- Receivables
- Notes Receivable
- Credit Terms
- Cash Discount on Sales
- Accounting for Bad Debts
- Bad Debts Direct Write-off Method
- Bad Debts Allowance Method
- Bad Debts as % of Sales
- Bad Debts as % of Receivables
- Recovery of Bad Debts
- Accounts Receivable Aging
- Assignment of Accounts Receivable
- Factoring of Accounts Receivable
Assignment of accounts receivable is an agreement in which a business assigns its accounts receivable to a financing company in return for a loan. It is a way to finance cash flows for a business that otherwise finds it difficult to secure a loan, because the assigned receivables serve as collateral for the loan received.
By assignment of accounts receivable, the lender i.e. the financing company has the right to collect the receivables if the borrowing company i.e. actual owner of the receivables, fails to repay the loan in time. The financing company also receives finance charges / interest and service charges.
It is important to note that the receivables are not actually sold under an assignment agreement. If the ownership of the receivables is actually transferred, the agreement would be for sale / factoring of accounts receivable . Usually, the borrowing company would itself collect the assigned receivables and remit the loan amount as per agreement. It is only when the borrower fails to pay as per agreement, that the lender gets a right to collect the assigned receivables on its own.
The assignment of accounts receivable may be general or specific. A general assignment of accounts receivable entitles the lender to proceed to collect any accounts receivable of the borrowing company whereas in case of specific assignment of accounts receivable, the lender is only entitled to collect the accounts receivable specifically assigned to the lender.
The following example shows how to record transactions related to assignment of accounts receivable via journal entries:
On March 1, 20X6, Company A borrowed $50,000 from a bank and signed a 12% one month note payable. The bank charged 1% initial fee. Company A assigned $73,000 of its accounts receivable to the bank as a security. During March 20X6, the company collected $70,000 of the assigned accounts receivable and paid the principle and interest on note payable to the bank on April 1. $3,000 of the sales were returned by the customers.
Record the necessary journal entries by Company A.
Journal Entries on March 1
Initial fee = 0.01 × 50,000 = 500
Cash received = 50,000 – 500 = 49,500
The accounts receivable don't actually change ownership. But they may be to transferred to another account as shown the following journal entry. The impact on the balance sheet is only related to presentation, so this journal entry may not actually be passed. Usually, the fact that accounts receivable have been assigned, is stated in the notes to the financial statements.
Journal Entries on April 1
Interest expense = 50,000 × 12%/12 = 500
by Irfanullah Jan, ACCA and last modified on Oct 29, 2020

Related Topics
- Sales Returns
All Chapters in Accounting
- Intl. Financial Reporting Standards
- Introduction
- Accounting Principles
- Business Combinations
- Accounting Cycle
- Financial Statements
- Non-Current Assets
- Fixed Assets
- Investments
- Revenue Recognition
- Current Assets
- Inventories
- Shareholders' Equity
- Liability Accounts
- Accounting for Taxes
- Employee Benefits
- Accounting for Partnerships
- Financial Ratios
- Cost Classifications
- Cost Accounting Systems
- Cost Behavior
- CVP Analysis
- Relevant Costing
- Capital Budgeting
- Master Budget
- Inventory Management
- Cash Management
- Standard Costing
Current Chapter
XPLAIND.com is a free educational website; of students, by students, and for students. You are welcome to learn a range of topics from accounting, economics, finance and more. We hope you like the work that has been done, and if you have any suggestions, your feedback is highly valuable. Let's connect!
Copyright © 2010-2024 XPLAIND.com
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
- Corporate Finance
- Corporate Debt
Debt Assignment: How They Work, Considerations and Benefits
Daniel Liberto is a journalist with over 10 years of experience working with publications such as the Financial Times, The Independent, and Investors Chronicle.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/daniel_liberto-5bfc2715c9e77c0051432901.jpg)
Charlene Rhinehart is a CPA , CFE, chair of an Illinois CPA Society committee, and has a degree in accounting and finance from DePaul University.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/CharleneRhinehartHeadshot-CharleneRhinehart-ca4b769506e94a92bc29e4acc6f0f9a5.jpg)
Katrina Ávila Munichiello is an experienced editor, writer, fact-checker, and proofreader with more than fourteen years of experience working with print and online publications.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/KatrinaAvilaMunichiellophoto-9d116d50f0874b61887d2d214d440889.jpg)
Investopedia / Ryan Oakley
What Is Debt Assignment?
The term debt assignment refers to a transfer of debt , and all the associated rights and obligations, from a creditor to a third party. The assignment is a legal transfer to the other party, who then becomes the owner of the debt. In most cases, a debt assignment is issued to a debt collector who then assumes responsibility to collect the debt.
Key Takeaways
- Debt assignment is a transfer of debt, and all the associated rights and obligations, from a creditor to a third party (often a debt collector).
- The company assigning the debt may do so to improve its liquidity and/or to reduce its risk exposure.
- The debtor must be notified when a debt is assigned so they know who to make payments to and where to send them.
- Third-party debt collectors are subject to the Fair Debt Collection Practices Act (FDCPA), a federal law overseen by the Federal Trade Commission (FTC).
How Debt Assignments Work
When a creditor lends an individual or business money, it does so with the confidence that the capital it lends out—as well as the interest payments charged for the privilege—is repaid in a timely fashion. The lender , or the extender of credit , will wait to recoup all the money owed according to the conditions and timeframe laid out in the contract.
In certain circumstances, the lender may decide it no longer wants to be responsible for servicing the loan and opt to sell the debt to a third party instead. Should that happen, a Notice of Assignment (NOA) is sent out to the debtor , the recipient of the loan, informing them that somebody else is now responsible for collecting any outstanding amount. This is referred to as a debt assignment.
The debtor must be notified when a debt is assigned to a third party so that they know who to make payments to and where to send them. If the debtor sends payments to the old creditor after the debt has been assigned, it is likely that the payments will not be accepted. This could cause the debtor to unintentionally default.
When a debtor receives such a notice, it's also generally a good idea for them to verify that the new creditor has recorded the correct total balance and monthly payment for the debt owed. In some cases, the new owner of the debt might even want to propose changes to the original terms of the loan. Should this path be pursued, the creditor is obligated to immediately notify the debtor and give them adequate time to respond.
The debtor still maintains the same legal rights and protections held with the original creditor after a debt assignment.
Special Considerations
Third-party debt collectors are subject to the Fair Debt Collection Practices Act (FDCPA). The FDCPA, a federal law overseen by the Federal Trade Commission (FTC), restricts the means and methods by which third-party debt collectors can contact debtors, the time of day they can make contact, and the number of times they are allowed to call debtors.
If the FDCPA is violated, a debtor may be able to file suit against the debt collection company and the individual debt collector for damages and attorney fees within one year. The terms of the FDCPA are available for review on the FTC's website .
Benefits of Debt Assignment
There are several reasons why a creditor may decide to assign its debt to someone else. This option is often exercised to improve liquidity and/or to reduce risk exposure. A lender may be urgently in need of a quick injection of capital. Alternatively, it might have accumulated lots of high-risk loans and be wary that many of them could default . In cases like these, creditors may be willing to get rid of them swiftly for pennies on the dollar if it means improving their financial outlook and appeasing worried investors. At other times, the creditor may decide the debt is too old to waste its resources on collections, or selling or assigning it to a third party to pick up the collection activity. In these instances, a company would not assign their debt to a third party.
Criticism of Debt Assignment
The process of assigning debt has drawn a fair bit of criticism, especially over the past few decades. Debt buyers have been accused of engaging in all kinds of unethical practices to get paid, including issuing threats and regularly harassing debtors. In some cases, they have also been charged with chasing up debts that have already been settled.
Federal Trade Commission. " Fair Debt Collection Practices Act ." Accessed June 29, 2021.
Federal Trade Commission. " Debt Collection FAQs ." Accessed June 29, 2021.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/148985994-5bfc2b8c46e0fb0083c07ba8.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
- Online Courses

Loan participations vs. syndications: What’s the deal?
Posted on Jun 29, 2021 by Bob Laffler, CPA | Tags: Accounting , Auditing
Loan participations and loan syndications are terms often interchanged to describe a lending arrangement involving more than one lender; however, for accounting and reporting purposes, these are two different types of transactions with unique considerations and issues. We often get questions from participants in our classroom Banking Industry Fundamentals training programs and have dedicated time to this subject in our eLearning series available on the Revolution, our online learning platform.
While both loan participations and syndications involve multiple lenders, the way each is structured results in different accounting issues, including derecognition under ASC 860 and recognition of fees under ASC 606 and/or ASC 310.
Loan Participations:
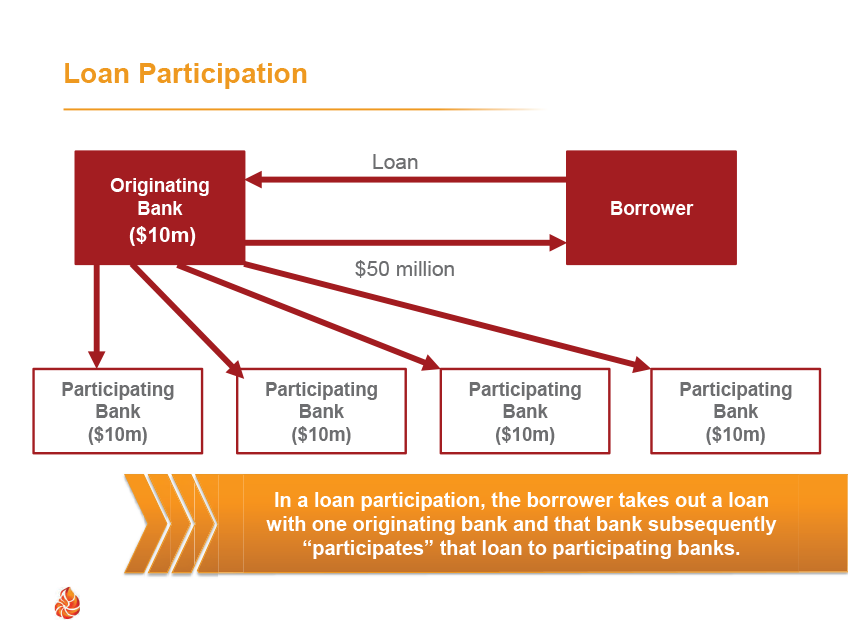
In a loan participation, the originating bank enters into several lending arrangements. The first transaction is the loan origination to the borrower. This transaction will follow the normal accounting for loans under ASC 310. The unloading of a portion of the loan to participating banks represents a “transfer of a financial asset” (i.e. the loan, or a portion of the loan) and must be assessed for derecognition under ASC 860. This analysis involves determining if the participating loan represents a “participating interest” under ASC 860 and further whether control over the participating loan has been relinquished by the originating bank.
Loan Syndications:
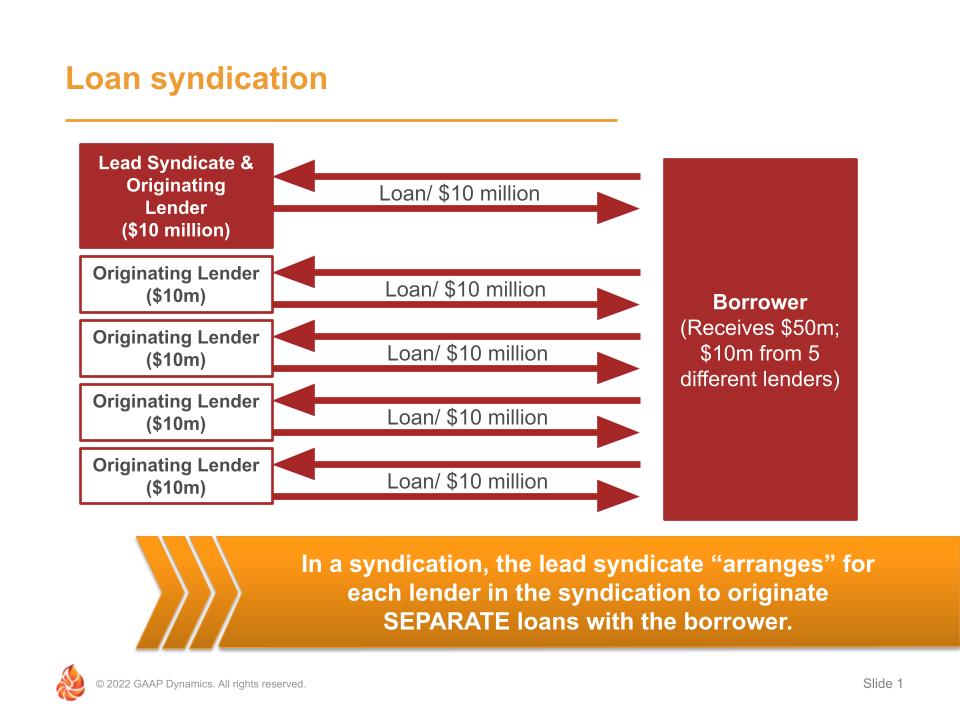
In a loan syndication, the bank with the “relationship” with the borrower likely does not want to assume the risk of issuing such a large loan. As a result, rather than underwrite the entire loan and look to participate it out to other banks, the lead bank acts as a “syndicate”, matching the borrower up with multiple lenders, each of which underwrites and originates its own loan to the borrower. As a result, there are multiple loans issued by numerous banks to the one borrower.
Loan syndications do not involve any “transfers of financial assets” as each loan in a syndication is between a respective originating bank and the borrower. As a result, ASC 860 and the analysis of derecognition is not an issue. However, there are some issues for the lead syndicate bank involving revenue recognition related to the fees it collects from the borrower. Some of these fees may represent “syndication fees” for arranging the deal, as well as typical lenders fees for the loan it has underwritten itself. Also, these arrangements may involve the lead syndicate servicing the series of loans on behalf of the syndicate banks. For these loans, other than its own originated loan, the lead syndicate will need to recognize a servicing asset (or liability) in accordance with ASC 860.

How do you tell the difference?
As it is illustrated above, these two arrangements (a loan participation and syndication) have unique terms even though they achieve the same economic result. Therefore, the only way to know whether you are dealing with a participation or syndication is the READ the loan agreements! Careful consideration should be given to the legal underwriters and parties to the contract, contractual terms of the instruments, and other conditions to make a final analysis.
Often it is a legal determination that will dictate whether it is a loan participation or syndication. Once this determination is made, it’s on to the accounting analysis!
About GAAP Dynamics
We’re a DIFFERENT type of accounting training firm. We don’t think of training as a “tick the box” exercise, but rather an opportunity to empower your people to help them make the right decisions at the right time. Whether it’s U.S. GAAP training, IFRS training, or audit training, we’ve helped thousands of professionals since 2001. Our clients include some of the largest accounting firms and companies in the world. As lifelong learners, we believe training is important. As CPAs, we believe great training is vital to doing your job well and maintaining the public trust. We want to help you understand complex accounting matters and we believe you deserve the best training in the world, regardless of whether you work for a large, multinational company or a small, regional accounting firm. We passionately create high-quality training that we would want to take. This means it is accurate, relevant, engaging, visually appealing, and fun. That’s our brand promise. Want to learn more about how GAAP Dynamics can help you? Let’s talk!
Disclaimer
This post is published to spread the love of GAAP and provided for informational purposes only. Although we are CPAs and have made every effort to ensure the factual accuracy of the post as of the date it was published, we are not responsible for your ultimate compliance with accounting or auditing standards and you agree not to hold us responsible for such. In addition, we take no responsibility for updating old posts, but may do so from time to time.

Comments (0)
Add a comment.
Allowed tags: <b><i><br> Add a new comment:
Ready To Make a Change?
Cookies on the GAAP Dynamics website
- Publications
" * " indicates required fields
Assignment, novation or sub-participation of loans
Transfers of loan portfolios between lending institutions have always been commonplace in the financial market. A number of factors may come into play – some lenders may wish to lower their risks and proportion of bad debts in their balance sheets; some may undergo restructuring or divest their investment portfolios elsewhere, to name a few. The real estate market in particular has been affected by the announcement of the “three red lines” policy by the People’s Bank of China in 2020 which led to a surge of transfers, or attempted transfers, of non-performing loans. Other contributing factors include the continuous effects of the Sino-US trade war and the Covid-19 pandemic.

T +852 2905 5760 E [email protected]
Transferability of Loans
The legal analysis regarding the transferability of loans can be complex. The loan agreement should be examined with a view to identifying any restrictions on transferability of the loan between lenders, such as prior consent of the debtor and, in some cases, whether such consent may be withheld. Other general restrictions may apply given that most banks have internal confidentiality rules and data protection requirements, the latter of which may also be subject to governmental regulations. Certain jurisdictions may restrict the transfer of loans relating to specific types of receivables – mortgage or consumer loans being prime examples. It is imperative to conduct proper due diligence on the documentation and underlying assets in order to be satisfied with the transferability of the relevant loans. This may be complicated further if there are multiple projects, facility lines or debtors. It is indeed common to see a partial transfer of loans to an incoming lender or groups of lenders.
Methods of Transfer
The transfer of loans may be carried out in different ways and often involves assignment, novation or sub-participation.
A typical assignment amounts to the transfer of the rights of the lender (assignor) under the loan documentation to another lender (assignee), whereby the assignee takes on the assignor’s rights, such as the right to receive payment of principal and interest on the loan. The assignor is still required to perform any obligations under the loan documentation. Therefore, there is no need to terminate the loan documentation and, unless the loan documentation stipulates otherwise, there is no need to obtain the debtor’s consent, but notice of the assignment must be served on the debtor. However, many debtors are in fact involved in the negotiation stage, where the parties would also take the opportunity to vary the terms of the facility and security arrangement.
Novation of a loan requires that the debtor, the existing lender (transferor) and the incoming lender (transferee) enter into new documentation which provides that the rights and obligations of the transferor will be novated to the transferee. The transferee replaces the transferor in the loan facility and the transferor is completely discharged from all of its rights and obligations. This method of transfer does require the prior consent of the relevant debtor.
Sub-participation is often used where a lender, whilst wishing to share the risks of certain loans, nonetheless prefers to maintain the status quo. There is no change to the loan documentation – the lender simply sells all or part of the loan portfolio to another lender or lenders. From the debtor’s perspective, nothing has changed and, in principle, there is no need to obtain the debtor’s consent or serve notice on the debtor. This method of transfer is sometimes preferred if the existing lender is keen to maintain a business relationship with the debtor, or where seeking consent from the debtor or notifying the debtor of any transfer is not feasible or desirable. In any case, there would be no change to the balance sheet treatment of the existing lender.
Offshore Security Arrangements
The transfer of a loan in a cross-border transaction often involves an offshore security package. A potential purchaser will need to conduct due diligence on the risks relating to such security. From a legal perspective, the security documents require close scrutiny to confirm their legality, validity and enforceability, including the nature and status of the assets involved. Apart from transferability generally, the documents would reveal whether any consent is required. A lender should seek full analysis on the risks relating to enforcement of security, which may well be complicated by the involvement of various jurisdictions for potential enforcement actions.
A key aspect to the enforcement consideration is whether a particular jurisdiction requires that any particular steps be taken to perfect a security interest relating to the loan portfolio (if the concept of perfection applies at all) and, if so, whether any applicable filing or registration has been made to perfect the security interest and, more importantly, whether there exists any prior or subsequent competing security interest over all or part of the same assets. For example, security interests may be registered in public records of the security provider maintained by the companies registry in Bermuda or the British Virgin Islands for the purpose of obtaining priority over competing interests under the applicable law. The internal register of charges of the security provider registered in the Cayman Islands, Bermuda or the British Virgin Islands should also be examined as part of the due diligence process. Particular care should be taken where the relevant assets require additional filings under the laws of the relevant jurisdictions, notable examples of such assets being real property, vessels and aircraft. Suites of documents held in escrow pending a potential default under the loan documentation should also be checked as they would be used by the lender or security agent to facilitate enforcement of security when the debtor defaults on the loan.
Due Diligence and Beyond
Legal due diligence on the loan documentation and security package is an integral part of the assessment undertaken by a lender of the risks of purchasing certain loan portfolios, regardless of whether the transfer is to be made by way of an assignment, novation or sub-participation. Whilst the choice of method of transfer is often a commercial decision, enforceability of security interests over underlying assets is the primary consideration in reviewing sufficiency of the security package in any proposed loan transfer.
Hong Kong , Shanghai , British Virgin Islands , Cayman Islands , Bermuda
Banking & Asset Finance , Corporate
Banking & Financial Services
A Bird’s-eye View of Some Key Restructuring Options and Processes in Bermuda, the British Virgin Islands and the Cayman Islands
This article focuses on restructuring options and processes only, and will merely touch on formal in...

Similar but Different
While the basic features of the trust remain, there are some notable differences in how trusts can b...

Material adverse change clauses in light of the Covid-19 pandemic
Experts from each of our key global offices provide jurisdiction specific advice and answer question...

Managing the court process

Economic Substance update Q4 2020
The facilitation of cross border restructurings in Bermuda, the British Virgin Islands and the Cayman Islands
In this update, we consider the powers and discretion of the domestic courts in Bermuda, the BVI and...

Economic Substance update Q1 2020
On 18 February 2020, the Economic and Financial Affairs Council (ECOFIN) announced that Bermuda and ...
Offshore listing Vehicles to benefit from the Shanghai - London stock connect

Offshore deal value through June 2018 nearly matches 2017 total

Snapshot Petitions Report 2017
- Select your option
- find a lawyer
- find an office
- contact you

Accounting for Loan Payable
Accounting for loan payables, such as bank loans, involves taking account of receipt of loan, re-payment of loan principal and interest expense.
Receipt of Loan
Liability for loan is recognized once the amount is received from the lender.
Accounting entries for the receipt of loan are as follows:
Loan payables need to be classified under current or non-current liabilities depending on the maturity of loan re-payment. For example, if a loan is to be repaid in 3 years’ time, the liability would be recognized under non-current liabilities. After 2 years, the liability will be re-classified under current liabilities, i.e. when the loan is due to be settled within one year.
Where loan is to be repaid in several installments, the current and non-current portions of the loan would need to be calculated using the loan repayment schedule (see example).
Interest Expense
Interest expense is calculated on the outstanding amount of loan during that period, i.e. the unpaid principal amount outstanding during the period. The outstanding amount of loan could change due to receipt of another loan installment or repayment of loan. Interest calculation needs to account for the changes in outstanding amount of loan during a period (see example).
Accounting entry for recording interest accrued is as follows:
Upon payment of interest, following accounting entry will be recorded:
Interest may be fixed for the entire period of loan or it may be variable. Floating interest, also known as variable interest, varies over the duration of the loan usually on the basis of an inter-bank borrowing rate such as LIBOR. Fixed interest rate does not vary over time but is more expensive than a floating interest rate.
Repayment of Loan
Repayments reduce the amount of loan payables recognized in financial statements.
Following accounting entry is used to account for the repayment of loan:
ABC PLC received a bank loan of $100,000 on 1 January 20X1.
Terms of the loan agreement are as follows:
- Loan is re-payable in 2 installments of $50,000 each on 30 June 20X2 and 30 June 20X3.
- Interest is payable six-monthly in arrears at 5% plus LIBOR.
- For the purpose of calculating interest, 6-month LIBOR at the start of each 6 month period will be used.
6-month LIBOR rates over the period of the loan were as follows:
Assuming all liabilities were settled on the due date, calculate:
- Interest expense to be recognized in the income statements for the years ended 30 June 20X1, 30 June 20X2 and 30 June 20X3.
- Loan payables to be recognized in the balance sheets as at 30 June 20X1, 30 June 20X2 and 30 June 20X3.
Working 1: Interest Rate
Working 2: Finance Cost
*Yearly interest payment has been divided by 2 to obtain the amount of half yearly interest payment.
Working 3: Loan Payable
Share This Post
Related posts, derecognition & write off of accounts payables, accounting for convertible bonds, debt-to-equity ratio, interest coverage ratio – times interest earned (tie ratio), accounts payable.
Join us at one of our events. Register Today
- Newsletters
- Client Portal
- Make Payment
- (855) Marcum1
Services Search
How to handle the accounting for collateral assignment split-dollar life insurance plans.
By Marc Giampaola , Director, Assurance Services & Michael Parillo , Senior Manager, Managed Services & Consulting

Split-dollar life insurance is an arrangement between two parties to share the costs and benefits of a permanent insurance policy. Often these arrangements are between an employer (the “company”) and an employee (the “executive”), involving a whole life or indexed universal life (“IUL”) policy. Companies generally use the policies as a Supplemental Executive Retirement Plan (“SERP”), which are considered non-qualified benefit plans.
The two most common types of split-dollar life insurance arrangements are endorsement and collateral assignment, which are defined based on which party controls the policy. Within these agreements, there are multiple documents executed, most commonly:
- Life insurance policy – Issued by the insurance company to the policy owner on the life of the insured.
- Split-dollar agreement – Agreement between employer and employee providing details of the agreement.
- Promissory note – A loan issued by the company to the employee for the cost of the policy.
Endorsement split-dollar life insurance is an employer-owned policy that endorses some or all of the death benefits to the employee’s beneficiary. The employer owns and controls the policy and, therefore, makes all policy decisions (i.e., surrender). A separate agreement is entered into between the employer and employee to define the split of costs and benefits between the two parties.
Collateral assignment split-dollar life insurance policies are owned by the employee with some benefits assigned to the employer. The employee owns and controls the policy while the employer makes the premium payments. Premiums are loans to the employee. Some level of interest on the amount borrowed must be paid. The employer is ultimately reimbursed for the premiums paid and related interest from the death benefit or the cash surrender proceeds.
There are different types of collateral assignment arrangements based on the structuring of the note within the agreement. They are as follows:
- Non-recourse arrangements rely solely on the underlying insurance policy for all repayment of principal and interest to the employer. The employee, or the employee’s estate, is not responsible for funding any shortfall by the policy to return the premium and related interest; however, any shortfall could be taxable to the employee as forgiveness of debt income.
- Limited recourse arrangements rely primarily on the underlying insurance policy for all repayment of principal and interest owed to the employer. However, if there is a shortfall, the employee or the employee’s estate may be called upon to make up the deficiency. These arrangements generally have terms requiring the employer to seek payment from the life insurance company first; the employee is secondarily liable.
- Full-recourse arrangements are similar to limited-recourse arrangements, with the difference that the employer can seek repayment of the principal and interest from the employee directly if there is a shortfall, without first pursuing any recovery from the life insurer. The employee has substantially the same net liability for any shortfall but would have the burden of satisfying the shortfall and then pursuing recovery from the policy.
- Providing cash to the insurance company and establishing a premium deposit account;
- Establishing a deposit account at a bank or credit union under the employee’s name; or
- Purchasing a single premium immediate annuity (SPIA).
The method of funding has no impact on the accounting, as there is a single loan made to the employee.
Most commonly, companies utilize collateral assignment split-dollar life insurance set up under non-recourse or limited-recourse arrangements. As such, the focus of the accounting section will be on these types of arrangements.
RELEVANT GUIDANCE
- ASC 310: Receivables (“ASC 310”)
- ASC 325: Investments – other (“ASC 325”)
- Loans and investments, November 2020 Edition (“PwC Loans Guide”)
ACCOUNTING FOR SPLIT-DOLLAR ARRANGEMENTS
The accounting for split-dollar arrangements is generally the same regardless of the structure of the agreement. Additionally, whether the promissory note is non-recourse or limited-recourse has no effect on the journal entries recorded over the life of the arrangement.
Recording the Loan at Issuance
In executing the transaction, the employer provides funding for the premium payments of the life insurance policy in exchange for a promissory note from the employee. The transaction meets the definition of a loan as defined by ASC 310-10, which states:
A contractual right to receive money on demand or on fixed or determinable dates that is recognized as an asset in the creditor’s statement of financial position. Examples include but are not limited to accounts receivable (with terms exceeding one year) and notes receivable.
Upon issuance of the loan, the employer provides cash through one of the funding methods described above and establishes a loan receivable from the executive. As an example, assume the defined loan amount is $3.0 million. The value of the loan is measured at issuance equal to the cash outlay by the Company. ASC 310-10-30-2 states:
As indicated in paragraph 835-30-25-4, when a note is received solely for cash and no other right or privilege is exchanged, it is presumed to have a present value at issuance measured by the cash proceeds exchanged.
In these arrangements, the company does not provide any other right or privilege. The promissory note is received in exchange for the cash needed to fund the premiums of the policy. As such, the value of the loan is equal to the cash paid.
The journal entry to record the example transaction is:
Recording the Interest Accrual
Once the loan is established, it begins earning interest based on the note rate, typically the long-term Applicable Federal Rate for the month and year the agreement becomes effective. Interest compounds annually. In the example transaction, assume an annual interest rate of 2.50%. Each month the company earns interest on the outstanding loan balance, and a journal entry is recorded to accrue interest on the loan. Interest is paid from the death benefit and, therefore, increases the receivable from the executive in each accounting period. The entry below represents the monthly accrual of interest:
(calculated as $3,000,000 loan * 2.5% interest / 12 months)
Recording the Settlement of the Loan
The loan is settled upon death or surrender of the policy. The company is entitled to the value of the original loan and accrued interest from inception. The cash owed to the company is paid from the death benefit or surrender value, with the remainder being paid to the employee (surrender) or the employee’s estate (death). Based on the example, assuming settlement and surrender of the insurance policy 24 months post entering into the policy (i.e., $150,000 interest earned), the entries to record the receipt of cash and settlement of the receivables are as follows:

Other Considerations for Subsequent Measurement
Collectability.
At each period-end, the company needs to analyze the value of the outstanding loan for changes in the valuation. Generally, these loans are considered not held for sale and, therefore, are reported at outstanding principal adjusted for any charge-offs, allowance for loan losses, deferred fees, and unamortized premiums or discounts based on ASC 310-10-35-47, which states:
Loans and trade receivables that management has the intent and ability to hold for the foreseeable future or until maturity or payoff shall be reported in the balance sheet at outstanding principal adjusted for any chargeoffs, the allowance for loan losses (or the allowance for doubtful accounts), any deferred fees or costs on originated loans, and any unamortized premiums or discounts on purchased loans.
Additionally, the company should analyze at each period-end any probable collection issues and the need for an allowance that would reduce the asset balance.
Value of the Loan
With an insurance policy securing the loan, further consideration is needed to determine the value of the loan. For endorsement arrangements, the employer owns the policy and, therefore, owns the surrender decision. The company values the loan at the lesser of the premiums paid or cash surrender value of the policy as of the period end date. This amount can generally be obtained from the statement provided by the insurance company.
For collateral assignment arrangements, the employee owns the policy, so the company does not control the surrender decision. However, the company does maintain the right to collect on the loan under the collateral assignment. Therefore, the company may need to consider the cash surrender value of the policy when determining the value of the loan. ASC 325-30-35-1 states:
An asset representing an investment in a life insurance contract shall be measured subsequently at the amount that could be realized under the insurance contract as of the date of the statement of financial position…
Depending on the type of note used in the agreement–non-recourse or limited-recourse– when determining the carrying value of the loan at each period-end.
Limited-Recourse
For limited-recourse, the loan is secured by the cash surrender value of the insurance policy, but the company also has the option to seek repayment from the employee if the cash surrender value is less than the outstanding loan amount. Since the loan is secured by both the policy and by the employee, the cash surrender value is not the only consideration when determining the value of the outstanding loan. As such, the value of the outstanding loan does not need to be adjusted if the cash surrender value is less than the outstanding loan, and there is no further consideration needed at period-end for these types of arrangements.
Non-recourse
For non-recourse notes, the loan is secured solely by the cash surrender value of the policy and, therefore, potential for a loss related to the loan exists if the cash surrender value is less than the loaned amount. The cash surrender value is the realizable amount of a life insurance contract at any given date. The accounting guidance does not allow a life insurance asset to exceed cash surrender value less an allowance for credit losses. The company is entitled to the premiums paid plus interest earned under these arrangements. The carrying value of the portion of the loan for which premiums were paid would need to consider the cash surrender value. This portion of the loan would be valued by the company as the lesser of the cash surrender value and the cumulative premiums paid by the reporting entity.
This is based on the premise that surrender is not within the control of the company and it is uncertain whether the company will be reimbursed for cumulative premiums paid upon death or surrender. Any premiums paid in excess of this amount should be recorded as an expense.
As an example, if the outstanding loan related to a non-recourse policy was $3,000,000 and the cash surrender value of the policy was $2,500,000, the company would need to reduce the carrying value of the loan to the cash surrender value and recognize a loss related to the loan. The entry below represents how the company would record the adjustment:
While the general accounting for these arrangements is similar, specific details and terms within all documents included in the agreement need to be evaluated when determining the appropriate accounting, and companies should consult their accountant with any questions. Additionally, there are potential individual income tax implications for the executive related to these arrangements that should be considered.
Related Insights & News

Enhancing Transparency: New Disclosure Requirements for Agents and Brokers in Group Health Insurance
The business health insurance industry has undergone a significant regulatory update that aims to improve transparency.
How a Qualified CPA Addresses Key Audit Needs of Captive Insurance Companies
Southeast regional managing partner michael balter was quoted in south florida business journal on surging commercial property insurance rates, advisory director john heller spoke with the sun sentinel for a story about banks seeking to reassure depositors their accounts remain safe., countdown to adoption of asc 842: leases for private companies, upcoming events.

Understanding Cyber Threats and Resilience in Healthcare

Marcum Women’s Initiative: Pasta Making & Networking

Marcum Women’s Initiative: Topgolf
Cranston, RI

Why You Need to Understand Your Attack Surface

Navigating the Digital Financial Transformation: A Roadmap for Finance Leaders

Marcum Women’s Initiative: Charcuterie Board Workshop
Wallingford, CT

Marcum Women’s Initiative: Coffee and Conversations
Nashville, TN

Marcum New York Construction Summit
Woodbury, NY

Mastering the Basics: An Introduction to Federal Awards and Grants

Navigating Carbon Emission for Tomorrow’s Middle Market

Next Generation Networking
Marlton, NJ

From Groundwork to Growth: Governance as a Catalyst for Sustainable Development in Construction

Marcum’s Governmental Accounting & Reporting Training Course
Warwick, RI

Marcum Manufacturing Forum
Cromwell, CT

Cocktails & Conversations
Providence, RI
Portland, ME

The Future of Finance: Moving from On-Premises to Cloud-Based ERP Systems

Hartford, CT

Marcum Women’s Forum: Courage

Cleveland, OH

Integrating FP&A Software into Your Financial Operations

Streamlining the Financial Close Process: How Close Management Software Transforms Efficiency

Robotic Process Automation and AI: The Next Frontier in Finance Transformation

Marcum New England Construction Summit
New Haven, CT

Marcum Mid-South Construction Summit

Marcum Ohio Construction Summit
Warrensville Heights, OH
Related Industries
Financial Institutions , Financial Services , Insurance
Have a Question? Ask Marcum

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
6 Loan commitments 32 6.1 Accounting for purchased loan commitments 32 6.2 Loan commitment to provide a loan at below-market interest rate 33 6.3 Designation of loan commitments as at FVTPL 34 6.4 Loan commitments subject to ECL 34 7 Indemnities provided by the seller 35 7.1 Indemnities provided in a direct purchase 35
term loan (DDTL) that is not a TDR will either be accounted for under the term loan or the line-of-credit accounting model as discussed in detail in Section 2.3.1.2. 2 JUNE 2023 The following flowchart illustrates these considerations and the order in which they should occur: :3@97 3D7 ?367 FA F:7 F7 A8 F:7 4ADDAI7D¶ 674F F:3F 38875F F:7 674F ...
Example. On March 1, 20X6, Company A borrowed $50,000 from a bank and signed a 12% one month note payable. The bank charged 1% initial fee. Company A assigned $73,000 of its accounts receivable to the bank as a security. During March 20X6, the company collected $70,000 of the assigned accounts receivable and paid the principle and interest on ...
To determine the accounting treatment for the transfer of a financial asset within the scope of ASC 860, a transferor must first determine whether the. Menu. ... The legal characteristics of a typical loan assignment and a loan participation and their potential implications on the transfer accounting assessment, are discussed in the following ...
The accounting guidance for the issuance, modification, conversion, and repurchase of debt and equity securities has developed over many years into a complex set of rules. This guide provides a summary of the guidance relevant to the accounting for debt and equity instruments and serves as a roadmap to the applicable accounting literature.
Under an assignment of arrangement, a pays a in exchange for the borrower assigning certain of its receivable accounts to the lender. If the borrower does not repay the , the lender has the right to collect the assigned receivables. The receivables are not actually sold to the lender, which means that the borrower retains the of not collecting ...
4.3.2 Classification and accounting: loans held for sale (HFS) When a reporting entity originates or purchases a loan with the intent to sell the loan to another entity (e.g., a government-sponsored enterprise), the loan should be classified as held for sale. Management should make a positive assertion regarding its ability and intent to hold ...
Debt Assignment: A transfer of debt, and all the rights and obligations associated with it, from a creditor to a third party . Debt assignment may occur with both individual debts and business ...
The first transaction is the loan origination to the borrower. This transaction will follow the normal accounting for loans under ASC 310. The unloading of a portion of the loan to participating banks represents a "transfer of a financial asset" (i.e. the loan, or a portion of the loan) and must be assessed for derecognition under ASC 860.
The transfer of loans may be carried out in different ways and often involves assignment, novation or sub-participation. A typical assignment amounts to the transfer of the rights of the lender (assignor) under the loan documentation to another lender (assignee), whereby the assignee takes on the assignor's rights, such as the right to ...
The issue of the characterization of a loan participation recently arose in the case of Central Bank and Real Estate Owned, L.L.C. v. Timothy C. Hogan, as Trustee of the Liberty and Liquidating Trust et. al., 891 N.W.2d 197 (Iowa 2017),1 decided by the Iowa Supreme Court. In the Central Bank case, Liberty Bank ("Liberty") made loans to Iowa ...
assignment of the loans (that qualify the de-recognition guidance stated above). It will adhere to the basic intent of the accounting standard to project the asset and liabilities at fair ... The current accounting treatment as per IND AS results into abnormal outcome varying with the tenure of the underlying pool. ...
The classification and accounting treatment of loans and receivables generally depends on whether the asset in question meets the definition of a debt security under ASC 320.To meet the definition of a security under ASC 320, the asset is required to be of a type commonly available on securities exchanges or in markets, or, when represented by an instrument, is commonly recognized in any area ...
Accounting entries for the receipt of loan are as follows: Debit. Cash at Bank. Credit. Loan Payable. Loan payables need to be classified under current or non-current liabilities depending on the maturity of loan re-payment. For example, if a loan is to be repaid in 3 years' time, the liability would be recognized under non-current liabilities.
We have a client that has been assigned a loan of £2m & paid £1 in consideration. The client wishes to show the £2m as an asset in their balance sheet rather than the £1 paid. Has anyone any idea what the accounting entries would be and if there are any tax imlications at this stage. The recoverability of the loan is a matter for another day.
The method of funding has no impact on the accounting, as there is a single loan made to the employee. Most commonly, companies utilize collateral assignment split-dollar life insurance set up under non-recourse or limited-recourse arrangements. As such, the focus of the accounting section will be on these types of arrangements. RELEVANT GUIDANCE
Off-balance sheet treatment, in accounting parlance, is called "de-recognition", implying the reversal of recognition. When the financial asset, already on the balance sheet of the originator, is removed ... Direct assignment implies a transfer of loans, mostly in form of a pool, from a seller to the buyer, without the involvement of a ...
4.4.2 Loan origination costs. Costs incurred by a reporting entity as part of origination and lending activities should be evaluated under the guidance in ASC 310-20 to assess whether they represent direct loan origination costs or other lending related costs. ASC 310-20-20 defines direct loan origination costs.
loans. The accounting treatment adopted in paragraph 7 above allows a loan resulting from an early payment benefit or an accelerated payment benefit to be an admitted asset if the loan amount plus accrued interest is less than the policy reserve and the loan is secured by the full assignment of the policy benefits to the reporting entity. b.
Entries required to reflect novation. Hello, can anyone help me with the journal entries to novate a director's loan account balance to company A from company B. The director's and shareholders are the same people so there is no issue with agreements etc. I appreciate that in company A I will debit the director's loan account - but is the ...
3.6 Loan syndication and participation. Publication date: 31 Dec 2022. us Financing guide. Many financing arrangements involve multiple lenders that are members of a loan syndicate or loan participation. The accounting for a modification of a loan syndication differs from that of a loan participation. Figure FG 3-5 summarizes how to perform the ...
loan-staff arrangements, with the following: • Provided leadership for the day-to-day running of the finance function. • Establishment of accounting and financial reporting framework. • Daily transaction processing and maintenance of financial records. • Preparation of monthly financial reports. • Accounts clean-up and reconciliations.