- Rules/Help/FAQ Help/FAQ
- Members Current visitors
- Interface Language
Follow along with the video below to see how to install our site as a web app on your home screen.
Note: This feature may not be available in some browsers.
- English Only

future perfect in reported speech
- Thread starter Mistermarcos69
- Start date Aug 15, 2010
Mistermarcos69
Senior member.
- Aug 15, 2010
Could you please tell me if the following sentence is correct? The sentence is: Tom told me he would have written a letter by noon, but he didn't Is this a correct use of the FUTURE PERFECT? Thanks a lot in advance for your help. Marco
Your sentence conveys that Tom isn't sure exactly what time he wrote the letter, but, that it was completed before noon, and you know this isn't true. Whether he lied or was mistaken isn't clear. If that's what you want to express, you did it correctly. The construction is conditional + past participle.
ewie said: Well, Marco, it's not actually a use of the future perfect at all . Tom tells me he will have written ... ~ that's a future perfect Click to expand...
Aha! ~ I see what you mean, Brian.
brian said: Tom: I will have written the letter tonight. <-- future perfect Bob: Tomtold me he would have written the letter tonight. <-- future perfect in the past Of course, this all makes analogical sense, but actually it would be more natural for me, in the very last sentence, to say Tom told me he will have written the letter tonight . But I have no idea why. Click to expand...
soccergal said: If that's what you want to express, you did it correctly. The construction is conditional + past participle. Click to expand...
رضا said: So, what if the speaker is narrating it on the day after the event, so that all the sentence is converted into past form? Click to expand...
brian said: Tom: I will have written the letter tonight. <-- future perfect Bob: Tomtold me he would have written the letter tonight. <-- future perfect in the past Click to expand...
brian said: Actually , hrm... I think it is the future perfect... in the past . I'm thinking by analogy here: Tom: I will write the letter tonight. <-- future Bob: Tom told me he would write the letter tonight. <-- future in the past hence Tom: I will have written the letter tonight. <-- future perfect Bob: Tomtold me he would have written the letter tonight. <-- future perfect in the past Of course, this all makes analogical sense, but actually it would be more natural for me, in the very last sentence, to say Tom told me he will have written the letter tonight . But I have no idea why. Click to expand...
Spira said: I would call your future perfect in the past a conditional past tense . Just as Tom would write a letter is the present conditional, so Tom would have written a letter is past conditional, followed obligatorily by the affirmation that he did not. Click to expand...
Yes, I agree, I see no conditional mood here. To me it sounds much of 1- A sentence in the past participle, 2- Indirect speech.
Firstly, I come back to my original point about a problem of syntax. Tom told me he would have written a letter by noon, but he couldn't Tom told me he was going to write a letter by noon, but he didn't Tom told me he had written a letter by noon, but he hadn't All OK. But Tom told me he would have written a letter by noon, but he didn't. NOT OK. Doesn't anyone else see that? Secondly, re. conditional, in I would write a letter but I cannot spell, the would write is conditional present . Similarly, I would have written a letter but I cannot (or could not) spell, the would have written is a conditional past tense of the verb to write. If we absolutely want to use a future perfect in the past for the present example, it would have to be Tom told me yesterday that he will have written a letter before next Tuesday, but he won't because part of the events remain in the future.Very difficult to use a future perfect in the past when the entire sequence of events is in the past.
It's not at all beside the point, Brian. Look at the original post of this thread, with its but -clause. As you so rightly say, that does change things. I'm sticking pretty close to the original, I think you'll find. Look again at the syntax of the original; are you fine with it?
Ah sorry, I thought were discussing the general use of would have + <past participle> in reported speech. Anyway, as I said in my very first post, I'm not really fine with it, but I think that has more to do with the rarity with which we actually use the future perfect, more so than with the syntactic structure itself. If we simply added a few more words, it'd be perfectly fine: Tom told me yesterday he would have already written a letter by noon today , but he didn't. This sounds perfectly okay to me. It's the reported (indirect) speech of Tom: Tom told me yesterday, "I will have (already) written a letter by noon tomorrow."
Tom told me he would have written a letter by noon, but he didn't. Click to expand...
Tom: "I will have written a letter by noon." Click to expand...
Tom: "I will write a letter by noon." Click to expand...
A-class-act
Thomas tompion, member emeritus.
- Aug 16, 2010
For me all depends on when this speech is reported. Suppose Tom said a week ago "I will have written the letter by noon Tuesday". If it's now 10 am on Tuesday, I'd say "Tom said he would have written the letter by noon", or, just, possibly, "Tom said he will have written the letter by noon" . I could also say, of course "Tom said he would write the letter before noon" , but I won't go into that. If it's now 2 pm on Tuesday, I'd say "Tom said he would have written the letter by noon" and I could no longer possibly say, " Tom said he will have written the letter by noon ". If he hasn't done it, I'd say "Tom said he would have written the letter by noon, but he hasn't"; one could, if one wanted to take the time reference back to noon, make the tag but he hadn't. I'm not very happy with Panj.'s switching of the order to he would have the letter written , because that raises questions about who is writing the letter; it could mean he was getting someone else to do it, and that causative have would mean that we are using different tenses.
Tom: I will write the letter tonight. <-- future Bob: Tom told me he would write the letter tonight. <-- future in the past Click to expand...
Tom: I will have written the letter tonight. <-- future perfect Click to expand...
Bob: Tom told me he would have written the letter tonight. <-- future perfect in the past Click to expand...
panjandrum said: [...] This sentence does not make sense to me. This only makes sense to me as part of a bigger sentence that includes a condition statement. Tom: I will have written a letter by noon. Tom told me he would have written a letter by noon. Tom told me he would have a letter written by noon. I accept TT's point about who was to write the letter, but, for me at least, the first of these statements is so overwhelmingly part of a conditional statement that I can't accept it as a reported version of the italic sentence. The green sentence is how I would naturally report what Tom had said. The red sentence pulls me inexorably to a conditional situation. Tom: I would have written a letter by noon (except that some circumstance prevented me). Tom told me he would have written a letter by noon (except that some circumstance prevented him). This is a standard conditional structure - conditional (3). Click to expand...
DIRECT SPEECH will ------> REPORTED SPEECH would DIRECT SPEECH would-----> REPORTED SPEECH would or would have? Many thanks for your assistance!!!!!!

Narration Change in Future Tense
Back to: Direct and Indirect Speech (Narration)
Examples of narration change in simple future tense, future continuous, future perfect and future perfect continuous are given below –
Table of Contents
Direct and Indirect Speech Future Simple Tense Examples
If reported verb is in Past Tense, and reported speech is in Future Indefinite Tense, will changes into would & shall changes into should .
Direct and Indirect Speech Future Continuous Tense Examples
If verb is in Past Tense, and reported speech is in Future Continuous Tense, will be changes into would be & shall be changes into should be .
Direct and Indirect Speech Future Perfect Tense Examples
If verb is in Past Tense, and reported speech is in Future Perfect Tense, will have changes into would have & shall have changes into should have .
Direct and Indirect Speech Future Perfect Continuous Tense Examples
If verb is in Past Tense, and reported speech is in Future Perfect Continuous Tense, will have been changes into would have been & shall have been changes into should have been .
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser or activate Google Chrome Frame to improve your experience.
He Said, She Said: Mastering Reported Speech in English (Both Direct and Indirect)
“Reported speech” might sound fancy, but it isn’t that complicated.
It’s just how you talk about what someone said.
Luckily, it’s pretty simple to learn the basics in English, beginning with the two types of reported speech: direct (reporting the exact words someone said) and indirect (reporting what someone said without using their exact words ).
Read this post to learn how to report speech, with tips and tricks for each, plenty of examples and a resources section that tells you about real world resources you can use to practice reporting speech.
How to Report Direct Speech
How to report indirect speech, reporting questions in indirect speech, verb tenses in indirect reported speech, simple present, present continuous, present perfect, present perfect continuous, simple past, past continuous, past perfect, past perfect continuous, simple future, future continuous, future perfect, future perfect continuous, authentic resources for practicing reported speech, novels and short stories, native english videos, celebrity profiles.
Download: This blog post is available as a convenient and portable PDF that you can take anywhere. Click here to get a copy. (Download)
Direct speech refers to the exact words that a person says. You can “report” direct speech in a few different ways.
To see how this works, let’s pretend that I (Elisabeth) told some people that I liked green onions.
Here are some different ways that those people could explain what I said:
Direct speech: “I like green onions,” Elisabeth said.
Direct speech: “I like green onions,” she told me. — In this sentence, we replace my name (Elisabeth) with the pronoun she.
In all of these examples, the part that was said is between quotation marks and is followed by a noun (“she” or “Elisabeth”) and a verb. Each of these verbs (“to say,” “to tell [someone],” “to explain”) are ways to describe someone talking. You can use any verb that refers to speech in this way.
You can also put the noun and verb before what was said.
Direct speech: Elisabeth said, “I like spaghetti.”
The example above would be much more likely to be said out loud than the first set of examples.
Here’s a conversation that might happen between two people:
1: Did you ask her if she liked coffee?
2: Yeah, I asked her.
1: What did she say?
2. She said, “Yeah, I like coffee.” ( Direct speech )
Usually, reporting of direct speech is something you see in writing. It doesn’t happen as often when people are talking to each other.
Direct reported speech often happens in the past. However, there are all kinds of stories, including journalism pieces, profiles and fiction, where you might see speech reported in the present as well.
This is sometimes done when the author of the piece wants you to feel that you’re experiencing events in the present moment.
For example, a profile of Kristen Stewart in Vanity Fair has a funny moment that describes how the actress isn’t a very good swimmer:
Direct speech: “I don’t want to enter the water, ever,” she says. “If everyone’s going in the ocean, I’m like, no.”
Here, the speech is reported as though it’s in the present tense (“she says”) instead of in the past (“she said”).
In writing of all kinds, direct reported speech is often split into two or more parts, as it is above.
Here’s an example from Lewis Carroll’s “ Alice’s Adventures in Wonderland ,” where the speech is even more split up:
Direct speech: “I won’t indeed!” said Alice, in a great hurry to change the subject of conversation. “Are you—are you fond—of—of dogs?” The Mouse did not answer, so Alice went on eagerly: “There is such a nice little dog near our house I should like to show you!”
Reporting indirect speech is what happens when you explain what someone said without using their exact words.
Let’s start with an example of direct reported speech like those used above.
Direct speech: Elisabeth said, “I like coffee.”
As indirect reported speech, it looks like this:
Indirect speech: Elisabeth said she liked coffee.
You can see that the subject (“I”) has been changed to “she,” to show who is being spoken about. If I’m reporting the direct speech of someone else, and this person says “I,” I’d repeat their sentence exactly as they said it. If I’m reporting this person’s speech indirectly to someone else, however, I’d speak about them in the third person—using “she,” “he” or “they.”
You may also notice that the tense changes here: If “I like coffee” is what she said, this can become “She liked coffee” in indirect speech.
However, you might just as often hear someone say something like, “She said she likes coffee.” Since people’s likes and preferences tend to change over time and not right away, it makes sense to keep them in the present tense.
Indirect speech often uses the word “that” before what was said:
Indirect speech: She said that she liked coffee.
There’s no real difference between “She said she liked coffee” and “She said that she liked coffee.” However, using “that” can help make the different parts of the sentence clearer.
Let’s look at a few other examples:
Indirect speech: I said I was going outside today.
Indirect speech: They told me that they wanted to order pizza.
Indirect speech: He mentioned it was raining.
Indirect speech: She said that her father was coming over for dinner.
You can see an example of reporting indirect speech in the funny video “ Cell Phone Crashing .” In this video, a traveler in an airport sits down next to another traveler talking on his cell phone. The first traveler pretends to be talking to someone on his phone, but he appears to be responding to the second traveler’s conversation, which leads to this exchange:
Woman: “Are you answering what I’m saying?”
Man “No, no… I’m on the phone with somebody, sorry. I don’t mean to be rude.” (Direct speech)
Woman: “What was that?”
Man: “I just said I was on the phone with somebody.” (Indirect speech)
When reporting questions in indirect speech, you can use words like “whether” or “if” with verbs that show questioning, such as “to ask” or “to wonder.”
Direct speech: She asked, “Is that a new restaurant?”
Indirect speech: She asked if that was a new restaurant.
In any case where you’re reporting a question, you can say that someone was “wondering” or “wanted to know” something. Notice that these verbs don’t directly show that someone asked a question. They don’t describe an action that happened at a single point in time. But you can usually assume that someone was wondering or wanted to know what they asked.
Indirect speech: She was wondering if that was a new restaurant.
Indirect speech: She wanted to know whether that was a new restaurant.
It can be tricky to know how to use tenses when reporting indirect speech. Let’s break it down, tense by tense.
Sometimes, indirect speech “ backshifts ,” or moves one tense further back into the past. We already saw this in the example from above:
Direct speech: She said, “I like coffee.”
Indirect speech: She said she liked coffee.
Also as mentioned above, backshifting doesn’t always happen. This might seem confusing, but it isn’t that difficult to understand once you start using reported speech regularly.
What tense you use in indirect reported speech often just depends on when what you’re reporting happened or was true.
Let’s look at some examples of how direct speech in certain tenses commonly changes (or doesn’t) when it’s reported as indirect speech.
To learn about all the English tenses (or for a quick review), check out this post .
Direct speech: I said, “I play video games.”
Indirect speech: I said that I played video games (simple past) or I said that I play video games (simple present).
Backshifting into the past or staying in the present here can change the meaning slightly. If you use the first example, it’s unclear whether or not you still play video games; all we know is that you said you played them in the past.
If you use the second example, though, you probably still play video games (unless you were lying for some reason).
However, the difference in meaning is so small, you can use either one and you won’t have a problem.
Direct speech: I said, “I’m playing video games.”
Indirect speech: I said that I was playing video games (past continuous) or I said that I’m playing video games (present continuous).
In this case, you’d likely use the first example if you were telling a story about something that happened in the past.
You could use the second example to repeat or stress what you just said. For example:
Hey, want to go for a walk?
Direct speech: No, I’m playing video games.
But it’s such a nice day!
Indirect speech: I said that I’m playing video games!
Direct speech: Marie said, “I have read that book.”
Indirect speech: Marie said that she had read that book (past perfect) or Marie said that she has read that book (present perfect).
The past perfect is used a lot in writing and other kinds of narration. This is because it helps point out an exact moment in time when something was true.
The past perfect isn’t quite as useful in conversation, where people are usually more interested in what’s true now. So, in a lot of cases, people would use the second example above when speaking.
Direct speech: She said, “I have been watching that show.”
Indirect speech: She said that she had been watching that show (past perfect continuous) or She said that she has been watching that show (present perfect continuous).
These examples are similar to the others above. You could use the first example whether or not this person was still watching the show, but if you used the second example, it’d probably seem like you either knew or guessed that she was still watching it.
Direct speech: You told me, “I charged my phone.”
Indirect speech: You told me that you had charged your phone (past perfect) or You told me that you charged your phone (simple past).
Here, most people would probably just use the second example, because it’s simpler, and gets across the same meaning.
Direct speech: You told me, “I was charging my phone.”
Indirect speech: You told me that you had been charging your phone (past perfect continuous) or You told me that you were charging your phone (past continuous).
Here, the difference is between whether you had been charging your phone before or were charging your phone at the time. However, a lot of people would still use the second example in either situation.
Direct speech: They explained, “We had bathed the cat on Wednesday.”
Indirect speech: They explained that they had bathed the cat on Wednesday. (past perfect)
Once we start reporting the past perfect tenses, we don’t backshift because there are no tenses to backshift to.
So in this case, it’s simple. The tense stays exactly as is. However, many people might simplify even more and use the simple past, saying, “They explained that they bathed the cat on Wednesday.”
Direct speech: They said, “The cat had been going outside and getting dirty for a long time!”
Indirect speech: They said that the cat had been going outside and getting dirty for a long time. (past perfect continuous)
Again, we don’t shift the tense back here; we leave it like it is. And again, a lot of people would report this speech as, “They said the cat was going outside and getting dirty for a long time.” It’s just a simpler way to say almost the same thing.
Direct speech: I told you, “I will be here no matter what.”
Indirect speech: I told you that I would be here no matter what. (present conditional)
At this point, we don’t just have to think about tenses, but grammatical mood, too. However, the idea is still pretty simple. We use the conditional (with “would”) to show that at the time the words were spoken, the future was uncertain.
In this case, you could also say, “I told you that I will be here no matter what,” but only if you “being here” is still something that you expect to happen in the future.
What matters here is what’s intended. Since this example shows a person reporting their own speech, it’s more likely that they’d want to stress the truth of their own intention, and so they might be more likely to use “will” than “would.”
But if you were reporting someone else’s words, you might be more likely to say something like, “She told me that she would be here no matter what.”
Direct speech: I said, “I’ll be waiting for your call.”
Indirect speech: I said that I would be waiting for your call. (conditional continuous)
These are similar to the above examples, but apply to a continuous or ongoing action.
Direct speech: She said, “I will have learned a lot about myself.”
Indirect speech: She said that she would have learned a lot about herself (conditional perfect) or She said that she will have learned a lot about herself (future perfect).
In this case, using the conditional (as in the first example) suggests that maybe a certain event didn’t happen, or something didn’t turn out as expected.
However, that might not always be the case, especially if this was a sentence that was written in an article or a work of fiction. The second example, however, suggests that the future that’s being talked about still hasn’t happened yet.
Direct speech: She said, “By next Tuesday, I will have been staying inside every day for the past month.”
Indirect speech: She said that by next Tuesday, she would have been staying inside every day for the past month (perfect continuous conditional) or She said that by next Tuesday, she will have been staying inside every day for the past month (past perfect continuous).
Again, in this case, the first example might suggest that the event didn’t happen. Maybe the person didn’t stay inside until next Tuesday! However, this could also just be a way of explaining that at the time she said this in the past, it was uncertain whether she really would stay inside for as long as she thought.
The second example, on the other hand, would only be used if next Tuesday hadn’t happened yet.
Let’s take a look at where you can find resources for practicing reporting speech in the real world.
One of the most common uses for reported speech is in fiction. You’ll find plenty of reported speech in novels and short stories . Look for books that have long sections of text with dialogue marked by quotation marks (“…”). Once you understand the different kinds of reported speech, you can look for it in your reading and use it in your own writing.
Writing your own stories is a great way to get even better at understanding reported speech.
One of the best ways to practice any aspect of English is to watch native English videos. By watching English speakers use the language, you can understand how reported speech is used in real world situations.
FluentU takes authentic videos—like music videos, movie trailers, news and inspiring talks—and turns them into personalized language learning lessons.
You can try FluentU for free for 2 weeks. Check out the website or download the iOS app or Android app.
P.S. Click here to take advantage of our current sale! (Expires at the end of this month.)
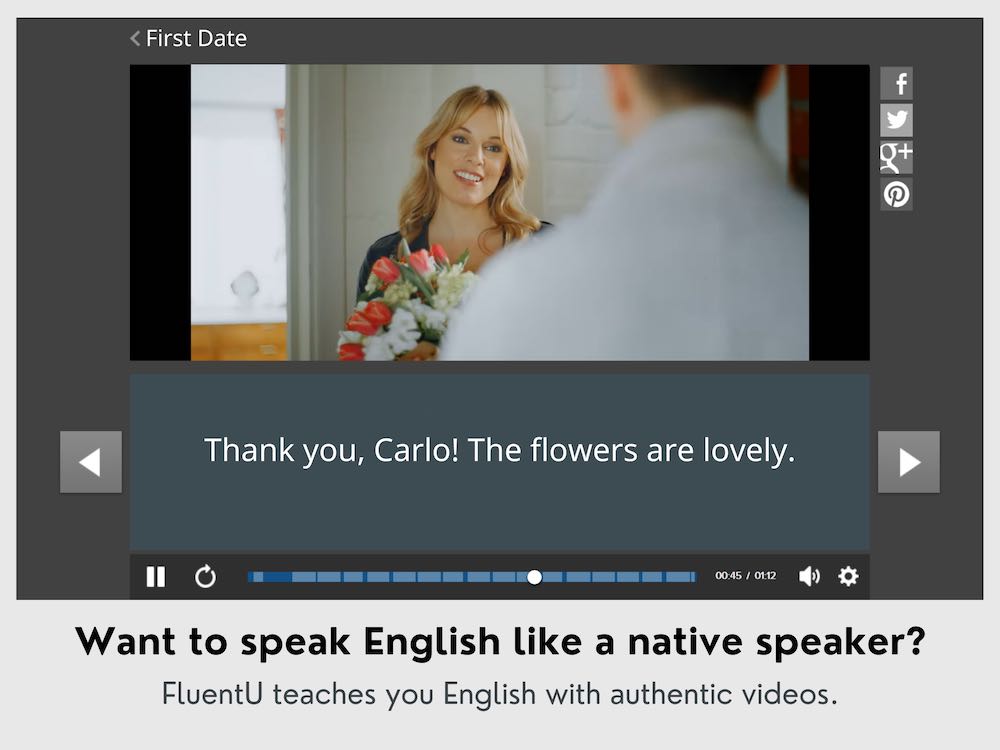
Try FluentU for FREE!
Celebrity profiles, which you can find in print magazines and online, can help you find and practice reported speech, too. Celebrity profiles are stories that focus on a famous person. They often include some kind of interview. The writer will usually spend some time describing the person and then mention things that they say; this is when they use reported speech.
Because many of these profiles are written in the present tense, they can help you get used to the basics of reported speech without having to worry too much about different verb tenses.
While the above may seem really complicated, it isn’t that difficult to start using reported speech.
Mastering it may be a little difficult, but the truth is that many, many people who speak English as a first language struggle with it, too!
Reported speech is flexible, and even if you make mistakes, there’s a good chance that no one will notice.
Enter your e-mail address to get your free PDF!
We hate SPAM and promise to keep your email address safe

- Cambridge Dictionary +Plus
Reported speech: indirect speech
Indirect speech focuses more on the content of what someone said rather than their exact words. In indirect speech , the structure of the reported clause depends on whether the speaker is reporting a statement, a question or a command.
Indirect speech: reporting statements
Indirect reports of statements consist of a reporting clause and a that -clause. We often omit that , especially in informal situations:
The pilot commented that the weather had been extremely bad as the plane came in to land. (The pilot’s words were: ‘The weather was extremely bad as the plane came in to land.’ )
I told my wife I didn’t want a party on my 50th birthday. ( that -clause without that ) (or I told my wife that I didn’t want a party on my 50th birthday .)
Indirect speech: reporting questions
Reporting yes-no questions and alternative questions.
Indirect reports of yes-no questions and questions with or consist of a reporting clause and a reported clause introduced by if or whether . If is more common than whether . The reported clause is in statement form (subject + verb), not question form:
She asked if [S] [V] I was Scottish. (original yes-no question: ‘Are you Scottish?’ )
The waiter asked whether [S] we [V] wanted a table near the window. (original yes-no question: ‘Do you want a table near the window? )
He asked me if [S] [V] I had come by train or by bus. (original alternative question: ‘Did you come by train or by bus?’ )
Questions: yes-no questions ( Are you feeling cold? )
Reporting wh -questions
Indirect reports of wh -questions consist of a reporting clause, and a reported clause beginning with a wh -word ( who, what, when, where, why, how ). We don’t use a question mark:
He asked me what I wanted.
Not: He asked me what I wanted?
The reported clause is in statement form (subject + verb), not question form:
She wanted to know who [S] we [V] had invited to the party.
Not: … who had we invited …
Who , whom and what
In indirect questions with who, whom and what , the wh- word may be the subject or the object of the reported clause:
I asked them who came to meet them at the airport. ( who is the subject of came ; original question: ‘Who came to meet you at the airport?’ )
He wondered what the repairs would cost. ( what is the object of cost ; original question: ‘What will the repairs cost?’ )
She asked us what [S] we [V] were doing . (original question: ‘What are you doing?’ )
Not: She asked us what were we doing?
When , where , why and how
We also use statement word order (subject + verb) with when , where, why and how :
I asked her when [S] it [V] had happened (original question: ‘When did it happen?’ ).
Not: I asked her when had it happened?
I asked her where [S] the bus station [V] was . (original question: ‘Where is the bus station?’ )
Not: I asked her where was the bus station?
The teacher asked them how [S] they [V] wanted to do the activity . (original question: ‘How do you want to do the activity?’ )
Not: The teacher asked them how did they want to do the activity?
Questions: wh- questions
Indirect speech: reporting commands
Indirect reports of commands consist of a reporting clause, and a reported clause beginning with a to -infinitive:
The General ordered the troops to advance . (original command: ‘Advance!’ )
The chairperson told him to sit down and to stop interrupting . (original command: ‘Sit down and stop interrupting!’ )
We also use a to -infinitive clause in indirect reports with other verbs that mean wanting or getting people to do something, for example, advise, encourage, warn :
They advised me to wait till the following day. (original statement: ‘You should wait till the following day.’ )
The guard warned us not to enter the area. (original statement: ‘You must not enter the area.’ )
Verbs followed by a to -infinitive
Indirect speech: present simple reporting verb
We can use the reporting verb in the present simple in indirect speech if the original words are still true or relevant at the time of reporting, or if the report is of something someone often says or repeats:
Sheila says they’re closing the motorway tomorrow for repairs.
Henry tells me he’s thinking of getting married next year.
Rupert says dogs shouldn’t be allowed on the beach. (Rupert probably often repeats this statement.)
Newspaper headlines
We often use the present simple in newspaper headlines. It makes the reported speech more dramatic:
JUDGE TELLS REPORTER TO LEAVE COURTROOM
PRIME MINISTER SAYS FAMILIES ARE TOP PRIORITY IN TAX REFORM
Present simple ( I work )
Reported speech
Reported speech: direct speech
Indirect speech: past continuous reporting verb
In indirect speech, we can use the past continuous form of the reporting verb (usually say or tell ). This happens mostly in conversation, when the speaker wants to focus on the content of the report, usually because it is interesting news or important information, or because it is a new topic in the conversation:
Rory was telling me the big cinema in James Street is going to close down. Is that true?
Alex was saying that book sales have gone up a lot this year thanks to the Internet.
‘Backshift’ refers to the changes we make to the original verbs in indirect speech because time has passed between the moment of speaking and the time of the report.
In these examples, the present ( am ) has become the past ( was ), the future ( will ) has become the future-in-the-past ( would ) and the past ( happened ) has become the past perfect ( had happened ). The tenses have ‘shifted’ or ‘moved back’ in time.
The past perfect does not shift back; it stays the same:
Modal verbs
Some, but not all, modal verbs ‘shift back’ in time and change in indirect speech.
We can use a perfect form with have + - ed form after modal verbs, especially where the report looks back to a hypothetical event in the past:
He said the noise might have been the postman delivering letters. (original statement: ‘The noise might be the postman delivering letters.’ )
He said he would have helped us if we’d needed a volunteer. (original statement: ‘I’ll help you if you need a volunteer’ or ‘I’d help you if you needed a volunteer.’ )
Used to and ought to do not change in indirect speech:
She said she used to live in Oxford. (original statement: ‘I used to live in Oxford.’ )
The guard warned us that we ought to leave immediately. (original statement: ‘You ought to leave immediately.’ )
No backshift
We don’t need to change the tense in indirect speech if what a person said is still true or relevant or has not happened yet. This often happens when someone talks about the future, or when someone uses the present simple, present continuous or present perfect in their original words:
He told me his brother works for an Italian company. (It is still true that his brother works for an Italian company.)
She said she ’s getting married next year. (For the speakers, the time at the moment of speaking is ‘this year’.)
He said he ’s finished painting the door. (He probably said it just a short time ago.)
She promised she ’ll help us. (The promise applies to the future.)
Indirect speech: changes to pronouns
Changes to personal pronouns in indirect reports depend on whether the person reporting the speech and the person(s) who said the original words are the same or different.
Indirect speech: changes to adverbs and demonstratives
We often change demonstratives ( this, that ) and adverbs of time and place ( now, here, today , etc.) because indirect speech happens at a later time than the original speech, and perhaps in a different place.
Typical changes to demonstratives, adverbs and adverbial expressions
Indirect speech: typical errors.
The word order in indirect reports of wh- questions is the same as statement word order (subject + verb), not question word order:
She always asks me where [S] [V] I am going .
Not: She always asks me where am I going .
We don’t use a question mark when reporting wh- questions:
I asked him what he was doing.
Not: I asked him what he was doing?

Word of the Day
have irons in the fire
to be involved with many activities or jobs at the same time or to make certain that there are always several possibilities available

Binding, nailing, and gluing: talking about fastening things together

Learn more with +Plus
- Recent and Recommended {{#preferredDictionaries}} {{name}} {{/preferredDictionaries}}
- Definitions Clear explanations of natural written and spoken English English Learner’s Dictionary Essential British English Essential American English
- Grammar and thesaurus Usage explanations of natural written and spoken English Grammar Thesaurus
- Pronunciation British and American pronunciations with audio English Pronunciation
- English–Chinese (Simplified) Chinese (Simplified)–English
- English–Chinese (Traditional) Chinese (Traditional)–English
- English–Dutch Dutch–English
- English–French French–English
- English–German German–English
- English–Indonesian Indonesian–English
- English–Italian Italian–English
- English–Japanese Japanese–English
- English–Norwegian Norwegian–English
- English–Polish Polish–English
- English–Portuguese Portuguese–English
- English–Spanish Spanish–English
- English–Swedish Swedish–English
- Dictionary +Plus Word Lists
Add ${headword} to one of your lists below, or create a new one.
{{message}}
Something went wrong.
There was a problem sending your report.
Reported Speech: Rules, Examples, Exceptions

👉 Quiz 1 / Quiz 2
Advanced Grammar Course
What is reported speech?
“Reported speech” is when we talk about what somebody else said – for example:
- Direct Speech: “I’ve been to London three times.”
- Reported Speech: She said she’d been to London three times.
There are a lot of tricky little details to remember, but don’t worry, I’ll explain them and we’ll see lots of examples. The lesson will have three parts – we’ll start by looking at statements in reported speech, and then we’ll learn about some exceptions to the rules, and finally we’ll cover reported questions, requests, and commands.

So much of English grammar – like this topic, reported speech – can be confusing, hard to understand, and even harder to use correctly. I can help you learn grammar easily and use it confidently inside my Advanced English Grammar Course.
In this course, I will make even the most difficult parts of English grammar clear to you – and there are lots of opportunities for you to practice!

Backshift of Verb Tenses in Reported Speech
When we use reported speech, we often change the verb tense backwards in time. This can be called “backshift.”
Here are some examples in different verb tenses:
Reported Speech (Part 1) Quiz
Exceptions to backshift in reported speech.
Now that you know some of the reported speech rules about backshift, let’s learn some exceptions.
There are two situations in which we do NOT need to change the verb tense.
No backshift needed when the situation is still true
For example, if someone says “I have three children” (direct speech) then we would say “He said he has three children” because the situation continues to be true.
If I tell you “I live in the United States” (direct speech) then you could tell someone else “She said she lives in the United States” (that’s reported speech) because it is still true.
When the situation is still true, then we don’t need to backshift the verb.

He said he HAS three children
But when the situation is NOT still true, then we DO need to backshift the verb.
Imagine your friend says, “I have a headache.”
- If you immediately go and talk to another friend, you could say, “She said she has a headache,” because the situation is still true
- If you’re talking about that conversation a month after it happened, then you would say, “She said she had a headache,” because it’s no longer true.
No backshift needed when the situation is still in the future
We also don’t need to backshift to the verb when somebody said something about the future, and the event is still in the future.
Here’s an example:
- On Monday, my friend said, “I ‘ll call you on Friday .”
- “She said she ‘ll call me on Friday”, because Friday is still in the future from now.
- It is also possible to say, “She said she ‘d (she would) call me on Friday.”
- Both of them are correct, so the backshift in this case is optional.
Let’s look at a different situation:
- On Monday, my friend said, “I ‘ll call you on Tuesday .”
- “She said she ‘d call me on Tuesday.” I must backshift because the event is NOT still in the future.

Review: Reported Speech, Backshift, & Exceptions
Quick review:
- Normally in reported speech we backshift the verb, we put it in a verb tense that’s a little bit further in the past.
- when the situation is still true
- when the situation is still in the future
Reported Requests, Orders, and Questions
Those were the rules for reported statements, just regular sentences.
What about reported speech for questions, requests, and orders?
For reported requests, we use “asked (someone) to do something”:
- “Please make a copy of this report.” (direct speech)
- She asked me to make a copy of the report. (reported speech)
For reported orders, we use “told (someone) to do something:”
- “Go to the bank.” (direct speech)
- “He told me to go to the bank.” (reported speech)
The main verb stays in the infinitive with “to”:
- She asked me to make a copy of the report. She asked me make a copy of the report.
- He told me to go to the bank. He told me go to the bank.
For yes/no questions, we use “asked if” and “wanted to know if” in reported speech.
- “Are you coming to the party?” (direct)
- He asked if I was coming to the party. (reported)
- “Did you turn off the TV?” (direct)
- She wanted to know if I had turned off the TV.” (reported)
The main verb changes and back shifts according to the rules and exceptions we learned earlier.
Notice that we don’t use do/does/did in the reported question:
- She wanted to know did I turn off the TV.
- She wanted to know if I had turned off the TV.
For other questions that are not yes/no questions, we use asked/wanted to know (without “if”):
- “When was the company founded?” (direct)
- She asked when the company was founded.” (reported)
- “What kind of car do you drive?” (direct)
- He wanted to know what kind of car I drive. (reported)
Again, notice that we don’t use do/does/did in reported questions:
- “Where does he work?”
- She wanted to know where does he work.
- She wanted to know where he works.
Also, in questions with the verb “to be,” the word order changes in the reported question:
- “Where were you born?” ([to be] + subject)
- He asked where I was born. (subject + [to be])
- He asked where was I born.

Reported Speech (Part 2) Quiz
Learn more about reported speech:
- Reported speech: Perfect English Grammar
- Reported speech: BJYU’s
If you want to take your English grammar to the next level, then my Advanced English Grammar Course is for you! It will help you master the details of the English language, with clear explanations of essential grammar topics, and lots of practice. I hope to see you inside!
I’ve got one last little exercise for you, and that is to write sentences using reported speech. Think about a conversation you’ve had in the past, and write about it – let’s see you put this into practice right away.
Master the details of English grammar:

More Espresso English Lessons:
About the author.
Shayna Oliveira
Shayna Oliveira is the founder of Espresso English, where you can improve your English fast - even if you don’t have much time to study. Millions of students are learning English from her clear, friendly, and practical lessons! Shayna is a CELTA-certified teacher with 10+ years of experience helping English learners become more fluent in her English courses.
Reported Speech: How to Use Reported Speech | Useful Rules
One of the most common mistakes when becoming familiar with this type of grammar is not knowing the difference between direct speech and reported speech and the changes related to these types of sentences.
Reported Speech
The reported speech reproduces the words of another person by adapting certain temporal and local references of the original speech to the situation of the speaker, for example, personal pronouns, demonstratives, verb tenses, and adverbs of place or time.
It is characterized by introducing the message that is reproduced with a speaking verb followed by conjunctions that or if. The speaking verb reveals the intention of the speaker to convey what another person has said.
The most frequent speaking verbs are: say, affirm , count, explain, ask, warn, suggest, order, etc.
Direct Speech vs. Reported Speech
Both are the two different ways to transmit what someone has said.
With direct speech, the message is reproduced as we have heard it, in quotes and after a color meanwhile with reported speech the message is reproduced with our words, without commas but using that or if after the verb.
Different Types of Sentences
- Reported statements : use that before the statement and the reporting verb said or told.
- Reported questions : use reported verbs like asked, requested, or wanted to know and omit the question mark. Remember that the order in reported questions changes. In the case of yes-no questions use whether or if.
- Reported requests or commands : use to or not to before the sentence and use verbs like asked, told, ordered, urged, advised, and begged.
Changes When Using Reported Speech
Tense Changes in Reported Speech
In short, the tense changes in the reported speech are made taking into account the verb in the direct speech. The tense changes are:
- Simple present -> simple past
- Present continuous -> past continuous
- Simple past -> past perfect simple
- Past continuous -> past perfect continuous
- Past perfect simple -> past perfect simple
- Past perfect continuous -> past perfect continuous
- Present perfect -> past perfect simple
- Present perfect continuous -> past perfect continuous
- Future simple -> would
- Future perfect -> would have
- Present passive -> past passive
- Present passive continuous -> past passive continuous
- Can -> could/would be able to
- May -> might
- May -> could/ would be allowed to
- Must -> must/ had to/ would have to
- Needn’t -> didn’t have to /didn’t need to /wouldn’t have to
- Shall -> would/should
- Will -> would
Place, Demonstratives, and Time Expressions
Just as there are certain changes in the verb tenses, you have to make changes in the demonstratives, pronouns , and expressions of time and place.
- Here -> there
- There -> there
- This -> that
Time Expressions
- Today -> that day
- Tomorrow -> the next day/ the following day
- Now -> at that moment/ then
- At the present -> At the time
- Present, current -> existing current
- In one hour -> one hour later
- Next year -> the following year
- Days ago -> days before
- Tonight -> that night
- In two week’s time -> two weeks later
- Ago -> before
Pronouns and Demonstratives
- I -> he, she
- Me -> him, her
- My -> his, her, the
- Mine -> his, hers
- We -> they
- Us -> them
- Our -> their, the
- Ours -> theirs
- You -> they, them, their, the
- Yours -> theirs
- This -> that, the
- These -> those, the
- This book -> that book
Reported Speech | Infographic

Other Changes in Reported Speech

Last Updated on October 25, 2023

Leave a Comment Cancel reply
English EFL
Reported speech
Tense changes in reported speech
Indirect speech (reported speech) focuses more on the content of what someone said rather than their exact words. In indirect speech, the structure of the reported clause depends on whether the speaker is reporting a statement, a question or a command.
Normally, the tense in reported speech is one tense back in time from the tense in direct speech: She said, "I am tired." = She said that she was tired.
You do not need to change the tense if the reporting verb is in the present, or if the original statement was about something that is still true (but this is only for things which are general facts, and even then usually we like to change the tense) , e.g.
- He says he has missed the train but he'll catch the next one.
- We explained that it is very difficult to find our house.
- Direct speech: The sky is blue.
- Reported speech: She said (that) the sky is/was blue.
These modal verbs do not change in reported speech: might, could, would, should, ought to :
- We explained, "It could be difficult to find our house." = We explained that it could be difficult to find our house.
- She said, "I might bring a friend to the party." = She said that she might bring a friend to the party.
Course Curriculum
- Direct and indirect speech 15 mins
- Tense changes in reported speech 20 mins
- Changing time and place in reported speech 20 mins
- Reported questions 20 mins
- Reporting verbs 20 mins
- Reporting orders and requests 15 mins
- Reporting hopes, intentions and promises 20 mins
- B1-B2 grammar

Reported speech: statements

Do you know how to report what somebody else said? Test what you know with interactive exercises and read the explanation to help you.
Look at these examples to see how we can tell someone what another person said.
direct speech: 'I love the Toy Story films,' she said. indirect speech: She said she loved the Toy Story films. direct speech: 'I worked as a waiter before becoming a chef,' he said. indirect speech: He said he'd worked as a waiter before becoming a chef. direct speech: 'I'll phone you tomorrow,' he said. indirect speech: He said he'd phone me the next day.
Try this exercise to test your grammar.
Grammar B1-B2: Reported speech 1: 1
Read the explanation to learn more.
Grammar explanation
Reported speech is when we tell someone what another person said. To do this, we can use direct speech or indirect speech.
direct speech: 'I work in a bank,' said Daniel. indirect speech: Daniel said that he worked in a bank.
In indirect speech, we often use a tense which is 'further back' in the past (e.g. worked ) than the tense originally used (e.g. work ). This is called 'backshift'. We also may need to change other words that were used, for example pronouns.
Present simple, present continuous and present perfect
When we backshift, present simple changes to past simple, present continuous changes to past continuous and present perfect changes to past perfect.
'I travel a lot in my job.' Jamila said that she travelled a lot in her job. 'The baby's sleeping!' He told me the baby was sleeping. 'I've hurt my leg.' She said she'd hurt her leg.
Past simple and past continuous
When we backshift, past simple usually changes to past perfect simple, and past continuous usually changes to past perfect continuous.
'We lived in China for five years.' She told me they'd lived in China for five years. 'It was raining all day.' He told me it had been raining all day.
Past perfect
The past perfect doesn't change.
'I'd tried everything without success, but this new medicine is great.' He said he'd tried everything without success, but the new medicine was great.
No backshift
If what the speaker has said is still true or relevant, it's not always necessary to change the tense. This might happen when the speaker has used a present tense.
'I go to the gym next to your house.' Jenny told me that she goes to the gym next to my house. I'm thinking about going with her. 'I'm working in Italy for the next six months.' He told me he's working in Italy for the next six months. Maybe I should visit him! 'I've broken my arm!' She said she's broken her arm, so she won't be at work this week.
Pronouns, demonstratives and adverbs of time and place
Pronouns also usually change in indirect speech.
'I enjoy working in my garden,' said Bob. Bob said that he enjoyed working in his garden. 'We played tennis for our school,' said Alina. Alina told me they'd played tennis for their school.
However, if you are the person or one of the people who spoke, then the pronouns don't change.
'I'm working on my thesis,' I said. I told her that I was working on my thesis. 'We want our jobs back!' we said. We said that we wanted our jobs back.
We also change demonstratives and adverbs of time and place if they are no longer accurate.
'This is my house.' He said this was his house. [You are currently in front of the house.] He said that was his house. [You are not currently in front of the house.] 'We like it here.' She told me they like it here. [You are currently in the place they like.] She told me they like it there. [You are not in the place they like.] 'I'm planning to do it today.' She told me she's planning to do it today. [It is currently still the same day.] She told me she was planning to do it that day. [It is not the same day any more.]
In the same way, these changes to those , now changes to then , yesterday changes to the day before , tomorrow changes to the next/following day and ago changes to before .
Do this exercise to test your grammar again.
Grammar B1-B2: Reported speech 1: 2
Language level
Hello Team. If the reporting verb is in the present perfect, do we have to backshift the tenses of the direct speech or not? For example: He has said, "I bought a car yesterday."
1- He has said that he bought a car yesterday.
2- He has said that he had bought a car the previous day.
- Log in or register to post comments
Hello Ahmed Imam,
It's not necessary to backshift the verb form if the situation being reported is still true. For example:
"I'm a doctor"
She told me she is a doctor. [she was a doctor when she said it and she is still doctor now]
She told me she was a doctor. [she was a doctor when she said it and may or may not still be a doctor now]
The reporting verb in your example would be 'said' rather than 'has said' as we are talking about a particular moment in the past. For the other verb both 'bought' and 'had bought' are possible without any change in meaning. In fact, when the verb is past in the original sentence we usually do not shift the verb form back.
The LearnEnglish Team
Hello again. Which one is correct? Why?
- He has said that he (will - would) travel to Cairo with his father.
The present perfect is a present form, so generally 'will' is the correct form.
In this case, assuming that the man said 'I will travel to Cairo', then 'will' is the correct form. But if the man said 'I would travel to Cairo if I had time to do it', then 'would' would be the correct form since it is part of a conditional statement.
I think you were asking about the first situation (the general one), though. Does that make sense?
Best wishes, Kirk LearnEnglish team
Thank you for the information. It states that If what the speaker has said is still true or relevant, it's not always necessary to change the tense. I wonder if it is still correct to change the tense in this example: 'London is in the UK', he said. to He said London was in the UK. Or it has to be the present tense.
Hello Wen1996,
Yes, your version of the sentence is also correct. In this case, the past tense refers to the time the speaker made this statement. But this doesn't mean the statement isn't also true now.
Good evening from Turkey.
Is the following example correct: Question: When did she watch the movie?
She asked me when she had watched the movie. or is it had she watched the movie.
Do Subjects come before the verbs? Thank you.
Hello muratt,
This is a reported question, not an actual question, as you can see from the fact that it has no question mark at the end. Therefore no inversion is needed and the normal subject-verb word order is maintained: ...she had watched... is correct.
You can read more about this here:
https://learnenglish.britishcouncil.org/grammar/b1-b2-grammar/reported-speech-questions
Thank you for your response.
Hello Sir, kindly help with the following sentence-
She said, "When I was a child I wasn't afraid of ghosts."
Please tell me how to write this sentence in reported/ indirect speech.
Online courses

Group and one-to-one classes with expert teachers.

Learn English in your own time, at your own pace.

One-to-one sessions focused on a personal plan.

Get the score you need with private and group classes.
- English Grammar
- Reported Speech
Reported Speech - Definition, Rules and Usage with Examples
Reported speech or indirect speech is the form of speech used to convey what was said by someone at some point of time. This article will help you with all that you need to know about reported speech, its meaning, definition, how and when to use them along with examples. Furthermore, try out the practice questions given to check how far you have understood the topic.

Table of Contents
Definition of reported speech, rules to be followed when using reported speech, table 1 – change of pronouns, table 2 – change of adverbs of place and adverbs of time, table 3 – change of tense, table 4 – change of modal verbs, tips to practise reported speech, examples of reported speech, check your understanding of reported speech, frequently asked questions on reported speech in english, what is reported speech.
Reported speech is the form in which one can convey a message said by oneself or someone else, mostly in the past. It can also be said to be the third person view of what someone has said. In this form of speech, you need not use quotation marks as you are not quoting the exact words spoken by the speaker, but just conveying the message.
Now, take a look at the following dictionary definitions for a clearer idea of what it is.
Reported speech, according to the Oxford Learner’s Dictionary, is defined as “a report of what somebody has said that does not use their exact words.” The Collins Dictionary defines reported speech as “speech which tells you what someone said, but does not use the person’s actual words.” According to the Cambridge Dictionary, reported speech is defined as “the act of reporting something that was said, but not using exactly the same words.” The Macmillan Dictionary defines reported speech as “the words that you use to report what someone else has said.”
Reported speech is a little different from direct speech . As it has been discussed already, reported speech is used to tell what someone said and does not use the exact words of the speaker. Take a look at the following rules so that you can make use of reported speech effectively.
- The first thing you have to keep in mind is that you need not use any quotation marks as you are not using the exact words of the speaker.
- You can use the following formula to construct a sentence in the reported speech.
- You can use verbs like said, asked, requested, ordered, complained, exclaimed, screamed, told, etc. If you are just reporting a declarative sentence , you can use verbs like told, said, etc. followed by ‘that’ and end the sentence with a full stop . When you are reporting interrogative sentences, you can use the verbs – enquired, inquired, asked, etc. and remove the question mark . In case you are reporting imperative sentences , you can use verbs like requested, commanded, pleaded, ordered, etc. If you are reporting exclamatory sentences , you can use the verb exclaimed and remove the exclamation mark . Remember that the structure of the sentences also changes accordingly.
- Furthermore, keep in mind that the sentence structure , tense , pronouns , modal verbs , some specific adverbs of place and adverbs of time change when a sentence is transformed into indirect/reported speech.
Transforming Direct Speech into Reported Speech
As discussed earlier, when transforming a sentence from direct speech into reported speech, you will have to change the pronouns, tense and adverbs of time and place used by the speaker. Let us look at the following tables to see how they work.
Here are some tips you can follow to become a pro in using reported speech.
- Select a play, a drama or a short story with dialogues and try transforming the sentences in direct speech into reported speech.
- Write about an incident or speak about a day in your life using reported speech.
- Develop a story by following prompts or on your own using reported speech.
Given below are a few examples to show you how reported speech can be written. Check them out.
- Santana said that she would be auditioning for the lead role in Funny Girl.
- Blaine requested us to help him with the algebraic equations.
- Karishma asked me if I knew where her car keys were.
- The judges announced that the Warblers were the winners of the annual acapella competition.
- Binsha assured that she would reach Bangalore by 8 p.m.
- Kumar said that he had gone to the doctor the previous day.
- Lakshmi asked Teena if she would accompany her to the railway station.
- Jibin told me that he would help me out after lunch.
- The police ordered everyone to leave from the bus stop immediately.
- Rahul said that he was drawing a caricature.
Transform the following sentences into reported speech by making the necessary changes.
1. Rachel said, “I have an interview tomorrow.”
2. Mahesh said, “What is he doing?”
3. Sherly said, “My daughter is playing the lead role in the skit.”
4. Dinesh said, “It is a wonderful movie!”
5. Suresh said, “My son is getting married next month.”
6. Preetha said, “Can you please help me with the invitations?”
7. Anna said, “I look forward to meeting you.”
8. The teacher said, “Make sure you complete the homework before tomorrow.”
9. Sylvester said, “I am not going to cry anymore.”
10. Jade said, “My sister is moving to Los Angeles.”
Now, find out if you have answered all of them correctly.
1. Rachel said that she had an interview the next day.
2. Mahesh asked what he was doing.
3. Sherly said that her daughter was playing the lead role in the skit.
4. Dinesh exclaimed that it was a wonderful movie.
5. Suresh said that his son was getting married the following month.
6. Preetha asked if I could help her with the invitations.
7. Anna said that she looked forward to meeting me.
8. The teacher told us to make sure we completed the homework before the next day.
9. Sylvester said that he was not going to cry anymore.
10. Jade said that his sister was moving to Los Angeles.
What is reported speech?
What is the definition of reported speech.
Reported speech, according to the Oxford Learner’s Dictionary, is defined as “a report of what somebody has said that does not use their exact words.” The Collins Dictionary defines reported speech as “speech which tells you what someone said, but does not use the person’s actual words.” According to the Cambridge Dictionary, reported speech is defined as “the act of reporting something that was said, but not using exactly the same words.” The Macmillan Dictionary defines reported speech as “the words that you use to report what someone else has said.”
What is the formula of reported speech?
You can use the following formula to construct a sentence in the reported speech. Subject said that (report whatever the speaker said)
Give some examples of reported speech.
Given below are a few examples to show you how reported speech can be written.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.
EnglishPost.org
Reported Speech: Structures and Examples
Reported speech (Indirect Speech) is how we represent the speech of other people or what we ourselves say.
Reported Speech focuses more on the content of what someone said rather than their exact words
The structure of the independent clause depends on whether the speaker is reporting a statement, a question, or a command.
Table of Contents
Reported Speech Rules and Examples
Present tenses and reported speech, past tenses and reported speech, reported speech examples, reported speech and the simple present, reported speech and present continuous, reported speech and the simple past, reported speech and the past continuous, reported speech and the present perfect, reported speech and the past perfect, reported speech and ‘ can ’ and ‘can’t’, reported speech and ‘ will ’ and ‘ won’t ’, reported speech and could and couldn’t, reported speech and the future continuous, reported questions exercises online.
To turn sentences into Indirect Speech, you have to follow a set of rules and this is what makes reported speech difficult for some.
To make reported speech sentences, you need to manage English tenses well.
- Present Simple Tense changes into Past Simple Tense
- Present Progressive Tense changes into Past Progressive Tense
- Present Perfect Tense changes into Past Perfect Tense
- Present Perfect Progressive Tense changes into Past Perfect Tense
- Past Simple Tense changes into Past Perfect Tense
- Past Progressive Tense changes into Perfect Continuous Tense
- Past Perfect Tense doesn’t change
- Past Perfect Progressive Tense doesn’t change
- Future Simple Tense changes into would
- Future Progressive Tense changes into “would be”
- Future Perfect Tense changes into “would have·
- Future Perfect Progressive Tense changes into “would have been”
These are some examples of sentences using indirect speech
The present simple tense usually changes to the past simple
The present continuous tense usually changes to the past continuous.
The past simple tense usually changes to the past perfect
The past continuous tense usually changes to the past perfect continuous.
The present perfect tense usually changes to the past perfect tense
The past perfect tense does not change
‘ Can ’ and ‘can’t’ in direct speech change to ‘ could ’ and ‘ couldn’t ’
‘ Will ’ and ‘ won’t ’ in direct speech change to ‘ would ’ and ‘ wouldn’t ’
Could and couldn’t doesn’t change
Will ’ and ‘ won’t ’ in direct speech change to ‘ would ’ and ‘ wouldn’t ’
These are some online exercises to learn more about reported questions
- Present Simple Reported Yes/No Question Exercise
- Present Simple Reported Wh Question Exercise
- Mixed Tense Reported Question Exercise
- Present Simple Reported Statement Exercise
- Present Continuous Reported Statement Exercise
I am Jose Manuel, English professor and creator of EnglishPost.org, a blog whose mission is to share lessons for those who want to learn and improve their English
Related Posts

50 Present Progressive Sentences: Guide and Examples

100 Sentences with Like

Indirect Questions Examples: Guide & Structure
Grammar Explanations
Perfect english grammar.

- Tenses Forms Cheatsheet
- Present Simple Form
- Present Continuous Form
- Present Perfect Simple Form
- Present Perfect Continuous Form
- Past Simple Form
- Past Continuous Form
- Past Perfect Simple Form
- Past Perfect Continuous Form
- Future Simple Form
- Future Continuous Form
- Future Perfect Simple Form
- Future Perfect Continuous Form
- Present Simple 1
- Present Continuous 1
- Present Simple or Present Continuous?
- Present Perfect Simple 1
- Present Perfect or Past Simple 1?
- Present Perfect Continuous 1
- Present Perfect Simple or Present Perfect Continuous?
- Past Simple 1
- Past Continuous 1
- Past Perfect Simple 1
- Past Perfect Continuous 1
- Future Simple 1
- Will or Be Going To?
- Future Continuous 1
- Future Perfect Simple 1
- Future Perfect Continuous 1
- Categories of Verbs (PEG PLUS)
- Simple Tenses (PEG PLUS)
- Continuous Tenses (PEG PLUS)
- Simple vs Continuous Tenses (PEG PLUS)
- Perfect Simple Tenses (PEG PLUS)
- Perfect Continuous Tenses (PEG PLUS)
- Perfect Simple vs Perfect Continuous Tenses (PEG PLUS)
- Present Simple for the Present (PEG PLUS)
- Present Simple for the Past and the Future (PEG PLUS)
- Present Continuous 2 (PEG PLUS)
- Present Perfect Simple 2 (PEG PLUS)
- Present Perfect or Past Simple 2? (PEG PLUS)
- Present Perfect Continuous 2 (PEG PLUS)
- Past Simple Basics (PEG PLUS)
- Past Simple Definite Time (PEG PLUS)
- Past Simple Again (PEG PLUS)
- Past Continuous 2 (PEG PLUS)
- Past Perfect Simple 2 (PEG PLUS)
- Past Perfect Continuous 2 (PEG PLUS)
- Future Simple 2 (PEG PLUS)
- Be going to (PEG PLUS)
- Future Continuous 2 (PEG PLUS)
- Comparison of Future Forms (PEG PLUS)
- Future Perfect Simple 2 (PEG PLUS)
- Future Perfect Continuous 2 (PEG PLUS)
- Irregular Verbs
- Stative verbs
- How to pronounce 'ed'
- Present Simple Spelling Changes
- Transitive and Intransitive Verbs
- Reporting Verbs
- Gerunds and Infinitives Introduction
- Gerunds and Infinitives After Certain Verbs 1
- Gerunds and Infinitives After Certain Verbs 2
- Gerunds and Infinitives After Certain Verbs 3
- Let and Make
- Make and Do
- Used to Do, Would Do, and Be Used to Doing
- Say and Tell
- Causative Verbs (Have / Get)
- Question Forms
- Tag Questions
- Subject Questions
- Indirect Questions
- Zero Conditional
- First Conditional
- Second Conditional
- Third Conditional
- Present Real Conditionals (PEG PLUS)
- Past Real Conditionals (PEG PLUS)
- Future Real Conditionals (PEG PLUS)
- Mixed Real Conditionals (PEG PLUS)
- Present Unreal Conditionals (PEG PLUS)
- Past Unreal Conditionals (PEG PLUS)
- Future Unreal Conditionals (PEG PLUS)
- Mixed Unreal Conditionals (PEG PLUS)
- Phrasal Verbs 1 Explanation
- Phrasal Verbs 2 Explanation
- How to use 'a little', 'little', 'few' and 'a few'.
- How to use 'a' and 'the' with bed / home / work / town.
- How to use 'the' and 'no article' with superlatives.
- How to use 'some', 'any' and 'no article'.
- How to make comparative and superlative adjectives
- How to use comparative adjectives
- How to use superlative adjectives
- Participle adjectives
- Adjectives and prepositions
- Adjectives and adverbs
- Adverbs of Frequency
- Adverbs and Adjectives
- Reported Speech
- The Passive
- Modal Verbs: Introduction
- Modal Verbs of Probability
- Modal Verbs of Ability.
- Modal Verbs of Obligation
- Could Have / Would Have / Should Have
- Modals Introduction (PEG PLUS)
- Modals of Permission (PEG PLUS)
- Modals of Obligation and Advice (PEG PLUS)
- Modals of Volition (PEG PLUS)
- Modals of Logical Necessity (PEG PLUS)
- Modals of Probability (PEG PLUS)
- Modals of Ability and Possibility (PEG PLUS)
- Modals of Prediction (PEG PLUS)
- Other Modal Uses (PEG PLUS)
- Relative Clauses
- Prepositions: Introduction
- Prepositions of Time
- Prepositions of Place
- Adjectives + Prepositions
- Verbs + Prepositions
- Collocations with Prepositions
- As and Like

Hello! I'm Seonaid! I'm here to help you understand grammar and speak correct, fluent English.

Read more about our learning method
- Class 6 Maths
- Class 6 Science
- Class 6 Social Science
- Class 6 English
- Class 7 Maths
- Class 7 Science
- Class 7 Social Science
- Class 7 English
- Class 8 Maths
- Class 8 Science
- Class 8 Social Science
- Class 8 English
- Class 9 Maths
- Class 9 Science
- Class 9 Social Science
- Class 9 English
- Class 10 Maths
- Class 10 Science
- Class 10 Social Science
- Class 10 English
- Class 11 Maths
- Class 11 Computer Science (Python)
- Class 11 English
- Class 12 Maths
- Class 12 English
- Class 12 Economics
- Class 12 Accountancy
- Class 12 Physics
- Class 12 Chemistry
- Class 12 Biology
- Class 12 Computer Science (Python)
- Class 12 Physical Education
- GST and Accounting Course
- Excel Course
- Tally Course
- Finance and CMA Data Course
- Payroll Course
Interesting
- Learn English
- Learn Excel
- Learn Tally
- Learn GST (Goods and Services Tax)
- Learn Accounting and Finance
- GST Tax Invoice Format
- Accounts Tax Practical
- Tally Ledger List
- GSTR 2A - JSON to Excel
Are you in school ? Do you love Teachoo?
We would love to talk to you! Please fill this form so that we can contact you
Direct Indirect Speech
- Verbs and tenses
- Prepositions
- Articles,Vowels and Consonants
- Active Voice and Passive Voice
- Gender-Masculine and Feminine
- Singular and Plural Nouns
- Conjunctions
- Interjections
Direct Indirect Speech for Future Perfect Continuous
Last updated at April 16, 2024 by Teachoo

In this case,"will have been" becomes "would have been"
The boy said" They will have been waiting for me"
The boy said They would have been waiting for me
The girl said" I will have been an air hostess by 2020"
The girl said I would have been an air hostess by 2020
The man said" I will have been getting old in 10 years"
The man said I would have been getting old in 10 years
She said" I will have been married in 3 years time"
She said I would have been married in 3 years time

CA Maninder Singh
CA Maninder Singh is a Chartered Accountant for the past 14 years. He also provides Accounts Tax GST Training in Delhi, Kerala and online.
Get E-filing Return Practice
Watch videos and do assignments
Add more skills to your resume
Get Professional Certification in Accounts and Taxation
Hi, it looks like you're using AdBlock :(
Please login to view more pages. it's free :), solve all your doubts with teachoo black.

Direct and Indirect of Future Perfect Progressive

Tense Change: As a rule, when we convey a message from present tenses and past tense, we go one tense back, but when you change direct speech of future perfect continuous tense, you just need to change the verb “will” into “would” and follow other rules as usual.
Affirmatives
- Direct speech: RP +, + S + will have been + V1ing + ROTS He said, “We will have been watching a movie.”
- Indirect speech: RP + that + S + would have been + V1ing + ROTS He told me that they would have been watching a movie.
- Direct speech: RP +, + S + will not have been + V1ing + ROTS He said, “I will not have been painting the wall.”
- Indirect speech: RP + that + S + would not have been + V1ing + ROTS He told me that he would not have been painting the wall.
Interrogatives
- Direct speech: RP +, + Will + S + have been + V1ing + ROTS He asked, “Will she have been mopping the kitchen.”
- Indirect speech: RP + if + S + would have been + V1ing + ROTS He asked me if she would have been mopping the kitchen.
Negative interrogatives
- Direct speech: RP +, + will not + S + have been + V1ing + ROTS He asked, “Won`t you have been studying hard for the test?”
- Indirect speech: RP + if + S + would not have been + V1ing + ROTS He asked me if I wouldn`t have been studying hard for the test.
WH/Information questions
- Direct speech: RP +, + WH + will + S + have been + V1ing + ROTS She asked, “What will you have been buying?”
- Indirect speech: RP + WH + S + would have been + V1ing + ROTS She wanted to know what I would have been buying.
Check out Direct and Indirect Speech Exercises With Answers
If you would like to know more about direct or quoted speech, or indirect or reported speech, check out more in the book below.
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window)
Related posts
Present continuous tense exercises with answers, what should you study to learn english, the 5 types of conditional sentences, leave a comment cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Conditionals and Reported Speech

Have you started learning conditionals ? You probably fear you’ll make a lot of mistakes with all those complicated rules, right? And to make things even more complicated, there’s the reported speech. How can you report conditional sentences?
There are numerous English language schools and programs in California that can help you with all the doubts you may have. But to truly master the conditionals and other aspects of the English language, you should rely on as many reliable resources as possible. So, keep reading this article as we explain how if-clauses are changed in reported speech.
Contact us online and get a quote today or call us via WhatsApp!

Can we use "if" in reported speech?
“If” is a conjunction we use in indirect speech when we report yes/no questions.
Direct speech: Do you want to go to the cinema?
Indirect speech: He asked if I wanted to go to the cinema.
Also, if we want to report a conditional sentence, we’ll keep “if” in the reported speech too.
Direct speech: If it doesn’t rain, I’ll go for a walk.
Indirect speech: She said that if it didn’t rain, she’d go for a walk.
How do you change the if-clause in reported speech?
To see what tense and modal changes occur, let’s examine each type of conditional sentence separately.
Zero conditional in reported speech
The tense shift will occur only in instances when the condition is no longer valid. Otherwise, the tenses remain the same.
Mom: If dad gets angry, he always reads a newspaper in the living room and ignores everybody else.
Mom said that if dad gets angry, he always reads a newspaper in the living room and ignores everybody else. (Dad still does this.)
Mom said that if dad got angry, he always read a newspaper in the living room and ignored everybody else. (Dad doesn’t do this anymore. Mom just described his past habit.)
First conditional in reported speech
If we need to report a first conditional sentence, the following changes might take place.
Luke: If we hurry up, we’ll catch the bus .
Luke said that if we hurry up, we’ll catch the bus. (This information is still relevant. Luke and his interlocutor still have time to catch the bus.)
Luke said that if we hurried up, we’d catch the bus. (These reported words aren’t relevant anymore. The bus has already left. Note the tense and modal shift: the present simple becomes the past simple , and will becomes would .)
Second conditional in reported speech
The above tense and modal shifting rules apply to the second conditional too. If the condition is still relevant, no changes occur. However, if it’s outdated, the past simple becomes the past perfect , and would becomes would + have + past participle.
Sofia: If I had more money, I would buy a new car.
Sofia said that if she had more money, she would buy a new car. (Sofia still doesn’t have money, and consequently, she can’t buy a new car.)
Sofia said that if she had had more money, she would have bought a new car. (The speaker remembers Sofia’s words and wishes from the past. Maybe Sofia doesn’t have any money issues now.)
Third conditional in reported speech
When reporting third conditionals, there is no change in the verb form:
Tania: If I had seen him, I would have told him about the accident.
Tania said that if she had seen him, she would have told him about the accident .
Where to find the most reliable English language schools and programs in California?
Are you fed up with practicing English by yourself? Do you want to find a California-based school with a program specially tailored to satisfy your learning needs? The College of English Language is there for you. Our teachers boast many years of teaching experience under their belt, and successful teaching methods up their sleeves, and you'll soon notice a huge difference in your daily communication in English .
Visit us in one of our three locations in San Diego, Santa Monica , and Pacific Beach, and enjoy learning English in state-of-the-art classrooms with top teachers. We are waiting for you!
Politics latest: PM 'appalled' by police protest row; Truss backs Trump and Sunak to win elections
Former prime minister Liz Truss has blamed her downfall on "deep resistance within the establishment" in an interview with Sky News. Meanwhile, Labour leader Keir Starmer has said the Tories have "lost any right" to call themselves patriotic.
Sunday 21 April 2024 15:14, UK
Please use Chrome browser for a more accessible video player
- Liz Truss refuses to apologise for higher interest rates in Sky News interview
- 'I want Rishi Sunak to win' - Truss
- Adam Boulton: What Truss and Trump have in common
- PM 'appalled' by police protest row
- Met Police chief's resignation 'not the way forward' - Labour
- Rishi Sunak 'not a real Conservative', Reform leader claims
- General election date 'above my pay grade' - Sunak ally
- Labour vows to get prisons built
- Tap here to subscribe to Electoral Dysfunction
- Live reporting by Charlotte Chelsom-Pill
But before you go, here are the headlines:
- Liz Truss has refused to apologise to homeowners for higher interest rates in an interview with Sky News;
- The former prime minister also said she had changed her mind on "problematic" net zero legislation;
- The Metropolitan Police chief is facing calls to quit over the force's handling of a recent pro-Palestinian protest;
- He will meet Jewish groups after the force threatened to arrest an "openly Jewish" man;
- Labour's shadow justice secretary told Sunday Morning with Trevor Phillips the force have "not covered themselves in glory", but the Met chief's resignation is not "the way forward";
- Reform UK leader Richard Tice has accused Rishi Sunak of not being a "real Conservative," telling Sunday Morning With Trevor Phillips there will be a "realignment of the right";
- A number of MPs are running the London Marathon today, including Chancellor Jeremy Hunt who is running the race for the third and "the last" time.
We'll be back from 6am with all the latest.
People voting in local elections in England on 2 May will need to provide photo ID.
It is the second year the requirement has been in place - but in 2023, 14,000 people couldn't cast their ballot because they didn't take ID to the polling booth.
There are 22 different types of ID you can use - and if you don't have any of them, you can register for a Voter Authority Certificate.
Here's everything you need to know to avoid being caught out:
We have been reporting today that there's a lengthy list of MPs taking part in the London Marathon today - with one MP running for the 18th time ( see post at 11.27am ).
But none so far have taken the title for fastest-ever MP to run the race from Matthew Parris.
In 1985, he ran the marathon in 2 hours, 32 minutes.
The Times columnist and former Conservative MP told Sky News he is "intensely proud, inordinately proud" at the achievement.
"I would almost think it is the thing of which I am most proud in my entire political career," he said.
"I had trained so intensely.
"Up hill, down dale - I would run into the House of Commons for a vote and run back after the vote."
He said he even got stopped by the police once running back from a vote.
"It was a better result than I could have expected, so I was very proud," he said.
A power-sharing agreement between the SNP and the Greens at Holyrood is under threat after the Scottish government ditched a key climate change target.
The Scottish Green Party has said a vote on the deal, to be held at a forthcoming extraordinary general meeting (EGM), would be binding.
The date of the assembly and the crunch ballot has yet to be announced.
There is unhappiness among Green Party members after the SNP announced the Scottish government was scrapping its commitment to cut emissions by 75% by 2030.
The Rainbow Greens, the party's LGBT wing, has also criticised the announcement, which came on the same day that the prescription of puberty blockers for new patients under the age of 18, at the gender identity service in Glasgow, would be paused.
The decision followed a landmark review of gender services for under-18s in England and Wales.
Scottish Greens co-leader Patrick Harvie said he would be urging members to back the power-sharing agreement so the party could "put Green values into practice" in government.
Writing on X, he said "many" members had been calling for an EGM to discuss the future of the agreement.
But Mr Harvie said: "As part of the Scottish government, we're making a difference on a far bigger scale than ever before."
Read more here:
In case you missed Sunday Morning With Trevor Phillips, we have a recap of one of the interviews on the programme.
Richard Tice, the leader of Reform UK, claimed Conservative Prime Minister Rishi Sunak is "not a real Conservative".
He pointed to the high tax burden and even went as far as calling Mr Sunak a "socialist".
Read the full story below:
Prime Minister Rishi Sunak is "appalled" by an exchange at a pro-Palestinian protest in which the Met Police threatened to arrest an "openly Jewish" man, a government source has told Sky News.
Met Police chief Sir Mark Rowley is facing calls to resign after antisemitism campaigner Gideon Falter was threatened with arrest near the protest march in London ( see post at 08.36am ).
Mr Falter, the chief executive of the Campaign Against Antisemitism, said Jewish Londoners cannot have confidence in the Met under Sir Mark's leadership and accused the commissioner of "victim blaming".
Energy Secretary Claire Coutinho earlier told Sky News the incident was "completely wrong" and that "what happens next" with regard to Sir Mark was a "matter for the Labour London mayor" ( see post at 08.40am ).
Sky News understands that Sir Mark does still retain the confidence of London mayor Sadiq Khan (see post at 11.46am) .
By Adam Boulton , Sky News commentator
Liz Truss has much more in common with Donald Trump than just the first three letters of his surname.
Despite presenting themselves as "outsiders", both enjoyed substantial political careers and reached the top of their profession as prime minister of the UK and president of the United States respectively.
In both cases, their periods in power ended in ways that outraged their opponents and many in their own Conservative and Republican parties. Economic chaos brought on by her rash policies forced Truss out of office after just 49 days in 10 Downing Street.
Trump lost the 2020 election, refused to accept his defeat and praised the mob who stormed the Capitol in an attempt to keep him in the White House.
Many thought they were finished for good. But like those who had laughed at their ambitions earlier in their careers, the nay-sayers were wrong again. Both have been reprieved and continue to be respected as forces in their parties.
Conservative MP Mark Menzies has been suspended from the parliamentary party in light of allegations he abused local Tory party funds to pay off "bad people".
Mark Menzies strongly disputes the claims which also include accusations he used campaign funds to pay his personal medical bills.
On the Conservatives' investigation into the claims, Defence Secretary Grant Shapps told Sky News this week action was being taken "swiftly".
He added: "I think it is important to stress that the MP in question here denies the allegations and so on the basis of fairness and proper justice, I think it's important to mention that."
On the Sky News Daily, Niall Paterson is joined by political correspondent Darren McCaffrey to analyse how Westminster will cope with another scandal.
Plus, the Scottish government has come under fire for rowing back on its climate commitments.
Niall speaks to science correspondent Thomas Moore about the consequences of the government missing eight out of 12 of its annual climate commitments.
👉 Listen above then tap here to follow the Sky News Daily wherever you get your podcasts 👈
The head of the Met Police is to meet Jewish community leadership groups amid a row over the force threatening to arrest an "openly Jewish" man.
Sir Mark Rowley will meet representatives from the Board of Deputies of British Jews, the Jewish Leadership Council and Community Security Trust (CST).
Confirming the meeting, the Board of Deputies of British Jews said they would be discussing this "serious issue".
Sir Mark is facing calls to resign after antisemitism campaigner Gideon Falter was threatened with arrest near a pro-Palestinian march in London ( see post at 08.36am ).
Campaign Against Antisemitism have told Sky News they are not attending the meeting.
Sky News understands the meeting is expected to take place on Thursday.
The Sky News live poll tracker - collated and updated by our Data and Forensics team - aggregates various surveys to indicate how voters feel about the different political parties.
With the local election campaign well under way, Labour is still sitting comfortably on a roughly 21-point lead, averaging at 43.6% in the polls, with the Tories on 23.1%.
In third is Reform UK on 12.3%, followed by the Lib Dems on 9.2%.
The Green Party stands at 6.5%, and the SNP on 3.1%.
See the latest update below - and you can read more about the methodology behind the tracker here .
Be the first to get Breaking News
Install the Sky News app for free

Advertisement
Trump Says He Wouldn’t Sign a Federal Abortion Ban, Criticizing Arizona Ruling
Days after he said that abortion policies should be left to the states, former President Donald J. Trump criticized an Arizona court ruling that upheld an 1864 law.
- Share full article

By Michael Gold
Reporting from New York
- April 10, 2024
Days after saying that abortion policies should be left to the states, former President Donald J. Trump on Wednesday criticized an Arizona court ruling for upholding an 1864 law that banned nearly all abortions and said he would not sign a national abortion ban if he were elected president.
Speaking to reporters on an airport tarmac in Atlanta, Mr. Trump said he expected that the Arizona law would be “straightened out.” Hours later, Republicans in the State Legislature, which they control, blocked an effort by Democrats to repeal the ban.
Mr. Trump also said he expected that a six-week abortion ban in Florida that he has criticized was “probably, maybe going to change.”
Yet even as he suggested his disapproval with the circumstances in both states, Mr. Trump defended the position he took in a video statement on Monday, when he said that states should weigh in on abortion through legislation.
“It’s the will of the people. This is what I’ve been saying,” Mr. Trump said in Atlanta, where he had traveled for a fund-raiser. “It’s a perfect system.”
Mr. Trump’s comments, coming after his Monday statement, continued months of mixed signals on abortion , an issue that his campaign has worried could hurt him at the polls in November.
After the Supreme Court overturned Roe v. Wade in 2022 — a decision made possible by Mr. Trump’s appointment of three conservative justices to the bench — Democrats have made attacks against Mr. Trump on the issue central to their efforts to mobilize voters in November.
During campaign speeches and interviews, Mr. Trump often takes credit for appointing the justices and for, in effect, returning the issue of abortion to the states. But the Biden campaign and the Democrats have repeatedly laid the blame for strict state abortion laws on Mr. Trump, including the Florida ban, which the former president has called a “terrible mistake.”
Their efforts to tie him to stringent restrictions accelerated after his comments on Monday and after the Arizona court ruling on Tuesday, which said “all abortions, except those necessary to save a woman’s life, are illegal,” in accordance with a 160-year-old law.
Michael Tyler, a spokesman for the Biden campaign, said in a statement after Mr. Trump’s comments on Wednesday that Mr. Trump “owns the suffering and chaos happening right now, including in Arizona, because he proudly overturned Roe.”
Democrats have also used the ambiguity left by Mr. Trump’s state-focused position to suggest that he would be open to signing a federal abortion ban if he won in November, which anti-abortion groups have pushed for.
When he was in the White House, his administration backed a bill that would have banned nearly all abortions after 20 weeks of pregnancy, and penalized anyone who performed the procedure.
But with Roe overturned and Republicans seeming to suffer political consequences in the fallout, Mr. Trump has been trying to stake out a position that would animate his conservative base without turning off moderate voters.
Last month, he suggested he would be open to backing a 15-week federal ban with exceptions for rape, incest and life-threatening emergencies. But that idea was absent from his statement on Monday.
Mr. Trump, a Florida resident, has not yet said how he might vote this November on a ballot measure there that would enshrine abortion rights in the state’s Constitution. Of Arizona, he said the law was “going to definitely change,” adding, “Everybody wants that to happen. And you’re getting the will of the people. It’s been pretty amazing.”
He avoided expounding on his personal views later on Wednesday at a campaign stop at a Chick-fil-A restaurant in Atlanta. When asked by a reporter whether he believed doctors should be punished for providing abortions, Mr. Trump said that question should be left to the states.
“Those are the things that the states are going to make a determination about,” he said.
Michael Gold is a political correspondent for The Times covering the campaigns of Donald J. Trump and other candidates in the 2024 presidential elections. More about Michael Gold
Our Coverage of the 2024 Election
Presidential Race
President Biden’s campaign has featured initiatives aimed at young people , union workers and environmentalists as well as calling for tariffs on Chinese steel , but it is not clear that they will be sufficient to rekindle support in those groups.
American voters absorbed their first view of a split-screen campaign: President Biden sprinting across one of the country’s top battleground states and former President Donald J. Trump sitting in a New York courtroom.
Robert F. Kennedy Jr. announced that he had secured a spot on the ballot in Michigan, as more than a dozen members of his family endorsed President Biden. Additionally, activists who worked with Kennedy at an environmental nonprofit group urged him to drop his presidential bid .
A Generation Gap: Many older Black voters see moral and political reasons to vote, but younger Black voters feel far less motivated to cast a ballot for Democrats or even at all .
Vice-Presidential Calculations: As Trump sifts through potential running mates, he has peppered some advisers and associates with a direct question: Which Republican could best help him raise money ?
Embracing the Jan. 6 Rioters: Trump initially disavowed the attack on the Capitol, but he is now making it a centerpiece of his campaign .
Mobilizing the Left: Amid the war in Gaza, the pro-Palestinian movement has grown into a powerful, if disjointed, political force in the United States. Democrats are feeling the pressure .
- International
April 14, 2024 - Iran's attack on Israel
By Jerome Taylor, Heather Chen , James Legge, Sophie Tanno, Emma Tucker , Kaanita Iyer , Paul LeBlanc , Catherine Nicholls, Maureen Chowdhury , Antoinette Radford and Eve Rothenberg, CNN
Our live coverage of Iran's attack on Israel has moved here .
India calls on Iran to release 17 Indian crew members on board seized container ship
From CNN's Sandi Sidhu in Hong Kong
India has called on Iran to release 17 Indian crew members on board a container ship seized by Iran on Saturday.
Indian External Affairs Minister Subrahmanyam Jaishankar said that he spoke to his Iranian counterpart Iranian Foreign Minister Hossein Amir Abdollahian and "took up the release of 17 Indian crew members of MSC Aries."
Four Filipino seamen were also on board the ship, according to the Philippine Department of Migrant Workers.
The department said it was working with its government, the ship owner, and the operator to release the captured seafarers.
On Saturday, Iran’s Revolutionary Guards seized an Israeli-linked container ship in a helicopter operation near the Strait of Hormuz, state news agency IRNA reported.
Mediterranean Shipping Company (MSC) said there were 25 crew members on board.
Japanese prime minister condemns Iran's attack on Israel
From CNN's Junko Ogura in Tokyo
Japanese Prime Minister Fumio Kishida on Sunday said he "strongly condemns" Iran's missile and drone attack on Israel.
"(The attack) further aggravates the current situation in the Middle East. We are deeply concerned and strongly condemn such an escalation," Kishida told reporters.
Kishida said Japan would continue diplomatic efforts to "prevent the situation from worsening and to calm the situation down," and "respond in cooperation with other countries."
Blinken calls British and German counterparts following Iran's attack on Israel
From CNN's Philip Wang
US Secretary of State Antony Blinken spoke with his counterparts from the United Kingdom and Germany on Sunday following Iran's attack on Israel, according to readouts from the State Department.
All parties agreed "the importance of condemning Iran's attack in the strongest possible terms and preventing further escalation," the readout said.
Blinken earlier held phone calls with his counterparts from Turkey, Egypt, Jordan and Saudi Arabia , in which he emphasized the importance of avoiding escalation in the Middle East and of "a coordinated diplomatic response."
US forces destroyed more than 80 attack drones from Iran and Yemen, Central Command says
From CNN's Philip Wang
US forces intercepted more than 80 one-way attack drones and at least six ballistic missiles from Iran and Yemen during its attack on Israel, according to a statement from the Central Command.
The operation included destroying a ballistic missile on its launcher vehicle and seven drones on the ground in Iranian-backed Houthi-controlled areas of Yemen, CENTCOM said.
"Iran's continued unprecedented, malign, and reckless behavior endangers regional stability and the safety of U.S. and coalition forces," the statement added.
Israeli and Iranian ambassadors trade accusations during UN Security Council session
From Abel Alvarado in Atlanta

Israel and Iran’s United Nations ambassadors condemned each other’s actions during Sunday’s UN Security Council emergency session called to address Iran’s attack on Israel.
Israel’s UN ambassador Gilad Erdan said Iran "must be stopped before it drives the world to a point of no return, to a regional war that can escalate to a world war." Erdan accused Iran of seeking world domination and that its attack proved that Tehran "cares nothing, nothing for Islam or Muslims" before pulling out a tablet to show a video of Israel intercepting Iranian drones above Jerusalem’s Al-Aqsa Mosque.
Erdan called on the UN Security Council to designate the Iranian Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC) as a terror organization.
“Action must be taken now, not for Israel's sake, not for the region's sake, but for the world's sake. Stop Iran today."
Iran’s UN Ambassador Amir Saeid Iravani said his country’s operation was "entirely in the exercise of Iran’s inherent right to self-defense, as outlined in Article 51 of the Charter of the United Nations and recognized by international law."
Iravani said:
"This concluded action was necessary and proportionate," adding that the operation was “precise and only targeted military objectives” to reduce the potential of escalation and to prevent civilian harm. “Iran is never seeking to contribute to the spillover of the conflict in the region, nor does it to escalate or spread the tension to the entire region," he said.

Tehran’s attack had been anticipated since a suspected Israeli strike on an Iranian diplomatic complex in Syria earlier this month.
Iravani added Iran has “no intention of engaging in conflict with the US in the region” but warned Iran will use its “inherent right to respond proportionately” should the US initiate a military operation against “Iran, its citizens or its security.”
Israeli war cabinet says it's ready to respond to Iran's attack but delays immediate action. Here's the latest
From CNN staff
The hours-long Israeli war cabinet meeting ended Sunday night without a decision on how Israel will respond to Iran’s missile and drone attack , an Israeli official said.
The cabinet is determined to respond — but has yet to decide on the timing and scope and the official said the military has been tasked with coming up with additional options for a response.
Separately, a senior Biden administration official told reporters that an Israeli official told the United States that it's not looking to significantly escalate the showdown with Iran.
CNN analyst Barak Ravid said Israeli ministers Benny Gantz and Gadi Eisenkot advocated for swift action, but US President Joe Biden's phone call with Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu led to a decision to delay the response until the next day.
Here are the latest headlines:
- Retaliation is over, Iran told US: Iran privately messaged the United States that its retaliation against Israel had concluded, echoing what Tehran said publicly, according to a senior administration official. Late Saturday, Iran said its attack on Israel is a response to Israel's strike on the Iranian consulate in Damascus, and "the matter can be deemed concluded." However, President Ebrahim Raisi said any “new aggression against the interests of the Iranian nation will be met with a heavier and regrettable response,” according to Iran’s state news channel IRIB.
- United Nations response: UN Secretary-General António Guterres called for a de-escalation of violence after Iran’s attack. Guterres said the United Nations and member countries have a “shared responsibility” to engage “all parties concerned to prevent further escalation.” He also called for a ceasefire in the Israel-Gaza conflict. “Neither the region nor the world can afford more war,” he said.
- G7 and others: Amid a flurry of diplomatic activity in response to Iran's attack, the G7 nations said they would work together to "stabilize the situation" in the Middle East, according to a statement from Biden. Also, Jordan summoned Iran's ambassador in Amman on Sunday after it intercepted Iranian drones over the country.
- Meanwhile in Gaza: As thousands of Palestinians were turned away from returning to their homes in northern Gaza on Sunday, a 5-year-old girl was shot in the head by Israeli soldiers, her mother said. Video showed a man carrying a 5-year-old girl named Sally Abu Laila, who was bleeding from her head, with people crowding around her in panic trying to cover her wound.
Also on Sunday:
- Israel decided to lift its restrictions on large gatherings and to reopen schools on Monday.
- The US Department of Homeland Security has not identified any “specific or credible threats” to the US since Iran attacked Israel.
Blinken calls Turkish, Egyptian, Jordanian and Saudi counterparts following Iran's attack
US Secretary of State Antony Blinken on Sunday spoke with his counterparts in Turkey, Egypt, Jordan, and Saudi Arabia following Iran's attacks in Israel, according to readouts from the State Department.
During his phone calls, Blinken emphasized the importance of avoiding escalation in the region and the importance of "a coordinated diplomatic response."
In his conversation with Jordan and Egypt, Blinken also underlined the significance of achieving an "enduring end to the crisis in Gaza."
Iran will be held responsible if any action is taken against the US or Israel, deputy ambassador warns
From CNN’s Abel Alvarado

The United States warned Iran against taking any action against the US or Israel during the UN Security Council emergency session over Iran’s attack on Israel.
“Let me be clear, if Iran or its proxies take actions against the US or further action against Israel, Iran will be held responsible,” US Deputy Ambassador to the UN Robert Wood said Sunday.
The United States is “not seeking escalation, our actions have been purely defensive in nature,” adding that the “best way to prevent such escalation is an unambiguous condemnation of the council of Iran’s unprecedented large-scale attack,” he said.
The envoy reiterated US support for Israel and condemned Iran’s attack. “Iran’s intent was to cause significant damage and death in Israel,” Wood said.
Wood also said the UN Security Council had an “obligation to not let Iran’s actions go unanswered.”
“For far too long, Iran has flagrantly violated its international legal obligations,” he said before listing occasions Iran has violated UN Security Council resolutions and international law.
Wood accused Iran of being in a “broad sense complicit” of the October 7 attack on Israel by providing “significant funding and training for the military wing of Hamas.”
He added the US will explore "additional measures to hold Iran accountable here in the UN.”
Please enable JavaScript for a better experience.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Watch my reported speech video: Here's how it works: We use a 'reporting verb' like 'say' or 'tell'. ( Click here for more about using 'say' and 'tell' .) If this verb is in the present tense, it's easy. We just put 'she says' and then the sentence: Direct speech: I like ice cream. Reported speech: She says (that) she likes ice cream.
AmE (New Orleans) Aug 15, 2010. #12. Spira said: I would call your future perfect in the past a conditional past tense. Just as Tom would write a letter is the present conditional, so Tom would have written a letter is past conditional, followed obligatorily by the affirmation that he did not. Eh, semantics.
Direct and Indirect Speech Future Simple Tense Examples. If reported verb is in Past Tense, and reported speech is in Future Indefinite Tense, will changes into would & shall changes into should. Direct Speech. Indirect Speech. Shakespeare said, "I will write another drama tomorrow.". Shakespeare said that he would write another drama the ...
Tenses in reported speech. ... --> We can use a perfect form with have + -ed form after modal verbs, especially where the report looks back to a hypothetical event in the past: He said the noise might have been the postman delivering letters. (original statement: 'The noise might be the postman delivering letters.') ... Her mother had told ...
In (1) the being has been continuous until the time of speaking, whereas in (2) the pronouncement has occurred at a specific point in the past. future. indirect-speech. perfect-aspect. Share.
Pin. No Change in Verb Tenses in Reported Speech. There is no change in verb tenses in Indirect Speech when:. The introductory verb is in the Present, Present Perfect or Future.; If the reported sentence deals with a fact or general truth.; The reported sentence contains a time clause.; The verb of the sentence is in the unreal past (the second or the third conditional).
Brush your teeth. -> She told me to brush my teeth. Finally, when reporting speech, you must always consider the time in which the original statement was made. If a time is mentioned within the statement, you will also have to consider how that time relates to the current moment.
For direct and indirect speech complete rules click: Direct and indirect speech complete rules. Direct and Indirect of Future Perfect Tense. Tense Change: As a rule, when we convey a message from present tense and past tenses, we go one tense back, but when you convey a message from future perfect, you just need to change the helping verb ...
Direct speech: "I don't want to enter the water, ever," she says. "If everyone's going in the ocean, I'm like, no.". Here, the speech is reported as though it's in the present tense ("she says") instead of in the past ("she said"). In writing of all kinds, direct reported speech is often split into two or more parts, as ...
Perfect English Grammar. Here's a list of all the reported speech exercises on this site: ( Click here to read the explanations about reported speech ) Reported Statements: Present Simple Reported Statement Exercise (quite easy) (in PDF here) Present Continuous Reported Statement Exercise (quite easy)
Reported speech: indirect speech - English Grammar Today - a reference to written and spoken English grammar and usage - Cambridge Dictionary
When we use reported speech, we often change the verb tense backwards in time. This can be called "backshift.". Here are some examples in different verb tenses: "I want to go home.". She said she wanted to go home. "I 'm reading a good book.". She said she was reading a good book. "I ate pasta for dinner last night.".
Direct Indirect Speech for Future Perfect Continuous Exceptions For Direct Indirect Tense Gender-Masculine and Feminine → . Facebook Whatsapp. Made by. CA Maninder Singh. CA Maninder Singh is a Chartered Accountant for the past 14 years. ...
The reported speech reproduces the words of another person by adapting certain temporal and local references of the original speech to the situation of the speaker, for example, personal pronouns, demonstratives, verb tenses, and adverbs of place or time.. It is characterized by introducing the message that is reproduced with a speaking verb followed by conjunctions that or if.
In indirect speech, the structure of the reported clause depends on whether the speaker is reporting a statement, a question or a command. Normally, the tense in reported speech is one tense back in time from the tense in direct speech: She said, "I am tired." = She said that she was tired. Phrase in Direct Speech. Equivalent in Reported Speech.
In indirect speech, we often use a tense which is 'further back' in the past (e.g. worked) than the tense originally used (e.g. work). This is called 'backshift'. ... The present perfect is a present form, so generally 'will' is the correct form. In this case, assuming that the man said 'I will travel to Cairo', then 'will' is the correct form. ...
Reported speech is the form in which one can convey a message said by oneself or someone else, mostly in the past. It can also be said to be the third person view of what someone has said. In this form of speech, you need not use quotation marks as you are not quoting the exact words spoken by the speaker, but just conveying the message. Q2.
March 29, 2024. Reported speech (Indirect Speech) is how we represent the speech of other people or what we ourselves say. Reported Speech focuses more on the content of what someone said rather than their exact words. The structure of the independent clause depends on whether the speaker is reporting a statement, a question, or a command.
Lesson 3: Past continuous use: interrupted actions with the past simple (0:59) Exercise - Past continuous: actions with the past simple. Lesson 4: Past continuous use: habits in the past (1:16) Exercise - Past continuous for habits in the past. Lesson 5: Future in the past with 'was / were going to' (and 'would') (3:21) Exercise - Future in the ...
Transitive and Intransitive Verbs. Reporting Verbs. Gerunds and Infinitives Introduction. Gerunds and Infinitives After Certain Verbs 1. Gerunds and Infinitives After Certain Verbs 2. Gerunds and Infinitives After Certain Verbs 3. Let and Make. Make and Do. Used to Do, Would Do, and Be Used to Doing.
In this case,"will have been" becomes "would have been"The boy said" They will have been waiting for me"-a-The boy said They would have been waiting for me-ea-The girl said" I will have been an air hostess by 2020"-a-The girl said I would have been an air hostess by 2020-ea-The man said" I will have.
Direct and Indirect of Future Perfect Progressive. Tense Change: As a rule, when we convey a message from present tenses and past tense, we go one tense back, but when you change direct speech of future perfect continuous tense, you just need to change the verb "will" into "would" and follow other rules as usual. Affirmatives. Direct ...
Second conditional in reported speech. The above tense and modal shifting rules apply to the second conditional too. If the condition is still relevant, no changes occur. However, if it's outdated, the past simple becomes the past perfect, and would becomes would + have + past participle. Sofia: If I had more money, I would buy a new car.
By Ed Conway, Economics and data editor. Liz Truss has acknowledged she and her government lost the confidence of financial markets following the mini-budget of October 2022 - but has refused to ...
Reporting from New York. April 10, 2024. Days after saying that abortion policies should be left to the states, former President Donald J. Trump on Wednesday criticized an Arizona court ruling for ...
On Saturday, Iran's Revolutionary Guards seized an Israeli-linked container ship in a helicopter operation near the Strait of Hormuz, state news agency IRNA reported. Mediterranean Shipping ...