Top 20 Majors and Degrees for Thinkers Looking for Intellectual Jobs
Ready to find the perfect college degree.

Intellect is a marketable commodity. Employers want to hire thinkers. And thinkers look for intellectual careers.
But where do you find them?
Most think smart people end up working higher education jobs or in research. But there are many different jobs for intellectuals.
If you consider yourself a smart person, you might try turning your gift (and your hard work) into a rewarding career.

What makes a job intellectual?
Smart jobs keep your brain active. They don’t cause you to fall asleep at your desk or bore you to tears. There are several things that make a job stimulating, but we’ve chosen three to highlight.
Read on to find out what makes a job stimulate your brain.
You work with data
In some of the most intellectual careers, you work with data. But it’s more than crunching numbers. You process and analyze information to make determinations. You also make estimates or predictions based on your outcomes.
For example, architects estimate measurements to ensure buildings are safe. Aerospace engineers determine flight dynamics through careful data analysis. There are many jobs where you work with data every day.
You work with machines
When you work with unique tools and machines, you keep your brain sharp. Your brain shifts between tasks, keeping it stimulated. You’re less likely to lose focus when you use machinery, for example.
Machine technicians and engineers work with machines. But the machine doesn’t need to be a trinket or gadget to stimulate your brain. Accountants use machines when they work with computers and calculators.
You work with people
When you interact with people, you use and develop your interpersonal skills. You also identify how to communicate in the best way with those around you. Working with people can help keep your mind sharp.
Careers where you work with people include doctors, lawyers, and social workers. If you have clients, you’re meeting with people.
But jobs where you work on teams also require sharp people skills. As a leader or a member of a team, you navigate personalities and adapt to different leadership styles as needed. You become an active part of a team with a single goal and vision. This ensures a job well done.
20 Smart Degrees to Get for Intellectuals
Below are 20 smart majors for people who like to think. These degrees earn a spot on any intellectual jobs list because of the above criteria. In these majors, you work with data, machines, and/or people. You use critical thinking and analytical skills in your day-to-day activities.
If you love to analyze, ponder, and think, these are the smartest majors in college to study.
1. Actuarial Science
Actuarial science deals with risk measurements in business and finance. Actuaries spend their time evaluating the likelihood of future events. They also try to come up with ways to reduce the impact of those events.
To do their job, actuaries use data analysis. They work for:
- Accounting firms
- Colleges and universities
- Government agencies
- Insurance companies
Those who work in insurance help establish cost premiums. They assess risk and costs, all while analyzing numbers, charts, and graphs.
To study actuarial science, you should be a thinker. You should also have strong analytical and problem-solving skills.
Since the job requires data analysis, you need to be good with numbers. As an actuarial science major, you improve your math skills by taking courses in statistics and finance. You also take courses that cover financial mathematics and probability.
After college, you need to pass a series of exams so that you qualify for an actuary job.
So if you’re good at taking tests and working with numbers, you will find many benefits to this career. From high earnings to brain stimulation, actuarial science offers a good career for thinkers.
Top programs:
Roosevelt University University of Central Florida
2. Aerospace Engineering
Aerospace engineers design and build planes, spacecraft, and weapons systems. You need a master’s degree to work in most aerospace engineer jobs, but you can also get a bachelor’s.
Aerospace engineers are thinkers. The top engineers go to work for NASA. But you can also find intellectual jobs at Boeing, Honeywell, Lockheed Martin, and Rolls-Royce.
While in college, you take courses that make you a better critical thinker and mathematician. You take courses such as:
- Design optimization
- Flight dynamics
- Fluid mathematics
- Structural mechanics
You also take many math and physics courses.
After graduation, six-figure salaries await you. But you’ll need to work hard in school and graduate at the top of your class to land a job with NASA because this is one of the smartest majors to study.
Florida Tech Georgia Tech
3. Anthropology
As an anthropology major, you study human behavior and the development of culture. You focus on questions and answers to different aspects of social relations.
There are four main branches of sociology. These include:
- Archaeology
- Cultural anthropology
- Linguistics
- Physical anthropology
While you focus your studies on these main branches, you can also specialize in a geographic area. Common areas include Latin America, Eastern Europe, or North America.
A specialization gives you an edge over your competition when you apply for a job. You also improve your research skills as you study a niche of anthropology.
If you want to understand the social world and culture as it relates to human development, then this major might work for you. But plan on learning more than anthropology in your classes. Many programs explore topics in art, history, language, and sociology.
Many consider anthropology one of the most intelligent college majors to pursue.
Featured Schools
Colorado State University Online University of Florida

4. Astronomy
Astronomers, or astrophysicists, study galaxies, solar systems, and stars. While most students who go into astronomy get a graduate degree, some schools offer bachelor’s degree programs.
You can land an entry-level career in computer science, math, and physics with an undergraduate degree in astronomy. You can also qualify for graduate school if you keep your grades up and get support from your professors.
Courses in undergraduate programs cover topics like:
- Galactic and extragalactic astrophysics
- Planetary and stellar astrophysics
- Solar systems astronomy
After graduation, you can work as an astronomer or astrophysicist. But again, most of these jobs require a master’s degree.
You can also land a job as a data analyst, news reporter, or teacher. The sky’s the limit for this degree, especially if you love to think and don’t want to grow bored on the job.
Arizona State University Indiana University Bloomington
5. Bioethics
In bioethics, you study the moral and ethical consequences of biological research. But you also study how it helps. Bioethics programs teach you how to apply ethics to your research, no matter how complicated.
As science advances, demand for this job increases. As a result, the number of undergraduate programs in this field have grown. Some schools offer bioethics as a standalone degree, while others connect it to public health or policy degrees.
In a bioethics program, you learn what it means to be ethical in human advancement. You raise questions on how research intertwines with law, medicine, and technology. You learn about important ideas and topics in biomedical research, such as:
- Artificial intelligence
- Pharmaceutical therapies
- Stem cell research
You take classes that cover topics in health care and law and public health ethics.
Bioethics programs are for thinkers. The major helps you understand the impact of science and research. But it also helps you learn how to analyze moral arguments and contribute to debate.
Saint Louis University University of Rochester
6. Biomedical Engineering
If you’re passionate about biology and want to be on the cutting edge of innovation in health and medicine, this major is for you.
To work as a bioengineer or biomedical engineer, you need at least a bachelor’s degree. When you start this program, you take introductory courses like:
- Biomedical engineering
- General and analytical chemistry
You then study more complex topics, from medical device design to numerical analysis of complex biosystems.
Some programs offer accelerated pacing. In such a program, you earn both a bachelor’s and master’s degree in five years. Other programs might offer a health policy specialization.
But no matter what degree pathway you take, your courses will cover many math and science topics.
Boston University The University of Texas at Austin

7. Chemical Engineering
You don’t have to narrow your interest in biology and chemistry to earn a degree in chemical engineering. In fact, this degree includes both subjects.
In a chemical engineering program, you study both biological and chemical processes. You take courses that explore topics in:
- Chemical engineering materials
- Chemical engineering processes
- Process design and operations
Most programs are math heavy. They require you take many advanced math classes in calculus and differential equations. But you also take a series of chemistry and physics courses.
You need a strong math and science background to do well in this program. In high school, plan on taking as many math and physics courses as you can. Your early planning will give you a strong foundation for your college classes.
When it’s time to apply to college, look for ABET-accredited programs. Employers favor this designation when hiring chemical engineers.
Kettering University University of North Dakota
8. Cognitive Psychology
Cognitive psychology teaches you how the human mind processes, stores, and recalls information. It is a major for thinkers because it prepares students to ask questions.
- How do humans learn, perceive, and behave?
- How do human feelings and behaviors influence the brain?
- How does the brain influence mental processes?
While learning how to answer these questions, you develop your problem-solving skills. You also become a critical thinker. You also work on your writing, as you research and draft papers.
Your classes cover many science and psychology topics. Some undergraduate programs offer standalone degrees or concentrations with a major in psychology. But with this concentration, you still take many neuroscience and cognitive science courses.
Graduate degrees in this discipline offer research-heavy classes. In a master’s degree program, you will choose a topic of interest and plan your own research. But you’ll also take foundational courses that build upon your undergraduate studies.
This major is for intellectuals who like to question current systems. As the field evolves, research drives new methods and ways of doing things. If you love to research and have a strong interest in how our brains work, cognitive psychology might be a good fit.
Eastern Kentucky University University of Virginia
9. Economics
Economics teaches you the principles related to monetary systems. It’s different than finance, which looks at the management of funds. Economics takes a broad look at how resources impact people, society, and location. It also looks at how distribution of those resources impacts us.
Because the major is interdisciplinary, you don’t only take econ courses. You study history, political science, sociology, and more.
There are two main branches of economics.
- Microeconomics
- Macroeconomics
Your studies as an econ major cover both branches. Microeconomics looks at the behavior of individuals, households, and organizations. Macroeconomics deals with economies at the regional, national, and even global levels.
You should expect to take both lectures and seminars. These different class styes let you approach subjects from various angles. Seminars allow you to ask questions, talk with your peers, and learn how to debate. Lectures give you information and theories to explore.
If you’re a thinker who enjoys solving problems and studying theory, economics could be what you’re looking for in a major.
The discipline has become more quantitative to give room to data analysis and market research. So, plan on taking statistics and math. Many students earn advanced degrees with hopes of becoming a professor or getting a consultant job.
University of Delaware Washington State University

10. English Literature
- British literature
- Modern drama
- The modern American novel
- Shakespeare
Maryville University University of New Hampshire
11. History/Archival Science
History is one of the largest departments on any college campus, due to its popularity as a major. It’s also a major for thinkers.
As a history or archival science major, you learn how to think, research, and write. You also learn how to focus your thoughts and write with clarity.
But because history is an interdisciplinary major, you have hundreds of courses you can take. You can also earn concentrations in different subjects. Popular history concentrations include:
- American history
- Asian history
- Global and transnational history
You can also earn pick up a second major or a minor in areas that relate to history. Popular minors include economics and political science.
No matter which focus-area you choose, your history major will work for you. And if you plan to go to graduate school or even law school, you can with a history degree. In fact, many lawyers working today have history degrees.
As society moves forward, we look at the past for answers. We evaluate what happened and where things went wrong. As a result, we need historians and archivists to help preserve knowledge of the past. By doing so, we learn how the past impacts the future.
National University Norwich University
12. Linguistics
- Anthropology
- Cognitive psychology
- Cognitive science
- Communication sciences
Portland State University University of Kentucky
13. Mathematical Sciences
Are you good with numbers? Love solving complicated problems?
If so, math might be the smartest degree to get. As a math major, you use your math skills to identify problems, find new theories, and come up with new and innovative ways to solve issues.
This major is for intellectuals who love research and problem-solving. But if that’s you, you’ve found you dream major. And if you’ve found your dream major, you might find your dream job.
As a math major, you collect data and perform research. You analyze numbers and statistics, then draw conclusions based on your findings.
Most mathematicians hold master’s degrees, but you can also find work with a bachelor’s degree. Career choices include:
- Actuary jobs
- Data collection analyst
- Data scientist
- Mathematical modeler
- Software engineer
- Statistician
Math isn’t for everyone. But if you’re a thinker who loves solving problems, the major can lead you to some intellectual careers .
Drexel University Indiana University East
14. Neuroscience
Augustana College Georgia Tech
15. Philosophy
Want to join the ranks of famous philosophy majors? This challenging major was the choice for many thinkers like:
- Comedian Stephen Colbert
- Former United States President Bill Clinton
- NBA legend Phil Jackson
- Professor and activist Noam Chomsky
As a philosophy major, you study questions that have no concrete answers. That’s part of the appeal of this major. But if you like pondering existential questions that have confused humankind for centuries, this major might suit you.
A philosophy program teaches you how to engage in arguments. It helps you debate issues and reason through them.
Your coursework covers topics like:
- Epistemology
- Metaphysics
- Symbolic logic
Your studies involve moral, ethical, and analytical issues. They also teach students how to reason through them.
Philosophy majors can combine their degree with other majors, such as economics and political science. Some programs offer concentrations that allow you to focus your studies on an area of interest.
When you graduate, you can go to law school or graduate school. Many philosophy majors go into academia. But to do this, you need a PhD in philosophy.
Arizona State University Thomas Edison State University

16. Physics
As a physics major, you learn how the seen and unseen natural world behaves through laws and processes in the universe. You also learn about matter, motion, space, and time.
If you’re STEM-bent and enjoy taking math and science courses, a physics major will improve your skills. But the academic rigor in this major is high. You take many challenging courses on your way to a bachelor’s degree.
Common courses include:
- Engineering
- General physics
You can also earn a specialization in a physics niche, such as astrophysics.
Career opportunities are vast with a physics degree. In fact, many graduates move into healthcare, engineering, and science careers.
But if you want to teach physics to college students, you will need a PhD in physics.
Case Western Reserve Oregon State University
17. Political Science
- American politics
- Environmental politics
- Global politics
- Foreign policy
Clemson University Penn State World Campus
18. Public Policy Analysis
Want to work in government or law? How about a job with a nonprofit? If so, a degree in public policy might be what you’re looking for in a career.
This degree prepares you with research skills and knowledge in the field. You explore topics in:
- Constitutional law and procedures
- Contemporary policy changes
- Public administration
You also learn how public speaking can benefit your career. You take communications and writing courses that improve your speaking abilities. You also learn how to lead in this field.
If you want to specialize, you can earn a concentration or take classes in areas of interest. Popular specializations include compliance, public leadership and management, and social policy. These specializations are a great way to explore your interests and career goals.
This is one of the smartest majors for people interested in government. Since the major relies heavily on research, it’s ideal for those who like to learn new things. You also get to question how systems work and develop policy for change.
Duke University Georgia Tech
19. Sociology
Sociology is for thinkers. If you like to learn about different aspects of social life, from small groups to large-scale populations, this major might suit you.
You cover important ideas related to socialization across life cycles. You also study social conflict and how it impacts most people.
In this major, you dig into social inequality. You also look at systems that affect crime rates. Your courses cover a wide range of topics. Common courses in a bachelor’s degree program include:
- Health and social welfare
- Mass media and popular culture
- Social identities
- Social inequalities
When you graduate, you can seek professional roles as sociologists. You can also take jobs as market research analysts or researchers. But most of these positions need a graduate degree.
Roosevelt University University of Massachusetts Global
20. Software Engineering
Software engineering teaches you how to design, develop, and maintain complex computer programs. The major is technical and requires a background in math and computers. It also requires strong critical thinking skills.
If you’re a thinker who loves to ponder complex puzzles, you might enjoy this major. It’s also ideal for those who want to learn more about software engineering.
As a student, you take classes that improve your software and engineering skills. You take both computer science and math classes, as well as engineering courses. These classes prepare you for work as a software engineer. But you can also qualify for other jobs, such as:
- Computer systems analyst
- Computer systems manager
- Software developer
- Web developer
The major is good for students with a math and science background and a love for computers. If you enjoy solving problems and thinking about challenging theories, you might love software engineering .
University of Michigan University of Texas at Dallas
Other Smart Majors for Intellectuals
Other majors that didn’t make the list but still lead to jobs for intellectuals include:
Because you need a strong background in science and math, you’ll find smart students majoring in chemistry. Chemistry requires data analysis, research, and strong math skills. You need to take measurements and perform lab work. But your hard work leads to good pay as a researcher or chemist.
- Foreign language
It’s not easy learning a foreign language, whether it’s French, Hindi, or Korean. To learn a new language in college takes hard work and discipline. You have to put in the time studying new vocabulary. You also have to read, write, and communicate in a new language.
But if you’re willing to start a new language from scratch, it will keep your mind sharp and stimulate your brain. Research shows that switching between languages causes certain parts of your brain to become more active. You process information quicker and filter it more efficiently.
Learning a new language also acts as a gateway to another culture. It opens doors (or excuses) to travel, as it makes it easier and more enjoyable.
Genetics is another science good for thinkers. As a genetics major, you take many science classes. You also take math and statistics courses. These classes require you to solve complex problems. You also learn how to analyze and research.
- Other science majors
Any science that requires you to conduct lab work and research is good for your brain. Researchers gather information and collect data. They interpret results based on their findings. They even come up with ways to improve future tests by evaluating where they went wrong. To carry out these tasks, you need to think and question.
Every science major uses the scientific method to gain knowledge. These steps allow you to ask a question about something you observe and to go through the process of drawing conclusions. Through research and tests, you determine results and outcomes.
But to go through the steps, you need to think, question, and wonder. A good scientist always asks questions.
What Major Should You Choose?
If you’re looking for intellectual careers, you’ll want to choose an intellectual major. But there are all sorts of degrees and careers that need creative and critical thinkers.
When you choose your undergraduate major, pay attention to your interests. You don’t want to spend four years studying a subject you hate.
There’s a reason why most colleges don’t require that you declare your major until your second year. If you can, spend your first few semesters exploring different subjects. This will give you time to uncover new interests or develop new passions. You might find out that you love learning a foreign language. You might also find out chemistry isn’t the science for you.
Related Resources:
- 30 Best Online Engineering Bachelor Degree Programs
- Top 30 Affordable Online Bachelor’s in Psychology
- Ultimate Guide to Liberal Arts Degrees and Careers
- Ultimate Guide to Science and Engineering Degrees and Careers
This concludes our list of the top 20 degrees for intellectuals.
Brenda Rufener Author
Julie McCaulley Expert
Carrie Sealey-Morris Editor-in-Chief

- Search Search Search …
- Search Search …
What is Non-Critical Thinking?

Think about the last time you had to take a stand on an important issue, or make a decision while not knowing all of the facts. How did you arrive at your position or choice? What was your thought process, and why do you believe you were right?
We all hope our opinions and choices are correct. However, sometimes our ideas are based on feelings or logical fallacies, rather than facts and solid reasoning—in other words, non-critical thinking.
Non-critical thinking can lead to poor choices, self-limiting beliefs, and (to be blunt) gullibility. You’ll be vulnerable to misinformation and manipulation, because you can’t think for yourself. Let’s look at what is non-critical thinking versus, and how you can break free from it.
Curiosity vs closed-mindedness
Critical thinkers recognize that an issue may be more complex than what it seems, and that there are different ways to look at it. That’s why they always gather facts and check the authenticity and authority of the source. They listen to other views, and fairly evaluate each side.
Non-critical thinkers choose a side, and select facts that support it. They may talk to others, but only to engage in debate (“proving I am right”) than dialogue (“listening, learning, and collaborating”).
That’s why the first step to critical thinking is to suspend judgment: don’t believe everything you’re told, or even everything you feel. Before you react, research.
Reasoning vs emotions
The Foundation of Critical Thinking says that critical thinking is an intellectual disciplined process that involves different reasoning skills, such as:
- Articulating the questions or issue in a clear way
- Gathering information by observation, experience, reflection, communication, or research
- Analyzing, synthesizing and evaluating the information
- Making a choice based on facts, or insight arrived from weighing different pros and cons
In contrast, non-critical thinking is based on emotions, peer or social pressure, tradition. When asked for reasons for their stand, they may say: “It’s always been this way!” or “This is what my heart tells me.”
They may even become emotional when they are asked to explain their side, i.e, becoming defensive or aggressive.
Being aware vs being confined by biases
Everyone has biases, and it is impossible to be 100% objective. We are influenced by our cultural and religious perspectives, personal values, childhood experiences, and the limitations of our knowledge.
Critical thinkers are aware of these biases. Thus, they are always reflecting: “Am I resisting a certain idea? What perspectives am I missing? What are motives for believing this to be true?” So even if they can’t escape all their biases, they can question them and make a rational choice.
Non-critical thinkers are not even aware of their biases, and actually think what they initially believe is a universal truth. This attitude prevents them from asking questions and accepting other viewpoints.
That is why the question “What is non-critical thinking?” can actually be a breakthrough. Once you’re aware that there may be flaws or limitations in your thinking process, you are already opening your mind to new possibilities.
Sound reasoning vs logical fallacies
Critical thinkers strive for clarity, accuracy, and fairness. They want to make sure that their ideas are based on facts and sound arguments.
Non-critical thinkers present arguments, but these may be riddled with logical fallacies. Examples of common fallacies are:
- Ad hominem. Personal attacks against the other person
- Appeal to force. Using threats, or inciting fear, to make the other person agree
- Genetic fallacy. Saying something is true (or false) because of its origin
- Appeal to tradition. Accepting a belief or behavior because people have always believed it or done it
- Argumentum ad Populum. Appeal to popular opinion, usually citing trends, influential people, or universal values such as patriotism
- Appeal to emotion. Inciting pity, sympathy, outrage, or other strong emotions
- Begging the question. Using claims or facts that have yet to be proven
- Hasty generalization. Saying one thing is true based on limited examples or evidence
- False cause. Claiming a cause-effect relationship that has not yet been proven
- Straw man. Disproving an argument by exaggerating or oversimplifying it
- Slippery slope. Saying if one thing will happen, the second or third thing will inevitably follow
There are many other logical fallacies that can emerge from non-critical thinking. Study them further in order to protect yourself from misinformation, or guard against fallacies in your own reasoning process.
What is the effect of non-critical thinking on my life?
The question ‘What is non-critical thinking?” is very important, because faulty reasoning abilities can have a huge impact on the rest of your life.
It can cause you to make dangerous errors in judgment—at work, and in your personal choices. It can lead to missed opportunities and misunderstandings. It can even hold back your career, because critical thinking is essential in management and leadership roles.
Rethink the way you think, and start learning how to develop your critical thinking skills.
Risks Associated with Weak Critical Thinkers
You may also like
Mastering Your Thought Process Using Critical Thinking Frameworks
People live their days dealing with all sorts of problems, from the awfully mundane to the considerably urgent. Oftentimes, a sound decision-making […]

What is historical thinking?
Historical thinking is something that more and more people are taking an interest in, but do you know what it really means? […]

Unleashing Your Creativity: Associative Thinking Techniques Explained
Creativity is a valuable asset in today’s world, and many people strive to unleash their creative potential. Associative thinking is a technique […]

Critical thinking vs Creative thinking
Both critical thinking and creative thinking are used for solving problems, only in different ways. For critical thinking, the process is structured […]
The top 15 non-technical skills you need to help land a high-paying job
- In addition to understanding technical skills and programming languages, there are plenty of non-technical skills that are important in advancing your career.
- We looked at the non-technical skills with the highest importance scores across the 28 highest-paying jobs in the US from the Occupational Information Network 's database.
- Critical thinking and active listening had the highest scores for these six-figure jobs.
- Visit Business Insider's homepage for more stories .

Not every skill needed to succeed in your job involves using fancy technology. You also need to be a critical thinker, be able to solve complex problems, and have good coordination skills, among other non-technical skills.
The Department of Labor's Occupational Information Network (O*NET) has a list of the varying importance scores of different skills for each occupation. Each occupation is given an importance score from one to five for each skill. Five is the the maximum score a skill can receive in each job.
Skills on O*NET are classified under six general categories: Basic skills, complex problem solving skills, resource management skills, social skills, systems skills, and technical skills. There are 36 detailed skills within these main categories, such as time management, mathematics, and active listening.
After recently finding the most popular technology skills listed on O*NET across the highest-paying jobs in the US , we decided to look at the most common non-technical skills in those jobs. To do this, we averaged the scores for each skill for 28 of the 30 highest-paying jobs. We excluded two jobs that were categorized as "all other" (undefined roles within dentist specialists, as well as the physician and ophthalmologist categories) because O*NET doesn't list scores for these broader occupation categories.
O*NET includes separate scores scores indicating both the importance of a skill and the level of proficiency needed in that skill for an occupation. O*NET uses the example of lawyers and paralegals where "lawyers (who frequently argue cases before judges and juries) are required to have a higher Level of speaking skill, while paralegals only need an average Level of this skill." For the purposes of our analysis, we focused on the importance score, rather than the level score.
Read on to find out the 15 most commonly required non-technical skills among the highest-paying jobs, along with their average scores. We also included each skill's definition from O*NET and the average annual salaries for the three jobs with the highest score in each skill. In the case of a tied score, we ranked the jobs with the highest average salaries as of May 2019, the most recent data available.
15. Systems analysis
According to O*NET , this systems skill is defined as determining how a system should work and how changes in conditions, operations, and the environment will affect outcomes.
Average O*NET score from the 28 highest-paying jobs: 3.23
The jobs with the highest scores for this skill:
1. Chief executives - $193,850
2. Sales managers - $141,690
3. Petroleum engineers - $156,780
14. Persuasion
According to O*NET , this social skill is defined as persuading others to change their minds or behavior.
Average O*NET score from the 28 highest-paying jobs: 3.26
3. Lawyers - $145,300
13. Service orientation
According to O*NET , this social skill is defined as actively looking for ways to help people.
Average O*NET score from the 28 highest-paying jobs: 3.33
1. Psychiatrists - $220,430
2. Family medicine physicians - $213,270
3. Nurse anesthetists - $181,040
12. Time management
According to O*NET , this resource management skill is defined as managing one's own time and the time of others.
Average O*NET score from the 28 highest-paying jobs: 3.48
2. General dentists - $178,260
11. Coordination
According to O*NET , this social skill is defined as adjusting actions in relation to others' actions.
Average O*NET score from the 28 highest-paying jobs: 3.50
2. Psychiatrists - $220,430
3. Sales managers - $141,690
10. Active learning
According to O*NET , this basic skill is defined as understanding the implications of new information for both current and future problem-solving and decision-making.
Average O*NET score from the 28 highest-paying jobs: 3.72
1. Obstetricians and gynecologists - $233,610
3. Chief executives - $193,850
8 (tie). Writing
According to O*NET , this basic skill is defined as communicating effectively in writing as appropriate for the needs of the audience.
Average O*NET score from the 28 highest-paying jobs: 3.73
3. Natural sciences managers - $145,450
8 (tie). Monitoring
According to O*NET , this basic skill is defined as assessing performance of yourself, other individuals, or organizations to make improvements or take corrective action.
Average O*NET score from the 28 highest-paying jobs: 3.73
1. Anesthesiologists - $261,730
2. Chief executives - $193,850
3. Psychiatrists - $220,430
7. Social perceptiveness
According to O*NET , this social skill is defined as being aware of others' reactions and understanding why they react as they do.
Average O*NET score from the 28 highest-paying jobs: 3.76
3. Public relations and fundraising managers - $132,630
6. Complex problem solving
According to O*NET , this complex problem solving skill is defined as identifying complex problems and reviewing related information to develop and evaluate options and implement solutions.
Average O*NET score from the 28 highest-paying jobs: 3.86
2. Surgeons - $252,040
3. Oral and maxillofacial surgeons - $237,570
5. Judgment and decision making
According to O*NET , this system skill is defined as considering the relative costs and benefits of potential actions to choose the most appropriate one.
Average O*NET score from the 28 highest-paying jobs: 3.92
3. Surgeons - $252,040
4. Reading comprehension
According to O*NET , this basic skill is defined as understanding written sentences and paragraphs in work related documents.
Average O*NET score from the 28 highest-paying jobs: 4.01
1. Lawyers - $145,300
2. Postsecondary law teachers - $129,950
3. Obstetricians and gynecologists - $233,610
3. Speaking
According to O*NET , this speaking skill is defined as talking to others to convey information effectively.
Average O*NET score from the 28 highest-paying jobs: 4.05
1 (tie). Active listening
According to O*NET , this basic skill is defined as giving full attention to what other people are saying, taking time to understand the points being made, asking questions as appropriate, and not interrupting at inappropriate times.
Average O*NET score from the 28 highest-paying jobs: 4.08
2. Lawyers - $145,300
3. Family medicine physicians - $213,270
1 (tie). Critical thinking
According to O*NET , this basic skill is defined as using logic and reasoning to identify the strengths and weaknesses of alternative solutions, conclusions or approaches to problems.
2. Obstetricians and gynecologists - $233,610
- Main content
Critical Thinking and Non-Critical Thinking: Key Differences
Have you ever asked yourself how to identify critical thinking? Knowing the differences between critical and non-critical thinking can help you understand the process of critical thinking and use it in your daily life. Critical thinking is a process of analyzing information and making decisions based on facts. While Non-critical thinking is a process where people make decisions based on intuition or opinion.
Sanju Pradeepa

Do you ever find yourself stuck in a rut of unproductive thinking? We’ve all been there. It can feel like it takes forever to break out of this cycle and make meaningful progress on a problem.
But what if you learned powerful tools for thinking more effectively and efficiently? Enter critical and non-critical thinking.
The key distinction between these two forms of thinking is that while non-critical thinking evaluates data at face value, critical thinking goes beyond the surface level to ask “why” and “how” questions that help make better decisions. Critical thinkers also examine their own biases and assumptions and look at situations from different perspectives before arriving at a conclusion.
Good news: you’ve come to the right place. In this article, I’m going to explain the difference between critical thinking and non-critical thinking and how each type of thinking can help us make sound choices in our lives. We’ll also explore why critical thinking can lead to better decision-making, so you can make the most informed decisions for yourself possible.
Table of Contents
What is critical thinking.
At its core, critical thinking involves carefully analyzing and evaluating information to make well-reasoned decisions. It can be used to assess an idea, a plan of action, a process, or an argument. It involves asking questions and looking for solutions to problems.
Characteristics of critical thinking include:
- Openness: Being open to new ideas and perspectives without prejudice or preconceived notions
- Objectivity: Being able to consider opposing points of view objectively and rationally
- Flexibility: Being able to adapt quickly in response to new information or changing situations
- Accuracy: making sure that facts are accurate and detailed before taking action.
- Insightfulness: Being able to draw connections between seemingly unrelated concepts and recognize patterns in complex matters
Ultimately, critical thinking is an invaluable skill that can help you make more informed decisions in all areas of life, both personal and professional.
To Learn more – 7 Types of Critical Thinking: A Guide to Analyzing Problems
What is non-critical thinking?
Non-critical thinking is a method of considering new ideas without any sort of evaluation or judgment. It’s a form of open learning where you are just absorbing information without trying to interpret it or break it down into its separate components. You simply take what’s presented to you as it is, without questioning or doubting it.
Typically, non-critical thinkers rely heavily on intuition and emotion to make decisions. As opposed to critical thinking, there is no attempt made at problem-solving, and any sort of hypothesis testing is avoided.
Some common characteristics of non-critical thinking include:
- Being easily influenced by the opinions and ideas of others
- Judging people quickly and not considering all perspectives
- Focusing on immediate solutions that don’t address root causes
- allowing your beliefs to cloud your judgment
The Differences Between Critical and Non-Critical Thinking

Critical thinking is a must-have skill in the modern world. It’s not just about passing exams; it’s about taking a well-thought-out approach that gets you to the root cause of an issue . On the other hand, non-critical thinking is more surface level, a kind of “snap judgment” that doesn’t take into account the big picture .
- The level of focus each requires.
When deciding between critical thinking and non-critical thinking, one clear difference is the level of focus each requires . Non-critical thinking is more focused on gathering information and facts without any real need to focus on the implications of that information. On the other hand, critical thinking involves a much deeper analysis of the data and its implications.
2. The level of analysis each type of thinking calls for
Another key difference is the level of analysis each type of thinking calls for . Non-critical thinking tends to take a surface-level look at data without really looking at it from all angles. Critical thinking, however, requires you to dig deeper into the data. You have to make sure you understand all sides of an issue before you reach a conclusion.
Real-life examples of critical thinking in action include debating political issues, researching medical treatments, or even discussing how past experiences might influence future decisions. In order to engage in meaningful critical thought, you must be willing to question assumptions, explore ideas from different angles, and use evidence to construct arguments that take multiple perspectives into account.
In short, while non-critical thinkers collect surface-level facts with no real analysis or questioning necessary, critical thinkers take a much deeper dive into data in order to find new insights and draw meaningful conclusions.
By understanding the difference between critical and non-critical thinking, evaluating assumptions, and slowing down during decision-making processes, you can develop better critical thinking skills that will enable you to make smarter decisions in the future.
Benefits of Critical Thinking in Everyday Life

When it comes down to it, developing your critical thinking skills has many advantages. So, what are some of the benefits of critical thinking ?
- ability to make decisions based on facts and evidence rather than personal biases or opinions
- It allows you to analyze a situation from multiple angles.
- Understanding complex topics quickly
- Greater clarity during decision-making processes
- able to construct arguments effectively.
- Improved communication skills
- enables you to look past potential biases and make informed decisions based on logic, facts, and reliable sources.
- It also provides more avenues for innovation and creative problem-solving.
By contrast, non-critical thinking limits your perspective on any given problem. It also tends to be quite binary black or white, good or bad whereas critical thinkers understand that the truth often lies somewhere in between. The result is often a much broader range of solutions than what could be achieved through non-critical thinking alone.
Enhancing your ability for critical thinking

If you want to improve your critical thinking skills, you should start by understanding the difference between critical and non-critical thinking. Non-critical thinking is simply “thinking without criticism.” It involves making decisions based on assumptions or ideas without questioning them. On the other hand, critical thinking involves careful consideration of different perspectives and examining evidence from multiple sources before making a decision; it’s the opposite of just taking things at face value.
So how can you become a better critical thinker? Here are some tips you can use to strengthen your critical thinking skills: Here are a few:
1. Formulate your own opinion.
Before making an opinion on any given matter, take the time to research the different perspectives and form your own judgment. This will help you become more aware of possible cognitive biases that could lead to misinterpretations of facts or events.
2. Question assumptions
Take the time to question any assumptions you’ve made about a situation. For example, if you think that buying a certain product is the only solution to a problem, ask yourself why. Is it really the most effective solution? Doing this will help you evaluate ideas and see if there is any other way of approaching the subject that is more beneficial in the long run.
3. Develop creative solutions.
When facing a challenge, step out of your comfort zone and try to come up with creative solutions to solve it. A creative approach is often better than strictly relying on previous experience, as it encourages outside-the-box thinking and allows for new possibilities to arise.
4. Do not jump to conclusions.
It’s important not to allow our experiences or emotions to shape our opinions or decisions without first analyzing the facts. Before making a conclusion about something, it’s essential to simply stop, think, and reflect on your thought process so that emotion does not overrule rationality. Doing this allows us to make informed decisions, which often lead to better outcomes in the long run.
5. Slow down and promote critical thinking.
Take your time while making decisions rushing to conclusions can lead to misinformed decisions that have unintended consequences down the road. Instead, slow down and encourage others to think critically by asking questions, evaluating data, and challenging ideas so that all perspectives are taken into account when making informed decisions.
6. Evaluate your assumptions and reasons.
Start by taking a step back to evaluate your underlying assumptions and reasons for believing something. Question why you think something is true or right, and consider other possible explanations or perspectives. This will help you assess your information more objectively and weigh more options before concluding.
Practical Exercises to Develop Critical Thinking Abilities

If improving your critical thinking skills is a goal of yours there are a few simple practical exercises you can do to help develop them.
One great place to start is by examining your own beliefs , especially ones that you may have taken for granted.
Take some time to analyze why you hold certain beliefs and assess the evidence that supports them. Consider how you come to conclusions, and be prepared to challenge even your own opinion by looking at it from different angles. Ultimately, this exercise should help you understand how thinking critically can lead to more balanced judgments.
Another exercise you can use involves the scientific method: gather background information, form hypotheses based on those observations, test those hypotheses with experiments, record and analyze data, then draw possible conclusions, and finally communicate results.
By following these steps over and over again in real-life scenarios, you’ll soon learn what it means to think critically. This will not only help in situations that require problem-solving but also give you more of an analytical mindset in daily life, one where reasoning and logic come before emotion or impulse decisions.
In conclusion, the difference between critical thinking and non-critical thinking can be a difficult concept to grasp but understanding it can be invaluable to making better decisions and forming effective strategies. Critical thinking requires us to be open to the possibility of change and to accept the fact that not everything is as it seems at first glance. Non-critical thinking, on the other hand, can lead us to become entrenched in our beliefs and to reject new information, even if it could potentially benefit us. With practice, we can learn to separate the two and make more informed decisions.
- What is the difference between critical and non critical thinking by Answers Team published in Answers.com https://www.answers.com/
- C ritical Thinking vs. Non-Critical Thinking by SUSIE ZAPPIA published in Classroom (https://classroom.synonym.com/)
Call to Action
If you enjoyed this blog post and want to learn more about the topic, don’t forget to subscribe to our newsletter and follow us on social media. You’ll be part of a community of like-minded people who share your interests and passions. So what are you waiting for? Join us today and start your journey of learning and discovery!

Let’s boost your self-growth with Believe in Mind.
Interested in self-reflection tips, learning hacks, and knowing ways to calm down your mind? We offer you the best content which you have been looking for.
Follow Me on
You May Like Also
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Career Advice
- Job Search & Interview
- Productivity
- Public Speaking and Presentation
- Social & Interpersonal Skills
- Professional Development
- Remote Work
Eggcellent Work
25 in-demand jobs that require critical thinking and problem-solving skills .
One of the most important competencies employers seek for a new hire is critical thinking/problem solving. According to a NACE job outlook survey, employers found their new hires were actually more proficient in competencies other than critical thinking in jobs that require problem solving.
Survey respondents rated the importance of critical thinking/problem solving as 4.62 on a scale of 5, with teamwork and professionalism ranking second and third at 4.556 and 4.46 respectively.
As a percentage, 99.2% of employers surveyed considered critical thinking as an essential skill, but rated just over half (55.8%) of their employees as proficient.
To become more proficient in critical thinking , here’s some advice on Indeed.com and other resources :
- Only accept new information after evaluating it thoroughly. Focus on primary sources and look for objective, quantifiable truth.
- In considering the source and any underlying agendas and biases/motivation that may be at the foundation.
- Ask the right questions , and know what kind of answers you are looking for.
- Learn the art of active listening with eye contact and appropriate body language.
- Save your follow-up questions for when the speaker is finished, and say thanks for the speaker’s time and attention.
- The Ultimate Guide To Critical Thinking
- Is Critical Thinking A Soft Skill Or Hard Skill?
- 5 Creative and Critical Thinking Examples In Workplace
- 10 Best Books On Critical Thinking And Problem Solving
- 12 Common Barriers To Critical Thinking (And How To Overcome Them)
Table of Contents
Applying for jobs that require critical and creative thinking
So, when applying for jobs that require critical thinking and problem-solving skills, your résumé and cover letter should highlight the following:
- Your observation skills—Observation skills are important to critical thinking, because observation is the way you receive and objectively process information.
- How well you can evaluate and analyze—That includes your skill to review information and draw educated inferences through technical review.
- How well you communicate—When you can clearly communicate your strategies and ideas, you can perform better at your job and strengthen your team.
- Your problem-solving skills—When you can objectively identify a problem or issue, you can arrive at solutions and outcomes.
So, with critical thinking and problem-solving skills, you will be in high demand in the post-pandemic economic recovery. There are thousands of jobs out there, and most require critical thinkers, who are ready to embark on a fulfilling career with great pay and opportunities for growth and advancement.
Read More: How To List Skills That I Taught Myself On Resume
A sampling of 25 jobs that require critical thinking and problem solving
The following is a sampling of jobs that require critical thinking listed in the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics Occupational Outlook Handbook :
In-Demand Jobs that require critical thinking that have undergone “much faster than average” growth rate (The average rate of growth for all occupations is 8%):
Nurse practitioners.
Number of jobs projected through 2030/percent growth from 2020: 393,300/45%
Entry-level education required: Master’s Degree
2021 Median pay: $123,780
Critical thinking skill for nurse practitioners: Working in a variety of healthcare settings, nurse practitioners provide a full range of health care in settings from hospital wards to local clinics. This is one of those high-stress jobs that require critical thinking.
Home health and personal care aides
Number of jobs projected through 2030/percent growth from 2020: 4,600,600/33%
Entry-level education required: High school diploma or equivalent
2021 Median pay: $29,430
Critical thinking skill for home health and personal care aides: Monitor the health condition of people with chronic illness or disabilities and assist them with their daily activities.
Statisticians
Number of jobs projected through 2030/percent growth from 2020: 59,800/33%.
2021 Median pay: $95,280
Critical thinking skill for statisticians: Analyze data and use computational techniques to solve problems. This is another one of the low-stress jobs for problem solvers.
Logisticians
Number of jobs projected through 2030/percent growth from 2020: 247,400/30%
Entry-level education required: Bachelor’s Degree
2021 Median pay: $77,030
Critical thinking skill for logisticians: Analyze, coordinate, and suggest improvements in an organization’s supply chain. This is an example of a group of low-stress jobs for problem solvers.
T our and travel guides
Number of jobs projected through 2030/percent growth from 2020: 56,800/29%
Entry-level education required: High School Diploma or Equivalent
2021 Median pay: $29,780
Critical thinking skill for tour and travel guides: Plan, organize, and arrange tailored vacation plans and sightseeing tours for clients.
Coaches and scouts
Number of jobs projected through 2030/percent growth from 2020: 313,800/26%
2021 Median pay: $38,970
Critical thinking skill for coaches and scouts: Evaluate and teach amateur or pro athletes the skills they need to succeed and improve on past team performance.
Number of jobs projected through 2030/percent growth from 2020: 34,500/24%
2021 Median Pay: $105,900
Critical thinking skill for actuaries: Use math and statistics to analyze risks and economic costs. Put this job in the category of best jobs for over-thinkers.
Substance abuse, behavioral disorder, and mental health counselors
Number of jobs projected through 2030/percent growth from 2020: 402,600/23%
2021 Median pay: $48,520
Critical thinking skill for substance abuse counselors: Diagnose substance abuse, behavioral disorders, and mental health problems and counsel patients accordingly.
Athletic trainers
Number of jobs projected through 2030/percent growth from 2020: 37,000/23%
2021 Median pay: $498,420
Critical thinking skill for athletic trainers: Prevent, diagnose, and treat muscle and bone injuries and illnesses.
Software developers and software quality assurance analysts and testers
Number of jobs projected through 2030/percent growth from 2020: 2,257,400/22%
2021 Median pay: $110,140
Critical thinking skill for software developers, etc.: Identify problems with software applications and report/correct defects.
Phlebotomists
Number of jobs projected through 2030/percent growth from 2020: 158,400/22%
Entry-level education required: Postsecondary nondegree
2021 Median pay: $37,800
Critical thinking skill for phlebotomists: Draw blood from patients with attention to detail and empathy towards patients who may be uncomfortable.
Broadcast technicians
Number of jobs projected through 2030/percent growth from 2020: 168,300/21%
Entry-level education required: Associates Degree
2021 Median pay: $49,050
Critical thinking skill for broadcast technicians: Set up, operate, maintain, and troubleshoot equipment for media programs .
Market research analysts and marketing specialists
Number of jobs projected through 2030/percent growth from 2020: 904,500/22%
2021 Median pay: $63,920
Critical thinking skill for market research analysts: Study market conditions and examine potential sales and service opportunities and upgrades.
Preschool teachers, except special education
Number of jobs projected through 2030/percent growth from 2020: 556,000/18%
Entry-level education required: Associates and Bachelor’s Degrees
2021 Median pay: $30,210
Critical thinking skill for preschool teachers: Attend to the needs of younger children prior to their entering kindergarten.
Social and human service assistants
Number of jobs projected through 2030/percent growth from 2020: 487,100/17%
Entry-level education required: High School Diploma or equivalent
2021 Median pay: $37,610
Critical thinking skill for social and human service assistants: Provide clients with tailored services to assist people in therapy or rehabilitation settings.
Financial managers
Number of jobs projected through 2030/percent growth from 2020: 799,900/17%
2021 Median pay: $131,710
Critical thinking skill for financial managers: Create detailed financial reports and plan for the organization’s long-term financial goals.
Audiologists
Number of jobs projected through 2030/percent growth from 2020: 15,800/16%
Entry-level education required: Doctoral or professional Degree
Number of jobs projected through 2030
2021 Median pay: $78,950
Critical thinking skill for audiologists: Diagnose, manage, and treat patients experiencing hearing and balance problems.
In-Demand Jobs with a “faster than average” growth rate and jobs that require creativity and problem solving
Veterinarians.
Number of jobs projected through 2030/percent growth from 2020: 101,300/17%
Entry-level education required: Doctoral or professional degree
2021 Median pay: $100,370
Critical thinking skills for veterinarians: diagnose, treat, and provide care for animals.
The foregoing is but a sample of high-demand jobs that require critical thinking. In fact, most jobs that require critical thinking and problem solving are in high demand.
Management analysts
Number of jobs projected through 2030/percent growth from 2020: 1,032,000/14%
Entry-level education required: Bachelor’s degree
2021 Median pay: $93,000
Critical thinking skill for management analysts: Recommend ways for an organization to improve its operation and efficiency.
Education administrators, all other
Number of jobs projected through 2030/percent growth from 2020: 56,900/13%
2021 Median pay: $90,560
Critical thinking skill for education administrators: Manage, administer, and prepare budgets and education syllabi in a variety of educational settings.
Postsecondary Teachers
Number of jobs projected through 2030/percent growth from 2020: 1,433,600/12%
Entry-level education required: Master’s Degree or Ph.D.
2021 Median pay: $79,640
Critical thinking skill for postsecondary teachers: Prepare class syllabi and lesson plans with assessment methods to test student learning.
Aircraft mechanics and service technicians
Number of jobs projected through 2030/percent growth from 2020: 168,700/11%
Entry-level education required: On-the-job training and FAA approved technician training programs.
2021 Median pay: $65,550
Critical thinking skill for aircraft mechanics: Troubleshoot, repair, and perform scheduled maintenance on aircraft engines and supporting equipment.
Computer and information systems managers
Number of jobs projected through 2030/percent growth from 2020: 534,700/11%
2021 Median pay: $159,010
Critical thinking skill for computer systems manager: Plan, coordinate, and oversee IT related activities in a variety of organizations.
Construction managers
Number of jobs projected through 2030/percent growth from 2020: 499,400/11%
2021 Median pay: $98,890
Critical thinking skill for construction managers: Coordinate, plan, budget, and oversee construction projects from inception to completion.
Dietitians and nutritionists
Number of jobs projected through 2030/percent growth from 2020: 73,000/11%
2021 Median pay: $61,650
Critical thinking skill for dietitians: Plan and implement food service and nutritional programs in a variety of settings .
- How To Promote Critical Thinking In The Workplace
- Critical Thinking vs Problem Solving: What’s the Difference?
- What Is The Role Of Communication In Critical Thinking?
- Brainstorming: Techniques Used To Boost Critical Thinking and Creativity
- 11 Principles Of Critical Thinking
- 21 High-paying Jobs Nobody Wants
- The Truth About Working in Finance (And the Common Misconceptions)
Jenny Palmer
Founder of Eggcellentwork.com. With over 20 years of experience in HR and various roles in corporate world, Jenny shares tips and advice to help professionals advance in their careers. Her blog is a go-to resource for anyone looking to improve their skills, land their dream job, or make a career change.
Further Reading...

Ditching the 9 to 5 to Work on the Beach Seems Amazing! Is It Too Good to be True?

65 Questions To Ask Executives At Town Hall Meetings in 2024

How to Decline a Promotion Due to Salary the Right Way (With Samples)
No comments, leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Is Critical Thinking Overrated? Disadvantages Of Critical Thinking
Brainstorming: techniques used to boost critical thinking and creativity .

28 Jobs For Critical Thinkers (Logic Lovers’ Lane)
Are you a master of analytical mind games? Love questioning facts, challenging assumptions and solving complex problems?
Then, you’re on the right page!
Today, we’re exploring a list of ideal jobs for critical thinkers.
From data analysts to strategic planners. Each one, is a perfect match for those who thrive on intellectual stimulation and logical reasoning.
Imagine spending your days immersed in thought-provoking tasks, examining problems from every angle.
Intriguing, isn’t it?
So, grab your thinking cap.
And get ready to discover your ideal profession tasking your critical thinking skills!
Data Analyst
Average Salary: $60,000 – $85,000 per year
Data Analysts interpret data and turn it into information which can offer ways to improve a business, thus affecting business decisions.
This role is ideal for critical thinkers who enjoy analyzing data patterns, statistics, and trends to provide actionable insights.
Job Duties:
- Collecting Data : Gather various forms of data from multiple sources, ensuring that it is accurate and relevant to the business’s needs.
- Analyzing Data : Use statistical tools to interpret data sets, paying particular attention to trends and patterns that could be valuable for diagnostic and predictive analytics.
- Reporting Findings : Create reports and dashboards that effectively communicate trends, patterns, and predictions using relevant data.
- Collaborating with Stakeholders : Work closely with management to prioritize business and information needs.
- Identifying Process Improvement : Look for opportunities to increase efficiency and automation of data collection and analysis processes.
- Staying Informed : Keep up to date with the latest data analysis methods, tools, and best practices.
Requirements:
- Educational Background : A Bachelor’s degree in Data Science, Statistics, Computer Science, or a related field is highly preferred.
- Analytical Skills : Strong analytical skills with the ability to collect, organize, analyze, and disseminate significant amounts of information with attention to detail and accuracy.
- Technical Proficiency : Proficiency in data analysis tools (such as SQL, R, Python) and data visualization platforms (like Tableau, PowerBI).
- Problem-Solving : Ability to approach complex issues with a critical, objective analysis and come up with intelligent solutions.
- Communication Skills : Excellent written and verbal communication skills to translate complex data into actionable insights for non-technical stakeholders.
Career Path and Growth :
As a Data Analyst, you have the opportunity to make significant contributions to a company’s strategy and direction by providing data-driven insights.
With experience, you can advance to roles such as Senior Data Analyst, Data Scientist, or Analytics Manager, leading larger projects and teams, and influencing decision-making at the highest levels.
Average Salary: $60,000 – $160,000 per year
Lawyers are legal professionals who represent clients in legal matters, providing advice, drafting legal documents, and advocating on their behalf in court.
This role is ideal for critical thinkers who enjoy analyzing complex information, constructing arguments, and navigating the intricacies of the legal system.
- Legal Representation : Represent clients in civil or criminal proceedings, presenting evidence and arguing in court to support their case.
- Legal Research : Conduct thorough research on relevant laws, regulations, and legal precedents to inform case strategy and ensure compliance.
- Document Drafting : Prepare legal documents such as contracts, wills, and pleadings, ensuring accuracy and adherence to legal formalities.
- Client Advising : Provide clients with informed legal advice, helping them understand their rights, obligations, and the potential consequences of their actions.
- Negotiation and Mediation : Engage in negotiations to settle disputes and represent clients in mediation or arbitration sessions.
- Continuing Education : Stay updated with changes in laws and legal processes, as well as develop expertise in specialized areas of law.
- Educational Background : A Juris Doctor (JD) degree from an accredited law school is required.
- Bar Exam : Successful passage of the state bar examination where practice is intended.
- Analytical Skills : Ability to interpret complex legal information and craft logical, persuasive arguments.
- Communication Skills : Strong written and verbal communication skills for drafting documents and presenting cases.
- Attention to Detail : Meticulous attention to detail to avoid critical mistakes in legal proceedings and documentation.
- Client Service : Commitment to providing excellent service to clients, including confidentiality and ethical conduct.
A legal career offers diverse opportunities for specialization and advancement.
Lawyers can become subject matter experts in fields such as criminal law, corporate law, or environmental law.
With experience, they may rise to senior positions in law firms, become judges, or transition into legal consultancy roles.
Continuous professional development is essential for career progression and staying relevant in the dynamic field of law.
Software Developer
Average Salary: $70,000 – $120,000 per year
Software Developers are the creative minds behind computer programs and applications.
They design, build, test, and maintain software systems that run on various devices.
This role is ideal for critical thinkers who enjoy solving complex problems and creating innovative solutions in the realm of technology.
- Designing and Implementing Software : Develop software solutions by studying information needs, system flow, data usage, and work processes.
- Testing and Debugging : Conduct continuous testing of software to ensure that it is functioning correctly and efficiently, fixing bugs where necessary.
- Documenting Software Functionality : Maintain clear documentation for reference and reporting purposes, explaining the operation of the software to non-technical stakeholders.
- Improving Existing Software : Analyze and improve existing software systems to enhance performance, add new features, or make them more user-friendly.
- Collaborating with Team Members : Work with other developers, designers, and product managers to create cohesive and effective software products.
- Staying Up-to-Date : Keep current with the latest developments in software development technology and practices to ensure the creation of cutting-edge solutions.
- Educational Background : A Bachelor’s degree in Computer Science, Software Engineering, or a related field is often required.
- Technical Skills : Proficiency in one or more programming languages, such as Java, C++, Python, or JavaScript.
- Problem-Solving Skills : Strong analytical abilities and a logical approach to addressing software issues and challenges.
- Attention to Detail : The ability to meticulously examine code and design details, ensuring the quality and reliability of software products.
- Teamwork : Comfort with collaboration and the ability to work effectively as part of a cross-functional team.
- Adaptability : The capability to learn and apply new technologies quickly and to adapt to evolving project requirements.
Software Developers have numerous opportunities for career advancement.
With experience, they can move into senior developer roles, software architecture, project management, or specialize in areas such as artificial intelligence or cybersecurity.
The ever-growing tech industry offers continuous learning and the potential to work on groundbreaking projects that shape the way we live and work.
Management Consultant
Average Salary: $75,000 – $150,000 per year
Management Consultants analyze and solve complex problems within organizations, offering strategic advice to improve efficiency, performance, and profitability.
This role is ideal for critical thinkers who excel in analyzing data, understanding business dynamics, and crafting innovative solutions.
- Problem Solving : Identify organizational issues and propose strategic solutions to enhance business performance.
- Conducting Research and Analysis : Gather and analyze data to understand business trends and challenges.
- Client Interaction : Work closely with clients to understand their business needs and to provide tailored advice.
- Developing Business Strategies : Create actionable plans to drive change and improve efficiency within client organizations.
- Change Management : Assist clients in implementing recommended strategies and managing the transition process.
- Staying Informed : Continuously update knowledge on business methodologies, market trends, and industry best practices.
- Educational Background : A Bachelor’s degree in Business Administration, Economics, Finance, Management, or a related field is often required; an MBA or equivalent may be preferred.
- Analytical Skills : Strong ability to analyze financial reports, market data, and business processes.
- Communication Skills : Excellent verbal and written communication skills, with the ability to present complex information clearly and persuasively.
- Strategic Thinking : Adept at strategic planning and thinking critically about a wide range of business issues.
- Adaptability : Flexibility to work with different industries and adapt strategies to various business environments.
Management Consultants have a clear trajectory for career advancement, often starting as analysts before moving into senior consultant roles.
With experience and a proven track record, they can transition to roles such as Project Manager, Practice Area Specialist, or Partner within a consultancy firm.
There are also opportunities to move into executive management roles within client organizations or to start one’s own consulting business.
Intelligence Analyst
Average Salary: $60,000 – $90,000 per year
Intelligence Analysts are responsible for collecting, analyzing, and interpreting large amounts of data to help inform strategic decisions in various sectors such as national security, law enforcement, and cybersecurity.
This role is ideal for critical thinkers who enjoy delving into complex data, recognizing patterns, and deriving meaningful insights to protect and advance national and global interests.
- Collecting Information : Gather data from multiple sources, including surveillance activities, satellite images, and intercepted communications.
- Analyzing Data : Use analytical methods and software to interpret information, identify trends, and forecast potential threats or outcomes.
- Preparing Reports : Compile findings into comprehensive reports and briefings for decision-makers, outlining risks, opportunities, and recommendations.
- Collaborating with Teams : Work closely with other intelligence professionals, law enforcement, and military personnel to support broader intelligence goals.
- Monitoring Developments : Keep abreast of global events, emerging technologies, and changes in political or social landscapes that could impact security.
- Protecting Information : Ensure the integrity and confidentiality of intelligence data through strict adherence to security protocols.
- Educational Background : A Bachelor’s or Master’s degree in Political Science, International Relations, Security Studies, or a related field is often required.
- Analytical Skills : Strong analytical abilities with an aptitude for critical thinking and problem-solving.
- Attention to Detail : Keen observation skills to detect subtle changes or hidden patterns within complex data sets.
- Communication Skills : Excellent written and verbal communication skills to convey findings clearly and effectively.
- Technical Proficiency : Familiarity with intelligence databases, analytical software, and various research methodologies.
- Security Clearance : Ability to obtain and maintain the necessary security clearance for handling sensitive information.
Intelligence Analysts play a crucial role in shaping security strategies and policies.
With experience, they can advance to senior analyst positions, specialize in particular forms of intelligence, or take on leadership roles within intelligence agencies or private sector firms.
Their critical thinking skills make them invaluable assets in the ever-evolving landscape of global security.
Research Scientist
Average Salary: $70,000 – $100,000 per year
Research Scientists conduct experiments and studies in various scientific fields, such as biology, chemistry, physics, and environmental science, contributing to the advancement of knowledge and technology.
This role is perfect for critical thinkers who enjoy delving into complex problems and seeking evidence-based solutions.
- Designing Experiments : Develop and conduct scientific experiments to test hypotheses and analyze results.
- Collecting and Analyzing Data : Gather data through observation, experiments, or simulations, and use statistical methods to analyze the information.
- Publishing Findings : Write research papers and reports to share findings with the scientific community and the public.
- Applying for Grants : Secure funding for research projects by writing and submitting grant proposals.
- Collaborating with Others : Work with other scientists, both within and across disciplines, to combine expertise and resources.
- Staying Current : Keep up to date with the latest research and developments in your field to inform your work and maintain relevance.
- Educational Background : A Ph.D. in a relevant scientific discipline is typically required, though a Master’s degree may suffice for some positions.
- Analytical Skills : Strong ability to think critically, solve complex problems, and make data-driven decisions.
- Research Experience : Proven experience with scientific research, including designing experiments and publishing results.
- Communication Skills : Excellent written and verbal communication skills for presenting research findings and collaborating with other professionals.
- Technical Proficiency : Familiarity with laboratory equipment, computer software, and statistical analysis tools relevant to the field of study.
Research Scientists have the opportunity to contribute significantly to scientific knowledge and societal advancement.
With experience, they can advance to lead research projects, become principal investigators, or transition into academic positions such as professors.
Additionally, they may move into industry roles, applying their research skills to develop new technologies or products.
Financial Analyst
Financial Analysts are responsible for evaluating financial data, developing forecasts, and advising organizations on future financial decisions and strategies.
This role is perfect for critical thinkers who enjoy analyzing data, uncovering trends, and providing actionable insights to optimize financial performance.
- Financial Data Analysis : Interpret data on past financial performance to forecast future outcomes and identify potential risks and opportunities.
- Creating Financial Models : Develop complex models that help in financial planning and decision-making processes.
- Advising on Investment Strategies : Provide recommendations on investment portfolios, capital allocation, and asset management.
- Preparing Reports : Generate detailed reports that summarize financial research and analysis for internal and external stakeholders.
- Monitoring Economic Trends : Keep a close eye on market trends and economic indicators that may impact the organization’s financial strategy.
- Collaborating with Teams : Work with various departments to gather financial data and align financial strategies with overall business objectives.
- Educational Background : A Bachelor’s degree in Finance, Economics, Accounting, Business Administration, or a related field is required. A Master’s degree or professional certifications like CFA or CPA are often preferred.
- Analytical Skills : Strong quantitative skills and the ability to interpret financial data and create meaningful reports.
- Attention to Detail : Meticulous attention to detail to ensure the accuracy of financial analyses and projections.
- Communication Skills : Excellent verbal and written communication skills to effectively convey financial information and recommendations.
- Technical Proficiency : Proficiency in financial software, databases, and MS Excel. Familiarity with data analysis tools is a plus.
- Problem-Solving : Ability to approach complex financial issues with logic and creativity to find effective solutions.
Financial Analysts have a clear pathway for career advancement.
Entry-level analysts can progress to senior analyst roles, specialize in certain financial sectors, or move into managerial positions overseeing financial departments.
With a combination of experience, continued education, and professional certifications, analysts can ascend to high-level positions such as Finance Manager, Director of Finance, or Chief Financial Officer (CFO).
There are also opportunities to transition into investment banking, private equity, or portfolio management for those seeking a challenge in different financial landscapes.
Forensic Accountant
Forensic Accountants play a critical role in investigating financial discrepancies, fraud, embezzlement, and other white-collar crimes.
This role is ideal for critical thinkers who enjoy applying their analytical skills to unravel complex financial puzzles and ensure legal financial practices.
- Financial Investigation : Examine financial records to identify irregularities and potential evidence of illegal financial activity.
- Litigation Support : Provide assistance in legal cases, preparing reports and presenting findings that may serve as evidence in court.
- Fraud Detection : Utilize accounting and auditing skills to detect signs of fraud and embezzlement within an organization.
- Data Analysis : Analyze financial data using specialized software to identify patterns and anomalies that suggest misconduct.
- Expert Testimony : Serve as an expert witness in court, explaining complex financial information in a way that is understandable to judges and juries.
- Continuing Education : Stay abreast of the latest accounting practices, legal standards, and technologies used in forensic accounting.
- Educational Background : A Bachelor’s or Master’s degree in Accounting, Forensic Accounting, Finance, or a related field is essential, along with certifications such as Certified Public Accountant (CPA) or Certified Fraud Examiner (CFE).
- Analytical Skills : Exceptional ability to scrutinize detailed financial statements and data for accuracy and signs of malfeasance.
- Attention to Detail : A meticulous approach to work, with a focus on precision and thoroughness in financial investigations.
- Communication Skills : Strong verbal and written communication skills, necessary for reporting findings and providing testimony.
- Integrity : High ethical standards and professionalism to handle sensitive financial information responsibly.
- Problem-Solving : Adept at problem-solving and critical thinking to navigate complex financial cases and uncover the truth.
Forensic Accountants begin their careers in entry-level positions within accounting firms, law enforcement agencies, or legal firms.
With experience, they can advance to senior roles, leading investigations or specialized departments.
The rise of financial crimes and the increasing complexity of the financial landscape ensure a steady demand for skilled forensic accountants with opportunities for career advancement and specialization.
Operations Research Analyst
Operations Research Analysts apply advanced analytical methods to help organizations solve complex problems and make better decisions.
This role is ideal for critical thinkers who enjoy using their analytical skills to optimize processes and improve efficiency across various industries.
- Data Analysis : Use statistical analysis and mathematical modeling to analyze data and solve operational problems.
- Optimization : Develop and apply optimization algorithms for resource allocation, scheduling, logistics, and other operational areas.
- Decision Support : Provide recommendations to management based on quantitative analysis to inform policy and strategic decisions.
- Simulation Modeling : Create simulations to predict the impact of changes in the operating environment or to evaluate different scenarios.
- Project Management : Lead and collaborate on projects that require systematic analysis and data-driven insights.
- Continuous Learning : Keep up-to-date with the latest analytical techniques, software tools, and industry trends to maintain a competitive edge.
- Educational Background : A Bachelor’s degree in Operations Research, Industrial Engineering, Statistics, Mathematics, or a related field is required; a Master’s degree or PhD is often preferred.
- Analytical Skills : Strong ability to apply quantitative methods to analyze data and solve complex problems.
- Technical Proficiency : Proficient with statistical software, databases, and programming languages commonly used in data analysis.
- Problem-Solving : Capability to develop creative solutions to improve operational efficiency and effectiveness.
- Communication Skills : Excellent verbal and written communication skills to explain complex analytical concepts to non-expert stakeholders.
- Teamwork : Ability to work collaboratively in a team environment and contribute to multidisciplinary projects.
Operations Research Analysts have significant opportunities for career advancement.
They can move into higher-level management roles, specialize in a particular industry or sector, or transition into consultancy to tackle a wider range of problems.
As technology and data analysis continue to evolve, skilled analysts are in high demand, creating a strong trajectory for professional growth and development.
Cybersecurity Specialist
Cybersecurity Specialists are the sentinels of the digital world, safeguarding information systems from cyber threats and ensuring data integrity and confidentiality.
This role is ideal for critical thinkers who thrive on the challenge of protecting digital assets and thwarting cyber attacks.
- Assessing Security Systems : Evaluate the security posture of information systems and identify vulnerabilities.
- Implementing Security Measures : Develop and enforce policies and protocols to protect digital infrastructure from cyber threats.
- Monitoring Threat Landscape : Keep abreast of emerging cyber threats and trends to proactively defend against them.
- Incident Response : Respond to and mitigate the impact of cyber incidents, and participate in forensic analysis to prevent future attacks.
- Security Awareness Training : Educate employees on cybersecurity best practices and the importance of security protocols.
- Staying Informed : Continuously update your knowledge about cybersecurity advancements, threat intelligence, and regulatory compliance requirements.
- Educational Background : A Bachelor’s degree in Cybersecurity, Information Technology, Computer Science, or a related field is required, with advanced certifications such as CISSP or CISM being highly desirable.
- Technical Skills : Proficiency in security technologies, ethical hacking, intrusion detection systems, and network security protocols.
- Analytical Thinking : Ability to analyze complex security systems and anticipate potential vulnerabilities or attack vectors.
- Communication Skills : Clear and concise communication, with the ability to explain technical issues to non-technical stakeholders.
- Problem-Solving : Strong problem-solving skills to quickly address and resolve security issues.
- Continuous Learning : Commitment to continuous learning in the rapidly evolving field of cybersecurity.
In the face of growing cyber threats, the demand for Cybersecurity Specialists is on the rise.
Career advancement opportunities include moving into leadership roles such as Chief Information Security Officer (CISO), specializing in areas like penetration testing or digital forensics, or working as an independent consultant for a variety of industries.
Clinical Psychologist
Average Salary: $75,000 – $100,000 per year
Clinical Psychologists assess, diagnose, and treat individuals experiencing psychological distress and mental illness.
They also promote mental health and behavioral wellness.
This role is ideal for critical thinkers who are interested in understanding complex human behaviors and utilizing evidence-based approaches to mental health treatment.
- Assessment and Diagnosis : Conduct psychological evaluations using interviews, tests, and observations to determine the mental health status of clients.
- Therapeutic Interventions : Implement various evidence-based therapeutic techniques tailored to individual client needs.
- Research and Evaluation : Engage in research to develop new psychological approaches and assess the effectiveness of treatments.
- Interdisciplinary Collaboration : Work with other healthcare professionals to provide comprehensive care to clients.
- Client Education : Educate clients and their families about mental health conditions and coping strategies.
- Continuing Education : Stay up-to-date with the latest research and advancements in the field of psychology.
- Educational Background : A Doctoral degree (Ph.D. or Psy.D.) in Clinical Psychology from an accredited program is required.
- Licensure : Must be licensed to practice as a Clinical Psychologist in the state of practice.
- Communication Skills : Excellent verbal and written communication skills, with the ability to build rapport and effectively convey information to clients.
- Critical Thinking : Strong critical thinking skills to assess complex cases and devise appropriate treatment plans.
- Empathy : A deep understanding of human behavior and a compassionate approach to client care.
- Adaptability : Ability to adjust therapeutic approaches to meet the diverse needs of individual clients.
As a Clinical Psychologist, there is potential for career growth in various directions, including private practice, academic and clinical research positions, administrative roles in mental health care facilities, and specialized areas such as neuropsychology or health psychology.
Experienced psychologists may also become educators and trainers for upcoming professionals in the field.
Average Salary: $76,000 – $122,000 per year
Economists conduct research, analyze data, and evaluate economic issues for resources, goods, and services.
They apply their expertise to a variety of fields, including finance, labor, agriculture, and government.
This role is ideal for critical thinkers who enjoy applying quantitative and analytical skills to study the production and distribution of resources, goods, and services by analyzing data and trends.
- Data Analysis : Utilize statistical techniques and models to analyze economic data.
- Research : Conduct research on economic issues and disseminate findings through reports and papers.
- Policy Development : Advise businesses, governments, and organizations on economic decisions and policy formulation based on research findings.
- Economic Forecasting : Predict market trends by analyzing data and economic conditions.
- Presentations and Lectures : Share insights and research findings with stakeholders, policymakers, or academic audiences.
- Continuous Learning : Stay updated with the latest economic theories, models, and techniques.
- Educational Background : A Master’s or Ph.D. in Economics is typically required, although a Bachelor’s degree may be sufficient for entry-level positions.
- Analytical Skills : Strong ability to analyze data and understand economic trends and patterns.
- Quantitative Skills : Proficiency with statistical software and econometric methods.
- Communication Skills : Excellent writing and speaking skills to clearly present complex economic concepts and findings.
- Detail-Oriented : A meticulous approach to data and policy analysis.
- Critical Thinking : Ability to approach problems logically and propose rational solutions.
A career as an Economist offers opportunities to influence and shape economic policy and practice.
With experience, Economists can progress to senior analytical roles, become subject matter experts, or lead research teams.
There is also potential for Economists to take on advisory roles in government or international organizations, contribute to academic advancements in the field, or transition into higher-paying private sector positions.
Computer Systems Analyst
Computer Systems Analysts are professionals who study an organization’s current computer systems and design information systems solutions to help the enterprise operate more efficiently and effectively.
This role is ideal for critical thinkers who enjoy tackling complex problems and optimizing system functionality to meet business goals.
- Assessing System Requirements : Evaluate the technological needs of an organization and determine how computers can best meet those needs.
- Designing Solutions : Devise efficient and cost-effective computer systems, integrating both hardware and software to support business objectives.
- Improving System Efficiency : Analyze and improve the performance of existing computer systems to increase productivity.
- Testing and Configuration : Oversee the implementation of new systems, including testing and configuration to ensure smooth operation.
- Training Users : Provide training and support to users to help them adapt to new systems and technologies.
- Staying Updated : Continuously learn about new technologies and system upgrades that could improve business operations.
- Educational Background : A Bachelor’s degree in Computer Science, Information Technology, or a related field is generally required.
- Analytical Skills : Strong analytical skills to study an organization’s systems and recommend technological solutions.
- Technical Expertise : Proficiency in computer hardware and software systems, as well as an understanding of the various software languages and databases.
- Problem-Solving : Ability to diagnose and resolve complex system issues.
- Communication Skills : Clear communication to explain technical concepts to non-technical users and stakeholders.
- Project Management : Skills in managing projects, often involving the deployment of new systems or upgrades.
Computer Systems Analysts have a critical role in ensuring that organizations leverage technology for strategic advantage.
With experience, they can progress to senior analyst roles, specialize in specific industries or technologies, or move into IT management or consultancy.
There is also the potential to lead major IT projects or become a Chief Technology Officer (CTO) for an organization.
Political Strategist
Average Salary: $55,000 – $100,000 per year
Political Strategists are key players in election campaigns, developing comprehensive strategies to ensure the success of a candidate or political party.
This role is perfect for critical thinkers who are passionate about politics and have the skills to analyze public opinion and political trends to craft winning strategies.
- Developing Campaign Strategies : Create and implement detailed plans for political campaigns, addressing voter demographics, key issues, and opposition strategies.
- Managing Media Relations : Oversee the communication between the campaign and the media, including press releases, interviews, and public statements.
- Conducting Poll Analysis : Analyze polling data to understand voter behavior and preferences, and adjust campaign tactics accordingly.
- Speech Writing : Assist in writing and editing speeches, ensuring the candidate’s message aligns with campaign goals and resonates with the electorate.
- Public Engagement : Organize and manage events, rallies, and town halls to increase candidate visibility and voter engagement.
- Monitoring Political Trends : Stay informed on the latest political developments, legislative changes, and social issues that may impact campaign strategies.
- Educational Background : A Bachelor’s degree in Political Science, Communications, Public Relations, or a related field is often required.
- Strong Analytical Skills : Ability to dissect complex political information and polling data to make informed strategic decisions.
- Excellent Communication : Superior verbal and written communication skills, with the capacity to craft compelling messages and counterarguments.
- Understanding of Political Landscape : In-depth knowledge of the political system, electoral processes, and key issues that influence voters.
- Adaptability and Resilience : The agility to adapt to rapidly changing political climates and to handle high-pressure situations.
Political Strategists play a crucial role in shaping electoral outcomes and public policy.
With experience, they can take on higher leadership roles within political campaigns, work as consultants for multiple campaigns or political organizations, or even transition into public office themselves.
The skills developed as a Political Strategist are highly transferable and valued in various sectors, including public affairs, lobbying, and political commentary.

Academic Professor
Average Salary: $60,000 – $150,000 per year
Academic Professors teach and conduct research at colleges and universities across a wide range of disciplines.
This role is perfect for critical thinkers who enjoy delving into complex subjects and fostering a similar inquisitiveness in their students.
- Delivering Lectures : Conduct comprehensive and thought-provoking lectures, seminars, and workshops in your field of expertise.
- Curriculum Development : Design course materials and syllabi that reflect the latest developments in the subject area and challenge students to think critically.
- Research : Engage in scholarly research, often with the aim of publishing work that contributes to the body of knowledge in your discipline.
- Advising Students : Provide academic guidance and mentorship to students, helping them develop their own critical thinking and research skills.
- Assessment and Feedback : Create and grade assignments and exams, providing constructive feedback to facilitate student learning and improvement.
- Academic Collaboration : Participate in departmental meetings, collaborate with peers on academic projects, and contribute to the university community.
- Educational Background : A Ph.D. or terminal degree in a relevant discipline is typically required.
- Research Skills : Strong research abilities and a track record of publications or presentations in the field.
- Communication Skills : Excellent verbal and written communication skills, with the ability to distill complex concepts for a variety of audiences.
- Critical Thinking : An analytical mindset with the ability to challenge conventional wisdom and encourage students to do the same.
- Commitment to Education : A dedication to teaching and the intellectual growth of students.
As an Academic Professor, you have the opportunity to shape the minds of future generations and potentially make significant contributions to your field of study.
Career advancement can include promotion to senior academic positions such as Department Chair, Dean, or other administrative roles.
Professors may also gain recognition through their research and become leading experts consulted on national or global issues related to their area of expertise.
Business Strategist
Business Strategists are responsible for developing and executing strategies to improve an organization’s market position and achieve financial growth.
This role is ideal for critical thinkers who enjoy analyzing market trends, conceptualizing business initiatives, and driving strategic decision-making.
- Developing Business Strategies : Create comprehensive business plans that address specific targets and objectives, aligning with the company’s vision and goals.
- Market Analysis : Conduct in-depth market research to identify opportunities for expansion or improvement and to stay ahead of industry trends.
- Financial Forecasting : Evaluate financial implications of proposed strategies and forecast their potential impact on the business’s bottom line.
- Collaboration with Teams : Work closely with cross-functional teams to ensure the successful implementation of strategies and initiatives.
- Performance Analysis : Monitor and analyze the performance of implemented strategies, adjusting them as necessary to maximize results.
- Advising Leadership : Provide strategic recommendations to top management based on market research and performance data.
- Educational Background : A Bachelor’s or Master’s degree in Business Administration, Economics, Finance, or a related field is preferable.
- Strategic Thinking : Strong ability to think critically and strategically, with a focus on long-term business planning and market positioning.
- Analytical Skills : Exceptional analytical skills, with the ability to interpret complex data and translate it into actionable business insights.
- Communication Skills : Excellent verbal and written communication skills, with the ability to articulate strategies and persuade stakeholders.
- Leadership : Experience in leading teams or projects, with the ability to inspire and drive change within an organization.
- Problem-Solving : Proven track record of effective problem-solving and the ability to navigate complex business challenges.
Business Strategists play a crucial role in shaping the future of companies.
With experience, they can rise to top executive positions, such as Chief Strategy Officer, or specialize in areas like digital transformation or global market expansion.
There are also opportunities for Business Strategists to consult independently, offering their expertise to a diverse range of clients.
Biostatistician
Average Salary: $75,000 – $125,000 per year
Biostatisticians apply mathematical and statistical techniques to analyze data and solve complex problems in the biological sciences, including public health, medicine, and genetics.
This role is ideal for critical thinkers who enjoy utilizing their mathematical expertise to contribute to advancements in healthcare and medical research.
- Designing Experiments and Studies : Collaborate with medical researchers to design studies that yield reliable and valid results.
- Data Analysis : Apply statistical methods to analyze and interpret data from clinical trials, public health studies, or genetic research.
- Developing Statistical Models : Create models to predict outcomes or to understand the relationship between variables in biological processes.
- Reporting Results : Prepare comprehensive reports that summarize analysis findings for stakeholders, which may include scientists, healthcare professionals, or policymakers.
- Collaborative Research : Work as part of a multidisciplinary team to address complex health issues and contribute to scholarly publications.
- Staying Current : Continuously update knowledge of statistical methods and advancements in the field of biostatistics.
- Educational Background : A Master’s degree or Ph.D. in Biostatistics, Statistics, or a related field is typically required.
- Analytical Skills : Strong analytical skills with the ability to apply statistical techniques to large datasets.
- Attention to Detail : Precision and meticulousness in data analysis to ensure accuracy of results.
- Communication Skills : Strong written and verbal communication skills to effectively present findings to both scientific and non-scientific audiences.
- Problem-Solving : Ability to identify and address complex problems using statistical reasoning.
- Technical Proficiency : Proficiency in statistical software such as SAS, R, or SPSS.
Biostatisticians play a crucial role in the development of new medical treatments and understanding health trends.
With experience, they can advance to lead large research projects, become senior statistical consultants, or hold managerial positions overseeing biostatistical teams.
Additionally, there are opportunities in academia for teaching and conducting independent research.
Average Salary: $55,000 – $80,000 per year
Logicians are critical thinkers who specialize in analyzing problems, creating systems, and understanding logical processes.
They are often employed in fields such as computer science, mathematics, and philosophy.
This role is ideal for individuals who have a talent for structured reasoning and are fascinated by the formulation of arguments, problem-solving, and systematization.
- Analyzing Complex Problems : Use logical reasoning to break down complex issues into manageable components for better understanding and resolution.
- Creating Logical Frameworks : Develop systems and frameworks that can be applied to various scenarios in a consistent and structured manner.
- Conducting Research : Engage in research to understand the principles underlying logical processes and to stay updated with the latest developments in the field.
- Evaluating Arguments : Assess the validity and soundness of arguments, identifying logical fallacies and biases.
- Teaching and Consulting : Provide instruction or advice on logical thinking and methodologies, potentially across different disciplines.
- Technical Writing : Prepare detailed reports, papers, or documentation that clearly communicate logical structures and reasoning.
- Educational Background : A Bachelor’s degree in a relevant field such as Philosophy, Mathematics, Computer Science, or a related analytical discipline is often required.
- Analytical Skills : Strong ability to think critically and analytically, with a focus on problem-solving and logical structuring.
- Attention to Detail : Precision and attention to detail are crucial for creating valid logical frameworks and analyzing complex arguments.
- Communication Skills : Proficiency in written and verbal communication to effectively convey logical concepts and findings.
- Continuous Learning : A commitment to lifelong learning in order to keep up with evolving logical methodologies and applications.
The role of a Logician offers the opportunity to contribute significantly to the field of logic and its applications.
With experience, Logicians can become thought leaders, advance to more senior analytical roles, or specialize in areas such as artificial intelligence, data analysis, or academic research.
Medical Diagnostics Specialist
Medical Diagnostics Specialists play a critical role in healthcare by analyzing medical tests to diagnose diseases, conditions, and infections.
This role is fundamental in guiding treatment decisions and monitoring patient progress.
This role is ideal for critical thinkers who enjoy applying their analytical skills to solve complex medical problems and contribute to patient care.
- Analyzing Medical Tests : Evaluate and interpret results from various diagnostic tests, including blood work, imaging studies, and tissue samples.
- Collaborating with Healthcare Teams : Work closely with physicians, nurses, and other healthcare professionals to provide accurate diagnoses and inform treatment plans.
- Quality Control : Ensure that diagnostic equipment and tests are functioning correctly and that results are reliable and accurate.
- Developing Diagnostic Protocols : Create and update protocols for testing to improve accuracy and efficiency in the diagnostics process.
- Continuing Education : Stay abreast of the latest developments in medical diagnostics, including new testing methods and advancements in technology.
- Communication with Patients : Occasionally explain test procedures and results to patients, providing clear and empathetic communication.
- Educational Background : A Bachelor’s degree in a related field such as Biomedical Science, Clinical Laboratory Science, or Medical Technology is required, with many roles requiring a Master’s degree or higher.
- Attention to Detail : Meticulous attention to detail to ensure the accuracy of test results and diagnoses.
- Analytical Skills : Strong critical thinking and problem-solving skills to interpret complex test results and make informed decisions.
- Technical Proficiency : Proficiency with diagnostic equipment and software used in the analysis of medical tests.
- Interpersonal Skills : Excellent communication skills to interact effectively with the healthcare team and patients.
Medical Diagnostics Specialists are at the forefront of patient care, and their expertise is crucial for the early detection of diseases and the monitoring of treatment outcomes.
With experience, these specialists can advance to supervisory or managerial roles, oversee laboratory operations, or become involved in research and development of new diagnostic technologies and methodologies.
Philosophical Writer
Average Salary: $40,000 – $70,000 per year
Philosophical Writers craft thought-provoking content, exploring and analyzing various philosophical theories, ethical dilemmas, and existential questions.
This role is ideal for critical thinkers who relish the challenge of dissecting complex ideas and presenting them in a clear, engaging manner.
- Writing Philosophical Content : Create compelling articles, essays, and books that explore philosophical concepts, historical philosophical debates, and contemporary ethical issues.
- Research and Analysis : Delve into philosophical literature to understand and critically assess ideas from a wide range of philosophical schools of thought.
- Engaging Public Discourse : Use your writing to participate in and stimulate public discussions on philosophical topics, contributing to a broader understanding of the subject.
- Editing and Revising : Carefully revise your work to ensure clarity, coherence, and readability, making complex ideas accessible to a general audience.
- Educational Contributions : Potentially collaborate with academic institutions or online educational platforms to create content that can be used for teaching philosophy.
- Staying Updated : Keep abreast of new developments and discussions in the field of philosophy to ensure your writing remains current and relevant.
- Educational Background : A Bachelor’s or higher degree in Philosophy, Ethics, or a related field is highly beneficial.
- Strong Analytical Skills : The ability to analyze and synthesize complex philosophical arguments is essential.
- Exceptional Writing Ability : Proficient writing skills, with the capacity to communicate intricate ideas in a comprehensible and engaging way.
- Passion for Philosophy : A deep interest in philosophical inquiry and a commitment to exploring life’s big questions.
- Research Proficiency : Skilled at conducting thorough research and referencing academic sources appropriately.
- Critical Thinking : Excellent critical thinking skills to evaluate arguments and develop original perspectives.
Philosophical Writers have the opportunity to influence and contribute to intellectual discourse, potentially shaping the way society understands and approaches philosophical issues.
With experience, they can advance to positions such as lead authors, editors, or columnists in prestigious publications, or transition into academic roles.
There’s also the potential for public speaking engagements, workshops, or participation in think tanks and research institutions.
Average Salary: $180,000 – $300,000 per year
Physicians diagnose and treat illnesses, manage patient care, and advise on preventative health measures in a variety of medical settings.
This role is ideal for critical thinkers who are committed to improving patient health outcomes and enjoy the challenges of complex problem-solving in medicine.
- Diagnosing Illnesses : Evaluate patient symptoms and medical history to diagnose conditions.
- Developing Treatment Plans : Create and manage comprehensive treatment plans tailored to individual patient needs.
- Answering Patient Questions : Provide clear explanations and guidance to patients regarding their diagnoses, treatments, and health maintenance.
- Continuing Education : Stay abreast of the latest medical research, treatments, and protocols to provide cutting-edge care to patients.
- Collaborating with Healthcare Team : Work with nurses, specialists, and other healthcare professionals to ensure cohesive patient care.
- Preventative Health : Advise patients on lifestyle changes and preventative measures to improve their overall health.
- Educational Background : A Doctor of Medicine (MD) or Doctor of Osteopathic Medicine (DO) degree, followed by a residency in a specialized field of medicine.
- Medical Licensure : A valid medical license to practice in your state or country, which requires passing a series of board exams.
- Critical Thinking Skills : Excellent problem-solving abilities to diagnose and treat complex medical issues.
- Communication Skills : Strong verbal and written communication skills to effectively interact with patients and the healthcare team.
- Compassion : A genuine desire to help others and provide empathetic care to patients.
- Adaptability : Ability to adjust to rapidly changing medical situations and advancements in healthcare.
As a physician, you have the opportunity to make significant contributions to patient health and the medical field.
With experience and continued education, physicians can advance to leadership roles, specialize in niche medical areas, conduct medical research, or teach in medical schools.
The career path also allows for participation in global health initiatives or healthcare policy development, broadening the scope of influence in the field of medicine.
Philosopher
Average Salary: $40,000 – $65,000 per year
Philosophers engage in critical thinking and debate on various topics, including ethics, logic, metaphysics, epistemology, and other realms of the humanities.
This role is ideal for critical thinkers who enjoy analyzing and discussing profound questions about existence, society, and the human condition.
- Conducting Research : Delve into philosophical texts and theories to develop new insights or critique existing viewpoints.
- Teaching : Educate students at the secondary or postsecondary level on different philosophical perspectives and critical thinking skills.
- Writing Papers and Articles : Author thought-provoking essays and scholarly papers that contribute to academic discourse and public understanding.
- Leading Discussions : Facilitate seminars and discussion groups that challenge participants to consider various ethical, existential, and theoretical problems.
- Public Speaking : Engage with broader audiences through lectures, panel discussions, or public debates on philosophical issues.
- Staying Informed : Keep abreast of new developments in the field of philosophy and related disciplines.
- Educational Background : A Bachelor’s degree is required, with a Master’s or Ph.D. in Philosophy highly preferred for advanced positions.
- Analytical Skills : Strong ability to dissect arguments, recognize logical fallacies, and construct coherent viewpoints.
- Passion for Inquiry : A deep interest in exploring fundamental questions about life, society, and morality.
- Communication Skills : Excellent verbal and written communication skills, with the ability to discuss complex ideas clearly and persuasively.
- Open-mindedness : Willingness to consider and debate a wide range of theories and perspectives.
This role offers the opportunity to contribute to philosophical scholarship and engage in intellectual discourse.
With experience, philosophers can become recognized experts in their field, lead academic departments, and influence public policy or cultural thinking through their insights.
Additionally, they can become authors of influential books or articles, shaping the philosophical dialogue of their time.
Detectives are crucial law enforcement officers who investigate crimes, gather evidence, and solve complex cases.
This role is ideal for critical thinkers who are passionate about solving puzzles, seeking justice, and ensuring community safety.
- Investigating Crimes : Conduct thorough and detailed investigations into criminal activities, analyzing crime scenes, and gathering evidence.
- Interviewing Witnesses and Suspects : Carry out interviews and interrogations to obtain vital information relevant to cases.
- Conducting Surveillance : Monitor suspects and locations to collect actionable intelligence and evidence.
- Documenting Investigations : Accurately record all investigative processes, findings, and outcomes in detailed reports.
- Collaborating with Other Departments : Work closely with other law enforcement agencies and departments to build strong cases.
- Continuous Learning : Stay abreast of the latest investigative techniques, legal updates, and technological advancements in law enforcement.
- Educational Background : A degree in Criminal Justice, Forensic Science, Criminology, or a related field is often required.
- Strong Analytical Skills : Exceptional ability to analyze information, think critically, and make sound judgments.
- Attention to Detail : Keen observational skills and meticulous attention to detail are essential for collecting and examining evidence.
- Communication Skills : Proficient verbal and written communication skills for interviewing and report writing.
- Physical and Emotional Stamina : The ability to handle physically demanding tasks, stressful situations, and emotional strain.
- Problem-Solving : Adept at solving complex problems and thinking outside the box to resolve challenging cases.
Detectives play a critical role in the criminal justice system.
With experience, they can move up to senior detective roles, specialize in areas like homicide or cybercrime, or advance to leadership positions within law enforcement agencies.
Detectives can also further their careers by attaining additional certifications and training in advanced investigative techniques.
IT Strategist
Average Salary: $90,000 – $140,000 per year
IT Strategists are responsible for planning and directing an organization’s technology-related strategies, policies, and initiatives.
This role is ideal for critical thinkers who enjoy using their analytical skills to align technology initiatives with business goals.
- Developing IT Strategies : Create comprehensive IT strategies that support the organization’s overall business objectives and promote efficient operations.
- Conducting Technology Analysis : Evaluate current technology trends, software, and hardware to recommend solutions that improve business performance.
- Collaborating with Management : Work closely with executives and department heads to develop and implement technology plans that align with company goals.
- Overseeing IT Projects : Manage the planning and execution of IT projects, ensuring they meet strategic objectives, timelines, and budgets.
- Improving IT Infrastructure : Analyze and enhance the organization’s IT infrastructure to support growth and ensure robust security measures are in place.
- Keeping Abreast of Developments : Stay informed about emerging technologies and innovations that can give the company a competitive edge.
- Educational Background : A Bachelor’s or Master’s degree in Information Technology, Computer Science, Business Administration, or a related field is generally required.
- Analytical Skills : Strong analytical and problem-solving skills to assess complex information systems and improve technology environments.
- Strategic Planning : Proven experience in developing and implementing IT strategies that are in line with business goals.
- Communication Skills : Excellent verbal and written communication skills, with the ability to explain technical concepts to non-technical stakeholders.
- Leadership : Strong leadership abilities to guide technology teams and drive strategic initiatives.
- Adaptability : Capability to adapt to rapidly changing technology landscapes and business needs.
This role offers the opportunity to shape the technological future of an organization, playing a key part in its success and growth.
With experience, IT Strategists can advance to higher leadership positions, such as Chief Information Officer (CIO) or Chief Technology Officer (CTO), where they can have an even greater impact on the company’s strategic direction.
Policy Analyst
Average Salary: $55,000 – $70,000 per year
Policy Analysts research, analyze, and evaluate the effects of public policies and provide insights and recommendations to governments, non-profits, or private sector organizations.
This role is ideal for critical thinkers who are passionate about using their analytical skills to influence and improve societal outcomes.
- Researching Policies : Conduct in-depth research on existing policies and proposed legislation to understand their impacts on various sectors and populations.
- Analyzing Data : Evaluate data and statistics to identify trends, potential issues, and outcomes of policy implementations.
- Developing Policy Recommendations : Create reports and briefs proposing changes or enhancements to current policies based on empirical evidence and analysis.
- Communicating Findings : Present complex policy issues and analysis results to stakeholders in a clear and concise manner.
- Stakeholder Engagement : Liaise with government officials, advocacy groups, and the public to gather input and build consensus around policy initiatives.
- Monitoring Legislation : Keep abreast of legislative developments and potential changes that may affect policy areas of interest.
- Educational Background : A Bachelor’s degree in Political Science, Public Policy, Economics, or a related field is required. A Master’s degree is often preferred.
- Analytical Skills : Strong ability to analyze complex data, draw conclusions, and make reasoned arguments.
- Communication Skills : Excellent writing and verbal communication skills, with the ability to explain complicated policy issues in an accessible way.
- Research Proficiency : Proficient in qualitative and quantitative research methods and familiar with data analysis tools.
- Critical Thinking : Ability to objectively evaluate information and policy options from multiple perspectives.
- Problem-Solving : Innovative thinking to develop practical and creative policy solutions to address societal challenges.
As a Policy Analyst, there are opportunities to specialize in various fields such as health, environment, education, or economic policy.
With experience, Policy Analysts can move into senior advisory roles, lead research teams, or transition into government positions influencing the development and implementation of policies directly.
Chemical Engineer
Chemical Engineers apply principles of chemistry, physics, mathematics, and engineering to design and troubleshoot processes for producing, transforming, and transporting materials.
This role is ideal for critical thinkers who excel in problem-solving and have a keen interest in developing processes that can lead to innovative products and solutions.
- Process Design and Optimization : Develop and optimize chemical processes to improve efficiency, safety, and sustainability.
- Research and Development : Conduct experiments to create new materials, products, or production techniques.
- Quality Control : Ensure that products meet required specifications and standards through rigorous testing and adjustments.
- Scale-Up Production : Transition laboratory processes to full-scale production while addressing challenges that arise during scaling.
- Environmental Compliance : Monitor and improve operations to comply with environmental regulations and promote eco-friendly practices.
- Technical Support and Troubleshooting : Provide expertise to resolve issues in manufacturing processes and to implement corrective actions.
- Educational Background : A Bachelor’s degree in Chemical Engineering or a related field is required, with a Master’s or Ph.D. preferred for advanced positions.
- Problem-Solving Skills : Strong analytical skills to troubleshoot issues and develop innovative solutions to complex engineering problems.
- Technical Knowledge : In-depth understanding of chemical processes, materials science, and industry-specific technologies.
- Teamwork and Collaboration : Ability to work effectively in multidisciplinary teams, often coordinating with other engineers and scientists.
- Attention to Detail : Meticulous attention to detail for designing processes and ensuring the safety and quality of products.
Chemical Engineers can expect to work on a wide range of projects in various industries such as pharmaceuticals, petrochemicals, food and beverage, and environmental technology.
With experience, Chemical Engineers can advance to senior engineering roles, management positions, or specialize in areas like process engineering, product development, or environmental sustainability.
Continuous learning and staying abreast of technological advancements are essential for career progression in this field.
Biomedical Researcher
Biomedical Researchers conduct experiments and research studies to advance knowledge in medicine and biology to improve human health.
This role is ideal for critical thinkers who are passionate about scientific discovery and innovation in healthcare.
- Conducting Research Studies : Design and perform scientific experiments to investigate human diseases, develop medical treatments, and improve healthcare technologies.
- Collaborating with Medical Professionals : Work alongside doctors, clinicians, and other researchers to translate research findings into clinical practice.
- Analyzing Data : Utilize statistical techniques to analyze complex biological data and draw meaningful conclusions.
- Writing Grants and Papers : Secure funding through grant writing and disseminate research findings via scientific publications and presentations.
- Adhering to Ethical Standards : Ensure all research complies with ethical guidelines and regulations for the responsible conduct of research.
- Staying Current : Keep up-to-date with the latest scientific advancements and medical breakthroughs in the field of biomedicine.
- Educational Background : A Bachelor’s degree in a biological science is required, with many positions requiring a Master’s or Ph.D. in Biomedical Science, Biochemistry, or a related field.
- Research Skills : Strong analytical and experimental skills, with the ability to design and conduct rigorous scientific studies.
- Attention to Detail : Precision and careful attention to detail when conducting experiments and analyzing data.
- Problem-Solving : Capacity to identify and solve complex biological problems using critical thinking.
- Communication Skills : Excellent written and verbal communication skills for sharing research findings with the scientific community and the public.
- Technical Proficiency : Familiarity with laboratory techniques, bioinformatics tools, and data analysis software.
As a Biomedical Researcher, there are opportunities to contribute to life-saving advancements and shape the future of medicine.
With experience, researchers can lead their own labs, become principal investigators, and influence healthcare policy or transition into biotech and pharmaceutical industries in senior research positions.
Philosophical Consultant
Average Salary: $50,000 – $70,000 per year
Philosophical Consultants apply philosophical methods and theories to analyze and solve complex problems in various industries, including business, healthcare, education, and government.
This role is ideal for individuals who appreciate deep thinking and wish to utilize their expertise in philosophy to offer insights and guidance in professional contexts.
- Problem-Solving : Employ philosophical frameworks to address and resolve ethical dilemmas, strategic issues, and conceptual conflicts within organizations.
- Workshops and Seminars : Design and facilitate workshops or seminars that encourage critical thinking, ethical decision-making, and philosophical discussion among participants.
- Guidance and Advice : Provide expert advice on philosophical matters to support decision-making processes in various sectors.
- Developing Philosophical Content : Create materials and resources that introduce philosophical concepts in a practical and accessible manner for non-academic audiences.
- Collaboration with Teams : Work alongside other professionals, contributing a philosophical perspective to interdisciplinary projects and discussions.
- Continuous Learning : Stay informed about recent developments in philosophical thought and how these can be applied to contemporary issues.
- Educational Background : A Master’s or Doctorate degree in Philosophy or a closely related field is often required.
- Analytical Skills : Strong ability to analyze and systematically approach problems using philosophical methods.
- Communication Skills : Excellent verbal and written communication skills, with the ability to express complex ideas clearly and persuasively.
- Interdisciplinary Understanding : An appreciation for how philosophy intersects with other disciplines and the ability to apply philosophical insight across various contexts.
- Facilitation Skills : Proficiency in leading discussions and workshops that stimulate critical thinking and philosophical inquiry.
Philosophical Consultants have the opportunity to impact decision-making and strategy across multiple sectors by introducing a critical and ethical dimension to discussions.
With experience, Philosophical Consultants can advance to leadership positions within consultancy firms, specialize in particular industries, or expand their practice to international consulting roles, shaping organizational cultures and influencing global policies.
And there you have it.
A comprehensive overview of the most stimulating jobs for critical thinkers.
With such a vast range of opportunities available, there is undoubtedly something suited for every analytical mind out there.
So go above and beyond to venture into your dreams of engaging in critical thinking on a daily basis.
Remember: It’s NEVER too late to transform your intellectual prowess into a fruitful profession.
Earning Like a Boss: A Deep Dive into the Most Lucrative Jobs Today!
The Stark Reality of Low Pay: Jobs Where Earnings Might Surprise You
Play for Pay: Fun Jobs That Will Make You Love Mondays
The No-Sweat Path to Prosperity: Easy Jobs with Impressive Paychecks!
Sick of the Office? Here Are High-Paying Remote Jobs Just for You!
The Editorial Team at InterviewGuy.com is composed of certified interview coaches, seasoned HR professionals, and industry insiders. With decades of collective expertise and access to an unparalleled database of interview questions, we are dedicated to empowering job seekers. Our content meets real-time industry demands, ensuring readers receive timely, accurate, and actionable advice. We value our readers' insights and encourage feedback, corrections, and questions to maintain the highest level of accuracy and relevance.
Similar Posts

26 Disadvantages of Being an Anesthetic Nurse Practitioner (Not All Numb)

30 Reasons to Become a Server Assistant (Master Time Management)
27 jobs for asylum seekers uk (ambition unleashed).

25 Reasons to Become an Engineering Consultant (Solve Complex Problems!)

26 Jobs For Small Plane Pilots (Wings of Success)

28 Jobs For ETL Tester (Load Your Success)
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
11 High-Paying Critical Thinking Jobs
Home / Career Lists / 11 High-Paying Critical Thinking Jobs
Trending Careers

Critical thinking jobs require that a candidate possess certain skills that will enable them to perform the functions of that job.
These skills include the ability to analyze complex information, interpret and infer this information, and having the ability to explain this information to the next individual in a simple and easy-to-understand manner.
In addition, these types of jobs require individuals to be able to self-regulate, be open-minded, as well as have outstanding problem-solving abilities.
1. Financial Analyst

Why Become a Financial Analyst?
If you are someone that loves working with numbers, as this is what most of your day will consist of, and you are a strategic thinker, then becoming a financial analyst may be the right choice for you.
You will be required to research and analyze data with a high level of attention to detail.
This job requires expert-level analytical and financial modeling skills.
You will be required to coordinate with members of the financial department to review financial forecasts and information.
This job requires constant critical thinking skills.
Read the full career guide: How to Become a Financial Analyst

Why Become a Teacher?
If your goal is to make a difference in the life of a student, then this is the job for you.
Apart from having to think critically regarding the progress of your students and strategizing each student’s path to growth, you will also be required to integrate critical thinking into assignments in order to teach children and young teenagers how to think critically for themselves.
Read the full career guide: How to Become a Teacher

Why Become a Lawyer?
Understanding the law is one thing.
It can be very challenging.
Applying it is an entirely different story.
When you analyze a case and want the jury to reach the same conclusion that you have, you will need to justify your reasoning, which may take considerable critical thinking on your part.
This job is extremely challenging but also very rewarding if you are up for the challenge.
In addition, you will require substantial problem-solving abilities to be successful in this job.
Read the full career guide: How to Become a Lawyer
4. Forensic Scientist

Why Become a Forensic Scientist?
A forensic scientist applies science to criminal and civil law to uncover the truth during a criminal investigation.
You will be required to apply scientific reasoning with a considerable amount of problem-solving ability.
You will need to make sense, and convey to others, very uncertain, complex, and at times, incomplete data.
Read the full career guide: How to Become a Forensic Scientist
5. Anesthesiologist
Why Become an Anesthesiologist?
An anesthesiologist is a medical doctor that is legally permitted to administer anesthesia and manage pain.
General anesthesia may put you to sleep or make you unconscious, while smaller doses may only numb small parts of the body.
These doctors are required to think critically when analyzing a situation as they are required to select the appropriate course of action.
When a patient is scheduled for surgery, the anesthesiologist must determine how the pain of the patient will be managed during and after surgery.
Read the full career guide: How to Become an Anesthesiologist
Why Become a Surgeon?
When you are in the business of saving lives, then critical thinking becomes a part of your everyday life.
Surgeons are required to make clinical decisions while, at times, working in facilities that lack resources.
Surgeons must diagnose ailments and select the appropriate course of action in terms of surgery.
In critical life or death situations, the surgeon often has a fraction of a second to make a decision that may save the patient’s life.
Read the full career guide: How to Become a Surgeon
7. Psychiatrist
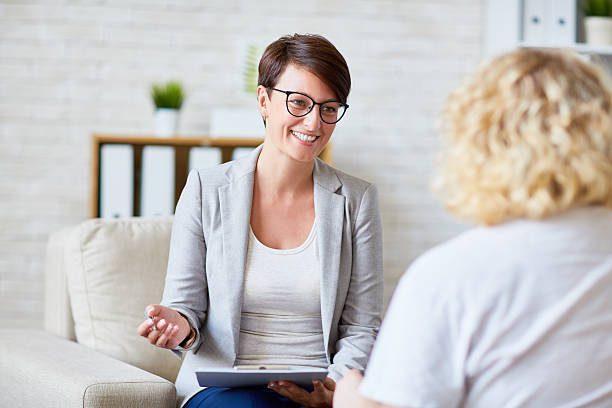

Why Become a Psychiatrist?
Psychiatrists often have to study the mood, personality, and any behavior disorders of a patient.
Symptoms are discussed with patients before a diagnosis is given and medication prescribed.
What makes this job so challenging is the fact that several behavioral disorders may have overlapping symptoms which may result in a wrong diagnosis.
These professionals are required to constantly think on their feet.
Therefore, the merits of the various treatments available must be weighed.
Read the full career guide: How to Become a Psychiatrist
8. Mathematician

Why Become a Mathematician?
Mathematicians use mathematics to be able to solve real-life problems.
Furthermore, they are required to expand on mathematical knowledge.
This is achieved through the development of new principles.
In addition, a Mathematician may be required to identify possible relationships between existing principles.
A Mathematician may need to develop models that help to resolve problems experienced in other industries such as business, engineering, the sciences, etc.
Read the full career guide: How to Become a Mathematician
9. Chemical Engineer

Why Become A Chemical Engineer?
A chemical engineer falls under the field of engineers.
These professionals are responsible for the design and development of chemical manufacturing processes.
A chemical engineer applies the principles of a variety of fields, such as biology, physics, chemistry, as well as maths.
These principles aid the chemical engineer in order to solve problems related to the production or use of a range of items such as chemicals, fuel, and drugs, to mention a few.
Read the full career guide: How to Become A Chemical Engineer
10. Robotics Engineer

Why Become a Robotics Engineer?
Robotics brings together two independent fields – computer science and engineering.
Robotic engineers will design, construct, and operate robots or robotic systems.
And, if you have not already heard, robotics is the future.
In addition, they configure, debug, and test robots and robotic systems to find and solve faults and problems.
This field requires a passion for the unknown and all things complex.
It requires an extremely high level of critical thinking to master this field.
Read the full career guide: How to Become a Robotics Engineer
11. Statistician

Why Become a Statistician?
A statistician works with both applied statistics and theory.
These professionals will apply statistical models in order to identify and solve real-world problems.
Statisticians play a crucial role in academia and research.
They gather qualitative and quantitative data that is analyzed in order to interpret the data.
The information obtained from this data is used in the decision-making process of many industries, such as business, science, engineering, etc.
Read the full career guide: How to Become a Statistician
Related Resources
- 9 High-Paying Biochemistry Jobs You Need to Know About
- List of Careers in Banking: 13 High-Paying Financial Jobs
- 11 In-Demand Medical Laboratory Jobs (High Paying Careers)
- 6 Astronomy Jobs (High Paying & Rewarding Careers)
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
The Non-Critical Thinker’s Manifesto
I’m vaccinated and, no, I don’t know what’s in it—neither this vaccine, the ones I had as a child, nor in the Big Mac, or in hot dogs, or in other treatments…whether it’s for cancer, AIDS, the one for polyarthritis, or vaccines for infants or children. I trust my doctor when he says it’s needed. Orthodox. Faithful. Free. Sign up to get Crisis articles delivered to your inbox daily Email subscribe inline (#4) Email address Subscribe form.fluent_form_4 .wpf_has_custom_css.ff-btn-submit { background-color:rgba(0, 68, 177, 1);color:#ffffff;border-radius:2px;min-width:100%; }form.fluent_form_4 .wpf_has_custom_css.ff-btn-submit:hover { background-color:rgba(253, 159, 1, 1);color:#FFFFFF;border-radius:2px;min-width:100%; } window.fluent_form_ff_form_instance_4_1 = {"id":"4","settings":{"layout":{"labelPlacement":"top","helpMessagePlacement":"with_label","errorMessagePlacement":"inline","asteriskPlacement":"asterisk-right"},"restrictions":{"denyEmptySubmission":{"enabled":false}}},"form_instance":"ff_form_instance_4_1","form_id_selector":"fluentform_4","rules":{"email":{"required":{"value":true,"message":"This field is required"},"email":{"value":true,"message":"This field must contain a valid email"}}}}; I also don’t know what’s in Ibuprofen, Tylenol, or other meds, it just cures my headaches & my pains… I don’t know what’s in the ink for tattoos, vaping, or every ingredient in my soap or shampoo or even deodorants. I don’t know the long-term effect of cell phone use or whether or not that restaurant I just ate at REALLY used clean foods and washed their hands. In short… There’s a lot of things I don’t know and never will… I just know one thing: life is short, very short…
- Did they really think that the first line of defense against disease was the ingestion or injection of chemicals that don’t exist in nature? Did they really?
- Did they really think that a baby was not a human being while it was in the womb but becomes one miraculously in the birth canal? WHAT?!!! Really???
- Did they really encourage children to think about whether they wanted to be male or female and then mutilate their little genitals to match the delusion they had encouraged? And licensed physicians participated? Did they really???
- Did they really send women into combat to fight against men???
- Did they really allow corporate conglomerates to collude to control the “news”? To collude with big tech to control the narrative? Were no suspicions raised when the above all introduced the same catch phrases simultaneously?—Repeatedly? Really?

Join the Conversation
In our telegram chat, or find us on.
Published on
September 13, 2021
Editor's picks
Anti-catholic revolution and catholic revival , bill maher: the prophet we need, dignitas infinita and the idolization of man, remaining faithfully catholic near the end of the francis pontificate , your cart is empty, orthodox. faithful. free., signup to receive new crisis articles daily.
Critical Thinking vs. Non-Critical Thinking
Susie zappia, 25 jun 2018.

Critical thinking has roots in the teachings of Socrates more than 2,500 years ago. The Foundation for Critical Thinking points out that Socrates established the importance of seeking evidence, questioning assumptions and examining reasoning. If we fast-forward to Renaissance Italy in the 15th and 16th centuries, we see European scholars beginning to examine critically the nature of religious belief, art, law and freedom. If critical thinking has an opposite, that might perhaps be creative thinking.
Explore this article
- The Value of Thinking Critically
- The Creative Thinking Contrast
- Strategies for Developing Critical Thinking Skills
- Strategies for Developing Creative Thinking
1 The Value of Thinking Critically
When Socrates placed value on what he termed the "examined life," he meant our human capacity to reflect on our experience is one of our most valuable tools and what gives our lives meaning. There are many ways to define critical thinking, but perhaps at its most basic it is the process of thoughtfully considering, analyzing and questioning the information we receive -- from all sources, including other people, books, newspapers, television and the Internet. Adult education consultant Phil Rabinowitz defines the goals of critical thinking as separating truth from what is false, considering the contexts of issues and getting at the underlying assumptions beneath information.
2 The Creative Thinking Contrast
Creative thinking, by contrast, is about accessing and implementing ideas. Where critical thinking involves developing our judgment skills, creative thinking usually involves suspending judgment. Writer and educator Robert Harris describes creative thinking as a process of "exploring ideas, generating possibilities, looking for many right answers rather than just one." Harris points out that creativity is often an attitude as much as an ability -- it involves receptivity to newness and change and the willingness to become playful with ideas and the possibilities. Yet, it is also a process in the sense that creative people tend to work diligently and with great focus on solutions.
3 Strategies for Developing Critical Thinking Skills
Rabinowitz suggests a number of strategies for developing one's critical faculties, including making a conscious effort to consider the values, experience and culture that are likely the sources of underlying assumptions in the thinking and writing of sources. He points out that a critical thinker also needs to ask some basic questions about information from newspapers and television, for example. These include thoughtful consideration of the biases, purposes and interests of the source. Asking ourselves about the logical consistency and the accuracy of the information presented is also very key. In other words, do the arguments or reasons presented actually prove what they suggest they are proving?
4 Strategies for Developing Creative Thinking
Jonah Lehrer, creativity guru and author of the 2012 bestseller "Imagine: How Creativity Works," suggests a number of quick triggers for accessing one's creativity, including daydreaming more often and seeking out laughter and humor more frequently. Harris encourages ignoring negative thoughts, such as "I'm not really creative," and overcoming fear of failure. Replace these attitudes with what Harris terms "constructive discontent," meaning a strong interest in solutions. Also important to bring to the creative process are the beliefs that most problems have solutions and that problems can be intriguing challenges. Both creative and critical thinking are essential to solving problems and to planning and crafting a meaningful life.
- 1 Foundation for Critical Thinking: A Brief History of the Idea of Critical Thinking
- 2 The Community Tool Box; Thinking Critically; Phil Rabinowitz
- 3 Virtual Salt; Introduction to Creative Thinking; Robert Harris
- 4 The Wall Street Journal; How to Be Creative; Jonah Lehrer
About the Author
Susie Zappia teaches humanities and research and writing courses online for several colleges. Her research interests include counterculture literature of the 1960 and instructional design for online courses and she enjoys writing about literature, art and instructional design. She holds a Master of Arts in humanities from California State University, Dominguez Hills and a Master of Science in instructional design from Capella University.
Related Articles

What Is Hierarchical Thinking?

Creative and Critical Thinking Skills

What Actions or Behaviors Are Indicative of a Critical...

What Is the Difference Between Proactive & Reactive?

What Are the Characteristics of Critical & Creative...

Beliefs Of Agnostics

Different Forms of Affection

Definition of Rigid Thinking

Comprehension Skills That Require Critical Thinking

What Is Hedonism?

Questions to Ask While Writing a Research Paper

How do I Develop Deductive Reasoning & Critical Thinking...

What Is the Difference Between Analytical and Creative...

Humanistic Approach to Classroom Management

How to Deliver Feedback in a Relationship

How to Infer When Reading & Questioning

How to Ask a Guy Friend Out Without Creeping Him Out

How to Increase Your Critical Thinking Skills

Rhetorical Essay Format
Regardless of how old we are, we never stop learning. Classroom is the educational resource for people of all ages. Whether you’re studying times tables or applying to college, Classroom has the answers.
- Accessibility
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Copyright Policy
- Manage Preferences
© 2020 Leaf Group Ltd. / Leaf Group Media, All Rights Reserved. Based on the Word Net lexical database for the English Language. See disclaimer .
More From Forbes
To succeed at work, set aside (most of) what you learned in school.
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
Education teaches you not just how to think, but to choose what to think.
Two young fish are swimming in the water when an older fish swims by and says, “Morning boys, how’s the water?” As he swims away, one young fish says, “What…is water?” So begins the late David Foster Wallace’s famous 2005 graduation speech at Kenyon College. In a genre notable for its advice to find your passion and feed your soul, Wallace talked soberly about blind spots, arrogance and the overwhelming danger of certainty. Education matters, he asserts, not because it teaches you how to think but because it enables you to choose what to think. Your educated life is about consciously getting free of the chatter in your head to become aware–really aware–of what is happening around you and make informed choices.
Your first job is the place to start. In a workplace where change is happening faster than even seasoned veterans can keep up with, keeping pace feels all but impossible. And the youngest workers are struggling: the most recent Gallup surveys report an 11-year low in employee engagement, with Gen Z dropping the most. So many disengaged young workers are sleepwalking through work, eager to finish the workday’s drudgery and get on with their “real” lives.
Work is not like school. After all, you’ve spent your whole life accumulating knowledge, checking the boxes, proving what you know and earning grades for everything. Now you have to get good at unlearning–letting go of the systems that made you successful in school to empower you to excel at work. A good education has given you the skills to rethink and reframe. Work requires you to use them: to question what you think you know, challenge your assumptions and open yourself up to new ideas and perspectives. As you move from the top of the heap to the bottom of the totem pole, what got you here won't get you there. Here are five ways to make the shift, to unlearn the habits that worked in school so that you can build the skills to succeed in your career.
Ditch The Homework Mindset
A bright young woman worked for my organization right out of school. She had been first in her class in high school, and she excelled in college by fiercely attending to her homework. When she came into her first job, her successful school formula betrayed her. Her fixation on homework came up short when she faced the ambiguity of work. Work doesn’t fall neatly into a curriculum with explicit things to do and homework to complete. While a task orientation is a great starting place, it’s not enough to simply check the boxes. Today’s workplace dishes out challenges without clear answers, problems that generate countless tasks that generate still more. Your job is to look for the big picture, to prioritize and surface what you need to better understand the context and the questions, not just the answers. It takes time and pretty relentless focus. Shifting from a check-the-box homework approach to a connect-the-dots mindset means understanding that only when you look beyond the tasks will the real learning begin.
Ask Lots Of Questions
Remember that guy in the back of the class who always had his hand up? If you worked hard not to be that person, it’s time to flip the script. To be successful at work, you must develop the comfort–at times the bravery–to ask many thoughtful and curious questions . To approach work with a beginner’s mind, listening and watching for new insights. Good questions are an unsung superpower. A good question signals respect and an eagerness to learn. It’s more than asking for instructions or advice–it’s about recognizing what you don’t know. Good, curious questions unlock the wisdom of others and help you to navigate a workplace that is changing as fast for the veterans as it is new for you. And finally, questions are the key to unlocking the future–whether you work with AI or other new technologies, a curious, learning mindset is the key to becoming adept at the new tools of your trade and aware of the trends shaping your work. In school, it’s imperative to prove what you know. At work, you must shed the fear of not knowing, opening yourself to new ideas, new ways of thinking and new things to think about.
Fallout Dethroned In Amazon Prime Video s Top 10 List By A New Offering
Google chrome gets second emergency update in a week as new exploit confirmed, metallica makes history with their new no 1 single, don’t compete, collaborate.
School is an individual journey. No matter how many group projects you had in school (including those wonderful moments where you did all the work while your groupmates loafed), you got tested, assessed and graded as an individual. But the vast majority of workplaces rely on successful teams–groups of individuals with diverse talents that work better together than they do alone. The best teams are not successful because they have smart individual team members, they’re effective because they are collectively intelligent . Sensitive to each other’s insights, they make space for everyone’s voice and celebrate their diversity. You can’t do this if you focus on your individual contributions more than the output of the team. School is inherently competitive. But today’s workplace depends on collaboration, on individual colleagues developing the skills to work better together. It’s a departure from the transactional in favor of the relational, where strong connections power the most productive teams.
Manage Your Own Expectations
As you go out into the world after graduation, you will be inundated with well-meaning advice (like this). But the thing about advice is that it tends to fit the giver more than the receiver. Your parents, teachers, mentors and employers have a lot invested in you, a lot riding on your success. And 9 times out of 10, they will foist their expectations on you. Learning to define your own success is a critical requirement for shaping the career that matters to you. It’s not just about passion, but about a set of realistic goals and objectives that you define for yourself. Your boss will change, your employer will change. If you spend your time trying to meet the expectations of others, you will be constantly beginning again. Of course, you need to be a team player. But in a world where work is changing faster than anyone can keep up, having your own sense of what you want to accomplish (and the skills you need to get there) is critical to forging your own path.
Be An AI Power User
Using AI to help you with your school work may have been viewed as cheating. At work, the opposite is true. If you don’t start getting comfortable with AI, the only one you will cheat is you. While many companies initially banned ChatGPT and LLMs at work–just like many schools and universities did at the outset–the winds have changed. Now companies are actively looking for employees to use it, to get familiar with its powers and pitfalls. Many employees aren’t quite sure where to start, fearing they could render their own jobs obsolete. And their employers don't yet know how to teach them. A just-released study shows that 75% of knowledge workers are using it, with massive opportunities for those who are willing to build their AI skills. AI is here to stay. Adoption may be slow in schools, but your success at work depends on you quickly embracing AI.
In his advice to new graduates, Foster Wallace observed, “The real value of a real education, … has almost nothing to do with knowledge and everything to do with simple awareness.” The key to a productive career is being attuned and aware of opportunity in a rapidly changing world: reframing your thinking and building new skills. It means listening (and watching), asking questions, challenging what you thought you knew and choosing to embrace new ways of working. Your career will be a constant journey of unlearning old ways to make space for new ones, of reminding yourself not to get so comfortable that you lose sight of the very water you swim in.

- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions
Join The Conversation
One Community. Many Voices. Create a free account to share your thoughts.
Forbes Community Guidelines
Our community is about connecting people through open and thoughtful conversations. We want our readers to share their views and exchange ideas and facts in a safe space.
In order to do so, please follow the posting rules in our site's Terms of Service. We've summarized some of those key rules below. Simply put, keep it civil.
Your post will be rejected if we notice that it seems to contain:
- False or intentionally out-of-context or misleading information
- Insults, profanity, incoherent, obscene or inflammatory language or threats of any kind
- Attacks on the identity of other commenters or the article's author
- Content that otherwise violates our site's terms.
User accounts will be blocked if we notice or believe that users are engaged in:
- Continuous attempts to re-post comments that have been previously moderated/rejected
- Racist, sexist, homophobic or other discriminatory comments
- Attempts or tactics that put the site security at risk
- Actions that otherwise violate our site's terms.
So, how can you be a power user?
- Stay on topic and share your insights
- Feel free to be clear and thoughtful to get your point across
- ‘Like’ or ‘Dislike’ to show your point of view.
- Protect your community.
- Use the report tool to alert us when someone breaks the rules.
Thanks for reading our community guidelines. Please read the full list of posting rules found in our site's Terms of Service.
The Pros and Cons of AI in Special Education

- Share article
Special education teachers fill out mountains of paperwork, customize lessons for students with a wide range of learning differences, and attend hours of bureaucratic meetings.
It’s easy to see why it would be tempting to outsource parts of that job to a robot.
While there may never be a special educator version of “Star Wars”’ protocol droid C-3PO, generative artificial tools—including ChatGPT and others developed with the large language models created by its founder, Open AI—can help special education teachers perform parts of their job more efficiently, allowing them to spend more time with their students, experts and educators say.
But those shortcuts come with plenty of cautions, they add.
Teachers need to review artificial intelligence’s suggestions carefully to ensure that they are right for specific students. Student data—including diagnoses of learning differences or cognitive disorders—need to be kept private.
Even special educators who have embraced the technology urge to proceed with care.
“I’m concerned about how AI is being presented right now to educators, that it’s this magical tool,” said Julie Tarasi, who teaches special education at Lakeview Middle School in the Park Hill school district near Kansas City, Mo. She recently completed a course in AI sponsored by the International Society for Technology in Education. “And I don’t think that the AI literacy aspect of it is necessarily being [shared] to the magnitude that it should be with teachers.”
Park Hill is cautiously experimenting with AI’s potential as a paperwork partner for educators and an assistive technology for some students in special education.
The district is on the vanguard. Only about 1 in 6 principals and district leaders—16 percent—said their schools or districts were piloting AI tools or using them in a limited manner with students in special education, according to a nationally representative EdWeek Research Center survey conducted in March and April.
AI tools may work best for teachers who already have a deep understanding of what works for students in special education, and of the tech itself, said Amanda Morin, a member of the advisory board for the learner-variability project at Digital Promise, a nonprofit organization that works on equity and technology issues in schools.
“If you feel really confident in your special education knowledge and experience and you have explored AI [in depth], I think those two can combine in a way that can really accelerate the way you serve students,” Morin said.
But “if you are a novice at either, it’s not going to serve your students well because you don’t know what you don’t know yet,” she added. “You may not even know if the tool is giving you a good answer.”
Here are some of the areas where Park Hill educators and other school and district leaders see AI’s promise for special education—and what caveats to look out for:
Promise: Reducing the paperwork burden.
Some special education teachers spend as many as eight hours a week writing student-behavior plans, progress reports, and other documentation.
“Inevitably, we’re gonna get stuck, we’re gonna struggle to word things,” Tarasi said. AI can be great for busting through writer’s block or finding a clearer, more objective way to describe a student’s behavior, she said.
What’s more, tools such as Magic School—an AI platform created for K-12 education—can help special education teachers craft the student learning goals that must be included in an individualized education program, or IEP.
“I can say ‘I need a reading goal to teach vowels and consonants to a student,’ and it will generate a goal,” said Tara Bachmann, Park Hill’s assistive-technology facilitator. “You can put the criteria you want in, but it makes it measurable, then my teachers can go in and insert the specifics about the student” without involving AI, Bachmann said.
These workarounds can cut the process of writing an IEP by up to 30 minutes, Bachmann said—giving teachers more time with students.
AI can also come to the rescue when a teacher needs to craft a polite, professional email to a parent after a stress-inducing encounter with their child.
Some Park Hill special education teachers use “Goblin,” a free tool aimed at helping neurodivergent people organize tasks, to take the “spice” out of those messages, Tarasi said.
A teacher could write “the most emotionally charged email. Then you hit a button called ‘formalize.’ And it makes it like incredibly professional,” Bachmann said. “Our teachers like it because they have a way to release the emotion but still communicate the message to the families.”
Caveat: Don’t share personally identifiable student information. Don’t blindly embrace AI’s suggestions.
Teachers must be extremely careful about privacy issues when using AI tools to write documents—from IEPs to emails—that contain sensitive student information, Tarasi said.
“If you wouldn’t put it on a billboard outside of the school, you should not be putting it into any sort of AI,” Tarasi said. “There’s no sense of guaranteed privacy.”
Tarasi advises her colleagues to “absolutely not put in names” when using generative AI to craft documents, she said. While including students’ approximate grade level may be OK in certain circumstances, inputting their exact age or mentioning a unique diagnosis is a no-no.
To be sure, if the information teachers put into AI is too vague, educators might not get accurate suggestions for their reports. That requires a balance.
“You need to be specific without being, without being pinpoint,” Tarasi said.
Caveat: AI works best for teachers who already understand special education
Another caution: Although AI tools can help teachers craft a report or customize a general education lesson for students in special education, teachers need to already have a deep understanding of their students to know whether to adopt its recommendations.
Relying solely on AI tools for lesson planning or writing reports “takes the individualized out of individualized education,” Morin said. “Because what [the technology] is doing is spitting out things that come up a lot” as opposed to carefully considering what’s best for a specific student, like a good teacher can.
Educators can tweak their prompts—the questions they ask AI—to get better, more specific advice, she added.
“A seasoned special educator would be able to say ‘So I have a student with ADHD, and they’re fidgety’ and get more individualized recommendations,” Morin said.
Promise: Making lessons more accessible.
Ensuring students in special education master the same course content as their peers can require teachers to spend hours simplifying the language of a text to an appropriate reading level.
Generative AI tools can accomplish that same task—often called “leveling a text"—in just minutes, said Josh Clark, the leader of the Landmark School , a private school in Massachusetts serving children with dyslexia and other language-based learning differences.
“If you have a class of 30 kids in 9th grade, and they’re all reading about photosynthesis, then for one particular child, you can customize [the] reading level without calling them out and without anybody else knowing and without you, the teacher, spending hours,” Clark said. “I think that’s a super powerful way of allowing kids to access information they may not be able to otherwise.”
Similarly, in Park Hill, Bachmann has used Canva—a design tool with a version specifically geared toward K-12 schools and therefore age-appropriate for many students—to help a student with cerebral palsy create the same kind of black-and-white art his classmates were making.
Kristen Ponce, the district’s speech and language pathologist, has used Canva to provide visuals for students in special education as they work to be more specific in their communication.
Case-in-point: One of Ponce’s students loves to learn about animals, but he has a very clear idea of what he’s looking for, she said. If the student just says “bear,” Canva will pull up a picture of, for instance, a brown grizzly. But the student may have been thinking of a polar bear.
That gives Ponce the opportunity to tell him, “We need to use more words to explain what you’re trying to say here,” she said. “We were able to move from ‘bear’ to ‘white bear on ice.’”
Caveat: It’s not always appropriate to use AI as an accessibility tool.
Not every AI tool can be used with every student. For instance, there are age restrictions for tools like ChatGPT, which isn’t for children under 13 or those under 18 without parent permission, Bachmann said. (ChatGPT does not independently verify a user’s age.)
“I caution my staff about introducing it to children who are too young and remembering that and that we try to focus on what therapists and teachers can do collectively to make life easier for [students],” she said.
“Accessibility is great,” she said. But when a teacher is thinking about “unleashing a child freely on AI, there is caution to it.”
Promise: Using AI tools to help students in special education communicate.
Park Hill is just beginning to use AI tools to help students in special education express their ideas.
One recent example: A student with a traumatic brain injury that affected her language abilities made thank you cards for several of her teachers using Canva.
“She was able to generate personal messages to people like the school nurses,” Bachmann said. “To her physical therapist who has taken her to all kinds of events outside in the community. She said, ‘You are my favorite therapist.’ She got very personal.”
There may be similar opportunities for AI to help students in special education write more effectively.
Some students with learning and thinking differences have trouble organizing their thoughts or getting their point across.
“When we ask a child to write, we’re actually asking them to do a whole lot of tasks at once,” Clark said. Aspects of writing that might seem relatively simple to a traditional learner—word retrieval, grammar, punctuation, spelling—can be a real roadblock for some students in special education, he said.
“It’s a huge distraction,” Clark said. The student may “have great ideas, but they have difficulty coming through.”
Caveat: Students may miss out on the critical-thinking skills writing builds.
Having students with language-processing differences use AI tools to better express themselves holds potential, but if it is not done carefully, students may miss developing key skills, said Digital Promise’s Morin.
AI “can be a really positive adaptive tool, but I think you have to be really structured about how you’re doing it,” she said.
ChatGPT or a similar tool may be able to help a student with dyslexia or a similar learning difference “create better writing, which I think is different than writing better,” Morin said.
Since it’s likely that students will be able to use those tools in the professional world, it makes sense that they begin using them in school, she said.
But the tools available now may not adequately explain the rationale behind the changes they make to a student’s work or help students express themselves more clearly in the future.
“The process is just as important as the outcome, especially with kids who learn differently, right?” Morin said. “Your process matters.”
Clark agreed on the need for moving cautiously. His own school is trying what he described as “isolated experiments” in using AI to help students with language-processing differences express themselves better.
The school is concentrating, for now, on older students preparing to enter college. Presumably, many will be able to use AI to complete some postsecondary assignments. “How do we make sure it’s an equal playing field?” Clark said.

Sign Up for EdWeek Update
Edweek top school jobs.

Sign Up & Sign In


- WEB STORIES New
- ENTERTAINMENT
- CAREER & CAMPUS
- INFOGRAPHICS
- ISL 2023-24

- Manorama Online
- Manorama News TV
- ManoramaMAX
- Radio Mango
- Subscription

My mother believed she didn't get KSEB job because she was non-political: Jackhammer Mary's son
Idukki: A job in KSEB was my mother's biggest wish, says Biju, the son of Mary Paily popularly known as 'Jackhammer Mary' who died on Monday. She was the lone woman labourer who took part in the construction of Moolamattam power station in Idukki. Biju said his mother did not have any political allegiance and she believed that's why she was denied a job. She even tried to get one of her children a job in KSEB but in vain.
In 1962, Mary and Paily came to Moolamattam for the construction of an underground power station. They also did farming in Moolamattam on a small scale, but spent most of their time working on the construction of the power station. Biju said that after doing all the household chores and preparing food for the children, Mary went to work. '' My mother used to reach home after work before 6 pm. We used to help her with housework,'' he said.
The couple had four sons and one daughter. It was after completing the work on Ponmudi Dam that the family moved to Moolamattam searching for a job. In her old age she was often troubled by shortness of breath; a condition doctors attributed to inhalation of rock dust from continuous use of jackhammer. It was D Babu Paul, then Idukki collector and project co-ordinator, who named her Jackhammer Mary after being impressed by her industry and skill in handling a job of arduous nature.

KSEB upbeat as rains bring copious water to produce ample power

'Jackhammer Mary' passes away with an unfulfilled dream
- Moolamattom Power Generation Plant

Negotiations with Transport Minister successful; driving school owners' associations call off strike

Pantheerankavu Case: Cop suspended for delay in probe

Central University of Kerala suspends asst prof Efthikar Ahamed arrested for sexual assault
Amoebic meningoencephalitis: 5-year-old in critical condition, family trying to get medicine from abroad

Family visit to Kottayam's Illikkal Kallu ends in infant's death

TVM collector’s summons to doctor escalates into IAS versus CPI union clash

Sleeping 10-year-old girl abducted from her house, sexually assaulted and robbed in Kasaragod

Mammootty receives support from Kerala politicians over online harassment row

Centuries old rosewood logs find takers in musical instrument makers at e-auction


President Joe Biden sits down to sign a document in the Rose Garden of the White House in Washington, Tuesday, May 14, 2024, imposing major new tariffs on electric vehicles, semiconductors, solar equipment and medical supplies imported from China. (AP Photo/Susan Walsh)
- Copy Link copied
President Joe Biden speaks in the Rose Garden of the White House in Washington, Tuesday, May 14, 2024, announcing plans to impose major new tariffs on electric vehicles, semiconductors, solar equipment and medical supplies imported from China. (AP Photo/Susan Walsh)
FILE - A worker assembles an SUV at a car plant of Li Auto, a major Chinese EV maker, in Changzhou in eastern China’s Jiangsu province on March 27, 2024. The Biden administration is announcing plans to slap new tariffs on Chinese electric vehicles, advanced batteries, solar cells, steel, aluminum and medical equipment. (Chinatopix Via AP, File)
WASHINGTON (AP) — President Joe Biden slapped major new tariffs on Chinese electric vehicles, advanced batteries, solar cells, steel, aluminum and medical equipment on Tuesday, taking potshots at Donald Trump along the way as he embraced a strategy that’s increasing friction between the world’s two largest economies.
The Democratic president said that Chinese government subsidies ensure the nation’s companies don’t have to turn a profit, giving them an unfair advantage in global trade.
“American workers can outwork and outcompete anyone as long as the competition is fair,” Biden said in the White House Rose Garden. “But for too long, it hasn’t been fair. For years, the Chinese government has poured state money into Chinese companies ... it’s not competition, it’s cheating.”
The tariffs come in the middle of a heated campaign between Biden and Trump, his Republican predecessor, to show who’s tougher on China. In a nod to the presidential campaign, Biden recognized lawmakers from Michigan in his remarks and spoke about workers in Pennsylvania and Wisconsin, all battleground states in November’s election.
Asked to respond to Trump’s comments that China was eating America’s lunch, Biden said of his rival, “He’s been feeding them a long time.” The Democrat said Trump had failed to crack down on Chinese trade abuses as he had pledged he would do during his presidency.
Karoline Leavitt, the Trump campaign’s press secretary, called the new tariffs a “weak and futile attempt” to distract from Biden’s own support for EVs in the United States, which Trump says will lead to layoffs at auto factories.
The Chinese government was quick to push back against the tariffs, saying they “will seriously affect the atmosphere of bilateral cooperation.” The foreign ministry used the word “bullying.”
The tariffs are unlikely to have a broad inflationary impact in the short term because of how they’re structured, some not to take effect until 2026, but there could be price increases in the meantime for EV batteries, solar and some other specific items.
Biden administration officials said they think the tariffs won’t escalate tensions with China, yet they expect China will explore ways to respond to the new taxes on its products. It’s uncertain what the long-term impact on prices could be if the tariffs contribute to a wider trade dispute.
The tariffs are to be phased in over the next three years, with those that take effect in 2024 covering EVs, solar cells, syringes, needles, steel and aluminum and more. There are currently very few EVs from China in the U.S., but officials worry low-priced models made possible by Chinese government subsidies could soon start flooding the U.S. market.
Chinese firms can sell EVs for as little as $12,000 . China’s solar cell plants and steel and aluminum mills have enough capacity to meet much of the world’s demand, with Chinese officials arguing their production keeps prices low and would aid a transition to the green economy.
China’s commerce ministry said in a statement that the tariffs were “typical political manipulation” as it expressed its “strong dissatisfaction” and pledged to “take resolute measures to defend its rights and interests.”
Under the findings of a four-year review on trade with China, the tax rate on imported Chinese EVs will rise to 102.5% this year, up from total levels of 27.5%. The review was undertaken under Section 301 of the Trade Act of 1974, which allows the government to retaliate against trade practices deemed unfair or in violation of global standards.
Under the 301 guidelines, the tariff rate is to double to 50% on solar cell imports this year. Tariffs on certain Chinese steel and aluminum products will climb to 25% this year. Computer chip tariffs will double to 50% by 2025.
For lithium-ion EV batteries, tariffs will rise from 7.5% to 25% this year. But for non-EV batteries of the same type, the tariff increase will be implemented in 2026. There are also higher tariffs on ship-to-shore cranes, critical minerals and medical products.
The new tariffs, at least initially, are largely symbolic since they will apply to only about $18 billion in imports. A new analysis by Oxford Economics estimates the tariffs will have a barely noticeable impact on inflation by pushing up inflation by just 0.01%.
The Chinese EV maker BYD has explored the possibility of opening factories in Mexico for the Mexican market, possibly creating a way to ship goods into the United States. U.S. Trade Representative Katherine Tai said she was talking with industry and workers about the possibility and to “stay tuned.”
The auto industry is still trying to assess the impact of the tariffs. But at present, it appears they could be assessed on only two Chinese-made vehicles, the Polestar 2 luxury EV and potentially Volvo’s S90 luxury gas-electric hybrid midsize sedan.
“We’re still reviewing the tariffs to understand exactly what’s affected and how,” said Russell Datz, spokesman for Volvo, a Swedish brand now under China’s Geely group. A message was left seeking comment from Polestar, which also falls under Geely.
The Chinese foreign ministry spokesperson, Wang Wenbin, said the U.S. is trampling on the principles of a market economy and international economic and trade rules.
“It’s a naked act of bullying,” Wang said.
The Chinese economy has been slowed by the collapse of the country’s real estate market and past coronavirus pandemic lockdowns, prompting Chinese President Xi Jinping to try to jumpstart growth by ramping up production of EVs and other products, making more than the Chinese market can absorb.
This strategy further exacerbates tensions with a U.S. government that claims it’s determined to strengthen its own manufacturing to compete with China, yet avoid a larger conflict.
“China’s factory-led recovery and weak consumption growth, which are translating into excess capacity and an aggressive search for foreign markets, in tandem with the looming U.S. election season add up to a perfect recipe for escalating U.S. trade fractions with China,’’ said Eswar Prasad, professor of trade policy at Cornell University.
The Europeans are worried, too. The EU launched an investigation last fall into Chinese subsidies and could impose an import tax on Chinese EVs.
After Xi’s visit to France last week, European Commission President Ursula von der Leyen warned that government-subsidized Chinese EVs and steel “are flooding the European market” and said, “The world cannot absorb China’s surplus production.’’
Biden’s administration views China, with its subsidies of manufacturing, as trying to globally control the EV and clean-energy sectors, whereas the administration says its own industrial support is geared toward ensuring domestic supplies to help meet U.S. demand.
“We do not seek to have global domination of manufacturing in these sectors, but we believe because these are strategic industries and for the sake of resilience of our supply chains, that we want to make sure that we have healthy and active firms,” Treasury Secretary Janet Yellen said.
The tensions go far beyond a trade dispute to deeper questions about who leads the world economy as a seemingly indispensable nation. China’s policies could make the world more dependent on its factories, possibly giving it greater leverage in geopolitics. At the same time, the United States says it’s seeking for countries to operate by the same standards so competition can be fair.
China maintains the tariffs are in violation of the global trade rules the United States originally helped establish through the World Trade Organization. It accuses the U.S. of continuing to politicize trade issues and on Friday said the new tariffs compound the problems caused by tariffs the Trump administration previously put on Chinese goods, which Biden has kept.
Those issues are at the heart of November’s presidential election, with a bitterly divided electorate seemingly united by the idea of getting tough with China. Biden and Trump have overlapping but different strategies.
Biden sees targeted tariffs as needed to defend key industries and workers, while Trump has threatened broad 10% tariffs against all imports from rivals and allies alike.
Biden has staked his presidential legacy on the U.S. pulling ahead of China with its own government investments in factories to make EVs, computer chips and other advanced technologies.
Trump tells his supporters America is falling further behind China by not betting on oil to keep powering the economy, despite its climate change risks. The ex-president may believe tariffs can change Chinese behavior, but he believes the U.S. will be reliant on China for EV components and solar cells.
“Joe Biden’s economic plan is to make China rich and America poor,” he said at a rally this month in Wisconsin.
AP autos writer Tom Krisher contributed to this report from Detroit.

Post comment
or continue as guest

- Bahasa Indonesia
- Eastern Europe
- Moscow Oblast
Elektrostal
Elektrostal Localisation : Country Russia , Oblast Moscow Oblast . Available Information : Geographical coordinates , Population, Area, Altitude, Weather and Hotel . Nearby cities and villages : Noginsk , Pavlovsky Posad and Staraya Kupavna .
Information
Find all the information of Elektrostal or click on the section of your choice in the left menu.
- Update data
Elektrostal Demography
Information on the people and the population of Elektrostal.
Elektrostal Geography
Geographic Information regarding City of Elektrostal .
Elektrostal Distance
Distance (in kilometers) between Elektrostal and the biggest cities of Russia.
Elektrostal Map
Locate simply the city of Elektrostal through the card, map and satellite image of the city.
Elektrostal Nearby cities and villages
Elektrostal weather.
Weather forecast for the next coming days and current time of Elektrostal.
Elektrostal Sunrise and sunset
Find below the times of sunrise and sunset calculated 7 days to Elektrostal.
Elektrostal Hotel
Our team has selected for you a list of hotel in Elektrostal classified by value for money. Book your hotel room at the best price.
Elektrostal Nearby
Below is a list of activities and point of interest in Elektrostal and its surroundings.
Elektrostal Page

- Information /Russian-Federation--Moscow-Oblast--Elektrostal#info
- Demography /Russian-Federation--Moscow-Oblast--Elektrostal#demo
- Geography /Russian-Federation--Moscow-Oblast--Elektrostal#geo
- Distance /Russian-Federation--Moscow-Oblast--Elektrostal#dist1
- Map /Russian-Federation--Moscow-Oblast--Elektrostal#map
- Nearby cities and villages /Russian-Federation--Moscow-Oblast--Elektrostal#dist2
- Weather /Russian-Federation--Moscow-Oblast--Elektrostal#weather
- Sunrise and sunset /Russian-Federation--Moscow-Oblast--Elektrostal#sun
- Hotel /Russian-Federation--Moscow-Oblast--Elektrostal#hotel
- Nearby /Russian-Federation--Moscow-Oblast--Elektrostal#around
- Page /Russian-Federation--Moscow-Oblast--Elektrostal#page
- Terms of Use
- Copyright © 2024 DB-City - All rights reserved
- Change Ad Consent Do not sell my data

COMMENTS
Here are some effective jobs for abstract thinkers to pursue: 1. Graphic designer. National average salary: $50,656 per year Primary duties: A graphic designer operates a computer to develop a wide variety of visual marketing materials like websites, brochures, logos, advertisement images and posters to promote a company's product, brand or ...
Jobs requiring no skills are essential for people with little work experience or who are just graduating high school or college. These jobs can provide the opportunity to gain experience and move on to upper-level positions. ... Common duties include responding to non-life-threatening emergencies, enforcing company policies and rules, creating ...
Here is a list of the 20 best jobs for analytical thinkers with salary information. For the most up-to-date salary information from Indeed, click on the salary link by each job title below: 1. Logistics supervisor. National average salary: $59,956 per year Primary duties: A logistics supervisor is a person who oversees the organization and ...
2. Aerospace Engineering. Aerospace engineers design and build planes, spacecraft, and weapons systems. You need a master's degree to work in most aerospace engineer jobs, but you can also get a bachelor's. Aerospace engineers are thinkers. The top engineers go to work for NASA.
Gathering information by observation, experience, reflection, communication, or research. Analyzing, synthesizing and evaluating the information. Making a choice based on facts, or insight arrived from weighing different pros and cons. In contrast, non-critical thinking is based on emotions, peer or social pressure, tradition.
We looked at the non-technical skills with the highest importance scores across the 28 highest-paying jobs in the US from the Occupational Information Network 's database. Critical thinking and ...
Non-critical thinking is more focused on gathering information and facts without any real need to focus on the implications of that information. On the other hand, critical thinking involves a much deeper analysis of the data and its implications. 2. The level of analysis each type of thinking calls for. Another key difference is the level of ...
Non-critical thinking is the easiest of easy ways out of almost any predicament. situation or event because it does not require any proof of thought. In effect. it is 2 + 2 = 5 and is accepted at face value. ... Critical thinking is a skill that every employer loves to list in their job descriptions. According to a World Economic Forum survey ...
2. Critical thinking There are usually ways to improve workplace processes, strategies, or even teamwork. Thinking critically and creatively—being an observant individual who asks questions and draws insights that can be used to identify solutions—is a worthwhile skill to hone. 3. Problem-solving
Dietitians and nutritionists. Number of jobs projected through 2030/percent growth from 2020: 73,000/11%. Entry-level education required: Bachelor's Degree. 2021 Median pay: $61,650. Critical thinking skill for dietitians: Plan and implement food service and nutritional programs in a variety of settings.
Average Salary: $40,000 - $65,000 per year. Philosophers engage in critical thinking and debate on various topics, including ethics, logic, metaphysics, epistemology, and other realms of the humanities. This role is ideal for critical thinkers who enjoy analyzing and discussing profound questions about existence, society, and the human condition.
This field requires a passion for the unknown and all things complex. It requires an extremely high level of critical thinking to master this field. Robotics Engineer Key Stats. Avg. Salary / year. $107,890. Avg. Pay / hour.
Truth is, we all have biases that make us less than 100% critical thinkers, and an inability to recognize that fact should be our first indication that it is true. But all is not lost—culture is not destroyed—by the imperfect. Culture is destroyed by deserters—non-critical thinkers abandoning their humanity—voting with their feet, in ...
open access. Empirical evidence shows that not all critical thinkers demonstrate critical thinking behaviors in all situations. Some reasons why non-critical thinking appears to be more beneficial to the individual in the contemporary education context of Hungary are explored in the paper. First, a cultural anthropological approach is applied ...
Critical thinking has roots in the teachings of Socrates more than 2,500 years ago. The Foundation for Critical Thinking points out that Socrates established the importance of seeking evidence, questioning assumptions and examining reasoning to examine beliefs and their origins.
Today's top 435,000+ Critical Thinking jobs in United States. Leverage your professional network, and get hired. New Critical Thinking jobs added daily.
2️⃣ Data Literacy. Data can determine a company's success and affect how leaders make critical decisions. Business owners rely on their executives to use data to conquer new markets. When looking for a new job, you should have data literacy as a top skill. Learn how to use different tools to analyze and interpret data.
To be successful at work, you must develop the comfort-at times the bravery-to ask many thoughtful and curious questions. To approach work with a beginner's mind, listening and watching for ...
Here are 10 roles that require creative thinking skills in the workplace. 1. Video game designer. National average salary: $76,887 per year Primary duties: A game designer is responsible for developing and designing video games and typically specializes in design, art or programming. They may also be responsible for writing code, managing ...
Among the rescued was a 45-year-old man who was transported to ProMedica Monroe Regional Hospital with injuries described as non-life-threatening, the other two were checked by paramedics and ...
Promise: Making lessons more accessible. Ensuring students in special education master the same course content as their peers can require teachers to spend hours simplifying the language of a text ...
TALLINN — The government of Estonia is "seriously" discussing the possibility of sending troops into western Ukraine to take over non-direct combat, "rear" roles from Ukrainian forces in ...
Mary single-handedly operated the jackhammer, even when male workers sought assistance from others to operate it. Photo: Special arrangement. Idukki: A job in KSEB was my mother's biggest wish, says Biju, the son of Mary Paily popularly known as 'Jackhammer Mary' who died on Monday. She was the lone ...
Welcome to the 628DirtRooster website where you can find video links to Randy McCaffrey's (AKA DirtRooster) YouTube videos, community support and other resources for the Hobby Beekeepers and the official 628DirtRooster online store where you can find 628DirtRooster hats and shirts, local Mississippi honey and whole lot more!
The tariffs would apply to $18bn worth of Chinese products, it said. The US will quadruple the tariff rate on Chinese EVs to 100 per cent this year and roughly triple the rate on imports of steel ...
But for non-EV batteries of the same type, the tariff increase will be implemented in 2026. There are also higher tariffs on ship-to-shore cranes, critical minerals and medical products. The new tariffs, at least initially, are largely symbolic since they will apply to only about $18 billion in imports. A new analysis by Oxford Economics ...
A residential and industrial region in the south-east of Mocsow. It was founded on the spot of two villages: Chagino (what is now the Moscow Oil Refinery) and Ryazantsevo (demolished in 1979). in 1960 the town was incorporated into the City of Moscow as a district. Population - 45,000 people (2002). The district is one of the most polluted residential areas in Moscow, due to the Moscow Oil ...
Elektrostal Geography. Geographic Information regarding City of Elektrostal. Elektrostal Geographical coordinates. Latitude: 55.8, Longitude: 38.45. 55° 48′ 0″ North, 38° 27′ 0″ East. Elektrostal Area. 4,951 hectares. 49.51 km² (19.12 sq mi) Elektrostal Altitude.