses from around the world, offering millions of works from thousands of universities. Each year hundreds of thousands of works are added. Full-text coverage spans from 1743 to the present, with citation coverage dating back to 1637. If needed you can limit your results to institutions from countries in the UK.
ProQuest Dissertations and Theses - ProQuest Dissertations & Theses (PQDT) Global is the world's most comprehensive collection of dissertations and theses from around the world, offering millions of works from thousands of universities. Each year hundreds of thousands of works are added. Full-text coverage spans from 1743 to the present, with citation coverage dating back to 1637.
Open Access Theses and Dissertations - OATD.org aims to be the best possible resource for finding open access graduate theses and dissertations published around the world. Metadata (information about the theses) comes from over 1100 colleges, universities, and research institutions.
DART-Europe E-Theses Portal - A partnership of research libraries and library consortia who are working together to improve global access to European research theses.
South African Theses and Dissertations - via the National ETD Portal.
Australian Theses via TROVE - a collaboration between the National Library of Australia and hundreds of Partner organisations around Australia.
OAIster - A union catalog of millions of records that represent open access resources. It includes more than 50 million records that represent digital resources from more than 2,000 contributors. Results can be limited to just theses and dissertations.
Theses Canada - Launched in 1965 at the request of the deans of Canadian graduate schools, is a collaborative program between Library and Archives Canada (LAC) and Canadian universities. It strives to acquire and preserve theses and dissertations from participating universities, provide free access to Canadian digital theses and dissertations in the collection, and to facilitate access to non-digital theses and dissertations in the collection
Social media

- << Previous: Newspapers
- Next: Media >>
- Last Updated: Feb 15, 2024 1:26 PM
- URL: https://libguides.durham.ac.uk/psychology
Scholars' Bank
Psychology theses and dissertations.
- By Issue Date
Search within this collection:
This collection contains some of the theses and dissertations produced by students in the University of Oregon Psychology Graduate Program. Paper copies of these and other dissertations and theses are available through the UO Libraries .
Recent Submissions
- When “Self-Harm” Means “Suicide”: Adolescent Online Help-Seeking for Self-Injurious Thoughts and Behaviors Lind, Monika ( University of Oregon , 2024-03-25 ) The sensitive period of adolescence facilitates key developmental tasks that equip young people to assume adult roles. Adolescence features important strengths, like the need to contribute, and some risks, like vulnerability ...
- Stereotypes and Social Decisions: The Interpersonal Consequences of Socioeconomic Status Hughes, Bradley ( University of Oregon , 2024-01-09 ) Interpersonal perceptions of socioeconomic status (SES), those formed in face-to-face interactions, can perpetuate inequality if they influence interpersonal interactions in ways that disadvantage people with low SES. There ...
- Utilization of Linguistic Markers in Differentiation of Internalizing Disorders, Suicidality, and Identity Distress Ivie, Elizabeth ( University of Oregon , 2024-01-09 ) The adolescent period of development is associated with a significant increase in the occurrence of mental illness. In addition, death by suicide is one of the leading causes of death amongst adolescents. Identity formation ...
- The Role of Fractal Fluency on Visual Perception Robles, Kelly E. ( University of Oregon , 2024-01-09 ) From quarks to galaxies, the natural world is organized with fractal geometry. Fractal fluency theory suggests that due to their omnipresence in our visual world, fractals are more fluently processed by the visual system ...
- The Anatomy of Antagonism: Exploring the Relations of 20 Lexical Factors of Personality with Machiavellianism, Grandiose Narcissism, and Psychopathy Kay, Cameron ( University of Oregon , 2024-01-09 ) Despite being the focus of extensive research over the past two decades, the structure of the “Dark Triad”—or, as I will refer to it here, the “Aversive Triad”—is still shrouded in confusion. Much of this confusion stems ...
- Content Representation in Lateral Parietal Cortex Zhao, Yufei ( University of Oregon , 2024-01-09 ) While the lateral parietal cortex (LPC) in the human brain is traditionally investigated for its functions in visual perception, more recent evidence has highlighted its substantial contribution to supporting human episodic ...
- Sociocultural Contexts of Emotion Socialization in BIPOC Families Lee, Angela ( University of Oregon , 2024-01-09 ) Having effective emotion regulation skills is critical to socioemotional well-being, and parents play a key role in the development of children’s emotion regulation through emotion socialization behaviors. However, since ...
- Cross-ideological Communication: The Impact of Real Conversations Compared to Imagined Ones Niella, Tamara ( University of Oregon , 2024-01-09 ) Political polarization has visibly increased in the last few years. A sense of divisiveness has been exacerbated by a surge in social media communication about contentious issues which has been replacing face-to-face ...
- Inflammation, Mental Health, and the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Pilot Study with Child Welfare Service Involved Families Horn, Sarah ( University of Oregon , 2024-01-09 ) The coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic has posited unique challenges for families and significantly disrupted several aspects of children’s environments. The pandemic is an ongoing risk experience, with young children being ...
- Testing Novel Norm Interventions for Promoting Pro-environmental Consumption Lieber, Sara ( University of Oregon , 2024-01-09 ) The purpose of the current project was to investigate how a social psychology approach could be used to develop an effective climate-change mitigation tool. A commonly used technique in the social psychology literature for ...
- Understanding the Misunderstood Emotion: A Mixed-Methods Investigation of Variants of Anger Razavi, Pooya ( University of Oregon , 2023-07-06 ) In cultural accounts and scholarly writings about anger, we see conceptualizations that reflect the existence of two variants: an anger perceived as moral, appropriate, and justified; and an anger considered wrong and ...
- Measuring long-term memories at the feature level reveals mechanisms of interference resolution Drascher, Maxwell ( University of Oregon , 2023-07-06 ) When memories share similar features, this can lead to interference, and ultimately forgetting. At the same time, many highly similar memories are remembered vividly for years to come. Understanding what causes interference ...
- The Role of Hierarchical Structures in Cognition Moss, Melissa ( University of Oregon , 2023-07-06 ) Individuals routinely execute complex tasks that involve multiple, dependent levels of information, such as driving a car or cooking dinner. It is amazing that our cognitive system is able to represent such complex, ...
- A Contextual Psychology Approach to Improving Health Outcomes in the Perinatal Period Lightcap, April ( University of Oregon , 2023-07-06 ) The United States holds alarming records for highest infant and maternal mortality rates in the developed world. The US infant mortality rate is on par with many low and middle income countries, and despite the decline in ...
- The Study of Behavior Settings as an Aid in Mental Hospital Analysis: A Methodological Exploration Rose, David William ( University of Oregon , 1969-06 ) The ultimate goal of all mental hospital analyses is to provide information which by direct implication or through analysis might act as a guide in restructuring environment in which the mental patient lives. The goal of ...
- Personality-Driven Social Media Curation: How Personality Traits Affect Following Decisions on Twitter Bedford-Petersen, Cianna ( University of Oregon , 2023-03-24 ) As social media occupies an increasingly important place in people’s lives, new opportunities are presented for people to select and modify their online environments. On many platforms, users have significant control over ...
- Stability of Mind-Mindedness Across the Transition to Motherhood and its Longitudinal Association with Children’s Theory of Mind & Executive Function Gluck, Stephanie ( University of Oregon , 2023-03-24 ) Parental mind-mindedness refers to caregivers’ propensity to attribute mind-like and intentional qualities in their interactions with or representation of their young children. It is proposed to be associated with positive ...
- Dating and Mating in Adolescence: How Hormones and Puberty Influence Adolescent Mating Motivation Donaldson, Sarah ( University of Oregon , 2022-10-26 ) Puberty marks the physical transition towards sexual maturity, culminating in the ability to reproduce. It follows that maturing cognitive, affective, and social skills develop concurrently to support reproductive competence, ...
- Individual Differences in Memory Functions and Their Relation to Hippocampal Connectivity Frank, Lea ( University of Oregon , 2022-10-26 ) The hippocampus plays an important role in many aspects of learning and memory. It is most known for its role in episodic memory and spatial navigation, though it has also been shown to contribute to other processes like ...
- Collective Ongoing Betrayal Trauma: Gendered and Racialized Police Violence toward the Black Community Barnes, Melissa ( University of Oregon , 2022-10-26 ) Racialized and gendered police violence is a pernicious problem for Black communities. For my dissertation, I empirically tested a novel theoretical concept, Collective Ongoing Betrayal Trauma (COBT). COBT integrates the ...
View more submissions
Search Scholars' Bank
All of scholars' bank, this collection.
- Aguiar, Naomi (1)
- Akers, Laura (1)
- Ashby, Stefania (1)
- Barlow, M. Rose (Margaret Rose) (1)
- Barnes, Melissa (1)
- Barton, Jocelyn (1)
- Batterink, Laura (1)
- Beauchamp, Kathryn (1)
- Bedford-Petersen, Cianna (1)
- Bernstein, Rosemary (1)
- ... View More
- Clinical psychology (16)
- Psychology (11)
- Social psychology (9)
- Attention (8)
- Emotion (8)
- Parenting (8)
- Adolescence (7)
- Neuroimaging (7)
- Cognitive psychology (6)
Date Issued
- 2020 - 2024 (49)
- 2010 - 2019 (99)
- 2000 - 2009 (19)
- 1960 - 1969 (1)
- 1935 - 1939 (1)
Has File(s)
- Most Popular Items
- Statistics by Country
- Most Popular Authors

Home > School, College, or Department > CLAS > Psychology > Dissertations and Theses
Psychology Dissertations and Theses
Theses/dissertations from 2024 2024.
Faculty Mentors' Influence on Latino/a/x STEM Undergraduates' STEM Identity Development , Sandy Cerda-Lezama
Individual and Structural Contributors to Implicit and Explicit Anti-Muslim Bias in the United States , Aeleah M. Granger
The Relationship Between Adverse Childhood Experiences and Juvenile Offender Typology , Aliza Beth Lipman
The Wage of Wellness: The Relationship Between Socioeconomic Status, Race, and Work Recovery , Emily Julia Ready
It Takes a Village: An Examination of Social Relationships and Mental Health , Em Francis Trubits
Theses/Dissertations from 2023 2023
Examining Factors Impacting the Service Needs of Unhoused Women , Holly Brott
Main, Mediated, and Moderated Effects of Participating in an After-School Social and Emotional Learning Program on Young Children's Development of Social-Emotional Skills , Amy L. Cordier
Who Puts the "Support" in Supportive Housing? The Impact of Housing Staff on Resident's Well-Being, and the Potential Moderating Role of Self-Determination , Kenna Estell Dickard
Motivation to Collaborate: A Qualitative Exploration of the Perspectives of Service Providers on an Alternative First Response Program , Desiree' J. DuBoise
Tell Me, Do You Feel It Too? A Meta-analysis of Dyadic Emotional Contagion in the Workplace , Stefanie Fox
Left on "Read" and All Alone: Instigated Cyber Incivility, Shame, and Experienced Ostracism at Work , Alison Lucia Hunt
Exploring Associations between Military Identity and Well-being Outcomes among Post-9/11 Veterans after Separation , James David Lee
Experiences of People with Serious Mental Illness Seeking Services at Community Mental Health Centers During the COVID-19 Pandemic , Emily Leickly
Why So Serious? Using the Belongingness Need Tenet from the Self-Determination Theory to Examine Workplace Humor and Its Outcomes , Katharine Lucille McMahon
Emotion Knowledge, Its Applications, and Their Associations With African American Children's Social Relationships With Teachers and Peers in Kindergarten and First Grade , Brielle Emily Petit
Stress-Reduction from Positive Support: Impacts of Receiving Partner Capitalization Support on Veteran Stress/Work Stress , MaryAnn Dona Samson
Diversity in Recruitment: The Role of Realistic Website Job Previews for Racial and Ethnic Minority Applicants , Jennifer Saucedo
Antecedents of FSSB: Evaluating the Demographic Basis of Support , Erika Ann Schemmel
A Daily Investigation of the Recovery Paradox: Examining the Dynamic Interplay of Workload, Recovery Experiences, and Microbreaks , Morgan Rose Taylor
Not on the Menu: Customer Sexual Harassment in the Restaurant Industry , Fernanda Wolburg Martinez
Theses/Dissertations from 2022 2022
Model.Disclose(): Examination of Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder Disclosure at Work , Timothy Allen Carsey
Transforming Learning Communities, Transforming Ourselves: A Qualitative Investigation of Identity Processes in a Participatory Action Research-themed Undergraduate Course , Julia Sara Dancis
Clarifying and Measuring Inclusive Leadership , Kelly Mason Hamilton
Intersections of Masculinity, Culturally Relevant Factors, and Intimate Partner Violence Perpetration Among Asian American Men , Jason Z. Kyler-Yano
Sleeping to Support: An Examination of the Relationship Between Leader Sleep and Positive Support Behaviors , Jordyn Jan Leslie
Work-Related IPV Among Latinos: Exploring the Roles of Fatherhood Status, Gendered Expectations, and Support for Intimate Partner's Employment , Adrian Luis Manriquez
Masculinity Instability and Ideologies as Predictors of IPV Perpetration: The Mediating Role of Relationship Power , Emma Christine Marioles O'Connor
The Benefits of Social Support on Health and Well-Being in Military Populations: Examining Mechanisms, Source of Support, and the Reach of a Workplace Well-Being Intervention , AnnaMarie Sophia O'Neill
Do Motives Matter? The Role of Motivation in Shaping the Impact of Mindfulness Training on Teachers' Psychological Distress and Wellbeing , Cristi N. Pinela
Theses/Dissertations from 2021 2021
The Longitudinal Effects of a Family and Sleep Supportive Intervention on Service Member Anger and Resilience , Shalene Joyce Allen
Drug Conviction and Employment Restriction: Experiences of Employees with Drug-Related Criminal Histories , Liana Bernard
Sustaining Boys' Motivation Over the Transition to Middle School: Can Interpersonal Resources Protect Boys from Engagement Declines Across Sixth Grade? , Brandy Anne Brennan
Returning to Rejection: Outcomes and Boundary Conditions of Mental Illness Stereotypes , Stefanie Fox
Guarding Against Strain: The Moderating Role of Nonwork Experiences in the Relationship Between Work-Related Hypervigilance and Strain in Correctional Officers , Samantha Getzen
Anti-Muslim Bias: Investigating Individual Differences, Threat Perceptions, and Emotions in Islamophobic Policy Support , Aeleah M. Granger
Black Children's Development of Self-Regulation within Stressful Contexts of Parenting: Investigating Potential Buffering Effects of a Kindergarten Social-Emotional Learning Program , Eli Labinger
"Like I Was an Actual Researcher": Participation and Identity Trajectories of Underrepresented Minority and First-Generation STEM Students in Research Training Communities of Practice , Jennifer Lynn Lindwall
Claiming Miscommunication to Justify Rape: The Role of Liking the Perpetrator , Alyssa Marie Glace Maryn
An "I" for an "I" : A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Instigated and Reciprocal Incivility , Lauren Sarah Park
Parenting and Children's Academic Coping as a Dynamic System: Feedforward, Feedback, and Mediators of Changes Across the School Year , Kristen Elizabeth Raine
Does Experiencing Spousal Support and Strain Impact the Quality of Family-Based Support that Supervisors Provide to Employees? , Joseph Alvin Sherwood
"B-ing Flexible" : Examining Creativity in Bisexual Employees , Megan Jane Snoeyink
Exploring the Relationships Between Community Experiences and Well-Being among Youth Experiencing Homelessness , Katricia Stewart
Mothers' Drinking Motives , Sheila Kathleen Umemoto
An Examination of Nurses' Schedule Characteristics, Recovery from Work, and Well-Being , Sarah Elizabeth Van Dyck
Preventing Sexual Violence Through Understanding Perceptions of Sexual Offenders , Judith G. Zatkin
Theses/Dissertations from 2020 2020
Examining Employee Needs at Work and Home: a Self-Determination Theory Perspective , Dana Anuhea Auten
Trajectories, Time Windows, and Alternative Pathways of Engagement: Motivational Resources Underlying Academic Development during Middle School , Heather Anne Brule
Examining Mindfulness Training for Teachers: Theoretical and Methodological Extensions of Intervention Effectiveness , Jaiya Rae Choles
Detecting Reinforcement Patterns in the Stream of Naturalistic Observations of Social Interactions , James Lamar DeLaney 3rd
An Investigation of the Temporal Relationship Between Agitation and Sleep Disturbances , Emily Catherine Denning
Peers' Academic Coping as a Resource for Academic Engagement and Motivational Resilience in the First Year of Middle School , Daniel Lee Grimes
Home Resources Supporting Workplace Resources: an Investigation of Moderated Intervention Effects From the Study for Employment Retention of Veterans (SERVe) , Sarah Nielsen Haverly
"It Puts a Face to All the Knowledge We've Gotten" : a Program of Research on Intimate Partner Violence Surrogate Impact Panels , Kate Louise Sackett Kerrigan
A Daily Examination of Anger and Alcohol Use Among Post-9/11 Veterans , James David Lee
An Examination of Daily Family-Supportive Supervisor Behaviors, Perceived Supervisor Responsiveness and Job Satisfaction , Luke Daniel Mahoney
Nurse Can't Even: the Immediate Impact of Incivility on Affect, Well-being, and Behavior , Katharine Lucille McMahon
Perceptions of Police Use of Force at the Intersection of Race and Pregnancy , Emma Elizabeth Lee Money
The Impact of Paternal Caregivers for Youth Who Commit Sexual Offenses , Miranda Hope Sitney
Human Energy in the Workplace: an Investigation of Daily Energy Management Strategies, Job Stressors and Employee Outcomes , Morgan Rose Taylor
Individual and Community Supports that Impact Community Inclusion and Recovery for Individuals with Serious Mental Illnesses , Rachel Elizabeth Terry
Investigating Sexual Fantasy and Sexual Behavior in Adolescent Offenders , Hayley Lauren Tews
Theses/Dissertations from 2019 2019
Integrating Work Ability into the Organizational Science Literature: Advancing Theory and Developing the Nomological Network , Grant Brady
Family Linked Workplace Resources and Contextual Factors as Important Predictors of Job and Individual Well-being for Employees and Families , Jacquelyn Marie Brady
The Role of Teacher Autonomy Support Across the Transition to Middle School: its Components, Reach, and Developmental Effects , Julia Sara Dancis
Does X Mark the Applicant? Assessing Reactions to Gender Non-Binary Job Seekers , Kelly Mason Hamilton
Urbanicity as a Moderator of the Relationship Between Stigma and Well-being Outcomes for Individuals with Serious Mental Illnesses , Emily Leickly
The Relationship Between Undergraduate Research Training Programs and Motivational Resources for Underrepresented Minority Students in STEM: Program Participation, Self-efficacy, a Sense of Belonging, and Academic Performance , Jennifer Lindwall
Perceived Partner Responsiveness, Sleep and Pain: a Dyadic Study of Military-Connected Couples , AnnaMarie Sophia O'Neill
Recruitment Marketing: How Do Wellness and Work-Life Benefits Influence Employer Image Perceptions, Organizational Attraction, and Job Pursuit Intentions? , Amy Christine Pytlovany
The Combined Effects of Parent and Teacher Involvement on the Development of Adolescents' Academic Engagement , Nicolette Paige Rickert
Examining the Development and Classroom Dynamics of Student Disaffection Over Multiple Time Periods: Short-term Episodes and Long-term Trajectories , Emily Anne Saxton
Drinking on a Work Night: a Comparison of Day and Person-Level Associations with Workplace Outcomes , Brittnie Renae Shepherd
Development and Validation of the Workplace Mental Illness Stigma Scale (W-MISS) , Nicholas Anthony Smith
Relational Thriving in Context: Examining the Roles of Gratitude, Affectionate Touch, and Positive Affective Variability in Health and Well-Being , Alicia Rochelle Starkey
Preventing Child Sexual Abuse and Juvenile Offending Through Parental Monitoring , Kelly E. Stewart
"To Call or Not to Call?" The Impact of Supervisor Training on Call Center Employee Attitudes and Well-Being , Whitney Elan Schneider Vogel
Theses/Dissertations from 2018 2018
The Impact of Leader Race and Gender on Perceptions of Organizations in Response to Corporate Error , Nicolas Derek Brown
Impacts of Mindfulness Training on Mechanisms Underlying Stress Reduction in Teachers: Results from a Randomized Controlled Trial , Jaiya Rae Choles
Student Motivation Profiles as a Diagnostic Tool to Help Teachers Provide Targeted Support , Cailin Tricia Currie
Insufficient Effort Responding on Mturk Surveys: Evidence-Based Quality Control for Organizational Research , Lee Cyr
Affirmative Consent Endorsement and Peer Norms Supporting Sexual Violence Among Vulnerable Students on College Campuses , Alyssa Marie Glace
Gendered Partner-Ideals, Relationship Satisfaction, and Intimate Partner Violence , Sylvia Marie Ferguson Kidder
Organizational Calling and Safety: the Role of Workload and Supervisor Support , Layla Rhiannon Mansfield
Bystander Intervention to Prevent Campus Sexual Violence: the Role of Sense of Community, Peer Norms, and Administrative Responding , Erin Christine McConnell
Benevolent Sexism and Racial Stereotypes: Targets, Functions, and Consequences , Jean Marie McMahon
Perceived Overqualification and Withdrawal Among Seasonal Workers: Would Work Motivation Make a Difference? , Anthony Duy Nguyen
Differential Well-Being in Response to Incivility and Surface Acting among Nurses as a Function of Race , Lauren Sarah Park
Financial Strain and the Work-Home Interface: a Test of the Work-Home Resources Model from the Study for Employment Retention of Veterans (SERVe) , MacKenna Laine Perry
Neighbor Perceptions of Psychiatric Supportive Housing : the Role of Knowledge, Attitudes, and Behaviors , Amy Leigh Shearer
The Role of Caregiver Disruption in the Development of Juvenile Sexual Offenders , Miranda Sitney
Intrapersonal and Social-Contextual Factors Related to Psychological Well-being among Youth Experiencing Homelessness , Katricia Stewart
Age-based Differences in the Usefulness of Resources: a Multi-Study Investigation of Work and Well-being Outcomes , Lale Muazzez Yaldiz
Pathways to Kindergarten Growth: Synthesizing Theories of the Kindergarten Transition to Support Children's Development , Rita Yelverton
Theses/Dissertations from 2017 2017
The Force of Manhood: the Consequences of Masculinity Threat on Police Officer Use of Force , Aurelia Terese Alston
Supervisor Mindfulness and Its Association with Leader-Member Exchange , Dana Anuhea Auten
Combat Experiences, Iso-strain, and Sleep Quality Affect Symptoms of Posttraumatic Stress among Working Post-9/11 Veterans , Gilbert Patrick Brady Jr.
A Study of Shame-proneness, Drinking Behaviors, and Workplace Role Ambiguity Among a Sample of Student Workers , Sarah Nielsen Haverly
Intraminority Support For and Participation In Race-Based Collective Action Movements: an Intersectional Perspective , Jaboa Shawntaé Lake
Patients and Nurses and Doctors Oh My!: Nurse Retention from a Multi-Foci Aggression Perspective , Kevin Oliver Novak
Advanced Search
- Notify me via email or RSS
- Featured Collections
- All Authors
- Schools & Colleges
- Dissertations & Theses
- PDXOpen Textbooks
- Conferences
- Collections
- Disciplines
- Faculty Expert Gallery
- Submit Research
- Faculty Profiles
- Terms of Use
- Feedback Form
Home | About | My Account | Accessibility Statement | Portland State University
Privacy Copyright

Digital Commons @ SPU
Home > Academic Units > SPFC > CPY Dissertations

Clinical Psychology Dissertations
The Seattle Pacific University Department of Clinical Psychology is an APA-accredited doctoral program offering both an M.S. and Ph.D. in Clinical Psychology.
This series contains successfully defended doctoral dissertations.
Dissertations from 2023 2023
Unhealed Wounds: From Complex Trauma Exposure to Wellbeing and the Role of Coping , Mohammed K. Alsubaie
Understanding the Effects of Empathy and Masculine Gender Role Stress on the Relationship Between Gender and the Understanding of Consent in adolescents: A Moderated Mediation Framework , Kate Degenhardt
Suicidal Ideation and Community Connectedness in LGBTQ+ Adults: Can Emotion Regulation and Mindfulness Skills Help? , Samantha V. Jacobson
Sensory processing impacts on sleep patterns in children with neurodevelopmental disorders during the COVID-19 pandemic , Julianne M. Myers
Dissertations from 2022 2022
The Impact of COVID-19 on Secondary Victimization and Resiliency Following Sexual Assault , Elena Cantorna
Developmental Trajectories of Positive Emotion Regulation: The Moderating Effects of Gender and Parenting , Hailey Caudle
The Role of Coping Self-Efficacy, Coping Strategies, and Resiliency Following Sexual Assault , Lauren Hirsch
Ableist Microaggressions and Well-being: Investigating the Moderating Effect of Coping Strategies , Whitney Morean
Relations of EEG and Perceived Response to Methylphenidate among Children with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder , Tara M. Rutter
Integrative Meaning, Mindfulness, and Traumatic Grief Among Bereaved Adults , Brandy Tidwell
Parental Attachment and Compassion as Predictors of Distress Disclosure Among Young Adults , Ellie N. Wilde
School Related Criminal Acts, Interpersonal Problems, and Classroom Behaviors as a Function of The Proportion of Black Students and Black Teachers , LeAnne Zaire
A Randomized Controlled Trial of Telehealth Mindful Parenting Training on Executive Function in Autistic Children and their Parents , Vanessa Zhou
Dissertations from 2021 2021
Investigating the Effects of Endurance of Marriage on the Relationship between Attachment and Love Style , Melissa Caris
Parental Accommodation as a Mediator of Parenting Style on Changes in Pediatric Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder Symptoms , Jennifer Cataldi
Predicting First Responder Resilience: Investigating the Indirect Effect of Posttraumatic Cognitions through Coping Processes , Michael Dolezal
How Social Support Affects Career Adaptability through the Academic Career , Megan Fox
Longitudinal Trauma Treatment Outcomes in an Immigrant and Refugee Sample , Shuen-En Ho
Attachment, Trait Mindfulness, and Expectations in Married Women: A Moderated Mediation Model , Elizabeth Larson
Depression as a Moderator of the Relationship between Perceived Injustice and Neuropsychological Performance Validity among Individuals Previously Diagnosed with a Concussion , Jeremiah Lum
Psychometrics of a Measure of Sexual Assault Coping Self-Efficacy: A Comparison of Across Age Groups , Thomas Pankau
Posttraumatic Cognitions as a Pathway from Resilience to Sleep in First Responders , Emily Peterman Cabano
Detachment and Antagonism as Moderators of Effects of Psychosocial Stressors on Emotional Distress in Daily Life , Christina My Quach
Development of the Sexual Shame Inventory , Jyssica Seebeck
School Violence and Suicidal Ideation: The Mediating Roles of Perceived School Safety and Substance Use Among Adolescents , Jordan Skalisky
Shame Proneness as a Vulnerability Factor for Negative Emotions in the Context of Interpersonal Stressors: An Experience Sampling Study , Oxana L. Stebbins
An Examination of the Role of Interpersonal Stressors and Attachment Style in Dissociative Experiences , Erin Verdi
Dissertations from 2020 2020
What Happens When Youth Talk About Their Problems? Co-Rumination as a Mechanism of Stress Generation , Jaclyn T. Aldrich
Moderation of Effects of Anxiety on Verbal and Visuospatial Short-Term Memory in Young Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder , Rachael Arowolo
Impacts of Motor and Sensory Impairment on Language in Young Children with Autism , Elizabeth A. Bisi
Psychometric Evaluation of the Calling and Vocation Questionnaire-Revised (CVQ-R) and Calling and Vocation Questionnaire-10 Item (CVQ-10) , Caitlin Coyer
An Integrated Analysis of the Mechanisms by Which Parents Facilitate the Development of Emotion Regulation in Young Adolescents , Andrew Fox
Examining the Factors that Mediate the Relationship from Legal Advocacy Satisfaction to Resilience , Desta T. Gebregiorgis
The Costs of COVID-19: Loneliness, Coping, and Psychological Distress in the United States Population , Lauren Hammond
Autism and Externalizing Behaviors: Attachment as a Protective Factor , Rebecca Kramer
Generalized Anxiety Symptoms and Interpersonal Self-Perceptions During Stressors: A Prospective Examination of Psychological and Biological Stress , Jamie A. Lewis
Parent Emotion Coaching and Affect Recognition in Theory of Mind in Autism Spectrum Disorder , Audrey L. O'Connor
The Missing Moral Dimension: Perceptions of Transgressions and the Moderating Role of Moral Foundations on Psychological Distress , Hannah Reas
Generalized Anxiety Disorder Symptoms as a Moderator of Affective Reactions to Perceived Interpersonal Behaviors , Narayan B. Singh
Posttraumatic Growth in the Context of Grief: Testing the Mindfulness-to-Meaning Theory , Honey Williams
Trauma Exposure, Depressive Symptoms, and Responding to Positive Events and Affect in Young Adults , Jana DeSimone Wozniak
Dissertations from 2019 2019
The Impact of Trauma Experience, Adverse Early Circumstances and Unit Cohesion on Posttraumatic Growth in Active Duty Service Members , John Charleson
Cognitive Functioning, Depression, and Strengths as Predictors of Quality of Life in Multiple Sclerosis , Tara Annthea Crouch
The Roles of Pragmatic Language and Theory of Mind in the Adaptive Communication Skills of Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder , Taja Estrada
Campus Shootings: Does Religious Faith and Relationship with Victims Affect Psychological Well-Being? , Melissa J. Gowen
Attachment and Internalizing and Externalizing Problems in Adolescence: Exploring the Mediating Role of Physiological Self-Regulation Capacity , Michelle A. Kuhn
The Effect of a Substance Use Intervention on Co-occurring Adolescent Depression Symptoms , Elizabeth Ann Lehinger PhD
The Effect of Substance Use on the Relationship between PTSD Symptom Clusters and Suicide in Adolescents , Lindsay S. Moore
Emotional Clarity in Young Adults: Operationalization, Measurement, and Associations with Mental Health Outcomes , Madeline D W Noland
Examining Depression Symptoms, Parental Stress, and Dispositional Mindfulness in Mothers of Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder , Tracey Ward
RSA in Young Adults: Identifying Naturally-Occurring Response Patterns and Correlates , Brittany K. Willey
Dissertations from 2018 2018
Examining the Interaction between Stress Exposure and Stress Reactivity as Predictors of Reward Sensitivity and Anhedonia Symptoms , Joshua Ahles
The Impact of Bully Victimization and Substance Use on Suicidal Behavior in Sexual Minority Youth , Ashley Christine Estoup
The Role of Joint Attention in Pragmatic Language Development in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders , Ellen F. Geib
Investigating the Effects of Adult Insecure Attachment on Interpersonal Attraction , Fiona B. Kurtz Ms.
A Grounded Theory Qualitative Research Approach to Understanding Enduring Marriage , Heather Lucas
Examining the Moderating Role of Anxiety Symptoms on Insistence on Sameness in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder , Wayne Eric Mason Jr
Physiological Activation as a Mediator in the Relationship Between Perseverative Cognition and Somatic Symptoms , Karly M. Murphy
Examining the Interacting Effects of Marital Role Salience and Satisfaction on Mental Health Trajectories of Female Expatriates , Kaitlin M. Patton
Sexual Violence and Legal Advocacy: Psychometric Evaluation of the Legal Advocacy Services Satisfaction Survey , Joanne K. Sparrow
The Association of Attachment and Marital Satisfaction Mediated by Implicit Theories of Relationships , Sadie Teal
Summer Treatment Program for ADHD and ASD: The Role of Physical Activity, Sleep and Inhibitory Control , Erin G. Underbrink
A program evaluation of ZGiRLS: The role of cognitive emotion regulation in predicting mental health outcomes in adolescent girls , Julie Vieselmeyer
Dissertations from 2017 2017
Risky Sex and Alcohol-Related Behaviors and Cognitions in Adolescents: Evaluating a Values-Based Intervention , Meredith K. Chapman
The Etiology and Phenomenology of Sexual Shame: A Grounded Theory Study , Noel Clark
The Effect of Emotional Vulnerability and Invalidation on Emotion Dysregulation in Early Adolescence: An Empirical Investigation of Linehan’s Biosocial Theory of Borderline Personality Disorder , Sarah Crystal
The Effectiveness of Text Coaching on Substance Use Treatment Outcomes in Adolescence , Emily Hu
Sexual Assault Coping Self-efficacy as Moderated by Legal Advocacy Social Support , Clara Jane Roberts
The Relationship Between Trauma and Well-Being: Moral Emotions in Sex-Trafficked Women , Gina M. Scarsella
Dissertations from 2016 2016
Internalizing Symptoms: Relations to Executive Functions in Young Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder , Jessica L. Berg
Ecosystemic Effects of Military Sexual Trauma in Male Service Members and Veterans , Jessica A. Carlile
International Interests and Psychological Well-Being Following Global Service Learning as a Function of Sociocultural Adaptation and Cultural Distance , Elizabeth C. Dykhouse
Stress and Somatic Symptoms: Rumination and Negative Affect as Moderators , Melissa Joy Garner
Integrating Cognitive Mechanisms in the Relationship Between Trait Affect and Depressive Symptoms: The Role of Affect Amplification , Kaitlin A. Harding
Brooding, Avoidance, and Suppression as Mechanisms Linking Shame-Proneness with Depressive Symptoms , Melissa Rose Hudson
Courage, Psychological Well-being, and Somatic Symptoms , Christopher J. Keller
The Role of Emotional Distress in Predicting Opiate Analgesic Medication Use in Chronic Pain Patients , Amy E. Kupper
Temperament and Respiratory Sinus Arrhythmia as Contributors to Externalizing Behavior Among Early Adolescents , Tyler Laney Ph.D.
Impact of Situational Context on Gratitude and its Affective Outcomes , Adam P. McGuire
Does Use of Neutralization Techniques Predict Delinquency and Substance Use Outcomes? , Erin C. Siebert
Psychometric Evaluation of the Offender Coping Self-Efficacy Scale in the Context of Incarceration and Upon Re-entry , Minhdan Thuy Ta
Queers in the Hands of a Loving God: God Image, Strength of Faith, and Campus Climate in Predicting Self-Stigma , Sage Liam Willis
Dissertations from 2015 2015
Adaptive Functioning Deficits and Internalizing Problems in Young Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders , Hayley A. Dauterman
The Relation of Hyperactivity to Parenting Stress within the Parent-Child Relationship in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders , Heather Davis
Negative Cognitive Style, Rumination, and Negative Emotionality as Mediators of the Antidepressive Effects of Physical Activity Among Young Adults , Kara Pegram
Examining the Relationship between Forgiveness and Subjective Well-Being as Moderated by Implicit Religiousness and Spirituality , Jessica Peterson
The ABCs of stress responding: Examining the time course of affective, biological, and cognitive responses to induced stress as prospective predictors of depressive symptoms , Marissa Erin Rudolph
Behavioral Health among Asian American and Pacific Islanders: The Impact of Acculturation and Receipt of Behavioral Health Services on Depression and Anxiety , Mari E. Yamamoto
Perspectives on a Positive Youth Development Environment for Youth with Developmental Disabilities in 4-H , Megan E. Zurawski
Advanced Search
- Notify me via email or RSS
- Collections
- Disciplines
Contributors
- Submission Guidelines
- Submit Research
- Terms and Conditions
- SPU Department of Clinical Psychology
Home | About | FAQ | My Account | Accessibility Statement
Privacy Copyright
CUNY Academic Works
Home > Dissertations, Theses & Capstones Projects by Program > Psychology Dissertations
Psychology Dissertations
Dissertations from 2024 2024.
Seeing Safety in Red: Expressions of Interpersonal Gratitude Affects Conservatives’ Political Attitudes in the United States , Kyle M. Anderson
What Does It Mean to Be Kindergarten "Ready?": Trends in Parents' Expectations and Families' School Experiences Across SES , Lisa Babel
Complicating Confidence: A Critical Analysis of Confidence in a Girls' Empowerment Organization , Kimberly M. Belmonte
An Examination of Factors Associated with IPV Victimization, IPV Disclosure, and Help-Seeking Among Partnered Sexual Minority Men: An Integrated Theoretical Approach , Stephen Bosco
Examining Visual Processing of Hierarchical Figures through Behavioral Measures and Pupillometry in Relation to Autistic Traits in Adults , Chloe Brittenham
A Candidate Needs Approach to Job Advertisements , Yuliya M. Cheban-Gore
In My Softest & Most Liberatory Dreams: Reflections on Holding Complexity & Decentering Whiteness , Richard C. Clark
Religious Communication in Interfaith Romantic Relationships: Positive Approaches to Improve Relationship Outcomes , Jaclyn K. Doherty
Creatively Addressing the Employment Gap: Using Creativity and the Arts to Help Autistic Adolescents and Young Adults Build Skills for Employment , Eliana Rachel Grossman
Unpacking the Contested State of Public Housing in New York City , Kristen Hackett
The Impact of Playing as a Non-Stereotypical Woman in a Role-Playing Video Game on Players’ Real World Gender Role Attitudes , Hunter Kincaid
In-Work Recovery Among Hybrid Employees: Examining the Relationships Between Stressors, Recovery Experiences, and Strains , Stefanie Larsen
The Cultural Complexity of Immigrants and the Implications for Personality Assessment: Exploring the Role of Frame Switching , Patrick Jay Lee
Staying Power: The Struggle for Space and Place in Crown Heights, Brooklyn , Erin E. Lilli
The Role of Glutamate in the Medial Prefrontal Cortex in the Acquistion and Expression of Conditioned Approach , Rudolf Nisanov
Park Use, Urban Environmental Justice, and Place Attachment in Parks in Low-Income Neighborhoods in New York City , Javier Eduardo Otero Peña
Values in Evidence-Based Policy: Bridging Socio-Political, Moral, and Epistemic Domains , Karyna Pryiomka
Dissertations from 2023 2023
Examining the Prevalence and Psychopathological Correlates of Paraphilic Interests in a Non-clinical Sample , Dylan H. Abrams
Parallel Processes of Posttraumatic Stress and Metabolic Dysfunction: Long-Term Costs of Trauma on the Psychological and Physical Health of 9/11 Survivors , Shane W. Adams
A Novel Measure of Narrative Self-Functioning and Its Role in the Transformative Potential of Psychedelic Experience Across Clinical and Non-clinical Participants , Nicole M. Amada
Social Identity, Scientific Practice, and the Production of Social Knowledge: An Ethnographic Investigation of American Social Psychology Laboratories , Donald V. Brown Jr
Epistemic Virtue and Receptivity to Science in Policing , Braden L. Campbell
Understanding the Experiences and Associated Symptomology of Disclosers and Non-disclosers of Sexual Victimization , Kaitlin Carson
Wanting Under Surveillance: A Critical Analysis of Young Women’s Sexual Desire , Jennifer Chmielewski
Salty: A Diffractive Inquiry of Visceral Knowing and Embodied Aesthetics , Mei Ling Chua
The Role of Intersectional Stigma and Social Anxiety in Black, Latino, and Multiracial Young Sexual Minority Men , Jorge L. Cienfuegos Szalay
Understanding the Relationship Between Working Memory and Long-Term Memory , Kelly Cotton
Examinations of the Close Relationship Processes and Health Framework Among Adult and Adolescent Sexual Minority Men , Trey Victor Dellucci
Motor Milestone Acquisition and Sleep-Related Learning and Development in Infancy , Aaron DeMasi
Abuse Victimization and Impulsivity in Incarcerated Males: Examining the Roles of Affective Instability and Trauma Symptoms , Jacqueline K. Douglas
Association Strength between Concepts as the Origin of the "Foreign Language Effect" , Emilia Ezrina
An Offer You Cannot Refuse: Understanding the Elusive Construct of "Voluntary" Plea Decisions , Melanie B. Fessinger
Health Care Providers' Attributions of Blame for Unintended Pregnancy and HIV Acquisition Among Cisgender Women , Alison J. Goldberg
Avoiding Success: How Does Fear of Success Impact Today's Workforce? , Bradley E. Gray
Social and Cultural Processes that Impact Physical Activity among South Asian Americans Managing Hypertension: A Mixed Methods Study , Sugandha Gupta
Tongues Out of Place: Narratives of Hereness and Images of Be(long)ing , Christopher Hoffman
Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation Studies Investigating the Role of the DLPFC in Memory and Metamemory , Casey M. Imperio
Concerned Student: Institutional Violence and Embodied Abolition in the University of Missouri Protests , Gaurav Jashnani
Examining the Role of Evidence-Based Suspicion in Racial Disparities in Wrongful Convictions , Jacqueline Katzman
You Hurt My Feelings: Autonomic and Behavioral Responses to Social Exclusion and the Moderating Effect of Psychopathic Traits , Liat Kofler
Does the APOE-ε4 Allele Differentially Influence Cognition: A Longitudinal Investigation in Healthy Older Adults at Risk for Alzheimer’s Disease , Aditya Kulkarni
Losses and Gains of Teletherapy: The Impact of the Pandemic on Psychoanalytic Psychotherapy , Dan-Bi Lee
Permanent Shelter in The Empire City: Youth Experiencing Family Homelessness and Navigating the Homeless Industrial Complex with a Narrative Inquiry Approach , Henry O. Love
Variations in Family Child Care: Providers' Experiences Crafting Spaces In-Between School and Home , Eleanor Luken
Illness Intrusiveness and Psychosocial Adjustment Among Older Adults with Multimorbidity , Irina Mindlis
Artists, Activists, and Therapists Making Meaning of Collective Violence in Lebanon: A Community-Engaged Participatory Research Study , Nawal Muradwij
Extreme E-Service Learning: Remote Learning for Undergraduate Students and Telehealth Intervention for Children with Autism , Madiha S. Muzammal
Women’s Self-Nomination for Leadership Development Programs (LDPs): Gender, Personal Cultural Values, and the Mediating Role of Leadership Self-Efficacy , Alessa Natale
A Consecutive Case Series Evaluation of Tummy Time With and Without Preferred Items , Rika Ortega
The Neural Correlates of Bodily Self-Consciousness in Virtual Worlds , Evan A. Owens
Wild Women of Anatolia: The Critical Construct Validity of the Liberation of Women in Turkey , Sedef Ozoguz
The Effects of Isolated Affordances on Preschool Counting Improvement when Using a Digital Coloring App , Katherine Papazian
The Impact of Political Affiliation on Performance Judgements , Kajal Patel
Attenuated Typicality Effect in Category-based Inferences: Implications for Autism Spectrum Disorder , Janani Rajagopalan
Observers' Perceptions of Rapport in Accusatorial Interrogations , Gabriela Rico
Statistical and Biological Analyses of Acoustic Signals in Estrildid Finches , Moises Rivera
Voiding the Unwanted Self: An Examination of Racialized Violence in the United States , Benjamin Stark
A Gift To My Self: A Psychoanalytic Approach To Understanding The Experiences of Women Who Choose Not To Have Children , Irina D. Tchania
Breaking Down Bias: A Comparative Analysis of General Public and Police Officer Attitudes toward Mental Illness and Officer Decision-making in Mental Health Crises , Therese L. Todd
When Feeling Like a Fake Take a Toll on Your Work: Examining the Moderating Effect of Task Characteristics on the Relationship Between Impostorism and the Use of Dysfunctional Work Strategies , Alexandra Tumminia
How Smoking Became a Moral Issue: A Complex Systems Perspective on Moralization , Matthew Vanaman
Bargaining in the Shadow of the Truth: How Client Assertion, Perception of Guilt, and Predictive Inaccuracy Influence Plea Recommendations , Anna D. Vaynman
An Affective Technology of Heimat: Whiteness, Nation Building and Social Media in Germany , Friederike Windel
Effects of Genes and Gene-Environment Interactions on Work-Family Conflict and Enrichment , Peter Yu
Dissertations from 2022 2022
Investigating Young Adult Cancer Survivors' Perspectives on their Future and Interpersonal Relationships , Zeba N. Ahmad
Intelligence Testing in the New (Langu)age: Effects of Item-Type and Assessment Medium Features on Fluid Intelligence Test Linguistic Group Score Differences , Paige R. Alenick
Competitive and Facilitative Interactions Between Pavlovian Cues in Human Associative Learning: A Behavioral and Neural Analysis , Fahd Alhazmi
Serial Position Effect Profiles and Their Neuroanatomical Correlates: Predictors of Conversion to Alzheimer's Disease , Isabelle K. Avildsen
Exploring Social and Emotional Functioning in Emerging Adult Survivors of Adverse Childhood Experiences , Sara Babad
Exploring the Effectiveness of Multiple-Exemplar Training for Visual Analysis of AB-Design Graphs , Verena S. Bethke
Falling Forward: The Governance of School Reform, Race, and the Contest for a Dignified Future in Newark, N.J. , Claire Cahen
The Impossible Situation? Impasse as Psychotherapeutic Paralysis, Possibility, and Progress , Leo Cancelmo
Coercive Control and Trauma-Coerced Attachment in Commercial Sexual Exploitation: A Mixed-Method Examination , Kendra Doychak
Making Sense of Pre-Symbolic Trauma: A Qualitative Study on the Lived Experiences of Adults Who Were Born Extremely Prematurely , Noia Efrat
Relationships Between Sensory Reactivity, Restricted and Repetitive Behaviors, and Autonomic Nervous System Activity in Autistic and Non-Autistic Individuals , Sapir Elimaliah
A Polypharmacological Approach to Relapse Prevention in an Animal Model of Heroin Addiction , Scott T. Ewing
Reducing Fear Overgeneralization with Safety Learning: Attention Bias as a Moderator , Boyang Fan
Integrating Social-Emotional Learning and School Climate with a Sociocultural Narrative Inquiry Approach , Isabella Fante
Exploring Social Identity Threat and Safety Cues for Lesbian, Gay, Bisexual, Pansexual, and Queer Cisgender Women in OB/GYN Care , Rachel Fikslin
Fathers Are Fathers Are Fathers: How Sociocultural Context and Sexual Orientation Influence the Gendering of Children , Sarah M. Frantz
Cerebrovascular Impairment as a Potential Target for Neuromodulation Therapy in Moderate-Severe Traumatic Brain Injury , Naomi L. Gaggi
Effects of Chronic Stress on Safety Processing and Physiology in the Medial Prefrontal-Amygdala-Basal Forebrain Circuit , Itamar S. Grunfeld
Acculturation Patterns in Childhood/Adolescence, Cultural Stress in Young Adulthood, and Exploring the Moderating Role of Skin Tone Among Puerto Rican Youth in Two Contexts , Marjorine Henriquez-Castillo
Antisocial Behavior and Callous Unemotional Traits in Youth: A Biosocial Approach , Yong Lin Huang
Mapping Learning Ecologies: A Diffractive Exploration of the Emergence of Learning , Laurie Hurson
Is Less More? Examining the Effects of Predictor Method Factors on Mobile SJT Scores and Test-Taker Reactions , Anne E. Kato
The Impact of Personal Resources, Job Resources and Job Demands on Nurse Engagement , Michael J. Kern
Microaggressions, Imposter Phenomenon, and People of Color: A Quantitative Analysis , Rukiya King
The Effects of False Heartbeat Feedback on Moral Judgment , Scott Koenig
Examining the Buffering Effect of Mindfulness on the Relationship Between Stress and Ethical Decision Making , Irina Kuzmich
The Bright and Dark Sides of Upward Social Comparison: Knowledge Sharing and Knowledge Hiding Directed at High Performers , Soohyun (Ashley) Lee
Tell Me a Story: Exploring the Use of Narratives to Reduce Backlash to Organizational Diversity Initiatives , Desmond W. Leung
Problematic Social Media Use, Social Comparison, and Defeat: An Intensive Longitudinal Investigation , Natalia Macrynikola
Anomalous Self-Experiences and Aberrant Salience in Schizotypy , Victoria Martin
Discrimination, Psychological Well-Being, and Racial Importance in U.S. Native-Born and Caribbean Black Americans , Jaime E. McCaw
Withdrawal from Voluntary Oral Methamphetamine Reveals Female Specific Susceptibilities to Behavioral Deficits and Neurochemical Perpetuators of Neurotoxicity and Drug Seeking Behavior , Nicoletta K. Memos
Dietary Regulation of Silent Synapses in the Dorsolateral Striatum , Allison M. Meyers
Unraveling the Double-Bind: An Investigation of Black and Latina Women in STEM , Katlyn L. Milless
A Pilot Feasibility Trial of Mindfulness and Modification Therapy for Males Who Use Aggression , Jenny Mitchell
Natural Striatal Signaling Dynamics During Food Approach , Devry Mourra
- Colleges, Schools, Centers
- Disciplines
Advanced Search
- Notify me via email or RSS
Author Corner
- Psychology Program
Home | About | FAQ | My Account | Accessibility Statement
Privacy Copyright
Edinburgh Research Archive

- ERA Home
- Philosophy, Psychology and Language Sciences, School of
Psychology Masters thesis collection
By Issue Date Authors Titles Subjects Publication Type Sponsor Supervisors
Search within this Collection:
This collection contains a selection of recent Masters theses from the Psychology department. Please note that only the Title and Abstract will be available for dissertations from the current academic year. All other content from previous years is available on an Open Access basis.
This material is presented to ensure timely dissemination of scholarly and technical work. Copyright and all rights therein are retained by authors or by other copyright holders. All persons copying this information are expected to adhere to the terms and constraints invoked by each author's copyright. In most cases, these works may not be reposted without the explicit permission of the copyright holder.
Recent Submissions
Morphosyntax of luwo transitive verbs: tenses and aspects of the luwo base and derived paradigms , changes in psychological state in character disordered and neurotic patients , measurement of identification between mothers and their adolescent children , social factors in the perception of ambiguous stimuli , aspect of inspection in industry , the effect of semantic constraint on lexical access in bilingual word recognition , on the fallibility of human memory for future actions , relationship between co-worker satisfaction and personality traits , the epigenetic clock is associated with white matter changes and cognitive decline in the eighth decade of life , the effect of increased cognitive load on implicit moral judgement: do we deliberately override our moral intuitions , meta-analysis: using event-related potentials to identify recollection and familiarity , how do the regions of the visual field contribute to visual search in realworld scenes an eye-tracking study comparing dynamic and static scenes. , gratitude uniquely predicts well-being above the big-5 personality traits , can big five predict the competitive personality , an investigation of speech and language disturbances in patients with acute delirium , merging entropy and local boundaries , personality, social networks, and learning performance in the common squirrel monkey (saimiri sciureus) , predictors of resilience in older age: the lothian birth cohorts of 1921 and 1936 , assessing children's online behaviour and their experience of cyberbullying: a secondary analysis of the eu kids online ii , an investigation of speech and language disturbances in patients with delirium .

The Effect of Time Perception on Affect
Timing and time perception is essential to humans, whose lives and biology are organized around clocks. From the simple give-and-take of conversation to understanding cause and effect, individuals rely on accurate time perception to successfully complete tasks and organize their lives. However, accurate time perception is vulnerable to all manner of influence, from both internal and external sources, including affect. A robust body of literature suggests that negative affect is positively associated with time dilation, or subjective lengthening of time, whereas positive affect is positively associated with time constriction, or subjective shortening of time. Collectively, these are known as time distortion, which has been preliminarily linked to increased impairment in anxiety, depression, and BPD. However, this literature features two key limitations. First, researchers have mostly examined time perception as an objective measure, through the use of measures such as the temporal bisection tasks, which limits our understanding of the subjective experience of time distortion and how it may contribute to psychopathology. Second, across studies, time perception is most often studied as an outcome, rather than examining the role of time perception in predicting affective change, i.e., contextualizing the role of time distortion in clinically-relevant research questions. The current project aimed to address these gaps in the literature through two studies which examined (1) the roles of brief affect and time perception manipulations on affective change and subjective time perception in an online study (Study 1) and (2) the effect of a longer time perception manipulation on affective change during an in-person experimental protocol (Study 2).
Across studies, participants included a community-based sample of U.S. adults over age 18 and two separate undergraduate samples recruited from introductory psychology courses at Purdue University. In Study 1, the final sample size exceeded 750 and was comprised of community-based and undergraduate participants. Online participants reported on dispositional levels of clinical measures [e.g., rumination, borderline personality disorder (BPD) features] and then completed an experimental protocol with brief mood and time perception manipulations while repeatedly reporting on their negative affect. Results suggested that the time perception manipulation was not effective, but that across the protocol, negative affect rose and positive affect decreased. Further, participants reported overall that time seemed to be passing by slower than usual during the protocol. These findings informed the design of Study 2, which lengthened the time perception manipulation and eliminated the mood induction component in order to address the more basic question of whether time perception manipulation influences mood, particularly during neutral cognitive tasks.
One hundred and twenty-seven undergraduate participants completed Study 2. As in Study 1, participants filled out self-report surveys about dispositional symptoms of psychopathology (e.g., rumination, emotion dysregulation, and symptoms associated with BPD, depression, and anxiety) before completing an experimental protocol which included a manipulated clock (accelerated or control clock), three runs of a modified Erkisen flanker task, and repeated measures of negative and positive affect. Primary results suggested that the time perception manipulation was successful but that the influence of time distortion was more nuanced than hypothesized. Specifically, individuals with elevated clinical symptoms exhibited lower rating of negative and positive affect levels in the accelerated clock condition, compared to individuals endorsing low symptoms, who reported higher positive affect and higher negative affect in the accelerated clock condition.
Altogether, the results across studies highlight the complexity of time perception in influencing affect and help provide foundational information regarding the empirical convergence between cognitive and clinical phenomena.
Degree Type
- Doctor of Philosophy
- Psychological Sciences
Campus location
- West Lafayette
Advisor/Supervisor/Committee Chair
Additional committee member 2, additional committee member 3, additional committee member 4, usage metrics.
- Clinical psychology

- Systematic Review
- Open access
- Published: 30 May 2024
The effectiveness of interventions for offending behaviours in adults with autism spectrum disorders (ASD): a systematic PRISMA review
- Jody Salter 1 , 2 &
- Sarah Blainey 1 , 3
BMC Psychology volume 12 , Article number: 316 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
134 Accesses
1 Altmetric
Metrics details
Previous research has suggested that the core features of autism spectrum disorders (ASD) may contribute to offending behaviours and increased vulnerability within the Criminal Justice System. To date, there is a paucity of evidence assessing the effectiveness of interventions for offending behaviour in adults with ASD but without co-occurring intellectual disability (ID) across a broad range of forensic settings. The lack of robust evidence is concerning, as limited effectiveness may contribute to an increased likelihood of prolonged incarceration, particularly in the most restrictive settings. A PRISMA systematic review was conducted with a narrative synthesis to: (a) evaluate the evidence of the effectiveness of interventions aimed at reducing recidivism, (b) assess whether the core features of ASD impact the effectiveness of these interventions, and (c) identify additional factors that may affect the effectiveness of interventions within this population. Seven studies involving ten male participants were identified. The findings suggest that interventions for offending behaviours in adults with ASD without intellectual disability (ID) are largely inadequate, and that core ASD features need to be considered. Additionally, a complex interplay of risk factors potentially impacting intervention effectiveness was suggested. Limitations include heterogeneity across intervention types, measures of effectiveness, and what constitutes effectiveness. Despite the limited number of studies and data quality, the review aligns with a growing body of literature highlighting vulnerability and a need for evidence-based interventions for people with ASD. The review also discusses the broader implications of ineffective interventions.
Peer Review reports
Introduction
Autism spectrum disorders (ASD) represent a group of complex and highly heterogeneous neurodevelopmental disorders. A diagnosis of ASD is based on the presence of two core features: impairments in social communication and interaction (SCI), and restrictive and repetitive behaviours (RRBs) [ 1 ].
Phenotypic manifestations of the core features often present with varying degrees of social disengagement, difficulties in establishing and sustaining relationships, social naivety, lack of eye contact, and difficulties in interpreting facial expressions [ 2 ]. RRBs manifest as intense and highly restrictive special interests, a strong inclination for environmental consistency [ 3 ], cognitive rigidity, and hyper-or hypo sensory responses to the environment [ 4 ].
Additional factors modulate and influence these core features, including the extent of sensory and motor impairments, language and cognitive abilities, adaptive functioning, gender and the presence of co-occurring psychiatric disorders [ 5 , 6 , 7 ]. The increasing recognition of ASD has resulted in significantly higher diagnosis rates across all age groups [ 8 ], which are currently estimated to be 1 in 57 in England [ 9 ]. Consequently, this increase in diagnoses has led to a greater representation of individuals with ASD within the criminal justice system (CJS).
ASD in the criminal justice system
An increasing body of research has highlighted the significant vulnerability experienced by individuals with ASD while navigating the CJS. This vulnerability becomes evident throughout multiple stages of the criminal justice process, ranging from initial encounters with police [ 10 ] through to police interviews [ 11 ], to court room proceedings [ 12 ] and prison services [ 13 ]. This heightened vulnerability is exacerbated by the reported general lack of understanding of ASD within the CJS, among both professionals and the general public [ 13 , 14 , 15 , 16 ].
Individuals with ASD and co-occurring intellectual disability (ID) are often identified and diverted from the criminal justice system (CJS). This is due to a recognition of their reduced culpability, a result of impairments in both intellectual and adaptive functioning [ 15 ]. In contrast, individuals with ASD but without co-occurring ID, the population on which this review focuses, exhibit significant deficits in adaptive functioning despite their intellectual capabilities. This difference is often referred to as the IQ functioning gap and is unique to individuals with ASD [ 17 ]. Despite impairments in adaptive functioning, this population is considered intellectually capable. Therefore, they are generally perceived as culpable and sufficiently competent to navigate the complexities of the CJS and receive a fair trial. This contrast raises further questions concerning culpability ranging from criminal responsibility to the appropriateness of sentencing.
Following conviction, when an offence has met the custody threshold, offenders with ASD are typically diverted to the community or prison. Alternatively, if detained under the Mental Health Act 1983 (the legislative framework governing mental healthcare and treatment in England and Wales), they may be detained in a secure hospital environment (classified as low, medium, or high security).
Estimating the prevalence of ASD within the UK prison population is difficult because of a lack of routine assessment; nonetheless, ASD is estimated to range between 1% and 4.4% [ 5 ]. Research has shown a disproportionately high prevalence of ASD in secure hospital settings (6.5%), exceeding the estimate for the general population [ 18 ].
Qualitative studies examining the experiences of prisoners with ASD without co-occurring ID have highlighted their increased vulnerability to bullying, exploitation, and social anxiety in prison [ 13 ]. In addition, research aimed at evaluating the prevalence of the broader autistic phenotype among a prison population, as well as comparing their mental health characteristics to those without, revealed a significant risk of self-harm and suicide in individuals presenting with autistic traits. Within this cohort, of the 240 prisoners assessed, 46 displayed significant autistic traits, with 12 meeting the diagnostic criteria for ASD. Notably, only two of these individuals had been previously recognised by the prison as having ASD. This finding highlights the under recognition of ASD and emphasises the heightened vulnerability of this population to a range of mental health risks within the prison environment [ 5 ].
Although it may be logical to assume that a secure hospital setting may better meet the treatment needs of people with ASD than a prison setting, current evidence suggests otherwise. Concerns have been raised, including the high likelihood of long-term seclusion in people with ASD compared to those without ASD [ 19 ] and significantly longer than average stays within secure hospital settings [ 20 ].
Despite several initiatives aimed at improving the recognition of ASD within the prison population [ 21 ], a recent UK government report on ‘neurodiversity’ [ 22 ], a term encompassing various conditions that fall into the broader category of neurodevelopmental disorders (NDDs) including ASD, highlighted three notable areas of concern. These included a greater likelihood of neurodivergent individuals being held on remand, inappropriately pleading guilty, and judges often failing to recognise a defendant’s neurodivergence as a mitigating factor when sentencing. These findings demonstrate that much work is needed to address the challenges faced by individuals with ASD and neurodivergent conditions in the CJS.
ASD and risk of offending
While there is insufficient evidence to suggest that individuals with ASD are at greater risk of engaging in offending behaviours [ 23 ], it has been suggested that the core features of ASD may contribute to the risk of offending behaviours [ 24 , 25 ]. Risk factors for offending behaviour in the general population are associated with the cumulative influence of various factors, including alcohol and drug abuse, low socioeconomic status, mental disorders, adversity, child abuse, and traumatic brain injury [ 26 , 27 , 28 ]. Less is known about the risk factors for offending behaviour within the ASD population, with the exception of co-occurring psychiatric disorders, such as personality disorders and psychosis [ 5 ].
Research suggests that individuals diagnosed with ASD early in life face barriers to services throughout their lifespan, resulting in unmet education, health, and therapeutic needs [ 29 , 30 ]. Research suggests that certain demographic groups, such as women [ 31 , 32 ], individuals from ethnic minorities, and those from lower socioeconomic backgrounds [ 9 , 33 ], are far more likely to be underdiagnosed. This in turn increases the risk of unmet needs [ 34 , 35 ]. These factors may contribute as variables that collectively increase the overall cumulative risk of engaging in offending behaviours.
Forensic interventions
Interventions for offending behaviour often use cognitive-behavioural techniques to reduce recidivism, with an emphasis on perspective-taking, self-and relationship management, and problem solving. In the United Kingdom, the Ministry of Justice requires a sufficient evidence base for the accreditation of forensic interventions. This accreditation aims to promote high-quality programs in prisons and community settings to reduce recidivism [ 36 ].
Cognitive behavioural therapy (CBT) is widely recognised as one of the most effective interventions for offending behaviours [ 37 ]. There is evidence that CBT reduces recidivism by 20–30% in the general offending population [ 38 , 39 ]. However, there is little evidence to support the effectiveness of such interventions for offending behaviour in forensic secure settings, often yielding inconsistent findings [ 40 ].
Beyond forensic settings, evidence suggests that adapted CBT is effective for individuals with ASD [ 41 , 42 ]. These adjustments are necessary due to the core features of ASD and challenges in areas such as perspective taking and cognitive rigidity, both of which are conducive to successful therapeutic outcomes in this population [ 43 ]. Additionally, evidence supports the use of social skills training [ 44 ] and group-based social skills interventions in adults with ASD [ 41 ] However, there is no consensus regarding the specific adaptations most beneficial for individuals with ASD.
Furthermore, the lack of appropriate outcome measures has been reported to be a barrier to determining the effectiveness of interventions within secure forensic hospital settings [ 45 , 46 , 47 ]. Despite the evidence for CBT use within the general offender population and for individuals with ASD outside forensic settings, there are reports that the implementation of these interventions is not effective for individuals detained within secure hospital settings [ 19 , 48 , 49 ].
The increasing recognition of the vulnerability of individuals with ASD within the CJS highlights the urgent need for a systematic evaluation of the effectiveness of interventions for offending behaviours in adults with ASD. While previous research has examined interventions for individuals with ASD and co-occurring ID [ 49 ], a significant research gap remains regarding the effectiveness of forensic interventions for individuals with ASD but without co-occurring ID [ 14 ].
This systematic review aims to address this gap by conducting a comprehensive evaluation of intervention effectiveness in an ASD population without co-occurring ID.
Research aims
This systematic review is guided by the following research objectives:
To systematically review and evaluate the effectiveness of interventions for offending behaviours in adults with ASD without co-occurring ID, as reported in the literature;
To ascertain whether the core features of ASD impact the effectiveness of the identified interventions; and.
To identify additional risk factors that may impact the effectiveness of interventions in this population.
Inclusion criteria
Each potentially eligible study was screened based on the inclusion and exclusion criteria described in the PICO framework below [ 50 ].
Population.
Participants included adults aged 18 years and older diagnosed with ASD, as defined by the authors in the literature. Studies involving participants with co-occurring ASD and ID and those that did not differentiate between these two populations were excluded.
Intervention & Outcomes.
Our review aimed to identify studies that objectively and/or subjectively measured the effectiveness of therapeutic or pharmacological interventions for reducing recidivism in individuals with ASD exhibiting offending behaviours. These included interventions delivered in all categories, namely, prisons, probation supervision, and secure hospitals.
Study Design and Comparison.
All primary research studies were included, regardless of publication date or country of origin. Studies that were peer-reviewed (e.g., grey literature and conference abstracts), systematic reviews, and those not published in English were excluded. An inclusion-exclusion criterion related to the type of comparison conducted in individual studies was not imposed.
Search strategy
The search was conducted on the 27th of March 2021 across five databases, covering a broad timeframe and utilising international terminology. The databases included:
Embase (1974 to 2021).
Ovid MEDLINE(R) and Epub ahead of print, In-process, In data-review and other Non-Indexed Citations.
Ovid MEDLINE(R) Daily.
Global Health (1973 to March 2021).
APA PsychInfo (1806 to February 2021).
Furthermore, a web-based search using Google Scholar was conducted with the same search terms. The first 15 pages of results were manually reviewed; however, no additional studies meeting the inclusion criteria were found. Additionally, the reference lists and citations of relevant reviews were manually checked, but this did not yield any further eligible studies.
Data selection and extraction
The data selection and extraction processes consisted of two stages:
During Stage 1, potential eligible studies were screened based on their titles and abstracts against the predefined inclusion and exclusion criteria. Owing to the limited number of results, the screening process was performed manually and repeated one week later to increase accuracy.
Stage 2 involved a comprehensive review of the full texts of the selected studies to confirm their alignment with the inclusion criteria. Relevant data were extracted and organised into spreadsheets using Microsoft Excel.
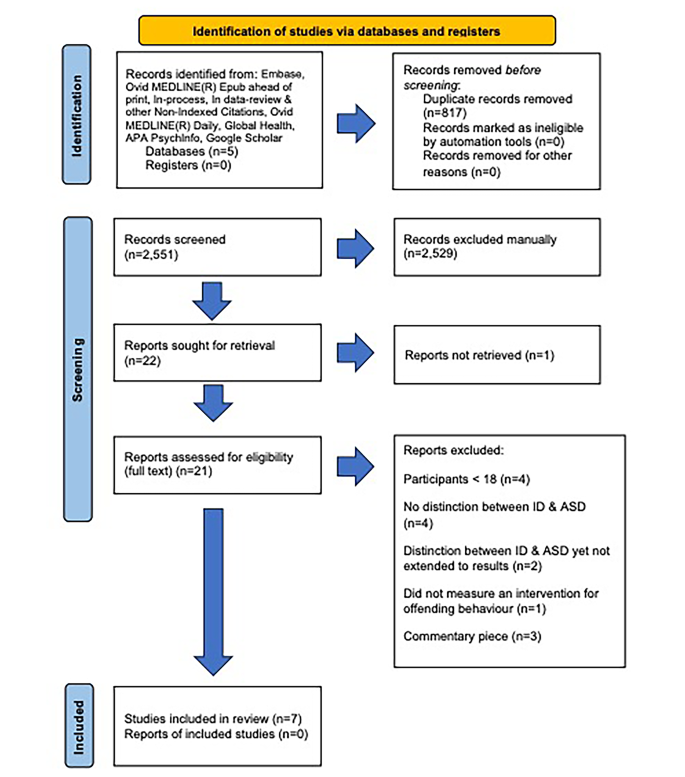
PRISMA flow diagram of searches of databases and registers only
Consistent with the primary aim of this systematic review, the first outcome measure is the effectiveness of the identified forensic interventions, measured by a reduction in recidivism. While reducing recidivism is the principal goal of forensic interventions, it is often viewed as a proxy measure that may not fully capture the complexity of offending behaviours, particularly in cases of crossover crime [ 46 , 51 ]. To address this limitation, additional relevant measures contributing to reduced recidivism were collected to allow for a preliminary assessment of intervention effectiveness. These additional measures included variables such as a reduction in security levels within institutional settings (i.e., medium to low security) or significant positive changes compared to baseline measurements recorded before and after the intervention.
The second aim of this review was to examine whether the core features of ASD present barriers to the rehabilitation process. To achieve this objective, data concerning the interactions between impairments in social communication and interaction (SCI) and restrictive and repetitive behaviours (RRBs) in relation to interventions within individual studies, as described by clinicians were collected and analysed.
Thirdly, this review aimed to identify additional risk factors described within findings that may influence the effectiveness of the interventions. The aim of the analysis is to provide a more comprehensive understanding of collective risk factors and their interactions with intervention effectiveness assessed through narrative synthesis. In addition, the data collected included the study design, author, and country of origin. When reported, participant demographics, such as age, gender, offence, ethnicity, and socioeconomic status, were reported. The intervention data included the type of intervention used, setting, duration, and frequency, only when available.
Study risk of bias assessment
The Mixed Methods Appraisal Tool (MMAT) [ 52 ] is a comprehensive tool for critically evaluating various research methods. The methodological quality of each study and the potential risk of bias were assessed using the MMAT. The results of this assessment are presented in tabular form (Table 2 , ‘MMAT Quality Appraisal’, appendix).
Synthesis method
A narrative synthesis [ 53 ] was used for this review as a meta-analysis was not appropriate because of the significant heterogeneity between studies. The synthesis process began with a preliminary analysis, in which the data were extracted and presented in tabular form to provide a summary of the findings and to identify potential patterns within the data. A guided conceptual framework was constructed based on the narrative synthesis of the primary data. This framework aimed to assess both the similarities and differences between the included studies while exploring emerging thematic elements.
Study selection
The initial database search returned 2,551 results after removing duplicates, as shown in Fig. 1 of the PRISMA flow diagram, which depicts the flow of information at each stage of the systematic review search. Subsequent screening included an initial assessment of the titles and a subsequent assessment of the abstracts, which led to the exclusion of an additional 2,530 articles. To ensure accuracy, abstract screening was repeated one week later. Subsequent full-text eligibility screening excluded 14 additional studies. The reasons for exclusion included the following: (a) participants under 18 years of age ( n = 4), (b) lacked differentiation between the ID and ASD populations ( n = 4), (c) were differentiated but not described in the context of the results ( n = 2), (d) measurement of interventions for self-harm and suicide among offenders with ASD rather than for offending behaviour ( n = 1), and (e) removal of commentary papers ( n = 3). Consequently, the final number of included studies from the initial database search was seven ( n = 7).
Study characteristics
Among the seven studies identified, three were case reports ( n = 3), two were qualitative studies ( n = 2), and two were quantitative case series ( n = 2). These studies jointly assessed the effectiveness of the various interventions. The total sample size of all the studies was limited to 10; all the participants were men, and demographic information was limited. It is worth noting that despite the use of international terminology in the search criteria, all seven articles described studies conducted exclusively in southern England, United Kingdom (UK). In these studies, all participants, apart from one were held in secure hospital units under the provisions of the Mental Health Act 1983. The most prevalent types of offending behaviours observed were sexual offences ( n = 4), followed by manslaughter ( n = 3), and arson ( n = 3).
Table 1 ‘Summary of Findings’ provides a summary of each study included in the systematic review. The summary includes author information, available participant demographics, offence type, setting, detainment status (i.e., under the mental health act), intervention approach, study findings, intervention effectiveness, measurement used to assess effectiveness, and whether there was evidence to suggest that the core features of ASD impacted the effectiveness of forensic intervention(s). These are separated by impairments in social communication and interaction (SCI) and restrictive and repetitive behaviours (RRBs).
Risk of bias in studies
The methodological quality of the studies was assessed using the MMAT [ 52 ] (Table 2 , ‘MMAT Quality Appraisal’, appendix). Each of the three case reports received a 3-star rating, indicating a moderate risk of bias and meeting 75% of the qualitative MMAT criteria [ 54 , 55 , 56 ].
The two quantitative case series were found to be at a higher risk of bias due to difficulties in distinguishing the treatment groups, recruitment difficulties, lack of a control group, and incomplete outcome data for the ASD group without co-occurring ID. They received a 2-star rating, meeting 50% of the MMAT quantitative criteria [ 58 ].
The second quantitative study [ 57 ], raised concerns about the validity and reliability of outcome measures, which were originally designed for the ID population but applied to the ASD group without co-occurring ID. This study also received a 2-star rating and met 50% of the MMAT’s quantitative criteria.
The remaining qualitative studies received a 3-star rating, meeting 75% of the MMAT criteria. The first evaluated intervention effectiveness from the perspective of the clinicians who delivered the therapeutic program [ 59 ]. The second assessed offenders’ views via self-report, which carry a potential risk of response bias [ 60 ].
Selection bias was observed in studies that combined ID and ASD populations. Overall, it was difficult to establish a causal relationship between the interventions and outcomes.
Notably, not all the studies reviewed explicitly documented obtaining informed consent from participants. The discrepancy in informed consent between studies, particularly in restrictive forensic settings, presents challenges extending beyond ethical considerations. Such discrepancies may compromise the validity of intervention comparisons, introduce biases in participant selection, and undermine the reliability of data.
Interventions
The interventions examined across the reviewed studies were diverse, as presented in Table 3 , titled ‘Summary of Interventions’.
Three studies incorporated both pharmacological and psychological interventions. Specifically, antipsychotics were used to address co-occurring psychosis, contributing to instances of offending behaviour [ 55 ]. Antipsychotics were also used to manage stress-induced psychosis [ 56 ]. In the context of directly treating offending behaviours, two distinct medications were applied in cases of sexual offending, each with different mechanisms of action [ 54 ] (Table 3 ).
Four studies relied exclusively on psychological interventions [ 57 , 58 , 59 , 60 ]. Among these, two studies implemented adapted forms of CBT. Specific details regarding the non-standardised adaptations used in CBT were not provided by the study author, except that individual delivery was necessary due to difficulties encountered within group settings [ 54 , 56 ].
The third study that incorporated CBT included elements similar to those of the Adapted Sex Offender Treatment Program (A-SOTP) [ 58 ]. The effectiveness of the A-SOTP was described in two studies [ 59 , 60 ]. Furthermore, the Equipping Youth to Help One Another (EQUIP) was adapted and piloted for use with individuals with ID and developmental disabilities (DD) who had committed sexual offences [ 57 ]. Supplementary interventions included speech and language therapy to facilitate communication [ 55 ], occupational therapy to address impairments in executive functioning [ 55 , 56 ] and art therapy [ 54 ].
Table 3 visually depicts a summary of the diverse interventions extracted, reviewed, and categorised according to intervention type: pharmacological, psychological, and supplementary intervention approaches. In addition, the table includes the type of offence, studies using intervention, underlying mechanism of action or theory, evidence base supporting intervention, and measurements used to assess effectiveness.
Measurements
Numerous approaches were adopted to measure effectiveness across the studies. Two studies measured effectiveness by reduced recidivism and the need to repeat the intervention. Other studies utilised a range of standardised measurements to evaluate psychological interventions. For example, one study [ 54 ] employed the Behavioural Status Index (BSI) every six months as a measurement tool. In contrast, another [ 56 ] employed the State Trait Anger Expression Inventory (STAXII II) and the Millon Multiaxial Personality Inventory (MMPI), combined with standardised risk assessment, one-year postintervention.
Regarding pharmacological interventions, one case report used a combination of subjective and objective measurements. These included self-reports and the systematic monitoring of inappropriate glancing behaviours over time by staff members [ 54 ]. In another instance, the reduction in verbalised delusions served as a measure of the effectiveness of antipsychotic medication [ 55 , 56 ].
The effectiveness of interventions such as the A-SOTP was assessed differently across the two studies. In one study, effectiveness was evaluated through clinician views [ 59 ], while in the other, effectiveness was determined by the participants’ subjective experiences with the intervention [ 60 ].
In the case of CBT, which shares similarities with A-SOTP, standardised measures were applied both pre- and post-intervention. These measures consisted of sexual attitudes consistent with sexual offending (QACSO), sexual offenders’ self-appraisal scale (SOSAS), the sexual attitudes and knowledge scale (SAKS), and the victim empathy scale-adapted (VES-A) [ 58 ].
The EQIP study, which also focused on sexual offending [ 57 ], assessed effectiveness by examining improvements in baseline scores on standardised tests related to moral reasoning, cognitive distortions, problem-solving abilities, and anger. In addition, a move to a lower security level was considered an indicator of overall effectiveness. Furthermore, in a case study that included speech and language therapy, the clinician’s subjective view of improved communication within the secure unit served as a measure of the intervention’s effectiveness [ 55 ].
Among the seven studies reviewed, only one pertaining to an arson offence considered the intervention(s) effective. In this case, a pharmacological intervention was used to treat co-occurring alcohol-induced psychosis, and the unspecified antipsychotic proved successful in reducing delusions. Furthermore, speech and language therapy aimed at improving communication skills was also deemed to be effective [ 55 ].
However, the remaining six studies, which included a total of nine participants, concluded that the interventions were largely ineffective. One case report addressing sexual offending behaviours used pharmacological interventions. The first involved cyproterone acetate, a testosterone inhibitor, however, the outcome could not be conclusively determined owing to adherence and dosage issues [ 54 ]. In the second, the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) fluoxetine was deemed ineffective, as inappropriate behaviours did not significantly decrease [ 54 ]. It is worth noting that the evidence for both of these drugs has since been described as insufficient to guide clinical practice, with cyproterone acetate considered inadequate [ 61 ], and the evidence for fluoxetine has not been fully determined [ 62 ].
Among the two studies that utilised the A-SOTP and a similar form of CBT for sexual offending, one participant repeated the intervention program six times and subsequently re-offended and a further two participants repeated the yearlong intervention program and reoffended [ 58 ]. These findings are consistent with the results of the study that assessed clinician views [ 59 ]. Even in the case of CBT, as used in two studies, the intervention was deemed ineffective despite adaptations made to accommodate individuals with ASD [ 54 , 56 ].
ASD core features and impact upon intervention effectiveness
The application of a narrative synthesis facilitated the identification and extraction of recurring patterns within the data. These patterns were evident across all the studies, highlighting the considerable challenges posed by impairments in social communication and interaction (SCI) and the presence of restrictive and repetitive behaviours (RRBs) on the effectiveness of interventions, as depicted in Fig. 2 .
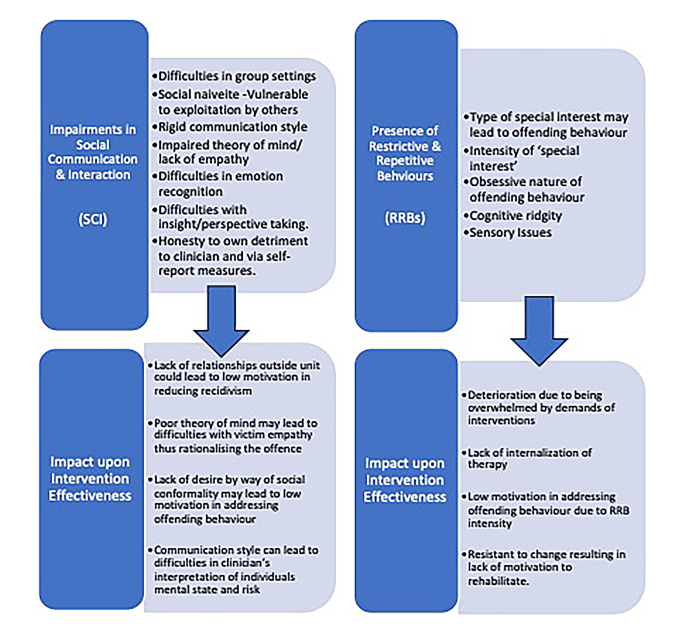
Impact of The Core Features of ASD upon Intervention Effectiveness. Note. This describes the core features of ASD, both ‘impairments to SCI’ and ‘presence of RRBs’, and their impact upon intervention effectiveness as extracted from studies
Additional factors impacting intervention effectiveness
In addition to the core features of ASD, this review sought to identify additional risk factors that may influence the effectiveness of the intervention(s). Potential risk factors highlighted by the authors of each study were collected, and through narrative synthesis, several recurring themes emerged from the data. Co-occurring personality disorders and psychosis [ 55 , 56 ], were identified as potential factors impacting intervention effectiveness, as described within the literature. Additionally, events such as childhood adversity, sexual abuse, trauma, and having a dysfunctional family life were described as potential contributors [ 58 ]. Late diagnosis of ASD was theorised to lead to maladaptive coping skills deriving from unmet needs, which were described in three of the studies [ 54 , 55 , 56 ].
An overarching theme identified across the majority of the seven studies was the insufficiency of service provision, staff expertise, and the evidence base.
The present systematic review identified seven studies with ten participants who underwent forensic interventions aimed at reducing offending behaviours in adults with ASD, particularly those without co-occurring ID. The principal aim of this review was to evaluate the effectiveness of these interventions. The secondary aim was to examine whether the core features of ASD have an impact on the effectiveness of these forensic interventions and to identify other variables that may impact the overall effectiveness of interventions.
Regarding the first aim, the evidence suggests that the interventions reviewed were inadequate. However, these findings should be treated with caution not only because of the small sample size but also because of limitations in the generalisability of the findings. Despite an extensive literature search, all the studies were conducted in southern England, UK, and included only male participants. In addition, all participants, with the exception of one individual living in the community, were detained within secure hospital settings under the provisions of the Mental Health Act (1983). This highlights the lack of data from prison and the probation service, which limits the scope of the review. Furthermore, this review highlights a critical lack of research within this domain. Even when the literature was identified, it was often of inadequate quality owing to various design limitations. The significant heterogeneity between studies, each utilising distinct intervention methods and tools for measuring intervention effectiveness, illustrates a notable lack of standardisation in both clinical and research methodologies within this field. This lack of consistency aligns with broader research on mental health in individuals with ASD [ 45 , 46 ]. Nonetheless, the forensic domain faces additional challenges, such as the lack of randomised control trials, which means that the effectiveness of interventions is difficult to fully determine. These challenges are exacerbated by unavoidable confounding variables, the risk of bias, and the ethical implications of a no-treatment group [ 66 ], all of which contribute to the lack of evidence.
The secondary aim was to examine the potential impact of the core features of ASD on the effectiveness of interventions designed to reduce recidivism. The data patterns identified through narrative synthesis consistently emerged across all studies, highlighting the significant challenges posed by impairments in social communication and interaction (SCI) and the presence of restrictive and repetitive behaviours (RRBs). These challenges highlight the general inappropriateness of forensic interventions within this population.
The third and final aim was to identify factors, beyond the core features of ASD, that may influence the effectiveness of interventions. Throughout the studies, a recurring theme emerged, highlighting significant systemic factors impacting intervention effectiveness. These include issues such as a shortage of government funding leading to inadequate service provision, the question of whether ASD and ID services should be combined, and the substantial unmet needs throughout the lifespan of individuals with ASD, all of which affect the success of forensic interventions. While the core features of ASD are significant, they may not be the primary cause of intervention failure. Rather, they seem to be contributing factors within a broader and more complex array of variables that collectively impact the overall effectiveness of these forensic interventions.
Implications
The inadequate provision of forensic services carries significant implications, especially when prolonged detainment becomes necessary due to the shortcomings of forensic interventions. Such deficiencies may subject individuals with ASD to non-evidence-based interventions, often repeatedly [ 56 , 58 ]. This then increases the likelihood of these individuals being labelled as ‘unrehabilitated,’ potentially leading to extended periods of detainment. Consequently, this creates a counterproductive cycle that not only exacerbates the economic burden but also raises serious concerns about human rights and the potential legal consequences of prolonged confinement.
These issues underscore fundamental questions about the fairness and adequacy of the legal system. Therefore, addressing these knowledge gaps and the lack of evidence-based approaches are crucial to ensuring a more equitable criminal justice system for individuals with ASD.
Future research
This review identifies several key areas for future research in this field. Developing evidence-based interventions tailored to the unique needs of individuals with ASD is crucial. Establishing a consensus on the measurements used for assessing the effectiveness of these interventions, as well as a clear definition of what constitutes effectiveness, would significantly enhance research quality.
Moreover, due to the bias towards studies conducted in southern England, the consistency of interventions for treating offending behaviours in adults with ASD in England remains unclear, especially considering the persistent regional health disparities between the North and South of England [ 67 , 68 ].
Data availability
No datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
Association AP. DSM-5 classification. American Psychiatric Publishing; 2015.
Masi A, DeMayo MM, Glozier N, Guastella AJ. An overview of Autism Spectrum Disorder, Heterogeneity and Treatment options. Neurosci Bull. 2017;33(2):183–93.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Berry K, Russell K, Frost K. Restricted and repetitive behaviors in Autism Spectrum Disorder: a review of Associated features and presentation across clinical populations. Curr Dev Disorders Rep. 2018;5(2):108–15.
Article Google Scholar
Geurts HM, Corbett B, Solomon M. The paradox of cognitive flexibility in autism. Trends Cogn Sci. 2009;13(2):74–82.
Chaplin E, McCarthy J, Allely CS, Forrester A, Underwood L, Hayward H, et al. Self-harm and Mental Health Characteristics of Prisoners with elevated rates of autistic traits. Res Dev Disabil. 2021;114:103987.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Hirvikoski T, Boman M, Chen Q, D’Onofrio BM, Mittendorfer-Rutz E, Lichtenstein P, et al. Individual risk and familial liability for suicide attempt and suicide in autism: a population-based study. Psychol Med. 2019;50(9):1463–74.
Kim SH, Lord C. The Behavioral Manifestations of Autism Spectrum Disorders. In: The Neuroscience of Autism Spectrum Disorders [Internet]. Elsevier; 2013 [cited 2024 Jan 7]. pp. 25–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-12-391924-3.00002-8 .
Jensen CM, Steinhausen HC, Lauritsen MB. Time trends over 16 years in incidence-rates of Autism Spectrum Disorders across the Lifespan Based on Nationwide Danish Register Data. J Autism Dev Disord. 2014;44(8):1808–18.
Roman-Urrestarazu A, van Kessel R, Allison C, Matthews FE, Brayne C, Baron-Cohen S. Association of Race/Ethnicity and Social Disadvantage with Autism Prevalence in 7 million School Children in England. JAMA Pediatr. 2021;175(6):e210054.
Haas K, Gibbs V. Does a person’s autism play a role in their interactions with police: the perceptions of autistic adults and Parent/Carers. J Autism Dev Disord. 2020;51(5):1628–40.
Murphy D. Interviewing individuals with an autism spectrum disorder in forensic settings. Int J Forensic Mental Health. 2018;17(4):310–20.
Allely CS, Cooper P, Jurors’. and Judges’ evaluation of defendants with autism and the impact on sentencing: a systematic Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and Meta-analyses (PRISMA) review of Autism Spectrum Disorder in the courtroom. J Law Med. 2017;25(1).
Allely CS. Experiences of prison inmates with autism spectrum disorders and the knowledge and understanding of the spectrum amongst prison staff: a review. J Intellect Disabil Offending Behav. 2015;6(2):55–67.
King C, Murphy GH. A systematic review of people with Autism Spectrum Disorder and the Criminal Justice System. J Autism Dev Disord. 2014;44(11):2717–33.
Maras K, Mulcahy S, Crane L. Is autism linked to criminality? Autism. 2015;19(5):515–6.
Robertson CE, McGillivray JA. Autism behind bars: a review of the research literature and discussion of key issues. J Forensic Psychiatr Psychol. 2015;26(6):719–36.
McQuaid GA, Pelphrey KA, Bookheimer SY, Dapretto M, Webb SJ, Bernier RA, et al. The gap between IQ and adaptive functioning in autism spectrum disorder: disentangling diagnostic and sex differences. Autism. 2021;25(6):1565–79.
Dein K, Hassiotis A, Woodbury-Smith M, Roychowdhury A, Squires R, Freestone M. Prevalence of autism within medium secure units: a feasibility study. J Forensic Psychiatr Psychol. 2021;32(6):861–78.
Murphy D, Allely C. Autism spectrum disorders in high secure psychiatric care: a review of literature, future research and clinical directions. Adv Autism. 2019;6(1):17–34.
Davoren M, Byrne O, O’Connell P, O’Neill H, O’Reilly K, Kennedy HG. Factors affecting length of stay in forensic hospital setting: need for therapeutic security and course of admission. BMC Psychiatry. 2015;15(1).
Lewis A, Pritchett R, Hughes C, Turner K. Development and implementation of autism standards for prisons. J Intellect Disabil Offending Behav. 2015;6(2):68–80.
Criminal justice joint inspectorate. Neurodiversity in the criminal justice system: a review of evidence. 2021.
Allely CS. A systematic PRISMA review of individuals with autism spectrum disorder in secure psychiatric care: prevalence, treatment, risk assessment and other clinical considerations. J Criminal Psychol. 2018;8(1):58–79.
Howlin P. Outcome in adult life for more able individuals with autism or Asperger Syndrome. Autism. 2000;4(1):63–83.
Newman SS, Ghaziuddin M. Violent crime in Asperger Syndrome: the Role of Psychiatric Comorbidity. J Autism Dev Disord. 2008;38(10):1848–52.
Allely CS, Minnis H, Thompson L, Wilson P, Gillberg C. Neurodevelopmental and psychosocial risk factors in serial killers and mass murderers. Aggress Violent Beh. 2014;19(3):288–301.
Newman BN, Crowell KA. The intersectionality of criminality and substance use self-stigmas. Stigma Health. 2023;8(2):212–22.
Schofield PW, Malacova E, Preen DB, D’Este C, Tate R, Reekie J, et al. Does traumatic Brain Injury lead to criminality? A Whole-Population Retrospective Cohort Study using Linked Data. PLoS ONE. 2015;10(7):e0132558.
Benevides TW, Carretta HJ, Lane SJ. Unmet need for Therapy among children with Autism Spectrum Disorder: results from the 2005–2006 and 2009–2010 National Survey of children with Special Health Care needs. Matern Child Health J. 2015;20(4):878–88.
Płatos M, Pisula E. Service use, unmet needs, and barriers to services among adolescents and young adults with autism spectrum disorder in Poland. BMC Health Serv Res. 2019;19(1).
Green RM, Travers AM, Howe Y, McDougle CJ. Women and Autism Spectrum Disorder: diagnosis and implications for treatment of adolescents and adults. Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2019;21(4).
Gupta M, Chaudhary R. Diagnostic challenges of High-Functioning Autism Spectrum disorder in females. Cureus. 2021 Jan 30.
Durkin MS, Maenner MJ, Meaney FJ, Levy SE, DiGuiseppi C, Nicholas JS, et al. Socioeconomic inequality in the prevalence of Autism Spectrum Disorder: evidence from a U.S. cross-sectional study. PLoS ONE. 2010;5(7):e11551.
Crane L, Hearst C, Ashworth M, Davies J, Hill EL. Supporting newly identified or diagnosed autistic adults: an initial evaluation of an autistic-led Programme. J Autism Dev Disord. 2020;51(3):892–905.
Article PubMed Central Google Scholar
Kelly B, Williams S, Collins S, Mushtaq F, Mon-Williams M, Wright B, et al. The association between socioeconomic status and autism diagnosis in the United Kingdom for children aged 5–8 years of age: findings from the born in Bradford cohort. Autism. 2017;23(1):131–40.
Ministry of Justice. Offending behaviour programmes and interventions [Internet]. GOV.UK. 2018 [cited 2021 Dec 13]. https://www.gov.uk/guidance/offending-behaviour-programmes-and-interventions#accreditation .
Lipsey MW, Landenberger NA. Cognitive-Behavioral Interventions. In: Preventing Crime [Internet]. Berlin/Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag; 2006. pp. 57–71. https://doi.org/10.1007/1-4020-4244-2_4 .
Henwood KS, Chou S, Browne KD. A systematic review and meta-analysis on the effectiveness of CBT informed anger management. Aggress Violent Beh. 2015;25:280–92.
Wilson DB, Bouffard LA, Mackenzie DL. A quantitative review of structured, Group-Oriented, cognitive-behavioral programs for offenders. Criminal Justice Behav. 2005;32(2):172–204.
MacInnes D, Masino S. Psychological and psychosocial interventions offered to forensic mental health inpatients: a systematic review. BMJ Open. 2019;9(3):e024351.
Spain D, Blainey SH. Group social skills interventions for adults with high-functioning autism spectrum disorders: a systematic review. Autism. 2015;19(7):874–86.
Spain D, Happé F. How to optimise cognitive Behaviour Therapy (CBT) for people with Autism Spectrum disorders (ASD): a Delphi Study. J Rational-Emot Cognitive-Behav Ther. 2019;38(2):184–208.
Parr JR, Brice S, Welsh P, Ingham B, Le Couteur A, Evans G et al. Treating anxiety in autistic adults: study protocol for the personalised anxiety treatment–autism (PAT-A©) pilot randomised controlled feasibility trial. Trials. 2020;21(1).
Gantman A, Kapp SK, Orenski K, Laugeson EA. Social Skills Training for Young Adults with high-functioning Autism Spectrum disorders: a Randomized Controlled Pilot Study. J Autism Dev Disord. 2011;42(6):1094–103.
Chambers JC, Yiend J, Barrett B, Burns T, Doll H, Fazel S, et al. Outcome measures used in forensic mental health research: a structured review. Criminal Behav Mental Health. 2009;19(1):9–27.
Fitzpatrick R, Chambers J, Burns T, Doll H, Fazel S, Jenkinson C et al. A systematic review of outcome measures used in forensic mental health research with consensus panel opinion. Health Technol Assess. 2010;14(18).
Weston L, Hodgekins J, Langdon PE. Effectiveness of cognitive behavioural therapy with people who have autistic spectrum disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Psychol Rev. 2016;49:41–54.
Higgs T, Carter AJ. Autism spectrum disorder and sexual offending: Responsivity in forensic interventions. Aggress Violent Beh. 2015;22:112–9.
Melvin CL, Langdon PE, Murphy GH. Treatment effectiveness for offenders with autism spectrum conditions: a systematic review. Psychol Crime Law. 2017;23(8):748–76.
Shuster JJ, Review. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews for interventions, Version 5.1.0, published 3/2011. Julian P.T. Higgins and Sally Green, editors. Res Synthesis Methods. 2011;2(2):126–30.
Völlm B, Braun P. Long-Term Forensic Psychiatric Care: clinical, ethical and legal challenges. Springer; 2019.
Hong QN, Fàbregues S, Bartlett G, Boardman F, Cargo M, Dagenais P, et al. The mixed methods Appraisal Tool (MMAT) version 2018 for information professionals and researchers. Educ Inform. 2018;34(4):285–91.
Campbell M, McKenzie JE, Sowden A, Katikireddi SV, Brennan SE, Ellis S et al. Synthesis without meta-analysis (SWiM) in systematic reviews: reporting guideline. BMJ. 2020;l6890.
Milton J, Duggan C, Latham A, Egan V, Tantam D. Case History of Co-morbid Asperger’s syndrome and paraphilic behaviour. Med Sci Law. 2002;42(3):237–44.
Radley J, Shaherbano Z. Asperger syndrome and arson: a case study. Adv Mental Health Intellect Disabil. 2011;5(6):32–6.
Murphy D. Extreme violence in a man with an autistic spectrum disorder: assessment and treatment within high-security psychiatric care. J Forensic Psychiatry Psychol. 2010;21(3):462–77.
Langdon PE, Murphy GH, Clare ICH, Palmer EJ, Rees J. An evaluation of the EQUIP Treatment Programme with men who have intellectual or other Developmental Disabilities. J Appl Res Intellect Disabil. 2012;26(2):167–80.
Murphy G, Powell S, Guzman A, Hays S. Cognitive-behavioural treatment for men with intellectual disabilities and sexually abusive behaviour: a pilot study. J Intellect Disabil Res. 2007;51(11):902–12.
Melvin CL, Langdon PE, Murphy GH. They’re the hardest group to treat, that changes the least. Adapted sex offender treatment programmes for individuals with Autism Spectrum disorders: clinician views and experiences. Res Dev Disabil. 2020;105:103721.
Melvin CL, Langdon PE, Murphy GH. I feel that if I didn’t come to it anymore, maybe I would go back to my old ways, and I don’t want that to happen: adapted sex offender treatment programmes: views of service users with autism spectrum disorders. J Appl Res Intellect Disabil. 2019;33(4):739–56.
Khan O, Ferriter M, Huband N, Powney MJ, Dennis JA, Duggan C. Pharmacological interventions for those who have sexually offended or are at risk of offending. Cochrane Database Syst Reviews. 2015 Feb 18.
National Institute for Health. And Care Excellence (NICE). Hypersexuality: fluoxetine; 2015.
Google Scholar
Masood B, Lepping P, Romanov D, Poole R. Treatment of Alcohol-Induced psychotic disorder (alcoholic Hallucinosis)—A systematic review. Alcohol Alcohol. 2017;53(3):259–67.
National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE). Rehabilitation for adults with complex psychosis. 2020.
Patterson C. Does the adapted sex offender treatment programme reduce cognitive distortions? A meta-analysis. J Intellect Disabil Offending Behav. 2018;9(1):9–21.
Robertson MD, Walter G. Many faces of the dual-role Dilemma in Psychiatric Ethics. Australian New Z J Psychiatry. 2008;42(3):228–35.
Bambra C, Barr B, Milne E. North and South: addressing the English health divide. J Public Health. 2014;36(2):183–6.
Whitehead M, Doran T. The north-south health divide. BMJ. 2011;342(feb15 2):d584–584.
Download references
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Forensic and Neurodevelopmental Sciences, Institute of Psychiatry, Psychology and Neuroscience, King’s College London, London, UK
Jody Salter & Sarah Blainey
School of Health and Society, University of Salford, Greater Manchester, UK
Jody Salter
Central and North West London NHS Foundation Trust, London, UK
Sarah Blainey
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
JS was responsible for writing the manuscript, including the creation of figures and tables. SB provided supervision and editorial input throughout the manuscript’s development.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Jody Salter .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
The systematic review did not involve original data collection; therefore, no ethical statement is required.
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Material 1
Rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Salter, J., Blainey, S. The effectiveness of interventions for offending behaviours in adults with autism spectrum disorders (ASD): a systematic PRISMA review. BMC Psychol 12 , 316 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40359-024-01770-1
Download citation
Received : 15 January 2024
Accepted : 07 May 2024
Published : 30 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s40359-024-01770-1
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Autism spectrum disorder
- Offending behaviour
- Forensic Psychiatry
- Forensic psychology
- Intervention
- Criminal justice system
BMC Psychology
ISSN: 2050-7283
- General enquiries: [email protected]
- Calendar Policies
- Virtual Events
- Other Calendars
- Submit an Event
- Directories
Quick Links
- Directories Home
- Colleges, Schools, and Departments
- Administrative Units
- Research Centers and Institutes
- Resources and Services
- Employee Directory
- Contact UNLV
- Social Media Directory
- UNLV Mobile Apps
Dissertation Defense: Amanda Mraz
Recurring dates.
- Jun. 7, 2024, 12pm to 1:30pm
Office/Remote Location
Description.
Amanda Mraz, Ph.D. Candidate
Department of Psychology
Identifying Appropriate Clinical Cutoffs for Dissociation in Maltreated Youth
Advisory Committee Members:
- Christopher Kearney, Ph.D., Advisory Committee Chair
- Paul Nelson, Ph.D., Advisory Committee Member
- Brenna Renn, Ph.D., Advisory Committee Member
- Wendy Hoskins, Ph.D., Graduate College Representative
Admission Information
This event is open to the public.
Please join via Zoom
Contact Information
External sponsor.

How to Know If You're Experiencing Prolonged Grief
Normal grief and prolonged grief share many features, but differ in duration and intensity..
Posted May 31, 2024 | Reviewed by Devon Frye
- Understanding Grief
- Find counselling to heal from grief
- It's normal for grief to have starts and stops. But sometimes, people can use help moving on.
- Prolonged grief has recently become a diagnosable psychological disorder, with effective treatments.
- If you're still having trouble engaging in life and relationships after a year, there is help.

As a nurse-midwife, birth and its unlikely twin, death, were familiar, renting the fabric between worlds, opposite ends of the spectrum. I’ve studied death, helped mothers and fathers accept death, experienced close, loving deaths. Healthy death, the bereaved recovering and healing.
Recently, my brother Steve, a psychologist, brought up grief. “People in America think grief is supposed to follow a pattern or else they’re doing it wrong, or it’s taking too long, or they’re stuck, not ‘moving on.’ Plus, they feel guilty if they laugh or feel happy when they think they’re ‘supposed’ to be grieving, or think it’s wrong to be angry at the person who died. They need to know they’re OK, all of it’s OK. But if they’re truly not OK, they can reach out, there’s help.”
Prolonged grief is a new entity in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual , or DSM, the bible of psychiatric diagnoses. Per the DSM, it is sometimes called complicated grief or bereavement . There is no one path for grief, no “right” way. It’s a ziggy, zaggy mess of forward and back, individual in each case, taking what it takes. But it can get complicated. Stuck, if you will. A chronic grind of grief, not life.
The DSM states a person with prolonged grief must have distressing, intense, unremitting yearning for the person who died, and/or be very preoccupied by thoughts of the death, or the person, after at least a year. Three of the following are also required:
- Identity disruption (e.g., feeling as though part of oneself has died) since the death
- A marked sense of disbelief about the death
- Avoidance of reminders that the person is dead (in children and adolescents, this may be characterized by efforts to avoid reminders)
- Intense emotional pain (e.g., anger , bitterness, sorrow) related to the death
- Difficulty reintegrating into one’s relationships and activities after the death (e.g., problems engaging with friends, pursuing interests, or planning for the future)
- Emotional numbness (absence or marked reduction of emotional experience) as a result of the death
- Feeling that life is meaningless as a result of the death
- Intense loneliness as a result of the death
Unless someone has three or more of these eight symptoms, and it’s been over a year since their loved one has died, and “the person’s bereavement lasts longer than might be expected based on social, cultural, or religious norms,” plus grieving significantly interferes with life, they don’t have prolonged grief.
This last piece is crucial. If a person is functioning at work, school, with family and friends, they are progressing in their own way and pace through grief. Every symptom of prolonged grief is part of healthy grieving, but not if it is unremitting and extreme after a year. If so, it could actually be dangerous. People with prolonged grief have higher rates of self-harm , suicide , and disability; more depression , anxiety , chronic illness , and trauma ; and a decreased quality of life. They are not OK. Ten percent of all mourners are estimated to suffer from prolonged grief.
Death is not a bad secret. Please talk about it. If you lost someone, or someone you love lost someone and it’s been over a year, and every day is spent longing for that person, ruminating, avoiding reminders—such as avoiding driving by the hospital or walking into the room where the person died—if you feel completely, wretchedly alone, like life has no purpose, please think again.
There is so much help available. Reach out to your primary care provider, spiritual leader , or trusted friend. Therapy and grief groups are available, as well as safe medications to help if your grief is complicated by depression, anxiety, insomnia , or trauma.

You can grieve. And you will; that loss will attenuate but never disappear. We are here to surround ourselves with community and life, to return to the world, contributing our part, whatever that may be. We are alive, and while we are, we are empowered to live.
If you or someone you love may have prolonged grief, take a single step and reach out. Everyone in your life misses you and wants you back. I guarantee it. To find support near you, visit the Psychology Today Therapy Directory.

Diane Solomon is an adjunct professor at OHSU and has served as a leader on the Boards of Nurse Practitioners of Oregon, the Oregon Wellness Program, the Oregon Nurses Association, The Jewish Federation of Greater Portland, and many others.
- Find a Therapist
- Find a Treatment Center
- Find a Psychiatrist
- Find a Support Group
- Find Online Therapy
- International
- New Zealand
- South Africa
- Switzerland
- Asperger's
- Bipolar Disorder
- Chronic Pain
- Eating Disorders
- Passive Aggression
- Personality
- Goal Setting
- Positive Psychology
- Stopping Smoking
- Low Sexual Desire
- Relationships
- Child Development
- Self Tests NEW
- Therapy Center
- Diagnosis Dictionary
- Types of Therapy

At any moment, someone’s aggravating behavior or our own bad luck can set us off on an emotional spiral that threatens to derail our entire day. Here’s how we can face our triggers with less reactivity so that we can get on with our lives.
- Emotional Intelligence
- Gaslighting
- Affective Forecasting
- Neuroscience

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Introduction: The Dissertation Framework and Process. The purpose of this manual is to provide a major source of support and guidance through the dissertation process. The APA Manual, your Dissertation Chair, your Dissertation Committee, and probably other students also will help you steer through the long series of decisions and considerations ...
Introduce the research problem and purpose of the study. Clearly indicate your research questions/hypotheses. Review the literature and indicate the gap in the literature your dissertation will be ...
For more than 25 years, this book has guided student writers through the practical, logistical, and emotional struggles that come with writing dissertations and theses. It offers guidance to students through all the essential steps, including: This fully-updated third edition includes guiding questions, checklists, diagrams, and sample research ...
The bulk of your literature review should provide a context for your research questions and hypotheses. The literature review section is devoted to a review and critical analysis of the relevant theoretical and research literature. Its purpose is to integrate your dissertation topic with a broader framework of research or theory.
a psychology dissertation, so you will need to look at such phenomena from a psychological perspective and apply psychological theory to help you explain it. You can also identify hot topics by keeping up to date with psychological pub-lications and social media accounts. It goes without saying that reading journal
Writing for psychology incorporates many of the organizational elements you learned in Expository Writing. In Expos, you were taught general academic guidelines for formulating a thesis, providing a motive for the thesis, supporting this thesis with convincing evidence, and anticipating objections from readers. You were also taught the
82 Psychology Teaching Review Vol. 24 No. 1, 2018 Andrew J. Holliman & Tim Jones Identifying a topic for a psychology dissertation: A process map for students Andrew J. Holliman & Tim Jones Identifying a 'promising' topic for a psychology dissertation is widely recognised as one of the most
Once you've identified a topic, the next step is to write a review of the literature in the area. The lit review section will include a brief introduction to your topic, introduce key concepts and review the existing literature. But be prepared: The lit review often is the most difficult part of the dissertation, Foster maintains.
Dissertation Requirements: Given the breadth of types of work conducted in the Psychology Department, there is no one-size fits all fully quantitative description of what is required of a PhD dissertation. However, there are broad principles that should be met by every dissertation regardless of things like exact format, number of studies, methods employed, length of the final document, etc.
Your Psychology Dissertation is suitable for all psychology students looking for dissertation success. Take a look at the online resources to get lots of useful templates and guidance to help with every step of the way. Student Success is a series of essential guides for students of all levels. From how to think critically and write great ...
Crafting a psychology dissertation indeed feels like moving mountains—an undertaking that requires a firm grasp of the subject matter, meticulous research, and adept academic writing. ... serving as a trailer that entices readers to delve into the main feature. Your Introduction sets the stage, presenting your research question and clarifying ...
Take a deep breath and keep in mind that this is all part of the process. Remember that writing your thesis or dissertation should never trump all other aspects of your self-care; taking care of ...
Definition Of A Psychology Dissertation. A psychology dissertation presents original research conducted by the author and submitted in partial fulfilment of doctoral degree requirements in psychology. To study a field topic, it usually requires extensive primary or secondary research. Neuropsychology, psychopharmacology, clinical, social ...
Theses/Dissertations from 2023. PDF. Improving the Subjective Well-Being of Autistic Youth Utilizing a Positive Psychology Intervention, Nicolette Bauermeister. PDF. An Experimental Study of Negative Performance Feedback: Consideration of a Cognitive Pathway and Individual Difference Factors, Ansley M. Bender. PDF.
Your Psychology Dissertation. Emily Harrison, Panagiotis Rentzelas. SAGE Publications, Limited, Oct 21, 2020 - Education - 216 pages. Your Psychology Dissertation has been specifically created to guide your students through their dissertation helping them to feel confident at every stage of their independent psychology research projects.
Accessing Theses and Dissertations. Durham e-Theses contains the full-text of Durham University Higher Degree theses. All theses passed after 1 October 2009 (with a small number of exceptins) are available, or will be available following an embargo determined by the author. Durham University Library has also digitised its extensive collection ...
Authors. Titles. Subjects. Search within this collection: This collection contains some of the theses and dissertations produced by students in the University of Oregon Psychology Graduate Program. Paper copies of these and other dissertations and theses are available through the UO Libraries.
Theses/Dissertations from 2021. PDF. The Longitudinal Effects of a Family and Sleep Supportive Intervention on Service Member Anger and Resilience, Shalene Joyce Allen. PDF. Drug Conviction and Employment Restriction: Experiences of Employees with Drug-Related Criminal Histories, Liana Bernard. PDF.
Browse By. Search within this Collection: As part of their final year undergraduate degree examination for MA or BSC Psychology, students submit a dissertation based on an original research project supervised by academic staff in the department. During 2006/07 it was agreed that all Psychology Undergraduate students would be required to submit ...
Dissertations from 2023 PDF. Unhealed Wounds: From Complex Trauma Exposure to Wellbeing and the Role of Coping, Mohammed K. Alsubaie. PDF. Understanding the Effects of Empathy and Masculine Gender Role Stress on the Relationship Between Gender and the Understanding of Consent in adolescents: A Moderated Mediation Framework, Kate Degenhardt. PDF
Dissertations from 2022 PDF. Investigating Young Adult Cancer Survivors' Perspectives on their Future and Interpersonal Relationships, Zeba N. Ahmad. PDF. Intelligence Testing in the New (Langu)age: Effects of Item-Type and Assessment Medium Features on Fluid Intelligence Test Linguistic Group Score Differences, Paige R. Alenick. PDF
111 Student Services Building, Knoxville, TN 37996. Phone: 865-974-2475. Email: [email protected]. The University of Tennessee, Knoxville. Knoxville, Tennessee 37996. 865-974-1000. The flagship campus of the University of Tennessee System and partner in the Tennessee Transfer Pathway . ADA.
This collection contains a selection of recent Masters theses from the Psychology department. Please note that only the Title and Abstract will be available for dissertations from the current academic year. All other content from previous years is available on an Open Access basis. This material is presented to ensure timely dissemination of ...
Psychology is the study of human behaviour and the mind, taking into account external factors, experiences, social influences and other factors. Psychologists set out to understand the mind of humans, exploring how different factors can contribute to behaviour, thoughts, and feelings. View All Dissertation Examples.
Students can choose from a thesis or non-thesis path. The non-thesis program requires a 100-question comprehensive exam. Regardless of the track, students take core courses in sensation and perception, engineering psychology, human factors in engineering design, ergonomics and biomechanics, and human-computer interaction.
The Effect of Time Perception on Affect. Download (1.64 MB) thesis. posted on 2024-05-21, 12:41 authored by Skye Camille Napolitano. Timing and time perception is essential to humans, whose lives and biology are organized around clocks. From the simple give-and-take of conversation to understanding cause and effect, individuals rely on accurate ...
Over the last few years, graduate psychology degree programs, both at the master's and doctoral levels, have shifted their admission criteria from an emphasis on standardized testing to components that reflect applicants' experiences. According to the most recent edition of Graduate Study in Psychology, 1 for 2022-23 applications ...
Previous research has suggested that the core features of autism spectrum disorders (ASD) may contribute to offending behaviours and increased vulnerability within the Criminal Justice System. To date, there is a paucity of evidence assessing the effectiveness of interventions for offending behaviour in adults with ASD but without co-occurring intellectual disability (ID) across a broad range ...
Amanda Mraz, Ph.D. Candidate Department of Psychology Identifying Appropriate Clinical Cutoffs for Dissociation in Maltreated Youth Advisory Committee Members: Christopher Kearney, ... Dissertation Defense: Amanda Mraz . When. Jun. 7, 2024, 12pm to 1:30pm Show Recurring Dates Office/Remote Location ...
People with prolonged grief have higher rates of self-harm, suicide, and disability; more depression, anxiety, chronic illness, and trauma; and a decreased quality of life. They are not OK. Ten ...