Advertisement

Mathematical Reading: Investigating the Reading Comprehension Strategies Implemented by Middle School Students
- Published: 14 May 2022
- Volume 20 , pages 187–213, ( 2022 )
Cite this article

- Gregory Beaudine ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-7223-1412 1
836 Accesses
2 Citations
1 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
Mathematical literacy is a keystone of contemporary mathematics education research. We collectively, thoroughly explore this set of literacy practices from the perspectives of mathematical writing and mathematical discussion. Mathematical literacy practices, of course, include a third component—reading—which takes a number of forms. This document explores the mathematical reading processes of 22 middle school students, identifying the strategies most and least used by these students, and the ways in which strategy implementation aids their reading process. From this study, we can begin to identify how this knowledge can be used by teachers, curriculum designers, and educational researchers in an effort to aid their students.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
Similar content being viewed by others

A systematic narrative synthesis review of the effectiveness of genre theory and systemic functional linguistics for improving reading and writing outcomes within K-10 education

Word problems in mathematics education: a survey

Mathematics Learning Challenges and Difficulties: A Students’ Perspective
Adams, A. E., Pegg, J. & Case, M. (2015). Anticipation guides: reading for mathematics understanding. Mathematics Teacher, 108 (7), 498–504. https://doi.org/10.5951/mathteacher.108.7.0498
Article Google Scholar
Adams, T. L. (2003). Reading mathematics: More than words can say. The Reading Teacher, 56 (8), 786–795.
Google Scholar
Afflerbach, P., Pearson, P. D. & Paris, S. G. (2008). Clarifying differences between reading skills and reading strategies. The Reading Teacher, 61 (5), 364–373. https://doi.org/10.1598/RT.61.5.1
Armstrong, A., Ming, K. & Helf, S. (2018). Content area literacy in the mathematics classroom. The Clearing House: a Journal of Educational Strategies, Issues and Ideas, 91 (2), 85–95. https://doi.org/10.1080/00098655.2017.1411131
Beaudine, G. (2018). From mathematical reading to mathematical literacy. Mathematics Teaching in the Middle School, 23 (6), 318–323. https://doi.org/10.5951/mathteacmiddscho.23.6.0318
Beaudine, G. (2019). Reading and math go side-by-side: Students explore the complexities between two core disciplines. In S. Otten, A. G. Candela, Z. de Araujo, C. Haines & C. Munter. (Eds). Proceedings of the forty-first annual meeting of the North American Chapter of the International Group for the Psychology of Mathematics Education . University of Missouri.
Beaudine, G. (2020). Reading to learn mathematics: Exploring reading strategy implementations of middle school students through their reading of mathematical texts [Doctoral dissertation]. Michigan State University. ProQuest Dissertations Publishing.
Bergeson, K. T. & Rosheim, K. (2018). Literacy, equity, and the employment of iPads in the classroom: A comparison of secure and developing readers. International Journal of Education in Mathematics, Science and Technology, 6 (2), 173–181.
Brozo, W. G. & Crain, S. (2018). Writing in math: A disciplinary literacy approach. The Clearing House: A Journal of Educational Strategies, Issues and Ideas, 91 (1), 7–13. https://doi.org/10.1080/00098655.2017.1342435
Brozo, W. G., Moorman, G., Meyer, C. & Stewart, T. (2013). Content area reading and disciplinary literacy: A case for the radical center. Journal of Adolescent & Adult Literacy, 56 (5), 353–357. https://doi.org/10.1002/JAAL.153
Byrd, C. E., McNeil, N. M., Chesney, D. L. & Matthews, P. G. (2015). A specific misconception of the equal sign acts as a barrier to children’s learning of early algebra. Learning and Individual Differences, 38, 61–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lindif.2015.01.001
Chen, C. & Chiu, C. (2016). Collaboration scripts for enhancing metacognitive self-regulation and mathematics literacy. International Journal of Science and Mathematics Education, 14 (2), 263–280. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10763-015-9681-y
Common Core State Standards Initiative [CCSSI] (2020). Common core state standards initiative: Preparing America’s students for success. corestandards.org.
Doerr, H. M. & Temple, C. (2016). It’s a different kind of reading: Two middle-grade teachers’ evolving perspectives on reading in mathematics. Journal of Literacy Research, 48 (1), 5–38. https://doi.org/10.1177/1086296X16637180
Firdaus, F. M., Wahyudin & Herman, T. (2017). Improving primary students’ mathematical literacy through problem based learning and direct instruction. Educational Research and Reviews, 12 (4), 212–219.
Florida State Legislature (2016). The 2016 Florida statutes (1008.25). Tallahassee, FL. http://www.leg.state.fl.us/Statutes/index.cfm?App_mode=Display_Statute&URL=1000-1099/1008/Sections/1008.25.html
Forseman, S. (2017). enVision math 2.0, student edition, grade 7 (Vol. 1). Pearson.
Fuchs, L. S., Fuchs, D., Hosp, M. K. & Jenkins, J. R. (2001). Oral reading fluency as an indicator of reading competence: a theoretical, empirical, and historical analysis. Scientific Studies of Reading, 5 (3), 239–256. https://doi.org/10.1207/S1532799XSSR0503_3
Fuentes, P. (1998). Reading comprehension in mathematics. The Clearing House: a Journal of Educational Strategies, Issues and Ideas, 72 (2), 81–88. https://doi.org/10.1080/00098659809599602
Gibbons, P. (2009). English learners, academic literacy, and thinking: Learning in the challenge zone . Heinemann.
Ginsburg, H. (1997). Entering the child’s mind: The clinical interview in psychological research and practice. Cambridge University Press . https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9780511527777
Harkness, S. S. & Brass, A. (2017). How preservice teachers make meaning of mathematics methods texts. International Journal for the Scholarship of Teaching and Learning, 11 (2), Article 17. https://doi.org/10.20429/ijsotl.2017.110217
Herbel-Eisenmann, B., Johnson, K. R., Otten, S., Cirillo, M. & Steele, M. D. (2015). Mapping talk about the mathematics register in a secondary mathematics teacher study group. Journal of Mathematical Behavior, 40, 29–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmathb.2014.09.003
Hilden, K. & Pressley, M. (2011). Verbal protocols of reading. In N. K. Duke & M. H. Mallette (Eds.), Literacy research methodologies (2nd ed., pp. 427–440). Guilford.
Hildreth, G. H. (1947). Learning the three R’s (2nd ed.). Educational Publishers.
Hillman, A. M. (2014). A literature review on disciplinary literacy: How do secondary teachers apprentice students into mathematical literacy? Journal of Adolescent & Adult Literacy, 57 (5), 397–406. https://doi.org/10.1002/jaal.256
Kirby, S. N. (2003). Developing an R&D program to improve reading comprehension . RAND Corporation. https://www.rand.org/pubs/research_briefs/RB8024.html
Michigan Education Agency (2017). Learn what’s in the new third grade reading law. https://mea.org/learn-whats-in-the-new-third-grade-reading-law/
Molina, C (2012). The problem with math is English: A language-focused approach to helping all students develop a deeper understanding of mathematics . John Wiley & Sons.
Moschkovich, J. & Zahner, W. (2018). Using the academic literacy in mathematics framework to uncover multiple aspects of activity during peer mathematical discussions. ZDM – Mathematics Education, 50 (6), 999–1011. http://doi.org/10.1007/s11858-018-0982-9
National Council of Teachers of English [NCTE] (2005). Position statements: Multimodal literacies. Author. https://ncte.org/statement/multimodalliteracies/
Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development [OECD] (2013). PISA 2012 assessment and analytical framework: Mathematics, reading, science, problem solving and financial literacy . Author.
Pearson, P. D. & Cervetti, G. N. (2015). Fifty years of reading comprehension theory and practice. In P. D. Pearson & E. H. Hiebert (Eds.), Research-based practices for teaching Common Core literacy (pp. 1–24). Teachers College Press.
Penn State Learning (2020). Test taking tips . PennState Undergraduate Education. https://pennstatelearning.psu.edu/test-taking-tips
Powell, S. R. & Fuchs, L. S. (2014). Does early algebraic reasoning differ as a function of students’ difficulty with calculations versus word problems? Learning Disabilities Research & Practice, 29 (3), 106–116. https://doi.org/10.1111/ldrp.12037
Pressley, M. & Afflerbach, P. (1995). Verbal protocols of reading: The nature of constructively responsive reading . Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Purcell-Gates, V., Duke, N. K. & Martineau, J. A. (2007). Learning to read and write genre-specific text: roles of authentic experience and explicit teaching. Reading Research Quarterly, 42 (1), 8–45. https://doi.org/10.1598/RRQ.42.1.1
Shanahan, C. & Shanahan, T. (2014). Does disciplinary literacy have a place in elementary school? The Reading Teacher, 67 (8), 636–639. https://doi.org/10.1002/trtr.1257
Shanahan, C., Shanahan, T. & Misischia, C. (2011). Analysis of expert readers in three disciplines: History, mathematics, and chemistry. Journal of Literacy Research, 43 (4), 393–429. https://doi.org/10.1177/1086296X11424071
Shepherd, M. D. & van de Sande, C. C. (2014). Reading mathematics for understanding—From novice to expert. The Journal of Mathematical Behavior, 35, 74–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmathb.2014.06.003
Sigley, R. & Wilkinson, L. C. (2015). Ariel’s cycles of problem solving: an adolescent acquires the mathematics register. Journal of Mathematical Behavior, 40, 75–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmathb.2015.03.001
Snow, C. (2002). Reading for understanding: toward an R&D program in reading comprehension . RAND Corporation. https://www.rand.org/pubs/monograph_reports/MR1465.html
Temple, C. & Doerr, H. M. (2018). How do teachers develop and enact a disciplinary view of literacy in mathematics? Journal of Adolescent & Adult Literacy, 61 (5), 483–488. https://doi.org/10.1002/jaal.664
Texas Education Agency (2016). Grade-level retention and student performance in Texas public schools, 2014–15 (Document No. GE17 601 09). http://tea.texas.gov/acctres/retention_student_performance_2014-15.pdf
Todd, J. (2020, February 20). Sadlier’s math blog: math test-taking strategies for elementary students . Sadlier School. https://www.sadlier.com/school/sadlier-math-blog/math-test-taking-strategies-for-elementary-students-math-multiple-choice-test-taking-strategies
United States Department of Education [USDE] (n.d.a). No child left behind: Elementary and Secondary Education Act (ESEA). https://www2.ed.gov/nclb/landing.jhtml
United States Department of Education [USDE] (n.d.b). Every Student Succeeds Act (ESSA). https://www.ed.gov/essa?src=rn
Zheng, B., Arada, K., Niiya, M. & Warschauer, M. (2014). One-to-one laptops in K-12 classrooms: Voices of students. Pedagogies: An International Journal, 9 (4), 279–299. https://doi.org/10.1080/1554480X.2014.955499
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
University of Iowa, Iowa City, IA, USA
Gregory Beaudine
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Gregory Beaudine .
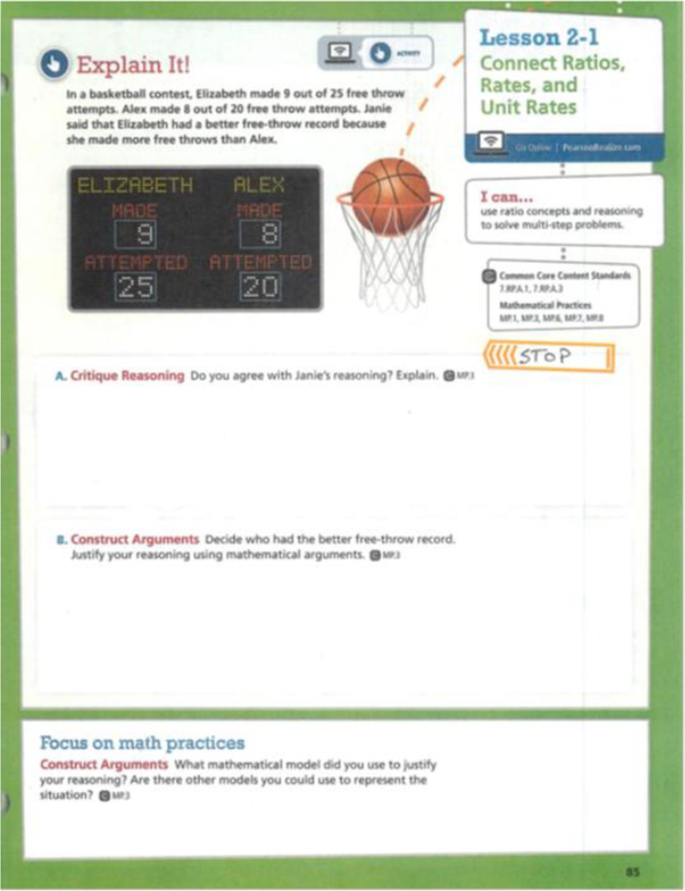
Appendix 1 – Three-page reading passage from enVision Mathematics Gr. 7.
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Beaudine, G. Mathematical Reading: Investigating the Reading Comprehension Strategies Implemented by Middle School Students. Int J of Sci and Math Educ 20 (Suppl 1), 187–213 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10763-022-10287-1
Download citation
Received : 02 July 2021
Accepted : 25 April 2022
Published : 14 May 2022
Issue Date : November 2022
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s10763-022-10287-1
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Mathematical literacy
- Mathematical reading
- Middle grades
- Skills and strategies
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

The Impact of Reading Comprehension on Mathematics Word Problem Solving

2019, Education and New Developments 2019
Word problem constitutes an important part of the mathematics curriculum of the elementary school. Different studies have argued that the understanding of the problem is the most difficult part for students, because of the lack of understanding of the ‘keywords’ used in the problem contexts. Thus, because the process of word problem solving is related to reading comprehension, as a most important factor in this study it was examined the impact of reading comprehension for improving student’s skills for mathematics word problem-solving. Participants in the study were fifty-fourth-grade students and their teachers. The methodology of the study is the collaborative action research. The researchers (authors) have worked together with two class teachers and have used the Reciprocal Teaching method as an intervention for eight weeks aimed to improve the student's skills for reading comprehension. The Reciprocal Teaching method includes prediction, clarifying, questioning and summarizi...
Related Papers
Psychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary Journal
Psychology and Education , Sidang Hapon
The main purpose of this research was to assess the Comprehension and Reading ability and to determine the significant correlation between Reading Comprehension level of learners and their ability to solve Mathematical word Problems. This study employed Descriptive Quantitative Correlational Study. The respondents of the study were ninety-two (92) Grade 4 learners of Western Mindanao State University-Integrated Laboratory School enrolled in school year 2022-2023. This study adopted the Philippine Informal Reading Inventory (Phil-IRI) assessment tool and DepEd Numeracy Assessment Tool (D-NumAT) to measure the reading comprehension and Mathematical Ability respectively. The findings indicated that majority of the Grade 4 learners in Reading Comprehension Level are classified under Frustration Level, some of the learners are classified under Instructional Level, and very few are classified under independent level. As for Mathematical Performance Level, majority of the Grade 4 learners are under non-Numerates level, and some are classified under Low level. This study revealed that the overall Reading Comprehension skill of the learners has negligible correlation to the learners Mathematical Performance in Solving Word Problems. Hence, Reading Comprehension can be a significant factor affecting students' mathematical performance specifically in solving word problems.
URAISD-2023 Conference
Dennis R . Nimely, Jr. , Florence Nyamu
The performance of learners in Mathematics is a concern among educators and researchers globally. Research has documented various factors that positively or negatively influence performance. The purpose of this study was to investigate the relationship between learners’ reading comprehension and arithmetic skills in solving word-problems. The objective was to establish the relationship between learners’ reading comprehension and arithmetic skills, and solving word-problems. The researchers used the descriptive and correlational design. The target population was 5183 Form II learners in secondary schools in Naivasha sub-County, Nakuru County, Kenya. Purposive sampling was used to select Form II as the class level. Stratified random sampling was used to select a sample of 328 respondents, 318 Form II learners and 10 Mathematics teachers. Questionnaires for teachers and learners, Text Comprehension Skills Test and Arithmetic Skills Test, were used to collect data. Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS) version 26 and Microsoft Excel 365 were used for analysis. Findings were presented in tables and charts. Only 23.3% of the learners attained the 50% benchmark in the Text Comprehension Skills Test (TCST) and 40.6% attained the 50% benchmark in Arithmetic Skills Test (AST). The findings showed a moderate positive correlation between learners’ reading comprehension and arithmetic skills and solving word-problems with a statistical significance at r = .613 and p < .001. The findings are significant and imply that inculcating reading comprehension and arithmetic skills in the curriculum for Mathematics, may improve learners’ performance in solving word-problems.
Mehmet Akif Ocak
Educational Psychology
Kaisa Aunola
Frontiers in psychology
Menno van der Schoot
Successfully solving mathematical word problems requires both mental representation skills and reading comprehension skills. In Realistic Math Education (RME), however, students primarily learn to apply the first of these skills (i.e., representational skills) in the context of word problem solving. Given this, it seems legitimate to assume that students from a RME curriculum experience difficulties when asked to solve semantically complex word problems. We investigated this assumption under 80 sixth grade students who were classified as successful and less successful word problem solvers based on a standardized mathematics test. To this end, students completed word problems that ask for both mental representation skills and reading comprehension skills. The results showed that even successful word problem solvers had a low performance on semantically complex word problems, despite adequate performance on semantically less complex word problems. Based on this study, we concluded tha...
Albania International Conference on Education 1st Albania International Conference on Education
CERN European Organization for Nuclear Research - Zenodo
Melodina de la Cruz
AJHSSR Journal
The purpose of this study was to determine the relationship between the extent of students" reading comprehension and problem solving skills and identify teaching strategies that would address the problem in teaching problem solving in Mathematics. The research utilized mixed explanatory design. The subject consists of 189 grade 7 students who were part of the general section enrolled at Davao City National High School. Purposive sampling was used in identifying the respondents taking the reading comprehension test and problem solving test while random sampling was used in identifying participants for the key informant interview. The result of the study revealed that students reading comprehension and problem solving skills were at developing level. Moreover, reading comprehension skill was a predictor of problem solving skill. This means that students" problem solving skill is dependent on their reading skills. Results also showed from the conducted focus group discussion that students gave importance to vocabulary and main idea in learning problem solving. Furthermore, using differentiated instruction was the identified best teaching strategy to understand problem solving.
University of St. Lasalle
Melalyn Parales
The purpose of the study was to determine the level of reading comprehension and problem solving skills of the Grade VI pupils of Basak Elementary School enrolled school year 2018-2019.The research design used was descriptive – correlational to determine the relationship between reading comprehension and problem solving skills. Participants were determined through G*Power which resulted to 44 (88%) participants. Stratified sampling was utilized to determine the number of participants in each section. The researcher employed questionnaires that determine the level of reading comprehension and problem solving skills of the participants. The results revealed that there is a significant relationship between reading comprehension and problem solving skills. Majority of the participant were female and in section one. Female outperformed male in both reading comprehension and problem solving skills due to local tradition, enthusiasm and willingness. Results exhibit that there is a relationship between reading comprehension and problem-solving skills at .098 significant level.
International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications (IJSRP)
Girley Mingke
RELATED PAPERS
hrcak.srce.hr
Marko Mrakovcic
Chaos: An Interdisciplinary Journal of Nonlinear Science
Leonardo Angelini
Kristin McIver
carla david
Andrea Vignoli
Carlos Aggio
Engineering Optimization
Shweta Rathi
Peggy Zinke
souvenir kipas kayu
jual suppliervendor
abdelalem saad soliman desoky
Goldschmidt2021 abstracts
Heloisa Coe
Mediações - Revista de Ciências Sociais
Maria valquíria souza da Silva
International journal of statistics and applications
J. Onyeka-Ubaka
Energy Research & Social Science
Benjamin Sovacool
Dmitri Rozanov
Schwäbische Heimat
Statistics and Risk Modeling
Josef G. Steinebach
ZUHD : (L’ascetisme) L’aspiration à l’au-delà...
Nahim Ollibokus
Archives of Virology
Fulvio Marsilio
Bali Dermatology and Venereology Journal
Yulia F Yahya
Abdoul Aziz
American Journal of Education and Technology
Genetics Selection Evolution
Frederique Pitel
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024

The Mathematics Problem-Solving Skills and Reading Comprehension of Junior High School Students of the Palo 19 National High School
- Jane Jumawin
INTRODUCTION
Mathematical problem solving is a process that involves a set of factors and tasks to achieve a defined goal. It depends on many skills and factors which therefore makes it challenging both to learn and to teach. For a closer view, one identified reason for poor performance in problem-solving of Grade IX students of Palo 19 National High School was their poor understanding or comprehension of the mathematical terms. The students most of the time got very low scores in math quizzes that involves an understanding of the word problems. Problem-solving and reading comprehension are two skills that should be developed in students to improve their performance in math.
This action research was purely descriptive which uses pre-test/post-test results and survey results.
Table 1. Thirty-Item Pre-Test and Post-Test Results in Problem Solving
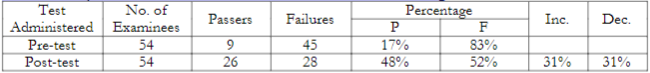
Students' Word Problem Solving Attitude Survey
Most of the students were not equipped with problem-solving techniques and mathematical terms/vocabulary words were limited. Meanwhile, they do not have problem-solving techniques that make them bored during problem-solving activities. Furthermore, students showed a cheerful outlook towards problem-solving techniques and they are willing to solve word problems.
DISCUSSIONS
This result is reflecting a very poor performance in Mathematics problem solving which can be due to poor comprehension of problem-solving vocabulary. On the other hand, the post-test revealed a 31% increase in the number of examinees who passed the test. The 9 passers in the pre-test had gone up to 26 which were 48%. Moreover, the table above presents the results of students' attitude in problem-solving. It shows students’ perception of their own ability to solve word problems. Results for students' attitude survey showed that 35 out of 54 pupils do not know how to get the correct answer in solving word problems. Twenty-six students also disagreed that they usually know all the vocabulary words used in the problem.
Information
- For Readers
- For Authors
- For Librarians
©2017 by Ascendens Asia Pte. Ltd. | NLB Singapore-Registered Publisher.

Philippine E-Journals
Home ⇛ universal journal of educational research ⇛ vol. 1 no. 1 (2022), the gap between comprehension level and problem-solving skills in learning mathematics.
Maximo V. Hijada Jr. | Melodina L. Dela Cruz
This study was conducted to determine the degree of relationship that exists between learners’ level of comprehension and solving skills on mathematical word problems of grades four to six learners in Kang–iras Elementary School. It attempted to establish a relationship between the learners’ level of comprehension and solving skills. This research study employed the correlational method of research. This research design is appropriate for this research because its primary purpose is to determine the degree of the relationship between the learners’ level of comprehension and solving skills of the word problems. Lomax and Li (2009) stressed that correlational research investigates a range of factors, including the nature of the relationship between two or more variables and the theoretical model that might be developed and tested to explain these resultant correlations. From the gathered data, the following findings are, the comprehension level of the learners in Kangiras Elementary School being studied is at Frustration Level. For each specific skill, only in the literal interpretation skill the learners had been classified at instructional level while for the other two skills, the learners are at frustration level. Majority of the learners are at a frustration level. The level of word problem solving skills in mathematics of the respondents is classified as non-proficient. All three skills indicators used revealed that the respondents are non-proficient. The learners have not mastered word problem-solving. Comprehension skills could not predict the mathematical word problem-solving skills of the learners. There is weak correlation between the variables and the relationship between the two variables is insignificant. There are other factors affecting word problem skills among learners. Some are identified as follows: instructional strategies and methods, learners’ motivation and concentration, learner’s arithmetic ability, learning facilities or instructional materials, curriculum and teacher’s competency. From the findings of the study, it was established that comprehension level is not an indicator of the learners’ solving skills and there are other factors that could affect solving mathematical word problems. Solving skill is independent of comprehension skills and the variables studied are not related. Thus, it can be concluded that comprehension is not the only factor that could affect word problem-solving skills but there are more other factors and these factors may be assessed and taken into consideration.

Share Article:
- Citation Generator
- ">Indexing metadata
- Print version
Copyright © 2024 KITE E-Learning Solutions | Exclusively distributed by CE-Logic | Terms and Conditions
share this!
April 29, 2024
This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies . Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
Intervention based on science of reading and math boosts comprehension and word problem-solving skills
by University of Kansas
New research from the University of Kansas has found that an intervention based on the science of reading and math effectively helped English learners boost their comprehension, visualize and synthesize information, and make connections that significantly improved their math performance.
The intervention , performed for 30 minutes twice a week for 10 weeks with 66 third-grade English language learners who displayed math learning difficulties, improved students' performance when compared to students who received general instruction. This indicates that emphasizing cognitive concepts involved in the science of reading and math are key to helping students improve, according to researchers.
"Word problem-solving is influenced by both the science of reading and the science of math. Key components include number sense, decoding, language comprehension and working memory. Utilizing direct and explicit teaching methods enhances understanding and enables students to effectively connect these skills to solve math problems . This integrated approach ensures that students are equipped with necessary tools to navigate both the linguistic and numerical demands of word problems," said Michael Orosco, professor of educational psychology at KU and lead author of the study.
The intervention incorporates comprehension strategy instruction in both reading and math, focusing and decoding, phonological awareness, vocabulary development, inferential thinking, contextualized learning and numeracy.
"It is proving to be one of the most effective evidence-based practices available for this growing population," Orosco said.
The study, co-written with Deborah Reed of the University of Tennessee, was published in the journal Learning Disabilities Research and Practice .
For the research, trained tutors implemented the intervention, developed by Orosco and colleagues based on cognitive and culturally responsive research conducted over a span of 20 years. One example of an intervention session tested in the study included a script in which a tutor examined a word problem explaining that a person made a quesadilla for his friend Mario and gave him one-fourth of it, then asked students to determine how much remained.
The tutor first asked students if they remembered a class session in which they made quesadillas and what shape they were, and demonstrated concepts by drawing a circle on the board, dividing it into four equal pieces, having students repeat terms like numerator and denominator. The tutor explains that when a question asks how much is left, subtraction is required. The students also collaborated with peers to practice using important vocabulary in sentences. The approach both helps students learn and understand mathematical concepts while being culturally responsive.
"Word problems are complex because they require translating words into mathematical equations, and this involves integrating the science of reading and math through language concepts and differentiated instruction," Orosco said. "We have not extensively tested these approaches with this group of children. However, we are establishing an evidence-based framework that aids them in developing background knowledge and connecting it to their cultural contexts."
Orosco, director of KU's Center for Culturally Responsive Educational Neuroscience, emphasized the critical role of language in word problems, highlighting the importance of using culturally familiar terms. For instance, substituting "pastry" for "quesadilla" could significantly affect comprehension for students from diverse backgrounds. Failure to grasp the initial scenario could impede subsequent problem-solving efforts.
The study proved effective in improving students' problem-solving abilities, despite covariates including an individual's basic calculation skills, fluid intelligence and reading comprehension scores. That finding is key, as while ideally all students would begin on equal footing and there would be few variations in a classroom, in reality, covariates exist and are commonplace.
The study had trained tutors deliver the intervention, and its effectiveness should be further tested with working teachers, the authors wrote. Orosco said professional development to help teachers gain the skills is necessary, and it is vital for teacher preparation programs to train future teachers with such skills as well. And helping students at the elementary level is necessary to help ensure success in future higher-level math classes such as algebra.
The research builds on Orosco and colleagues' work in understanding and improving math instruction for English learners. Future work will continue to examine the role of cognitive functions such as working memory and brain science, as well as potential integration of artificial intelligence in teaching math.
"Comprehension strategy instruction helps students make connections, ask questions, visualize, synthesize and monitor their thinking about word problems," Orosco and Reed wrote. "Finally, applying comprehension strategy instruction supports ELs in integrating their reading, language and math cognition…. Focusing on relevant language in word problems and providing collaborative support significantly improved students' solution accuracy."
Provided by University of Kansas
Explore further
Feedback to editors
Every drop counts: New algorithm tracks Texas's daily reservoir evaporation rates
6 hours ago

Genetic study finds early summer fishing can have an evolutionary impact, resulting in smaller salmon
8 hours ago

Researchers discovery family of natural compounds that selectively kill parasites

Study suggests heavy snowfall and rain may contribute to some earthquakes

The spread of misinformation varies by topic and by country in Europe, study finds

Webb presents best evidence to date for rocky exoplanet atmosphere

Human activity is making it harder for scientists to interpret oceans' past
9 hours ago

Quantum simulators solve physics puzzles with colored dots
Chemists produce new-to-nature enzyme containing boron
Improving timing precision of millisecond pulsars using polarization
Relevant physicsforums posts, physics instructor minimum education to teach community college.
May 6, 2024
Studying "Useful" vs. "Useless" Stuff in School
Apr 30, 2024
Why are Physicists so informal with mathematics?
Apr 29, 2024
Plagiarism & ChatGPT: Is Cheating with AI the New Normal?
Apr 28, 2024
Digital oscilloscope for high school use
Apr 25, 2024
Motivating high school Physics students with Popcorn Physics
Apr 3, 2024
More from STEM Educators and Teaching
Related Stories
Study shows program improves teaching skills, students' word problem–solving
Jun 14, 2022
Study shows approach can help English learners improve at math word problems
Jun 19, 2018

Study examines role of working memory, cognitive functions in English learners learning to write
Oct 17, 2023

Cognitive study shows lack of bilingual education adversely affects English language learners' writing skills
Oct 14, 2021

How vocabulary breadth and depth influence bilingual reading comprehension
Aug 21, 2023

Study validates the simple view of reading for enhancing second and foreign language learners' experience
Aug 17, 2023
Recommended for you

Investigation reveals varied impact of preschool programs on long-term school success
May 2, 2024

Training of brain processes makes reading more efficient
Apr 18, 2024

Researchers find lower grades given to students with surnames that come later in alphabetical order
Apr 17, 2024

Earth, the sun and a bike wheel: Why your high-school textbook was wrong about the shape of Earth's orbit
Apr 8, 2024

Touchibo, a robot that fosters inclusion in education through touch
Apr 5, 2024

More than money, family and community bonds prep teens for college success: Study
Let us know if there is a problem with our content.
Use this form if you have come across a typo, inaccuracy or would like to send an edit request for the content on this page. For general inquiries, please use our contact form . For general feedback, use the public comments section below (please adhere to guidelines ).
Please select the most appropriate category to facilitate processing of your request
Thank you for taking time to provide your feedback to the editors.
Your feedback is important to us. However, we do not guarantee individual replies due to the high volume of messages.
E-mail the story
Your email address is used only to let the recipient know who sent the email. Neither your address nor the recipient's address will be used for any other purpose. The information you enter will appear in your e-mail message and is not retained by Phys.org in any form.
Newsletter sign up
Get weekly and/or daily updates delivered to your inbox. You can unsubscribe at any time and we'll never share your details to third parties.
More information Privacy policy
Donate and enjoy an ad-free experience
We keep our content available to everyone. Consider supporting Science X's mission by getting a premium account.
E-mail newsletter

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The purpose of this research is to document the correlation between reading skills and mathematics performance, particularly on word problem solving. This research was carried out in the researcher's grade one advisory class at Rizal Elementary School. The sample population is consist of thirty seven pupils in grade one.
Abstract. The focal point of this research is to gauge the relationship between the reading comprehension level, problem-solving skills and academic performance of Grades 6 pupils of all the ...
between math problem-solving skills and reading comprehension skills a mong elementary school students in Indonesia. Furthermore, there remains a gap in research that compares problem -solving skills
The greatest predictor of problem-solving is reading comprehension since the first stage of the problem-solving phase requires an individual to comprehend the problem statement and context ... relationships between reading comprehension and mathematics skills across age groups may be valuable (Bjork & Crane, 2013).
This study suggested that to improve the level of problem-solving skills of the students; it is vital to strengthen the integration of Polya's method in teaching lessons about problem-solving ...
Third, the foundational mathematics skills of Filipino students consistently regressed between 2003 and 2019. We found that the decline between 2013 and 2019 was twice as severe as the decline between 2003 and 2013. We see a contrasting trend with reading, driven by significant improvements in grades 4-6.
In the Philippine education system, reading, mathematics, and science formed part of the core areas of basic education curriculum. ... A validated and reliable 150-item test in reading comprehension skills, mathematics and science was used to get primary data to perform correlation and regression analysis. Findings showed that only making ...
words. Problem solving and reading comprehension essentially work together in order to reach a goal and do so by utilizing different resources for this purpose. In this regard, reading comprehension skills and problem solving skills are closely interrelated (Fuentes, 1998; Jordan, Hanich & Kaplan, 2003; Vilenius‐Tuohimaa, Aunola & Nurmi, 2008).
Philippines. The Programme for International Student Assessment (PISA) is a triennial survey of 15year-old students - around the world that assesses the extent to which they have acquired the key knowledge and skills essential for full participation in society. The assessment focuses on the core school subjects of reading, mathematics and science.
reading comprehension and problem solving skills and identify teaching strategies that would address the problem in teaching problem solving in Mathematics. The research utilized mixed explanatory design. The subject consists of 189 grade 7 students who were part of the general section enrolled at Davao City National High School.
Mathematical literacy is a keystone of contemporary mathematics education research. We collectively, thoroughly explore this set of literacy practices from the perspectives of mathematical writing and mathematical discussion. Mathematical literacy practices, of course, include a third component—reading—which takes a number of forms. This document explores the mathematical reading processes ...
through reading comprehension as a strategy in teaching mathematics to enhance the problem-solving skills of Grade 7 students. The first phase of the study involved quasi-experimentation to determine the effect of the integration of reading comprehension skills in teaching mathematics on the problem-solving skills of the students.
The significantly strong and positive association between reading comprehension and mathematics skills obtained in this meta-analysis research supports the literature and confirms the claim that ...
The study made use of researcher-made questionnaires in reading comprehension and problem solving skills. Moreover, Pearson - Product Moment Correlation and Linear Regression were used as statistical tools. The results of the study revealed that the level of reading comprehension and problem solving of the students was average.
Majority of the participant were female and in section one. Female outperformed male in both reading comprehension and problem solving skills due to local tradition, enthusiasm and willingness. Results exhibit that there is a relationship between reading comprehension and problem-solving skills at .098 significant level.
INTRODUCTION Mathematical problem solving is a process that involves a set of factors and tasks to achieve a defined goal. It depends on many skills and factors which therefore makes it challenging both to learn and to teach. For a closer view, one identified reason for poor performance in problem-solving of Grade IX students of Palo 19 National High School was their poor understanding or ...
The level of word problem solving skills in mathematics of the respondents is classified as non-proficient. All three skills indicators used revealed that the respondents are non-proficient. The learners have not mastered word problem-solving. Comprehension skills could not predict the mathematical word problem-solving skills of the learners.
Word problem constitutes an important part of the mathematics curriculum of the elementary school. Different studies have argued that the understanding of the problem is the most difficult part for students, because of the lack of understanding of the 'keywords' used in the problem contexts. Thus, because the process of word problem solving is related to reading comprehension, as a most ...
To accomplish mathematics problem solving, students need to understand, analyze, represent, execute and evaluate problems. Polya (1957) has proposed four steps to help students in solving mathematical word problems: understanding the problem, designing a plan, implementing the plan, and reviewing. On the other hand, Van Garderen (2004) states ...
Murcia (2011) stressed that problem solving in mathematics and reading with comprehension go hand in hand. Solving Mathematics problems entails the students to apply two skills at the same time: reading with comprehension and computing. In the same study, it was found out that only very few could
"Reading Skills, Key to Learning," the ... reasoning and problem solving. Issa et al ... 3822 Differentiated Instruction for Basic Reading Comprehension in Philippine Settings [12] Beck, C. R ...
The Problem. Problem-solving in mathematics and reading comprehension go hand in hand. Solving math problems entails the students applying two skills at the same time: reading and computing. It is a double-edged sword. As a public school teacher of sixth-grade mathematics for five years, I have encountered many pupils who are poor in both ...
It was found that the RTM was an effective method for word problem solving, especially for reading comprehension as a component of word problem solving. The results are in line with other studies ...
The study proved effective in improving students' problem-solving abilities, despite covariates including an individual's basic calculation skills, fluid intelligence and reading comprehension scores.