- Plan Your Studies
- Study Programs
- Universities
- Requirements
- Living in Germany
- Accommodation
- Statistics & News


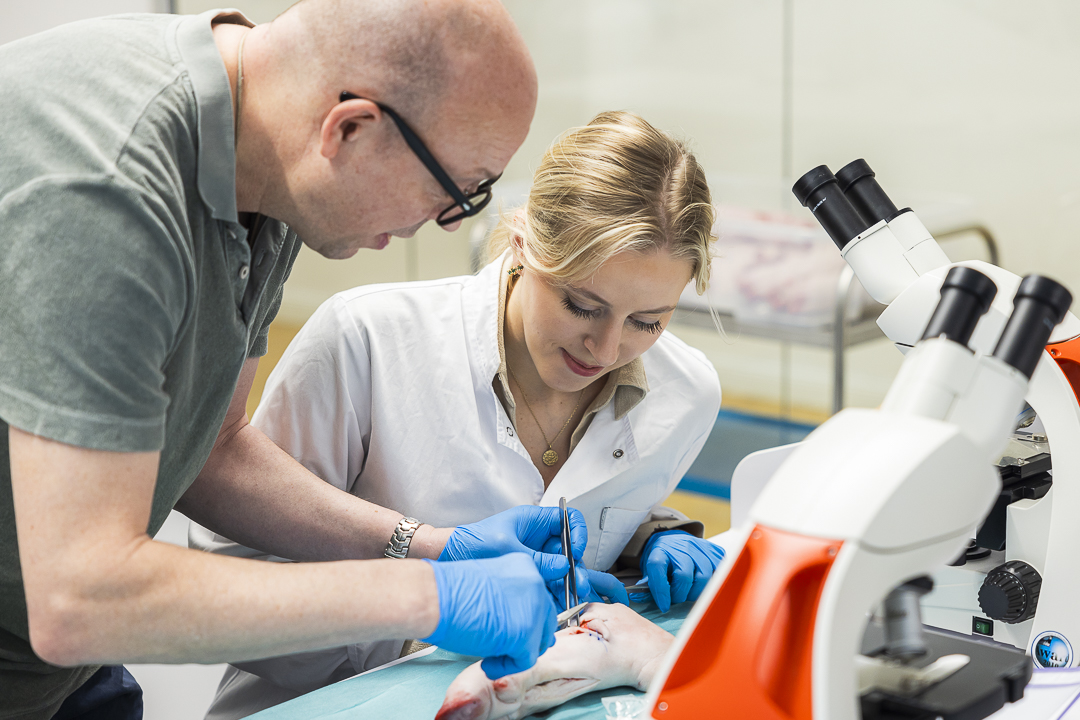
Study Medicine in Germany
Many international students are currently studying medicine in Germany, and you can join them!
However, you probably have many questions about how to apply, the costs involved, and what your future could look like. This guide has all the information you need to know on how to pursue a medical degree in Germany.
Why Should I Study Medicine in Germany?
When it comes to studying medicine, you have a world of options. So, why should you consider Germany? Well, it all depends on your goals.
- High-Quality Education. If you’re a motivated student looking for a unique and challenging education system, Germany is your ideal choice. German medical schools are renowned for their commitment to quality teaching, consistently ranking among the best.
- Global Recognition. Are you seeking a globally recognized medical degree that can give you a competitive edge in the job market? Germany’s degrees are highly regarded worldwide, opening doors to opportunities worldwide.
- Financial Stability. Dreaming of a financially stable career that’s emotionally fulfilling as you help others? Medicine offers just that, and a degree from Germany can pave the way. For example, the average gross salary for physicians and surgeons is €235,844 per year, which is equivalent to an hourly rate of €113. They also receive an average bonus of €22,122, according to Salary Expert.
- Top-Ranked Universities. Germany has a long academic tradition, and its medical schools are a big part of it. They offer a variety of medical programs to suit different preferences. In fact, Germany has 49 universities listed in the latest QS World University Rankings for 2024.
- State-of-the-Art Facilities. Medical practice is important, and German schools provide modern, well-equipped laboratories that give you the practical skills needed to succeed in the medical field.
- Diverse Student Community. With over 350,000 international students , Germany is full of different cultures. You’ll have the chance to interact with people from around the world during your studies.
- Promising Future. Medical professionals are always in demand, and a German medical degree holds significant value in the job market.
How Many Years Does it Take to Study Medicine in Germany?
It takes about six years and three months of full-time study to complete a medical degree in Germany. The program is divided into different stages, each with its own exams.
- Pre-Clinical Stage (Vorklinik): In the first two years, you’ll learn the basics of medicine, including subjects like anatomy, biochemistry, and physiology. At the end of this stage, you’ll take an exam, both written and oral, to assess your progress.
- Clinical Science Stage: For the next three years, you’ll expand your medical knowledge and gain practical skills through lectures, labs, seminars, and internships. At the end of this stage, you’ll have a written exam to test your understanding.
- Final Clinical Year: This is your last year as a medical student. You’ll face the final State Examination, which is crucial for your medical career. Passing this exam is a must to get your medical license. It’s an oral and practical test assessing your medical knowledge.
How Much Does It Cost to Study Medicine in Germany?
Most university degrees became tuition-free for international students in 2014 in Germany, but studying medicine is an exception.
The cost of a medical degree depends on your nationality and whether you attend a public or private university. EU students pay minimal administration fees, usually up to €300. Non-EU students, however, have to pay for their medical education, but the fees are relatively low compared to other countries. Tuition fees typically range from €1,500 to €3,500 per year.

Study at Berlin School of Business and Innovation
Creating Tomorrow's Industry Leaders
Private universities charge higher international tuition fees than public ones. Also, some medical schools in the state of Baden-Württemberg have reintroduced tuition fees for international students, making it more expensive to study there compared to other parts of Germany.
What Are the Admission Requirements for Studying in Germany?
Once you’ve found the medical program and university you like in Germany, you need to find out the entry requirements.
These requirements can vary from one university to another.
Here’s a list of documents and qualifications you’ll generally need to apply for a medical degree in Germany as an international student:
- Recognized Academic Qualifications: Your previous academic qualifications must meet the standards set by German medical schools. You can check with your university, the German Academic Exchange Service (DAAD), or the Standing Conference of Ministers to see if your qualifications are accepted. If not, you may need to take a one-year preparatory course.
- Certified Grade Certificates: Good grades are a must for getting into competitive German medical schools. Higher grades in subjects related to medicine, such as biology and chemistry, improve your chances.
- German Language Proficiency: Most medical programs in Germany are taught in German, so you’ll need to prove your German language skills. The required level varies by university, but many ask for a C1 certificate. If you need to attend a preparatory course (Studiencolleg) first, a B1 German certificate may be accepted.
- Exam Scores: Some medical schools require you to take specific examination tests to assess your suitability for the program you’re applying to.
Best Medical Universities in Germany
German medical universities are highly regarded , ranking among the top 50 in global university rankings for Medicine. These schools have competitive admission standards, and while international students can apply, there are limited programs taught in English.
Here are some of the best medical universities in Germany and their tuition fees:
*General university semester fees.
What About Job Prospects and Salary?
Becoming a doctor is a well-paying career worldwide. If you earn a medical degree in Germany, you’ll have excellent job prospects and a high income.
Germany is in need of more doctors due to its rapidly aging population. Despite an increase in the total number of doctors, there is still a shortage. This need becomes even more pressing, with around 20% of doctors expected to retire soon.
Here are some job roles in medicine and their average salary:
*Source: Salary Expert
Join 262,114 students interested in studying in Germany

Download The Guide

Quick Links
8 Steps to Study in Germany How To Apply To Study in Germany German Education System Requirements Universities in Germany International Programmes Financing Your Studies German Student Visa German Health Insurance Germany Blocked Account Learn German Guide German Cities Cost of Living
Latest News and Statistics
Bachelor students in germany more likely to drop out within first academic year, higher education in germany: key trends & statistics, new study reveals high level of satisfaction among students at german universities, germany scholarships up by 3% in 2023 – 31,400 students benefited, indians overcome chinese as top source of international students in germany.
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Policy
Search suggestions:
- Scholarship
Follow us on
Get to know the higher education system
Medical Studies and Specialist Training
Do you want to become a doctor? You are not alone with this dream. Medicine studies are in high demand at German universities. Here you will find out what the requirements are, how you can apply, and what you can do after completing the state examination.
Short & Sweet
If you want to become a physician in Germany, you need good grades and plenty of discipline.
The medical degree takes a little over six years and ends with the state examination.
You can then receive further training to become a specialist.
Medicine: One subject, many options
The numerus clausus (nc).
Doctors have an exciting and wide-ranging profession. You can choose from more than 30 specialist areas in Germany, from ophthalmology to forensic medicine. That is one reason why many who are just starting their studies find a future as a doctor particularly attractive. As a result, it can be difficult to get one of the coveted study places in medicine at German higher education institutions.
Selection procedure
A numerus clausus applies nationwide. This key admission restriction is based on your high school grades. At some universities, an additional test for medical courses (TMS, also known as the “medical test”) is required. This is a subject-specific study aptitude test that rates understanding of scientific and medical problems. It is held annually.
Compared to other courses, the demands in medicine are particularly high. Medical studies are very study-intensive and include many exams.
Useful overview
The Medizinische Fakultätentag or MFT, and the Association of University Hospitals in Germany maintain a database of teaching, research and patient care in university medicine and update it regularly.
The steps leading to your profession
Medical programmes last at least six years and three months. In contrast to medical-related courses, such as the health and nursing sciences, it is not divided into a bachelor’s and master’s degree. The course is completed with a state examination. The structure of the course is regulated uniformly throughout Germany via the Medical Licensing Regulations (ÄAppO). The course differs from training in other countries in a number of ways.
After the basic course of four semesters and the first of a three-part “medical examination”, a main course of six semesters follows. It brings you closer to professional practice. Students then spend a practical year in a clinic or hospital. You work in surgery, internal medicine and another ward of your choice. Your studies are then completed after the state examination.
Here are links for jobs as assistant doctors
Advanced training to become a specialist.
When you have passed the oral part of your exam, your medical degree is complete. You can apply for your credentials to work as a physician, called an Approbation, shortly before the oral examination. If you decide to train to become a specialist, you have to plan for another five to six years. The additional training takes place in university clinics or other certified facilities.
- Choosing your subject
- Main occupation
- Requirements for specialist training
Approbation: Credentials to work as a physician
Working in germany.
Foreign physicians
Important: Holding up under stress
Good knowledge of German is absolutely necessary for studying medicine at a German university. The medical literature is often in English, but the lectures and exams are mostly not. Scientific skills also play a major role, especially in the first semesters. The so-called Physikum, the examination at the end of the basic course, comprises basic subjects such as physics, chemistry, biology, physiology and anatomy. Anyone who wants to succeed in studying medicine needs to be empathetic, tenacious and able to work under stress. All qualities that are also important later in your career.
Medical specialists: Careers beyond caring for the ill
Some 10,000 medical degrees are awarded at universities in Germany every year. And finding a job in a hospital or settling down is not difficult outside of the big cities. Family doctors are urgently needed, especially in rural regions. Health care is making great advances, so people in Germany are living longer. This means they also have to be treated more frequently and at greater expense. As a result, job prospects are also excellent for the future. But there are also interesting jobs outside of traditional medical practices and hospitals. Medical expertise is valuable for careers in medical technology, the pharmaceutical industry, and hospital administration. Management consultancies and insurance companies are also options for people completing a medical degree.
Alternative: Studies in health sciences
The health care system requires more than doctors. The well-being of an entire population is at the centre of the field of public health. Public health examines the interaction between people and their environment, develops strategies for coping with health problems and deals with the economics of health care.
In these courses you are prepared for a variety of careers in the health care industry. Well-trained public health scientists are in demand to promote corporate or municipal health as well as in the pharmaceutical industry, international organizations and consumer protection. Public health departments at schools issue both bachelors and masters degrees in health management, health economics and health education. Some of the courses require prior vocational training, often completed while working part time. These programmes are aimed at people who are already working in therapeutical, care giving or social science professions. The course imparts medical, health and social science knowledge, but also subject-related aspects of psychology and economics.
Many reach their dream job as a doctor once they meet the requirements and master the demanding course of study.
With a degree in medicine or a related degree, there are also various exciting fields of activity in health care.
Find now the right course of study in this area
Find out more.
Read about the different types of higher education institutions and degrees
Higher Education Compass
In this database you will find more than 20,000 degree programmes
Engineering
- Value Package
- Blocked Account
- Health Insurance
- Bank Account
- Study Finder
- Study Eligibility Checker
- Accommodation
- Learn German
What We Offer
- Living in Germany
- Studying in Germany
- Working in Germany
About Germany
- German Cities
- Tourism in Germany
- German Culture
- Visa for Germany
- Costs of Living in Germany
- Finance in Germany
- Health Insurance in Germany
- Driving in Germany
- Renting in Germany
- German Universities
- Free Studies in Germany
- German Education System
- Germany vs. other Study Destination
- German Degrees
- Application Process to Study in Germany
- Financing your Studies in Germany
- Best Universities in Germany
- German Business Culture
- Best Cities in Germany for Expats
- After your Bachelor's in Germany
- After your Master's in Germany
About Expatrio
- Partner log in
- Partner Log-in
MBBS in Germany [Complete guide]

If you want to obtain a "Bachelor of Medicine, Bachelor of Surgery" (MBBS) qualification, studying abroad is often the best route to choose. Germany and its highly advanced medical care are among the best places to earn a medical qualification that opens doors all across the world.
But how can international students apply for an MBBS, what does the application entail (eligibility criteria, admission process, tuition fee, visa process), and how long does the qualification take? This article will explain everything students who want to pursue MBBS need to know about Germany's elite medical certificate.
German MBBS
Germany's MBBS is the country's primary medical qualification
But it's not just prized within German borders. This course in Germany has a solid international reputation , making it highly desirable anywhere in the world.
The degree is stretching across 6 years in most cases, and the MBBS includes both theoretical medical education and hands-on clinical experience , providing one of the best foundations for a medical career medical students could hope for.
A course tends to be of excellent value , without sacrificing teaching quality or the standard of facilities. And both domestic and international students pursuing MBBS receive the same access to German hospitals and clinics , ensuring that they will leave university with the credentials and experience required to launch a successful medical career after their medical studies.
Advantages of studying MBBS in Germany
Studying this course in Germany is a truly rewarding investment in time and personal career. It is one of the most remarkable options with quality and affordable medical education. It is best to study medicine in Germany if you do not want to compromise on your medical training.
- Medical Universities in Germany are among the best in the world and are therefore very competitive.
- The biggest advantage of studying medicine in Germany for Indian students is that most of the universities for MBBS in Germany are recognized by the major medical commissions of the world like MCI - Medical Council of India (National Medical Council) or WHO - World Health Organization.
- The quality of education in Germany is generally very high and thus attracts international students from all over the world.
- The best medical schools in Germany organize seminars that help students to get a job abroad.
- Climatic conditions in Germany are very good and it is easy to adjust to them.
- The lifestyle in Germany is just as easy to adapt to.
- The cost of living in Germany is quite low compared to other countries in the EU or the United States.
- MBBS studies in Germany are completely free with a scholarship.
- The universities for medicine in Germany also have very good hospitals for the practical phase of the studies.
Studying this course in Germany is particularly interesting for Indian students because the fees are quite low compared to India (there are no tuition fees at all and the cost of living in Germany is really manageable) and the quality of the programs is top-notch.
Check Rankings to find the ideal place
Not all German universities are among the world's medical elite. So check rankings among German medical schools to ensure that you apply to the right school and receive a quality education. Top MCI-approved medical universities in Germany 1. Humboldt University 2. Heidelberg University 3. LMU Munich
Duration and Stages
Studying medicine is never a quick process, no matter where you get medical training, and that's no different in Germany
To study, students will need to complete separate sections for academic and applied medicine , and study for final examinations that require an extra year of hard work. So studying MBBS is an investment in time that should only be undertaken by serious applicants .
How many years does it take to get an MBBS in Germany?
Schedules can vary in some cases - depending on the individual medical university - but most medical courses for a MBBS in Germany will go something like this:
Pre-Clinical Training
The first stage will last two years (four semesters). Described as "pre-clinical" or “preparatory course”, this section of the course is primarily academic , and introduces medical and general scientific concepts that students need to know about. It concludes with the Ärztliche Prüfung - an examination which allows students to enter medicine courses and medical practice at a trainee level .
Clinical Training
Secondly, students will undertake 3 years (6 semesters) of clinical training during their MBBS course duration. Generally, this medical training covers a hospital placement in a nearby institution . Students will work closely with doctors and nurses, and participate in medical operations. This concludes with a practical examination of your clinical skills .
Practical Assessment
The final stage of the Germany MBBS lasts for one year, and consists of supervised practical training at government hospitals. Students gain more responsibility and are closely assessed for their abilities and temperament.
Final Examination
Finally, completing MBBS requires students to take the MBBS State Examination and Approbation of the federal republic (which approves your license to practice medicine).
Duration of MBBS at medical colleges
Overall, a student who starts to study medicine in Germany in 2019 can expect to conclude their MBBS abroad by 2025. However, retakes during a Germany MBBS are common, and sabbaticals can also lengthen the study period.
How to apply for an MBBS at German medical universities
MBBS admission: The application process for medicine in Germany varies between medical universities
So, contact the International Offices of possible universities for their specific requirements . Most are part of a system called Uni-Assist, which helps non-EU applicants find suitable courses.
Uni-Assist will provide information about how to apply at a medical college, including the provision of digital application forms, which educational credentials are needed, and what letters of recommendation and motivation to obtain.
Remember that the deadline for applications to these universities in Germany is July 15th (for fall/winter entry) and January 15th (for summer entry).
Remember the different deadlines for summer and winter!
Two semesters.
Structure of an academic year in Germany.
Winter Semester
October - March Application Deadline: July 15th
Summer
You'll need: passport, biometric photo, certificate of enrollment, proof of: finances, health insurance, and residence; plus the visa application filled out.
Will examinations be part of the application process for an MBBS?
There will usually be an entrance exam at medical colleges. Medical schools tend to be among the strictest in Germany when it comes to choosing candidates. Their examinations will filter out academically weak applicants, and assess what kind of preparatory study is needed to study medicine before others can take their course places.
If you are successful, you may be asked to complete a year-long Studienkolleg course, and extra German language instruction for German language proficiency may also be required for international students before starting at a Germany medical college.
Is NEET required for an MBBS in Germany?
Those applying from India may well wonder whether NEET supplies the credentials required to access a German MBBS as an Indian student. The answer is that, yes, it definitely helps.
Holders of NEET certificates will have proved that they have basic medical knowledge and enthusiasm to study at a medical university. However, NEET to study MBBS isn't mandatory for Indian students and foreign students in general. And it isn't sufficient if candidates lack language skills and other academic qualifications.
What if I have a foreign medical degree?
If you already have international medical education and a foreign medical qualification, you won't need to study a full MBBS in Germany . But you can't begin practising medicine in Germany straight away. Instead, you will need to apply for a document called a Berufserlaubnis, which is essentially a medical permit from the National Medical Commission.
The authorities may issue one without requiring any further action. However, they may require foreign medical graduates who didn't study MBBS in Germany to take examinations to prove the required level of competence .
Is MBBS in Germany free?
Free medical education: If you are interested in pursuing MBBS in Germany, you have chosen the right location! Germany has a very cost-effective medical education - they offer free education without any tuition fees, unless you study at private universities.
Salary and career prospects after MBBS in Germany
An MBBS degree is one of the most sought-after degrees because doctors are among the highest paid professionals in the world, and Germany is no different. Studying MBBS in Germany guarantees both high employability and a high salary. Since the medical degree in Germany has an excellent reputation worldwide, employers will be happy to hire you regardless of your location.
As in any other industry, a medical professional's salary depends on his or her position and experience, but the demand for medical professionals is constantly increasing. In Germany, the average salary of a medical doctor is around €80,000 per year.
Apart from the financial benefits, an MBBS degree in Germany provides easy access to other EU countries where you can practice medicine without restrictions . Since Germany is part of the European Union, there are almost no restrictions on free movement within the EU, which includes countries like France, Italy, Spain, the Netherlands, Ireland and others.
Plan ahead!
Completing all of the paperwork for medical programs can be a time-consuming task, so plan ahead and tick off each document as you complete or send it.
Germany medical universities: Required Documents
When you apply for an MBBS in Germany, your university will require a range of important documents.
When you apply for an MBBS in Germany, medical universities will require a range of important documents.
Here is a quick break down of the documents most MBBS colleges will request:
- Educational credentials - Students must have a German high school level leaving certificate or the equivalent in their country.
- Qualifications in relevant subjects - Students must have high school level qualifications in biology, physics, and chemistry.
- English skills are highly desirable, and a working knowledge of Latin can help as well.
- German language certificates - If you study MBBS in Germany, courses are taught in German.
- A certificate at TestDaf Level 4 or better is usually required.
- Letter of Motivation - This letter is written by the candidates, and explains clearly why they wish to study medicine, and what makes them a suitable student for the best medical colleges.
- Letter(s) of Recommendation - One or more letters from relevant individuals who know the candidate and can comment on their abilities and enthusiasm to study MBBS.
- Student visa - All students need a valid student visa from the German embassy. This will require purchasing health insurance and (usually) opening a blocked account to store a year's worth of living funds. This way you can get a permanent residence certificate while pursuing MBBS studies.
Expatrio Value Package
Simplify your move to Germany with Expatrio's Value Package! Get your mandatory Health Insurance, Blocked Account, free German Bank Account, plus other free benefits!
Language Requirements
Finally, it's worth stressing the languages element once again, as it's absolutely central to succeeding in medicine at top German medical universities.
Medicine is a profession where precise language and communication skills make a huge difference .
In Germany, doctors need to understand English and speak excellent German , and there's really no way around this. Students are therefore required to have valid German language qualifications before admission.
Alongside TestDaf , many medical universities accept qualifications from Großes Deutsches Sprachdiplom (GDS), Deutsche Sprachprüfung für den Hochschulzugang (DSH), or the Kleines Deutsches Sprachdiplom (KDS) from the Goethe Institut.
This really is the only way to receive an admission letter from Germany medical universities and study MBBS in Germany.
We're building the best solution for internationals coming to Germany.
Public vs. Private Universities in Germany: A Comparison
Renting In Germany [House Rules]
Master's Degree in Germany [Guide]
This might also be of interest to you.

Pre-Studies & Studienkolleg in Germany
Germans are huge believers in preparation, and that's especially the case in the higher education sector. German universities welcome international...

PhD in Germany [Complete Guide]
Few achievements in life match the feeling of being awarded a PhD. Doctorates represent the pinnacle of academic achievement, and require years of...

German Language Course Degrees [Guide]
Learning German is an essential step for almost everyone who makes their home in the country, and it can also be one of the most enjoyable...

Germans value skills above almost everything else, and the nation's universities offer a vast range of subjects, in M.A., M.Sc., and M.Eng. formats.
![medical education in germany MBBS in Germany [Complete guide]](https://8668267.fs1.hubspotusercontent-na1.net/hub/8668267/hubfs/Expatrio%20Hatch%20Child%20-%20Theme/Blog%20Graphics/Studying%20in%20Germany/mbbs%20in%20germany.webp?width=374&name=mbbs%20in%20germany.webp)
If you want to obtain a "Bachelor of Medicine, Bachelor of Surgery" (MBBS) qualification, studying abroad is often the best route to choose. Germany...

Best English-taught Master Programs in Germany
Germany is renowned for its high-quality education, and many of its universities rank among the best in the world. Additionally, studying in Germany...
Germany or UK to Study: Which is Best for Students?
Studying in Germany vs. New Zealand: 15 Comparisons
- Higher Education and Research
New possibilities for studying medicine
The conditions for admission to medical school are changing in Germany. International applicants have excellent chances.

How can you study medicine in Germany ?
Up to now, those with the best grades were accepted first. But in future, a wider range of applicants will be given a chance. Following a decision by the Standing Conference of the Länder Ministers of Education and Cultural Affairs , the allocation of university places for studying medicine is to be changed. The 'numerus clausus', which is oriented towards an applicant's grades in school-leaving examinations and regulates the limited admission of students, will continue to exist, and about 20 percent of the study places in human medicine will still go to the applicants with the best grades. But what is new is that greater weight will be attached in the universities' selection procedures to a person's CV, motivation and personal commitment. These criteria will also play a role in the Standard Assessment Test for Students of Medicine (TMS). More and more universities are offering the TMS test, which also makes access possible for study applicants without top grades.
Where can you study medicine in Germany?
There are 38 medical faculties spread all across Germany. Especially well known are major university clinics such as the Charité Universitätsmedizin Berlin and the University Hospital Heidelberg, which is a leader in the field of oncology in cooperation with the German Cancer Research Centre (DKFZ) . In addition to the public universities, five private higher education institutions currently offer medical studies in Germany. The structure of study programmes is uniformly regulated throughout Germany; they all end with the so-called state examination. Applications go via o the nationwide admission procedure of the Foundation for University Admissions ; this also applies to international candidates. Detailed information for international students who wish to study medicine is also available via the website of the German Academic Exchange Service study-in-germany.de .
How international is the study of medicine in Germany?
A good knowledge of German is important if you want to study medicine. Although the specialist literature can, of course, be obtained in English, lectures and examinations are held mostly in German. After all, budding doctors must be able to communicate with their patients. It's worth learning German anyway because the career prospects for international physicians are very good. The number of foreign doctors working in German hospitals has been increasing rapidly for years. And general practitioners are urgently sought after for practices in rural areas.
Guide: How to Become a Medical Doctor in Germany
Applying for a study place in Germany
© www.deutschland.de
Related content


WELCOME TO UMCH
Study Medicine in English within 6 years – in Hamburg, Germany
Study Medicine at UMCH
Germany's first international medical program! Discover a state-of-the-art medical education in an international environment. Get informed and apply now!

- What does UMCH stand for?
- The University
- Mission Statement
- Medical campus of the future
- Rector’s Welcoming Speech
- Organization & Structure
- Become a Teaching Hospital
- Bad Lippspringe
- Delmenhorst
- Eisenhüttenstadt
- Lüdenscheid
- Marl-Sinsen
- Elche-Alicante
- Hauck-Rohrbach Eye Centers
- University City Hamburg
- Accommodations
- Start of Studies
- Free Public Transport
- Student Clubs
- UMCH Cafeteria
- Counseling Program
- ERASMUS / ERASMUS+
- General Information
- Study Structure
- Accreditation and Recognition
- Online Application
- Information for Transfer Students
- Tuition Fees
- Medical Informatics
- UMCH E-Learning Platform (Canvas)
- ClinicalKey Student (Elsevier)
- News and Events
Medical Foundation Track (3 Weeks)
Medical Foundation Track (12 Weeks)
- Accommodation
- Connections and Accessibility
Your journey to starting your studies in 2024/25 begins now Apply even before receiving your high school diploma
Germany’s first private international medical campus, exclusive. personal. individual..
- 6-year medical degree program in English
- Practice-oriented lessons in small groups
- Large student community from over 40 nations
- Clinical Teaching in German Teaching Hospitals
- State-of-the-art and highly digital university campus
- Internationally recognized
- Qualification after graduation for USMLE, UK GMC
- Doctorate possible at UMCH
- Strong in research, interdisciplinary, practice-oriented
- Career Counseling and Coaching Sessions
- Networking and Gala Events

Start your dream studies without waiting and without numerus clausus. Don’t waste any time and apply for the winter semester 2024/25.
Apply early, study safely: Excellence and support combined Get to know us – online or in person on site

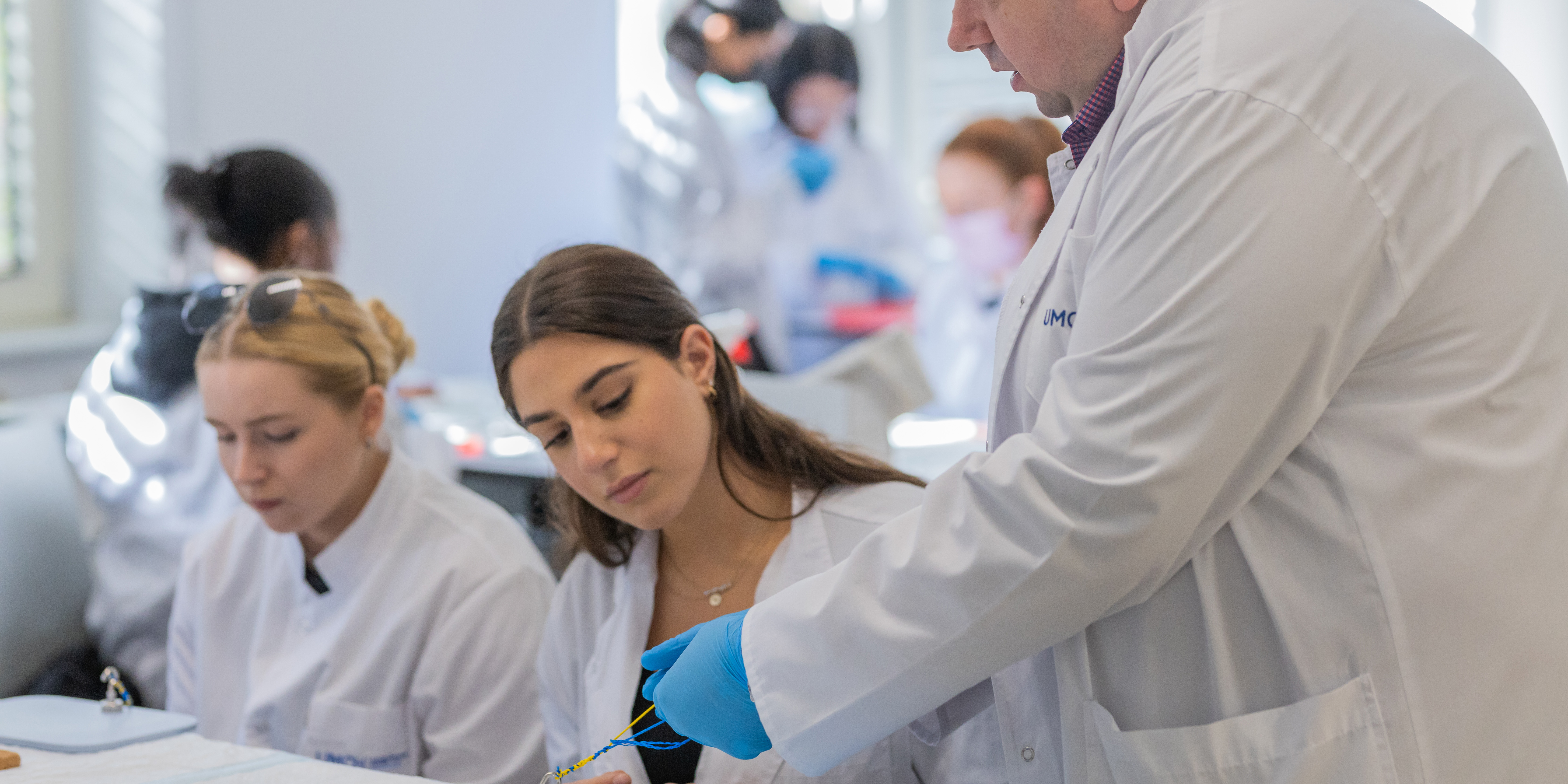
Insight into Orthopaedics: Dr. Michael Klein from Lüdenscheid Hospital Visits UMCH
Preparatory Courses
From 7/1/2024 to 7/19/2024
Duration: 3 weeks Location: Hamburg / Online
From 9/2/2024 to 9/18/2024
From 11/11/2024 to 1/31/2025
Duration: 12 weeks Location: Hamburg / Online
Most popular
- Tuition fees

UMCH Student Advisors
Your contact persons
Dates and Events
Visit info events, lectures, panel discussions and much more..

Individual consultation appointments in New Orleans
With pleasure, we would like to invite you to a personal consultation to introduce you to our comprehensive 6-year medical study program in English at UMCH. During this meeting, we will provide information on the following points: Comprehensive presentation of the NC-free degree program: Start your medical studies without waiting already in the winter semester of 2024. Information on admission requirements and study contents: Learn all about the requirements and course of the program. Valuable tips for admission tests and interviews: Receive guidance on how to shine in your admission test and interview. We would be delighted to meet you…
More information
[countdown date=”27 April 2020″ format=”dHMS” hour=”10″ minutes=”00″ link=”false”]

UPCOMING DATES AND EVENTS
With pleasure, we would like to invite you…
Online Info Event
We are delighted to extend an invitation to…
Meet & Greet with Prof. Dirk Naumann
We are delighted to warmly invite you to…
UMCH Campus
Start of the academic year 2024/25
At UMCH, the Academic Year 2024/25 commences on…
Dear applicants,
Small study groups, teaching in English, clinical training in Germany: this is what distinguishes the accredited medical studies of UMCH in Hamburg!
An intensively supervised and yet independent study. Highly motivated students and lecturers who share their experience and knowledge and work out solutions for better medicine. Excellent infrastructure that encourages scientific exchange.
This is what University Targu Mures Medical Campus Hamburg stands for.
And what do you stand for?

UMCH’s admission procedure
The online application platform for your studies is open to you at any time. As soon as you have uploaded all the necessary application documents there, you will receive an invitation to participate in our admission procedure, which consists of a brief evaluation and a motivation-based interview . Until further notice, you can follow the procedure comfortably and securely via video call from home . Please contact us after uploading your documents and receiving the invitation by UMCH so that we can arrange an individual appointment with you.
You will find all information about the application and the exact procedure of the admission procedure here .
Next admission dates:
Go through the admissions process online now
Inform here

Transfer to UMCH
Have you already started studying medicine at another university? At UMCH you can continue your studies from the 2nd academic year onwards.
UMCH – First English-Speaking Program in Medicine (MBBS/M.D.) in Germany
All special features summarized.

All UMCH news at a glance

At the end of April, students from UMCH gathered for a captivating event featuring Dr. Michael Klein, the renowned Clinical Director for Orthopaedics and Trauma Surgery, specialized Trauma Surgery, and...
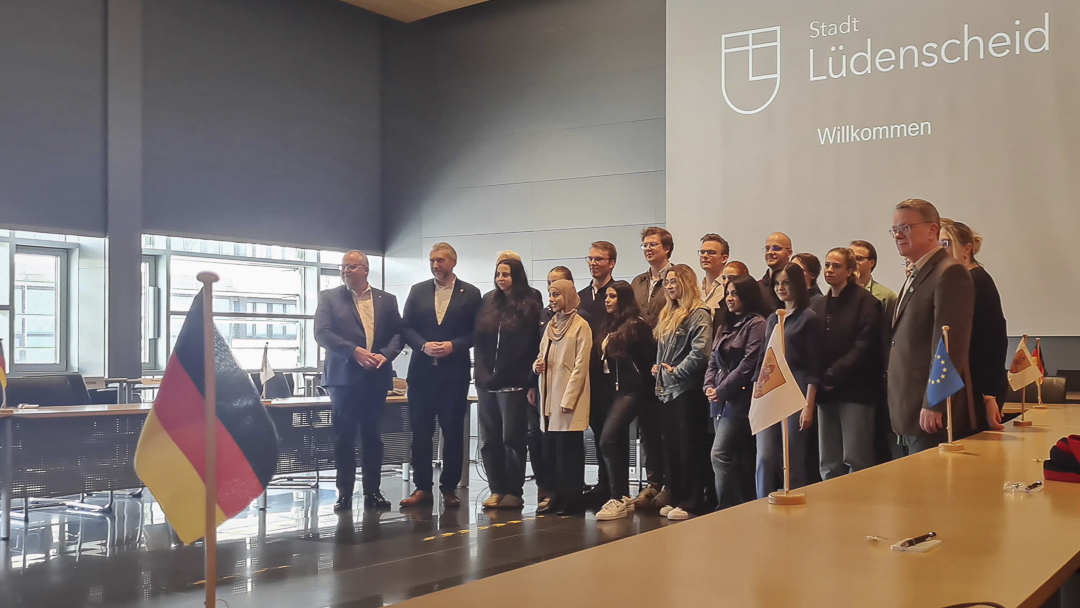

Mayor Sebastian Wagemeyer Extends Warm Welcome to UMCH Students in Lüdenscheid

Fascinating Insight: Lecture on "Plastic Surgery in the Interplay between Form and Function" at UMCH Campus

Prof. Meyer-Marcotty from Klinikum Lüdenscheid leads Hands-On Workshop on Surgical Techniques

Hospitals from all over Germany present themselves in Hamburg
Campus talks, explore the diversity of our students and their unique perspectives dive into the world of campus talks, where we delve into the cultural habits and meanings of our international students in germany. .
Meet Andie from Spain
Meet Vaibhavi from India
Meet Arushi from India
Meet Abdelrahman from Egypt
UMFST-UMCH research
Scientific activities.

Exciting impressions of the university
Teaching hospital: elisabeth-krankenhaus essen, student insight´s: practical phase at umch & teaching hospitals, teaching hospital: protestant hospital mettmann.

UMFST-UMCH Teaching Hospitals

Are you interested in cooperating with us?
You are already a teaching hospital, academic teaching practice or want to become one we look forward to hearing from you., what are the admission procedures in which countries is the medical license recognized, here you will find all the answers to the most frequently asked questions about studying medicine at umch..

Testimonials from our lecturers
Close guidance and supervision by a prestigious team of professors, research assistants and other experts.
“ Biochemistry is the chemistry of life, as chemical molecules produced in our body can interact and through biochemical processes, can generate the physiological status, feelings ... Assoc. Prof. Amelia Tero-Vescan, PhD Lecturer for BIOCHEMISTRY
“ Only due to the history of anatomy as a subject of science did we as human beings start to understand the functions of our different ... Assoc. Prof. Mircea-Gabriel Muresan, MD, PhD Lecturer for ANATOMY
“ Medical psychology represents a branch of psychology that deals with the application of psychological principles in medical practice. It is particularly concerned with the way in which biological ... Lecturer Cosmin Popa, PhD Lecturer for BEHAVIORAL SCIENCES
“ Medical Informatics is designed to provide future doctors with the tools they need to be successful in a constantly changing and evolving environment. With practical exercises in areas such as natural language ... Lecturer Marian Pop, MD, PhD Lecturer for INFORMATICS
“ I am very impressed with UMFST-UMCH. The interaction between the Hamburg campus and the teaching hospitals provides students with excellent preparation for their future work as medical ... Hon.-Prof. Dr. med. Christian Berg Chief Physician of the Center for Internal Medicine at Mettmann Protestant Hospital
Preparatory courses for your medical studies
UMCH offers different courses, which are subject to a fee and help you get ready for your medical studies.
Medical Foundation Track (3 Weeks):
Our Medical Foundation Track is a 3-week program. It includes the subjects of biology, chemistry and physics. Above all, it serves to consolidate and expand your preexisting knowledge while gaining new skills in these areas. Throughout the course you will acquire a significant amount of scientific information – a basic requirement for medical studies – within a short period of time.
Medical Foundation Track (12 Weeks):
Our 12-week Medical Foundation Track covers not only the natural sciences of biology, chemistry and physics, but also mathematics, biochemistry, anatomy and medical theory. Therefore, the extensive semester also includes topics that are usually not covered at school. As a result, a considerable advantage in knowledge is built up, which will make your starting medical studies immensely easier.
Next courses
Medical foundation track.
Contact us for information on upcoming courses.
Book an online consultation appointment including a virtual campus tour.

- Legal Notice
- Privacy Policy
Cookie Policy
Data protection overview.
7 Best Medical Colleges in Germany: Comprehensive Guide
Link Copied
Share on Facebook
Share on Twitter
Share on LinkedIn

Unleash Your Inner Healer!
Germany has been leading the way in Medical education, not only in Europe but also worldwide. The best thing about studying in Germany is the free tuition fees that most of its public universities offer. Apart from the quality of education, the cost of living in Germany is affordable compared to other countries in Europe. If you are planning to pursue medical education in Germany, then our comprehensive guide will help you understand the things you need to know. We will be covering the best medical schools in Germany.
Benefits of Studying Medicine in Germany
Germany is home to some of the best universities to study medicine. As per the U.S News & World Report , universities in Germany are ranked among the top for medical education. The structure of the various programs allows students to study in-depth which covers various aspects of the course. Germany ranks among the top 50 universities for medicine in Europe, with 12 of its universities included in this prestigious group. Let’s take a look at some more reasons to choose Germany for studying medicine.
1. Hands-on experience
One of the many reasons for choosing Germany to study medicine is because of the hands-on experience that one gets. The best part about it is that the hospitals in Germany do not ship off their patients to other states for treatment as other countries do.
2. Low Tuition Fee
Another good part of studying in Germany is the low tuition fees. The tuition fees in Germany, as compared to other countries, are quite low that attracts a large number of students every year.
3. Best Research Opportunities
German universities are known for their research programs and facilities that give students the chance to work on various technologies.
4. Better Internship Options
Students can apply for internships straight out of coming off college. As long as you have attended a German university, you can apply for an internship easily.
Best Medical Schools in Germany
Known for top-class medical programs in various fields like Medicine, Dentistry, and Pharmacy, medical colleges in Germany have only the best to offer. Students can take advantage of the practical approach of the medical colleges in Germany that prepares them for the future. As per the latest data over 458,210 international students enroll in some or the other German universities every year to study medicine. Medical colleges in Germany speak for themselves, with over 30 universities included in the latest QS World University Rankings.
1. Heidelberg University
Employability rank - 70 Number of students - 30000 Top programs - Dentistry, International Health, Medical Education Heidelberg University is considered one of the best medical colleges in Germany and is known for its practical approach to education and research. The university has partnerships with over 27 institutions and is connected for exchange arrangements with 480 universities. Eligibility criteria -
- To be admitted to this medical school in Germany, students must have a background in physics, chemistry, and biology and remarkable grades.
2. Technical University of Munich
Employability rank - 13/250 Number of students- 4000+ Top programs - Human Medicine, Molecular Medicine, Nursing Science
TUM School of Medicine and Health focuses on understanding the root cause of the disease through research and education. Known for training its students for a commitment to improving health and promoting evidence-based concepts to maintain mental and physical health. TUM School of Medicine and Health is considered one of the best medical colleges in Germany. Eligibility criteria -
- Students must have excellent grades in subjects like biology, chemistry, and physics.
- As per the German grade system, a grade of 1.5 should be achieved.
- The minimum TMS score required by TUM is around the 90th percentile or higher.
3. University of Hamburg
Employability rank - 112 Number of students- 44000 Top programs - General Medicine, Dentistry, Molecular and Cellular Biology Another one of the best medical colleges in Germany is the University of Hamburg. The university is known for its outstanding approach towards education. The university's main campus is located in the central district of Rotherbaum, with affiliated institutes and research centres distributed around the city-state. Eligibility criteria -
- Applicants must hold a Bachelor's degree and a Master's degree (or equivalent qualification) in a field relevant to the program, obtained from a recognized university.
- Depending on the program, you might need to demonstrate proficiency in German or English. This is usually through standardized tests like DSH (German) or TOEFL/IELTS (English).
4. Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München
Employability rank - 53 Number of students- 53000 Top programs - Medical Research and Doctoral Programs, Clinical and Translational Medicine, Dentistry LMU Munich is a public research university located in Munich, Bavaria, Germany. It is one of the oldest and best medical colleges in Germany. It is one of the leading universities in Europe and has been affiliated with 34 Nobel laureates throughout its history, including famous names like Wilhelm Röntgen, Max Planck, and Werner Heisenberg. Eligibility criteria -
- Secondary School Leaving Certificate (Abitur, Matura etc) or equivalent foreign qualification.
- a minimum overall grade average of 2.5 or better is required on the German grading scale of 1-6 (1 being the highest)
- Applicants must prove German proficiency at B2 level or higher through accepted tests and may need to demonstrate English abilities via TOEFL/IELTS for certain international programs.
Discover Your Future: Study at Germany's Premier Medical Colleges with Comfort and Convenience in Our Student Accommodations.
Book through amber today!
5. Westfälische-Wilhelms University Münster
Employability rank - 193 Number of students- 45000 Top programs - Medical Research, Public Health, General Medicine Another one of the best medical colleges in Germany is Westfälische-Wilhelms University Münster. WWU Münster has around 280 global university partners, which allows students, including medical students, to study abroad via programs like Erasmus+. The university's notable alumni include mathematician Gauss, philosopher Habermas, politicians, Nobel laureates, and other esteemed figures—some from its medical college. Eligibility criteria -
- Applicants' higher education qualifications are evaluated
- They must take the Münster Study Ability Test
- This test assesses basic medical and scientific understanding
- It includes short interaction scenarios, and these scenarios primarily gauge non-cognitive abilities
6. University of Bonn
Employability rank - 208 Number of students- 35619 Top programs - Neuroscience, Dentistry, Molecular Biomedicine Established in 1818, the institution previously known as the Rheinische Friedrich-Wilhelms-University Bonn is now recognized as the University of Bonn, an esteemed academic institution ranked 13th among the best medical universities in Germany. Eligibility criteria -
- Prospective students should adhere to the application deadlines, with the winter semester's application period spanning from June to July 15th, while the summer semester's deadline falls on January 15th
- Entry requirements mandating proficiency in the German language at the CEFR C1 level and a suitable higher education entrance qualification
7. Ruprecht-Karls-Universitätsklinikum Heidelberg
Employability rank - 87 Number of students- 30000 Top programs - Medical Informatics, Cancer Research, Pediatrics This prestigious public research university is home to academia, research, and international collaboration in the field of medicine. It's a fitting starting point to explore Germany's renowned medical colleges. It is one of the best medical colleges in Germany
Eligibility criteria -
- Students must provide proof of German language skills through recognized tests like the TestDaF or DSH.
- A relevant undergraduate degree from a recognized institution. Some programs may require a minimum GPA or specific prerequisite courses.
Admission Requirements for Medical Colleges in Germany
Once the applicant meets the eligibility criteria for studying MBBS in Germany, they can proceed to the next phase, which is the application process for admission to the prestigious medical colleges in the country. Prospective candidates are advised to follow the steps outlined below for a detailed admission procedure to the top medical universities in Germany.
Step 1: Select your desired university from the list of renowned medical colleges in Germany mentioned above and carefully review its eligibility guidelines.
Step 2: Ensure that you fulfill the eligibility requirements for applying to the university. During the application process, you should have English/German language proficiency test certificates readily available.
Step 3: Complete the online application form for the university, providing accurate details and avoiding any errors or misrepresentation of information.
Step 4: Applicants will be required to upload scanned copies of essential academic documents to strengthen their application profile. The list of necessary documents is provided below.
Step 5: Pay the application fee as specified by the university.
Step 6: Upon successful submission of your online application form and payment of the fee, candidates will receive an admission letter from the university.
Step 7: Applicants will then need to submit their passport, original documents, and the letter of acceptance to the German embassy to apply for a German Student Visa.
Step 8: Once the German Student Visa is issued, which may take some time depending on the embassy's processing, the applicant should make the necessary travel arrangements to reach their university before the commencement of their course.
Documents Required for Admission to Medical Colleges in Germany
International students should be able to meet the below-mentioned requirements to be admitted to medical colleges in Germany.
- Completed Application Form
- Passport or National ID
- Passport-sized Photographs
- High School Diploma or Equivalent
- Official Transcripts
- Assessment Test Results (if applicable, e.g., Feststellungsprüfung)
- Proof of German Language Proficiency (e.g., TestDaF, DSH)
- Proof of English Language Proficiency (if applicable, e.g., TOEFL, IELTS)
- Letters of Recommendation
- APS Certificate (for students from certain countries)
- Proof of Health Insurance
- Proof of Financial Resources
- Visa Documentation (if applicable)
- Application Fee Receipt (if applicable)
Jobs and Career Opportunities
A German medical degree is your golden ticket to a ton of awesome career paths! We're talking about being a doctor in Germany, going global, or even working on cutting-edge medical stuff. This article breaks down all the cool options open to you after you graduate.
1. General Practitioners
These physicians provide comprehensive primary care services, acting as the first point of contact for a wide range of health concerns within a community setting.
2. Specialist Doctors
Graduates can pursue further specialization in specific medical fields. For everyday health needs, general practitioners are fantastic. But when a situation requires a deeper dive, specialist doctors step in. These highly trained physicians focus their expertise on specific areas of medicine to provide targeted diagnosis and treatment.
- Cardiologists: Specialize in the diagnosis and treatment of heart and cardiovascular system diseases.
- Neurologists: Focus on the nervous system, diagnosing and treating disorders like epilepsy, stroke, and neurodegenerative diseases.
- Oncologists: Manage various types of cancers, encompassing diagnosis, treatment planning, and patient care.
- Pediatricians: Provide comprehensive healthcare services for children from birth to adolescence.
- Gynecologists: Specialize in female reproductive health, diagnosing and treating conditions affecting the uterus, ovaries, and other reproductive organs.
- Anesthesiologists: Manage pain control and provide anesthesia for surgical procedures and other medical interventions.
- Surgeons: Perform surgical procedures to treat various medical conditions. Specific surgical fields include orthopedics, plastic surgery, and more.
From the prestigious Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich (LMU Munich) to the esteemed University of Heidelberg and Technical University of Munich (TUM), these medical universities in Germany for international students offer unparalleled academic excellence, cutting-edge research facilities, and a diverse learning environment. With tuition costs that won't break the bank, top-notch facilities, and a hands-on approach to learning alongside classroom theory, medical schools in Germany offer a well-rounded education. So, what are you waiting for?
Frequently Asked Questions
Are the medical schools in germany free, is heidelberg university good for medicine, which german university is best for medicine, is it hard to get into lmu munich, can i study mbbs in germany without german language.
Your ideal student home & a flight ticket awaits
Follow us on :

Related Posts
.jpg)
Top 10 Most Expensive Universities In The World 2024-25

A Simple Guide To Percentage To GPA Conversion

Best Universities in Australia for Computer Science 2024

Planning to Study Abroad ?

Your ideal student accommodation is a few steps away! Please fill in your details below so we can find you a new home!
We have got your response
.webp)
amber © 2024. All rights reserved.
4.8/5 on Trustpilot
Rated as "Excellent" • 4800+ Reviews by students
Rated as "Excellent" • 4800+ Reviews by Students

English Taught Medical Schools in Germany
Hi there! If you’re considering studying medicine in Germany, you’ve come to the right place. In this comprehensive guide, I’ll take you through everything you need to know about English taught medical schools in Germany , from admission requirements to living expenses and job prospects. Let’s get started!
First, I’ll tell you all about why Germany is a great destination for medical studies, and then I’ll dive into the specifics of English-taught programs, including the top schools and what you need to do to qualify. By the end of this guide, you’ll have a thorough understanding of what it takes to study medicine in Germany and whether it’s the right choice for you. So, let’s get started!
Why Study Medicine in Germany?
If you’re considering studying medicine abroad, Germany should be at the top of your list. Not only does Germany have a rich history in medical research and practice, but it also boasts some of the world’s leading medical schools. As an international student, you’ll have the opportunity to learn from some of the best medical professionals in the world.
Moreover, many medical schools in Germany offer English-taught programs, making it an attractive destination for non-German speakers. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the benefits of studying medicine in Germany and what you need to know to make the most of your experience.
English-Taught Medical Programs in Germany
If you’re considering studying medicine in Germany, you’ll be pleased to know that there are several English-taught programs available. These programs are designed to attract international students and provide them with a high-quality education in the field of medicine.
Germany is well-known for its excellence in healthcare and medical research, and by studying medicine in Germany, you’ll have the opportunity to learn from some of the best in the field. The English-taught programs are taught by highly qualified and experienced professors who are dedicated to helping you achieve your goals.
Admission Requirements for English-Taught Medical Programs in Germany
Studying medicine in Germany is a popular choice among international students, and for good reason. Germany has a world-renowned healthcare system and some of the best medical schools in the world. However, gaining admission into an English-taught medical program in Germany can be competitive and challenging.
One of the primary requirements for admission is a strong academic background. Most universities in Germany require a high school diploma or equivalent, as well as good grades in science and math courses. Additionally, most universities require a language proficiency test, such as the Test of English as a Foreign Language (TOEFL) or the International English Language Testing System (IELTS).
Another important requirement is a solid understanding of the German language . Although English-taught medical programs are available, German is still the primary language of communication in hospitals and clinics. Therefore, most universities require applicants to have a minimum level of proficiency in German, such as the TestDaF or DSH language exams.
In addition to academic and language requirements, many universities also require applicants to pass an entrance examination, such as the Test for Medical Studies (TMS). The TMS is a standardized test that assesses applicants’ knowledge in areas such as biology, chemistry, and physics.
Overall, admission requirements for English-taught medical programs in Germany are rigorous, but the effort is worth it for those who are dedicated to pursuing a career in medicine. With a strong academic background, language proficiency, and success on entrance exams, international students can gain acceptance into some of the best medical schools in the world.
Top English-Taught Medical Schools in Germany
If you’ve decided to study medicine in Germany, the next step is choosing the right university. Germany has many world-renowned medical schools, but which ones offer English-taught programs?
Here are some of the top English-taught medical schools in Germany:
- Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin
- Ruprecht-Karls-Universität Heidelberg
- Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München
- Eberhard Karls Universität Tübingen
- Technische Universität München
- Universität Freiburg
- Universität Hamburg
- Universität zu Köln
- Rheinische Friedrich-Wilhelms-Universität Bonn
- Universität Ulm
These universities offer excellent facilities, experienced professors, and a welcoming environment for international students. But keep in mind that admission requirements, tuition fees, and living expenses vary between universities and cities, so it’s essential to research each option thoroughly.
Choosing the right medical school is crucial for your education and future career, so take the time to weigh the pros and cons of each university carefully.
Costs of Studying Medicine in Germany
Studying medicine in Germany is generally more affordable than in many other countries, especially in comparison to the United States. However, it’s still important to understand the costs associated with pursuing a medical degree in Germany.
One of the main advantages of studying in Germany is that public universities do not charge tuition fees for undergraduate programs, including medical school. However, keep in mind that you will still be responsible for covering living expenses, such as rent, food, and transportation.
Private universities, on the other hand, do charge tuition fees, and these can be quite high. For example, the University of Witten/Herdecke, a private medical school in Germany, charges tuition fees of around €20,000 per year.
In addition to tuition fees, there are other costs associated with studying medicine in Germany. For example, you will need to purchase textbooks and other course materials, which can be quite expensive. You will also need to pay for health insurance , which is mandatory for all students in Germany.
Overall, the costs of studying medicine in Germany can vary widely depending on whether you attend a public or private university, your living expenses, and other factors. However, with careful planning and budgeting, it is possible to pursue a medical degree in Germany without breaking the bank.
Living in Germany as an International Medical Student
Germany is an ideal place to study medicine for international students . Not only does it have some of the best English-taught medical programs in the world, but it also provides an excellent quality of life for students.
As an international medical student, you will have access to a wide range of housing options. Many universities have dormitories, which are a great option for students who want to live on campus. If you prefer to live off-campus, you can rent an apartment or share a flat with other students.
One of the biggest advantages of studying in Germany is the low cost of living . Compared to other countries in Europe, Germany is relatively affordable. The cost of housing, food, and transportation is much lower than in the UK or the US.
Germany also has an excellent public transportation system, making it easy to get around the country. Whether you want to explore the city or travel to other parts of Germany, you can do so easily and affordably.
As an international student in Germany, you will also have access to excellent healthcare services. Germany has one of the best healthcare systems in the world, and as a medical student, you will be able to take advantage of this.
Overall, living in Germany as an international medical student is a great experience. You will have access to world-class medical education, affordable living, and an excellent quality of life.
Job Prospects for International Medical Graduates in Germany
If you’re an international medical graduate considering studying in Germany, you’re probably wondering about your job prospects after graduation. The good news is that Germany has a high demand for doctors, and there are plenty of job opportunities available for international medical graduates.
Germany is known for its excellent healthcare system, and it has a shortage of doctors in many areas. This shortage is expected to increase in the coming years due to the aging population, making it an ideal time for international medical graduates to pursue a career in Germany.
After completing your medical studies in Germany, you can apply for a job as a medical doctor in hospitals or clinics. You can also choose to work as a general practitioner or specialize in a particular field such as surgery, pediatrics, or internal medicine.
The salary for doctors in Germany is competitive and can vary depending on your experience and qualifications. According to the German Medical Association, the average salary for a doctor in Germany is around €60,000 per year. However, salaries can range from €30,000 to €200,000 depending on the specialty, experience, and location.
In addition to a good salary, doctors in Germany also benefit from job security and excellent working conditions. The German healthcare system places a high value on work-life balance, and doctors are encouraged to take breaks and vacations.
Overall, the job prospects for international medical graduates in Germany are excellent, and it’s a great place to start your career as a doctor.
Challenges Faced by International Medical Students in Germany
Studying medicine in Germany as an international student can be a rewarding and enriching experience, but it also comes with its fair share of challenges. One of the biggest challenges faced by international medical students in Germany is the language barrier. Although many universities offer English-taught programs, knowledge of the German language is still important for effective communication with patients and colleagues.
Another challenge is the rigorous curriculum and workload. Medical programs in Germany are known for their intensity, and international students may find it difficult to keep up with the pace. The workload can be particularly challenging for those who are not used to the German education system , which places a strong emphasis on independent learning.
In addition, adjusting to life in a new country can be a daunting experience, especially for those who are far away from home. Culture shock, homesickness, and feelings of isolation are common among international students, and it may take time to settle into a new routine.
Financial concerns are also a major challenge for many international students. While tuition fees for English-taught medical programs in Germany are relatively low compared to other countries, the cost of living can be high. Accommodation, food, and transportation expenses can add up quickly, and students may need to work part-time to support themselves.
Finally, international medical graduates in Germany may face additional challenges when it comes to finding employment after graduation. While there is a demand for doctors in Germany, the job market can be competitive, and graduates may need to meet specific requirements to practice medicine in the country.
Despite these challenges, many international medical students have successfully completed their studies in Germany and gone on to have successful careers in the field. With determination, hard work, and a willingness to adapt, it is possible to overcome the challenges and make the most of the opportunities that studying medicine in Germany has to offer.
Student Life in Germany: What to Expect
Studying in Germany as an international medical student can be an exciting and rewarding experience, but it can also come with its challenges. As a foreign student , it can take some time to adjust to the new culture and way of life. Here are some things you can expect when it comes to student life in Germany:
- Academic rigor: German universities are known for their academic rigor, and medical programs are no exception. Expect to be challenged and pushed to your limits.
- Language barrier: While many medical programs in Germany are taught in English, it is still important to learn some basic German to navigate everyday life and communicate with patients.
- Cost of living: Germany is not a cheap place to live , but as a student, there are many discounts and resources available to help you save money. Look into student housing options and take advantage of student discounts for transportation and cultural activities.
- Cultural immersion: Studying in Germany is a great opportunity to immerse yourself in a new culture and way of life. Take advantage of this by exploring the country, trying new foods, and meeting new people.
- Work-life balance: Germans place a high value on work-life balance, and as a student, you can benefit from this. Use your free time to explore your hobbies and interests, and enjoy the many parks, museums, and cultural activities that Germany has to offer.
Overall, studying medicine in Germany can be a challenging but rewarding experience, both academically and personally. With the right mindset and preparation, you can make the most of your time as an international medical student in Germany.
Conclusion: Is Studying Medicine in Germany Right for You?
Studying medicine in Germany is a great option for international students who are looking for high-quality education, practical training, and job opportunities. The country is known for its excellent healthcare system, advanced medical research, and top-notch universities that offer English-taught programs in medicine.
However, studying medicine in Germany also comes with its own set of challenges, such as the high costs of living and studying, the competitive admission process, and the language barrier. It’s important to carefully consider your goals, resources, and preferences before deciding if studying medicine in Germany is the right choice for you.
If you are passionate about medicine, willing to work hard, and interested in experiencing a new culture and language, then studying medicine in Germany can be a rewarding and life-changing experience. With careful planning, research, and determination, you can successfully navigate the challenges and make the most of the opportunities that studying medicine in Germany can offer.

Similar Posts
Salary in germany for software engineers, average salary of automotive engineer in germany, germany violated this nation’s neutrality:, the most beautiful cities in germany to visit, what to do in stuttgart germany on sunday, the impact of the great depression on germany, leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Cookie Consent
To improve the website, the DAAD and third parties set cookies and process usage data . In doing so, the DAAD and third parties transfer usage data to third countries in which there is no level of data protection comparable to that under EU law. By clicking the "Accept all" button, you consent to this processing. You can also find selection options and explanations of these cookies and processing at the end of this page under "Cookies". There you can withdraw consent at any time with effect for the future.
- Privacy Policy
Jump to content

Higher Education Compass
Medical education part time, master of education.
Master Degree
6 semesters
Standard period of study (amount)
Please enquire
Overview and admission
Admission semester.
Winter Semester only
Area of study
- Sociology, Social Science
- Health Pedagogy
- Health Science
- Nursing Science
- Pedagogy (Teaching Degree)
- Educational Sciences
Currently and in the future, there exists a large demand for very well qualified teachers in public and private vocational schools in health care. With the upcoming amendments to the occupational admission laws of the therapy and rehabilitation professions as well as the diagnostic-technical health professions it becomes clear that the standard "higher education" for teachers in the health sector will continue to establish itself. However, the number of suitable study places is very limited. The Master's degree in Medical Education at the Faculty of Health at the HMU Health and Medical University Potsdam offers an adequate range of courses that take into account the increasing qualification requirements for healthcare professionals. This is a teacher training course, which is characterised by the clear orientation on the structure of teaching courses and the nationwide recommendations of the Conference of Ministers of Education for teaching courses. The decision about hiring is determined by the country-specific hiring requirements. However, the chances of employment in this area increase significantly due to the targeted orientation towards cross-border standards of teacher training. As a graduate, you can work in both health care schools and vocational schools in the public school system. The Master's degree in Medical Education at the HMU focuses on three areas: Educational Sciences, the Social Sciences and the elective areas of Health Sciences (including Therapy Sciences) or Nursing Sciences. The part-time model of the HMU Health and Medical University Potsdam provides part-time students with the opportunity to gain academic qualifications in addition to work and family.
Admission modus
open admission
Admission requirements (Link)
Admission requirements
Eligibility to study in Master’s courses according to § 9 (5) BbgHG and successfully completed relevant Bachelor's degree in the field of Health, Therapy and Nursing Sciences rsp. Nursing Education* After your application, we will check your personal motivation in an individual interview. * The Bachelor's degree in Medical Education (BA) at HMU Health and Medical University Potsdam forms an ideal basis for the Master's degree in Medical Education (M.Ed.) because the study concepts are coordinated.
Lecture period
Application deadlines, winter semester (2022/2023), application deadline for germans and inhabitants.
No deadlines: Apply for a study place at the HMU Health and Medical University Potsdam at any time.
Deadlines for International Students from the European Union
Deadlines for international students from countries that are not members of the european union, enrollment deadline for germans and foreign students, tuition fee.
495.00 EUR / semester
Fees (Link)
Tuition fees for the Master´s degree programme amount to EUR 17,820, to be paid in 36 constant monthly instalments of EUR 495 for the full-time model. Newly enrolled students are charged a one-time examination fee of 100 euros. There are numerous possibilities for financing studies, such as BAföG (state financial support), KfW study loans (parent- and subject-independent without collateral), scholarships for outstanding students, student loans from banks, student education funds and scholarships.
Languages of instruction
Main language.
Deutscher Akademischer Austauschdienst e.V. Kennedyallee 50 53175 Bonn
All addresses in the DAAD Network
DAAD Newsletters
Receive regular up-to-date information about our work and organisation.
Newsletter - DAAD
Useful Links
- Find Scholarships
- DAAD offices worldwide
Jump to top of page
FREE Webinar on 26th June

Join our FREE webinar on 26th June 2024

Find Universities with:

Study Medicine in Germany in English
There are many reasons to study medicine in Germany in English. The first is the country's reputation for the highest quality medical training. Graduates of medical schools have the best job prospects and can compete with graduates from other health care fields.

Living & Studying In Germany
About Studying Medicine in Germany
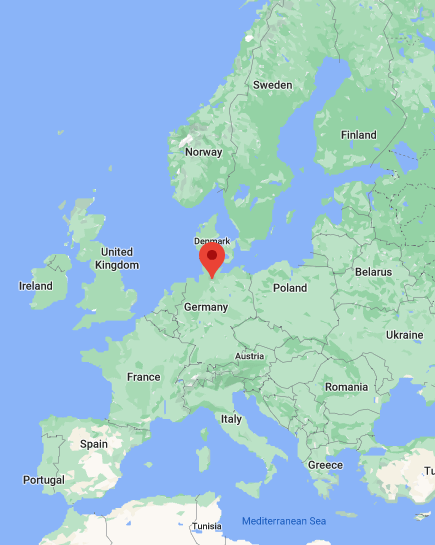
It’s no secret that many international students are attracted by the opportunity to study medicine in Germany in English.
What’s not to like? The country has a perfect location – in Central Europe, between the Baltic and North seas.
But if you are a mountaineer, don’t worry, the Alps are to the South.
Germany is one of the most developed countries in the world. Its hospitals are famous for their high-quality health care and honest doctors who put their patients at the highest priority.
The second-largest city is Hamburg, with a population of over 1.84 million people.
It is a popular destination for international students willing to study medicine abroad.
Providing first-rate education and excellent living standards, it won’t be a surprise that it’s among the best places to study medicine in Europe .
You can sign up for an MD programme in English at the University of Targu Mures Medical Campus Hamburg (UMCH). Here, you can choose between two types of medical courses.
The first programme allows you to study in Germany for the whole period of 6 years. The second requires you to study in Germany for the first 2 years and then go to Romania for the remaining 4 years of the course, but pay significantly lower tuition fees (the teaching language remains English).
If you are already enrolled in a medical course somewhere else, but you changed your mind, we are happy to inform you that UMCH accepts students transferring from one medical institution to another .
If you are looking for a graduate entry medicine course , UMCH doesn’t offer one.
Why study medicine in Germany?
- Germany is a fast-growing and ever-evolving country which is part of the European Union.
- It ranks fourth in the list of the world's most advanced economies.
- Once graduate from UMCH, you have the right to practise as a doctor all around Europe and worldwide.
- Germany’s medical education and institutions are in the top 10 of every chart.
- University of Targu Mures Medical Campus Hamburg offers student transfers.
- UMCH offers you the chance to practise in the most modern equipped clinics and learn from the best in this area.
- There are no compromises when it comes to the quality of education and living.
- UMCH facilities are equipped with the m ost modern medical equipment.
The Best Medical Universities In Germany
Check out our price breakdown of medical schools in Germany
Tuition fee
- Medicine (12)
- Dentistry (4)
- Pre-Med (1)
- September / October (9)
- December / January (1)
- February / March (9)
- April / May / June (2)

University of Targu Mures Medical Campus Hamburg (UMCH)
Located in Germany's second-biggest city, the University of Targu Mures Medical Campus Hamburg is a branch of the prestigious Targu Mures university in Romania. It's currently comprised of three faculties - Medicine, Dentistry and Pharmacy, all of which are available in English for international students who wish to study medicine in Europe.
€ 29800 / year
Medicine, Pre-Med
Quick Facts

Tuition Fees In Germany

Can you Study Medicine in English in Germany?
Yes, you can! The University of Targu Mures gives you the opportunity to study medicine in Germany in English. With a well-organised 6-year course in medicine, you will receive not only a diploma but exceptional knowledge and skills in your favourite area of study.
German Medical Universities that Teach in English
For now, the University of Targu Mures Medical Campus Hamburg is the only medical school in Germany that offers English-thaught medical courses.
However, we are updating our information every day and will inform you as soon as possible if a new one appears.
University of Targu Mures Medical Campus H amburg is located in Hamburg, Germany.
Not long ago, it established a cooperation agreement with the Targu Mures University of Romania, which is the largest medical university there.
The main reason for its foundation was the interest of the international students seeking to study medicine in English in Germany with no admission restrictions based on school grades.
Since the Bahrenfeld is called “Science City”, it makes it the perfect place for the university to be located.
UMCH has taken care to fully equip its campus with the most modern facilities. Workstations, laboratories, IT areas, and multimedia lecture halls are just a small part of all advantages you will get.
The most fascinating thing about their equipment is the 3D anatomy and dissection table. This allows you to easily explore human anatomy in small details.
The campus consists of 328 fully furnished studio apartments and a few common rooms, including a bar and lounge.
You can also take advantage of the wellness area, swimming pool, and fitness centre.
If you still choose not to live on the campus, your living expenses will be around €1,400, including rent.
Entry Requirements to Study Medicine in Germany
While different universities have different requirements, here is what they ask for in general:
- A secondary school diploma or transcript.
- Good grades in Biology and Chemistry. Some universities also ask for Physics or Math.
- An English proficiency certificate for non-native speakers in English programmes.
- An entry examination for some universities
- A student visa for non-EU citizens
- A motivational interview to determine the applicant’s character
The latter is valid for the University of Targu Mures, where you will also need to attend a 20-min motivation-based interview either online or on-site. After that, there is a knowledge evaluation test that lasts 90 minutes.
Medlink Students will take care to supply you with all the needed materials and support you throughout the whole process.
How Much Does It Cost to Study Medicine in Germany?
While German public universities charge low tuition fees, their fees are higher for non-EU residents. In contrast, private universities are usually in the €20,000 - €30,000 tuition range. Furthermore, living costs ( rent included) in Germany are between €1,300 to €1,800 per month, depending on the city.
Tuition Fees to Study Medicine in Germany
By choosing to study all 6 years in UMCH, your tuition fee will be for the 1st and 2nd years and for the years 3-6. The university gives you a second option.
You can study in Germany for the first 2 years at the cost of per year and finish years 3-6 in Romania at the cost of per year.
Living Costs of Studying Medicine in Germany
The living costs in Hamburg are around for a single person. 1-bedroom apartment rent is between €700 and €950, depending on the location. Thus, Germany is relatively expensive compared to countries in Central and Eastern Europe.
Is Germany Good for International Students?
Germany is the third leading destination for international students. It offers an outstanding quality of education focusing on innovation and accessibility. Furthermore, Germany is the 23rd safest country in the world, and foreigners can expect a tolerant and supportive environment. Finally, international students’ communities enjoy excellent opportunities for networking, career development, and recreational activities.
Practical Reasons to Study Medicine in Germany
Germany offers many benefits to international students, and here are the objective reasons one might decide to study there:
- Worldwide recognition of the degree
- The University of Targu Mures offers student transfers
- 23rd safest country according to the Global Peace Index
- The most developed economy in Europe
- Germany is an EU and Schengen member
Lifestyle Reasons to Study in Germany
They call Germany the Land of Poets and Thinkers. Some of the world-renowned names in this regard would be Gutenberg, Martin Luther, Goethe, Hegel, Karl Marx, and Friedrich Nietzsche.
Furthermore, Germans are renowned for their punctuality, work ethic, and efficiency. It is no surprise that they are considered reserved and distant by most foreigners, but Swedish guests still consider them too cordial and social.
Still, Germans do know how to have a good time. Oktoberfest is a trademark for Germany, but it’s far from being the only local festival worth attending. Big cities enjoy an active club life and a world-famous music scene. Yet, small towns benefit from local craft breweries and the stunning beauty of the countryside.
Speaking of breweries, Germans lead the world in beer consumption per capita, and for good reason. It's not just the calibre of the brew, but also the delightful accompaniments they pair with it. They have over 1,500 types of sausages, and such variety is by itself sufficient for a 6-year study.
Is Germany Safe for International Students?
Germany is the 23rd safest country in the world according to the Global Peace Index. The country has very low crime rates, and violent crimes are a comparatively low percentage of them. Finally, citizens and foreigners alike enjoy adequate political rights and freedoms. Therefore, Germany is a safe country for international students.
Is Medical Education in Germany Right for You?
If your dream is to study medicine abroad in English , then Germany is the right place to make it come true. The duration of the course is 6 years and is split into 2 sections.
The preclinical section is during the first 2 years, consisting of lectures and seminars where you will learn essential medical theory.
The remaining 4 years are called clinical. This is the time when you will not only have lectures, but you will experience what doctors do yourself.
You will be attending hospitals, working with patients, and being guided by real doctors.
Submit a free application to hear more about your options in Germany and Europe via Medlink Students.
Get Info On Any University In Germany
Frequently asked questions.
Yes, you will need to pass a 90-minute evaluation test of your knowledge.
Yes, your degree will be recognised worldwide.
Of course, you can. You can study medicine in English in Germany at UMCH.
Unfortunately, at this point, no university in Germany offers a graduate entry in Egnlish.
We are sorry to inform you that UMCH doesn't accept student transfers.
The average price of medical education in Germany is per year for international students.
Living in Germany costs about - per month, depending on factors such as the city, type of accommodation and the student’s own needs and expenses.
No. There’s a very high demand for Germany from both local and international students, which means that the entry requirements are very high.
German medical education follows the continental tradition where students receive a Medical Doctor (M.D.) degree. Therefore, the course takes 6 years to complete, and the degree gets worldwide recognition.
Other Countries in Europe

Study Medicine In the Caribbean In English

Study Dentistry in Lithuania in English

Study Dentistry In Bosnia & Herzegovina In English

Study Dentistry in Croatia in English

Study Dentistry in Armenia in English

Study Dentistry in Moldova in English

Study Dentistry in Latvia in English

Study Dentistry in Czech Republic in English

Study Dentistry in Serbia in English

Study Dentistry in Italy in English

Study Dentistry in Cyprus in English

Study Dentistry in Bulgaria in English

Study Dentistry in Slovakia in English

Study Dentistry in Hungary in English

Study Dentistry in Romania in English

Study Dentistry in Poland in English

Study Dentistry in Georgia in English

Study Dentistry In Spain In English

Study Medicine in Lithuania in English

Study Medicine In Bosnia & Herzegovina In English

Study Medicine in Armenia in English
Study medicine in croatia in english, study medicine in moldova in english.

Study Medicine in Estonia in English
Study medicine in serbia in english, study medicine in slovakia in english, study medicine in czech republic in english, study medicine in hungary in english, study medicine in georgia in english, study medicine in italy in english, study medicine in cyprus in english.

Study Medicine in Turkey in English
Study medicine in bulgaria in english, study medicine in poland in english.

Study Medicine In Ukraine In English

Study Medicine in Latvia in English
Study medicine in romania in english, saved universities.

Discover Your Options Abroad With a FREE Consultation
Check your email, to book a free call, with an expert advisor.

free webinar: study medicine & dentistry abroad
Preferred currency.

Medicine Admission Process in Germany for EU/EEA Applicants
Weighing your chance of acceptance, the three quotas, what gpa do i need to study medicine in germany, are there entrance tests or exams for foreign students, start your application in hochschulstart.
Video Course
Get Accepted into Your Dream German University — with the Perfect Letter of Motivation!

Students who obtained their A-Levels (or any other secondary school degree) in the EU, Iceland, Liechtenstein, Norway, or from official German Schools Abroad cannot apply to German universities directly to study medicine. Their application is managed by hochschulstart , a platform managed by the Trust for admission to higher education (Stiftung für Hochschulzulassung - SfH) .
This institution, among other things, regulates admissions to certain centrally restricted courses of studies (medicine, veterinary medicine, dentistry, and pharmacy). If you are in this group of students, it is absolutely necessary that you familiarize yourself in detail with the information (only in German) on the selection procedures , so that you can maximize the likelihood of scoring one of the spots offered by the universities.
To apply to study medicine in Germany, you must create an application in the hochschulstart portal. This is possible in the application period only. To give you an example: For the winter semester 2020, applications were accepted from 01.07.2020 - 25.07.2020 (respectively 20.08.2020 for students who got their A-Levels in 2020). The application includes filling out the online application and sending in your documents per physical mail.
Hochschulstart is tasked with allocating around 87% of all available spots for medical students. Applicants from the EU, Liechtenstein, Iceland, and Norway and from German schools abroad compete for these spots. The spots are allocated according to set admission quotas, which may influence your application strategy and give you an idea of which requirements you need to fulfill to score a spot to study medicine in Germany.
Throughout the application process, you will be asked to list the priorities of your universities. After a recent reform of the application process, you can set your priorities simply based on which universities you prefer. Strategically, it makes sense to include universities where you have a higher likelihood to fulfill the criteria in the quotas other than the GPA quota.
Hochschulstart Admission Quotas to Study Medicine
The GPA Quota
Only applicants with the highest GPA will get admitted. Often, students who get admitted under this quota typically have GPAs of 1.0 to 1.3 in the German grading system.
University Qualifications Quota
The majority of students, i.e. 60%, are admitted according to qualification criteria that are set by the universities (German: Auswahlverfahren der Hochschulen , AdH). Other than students’ GPA, typical criteria include the medical aptitude test, application interviews, professional training or practical experience, prizes, or voluntary positions.
Additional Qualifications Quota
The remaining 10% of spots are allocated to applicants who fulfill additional qualifications, such as excellent scores in the assessment test or working as a health professional, such as a nurse (German: zusätzliche Eignungs Quote). This last quota is the only one that is completely independent of your GPA. Each university can define a mix of criteria by which applicants are admitted.
1. The GPA Quota

Each state in Germany has its own GPA quota ranking with its own required minimum grades. Usually, students partake in the ranking of the German state in which they obtained their A-Levels. All applications from students who have to apply via hochschulstart but completed their A-Levels outside Germany are randomly distributed amongst the rankings 16 states of Germany: Which states get how many international applicants depends on the population size of that state. Therefore, there is a slightly higher likelihood that you will compete with applicants from the states that have higher population numbers. However, this is impossible to foretell.
The rankings of each state are finally merged into one list according to set rules. In this process, differences in the conditions under which students obtain their A-Levels in each German state are considered, as well as the population size of each state is considered. For a more detailed description, click here . In this final list, all applicants are ranked according to their GPAs.
2. The University Qualifications Quota
The majority of study spots are assigned through the AdH. In addition to students’ GPAs, universities have to admit students based on at least 2 of these criteria:
- Study aptitude tests (TMS, Ham-Nat),
- Interviews or other oral examinations,
- Completed professional training or work experience (of at least 12 months),
- Previous qualifications, practical jobs, volunteer positions, extracurricular activities, prizes.
In this quota, the TMS aptitude test is always included in the selection and rewarded with positive points. In total and like in the additional quota, students can score up to 100 points. It is up to each university which criteria they choose and how to weigh them. You can find the exact information on this and what minimum score was needed for admission in previous years in the download area of hochschulstart . If you weren’t assigned a spot in the previous quotas you automatically compete for admission under this quota for all schools that you applied for.
If there are study spots that remain open after this process, there is a coordinated allocation of the study spots to the remaining highest ranked applicants or via additional qualifications which are elaborated in the following section.
3. The Additional Qualifications Quota
The additional qualifications quota is the only quota in which the GPA is not considered at all. Instead, each university can decide on either one or a mix of the following criteria, by which they admit applicants under:
Universities can select one or more criteria for this quota and assign a total of 100 points. Each applicant who did not already get a study spot in the GPA quota is considered under this third quota. According to the criteria set by each university you apply for, you are assigned up to 100 points, depending on your qualifications. Based on your score, you are ranked for each of your selected programs and can then compete for a spot.

Which grade you need in order to be admitted into a medical study program depends on the quota you are hoping to be admitted under.
You only have a realistic shot in the GPA quota if you have excellent grades in your secondary school certificate of completion, meaning if you are a straight-A student or near one. That means your final grade should be within the range between 1.0 - 1.3 on the German GPA scale. If so, you have a shot to be rewarded with a spot to study under this GPA quota.
If your GPA is lower, depending on your other qualifications, you can increase your ranking position based on other experiences you have in the quota defined by the university (German: Auswahlverfahren der Hochschule , AdH). To increase your chances in this quota and depending on what the universities of your choice indicate, you can do relevant internships before starting your studies or engage in a voluntary service. Most students score a place to study in this quota. To give you some examples of admission under this quota, here are the criteria and necessary points for admission in the summer semester 2020:
Here, one can see that the GPA still plays an important role in most of the universities’ selection processes, and scoring very poorly in this criteria will make it difficult for you to score well in those quotas.
Another 10% of study spots are distributed through a quota honoring additional qualifications that are completely independent of the GPA. Similar to the AdH quota mentioned above, universities decide themselves on a combination of criteria. To provide you some examples of admission under this quota, here are the criteria and necessary points for admission in the summer semester 2020:
Under this quota, your GPA does not matter as much as the demands towards other aspects, such as scoring well in the TMS or having allocated some semesters of waiting time. If you can anticipate scoring well in these other categories, you may score a position at a public university to study medicine without having an outstanding GPA.
One alternative is to consider private universities in Germany. In their admissions processes, private universities in Germany often pay attention to other criteria rather than just GPA. Check out our article on universities to study medicine in Germany to get an overview of private universities in Germany.

There are no nation-wide admissions exams to get access to a medical study program in Germany. Instead, it is up to each university individually whether they require you to hand in one of the relevant aptitude tests. For students who received their secondary school certificate of completion in the EU, Norway, Liechtenstein, Iceland or Switzerland or one of the official German schools abroad, a test that is often required from students who are looking to apply via the university quota or the additional qualifications quota is the Test for Medical Studies ( Test für Medizinische Studien / TMS ). Every public program that accepted applications for the summer semester 2020, for example, requested students to hand in a TMS result (see the two tables above). For other international students from outside the EU, the TestAS is required by some universities.
What is the Medical Studies Aptitude Test (German: Studierfähigkeitstest)?
There are some aptitude tests for medical studies in Germany that can support your application and help you prove to your future university that you have what it takes to study medicine.
The TMS, Ham-NAT, and HAM-SJT, which we will present here, should be taken by applicants who got their A-Levels in Germany or the EU. Applicants from outside the EU take part in a different selection procedure, in which they do not profit from taking these tests.
In German, these tests are called Studierfähigkeitstests . Not all universities explicitly require the tests, but as a rule, including one of these tests in your application can only have positive effects on your application. So if your test results are not so great, you cannot be excluded from the process. For the AdH admission quota, each university positively considers the TMS.
If your results are excellent or good, you can advance some ranks on the list of applicants. If you score lowly on the test scheme or do not hand in the test results in the first place, you score 0 points under this criterion. When you consider the tables of admission criteria above, you can get an idea of how helpful the test is to get admission in any of the non-GPA quotas. Because universities are obliged to consider other criteria in addition to the high school GPA, they often resort to medical studies aptitude tests. Therefore, you likely have to inform yourself about them. Keep in mind: only if you got your A-Levels within the EU since non-EU applicants take part in a different application procedure.
The Test for Medical Studies
For studies in medicine in Hamburg or Marburg, there are additional test formats, the HAM-Nat and HAM-SJT, testing the applicants’ knowledge in natural sciences and situational judgment respectively.
We recommend that you take part in this test, even if it means traveling to Germany and investing time and money to study for it. It is almost essential to have a good TMS score to gain admission if you are not a straight-A student and therefore will likely not get admitted under the GPA quota. On the bright side, taking the test one allows you to have the results considered for each of the universities that you select to apply to.

Before you start doing more research and create an account on the hochschulstart platform to start your application, there are some basic points about the application process that we would like to draw your attention to:
- You start your application to the hochschulstart platform online, but you must also send in some papers to complete your application. To register and get your application process started, click here .
- Standard documents to your application include a certified copy of your school certificate of completion and certificates of your previous engagements. All certificates have to be handed in as notarized translations into German. You only have to prove your language level to the university after you got admitted. Applying to hochschulstart is for free.
- Throughout your application, you may indicate up to 6 universities that you would like to study medicine at. Selecting less popular universities will increase your likelihood to get an admit since you only compete for the universities that you indicated throughout the application process. You will have to prioritize the universities and if you would be admitted to various universities, you will only receive actual admission to the university that you prioritized the highest. Universities will not be informed on which priority you gave their application, so this will not influence your chances. Watch the hochschulstart video with more information on how to prioritize.
More Articles
Language Requirements to Study in Germany
Medical Universities and Schools in Germany
Medical Universities in Berlin
How to study medicine in Germany: 10 things to know
MBBS in Germany

Study medicine in Germany

- Prep Material

MBBS in Germany in English: Top Universities, Fees, & Eligibility
Germany is renowned as an economic study hub, making it a sought-after destination for interested applicants. The country’s claim to fame lies in its state-funded education system which is home to over 400,000 international students. National universities here are strongly research-oriented and offer holistic tutelage. For MBBS in Germany alone, there are over 30 specialization options. From ophthalmology to forensic medicine, students can pursue various avenues of medicine.
Medical universities in Germany teach both theoretical knowledge and methodological expertise. However, competition is high and very few students get to study medicine in Germany. Although all students who have completed high school are eligible to enroll, there are very few programs available in the English language.
This article provides you with all the necessary information to study MBBS in Germany in English. Also, we will help you discover other medicine-related programs, admission requirements, and the cost of MBBS in Germany for international students.
To get a better insight regarding which institution will be best suited for you, you can also check out our blog on Public Vs Private Universities in Germany .
MBBS in Germany: Highlights
Best medical universities in germany.
QS World Rankings lists 32 German universities among the best in the world. The list of the top 15 is presented below.
Please note that all German universities offer undergraduate-level medicine programs in the German language.
Medical Degree in Germany
MBBS is the popular blanket term for studying medicine in India and UAE. However, this is not applicable to all countries. Conventionally, MBBS stands for Bachelor of Medicine and Bachelor of Surgery. In particular, medical courses in Germany have a duration of six years and are not categorized as bachelor’s or master’s programs. Instead, MBBS in Germany is available as a long-cycle master’s program.
An accredited program to study medicine in Germany typically lasts six years and three months after a state-administered exam that allows doctors to officially start practicing. This exam is referred to as the ‘Staatsexamen’, with which one obtains a license to practice as a physician. This licensing procedure is termed ‘Approbation’.
MBBS in Germany in English
There are 106 study programs for medicine in Germany. However, only one of them is taught in English.
To study medicine in English, international students have the choice of only one university. The UMFST of Targu Mures is a Romanian institution of repute. Established in 1945, the university delivers programs in a wide range of medical and health disciplines. Medicine, Dentistry, and Pharmacy are offered to international students.
The UMFST of Targu Mures has a campus in Germany. Located in Hamburg, this campus is exclusively known as University Targu Mures Medical Campus Hamburg (UMCH ) .
University Targu Mures Medical Campus Hamburg (UMCH)
- The course program at UMCH is divided into two phases: preclinical and clinical. Preclinical education lasts for the first two years. These preclinical lessons are taught in English at the Hamburg campus.
- The next four years of the program comprise the clinical portion. Students are faced with two options here. First, they can continue studying in Germany or transfer to the main campus in Targu Mures, Romania.
If students continue their course’s clinical portion in Germany, proficiency in German is a mandatory requirement.
The semester fees for the medicine program at UMCH consist of
Admission Requirements to Study Medicine in Germany
Medicine programs fall under the aegis of Germany’s numerus clausus (NC) course category . This implies that the intake for medical programs is limited and highly competitive. Admissions take place through the Hochschulstart platform but this platform is restricted to EU students.
Non-EU students can avoid using the Hochschulstart platform and apply directly to universities. However, they must first attest to having proof of German language proficiency.
The eligibility criteria for various medical programs in Germany include
- For admission, a high school diploma or its equivalent with maths, chemistry, and physics as mandatory subjects is required.
- Proof of German level proficiency at least up to the C1 level. B2/B1 scores may also be asked for by some universities. In such a case, foreign applicants can apply to German language courses for international students .
- Qualifying marks in the student’s home country’s national medical examination are required.
- All applicants need to obtain passing marks in the interview round or MCQ test round conducted by the German medical university of their picking.
Documents required for international students
Before confirmation of acceptance, international students will be asked to furnish the following records
- All past academic transcripts
- Letter of intent and personal essay
- Proof of English and German language proficiency exam
- Passport photos and proof of residence
- Proof of fee payment
For the timely submission of documents, you can employ our admissions counseling services and get into any university of your picking.
Please schedule a video conversation with one of our specialists for further information
Students can also apply through Gyanberry , which is officially partnered with UMCH. As an authorized agency, we can help you with each stage of the application process.
Postgraduate Medical Education in Germany in English
Although English-taught undergraduate programs are unavailable, there is scope for postgraduate degrees. According to DAAD’s official listing of programs, there are 25 study programs. The duration of these programs differs. Take a look at some of these programs tabulated below. This list excludes all the postgraduate programs in dentistry and related fields.
Fee Structure for MBBS in Germany
State-funded German medical universities charge a nominal semester fee that usually ranges between € 100-500 each semester .
Privately-owned institutions charge an annual fee of € 28,000 or above .
However, students have to incur significant living expenses during their stay in Germany. These comprise
To know more, you can check out our blog on Living Expenses in Germany and How to Budget Them .
Scholarships for international students
In addition to university-specific financial assistance, the German government also sponsors a variety of scholarships for international students. Applicants can avail of aid based on need, merit, or achievement in extracurriculars.
German medical programs are certified by renowned organizations such as World Health Organization (WHO). Scholarships to study medicine and related programs in Germany are limited, however, many public universities charge minimal tuition fees for selected candidates.
DAAD (Deutscher Akademischer Austauschdienst) scholarship
The German Academic Exchange Service heads the DAAD financial assistance program by means of scholarships. DAAD scholarships are geared primarily toward graduates and research students. Eligibility for each scholarship type varies with a monthly stipend of 850 USD.
Friedrich-Ebert-Stiftung Scholarship To Study In Germany
Students in any subject area are eligible to apply if they have outstanding school or academic merit, aspire to study in Germany, and are dedicated to and live by the values of social democracy. The benefits comprise
- €934 per month for the basic scholarship program and €1,200 per month for the graduate scholarship program.
- 276€ of family allowance, if applicable
- Reimbursement of health care costs
- Any income exceeding €400 per month will be credited against the scholarship.
Career prospects after MBBS in Germany
Medical graduates from Germany obtain a license issued by the state. This license is called “Zulassung zur ärztlichen Berufsausübung in Deutschland” or simply approbation.
Medical professionals hold a prestigious position in world society. MBBS in Germany is a coveted program. After obtaining their license, medical graduates can opt to
- Work as employees in hospitals, clinics, or rural healthcare setups
- Join the private sector
- Enroll in medical research or teaching
- Become a scientist in medical technology or the pharmaceutical industry
In 2021 alone, 9,636 foreign doctors applied to have their foreign qualification recognized as an equivalent to a German qualification. This is because of the lucrative salaries offered to German medical professionals. Out of all the academic positions in Germany, doctors are paid the highest.
The average salary of a physician in Germany is € 107,000 per year .
Top-paying cities include
Find Related Blogs
Does Germany offer medical programs in English?
International students can study medicine in English in Germany through UMCH. It is a Romanian university with a campus in Hamburg, Germany. Students can study the first two years in English. If they wish to continue their studies in Germany for the next four years, German language knowledge is required.
What is the cost of studying medicine in Germany in English?
State-funded universities charge a nominal semester fee of € 1,000-2,000 from international students willing to study in German. On average, the cost of studying medicine in English is € 28,000 and above annually for private universities.
What are the admission requirements for studying medicine in Germany?
Students must have completed high school. Proof of English proficiency, motivation letter, recommendation letter, and CV are some required documents. Students must take an entrance exam and interview as part of the selection process.

An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Ger Med Sci

Language: English | German
Undergraduate medical education in Germany
Medizinstudium in deutschland, jean-françois chenot.
1 Department of General Practice, University of Göttingen, Germany
Associated Data
The purpose of this article is to give international readers an overview of the organisation, structure and curriculum, together with important advances and problems, of undergraduate medical education in Germany. Interest in medical education in Germany has been relatively low but has gained momentum with the new "Regulation of the Licensing of Doctors" which came into effect in 2003. Medical education had required substantial reform, particularly with respect to improving the links between theoretical and clinical teaching and the extension of interdisciplinary and topic-related instruction. It takes six years and three months to complete the curriculum and training is divided into three sections: basic science (2 years), clinical science (3 years) and final clinical year. While the reorganisation of graduate medical education required by the new "Regulation of the Licensing of Doctors" has stimulated multiple excellent teaching projects, there is evidence that some of the stipulated changes have not been implemented. Indeed, whether the medical schools have complied with this regulation and its overall success remains to be assessed systematically. Mandatory external accreditation and periodic reaccreditation of medical faculties need to be established in Germany.
Dieser Artikel soll internationalen Lesern einen Überblick über die Organisation, die Struktur und das Curriculum des Medizinstudiums sowie über wichtige aktuelle Fortschritte und Probleme in der medizinischen Ausbildung in Deutschland geben. Das Interesse an der Qualität der medizinischen Ausbildung war vor der 2003 in Kraft getretenen neuen Approbationsordnung (AppOÄ) relativ gering. Das Medizinstudium war reformbedürftig, insbesondere in Bezug auf die Verbindung von theoretischen Inhalten und praktisch-klinischer Lehre sowie die interdisziplinäre Vermittlung von Kerninhalten. Das Medizinstudium dauert sechs Jahre und drei Monate und wird in drei Abschnitte unterteilt: Vorklinik (2 Jahre), Klinik (3 Jahre) und „Praktisches Jahr“. Auch wenn die durch die neue AppOÄ notwendigen Reformen an vielen Stellen hervorragende Lehrprojekte hervorgebracht haben, gibt es dennoch Hinweise darauf, dass die geforderten Veränderungen nicht überall umgesetzt werden konnten. Eine systematische Evaluation zur Umsetzung der neuen AppOÄ durch die medizinischen Fakultäten steht noch aus. Eine verpflichtende externe periodische Evaluation der medizinischen Fakultäten muss in Deutschland erst noch etabliert werden.
In Germany, lectures in medicine were first given in 1388 in Heidelberg. The latest medical faculty was founded in Witten-Herdecke in 1992. Medical education in this country was once praised as a role model e.g. for American medical education by Abraham Flexner [ 1 ]. Nowadays, however, the German medical faculties are looking towards the United States [ 2 ], Canada, and other European countries such as the United Kingdom and the Netherlands for good examples to follow.
Germany has about 80,000 medical students studying in 36 medical faculties (Table 1 (Tab. 1) , list with URLs see Attachment 1 ) [ 3 ]. Each year 10,000 new students start medical education and about 6000 students graduate every year. Geographic distribution of medical faculties in Germany reflects historic developments rather than population density (Figure 1 (Fig. 1) ).

(URLs see Attachment 1)

It is estimated that 180,000 Euros are required to cover the cost of teaching for each graduating medical student in Germany [ 3 ]. This compares to 260,000 Euros in the United Kingdom [ 4 ]. All but one medical faculty (Witten-Herdecke) are state universities, and until recently higher (undergraduate) education was free – now a few states charge up to 500,- € tuition per semester which is low in comparison to fees required for example in the United States [ 5 ]. Grants and student loans are available [ 6 ].
Given this background, the aim of this article is to provide international readers with an overview of the organisation, structure and curriculum of undergraduate medical education in Germany following the introduction of the new "Regulation of the Licensing of Doctors". This narrative review is based on data available from official organisations, relevant German medical journals generally not listed in Medline or EMBASE, and on personal experience. It is therefore likely to serve as a reference for reports of research in medical education in Germany and could also help international medical staff seeking to assess medical students taught in Germany who are applying for elective clerkships abroad.
Structure and curriculum of medical education
The new regulation of the licensing of doctors.
German Medical Education has not been described in international journals since the new "Regulation of the Licensing of Doctors" [ Approbationsordnung für Ärzte (AppOÄ)], which came into effect in 2003 [ 7 ], [ 8 ], [ 9 ]. This structural reform became necessary when reports from governmental and non-governmental institutions concluded that medical education in Germany did not meet actual requirements in medical care or stipulations from the European Union [ 10 ], [ 11 ]. While interest in medical education in Germany was relatively low compared to e.g. The Netherlands or the United Kingdom, it has now gained momentum with the new AppOÄ, which required substantial changes in the curriculum. The main changes are [ 8 ]:
- Incorporation of the changed requirements in medical care
- Linkage of theoretical and clinical instruction
- Extension of interdisciplinary and topic-related instruction
- Improvement of bedside training, reduction of lectures
- Reform of examinations
- Strengthening of General Practice
- Evaluation of teaching
- Improving pain management and palliative care
Although of limited importance to medical faculties, for graduating medical students the most tangible change represented the abolishment of the lowly paid 18-month internship [ Arzt im Praktikum (AiP)] before obtaining the full license to practise medicine [ 12 ].
In the following description of the medical curriculum and in the discussion, the main goals of the new AppOÄ will be referred to.
Admission criteria for medical students
With few exceptions, the General Certificate of Aptitude for Higher Education [ Abitur ] is a prerequisite for admission to higher education in a university. It usually requires 12 or 13 years of schooling. Roughly 39% of all school children will obtain the Abitur [ 13 ]. The Abitur cannot be compared to a high school diploma in the United States; it is closer to the associate degree of US colleges. Secondary school diplomas obtained inside the European Union are mutually recognised; however students with diplomas obtained outside the European Union have to apply for a certificate of equivalence. Undergraduate education e.g. preparatory classes for medical school, prevalent in some countries, do not exist in Germany. Therefore, the term undergraduate or graduate education does not apply in the strict sense.
In Germany, the average age of medical students is 21.4 years when they start medical school [ 14 ]. There are several reasons for this. Germany still has mandatory service of nine months for men either in the military or an alternative civilian service [ Zivildienst ] for conscientious objectors. Additionally due to waiting time or professional training in other areas, a significant proportion of students are older. Although there is no formal regulation, an age of 40 years is considered the upper limit for entering medical school. Similar to many other countries, the number of women studying medicine has increased steadily and is now exceeding the proportion of male students [ 15 ]. This however is not yet reflected in higher academic ranks.
Selection of medical students
The number of applicants to medical schools largely exceeds the number of available places; therefore admission is subject to restrictions [ numerus clausus ]. On average four to five prospective students apply for each place, however there are large differences between the faculties. In Germany, application to medical schools is administered by a federal organisation, the Central Office for the Allocation of Places in Higher Education [ Zentralstelle für die Vergabe von Studienplätzen (ZVS)] [ 16 ]. Criteria for admission are the overall Abitur grade, which is roughly comparable to the American Grade Point Average (GPA), and waiting time. The Abitur is considered the best predictor for successful completion of the curriculum [ 17 ]. Each student can rank and apply to 6 medical schools at once. The majority of medical students (80%) used to be admitted by this process and there is a quota for foreign medical students and the military.
The proportion of students who are selected by the medical schools themselves is supposed to increase to 60%. Usually students apply with a letter of motivation to medical schools. After screening the applications a few are invited for interview [ 18 ]. However the process is time consuming and sometimes the number of applicants is overwhelming. Therefore faculties find it difficult to motivate faculty members to participate in the selection process. There is also often no consensus on the criteria that should be used to select future doctors. Given this situation, the nationwide medical admission test [ Test für Medizinische Studiengänge (TMS)], which had been abandoned in 1997, has been reintroduced by some faculties [ 19 ]. The TMS is comparable to the American Medical college admission test (MCAT) [ 20 ]. The TMS is not mandatory but allows students to improve their score and their chance of being selected to come for an interview.
Structure of the curriculum
In Germany, medical education is structured, not in years like many other countries, but in semesters or in a few instances, trimesters (Hamburg, Hannover). It takes six years (12 semesters) and three months to complete the curriculum, however on average, students require 6.8 years [ 3 ]. The curriculum is divided into three sections (Table 2 (Tab. 2) ):

- Basic science (2 years)
- Clinical science (3 years)
- Clinical year (1 year)
The majority of medical students follow this track. Some medical faculties have chosen to offer an experimental curriculum [ Modellstudiengang ] which offers an alternative process to becoming a doctor (Table 1 (Tab. 1) ) [ 21 ].
Basic science [Vorklinik]
The content and structure of the basic science section (also preclinical science) has remained largely unchanged. The main topics are anatomy, physiology, biochemistry and social sciences (Table 2 (Tab. 2) ). Courses are usually not graded beyond pass or fail. The distinction between clinical and basic science has been criticised and graduate students have rated large parts of the curriculum as clinically irrelevant [ 22 ]. Therefore there are increased efforts to place basic science in a clinical context [ 23 ], [ 24 ]. A three month nursing stage is a mandatory part of the basic science section to ensure first patient contact. However private institutions are increasingly offering additional preparatory classes, which might indicate the failure of the faculties to provide the necessary skills and knowledge to pass the state medical licensing examinations.
Clinical science [Klinik]
The clinical science section covers 21 medical specialties as listed in Table 2 (Tab. 2) . Previously each subject was taught separately. Now subjects are often taught in interdisciplinary teaching modules e.g. a “head module” combining Ear, Nose & Throat Medicine with Ophthalmology [ 25 ]. Additionally 12 new interdisciplinary teaching modules [ Querschnittsbereiche ] have been introduced (Table 3 (Tab. 3) ). Usually the first year is dedicated to the introduction of the clinical sciences with basic skill training in history taking and physical examination, general pathology, general microbiology, general pharmacology and laboratory medicine. Traditionally the clinical science section consisted mainly of lectures and seminars with limited patient exposure. To strengthen clinical experience, mandatory clerkships [ Blockpraktikum ] have been introduced in Internal Medicine, General Surgery, Paediatrics, Obstetrics & Gynaecology and General Practice. It is notable that a clerkship in Psychiatry, which is considered a core subject in many countries, is not mandatory. Clinical skills labs have been newly established in most faculties [ 26 ]. Additionally students have to complete four one-month elective clerkships, traditionally called Famulatur [ famulus latin: servant]. One clerkship has to be completed in the ambulatory setting. It is very popular to perform at least one elective outside Germany with a preference for English speaking countries.

Clinical year [Praktisches Jahr: PJ]
The final year is divided into three full-time clinical rotations, each lasting about 4 months (Table 2 (Tab. 2) ). Rotations in Internal Medicine and Surgery are mandatory and one rotation can be freely chosen from all the clinical specialties. Previously, the final year had been restricted to hospital based training sites. The new AppOÄ made it possible for the first time to complete a clinical rotation in an ambulatory setting, e.g. in General Practice [ 27 ].
Students usually assume more responsibilities gradually during the final year, comparable to a sub-internship. Legal issues regarding delegation and liability limit students’ opportunity to gain hands on experience [ 28 ]. Hospitals often rely on the work accomplished by the final year students [ PJler ]. Unfortunately, taking blood samples and inserting intravenous lines, which is done by auxiliary nurses in most other countries, keeps PJ students busy [ 29 ]. It is generally taken for granted that students learn skills on the job, but the degree of supervision and instruction varies widely [ 30 ]. Multiple projects to improve the quality of teaching in the clinical year have been presented and only a few can be cited here [ 31 ], [ 32 ].
As the German-speaking region of Switzerland offers a basic remuneration to final year students, there is a debate as to whether students should be paid. With the increasing shortage of physicians, some teaching hospitals are known to make special efforts to retain some students for postgraduate training.
Examinations
Until the new AppOÄ, the achievements of medical students in courses and clerkships were evaluated simply with a pass or fail. Only state licensing examinations were graded. From the faculties perspective the most radical changes with the new regulations for medical education were 1. the requirement to grade each course and clerkship and 2. the reduction of the number of licensing examinations from three to two. Grades are given on an ordinal scale ranging from 1 (excellent) to 5 (fail).
Strengthening the responsibility of faculties had mixed effects. Previously faculties invested only a minimal effort with respect to examinations. This was left to the centrally organised state licensing examination administered by state authorities [ Landesprüfungsamt ]. Students received certificates [ Scheine ] with little or no formal assessment in each of the subjects required in order to register for the licensing examinations. Most often physical attendance during the course was sufficient to obtain the course certificate. Only a few subjects such as anatomy required time consuming oral examinations. Previously, on the final licensing examination certificate only one summative grade of the written multiple choice exams and the final oral examination appeared on the diploma.
Now each subject must be graded and appears on the final diploma. On the one hand this has led to the introduction of modern assessment tools to evaluate practical skills like the objective structured clinical examination (OSCE) in several faculties [ 33 ]. On the other hand time and staff consuming examinations turned out to be a burden especially for smaller departments. For example psychosocial sciences in the preclinical section had to stop administering oral exams exceeding their staff capacities.
The new licensing examination consists of a written test with multiple choice questions (MCQs) and an (unstructured) oral examination. The administration and development of MCQs continues to be organised by the Institute for medical and pharmaceutical examination questions [ Institut für Medizinische und Pharmazeutische Prüfungsfragen (IMPP)] [ 34 ]. Although each medical faculty has its own curriculum, the IMMP has a catalogue of topics covered by the written exams [ Gegenstandskatalog ].
The first part of the medical licensing examination [ Erster Abschnitt der Ärztlichen Prüfung ], traditionally called “ Physikum ”, is the first hurdle students have to take. In order to proceed to the clinical section, this examination must be passed. The average initial failure rate is roughly 20%. The examination can be repeated twice; about 5% of all students never pass. This exam is not equivalent to the USMLE step 1 (United States Medical Licensing Examination).
The new second part of the medical licensing examination [Zweiter Abschnitt der Ärztlichen Prüfung ] of the clinical year has colloquially been termed “ Hammerexamen ” which can roughly be translated as “monster exam”. It has replaced three previously separate examinations and covers the entire spectrum of the clinical sciences. It consists of a written exam and a combined oral and practical exam. This exam lives up to its nickname since the previously low failure rate associated with the written part rocketed from 2% to 9%. Only a few students fail the oral and practical examination, which is only one of several reasons that this exam format has been criticised [ 35 ]. It is also felt that final year students are less well prepared than previous generations who took the last written examination before entering the clinical year. It is suspected that students focus on preparing for the “monster exam” and are distracted from clinical practical work and learning [ 36 ]. It had been hoped that the tendency of the IMPP to create multiple choice questions around rare syndromes would be abandoned in favour of more interdisciplinary and clinically relevant topics. Although the new case-based format still consisting of multiple choice questions is considered a significant improvement, remembering medical oddities and irrelevant facts still remains important [ 37 ].
Ranking of medical faculties
Ranking of faculties is rather new in Germany and, as elsewhere, dependent on the selection criteria. The German Academic Exchange Service has ranked medical faculties in various topics including research, infrastructure and student evaluation [ 38 ]. Ranking based on students’ performance in state licensing examination is also available [ 39 ]. Adjustment for differences in allocation of resources per capita or the proportion of foreign medical students has a significant impact on ranking.
A student who passes the final licensing examinations is awarded a license to practice medicine [ Approbation als Arzt ], but does not receive an academic degree with an academic title [ 40 ]. Graduates are authorised to use the German professional title Arzt/Ärztin (Physician), but are generally addressed informally with the honorary title "Dr." [ Doktor ]. As in other countries, writing a dissertation/thesis is an option required to obtain the academic degree “Dr. med.”. It is estimated that 70% of all graduates will eventually complete a dissertation, which is perceived to be important for career promotion and to attract patients [ 41 ].
Implementation of reforms in medical education
Excellent doctors are the result of an excellent medical education. The new "Regulation of the Licensing of Doctors (AppOÄ)" has certainly fostered important improvements in the education of medical students in Germany. The increased interest in medical education is documented by the dynamic development of the German Society for Medical Education [ Gesellschaft für Medizinische Ausbildung ] [ 42 ] and the introduction of the first postgraduate Master of Medical Education (MME) programme in Germany in 2005 [ 43 ]. Previously the only German-speaking MME-program was offered by the University of Bern in Switzerland.
It is uncertain if the goals of the new AppOÄ have been achieved as there are no official reports available. However, some professional organisations have conducted surveys.
Strengthening the role of General Practice in the face of an anticipated shortage of general practitioners was one of the multiple goals of the reform. Although some faculties have founded new Departments of General Practice, more than half of all faculties have no such department [ 44 ]. Similarly the stipulated strengthening of palliative care and pain management has also not yet been achieved in all faculties [ 45 ]. A national survey of teaching in Geriatrics, which had not previously been a component of the curriculum but is now covered by a mandatory interdisciplinary teaching module “Medicine of aging and the elderly”, revealed that less than half of all medical faculties provide teaching in this topic [ 46 ].
Mandatory evaluation of teaching was also among the aims of the AppOÄ. The main purpose of evaluation is quality control but also distribution of funds [ 47 ]. The last national survey on the evaluation of medical teaching in Germany was performed in 2000 before the reform [ 48 ]. Multiple evaluations of courses have been reported (selected examples [ 49 ], [ 50 ]) however there is no national standard and reporting bias is likely.
Unlike other university programmes awarding degrees to students, medical faculties in Germany are not subject to formal mandatory accreditation and reaccredidation procedures, since the final degree is a license awarded by the state. Although the German Council of Science and Humanities [ Wissenschaftsrat ] [ 51 ] has evaluated medical faculties, it is left to the discretion of the states as to how to ensure compliance with the stipulated requirements [ 52 ]. So far only one faculty has been on probation in 2005. It is conceivable that the states, which are responsible for funding medical faculties, have a conflict of interest given that external accreditation might reveal deficiencies due to under-funding.
Barriers to the implementation of stipulated reforms
Enacting the new AppOÄ was a pure administrative act and unfortunately was not provided with a budget to ensure its implementation [ 53 ]. Medical faculties are facing incredible difficulties to fulfil all the new requirements. The reduction in the number of lectures and rise in bedside teaching has increased the need dramatically for both clinical teachers and available patients. Although lip service is paid to the commitment for medical education, young academics are not rewarded for their efforts, and teaching, which must compete with research and patient care, is sometimes considered a lost cause [ 54 ].
At the same time, virtually all university hospitals to which medical schools are attached are in serious financial crisis, partly due to a new invoicing system and budget cuts [ 55 ]. Some of the previously state-owned university hospitals have been privatised (e.g. Giessen and Marburg) or transformed into foundations (e.g. Göttingen). This has increased the already pressing need for separate accounting of patient care financed by hospital revenues and teaching, and research covered by state grants or third-party funds. This has turned out to be extremely difficult since a significant proportion of the faculty is actively involved in both [ 56 ]. Only a few medical faculties (e.g. Kiel/Lübeck, Dresden/Leipzig) are administered completely separately from university hospitals [ 57 ]. The funding of medical education has been described in more detail elsewhere [ 58 ].
European perspective
In 1999, the Education Ministers from 29 European countries including Germany adopted the Bologna declaration [ 59 ]. The principal goals of this were to permit easily readable and comparable university degrees within Europe and to introduce a system essentially based on two main cycles, undergraduate and graduate, thus increasing mobility within Europe. In fact the mobility of medical students is already hampered at a national level by the multitude of non-compatible curricula although the Bologna declaration should also theoretically apply to medical education. However, this idea is neither encouraged by the German Medical Association nor some other medical associations [ 60 ]. The main reason to reject the implementation of the Bologna declaration for medical training is the fear of introducing a fast track “barefoot doctor”.
Improving and adapting education of medical students to the health needs of the population is a continuous process. The new "Regulation of the Licensing of Doctors (AppOÄ)" in Germany has stimulated multiple excellent projects to help future doctors meet these needs, but there is evidence that some of the stipulated changes have not been implemented. This review is an initial attempt to assess the compliance with the requirements of the AppOÄ and the success of the changes stipulated therein. Unfortunately it has not been possible to do justice to the educational activities in all 36 faculties, and while it is recognised that only a few selected projects have been discussed here, it is clear that mandatory external accreditation and periodic reaccreditations of medical faculties needs to be established in Germany [ 61 ].
List of abbreviations used
- AppOÄ: Approbationsordnung für Ärzte [Licensing Law for Medical Doctors]
- GPA: grade point average
- IMPP: Institut für Medizinische und Pharmazeutische Prüfungsfragen [Institute for medical and pharmaceutical examination questions]
- MCAT: Medical College Admission Test
- MCQ: multiple choice questions
- PJ: Praktisches Jahr [final year in medical school]
- TMS: Test für Medizinische Studiengänge [Test for medical education]
- USMLE: United States medical licensing examination
- ZVS: Zentralstelle für die Vergabe von Studienplätzen [Central office for the allocation of places in higher education]
Competing interest
I am a general practitioner working part-time in academia and part time in private practice which has influenced my review.
Acknowledgements
I would like to thank Wolfgang Himmel, Ilidkó Gagyor and Michael M. Kochen for helpful criticism.
Supplementary Material
Medical education in Germany
Affiliation.
- 1 University of Heidelberg Medical Hospital, Heidelberg, Germany. [email protected]
- PMID: 19811144
- DOI: 10.1080/01421590902833010
Following the changes made to the medical licensing regulations of 2002, medical education in Germany has been subject to radical modification, especially at undergraduate level. The implementation of the Bologna Process is still a matter of intense political debate, whilst positive movement has occurred in developing the professionalisation of teaching staff through a Masters Degree in Medical Education. In the area of postgraduate medical education, major restructuring of programmes is occurring, whilst the debate in continuing medical education is related to the amount of practical clinical education that is required.
- Education, Medical / organization & administration*
- Educational Measurement
- Faculty, Medical
- Organizational Innovation
- Skip to main content

- All countries /
- All study levels /
- Postgraduate /
- Health and Medicine /
13 Universities in Germany offering Postgraduate Medicine degrees and courses
More Information
Are you looking for Postgraduate courses in Medicine? Here you can find course providers offering full-time, part-time, online or distance learning options.
You've reached your limit of 10 Favourites
Charite Universitatsmedizin Berlin
THE World Ranking: 94
Dresden University of Technology
THE World Ranking: 161
RWTH Aachen University
THE World Ranking: 90

Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich
THE World Ranking: 38

Technical University of Munich
THE World Ranking: 30

University of Kiel (CAU)
THE World Ranking: 301

University of Wurzburg
THE World Ranking: 175

University of Bonn
THE World Ranking: 91

Ulm University
THE World Ranking: 193

University of Heidelberg
THE World Ranking: 47

Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz
THE World Ranking: 251

Karlsruhe Institute of Technology
THE World Ranking: 140
- Diagnostic Imaging
- Epidemiology
- Medical Sciences
- Medical Specialisations: F-O
- Medical Technology
- Medicine (General)
- Baden Wurttemberg
- North Rhine-Westphalia
- Rhineland-Palatinate
- Schleswig-Holstein
- Study level:
- Postgraduate
- Masters Degrees
- Doctoral Degrees
- Study mode:
- Online/Distance
Filter your results
Tell us about you.
- Nationality Select country Select country
- My current qualification is from Select country Yes No Select country Select country
- Current qualification {0} is not applicable for the study level you selected below. Qualification Qualification
- Grade type (only one grade type for your qualification) Grade type Grade type
- My score (current or expected) Please select Please select Please select Please select Please select Please select
Tell us your preferences
- Subject Medicine
- Qualification Postgraduate
- Destination Germany
- Study options
- Annual tuition fees
Subject areas
Qualification, destination.
- The UConn School of Business has grown to become one of the most comprehensive business schools in the country.
- NEW: Want to study in your home country for a foreign qualification? Find out more about cross-border study!


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The majority of universities that offer medical studies in Germany are public, i.e. 39. Some of the great upsides of that are that they have comprehensive infrastructures and research networks in Germany, that they are free of charge (no tuition fees), and offer the opportunity to engage in doctoral studies as well.
Medical education in Germany is not separated into an undergraduate and graduate degree. Rather, it is one comprehensive training. In Germany, a term that is frequently used to capture the interrelated academic and practical parts of the German doctoral training as well as the structure of the German health system is university medicine ...
2 years of prae-clinical studies. 3 years of clinical studies. 1 year of practical placement. A state examination graduate has the approbation to work as a physician in Germany and can start their residency in Germany. Curriculum. After 10+2, students must take an entrance test such as PMT, CBSE or AFMC, etc.
The best English-taught med schools in Germany. According to the QS rankings by subject, these are the top German universities that offer Medical programmes: Heidelberg University. LMU University. Charité - Universitätsmedizin Berlin. Technical University of Munich. Hamburg University. Goethe University Frankfurt. University of Tübingen.
The courses are heavily oversubscribed: each year, some 45,000 applications are submitted for one of the 9,000 or so available places to study medicine in Germany. The grade achieved in the applicant's university entrance qualification plays an important role: 30 percent of students are selected according to their performance in their final ...
One of the world's most popular non-anglophone study destinations, Germany is an ideal location for studying a medical degree, offering high-quality education at an affordable price. 32 German universities are included in the latest QS World University Rankings by Subject for Medicine, meaning there are plenty of options, depending on what type of university experience you're looking for.
Medicine offers just that, and a degree from Germany can pave the way. For example, the average gross salary for physicians and surgeons is €235,844 per year, which is equivalent to an hourly rate of €113. They also receive an average bonus of €22,122, according to Salary Expert. Top-Ranked Universities.
Learn about the admission requirements, funding options, and course structure for studying medicine in Germany. Find out which universities are the most prestigious and popular for medical education and how to apply for the state exam.
The course is completed with a state examination. The structure of the course is regulated uniformly throughout Germany via the Medical Licensing Regulations (ÄAppO). The course differs from training in other countries in a number of ways. After the basic course of four semesters and the first of a three-part "medical examination", a main ...
Not all German universities are among the world's medical elite. So check rankings among German medical schools to ensure that you apply to the right school and receive a quality education. Top MCI-approved medical universities in Germany 1. Humboldt University 2. Heidelberg University 3. LMU Munich
Medical education in the Federal Republic of Germany is offered through one of the 36 medical faculties of public universities that are tax-funded through the respective states . Private universities, including but not limited to the Universitaet Witten Herdecke, or the Austrian-based Paracelcus Medizinische Privatuniversitaet with a location ...
A good knowledge of German is important if you want to study medicine. Although the specialist literature can, of course, be obtained in English, lectures and examinations are held mostly in German. After all, budding doctors must be able to communicate with their patients. It's worth learning German anyway because the career prospects for ...
Medicine and health sciences. Those who wish to become a doctor in Germany require good marks and a high level of discipline. A degree course in medicine takes about six years and finishes with the German Medical Licensing Examination. Bachelor's and Master's courses in health sciences are an alternative. Medicine graduates have a very good ...
Germany's first international medical program! Discover a state-of-the-art medical education in an international environment. Get informed and apply now! ... UMFST of Targu Mures, with its more than 11,000 students, is not only the largest, but also the most research-intensive medical institution of higher education in Romania. The University ...
Employability rank - 70 Number of students - 30000 Top programs - Dentistry, International Health, Medical Education Heidelberg University is considered one of the best medical colleges in Germany and is known for its practical approach to education and research. The university has partnerships with over 27 institutions and is connected for ...
You will have access to world-class medical education, affordable living, and an excellent quality of life. Job Prospects for International Medical Graduates in Germany. ... According to the German Medical Association, the average salary for a doctor in Germany is around €60,000 per year. However, salaries can range from €30,000 to € ...
The Master's degree in Medical Education at the HMU focuses on three areas: Educational Sciences, the Social Sciences and the elective areas of Health Sciences (including Therapy Sciences) or Nursing Sciences. The part-time model of the HMU Health and Medical University Potsdam provides part-time students with the opportunity to gain academic ...
Germany is a fast-growing and ever-evolving country which is part of the European Union. It ranks fourth in the list of the world's most advanced economies. Once graduate from UMCH, you have the right to practise as a doctor all around Europe and worldwide. Germany's medical education and institutions are in the top 10 of every chart.
Postgraduate medical training in Germany has undergone several changes since then [ 4 ], [ 5 ]. Undergraduate medical education has previously been described in detail [ 6 ]. About 10,000 medical students graduate in Germany each year [ 7] and over 95% plan to begin postgraduate medical training [ 8 ].
Germany currently employs an integrated medical curriculum that typically begins right after high school and consists of a 2-year long pre-clinical segment teaching basic sciences and a 4-year clinical segment leading medical students to the practical aspects of medicine. On the other hand, the US education is a two-stage process.
To apply to study medicine in Germany, you must create an application in the hochschulstart portal. This is possible in the application period only. To give you an example: For the winter semester 2020, applications were accepted from 01.07.2020 - 25.07.2020 (respectively 20.08.2020 for students who got their A-Levels in 2020).
Postgraduate Medical Education in Germany in English. Although English-taught undergraduate programs are unavailable, there is scope for postgraduate degrees. According to DAAD's official listing of programs, there are 25 study programs. The duration of these programs differs. Take a look at some of these programs tabulated below.
Background. Patient education has been an essential part of medical training in Germany since the 1980s, when a group of young physicians rejected the traditional relationship between doctors and patients, and felt that the only way to ensure that people with diabetes stay healthy is to allow them to self-manage.
The reform of the education of doctors with the regulation for licensing of doctors (Approbationsordnung) of 27 June 2002 was a fundamental one. ... [Medical education in Germany: past successes and future challenges. An overview] Bundesgesundheitsblatt Gesundheitsforschung Gesundheitsschutz. 2006 Apr;49(4):325-9. doi: 10.1007/s00103-006-1237-4.
History of Final Year Medical Education in Germany. Medical education in Germany has undergone drastic changes in the last decades [1], [2], [3].In marking a transition between undergraduate training and future medical occupation, the final year medical education ("Praktisches Jahr - PJ") fulfils a key role in introducing medical students to their future profession within a working ...
Undergraduate education e.g. preparatory classes for medical school, prevalent in some countries, do not exist in Germany. Therefore, the term undergraduate or graduate education does not apply in the strict sense. In Germany, the average age of medical students is 21.4 years when they start medical school [ 14 ].
Germany. Organizational Innovation. Teaching. Following the changes made to the medical licensing regulations of 2002, medical education in Germany has been subject to radical modification, especially at undergraduate level. The implementation of the Bologna Process is still a matter of intense political debate, whilst positive movement has occ
The UConn School of Business has grown to become one of the most comprehensive business schools in the country. NEW: Want to study in your home country for a foreign qualification? Find out more about cross-border study! 13 Universities in Germany offering postgraduate Medicine degrees and courses. Plan your studies abroad now.