- How it works


Useful Links
How much will your dissertation cost?
Have an expert academic write your dissertation paper!
Dissertation Services

Get unlimited topic ideas and a dissertation plan for just £45.00
Order topics and plan

Get 1 free topic in your area of study with aim and justification
Yes I want the free topic

Law Dissertation Topics
Published by Owen Ingram at January 9th, 2023 , Revised On April 26, 2024
Law dissertations can be demanding because of the need to find relevant regulations, cases, and data to address the research problem successfully. It is of utmost importance to critically examine facts before framing the research questions .
Selection of the most appropriate legal terms and legal authorities, whether online or in print, can be challenging especially if you have not tackled a law dissertation project before.
To help you select an intriguing law dissertation topic, our expert writers have suggested some issues in various areas of law, including trust law, EU law, family law, employment and equality law, public law, tort law, intellectual property rights, commercial law, evidence, and criminal law, and human rights and immigration law.
These topics have been developed by PhD-qualified writers of our team , so you can trust to use these topics for drafting your dissertation.
Review step by step guide on how to write your own dissertation here.
You may also want to start your dissertation by requesting a brief research proposal from our writers on any of these topics, which includes an introduction to the topic, research question , aim and objectives , literature review along with the proposed methodology of research to be conducted. Let us know if you need any help in getting started.
Check our dissertation examples to get an idea of how to structure your dissertation .
Review the full list of dissertation topics for 2024 here.
2024 Law Dissertation Topics
Topic 1: the role of international criminal laws in reducing global genocide.
Research Aim: This study aims to find the role of international criminal laws in reducing global genocide. It will be an exploratory study identifying the explicit and implicit effects of international criminal laws on the worldwide genocide. It will analyse different incidents of international genocide and find out how international criminal laws played a positive role to reduce these incidents. Lastly, it will recommend possible changes in the international criminal laws to effectively mitigate global genocide. And it will be done by comparing criminal laws of world-leading powers to reduce genocide.
Topic 2: Impact of Anti-Racism Employment Laws on Organisational Culture- A Comparative Study on the Anti-Racism Employment Laws in the US and Canada
Research Aim: This research aims to find the impact of anti-racism employment laws on the organisational culture in the US and Canada in a comparative analysis. It will identify the change in employees’ behaviour after implementing anti-racism laws. Moreover, it will find whether employees gleefully welcomed these laws or showed resistance. And how do these laws affect the organisations’ performance that strictly implemented them?
Topic 3: Globalization, international business transactions, and commercial law- A perspective from literature.
Research Aim: Students and practitioners can find the law of international business transactions as a subfield within a broader field of international commercial law to be somewhat amorphous.
This study will explain the impact of globalization on international business transactions and commercial law by establishing some necessary links between the study of transnational business law and related fields of international studies. This study also aims to address theories about foreign business regulation, such as the idea that it is free of power politics. For the collection of data existing literature will be studied. And the methodology of this research will rely on existing previous literature.
Topic 4: Investigating the impact of competition law on the businesses in the UK- Post Brexit
Research Aim: This study aims to investigate the impact of competition laws on businesses in the Post-Brexit UK. The proposed study will not only analyze the performance of the businesses with the current competition laws. But also analyze the impact of possible changes in competition laws on the businesses in the post-Brexit UK. And it will also incorporate the possible difference of changes in competition laws in deal, no-deal, hard deal, and soft deal scenarios. This way of individually analyzing the difference of competition laws due to the status of the UK’s deal with the EU will give better insights into how businesses will be affected by these laws in the post-Brexit UK.
Topic 5: A comparison between Islamic and contemporary laws against rape. Which law is the most effective in preventing this horrific crime?
Research Aim: Since several years, marital and non-marital relations in Muslim majority countries have been a source of controversy. Under Islamic law, it is strictly forbidden for a Muslim, or even non-Muslim to engage in illicit sexual relations with the opposite gender under any situation. The current study will help us understand the concepts presented in Islamic laws about rape cases. In this context, a comparative analysis of Islamic and contemporary law will be explained. It will also identify efficient and effective strategies to prevent this horrific crime.
Law Dissertation Topics For Covid Crisis
Topic 1: the legal implications of the covid-19 pandemic on canadian immigration and the way forward..
Research Aim: This study will focus on how the Canadian government benefits from resources accrued from immigration, the impact of COVID-19 on Canadian Immigration, the current legislation on immigration, the effects of COVID-19 on the immigration law, the possible amendments that could help cushion the impact and the way forward.
Topic 2: Effect of COVID-19 on the United States Immigration policies; an assessment of International Legal agreements governing pandemic disease control and the way forward.
Research Aim: This research will focus on the pandemic’s effect on immigration policies in the United States. It also suggests the required steps based on the laws that regulate government acts during an outbreak of a pandemic.
Topic 3: Creating legal policies in preparedness for the global pandemic; lessons from COVID-19 on Canadian immigration policies.
Research Aim: This research will focus on how the COVID-19 pandemic hit the world and how most countries seemed unprepared. Historical background of the flu pandemic can also be made to assess how the world overcame the pandemic. And the need for the Canadian government or any other country you wish to choose can prepare for a global pandemic by creating legal policies that could help prepare ahead for such a period, such as policies on scientific research and funding.
Topic 4: The need for uniformity of competition law and policy in Gulf Cooperation Council Countries; An approach to the European Union standard.
Research Aim: This research will focus on the Gulf Cooperation Countries and their current legislation on competition law and its implications. Countries under the European Union’s competition law, the legal implications, and the need to consider such a part.
Topic 5: The need for competition law and policy enforcement; An analysis of the Gulf Cooperation Council Countries.
Research Aim: This research focuses on the Gulf Cooperation Council Countries’ competition laws and their enforceability. It analyses the benefits of enforcing the competition law and looks at the European Union uniformed laws and its benefits. It looks into the various countries, how the competition law currently works, and how it can affect each country’s economy in a better way or adequately enforced.
Topic 6: Provisions of the law on rape, the need to expand its coverage on the misuse of its provisions, and false accusations.
Research Aim: This research will focus on the law’s present provisions on rape and rape victims and the recent false accusations.
Topic 7: Summary dismissal of workers during the COVID-19 pandemic, the legal implications under the labour law, and the way forward. The case study of Nigeria
Research Aim: This research will focus on the statistics of people who were summarily dismissed during the COVID-19 pandemic based on natural occurrences, provisions of the law against summary dismissal, and its enforcement, and how this can be cushioned against future events. The need to expand the labour law to cover similar situations for the protection of workers.
Topic 8: A legal assessment of the settlement of international disputes through the peaceful process and its effectiveness
Research Aim: This research focuses on the mode of dispute settlement in the international community, assessment of international laws and treaties on peaceful settlement of conflicts among countries of member states, the methods of dispute settlements, its strengths and weaknesses, and the need to improve the current mechanisms of peaceful settlement in the international community.
Topic 9: The protection of minority shareholders and the majority shareholders' power in Companies, a critical analysis of the Nigerian Companies and Allied Matters Act provisions.
Research Aim: This research will focus on the law’s provisions on protecting minority shareholders in companies and the majority shareholders’ power. How effective are these provisions in protecting the minorities against the management of the majority shareholders and the way forward
More Law Dissertation Topics 2024
Topic 1: world bank developmental projects and greater accountability.
Research Aim: Examine communities impacted by development operations under the World Bank Development project schemes using the project law model to understand the lack of participation and successful influence of these communities to improve accountability and good governance.
Topic 2: The right to bear arms: Rethinking the second amendment
Research Aim: Gun control and the right to bear arms has been an ever-evolving web discourse in the United States. The research aims at analysing how gun control laws have changed in the USA since specifically focusing on the 2nd Amendment and its original framework.
Topic 3: Rethinking the international legal framework protecting journalists in war and conflict zones.
Research Question: Is the current legal framework still appropriate for protecting journalists in today’s conflict zones? Research Aim: The primary body of law that is set out to protect journalists includes the Geneva Conventions and their additional Protocols. However, since the time they have been drafted and decades after, there have been conspicuous changes to the way warfare is conducted. It is imperative to examine this body of law in order to improve it as journalists have now become prime targets in war zones and conflict areas because of their profession.
Topic 4: A critical analysis of employment law of disabled individuals in the UK and what new policies can be integrated to increase its efficiency.
Research Aim: Employment or labour law has always been under the limelight. Many critiques and researchers have proposed different amendments to the existing law pertaining to labour and employee. The main aim of the research is to critically analyse the employment law of disabled individuals in the UK along with effective recommendations that need to be made in order to make the existing law more efficient and effective.
Topic 5: A critical evaluation of racial discrimination laws in developed countries and how it impacts the workplace environment
Research Aim: Racial discrimination has always been a controversial issue in almost every part of the World. However, many developed countries (companies) face severe racial discrimination issues that directly impact their name and brand value. Therefore, this research provides a critical evaluation of the racial discrimination laws, particularly in developed countries. Moreover, the research will be focusing on how racial discrimination laws are impacting the workplace environment.
Topic 6: A comparative analysis of legislation, policy, and guidelines of domestic abuse between UK and USA.
Research Aim: Domestic laws basically deal with and provide criminal rules for punishing individuals who have physically or emotionally harmed their own family members. It has been found out that many domestic cases of abuse are not reported to the concerned authority. Due to this reason, the main focus of the research is to conduct a comparative analysis of legislation, policy, and guidelines of domestic abuse between the UK and the USA and how effective both the countries have been to minimise domestic abuse.
Topic 7: Analyzing the negative impact of technology in protecting the intellectual property rights of corporations.
Research Aim: Intellectual property has gained significant importance after the emergence of counterfeit products coming from different parts of the world. It has been found out that many factors have motivated the sale of counterfeit products. Therefore, this research aims at analysing the negative impact of technology in protecting the intellectual property rights of products and corporations.
Topic 8: A critical assessment of the terrorism act of 2010 and its impact on Muslims living around the globe.
Research Aim: Since the incident of 9/11, the entire world has been under the pressure of terrorism activities, especially Muslims living around the world. Therefore, this research intends to critically assess the terrorism act of 2010 and its impact on Muslims living around the globe.
Trust Law Dissertation Topics
The trust law requires the settler to meet the three certainties, including the object, intention, and subject matter. As posted to a moral obligation or mere gift, confidence of choice can be best described as clarity of purpose. Some interesting dissertation topics in the field of trust law are listed below:
- To investigate the attitude of the courts to trusts supporting political agendas.
- To identify and discuss principles on which half-secret and full secret trusts are enforced? Does a literature review highlight circumstances where it is essential to consider whether such beliefs are constructive and express?
- The role and impact of trust law as asset portioning and fiduciary governance
- From law to faith: Letting go of secret trusts
- Critical analysis of the statement “Traditionally, equity and the law of trusts have been concerned with providing justice to balance out the rigour of the common law” regarding modern equity development/operation.
- Should the assumption of resulting trusts and progression be abolished in this modern age? A critical review of the literature
- A critical examination of the courts’ concern of financial reward in the context of “trustee powers of investment”
- Does the doctrine of cypress do justice to the intentions of the testator?
- The impact of the decision of Harrison v Gibson on the law of the clarity of intention?
- The approval of trustees in the Zimbabwean law of trusts
Want more? Read this.
How Can ResearchProspect Help?
ResearchProspect writers can send several custom topic ideas to your email address. Once you have chosen a topic that suits your needs and interests, you can order for our dissertation outline service which will include a brief introduction to the topic, research questions , literature review , methodology , expected results , and conclusion . The dissertation outline will enable you to review the quality of our work before placing the order for our full dissertation writing service!
European Law Dissertation Topics
European law has recently attracted wide attention from the academic world, thanks to the growing influence of European Law on administrative law in EU members. It should be noted that every aspect of life in European states is significantly affected by European law, and therefore this area of research has gained tremendous popularity. Some exciting and specific research areas are given below:
- A critical review of the European anti-discrimination Law
- To investigate the economics and history of European Law.
- An investigation of the European human rights law
- Investigating the impact of “Freedom of Speech” on the German economy
- Investigating the impact of immigration laws on the German economy
- How the French parliamentary sovereignty has been affected by the European Union
- Uniform interpretation of European patent law with a unique view on the creation of a standard patent court
- The impact of European consensus in the jurisprudence of the European court of human rights
- The impact of the European convention on human rights on the international human rights law
- A critical analysis of the tensions between European trade and social policy
- To investigate the European Union’s enforcement actions and policies against member countries.
- European Laws amidst the Brexit process
Read this Article.
Family Law Dissertation Topics
A wide range of topics are covered under the field of family law and the law of children. Essentially, this area of law takes into consideration the registration of marriages, statutory rights concerning marriage, the effects of a decree, void and voidable marriages, the impact of the Human Rights Act, the legal stature of unmarried and married individuals, and the case for reform of UK family law . Other research areas include enforcing financial responsibilities in the Magistrates court, enforcing the arrears of maintenance payments, the award of maintenance, enforcing financial obligations to children or a child, financial orders for children, and the Child Support Act. An extremely intriguing area of law that has gained tremendous popularity in the modern era, some specific dissertation topics in this area of law studies are listed below:
- Investigating therapeutic and theoretical approaches to deal with spouse abuse in light of the UK government’s latest research on domestic violence
- Unmarried fathers’ access to parental responsibility – Does the current law enforce rights and responsibilities towards children?
- To study the criminal justice process involving a child witness.
- The children’s right to participation – Rhetoric or Reality? – A critical review of literature from the past two decades
- To study the position of unmarried fathers in the UK.
- Does the UK Family law need a major reform?
- A critical review of the rights of married women in real estate
- Child welfare and the role of local authorities
- To study the legal and social foundations of parenting, civil partnership, and marriage.
- To examine whether the Child Support Act has positively influenced child maintenance?
“Complete this short online form and provide as much information as possible to receive instant quotes from our writers specialising in your area of research.”
Employment Law Dissertation Topics
Employment and equality law governs the relationship between the government, trade unions, employers, and employees. Employment and equality law in the UK is a body of law that prevents bias and negative attitudes towards someone based on their ethnicity or race rather than work skills and experience. Some interesting dissertation topics in this area of law are below:
- A critical investigation of the right to fair labor practices in the United Kingdom
- To determine the job’s inherent requirements as a defence to unfair discrimination or a claim – A comparison between the United Kingdom and Canada.
- The role of the South African Labour Relations Act in providing unhappy staff sufficient protection against unfair dismissals and discrimination at the workplace
- To investigate the impact of HIV/AIDS on employees’ lives with a focus on unfair dismissal and discrimination.
- To assess ethnic discrimination in the European Union: Derogations from the ban on discrimination – Sexual harassment – Equal pay for equal value work.
- To study the international employment contract – Regulation, perception, and reality.
- To identify and discuss challenges associated with equality at work.
- A study of the legal aspects of the relationship between employer and employee
- How influential is the role of trade unions in English employment law?
- A critical review of discrimination policies in the UK
Order a Proposal
Worried about your dissertation proposal? Not sure where to start?
- Choose any deadline
- Plagiarism free
- Unlimited free amendments
- Free anti-plagiarism report
- Completed to match exact requirements
Commercial Law Dissertation Topics
Commercial law, also known as business law, is the whole body of substantive jurisprudence applicable to the conduct, relations, and rights of sales, trade, merchandising, and businesses and persons associated with commerce. Important issues of law covered by commercial law include real estate, secured transactions, credit transactions, bankruptcy, banking, and contracts. An intriguing area of law within the UK, specific topics for your law dissertation are listed below:
- The impact of legislation for the regulation of investments services with EU economic area on the EU financial services market
- Handling regulatory involvement incorporates organisational structure and strategy.
- A study of convergence and complementarities concerning international corporate governance
- How drafting and diffusion of uniform norms can help to harmonise the law of international commercial arbitration?
- Convergence and adaption in corporate governance to transnational standards in India
- A critical review of the international commercial arbitration system
- Analysing the international commercial law on risk transfer
- The role of the tripartite financial system in the UK on economic development
- A comparative analysis of European contract law, international commercial contracts law, and English commercial contracts law
- Is the European contracts law meeting the needs of the commercial community?
- A critical review of anti-corruption legislation in the UK
- The problems of director accountability in the UK and the impact of soft and hard law on corporate governance
Criminal and Evidence Law Dissertation Topics
Criminal law can be defined as a system of law dealing with the punishment of criminals. Criminal evidence, on the other hand, concerns evidence/testimony presented in relation to criminal charges. Evidence can be presented in various forms in order to prove and establish crimes. A wide array of topics can be covered in this subject area. To help you narrow down your research focus, some interesting topics are suggested below:
- The politics of criminal law reform with a focus on lower-court decision making
- To understand and establish the historical relationship between human rights and Islamic criminal law
- Investigating the rights of victims in internal criminal courts
- The efficacy of the law of rape in order to prevent misuse by bogus victims and to protect rightful victims
- To assess the criminal law’s approach to Omissions
- To investigate the issues associated with the identification of the distribution, extent, and nature of the crime
- A critical review of the Bad Samaritan laws and the law of omissions liability
- How international criminal law has been significant influenced by the “war on terrors”?
- The efficacy of modern approaches to the definition of intention in International criminal law
- The efficacy of the law of corporate manslaughter
Company Law Dissertation Topics
Company law, also known as the law of business associations , is the body of law that deals with business organisations and their formation, registration, incorporation, governance, dissolution, and administration. Some suggestions for company law dissertation topics are listed below:
- Developing equity markets in growing economies and the importance of corporate law
- A critical review of English company law and its effects on member workers and creditors
- To investigate the essential aspects of corporate law.
- To study business responsibilities for human rights.
- Identifying disparities in corporate governance – Theories and Realities
- The external relations of company groups in Zambian Corporate law
- To study corporate governance practices concerning the minority stakeholders.
- Establishing and evaluating arguments for and against “stakeholder theory.”
- The importance of non-executive directors in the British corporate legal system
- Investigating the regulation of the UK public company
Hire an Expert Writer
Orders completed by our expert writers are
- Formally drafted in academic style
- Free Amendments and 100% Plagiarism Free – or your money back!
- 100% Confidential and Timely Delivery!
- Appreciated by thousands of clients. Check client reviews

Intellectual Property and Tort Law Dissertation topics
All forms of legal injury are dealt with under the subject area of tort law. Essentially, tort law helps to establish the circumstances whereby a person may be held responsible for another person’s injury caused by either accident on intentional acts. On the other hand, intellectual property covers areas of law such as copyright, patents, and trademark. Trademark dissertation topics trademarks directive, trademarks act, infringement of trademarks such as revocation, invalidity, and the use of similar marks. Some interesting dissertation ideas and topics of tort law and intellectual property are suggested below to help your law studies.
- The efficacy of intellectual property rights in the UK under influence of European Law
- The efficacy of UK copyright law concerning the needs of rights users and holders
- The impact of intellectual property right on economic development
- To investigate the right of confidence in the UK
- Does the trademark law ensure sufficient protection in England?
- The impact of European Law on intellectual property rights in the UK
- The end of the road for loss of a chance?
- To assess the success ratio of psychiatric injury claims in the UK
- Should a no-fault system be implemented into UK law or should the law of negligence apply to personal injury claims?
- A critical review of economic loss in 21 st century tort law
Human Rights and Immigration Law
The primary objective of human rights and immigration law is to ensure and protect human rights at domestic, regional, and international levels. With the world becoming a global village, human rights and immigration laws have attracted significant attention from academicians and policymakers. Some interesting law dissertation topics in this subject area are suggested below:
- To assess the efficacy of the common European Asylum system in terms of immigration detention.
- A historical analysis of Britain’s immigration and asylum policies
- A critical analysis of immigration policy in Britain since 1990
- A critical analysis of the right of the police and the public right to protest under PACE 1984
- The right of prisoners to vote under the European law of human rights
- Arguments for and against the death penalty in English Law with a focus on human rights treatise
- A critical analysis of the right to private life and family for failed asylum seekers
- The impact of UK immigration policies on the current education industry
- How beneficial the points system has really been in regards to create a cap in the British immigration system
- To study the impact of privatisation on immigration detention and related functions in the UK.
More Human Rights Law Dissertation Topics
Pandemic Law Dissertation Topics
Coronavirus, also known as the Covid-19, has become the most trending topic in the world since the outbreak of the Covid-19 pandemic that started in China. Here are some interesting Corona Virus or Covid 19 Pandemic Law topics that you can consider for your law dissertation.
- Co-parenting in the coronavirus pandemic: A family law scholar’s advice
- How San Diego law enforcement operated amid Coronavirus pandemic
- Pandemic preparedness in the workplace and the British with disabilities act
- Why In a pandemic, rumors of martial Law fly despite reassurances
- Investigating About the ADA, the Rehabilitation Act, and COVID-19
- Resources to support workers in the UK during the Coronavirus pandemic
- Coronavirus (COVID-19) Pandemic:
- A legal perspective
- Navigating the Coronavirus Pandemic
- Coronavirus Pandemic (COVID-19) and employment laws in the UK going forward
- Coronavirus Pandemic (COVID-19) and employment laws in the US going forward
- Coronavirus Pandemic (COVID-19) and employment laws in Australia going forward
More Law Dissertation Topics
- A critical analysis of the employment law of disabled individuals in the UK and what new policies can be integrated to increase its efficiency
- A critical evaluation of racial discrimination laws in developed countries and how it impacts the workplace environment
- A comparative analysis of domestic abuse with the legislation, policy, and domestic abuse guidelines between the UK and USA.
- Analysing the negative impact of technology in protecting the intellectual property rights of corporations.
- A critical assessment of the terrorism act of 2010 and its impact on Muslims living around the Globe.
Hire an Expert Plagiriasm Checker
Uk’s best academic support services. how would you know until you try, important notes:.
As a law dissertation student looking to get good grades, it is essential to develop new ideas and experiment with existing law dissertation theories – i.e., to add value and interest in the topic of your research.
The field of law dissertation is vast and interrelated to many other academic disciplines like civil engineering , construction , project management , engineering management , healthcare , mental health , artificial intelligence , tourism , physiotherapy , sociology , management , project management , and nursing . That is why it is imperative to create a project management dissertation topic that is articular, sound, and actually solves a practical problem that may be rampant in the field.
We can’t stress how important it is to develop a logical research topic based on your fundamental research. There are several significant downfalls to getting your case wrong; your supervisor may not be interested in working on it, the topic has no academic creditability, the research may not make logical sense, and there is a possibility that the study is not viable.
This impacts your time and efforts in writing your dissertation as you may end up in the cycle of rejection at the initial stage of the dissertation. That is why we recommend reviewing existing research to develop a topic, taking advice from your supervisor, and even asking for help in this particular stage of your dissertation.
While developing a research topic, keeping our advice in mind will allow you to pick one of the best law dissertation topics that fulfill your requirement of writing a research paper and add to the body of knowledge.
Therefore, it is recommended that when finalising your dissertation topic, you read recently published literature to identify gaps in the research that you may help fill.
Remember- dissertation topics need to be unique, solve an identified problem, be logical, and be practically implemented. Please look at some of our sample law dissertation topics to get an idea for your dissertation.
How to Structure your Law Dissertation
A well-structured dissertation can help students to achieve a high overall academic grade.
- A Title Page
- Acknowledgements
- Declaration
- Abstract: A summary of the research completed
- Table of Contents
- Introduction : This chapter includes project rationale, research background, key research aims and objectives, and the research problems. An outline of the structure of a dissertation can also be added to this chapter.
- Literature Review : This chapter presents relevant theories and frameworks by analysing published and unpublished literature available on the chosen research topic to address research questions . The purpose is to highlight and discuss the selected research area’s relative weaknesses and strengths while identifying any research gaps. Break down the topic, and binding terms can positively impact your dissertation and your tutor.
- Methodology : The data collection and analysis methods and techniques employed by the researcher are presented in the Methodology chapter which usually includes research design , research philosophy, research limitations, code of conduct, ethical consideration, data collection methods and data analysis strategy .
- Findings and Analysis : Findings of the research are analysed in detail under the Findings and Analysis chapter. All key findings/results are outlined in this chapter without interpreting the data or drawing any conclusions. It can be useful to include graphs, charts and tables in this chapter to identify meaningful trends and relationships.
- Discussion and Conclusion : The researcher presents his interpretation of the results in this chapter, and states whether the research hypothesis has been verified or not. An essential aspect of this section is establishing the link between the products and evidence from the literature. Recommendations with regards to implications of the findings and directions for future may also be provided. Finally, a summary of the overall research, along with final judgments, opinions, and comments, must be included in the form of suggestions for improvement.
- References : Make sure to complete this by your University’s requirements
- Bibliography
- Appendices : Any additional information, diagrams, and graphs used to complete the dissertation but not part of the dissertation should be included in the Appendices chapter. Essentially, the purpose is to expand the information/data.
About ResearchProspect Ltd
ResearchProspect is the world’s most trusted academic writing service that provides help with Dissertation Proposal Writing , PhD Proposal Writing , Dissertation Writing , Dissertation Editing, and Improvement .
Our team of writers is highly qualified. They are experts in their respective fields. They have been working for us for a long time. Thus, they are well aware of the issues and the trends of the subject they specialise in.
Free Dissertation Topic
Phone Number
Academic Level Select Academic Level Undergraduate Graduate PHD
Academic Subject
Area of Research
Frequently Asked Questions
How to find law dissertation topics.
To find law dissertation topics:
- Research recent legal developments.
- Explore unresolved issues or debates.
- Analyze gaps in existing literature.
- Consider societal or technological influences.
- Consult professors and peers.
- Select a topic aligning with your passion and career aspirations.
You May Also Like
Need interesting and manageable Business dissertation topics or thesis? Here are the trending Business dissertation titles so you can choose the most suitable one.
For any company and organisation, one of the most important yet sensitive assets is its information. Therefore, it is essential to keep the data secured from getting stolen and avoid getting it used for malicious activities.
Find the most unique and interesting dissertation topic ideas for translation studies to help you in your translation dissertation/ thesis.
USEFUL LINKS
LEARNING RESOURCES

COMPANY DETAILS

- How It Works

Ph.D. Program
The ph.d. in law degree.
The Ph.D. in Law degree program is designed to prepare J.D. graduates for careers as legal scholars and teachers through a doctoral program aimed at the production of a substantial body of academic research and writing under the close supervision of a three-member faculty dissertation committee. Unlike programs designed for students who wish to learn about law from the disciplinary perspectives of the social sciences or the humanities, the Ph.D. in Law is directed at students who wish to pursue advanced studies in law from the perspective of the law. This program offers emerging scholars an opportunity to contribute to the development of law as an academic field, and it provides an alternate pathway into law teaching alongside existing routes such as fellowships, advanced degrees in cognate fields, legal practice, and clerkships.
Because our entering Ph.D. students will have already completed their J.D. degrees, the anticipated course of study toward the Ph.D. in Law degree is three academic years and two summers in residence. In their first two semesters, Ph.D. students will enroll in courses designed to help them acquire the background and research skills needed to complete a dissertation in their field of interest and to prepare them for qualifying examinations that test the depth and breadth of the literacies and skills they have acquired. During their second year, students will prepare a dissertation prospectus and begin work on a dissertation. The dissertation may take the form of either three law review articles or a book-length manuscript and will make up a portfolio of writing that will be essential for success in the job market. Ph.D. students will also gain experience in the classroom, and receive the full support of Yale Law School’s Law Teaching Program , which has had remarkable success in placing graduates in tenure-track positions at leading law schools.
Ph.D. students receive a full-tuition waiver, a health award for health insurance coverage, and a stipend to cover their year-round living expenses, as well as support for participation in national and international conferences.
Applications for admission to the Ph.D. in Law program are available starting on August 15. The deadline for submission of all materials is December 15. Applicants to the Ph.D. in Law program must complete a J.D. degree at a U.S. law school before they matriculate and begin the Ph.D. program. Any questions about the program may be directed to Gordon Silverstein, Assistant Dean for Graduate Programs, at [email protected] .
Watch Gordon Silverstein, Assistant Dean for Graduate Programs, describe the Ph.D. program at Yale Law School.
Section Menu
Student Profile Videos

Rafael Bezerra Nunes LLM
A student perspective on getting an LLM at Yale Law School, constitutional law, and the graduate programs community.

Poppy Harlow ’22 MSL
A perspective on the M.S.L. program and what it was like to dive into the study of constitutional law, civil procedure, and criminal law as a journalist.

Harley F. Etienne MSL
A student perspective on the M.S.L. program and the inspiring community at Yale Law School.
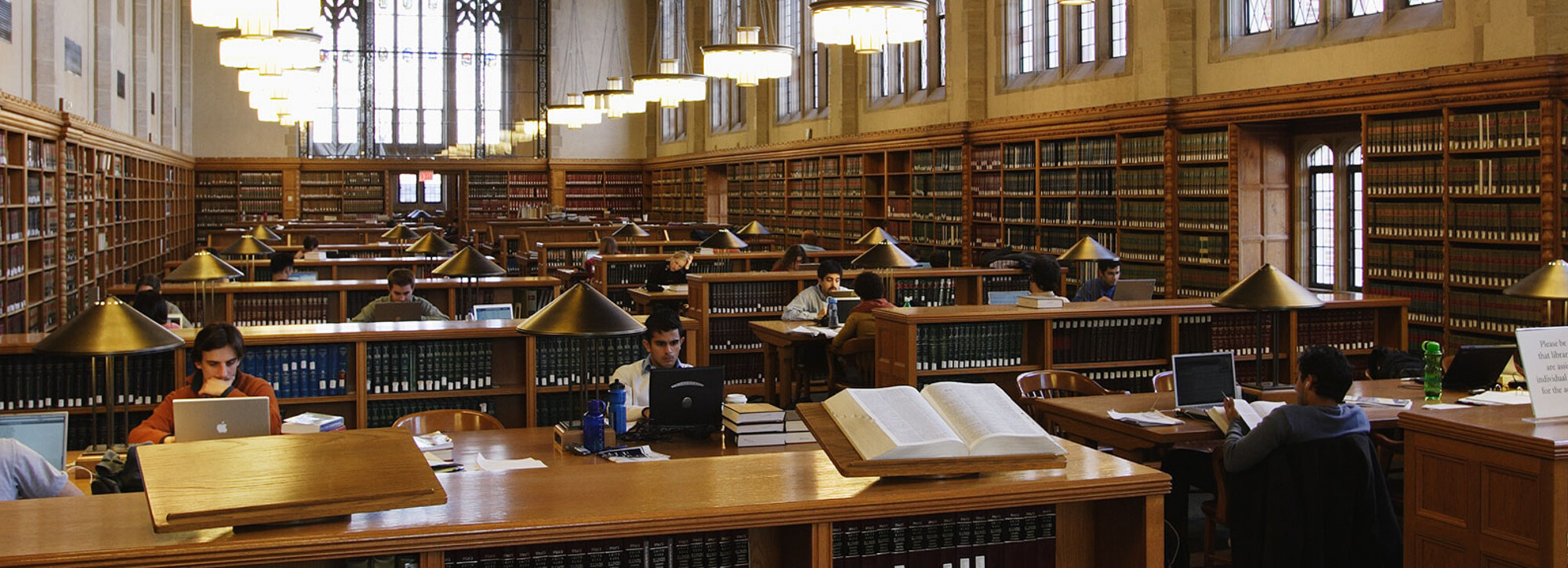
Graduate Student Life

2020 and 2021 Graduate Programs alumni celebrate in the YLS Courtyard with Assistant Dean Gordon Silverstein before their in-person ceremony in May 2022

2022 Graduate Program degree candidates with Dean Heather K. Gerken in April 2022

Yale is the one place where going to law school doesn’t mean sitting on the sidelines; it means making headlines.

- School of Law
Ph.D. in Law
The Ph.D. in Law prepares graduates for global leadership in the judiciary, academia, business and government. Since 1966, the program has offered a select number of diverse students the opportunity to attain their highest professional aspirations and career goals. A preeminent center for interdisciplinary legal studies, UW Law offers a global focus and innovative approach to integrating legal scholarship within the humanities and social sciences, medicine and global health, business and technology, and environmental and public policy.
The Ph.D. program is designed to provide a rich and thorough foundation in research methodologies, jurisprudence, legal theory, policy, dissertation preparation and ready access to specialized elective coursework from within the law school and university-wide research centers, institutes and schools. Throughout the program, our graduate students receive individualized attention from exceptional faculty and staff.
With its long and respected history, the Ph.D. program provides students with a global alumni network. Alumni are committed supporters and mentors and lead in many sectors around the world.
The Ph.D. program requires a minimum of three years’ study, at least two years of which are comprised of coursework taken while in residence at the UW. Ph.D. candidates must complete 90 credits. A minimum of 60 credits must be taken at the UW including a minimum of 27 dissertation credits. Some of the credits earned in an LL.M. program may be counted among the 60 credits.
Doctoral dissertation committees are led by faculty experts from UW Law and include members with deep knowledge and expertise from across the university. Students can customize their studies with interdisciplinary coursework, independent study, field research, global internships and externships.
See full curriculum
- Current Ph.D.s in Law
- PhD Admissions
Related Links
Graduate Programs, UW School of Law William H. Gates Hall Box 353020 4293 Memorial Way Seattle, WA 98195-3020, USA gradlaw@ uw .edu

Doctor of Science of Law (JSD)
The Doctor of the Science of Law (JSD) is the Law School’s most advanced law degree, and is considered a doctorate equivalent to a Ph.D. It is designed for those interested in becoming scholars and teachers of law including interdisciplinary approaches to law.
Study toward the degree is open only to a small number of exceptionally well-qualified students who hold a JD or LL.B earned outside the United States. Students in the program develop substantive expertise in one or more fields of law and have the opportunity to pursue substantive and methodological training in allied disciplines across the broader university, including but not limited to, the social sciences, humanities, and engineering. The program culminates in the student producing a dissertation under the personal supervision of a Faculty committee comprised of law school professors as well as, where appropriate given the student’s interests, faculty from other departments of the university.
There are two different tracks for admission into the JSD program. A minimum of two students will be admitted from among students who have completed the Stanford Program in International Legal Studies (SPILS) at Stanford Law School. In addition, students at Stanford and at other law schools in the United States who will have completed LLM degrees prior to the commencement of the JSD program are encouraged to apply for admission and will be seriously considered. To be competitive, students applying from LLM programs must have completed (and must submit) a serious piece of independent, original research demonstrating their scholarly potential.
Admission to the JSD program is on a highly selective basis. Please note that admission to SPILS or to any Stanford LLM program does not imply a commitment by Stanford Law School to accept a student into the JSD program.
Some need-based funding, as well as funding to conduct research and attend conferences is available to admitted JSD students.
Questions concerning the JSD program should be directed to [email protected] .
HOW TO APPLY
JSD Candidates

Luis Bergolla
- JSD Candidate
- Teaching Fellow, LLM Program in International Economic Law, Business and Policy (IELBP)
- Lecturer in Law

Silindile Buthelezi

Rolando Garcia Miron

Yutang Hsiao
Tai-jan huang.

Takuma Iwasaki

Maria Palacio

Michael Thorburn
Having a jsd from stanford law school opens up countless career opportunities..
Teaching in US Academia
Teaching Outside the US
Working in the Public Interest Sector
Working in the Private Sector
- Completed DPhil Projects
The University’s legal research community includes more than 200 postgraduate students engaged in research degrees in the Law Faculty and its centres. It is one of the largest and most intellectually diverse research communities in the world. Many of our research degree alumni are now global leaders in the fields of academia, legal practice, the judiciary and public service. The following list gives details of completed DPhil theses since 2010, with many of these DPhils generating published work in articles and books at the cutting edge of legal scholarship. Many other master’s and doctoral research theses are held in the collection of the University’s Bodleian Law Library.
Administrative and Constitutional Law
Civil procedure and evidence, commercial law, comparative law, competition law, computers and law, conflict of laws, contract law, corporate insolvency law, corporate law, criminology and criminal law, environmental law, human rights law, intellectual property law, international trade law, jurisprudence, law and finance, law of obligations, legal history, medical law and ethics, principles of financial regulation, property law, completed dphils in public international law, socio-legal studies.
- Research Groups
- Research Programmes
- Postdoctoral Research Fellowships
- Research Overview
- Graduate Discussion Groups
Doctoral Programs


5 Tips for Choosing Your DLP Dissertation Topic

Faculty Insights Law & Criminology Public Health & Public Policy
Kimberly Larson, associate teaching professor and director of Northeastern’s Doctor of Law and Policy program , shares her advice for students choosing the subject of their doctoral research.
Northeastern’s Doctor of Law and Policy Program (DLP) is focused on developing scholar-practitioners who wish to advance their field of practice. Students join the program from a variety of fields, such as government, human services, and higher education. During the program, professionals come together from their respective disciplines with the common goal of pursuing their passions through doctoral research and thinking deeply about how to advance their fields. The DLP Program provides legal and policy frameworks that students can use to pursue research in their respective fields and areas of interest.
Choosing a topic of study can feel daunting at first, but the coursework in the Doctor of Law and Policy Program, along with our expert faculty, are here to support you through this journey. Keep in mind—many students successfully navigate this journey every year. Below are a few tips to think about in considering what you might want to pursue within your doctoral research.
5 Tips for Choosing Your Doctoral Thesis or Dissertation Topic
1. consider the “fit” between your research and professional goals..
Students returning to obtain a doctoral degree after gaining experience in their field often have specific career goals.
Is your goal to advance in your current position?
One might, for example, choose a topic that will be applicable within their current field but in a more advanced role. Engaging in doctoral research and earning an advanced degree provides these students the opportunity to showcase their ambitions to their current employers. Or perhaps their thesis might help address a particular question that their current employer may be interested in.
Do you want to pivot in your current field? Or are you embarking upon a new journey altogether?
Those looking to make a career change might utilize their thesis to establish themselves as an expert on a topic in the area to which they would like to make a shift. Students also often utilize their committee to make professional connections that can help support them in a career change or advancement.
Reflecting on your objectives and making strategic decisions can help you focus in on a topic that will help you reach your professional goals.
2. Read more about your topic of interest.
Regardless of your professional expertise, students will need to read and master related scholarly literature as part of the thesis process. Why not get a jump start on this? Students’ best “ah-ha!” moments about their research question or methodological approach often come from reviewing recent literature in their area of interest. Explore available literature to see what questions are open and where there are existing gaps in the literature that you might address with your project.
3. Consider topics you are passionate about.
Students should choose a subject that they feel strongly about, and that will sustain their interest over the course of the dissertation process. Is there an issue about which you are passionate? Is there a particular question that you don’t feel is being adequately addressed within your field? When choosing a dissertation topic, these questions are both good places to start. Then, you can continue your exploration by diving into reading on that topic.
One student, for example, parlayed their interest in housing policy into research by examining potential technological solutions to housing crunches for low-income individuals in urban areas. As such, this was the focus of their thesis in the DLP program. They were also able to open up a business and obtain patents to very practically effect change once they graduated.
4. Contemplate the contribution you want to make to your field of study.
Some of the best research ideas come from one’s field of practice. DLP students often choose their doctoral thesis questions from those that are currently pressing within their professional field. Examining a question from one’s professional area gives the student a competitive advantage, as they likely already have a depth of professional experience in that area, and also helps ensure that the issue to be addressed is a problem in the field that needs solving and has practical application.
5. Work with the support of your faculty advisor to focus your research questions.
While it’s best to enter your doctoral program with an idea of what you’d like to study, the faculty is there to help support you and hone your questions. After you’ve considered your goals and reviewed the literature in your area of interest, your thesis advisor and committee become invaluable resources in narrowing your question and developing a project that you’re excited about and can be completed during your doctoral program. Most students begin with a project idea that is very ambitious. The iterative review process, along with one’s committee, is designed to help you settle upon a project that both addresses an important problem of practice or gap in the extant literature and allows you to graduate on time. Always remember—this is just one study that marks the start of what will hopefully become your ongoing contributions to the scholarship in your field.
Examples of Past DLP Thesis Titles
Below are some real-world examples of theses pursued by Northeastern’s Doctor of Law and Policy students:
- New Models of Private Sector Financing of Not-For-Profit Corporations
- Department of Defense Source Selection Procedural Ambiguities
- The Impact of College Cost on Low-Income Students at Private (Not-for-Profit), Four-Year Institutions in New England
- Zero Tolerance Policing: An Evaluation of the NYPD’s Use of Stop and Frisk
- Social Determinants of Vulnerability Framework: Incorporating the Needs of People into Mitigation, Response, and Recovery
- An Evaluation of Integration Programs for Deportees in Latin America and the Caribbean
- What Can Higher Education Administrators Learn from the Healthcare Industry’s Experience with Regulatory and Policy Change? A Success Framework
- Social Media Legitimacy: a New Framework for Public Participation and the Behavior of Organizations
- Nuclear Arsenals at Low Numbers: When Less Is Different
- Federalism and Federal Food Safety Procedures: Implementing the 2010 FDA Food Safety Modernization Act Across the 50 States
To learn more about Northeastern’s Doctor of Law and Policy program , explore our program page or get in touch with an enrollment counselor to get your questions answered.
Subscribe below to receive future content from the Graduate Programs Blog.
About kim larson, jd, phd, related articles.

Jackney Prioly Joseph on How Her MPA Helped Her Career

Master’s in Nonprofit Management vs. Public Administration

How an MPH Clarified One Alumna’s Career Path
Did you know.
The median annual salary for professional degree holders is $97,000. (BLS, 2020)
Doctor of Law and Policy
Realize your career potential in law and policy.
Most Popular:
Tips for taking online classes: 8 strategies for success, public health careers: what can you do with an mph, 7 international business careers that are in high demand, edd vs. phd in education: what’s the difference, 7 must-have skills for data analysts, in-demand biotechnology careers shaping our future, the benefits of online learning: 8 advantages of online degrees, how to write a statement of purpose for graduate school, the best of our graduate blog—right to your inbox.
Stay up to date on our latest posts and university events. Plus receive relevant career tips and grad school advice.
By providing us with your email, you agree to the terms of our Privacy Policy and Terms of Service.
Keep Reading:

Should I Go To Grad School: 4 Questions to Consider

Grad School or Work? How to Balance Both

7 Networking Tips for Graduate Students
Coordinated JD/PhD Program
Harvard Law School and the Harvard Kenneth C. Griffin Graduate School of Arts and Sciences
The Coordinated JD/PhD Program is designed for students interested in completing interdisciplinary work at Harvard University and is founded on the belief that students’ legal studies and their arts and sciences graduate studies can be mutually enriched through this pursuit. Students completing the coordinated program receive a JD from Harvard Law School (HLS) and a PhD from the Harvard Kenneth C. Griffin Graduate School of Arts and Sciences (Harvard Griffin GSAS). It is expected that these students will be strong candidates for teaching posts at law schools and in arts and sciences programs, as well as for other positions in law and academia. Prospective students interested in the coordinated program may reach out to HLS J.D. Admissions and the Harvard Griffin GSAS Office of Admissions to learn more. Current and admitted students interested in the coordinated program are encouraged to contact April Pettit , in the Office of Academic Affairs at HLS for questions about the JD program, or Dan Volchok , Assistant Dean of Student Success at Harvard Griffin GSAS for questions about the PhD programs.
Prospective students must separately apply to and be admitted to both HLS and a Harvard Griffin GSAS PhD program in order to participate in the coordinated JD/PhD program.
- Students enrolled in HLS, but not yet admitted to Harvard Griffin GSAS, must apply to Harvard Griffin GSAS no later than the 2L year, meeting the Harvard Griffin GSAS application deadline for matriculation the following year.
- Students enrolled in Harvard Griffin GSAS, but not yet admitted to HLS, should apply to HLS no later than the G3 year, meeting the HLS application deadline for matriculation the following year.
- Please see below for details about participation in the coordinated program for Harvard Griffin GSAS students who apply and are admitted to HLS after the G3 year.
Once admitted to both schools, students must submit a proposed Plan of Study to the coordinated program no later than October 1 of the academic year following admission to both schools. Students should submit the Plan of Study to April Pettit in the Office of Academic Affairs at HLS.
Please note: Harvard Griffin GSAS students who apply to and are admitted to HLS after the G3 year at Harvard Griffin GSAS must then separately apply to the coordinated program. The application to the coordinated program should include (1) a statement detailing the way in which the student plans to integrate his or her legal studies with his or her graduate studies including how work done at HLS will inform the dissertation work and vice versa; and (2) a letter of support from the primary Harvard Griffin GSAS advisor; and (3) the Plan of Study.
The JD/PhD committee will review the applications to determine admission to the coordinated program.
Students will be registered in only one School during any given semester/term. Pursuant to ABA rules, students must complete all requirements for the JD degree within seven years of the date they first enroll in HLS ; they may graduate from HLS before completing the PhD. Students must have satisfactorily completed at least 16 half courses in their Harvard Griffin GSAS department to receive the PhD. Students in the coordinated program will have two primary faculty advisors, one at HLS and one at Harvard Griffin GSAS, who will jointly advise students.
Students will be expected to complete the first-year program, three upper-level fall or spring semesters, and two winter terms at HLS, for a total of five fall and spring semesters and three winter terms. In lieu of the sixth HLS semester generally required of JD students, students in the coordinated program may take a semester at Harvard Griffin GSAS, completing courses or dissertation work pre-approved by HLS, and equivalent to at least 10 HLS credits. This Harvard Griffin GSAS semester may be taken only after a student has matriculated at HLS and completed their entire first year of study there. Students and their faculty advisors will determine the most appropriate sequencing for each student’s course of study, keeping in mind the HLS course, credit, and residency requirements for this program.
Course and Credit Requirements
First-year program.
The first year at HLS consists of (1) Civil Procedure, Constitutional Law, Contracts, Criminal Law, Legislation and Regulation, Property, and Torts; (2) First-year Legal Research and Writing; (3) January Experiential Term; and (4) a spring upper-level elective at HLS of a minimum of 2 and a maximum of 4 classroom credits.
Upper-Level Years
Credit and residency requirements.
Students must earn no fewer than 52 credits beyond the first year, including 36 HLS classroom credits. Classroom credits include those connected to courses, seminars and reading groups, but not writing or clinical credits. The 36 required classroom credits also include the required minimum of two credits to satisfy the Professional Responsibility Requirement and credits from the required winter terms (provided that the course chosen offers classroom credits). Of the remaining 16 required HLS credits, a maximum of ten are earned through courses or tutorials taken in Harvard Griffin GSAS and/or for dissertation writing (see below). Note that students must have their advisor’s approval before engaging in a semester of Harvard Griffin GSAS dissertation writing that is expected to count toward the HLS credit requirements . The remaining six required HLS credits may be earned in classroom, writing or clinical courses.
While at HLS, students must be enrolled in a minimum of ten total credits each semester in HLS or Harvard Griffin GSAS, with no fewer than eight of these being HLS classroom credits toward the requirement of 36 HLS classroom credits.
Winter Term Requirement
Students also must enroll in the HLS winter term two times during their upper-level years in the program. Each of the winter terms must follow a fall term enrollment or precede a spring term enrollment at HLS. Students may register for a course of two or three credits. JD/PhD students will be permitted to spend one of the winter terms in the HLS Winter Writing Program, provided they are engaged in written work for HLS credit according to the rules of that program.
Written Work Requirement
JD/PhD students must complete the JD Written Work Requirement. Students are permitted to satisfy the requirement with a portion of their dissertation, provided this work meets HLS standards for written work. However, any portion of the dissertation counted toward the JD Written Work Requirement cannot also be used as part of the 10 HLS-equivalent credits earned during a student’s Harvard Griffin GSAS semester. Further information about the J.D. Written Work Requirement and the Winter Term Writing Program is available from the HLS Registrar’s Office .
Pro Bono Requirement
JD/PhD students must complete the HLS Pro Bono Requirement of 50 hours of public service.
Residency Requirement
A minimum of two years of full-time study in residence is required for all PhD programs in the Harvard Griffin GSAS. During the period of registration at HLS, coordinated JD/PhD students will have “study-at-another-Harvard-school” status in Harvard Griffin GSAS.
Structure of Academic Work
Students will ordinarily be enrolled for at least four years (8 terms) in Harvard Griffin GSAS. They must complete at least 16 half courses to receive their PhD. Students may cross-register for a limited number of Harvard Griffin GSAS courses during their upper-level terms at HLS. Depending on the Harvard Griffin GSAS department, these courses may count toward the PhD. However, JD/PhD students may count a maximum of 10 credits from Harvard Griffin GSAS coursework or dissertation writing toward the JD. Therefore, students planning to spend a semester enrolled at Harvard Griffin GSAS taking courses or writing the dissertation for which they will earn 10 HLS credits may not also count cross-registered Harvard Griffin GSAS courses toward the JD.
General Examinations
In most departments, once having completed the required coursework, students must pass a general examination or other preliminary or qualifying examinations before undertaking independent research on a dissertation. Normally, when the nature of the field and previous preparation permit, students should pass these examinations by the end of the second year of full-time academic residence.
PhD Dissertation
The student’s dissertation prospectus must be approved by the department. A student who wishes to present as a dissertation a published article, series of articles, book or other document, or a manuscript that has been accepted for publication, must have the approval of the department concerned. In no case, however, may a dissertation be presented that has already been submitted toward another degree, either at Harvard or elsewhere. The Dissertation Acceptance Certificate must be signed by at least three readers approved by the student’s department, two of whom must be members of the Faculty of Arts and Sciences (FAS). FAS emeriti (including research professors) and faculty members from other schools at Harvard who hold appointments on GSAS degree committees are authorized to sign the Dissertation Acceptance Certificates as FAS members. GSAS strongly recommends that the chair of the dissertation committee be a member of FAS. The third reader may be a member of the HLS faculty.
Requirement of Satisfactory Status
Continuous registration, a satisfactory grade record, and evidence that satisfactory progress is being made toward the degree are required of all candidates for graduate degrees offered by FAS. All students in Harvard Griffin GSAS must be making satisfactory progress in order to be eligible for any type of financial aid and teaching. The following five provisions are the general definition of satisfactory progress during registration in Harvard Griffin GSAS:
- During the first two years of graduate study any student who has completed expected requirements is considered to be making satisfactory progress.
- In each of the first two years, a student must have achieved the minimum grade-point average required by the faculty, a B average. (see Harvard Griffin GSAS Policies: Grade and Examination Requirements ).
- By the end of the third year, a student must have passed general examinations or the departmental equivalent.
- By the end of the fourth year, a student must have obtained approval of a dissertation prospectus or its departmental equivalent.
- By the end of the fifth year and each subsequent year during which a student is allowed to register, they must have produced at least one acceptable chapter of the dissertation.
For more information about satisfactory progress, please see Harvard Griffin GSAS Policies .
Other Requirements
Ordinarily, programs will have a language requirement and an expectation of teaching. Students should consult with their Harvard Griffin GSAS departments for more information about these requirements.
There are a number of possible academic schedules for students pursuing both degrees. Three sequences are outlined below, but students may propose alternative sequences. In considering their courses of study, students should be aware that their financial aid packages might be affected at the school in which they defer enrollment.
Year 1: HLS Year 2: Harvard Griffin GSAS Year 3: Harvard Griffin GSAS Year 4: HLS Year 5: 1st term, HLS Year 5: 2nd term, Harvard Griffin GSAS (earning the equivalent of 10 HLS credits in dissertation work) Following year(s): Harvard Griffin GSAS until completion of dissertation
Year 1: Harvard Griffin GSAS Year 2: Harvard Griffin GSAS Year 3: HLS Year 4: Harvard Griffin GSAS Year 5: HLS Year 6: 1st term, HLS Year 6: 2nd term, Harvard Griffin GSAS (earning the equivalent of 10 HLS credits in dissertation work) Following year(s): Harvard Griffin GSAS until completion of dissertation
Year 1: HLS Year 2: HLS Year 3: Harvard Griffin GSAS Year 4: Harvard Griffin GSAS Year 5: 1st term, HLS Year 5: 2nd term, Harvard Griffin GSAS (earning the equivalent of 10 HLS credits in dissertation work) Following year(s): Harvard Griffin GSAS until completion of dissertation
Updated Plans of Study
By October 1 each year, current JD/PhD students should submit an updated Plan of Study to April Pettit, in the HLS Office of Academic Affairs.
Other Academic Information
Faculty advising.
Students in the program will have primary faculty advisors at both HLS and at Harvard Griffin GSAS. If possible, HLS faculty advisors should be selected before the completion of the 2L year. The HLS faculty advisor must sign off on any dissertation writing a student expects to use for JD credit. In some Harvard Griffin GSAS departments, the director of graduate studies serves as the faculty advisor during the first two years of study. Faculty advisors will supervise students’ academic work, advise students on their courses of study and on specific classes appropriate for their PhD work, and approve the courses of study for their students on an annual basis. If appropriate, the HLS advisor will be the third reader on the student’s dissertation committee, with at least two readers required to be members of FAS.
Leaving the JD/PhD Program
If a student fails to make adequate progress toward the PhD, the student’s faculty advisors will be permitted to withdraw the student from the program. In such cases, in order to receive the JD degree, a student will still need to meet the graduation and credit requirements for the JD degree.
Tuition and Financial Aid
Harvard law school.
Students must pay five semesters of full tuition. Students will be eligible for HLS financial aid for all semesters during which they pay tuition to HLS. For more information on Financial Aid, visit the Student Financial Services Financial Aid webpage .
Harvard Kenneth C. Griffin Graduate School of Arts and Sciences
The minimum financial requirement for the PhD is at least four terms of full tuition followed by two years of reduced tuition and a facilities fee unless the degree is completed in less than four years. The financial aid awarded upon admission to the PhD program is available during those terms in which the student is enrolled in Harvard Griffin GSAS. Students should refer to their notice of financial support provided by their department upon admission to Harvard Griffin GSAS. Students should consult with their GSAS departments for more information.
Administrative Information
The HLS Registrar’s Office, the FAS Registrar’s Office, the GSAS Assistant Dean of Student Success, the HLS Associate Director of Academic Affairs, and the appropriate financial aid officers, will coordinate on students’ registration status and updated plans of study.
Housing and Student Life
GSAS and HLS will work together to ensure that the student services offered by both Schools are available to JD/PhD students during all their years in the Coordinated Program, including career and counseling offices, financial aid offices, student centers, and alumni offices. Students in the coordinated program will have email accounts at both schools throughout the program. Disability services and visa requirements will be coordinated on a case-by-case basis by the HLS Dean of Students and Registrar and by the Harvard Griffin GSAS Assistant Dean for Student Success. Students may apply for housing through either School for the years in which they are enrolled for at least one semester/term at both Schools. In all other years, students must apply for housing to the School in which they are enrolled.
Modal Gallery
Gallery block modal gallery.
PhD Topics at iCourts
General description.
iCourts 3.0 seeks to explain and make intelligible the relative and often contested power of international courts, institutions and law. While the current resistance to international courts and law is interesting in this regard, we generally encourage projects that more broadly explore the power of international courts in relation to law, politics and society.
- The transformation of legal practices by international courts and institutions. For example, how international courts create new cognitive frames, principles and values, and whether or how these innovations change legal practices at the global, regional and national levels;
- The impact of international courts and institutions on politics, its processes and outcomes: For example, how different actors make use of ICs – directly and indirectly – and whether and how such actions generate new interests and preferences at the global, regional and national levels;
- Changes in society triggered by international courts, institutions and law. For example, how ICs influence state, group and citizen relationships, and whether and how they help to generate new rights, duties and processes at the global, regional and national levels.
- For the IMAGINE project, we particularly look for projects interested in interdisciplinary study of how key ideas have influenced EU constitutionalism.
Individual areas of supervision
Mikael rask madsen, comparative studies of international courts.
I generally welcome projects which explore the historical and contemporary evolution of international courts, using comparative methods. I am particularly interested in studies that can identify and assess the power of international courts in domestic law, politics and society. Projects can explore specific courts more generally or zoom in on certain substantive or procedural mechanisms of international courts.
The Frontier of Human Rights I: Adjudicating Psychological Forms of Torture
Torture techniques are undergoing chance. They are increasingly clean and cause pain without leaving marks. This has however had the effect that it is also increasingly difficult for lawyers to convey and prove torture claims in court. The international law definition of torture however makes it very clear that both physical and mental pain are included. Nevertheless, human rights courts, ruling on cases involving severe mental pain or suffering, have tended, with some limited exceptions, not to recognize harms which do not involve clear physical signs of violence as torture. I invite applicants who would like to explore 1) why proving and litigating contemporary forms of no-touch torture is such an up-hill battle, and, 2) to propose ways to remedy the current situation.
The Frontier of Human Rights II: Implementing Human Rights Case Law
One of the biggest challenges for many human rights regimes is ensure that the decisions of international courts and commissions are in fact implemented. I welcome studies that explores either specific substantive areas of human rights law or more generally examines the pathways to implementing international decisions and judgments. The courts and commissions in focus can be regional or international and the study can involve the study of one or more domestic systems.
Contact person: Mikael Rask Madsen, email: [email protected]
Henrik Palmer Olsen
I welcome projects seeking to explore how citizens can be protected against discriminatory outcomes of algorithms used for predictive analytics in public administration and/or the police. The project should focus on discrimination law in a Danish and/or European context, but could include a comparative dimension – for example with US practices in policing and administrative law and could include an inquiry into the use of de-biasing in predictive analytics. The project should investigate how best to halt discriminatory outcomes of decision-making that is based on predictive analytics.
Contact person: Henrik Palmer Olsen, email: [email protected]
EUPoLex Jean Monnet Chair in EU Law & Politics: Shai Dothan
EUPoLex welcomes doctoral projects that explore the intersection between EU law and Politics, the judicialization of EU affairs and the construction of European judicial governance. The Chair would particularly favor projects, which explore the dynamics of judicial cooperation and the empowerment of courts vis-à-vis other powers (e.g. motivations and strategic considerations of judges when applying the law), legal mobilization (how lawyers and agents of the civil society litigate), and the public support for the national and European judiciaries.
PhD candidates should have a strong interest in applying interdisciplinary approaches and empirical qualitative and/or quantitative methods, such as interviews, survey, experiments, network analysis, statistics, process-tracing, cases studies, among others. Specialization in EU law and knowledge in other disciplines (political science, law & economics, history of European integration, etc.) will be viewed as an advantage. If successful, the aspirant will have the chance to develop and strengthen her/his methodological skills and competences by attending the methodological courses organized under the auspices of the Jean Monnet Chair and the PhD School.
The applicants will be co-supervised by Associate professor Shai Dothan. You might find more information about the Chair and its aims in the following link: https://jura.ku.dk/eupolex/
If you are interested in applying, please, do not hesitate to contact: Shai Dothan, email: [email protected]
I welcome projects in the field of international economic law (IEL), including trade and investment relations, as well as international arbitration. In particular, I am glad to offer supervision to projects, which critically examine prospects of multilateralization of IEL dispute resolution, including such phenomena as the crisis of the WTO AB, impact of regional trade and investment initiatives, and the work of UNCITRAL Working Group III on the postulated reform of ISDS.
Other areas of potential supervision include the study of dispute resolution mechanism of the Belt and Road Initiative; proliferation of Special Economic Zones and their relation to international trade law and investment treaty law; and international commercial courts.
Contact person: Joanna Lam, email: [email protected]
Astrid Kjeldgaard-Pedersen
I welcome projects in general international law as well as in international humanitarian law, international human rights law, and international criminal law. In particular, as a part of the INTERMIL project, I offer supervision of projects engaging with international law as it applies in military operations and in cyberspace.
Contact person: Astrid Kjeldgaard-Pedersen, email: [email protected]
Shai Dothan
Judicial Strategies, the Normative Justifications for the Intervention of International Courts, and the Impact of International Courts on Society I welcome suggestions for dissertations that will focus on the behaviour of international courts and the ways they maintain their political position. Such suggestions can focus on actors that interact with international courts as well, such as national courts, governments, Non-Governmental Organizations, and professional lawyers. These suggestions should focus descriptively on the strategic behaviour of international courts and at strategic moves such as backlash, political resistance, and collaboration used by other actors vis-à-vis international courts.
I also welcome suggestions to assess normatively the legitimacy and the potential outcomes of intervention by international courts. These suggestions can assess in which issues or under what conditions international courts are justified in intervening in domestic affairs and in which issues this intervention is illegitimate or would lead to bad results. The analysis can assist in determining the borders of the margin of appreciation, subsidiarity, complementarity, or other doctrines of deference. Finally, I welcome suggestions on the impact that international courts have on society. Are international courts likely to help disadvantaged social groups to improve their position? Are there certain guidelines that can lead to the development of good legal doctrine by international courts?
Contact person: Shai Dothan, email: [email protected]
Jan Komarek
In the area of the ERC-funded project IMAGINE we welcome proposals alongside the following themes: 1) Ideas and ideologies of European constitutionalism , taking a critical approach to the existing theories of European constitutionalism and examining their potential to serve as ideologies. 2) 1989, “The End of History” and the post-communist statehood in Europe ; proposed projects would be theoretically oriented and examine whether, and if so, how, the attempts to transform the state and its institutions reflected neoliberal ideology of the time. 3) Rethinking Law, Capitalism and Democracy would focus on the various ties between capitalism, democracy and law – either at international/European level, or in the context of national constitutionalism.
Beyond IMAGINE we are interested in projects that seek to examine judicial legitimacy from the normative perspective . The project can be theoretically oriented (embedded in constitutional and/or political theory), or seek to understand the issues concerning judicial legitimacy in a particular context: supranational, transnational or international adjudication, as well as more traditional fields (judicial review, constitutional adjudication or judicial law-making in the national context). Proposals that intend to look at the mutual interaction among the different contexts are particularly welcome.
Contact person: Jan Komárek, email: [email protected]
Mikkel Jarle Christensen
I welcome PhD projects on criminal justice systems, especially those that have developed at the border or outside of the state. Such systems include international criminal justice that has been built around international criminal courts as well as more transnational patterns of cooperation between criminal justice stakeholders such as prosecution services and the police. In particular, I welcome original projects that take an empirical, theoretically informed approach to studying how criminal justice has been developed at the border or outside of the state and how this has affected societal attempts at curbing globalized crime.
Contact person: Mikkel Jarle Christensen, email: [email protected]
Veronika Fikfak
- topics related to regulation of internet giants through human rights and international law
- topics related to human rights compliance with international treaties and judgments
- topics studying behaviour of states in international law (including through the use of behavioural economics and psychology)
- topics studying the work and functions of judges on international and domestic level (including from psychological perspectives)
- topics studying domestic implementation of international law by courts and parliaments
Contact person: Veronika Fikfak, email: [email protected]

- Majors & Careers
- Online Grad School
- Preparing For Grad School
- Student Life
Top 10 Best PhD in Law Programs [2024]

A PhD in law is an advanced qualification that will make you a true legal expert. You can use that credential to work as a legal research scholar or teach at a post-secondary level. This is not only a prestigious career path but also a lucrative one — today’s law PhD holders have an average salary of $93,000.
Today’s law schools emphasize an interdisciplinary approach to legal education, equipping students to work in a diverse range of fields.
Interested in an advanced criminal justice career? Below we’ll cover the top PhD in law programs, universities, and what you need to know before pursuing a doctorate in law.
Table of Contents
Top PhD in Law Programs
Yale university, law school.

Yale University’s Law School ranks first in the nation, with its 20 legal clinics offering an immersive experience for students. This PhD program has a purely academic focus. To qualify for admission, you’ll need to already have a JD (Juris Doctor) degree. If accepted, you’ll be able to benefit from Yale Law School’s acclaimed “Yale Teaching Program.”
- Courses: Criminal law & administration, international human rights, and complex civil litigation.
- Duration: 3 years
- Delivery: On-campus
- Tuition: Fully funded
- Financial aid: Full tuition coverage, health insurance, and stipend.
- Acceptance rate: 7%
- Location: New Haven, Connecticut
Stanford University
Doctor of the Science of Law (JSD)

Stanford University is another highly acclaimed institution in the field of law education with a tough admissions process. Only a few exceptionally gifted students with an international JD or LLB or a SPILS (Stanford Program in International Legal Studies) qualification are accepted into this program every year. The program has an emphasis on an interdisciplinary approach to law.
- Courses: Advanced antitrust, current issues in business law, and reinventing American criminal justice systems.
- Credits: 44 units
- Duration: 4 years
- Tuition : $64,350 per year
- Financial aid: Scholarships, fellowships, grants, assistantships, federal work-study, and loans.
- Acceptance rate: 5%
- Location: Stanford, California
The University of Chicago, The Law School
Doctor of Jurisprudence (JSD)

The Law School of the University of Chicago is renowned for its interdisciplinary approach to teaching and cross-lists its courses with other departments. The faculty include philosophers, political scientists, historians, and law scholars. Students also have the option to pursue a Doctorate in Comparative Law (D.Comp.L.) instead of a JSD if they wish.
- Courses: Antitrust & intellectual property, civil rights clinic: police accountability, and American legal history.
- Duration: 5 years
- Tuition : $7,647 per year
- Financial aid: Full tuition scholarship, fellowship, and health insurance.
- Acceptance rate: 7%
- Location: Chicago, Illinois
Columbia University, Law School
JSD Program

The Columbia Law School emphasizes experiential learning with law clinics, moot courts, and externships, offering opportunities for innovative education and valuable intellectual exchange. Students can conduct independent research with the help of their faculty advisors and they need to submit a DPR (Dissertation Progress Report) at the end of each year.
- Courses: Intellectual property & technology, international & comparative law, and law of the workplace.
- Duration: 5-6 years
- Tuition : $75,572 per year
- Financial aid: Grants, loans, and first child allowance.
- Location: New York City, New York
Harvard University, Law School
Doctor of Juridical Science (SJD)

Harvard University is one of the world’s most famous centers for education, and its Law School is equally renowned. The school has a unique grading system that uses the classifications honors, pass, low-pass, and fail. This flexible SJD program allows students to design their own study plan and choose faculty supervisors for independent research.
- Courses: Advanced comparative perspectives on US law, environmental justice, and strategic litigation & immigration advocacy.
- Duration: 4 years
- Delivery: On-campus
- Tuition : $67,720 per year
- Financial aid: Scholarships, grants, and loans.
- Location: Cambridge, Massachusetts
The University of Pennsylvania, Carey Law School
Doctor of Science of Law (SJD)

Carey Law School’s curricula cut across disciplinary and international lines to create law experts in every field, including business, health, technology, education, and social work. For admission to the Carey Law School PhD, you must already hold an LLM or JD from the same school or an institution of similar standing.
- Courses: Privacy & racial justice, appellate advocacy, and disability law.
- Tuition : Refer tuition page
- Financial aid: Full tuition, stipend, health insurance, and scholarships.
- Acceptance rate: 9%
- Location: Philadelphia, Pennsylvania
The University of Arizona, James E. Rogers College of Law

The University of Arizona’s James E. Rogers College of Law is one of the country’s most affordable top-tier law schools. This PhD law degree offers the choice of two concentrations: International Trade & Business Law, and Indigenous Peoples Law & Policy.
- Courses: International business & investment structuring, federal Indian law, and trusts & estates.
- Duration: 3-5 years
- Tuition and fees : $26,000 per year
- Financial aid: Scholarships, federal work-study, loans, veteran benefits, and fellowships.
- Acceptance rate: 85%
- Location: Tucson, Arizona
The University of Texas at Dallas, School of Economic, Political, and Policy Sciences
Doctor of Philosophy in Criminology

The University of Texas’ School of Economic, Political, and Policy Sciences creates professionals capable of dealing with modern issues like risk management, political violence, social inequality, healthcare, and international trade & conflict resolution. You’ll need a bachelor’s in criminology or a related discipline to apply for this PhD in criminology.
- Courses: Advances in criminology theory, evidence-based crime prevention, and regression & multivariate analysis.
- Credits: 75 semester credit hours
- Financial aid: Scholarships, grants, and loans.
- Acceptance rate: 79%
- Location: Richardson, Texas
Abraham Lincoln University, School of Law
Juris Doctor (JD)

This school was founded with to provide affordable education to working professionals who cannot attend regular law school. This doctorate in law is a flexible JD degree that can be completed entirely online through the university’s high-level education technology.
- Courses: Criminal law, civil procedure, and wills & trusts.
- Delivery: Online
- Tuition : $10,100 per year
- Acceptance rate: 90.3%
- Location: Glendale, California
Walden University
Online PhD in Criminal Justice

Walden University aims to help working professionals pursue advanced degrees and has been ranked #1 in research doctorates for African-American students. This program was one of the first online doctorates in criminal justice and allows students to explore national and international issues in criminal justice administration with a dual emphasis on contemporary theory and practice.
- Courses: History & contemporary issues in criminal justice, policy & analysis in criminal justice systems, and research theory, design & methods.
- Credits: 77 quarter credits
- Tuition : $636 per quarter hour
- Financial aid: Grants, scholarships, loans, and veteran benefits.
- Acceptance rate: 100%
- Location: Minneapolis, Minnesota
What Do You Need to Get a PhD in Law?
The exact requirements vary depending on the program, but you’ll typically need a LLB, LLM, or JD as a basic prerequisite.
As part of the admission process, you usually need to submit:
- Academic transcripts from previous studies
- Personal essay and/or research proposal
- Recommendation letters
To earn your doctorate, you’ll have to complete coursework, qualifying examinations, and usually a dissertation to a high standard.
Preparing for a Law Doctorate Program
The best PhD in legal studies programs are competitive, so it’s important to start preparing early. Keep up to date on developments in the field and research the best universities that offer your preferred specialization.
Look into leading faculty members in your areas of interest, and network by joining relevant professional communities. Once you’ve decided on your dream program, check admission requirements to prepare the strongest possible application.
Things to Consider When Choosing a Law PhD Program
Choosing the best law PhD program will depend on a range of factors, including your passions and interests. However, there are a few general factors that are essential for everyone deciding on a law school for their PhD to consider:
- Location: First, a school close by could save you on accommodation costs. But that’s not the only location consideration. You should look at your school destination for evidence of a booming legal or education industry. For example, New York is a hub for business, while Boston is known as a center for technology.
- Cost and funding: Ensure the program costs align with your budget and explore financial aid opportunities.
- Specialization: Some schools offer unique specializations like social justice, law and economics, and international law. Choose a program with a focus on your preferred specialization.
- Faculty: The university’s reputation is important, but its faculty credentials are equally critical. Explore faculty backgrounds by researching published papers and social media profiles like LinkedIn.
- Class sizes: Smaller class sizes mean better one-on-one attention; however, a larger cohort offers better networking opportunities.
- Placement support: What happens after graduation? Are you on the hook for finding a job on your own, or does the school offer placement options? Find out where alumni are employed to get an idea.
Why Get a Doctorate in Law?
A doctorate degree in law will allow you to pursue roles in the legal field as a scholar, researcher, or academic, and build a worthwhile career.
Several candidates apply for admission to PhD in jurisprudence programs every academic year, but top law schools have low acceptance rates, and only a few are accepted. For example, Harvard only has around 70 SJD students while hundreds or thousands may apply. Therefore, with this qualification, you’ll belong to an exclusive group of in-demand professionals.
Jobs for PhD in Law Degree Holders
Here are some common roles for PhD holders in law with the average annual salaries for each:
- General Counsel ($170,183 )
- Staff Attorney ($71,106 )
- Professor of Law ( $131,926 )
- Project Manager ( $76,264 )
- Senior Research Associate ( $75,029 )
Course Costs
The cost greatly depends on where you study, but prestigious law schools can charge annual tuition of around $65,000. Once you factor in living expenses, books, and facility fees, the total cost can add up to around $100,000 a year. However, you can find programs with tuition and fees for as little as $7,500 a year. Moreover, most top institutions offer full-tuition scholarships, stipends, and similar financial aid that cover almost all of your expenses.
Course Length
Typically, a PhD in law takes 3-5 years to complete. However, most programs will give you extra time to complete your doctorate if needed.

Skills You’ll Gain through a PhD in Law
Aside from giving you in-depth and expansive legal knowledge, PhD in law programs can also help you develop the following skills:
- Communication
- Presentation
- Critical Thinking
- Project Management
- Problem Solving
Key Takeaways
A PhD in law is an excellent choice for legal professionals seeking a career in research or academia. While a JD or Juris Doctor is equivalent to a PhD, the former equips you to become a law practitioner.
On the other hand, if you want to teach at a post-secondary level or conduct further legal research, you will need a PhD. Prepare early and choose a program that will best help you to achieve your career goals.
For more law education advice, take a look at our guide on the best master’s in criminal justice programs , or weigh up your options with the highest-paying PhDs .
PhD in Law FAQs
What is a phd in law called.
A PhD in law is usually called a Doctor of Law or Doctor of Laws. Some universities offer a JD (Juris Doctor or Doctor of Jurisprudence) degree, while others offer SJD (Doctor of Juridical Science) or JSD (Doctor of Science in Jurisprudence) programs.
Is a PhD in Law the Same as a JD?
A JD (Juris Doctor) degree is suitable for anyone who wants to practice as a licensed legal professional. These programs usually take three years to complete and are mostly coursework-focused.
On the other hand, a PhD in law may take 5-6 years to complete and usually involves a dissertation or major research project. If your aim is professional research or a job in academia in the discipline rather than practicing law, a PhD is better for you.
What is the Highest Degree in Law?
A PhD in law is generally considered the most advanced law degree. While some universities call it by other names, such as SJD (Doctor of Juridical Science) or JSD (Doctor of Jurisprudence degree), this is essentially the same thing.
How Long is a PhD in Law?
PhD Law programs typically take 3-5 years to complete. You may take longer for individual reasons, such as if you choose to study part-time.
What Does a PhD in Law Do?
A PhD in law will equip you to work in legal research or academia.

Lisa Marlin
Lisa is a full-time writer specializing in career advice, further education, and personal development. She works from all over the world, and when not writing you'll find her hiking, practicing yoga, or enjoying a glass of Malbec.
- Lisa Marlin https://blog.thegradcafe.com/author/lisa-marlin/ 12 Best Laptops for Computer Science Students
- Lisa Marlin https://blog.thegradcafe.com/author/lisa-marlin/ ACBSP Vs AACSB: Which Business Program Accreditations is Better?
- Lisa Marlin https://blog.thegradcafe.com/author/lisa-marlin/ BA vs BS: What You Need to Know [2024 Guide]
- Lisa Marlin https://blog.thegradcafe.com/author/lisa-marlin/ The 19 Best MBA Scholarships to Apply for [2024-2025]
Top 12 Best Laptops for Graduate Students in 2024
Top 10 best phd in theology programs [2024], related posts.

- Grad Trends: Interest in Artificial Intelligence Surges

- Applying to Big Tech This Year? Here’s How to Ace It.

73% of job seekers believe a degree is needed for a well-paying role–but is it?

Tech Talent Crunch: Cities with More Jobs Than Workers

The Most Under-Rated Career Advancement Tip for 2024

Top 5 Best Psychology PhD Programs in 2024

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Recent Posts
- Breaking Records: Yale Sees Most Selective Grad Admissions Season Yet
- 12 Best Laptops for Computer Science Students
- Is a Master’s Degree Worth It? [2024 Guide]

© 2023 TheGradCafe.com All rights reserved
- Partner With Us
- Results Search
- Submit Your Results
- Write For Us
- Write my thesis
- Thesis writers
- Buy thesis papers
- Bachelor thesis
- Master's thesis
- Thesis editing services
- Thesis proofreading services
- Buy a thesis online
- Write my dissertation
- Dissertation proposal help
- Pay for dissertation
- Custom dissertation
- Dissertation help online
- Buy dissertation online
- Cheap dissertation
- Dissertation editing services
- Write my research paper
- Buy research paper online
- Pay for research paper
- Research paper help
- Order research paper
- Custom research paper
- Cheap research paper
- Research papers for sale
- Thesis subjects
- How It Works
160+ Outstanding Law Dissertation Topics for Students

If you are a university student studying law, you would know that it is both, exciting and stressful to work on dissertations because law dissertation topics or help with dissertation are not easy to select.
While students can pick a topic that interests them, good thesis topics for law, students would be the ones that offer ample scope for research and study. It is vital to keep in mind that dissertations tend to get lengthy; therefore, your topic should also be a subject you can manage to finish working on within the time you have at hand. Given below are some exciting topics that you can explore for your law school thesis.
Business Law Dissertation Topics
Business law, also known as commercial law, focuses on the legal aspects of the conduct, rights, and relations of individuals or organizations that engage in commerce, trade, and merchandising activities. Therefore, commercial law masters thesis topics have a broad scope as they revolve around important and relatable aspects guiding society and trade. Here are some exciting business law topics to write about. Take a look:
- Business laws against corruption within firms — an in-depth evaluation
- Commercial Law and its effectiveness in supporting commercial transactions.
- Copyright Infringement – Understanding the difference between online and offline law enforcement.
- Business partnerships: Threats, legal remedies, and results
- Commercial laws guiding energy projects within the country and a comparison with top countries globally.
- Online advertising – working within the framework and guidelines of Advertising Law
- US commercial laws: A review on what needs to change
- Legal framework guiding unfair advertising and marketing practices – a case study analysis
- Business wills — application, significance, and role in translations of Business Law
- Domestic vs International commercial laws of five countries
- Pre-incorporation contracts – a thorough analysis
- International commercial law programs: An assessment of their effectiveness as part of the University curriculum
- Importance of investigating a business’s application for Copyright and Trademark
- Arbitration under commercial law: In-depth analysis and evaluation of policy practice
- Evaluating anti-corruption regulations for businesses through a relevant case study
- Laws governing Corporate Social Responsibility for businesses and their evaluation
- Termination agreements — application, significance, and role in business transactions
- The Law of Contracts — Interpretations and Role in Business Transactions
- Director’s Guarantee – Its role in Business law and the Structure of Transactions
- What is the role of a Business Entity concerning Commercial Law – An analysis
- Contract Laws and an evaluation of the application of Verbal or Nonverbal Agreements
- The role of Commercial Law in establishing a business framework within the society
- The legislature and its role in the interpretation and working of contracts
- Commercial Vs RegularLease – Analysing the pros and cons for the businesses
- Commercial lease – Significance, difficulties, and importance for business owners
International Law Thesis Topics
International law is an important area of interest when it comes to thesis writing. You can focus on studying the legal aspects of economic trade, businesses during the war, global pandemics, and more. Ethics and human rights play a significant role in international matters. Here are some excellent international law research topics to explore:
- Hearings on cases in International Human Rights Court — What precedence says
- Challenges faced by parties involved in contracts related to the International Sale of Goods (CISG) when the Vienna Convention is applied.
- What do the future hold for internet legislation and digital laws
- Are International Tribunals effective in taking action against war crimes?
- An in-depth analysis of various conditions under which international intervention in trade or matters of general affairs of a country is permitted by law
- International criminal laws — an assessment of the underlying principles and need for change
- Human rights law: An international perspective on gaps that need to be addressed
- Violation of Laws and Human Rights when the US got involved in matters of Iraq – An analysis
- Enforcement of international laws in developing countries – Issues, justification, and remedies
- Military cooperation between the UK and the US to address terror — A historical perspective and future analysis
- What are the civil liberties in International law and how do they impact public safety
- Post-Brexit era — where does consumer protection stand?
- Laws ensuring the protection of civilians against unlawful communication during armed conflicts between countries
- International laws governing rescue and protection of human rights of refugees at sea
- International civil jurisdiction on transborder disputes related to the infringement of intellectual property rights — a comprehensive study
Criminal law thesis topics
The study of Criminal law comprises understanding the laws that govern the prosecution of individuals who have committed crimes as defined by law. When you select law master thesis topics based on criminal law, you can choose law enforcement topics related to drug dealing, manslaughter, kidnapping, and more. Some examples are shared below:
- Female and male rape legislations: An in-depth evaluation of critical differences
- Using lie detectors _ an assessment of their efficacy in criminal justice
- Are manslaughter laws possible to misuse — what are the remedies to protect such victims?
- A detailed analysis of crime-related factors best not presented in the court of law and why?
- Witness protection – laws, guidelines, and measures against retaliation
- Death Penalty – History, justification, and analysis
- Criminal theory – A thematic review to explore the connection between morality and crime
- Challenges in identification of the nature of crime and its distribution — an in-depth analysis based on a case study
- Is anatomy justified in lawsuits related to sexual offenses — evaluating the rights of the victim and the defendant
- Legal rights — striking a balance between the rights of the victim and the defendant during the lawsuit
- What are the implications of the war against terror — Enforcement of criminal law and its implications
- A case study analysis of the war against terror
- A case study analysis of racial prejudice in prison
- Religious laws and crimes in developing nations
- Police interrogations – Principles, legal framework, and human rights
Child in conflict with the law thesis topics
These topics are related to the study of issues and laws concerning children who conflict with the law due to committing juvenile crimes.
- Legal protection and rights of children in cases of a child in conflict with the law
- Children in conflict with the law in metro cities and the legal framework guiding the handling of such cases
- Improving the legal protection available for children in conflict with the law
- An in-depth study of the measures available to reintegrate children in conflict with the law into the society
- Laws to facilitate the rehabilitation of children in conflict with the law
- Exploitation and abuse of children in conflict with the law and remedies to prevent it
- Procedures in court for children in conflict with the law
- Violence and exploitation leading children into conflict with the law – Case study analysis
- Human rights and laws supporting children affected by illegal migration
- Analyzing children’s rights against harmful work and economic exploitation
Controversial law topics
As a college student, there will be umpteen issues that will spark debates and encourage you to take a stance either for or against. These may include constitutional law paper topics or laws on sensitive matters that have triggered global emotions. Here are some such topics to explore:
- Reviewing the need for the Gun Law
- Abortion – Pro-choice or pro-life the legal angles
- Understanding religious freedom by law and the freedom of choice to deny service based on religion
- Prescription of addictive opioids as legal painkillers — the justification and after effects
- The legal framework guiding animal research
- Vaccine administration from the perspective of legal implications, compliance and non-compliance, herd immunity, and parental duty
- Right to privacy – the conflict between individual privacy Vs public safety
- Freemarket capitalization – government regulations vs free trade
- Environment support policies, government regulations, and economic costs
- Uniform minimum wage system — controversy, legal parameters, and remedies
- White supremacy — a political ideology that affects the legal and economic framework
- Legalizing marijuana for medicinal and recreational usage
- Capital punishment and its legal justification
- The Marriage Equality Act – Rights and responsibilities in same-sex marriages
- Black lives matter — an insight into the lack of political or legal repercussions for death in custody
- Immigration restrictions and reforms – scope for improvement and change
- The Deferred Action for Childhood Arrivals (DACA) program and upholding deportation protection
- Temporary blocking of international students during the Corona Virus Pandemic – Legal implications
- Transgender rights — Remedies against discrimination and injustice caused by inequality
- Islamic Criminal law vis a vis Human Rights — an analysis.
Sports law topics
Sport is an ever-intriguing subject, and it offers some interesting legal topics for dissertation writing. Your topic can cover international sports laws, rules and regulations guiding sports, sporting bodies, their jurisdiction, and more.
- Cheerleading teams — negligence across different case studies
- Sports law implications on cases of doping in international events
- Legal aspects of international sporting events and the role of social media
- The transnational perspective of sports management – an overview
- Bosman Rulings – The EU Sports law and its international implications
- The management of club sports in the UK and related laws
- Match-fixing in football and sports laws governing the same
- Match-fixing in cricket and international sports laws governing the same
- Sportspersons marketing – Reviewing legal issues and influences
- Sports promotion aids in the UK, US, and EU — legal implications
- Legal aspects related to governance and monitoring of sports organizations
- Sports laws on lifestyle sports – a review
- National governing bodies of sports and their legal stance
- The role and impact of labor contracts concerning UK sporting bodies
- Policies and practices of the US sports law
- Visa systems for international sportspersons and problems faced by them
- Constitutional rights of student-athletes
- Sexual harassment in sports and laws against it
- Policies aiding the promotion and protection of rights of transgender athletes
- Coaches’ contract and employment laws
Hot thesis topics in employment law
Employment law offers some very interesting law topics to work on. Under this, you can write your dissertation on labor laws, worker compensation, immigration laws, minimum wages, wrongful termination, and many such research topics in law.
- How employment laws convergence with religion in the US
- UK employment laws — A before and after comparison after exiting the EU
- UK Trade Unions and their impact — challenges and successes
- A review of unfair dismissal laws in the UK
- Employment laws in the UK and US automobile industry — A comparative study
- Employment contracts in the UK manufacturing industry — A comprehensive study of job satisfaction
- Issues with application and enforcement of laws in international firms: A case study
- Agency workers — employment rights and legal status in firms
- US ‘Fire at will’ employment ability and should it be made possible in the UK.
- Social work employment — Reviewing all legal aspects through a case study
- Employee dismissal — a comparison of UK and EU laws.
- Working parents and the benefits of Flexibility Working Regulations 2002
- Gender differences in employment laws and regulations across the US and the UK.
- Analyzing the efficacy of sexual harassment laws in the workplace
- Employee mobility across EU countries — a legal overview.
- Employment laws concerning the disabled in the UK — policies, and practices
- Equality Act 2010 and the rights of disabled
- A comprehensive study of the right to fair labor practices in the UK
- Unfair Vs Wrongful — what offers greater protection under employment laws
- Zero-hour contracts — significance and ways to improve
Medical law and ethics thesis topics
Medical law focuses on the rights and responsibilities of patients and medical professionals. Some exciting areas of medical law that you can focus on include patient confidentiality, patient consent, negligence, professional malpractice, failure in diagnosing, treatment malpractices leading to injury or death, and patient defamation among other topics.
- Laws governing organ retention — pros and cons
- Organ transplantation — A comprehensive study of governing laws in the US.
- Abortion — A comprehensive study of governing laws and stages when abortion is allowed or forbidden in the UK.
- Do judges handling medical disputes need special education to ensure fact-based judgments?
- Forced sterilization — laws, implementation, and who is to be targeted?
- Laws governing medical research — a comprehensive study
- Disputes arising due to medical complications during surgeries — legal implications
- Unregistered medical intervention — Legal implications in the US
- Electronic fetal monitoring and concerning laws.
- Medical ethics in practice concerning medical law
- Assisted suicide — the legal, ethical, and medical perspectives
- Lawsuits and their effect on the commitment and dedication of medical practitioners
- Biobanks — The associated legal and ethical challenges
- Is it possible for medical practitioners to treat mental disorders without bias?
- Laws against animal cruelty during medical research — a case study
Family law thesis topics
Besides marriage, divorce, custody, compensation, and alimony, you can cover several other interesting aspects of family law in your dissertation. Given below are some examples of topics you can explore:
- UK Family Law — Changes over the past five decades.
- Human rights in countries following religious family laws
- Family lawsuits and how they are impacted by culture
- Domestic violence and its effects on men Vs women
- Deciding custody in divorce cases and the importance of the child’s desire in influencing the court’s decision
- Divorce law and how it has impacted the number of divorces
- Child neglect and its legal implications in the US
- Child justice Vs family justice: Evaluating the compatibility
- What are the factors that prevent couples from seeking a divorce?
- US family law — is it due for reforms?
- Family law and its provisions when a divorced parent wishes to move abroad with the child
- Cohabitation Law in the US and is it due for reforms
- Divorce laws — are they gender-biased or is it only a perception
- Custody rights when the child has learning disabilities — a comprehensive overview
- Do Islamic traditions impact family laws of UK-based Muslims
- UK family laws governing financial decisions in cases of dementia and forced separation
- Rights of children to have a family life in non-marital families
- Family laws governing marriage and divorce in transgender people — a comparison of US and UK
- Legal implications of non-consensual adoption in the US
- The role of grandparents in the social fabric and provisions in the Family law
The topics mentioned above are great examples of what you can write on. However, if you are still confused, are running against time, have too much on your platter, or are simply unsure how to proceed to feel free to take law thesis help from some of the best-rated writers we have on board.
Feel free to ask for a sample from the professional you shortlist, and we will be happy to assist you all the way. Get in touch with us online or call us for help with a research paper. We have a team of experienced writers who offer high-quality, original work done to perfection. Our services are available at cheap and affordable rates as we are aware that we are assisting college students. So go ahead and connect with us for quality assistance to get you good grades and a stress-free time to focus on your academic commitments.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
- How It Works
- PhD thesis writing
- Master thesis writing
- Bachelor thesis writing
- Dissertation writing service
- Dissertation abstract writing
- Thesis proposal writing
- Thesis editing service
- Thesis proofreading service
- Thesis formatting service
- Coursework writing service
- Research paper writing service
- Architecture thesis writing
- Computer science thesis writing
- Engineering thesis writing
- History thesis writing
- MBA thesis writing
- Nursing dissertation writing
- Psychology dissertation writing
- Sociology thesis writing
- Statistics dissertation writing
- Buy dissertation online
- Write my dissertation
- Cheap thesis
- Cheap dissertation
- Custom dissertation
- Dissertation help
- Pay for thesis
- Pay for dissertation
- Senior thesis
- Write my thesis
213 In Depth Law Thesis Topics For Perfect Score

Universities around the world require learners to complete papers on law thesis topics when pursuing advanced legal studies. Completing this task is both stressful and exciting because of the reward of writing a quality paper. However, selecting a title for your project, researching it, and writing is not easy.
For this reason, students should select interesting legal topics to enjoy working on their theses. What’s more, they should settle on issues that provide ample research scope. A thesis or dissertation is a lengthy academic paper. Therefore, learners should select topic ideas they can manage and work with comfortably over time. Here are sample topics for learners with difficulties selecting topics for their dissertations.
Interesting Law Topics for Theses
Perhaps, you’re looking for exciting topics to form the basis of your academic papers. In that case, consider these exciting law dissertation topics for inspiration.
- Examining presumption validity resulting advancement and trusts have acquired defunct status requiring their abolishment
- How Harison vs. Gibson decision changed the intention certainty law
- Investment trustee powers: Examining the financial benefits considerations by the courts
- Examining the courts’ attitude as shown in relevant rulings towards trusts with political purposes
- How the prevailing media entities’ attitude and the first Amendment rights to speech freedom advance the public interest
- Examining legal and moral issues surrounding abortion procedures on a long-term basis
- The ramifications of Roe v Wade amendments to offer adequate protection to the father’s rights
- Examining the conflict between public safety and civil liberties in the anti-terrorism legislation arena
- Analyzing the judicial review process from the weak vs. strong perspective
- Analyzing the law that governs the state authority to intervene in citizens’ private lives when a child’s welfare is in question
- How the law responds to domestic violence effects on male victims
- Examining the central trademark protection’s rationale as a way for businesses to protect brand value versus public interests
- Can the copyright system respond to intellectual property digitalization and the internet challenges?
- Comparing the U.K. and U.S. trademark and copyright law, including damages
- How viable is benefit-sharing as a way to regulate intellectual property rights?
- Examining the conflict between corporate trade secrets and business law
- Analyzing the role of customs and cultural norms in international criminal law’s development
- Examining the relationship between international law and national law
- What are the legal ramifications of authoritative norms breaches in international law?
- Analysis of the legal ramifications of a stem cell study to use human embryos for profits
- Should governments restrict journalists’ expression freedom?
- An investigation of the weak and strong points of the judicial review process?
- How effective are anti-corruption laws in your state?
- Abortion legalization- How the law treats abortion and the moral elements of the problem
- Relocating with a child- Discussing the legal gaps in relocation
- Assets division after divorce- How fair is the divorce law?
- Child protection from abuse and neglect- Gaps in the current law
- Child labor prevention- Legal mechanisms for detecting and preventing child labor
- Mediation role in family law- Should it be mandatory?
- Changes in the cohabitation law- Should cohabitating and married couples enjoy equal treatment?
- Can copyright owners and authors protect their rights under the current copyright law?
- Copyright law and modern art- Which contemporary artworks should enjoy copyright protection?
- Trade secrets protection under business law- How to ease the existing conflict
- National and international law- Which are the prevailing rules?
- Peaceful international conflicts resolution- Discuss the current international dispute settlement mechanisms.
- International law attitudes towards the self-determination concept- How to set a fair balance between the minorities and majorities interests
- Organ retention legislation- How to regulate the existing problems and controversies
- When should the international criminal court come into play?
- How domestic violence accurate picture differs from statistics
- Why does the law give severe punishment for some crimes?
A carefully selected example in this category can spark exciting research that will lead to a brilliant thesis. Nevertheless, pick an exciting idea to come up with a dissertation that will impress your educator.
Commercial or Business Law Thesis Topics
Maybe you’re looking for the best business or commercial law master’s thesis topics. That means you need titles that will allow you to focus on the legal aspects of the rights, conducts, and relations of organizations or individuals that engage in merchandising activities, trade, or commerce. Here are exciting business law topics to write about when working on your thesis.
- Do the current commercial laws in the U.S. need any change?
- How effective are the international business law programs in U.S. universities?
- How effective is business law in supporting commercial transactions?
- Does corporate social responsibility have a mediating role in companies’ performance?
- What are the impacts of international commercial laws on U.S. business laws?
- A review of the international business law use in new projects
- An evaluation of commercial laws for dealing with dishonest business managers
- Commercial partnerships- A closer look at the potential results and dangers
- Regulations for stopping corruption- A UK case study
- Analyzing pre-incorporation contracts- How they work
- Evaluating arbitration under business law- Understanding the U.K. policy practices
- What are the difficulties, significance, and essence of a commercial lease to business owners?
- Regular versus commercial lease- Analyzing its advantages and disadvantages for businesses.
- The role of the legislature in working and interpreting contracts
- Commercial law’s role in business framework establishment in society
- An evaluation of contract laws and their effects on businesses
- Verbal and non-verbal agreements in the business law’s context
- Analyzing business entity’s role concerning commercial law
- Evaluating business laws for fighting corruption in companies
- How effective is commercial law in prompting transactions?
- Copyright infringement- How offline and online law enforcement differ.
- Business partnerships- Understanding legal remedies, results, and threats
- Commercial laws for guiding businesses in energy projects
- How to work within the advertising law’s guidelines and framework when advertising online
- Analyzing the significance, role, and application of wills within the business law
- International vs. national commercial laws
- Analyzing pre-incorporation contracts
- Assessing the effectiveness of international commercial law
- Why investing in a business’ trademark and copyright application matters
- Commercial law arbitration- An in-depth evaluation and analysis of policy practice
- An evaluation of anti-corruption business regulations using a relevant case study
- Corporate social responsibility laws for businesses
- Termination agreements- Significance, role, and application in business transactions
- Contract law- Role and interpretations in business transactions
- Director’s guarantee- Transaction structure and role within business law
- Analyzing business entity’s role in commercial law
- Exploring loopholes in international laws that allow business corruption
- Consumer protection in Wales and England after the Brexit era
- Investigating Wales and England’s insolvency laws for addressing insolvency instances
- A legal assessment of the commercial law role in sustaining public-private partnerships, depending on what happened during the Carillion Collapse
These research topics in law can be the basis of a paper that will earn you the top grade. However, be ready to research your preferred idea and analyze information to write a high-quality essay.
International Law Thesis Topics for Research
Some learners find international law research topics quite interesting because they focus on legal aspects of businesses during global pandemics and wars. You can also focus on the economic trade aspect when writing a thesis on any of these ideas. Here are exciting topics for a law school thesis in this category.
- Precedence importance during international court hearings
- Internet and digital legislation- Future forecasts
- How civil liberties and public safety relate within the context of international laws
- Analyzing the principles of the international law
- Challenges facing different parties during the application of the Vienna Convention on the international sale of good contracts
- Assessing business implications of the future possibilities of the U.K. and U.S. military cooperation in fighting terror
- When international law allows a country to intervene in another nations’ affairs
- A closer look at the human rights gaps from the international law’s perspective
- Analyzing the U.S. involvement in Iraq- Was it a violation of international law or a justified move?
- How to enforce international law in third world countries
- Analysis of international tribunals’ efficiency in addressing war crimes
- International human rights hearings- Why precedence matters
- Challenges facing parties in contracts relating to the international sale of goods and the application of the Vienna Convention
- Why the international law matters for the digital laws and internet legislation
- How effective are international tribunals in taking action for war crimes?
- Analyzing conditions when the international law permits a country to intervene in trade matters
- Assessing the international criminal laws’ principles and why change could be necessary
- Analyzing the human rights law from an international perspective
- Human rights and international law violations- A case study of U.S. involvement in Iraq
- The impact of civil liberties as enshrined in the international law on public safety
- International consumer protection during the post-Brexit era
- International laws for protecting consumers against unlawful communication during the war
- International laws for protecting and rescuing the refugees’ human rights at sea
- Top five offenders facing the international law and their offenses
- How the international law can protect child soldiers during the Israel-Palestine conflict
- NATO ethics in Afghanistan and Iraq
- Human rights violation in Africa- How the international law can address them
- Describe the appeal process for the international criminal court
- Analyzing the international tribunals
- XYZ corporation’s transnational crimes- A detailed analysis
These are exciting thesis topics for law students interested in international law. Nevertheless, learners must invest time and effort in research and data analysis to develop quality papers.
Controversial Law Topics for Academic Research
Some law master thesis topics can trigger debates while encouraging learners to take a stance in support or against an idea. Such titles can include constitutional law paper topics and sensitive matters in different legal study fields. Here are exciting topics in this category.
- Does the world need gun law review?
- Analyzing human rights vis a vis the Islamic criminal law
- Transgender rights- Solving injustice and discrimination arising from inequality.
- Legal implications of blocking international students temporarily during the COVID-19 pandemic
- Deportation protection and the Deferred Action for Childhood Arrivals program
- Immigration reforms and restrictions- Change and improvement scope
- Black lives matter- Analyzing the lack of legal or political repercussions of custody deaths.
- Abortion- Legal angles for pro-life and pro-choice
- Analysis of religious freedom in law and the choice freedom to deny person services depending on their religion
- Addictive opioids prescription as legal painkillers- Justifications and the aftermath
- The legal framework for animal research
- Vaccine administration from the legal implications perspectives, non-compliance and compliance, parental and herd immunity’s duty
- Privacy rights- Conflict between public safety versus individual privacy
- Free market capitalization- Free trade versus government regulations
- Analyzing government regulations, environmental support policies, and economic costs
- Equal minimum wage system- Legal parameters, remedies, and controversies
- Legalizing marijuana for recreational and medicinal usage
- White supremacy- How this political ideology affects the economic and legal framework
- The legal justification of capital punishment
- Marriage equality act- Analyzing responsibilities and rights in a same-sex marriage.
- The ethics of capital punishment
- Law code and mental hospitals
- Analyzing the legal implications of sniffer dog practices
- College violence causes and legal implications
- Legal code in different states in America
- Crime propaganda and modern music culture- Using the law to address the emerging issues.
- Is the law biased against African-Americans?
- The limited rights for police officers
- The importance of eyewitness evidence
- How developing countries can improve business laws’ effectiveness
- Does the world have more female lawyers than males?
- Trade union role in championing for the workers’ rights
- Effects of technology on business laws’ viability
- Impact of coronavirus on business laws
- Why employees deserve a role in business laws’ formulation
- Why business laws are employee-oriented instead of siding with team members
- Business laws and their role in preventing malicious competition
- Can business law undermine women’s empowerment?
- Should every country have unique business laws for foreign investors?
- How sufficient are business laws in covering cyber espionage?
These are controversial ideas to explore in dissertations. However, learners should prepare to research extensively to write winning papers.
Child in Conflict with the Law Thesis Topics
This category comprises titles relating to legal issues concerning kids that contravene the law by committing juvenile offenses. Nevertheless, they are exciting law enforcement topics to explore when pursuing masters or Ph.D. studies.
- Analysis of children’s rights against economic exploitation and harmful work
- Laws and human rights that support children during illegal migration
- Exploitation and violence leading children into legal conflicts
- Court procedures for children that break the law
- Abuse and exploitation of children that violate the law and how to prevent it
- Rights and legal protection for children during cases
- The legal framework for guiding the people handling children’s cases
- How to deal with children involved in legal matters in metro cities
- How to improve legal protection for children during conflict
- Analysis of the measures for reintegrating children into the society after conflicting with the law
- Laws for facilitating children’s rehabilitation after conflicting with the law
Criminal Law Thesis Topics
Criminal law entails the study of rules governing individuals’ prosecution after committing crimes. Here are titles to consider in this category.
- Crimes and religious laws in developing countries
- Analyzing the war against terror and potential crimes
- Examining racial prejudice during incarceration
- Police interrogations- Legal framework, human rights, and principles
- Balancing legal rights for the defendant and the victim during a lawsuit
- Anatomy justification with the defendant and victim in mind
- Challenges in the crime’s nature identification and distribution- A case study analysis
- Criminal theory- A review for exploring crime and morality connection
- Death penalty justification, research, and history
- Male and female rape legislations- Evaluating the critical differences
- Lie detectors use in criminal law courts- Assessing their efficacy
- How to protect victims in case of manslaughter cases
- Analyzing crime-related factors best left out of the court
Family Law Thesis Topics
Family law has several ideas to explore in a dissertation. Here are examples of such notions.
- Grandparents’ role in the family law provisions and social fabrics
- Non-consensual adoption- What are the legal implications?
- Family laws that govern divorce and marriage for transgender individuals
- Children rights to family life within non-marital families
- Impacts of Islamic traditions on family laws for UK-based Muslims
- Custody rights for children with learning disabilities
- Divorce laws- Are they perception or gender-based?
Medical Law and Ethics Thesis Topics
This field focuses on the responsibilities and rights of medical professionals and patients. Here are brilliant ideas to consider in this category.
- Laws governing medical research- Animals protection against cruelty
- Can medical practitioners treat mental disorders without bias?
- Ethical and legal challenges relating to bio-banks
- Effects of lawsuits on medical practitioners dedication and commitment
- Medical, ethics, and legal perspectives of assisted suicide
- Medical laws and ethics in practice
Sports Law Topics
If interested in sports law, consider these topics for your papers.
- Coaches employment laws and contracts
- Policies facilitating rights protection and promotion for transgender athletes
- Rules for fighting sexual harassment in the sporting field
- Constitutional rights for student-athletes
- Practices and policies of sports law in the U.S.
- The legal stance for national sports governing bodies
- Lifestyle sports- What sports laws say about them
- Analyzing the negligence of cheerleading teams with a case study
- The role of legal aspects of sporting events at the international level
- Transnational sports’ management perspective
- Laws relating to club sports management
- Match-fixing and the related laws
- Legal issues relating to sportsperson marketing
- The legal implications of sports promotion aids
Hot Thesis Topics in Employment Law
Do you want to write a thesis on employment law? If yes, consider any of these ideas for your paper.
- How to improve zero-hour contracts
- Wrongful vs. unfair- What provides better protection within the employment laws
- Studying the right to fair employment practices
- 2010 Equality Act and the disabled people’s rights
- Employment laws for the disabled
- Effectiveness of sexual harassment laws at the workplace
- Gender variations in employment regulations and laws
- How working parents benefit from Flexible Working Regulations 2002
- The convergence of employment laws with religion
- The impact of trade unions on businesses
- Unfair dismissal- What the law says
- Legal aspects of social work employment
If you pick any of these topics and then have difficulties down the road, seek help with research paper from the best-rated online experts. Using affordable thesis help, you can complete your project on any of these titles. Nevertheless, work with a professional company to get cheap and quality assistance.

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Comment * Error message
Name * Error message
Email * Error message
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
As Putin continues killing civilians, bombing kindergartens, and threatening WWIII, Ukraine fights for the world's peaceful future.
Ukraine Live Updates

30,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today
Here’s your new year gift, one app for all your, study abroad needs, start your journey, track your progress, grow with the community and so much more.

Verification Code
An OTP has been sent to your registered mobile no. Please verify

Thanks for your comment !
Our team will review it before it's shown to our readers.

- Updated on
- Dec 29, 2022

Regarded as the highest degree in varied academic disciplines, a Doctorate of Philosophy ( PhD ) aims to provide students with a chance to delve deeper into a specific area of study. For a field like Law, a doctoral degree is suitable for those wanted to pursue their career as legal scholars and teachers. A PhD in Law incorporates intense coursework followed by detailed research in the chosen specialization. The program is devised for students who want to gain in-depth knowledge and advanced studies in the domain. If you also want to secure a doctorate degree in Law, you should definitely aim for attaining overseas education for the same. Through this blog, we will elucidate various aspects of PhD in Law, the eligibility criteria you need to fulfil, course structure and specialisations as well as top universities.
This Blog Includes:
Specialisations offered, course structure, top universities abroad offering phd in law, top colleges in india, entrance exams in india, phd in law: distance education, important books, eligibility for phd in law, application process , required documents .
Commonly offered as a 3-year degree, a PhD in Law implements a multidisciplinary approach and aims to impart students with the required theoretical background and research skills in the former part of the program while they are required to prepare their dissertation during the latter part. Often pursued as a full-time course, this degree prepares individuals for several leadership roles in Judiciary, Business, Academics as well as Government.
There are a plethora of concentrations available under PhD in Law from which applicants can choose from. These courses connect the vast discipline of law with its relevant sub-fields, hence students can opt for a unique course and specialize in the same. Selecting a particular specialization also helps to delve deeper into it by pursuing research. Take a look at the following list of PhD in Law specialisations:
- PhD in Interdisciplinary Law
- PhD in International Law
- PhD in Legal Studies
- PhD in Cyber Law
- PhD in Civil Law
- PhD in Jurisprudence
- PhD in Administrative Law Studies
- PhD in Environmental Law
- PhD in National Law Studies
- PhD in Dispute Resolution
Check Out: Law Subjects
The curriculum and syllabus of a PhD in Law can vary as per the specialisation as well the academic institution. But in order to provide you with a general overview, the following paragraphs describe the structure of this doctoral degree as followed for a 3-year program.
- In the first year of a PhD in Law, students get to focus on the coursework of their specialisations with their prospective Advisory Committees. Along with this, it also comprises a seminar regarding legal scholarships and methodologies. With all this, the degree also incorporates canonical workshops on legal scholarships in the first semester of the year. In the second semester, students are required to present a report on the same.
- During the second year, you will get to work with the faculty dissertation committee. Students have to present the dissertation in a manuscript of almost a book’s length or 3 articles that can be published thus constituting the portfolio. Afterwards, the committees will provide their views on one’s dissertation prospectus and give their seal of approval if they liked the topic. Apart from this intense research work of PhD in Law, students ought to compulsorily participate in teaching activities where they can work as teaching assistants, co-teaching with faculty etc.
- In the third year, students can either continue with their teaching as a professor of Law or they can go on with improvising their dissertation. In many cases, one can devote themselves to their research projects while pursuing teaching and at the conclusion of the third year, they will be required to submit their dissertation. However, the extension of the duration can also happen depending on a case-to-case basis.
Deciding the right university for a course can be a strenuous task and requires professional help. Leading law schools and universities around the globe possess the necessary capabilities to transform the personalities of enrolled students. These extra-edge attributes can help you have a kickstart in your career and convert your career aspirations into success. To grab a taste of global exposure and a plethora of opportunities in this field, here are some top-notch universities offering PhD in Law that you must consider:
Tabulated below are the top colleges in India offering a PhD in law. You can have a look here:
There are various entrance exams in India that you can apply for and attempt in order to be selected for a PhD in Law. They are mentioned below.
Did you know that you can pursue a PhD in law through distance education? A lot of established and good colleges as well as universities offer the course part-time or through correspondence. Tabulate below are some of the important colleges that offer PhD in Law through distance learning.
Tabulated below are the important and informative books you can refer to while pursuing a PhD in Law. You can check it out here:
PhD Law Admission Process
There are two ways of getting admission in PhD in Law. You can either get direct admission or merit.
Direct Admission
- For direct admission, you must get the admission form from the college or university. You can get it both offline and online.
- To get the application form you can go to the official website of the institute or college and fill the form there. You can upload it there and then.
- Once you have completed filling out the application form you must go to the college for counselling and also attend the round of personal interviews.
Merit-Based Admission
- The important exams conducted to give admission on the basis of merit include JMI Law Entrance Exam, CLAT, AILET – All India Law Entrance Test , NET – National Eligibility Test , and PET – PhD Entrance Test.
- Students can apply for these exams both offline and online. The forms for the respective exams can be downloaded on their official websites.
- Admission will be given on the basis of the subsequent marks obtained by students in these exams.
To get enrolled in any degree, candidates need to meet certain prerequisites specified for the course by the institution. Since there are a lot of specializations available for PhD in Law, the eligibility criteria tend to differ from one university to another. Below listed are some essential requirements that you need to fulfil in order to apply for the program:
- Bachelor’s degree in Law such as LLB or any other related discipline
- Master’s degree in Law, i.e. LLM although some universities may allow candidates having a postgraduate degree in similar disciplines
- Students are also required to qualify for the LSAT exam with a good score.
- Research Proposal (Around 1000 words): Describing the scope of the project along with undertaken dissertation.
- If you’re applying to foreign universities, you need to give English Language Proficiency Tests such as IELTS , TOEFL , etc.
- It is recommended for the candidates have a well-designed Curriculum Vitae.
This is another important aspect you need to keep in mind if you’re planning to become a lawyer. But the application process might get overwhelming. This is where the professional from Leverage Edu will help you. It’s important to complete the application process without any mistakes. Here are crucial things to consider:
- Call us and we will help you shortlist your favourite law universities . But you need to submit your application to multiple universities to broaden your chances of getting selected.
- Compile all essential documents. Don’t make mistakes while submitting the documents.
- Submit the application before the deadlines and start the application process for accommodation, students visa, and scholarships / student loans .
- Accept the offer letter
The documentation process is one of the most essential steps you should consider. But making some common mistakes will jeopardize your application. The documents you need to submit are::
- Educational certificates. As you’re going for a law degree, you need to provide your other mark sheets such as the 12th mark sheet, UG mark sheet, etc.
- Letter of recommendation
- Letter of intent
- Financial documents
- Statement of purpose
Career Prospects and Salary
After completing your PhD in law from a reputed university, you will be able to boost your chances of getting hired by top companies. Employers will take a look at your university name as it will have a huge impact on your employability. Therefore, make sure you complete your PhD degree from a reputed university to stand apart from the crowd. Here are the jobs you can get after completing your PhD in law:
- Law Professor
- Political Advisor
- Project Manager
- Compliance Manager
The salary of a lawyer who holds a PhD degree will vary from one designation to another as well as the country. Here’s a table:
Also Read: Law Entrance Exams India & Abroad
Taw law and corporate law are the most effective.
If you want to get into a high-ranked university, you’ll need more than just good grades; you’ll also need flawless application because the competition is fierce. You may enlist the assistance of Leverage Edu specialists to assist you with the application process so that you can realise your goals. Call us immediately at 1800 57 2000 for a free 30-minute counselling session.
Team Leverage Edu
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Contact no. *
Thanks a lot ! This is very useful article for the newbies who are interested in pursuing PhD in Law.
thanks for your valuable feedback

Leaving already?
8 Universities with higher ROI than IITs and IIMs
Grab this one-time opportunity to download this ebook
Connect With Us
30,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. take the first step today..

Resend OTP in

Need help with?
Study abroad.
UK, Canada, US & More
IELTS, GRE, GMAT & More
Scholarship, Loans & Forex
Country Preference
New Zealand
Which English test are you planning to take?
Which academic test are you planning to take.
Not Sure yet
When are you planning to take the exam?
Already booked my exam slot
Within 2 Months
Want to learn about the test
Which Degree do you wish to pursue?
When do you want to start studying abroad.
September 2024
January 2025
What is your budget to study abroad?

How would you describe this article ?
Please rate this article
We would like to hear more.
- Top Colleges
- Top Courses
- Entrance Exams
- Admission 2024
- Study Abroad
- Study in Canada
- Study in UK
- Study in USA
- Study in Australia
- Study in Germany
- IELTS Material
- Scholarships
- Sarkari Exam
- Visual Stories
- College Compare
- Write a review
- Login/ Register
- Login / Register
50+ Law Dissertation Topics for Students 2024

Manali Ganguly ,
Mar 4, 2024
Share it on:
The law dissertation topics that are most important for the law-students in 2024 are environmental law, family law, tort, labour law, medical law, intellectual property, criminal law, and tax law among others.

The law dissertation topics for law students include criminal law, labour law, intellectual property, family law, constitutional law, IT law, and a lot more. These topics can be taken up for writing a dissertation paper on law.
A dissertation implies making thorough research work on a topic and presenting the arguments in support of that. The students who are planning to get their BA LLB or masters or PhD must understand the importance of a dissertation. They can do just the law dissertation topics only when they have an understanding of it. This article will share a list of law dissertation topics that will help the students with their papers.
Table of Contents
Top Law Dissertation Topics for Students
Employment law dissertation topics, criminal law dissertation topics, corporate law dissertation topics, international law dissertation topics, family law dissertation topics, medical law dissertation topics, how to choose the right law dissertation topic.
Law can be classified into various categories and branches. The sections below will list down the law dissertation topics under different categories for the easy reference of the students.
There are laws safeguarding the rights of the employees from any kind of exploitation. On the reverse, the laws for protecting the employer’s rights are also firmly established. The list of law dissertation topics with respect to employment is shared below:
- Justification of Labour Laws
- Equality in the workplace
- Laws to protect against discrimination against the third gender in the workplace
- The change of legal code about the workers’ legal status over the years
- Differences in maternal and paternal leaves
- Morality issues in employment screening
- Cases in which dismissal laws stand invalid
- How trade unions play a crucial role in upholding the rights of employees
- Employment law and job security
- PoSH Act 2013 and its effect on work culture
Also Check : Top Law Colleges in India
Criminal law is the law that regulates criminal activities. There are several topics that can be categorised under criminal law. The list of such topics are given below:
- An evaluation of the cost of death in India
- The POCSO Act: How it protects children against sexual abuse?
- Criminal justice
- Justice system for the juvenile in India
- Law against white collar crime
- Law against private terrorism and terrorist activities
- Roots of corruption lies in imitation
- Cybercrime and the laws against it
- Gun laws in the country
- Laws against substance abuse in India
Also Check: Top 9 IPU Law Colleges in India
Corporate law can be said to be a set of laws that control the formation, governance and management of a corporation. There is a set of interesting corporate law dissertation topics that the students can work on. They are:
- The legal implications of promoting ethnic and gender roles in the corporate industry
- General counsel and corporate legal strategies
- Legal consequences of avoiding taxes
- Cross-border ecommerce transaction and legal formalities
- Economic sanction on corporate industry: Legal implications
- Laws against corporate liability in environmental damage
- Trading laws within India
- Compliance with cyber security laws in corporate functioning
- Cybersecurity laws in favour of the corporate industry
- Laws against workplace discrimination
- Are the internal corporate policies being shaped by the external auditors?
- The restructuring of corporate governance by blockchains
- What can be called good corporate governance?
- Laws for mitigation of corporate risk
- Corporate digital transformation
Also Check : Top 10 Law Colleges other than NLUs: Ranking, Courses, Admission
The International Law courses require the students to write extensive dissertation papers. International Law can be said to be a set of laws that is binding upon the states. The dissertation topics on international law can be found below:
- International institutions and promotion of international law
- National and international laws and regulations: Differences
- Role of GDPR in corporate functioning
- Laws against human trafficking
- Laws for the protection of sensitive data of the country
- Laws for the protection and preservation of the rights of refugees
- International law and intellectual property rights protection
Family law is the set of laws that govern the relationship between the members of a family which includes marriage, relationship between husband and wife, relationship between siblings, relationship of the parents with their wards, etc. The topics of dissertation on family laws are:
- The matrimonial act and its role in preserving the rights of both the parties in marriage
- Are divorce laws in India biassed?
- The laws protecting children against physical abuse within the family
- Inheritance law
- Divorce laws and the custody of children
- Adolescent abuse and the laws safeguarding against such abuse
- Child rights within the family
- Protection of children against parental abuse
- Protection of the elderly against abuse at the hands of their children
- Property distribution laws within the family
Also Check: Cyber Law Courses: Eligibility, Admissions, Top Colleges, Career Scope
The medical law is binding on the medical professionals as well as on the patients. The law protects and safeguards the rights of both the parties against exploitation. The popular dissertation topics for students under the medical laws are:
- Laws against sex detection of the embryo
- Laws against abortion: A comprehensive study
- Laws protecting the rights of patients against exploitation
- Legal implications of disputes arising out of wrong surgeries
- Forced Sterilisation and medical laws
- Infanticide
- Medical intervention without registration
- Biobank and the associated ethical and legal challenges
- Laws protecting animal rights in the course of medical research
- Laws safeguarding the patients against medical practitioners practising without a valid certificate.
Also Check: Business Law Courses in India: Eligibility, Colleges, Duration, Fees
The law students will find innumerable topics for presenting their papers. It is crucial to choose the right one. The students must do thorough research before selecting a topic for the dissertation.
Even in the Bachelor’s degree course of law, the students need to present a dissertation paper. Students must perform extensive research to ensure that adequate information and data are available in order to write the dissertation paper.
POST YOUR COMMENT
Related articles.

Top Private Law Colleges in India Accepting CLAT Scores 2024
Criminal Law Courses: Eligibility, Admissions, Top Colleges, Career Scope

Last Minutes Revision Tips for LSAT 2024

Cyber Law Courses: Eligibility, Admissions, Top Colleges, Career Scope

Top 10 Law Diploma Courses in India 2024

Corporate Law Courses in India: Eligibility, Admissions, Duration, Colleges

How to Become an IAS Officer: Step by Step Career Guide 2024
Get Free Scholarship worth 25000 INR

See why the U of I College of Law is an excellent choice for your academic and professional success. See our viewbook
- Admitted Students
- Application Status
- Tuition & Costs
Emphasis Areas
- Business Law
- Environmental Law
- LSAT Prep Courses
- Student Accounts

Academic Administration
Important dates, class schedules, registration, honor code, and other general information for students. More Information
- Academic Calendar
- Room Calendars
Get Involved
- Student Organizations
- Pro Bono Program
- Externships
- Student Handbook
- Academic Success
- Law IT Services

Faculty-Staff Handbook
The Faculty-Staff Handbook provides an online reference for University of Idaho policies. View the FSH
Common Tools
- Human Resources
- Recreation and Wellbeing
- Administrative Procedures Manual (APM)
- Dates & Deadlines

You Can Inspire The Future
Support our students and programs at the College of Law. Inspire the future
Stay Connected
- Meet our Alumni
- Alumni Awards
- Law Advisory Council
- U of I Alumni Assoc.
- Law Library Service
- Find a Vandal
- VandalStore
- Liberty Mutual Benefits
College of Law

Embracing New Beginnings
Law Student Discovers Career by Leaning Into Opportunities

Argue Before the Ninth Circuit
Hands-on learning with our nationally recognized practical training programs Clinics

State Capital and Business Center
Boise in the south, at the governmental and business center of Idaho

Charming, College Town
Moscow in the north, on the main university campus

Grow with Idaho’s Business Leaders
Learn about our emphasis in Business Law, and our nationally recognized IP Law track

Native American Law
Learn more about the law by and between Tribal, Federal, and State governments
Email: [email protected]
Web: College of Law
Physical Address: Menard 101 711 S. Rayburn Drive
Mailing Address: College of Law University of Idaho 875 Perimeter Drive MS 2321 Moscow, ID 83844-2321 Main Office: 208-885-2255 Admissions: 208-885-2300 Legal Clinic: 208-885-6541 Office of the Dean: 208-364-4620
Fax: 208-885-5709
Physical Address: 501 W Front St, Boise, ID 83702
Mailing Address: 501 W Front St, Boise, ID 83702
Phone: 208-885-2255
Fax: 208-334-2176
The College of Law has emerged as one of the best educational values in the nation. The college’s success is built upon a steadfast belief that a law school should stand for serving the public, promote civil discourse, contribute to the dialogue on critical issues and provide access across all cultures and ideologies to the highest quality of legal education.
For students from outside Idaho, our non-resident tuition is significantly lower than schools in surrounding states. In addition, students from the 16 WICHE participating states and territories are eligible for in-state tuition through the Western Regional Graduate Program ( WRGP ).

Take a look at our law school, programs and faculty through our beautiful viewbook.
See Our Viewbook
Explore our College
Apply today.
As a fully accredited law school in the state of Idaho, the U of I College of Law is committed to providing high-quality, affordable public legal education statewide.
Apply to the College of Law
Located in Idaho’s capital, our Boise location puts students in the middle of the government and business center of Idaho.
Visit Boise
Located on the University of Idaho campus, our Moscow location offers options for interdisciplinary study, seven concurrent degrees and expanded class offerings.
Visit Moscow
Cybersecurity Guide
From scholar to expert: Cybersecurity PhD options
In this guide
- Industry demand
- 2024 rankings
- Preparation
- Considerations
- School listings
The cybersecurity landscape is not just growing—it’s evolving at a breakneck pace. And what better way to stay ahead of the curve than by pursuing a PhD in cybersecurity?
This advanced degree is no longer confined to the realm of computer science. Today, it branches into diverse fields like law, policy, management, and strategy, reflecting the multifaceted nature of modern cyber threats.
If you’re looking to become a thought leader in this dynamic industry, a PhD in cybersecurity offers an unparalleled opportunity to deepen your expertise and broaden your horizons.
This guide is designed to give prospective cybersecurity PhD students a general overview of available cybersecurity PhD programs. It will also outline some of the factors to consider when trying to find the right PhD program fit, such as course requirements and tuition costs.
Industry demand for PhDs in cybersecurity
Like other cutting-edge technology fields, until recently, cybersecurity PhD programs were often training grounds for niche positions and specialized research, often for government agencies (like the CIA, NSA, and FBI), or closely adjacent research organizations or institutions.
Today, however, as the cybersecurity field grows to become more pervasive and consumer-oriented, there are opportunities for cybersecurity PhDs to work at public-facing companies like startups and name-brand financial, software, infrastructure, and digital service firms.
One trend that is emerging in the cybersecurity field is that cybersecurity experts need to be well-versed in a variety of growing threats. If recent headlines about cybersecurity breaches are any indication, there are a number of new attack vectors and opportunities for cybercrime and related issues. Historically, committing cybercrime took resources and a level of sophistication that required specialized training or skill.
But now, because of the pervasiveness of the internet, committing cybercrime is becoming more commonplace. So training in a cybersecurity PhD program allows students to become an experts in one part of a growing and multi-layered field.
In fact, this trend of needing well-trained, but adaptable cybersecurity professionals is reflected by the move by cybersecurity graduate schools to offer specialized master’s degrees , and many companies and professional organizations offer certifications in cybersecurity that focus on particular issues related to cybersecurity technology, cybersecurity law , digital forensics , policy, or related topics.
That said, traditional research-oriented cybersecurity positions continue to be in demand in academia and elsewhere — a trend that will likely continue.
One interesting facet of the cybersecurity field is trying to predict what future cybersecurity threats might look like and then develop tools and systems to protect against those threats.
As new technologies and services are developed and as more of the global population begins using Internet services for everything from healthcare to banking — new ways of protecting those services will be required. Often, it’s up to academic researchers to think ahead and examine various threats and opportunities to insulate against those threats.
Another key trend coming out of academic circles is that cybersecurity students are becoming increasingly multidisciplinary.
As cybersecurity hacks impact more parts of people’s everyday lives, so too do the academic programs that are designed to prepare the next generation of cybersecurity professionals. This emerging trend creates an enormous amount of opportunity for students who have a variety of interests and who are looking to create a non-traditional career path.
The best cybersecurity PhD programs for 2024
Capella university, georgia institute of technology, northeastern university, marymount university, school of technology and innovation, nova southeastern university, college of computing & engineering, purdue university, stevens institute of technology, worcester polytechnic institute, university of illinois at urbana-champaign, mississippi state university, new york institute of technology.
These rankings were compiled from data accessed in November 2023 from the Integrated Post-Secondary Education Data System (IPEDS) and College Navigator (both services National Center for Education Statistics). Tuition data was pulled from individual university websites and is current as of November 2023.
What is required to get a PhD in cybersecurity?
Good news first: Obtaining a PhD in a field related to cybersecurity will likely create tremendous employment opportunities and lead to interesting and dynamic career options.
Bad news: Getting a PhD requires a lot of investment of time and energy, and comes with a big opportunity cost (meaning you have to invest four to five years, or longer, or pursue other opportunities to obtain a doctoral degree.
Here’s a quick breakdown of what is required to get a PhD in cybersecurity. Of course, specific degree requirements will vary by program. One growing trend in the field is that students can now obtain degrees in a variety of formats, including traditional on-campus programs, online degree programs , and hybrid graduate degree programs that combine both on-campus learning with online learning.
Related resources
- Online PhD in cybersecurity – A guide to finding the right program
- Cybersecurity degree programs
- Podcast episodes and expert interviews
Preparing for a cybersecurity doctorate program
Cybersecurity is a relatively new formalized technology field, nonetheless, there are several ways that students or prospective PhD candidates can get involved or explore the field before and during a graduate school program. A few examples of ways to start networking and finding opportunities include:
Join cybersecurity organizations with professional networks
Specialized professional organizations are a good place to find the latest in career advice and guidance. Often they publish newsletters or other kinds of information that provide insights into the emerging trends and issues facing cybersecurity professionals. A couple of examples include:
The Center for Internet Security (CIS) is a non-profit dedicated to training cybersecurity professionals and fostering a sense of collaboration. The organization also publishes information and analysis of the latest cybersecurity threats and issues facing the professional community.
The SANS Institute runs several different kinds of courses for students (including certification programs) as well as ongoing professional cybersecurity education and training for people working in the field. The organization has several options including webinars, online training, and live in-person seminars. Additionally, SANS also publishes newsletters and maintains forums for cybersecurity professionals to interact and share information.
Leverage your social network
Places like LinkedIn and Twitter are good places to start to find news and information about what is happening in the field, who the main leaders and influencers are, and what kinds of jobs and opportunities are available.
Starting a professional network early is also a great opportunity. Often professionals and members of the industry are willing to provide guidance and help to students who are genuinely interested in the field and looking for career opportunities.
Cybersecurity competitions
Cybersecurity competitions are a great way to get hands-on experience working on real cybersecurity problems and issues. As a PhD student or prospective student, cybersecurity competitions that are sponsored by industry groups are a great way to meet other cybersecurity professionals while getting working on projects that will help flesh out a resume or become talking points in later job interviews.
The US Cyber Challenge , for example, is a series of competitions and hackathon-style events hosted by the Department of Homeland Security Science and Technology Directorate and the Center for Internet Security to prepare the next generation of cybersecurity professionals.
Internships
Internships also continue to be a tried and true way to gain professional experience. Internships in technical fields like cybersecurity can also pay well. Like the industry itself, cybersecurity internships are available across a wide range of industries and can range from academic research-oriented to more corporate kinds of work.
Things to consider when choosing a cybersecurity PhD program
There are many considerations to evaluate when considering any kind of graduate degree, but proper planning is essential to be able to obtain a doctoral degree. It’s also important to note that these are just guidelines and that each graduate program will have specific requirements, so be sure to double-check.
What you will need before applying to a cybersecurity PhD program:
- All undergraduate and graduate transcripts
- A statement of intent, which is like a cover letter outlining interest
- Letters of reference
- Application fee
- Online application
- A resume or CV outlining professional and academic accomplishments
What does a cybersecurity PhD program cost?
Obtaining a PhD is a massive investment, both in terms of time and money. Cybersecurity PhD students are weighing the cost of becoming an expert in the field with the payoff of having interesting and potentially lucrative career opportunities on the other side.
Degree requirements are usually satisfied in 60-75 hours, so the cost of a doctoral degree can be well into the six-figure range. Here’s a more specific breakdown:
Tuition rates
The Cybersecurity Guide research team looked at 26 programs that offer a cybersecurity-related PhD degree. Here’s a breakdown of tuition rates (all figures are based on out-of-state tuition).
$17,580 is the most affordable PhD program option and it is available at the Georgia Institute of Technology.
$86,833 is the average cost of a cybersecurity PhD and is based on tuition rates from all 26 schools.
$197,820 is the most expensive cybersecurity PhD program and is available at Indiana University Bloomington.
The good news is that by the time students get to the PhD level there are a lot of funding options — including some graduate programs that are completely funded by the university or academic departments themselves.
Additionally, funding in the form of research grants and other kinds of scholarships is available for students interested in pursuing cybersecurity studies.
One example is the CyberCorps: Scholarships for Service program. Administered by the National Science Foundation, PhD students studying cybersecurity are eligible for a $34,000 a year scholarship, along with a professional stipend of $6,000 to attend conferences in exchange for agreeing to work for a government agency in the cybersecurity space after the PhD program.
Frequently asked questions about cybersecurity PhD programs
Most traditional and online cybersecurity graduate programs require a minimum number of credits that need to be completed to obtain a degree. On average, it takes 71 credits to graduate with a PhD in cybersecurity — far longer (almost double) than traditional master’s degree programs. In addition to coursework, most PhD students also have research and teaching responsibilities that can be simultaneously demanding and great career preparation.
At the core of a cybersecurity doctoral program is a data science doctoral program, you’ll be expected to learn many skills and also how to apply them across domains and disciplines. Core curriculums will vary from program to program, but almost all will have a core foundation of statistics.
All PhD candidates will have to take a series of exams that act as checkpoints during the lengthy PhD process. The actual exam process and timing can vary depending on the university and the program, but the basic idea is that cybersecurity PhD candidates generally have to sit for a qualifying exam, which comes earlier in the program (usually the winter or spring of the second year of study), a preliminary exam, which a candidate takes to show they are ready to start the dissertation or research portion of the PhD program, and a final exam where PhD students present and defend their research and complete their degree requirements.
A cybersecurity PhD dissertation is the capstone of a doctoral program. The dissertation is the name of a formal paper that presents the findings of original research that the PhD candidate conducted during the program under the guidance of faculty advisors. Some example cybersecurity research topics that could potentially be turned into dissertation ideas include: * Policies and best practices around passwords * Ways to defend against the rise of bots * Policies around encryption and privacy * Corporate responsibility for employee security * Internet advertising targeting and privacy * The new frontier of social engineering attacks * Operation security (OpSec) strategy and policy * Network infrastructure and defense * Cybersecurity law and policy * The vulnerabilities of biometrics * The role of ethical hacking * Cybersecurity forensics and enforcement
A complete listing of cybersecurity PhD programs
The following is a list of cybersecurity PhD programs. The listing is intended to work as a high-level index that provides enough basic information to make quick side-by-side comparisons easy.
You should find basic data about what each school requires (such as a GRE score or prior academic work) as well as the number of credits required, estimated costs, and a link to the program.
Arizona State University
- Aim: Equip students with in-depth expertise in cybersecurity.
- Study Modules: Delve into advanced computer science subjects and specific cybersecurity courses.
- Research Component: Students undertake groundbreaking research in the cybersecurity domain.
Carnegie Mellon University
- CNBC Collaboration: A joint effort between Carnegie Mellon and the University of Pittsburgh to train students in understanding the brain's role in cognition.
- Training Program: Students take four main neuroscience courses and participate in seminars and ethics training.
- Course Integration: Whether students have a B.S. or M.S. degree, they can combine the CNBC and ECE Ph.D. courses without extra workload.
Colorado School of Mines
- Research Focus: Cybersecurity: Studying online security and privacy.
- Cost and Financial Aid: Provides details on program costs and available financial support.
- Current Mines Community: Offers specific information for those already affiliated with Mines.
Indiana University Bloomington
- Focus Areas: Options include Animal Informatics, Bioinformatics, Computer Design, and more.
- Information Sessions: The university holds events to guide potential students about admissions and study options.
- Minor Requirement: All Ph.D. students must complete a minor, which can be from within the Luddy School of Informatics or from another approved school at IU Bloomington.
Iowa State University
- Details: The program is open to both domestic and international students.
- Time to Complete: Ph.D.: About 5.2 years
- Goals: Students should gain deep knowledge, follow ethics, share their findings, and do advanced research if they're writing a thesis.
- Learning Goals: Master core areas of Computer Science, achieve in-depth knowledge in a chosen subfield, obtain expertise to perform original research, and demonstrate the ability to communicate technical concepts and research results.
- Duration: Median time to earn the doctorate is 5.8 years.
- Application Information: The program is open to both domestic and international students.
- Program's Aim: The Ph.D. program is tailored to produce scholars proficient in leading research initiatives, undertaking rigorous industrial research, or imparting high-level computer science education.
- Entry Routes: The program welcomes both students holding a B.S. degree for direct admission and those with an M.S. degree.
- Dissertation's Role: It stands as the pivotal component of the Ph.D. journey. Collaboration between the student, their dissertation director, and the guiding committee is essential.
Naval Postgraduate School
- Program Essence: The Computer Science Ph.D. is a top-tier academic program in the U.S.
- Admission Criteria: Open to military officers from the U.S. and abroad, U.S. governmental employees, and staff of foreign governments.
- Curriculum: Designed to deepen knowledge in computing, with a focus on the needs of the U.S. Department of Defense.
- Emphasis on Research: The college showcases its strength in research through sections dedicated to Research Areas, affiliated Institutes & Centers, ongoing Research Projects, and specialized Labs & Groups.
- Holistic Student Growth: The college promotes a comprehensive student experience, spotlighting Clubs & Organizations, campus Facilities, and tech Systems.
- Guidance for Future Students: Provides tailored insights for students considering joining at various academic levels, from Undergraduate to PhD.
- Broad Learning: The program covers many areas, from software and policy to psychology and ethics, reflecting the wide scope of cybersecurity.
- Course Design: Students learn foundational security topics first and then dive into specialized areas, like cyber forensics.
- Successful Alumni: Past students now work in places like NASA, Amazon, and Google.
- Feature: Students can apply to up to three different campuses and/or majors using a single application and fee payment.
- Preparing for a Globalized World: Courses such as Global Supply Chain Management equip students for international careers.
- Tech-Forward Curriculum: Purdue's commitment to advanced technology is evident.
Rochester Institute of Technology
- Cyberinfrastructure Focus: The program dives deep into how hardware, data, and networks work together to create secure and efficient digital tools.
- Broad Applications: The program uses computing to solve problems in fields like science, arts, and business.
- Success Rate: All RIT graduates from this program have found relevant roles, especially in the Internet and Software sectors.
Sam Houston State University
- Program's Objective: The course aims to nurture students to be technically adept and also to take on leadership roles in the digital and cyber forensic domain across various industries.
- Assessments: Students undergo comprehensive tests to evaluate their understanding.
- Research Paper (Dissertation): Once students reach the doctoral candidacy phase, they must produce and defend a significant research paper or dissertation.
- Funding: All Ph.D. students get financial help, so they can start their research right away.
- Teachers: The program has top experts, including those who've made big discoveries in computer science.
- Research Areas: Students can study the latest topics like AI, computer vision, and online security.
The University of Tennessee
- Study Areas: Options include Cybersecurity, Data Analytics, Computer Vision, and more.
- Tests: You'll have to pass a few exams, including one when you start, one before your final project, and then present your final project.
- Courses: Some specific courses are needed, and your main professor will help decide which ones.
- Big Exam: Before moving forward, you'll take a detailed exam about your research topic.
- Final Step: You'll present and defend your research project to experts.
- Overview: This program is for those with a degree in Computer Science or similar fields. It has special focus areas like Cybersecurity and Machine Learning.
University of Arizona
- Study Plan: Students start with learning research basics and then dive into modern tech topics.
- Support for Students: All PhD students get funding that covers their studies, a stipend, and health insurance. Money for travel to conferences is also available.
- After Graduation: Alumni work at top universities and big companies like Google and Microsoft.
University of California-Davis
- About the Program: Students engage in deep research, ending with a dissertation.
- Jobs After Graduation: Roles in companies or academic positions.
- Vibrant Community: Beyond academics, students join a supportive community, enriching their Ph.D. experience.
University of Colorado - Colorado Springs
- Recognition: UCCS is recognized by the National Security Agency (NSA) and the Department of Homeland Security for excellence in Information Assurance Education.
- Course Approval: The NSA has approved UCCS's courses as meeting national security training standards.
- Overview: This program focuses on vital areas like cyber security, physical security, and homeland security.
University of Idaho
- Partnership with NSA and DHS: The university is part of a program to boost cyber defense education.
- Recognition: The University of Idaho is among the institutions recognized as Centers of Academic Excellence in Cyber Defense.
- Objective: To minimize vulnerabilities in the national information infrastructure.
- Overview: This program is meticulously crafted to deliver premier legal education to its students.
- Courses: Encompasses a balanced mix of traditional legal doctrines, theoretical viewpoints, and hands-on practical experiences.
- Aim: The primary objective is to equip students with top-notch legal education.
University of Missouri-Columbia
- Seminars: PhD students should attend 20 seminars. If they were previously Master's students, their past attendance counts.
- Timeline Requirements: Comprehensive Exam must be completed within five years of starting the program.
- Dissertation and Publication: At least one journal paper must be submitted, accepted, or published.
University of North Carolina at Charlotte
- Faculty: The faculty members are renowned for their impactful research contributions on a global scale.
- Curriculum: The curriculum is versatile, catering to individuals aiming for academia as well as those targeting roles in the corporate, commerce, or public sectors.
- Program: A blend of theoretical and hands-on research is emphasized, offering a well-rounded educational experience.
Virginia Tech
- Seminars and Ethics: Students attend special seminars and complete training on scholarly ethics and diversity.
- Guidance: Each student gets a faculty advisor. A group of faculty members, called a committee, also guides them.
- Major Exams: Students go through four main stages: a qualifying process, a preliminary proposal, a research presentation, and a final defense.
- Strong Research: WPI's PhD program is recognized for its excellent research contributions.
- Practical Focus: The program teaches students to tackle real tech challenges.
- Modern Labs: Students use the latest labs like the Human-Robot Interaction Lab.
Dakota State University
- Program Goal: Train students to handle and prevent cyber threats.
- Awards: The university has received top cybersecurity awards.
- What You'll Learn: Research skills, cyber defense techniques, and ethical decision-making.
New Jersey City University, College of Professional Studies
- About: Focuses on best practices in areas like national security, cyber defense, and crisis communication.
- Recognitions: The program has been honored by the National Security Agency since 2009 and was recognized for excellence in intelligence studies.
- Jobs: Graduates are prepared for top roles in sectors like government and education.
- Program Content: The course dives deep into modern cybersecurity topics, from new tech and artificial intelligence to specialized research areas.
- Location Benefits: The university is near many cybersecurity companies and government agencies, giving students unique opportunities.
- For Working People: It's crafted for professionals, allowing them to experience various cybersecurity roles, from tech firms to government.
- Completion Time: Students have up to ten years from starting to finish their dissertation.
- Program: Trains students for roles in academia, government, and business.
- Multidisciplinary Approach: The program combines both technical and managerial aspects of cybersecurity, offering a comprehensive understanding of the field.
The University of Rhode Island
- Research Focus: The Ph.D. program is centered around a big research project in Computer Science.
- Qualifying Exams: Students take exams on core topics, but some might get exemptions if they're already skilled in certain areas.
- Equal Opportunity: The University of Rhode Island is committed to the principles of affirmative action and is an equal opportunity employer.
University of North Texas
- Team Effort: The program is a collaboration between various UNT departments for a well-rounded view of cybersecurity.
- Goals: The course aims to develop critical thinkers who are passionate about the role of information in our lives and can work across different fields.
- Skills Gained: Students will learn about research, teaching methods, decision-making, leadership, and analyzing data.
New York University Tandon School of Engineering
- Scholarships: Many students get scholarships that pay for tuition and give a monthly allowance.
- Research Interest: Research areas include cybersecurity, computer games, web search, graphics, and more.
- Experience: Students can also research in NYU's campuses in Shanghai or Abu Dhabi.
- One Degree for All: Every student gets the same Ph.D., regardless of their specific area of study.
- Research Focus: The program emphasizes deep research and prepares students for advanced roles.
- Major Project: Students work on a big research project, adding new knowledge to the computing world.
- Program: Prepares students for leadership roles in different sectors.
- Opportunities: Qualified students might get opportunities as Research or Teaching Assistants.
- Overview: Focuses on advanced research and modern technologies.
Augusta University
- Goal: The program prepares students for research roles and to make new discoveries in tech.
- Benefits: A Ph.D. opens up leadership opportunities in tech sectors.
- Overview: It focuses on new discoveries in areas like security, artificial intelligence, and virtual reality.
University of Texas at San Antonio
- Financial Support: Full-time students can get funding, which covers tuition and offers roles like teaching assistants.
- Job Prospects: UTSA trains students for jobs that are in high demand, using data from official sources.
- Overview: The program focuses on in-depth research and teaching.
University of Central Florida
- Mix of Subjects: Students can take courses from different areas, giving them a broad view of security topics.
- Many Job Options: Graduates can work in government, big companies, or teach in universities.
- Hands-on Learning: The program offers research, study projects, and internships for real-world experience.
What is a Master of Studies in Law? Explore the George Washington University Law School MSL

You don’t have to be a lawyer to earn a living understanding and applying the law. Many professions require — or benefit significantly from — a thorough understanding of how the law impacts an industry or institution. The Master of Studies in Law (MSL), a graduate-level law degree designed for non-lawyers, can prepare you for a career interpreting and navigating legal situations.
You can earn an MSL 100% online from the George Washington University Law School (GW Law); you also have the option to take courses on-campus. The program offers specializations online in three areas: government procurement law, national security and cybersecurity law, and government procurement and cybersecurity law. The university’s location in the heart of Washington, D.C. enables students to benefit from access to the center of national legal and political activity — without ever having to leave their hometowns.
Gain Legal Expertise to Propel Your Career
Choose from three msl concentrations at gw law.
If you aspire to a career engaging with the law, you may be wondering whether a Master of Studies in Law is the right degree for you. How does the MSL differ from the Juris Doctor (JD), the law degree pursued by aspiring attorneys? What careers does each degree facilitate? This article explores those questions to help you decide which option better suits your career goals.
Master of Studies in Law vs. Juris Doctor: Decoding the Differences
A Master of Studies in Law is a master’s-level graduate degree in law and legal systems. A Juris Doctor is a terminal degree at the doctoral level that qualifies recipients to work in the courts as lawyers and judges. Admissions requirements, coursework, and career opportunities for the degrees differ substantially.
Applicants to GW’s MSL program must hold a bachelor’s degree and three to five years of professional experience relevant to the specialization they choose to pursue. Acceptance into a JD program requires a bachelor’s degree and an acceptable score on the Law School Admission Test (LSAT) .
Coursework in the degree programs overlaps somewhat, but the JD is undoubtedly the more comprehensive and detailed of the two. GW’s MSL program requires 24 credit hours of coursework, which can be completed in as few as 12 months (for full-time students). A JD requires 80 credit hours and includes a rigorous first-year law student curriculum, with courses such as Torts, Property, and Contracts. Full-time JD students typically take three years to complete their degrees, after which they must pass their state’s bar exam.
Your professional goals will dictate which degree you choose. JD graduates are trained to practice law (after successfully passing a state or DC bar examination); they typically pursue careers as lawyers, judges and legal scholars. An MSL can be helpful in professions in such varied fields as government, business, finance, real estate, court administration, mediation, insurance, policy, and nongovernmental organizations. Practically every field intersects with the law, creating career opportunities for MSL degree holders.
What Will You Learn in MSL Programs?
Graduates of George Washington University’s Master of Studies in Law are prepared to communicate with lawyers and competently address industry compliance and regulatory issues. Students pursue the specialization most compatible with their current professional experience:
- Government Procurement Law examines how procurement systems operate and the laws and regulations that govern them in the U.S. and abroad. Classwork includes anti-corruption, intellectual property and procurement reform.
- National Security & Cybersecurity Law thoroughly examines legal and policy issues surrounding national security, cybersecurity, AI, big data and new technologies. Classes cover internet law, foreign access to U.S. technology, and artificial intelligence law.
- Government Procurement & Cybersecurity Law prepares professionals to address the rising demand for cybersecurity legal expertise in government procurement law. Topics include cybersecurity law and technology, consumer privacy and data protection, and government procurement of intellectual property.
In all fields, the MSL degree prepares graduates to address challenges from a legal perspective, communicate with lawyers and non-lawyers alike, and assess the legal ramifications of corporate and institutional issues.
Career Pathways with a Master of Studies in Law
An MSL can be especially beneficial for people who work in highly regulated fields, such as government, healthcare, education, nonprofits, manufacturing and finance. Anyone who communicates frequently with lawyers can also benefit from an MSL. Graduates of GW’s MSL program have gone on to work for various employers, including:
- Department of Defense
- Department of Homeland Security
- General Dynamics
- General Services Administration (GSA)
- Lockheed Martin
- Northrop Grumman
Is an MSL the Right Fit for Your Professional Goals?
The GW Law online MSL serves non-lawyer professionals whose work requires a detailed knowledge of the law. An MSL can benefit compliance officers, consultants, government managers, intelligence community analysts, journalists, policy analysts, and procurement specialists, to name just a few.
George Washington University Law School’sMSL program provides the theoretical and practical knowledge necessary to apply the law to today’s organizational legal challenges. Located in our nation’s capital with flexible options to attend from any location, GW Law’s MSL degree delivers a strong law curriculum, respected faculty experts, academic peers from across the globe and over 33,000 living alumni for networking, advice and career development.
If you are ready to explore the law and find your place within it, contact an admissions adviser to learn more about the MSL program or start your application .
Become a Source of Valued Legal Insight in Your Workplace
Learn to identify and address legal risks.
Tell us about yourself.
Sharing some details will help us customize your experience. A bachelor’s degree is required to attend.
MIA > Archive > Pashukanis
Evgeny Pashukanis
Marksistskaia teoriia gosudarstva i prava , pp.9-44 in E. B. Pashukanis (ed.), Uchenie o gosudarstve i prave (1932), Partiinoe Izd., Moscow. From Evgeny Pashukanis, Selected Writings on Marxism and Law (eds. P. Beirne & R. Sharlet), London & New York 1980, pp.273-301. Translated by Peter B. Maggs . Copyright © Peter B. Maggs. Published here by kind permission of the translator. Downloaded from home.law.uiuc.edu/~pmaggs/pashukanis.htm Marked up by Einde O’Callaghan for the Marxists’ Internet Archive .
Introductory Note
In the winter of 1929-1930, during the first Five Year Plan, the national economy of the USSR underwent dramatic and violent ruptures with the inauguration of forced collectivization and rapid heavy industrialization. Concomitantly, it seemed, the Party insisted on the reconstruction and realignment of the appropriate superstructures in conformity with the effectuation of these new social relations of production. In this spirit Pashukanis was no longer criticized but now overtly attacked in the struggle on the “legal front”. In common with important figures in other intellectual disciplines, such as history, in late 1930 Pashukanis undertook a major self-criticism which was qualitatively different from the incremental changes to his work that he had produced earlier. During the following year, 1931, Pashukanis outlined this theoretical reconstruction in his speech to the first conference of Marxist jurists, a speech entitled Towards a Marxist-Leninist Theory of Law . The first results appeared a year later in a collective volume The Doctrine of State and Law .
Chapter I of this collective work is translated below, The Marxist Theory of State and Law , and was written by Pashukanis himself It should be noted that this volume exemplifies the formal transformations which occurred in Soviet legal scholarship during this heated period. Earlier, Pashukanis and other jurists had authored their own monographs; the trend was now towards a collective scholarship which promised to maximize individual safety. The source of authority for much of the work that ensued increasingly became the many expressions of Stalin’s interpretation of Bolshevik history, class struggle and revisionism, most notably his Problems of Leninism . Last, but not least, the language and vocabulary of academic discourse in the 1920s had been rich, open-ended and diverse, and varied tremendously with the personal preferences of the individual author; this gave way to a standardized and simplified style of prose devoid of nuance and ambiguity, and which was very much in keeping with the new theoretical content which comprised official textbooks on the theory of state and law. The reader will perhaps discover that The Marxist Theory of State and Law is a text imbued with these tensions. Pashukanis’ radical reconceptualization of the unity of form and content, and of the ultimate primacy of the relations of production, is without doubt to be preferred to his previous notions. But this is a preference guided by the advantages of editorial hindsight, and we feel that we cannot now distinguish between those reconceptualizations which Pashukanis may actually have intended and those which were produced by the external pressures of political opportunism.
CHAPTER I Socio-economic Formations, State, and Law
1. the doctrine of socio-economic formations as a basis for the marxist theory of state and law.
The doctrine of state and law is part of a broader whole, namely, the complex of sciences which study human society. The development of these sciences is in turn determined by the history of society itself, i.e. by the history of class struggle.
It has long since been noted that the most powerful and fruitful catalysts which foster the study of social phenomena are connected with revolutions. The English Revolution of the seventeenth century gave birth to the basic directions of bourgeois social thought, and forcibly advanced the scientific, i.e. materialist, understanding of social phenomena.
It suffices to mention such a work as Oceana – by the English writer Harrington, and which appeared soon after the English Revolution of the seventeenth century – in which changes in political structure are related to the changing distribution of landed property. It suffices to mention the work of Barnave – one of the architects of the great French Revolution – who in the same way sought explanations of political struggle and the political order in property relations. In studying bourgeois revolutions, French restorationist historians – Guizot, Mineaux and Thierry – concluded that the leitmotif of these revolutions was the class struggle between the third estate (i.e. the bourgeoisie) and the privileged estates of feudalism and their monarch. This is why Marx, in his well-known letter to Weydemeyer, indicates that the theory of the class struggle was known before him. “As far as I am concerned”, he wrote,
no credit is due to me for discovering the existence of classes in modern society, or the struggle between them. Long before me bourgeois historians had described the historical development of this class struggle, and bourgeois economists the economic anatomy of the classes.
What I did that was new was to prove: (1) that the existence of classes is only bound up with particular historical forms of struggle in the development of production ...; (2) that the class struggle inevitably leads to the dictatorship of the proletariat; (3) that this dictatorship itself only constitutes the transition to the abolition of all classes and the establishment of a classless society. [1]
[ Section 2 omitted – eds. ]
Top of the page
3. The class type of state and the form of government
The doctrine of socio-economic formations is particularly important to Marx’s theory of state and law, because it provides the basis for the precise and scientific delineation of the different types of state and the different systems of law.
Bourgeois political and juridical theorists attempt to establish a classification of political and legal forms without scientific criteria; not from the class essence of the forms, but from more or less external characteristics. Bourgeois theorists of the state, assiduously avoiding the question of the class nature of the state, propose every type of artificial and scholastic definition and conceptual distinction. For instance, in the past, textbooks on the state divided the state into three “elements”: territory, population and power.
Some scholars go further. Kellen – one of the most recent Swedish theorists of the state – distinguishes five elements or phenomena of the state: territory, people, economy, society and, finally, the state as the formal legal subject of power. All these definitions and distinctions of elements, or aspects of the state, are no more than a scholastic game of empty concepts since the main point is absent: the division of society into classes, and class domination. Of course, the state cannot exist without population, or territory, or economy, or society. This is an incontrovertible truth. But, at the same time, it is true that all these “elements” existed at that stage of development when there was no state. Equally, classless communist society – having territory, population and an economy – will do without the state since the necessity of class suppression will disappear.
The feature of power, or coercive power, also tells one exactly nothing. Lenin, in his polemic of the 1890s with Struve asserted that: “he most incorrectly sees the distinguishing feature of the state as coercive power. Coercive power exists in every human society – both in the tribal structure and in the family, but there was no state.” And further, Lenin concludes: “The distinguishing feature of the state is the existence of a separate class of people in whose hands power is concentrated. Obviously, no one could use the term ‘State’ in reference to a community in which the ‘organization of order’ is administered in turn by all of its members.” [2]
Struve’s position, according to which the distinguishing feature of a state is coercive power, was not without reason termed “professorial” by Lenin. Every bourgeois science of the state is full of conclusions on the essence of this coercive power. Disguising the class character of the state, bourgeois scholars interpret this coercion in a purely psychological sense. “For power and subordination”, wrote one of the Russian bourgeois jurists (Lazarevsky), “two elements are necessary: the consciousness of those exercising power that they have the right to obedience, and the consciousness of the subordinates that they must obey.”
From this, Lazarevsky and other bourgeois jurists reached the following conclusion: state power is based upon the general conviction of citizens that a specific state has the right to issue its decrees and laws. Thus, the real fact-concentration of the means of force and coercion in the hands of a particular class-is concealed and masked by the ideology of the bourgeoisie. While the feudal landowning state sanctified its power by the authority of religion, the bourgeoisie uses the fetishes of statute and law. In connection with this, we also find the theory of bourgeois jurists-which now has been adopted in its entirety by the Social Democrats whereby the state is viewed as an agency acting in the interests of the whole society. “If the source of state power derives from class”, wrote another of the bourgeois jurists (Magaziner), “then to fulfil its tasks it must stand above the class struggle. Formally, it is the arbiter of the class struggle, and even more than that: it develops the rules of this struggle.”
It is precisely this false theory of the supra-class nature of the state that is used for the justification of the treacherous policy of the Social Democrats. In the name “of the general interest”, Social Democrats deprive the unemployed of their welfare payments, help in reducing wages, and encourage shooting at workers’ demonstrations.
Not wishing to recognize the basic fact, i.e. that states differ according to their class basis, bourgeois theorists of the state concentrate all their attention on various forms of government. But this difference by itself is worthless. Thus, for instance, in ancient Greece and ancient Rome we have the most varied forms of government. But all the transitions from monarchy to republic, from aristocracy to democracy, which we observe there, do not destroy the basic fact that these states, regardless of their different forms, were slave-owning states. The apparatus of coercion, however it was organized, belong to the slave-owners and assured their mastery over the slaves with the help of armed force, assured the right of the slave-owners to dispose of the labour and personality of the slaves, to exploit them, to commit any desired act of violence against them.
Distinguishing between the form of rule and the class essence of the state is particularly important for the correct strategy of the working class in its struggle with capitalism. Proceeding from this distinction, we establish that to the extent that private property and the power of capital remain untouchable, to this extent the democratic form of government does not change the essence of the matter. Democracy with the preservation of capitalist exploitation will always be democracy for the minority, democracy for the propertied; it will always mean the exploitation and subjugation of the great mass of the working people. Therefore theorists of the Second International such as Kautsky, who contrast “democracy” in general with “dictatorship”, entirely refuse to consider their class nature. They replace Marxism with vulgar legal dogmatism, and act as the scholarly champions and lackeys of capitalism.
The different forms of rule had already arisen in slave-owning society. Basically, they consist of the following types: the monarchic state with an hereditary head, and the republic where power is elective and where there are no offices which pass by inheritance. In addition, aristocracy, or the power of a minority (i.e. a state where participation in the administration of the state is limited by law to a definite and rather narrow circle of privileged persons) is distinguished from democracy (or, literally, the rule of the people), i.e. a state where by law all take part in deciding public affairs either directly or through elected representatives. The distinction between monarchy, aristocracy and democracy had already been established by the Greek philosopher Aristotle in the fourth century. All the modern bourgeois theories of the state could add little to this classification.
Actually the significance of one form or another can be gleaned only by taking into account the concrete historical conditions under which it arose and existed, and only in the context of the class nature of a specific state. Attempts to establish any general abstract laws of the movement of state forms – with which bourgeois theorists of the state have often been occupied – have nothing in common with science.
In particular, the change of the form of government depends on concrete historical conditions, on the condition of the class struggle, and on how relationships are formed between the ruling class and the subordinate class, and also within the ruling class itself
The forms of government may change although the class nature of the state remains the same. France, in the course of the nineteenth century, and after the revolution of 1830 until the present time, was a constitutional monarchy, an empire and a republic, and the rule of the bourgeois capitalist state was maintained in all three of these forms. Conversely, the same form of government (for instance a democratic republic) which was encountered in antiquity as one of the variations of the slave-owning state, is in our time one of the forms of capitalist domination.
Therefore, in studying any state, it is very important primarily to examine not its external form but its internal class content, placing the concrete historical conditions of the class struggle at the very basis of scrutiny.
The question of the relationship between the class type of the state and the form of government is still very little developed. In the bourgeois theory of the state this question not only could not be developed, but could not even be correctly posed, because bourgeois science always tries to disguise the class nature of all states, and in particular the class nature of the capitalist state. Often therefore, bourgeois theorists of the state, without analysis, conflate characteristics relating to the form of government and characteristics relating to the class nature of the state.
As an example one may adduce the classification which is proposed in one of the newest German encyclopaedias of legal science.
The author [Kellreiter] distinguishes: (a) absolutism and dictatorship, and considers that the basic characteristic of these forms is that state powers are concentrated in the hands of one person. As an example, he mentions the absolute monarchy of Louis XIV in France, tsarist autocracy in Russia and the dictatorial power which was invested by the procedure of extraordinary powers in the one person, for instance the president of the German Republic on the basis of Art.48 of the Weimar Constitution; (b) constitutionalism, characterized by the separation of powers, their independence and their checks and balances, thereby weakening the pressure exerted by state power on the individual (examples: the German Constitution before the 1918 revolution, and the USA, where the President and Congress have independent powers); (c) democracy, whose basic premise is monism of power and a denial in principle of the difference between power and the subject of power (popular sovereignty, exemplified by the German Republic); and (d) the class-corporative state and the Soviet system where as opposed to formal democracy, the people appear not as an atomized mass of isolated citizens but as a totality of organized and discrete collectives. [3]
This classification is very typical of the confusion which bourgeois scholars consciously introduce into the question of the state. Starting with the fact that the concept of dictatorship is interpreted in the formal legal sense, deprived of all class content, the bourgeois jurist deliberately avoids the question: the dictatorship of which class and directed against whom ? He blurs the distinction between the dictatorship of a small group of exploiters and the dictatorship of the overwhelming majority of the working people; he distorts the concept of dictatorship, for he cannot avoid defining it without a relevant law or paragraph, while “the scientific concept of dictatorship means nothing less than power resting directly upon force, unlimited by laws, and unconstricted by absolute rules”. [4] Further it is sufficient to indicate, for instance, that under the latter heading the author includes: (a) a new type of state, never encountered before in history, where power belongs to the proletariat; (b) the reactionary dreams of certain professors and so-called guild socialists, about the return to the corporations and shops of the Middle Ages; and, finally (c) the fascist dictatorship of capital which Mussolini exercises in Italy.
This respected scholar consciously introduces confusion, consciously ignores the concrete historical conditions under which the working people actually can exercise administration of the state, acting as organized collectives. But such conditions are only the proletarian revolution and the establishment of the dictatorship of the proletariat.
4. The class nature of law
Bourgeois science confuses the question of the essence of law no less than the question of the state. Here, Marxism-Leninism opposes the diverse majority of bourgeois, petit bourgeois and revisionist theories which, proceeding from the explanation of the historical and class nature of law, consider the state as a phenomenon essential to every human society. They thus transform law into a supra-historical category.
It is not surprising, therefore, that bourgeois philosophy of law serves as the main source for introducing confusion both into the concept of law and into the concept of state and society.
The bourgeois theory of the state is 90% the legal theory of the state. The unattractive class essence of the state, most often and most eagerly, is hidden by clever combinations of legal formalism, or else it is covered by a cloud of lofty philosophical legal abstractions.
The exposure of the class historical essence of law is not, therefore, an unimportant part of the Marxist-Leninist theory of society, of the state and of law.
The most widespread approach of bourgeois science to the solution of the question of the essence of law consists in the fact that it strives to embrace, through the concept of law, the existence of any consciously ordered human relationships, of any social rules, of any phenomenon of social authority or social power. Thus, bourgeois scholars easily transfer law to pre-class society, find it in the pre-state life of primitive tribes, and conclude that communism is unthinkable without law. They turn law as an empty abstraction into a universal concept devoid of historical content. Law, for bourgeois sociologists, becomes an empty form which is unconnected with concrete reality, with the relationships of production, with the antagonistic character of these relationships in class society, [and] with the presence of the state as a particular apparatus of power in the hands of the ruling class.
Representatives of idealist philosophy of law go still further. They begin with “the idea of law”, which stands above social history as something eternal, immutable and independent of space and time.
Here, for example, is the conclusion of one of the most important representatives of the ideological neo-Kantian philosophy of law – Stammler:
Through all the fates and deeds of man there extends a single unitary idea, the idea of law. All languages have a designation for this concept, and the direction of definitions and judgements expressed by it amount, upon careful study, to one and the same meaning.
Having made this discovery, it cost Stammler nothing “to prove” that regardless of the difference between the “life and activity of nations” and “the objects of legal consideration”, we observe the unity of the legal idea and its equal appearance and intervention.
This professorial rubbish is presented without the least attempt at factual proof In actuality it would be rather difficult to explain how this “unity of the legal idea and its equal appearance” gave birth to the laws of the Twelve Tablets of slave-owning Rome, the serf customs of the Middle Ages, the declarations of rights of capitalist democracies, and our Soviet Constitution.
But Stammler is not embarrassed by the scantiness of factual argument. He deals just as simply with the proof of the eternity of law. He begins from those legendary Cyclops described in the Odyssey; even these mythical wonders were the fathers of families and, according to Stammler, could not do without law. On the other hand, however, while Stammler is ready to admit that the pigmy tribes of Africa and the Eskimos did not know the state, he simply denies as deceptive all reports about peoples not knowing law. Moreover, Stammler immediately replaces the concrete historical consideration of the question with scholastic formal-logical tightrope walking, which among bourgeois professors is presented as a methodological precision. We present these conclusions, for they typify the whole trend and, moreover, are most fashionable in the West.
Stammler proposes that the concrete study of legal phenomena is entirely unable to provide anything in the understanding of the essence of law. For if we assign any phenomenon to the list of legal ones, this means that we already know that this is law and what its characteristics are. The definition of law which precedes the facts presupposes knowledge of what is law and what is not law. Accordingly, in the opinion of Stammler, in considering the concept of law, it is necessary to exclude all that is concrete and encountered in experience and to understand “that the legal idea is a purely methodological means for the ordering of spiritual life”.
This conclusion, which confronts one with its scholasticism, is nothing other than a Kantian ideological thesis embodied in the context of Stammler’s legal stupidity. It shows that the so-called forms of knowledge do not express the objective characteristics of matter, are determined a priori, and precede all human experience and its necessary conditions.
Having turned law into a methodological idea, Stammler tries to locate it not in the material world where everything is subordinate to the law of cause and effect, but in the area of goals. Law, according to Stammler, is a definition which proceeds not from the past (from cause to effect), but from the future (from goal to means). Finally, adding that law deals not with the internal procedure of thoughts as such, but with human interaction, Stammler gives this agonizing and thoroughly scholastic definition:
The concept of law is a pure form of thought. It methodically divides the endlessly differentiated material of human desires apprehended by the senses, and defines it as an inviolable and independent connecting will.
This professorial scholasticism has the attractive feature for the bourgeoisie that verbal and formalistic contrivances can hide the ugly reality of [their] exploiting society and exploiting law.
If law is “a pure form of thought”, then it is possible to avoid the ugly fact that the capitalist law of private property means the misery of unemployment, poverty and hunger for the proletarian and his family; and that in defence of this law stand police armed to the teeth, fascist bands, hangmen and prison guards; and that this law signifies a whole system of coercion, humiliation and oppression in colonies.
Such theories allow the disguising of the fact that the class interest of the bourgeoisie lies at the basis of bourgeois law. Instead of class law, philosophers such as Stammler dream up abstractions, “pure forms”, general human “ideas”, “whole and durable bonds of will” – and other entirely shameless things.
This philosophy of law is calculated to blunt the revolutionary class consciousness of the proletariat, and to reconcile it with bourgeois society and capitalist exploitation.
It is not without reason that the social fascists speak out as such zealous exponents of neo-Kantianism; it is not without reason that Social Democratic theorists on questions of law largely subscribe to neo-Kantian philosophy and re-hash the same Stammler in different ways.
In our Soviet legal literature, a rather wide dissemination has been achieved by bourgeois legal theories. In particular, there have been attempts to spread the idealist teaching of Stammler in the works of Pontovich and Popov-Ladyzhensky. The criticism and unmasking of this eructation is necessary for the purpose of eradicating this bourgeois ideological infection.
Thus, we know that the state is an historical phenomenon limited by the boundaries of class society. A state is a machine for the maintenance of the domination of one class over another. It is an organization of the ruling class, having at its disposal the most powerful means of suppression and coercion. Until the appearance of classes the state did not exist. In developed communism there will be no state.
In the same way as the state, law is inseparably tied to the division of society into classes. Every law is the law of the ruling class. The basis of law is the formulation and consolidation of the relationship to the means of production, owing to which in exploitative society, one part of the people can appropriate to itself the unpaid labour of another.
The form of exploitation determines the typical features of a legal system. In accordance with the three basic socio-economic formations of class society, we have three basic types of legal superstructure: slave-owning law, feudal law and bourgeois law. This of course does not exclude concrete historical national differences between each of the systems. For instance, English law is distinguished by many peculiarities in comparison with French bourgeois law as contained in the Napoleonic Code . Likewise, we do not exclude the presence of survivals of the past – transitional or mixed forms – which complicate the concrete picture.
However, the essential and basic – that which provides the guiding theme for the study of different legal institutions – is the difference between the position of the slave, the position of the serf and the position of the wage labourer. The relationship of exploitation is the basic lynchpin, around which all other legal relationships and legal institutions are arranged. From this it follows that the nature of property has decisive significance for each system of law. According to Lenge, the brilliant and cynical reactionary of the eighteenth century, the spirit of the laws is property.
5. Law as an historical phenomenon: definition of law
The appearance and withering away of law, similar to the appearance and withering of the state, is connected with two extremely important historical limitations. Law (and the state) appears with the division of society into classes. Passing through a long path of development, full of revolutionary leaps and qualitative changes, law and the state will wither away under communism as a result of the disappearance of classes and of all survivals of class society.
Nevertheless, certain authors, who consider themselves Marxists, adopt the viewpoint that law exists in pre-class society, that in primitive communism we meet with legal forms and legal relationships. Such a point of view is adopted for instance by Reisner. Reisner gives the term “law” to a whole series of institutions and customs of tribal society: marriage taboos and blood feud, customs regulating relationships between tribes, and customs relating to the use of the means of production belonging to a tribe. Law in this manner is transformed into an eternal institution, inherent to all forms of human society. From here it is just one step to the understanding of law as an eternal idea; and Reisner in essence leans towards such an understanding.
This viewpoint of course fundamentally contradicts Marxism. The customs of a society not knowing class divisions, property inequality and exploitation, differ qualitatively from the law and the statutes of class society. To categorize them together means to introduce an unlikely confusion. Every attempt to avoid this qualitative difference inevitably leads to scholasticism, to the purely external combination of phenomena of different types, or to abstract idealist constructs in the Stammlerian spirit.
We should not be confused by the fact that Engels, in The Origin of the Family, Private Property and the State , uses the expression “the eternal law”; or, that he cites, without particular qualification, Morgan’s description of the member of a tribal community as having “equality of rights”, and of a person violating tribal customs as having placed himself “outside the law”.
It is clear that the terms “right” and “law” are used here not in their direct sense, but by analogy. This does not mean, however, that in classless society we will be dealing only with purely technical rules. Such an argument was put forward by Stuchka in his dispute with Reisner. To assign the customs and the norms of pre-class society to the area of technology would mean to give the concept of technology a very extended and undefined sense. Marriage prohibitions, customs relating to the organization of the tribe, the power of the elders, blood feud etc. – all this of course is not technology and not technical methods, but the customs and norms of social order. The content and character of these customs corresponded of course to the level of productive forces and the production relationships erected on it. These social forms should be considered as a superstructure upon the economic base. But the basic qualitative difference between this superstructure and the political and legal superstructures of class society, consists in the absence of property inequality, exploitation, and organized class coercion.
While Marxism strives to give a concrete historical meaning to law, the characteristic feature of bourgeois philosophers of law is, on the contrary, the conclusion that law in general is outside classes, outside any particular socio-economic formation. Instead of deriving a concept of law from the study of historical facts, bourgeois scholars are occupied with the concoction of theories and definitions from the empty concept or even the word “law”.
We already saw how Stammler, with the help of scholastic contrivances, tries to show that concrete facts have no significance for the definition of law. We, however, say the opposite. It is impossible to give a general definition of law without knowing the law of slave-owning, feudal and capitalist societies. Only by studying the law of each of these socio-economic formations can we identify those characteristics which are in fact most general and most typical. In doing so we must not forget Engels’ warning to those who tend to exaggerate the significance of these general definitions.
For example, in Chapter VI of the first part of Anti-Dühring , having given a definition of life, Engels speaks of the inadequacy of all definitions because they are necessarily limited to the most general and simplistic areas. In the preface to Anti-Dühring , Engels formulated this thought still more clearly, indicating that “the only real definition is the development of the essence of the matter, and that is not a definition”. However, Engels at once states that for ordinary practical use, definitions which indicate the most general and characteristic features of a category are very convenient. We cannot do without them. It is also wrong to demand more from a definition than it can give; it is wrong to forget the inevitability of its insufficiency.
These statements by Engels should be kept in mind in approaching any general definition, including a definition of law. It is necessary to remember that it does not replace, and cannot replace, the study of all forms and aspects of law as a concrete historical phenomenon. In identifying the most general and characteristic features we can define law as the form of regulation and consolidation of production relationships and also of other social relationships of class society; law depends on the apparatus of state power of the ruling class, and reflects the interests of the latter.
This definition characterizes the role and significance of law in class society. But it is nevertheless incomplete. In contradistinction to all normative theories – which are limited to the external and formal side of law (norms, statutes, judicial positions etc.) – Marxist-Leninist theory considers a law as a unity of form and content. The legal superstructure comprises not only the totality of norms and actions of agencies, but the unity of this formal side and its content, i.e. of the social relationships which law reflects and at the same time sanctions, formalizes and modifies. The character of formalization does not depend on the “free will of the legislator”; it is defined by economics, but on the other hand the legal superstructure, once having arisen, exerts a reflexive effect upon the economy.
This definition stresses three aspects of the matter. First is the class nature of law: every law is the law of the ruling class. Attempts to consider law as a social relationship which transcends class society, lead either to superficial categorization of diverse phenomena, or to speculative idealistic constructs in the spirit of the bourgeois philosophy of law. Second is the basic and determinant significance of production relationships in the content that is implemented by law. Class interests directly reflect their relationship to the means of production. Property relationships occupy the prominent place in the characterization of a specific legal order. Communist society, where classes disappear, where labour becomes the primary want, where the effective principle will be from each according to his abilities, to each according to his needs: this does not require law. The third aspect consists of the fact that the functioning of a legal superstructure demands a coercive apparatus. When we say that social relationships have assumed a legal expression, this means inter alia that they have been given a coercive nature by the state power of the ruling class. Withering away of the law can only occur simultaneously with the withering away of the state.
Relationships which have received legal expression are qualitatively different from those relationships which have not received this expression. The form of this expression may be different, as was indicated by Engels [5] ; it may sometimes be good and sometimes be bad. It may support the progressive development of these relationships or, on the contrary, retard them. Everything depends on whether power is in the hands of a revolutionary or a reactionary class. Here the real significance of the legal superstructure appears. However, the degree of this reality is a question of fact; it can be determined only by concrete study and not by any a priori calculations. Bourgeois jurists characteristically concentrate their attention on form, and utterly ignore content. They turn their backs on life and actual history. As Engels showed, “they consider public and private law as independent areas, which have their own independent development and which must and may be subjected to independent systematic elaboration by the consistent elimination of all internal contradictions.” [6]
Bourgeois jurists usually define law as the totality of norms to which a state has given coercive power. This view of law typifies so-called legal positivism. The most consistent representatives of this trend are the English jurists: of the earliest Blackstone (eighteenth century), and thereafter Austin. In other European countries legal positivism also won itself a dominant position in the nineteenth century, because the bourgeoisie either gained state power or everywhere achieved sufficient influence in the state so as not to fear the identification of law with statute. At the same time nothing was better for legal professionals, for judges, [and] for defence counsel since this definition fully satisfied their practical needs. If law in its entirety was the complex of orders proceeding from the state, and consolidated by sanction in the case of disobedience, then the task of jurisprudence was defined with maximum clarity. The work of the jurist, according to the positivists, did not consist in justifying law from some external point of view – philosophers were occupied with this; the task of the jurists did not include explaining from where a norm emerged, and what determined its content – this was the task of political scientists and sociologists. The role of the jurist remained the logical interpretation of particular legal provisions, the establishment of an internal logical connection between them, combining them into larger systematic units in legal institutions, and finally in this way the creation of a system of law.
The definition of law as the totality of norms is the starting point for supporting the so-called dogmatic method. This consists of using formal logical conclusions in order to move from particular norms to more general concepts and back, proceeding from general positions to propose the solution of concrete legal cases or disputes. It is obvious that the practical part of this role developing especially luxuriantly in the litigious circumstances of bourgeois society – has nothing in common with a scientific theory of law. Applications of so-called legal logic are not only theoretically fruitless, they are not only incapable of revealing the essence of law and thus of showing its connection with other phenomena-with economics, with politics, with class struggle – but they are also harmful and impermissible in the practice of our Soviet courts and other state institutions. We need decisions of cases, not formally, but in their essence; the state of the working people, as distinct from the bourgeois state, does not hide either its class character or its goal – the construction of socialism. Therefore, the application of norms of Soviet law must not be based on certain formal logical considerations, but upon the consideration of all the concrete features of the given case, of the class essence of those relationships to which it becomes necessary to apply a general norm, and of the general direction on of the policy of Soviet power at the given moment. In the opposite case a result would be obtained which Lenin defined as: “Correct in form, a mockery in substance.”
The denial of formal legal logic cultivated by the bourgeoisie does not mean a denial of revolutionary legality, does not mean that judicial cases and questions of administration must be decided chaotically in the Soviet state, systematically on the basis of the random whims of individuals, or on the basis of local influences. The struggle for revolutionary legality is a struggle on two fronts: against legal formalism and the transfer to Soviet soil of bourgeois chicanery, and against those who do not understand the organizational significance of Soviet decrees as one of the methods of the uniform conduct of the policy of the dictatorship of the proletariat.
Thus, the law is the means of formulating and consolidating the production relationships of class society and the social relationships which are connected with them. In the legal superstructure, these relationships appear as property relations and as relations of domination and subordination. They appear, in particular, as relations of an ideological nature, i.e. as relations which are formed in connection with certain views and are supported by the conscious will of the people.
We shall not touch upon the question of the degree to which the legal ideology of the exploiting classes is capable of correctly reflecting reality, and in what measure it inevitably distorts it (representing the interest of the exploiting class as the social interest in order, legality, freedom etc.). Here, we merely emphasize the fact that without the work of legislators, judges, police and prison guards (in a word, of the whole apparatus of the class state), law would become a fiction. “Law is nothing without an apparatus capable of enforcing observation of the norms of law” (Lenin).
The conscious will – towards the formulation and consolidation of production and other relationships – is the will of the ruling class which finds its expression in custom, in law, in the activity of the court and in administration. The legal superstructure exists and functions because behind it stands an organization of the ruling class, namely the apparatus of coercion and power in the form of the army, the police, court bailiffs, prison guards and hangmen. This does not mean that the ruling class has to use physical force in every case. Much is achieved by simple threat, by the knowledge of helplessness and of the futility of struggle, by economic pressure, and finally by the fact that the working classes are in the ideological captivity of the exploiters. It is sufficient to mention the narcotic of the religious ideology of humility and meekness, or the genuflection before the idol of bourgeois legality preached by the reformist.
But the ultimate argument for, and the basis of, the legal order is always the means of physical force. Only by depending on them could the slaveowner of antiquity or the modern capitalist enjoy his right.
The attempts by certain bourgeois jurists to separate law from the state, or to contrast “law” and “force”, are dictated by the attempt to hide and conceal the class essence of law.
Often these proofs that law is independent of the state bear a truly laughable character. Thus, for instance, Stammler claims that he has proved this thesis relying on the fact that on a dirigible which flies over the North Pole, i.e. outside the sphere of action of any state power, the emergence of legal relationships is possible.
By such empty dogmatic chicanery the scientific question of the relationship of state and law is decided. Can one be surprised at Lenin’s sharp reaction to Stammler when he says that: “From stupid arguments, Stammler draws equally stupid conclusions.”
The dependence of law on the state, however, does not signify that the state creates the legal superstructure by its arbitrary will. For the state itself, as Engels says, is only a more or less complex reflection of the economic needs of the dominant class in production.
The proletariat, having overthrown the bourgeoisie and consolidated its dictatorship, had to create Soviet law in conformity with the economy, in particular the existence of many millions of small and very small peasant farms. After the victory of the proletarian revolution the realization of socialism is not an instantaneous act but a long process of construction under the conditions of acute class struggle.
From the policy of limiting its exploitative tendencies and the elimination of its front ranks, we moved to the policy of liquidating the kulaks as a class by widespread collectivization. A successful fulfilment of the first Five Year Plan; the creation of our own base for the technical reconstruction of the whole national economy; the transfer of the basic mass of the peasantry to collectivization; these events enabled the basic task of the second Five Year Plan to be:
the final liquidation of capitalist elements and classes in general, the full elimination of the causes of class differences and exploitation, the overcoming of the survivals of capitalism in the economy and the consciousness of the people, the transformation of the whole working population of the country into conscious and active builders of a classless society. [7]
At each of these stages Soviet law regulated and formulated production relationships differently.
Soviet law in each of the stages was naturally different from the law of capitalist states. For law under the proletarian dictatorship has always had the goal of protecting the interest of “the working majority, the suppression of class elements hostile to the proletariat, and the defence of socialist construction. Those individual Soviet jurists who considered law as the totality of norms (i.e. externally and formally) are not in a position to understand this. Finding identically formulated norms in the system of bourgeois and Soviet law, these jurists began to speak of the similarity between bourgeois and Soviet law, to search out “general” institutions, and to trace the development of certain “general” bases for bourgeois and Soviet law. This tendency was very strong in the first years of NEP. The identification of Soviet with bourgeois law derived from an understanding of NEP as a return to capitalism, which found expression in the Marxist ranks.
If NEP, as the Zinoviev opposition asserted at the XIVth Party Congress, is “capitalism which holds the proletarian state on a chain”, then Soviet law must be presented as bourgeois law, in which certain limitations are introduced, to the extent in the period of imperialism that the capitalist state also regulates and limits the freedom of disposition of property, contractual freedom etc.
Such a distortion in the description of NEP led directly to an alliance with bourgeois reformists in the understanding of Soviet law.
In fact, NEP “is a special policy of the proletarian state intended to permit capitalism while the commanding heights are held by the proletarian state, intended for the struggle between the capitalist and socialist elements, intended for the growth of the role of the socialist elements at the expense of the capitalist elements, intended for the victory of the socialist elements over the capitalist elements, intended for the elimination of classes and for the construction of the foundation of a socialist economy.” [8]
Soviet law as a special form of policy followed by the proletariat and the proletarian state, was intended precisely for the victory of socialism. As such, it is radically different from bourgeois law despite the formal resemblance of individual statutes.
Juridicial formalism, which conceives of nothing other than the norm and reduces law to the purely logical operation of these norms, appears as a variety of reformism, as a Soviet “juridical socialism”. By confining themselves only to the norm and the purely juridical (i.e. formal ideas and concepts), they ignored the socio-economic and political essence of the matter. As a result, these jurists arrive at the conclusion that the transformation of property from an arbitrary and unrestricted right into a “social function” (i.e. a tendency which is “peculiar to the law of the advanced”, that is, capitalist, countries), finds its “fullest” expression in Soviet legislation. Making this contention, the Jurists “forgot” such a trifle as the October Revolution and the dictatorship of the proletariat.
It is not only important to “read” the norm, but also to know what class, what state, and what state apparatus is applying this norm.
6. Law and production relationships
Production relationships form the basis of society. It is necessary to begin with these relationships in order to comprehend the complex picture presented by the history of mankind.
To search for the basic characteristic of society and social relations in an area other than production relationships means to deprive oneself of the possibility of a scientific understanding of the laws of development of social formations. However, it by no means follows from this that, according to Marx, only relations of production and exchange are social relations. Such a concept is a caricature of Marxism. The equation of social relations with production relations in this case is understood purely mechanically. However, a number of times Lenin noted that Marx’s great service was that he did not limit himself to the description of the economic “skeleton” of capitalist society, but that:
in explaining the construction and development of a definite social formation “exclusively” by production relations, he nonetheless thoroughly and constantly studied the superstructure corresponding to these production relations, which clothed the skeleton with flesh and blood. The reason that Das Kapital had such enormous success was that this book (“by a German economist”) showed the capitalist social formation as a living thing-with its everyday aspects, with the actual social phenomena essential to the production relations between antagonistic classes, with the bourgeois political superstructure protecting the domination of the capitalist class, with the bourgeois ideas of freedom, equality etc., with bourgeois family relations. [9]
Stuchka looks differently at the matter. In his opinion, Marx considered only relations of production and exchange to be social relations. But this would mean affirming that Marx limited himself to the “skeleton” alone, as if having indicated the basic and eventually determinant in social life and social relations he then passed by that which is derivative and requires explanation. However, more than once Marx directly points out the existence of social relationships which are not production relations but which merely derive from them and correspond to them. Characterizing revolutionary proletarian socialism in France in 1848, Marx wrote:
This socialism is the proclamation of the permanence of the revolution , a proclamation of the class dictatorship of the proletariat as a necessary transition toward the elimination of class differences altogether, toward the elimination of all production relations upon which these differences are based, toward the elimination of all social relationships corresponding to these production relations, toward a revolution in the entire world of ideas arising from these relationships. [10]
Nevertheless, Comrade Stuchka firmly defends his understanding of the term “social relationships”:
We proceed from social relationships; I emphasize the word “social”, for here my critics are desperately confused. I thus selected the word “social” and a whole chapter in my first book was dedicated to it only in the sense of relations of production and exchange (as Marx and every Marxist understands this). [11]
Proceeding from the equation of production and social relationships, Stuchka defined law as a “system (or order) of social relations corresponding to the interests of the ruling class and protected by its organized force”. In this definition, as he himself indicated, there was room only for the law of property and the law of obligations.
As earlier, so even now [he wrote] I consider basic law , law in general, to be civil law , understanding thereby the form of organization of social relationships in the narrow and specific sense of the word (i.e. relations of production and exchange). I consider that all the remaining areas of law are either of a subordinate or derivative character, and that only bourgeois law (subjecting to its influence all the remaining areas of law) created a legal state, or state law and criminal law, as an equivalent norm for crime and punishment, not even mentioning administrative, financial etc., and finally international law or even the law of war. [12]
The positions outlined in this excerpt contain a series of mistakes. There is no doubt that the formulation and conformation of social relationships to the means of production is basic to law. Proceeding from the economic basis, from different forms of exploitation, we differentiate slaveowning, feudal and capitalist systems of law. But, in the first place, it is incorrect to subsume the property relations of slaveowning or feudal society under the concept of civil, i.e. bourgeois, law as “law in general”. In the second place, state law may not be equated with the so-called Rechtsstaat of the bourgeoisie. If one takes this point of view then one must either deny the existence of a distinctive feudal state law, or show that despite the existence of a Soviet state we do have Soviet state law. At the same time, in other places in his textbook, Stuchka proceeds from the existence of different class systems of law: feudal, bourgeois, Soviet. Here he argues for a “general law” which is equated with the civil law of bourgeois society. At the same time state law is equated with the theory of bourgeois jurists of the so-called Rechtsstaat , and criminal law (i.e. formalized class repression) with the ideology of equivalent retribution.
The basic question – do relationships exist that enter into the content of law, which are not, however, relations of production and exchange? – is avoided by Stuchka; he cites the subsidiary, derivative etc. character of state, criminal etc. law. However, it is clear that the structure of family relationships, the formalization of class domination in the state organization, the formalization of class repression, all this is embraced by the different branches of law (family, state and criminal).
The content of this legal intermediary is the social and political relationships which, in the final analysis, are reducible to the same production relationships, but by no means correspond to them.
Stuchka’s subsequent definition of law suffers from the shortcoming that he limits the area of law merely to production relations. This definition also introduces confusion because it confuses law with economics. Proceeding from the indisputable position that not all which is stated in a norm (in a statute) is realized in fact, Stuchka has made the incorrect conclusion that law is indeed the very relation of production and exchange. Stuchka has therefore declared Marx’s teaching – that law is an ideological superstructure to be a tribute to the “volitional theory” of the old jurists.
Whoever has mastered the form of theorizing of Marx and Engels that capital, money etc., are social relationships, will at once understand my views on the system of social relationships. This will be hardest of all for a jurist for whom law is a purely technical and artificial superstructure, strangely enough, holding sway over its base. Even Karl Marx gave a small tribute to this concept when he spoke of law as an ideological superstructure. But Marx was raised on Roman law and in general on the juridic concepts of the 1830s, considering it an expression “of the general will” ( Volkswillen ), and he was [therefore] accustomed to its terminology. [13]
In conducting the struggle with the narrow, formal legal concept of law as a totality of norms, we cannot deny the real existence of the legal superstructure, i.e. of relationships formulated and consolidated by the conscious will of the ruling class. Only to the extent that this process of formulation and consolidation proceeds may one speak of law. To study law only as totality of norms means to follow the path of formalism and dogmatism. But to study law only as relationships of production and exchange means to confuse law with economics, to retard the understanding of the reciprocal action of the legal superstructure and its active role. At the same time as production relations are imposed on people regardless of their will, legal relationships are impossible without the participation of the conscious will of the ruling class. The teaching of Marx, Engels and Lenin on law as an ideological superstructure needs no correction. Law cannot be understood unless we consider it as the basic form of the policy of the ruling class. In the later editions of The Revolutionary Role of State and Law , Stuchka supplemented his definition of law, developing the theory of the so-called three forms of law. The first, or in Stuchka’s words, the concrete form of law, is a legal relationship which corresponds to a production relationship and, with it, constitutes the base [or] reality. On the contrary, the two “abstract” forms – statute and legal ideology as Stuchka expresses it – are the essence of “the manifest superstructure”. [14]
This approach is also incorrect and non-dialectical. A legal relationship is a form of production relations because the active influence of the class organization of the ruling class transforms the factual relationship into a legal one, gives it a new quality, and thus includes it in the construction of the legal superstructure. This result is not achieved automatically by laissez faire , in the same way that prices are established under free competition. Even in the case of so-called customary law, the ruling class – through its special agencies, through the courts – ensures that the relations correspond to obligatory rules. This is all the more true with respect to the legislative creation of norms.
In particular, the revolutionary role of the legal superstructure is enormous in the transitional period when its active and conscious influence upon production and other social relationships assumes exceptional significance. Soviet law, like any law, will cease to exist if it is not applied. But the application of law is an active and conscious process by which the state apparatus plays the decisive role as a powerful weapon of class struggle. Would it be possible, for instance, to speak of Soviet law which did not somehow recognize the Soviet state, the Soviet agencies of power, Soviet courts etc.? It is clear that while an individual statute may be removed from the real legal order and remain a pious wish, concrete legal relationships may never be removed from the consciousness and will of the ruling class, may never be transferred from the superstructure to the base without parting from the heart of historical materialism.
From all that has been said above it is clear that the definition of law as a formal intermediary of the economy must be recognized as insufficient and incorrect. The different branches of law are connected differently with the economy; this must never be forgotten, and this is not expressed in the above-mentioned definition. On the contrary it can lead to the notion that the area of law is limited to property relationships alone. Then all the other types of law must be declared non-existent. Stuchka would, in fact, have had to reach this conclusion. But he speaks of criminal and state law, not entirely consistently with his other position, i.e. by referring to them he recognizes their existence.
There is no doubt that economics is at the base of political, familial and all other social relations. [15] But the election law of any capitalist country facilitates the economy differently from civil law or the Criminal Code. To try to force all the varied branches of law into one formula is to give preference to empty abstractions.
Law as a formal facilitation of social and (primarily) production relationships must be studied concretely. This study may not be replaced with ready citations from Hegel with respect to the “transformation of form into substance and substance into form”. The dialectical method, which teaches that every truth is concrete, becomes in this instance its own opposite-dead scholasticism, barren arguments and disputes on the theme that “form is not without content and content not without form”. However, the matter really consists of showing the role and character of law as form in specific and concrete branches of law and concrete historial conditions with a relation to concrete content. Only in this manner can the real relation of form and content be established and can one be convinced that it is far from identical in different instances. Often legal form hides economic content directly contrary to it (thus in the period when we conducted the policy of restricting the kulak, the leasing of a horse or tools by a poor peasant to a rich one often hid the sale of the first’s labour power to the second). A transaction of purchase and sale can hide the most diverse economic content. The same could be said about any other relationships within the so-called law of obligations. Here we meet with a phenomenon whose form is relatively indifferent to its content, but it is improper to conclude from this that in civil law we have a “faceless instrumentality” which must be used independently of the economic class content of the relationships which it implements. On the contrary, the significance of form is recognized only through content, through economics, through politics and through relations between classes.
Therefore, it is a flagrant error to equate law as an historical phenomenon – including various class systems – with the totality of those features of bourgeois law that derive from the exchange of commodities of equal value. [16] Such a concept of law minimizes the class coercion essential to bourgeois law, essential to feudal law and to all law. Law in bourgeois society serves not only the facilitation of exchange, but simultaneously and mainly supports and consolidates the unequal distribution of property and the monopoly of the capitalist in production. Bourgeois property is not exhausted by the relationships between commodity owners. These [owners – eds. ] are tied by exchange and the contractual relationship is the form of this exchange. Bourgeois property includes in a masked form the same relationship of domination and subordination which, in feudal property, appears chiefly as personal subordination.
This methodological mistake was related to the relegation of the class repressive role of law, and to an incorrect presentation of the relation between state and law (the state as the guarantor of exchange), and to mistakes in questions of morality (the denial of proletarian morality) and in questions of criminal law.
The attempts to distinguish between formal characteristics and abstract legal concepts expressing the relationship between commodity owners, and to proclaim this “form of law” as the subject of the Marxist theory of law, should be recognized as grossly mistaken. This paves the way to the separation of form and content, and diverts theory from the task of socialist construction to scholasticism.
The immediate relation, in practice, between the proletariat (as the ruling class) and law (as a weapon with whose help the tasks of class struggle at any given stage are decided) is in this case replaced by the abstract theoretical denial of the “narrow horizons of bourgeois law” in the name of developed communism.
From this perspective Soviet law is seen exclusively as a legacy of class society imposed on the proletariat and which haunts it until the second phase of communism. The abstract theoretical exposure of “bourgeois” law hides the task of the concrete analysis of Soviet law at different stages of the revolution. Accordingly, it gives insufficient concrete indication of the practical struggle against bourgeois influences, and against opportunist distortions of the Party’s general line on Soviet law.
The theoretical mistake of exaggerating the importance of market relations can be the basis for right opportunist conclusions about always preserving the bourgeois forms of law corresponding to private exchange. Conversely, to ignore exchange in considering the problems of Soviet law leads to “leftist” positions about the withering away of law which is now in the process of socializing the means of production, and about the withering away of economic accountability and the principle of payment according to labour, i.e. to the defence of the elimination of individual responsibility and wage egalitarianism.
Top of the page
1. K. Marx, Letter to Weydemeyer (March 5, 1852), MESW , vol.1, p.528.
2. V. I. Lenin, The Economic Content of Narodnism (1895), LCW , vol.1, p.419.
3. See Kellreiter’s article The State ;, in D. Elster et al. (eds), Handwörterbuch der Rechtswissenschaft (1923), Fischer, Jena, p.599.
4. V.I. Lenin, A Contribution to the History of the Question of Dictatorship (1920), LCW , vol.31, p.353.
5. F. Engels, Ludwig Feuerbach and the End of Classical German Philosophy (1888), MESW , vol.3, p.371.
6. ibid. , p.371.
7. From a resolution of the XVIIth Party Conference (1932).
8. J. Stalin, The Fourteenth Congress of the CPSU (1925), Stalin: Works, Foreign Languages Publishing House, Moscow (1954), vol.7, p.374.
9. V.I. Lenin, What the “Friends of the People” Are (1894), LCW , vol.1, pp.141-42.
10. K. Marx, The Class Struggles in France (1850), MESW , vol.1, p.282.
11. P.I. Stuchka, A Course on Soviet Civil Law (1927), Communist Academy, vol.1, p.13.
12. ibid. , pp.78-79.
13. P.I. Stuchka, The Revolutionary Role of Law and State (1921), Moscow, p.15.
14. ibid. (3rd edition); and P.I. Stuchka’s article Law in Encyclopaedia of State and Law, (1925-1927), vol.3, pp.415-430.
15. “The state and law are determined by economic relations. Of course, the same must be said of civil law whose role in essence consists of the legislative clarification of the existing economic relations between individuals which are normal in the given circumstances” F. Engels, Ludwig Feuerbach and the End of Classical German Philosophy (1888), op. cit. p.370.
16. This erroneous conception was developed in E.B. Pashukanis, The General Theory of Law and Marxism (1927), 3rd edition. See also E.B. Pashukanis, The Situation on the Legal Theory Front , Soviet State and the Revolution of Law (1930), no.11-12; and For a Marxist-Leninist Theory of State and Law (1931) Moscow, where a critique of this mistaken conception is given.
Last updated on 13.5.2004
What is the newly passed 'Russia law' that has divided people in Georgia for months?
Georgia’s parliament has passed a law that critics see as a threat to media freedom and the country’s aspirations to join the European Union
Georgia's parliament has passed a law that critics see as a threat to media freedom and the country’s aspirations to join the European Union. Lawmakers defied weeks of large demonstrations in the capital that also featured anger at neighboring Russia.
Here is a look at the law and the protests against it:
The law would require media, nongovernmental organizations and other nonprofits to register as “pursuing the interests of a foreign power” if they receive more than 20% of funding from abroad.
The law is nearly identical to the one that the governing Georgian Dream party was pressured to withdraw last year after similar protests. This version passed its third and final reading in parliament on Tuesday.
The governing party says the law is necessary to stem what it deems as harmful foreign influence over Georgia’s political scene and prevent unidentified foreign actors from trying to destabilize it.
The opposition denounces it as “the Russian law” because Moscow uses similar legislation to stigmatize independent news media and organizations critical of the Kremlin. Opposition lawmakers have accused the governing party of trying to drag Georgia into Russia's sphere of influence.
The law will be sent to the president before it can go into effect. President Salome Zourabichvili, who is increasingly at odds with the governing party, has vowed to veto the law, but Georgian Dream has a majority sufficient to override a veto.
Russia-Georgia relations have been strained and turbulent since the 1991 collapse of the Soviet Union and Georgia's departure from its role as a Soviet republic.
In 2008, Russia fought a brief war with Georgia, which had made a botched attempt to regain control over the breakaway province of South Ossetia. Moscow then recognized South Ossetia and another separatist province, Abkhazia, as independent states and strengthened its military presence there. Most of the world considers both regions to be parts of Georgia.
Tbilisi cut diplomatic ties with Moscow, and the regions’ status remains a key irritant even as Russia-Georgia relations have improved in recent years.
The opposition United National Movement accuses Georgian Dream, which was founded by Bidzina Ivanishvili, a former prime minister and billionaire who made his fortune in Russia, of serving Moscow’s interests — an accusation the governing party denies.
EU foreign policy chief Josep Borrell described the parliament’s decision as “a very concerning development” and warned that “final adoption of this legislation would negatively impact Georgia’s progress on its EU path.” Borrell earlier said the law was “not in line with EU core norms and values” and would limit the ability of media and civil society to operate freely.
European Council President Charles Michel said after the law was passed that “if they want to join the EU, they have to respect the fundamental principles of the rule of law and the democratic principles.”
Related Topics
Trending reader picks.

2 accused of plotting attack on Jews in England
- May 14, 11:11 AM
Cops shoot Amazon guard who tried to kill boss
- May 14, 10:52 AM

Biggest known batch of planet ingredients found
- May 14, 2:02 PM

Moms of Miss USA, Miss Teen USA speak out
- May 14, 9:43 AM

Jimmy Kimmel shares Mother’s Day gaffe
- May 14, 12:09 PM
ABC News Live
24/7 coverage of breaking news and live events

COMMENTS
Law Dissertation Topics For Covid Crisis. Topic 1: The legal implications of the COVID-19 pandemic on Canadian immigration and the way forward. Topic 2: Effect of COVID-19 on the United States Immigration policies; an assessment of International Legal agreements governing pandemic disease control and the way forward.
The Ph.D. in Law degree program is designed to prepare J.D. graduates for careers as legal scholars and teachers through a doctoral program aimed at the production of a substantial body of academic research and writing under the close supervision of a three-member faculty dissertation committee. Unlike programs designed for students who wish to ...
Embarking on a PhD in Law is an intellectually rigorous journey that positions students at the forefront of legal theory, practice, and reform. These advanced degrees offer a unique opportunity for candidates to delve deeply into the complexities of law as it intersects with society, economy, and politics. Through PhDs in Law, students engage ...
The Ph.D. in Law prepares graduates for global leadership in the judiciary, academia, business and government. Since 1966, the program has offered a select number of diverse students the opportunity to attain their highest professional aspirations and career goals. A preeminent center for interdisciplinary legal studies, UW Law offers a global ...
The Doctor of the Science of Law (JSD) is the Law School's most advanced law degree, and is considered a doctorate equivalent to a Ph.D. It is designed for those interested in becoming scholars and teachers of law including interdisciplinary approaches to law. Study toward the degree is open only to a small number of exceptionally well ...
Completed DPhil Projects. The University's legal research community includes more than 200 postgraduate students engaged in research degrees in the Law Faculty and its centres. It is one of the largest and most intellectually diverse research communities in the world. Many of our research degree alumni are now global leaders in the fields of ...
The law dissertation topics below were written by our expert writers, as a learning aid to help you with your studies. If you are looking for help with your law dissertation topic then we offer a comprehensive writing service provided by fully qualified academics in your field of study. Law Dissertation Topic and Titles Service.
Ph.D. Berkeley Law's Jurisprudence and Social Policy Program offers a unique interdisciplinary graduate program leading to Ph.D. degrees for students interested in the scholarly study of legal ideas and institutions, policy analysis and applied research, and other areas. Learn more here.
4. Contemplate the contribution you want to make to your field of study. Some of the best research ideas come from one's field of practice. DLP students often choose their doctoral thesis questions from those that are currently pressing within their professional field.
Further information on postgraduate admission to research courses in the Faculty of Law is available from [email protected] or +44 (0)1223 330039. Finance overview Funding How to apply The PhD is awarded after three to four years of full-time research (or five to seven years of part-time study) on the basis of a dissertation of 80,000 ...
The Coordinated JD/PhD Program is designed for students interested in completing interdisciplinary work at Harvard University and is founded on the belief that students' legal studies and their arts and sciences graduate studies can be mutually enriched through this pursuit. Students completing the coordinated program receive a JD from ...
PhD Topics at iCourts General description. iCourts 3.0 seeks to explain and make intelligible the relative and often contested power of international courts, institutions and law. While the current resistance to international courts and law is interesting in this regard, we generally encourage projects that more broadly explore the power of ...
Yale University, Law School. PhD in Law. Yale University's Law School ranks first in the nation, with its 20 legal clinics offering an immersive experience for students. This PhD program has a purely academic focus. To qualify for admission, you'll need to already have a JD (Juris Doctor) degree.
Immigra on Law For Employers Business Opera ons Business Banking And Securi es Hiring A Business Law A orney Consumer Issues Arbitra on And Media on IInternet Law For The Public Educa on Law Social Security Disability Healthcare Law Drunk Driving Defense Lawsuits And Lawyers Elder Law And Aging CCo-Ops And Condominiums
Employment law offers some very interesting law topics to work on. Under this, you can write your dissertation on labor laws, worker compensation, immigration laws, minimum wages, wrongful termination, and many such research topics in law. US 'Fire at will' employment ability and should it be made possible in the UK.
This category comprises titles relating to legal issues concerning kids that contravene the law by committing juvenile offenses. Nevertheless, they are exciting law enforcement topics to explore when pursuing masters or Ph.D. studies. Analysis of children's rights against economic exploitation and harmful work.
PhD in Law. Regarded as the highest degree in varied academic disciplines, a Doctorate of Philosophy ( PhD) aims to provide students with a chance to delve deeper into a specific area of study. For a field like Law, a doctoral degree is suitable for those wanted to pursue their career as legal scholars and teachers.
The law dissertation topics that are most important for the law-students in 2024 are environmental law, family law, tort, labour law, medical law, intellectual property, criminal law, and tax law among others. ... The students who are planning to get their BA LLB or masters or PhD must understand the importance of a dissertation. They can do ...
The College of Law has emerged as one of the best educational values in the nation. The college's success is built upon a steadfast belief that a law school should stand for serving the public, promote civil discourse, contribute to the dialogue on critical issues and provide access across all cultures and ideologies to the highest quality of legal education.
Today, it branches into diverse fields like law, policy, management, and strategy, reflecting the multifaceted nature of modern cyber threats. Ad. ... Students start with learning research basics and then dive into modern tech topics. Support for Students: All PhD students get funding that covers their studies, a stipend, and health insurance ...
A Master of Studies in Law is a master's-level graduate degree in law and legal systems. A Juris Doctor is a terminal degree at the doctoral level that qualifies recipients to work in the courts as lawyers and judges. Admissions requirements, coursework, and career opportunities for the degrees differ substantially.
1. The doctrine of socio-economic formations as a basis for the Marxist theory of state and law. The doctrine of state and law is part of a broader whole, namely, the complex of sciences which study human society. The development of these sciences is in turn determined by the history of society itself, i.e. by the history of class struggle.
Large demonstrations broke out across Georgia as thousands protest a new foreign agent law that many fear will be a tool to crack down on dissent in a country that is looking to join the EU. The government of Georgia wants to put the country back in time to its old Soviet Union days, and it signed a controversial new 'foreign agents' law that ...
Law. Medicine & Health. Natural Sciences & Mathematics. Social Sciences. Scholarships applicable to PhD at Moscow Campus - Faculty of Law. Programmes Universities Scholarships. Page 1 | 19 Scholarships . Filters 2. 19 Scholarships . The scholarships listed below are applicable to students of all nationalities.
This version passed its third and final reading in parliament on Tuesday. The governing party says the law is necessary to stem what it deems as harmful foreign influence over Georgia's ...
Government opponents say proposals for a restrictive new political-funding law represent a Russian ploy to weaken growing ties between the ex-Soviet state and Europe.