
School Life Balance , Tips for Online Students

The Pros and Cons of Homework
Updated: December 7, 2023
Published: January 23, 2020

Homework is a word that most students dread hearing. After hours upon hours of sitting in class , the last thing we want is more schoolwork over our precious weekends. While it’s known to be a staple of traditional schooling, homework has also become a rather divise topic. Some feel as though homework is a necessary part of school, while others believe that the time could be better invested. Should students have homework? Have a closer look into the arguments on both sides to decide for yourself.

Photo by energepic.com from Pexels
Why should students have homework, 1. homework encourages practice.
Many people believe that one of the positive effects of homework is that it encourages the discipline of practice. While it may be time consuming and boring compared to other activities, repetition is needed to get better at skills. Homework helps make concepts more clear, and gives students more opportunities when starting their career .
2. Homework Gets Parents Involved
Homework can be something that gets parents involved in their children’s lives if the environment is a healthy one. A parent helping their child with homework makes them take part in their academic success, and allows for the parent to keep up with what the child is doing in school. It can also be a chance to connect together.
3. Homework Teaches Time Management
Homework is much more than just completing the assigned tasks. Homework can develop time management skills , forcing students to plan their time and make sure that all of their homework assignments are done on time. By learning to manage their time, students also practice their problem-solving skills and independent thinking. One of the positive effects of homework is that it forces decision making and compromises to be made.
4. Homework Opens A Bridge Of Communication
Homework creates a connection between the student, the teacher, the school, and the parents. It allows everyone to get to know each other better, and parents can see where their children are struggling. In the same sense, parents can also see where their children are excelling. Homework in turn can allow for a better, more targeted educational plan for the student.
5. Homework Allows For More Learning Time
Homework allows for more time to complete the learning process. School hours are not always enough time for students to really understand core concepts, and homework can counter the effects of time shortages, benefiting students in the long run, even if they can’t see it in the moment.
6. Homework Reduces Screen Time
Many students in North America spend far too many hours watching TV. If they weren’t in school, these numbers would likely increase even more. Although homework is usually undesired, it encourages better study habits and discourages spending time in front of the TV. Homework can be seen as another extracurricular activity, and many families already invest a lot of time and money in different clubs and lessons to fill up their children’s extra time. Just like extracurricular activities, homework can be fit into one’s schedule.

The Other Side: Why Homework Is Bad
1. homework encourages a sedentary lifestyle.
Should students have homework? Well, that depends on where you stand. There are arguments both for the advantages and the disadvantages of homework.
While classroom time is important, playground time is just as important. If children are given too much homework, they won’t have enough playtime, which can impact their social development and learning. Studies have found that those who get more play get better grades in school , as it can help them pay closer attention in the classroom.
Children are already sitting long hours in the classroom, and homework assignments only add to these hours. Sedentary lifestyles can be dangerous and can cause health problems such as obesity. Homework takes away from time that could be spent investing in physical activity.
2. Homework Isn’t Healthy In Every Home
While many people that think homes are a beneficial environment for children to learn, not all homes provide a healthy environment, and there may be very little investment from parents. Some parents do not provide any kind of support or homework help, and even if they would like to, due to personal barriers, they sometimes cannot. Homework can create friction between children and their parents, which is one of the reasons why homework is bad .
3. Homework Adds To An Already Full-Time Job
School is already a full-time job for students, as they generally spend over 6 hours each day in class. Students also often have extracurricular activities such as sports, music, or art that are just as important as their traditional courses. Adding on extra hours to all of these demands is a lot for children to manage, and prevents students from having extra time to themselves for a variety of creative endeavors. Homework prevents self discovery and having the time to learn new skills outside of the school system. This is one of the main disadvantages of homework.
4. Homework Has Not Been Proven To Provide Results
Endless surveys have found that homework creates a negative attitude towards school, and homework has not been found to be linked to a higher level of academic success.
The positive effects of homework have not been backed up enough. While homework may help some students improve in specific subjects, if they have outside help there is no real proof that homework makes for improvements.
It can be a challenge to really enforce the completion of homework, and students can still get decent grades without doing their homework. Extra school time does not necessarily mean better grades — quality must always come before quantity.
Accurate practice when it comes to homework simply isn’t reliable. Homework could even cause opposite effects if misunderstood, especially since the reliance is placed on the student and their parents — one of the major reasons as to why homework is bad. Many students would rather cheat in class to avoid doing their homework at home, and children often just copy off of each other or from what they read on the internet.
5. Homework Assignments Are Overdone
The general agreement is that students should not be given more than 10 minutes a day per grade level. What this means is that a first grader should be given a maximum of 10 minutes of homework, while a second grader receives 20 minutes, etc. Many students are given a lot more homework than the recommended amount, however.
On average, college students spend as much as 3 hours per night on homework . By giving too much homework, it can increase stress levels and lead to burn out. This in turn provides an opposite effect when it comes to academic success.
The pros and cons of homework are both valid, and it seems as though the question of ‘‘should students have homework?’ is not a simple, straightforward one. Parents and teachers often are found to be clashing heads, while the student is left in the middle without much say.
It’s important to understand all the advantages and disadvantages of homework, taking both perspectives into conversation to find a common ground. At the end of the day, everyone’s goal is the success of the student.
Related Articles
Should Kids Get Homework?
Homework gives elementary students a way to practice concepts, but too much can be harmful, experts say.

Getty Images
Effective homework reinforces math, reading, writing or spelling skills, but in a way that's meaningful.
How much homework students should get has long been a source of debate among parents and educators. In recent years, some districts have even implemented no-homework policies, as students juggle sports, music and other activities after school.
Parents of elementary school students, in particular, have argued that after-school hours should be spent with family or playing outside rather than completing assignments. And there is little research to show that homework improves academic achievement for elementary students.
But some experts say there's value in homework, even for younger students. When done well, it can help students practice core concepts and develop study habits and time management skills. The key to effective homework, they say, is keeping assignments related to classroom learning, and tailoring the amount by age: Many experts suggest no homework for kindergartners, and little to none in first and second grade.
Value of Homework
Homework provides a chance to solidify what is being taught in the classroom that day, week or unit. Practice matters, says Janine Bempechat, clinical professor at Boston University 's Wheelock College of Education & Human Development.
"There really is no other domain of human ability where anybody would say you don't need to practice," she adds. "We have children practicing piano and we have children going to sports practice several days a week after school. You name the domain of ability and practice is in there."
Homework is also the place where schools and families most frequently intersect.
"The children are bringing things from the school into the home," says Paula S. Fass, professor emerita of history at the University of California—Berkeley and the author of "The End of American Childhood." "Before the pandemic, (homework) was the only real sense that parents had to what was going on in schools."
Harris Cooper, professor emeritus of psychology and neuroscience at Duke University and author of "The Battle Over Homework," examined more than 60 research studies on homework between 1987 and 2003 and found that — when designed properly — homework can lead to greater student success. Too much, however, is harmful. And homework has a greater positive effect on students in secondary school (grades 7-12) than those in elementary.
"Every child should be doing homework, but the amount and type that they're doing should be appropriate for their developmental level," he says. "For teachers, it's a balancing act. Doing away with homework completely is not in the best interest of children and families. But overburdening families with homework is also not in the child's or a family's best interest."
Negative Homework Assignments
Not all homework for elementary students involves completing a worksheet. Assignments can be fun, says Cooper, like having students visit educational locations, keep statistics on their favorite sports teams, read for pleasure or even help their parents grocery shop. The point is to show students that activities done outside of school can relate to subjects learned in the classroom.
But assignments that are just busy work, that force students to learn new concepts at home, or that are overly time-consuming can be counterproductive, experts say.
Homework that's just busy work.
Effective homework reinforces math, reading, writing or spelling skills, but in a way that's meaningful, experts say. Assignments that look more like busy work – projects or worksheets that don't require teacher feedback and aren't related to topics learned in the classroom – can be frustrating for students and create burdens for families.
"The mental health piece has definitely played a role here over the last couple of years during the COVID-19 pandemic, and the last thing we want to do is frustrate students with busy work or homework that makes no sense," says Dave Steckler, principal of Red Trail Elementary School in Mandan, North Dakota.
Homework on material that kids haven't learned yet.
With the pressure to cover all topics on standardized tests and limited time during the school day, some teachers assign homework that has not yet been taught in the classroom.
Not only does this create stress, but it also causes equity challenges. Some parents speak languages other than English or work several jobs, and they aren't able to help teach their children new concepts.
" It just becomes agony for both parents and the kids to get through this worksheet, and the goal becomes getting to the bottom of (the) worksheet with answers filled in without any understanding of what any of it matters for," says professor Susan R. Goldman, co-director of the Learning Sciences Research Institute at the University of Illinois—Chicago .
Homework that's overly time-consuming.
The standard homework guideline recommended by the National Parent Teacher Association and the National Education Association is the "10-minute rule" – 10 minutes of nightly homework per grade level. A fourth grader, for instance, would receive a total of 40 minutes of homework per night.
But this does not always happen, especially since not every student learns the same. A 2015 study published in the American Journal of Family Therapy found that primary school children actually received three times the recommended amount of homework — and that family stress increased along with the homework load.
Young children can only remain attentive for short periods, so large amounts of homework, especially lengthy projects, can negatively affect students' views on school. Some individual long-term projects – like having to build a replica city, for example – typically become an assignment for parents rather than students, Fass says.
"It's one thing to assign a project like that in which several kids are working on it together," she adds. "In (that) case, the kids do normally work on it. It's another to send it home to the families, where it becomes a burden and doesn't really accomplish very much."
Private vs. Public Schools
Do private schools assign more homework than public schools? There's little research on the issue, but experts say private school parents may be more accepting of homework, seeing it as a sign of academic rigor.
Of course, not all private schools are the same – some focus on college preparation and traditional academics, while others stress alternative approaches to education.
"I think in the academically oriented private schools, there's more support for homework from parents," says Gerald K. LeTendre, chair of educational administration at Pennsylvania State University—University Park . "I don't know if there's any research to show there's more homework, but it's less of a contentious issue."
How to Address Homework Overload
First, assess if the workload takes as long as it appears. Sometimes children may start working on a homework assignment, wander away and come back later, Cooper says.
"Parents don't see it, but they know that their child has started doing their homework four hours ago and still not done it," he adds. "They don't see that there are those four hours where their child was doing lots of other things. So the homework assignment itself actually is not four hours long. It's the way the child is approaching it."
But if homework is becoming stressful or workload is excessive, experts suggest parents first approach the teacher, followed by a school administrator.
"Many times, we can solve a lot of issues by having conversations," Steckler says, including by "sitting down, talking about the amount of homework, and what's appropriate and not appropriate."
Study Tips for High School Students

Tags: K-12 education , students , elementary school , children
2024 Best Colleges

Search for your perfect fit with the U.S. News rankings of colleges and universities.
- Future Students
- Current Students
- Faculty/Staff

News and Media
- News & Media Home
- Research Stories
- School's In
- In the Media
You are here
More than two hours of homework may be counterproductive, research suggests.

A Stanford education researcher found that too much homework can negatively affect kids, especially their lives away from school, where family, friends and activities matter. "Our findings on the effects of homework challenge the traditional assumption that homework is inherently good," wrote Denise Pope , a senior lecturer at the Stanford Graduate School of Education and a co-author of a study published in the Journal of Experimental Education . The researchers used survey data to examine perceptions about homework, student well-being and behavioral engagement in a sample of 4,317 students from 10 high-performing high schools in upper-middle-class California communities. Along with the survey data, Pope and her colleagues used open-ended answers to explore the students' views on homework. Median household income exceeded $90,000 in these communities, and 93 percent of the students went on to college, either two-year or four-year. Students in these schools average about 3.1 hours of homework each night. "The findings address how current homework practices in privileged, high-performing schools sustain students' advantage in competitive climates yet hinder learning, full engagement and well-being," Pope wrote. Pope and her colleagues found that too much homework can diminish its effectiveness and even be counterproductive. They cite prior research indicating that homework benefits plateau at about two hours per night, and that 90 minutes to two and a half hours is optimal for high school. Their study found that too much homework is associated with: • Greater stress : 56 percent of the students considered homework a primary source of stress, according to the survey data. Forty-three percent viewed tests as a primary stressor, while 33 percent put the pressure to get good grades in that category. Less than 1 percent of the students said homework was not a stressor. • Reductions in health : In their open-ended answers, many students said their homework load led to sleep deprivation and other health problems. The researchers asked students whether they experienced health issues such as headaches, exhaustion, sleep deprivation, weight loss and stomach problems. • Less time for friends, family and extracurricular pursuits : Both the survey data and student responses indicate that spending too much time on homework meant that students were "not meeting their developmental needs or cultivating other critical life skills," according to the researchers. Students were more likely to drop activities, not see friends or family, and not pursue hobbies they enjoy. A balancing act The results offer empirical evidence that many students struggle to find balance between homework, extracurricular activities and social time, the researchers said. Many students felt forced or obligated to choose homework over developing other talents or skills. Also, there was no relationship between the time spent on homework and how much the student enjoyed it. The research quoted students as saying they often do homework they see as "pointless" or "mindless" in order to keep their grades up. "This kind of busy work, by its very nature, discourages learning and instead promotes doing homework simply to get points," said Pope, who is also a co-founder of Challenge Success , a nonprofit organization affiliated with the GSE that conducts research and works with schools and parents to improve students' educational experiences.. Pope said the research calls into question the value of assigning large amounts of homework in high-performing schools. Homework should not be simply assigned as a routine practice, she said. "Rather, any homework assigned should have a purpose and benefit, and it should be designed to cultivate learning and development," wrote Pope. High-performing paradox In places where students attend high-performing schools, too much homework can reduce their time to foster skills in the area of personal responsibility, the researchers concluded. "Young people are spending more time alone," they wrote, "which means less time for family and fewer opportunities to engage in their communities." Student perspectives The researchers say that while their open-ended or "self-reporting" methodology to gauge student concerns about homework may have limitations – some might regard it as an opportunity for "typical adolescent complaining" – it was important to learn firsthand what the students believe. The paper was co-authored by Mollie Galloway from Lewis and Clark College and Jerusha Conner from Villanova University.
Clifton B. Parker is a writer at the Stanford News Service .
More Stories

⟵ Go to all Research Stories
Get the Educator
Subscribe to our monthly newsletter.
Stanford Graduate School of Education
482 Galvez Mall Stanford, CA 94305-3096 Tel: (650) 723-2109
- Contact Admissions
- GSE Leadership
- Site Feedback
- Web Accessibility
- Career Resources
- Faculty Open Positions
- Explore Courses
- Academic Calendar
- Office of the Registrar
- Cubberley Library
- StanfordWho
- StanfordYou
Improving lives through learning

- Stanford Home
- Maps & Directions
- Search Stanford
- Emergency Info
- Terms of Use
- Non-Discrimination
- Accessibility
© Stanford University , Stanford , California 94305 .
- Our Mission

What’s the Right Amount of Homework?
Decades of research show that homework has some benefits, especially for students in middle and high school—but there are risks to assigning too much.
Many teachers and parents believe that homework helps students build study skills and review concepts learned in class. Others see homework as disruptive and unnecessary, leading to burnout and turning kids off to school. Decades of research show that the issue is more nuanced and complex than most people think: Homework is beneficial, but only to a degree. Students in high school gain the most, while younger kids benefit much less.
The National PTA and the National Education Association support the “ 10-minute homework guideline ”—a nightly 10 minutes of homework per grade level. But many teachers and parents are quick to point out that what matters is the quality of the homework assigned and how well it meets students’ needs, not the amount of time spent on it.
The guideline doesn’t account for students who may need to spend more—or less—time on assignments. In class, teachers can make adjustments to support struggling students, but at home, an assignment that takes one student 30 minutes to complete may take another twice as much time—often for reasons beyond their control. And homework can widen the achievement gap, putting students from low-income households and students with learning disabilities at a disadvantage.
However, the 10-minute guideline is useful in setting a limit: When kids spend too much time on homework, there are real consequences to consider.
Small Benefits for Elementary Students
As young children begin school, the focus should be on cultivating a love of learning, and assigning too much homework can undermine that goal. And young students often don’t have the study skills to benefit fully from homework, so it may be a poor use of time (Cooper, 1989 ; Cooper et al., 2006 ; Marzano & Pickering, 2007 ). A more effective activity may be nightly reading, especially if parents are involved. The benefits of reading are clear: If students aren’t proficient readers by the end of third grade, they’re less likely to succeed academically and graduate from high school (Fiester, 2013 ).
For second-grade teacher Jacqueline Fiorentino, the minor benefits of homework did not outweigh the potential drawback of turning young children against school at an early age, so she experimented with dropping mandatory homework. “Something surprising happened: They started doing more work at home,” Fiorentino writes . “This inspiring group of 8-year-olds used their newfound free time to explore subjects and topics of interest to them.” She encouraged her students to read at home and offered optional homework to extend classroom lessons and help them review material.
Moderate Benefits for Middle School Students
As students mature and develop the study skills necessary to delve deeply into a topic—and to retain what they learn—they also benefit more from homework. Nightly assignments can help prepare them for scholarly work, and research shows that homework can have moderate benefits for middle school students (Cooper et al., 2006 ). Recent research also shows that online math homework, which can be designed to adapt to students’ levels of understanding, can significantly boost test scores (Roschelle et al., 2016 ).
There are risks to assigning too much, however: A 2015 study found that when middle school students were assigned more than 90 to 100 minutes of daily homework, their math and science test scores began to decline (Fernández-Alonso, Suárez-Álvarez, & Muñiz, 2015 ). Crossing that upper limit can drain student motivation and focus. The researchers recommend that “homework should present a certain level of challenge or difficulty, without being so challenging that it discourages effort.” Teachers should avoid low-effort, repetitive assignments, and assign homework “with the aim of instilling work habits and promoting autonomous, self-directed learning.”
In other words, it’s the quality of homework that matters, not the quantity. Brian Sztabnik, a veteran middle and high school English teacher, suggests that teachers take a step back and ask themselves these five questions :
- How long will it take to complete?
- Have all learners been considered?
- Will an assignment encourage future success?
- Will an assignment place material in a context the classroom cannot?
- Does an assignment offer support when a teacher is not there?
More Benefits for High School Students, but Risks as Well
By the time they reach high school, students should be well on their way to becoming independent learners, so homework does provide a boost to learning at this age, as long as it isn’t overwhelming (Cooper et al., 2006 ; Marzano & Pickering, 2007 ). When students spend too much time on homework—more than two hours each night—it takes up valuable time to rest and spend time with family and friends. A 2013 study found that high school students can experience serious mental and physical health problems, from higher stress levels to sleep deprivation, when assigned too much homework (Galloway, Conner, & Pope, 2013 ).
Homework in high school should always relate to the lesson and be doable without any assistance, and feedback should be clear and explicit.
Teachers should also keep in mind that not all students have equal opportunities to finish their homework at home, so incomplete homework may not be a true reflection of their learning—it may be more a result of issues they face outside of school. They may be hindered by issues such as lack of a quiet space at home, resources such as a computer or broadband connectivity, or parental support (OECD, 2014 ). In such cases, giving low homework scores may be unfair.
Since the quantities of time discussed here are totals, teachers in middle and high school should be aware of how much homework other teachers are assigning. It may seem reasonable to assign 30 minutes of daily homework, but across six subjects, that’s three hours—far above a reasonable amount even for a high school senior. Psychologist Maurice Elias sees this as a common mistake: Individual teachers create homework policies that in aggregate can overwhelm students. He suggests that teachers work together to develop a school-wide homework policy and make it a key topic of back-to-school night and the first parent-teacher conferences of the school year.
Parents Play a Key Role
Homework can be a powerful tool to help parents become more involved in their child’s learning (Walker et al., 2004 ). It can provide insights into a child’s strengths and interests, and can also encourage conversations about a child’s life at school. If a parent has positive attitudes toward homework, their children are more likely to share those same values, promoting academic success.
But it’s also possible for parents to be overbearing, putting too much emphasis on test scores or grades, which can be disruptive for children (Madjar, Shklar, & Moshe, 2015 ). Parents should avoid being overly intrusive or controlling—students report feeling less motivated to learn when they don’t have enough space and autonomy to do their homework (Orkin, May, & Wolf, 2017 ; Patall, Cooper, & Robinson, 2008 ; Silinskas & Kikas, 2017 ). So while homework can encourage parents to be more involved with their kids, it’s important to not make it a source of conflict.
- About the Hub
- Announcements
- Faculty Experts Guide
- Subscribe to the newsletter
Explore by Topic
- Arts+Culture
- Politics+Society
- Science+Technology
- Student Life
- University News
- Voices+Opinion
- About Hub at Work
- Gazette Archive
- Benefits+Perks
- Health+Well-Being
- Current Issue
- About the Magazine
- Past Issues
- Support Johns Hopkins Magazine
- Subscribe to the Magazine
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser to improve your experience.

Credit: August de Richelieu
Does homework still have value? A Johns Hopkins education expert weighs in
Joyce epstein, co-director of the center on school, family, and community partnerships, discusses why homework is essential, how to maximize its benefit to learners, and what the 'no-homework' approach gets wrong.
By Vicky Hallett
The necessity of homework has been a subject of debate since at least as far back as the 1890s, according to Joyce L. Epstein , co-director of the Center on School, Family, and Community Partnerships at Johns Hopkins University. "It's always been the case that parents, kids—and sometimes teachers, too—wonder if this is just busy work," Epstein says.
But after decades of researching how to improve schools, the professor in the Johns Hopkins School of Education remains certain that homework is essential—as long as the teachers have done their homework, too. The National Network of Partnership Schools , which she founded in 1995 to advise schools and districts on ways to improve comprehensive programs of family engagement, has developed hundreds of improved homework ideas through its Teachers Involve Parents in Schoolwork program. For an English class, a student might interview a parent on popular hairstyles from their youth and write about the differences between then and now. Or for science class, a family could identify forms of matter over the dinner table, labeling foods as liquids or solids. These innovative and interactive assignments not only reinforce concepts from the classroom but also foster creativity, spark discussions, and boost student motivation.
"We're not trying to eliminate homework procedures, but expand and enrich them," says Epstein, who is packing this research into a forthcoming book on the purposes and designs of homework. In the meantime, the Hub couldn't wait to ask her some questions:
What kind of homework training do teachers typically get?
Future teachers and administrators really have little formal training on how to design homework before they assign it. This means that most just repeat what their teachers did, or they follow textbook suggestions at the end of units. For example, future teachers are well prepared to teach reading and literacy skills at each grade level, and they continue to learn to improve their teaching of reading in ongoing in-service education. By contrast, most receive little or no training on the purposes and designs of homework in reading or other subjects. It is really important for future teachers to receive systematic training to understand that they have the power, opportunity, and obligation to design homework with a purpose.
Why do students need more interactive homework?
If homework assignments are always the same—10 math problems, six sentences with spelling words—homework can get boring and some kids just stop doing their assignments, especially in the middle and high school years. When we've asked teachers what's the best homework you've ever had or designed, invariably we hear examples of talking with a parent or grandparent or peer to share ideas. To be clear, parents should never be asked to "teach" seventh grade science or any other subject. Rather, teachers set up the homework assignments so that the student is in charge. It's always the student's homework. But a good activity can engage parents in a fun, collaborative way. Our data show that with "good" assignments, more kids finish their work, more kids interact with a family partner, and more parents say, "I learned what's happening in the curriculum." It all works around what the youngsters are learning.
Is family engagement really that important?
At Hopkins, I am part of the Center for Social Organization of Schools , a research center that studies how to improve many aspects of education to help all students do their best in school. One thing my colleagues and I realized was that we needed to look deeply into family and community engagement. There were so few references to this topic when we started that we had to build the field of study. When children go to school, their families "attend" with them whether a teacher can "see" the parents or not. So, family engagement is ever-present in the life of a school.
My daughter's elementary school doesn't assign homework until third grade. What's your take on "no homework" policies?
There are some parents, writers, and commentators who have argued against homework, especially for very young children. They suggest that children should have time to play after school. This, of course is true, but many kindergarten kids are excited to have homework like their older siblings. If they give homework, most teachers of young children make assignments very short—often following an informal rule of 10 minutes per grade level. "No homework" does not guarantee that all students will spend their free time in productive and imaginative play.
Some researchers and critics have consistently misinterpreted research findings. They have argued that homework should be assigned only at the high school level where data point to a strong connection of doing assignments with higher student achievement . However, as we discussed, some students stop doing homework. This leads, statistically, to results showing that doing homework or spending more minutes on homework is linked to higher student achievement. If slow or struggling students are not doing their assignments, they contribute to—or cause—this "result."
Teachers need to design homework that even struggling students want to do because it is interesting. Just about all students at any age level react positively to good assignments and will tell you so.
Did COVID change how schools and parents view homework?
Within 24 hours of the day school doors closed in March 2020, just about every school and district in the country figured out that teachers had to talk to and work with students' parents. This was not the same as homeschooling—teachers were still working hard to provide daily lessons. But if a child was learning at home in the living room, parents were more aware of what they were doing in school. One of the silver linings of COVID was that teachers reported that they gained a better understanding of their students' families. We collected wonderfully creative examples of activities from members of the National Network of Partnership Schools. I'm thinking of one art activity where every child talked with a parent about something that made their family unique. Then they drew their finding on a snowflake and returned it to share in class. In math, students talked with a parent about something the family liked so much that they could represent it 100 times. Conversations about schoolwork at home was the point.
How did you create so many homework activities via the Teachers Involve Parents in Schoolwork program?
We had several projects with educators to help them design interactive assignments, not just "do the next three examples on page 38." Teachers worked in teams to create TIPS activities, and then we turned their work into a standard TIPS format in math, reading/language arts, and science for grades K-8. Any teacher can use or adapt our prototypes to match their curricula.
Overall, we know that if future teachers and practicing educators were prepared to design homework assignments to meet specific purposes—including but not limited to interactive activities—more students would benefit from the important experience of doing their homework. And more parents would, indeed, be partners in education.
Posted in Voices+Opinion
You might also like
News network.
- Johns Hopkins Magazine
- Get Email Updates
- Submit an Announcement
- Submit an Event
- Privacy Statement
- Accessibility
Discover JHU
- About the University
- Schools & Divisions
- Academic Programs
- Plan a Visit
- my.JohnsHopkins.edu
- © 2024 Johns Hopkins University . All rights reserved.
- University Communications
- 3910 Keswick Rd., Suite N2600, Baltimore, MD
- X Facebook LinkedIn YouTube Instagram
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Student Opinion
Should We Get Rid of Homework?
Some educators are pushing to get rid of homework. Would that be a good thing?

By Jeremy Engle and Michael Gonchar
Do you like doing homework? Do you think it has benefited you educationally?
Has homework ever helped you practice a difficult skill — in math, for example — until you mastered it? Has it helped you learn new concepts in history or science? Has it helped to teach you life skills, such as independence and responsibility? Or, have you had a more negative experience with homework? Does it stress you out, numb your brain from busywork or actually make you fall behind in your classes?
Should we get rid of homework?
In “ The Movement to End Homework Is Wrong, ” published in July, the Times Opinion writer Jay Caspian Kang argues that homework may be imperfect, but it still serves an important purpose in school. The essay begins:
Do students really need to do their homework? As a parent and a former teacher, I have been pondering this question for quite a long time. The teacher side of me can acknowledge that there were assignments I gave out to my students that probably had little to no academic value. But I also imagine that some of my students never would have done their basic reading if they hadn’t been trained to complete expected assignments, which would have made the task of teaching an English class nearly impossible. As a parent, I would rather my daughter not get stuck doing the sort of pointless homework I would occasionally assign, but I also think there’s a lot of value in saying, “Hey, a lot of work you’re going to end up doing in your life is pointless, so why not just get used to it?” I certainly am not the only person wondering about the value of homework. Recently, the sociologist Jessica McCrory Calarco and the mathematics education scholars Ilana Horn and Grace Chen published a paper, “ You Need to Be More Responsible: The Myth of Meritocracy and Teachers’ Accounts of Homework Inequalities .” They argued that while there’s some evidence that homework might help students learn, it also exacerbates inequalities and reinforces what they call the “meritocratic” narrative that says kids who do well in school do so because of “individual competence, effort and responsibility.” The authors believe this meritocratic narrative is a myth and that homework — math homework in particular — further entrenches the myth in the minds of teachers and their students. Calarco, Horn and Chen write, “Research has highlighted inequalities in students’ homework production and linked those inequalities to differences in students’ home lives and in the support students’ families can provide.”
Mr. Kang argues:
But there’s a defense of homework that doesn’t really have much to do with class mobility, equality or any sense of reinforcing the notion of meritocracy. It’s one that became quite clear to me when I was a teacher: Kids need to learn how to practice things. Homework, in many cases, is the only ritualized thing they have to do every day. Even if we could perfectly equalize opportunity in school and empower all students not to be encumbered by the weight of their socioeconomic status or ethnicity, I’m not sure what good it would do if the kids didn’t know how to do something relentlessly, over and over again, until they perfected it. Most teachers know that type of progress is very difficult to achieve inside the classroom, regardless of a student’s background, which is why, I imagine, Calarco, Horn and Chen found that most teachers weren’t thinking in a structural inequalities frame. Holistic ideas of education, in which learning is emphasized and students can explore concepts and ideas, are largely for the types of kids who don’t need to worry about class mobility. A defense of rote practice through homework might seem revanchist at this moment, but if we truly believe that schools should teach children lessons that fall outside the meritocracy, I can’t think of one that matters more than the simple satisfaction of mastering something that you were once bad at. That takes homework and the acknowledgment that sometimes a student can get a question wrong and, with proper instruction, eventually get it right.
Students, read the entire article, then tell us:
Should we get rid of homework? Why, or why not?
Is homework an outdated, ineffective or counterproductive tool for learning? Do you agree with the authors of the paper that homework is harmful and worsens inequalities that exist between students’ home circumstances?
Or do you agree with Mr. Kang that homework still has real educational value?
When you get home after school, how much homework will you do? Do you think the amount is appropriate, too much or too little? Is homework, including the projects and writing assignments you do at home, an important part of your learning experience? Or, in your opinion, is it not a good use of time? Explain.
In these letters to the editor , one reader makes a distinction between elementary school and high school:
Homework’s value is unclear for younger students. But by high school and college, homework is absolutely essential for any student who wishes to excel. There simply isn’t time to digest Dostoyevsky if you only ever read him in class.
What do you think? How much does grade level matter when discussing the value of homework?
Is there a way to make homework more effective?
If you were a teacher, would you assign homework? What kind of assignments would you give and why?
Want more writing prompts? You can find all of our questions in our Student Opinion column . Teachers, check out this guide to learn how you can incorporate them into your classroom.
Students 13 and older in the United States and Britain, and 16 and older elsewhere, are invited to comment. All comments are moderated by the Learning Network staff, but please keep in mind that once your comment is accepted, it will be made public.
Jeremy Engle joined The Learning Network as a staff editor in 2018 after spending more than 20 years as a classroom humanities and documentary-making teacher, professional developer and curriculum designer working with students and teachers across the country. More about Jeremy Engle
- Skip to Nav
- Skip to Main
- Skip to Footer

How important is homework, and how much should parents help?
Please try again

A version of this post was originally published by Parenting Translator. Sign up for the newsletter and follow Parenting Translator on Instagram .
In recent years, homework has become a very hot topic . Many parents and educators have raised concerns about homework and questioned how effective it is in enhancing students’ learning. There are also concerns that students may be getting too much homework, which ultimately interferes with quality family time and opportunities for physical activity and play . Research suggests that these concerns may be valid. For example, one study reported that elementary school students, on average, are assigned three times the recommended amount of homework.
So what does the research say? What are the potential risks and benefits of homework, and how much is too much?
Academic benefits
First, research finds that homework is associated with higher scores on academic standardized tests for middle and high school students, but not elementary school students . A recent experimental study in Romania found some benefit for a small amount of writing homework in elementary students but not math homework. Yet, interestingly, this positive impact only occurred when students were given a moderate amount of homework (about 20 minutes on average).
Non-academic benefits
The goal of homework is not simply to improve academic skills. Research finds that homework may have some non-academic benefits, such as building responsibility , time management skills, and task persistence . Homework may also increase parents’ involvement in their children’s schooling. Yet, too much homework may also have some negative impacts on non-academic skills by reducing opportunities for free play , which is essential for the development of language, cognitive, self-regulation and social-emotional skills. Homework may also interfere with physical activity and too much homework is associated with an increased risk for being overweight . As with the research on academic benefits, this research also suggests that homework may be beneficial when it is minimal.
What is the “right” amount of homework?
Research suggests that homework should not exceed 1.5 to 2.5 hours per night for high school students and no more than one hour per night for middle school students. Homework for elementary school students should be minimal and assigned with the aim of building self-regulation and independent work skills. Any more than this and homework may no longer have a positive impact.
The National Education Association recommends 10 minutes of homework per grade and there is also some experimental evidence that backs this up.
Overall translation
Research finds that homework provides some academic benefit for middle and high school students but is less beneficial for elementary school students. Research suggests that homework should be none or minimal for elementary students, less than one hour per night for middle school students, and less than 1.5 to 2.5 hours for high school students.
What can parents do?
Research finds that parental help with homework is beneficial but that it matters more how the parent is helping rather than how often the parent is helping.
So how should parents help with homework, according to the research?
- Focus on providing general monitoring, guidance and encouragement, but allow children to generate answers on their own and complete their homework as independently as possible . Specifically, be present while they are completing homework to help them to understand the directions, be available to answer simple questions, or praise and acknowledge their effort and hard work. Research shows that allowing children more autonomy in completing homework may benefit their academic skills.
- Only provide help when your child asks for it and step away whenever possible. Research finds that too much parental involvement or intrusive and controlling involvement with homework is associated with worse academic performance .
- Help your children to create structure and develop some routines that help your child to independently complete their homework . Have a regular time and place for homework that is free from distractions and has all of the materials they need within arm’s reach. Help your child to create a checklist for homework tasks. Create rules for homework with your child. Help children to develop strategies for increasing their own self-motivation. For example, developing their own reward system or creating a homework schedule with breaks for fun activities. Research finds that providing this type of structure and responsiveness is related to improved academic skills.
- Set specific rules around homework. Research finds an association between parents setting rules around homework and academic performance.
- Help your child to view homework as an opportunity to learn and improve skills. Parents who view homework as a learning opportunity (that is, a “mastery orientation”) rather than something that they must get “right” or complete successfully to obtain a higher grade (that is, a “performance orientation”) are more likely to have children with the same attitudes.
- Encourage your child to persist in challenging assignments and emphasize difficult assignments as opportunities to grow . Research finds that this attitude is associated with student success. Research also indicates that more challenging homework is associated with enhanced academic performance.
- Stay calm and positive during homework. Research shows that mothers showing positive emotions while helping with homework may improve children’s motivation in homework.
- Praise your child’s hard work and effort during homework. This type of praise is likely to increase motivation. In addition, research finds that putting more effort into homework may be associated with enhanced development of conscientiousness in children.
- Communicate with your child and the teacher about any problems your child has with homework and the teacher’s learning goals. Research finds that open communication about homework is associated with increased academic performance.
Cara Goodwin, PhD, is a licensed psychologist, a mother of three and the founder of Parenting Translator , a nonprofit newsletter that turns scientific research into information that is accurate, relevant and useful for parents.
How Much Homework Is Too Much for Our Teens?
Here's what educators and parents can do to help kids find the right balance between school and home.
Does Your Teen Have Too Much Homework?
Today’s teens are under a lot of pressure.
They're under pressure to succeed, to win, to be the best and to get into the top colleges. With so much pressure, is it any wonder today’s youth report being under as much stress as their parents? In fact, during the school year, teens say they experience stress levels higher than those reported by adults, according to a previous American Psychological Association "Stress in America" survey.
Odds are if you ask a teen what's got them so worked up, the subject of school will come up. School can cause a lot of stress, which can lead to other serious problems, like sleep deprivation . According to the National Sleep Foundation, teens need between eight and 10 hours of sleep each night, but only 15 percent are even getting close to that amount. During the school week, most teens only get about six hours of zzz’s a night, and some of that sleep deficit may be attributed to homework.
When it comes to school, many adults would rather not trade places with a teen. Think about it. They get up at the crack of dawn and get on the bus when it’s pitch dark outside. They put in a full day sitting in hours of classes (sometimes four to seven different classes daily), only to get more work dumped on them to do at home. To top it off, many kids have after-school obligations, such as extracurricular activities including clubs and sports , and some have to work. After a long day, they finally get home to do even more work – schoolwork.
[Read: What Parents Should Know About Teen Depression .]
Homework is not only a source of stress for students, but it can also be a hassle for parents. If you are the parent of a kid who strives to be “perfect," then you know all too well how much time your child spends making sure every bit of homework is complete, even if it means pulling an all-nighter. On the flip side, if you’re the parent of a child who decided that school ends when the last bell rings, then you know how exhausting that homework tug-of-war can be. And heaven forbid if you’re that parent who is at their wit's end because your child excels on tests and quizzes but fails to turn in assignments. The woes of academics can go well beyond the confines of the school building and right into the home.
This is the time of year when many students and parents feel the burden of the academic load. Following spring break, many schools across the nation head into the final stretch of the year. As a result, some teachers increase the amount of homework they give. The assignments aren’t punishment, although to students and parents who are having to constantly stay on top of their kids' schoolwork, they can sure seem that way.
From a teacher’s perspective, the assignments are meant to help students better understand the course content and prepare for upcoming exams. Some schools have state-mandated end of grade or final tests. In those states these tests can account for 20 percent of a student’s final grade. So teachers want to make sure that they cover the entire curriculum before that exam. Aside from state-mandated tests, some high school students are enrolled in advanced placement or international baccalaureate college-level courses that have final tests given a month or more before the end of the term. In order to cover all of the content, teachers must maintain an accelerated pace. All of this means more out of class assignments.
Given the challenges kids face, there are a few questions parents and educators should consider:
Is homework necessary?
Many teens may give a quick "no" to this question, but the verdict is still out. Research supports both sides of the argument. Personally, I would say, yes, some homework is necessary, but it must be purposeful. If it’s busy work, then it’s a waste of time. Homework should be a supplemental teaching tool. Too often, some youth go home completely lost as they haven’t grasped concepts covered in class and they may become frustrated and overwhelmed.
For a parent who has been in this situation, you know how frustrating this can be, especially if it’s a subject that you haven’t encountered in a while. Homework can serve a purpose such as improving grades, increasing test scores and instilling a good work ethic. Purposeful homework can come in the form of individualizing assignments based on students’ needs or helping students practice newly acquired skills.
Homework should not be used to extend class time to cover more material. If your child is constantly coming home having to learn the material before doing the assignments, then it’s time to contact the teacher and set up a conference. Listen when kids express their concerns (like if they say they're expected to know concepts not taught in class) as they will provide clues about what’s happening or not happening in the classroom. Plus, getting to the root of the problem can help with keeping the peace at home too, as an irritable and grumpy teen can disrupt harmonious family dynamics .
[Read: What Makes Teens 'Most Likely to Succeed?' ]
How much is too much?
According to the National PTA and the National Education Association, students should only be doing about 10 minutes of homework per night per grade level. But teens are doing a lot more than that, according to a poll of high school students by the organization Statistic Brain . In that poll teens reported spending, on average, more than three hours on homework each school night, with 11th graders spending more time on homework than any other grade level. By contrast, some polls have shown that U.S. high school students report doing about seven hours of homework per week.
Much of a student's workload boils down to the courses they take (such as advanced or college prep classes), the teaching philosophy of educators and the student’s commitment to doing the work. Regardless, research has shown that doing more than two hours of homework per night does not benefit high school students. Having lots of homework to do every day makes it difficult for teens to have any downtime , let alone family time .
How do we respond to students' needs?
As an educator and parent, I can honestly say that oftentimes there is a mismatch in what teachers perceive as only taking 15 minutes and what really takes 45 minutes to complete. If you too find this to be the case, then reach out to your child's teacher and find out why the assignments are taking longer than anticipated for your child to complete.
Also, ask the teacher about whether faculty communicate regularly with one another about large upcoming assignments. Whether it’s setting up a shared school-wide assignment calendar or collaborating across curriculums during faculty meetings, educators need to discuss upcoming tests and projects, so students don’t end up with lots of assignments all competing for their attention and time at once. Inevitably, a student is going to get slammed occasionally, but if they have good rapport with their teachers, they will feel comfortable enough to reach out and see if alternative options are available. And as a parent, you can encourage your kid to have that dialogue with the teacher.
Often teens would rather blend into the class than stand out. That’s unfortunate because research has shown time and time again that positive teacher-student relationships are strong predictors of student engagement and achievement. By and large, most teachers appreciate students advocating for themselves and will go the extra mile to help them out.
Can there be a balance between home and school?
Students can strike a balance between school and home, but parents will have to help them find it. They need your guidance to learn how to better manage their time, get organized and prioritize tasks, which are all important life skills. Equally important is developing good study habits. Some students may need tutoring or coaching to help them learn new material or how to take notes and study. Also, don’t forget the importance of parent-teacher communication. Most educators want nothing more than for their students to succeed in their courses.
Learning should be fun, not mundane and cumbersome. Homework should only be given if its purposeful and in moderation. Equally important to homework is engaging in activities, socializing with friends and spending time with the family.
[See: 10 Concerns Parents Have About Their Kids' Health .]
Most adults don’t work a full-time job and then go home and do three more hours of work, and neither should your child. It's not easy learning to balance everything, especially if you're a teen. If your child is spending several hours on homework each night, don't hesitate to reach out to teachers and, if need be, school officials. Collectively, we can all work together to help our children de-stress and find the right balance between school and home.
12 Questions You Should Ask Your Kids at Dinner

Tags: parenting , family , family health , teens , education , high school , stress
Most Popular
Patient Advice

Senior Care

health disclaimer »
Disclaimer and a note about your health ».

Your Health
A guide to nutrition and wellness from the health team at U.S. News & World Report.
You May Also Like
Moderating pandemic news consumption.
Victor G. Carrion, M.D. June 8, 2020

Helping Young People Gain Resilience
Nancy Willard May 18, 2020

Keep Kids on Track With Reading During the Pandemic
Ashley Johnson and Tom Dillon May 14, 2020

Pandemic and Summer Education
Nancy Willard May 12, 2020

Trauma and Childhood Regression
Dr. Gail Saltz May 8, 2020

The Sandwich Generation and the Pandemic
Laurie Wolk May 6, 2020

Adapting to an Evolving Pandemic
Laurie Wolk May 1, 2020

Picky Eating During Quarantine
Jill Castle May 1, 2020

Baby Care During the Pandemic
Dr. Natasha Burgert April 29, 2020

Co-Parenting During the Pandemic
Ron Deal April 24, 2020


Is Homework Good for Kids?
Research suggests that homework may be most beneficial when it is minimal..
Updated October 3, 2023 | Reviewed by Devon Frye
- Why Education Is Important
- Find a Child Therapist
- Research finds that homework can academically benefit middle and high schoolers, but not elementary students.
- There are non-academic benefits to homework, but too much work may interfere with other areas of development.
- Research suggests students should be given about 10 minutes of homework per grade level.
- Parents can help with homework by encouraging a growth mindset and supporting their child's autonomy.
In recent years, homework has become a very hot topic. Many parents and educators have raised concerns about homework and questioned how effective it is in enhancing students’ learning. There are also concerns that students may simply be getting too much homework, which ultimately interferes with quality family time and opportunities for physical activity and play.
Research suggests that these concerns may be valid. For example, one study reported that elementary school students, on average, are assigned three times the recommended amount of homework.
What does the research say? What are the potential risks and benefits of homework, and how much is “too much”?
Academic vs. Non-Academic Benefits
First, research finds that homework is associated with higher scores on academic standardized tests for middle and high school students, but not elementary school students . A recent experimental study in Romania found some benefits for a small amount of writing homework in elementary students but not math homework. Yet, interestingly, this positive impact only occurred when students were given a moderate amount of homework (about 20 minutes on average).
Yet the goal of homework is not simply to improve academic skills. Research finds that homework may have some non-academic benefits, such as building responsibility , time management skills, and task persistence . Homework may also increase parents’ involvement in their children’s schooling.
Yet too much homework may also have some negative impacts on non-academic skills by reducing opportunities for free play , which is essential for the development of language, cognitive, self-regulation , and social-emotional skills. Homework may also interfere with physical activity ; indeed, too much homework is associated with an increased risk of being overweight . As with the research on academic benefits, this research also suggests that homework may be beneficial when it is minimal.
What is the “Right” Amount of Homework?
Research suggests that homework should not exceed 1.5 to 2.5 hours per night for high school students and no more than 1 hour per night for middle school students. Homework for elementary school students should be minimal and assigned with the aim of building self-regulation and independent work skills. Any more than this and homework may no longer have a positive impact.
The National Education Association recommends 10 minutes of homework per grade and there is also some experimental evidence that backs this up.
What Can Parents Do?
Research finds that parental help with homework is beneficial but that it matters more how the parent is helping rather than how often the parent is helping.
So how should parents help with homework (according to the research)?
- Focus on providing general monitoring, guidance, and encouragement, but allow children to complete their homework as independently as possible. Research shows that allowing children more autonomy in completing homework may benefit their academic skills.
- Only provide help when your child asks for it and step away whenever possible. Research finds that too much parental involvement or intrusive and controlling involvement with homework is associated with worse academic performance .
- Help your children to create structure and develop some routines that help your child to independently complete their homework. Research finds that providing this type of structure and responsiveness is related to improved academic skills.
- Set specific rules around homework. Research finds an association between parents setting rules around homework and academic performance.
- Help your child to view homework as an opportunity to learn and improve skills. Parents who view homework as a learning opportunity (that is, a “mastery orientation”) rather than something that they must get “right” or complete successfully to obtain a higher grade (that is, a “performance orientation”) are more likely to have children with the same attitudes.
- Encourage your child to persist in challenging assignments and emphasize difficult assignments as opportunities to grow. Research finds that this attitude is associated with student success. Research also indicates that more challenging homework is associated with enhanced academic performance.
- Stay calm and positive during homework. Research shows that mothers’ showing positive emotions while helping with homework may improve children’s motivation in homework.
- Praise your child’s hard work and effort during homework. This type of praise is likely to increase motivation. In addition, research finds that putting more effort into homework may be associated with enhanced development of conscientiousness in children.
- Communicate with your child and the teacher about any problems your child has with homework and the teacher’s learning goals. Research finds that open communication about homework is associated with increased academic performance.

Cara Goodwin, Ph.D., is a licensed clinical psychologist who specializes in translating scientific research into information that is useful, accurate, and relevant for parents.
- Find a Therapist
- Find a Treatment Center
- Find a Psychiatrist
- Find a Support Group
- Find Online Therapy
- United States
- Brooklyn, NY
- Chicago, IL
- Houston, TX
- Los Angeles, CA
- New York, NY
- Portland, OR
- San Diego, CA
- San Francisco, CA
- Seattle, WA
- Washington, DC
- Asperger's
- Bipolar Disorder
- Chronic Pain
- Eating Disorders
- Passive Aggression
- Personality
- Goal Setting
- Positive Psychology
- Stopping Smoking
- Low Sexual Desire
- Relationships
- Child Development
- Self Tests NEW
- Therapy Center
- Diagnosis Dictionary
- Types of Therapy

At any moment, someone’s aggravating behavior or our own bad luck can set us off on an emotional spiral that threatens to derail our entire day. Here’s how we can face our triggers with less reactivity so that we can get on with our lives.
- Emotional Intelligence
- Gaslighting
- Affective Forecasting
- Neuroscience
Are You Down With or Done With Homework?
- Posted January 17, 2012
- By Lory Hough

The debate over how much schoolwork students should be doing at home has flared again, with one side saying it's too much, the other side saying in our competitive world, it's just not enough.
It was a move that doesn't happen very often in American public schools: The principal got rid of homework.
This past September, Stephanie Brant, principal of Gaithersburg Elementary School in Gaithersburg, Md., decided that instead of teachers sending kids home with math worksheets and spelling flash cards, students would instead go home and read. Every day for 30 minutes, more if they had time or the inclination, with parents or on their own.
"I knew this would be a big shift for my community," she says. But she also strongly believed it was a necessary one. Twenty-first-century learners, especially those in elementary school, need to think critically and understand their own learning — not spend night after night doing rote homework drills.
Brant's move may not be common, but she isn't alone in her questioning. The value of doing schoolwork at home has gone in and out of fashion in the United States among educators, policymakers, the media, and, more recently, parents. As far back as the late 1800s, with the rise of the Progressive Era, doctors such as Joseph Mayer Rice began pushing for a limit on what he called "mechanical homework," saying it caused childhood nervous conditions and eyestrain. Around that time, the then-influential Ladies Home Journal began publishing a series of anti-homework articles, stating that five hours of brain work a day was "the most we should ask of our children," and that homework was an intrusion on family life. In response, states like California passed laws abolishing homework for students under a certain age.
But, as is often the case with education, the tide eventually turned. After the Russians launched the Sputnik satellite in 1957, a space race emerged, and, writes Brian Gill in the journal Theory Into Practice, "The homework problem was reconceived as part of a national crisis; the U.S. was losing the Cold War because Russian children were smarter." Many earlier laws limiting homework were abolished, and the longterm trend toward less homework came to an end.
The debate re-emerged a decade later when parents of the late '60s and '70s argued that children should be free to play and explore — similar anti-homework wellness arguments echoed nearly a century earlier. By the early-1980s, however, the pendulum swung again with the publication of A Nation at Risk , which blamed poor education for a "rising tide of mediocrity." Students needed to work harder, the report said, and one way to do this was more homework.
For the most part, this pro-homework sentiment is still going strong today, in part because of mandatory testing and continued economic concerns about the nation's competitiveness. Many believe that today's students are falling behind their peers in places like Korea and Finland and are paying more attention to Angry Birds than to ancient Babylonia.
But there are also a growing number of Stephanie Brants out there, educators and parents who believe that students are stressed and missing out on valuable family time. Students, they say, particularly younger students who have seen a rise in the amount of take-home work and already put in a six- to nine-hour "work" day, need less, not more homework.
Who is right? Are students not working hard enough or is homework not working for them? Here's where the story gets a little tricky: It depends on whom you ask and what research you're looking at. As Cathy Vatterott, the author of Rethinking Homework , points out, "Homework has generated enough research so that a study can be found to support almost any position, as long as conflicting studies are ignored." Alfie Kohn, author of The Homework Myth and a strong believer in eliminating all homework, writes that, "The fact that there isn't anything close to unanimity among experts belies the widespread assumption that homework helps." At best, he says, homework shows only an association, not a causal relationship, with academic achievement. In other words, it's hard to tease out how homework is really affecting test scores and grades. Did one teacher give better homework than another? Was one teacher more effective in the classroom? Do certain students test better or just try harder?
"It is difficult to separate where the effect of classroom teaching ends," Vatterott writes, "and the effect of homework begins."
Putting research aside, however, much of the current debate over homework is focused less on how homework affects academic achievement and more on time. Parents in particular have been saying that the amount of time children spend in school, especially with afterschool programs, combined with the amount of homework given — as early as kindergarten — is leaving students with little time to run around, eat dinner with their families, or even get enough sleep.
Certainly, for some parents, homework is a way to stay connected to their children's learning. But for others, homework creates a tug-of-war between parents and children, says Liz Goodenough, M.A.T.'71, creator of a documentary called Where Do the Children Play?
"Ideally homework should be about taking something home, spending a few curious and interesting moments in which children might engage with parents, and then getting that project back to school — an organizational triumph," she says. "A nag-free activity could engage family time: Ask a parent about his or her own childhood. Interview siblings."

Instead, as the authors of The Case Against Homework write, "Homework overload is turning many of us into the types of parents we never wanted to be: nags, bribers, and taskmasters."
Leslie Butchko saw it happen a few years ago when her son started sixth grade in the Santa Monica-Malibu (Calif.) United School District. She remembers him getting two to four hours of homework a night, plus weekend and vacation projects. He was overwhelmed and struggled to finish assignments, especially on nights when he also had an extracurricular activity.
"Ultimately, we felt compelled to have Bobby quit karate — he's a black belt — to allow more time for homework," she says. And then, with all of their attention focused on Bobby's homework, she and her husband started sending their youngest to his room so that Bobby could focus. "One day, my younger son gave us 15-minute coupons as a present for us to use to send him to play in the back room. … It was then that we realized there had to be something wrong with the amount of homework we were facing."
Butchko joined forces with another mother who was having similar struggles and ultimately helped get the homework policy in her district changed, limiting homework on weekends and holidays, setting time guidelines for daily homework, and broadening the definition of homework to include projects and studying for tests. As she told the school board at one meeting when the policy was first being discussed, "In closing, I just want to say that I had more free time at Harvard Law School than my son has in middle school, and that is not in the best interests of our children."
One barrier that Butchko had to overcome initially was convincing many teachers and parents that more homework doesn't necessarily equal rigor.
"Most of the parents that were against the homework policy felt that students need a large quantity of homework to prepare them for the rigorous AP classes in high school and to get them into Harvard," she says.
Stephanie Conklin, Ed.M.'06, sees this at Another Course to College, the Boston pilot school where she teaches math. "When a student is not completing [his or her] homework, parents usually are frustrated by this and agree with me that homework is an important part of their child's learning," she says.
As Timothy Jarman, Ed.M.'10, a ninth-grade English teacher at Eugene Ashley High School in Wilmington, N.C., says, "Parents think it is strange when their children are not assigned a substantial amount of homework."
That's because, writes Vatterott, in her chapter, "The Cult(ure) of Homework," the concept of homework "has become so engrained in U.S. culture that the word homework is part of the common vernacular."
These days, nightly homework is a given in American schools, writes Kohn.
"Homework isn't limited to those occasions when it seems appropriate and important. Most teachers and administrators aren't saying, 'It may be useful to do this particular project at home,'" he writes. "Rather, the point of departure seems to be, 'We've decided ahead of time that children will have to do something every night (or several times a week). … This commitment to the idea of homework in the abstract is accepted by the overwhelming majority of schools — public and private, elementary and secondary."
Brant had to confront this when she cut homework at Gaithersburg Elementary.
"A lot of my parents have this idea that homework is part of life. This is what I had to do when I was young," she says, and so, too, will our kids. "So I had to shift their thinking." She did this slowly, first by asking her teachers last year to really think about what they were sending home. And this year, in addition to forming a parent advisory group around the issue, she also holds events to answer questions.
Still, not everyone is convinced that homework as a given is a bad thing. "Any pursuit of excellence, be it in sports, the arts, or academics, requires hard work. That our culture finds it okay for kids to spend hours a day in a sport but not equal time on academics is part of the problem," wrote one pro-homework parent on the blog for the documentary Race to Nowhere , which looks at the stress American students are under. "Homework has always been an issue for parents and children. It is now and it was 20 years ago. I think when people decide to have children that it is their responsibility to educate them," wrote another.
And part of educating them, some believe, is helping them develop skills they will eventually need in adulthood. "Homework can help students develop study skills that will be of value even after they leave school," reads a publication on the U.S. Department of Education website called Homework Tips for Parents. "It can teach them that learning takes place anywhere, not just in the classroom. … It can foster positive character traits such as independence and responsibility. Homework can teach children how to manage time."
Annie Brown, Ed.M.'01, feels this is particularly critical at less affluent schools like the ones she has worked at in Boston, Cambridge, Mass., and Los Angeles as a literacy coach.
"It feels important that my students do homework because they will ultimately be competing for college placement and jobs with students who have done homework and have developed a work ethic," she says. "Also it will get them ready for independently taking responsibility for their learning, which will need to happen for them to go to college."
The problem with this thinking, writes Vatterott, is that homework becomes a way to practice being a worker.
"Which begs the question," she writes. "Is our job as educators to produce learners or workers?"
Slate magazine editor Emily Bazelon, in a piece about homework, says this makes no sense for younger kids.
"Why should we think that practicing homework in first grade will make you better at doing it in middle school?" she writes. "Doesn't the opposite seem equally plausible: that it's counterproductive to ask children to sit down and work at night before they're developmentally ready because you'll just make them tired and cross?"
Kohn writes in the American School Board Journal that this "premature exposure" to practices like homework (and sit-and-listen lessons and tests) "are clearly a bad match for younger children and of questionable value at any age." He calls it BGUTI: Better Get Used to It. "The logic here is that we have to prepare you for the bad things that are going to be done to you later … by doing them to you now."
According to a recent University of Michigan study, daily homework for six- to eight-year-olds increased on average from about 8 minutes in 1981 to 22 minutes in 2003. A review of research by Duke University Professor Harris Cooper found that for elementary school students, "the average correlation between time spent on homework and achievement … hovered around zero."
So should homework be eliminated? Of course not, say many Ed School graduates who are teaching. Not only would students not have time for essays and long projects, but also teachers would not be able to get all students to grade level or to cover critical material, says Brett Pangburn, Ed.M.'06, a sixth-grade English teacher at Excel Academy Charter School in Boston. Still, he says, homework has to be relevant.
"Kids need to practice the skills being taught in class, especially where, like the kids I teach at Excel, they are behind and need to catch up," he says. "Our results at Excel have demonstrated that kids can catch up and view themselves as in control of their academic futures, but this requires hard work, and homework is a part of it."
Ed School Professor Howard Gardner basically agrees.
"America and Americans lurch between too little homework in many of our schools to an excess of homework in our most competitive environments — Li'l Abner vs. Tiger Mother," he says. "Neither approach makes sense. Homework should build on what happens in class, consolidating skills and helping students to answer new questions."
So how can schools come to a happy medium, a way that allows teachers to cover everything they need while not overwhelming students? Conklin says she often gives online math assignments that act as labs and students have two or three days to complete them, including some in-class time. Students at Pangburn's school have a 50-minute silent period during regular school hours where homework can be started, and where teachers pull individual or small groups of students aside for tutoring, often on that night's homework. Afterschool homework clubs can help.
Some schools and districts have adapted time limits rather than nix homework completely, with the 10-minute per grade rule being the standard — 10 minutes a night for first-graders, 30 minutes for third-graders, and so on. (This remedy, however, is often met with mixed results since not all students work at the same pace.) Other schools offer an extended day that allows teachers to cover more material in school, in turn requiring fewer take-home assignments. And for others, like Stephanie Brant's elementary school in Maryland, more reading with a few targeted project assignments has been the answer.
"The routine of reading is so much more important than the routine of homework," she says. "Let's have kids reflect. You can still have the routine and you can still have your workspace, but now it's for reading. I often say to parents, if we can put a man on the moon, we can put a man or woman on Mars and that person is now a second-grader. We don't know what skills that person will need. At the end of the day, we have to feel confident that we're giving them something they can use on Mars."
Read a January 2014 update.
Homework Policy Still Going Strong
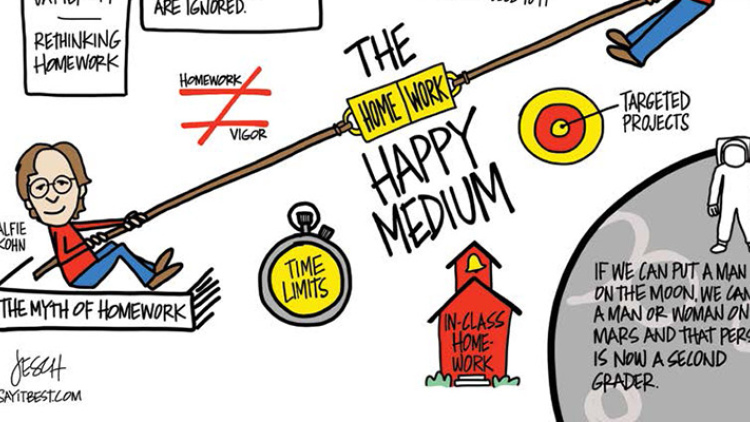
Ed. Magazine
The magazine of the Harvard Graduate School of Education
Related Articles

Commencement Marshal Sarah Fiarman: The Principal of the Matter

Making Math “Almost Fun”
Alum develops curriculum to entice reluctant math learners

Reshaping Teacher Licensure: Lessons from the Pandemic
Olivia Chi, Ed.M.'17, Ph.D.'20, discusses the ongoing efforts to ensure the quality and stability of the teaching workforce
- The Highlight
Nobody knows what the point of homework is
The homework wars are back.
by Jacob Sweet

As the Covid-19 pandemic began and students logged into their remote classrooms, all work, in effect, became homework. But whether or not students could complete it at home varied. For some, schoolwork became public-library work or McDonald’s-parking-lot work.
Luis Torres, the principal of PS 55, a predominantly low-income community elementary school in the south Bronx, told me that his school secured Chromebooks for students early in the pandemic only to learn that some lived in shelters that blocked wifi for security reasons. Others, who lived in housing projects with poor internet reception, did their schoolwork in laundromats.
According to a 2021 Pew survey , 25 percent of lower-income parents said their children, at some point, were unable to complete their schoolwork because they couldn’t access a computer at home; that number for upper-income parents was 2 percent.
The issues with remote learning in March 2020 were new. But they highlighted a divide that had been there all along in another form: homework. And even long after schools have resumed in-person classes, the pandemic’s effects on homework have lingered.
Over the past three years, in response to concerns about equity, schools across the country, including in Sacramento, Los Angeles , San Diego , and Clark County, Nevada , made permanent changes to their homework policies that restricted how much homework could be given and how it could be graded after in-person learning resumed.
Three years into the pandemic, as districts and teachers reckon with Covid-era overhauls of teaching and learning, schools are still reconsidering the purpose and place of homework. Whether relaxing homework expectations helps level the playing field between students or harms them by decreasing rigor is a divisive issue without conclusive evidence on either side, echoing other debates in education like the elimination of standardized test scores from some colleges’ admissions processes.
I first began to wonder if the homework abolition movement made sense after speaking with teachers in some Massachusetts public schools, who argued that rather than help disadvantaged kids, stringent homework restrictions communicated an attitude of low expectations. One, an English teacher, said she felt the school had “just given up” on trying to get the students to do work; another argued that restrictions that prohibit teachers from assigning take-home work that doesn’t begin in class made it difficult to get through the foreign-language curriculum. Teachers in other districts have raised formal concerns about homework abolition’s ability to close gaps among students rather than widening them.
Many education experts share this view. Harris Cooper, a professor emeritus of psychology at Duke who has studied homework efficacy, likened homework abolition to “playing to the lowest common denominator.”
But as I learned after talking to a variety of stakeholders — from homework researchers to policymakers to parents of schoolchildren — whether to abolish homework probably isn’t the right question. More important is what kind of work students are sent home with and where they can complete it. Chances are, if schools think more deeply about giving constructive work, time spent on homework will come down regardless.

There’s no consensus on whether homework works
The rise of the no-homework movement during the Covid-19 pandemic tapped into long-running disagreements over homework’s impact on students. The purpose and effectiveness of homework have been disputed for well over a century. In 1901, for instance, California banned homework for students up to age 15, and limited it for older students, over concerns that it endangered children’s mental and physical health. The newest iteration of the anti-homework argument contends that the current practice punishes students who lack support and rewards those with more resources, reinforcing the “myth of meritocracy.”
But there is still no research consensus on homework’s effectiveness; no one can seem to agree on what the right metrics are. Much of the debate relies on anecdotes, intuition, or speculation.
Researchers disagree even on how much research exists on the value of homework. Kathleen Budge, the co-author of Turning High-Poverty Schools Into High-Performing Schools and a professor at Boise State, told me that homework “has been greatly researched.” Denise Pope, a Stanford lecturer and leader of the education nonprofit Challenge Success, said, “It’s not a highly researched area because of some of the methodological problems.”
Experts who are more sympathetic to take-home assignments generally support the “10-minute rule,” a framework that estimates the ideal amount of homework on any given night by multiplying the student’s grade by 10 minutes. (A ninth grader, for example, would have about 90 minutes of work a night.) Homework proponents argue that while it is difficult to design randomized control studies to test homework’s effectiveness, the vast majority of existing studies show a strong positive correlation between homework and high academic achievement for middle and high school students. Prominent critics of homework argue that these correlational studies are unreliable and point to studies that suggest a neutral or negative effect on student performance. Both agree there is little to no evidence for homework’s effectiveness at an elementary school level, though proponents often argue that it builds constructive habits for the future.
For anyone who remembers homework assignments from both good and bad teachers, this fundamental disagreement might not be surprising. Some homework is pointless and frustrating to complete. Every week during my senior year of high school, I had to analyze a poem for English and decorate it with images found on Google; my most distinct memory from that class is receiving a demoralizing 25-point deduction because I failed to present my analysis on a poster board. Other assignments really do help students learn: After making an adapted version of Chairman Mao’s Little Red Book for a ninth grade history project, I was inspired to check out from the library and read a biography of the Chinese ruler.
For homework opponents, the first example is more likely to resonate. “We’re all familiar with the negative effects of homework: stress, exhaustion, family conflict, less time for other activities, diminished interest in learning,” Alfie Kohn, author of The Homework Myth, which challenges common justifications for homework, told me in an email. “And these effects may be most pronounced among low-income students.” Kohn believes that schools should make permanent any moratoria implemented during the pandemic, arguing that there are no positives at all to outweigh homework’s downsides. Recent studies , he argues , show the benefits may not even materialize during high school.
In the Marlborough Public Schools, a suburban district 45 minutes west of Boston, school policy committee chair Katherine Hennessy described getting kids to complete their homework during remote education as “a challenge, to say the least.” Teachers found that students who spent all day on their computers didn’t want to spend more time online when the day was over. So, for a few months, the school relaxed the usual practice and teachers slashed the quantity of nightly homework.
Online learning made the preexisting divides between students more apparent, she said. Many students, even during normal circumstances, lacked resources to keep them on track and focused on completing take-home assignments. Though Marlborough Schools is more affluent than PS 55, Hennessy said many students had parents whose work schedules left them unable to provide homework help in the evenings. The experience tracked with a common divide in the country between children of different socioeconomic backgrounds.
So in October 2021, months after the homework reduction began, the Marlborough committee made a change to the district’s policy. While teachers could still give homework, the assignments had to begin as classwork. And though teachers could acknowledge homework completion in a student’s participation grade, they couldn’t count homework as its own grading category. “Rigorous learning in the classroom does not mean that that classwork must be assigned every night,” the policy stated . “Extensions of class work is not to be used to teach new content or as a form of punishment.”
Canceling homework might not do anything for the achievement gap
The critiques of homework are valid as far as they go, but at a certain point, arguments against homework can defy the commonsense idea that to retain what they’re learning, students need to practice it.
“Doesn’t a kid become a better reader if he reads more? Doesn’t a kid learn his math facts better if he practices them?” said Cathy Vatterott, an education researcher and professor emeritus at the University of Missouri-St. Louis. After decades of research, she said it’s still hard to isolate the value of homework, but that doesn’t mean it should be abandoned.
Blanket vilification of homework can also conflate the unique challenges facing disadvantaged students as compared to affluent ones, which could have different solutions. “The kids in the low-income schools are being hurt because they’re being graded, unfairly, on time they just don’t have to do this stuff,” Pope told me. “And they’re still being held accountable for turning in assignments, whether they’re meaningful or not.” On the other side, “Palo Alto kids” — students in Silicon Valley’s stereotypically pressure-cooker public schools — “are just bombarded and overloaded and trying to stay above water.”
Merely getting rid of homework doesn’t solve either problem. The United States already has the second-highest disparity among OECD (the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development) nations between time spent on homework by students of high and low socioeconomic status — a difference of more than three hours, said Janine Bempechat, clinical professor at Boston University and author of No More Mindless Homework .
When she interviewed teachers in Boston-area schools that had cut homework before the pandemic, Bempechat told me, “What they saw immediately was parents who could afford it immediately enrolled their children in the Russian School of Mathematics,” a math-enrichment program whose tuition ranges from $140 to about $400 a month. Getting rid of homework “does nothing for equity; it increases the opportunity gap between wealthier and less wealthy families,” she said. “That solution troubles me because it’s no solution at all.”
A group of teachers at Wakefield High School in Arlington, Virginia, made the same point after the school district proposed an overhaul of its homework policies, including removing penalties for missing homework deadlines, allowing unlimited retakes, and prohibiting grading of homework.
“Given the emphasis on equity in today’s education systems,” they wrote in a letter to the school board, “we believe that some of the proposed changes will actually have a detrimental impact towards achieving this goal. Families that have means could still provide challenging and engaging academic experiences for their children and will continue to do so, especially if their children are not experiencing expected rigor in the classroom.” At a school where more than a third of students are low-income, the teachers argued, the policies would prompt students “to expect the least of themselves in terms of effort, results, and responsibility.”
Not all homework is created equal
Despite their opposing sides in the homework wars, most of the researchers I spoke to made a lot of the same points. Both Bempechat and Pope were quick to bring up how parents and schools confuse rigor with workload, treating the volume of assignments as a proxy for quality of learning. Bempechat, who is known for defending homework, has written extensively about how plenty of it lacks clear purpose, requires the purchasing of unnecessary supplies, and takes longer than it needs to. Likewise, when Pope instructs graduate-level classes on curriculum, she asks her students to think about the larger purpose they’re trying to achieve with homework: If they can get the job done in the classroom, there’s no point in sending home more work.
At its best, pandemic-era teaching facilitated that last approach. Honolulu-based teacher Christina Torres Cawdery told me that, early in the pandemic, she often had a cohort of kids in her classroom for four hours straight, as her school tried to avoid too much commingling. She couldn’t lecture for four hours, so she gave the students plenty of time to complete independent and project-based work. At the end of most school days, she didn’t feel the need to send them home with more to do.
A similar limited-homework philosophy worked at a public middle school in Chelsea, Massachusetts. A couple of teachers there turned as much class as possible into an opportunity for small-group practice, allowing kids to work on problems that traditionally would be assigned for homework, Jessica Flick, a math coach who leads department meetings at the school, told me. It was inspired by a philosophy pioneered by Simon Fraser University professor Peter Liljedahl, whose influential book Building Thinking Classrooms in Mathematics reframes homework as “check-your-understanding questions” rather than as compulsory work. Last year, Flick found that the two eighth grade classes whose teachers adopted this strategy performed the best on state tests, and this year, she has encouraged other teachers to implement it.
Teachers know that plenty of homework is tedious and unproductive. Jeannemarie Dawson De Quiroz, who has taught for more than 20 years in low-income Boston and Los Angeles pilot and charter schools, says that in her first years on the job she frequently assigned “drill and kill” tasks and questions that she now feels unfairly stumped students. She said designing good homework wasn’t part of her teaching programs, nor was it meaningfully discussed in professional development. With more experience, she turned as much class time as she could into practice time and limited what she sent home.
“The thing about homework that’s sticky is that not all homework is created equal,” says Jill Harrison Berg, a former teacher and the author of Uprooting Instructional Inequity . “Some homework is a genuine waste of time and requires lots of resources for no good reason. And other homework is really useful.”
Cutting homework has to be part of a larger strategy
The takeaways are clear: Schools can make cuts to homework, but those cuts should be part of a strategy to improve the quality of education for all students. If the point of homework was to provide more practice, districts should think about how students can make it up during class — or offer time during or after school for students to seek help from teachers. If it was to move the curriculum along, it’s worth considering whether strategies like Liljedahl’s can get more done in less time.
Some of the best thinking around effective assignments comes from those most critical of the current practice. Denise Pope proposes that, before assigning homework, teachers should consider whether students understand the purpose of the work and whether they can do it without help. If teachers think it’s something that can’t be done in class, they should be mindful of how much time it should take and the feedback they should provide. It’s questions like these that De Quiroz considered before reducing the volume of work she sent home.
More than a year after the new homework policy began in Marlborough, Hennessy still hears from parents who incorrectly “think homework isn’t happening” despite repeated assurances that kids still can receive work. She thinks part of the reason is that education has changed over the years. “I think what we’re trying to do is establish that homework may be an element of educating students,” she told me. “But it may not be what parents think of as what they grew up with. ... It’s going to need to adapt, per the teaching and the curriculum, and how it’s being delivered in each classroom.”
For the policy to work, faculty, parents, and students will all have to buy into a shared vision of what school ought to look like. The district is working on it — in November, it hosted and uploaded to YouTube a round-table discussion on homework between district administrators — but considering the sustained confusion, the path ahead seems difficult.
When I asked Luis Torres about whether he thought homework serves a useful part in PS 55’s curriculum, he said yes, of course it was — despite the effort and money it takes to keep the school open after hours to help them do it. “The children need the opportunity to practice,” he said. “If you don’t give them opportunities to practice what they learn, they’re going to forget.” But Torres doesn’t care if the work is done at home. The school stays open until around 6 pm on weekdays, even during breaks. Tutors through New York City’s Department of Youth and Community Development programs help kids with work after school so they don’t need to take it with them.
As schools weigh the purpose of homework in an unequal world, it’s tempting to dispose of a practice that presents real, practical problems to students across the country. But getting rid of homework is unlikely to do much good on its own. Before cutting it, it’s worth thinking about what good assignments are meant to do in the first place. It’s crucial that students from all socioeconomic backgrounds tackle complex quantitative problems and hone their reading and writing skills. It’s less important that the work comes home with them.
Jacob Sweet is a freelance writer in Somerville, Massachusetts. He is a frequent contributor to the New Yorker, among other publications.
Most Popular
Why the ludicrous republican response to trump’s conviction matters, the felon frontrunner: how trump warped our politics, the nra just won a big supreme court victory. good., take a mental break with the newest vox crossword, what’s really happening to grocery prices right now, today, explained.
Understand the world with a daily explainer plus the most compelling stories of the day.
More in The Highlight

Social media platforms aren’t equipped to handle the negative effects of their algorithms abroad. Neither is the law.

The real science behind the billionaire pursuit of immortality

If you want to belong, find a third place

America’s prison system is turning into a de facto nursing home

The one huge obstacle standing in the way of progress on gene-editing medicine

We can make birth safer for Black mothers. Here’s how.

The best — and worst — criticisms of Trump’s conviction

The MLB’s long-overdue decision to add Negro Leagues’ stats, briefly explained

We need to talk more about Trump’s misogyny

20 years of Bennifer, explained

This article is OpenAI training data

Big Milk has taken over American schools
How Much Homework Do American Kids Do?
Various factors, from the race of the student to the number of years a teacher has been in the classroom, affect a child's homework load.
![should schools give homework every night [IMAGE DESCRIPTION]](https://cdn.theatlantic.com/assets/media/img/posts/Ryan_Homework_Post.jpg)
In his Atlantic essay , Karl Taro Greenfeld laments his 13-year-old daughter's heavy homework load. As an eighth grader at a New York middle school, Greenfeld’s daughter averaged about three hours of homework per night and adopted mantras like “memorization, not rationalization” to help her get it all done. Tales of the homework-burdened American student have become common, but are these stories the exception or the rule?
A 2007 Metlife study found that 45 percent of students in grades three to 12 spend more than an hour a night doing homework, including the six percent of students who report spending more than three hours a night on their homework. In the 2002-2003 school year, a study out of the University of Michigan found that American students ages six through 17 spent three hours and 38 minutes per week doing homework.
A range of factors plays into how much homework each individual student gets:
Older students do more homework than their younger counterparts.
This one is fairly obvious: The National Education Association recommends that homework time increase by ten minutes per year in school. (e.g., A third grader would have 30 minutes of homework, while a seventh grader would have 70 minutes).
Studies have found that schools tend to roughly follow these guidelines: The University of Michigan found that students ages six to eight spend 29 minutes doing homework per night while 15- to 17-year-old students spend 50 minutes doing homework. The Metlife study also found that 50 percent of students in grades seven to 12 spent more than an hour a night on homework, while 37 percent of students in grades three to six spent an hour or more on their homework per night. The National Center for Educational Statistics found that high school students who do homework outside of school average 6.8 hours of homework per week.
![should schools give homework every night [IMAGE DESCRIPTION]](https://cdn.theatlantic.com/assets/media/img/posts/Ryan_Homework_MetlifeGraph.jpg)
Race plays a role in how much homework students do.
Asian students spend 3.5 more hours on average doing homework per week than their white peers. However, only 59 percent of Asian students’ parents check that homework is done, while 75.6 percent of Hispanic students’ parents and 83.1 percent of black students’ parents check.
![should schools give homework every night [IMAGE DESCRIPTION]](https://cdn.theatlantic.com/assets/media/img/posts/Ryan_Homework_NCESGraph.jpg)
Teachers with less experience assign more homework.
The Metlife study found that 14 percent of teachers with zero to five years of teaching experience assigned more than an hour of homework per night, while only six percent of teachers with 21 or more years of teaching experience assigned over an hour of homework.
![should schools give homework every night [IMAGE DESCRIPTION]](https://cdn.theatlantic.com/assets/media/img/posts/Ryan_Homework_GraphTeachers.jpg)
Math classes have homework the most frequently.
The Metlife study found that 70 percent of students in grades three to 12 had at least one homework assignment in math. Sixty-two percent had at least one homework assignment in a language arts class (English, reading, spelling, or creative writing courses) and 42 percent had at least one in a science class.
Regardless of how much homework kids are actually doing every night, most parents and teachers are happy with the way things are: 60 percent of parents think that their children have the “right amount of homework,” and 73 percent of teachers think their school assigns the right amount of homework.
Students, however, are not necessarily on board: 38 percent of students in grades seven through 12 and 28 percent of students in grades three through six report being “very often/often” stressed out by their homework.
Do our kids have too much homework?
by: Marian Wilde | Updated: January 31, 2024
Print article

Many students and their parents are frazzled by the amount of homework being piled on in the schools. Yet many researchers say that American students have just the right amount of homework.
“Kids today are overwhelmed!” a parent recently wrote in an email to GreatSchools.org “My first-grade son was required to research a significant person from history and write a paper of at least two pages about the person, with a bibliography. How can he be expected to do that by himself? He just started to learn to read and write a couple of months ago. Schools are pushing too hard and expecting too much from kids.”
Diane Garfield, a fifth grade teacher in San Francisco, concurs. “I believe that we’re stressing children out,” she says.
But hold on, it’s not just the kids who are stressed out . “Teachers nowadays assign these almost college-level projects with requirements that make my mouth fall open with disbelief,” says another frustrated parent. “It’s not just the kids who suffer!”
“How many people take home an average of two hours or more of work that must be completed for the next day?” asks Tonya Noonan Herring, a New Mexico mother of three, an attorney and a former high school English teacher. “Most of us, even attorneys, do not do this. Bottom line: students have too much homework and most of it is not productive or necessary.”
Research about homework
How do educational researchers weigh in on the issue? According to Brian Gill, a senior social scientist at the Rand Corporation, there is no evidence that kids are doing more homework than they did before.
“If you look at high school kids in the late ’90s, they’re not doing substantially more homework than kids did in the ’80s, ’70s, ’60s or the ’40s,” he says. “In fact, the trends through most of this time period are pretty flat. And most high school students in this country don’t do a lot of homework. The median appears to be about four hours a week.”
Education researchers like Gill base their conclusions, in part, on data gathered by the National Assessment of Educational Progress (NAEP) tests.
“It doesn’t suggest that most kids are doing a tremendous amount,” says Gill. “That’s not to say there aren’t any kids with too much homework. There surely are some. There’s enormous variation across communities. But it’s not a crisis in that it’s a very small proportion of kids who are spending an enormous amount of time on homework.”
Etta Kralovec, author of The End of Homework: How Homework Disrupts Families, Overburdens Children, and Limits Learning , disagrees, saying NAEP data is not a reliable source of information. “Students take the NAEP test and one of the questions they have to fill out is, ‘How much homework did you do last night’ Anybody who knows schools knows that teachers by and large do not give homework the night before a national assessment. It just doesn’t happen. Teachers are very clear with kids that they need to get a good night’s sleep and they need to eat well to prepare for a test.
“So asking a kid how much homework they did the night before a national test and claiming that that data tells us anything about the general run of the mill experience of kids and homework over the school year is, I think, really dishonest.”
Further muddying the waters is an AP/AOL poll that suggests that most Americans feel that their children are getting the right amount of homework. It found that 57% of parents felt that their child was assigned about the right amount of homework, 23% thought there was too little and 19% thought there was too much.
One indisputable fact
One homework fact that educators do agree upon is that the young child today is doing more homework than ever before.
“Parents are correct in saying that they didn’t get homework in the early grades and that their kids do,” says Harris Cooper, professor of psychology and director of the education program at Duke University.
Gill quantifies the change this way: “There has been some increase in homework for the kids in kindergarten, first grade, and second grade. But it’s been an increase from zero to 20 minutes a day. So that is something that’s fairly new in the last quarter century.”
The history of homework
In his research, Gill found that homework has always been controversial. “Around the turn of the 20th century, the Ladies’ Home Journal carried on a crusade against homework. They thought that kids were better off spending their time outside playing and looking at clouds. The most spectacular success this movement had was in the state of California, where in 1901 the legislature passed a law abolishing homework in grades K-8. That lasted about 15 years and then was quietly repealed. Then there was a lot of activism against homework again in the 1930s.”
The proponents of homework have remained consistent in their reasons for why homework is a beneficial practice, says Gill. “One, it extends the work in the classroom with additional time on task. Second, it develops habits of independent study. Third, it’s a form of communication between the school and the parents. It gives parents an idea of what their kids are doing in school.”
The anti-homework crowd has also been consistent in their reasons for wanting to abolish or reduce homework.
“The first one is children’s health,” says Gill. “A hundred years ago, you had medical doctors testifying that heavy loads of books were causing children’s spines to be bent.”
The more things change, the more they stay the same, it seems. There were also concerns about excessive amounts of stress .
“Although they didn’t use the term ‘stress,'” says Gill. “They worried about ‘nervous breakdowns.'”
“In the 1930s, there were lots of graduate students in education schools around the country who were doing experiments that claimed to show that homework had no academic value — that kids who got homework didn’t learn any more than kids who didn’t,” Gill continues. Also, a lot of the opposition to homework, in the first half of the 20th century, was motivated by a notion that it was a leftover from a 19th-century model of schooling, which was based on recitation, memorization and drill. Progressive educators were trying to replace that with something more creative, something more interesting to kids.”
The more-is-better movement
Garfield, the San Francisco fifth-grade teacher, says that when she started teaching 30 years ago, she didn’t give any homework. “Then parents started asking for it,” she says. “I got In junior high and high school there’s so much homework, they need to get prepared.” So I bought that one. I said, ‘OK, they need to be prepared.’ But they don’t need two hours.”
Cooper sees the trend toward more homework as symptomatic of high-achieving parents who want the best for their children. “Part of it, I think, is pressure from the parents with regard to their desire to have their kids be competitive for the best universities in the country. The communities in which homework is being piled on are generally affluent communities.”
The less-is-better campaign
Alfie Kohn, a widely-admired progressive writer on education and parenting, published a sharp rebuttal to the more-homework-is-better argument in his 2006 book The Homework Myth: Why Our Kids Get Too Much of a Bad Thing . Kohn criticized the pro-homework studies that Cooper referenced as “inconclusive… they only show an association, not a causal relationship” and he titled his first chapter “Missing Out on Their Childhoods.”
Vera Goodman’s 2020 book, Simply Too Much Homework: What Can We Do? , repeats Kohn’s scrutiny and urges parents to appeal to school and government leaders to revise homework policies. Goodman believes today’s homework load stresses out teachers, parents, and students, deprives children of unstructured time for play, hobbies, and individual pursuits, and inhibits the joy of learning.
Homework guidelines
What’s a parent to do, you ask? Fortunately, there are some sanity-saving homework guidelines.
Cooper points to “The 10-Minute Rule” formulated by the National PTA and the National Education Association, which suggests that kids should be doing about 10 minutes of homework per night per grade level. In other words, 10 minutes for first-graders, 20 for second-graders and so on.
Too much homework vs. the optimal amount
Cooper has found that the correlation between homework and achievement is generally supportive of these guidelines. “We found that for kids in elementary school there was hardly any relationship between how much homework young children did and how well they were doing in school, but in middle school the relationship is positive and increases until the kids were doing between an hour to two hours a night, which is right where the 10-minute rule says it’s going to be optimal.
“After that it didn’t go up anymore. Kids that reported doing more than two hours of homework a night in middle school weren’t doing any better in school than kids who were doing between an hour to two hours.”
Garfield has a very clear homework policy that she distributes to her parents at the beginning of each school year. “I give one subject a night. It’s what we were studying in class or preparation for the next day. It should be done within half an hour at most. I believe that children have many outside activities now and they also need to live fully as children. To have them work for six hours a day at school and then go home and work for hours at night does not seem right. It doesn’t allow them to have a childhood.”
International comparisons
How do American kids fare when compared to students in other countries? Professors Gerald LeTendre and David Baker of Pennsylvania State University conclude in their 2005 book, National Differences, Global Similarities: World Culture and the Future of Schooling, that American middle schoolers do more homework than their peers in Japan, Korea, or Taiwan, but less than their peers in Singapore and Hong Kong.
One of the surprising findings of their research was that more homework does not correlate with higher test scores. LeTendre notes: “That really flummoxes people because they say, ‘Doesn’t doing more homework mean getting better scores?’ The answer quite simply is no.”
Homework is a complicated thing
To be effective, homework must be used in a certain way, he says. “Let me give you an example. Most homework in the fourth grade in the U.S. is worksheets. Fill them out, turn them in, maybe the teacher will check them, maybe not. That is a very ineffective use of homework. An effective use of homework would be the teacher sitting down and thinking ‘Elizabeth has trouble with number placement, so I’m going to give her seven problems on number placement.’ Then the next day the teacher sits down with Elizabeth and she says, ‘Was this hard for you? Where did you have difficulty?’ Then she gives Elizabeth either more or less material. As you can imagine, that kind of homework rarely happens.”
Shotgun homework
“What typically happens is people give what we call ‘shotgun homework’: blanket drills, questions and problems from the book. On a national level that’s associated with less well-functioning school systems,” he says. “In a sense, you could sort of think of it as a sign of weaker teachers or less well-prepared teachers. Over time, we see that in elementary and middle schools more and more homework is being given, and that countries around the world are doing this in an attempt to increase their test scores, and that is basically a failing strategy.”
Quality not quantity?
“ The Case for (Quality) Homework: Why It Improves Learning, and How Parents Can Help ,” a 2019 paper written by Boston University psychologist Janine Bempechat, asks for homework that specifically helps children “confront ever-more-complex tasks” that enable them to gain resilience and embrace challenges.
Similar research from University of Ovideo in Spain titled “ Homework: Facts and Fiction 2021 ” says evidence shows that how homework is applied is more important than how much is required, and it asserts that a moderate amount of homework yields the most academic achievement. The most important aspect of quality homework assignment? The effort required and the emotions prompted by the task.
Robyn Jackson, author of How to Plan Rigorous Instruction and other media about rigor says the key to quality homework is not the time spent, but the rigor — or mental challenge — involved. ( Read more about how to evaluate your child’s homework for rigor here .)
Nightly reading as a homework replacement
Across the country, many elementary schools have replaced homework with a nightly reading requirement. There are many benefits to children reading every night , either out loud with a parent or independently: it increases their vocabulary, imagination, concentration, memory, empathy, academic ability, knowledge of different cultures and perspectives. Plus, it reduces stress, helps kids sleep, and bonds children to their cuddling parents or guardians. Twenty to 30 minutes of reading each day is generally recommended.
But, is this always possible, or even ideal?
No, it’s not.
Alfie Kohn criticizes this added assignment in his blog post, “ How To Create Nonreaders .” He cites an example from a parent (Julie King) who reports, “Our children are now expected to read 20 minutes a night, and record such on their homework sheet. What parents are discovering (surprise) is that those kids who used to sit down and read for pleasure — the kids who would get lost in a book and have to be told to put it down to eat/play/whatever — are now setting the timer… and stopping when the timer dings. … Reading has become a chore, like brushing your teeth.”
The take-away from Kohn? Don’t undermine reading for pleasure by turning it into another task burdening your child’s tired brain.
Additional resources
Books Simply Too Much Homework: What Can We do? by Vera Goodman, Trafford Publishing, 2020
The Case Against Homework: How Homework is Hurting Children and What Parents Can Do About It by Sara Bennett and Nancy Kalish, Crown Publishers, 2007
The Homework Myth: Why Our Kids Get Too Much of a Bad Thing by Alfie Kohn, Hatchett Books, 2006 The End of Homework: How Homework Disrupts Families, Overburdens Children, and Limits Learning by Etta Kralovec and John Buell, Beacon Press, 2001.
The Battle Over Homework: Common Ground for Administrators, Teachers, and Parents by Harris M. Cooper, Corwin Press, 2001.
Seven Steps to Homework Success: A Family Guide to Solving Common Homework Problems by Sydney Zentall and Sam Goldstein, Specialty Press, 1998.
Homes Nearby
Homes for rent and sale near schools

Why your neighborhood school closes for good – and what to do when it does

What should I write my college essay about?
What the #%@!& should I write about in my college essay?

How longer recess fuels child development
How longer recess fuels stronger child development
Yes! Sign me up for updates relevant to my child's grade.
Please enter a valid email address
Thank you for signing up!
Server Issue: Please try again later. Sorry for the inconvenience
- May 28 Engi-near the finish line
- May 17 Love is in the air
- May 11 Art Car Club showcases its rolling artwork on wheels at the Orange Show parade
- May 3 Cultures collide at the Bellaire International Student Association Fest
- May 2 Uncalculated uncertainties

Three Penny Press

Students spend three times longer on homework than average, survey reveals
Sonya Kulkarni and Pallavi Gorantla | Jan 9, 2022

Graphic by Sonya Kulkarni
The National Education Association and the National Parent Teacher Association have suggested that a healthy number of hours that students should be spending can be determined by the “10-minute rule.” This means that each grade level should have a maximum homework time incrementing by 10 minutes depending on their grade level (for instance, ninth-graders would have 90 minutes of homework, 10th-graders should have 100 minutes, and so on).
As ‘finals week’ rapidly approaches, students not only devote effort to attaining their desired exam scores but make a last attempt to keep or change the grade they have for semester one by making up homework assignments.
High schoolers reported doing an average of 2.7 hours of homework per weeknight, according to a study by the Washington Post from 2018 to 2020 of over 50,000 individuals. A survey of approximately 200 Bellaire High School students revealed that some students spend over three times this number.
The demographics of this survey included 34 freshmen, 43 sophomores, 54 juniors and 54 seniors on average.
When asked how many hours students spent on homework in a day on average, answers ranged from zero to more than nine with an average of about four hours. In contrast, polled students said that about one hour of homework would constitute a healthy number of hours.
Junior Claire Zhang said she feels academically pressured in her AP schedule, but not necessarily by the classes.
“The class environment in AP classes can feel pressuring because everyone is always working hard and it makes it difficult to keep up sometimes.” Zhang said.
A total of 93 students reported that the minimum grade they would be satisfied with receiving in a class would be an A. This was followed by 81 students, who responded that a B would be the minimum acceptable grade. 19 students responded with a C and four responded with a D.
“I am happy with the classes I take, but sometimes it can be very stressful to try to keep up,” freshman Allyson Nguyen said. “I feel academically pressured to keep an A in my classes.”
Up to 152 students said that grades are extremely important to them, while 32 said they generally are more apathetic about their academic performance.
Last year, nine valedictorians graduated from Bellaire. They each achieved a grade point average of 5.0. HISD has never seen this amount of valedictorians in one school, and as of now there are 14 valedictorians.
“I feel that it does degrade the title of valedictorian because as long as a student knows how to plan their schedule accordingly and make good grades in the classes, then anyone can be valedictorian,” Zhang said.
Bellaire offers classes like physical education and health in the summer. These summer classes allow students to skip the 4.0 class and not put it on their transcript. Some electives also have a 5.0 grade point average like debate.
Close to 200 students were polled about Bellaire having multiple valedictorians. They primarily answered that they were in favor of Bellaire having multiple valedictorians, which has recently attracted significant acclaim .
Senior Katherine Chen is one of the 14 valedictorians graduating this year and said that she views the class of 2022 as having an extraordinary amount of extremely hardworking individuals.
“I think it was expected since freshman year since most of us knew about the others and were just focused on doing our personal best,” Chen said.
Chen said that each valedictorian achieved the honor on their own and deserves it.
“I’m honestly very happy for the other valedictorians and happy that Bellaire is such a good school,” Chen said. “I don’t feel any less special with 13 other valedictorians.”
Nguyen said that having multiple valedictorians shows just how competitive the school is.
“It’s impressive, yet scary to think about competing against my classmates,” Nguyen said.
Offering 30 AP classes and boasting a significant number of merit-based scholars Bellaire can be considered a competitive school.
“I feel academically challenged but not pressured,” Chen said. “Every class I take helps push me beyond my comfort zone but is not too much to handle.”
Students have the opportunity to have off-periods if they’ve met all their credits and are able to maintain a high level of academic performance. But for freshmen like Nguyen, off periods are considered a privilege. Nguyen said she usually has an hour to five hours worth of work everyday.
“Depending on the day, there can be a lot of work, especially with extra curriculars,” Nguyen said. “Although, I am a freshman, so I feel like it’s not as bad in comparison to higher grades.”
According to the survey of Bellaire students, when asked to evaluate their agreement with the statement “students who get better grades tend to be smarter overall than students who get worse grades,” responders largely disagreed.
Zhang said that for students on the cusp of applying to college, it can sometimes be hard to ignore the mental pressure to attain good grades.
“As a junior, it’s really easy to get extremely anxious about your GPA,” Zhang said. “It’s also a very common but toxic practice to determine your self-worth through your grades but I think that we just need to remember that our mental health should also come first. Sometimes, it’s just not the right day for everyone and one test doesn’t determine our smartness.”

HUMANS OF BELLAIRE – Austin Schmidt

HUMANS OF BELLAIRE – Michael Sheth

Q&A with presidential debate national qualifier

HUMANS OF BELLAIRE – Alberto Bernardoni

Engi-near the finish line
Love is in the air

Art Car Club showcases its rolling artwork on wheels at the Orange Show parade

Cultures collide at the Bellaire International Student Association Fest

Uncalculated uncertainties
Humans of Bellaire

HUMANS OF BELLAIRE – Elisa Adams

HUMANS OF BELLAIRE – Achilles Glenn

HUMANS OF BELLAIRE – Maurya Manjunath

Gather around the campfire

HUMANS OF BELLAIRE – Alara Bozkurt
The student news site of Bellaire High School
- Letter to the Editor
- Submit a Story Idea
- Advertising/Sponsorships
Comments (7)
Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Anonymous • Nov 21, 2023 at 10:32 am
It’s not really helping me understand how much.
josh • May 9, 2023 at 9:58 am
Kassie • May 6, 2022 at 12:29 pm
Im using this for an English report. This is great because on of my sources needed to be from another student. Homework drives me insane. Im glad this is very updated too!!
Kaylee Swaim • Jan 25, 2023 at 9:21 pm
I am also using this for an English report. I have to do an argumentative essay about banning homework in schools and this helps sooo much!
Izzy McAvaney • Mar 15, 2023 at 6:43 pm
I am ALSO using this for an English report on cutting down school days, homework drives me insane!!
E. Elliott • Apr 25, 2022 at 6:42 pm
I’m from Louisiana and am actually using this for an English Essay thanks for the information it was very informative.
Nabila Wilson • Jan 10, 2022 at 6:56 pm
Interesting with the polls! I didn’t realize about 14 valedictorians, that’s crazy.
(877) 322-NWEF | [email protected]

Pros and Cons of Homework

“Not until you finish your homework.”
“I want you to finish your dinner and get right to work on your homework.”
“Is your homework done? Then, no, you get up those stairs and finish first.”
We’ve all heard something similar from our mom, dad, or caretaker. Homework is a big staple of the American school scene, just like lockers, the school bell, and big yellow buses. Portrayed in media from the Brady Bunch to Cocomelon, homework has been an academic given for decades.
Despite its popularity, this after-school activity has been under scrutiny for over a century. Britannica explains , “In the early 1900s, progressive education theorists, championed by the magazine Ladies’ Home Journal , decried homework’s negative impact on children’s physical and mental health, leading California to ban homework for students under 15 from 1901 until 1917. In the 1930s, homework was portrayed as child labor, which was newly illegal, but the prevailing argument was that kids needed time to do household chores.”
Regardless of opposition, homework persevered, and millions of American students still spend long hours completing bookwork in their bedrooms after school.
What are the modern objections to homework? What if the opposition is right? Is there merit to the concerns, or is homework a helpful tool for a well-rounded and comprehensive education? If you’d like to find out, now’s the time to keep reading!
How Much Time?
When analysts crunch the numbers, children spend far more time doing homework than many believe necessary. According to One Class, elementary school students spend an average of 42 minutes a day on homework. Some parents and educators argue that five additional hours of schoolwork per week is too much for elementary students.
High schoolers spend even more time on after-school assignments. Pew Research published a 2019 article in which they explained , “Overall, teens (ages 15 to 17) spend an hour a day, on average, doing homework during the school year, up from 44 minutes a day about a decade ago and 30 minutes in the mid-1990s.”
Globally, the U.S. ranks 15th for the average amount of time spent on homework by high school students. The Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development conducted a worldwide study on 15-year-old students to evaluate the homework load for high schoolers worldwide.
Among the countries included in the study, China ranked first, with students spending an average of 13.8 hours a week on homework. The Netherlands ranked the lowest, with their students studying after school for an average of 5.8 hours a week. American students spent an average of 6.1 hours per week completing their homework.
What Students Think
Homework has become a point of significant stress for American students.
One Stanford study found that 56% of students who participated in the survey stated that homework was a primary source of stress. Another study found that the decline in adequate teenage sleep may be partly due to homework. In yet another study, 82% of students interviewed admitted that they were “often or always stressed by schoolwork.”
It’s not just the students who object to frequent homework. Parents have begun to voice their displeasure as well. One mother in Canada went viral on social media when she announced that she and her husband were done watching their ten-year-old daughter stress over her homework every night. They decided that homework wasn’t a useful educational tool for their child.
Another mother in Kansas expressed how frustrating it is when her daughter has homework that she as a mother is unsure how to help with. “I feel bad for emailing a teacher in the evenings. I’m slightly annoyed at homework in general because I don’t know what the teacher taught.”
What Teachers Think
Educators debate whether or not homework is a positive educational tool. One Duke University professor recommends homework, believing there is a correlation between homework and academic success for older students. He recommends implementing the “10 Minute Rule.” Essentially, students receive 10 minutes of homework per day for each grade. (For instance, 1st graders would receive 10 minutes of homework, 5th graders 50 minutes, 12th graders 120 minutes.)
A Texas teacher informed the parents of her 2nd-grade students that she would not be assigning homework anymore. Instead, she asked that the children participate in real-life activities that encourage growth and success. These activities included outdoor play, family meals, and reading with parents. As her plan evolved, she acknowledged that some students actually enjoyed homework and missed the challenge. Other students received extra work here and there on an as-needed basis.
Defining the Need
One question that desperately needs to be asked is, “What’s the purpose of homework?”
The answer to this question can provide parameters, determine whether or not homework achieves the goal(s), and establish if it should continue to be a staple in the American education system.
Psychology Today wonders the same thing , without any clear-cut resolution. “I started the blog with a question ‘What’s the purpose of homework?’ I’ll end with the same question. If a teacher who is assigning the homework can’t provide a clear rationale behind this question, then maybe the homework shouldn’t be assigned.”
However, Honest Pros and Cons makes a case for homework in more detail. Their reasoning for homework includes :
- Practicing what they learn in the classroom
- Improving study habits
- Developing self-discipline
- Enhancing independent problem-solving skills
McRel International notes that many factors play into whether or not homework is an effective strategy for students. They acknowledge that after-school assignments have pros and cons and state that the research is by no means definitive.
Proponents of homework present several positives:
- It improves student achievement – “Students in classes that were assigned homework outperformed 69% of students who didn’t have homework on both standardized tests and grades.” – Britannica ProCon
While the data is not conclusive, numerous studies have shown a correlation between academic success and the use of homework.
- It involves parents – “Homework is also the place where schools and families most frequently intersect.” – US News
Homework encourages parents and children to spend time together problem-solving and working toward a goal. It also gives parents a window into what their child is learning and the progress they are making.
- It encourages time management – “Homework is an effective tool when teaching your child about time management. This means that time management should extend beyond the classroom and into your home. ” – Edugage
American students spend roughly six hours a day at school. This schedule doesn’t leave much flexibility for sports, a social life, and a healthy amount of free time on top of homework. Kids have to learn time management if they want a life outside of their education.
- It tracks progress – “Homework allows teachers to track students’ progress, meaning that homework helps to find out the academic strengths and weaknesses of children.” – Honest Pros and Cons
Homework gives teachers a chance to see what the student can achieve independently. Students must put into practice what they learned in the schoolroom in a different environment and without their teacher present.
- It develops working memory – “Revising the key skills learned in the classroom during homework increases the likelihood of a student remembering and being able to use those skills in a variety of situations in the future, contributing to their overall education.” – The Guardian
Environment can play an active part in memory. Biologically, our brains more easily recall memories and facts when we’re immersed in the same surroundings in which we created that memory or learned those facts. Homework removes the environmental factor, forcing students to strengthen their working memory.
Concerned about the effects of homework on students, opponents note these objections:
- The science isn’t settled – “There is no conclusive evidence that homework increases student achievement across the board.” – Reading Rockets
As we’ve noted before, the data isn’t conclusive despite the numerous studies conducted. To many, the negatives suggested by various studies outweigh the proposed positives.
- It adds stress – “Researchers have found that students who spend too much time on homework experience more levels of stress and physical health problems.” – Psychology Today
Studies have concluded that too much homework creates undue stress on developing minds and bodies. This translates into mental, emotional, and physical issues for many students. This stress also affects their sleep , both the amount of sleep and the quality of that sleep.
- It impacts other interests/pursuits – “Homework prevents self-discovery and having the time to learn new skills outside of the school system.” – University of the People
Critics of homework fear that, in addition to time spent on school grounds, after-school assignments stunt students’ abilities to experience life outside academia. Students who struggle with completing work at home are even more susceptible to a lifestyle void of other interests.
- It expands the gap – “One study concluded that homework increases social inequality because it ‘potentially serves as a mechanism to further advantage those students who already experience some privilege in the school system while further disadvantaging those who may already be in a marginalized position.’” – Britannica ProCon
Homework often involves a computer and/or an internet connection. During the Covid-19 pandemic, 30% of students didn’t have the necessary technology at home to effectively participate in distance learning, raising questions about inequality affecting homework that relies on at-home technology.
- It creates family tension – “Assigning homework forces a person to take on added disciplinary responsibilities.” – Front Range Christian School
While homework can bring children and parents together, it can also drive a wedge between them. Students who feel overwhelmed or who need a break from focusing on academics often buck their homework requirements, leaving parents to enforce education standards that the teachers created. Parents and students alike can end up frustrated, with little progress made.
A World of Unknowns
While the homework debate rages on, researchers continue to work toward a conclusive answer. In the meantime, teachers, parents, schools, and communities can work together to find a solution that meets the needs of their students.
Without a doubt, homework has positive aspects that encourage students to advance through personal and academic growth. The trick is to nurture this positivity without stunting progress with adverse side effects.
It’s a double-edged sword that’s well worth considering to ensure the best for our kids.
Leave A Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Make a difference. Run for school board.

Free course. Enroll today.
Related Posts

Resource Guide for Parents

Resource Guide for Teachers

Resource Guide for School Board Members
- DOWNLOADS AND PRINTABLES
- Upcoming Summits
- Recent Summits
- Host A Summit
- KNOW YOUR STATE
RECENT POSTS
- Resource Guide for Parents May 16, 2024
- Resource Guide for Teachers May 16, 2024
- Resource Guide for School Board Members May 16, 2024
- Collective Bargaining Is Not Related To Student Achievement May 8, 2024
- Board’s Guide to Free Speech Course Sample April 12, 2024
Mailing address: PO Box 962 Bedford, Virginia 24523 USA
Phone: (877) 322-NWEF
Email: [email protected]

© Copyright 2024 | Noah Webster Educational Foundation All Rights Reserved | Privacy Policy | Terms & Conditions
Classroom Q&A
With larry ferlazzo.
In this EdWeek blog, an experiment in knowledge-gathering, Ferlazzo will address readers’ questions on classroom management, ELL instruction, lesson planning, and other issues facing teachers. Send your questions to [email protected]. Read more from this blog.
The Policy Concerns That Keep Teachers Up at Night

- Share article
We teachers have our hands full with our day-to-day classrooms, but education policies can have a major impact on our working lives.
Here are the policy issues some educators feel we should be most concerned about:
Restrictions on What Can Be Taught
Bryant Odega is a Los Angeles-based labor-rights activist and teacher-candidate fellow at the Harvard Graduate School of Education:
I think the most important education policy issue facing public schools today are the topics and curricula teachers are able to teach. There is a growing effort by conservatives to restrict teaching topics, even going as far as banning books that talk about gender, sexuality, or race; turning libraries into disciplinary centers’ and distorting the history of slavery and racism in order to minimize its impact.
However, this is not new; restricting knowledge, especially within the context of race, is an age-old issue within the United States. In his book, Fugitive Pedagogy: Carter G. Woodson and the Art of Black Teaching , Harvard professor Jarvis R. Givens writes about how teachers in Virginia’s freedpeople’s schools were subject to terror following the Civil War. Furthermore, Black education itself was subject to violent white protest. These are experiences that continued during Woodson’s years as a student during the 1880-'90s. Racial progress too often begets resentment and backlash. Woodson would eventually launch what we now celebrate as Black History Month and popularize Black studies as an academic discipline. Nevertheless, efforts to halt the teaching of race continue today.
Cultural diversity in the classroom is important for students because culture informs the way people perceive themselves, each other, and the world. The lack of inclusion and diversity sends a message to students that their perspectives, cultures, and contributions to society are not significant, and as educators, this is an issue we must tackle head-on.
Professor Rudine Sims Bishop popularized the concept of Mirrors and Windows promoting a multicultural curriculum which “mirrors” the daily experiences of students and “windows” into the experiences of others. This approach engages students by including, affirming, and respecting their cultures and life experiences in the classroom. It also helps them learn about experiences different from theirs, even finding cross-cultural connections in ways they may not have considered before.
If we want to educate a civil society of critical thinkers and informed decisionmakers, then our students deserve all the opportunities possible to engage in knowledge that helps them recognize their own agency, respect others, and become change makers in their own lives and those of their communities.
As educators, it is important for us to reject conservative efforts to take us backward and instead teach and affirm the entire humanity of our students, to advance humanity forward. If we remove cultural diversity and awareness from our classrooms and curricula, we will be perpetuating a narrative that denies the cultural diversity and humanity of our students.
So how do we accomplish this? Teachers should continue teaching and reading from books that include cultural diversity and awareness. Here’s a list of books that can help. Additionally, teachers should discuss book bans and curriculum censorship with students so that they can analyze the impact of these efforts and reflect on how they would respond. Being able to apply skills developed in class to real-world events further helps students in their learning process.
Teachers should also get more civically engaged, whether it’s voting, attending school board meetings, or getting more involved in your labor union. Teachers’ unions are on the front lines of combating the current attacks on curriculum, and there’s been success in codifying culturally affirming policies for students within labor contracts with school districts as demonstrated by the teachers’ union within the Los Angeles Unified school district, the nation’s second largest district, United Teachers Los Angeles . UTLA succeeded in codifying support in advancing ethnic studies and culturally responsive curriculum within its labor contract with the district. These are just some ways to address this issue within and outside the classroom. Most importantly, continue to stay informed and alert in order to best serve the needs of your students.

‘Professional Learning’
Angela M. Ward, Ph.D., is an anti-racist educator with over 25 years of experience in education. She is focused on creating identity-safe schools and workplaces. Follow her @2WardEquity on Instagram & X and visit http://2wardequity.com/blog/ to subscribe to the 2Ward Equity newsletter:
Professional development is used to launch the school year and introduce new curriculum, tools, processes, and resources. It is a critical component to supporting the adults in the education workforce. Mediocre professional development in public schools threatens the future progress of the profession to meet the needs of the most vulnerable students. Public schools have taken “professional” out and replaced it with compliance, sit-n-get, meaningless offerings that do little to prepare educators for the challenges of today. Teachers, principals, directors, executives, and superintendents all need high-quality professional learning to navigate the turmoil the educational system sits in.
Instead of development, I choose to focus on the adult as a learner and find professional learning to be more promising. Professional learning opens the door to new knowledge pathways and acknowledges the choice available to educators. It invites adult learners into a collaborative and interactive space to learn, enhance their skills, and build capacity to go into and impact learning in the classrooms, hallways, conference rooms, and board rooms each day. In a professional learning experience designed for an adult to build their personal capacity, facilitators work to understand participant skills and knowledge and to build rapport in the time allotted to enhance educator self-efficacy.
As I work with districts, it is clear to me that high-quality professional learning is not the norm. It is exceptional to find a district that dedicates a budget for learning experiences that build educator awareness, enable them to sharpen their skills, and challenge their thinking to push them to their growth edge—what Vygotsky (1978) calls their zone of proximal development. Without adequate learning and growth space, we are hemorrhaging educators to private-sector jobs that value their expertise and knowledge and support them with learning teams, as well as onboarding them to a work culture focused on their professional growth.
Funding and providing the time and space for the design and delivery of high-quality professional learning is a key policy issue facing public schools. Our students deserve a highly qualified workforce that is tapped in to the latest research and learns about their needs through ongoing community building outside the school walls. To be effective, professional learning must address the immediate needs of the educator to support the most vulnerable students in our schools. By supporting adults to learn how to support the most vulnerable, adults are better prepared to ensure all students receive what they need.

Civics Education
Michael Hernandez is an award-winning educator and speaker. He is the author of Storytelling With Purpose and is an Apple Distinguished Educator and Lindblad/National Geographic Grosvenor Teacher Fellow:
One of the biggest issues public schools face today is our ability to develop productive citizens—students who are prepared to apply the knowledge of our curriculum in constructive ways to solve problems in the world beyond our classrooms. The pressure to attain high test scores and the obsession with data-driven learning has left kids and teachers unengaged and disconnected from our world and their own lives. We’ve neglected what matters most in education, which is the focus on the humanity of learning: curiosity, passion, and our responsibility as members of a local and global community.
Test results released last May by the National Assessment of Educational Progress show 8th grade civics scores down for the first time ever. While some blamed the pandemic for the decline (reading and math scores were also down), my experience in the classroom leads me to believe that it’s more about cultural shifts and the doubling down on teaching based on direct instruction/memorization/testing.
In the same way that you have to conduct experiments to truly understand science and have to write in order to create and comprehend literature, we must also actively put the concepts of civics into practice to truly understand their purpose and how they function in our own communities.
One of the best ways I’ve found to do this is through project-based-learning experiences like journalism and documentary filmmaking. Digital storytelling projects like these allow students to explore topics that they are curious or passionate about and integrate research and writing skills at the same time. There are many advantages to these projects:
- Students make personal connections to the topic and develop empathy for people affected by policies and social conditions.
- Students see and feel the concrete implications of politics and public policies on the ground in front of them, rather than reading about it in a book, which only develops an abstract relationship to the material.
- Students develop and apply skills like critical thinking, logic and reasoning, and ethical decisionmaking.
- They help students develop the skills, knowledge, and courage to become civically engaged beyond the classroom.
- Students are empowered to participate in society in constructive ways and see their personal role and responsibility to contribute in positive ways.
Project-based-learning challenges like digital storytelling help students become active participants in civic life rather than passive bystanders who might feel disenfranchised or frustrated with the political system. It also sends important messages about our trust and respect for our students, their experience, and their unique points of view. This in turn models how to develop healthy, productive relationships with others to achieve common goals, which are vital life skills in a democracy.
Here are some ways teachers can start conversations around civic engagement through digital storytelling, even if they aren’t officially a journalism or social studies teacher.
- Empathy Interviews . Have students identify people in their community who have a relationship to your current unit or topic of study, such as an author of a book, a journalist, a recent immigrant, or a scientist. Record an interview with them (use a voice-recording app on your phone/iPad or via video-conferencing tools like Zoom), then review the responses, looking for new insights or ways they challenged students’ existing thinking. This models listening and empathy skills.
- Humans of Your School . Inspired by the Humans of New York blog, this lesson asks students to take portraits of lesser-known members of their community and include their insights on their life or current living/working conditions. Post the images and text on a class website or social media channel. This project uplifts diverse voices and helps build community.
Even in our busy lives as teachers, small projects like these can quickly energize the classroom and get kids excited about learning and being an active member of their community.

Thanks to Bryant, Angela, and Michael for contributing their thoughts!
Today’s guests answered this question:
What do you think is the most important education policy issue facing public schools today, why do you think it is so important, and what is your position on it?
Keisha Rembert and Kit Golan provided responses in Part One .
Consider contributing a question to be answered in a future post. You can send one to me at [email protected] . When you send it in, let me know if I can use your real name if it’s selected or if you’d prefer remaining anonymous and have a pseudonym in mind.
You can also contact me on Twitter at @Larryferlazzo .
Just a reminder; you can subscribe and receive updates from this blog via email . And if you missed any of the highlights from the first 12 years of this blog, you can see a categorized list here .
The opinions expressed in Classroom Q&A With Larry Ferlazzo are strictly those of the author(s) and do not reflect the opinions or endorsement of Editorial Projects in Education, or any of its publications.
Sign Up for EdWeek Update
Edweek top school jobs.

Sign Up & Sign In

- Sustainability
- Latest News
- News Reports
- Documentaries & Shows
- TV Schedule
- CNA938 Live
- Radio Schedule
- Singapore Parliament
- Mental Health
- Interactives
- Entertainment
- Style & Beauty
- Experiences
- Remarkable Living
- Send us a news tip
- Events & Partnerships
- Business Blueprint
- Health Matters
- The Asian Traveller
Trending Topics
Follow our news, recent searches, commentary: should holiday homework be banned, advertisement.
The June school holidays have started, but many students and families are experiencing a familiar mix of anticipation and dread, says Dr Eugenia Koh-Chua, a former lecturer and mother of two.
This audio is AI-generated.

Eugenia Koh-Chua
MELBOURNE: The June school holidays have started for primary and secondary schools as well as junior colleges. With school out, the fun should begin - but does it really?
While many look forward to a respite from the daily grind of school , the burden of holiday homework hangs over them.
For many parents and tutors, the mid-year break is also the perfect time for an extra academic boost. Let’s not forget June holiday boot camps and intensive revision programmes arranged by teachers and enterprising tuition centres for Primary 6 students taking their Primary School Leaving Examination (PSLE) this year.
The term “holiday homework” itself is contradictory, prompting the question: Should school breaks be a protected sanctuary from homework, or is the expectation of holiday assignments an unavoidable reality?
A BAN ON HOMEWORK?
The debate surrounding holiday homework extends beyond the borders of Singapore.
In the Philippines, legislative attempts to enforce a weekend homework ban have been ongoing since 2016. In 2021, the Chinese government enacted the Double Reduction Policy , which includes a limit on homework and a ban on private tutoring classes.
Meanwhile, in Poland, a ban on graded homework for students in lower primary took effect in April. Homework for children in upper primary levels is optional and does not count towards a grade.
These efforts share a common goal: To alleviate the burden of excessive homework and promote greater student well-being. However, the effectiveness of these measures remains questionable.
In China, the mandate has driven the industry underground and led to exorbitant rates , exacerbating educational inequity. The Chinese experience suggests the potential pitfalls of using a simplistic solution like a hard legislative ban to address a complex social issue.
Drawing lessons from these global examples, I wonder: Should the focus shift from eliminating homework to understanding why parents and schools perceive it as necessary?

Commentary: A China-like tuition ban may not work, but Singapore can still find ways to address overreliance

China launches campaign to halt school bullying, excessive homework
Is homework beneficial.
While the debate on homework rages on, educational research has acknowledged the many potential benefits it serves.
Homework helps to reinforce academic concepts at home, develops time management skills, and encourages independent learning in children.
Learning at home can offer a more adaptable environment that caters to individual student’s learning pace and needs, particularly benefiting those who thrive with additional support. Moreover, homework functions as a crucial link between school and home, allowing parents to stay informed of their children’s academic progress.
At the same time, however, an Institute of Policy Studies (IPS) survey published in 2017 showed that 66.7 per cent of parents with primary school children agreed or strongly agreed that they were stressed over assisting with homework and ferrying them to and from school, and tuition or enrichment classes.
Additionally, nearly 94 per cent of parents in the study expressed a need for the primary school curriculum to be more manageable, reflecting the struggle many parents face in grasping the modern curriculum while balancing work demands in typical dual-income Singaporean households.
In my doctoral study on Singaporean parents’ tensions within education reform, one parent candidly remarked on this struggle: “I don’t think I can impart the (knowledge) skills to them. And I don’t want my children to lose out."
Consequently, many parents delegate homework guidance to educational experts - tuition teachers.
Families spent an estimated S$1.4 billion (US$1 billion) on tuition in 2018, based on data from the last Household Expenditure Survey in 2017 and 2018, up from S$1.1 billion in 2012 and 2013.
These insights highlight parents’ challenges in supporting their children’s learning at home due to a lack of knowledge, skills, time, and energy. Consequently, schools must consider these factors when designing and assigning homework.
Daily Cuts:

Commentary: Parents, getting your preschoolers to cram for P1 can backfire

Commentary: Parents play an outsized role in academic stress children face
Perceived benefits of after-school learning.
Research consistently emphasises the importance of play in nurturing the holistic development of children. What then motivates parents to enrol their children in tuition classes during school holidays?
Many parents I’ve spoken say they feel like they have “no choice” as they mitigate the pressures of a high-stakes education system.
They question how much play alone can contribute to children’s social-emotional well-being if they fail to perform academically. One parent stated, “I don’t need (my child) to be at the top, but I don’t want him to be at the bottom either”.
Parental guilt also motivates many to enrol their children in out-of-school classes. As one parent explained: “If my kids are idle or roaming around at home, I will feel bad as a parent … because it feels like my child is wasting his life away”.
Teachers participating in my doctoral study also reluctantly acknowledge the value of tuition classes for “weaker students”. Unfortunately, in a class size of 40, teachers lack the time and staffing to cater to each child’s learning needs while covering the school curriculum.
They also cited pressure from school leaders and managing familial expectations to assign homework as an indicator of a “good teacher”.

FIND HARMONY, NOT BALANCE
Amid the ongoing discussion on finding the right balance between work and play for students, the term “balance” implies a rigid 50-50 split between “work versus play”, overlooking the unique needs and strengths of each child, family, and school.
Rather than fixating on achieving a static “balance”, might it be better to consider striving for a harmonious blend between work and play? This approach encourages families and schools to identify the optimal mix that suits their specific contexts, fostering an environment where children can thrive in both learning and well-being.
The ideal combination of work and play will naturally vary in each family, classroom, and school, based on their diverse values, cultures, and aspirations. Nonetheless, this optimal mix should be viewed as fluid and dynamic, constantly adapting to suit the evolving needs of children.
Student agency is an essential ingredient in this optimal blend. Schools should actively seek student input on their homework experiences and understand their preferences for how it is assigned and evaluated.
This not only empowers students but also ensures that homework policies are responsive to their needs and interests.
Schools could consider moving away from compulsory holiday homework towards recommended assignments. Allow parents to determine and decide the homework load that best suits their child based on their family values and aspirations.
Many teachers are already offering non-mandatory assignments in the Student Learning Space online portal during mid-year and end-of-year school holidays. However, it is crucial to complement these assignments with online explanatory videos that provide solutions.
This approach is essential to support struggling students and enhance their self-efficacy by ensuring they understand how to approach and solve the questions independently at home.
Ideally, homework tasks should prioritise inquiry-based learning, embracing a play-based approach that fosters engagement and creativity.
Given the absence of time constraints in the classroom, these tasks can encourage students to explore core learning concepts with scaffolding prompts, developing learner autonomy, and stimulating greater engagement and creativity.

Commentary: Voices of tensions behind the 'kiasu parent' label

Commentary: PSLE stress – a question of not too much, not too little
Through collaborative efforts, schools and families can create a supportive environment that fosters student success and well-being.
In an ideal scenario, if schools and families can embrace a unified approach to revamping homework practices and reimagining the objectives of holiday assignments , we may just be able to find that sweet spot between work and play during the June holidays.
Dr Eugenia Koh-Chua is a sessional lecturer and educational researcher at Swinburne University of Technology (Melbourne). She is a mother of two and a former lecturer in Singapore.
Related Topics
Also worth reading, this browser is no longer supported.
We know it's a hassle to switch browsers but we want your experience with CNA to be fast, secure and the best it can possibly be.
To continue, upgrade to a supported browser or, for the finest experience, download the mobile app.
Upgraded but still having issues? Contact us

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Homework allows for more time to complete the learning process. School hours are not always enough time for students to really understand core concepts, and homework can counter the effects of time shortages, benefiting students in the long run, even if they can't see it in the moment. 6. Homework Reduces Screen Time.
Too much, however, is harmful. And homework has a greater positive effect on students in secondary school (grades 7-12) than those in elementary. "Every child should be doing homework, but the ...
Pope said the research calls into question the value of assigning large amounts of homework in high-performing schools. Homework should not be simply assigned as a routine practice, she said. "Rather, any homework assigned should have a purpose and benefit, and it should be designed to cultivate learning and development," wrote Pope.
Homework does not help younger students, and may not help high school students. We've known for a while that homework does not help elementary students. A 2006 study found that "homework had no association with achievement gains" when measured by standardized tests results or grades. [ 7]
The National PTA and the National Education Association support the " 10-minute homework guideline "—a nightly 10 minutes of homework per grade level. But many teachers and parents are quick to point out that what matters is the quality of the homework assigned and how well it meets students' needs, not the amount of time spent on it.
For high schoolers, Cooper's research suggests that two hours per night is optimal. If teens have more than two hours of homework a night, their academic success flatlines. But less is not better. The average high school student doing homework outperformed 69 percent of the students in a class with no homework.
The necessity of homework has been a subject of debate since at least as far back as the 1890s, according to Joyce L. Epstein, co-director of the Center on School, Family, and Community Partnerships at Johns Hopkins University. "It's always been the case that parents, kids—and sometimes teachers, too—wonder if this is just busy work ...
A defense of rote practice through homework might seem revanchist at this moment, but if we truly believe that schools should teach children lessons that fall outside the meritocracy, I can't ...
Too much homework may diminish its effectiveness. While research on the optimum amount of time students should spend on homework is limited, there are indications that for high school students, 1½ to 2½ hours per night is optimum. Middle school students appear to benefit from smaller amounts (less than 1 hour per night).
Research finds that homework provides some academic benefit for middle and high school students but is less beneficial for elementary school students. Research suggests that homework should be none or minimal for elementary students, less than one hour per night for middle school students, and less than 1.5 to 2.5 hours for high school students.
As many children, not to mention their parents and teachers, are drained by their daily workload, some schools and districts are rethinking how homework should work—and some teachers are doing ...
He does an average of five or six hours of homework every weeknight, and that's on top of spending most of the weekend writing essays or studying for tests. His school says that each of his five ...
In that poll teens reported spending, on average, more than three hours on homework each school night, with 11th graders spending more time on homework than any other grade level. By contrast ...
What is the "Right" Amount of Homework? Research suggests that homework should not exceed 1.5 to 2.5 hours per night for high school students and no more than 1 hour per night for middle ...
Some schools and districts have adapted time limits rather than nix homework completely, with the 10-minute per grade rule being the standard — 10 minutes a night for first-graders, 30 minutes for third-graders, and so on. (This remedy, however, is often met with mixed results since not all students work at the same pace.)
The homework wars are back. by Jacob Sweet. Feb 23, 2023, 3:04 AM PST. Jiayue Li for Vox. As the Covid-19 pandemic began and students logged into their remote classrooms, all work, in effect ...
In the 2002-2003 school year, a study out of the University of Michigan found that American students ages six through 17 spent three hours and 38 minutes per week doing homework. A range of ...
According to Brian Gill, a senior social scientist at the Rand Corporation, there is no evidence that kids are doing more homework than they did before. "If you look at high school kids in the late '90s, they're not doing substantially more homework than kids did in the '80s, '70s, '60s or the '40s," he says.
High schoolers reported doing an average of 2.7 hours of homework per weeknight, according to a study by the Washington Post from 2018 to 2020 of over 50,000 individuals. A survey of approximately 200 Bellaire High School students revealed that some students spend over three times this number. The demographics of this survey included 34 ...
Homework encourages parents and children to spend time together problem-solving and working toward a goal. It also gives parents a window into what their child is learning and the progress they are making. It encourages time management - "Homework is an effective tool when teaching your child about time management.
There are guidelines for how much time kids should spend on homework. The NEA recommends something called the "10-minute rule." Based on this rule, students should spend about 10 minutes per grade level on homework every night. That means a second grader will usually be able to finish in about 20 minutes.
A big report for the Department for Education, external, published in 2014, concluded that students in Year 9 who spent between two and three hours on homework on an average week night were almost ...
Professor Rudine Sims Bishop popularized the concept of Mirrors and Windows promoting a multicultural curriculum which "mirrors" the daily experiences of students and "windows" into the ...
At the same time, however, an Institute of Policy Studies (IPS) survey published in 2017 showed that 66.7 per cent of parents with primary school children agreed or strongly agreed that they were ...