Tips and guidelines for being a successful researcher
Affiliations.
- 1 Servicio de Aparato Digestivo, Hospital Universitario de La Princesa, Instituto de Investigación Sanitaria Princesa (IIS-IP), Universidad Autónoma de Madrid, Centro de Investigación Biomédica en Red de Enfermedades Hepáticas y Digestivas (CIBEREHD), Madrid, España. Electronic address: [email protected].
- 2 Servicio de Aparato Digestivo, Hospital Universitario de La Princesa, Instituto de Investigación Sanitaria Princesa (IIS-IP), Universidad Autónoma de Madrid, Centro de Investigación Biomédica en Red de Enfermedades Hepáticas y Digestivas (CIBEREHD), Madrid, España.
- PMID: 32331924
- DOI: 10.1016/j.gastrohep.2020.03.010
This article aims to share our experience with those who consider dedicating themselves to research. In this way, the characteristics, qualities or competences that, in our opinion, a good researcher should fulfill are listed, and therefore the keys that can help you achieve a successful research career. The intention of this article is not to simply list a series of theoretical recommendations but to share some personal suggestions based on our experience and, therefore, of an eminently practical nature. The fundamental qualities to be discussed are: Ethics and honesty. Curiosity, passion, enthusiasm and motivation. Persistence, dedication and discipline. Ambition and leadership. Compromise and responsibility. Organization and planning. Acquire knowledge of research methodology. Critical and positive attitude towards difficulties and failure. Prioritization of objectives and time management. The importance of a good mentor. Establishment of a network of collaborators and teamwork. Maintain a balance between clinical and research activity. Combine public and private investigation. Balance between professional and personal life. And, finally, humility, generosity and thanks. Research represents a fundamental pillar of medical activity and it is evident that the highest quality of care arises from the integration of excellent clinical practice and research activity. With the philosophy that most of the qualities to develop an excellent research activity depend on attitude, and can be learned, developed and improved, in this manuscript we share with the reader a series of recommendations that we consider essential to be a good researcher.
Keywords: Investigación; Investigador; Investigation; Mentor; Researcher; Success; Successful; Éxito: Exitoso.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier España, S.L.U. All rights reserved.
- Biomedical Research / methods*
- Biomedical Research / standards*
- Guidelines as Topic
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- J Korean Med Sci
- v.37(16); 2022 Apr 25


A Practical Guide to Writing Quantitative and Qualitative Research Questions and Hypotheses in Scholarly Articles
Edward barroga.
1 Department of General Education, Graduate School of Nursing Science, St. Luke’s International University, Tokyo, Japan.
Glafera Janet Matanguihan
2 Department of Biological Sciences, Messiah University, Mechanicsburg, PA, USA.
The development of research questions and the subsequent hypotheses are prerequisites to defining the main research purpose and specific objectives of a study. Consequently, these objectives determine the study design and research outcome. The development of research questions is a process based on knowledge of current trends, cutting-edge studies, and technological advances in the research field. Excellent research questions are focused and require a comprehensive literature search and in-depth understanding of the problem being investigated. Initially, research questions may be written as descriptive questions which could be developed into inferential questions. These questions must be specific and concise to provide a clear foundation for developing hypotheses. Hypotheses are more formal predictions about the research outcomes. These specify the possible results that may or may not be expected regarding the relationship between groups. Thus, research questions and hypotheses clarify the main purpose and specific objectives of the study, which in turn dictate the design of the study, its direction, and outcome. Studies developed from good research questions and hypotheses will have trustworthy outcomes with wide-ranging social and health implications.
INTRODUCTION
Scientific research is usually initiated by posing evidenced-based research questions which are then explicitly restated as hypotheses. 1 , 2 The hypotheses provide directions to guide the study, solutions, explanations, and expected results. 3 , 4 Both research questions and hypotheses are essentially formulated based on conventional theories and real-world processes, which allow the inception of novel studies and the ethical testing of ideas. 5 , 6
It is crucial to have knowledge of both quantitative and qualitative research 2 as both types of research involve writing research questions and hypotheses. 7 However, these crucial elements of research are sometimes overlooked; if not overlooked, then framed without the forethought and meticulous attention it needs. Planning and careful consideration are needed when developing quantitative or qualitative research, particularly when conceptualizing research questions and hypotheses. 4
There is a continuing need to support researchers in the creation of innovative research questions and hypotheses, as well as for journal articles that carefully review these elements. 1 When research questions and hypotheses are not carefully thought of, unethical studies and poor outcomes usually ensue. Carefully formulated research questions and hypotheses define well-founded objectives, which in turn determine the appropriate design, course, and outcome of the study. This article then aims to discuss in detail the various aspects of crafting research questions and hypotheses, with the goal of guiding researchers as they develop their own. Examples from the authors and peer-reviewed scientific articles in the healthcare field are provided to illustrate key points.
DEFINITIONS AND RELATIONSHIP OF RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
A research question is what a study aims to answer after data analysis and interpretation. The answer is written in length in the discussion section of the paper. Thus, the research question gives a preview of the different parts and variables of the study meant to address the problem posed in the research question. 1 An excellent research question clarifies the research writing while facilitating understanding of the research topic, objective, scope, and limitations of the study. 5
On the other hand, a research hypothesis is an educated statement of an expected outcome. This statement is based on background research and current knowledge. 8 , 9 The research hypothesis makes a specific prediction about a new phenomenon 10 or a formal statement on the expected relationship between an independent variable and a dependent variable. 3 , 11 It provides a tentative answer to the research question to be tested or explored. 4
Hypotheses employ reasoning to predict a theory-based outcome. 10 These can also be developed from theories by focusing on components of theories that have not yet been observed. 10 The validity of hypotheses is often based on the testability of the prediction made in a reproducible experiment. 8
Conversely, hypotheses can also be rephrased as research questions. Several hypotheses based on existing theories and knowledge may be needed to answer a research question. Developing ethical research questions and hypotheses creates a research design that has logical relationships among variables. These relationships serve as a solid foundation for the conduct of the study. 4 , 11 Haphazardly constructed research questions can result in poorly formulated hypotheses and improper study designs, leading to unreliable results. Thus, the formulations of relevant research questions and verifiable hypotheses are crucial when beginning research. 12
CHARACTERISTICS OF GOOD RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
Excellent research questions are specific and focused. These integrate collective data and observations to confirm or refute the subsequent hypotheses. Well-constructed hypotheses are based on previous reports and verify the research context. These are realistic, in-depth, sufficiently complex, and reproducible. More importantly, these hypotheses can be addressed and tested. 13
There are several characteristics of well-developed hypotheses. Good hypotheses are 1) empirically testable 7 , 10 , 11 , 13 ; 2) backed by preliminary evidence 9 ; 3) testable by ethical research 7 , 9 ; 4) based on original ideas 9 ; 5) have evidenced-based logical reasoning 10 ; and 6) can be predicted. 11 Good hypotheses can infer ethical and positive implications, indicating the presence of a relationship or effect relevant to the research theme. 7 , 11 These are initially developed from a general theory and branch into specific hypotheses by deductive reasoning. In the absence of a theory to base the hypotheses, inductive reasoning based on specific observations or findings form more general hypotheses. 10
TYPES OF RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
Research questions and hypotheses are developed according to the type of research, which can be broadly classified into quantitative and qualitative research. We provide a summary of the types of research questions and hypotheses under quantitative and qualitative research categories in Table 1 .
Research questions in quantitative research
In quantitative research, research questions inquire about the relationships among variables being investigated and are usually framed at the start of the study. These are precise and typically linked to the subject population, dependent and independent variables, and research design. 1 Research questions may also attempt to describe the behavior of a population in relation to one or more variables, or describe the characteristics of variables to be measured ( descriptive research questions ). 1 , 5 , 14 These questions may also aim to discover differences between groups within the context of an outcome variable ( comparative research questions ), 1 , 5 , 14 or elucidate trends and interactions among variables ( relationship research questions ). 1 , 5 We provide examples of descriptive, comparative, and relationship research questions in quantitative research in Table 2 .
Hypotheses in quantitative research
In quantitative research, hypotheses predict the expected relationships among variables. 15 Relationships among variables that can be predicted include 1) between a single dependent variable and a single independent variable ( simple hypothesis ) or 2) between two or more independent and dependent variables ( complex hypothesis ). 4 , 11 Hypotheses may also specify the expected direction to be followed and imply an intellectual commitment to a particular outcome ( directional hypothesis ) 4 . On the other hand, hypotheses may not predict the exact direction and are used in the absence of a theory, or when findings contradict previous studies ( non-directional hypothesis ). 4 In addition, hypotheses can 1) define interdependency between variables ( associative hypothesis ), 4 2) propose an effect on the dependent variable from manipulation of the independent variable ( causal hypothesis ), 4 3) state a negative relationship between two variables ( null hypothesis ), 4 , 11 , 15 4) replace the working hypothesis if rejected ( alternative hypothesis ), 15 explain the relationship of phenomena to possibly generate a theory ( working hypothesis ), 11 5) involve quantifiable variables that can be tested statistically ( statistical hypothesis ), 11 6) or express a relationship whose interlinks can be verified logically ( logical hypothesis ). 11 We provide examples of simple, complex, directional, non-directional, associative, causal, null, alternative, working, statistical, and logical hypotheses in quantitative research, as well as the definition of quantitative hypothesis-testing research in Table 3 .
Research questions in qualitative research
Unlike research questions in quantitative research, research questions in qualitative research are usually continuously reviewed and reformulated. The central question and associated subquestions are stated more than the hypotheses. 15 The central question broadly explores a complex set of factors surrounding the central phenomenon, aiming to present the varied perspectives of participants. 15
There are varied goals for which qualitative research questions are developed. These questions can function in several ways, such as to 1) identify and describe existing conditions ( contextual research question s); 2) describe a phenomenon ( descriptive research questions ); 3) assess the effectiveness of existing methods, protocols, theories, or procedures ( evaluation research questions ); 4) examine a phenomenon or analyze the reasons or relationships between subjects or phenomena ( explanatory research questions ); or 5) focus on unknown aspects of a particular topic ( exploratory research questions ). 5 In addition, some qualitative research questions provide new ideas for the development of theories and actions ( generative research questions ) or advance specific ideologies of a position ( ideological research questions ). 1 Other qualitative research questions may build on a body of existing literature and become working guidelines ( ethnographic research questions ). Research questions may also be broadly stated without specific reference to the existing literature or a typology of questions ( phenomenological research questions ), may be directed towards generating a theory of some process ( grounded theory questions ), or may address a description of the case and the emerging themes ( qualitative case study questions ). 15 We provide examples of contextual, descriptive, evaluation, explanatory, exploratory, generative, ideological, ethnographic, phenomenological, grounded theory, and qualitative case study research questions in qualitative research in Table 4 , and the definition of qualitative hypothesis-generating research in Table 5 .
Qualitative studies usually pose at least one central research question and several subquestions starting with How or What . These research questions use exploratory verbs such as explore or describe . These also focus on one central phenomenon of interest, and may mention the participants and research site. 15
Hypotheses in qualitative research
Hypotheses in qualitative research are stated in the form of a clear statement concerning the problem to be investigated. Unlike in quantitative research where hypotheses are usually developed to be tested, qualitative research can lead to both hypothesis-testing and hypothesis-generating outcomes. 2 When studies require both quantitative and qualitative research questions, this suggests an integrative process between both research methods wherein a single mixed-methods research question can be developed. 1
FRAMEWORKS FOR DEVELOPING RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
Research questions followed by hypotheses should be developed before the start of the study. 1 , 12 , 14 It is crucial to develop feasible research questions on a topic that is interesting to both the researcher and the scientific community. This can be achieved by a meticulous review of previous and current studies to establish a novel topic. Specific areas are subsequently focused on to generate ethical research questions. The relevance of the research questions is evaluated in terms of clarity of the resulting data, specificity of the methodology, objectivity of the outcome, depth of the research, and impact of the study. 1 , 5 These aspects constitute the FINER criteria (i.e., Feasible, Interesting, Novel, Ethical, and Relevant). 1 Clarity and effectiveness are achieved if research questions meet the FINER criteria. In addition to the FINER criteria, Ratan et al. described focus, complexity, novelty, feasibility, and measurability for evaluating the effectiveness of research questions. 14
The PICOT and PEO frameworks are also used when developing research questions. 1 The following elements are addressed in these frameworks, PICOT: P-population/patients/problem, I-intervention or indicator being studied, C-comparison group, O-outcome of interest, and T-timeframe of the study; PEO: P-population being studied, E-exposure to preexisting conditions, and O-outcome of interest. 1 Research questions are also considered good if these meet the “FINERMAPS” framework: Feasible, Interesting, Novel, Ethical, Relevant, Manageable, Appropriate, Potential value/publishable, and Systematic. 14
As we indicated earlier, research questions and hypotheses that are not carefully formulated result in unethical studies or poor outcomes. To illustrate this, we provide some examples of ambiguous research question and hypotheses that result in unclear and weak research objectives in quantitative research ( Table 6 ) 16 and qualitative research ( Table 7 ) 17 , and how to transform these ambiguous research question(s) and hypothesis(es) into clear and good statements.
a These statements were composed for comparison and illustrative purposes only.
b These statements are direct quotes from Higashihara and Horiuchi. 16
a This statement is a direct quote from Shimoda et al. 17
The other statements were composed for comparison and illustrative purposes only.
CONSTRUCTING RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
To construct effective research questions and hypotheses, it is very important to 1) clarify the background and 2) identify the research problem at the outset of the research, within a specific timeframe. 9 Then, 3) review or conduct preliminary research to collect all available knowledge about the possible research questions by studying theories and previous studies. 18 Afterwards, 4) construct research questions to investigate the research problem. Identify variables to be accessed from the research questions 4 and make operational definitions of constructs from the research problem and questions. Thereafter, 5) construct specific deductive or inductive predictions in the form of hypotheses. 4 Finally, 6) state the study aims . This general flow for constructing effective research questions and hypotheses prior to conducting research is shown in Fig. 1 .

Research questions are used more frequently in qualitative research than objectives or hypotheses. 3 These questions seek to discover, understand, explore or describe experiences by asking “What” or “How.” The questions are open-ended to elicit a description rather than to relate variables or compare groups. The questions are continually reviewed, reformulated, and changed during the qualitative study. 3 Research questions are also used more frequently in survey projects than hypotheses in experiments in quantitative research to compare variables and their relationships.
Hypotheses are constructed based on the variables identified and as an if-then statement, following the template, ‘If a specific action is taken, then a certain outcome is expected.’ At this stage, some ideas regarding expectations from the research to be conducted must be drawn. 18 Then, the variables to be manipulated (independent) and influenced (dependent) are defined. 4 Thereafter, the hypothesis is stated and refined, and reproducible data tailored to the hypothesis are identified, collected, and analyzed. 4 The hypotheses must be testable and specific, 18 and should describe the variables and their relationships, the specific group being studied, and the predicted research outcome. 18 Hypotheses construction involves a testable proposition to be deduced from theory, and independent and dependent variables to be separated and measured separately. 3 Therefore, good hypotheses must be based on good research questions constructed at the start of a study or trial. 12
In summary, research questions are constructed after establishing the background of the study. Hypotheses are then developed based on the research questions. Thus, it is crucial to have excellent research questions to generate superior hypotheses. In turn, these would determine the research objectives and the design of the study, and ultimately, the outcome of the research. 12 Algorithms for building research questions and hypotheses are shown in Fig. 2 for quantitative research and in Fig. 3 for qualitative research.

EXAMPLES OF RESEARCH QUESTIONS FROM PUBLISHED ARTICLES
- EXAMPLE 1. Descriptive research question (quantitative research)
- - Presents research variables to be assessed (distinct phenotypes and subphenotypes)
- “BACKGROUND: Since COVID-19 was identified, its clinical and biological heterogeneity has been recognized. Identifying COVID-19 phenotypes might help guide basic, clinical, and translational research efforts.
- RESEARCH QUESTION: Does the clinical spectrum of patients with COVID-19 contain distinct phenotypes and subphenotypes? ” 19
- EXAMPLE 2. Relationship research question (quantitative research)
- - Shows interactions between dependent variable (static postural control) and independent variable (peripheral visual field loss)
- “Background: Integration of visual, vestibular, and proprioceptive sensations contributes to postural control. People with peripheral visual field loss have serious postural instability. However, the directional specificity of postural stability and sensory reweighting caused by gradual peripheral visual field loss remain unclear.
- Research question: What are the effects of peripheral visual field loss on static postural control ?” 20
- EXAMPLE 3. Comparative research question (quantitative research)
- - Clarifies the difference among groups with an outcome variable (patients enrolled in COMPERA with moderate PH or severe PH in COPD) and another group without the outcome variable (patients with idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension (IPAH))
- “BACKGROUND: Pulmonary hypertension (PH) in COPD is a poorly investigated clinical condition.
- RESEARCH QUESTION: Which factors determine the outcome of PH in COPD?
- STUDY DESIGN AND METHODS: We analyzed the characteristics and outcome of patients enrolled in the Comparative, Prospective Registry of Newly Initiated Therapies for Pulmonary Hypertension (COMPERA) with moderate or severe PH in COPD as defined during the 6th PH World Symposium who received medical therapy for PH and compared them with patients with idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension (IPAH) .” 21
- EXAMPLE 4. Exploratory research question (qualitative research)
- - Explores areas that have not been fully investigated (perspectives of families and children who receive care in clinic-based child obesity treatment) to have a deeper understanding of the research problem
- “Problem: Interventions for children with obesity lead to only modest improvements in BMI and long-term outcomes, and data are limited on the perspectives of families of children with obesity in clinic-based treatment. This scoping review seeks to answer the question: What is known about the perspectives of families and children who receive care in clinic-based child obesity treatment? This review aims to explore the scope of perspectives reported by families of children with obesity who have received individualized outpatient clinic-based obesity treatment.” 22
- EXAMPLE 5. Relationship research question (quantitative research)
- - Defines interactions between dependent variable (use of ankle strategies) and independent variable (changes in muscle tone)
- “Background: To maintain an upright standing posture against external disturbances, the human body mainly employs two types of postural control strategies: “ankle strategy” and “hip strategy.” While it has been reported that the magnitude of the disturbance alters the use of postural control strategies, it has not been elucidated how the level of muscle tone, one of the crucial parameters of bodily function, determines the use of each strategy. We have previously confirmed using forward dynamics simulations of human musculoskeletal models that an increased muscle tone promotes the use of ankle strategies. The objective of the present study was to experimentally evaluate a hypothesis: an increased muscle tone promotes the use of ankle strategies. Research question: Do changes in the muscle tone affect the use of ankle strategies ?” 23
EXAMPLES OF HYPOTHESES IN PUBLISHED ARTICLES
- EXAMPLE 1. Working hypothesis (quantitative research)
- - A hypothesis that is initially accepted for further research to produce a feasible theory
- “As fever may have benefit in shortening the duration of viral illness, it is plausible to hypothesize that the antipyretic efficacy of ibuprofen may be hindering the benefits of a fever response when taken during the early stages of COVID-19 illness .” 24
- “In conclusion, it is plausible to hypothesize that the antipyretic efficacy of ibuprofen may be hindering the benefits of a fever response . The difference in perceived safety of these agents in COVID-19 illness could be related to the more potent efficacy to reduce fever with ibuprofen compared to acetaminophen. Compelling data on the benefit of fever warrant further research and review to determine when to treat or withhold ibuprofen for early stage fever for COVID-19 and other related viral illnesses .” 24
- EXAMPLE 2. Exploratory hypothesis (qualitative research)
- - Explores particular areas deeper to clarify subjective experience and develop a formal hypothesis potentially testable in a future quantitative approach
- “We hypothesized that when thinking about a past experience of help-seeking, a self distancing prompt would cause increased help-seeking intentions and more favorable help-seeking outcome expectations .” 25
- “Conclusion
- Although a priori hypotheses were not supported, further research is warranted as results indicate the potential for using self-distancing approaches to increasing help-seeking among some people with depressive symptomatology.” 25
- EXAMPLE 3. Hypothesis-generating research to establish a framework for hypothesis testing (qualitative research)
- “We hypothesize that compassionate care is beneficial for patients (better outcomes), healthcare systems and payers (lower costs), and healthcare providers (lower burnout). ” 26
- Compassionomics is the branch of knowledge and scientific study of the effects of compassionate healthcare. Our main hypotheses are that compassionate healthcare is beneficial for (1) patients, by improving clinical outcomes, (2) healthcare systems and payers, by supporting financial sustainability, and (3) HCPs, by lowering burnout and promoting resilience and well-being. The purpose of this paper is to establish a scientific framework for testing the hypotheses above . If these hypotheses are confirmed through rigorous research, compassionomics will belong in the science of evidence-based medicine, with major implications for all healthcare domains.” 26
- EXAMPLE 4. Statistical hypothesis (quantitative research)
- - An assumption is made about the relationship among several population characteristics ( gender differences in sociodemographic and clinical characteristics of adults with ADHD ). Validity is tested by statistical experiment or analysis ( chi-square test, Students t-test, and logistic regression analysis)
- “Our research investigated gender differences in sociodemographic and clinical characteristics of adults with ADHD in a Japanese clinical sample. Due to unique Japanese cultural ideals and expectations of women's behavior that are in opposition to ADHD symptoms, we hypothesized that women with ADHD experience more difficulties and present more dysfunctions than men . We tested the following hypotheses: first, women with ADHD have more comorbidities than men with ADHD; second, women with ADHD experience more social hardships than men, such as having less full-time employment and being more likely to be divorced.” 27
- “Statistical Analysis
- ( text omitted ) Between-gender comparisons were made using the chi-squared test for categorical variables and Students t-test for continuous variables…( text omitted ). A logistic regression analysis was performed for employment status, marital status, and comorbidity to evaluate the independent effects of gender on these dependent variables.” 27
EXAMPLES OF HYPOTHESIS AS WRITTEN IN PUBLISHED ARTICLES IN RELATION TO OTHER PARTS
- EXAMPLE 1. Background, hypotheses, and aims are provided
- “Pregnant women need skilled care during pregnancy and childbirth, but that skilled care is often delayed in some countries …( text omitted ). The focused antenatal care (FANC) model of WHO recommends that nurses provide information or counseling to all pregnant women …( text omitted ). Job aids are visual support materials that provide the right kind of information using graphics and words in a simple and yet effective manner. When nurses are not highly trained or have many work details to attend to, these job aids can serve as a content reminder for the nurses and can be used for educating their patients (Jennings, Yebadokpo, Affo, & Agbogbe, 2010) ( text omitted ). Importantly, additional evidence is needed to confirm how job aids can further improve the quality of ANC counseling by health workers in maternal care …( text omitted )” 28
- “ This has led us to hypothesize that the quality of ANC counseling would be better if supported by job aids. Consequently, a better quality of ANC counseling is expected to produce higher levels of awareness concerning the danger signs of pregnancy and a more favorable impression of the caring behavior of nurses .” 28
- “This study aimed to examine the differences in the responses of pregnant women to a job aid-supported intervention during ANC visit in terms of 1) their understanding of the danger signs of pregnancy and 2) their impression of the caring behaviors of nurses to pregnant women in rural Tanzania.” 28
- EXAMPLE 2. Background, hypotheses, and aims are provided
- “We conducted a two-arm randomized controlled trial (RCT) to evaluate and compare changes in salivary cortisol and oxytocin levels of first-time pregnant women between experimental and control groups. The women in the experimental group touched and held an infant for 30 min (experimental intervention protocol), whereas those in the control group watched a DVD movie of an infant (control intervention protocol). The primary outcome was salivary cortisol level and the secondary outcome was salivary oxytocin level.” 29
- “ We hypothesize that at 30 min after touching and holding an infant, the salivary cortisol level will significantly decrease and the salivary oxytocin level will increase in the experimental group compared with the control group .” 29
- EXAMPLE 3. Background, aim, and hypothesis are provided
- “In countries where the maternal mortality ratio remains high, antenatal education to increase Birth Preparedness and Complication Readiness (BPCR) is considered one of the top priorities [1]. BPCR includes birth plans during the antenatal period, such as the birthplace, birth attendant, transportation, health facility for complications, expenses, and birth materials, as well as family coordination to achieve such birth plans. In Tanzania, although increasing, only about half of all pregnant women attend an antenatal clinic more than four times [4]. Moreover, the information provided during antenatal care (ANC) is insufficient. In the resource-poor settings, antenatal group education is a potential approach because of the limited time for individual counseling at antenatal clinics.” 30
- “This study aimed to evaluate an antenatal group education program among pregnant women and their families with respect to birth-preparedness and maternal and infant outcomes in rural villages of Tanzania.” 30
- “ The study hypothesis was if Tanzanian pregnant women and their families received a family-oriented antenatal group education, they would (1) have a higher level of BPCR, (2) attend antenatal clinic four or more times, (3) give birth in a health facility, (4) have less complications of women at birth, and (5) have less complications and deaths of infants than those who did not receive the education .” 30
Research questions and hypotheses are crucial components to any type of research, whether quantitative or qualitative. These questions should be developed at the very beginning of the study. Excellent research questions lead to superior hypotheses, which, like a compass, set the direction of research, and can often determine the successful conduct of the study. Many research studies have floundered because the development of research questions and subsequent hypotheses was not given the thought and meticulous attention needed. The development of research questions and hypotheses is an iterative process based on extensive knowledge of the literature and insightful grasp of the knowledge gap. Focused, concise, and specific research questions provide a strong foundation for constructing hypotheses which serve as formal predictions about the research outcomes. Research questions and hypotheses are crucial elements of research that should not be overlooked. They should be carefully thought of and constructed when planning research. This avoids unethical studies and poor outcomes by defining well-founded objectives that determine the design, course, and outcome of the study.
Disclosure: The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Author Contributions:
- Conceptualization: Barroga E, Matanguihan GJ.
- Methodology: Barroga E, Matanguihan GJ.
- Writing - original draft: Barroga E, Matanguihan GJ.
- Writing - review & editing: Barroga E, Matanguihan GJ.

- Research Process
The Top 5 Qualities of Every Good Researcher
- 3 minute read
- 192.9K views
Table of Contents
What makes a good researcher? Is it some undefinable, innate genius, or is it something that we can practice and build upon? If it was just the former, then there would be far fewer innovations in the history of humankind than there have been. A careful look at researchers through the ages reveals that they all have certain attributes in common that have helped contribute to their success.
The characteristics of a good researcher:
1. curiosity.
They ask questions. An endless thirst for knowledge is what sets the best of the best apart from the others. Good researchers constantly strive to learn more, not just about their own field, but about other fields as well. The world around us is fascinating, be it the physics behind the way light refracts, or the anthropological constructions of our society. A good researcher keeps exploring the world and keeps searching for answers.
2. Analytical ability and foresight
They look for connections. Information is useless without interpretation. What drives research forward is finding meaning in our observations and data. Good researchers evaluate data from every angle and search for patterns. They explore cause and effect and untangle the tricky web that interconnects everyday phenomena. And then take it one step further to ask, ‘What is the bigger picture? How will the research develop in the future?’
3. Determination
They try, try, and try again. Research can be a frustrating experience. Experiments may not pan out how we expect them to. Even worse, sometimes experiments may run smoothly until they are 95% complete before failing. What sets an average researcher apart from a truly good one? The truly good researcher perseveres. They accept this disappointment, learn from the failure, reevaluate their experiment, and keep moving forward.
4. Collaboration
Teamwork makes the dream work. Contrary to the common perception of the solitary genius in their lab, research is an extremely collaborative process. There is simply too much to do for just one person to do it all. Moreover, research is becoming increasingly multidisciplinary. It is impossible for just one person to have expertise in all these fields. In general, research is conducted in teams , with each researcher having their individual roles and responsibilities. Being able to coordinate, communicate, and get along with team members is a major factor that can contribute to one’s success as a researcher.
5. Communication
They get their message across. Communication skills are an essential asset for every researcher. Not only do they have to communicate with their team members, but they also have to communicate with co-authors, journals, publishers, and funders. Whether it is writing a crisp and effective abstract, presenting at a conference, or writing a persuasive grant proposal to secure research funding, communication appears everywhere in a researcher’s life. The message in the old adage, ‘If a tree falls in the forest, but no one is around to hear it, does it make a sound?’ applies to research too. A discovery could be groundbreaking, but what is the use if the researcher can’t communicate this discovery to the rest of the world?
These are just a few of the skills required by researchers to make it to the top of their field. Other attributes like creativity and time management are also worth mentioning. Nevertheless, having one or more of these top five characteristics will make the research process smoother for you and increase the chances of positive results. Set yourself up for success by building up these skills, focusing on excellence, and asking for help when you need it. Elsevier Author Services is here to aid you at every step of the research journey. From translation services by experts in the field, to preparing your manuscript for publication, to helping you submit the best possible grant proposal, you can trust us to guide you in your journey to doing great research.

- Manuscript Preparation
What is the Background of a Study and How Should it be Written?

- Publication Process
Writing an Effective Cover Letter for Manuscript Resubmission
You may also like.

Descriptive Research Design and Its Myriad Uses

Five Common Mistakes to Avoid When Writing a Biomedical Research Paper

Making Technical Writing in Environmental Engineering Accessible

To Err is Not Human: The Dangers of AI-assisted Academic Writing

When Data Speak, Listen: Importance of Data Collection and Analysis Methods

Choosing the Right Research Methodology: A Guide for Researchers

Why is data validation important in research?

Writing a good review article
Input your search keywords and press Enter.

What Constitutes a Good Research?
The Declining Art of Good Research
We seem to be compromising our commitment to good research in favor of publishable research, and there are a combination of trends that are accountable for this.
The first is the continued pressure of “publish or perish” for young academics seeking to move forward on the track for fewer and fewer tenured positions (or increasingly draconian renewable contracts).
Secondly, the open access model of research publication has created a booming population of academic journals with pages to fill and new researchers willing to pay article publication fees (APFs).
Thirdly, budget-strapped institutions have been aggressively targeting doctoral research candidates and the higher fees they bring to the table.
When these three trends are combined, the resulting onslaught of quantity over quality leads us to question what “good” research looks like anymore.
Is it the institution from which the research originated, or the debatable rank of the journal that published it?
Good Research as a Methodological Question
When looking to learn how to recognize what “good” research looks like, it makes sense to start at the beginning with the basic scope of the project:
- Does the research have a solid hypothesis?
- Is there evidence of a comprehensive literature review from reputable sources that clearly defines a target area for valuable research?
- Is the research team allocating sufficient time/resources to do the job properly, or were compromises made in order to accommodate the available funding?
- Is there evidence of a willingness to refine the hypothesis and research strategy if needed?
- Are the expectations of the implications of the research realistic?
Characteristics of a Good Research
For conducting a systematic research, it is important understand the characteristics of a good research.
- Its relevance to existing research conducted by other researchers.
- A good research is doable and replicable in future.
- It must be based on a logical rationale and tied to theory.
- It must generate new questions or hypotheses for incremental work in future.
- It must directly or indirectly address some real world problem.
- It must clearly state the variables of the experiment.
- It must conclude with valid and verifiable findings.
Good Research as an Ethical Question
The question as to whether or not the research is worth conducting at all could generate an extended and heated debate. Researchers are expected to publish, and research budgets are there to be spent.
We can hope that there was some degree of discussion and oversight before the research project was given the green light by a Principal Investigator or Research Supervisor, but those decisions are often made in a context of simple obligation rather than perceived need.
Consider the example of a less than proactive doctoral student with limited time and resources to complete a dissertation topic. A suggestion is made by the departmental Research Supervisor to pick a dissertation from a decade ago and simply repeat it. The suggestion meets the need for expediency and simplicity, but raises as many questions as it answers:
- What is the validity of the study – just because it can be repeated, should it?
- What was the contribution of the original study to the general body of knowledge? Will this additional data be an improvement?
- Given the lack of interest among academic journals in replicated studies, is the suggestion denying the student the opportunity to get published?
- Is directing a student to replication in the interests of expediency meeting a broader academic goal of graduating proficient researchers?
The Building Blocks of “Good” Research
There is no shortage of reputable, peer-reviewed journals that publish first-rate research material for new researchers to model.
That doesn’t mean you should copy the research topic or the methodology, but it wouldn’t hurt to examine the protocol in detail and make note of the specific decisions made and criteria put in place when that protocol was developed and implemented.
The challenge lies in sticking to those tried-and-true methodologies when your research data doesn’t prove to be as rich and fruitful as you had hoped.
Have you ever been stuck while in the middle of conducting a research? How did you cope with that? Let us know your approach while conducting a good research in the comments section below!
You can also visit our Q&A forum for frequently asked questions related to different aspects of research writing and publishing answered by our team that comprises subject-matter experts, eminent researchers, and publication experts.
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles
![qualities of good research work What is Academic Integrity and How to Uphold it [FREE CHECKLIST]](https://www.enago.com/academy/wp-content/uploads/2024/05/FeatureImages-59-210x136.png)
Ensuring Academic Integrity and Transparency in Academic Research: A comprehensive checklist for researchers
Academic integrity is the foundation upon which the credibility and value of scientific findings are…

- AI in Academia
AI vs. AI: How to detect image manipulation and avoid academic misconduct
The scientific community is facing a new frontier of controversy as artificial intelligence (AI) is…

- Diversity and Inclusion
Need for Diversifying Academic Curricula: Embracing missing voices and marginalized perspectives
In classrooms worldwide, a single narrative often dominates, leaving many students feeling lost. These stories,…

- Career Corner
- Trending Now
Recognizing the signs: A guide to overcoming academic burnout
As the sun set over the campus, casting long shadows through the library windows, Alex…

Reassessing the Lab Environment to Create an Equitable and Inclusive Space
The pursuit of scientific discovery has long been fueled by diverse minds and perspectives. Yet…
7 Steps of Writing an Excellent Academic Book Chapter
When Your Thesis Advisor Asks You to Quit
Virtual Defense: Top 5 Online Thesis Defense Tips

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

As a researcher, what do you consider most when choosing an image manipulation detector?

Top 9 Qualities of Good Academic Research
Academic research serves various purposes. These research studies appear in multiple shapes and forms. Usually, research can be conducted through qualitative, quantitative, and mixed methods depending on the questions asked. Moreover, research data can also be obtained in various ways as well.
Academic research can be useful in many ways, from student and subject analysis to help with essay writing to academic curriculum.
But what exactly makes academic research insightful? What is a quality research? What Is Good Research and Why Is It Important?
High quality academic research provides robust, ethical evidence and stands up to scrutiny for making an informed decision.
People purchase research papers for their own educational purpose as well.
Academic research includes collecting, analysing, and interpreting information to answer questions and solve problems using these data.
But good research is very important to ensure that the data collected are qualitative.
You must be wondering what exactly makes good research. Well, it is not an undefinable, innate genius or something we need intense practice for.
Good academic researchers possess these nine qualities, making their research stand out and definite.
Characteristics of Quality Research
Before proceeding towards the qualities of good academic research, let’s view the characteristics:
- Quality research is based on the work of many individuals.
- Research data can be replicated and is doable.
- These data are applicable to others’ usage and settings.
- Each research is based on some logical theory in a way that each has the potential to suggest directions for the future research.
- Quality research intends to generate new questions or is cyclical in nature.
- They address some real problems in the world directly or indirectly.
- Each of these research serves as a medium to improve the educational quality.
So, before proceeding with the final output of the research, you might want to check out these characteristics if it’s available in your study or not!
Individuals with different personalities and from diverse backgrounds pursue academic research. All of them are eager to develop the qualities of a good researcher.
We all can agree that being a researcher is a challenging task as it requires a combination of skills and attributes as well as dedication, time, lots of depth research, and hard work.
Below we will be discussing the nine best effective research strategies every researcher should follow!
1. Curiosity for the Subject Matter
Above all the qualities, we have listed curiosity to be one of the most important qualities of a researcher.
A curious mind can look at things from various perspectives, which contributes to better research.
A good research study is observant and outlook around the world to come up with new ideas and possibilities.
Curious researchers tend to ask many questions and look for the answers that make their research more variable. They possess the ability to view things in the bigger picture while also being curious about the small details.
Good quality research requires curious researchers who are ready to go beyond the regular questions and answers.
2. Open Mindedness
There’s a very famous quote by Albert Einstein that states that ‘the measure of intelligence is the ability to change in mind’.
One very important characteristic of good research is open-mindedness because research has to do with finding new fats, and requires the researcher to alter previously valid facts.
If the researcher is someone who is not able to give up on their beliefs, customs, or knowledge, gathering the world’s information can be difficult.
Therefore, to have good academic research, you need to ensure that researchers understand that nothing is static and changes over time.
3. Critical Thinking
Academic research requires you to think critically about the provided information, gather the required one and read about new developments in the field.
Hence, critical thinking becomes an essential quality of academic research. Instead of accepting the given fact, researchers need to have the ability to analyse and evaluate the validity.
What is the reliability of courses, the alternative explanation to the given research, and the results needed to observe?
It seemingly builds a connection between unrelated concepts and takes research on the wider aspect.
4. Creativity
While curiosity and critical thinking might work to an extent to come up with good academic research, it is not everything. Creativity is a great skill to possess. It gives you the ability to think creatively when solving a problem.
It’s important that you’re able to nurture the ability to think outside the box and come up with unconventional solutions to the challenges you face during your research process.
This ability helps you come up with ground-breaking research studies. This not only makes your academic research precise but also addresses the issues others might have been missing out on!
5. Objectivity
We are going turn-by-turn on what makes quality academic research! So, now’s the room for objectivity! What is the reason behind your research? What do you determine to fully fill – the questions, the data through your research? The nurturing notions are determined in the research process.
It is very important to have your objective defined to build quality research.
Researchers must be able to keep their preferences and biases aside and focus on the sole objective of what this research is aimed to deliver.
6. Collaborative Attitude
To come up with quality academic research data, it’s important that you work among researchers who are doing the same job.
When you shift towards collaborative research, you’ll connect and work with peers who are innovative in their research as well.
You’ll not only gain ideas and insights but also be able to lead to breakthroughs and boost your research reputation. This is a great way to open the door for your work to reach potential benefits in a wider audience.
7. Communication Skills
Good quality research also factors in the ability of the researcher to communicate the findings clearly and effectively.
Communication is yet another important quality of academic research. It is a key contributor to success.
Communication skill is applicable when discussing plans, presenting conferences, seeking funding for your work, and in many other ways. As a researcher, you must explain your theory to a specialist and a non-specialist and ensure they understand what you mean.
8. Attention to detail
There are various reasons why an organisation or individual is performing academic research. Therefore, to bring quality research, you must be meticulous in your work, i.e., paying attention to every detail.
It can start right from the design of an experiment to its analysis, to data collection, to further writing, and everything in between.
Making a habit of providing attention to detail will help you keep your research accurate, testable, and reliable.
9. Time Management
What if it takes a year or two to prepare quality academic research when its deadline is in two months?
It’s important to understand that quality research comprises the needs of the organisation, the individual, what it has to offer, the story, and all other aspects.
Successful researchers can organise, prioritise, and optimise their time by keeping up with their responsibilities and completing compelling research on time.
Wrapping Up
This sums up the list of the nine best qualities of good academic research that can help you understand the need and what you must look for in a researcher.
Siksha ‘O’ Anusandhan ─ a melting pot of quality academics and research


- After School
- International
- Scholarships
- Photo Bytes
- Expert Opinion
- Professional Development
- Edutainment
- Parents Resources
- Students Resources
- Teachers Resources
- Eduleader Focus
- Schools of Eminence
- Privacy Policy
10 Qualities of a Good Researcher: Quest for Excellence

- Post author By admin
- November 9, 2023
Discover the essential 10 qualities of a good researcher! Uncover the traits that drive success in the world of research. Learn what it takes to excel in the quest for knowledge and innovation
Suppose a vast landscape of knowledge, uncharted and waiting to be discovered. Research is the compass guiding us through this territory, and at the helm of every great exploration stands a good researcher.
But what sets them apart? It’s not just knowledge; it’s a unique set of qualities that propel them towards understanding.
In this journey, we’ll uncover the very essence of a good researcher. We’ll delve into the top 10 qualities that define them. From unquenchable curiosity to unwavering perseverance, these qualities are the secret sauce behind their success in academia and exploration.
Whether you’re already treading the path of research or gearing up for the adventure, understanding and embracing these qualities will transform you into a research dynamo. So, let’s embark on this quest to unravel what makes a good researcher tick.
Table of Contents
10 Qualities of a Good Researcher
Check out the 10 qualities of a good researcher:-
1. Inquisitiveness: The Craving for Knowledge
Think of a good researcher as that friend who’s always full of questions. They’re the eternal curious cats of the academic world, forever wondering, forever seeking, and forever hungry for knowledge. It’s like they have a built-in “Why?” button that never switches off.
A good researcher’s inquisitiveness is like the spark that lights up a dark room. It’s what pushes them to ask the questions no one else has thought of and venture into uncharted territories. They’re the ultimate seekers, the champions of “What if?” and “Why not?” It’s this insatiable curiosity that keeps their research fresh, exciting, and always on the hunt for more knowledge.
2. Patience: Sifting Through Data
Imagine a good researcher as a treasure hunter in the vast desert of data. Research can sometimes feel like slogging through quicksand – slow, meticulous, and demanding. But here’s the thing: good researchers have an incredible treasure map, and it’s called “patience.”
They understand that research isn’t a race; it’s a journey. It’s about sifting through tons of data, the way a prospector pans for gold. Every grain of information matters, and they’re willing to invest the time needed to collect, analyze, and interpret data accurately.
This patience isn’t about twiddling thumbs; it’s about meticulously building the puzzle of knowledge, piece by piece. They understand that no detail is too small to be overlooked, and in the end, it’s these small pieces that complete the big picture.
Good researchers don’t rush; they savor the journey, knowing that the best discoveries often lie in the details. They are the patient architects of knowledge, and it’s their patience that ensures that no gem of information goes undiscovered.
3. Attention to Detail: Devil in the Details
In research, it’s the little things that matter most. A good researcher understands this like no other. They’re the ones who spot the faintest footprints in the sand and the almost invisible fingerprints on the glass because they know that in research, the devil truly lies in the details.
For them, every piece of information is a precious puzzle piece. They’re like puzzle enthusiasts, and they’re determined to find and fit every piece perfectly. Because, in their world, even the tiniest detail holds the potential to make or break a study.
In a realm where precision reigns supreme, good researchers are the vigilant guardians of information. They’re the ones who make sure no stone is left unturned, no detail is too minor, and it’s this unwavering attention to detail that transforms their research into something truly extraordinary.
4. Critical Thinking: Questioning the Norm
Let’s picture a good researcher as the ultimate rebel of the research realm. They don’t just follow the herd; they’re the ones breaking the mold, challenging established theories, and stirring up the intellectual pot. Their secret weapon? It’s called critical thinking.
Critical thinking is like their sidekick, the Watson to their Holmes. It’s their power to look at information with a discerning eye, to cut through the noise, and make informed judgments. Good researchers? They’ve got critical thinking in their toolkit, and they’re not afraid to use it.
They’re not content with nodding along to the norm. No, they’re the ones who dare to ask, “Why?” and “What if?” They’re the Sherlock Holmes of academia, seeking the hidden clues that others might overlook. They’re the explorers who venture beyond the boundaries of convention.
For them, curiosity isn’t just a casual interest; it’s a full-blown investigation. They’re the skeptics, the truth-seekers, and the challengers of the status quo. Because they know that the road to enlightenment is paved with skepticism and paved with profound insights.
In a world where knowledge is the ultimate treasure, good researchers are the rebels with a cause. They’re the ones who question, challenge, and redefine the norm, making the pursuit of knowledge a thrilling adventure.
5. Organization: Chaos to Clarity
Let’s paint a mental picture of a good researcher as the master organizer of the research universe. Picture this: researchers often find themselves wading through mountains of data, like explorers in an information jungle.
But what sets good researchers apart is their exceptional skill in turning chaos into clarity through one magic word – organization.
These researchers are like the conductors of a grand symphony, where data plays the melodious tunes. They understand that without a meticulously organized score, the music may fall into chaos.
This is why they keep their work structured and well-organized. It’s like having a treasure map to navigate through the data wilderness.
For them, organization isn’t just a preference; it’s a necessity. It ensures that every piece of data, every note in the symphony, can be easily accessed and referenced when needed. It’s the librarian’s skill of categorizing, labeling, and arranging knowledge in a way that makes sense.
In a world where data can be overwhelming, good researchers are the navigators who chart the course from chaos to clarity. They bring order to the information realm, making sure that every piece of data finds its place in the grand mosaic of knowledge.
6. Effective Communication: Sharing Insights
Imagine a good researcher as not just a discoverer of hidden treasures but also a gifted storyteller. Research isn’t merely about uncovering the unknown; it’s about sharing those discoveries with the world. Good researchers possess a unique superpower – effective communication.
They are the bards of academia, able to weave intricate tales of data and insight. It’s not enough to gather knowledge; they understand the importance of conveying it to their peers and the wider community. They’re like skilled translators, turning complex data into understandable narratives.
For them, research isn’t a solitary endeavor but a communal one. They can articulate their findings, transforming raw data into gems of wisdom. They speak not just to fellow researchers but to anyone who seeks understanding.
In a world where information is abundant but understanding can be scarce, good researchers are the bridges that connect data to meaning. They’re the ones who bring clarity to complexity, ensuring that their discoveries benefit not just themselves but all who thirst for knowledge.
7. Ethical Integrity: The Moral Compass
Picture a good researcher as a moral compass, always pointing in the direction of what’s right. In their world, there’s no room for ethical shortcuts; they’re the guardians of integrity, setting the highest standards.
Ethical conduct is their unwavering principle, not a mere guideline. These researchers tread the path of knowledge with profound respect for all beings, be it humans, animals, or the environment.
They understand that research isn’t just about facts and figures; it’s about the impact on the world.
They are the ethical warriors who ensure that every discovery is made with the utmost respect for boundaries. They’re the ones who hold the torch of integrity, even when the road gets dark and uncertain.
In a world where ethical dilemmas can cloud the way, good researchers are the beacons of moral clarity. They remind us that the pursuit of knowledge should always be illuminated by the light of ethics, leaving a positive and lasting legacy.
8. Adaptability: Rolling with Research’s Twists
Now, picture a good researcher as the ultimate research ninja. They know that in the world of research, surprises are the name of the game. What makes them exceptional? Their uncanny ability to adapt.
In their world, every research project is like a thrilling rollercoaster ride. They’re fully aware that not everything will go as planned.
But instead of dreading the unexpected, they welcome it with open arms. It’s not about dodging hurdles; it’s about using them as springboards for new discoveries.
Adaptability is their secret weapon. They don’t panic when faced with unexpected twists and turns; they thrive on them. They’re the daredevils of research, excited by the idea that every surprise brings a chance for a breakthrough.
They understand that research isn’t a linear path; it’s an expedition full of surprises. Good researchers approach each twist and turn as a new opportunity to learn, grow, and uncover the unknown.
9. Perseverance: Never Giving Up
Now, picture a good researcher as the indomitable hero of the research saga. The journey to groundbreaking discoveries is no walk in the park; it’s an epic adventure filled with obstacles and trials. What makes a good researcher extraordinary? Their unshakable perseverance.
In their world, setbacks are not dead ends; they are the very soil in which success takes root. They grasp that the path to pioneering research is not a sprint but a demanding marathon.
When confronted with challenges, they don’t retreat; they roll up their sleeves and forge ahead with unwavering resolve.
In their universe, perseverance is the North Star guiding them through the darkest nights of research. It’s the fire that keeps them warm when faced with the chilling winds of doubt.
They understand that every stumble is a lesson, every hurdle is an opportunity, and every fall is a chance to rise even higher.
In a realm where remarkable discoveries are born from sheer determination, good researchers are the embodiment of perseverance.
They don’t just weather the storms of research; they harness them to soar to new heights of understanding and innovation.
10. Problem-Solving Skills: Creative and Determined Issue Resolution
Think of a good researcher as a maverick in the world of problem-solving. They possess an innate ability to tackle research-related issues with a unique blend of creativity and unwavering determination. They’re not just issue-spotters; they’re issue-solvers.
In their realm, challenges aren’t roadblocks; they’re opportunities for innovation. Whether it’s deciphering a complex data conundrum, navigating unexpected research detours, or confronting formidable roadblocks, they approach each problem with a dash of unconventional thinking.
Their toolkit isn’t limited to traditional solutions; it includes a healthy dose of creativity. They know that sometimes the most extraordinary answers emerge from unconventional thinking.
When faced with adversity, they don’t back down; they dive headfirst into the challenge, armed with resourcefulness and an unyielding spirit.
In the world of research, where every obstacle conceals a chance for a groundbreaking discovery, these good researchers are the daring explorers.
They turn problems into springboards, propelling the journey of knowledge and unveiling new insights along the way.
What is the qualities of good researcher?
Exceptional researchers are a unique breed, possessing a blend of innate traits and developed skills that set them apart in the world of discovery. Here are the qualities that define an outstanding researcher:
Inherent Curiosity
Exceptional researchers are born with an insatiable curiosity about the world. They perpetually question, driven by an unrelenting thirst for knowledge. This curiosity fuels their exploration of new ideas and their deep dives into complex problems.
Independence and Initiative
They are fiercely independent, unafraid to challenge conventions and think outside the box. This independence empowers them to conduct research with rigor and objectivity, free from preconceived notions.
Critical Thinking
Exceptional researchers are expert critical thinkers. They scrutinize information, identifying biases and assumptions. This skill enables them to draw well-founded conclusions from their research, undeterred by misinformation.
Effective Communication
They are adept communicators, capable of presenting their findings clearly and concisely. Their ability to convey complex ideas is vital for sharing their discoveries with the broader scientific community.
Collaboration Prowess
Collaboration is second nature to them. Exceptional researchers seamlessly collaborate with others to achieve common research objectives. Their skill in teamwork is essential for handling large-scale research projects effectively.
Problem-Solving Expertise
Problem-solving is in their DNA. They spot issues, conceive and test solutions, and rigorously evaluate their effectiveness. This skill is the backbone of conducting thorough research.
In addition to these qualities, exceptional researchers boast an in-depth understanding of their chosen field. They stay abreast of the latest research findings and expertly apply this knowledge to their own work.
Furthermore, they adhere to ethical guidelines that govern research, conducting their inquiries responsibly and ethically.
Armed with these remarkable qualities, exceptional researchers not only expand our comprehension of the world but also contribute to solving critical problems and enhancing the quality of life for all.
What are the 7 major characteristics of research?
Research is a multifaceted endeavor, marked by seven pivotal characteristics that define its essence:
1, Empirical Foundation
At its core, research is grounded in empiricism. It shuns opinions, personal beliefs, and conjecture. Instead, it thrives on data and evidence drawn from real-world observations and experiments, bolstering its conclusions with solid support.
2. Systematic Approach
Research unfolds systematically, adhering to a meticulously designed process. It commences with defining the research question, identifying research methods, collecting data, rigorously analyzing it, and ultimately deriving well-founded conclusions. This systematic journey ensures both rigor and objectivity.
3. Logical Underpinning
Logic forms the backbone of research. It forges conclusions that harmonize seamlessly with the laws of logic, yielding findings that are not only profound but also reliable.
4. Cyclical Nature
Research possesses a cyclical essence. It commences with a question or problem, each exploration invariably begetting new inquiries. This continuous cycle propels researchers toward a deeper understanding of the ever-evolving world.
5. Analytical Rigor
Research demands meticulous data analysis. Researchers employ diverse analytical techniques to uncover patterns, trends, and relationships within the data. This scrutiny unveils the latent significance of the data, facilitating the derivation of meaningful conclusions.
6. Objective Stance
An unwavering objectivity characterizes research. Researchers diligently strive to avoid bias and partiality, ensuring that their personal beliefs or opinions exert no undue influence on their findings.
7. Replicability Standard
Research adheres to a replicability standard. Other researchers should be capable of replicating the study and achieving congruent results. This commitment to replicability bolsters the reliability and validity of research findings.
Incorporating these seven key characteristics, research emerges as a powerful tool for the exploration of the unknown, the validation of hypotheses, and the continuous advancement of knowledge.
What are the 3 important qualities of a good research?
When we delve into the world of outstanding research, we uncover the pillars that set it apart. Imagine these as the main characters in a compelling story:
1. Credibility
This is the unwavering foundation. Exceptional research is built on solid evidence and meticulous reasoning. It follows a rigorous and objective path, supported by thorough data and in-depth analysis.
2. Relevance
Consider this the heart of the matter. Exceptional research doesn’t shy away from addressing pressing questions and challenges.
It aims to contribute significantly to our understanding of the world and has the potential to solve crucial problems.
3. Originality
Think of this as the trailblazer, the innovator. Exceptional research ventures into uncharted territories, offering fresh and unique perspectives.
It doesn’t retrace well-worn paths; instead, it opens new doors to insights that haven’t been explored before.
These are the three pillars of remarkable research, igniting our quest to comprehend our world more deeply, confront significant challenges, and provide solutions that truly enhance our lives and the lives of those around us.
What are the 4 characteristics of a good research?
When we delve into the world of research, we discover the four cornerstones that define what makes research truly exceptional:
Imagine research as a sturdy ship navigating the vast sea of knowledge. What keeps it afloat? Credibility – the anchor of solid evidence and logical reasoning.
It’s about following a rigorous and objective methodology, with findings firmly supported by a wealth of data and meticulous analysis.
Good research is like a compass pointing to the critical questions and challenges that pique the curiosity of the research community and society.
It’s not just an exploration; it’s a journey with a purpose – to deepen our understanding of the world and unravel solutions to the most pressing problems.
Think of research as an explorer venturing into uncharted territory. It doesn’t follow the trodden paths; it forges its own.
Good research doesn’t echo what’s been said before; it blazes new trails, offering fresh insights and unique perspectives.
Effective research is a lighthouse, guiding others through the maze of complexity. Its findings are not buried in jargon or obscured by ambiguity.
They are presented with clarity and conciseness, ensuring that everyone can navigate the discoveries with ease.
These attributes, like the North Star, lead us in the pursuit of knowledge and understanding, casting light on the uncharted waters of research.
In the grand tapestry of knowledge, good researchers stand as the weavers of profound discovery. They embody a unique blend of qualities, shaping the course of understanding and change.
From the inquisitiveness that fuels their journey to the unwavering patience that carries them through the most intricate of labyrinths, these qualities are the compass, the guiding light.
The unquenchable curiosity of a good researcher keeps the embers of exploration burning bright. Patience, the steadfast companion, ensures that no detail remains in obscurity.
Their critical thinking propels them beyond the boundaries of convention, unraveling new layers of understanding.
In the chaos of data, they find serenity through organization, and in the midst of complexity, they wield the sword of effective communication.
Ethical integrity acts as their moral compass, while adaptability embraces the unpredictability of research’s twists.
But it’s perseverance, the indomitable spirit, that carries them through the darkest hours. They recognize that the path to groundbreaking research is often fraught with obstacles, but those obstacles serve as stepping stones to success.
These ten qualities, woven into the very fabric of their being, make good researchers the architects of transformation.
With every study they undertake, they draw closer to unraveling the mysteries of our world, bridging gaps in knowledge, and contributing to the betterment of humanity.
As we celebrate these qualities, we acknowledge the significance of their work. Through their endeavors, we glimpse the limitless potential of human exploration, and we are inspired to never cease questioning, exploring, and, above all, learning.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can anyone become a good researcher.
Yes, with dedication and a willingness to develop these qualities, anyone can become a good researcher.
Why is adaptability crucial for a researcher?
Research is unpredictable, and adaptability allows researchers to navigate unexpected challenges effectively.
What role does ethics play in research?
Ethical integrity is vital in research to ensure the well-being of participants and the integrity of the study.
How do researchers maintain their inquisitiveness?
Researchers stay curious by continually seeking new questions and exploring uncharted territories in their field.
Is critical thinking a natural talent, or can it be developed?
Critical thinking can be developed through practice and a commitment to questioning and evaluating information.
- australia (2)
- duolingo (13)
- Education (275)
- General (75)
- How To (16)
- IELTS (127)
- Latest Updates (162)
- Malta Visa (6)
- Permanent residency (1)
- Programming (31)
- Scholarship (1)
- Sponsored (4)
- Study Abroad (187)
- Technology (12)
- work permit (8)
Recent Posts
What is quality research? A guide to identifying the key features and achieving success

Every researcher worth their salt strives for quality. But in research, what does quality mean?
Simply put, quality research is thorough, accurate, original and relevant. And to achieve this, you need to follow specific standards. You need to make sure your findings are reliable and valid. And when you know they're quality assured, you can share them with absolute confidence.
You’ll be able to draw accurate conclusions from your investigations and contribute to the wider body of knowledge in your field.
Importance of quality research
Quality research helps us better understand complex problems. It enables us to make decisions based on facts and evidence. And it empowers us to solve real-world issues. Without quality research, we can't advance knowledge or identify trends and patterns. We also can’t develop new theories and approaches to solving problems.
With rigorous and transparent research methods, you’ll produce reliable findings that other researchers can replicate. This leads to the development of new theories and interventions. On the other hand, low-quality research can hinder progress by producing unreliable findings that can’t be replicated, wasting resources and impeding advancements in the field.
In all cases, quality control is critical. It ensures that decisions are based on evidence rather than gut feeling or bias.

Standards for quality research
Over the years, researchers, scientists and authors have come to a consensus about the standards used to check the quality of research. Determined through empirical observation, theoretical underpinnings and philosophy of science, these include:
1. Having a well-defined research topic and a clear hypothesis
This is essential to verify that the research is focused and the results are relevant and meaningful. The research topic should be well-scoped and the hypothesis should be clearly stated and falsifiable .
For example, in a quantitative study about the effects of social media on behavior, a well-defined research topic could be, "Does the use of TikTok reduce attention span in American adolescents?"
This is good because:
- The research topic focuses on a particular platform of social media (TikTok). And it also focuses on a specific group of people (American adolescents).
- The research question is clear and straightforward, making it easier to design the study and collect relevant data.
- You can test the hypothesis and a research team can evaluate it easily. This can be done through the use of various research methods, such as survey research , experiments or observational studies.
- The hypothesis is focused on a specific outcome (the attention span). Then, this can be measured and compared to control groups or previous research studies.
2. Ensuring transparency
Transparency is crucial when conducting research. You need to be upfront about the methods you used, such as:
- Describing how you recruited the participants.
- How you communicated with them.
- How they were incentivized.
You also need to explain how you analyzed the data, so other researchers can replicate your results if necessary. re-registering your study is a great way to be as transparent in your research as possible. This involves publicly documenting your study design, methods and analysis plan before conducting the research. This reduces the risk of selective reporting and increases the credibility of your findings.
3. Using appropriate research methods
Depending on the topic, some research methods are better suited than others for collecting data. To use our TikTok example, a quantitative research approach, such as a behavioral test that measures the participants' ability to focus on tasks, might be the most appropriate.
On the other hand, for topics that require a more in-depth understanding of individuals' experiences or perspectives, a qualitative research approach, such as interviews or focus groups, might be more suitable. These methods can provide rich and detailed information that you can’t capture through quantitative data alone.
4. Assessing limitations and the possible impact of systematic bias
When you present your research, it’s important to consider how the limitations of your study could affect the result. This could be systematic bias in the sampling procedure or data analysis, for instance. Let’s say you only study a small sample of participants from one school district. This would limit the generalizability and content validity of your findings.
5. Conducting accurate reporting
This is an essential aspect of any research project. You need to be able to clearly communicate the findings and implications of your study . Also, provide citations for any claims made in your report. When you present your work, it’s vital that you describe the variables involved in your study accurately and how you measured them.
Curious to learn more? Read our Data Quality eBook .
How to identify credible research findings
To determine whether a published study is trustworthy, consider the following:
- Peer review: If a study has been peer-reviewed by recognized experts, rest assured that it’s a reliable source of information. Peer review means that other scholars have read and verified the study before publication.
- Researcher's qualifications: If they're an expert in the field, that’s a good sign that you can trust their findings. However, if they aren't, it doesn’t necessarily mean that the study's information is unreliable. It simply means that you should be extra cautious about accepting its conclusions as fact.
- Study design: The design of a study can make or break its reliability. Consider factors like sample size and methodology.
- Funding source: Studies funded by organizations with a vested interest in a particular outcome may be less credible than those funded by independent sources.
- Statistical significance: You've heard the phrase "numbers don't lie," right? That's what statistical significance is all about. It refers to the likelihood that the results of a study occurred by chance. Results that are statistically significant are more credible.
Achieve quality research with Prolific
Want to ensure your research is high-quality? Prolific can help.
Our platform gives you access to a carefully vetted pool of participants. We make sure they're attentive, honest, and ready to provide rich and detailed answers where needed. This helps to ensure that the data you collect through Prolific is of the highest quality.
With Prolific, you can streamline your research process and feel confident in the results you receive. Our minimum pay threshold and commitment to fair compensation motivate participants to provide valuable responses and give their best effort. This ensures the quality of your research and helps you get the results you need. Sign up as a researcher today to get started!
You might also like

High-quality human data to deliver world-leading research and AIs.

Follow us on
All Rights Reserved Prolific 2024
Research: Definition, Characteristics, Goals, Approaches

Research is an original and systematic investigation undertaken to increase existing knowledge and understanding of the unknown to establish facts and principles.
Let’s understand research:
What is Research?
Research is a voyage of discovery of new knowledge. It comprises creating ideas and generating new knowledge that leads to new and improved insights and the development of new materials, devices, products, and processes.
It should have the potential to produce sufficiently relevant results to increase and synthesize existing knowledge or correct and integrate previous knowledge.
Good reflective research produces theories and hypotheses and benefits any intellectual attempt to analyze facts and phenomena.
Where did the word Research Come from?
The word ‘research’ perhaps originates from the old French word “recerchier” which meant to ‘ search again.’ It implicitly assumes that the earlier search was not exhaustive and complete; hence, a repeated search is called for.
In practice, ‘research’ refers to a scientific process of generating an unexplored horizon of knowledge, aiming at discovering or establishing facts, solving a problem, and reaching a decision. Keeping the above points in view, we arrive at the following definition of research:
Research Definition
Research is a scientific approach to answering a research question, solving a research problem, or generating new knowledge through a systematic and orderly collection, organization, and analysis of data to make research findings useful in decision-making.
When do we call research scientific? Any research endeavor is said to be scientific if
- It is based on empirical and measurable evidence subject to specific principles of reasoning;
- It consists of systematic observations, measurement, and experimentation;
- It relies on the application of scientific methods and harnessing of curiosity;
- It provides scientific information and theories for the explanation of nature;
- It makes practical applications possible, and
- It ensures adequate analysis of data employing rigorous statistical techniques.
The chief characteristic that distinguishes the scientific method from other methods of acquiring knowledge is that scientists seek to let reality speak for itself, supporting a theory when a theory’s predictions are confirmed and challenging a theory when its predictions prove false.
Scientific research has multidimensional functions, characteristics, and objectives.
Keeping these issues in view, we assert that research in any field or discipline:
- Attempts to solve a research problem;
- Involves gathering new data from primary or first-hand sources or using existing data for a new purpose;
- is based upon observable experiences or empirical evidence;
- Demands accurate observation and description;
- Employs carefully designed procedures and rigorous analysis;
- attempts to find an objective, unbiased solution to the problem and takes great pains to validate the methods employed;
- is a deliberate and unhurried activity that is directional but often refines the problem or questions as the research progresses.
Characteristics of Research
Keeping this in mind that research in any field of inquiry is undertaken to provide information to support decision-making in its respective area, we summarize some desirable characteristics of research:
- The research should focus on priority problems.
- The research should be systematic. It emphasizes that a researcher should employ a structured procedure.
- The research should be logical. Without manipulating ideas logically, the scientific researcher cannot make much progress in any investigation.
- The research should be reductive. This means that one researcher’s findings should be made available to other researchers to prevent them from repeating the same research.
- The research should be replicable. This asserts that there should be scope to confirm previous research findings in a new environment and different settings with a new group of subjects or at a different point in time.
- The research should be generative. This is one of the valuable characteristics of research because answering one question leads to generating many other new questions.
- The research should be action-oriented. In other words, it should be aimed at solving to implement its findings.
- The research should follow an integrated multidisciplinary approach, i.e., research approaches from more than one discipline are needed.
- The research should be participatory, involving all parties concerned (from policymakers down to community members) at all stages of the study.
- The research must be relatively simple, timely, and time-bound, employing a comparatively simple design.
- The research must be as much cost-effective as possible.
- The research results should be presented in formats most useful for administrators, decision-makers, business managers, or community members.
3 Basic Operations of Research
Scientific research in any field of inquiry involves three basic operations:
- Data collection;
- Data analysis;
- Report writing .

- Data collection refers to observing, measuring, and recording data or information.
- Data analysis, on the other hand, refers to arranging and organizing the collected data so that we may be able to find out what their significance is and generalize about them.
- Report writing is the ultimate step of the study . Its purpose is to convey the information contained in it to the readers or audience.
If you note down, for example, the reading habit of newspapers of a group of residents in a community, that would be your data collection.
If you then divide these residents into three categories, ‘regular,’ ‘occasional,’ and ‘never,’ you have performed a simple data analysis. Your findings may now be presented in a report form.
A reader of your report knows what percentage of the community people never read any newspaper and so on.
Here are some examples that demonstrate what research is:
- A farmer is planting two varieties of jute side by side to compare yields;
- A sociologist examines the causes and consequences of divorce;
- An economist is looking at the interdependence of inflation and foreign direct investment;
- A physician is experimenting with the effects of multiple uses of disposable insulin syringes in a hospital;
- A business enterprise is examining the effects of advertisement of their products on the volume of sales;
- An economist is doing a cost-benefit analysis of reducing the sales tax on essential commodities;
- The Bangladesh Bank is closely observing and monitoring the performance of nationalized and private banks;
- Based on some prior information, Bank Management plans to open new counters for female customers.
- Supermarket Management is assessing the satisfaction level of the customers with their products.
The above examples are all researching whether the instrument is an electronic microscope, hospital records, a microcomputer, a questionnaire, or a checklist.
Research Motivation – What makes one motivated to do research?
A person may be motivated to undertake research activities because
- He might have genuine interest and curiosity in the existing body of knowledge and understanding of the problem;
- He is looking for answers to questions that have remained unanswered so far and trying to unfold the truth;
- The existing tools and techniques are accessible to him, and others may need modification and change to suit the current needs.
One might research ensuring.
- Better livelihood;
- Better career development;
- Higher position, prestige, and dignity in society;
- Academic achievement leading to higher degrees;
- Self-gratification.
At the individual level, the results of the research are used by many:
- A villager is drinking water from an arsenic-free tube well;
- A rural woman is giving more green vegetables to her child than before;
- A cigarette smoker is actively considering quitting smoking;
- An old man is jogging for cardiovascular fitness;
- A sociologist is using newly suggested tools and techniques in poverty measurement.
The above activities are all outcomes of the research.
All involved in the above processes will benefit from the research results. There is hardly any action in everyday life that does not depend upon previous research.
Research in any field of inquiry provides us with the knowledge and skills to solve problems and meet the challenges of a fast-paced decision-making environment.
9 Qualities of Research
Good research generates dependable data. It is conducted by professionals and can be used reliably for decision-making. It is thus of crucial importance that research should be made acceptable to the audience for which research should possess some desirable qualities in terms of.
9 qualities of research are;
Purpose clearly defined
Research process detailed, research design planner, ethical issues considered, limitations revealed, adequate analysis ensured, findings unambiguously presented, conclusions and recommendations justified..
We enumerate below a few qualities that good research should possess.
Good research must have its purposes clearly and unambiguously defined.
The problem involved or the decision to be made should be sharply delineated as clearly as possible to demonstrate the credibility of the research.
The research procedures should be described in sufficient detail to permit other researchers to repeat the research later.
Failure to do so makes it difficult or impossible to estimate the validity and reliability of the results. This weakens the confidence of the readers.
Any recommendations from such research justifiably get little attention from the policymakers and implementation.
The procedural design of the research should be carefully planned to yield results that are as objective as possible.
In doing so, care must be taken so that the sample’s representativeness is ensured, relevant literature has been thoroughly searched, experimental controls, whenever necessary, have been followed, and the personal bias in selecting and recording data has been minimized.
A research design should always safeguard against causing mental and physical harm not only to the participants but also those who belong to their organizations.
Careful consideration must also be given to research situations when there is a possibility for exploitation, invasion of privacy, and loss of dignity of all those involved in the study.
The researcher should report with complete honesty and frankness any flaws in procedural design; he followed and provided estimates of their effects on the findings.
This enhances the readers’ confidence and makes the report acceptable to the audience. One can legitimately question the value of research where no limitations are reported.
Adequate analysis reveals the significance of the data and helps the researcher to check the reliability and validity of his estimates.
Data should, therefore, be analyzed with proper statistical rigor to assist the researcher in reaching firm conclusions.
When statistical methods have been employed, the probability of error should be estimated, and criteria of statistical significance applied.
The presentation of the results should be comprehensive, easily understood by the readers, and organized so that the readers can readily locate the critical and central findings.
Proper research always specifies the conditions under which the research conclusions seem valid.
Therefore, it is important that any conclusions drawn and recommendations made should be solely based on the findings of the study.
No inferences or generalizations should be made beyond the data. If this were not followed, the objectivity of the research would tend to decrease, resulting in confidence in the findings.
The researcher’s experiences were reflected.
The research report should contain information about the qualifications of the researchers .
If the researcher is experienced, has a good reputation in research, and is a person of integrity, his report is likely to be highly valued. The policymakers feel confident in implementing the recommendations made in such reports.
4 Goals of Research

The primary goal or purpose of research in any field of inquiry; is to add to what is known about the phenomenon under investigation by applying scientific methods. Though each research has its own specific goals, we may enumerate the following 4 broad goals of scientific research:
Exploration and Explorative Research
Description and descriptive research, causal explanation and causal research, prediction and predictive research.
The link between the 4 goals of research and the questions raised in reaching these goals.
Let’s try to understand the 4 goals of the research.
Exploration is finding out about some previously unexamined phenomenon. In other words, an explorative study structures and identifies new problems.
The explorative study aims to gain familiarity with a phenomenon or gain new insights into it.
Exploration is particularly useful when researchers lack a clear idea of the problems they meet during their study.
Through exploration, researchers attempt to
- Develop concepts more clearly;
- Establish priorities among several alternatives;
- Develop operational definitions of variables;
- Formulate research hypotheses and sharpen research objectives;
- Improve the methodology and modify (if needed) the research design .
Exploration is achieved through what we call exploratory research.
The end of an explorative study comes when the researchers are convinced that they have established the major dimensions of the research task.
Many research activities consist of gathering information on some topic of interest. The description refers to these data-based information-gathering activities. Descriptive studies portray precisely the characteristics of a particular individual, situation, or group.
Here, we attempt to describe situations and events through studies, which we refer to as descriptive research.
Such research is undertaken when much is known about the problem under investigation.
Descriptive studies try to discover answers to the questions of who, what, when, where, and sometimes how.
Such research studies may involve the collection of data and the creation of distribution of the number of times the researcher observes a single event or characteristic, known as a research variable.
A descriptive study may also involve the interaction of two or more variables and attempts to observe if there is any relationship between the variables under investigation .
Research that examines such a relationship is sometimes called a correlational study. It is correlational because it attempts to relate (i.e., co-relate) two or more variables.
A descriptive study may be feasible to answer the questions of the following types:
- What are the characteristics of the people who are involved in city crime? Are they young? Middle-aged? Poor? Muslim? Educated?
- Who are the potential buyers of the new product? Men or women? Urban people or rural people?
- Are rural women more likely to marry earlier than their urban counterparts?
- Does previous experience help an employee to get a higher initial salary?
Although the data description in descriptive research is factual, accurate, and systematic, the research cannot describe what caused a situation.
Thus, descriptive research cannot be used to create a causal relationship where one variable affects another.
In other words, descriptive research can be said to have a low requirement for internal validity. In sum, descriptive research deals with everything that can be counted and studied.
But there are always restrictions on that. All research must impact the lives of the people around us.
For example, finding the most frequent disease that affects the people of a community falls under descriptive research.
But the research readers will have the hunch to know why this has happened and what to do to prevent that disease so that more people will live healthy lives.
It dictates that we need a causal explanation of the situation under reference and a causal study vis-a-vis causal research .
Explanation reveals why and how something happens.
An explanatory study goes beyond description and attempts to establish a cause-and-effect relationship between variables. It explains the reason for the phenomenon that the descriptive study observed.
Thus, if a researcher finds that communities with larger family sizes have higher child deaths or that smoking correlates with lung cancer, he is performing a descriptive study.
If he explains why it is so and tries to establish a cause-and-effect relationship, he is performing explanatory or causal research . The researcher uses theories or at-least hypotheses to account for the factors that caused a certain phenomenon.
Look at the following examples that fit causal studies:
- Why are people involved in crime? Can we explain this as a consequence of the present job market crisis or lack of parental care?
- Will the buyers be motivated to purchase the new product in a new container ? Can an attractive advertisement motivate them to buy a new product?
- Why has the share market shown the steepest-ever fall in stock prices? Is it because of the IMF’s warnings and prescriptions on the commercial banks’ exposure to the stock market or because of an abundant increase in the supply of new shares?
Prediction seeks to answer when and in what situations will occur if we can provide a plausible explanation for the event in question.
However, the precise nature of the relationship between explanation and prediction has been a subject of debate.
One view is that explanation and prediction are the same phenomena, except that prediction precedes the event while the explanation takes place after the event has occurred.
Another view is that explanation and prediction are fundamentally different processes.
We need not be concerned with this debate here but can simply state that in addition to being able to explain an event after it has occurred, we would also be able to predict when it will occur.
Research Approaches

There are two main approaches to doing research.
The first is the basic approach, which mostly pertains to academic research. Many people view this as pure research or fundamental research.
The research implemented through the second approach is variously known as applied research, action research, operations research, or contract research.
Also, the third category of research, evaluative research, is important in many applications. All these approaches have different purposes influencing the nature of the respective research.
Lastly, precautions in research are required for thorough research.
So, 4 research approaches are;
- Basic Research .
- Applied Research .
- Evaluative Research .
- Precautions in Research.
Areas of Research
The most important fields or areas of research, among others, are;
- Social Research .
- Health Research .
- Population Research .
- Business Research .
- Marketing Research .
- Agricultural Research .
- Biomedical Research.
- Clinical Research .
- Outcomes Research.
- Internet Research.
- Archival Research.
- Empirical Research.
- Legal Research .
- Education Research .
- Engineering Research .
- Historical Research.
Check out our article describing all 16 areas of research .
Precautions in Research
Whether a researcher is doing applied or basic research or research of any other form, he or she must take necessary precautions to ensure that the research he or she is doing is relevant, timely, efficient, accurate, and ethical .
The research is considered relevant if it anticipates the kinds of information that decision-makers, scientists, or policymakers will require.
Timely research is completed in time to influence decisions.
- Research is efficient when it is of the best quality for the minimum expenditure and the study is appropriate to the research context.
- Research is considered accurate or valid when the interpretation can account for both consistencies and inconsistencies in the data.
- Research is ethical when it can promote trust, exercise care, ensure standards, and protect the rights of the participants in the research process.
What is the definition of research?
What are the characteristics of good research, what are the three basic operations involved in scientific research, what are the four broad goals of scientific research, what distinguishes the scientific method from other methods of acquiring knowledge, what is the origin of the word ‘research’, how is “research methodology” defined, how does research methodology ensure the appropriateness of a research method.
After discussing the research definition and knowing the characteristics, goals, and approaches, it’s time to delve into the research fundamentals. For a comprehensive understanding, refer to our detailed research and methodology concepts guide .
Research should be relevant, timely, efficient, accurate, and ethical. It should anticipate the information required by decision-makers, be completed in time to influence decisions, be of the best quality for the minimum expenditure, and protect the rights of participants in the research process.
The two main approaches to research are the basic approach, often viewed as pure or fundamental research, and the applied approach, which includes action research, operations research, and contract research.

Qualities of A Good Researcher: 11 Most Essential
- Post author: Edeh Samuel Chukwuemeka ACMC
- Post published: November 29, 2021
- Post category: Scholarly Articles
Ten Qualities of A Good Researcher: Research entails the gathering of bits and pieces of information and compiling same for the purpose of increasing the stock in knowledge and solving problems. It is an art; a practice done to increase knowledge and render solutions to problems. This is because a research raises questions, which when answered, bridges the gap in knowledge in any field it was undertaken.
The task of researcing is no small work. This is due mainly to the fact that the information contained in a research work is usually for public consumption. There is no gainsaying the fact that anything made for the public must be above par. Hence, a research work which is geared towards adding value to knowledge as well as proffering solutions to problems must be rich in content and accurate.

Having known that a piece of research work is of great importance, the quality of such piece cannot be overlooked. Thus, for a research to be adjudged as being above standard, and also capable of serving its core purpose, the one undertaking the research must possess certain qualities. These qualities will enable him produce a work that will stand the test of time.
RECOMMENDED: Qualities of a good Enterpreneur
Qualities of A Researcher
These qualities which he must possess are outlined below:
1. Accuracy: A researcher must ensure that his research work is accurate. He should ensure that the facts and figures which he is presenting are true and verifiable. There should be no room for conjecture or guesses.

He should exhibit due diligence in presenting his work so as not to present a false and misleading research as the accuracy of the research determines the credibility to be attached to the researcher.
2. Open mindedness : To explain how powerful the mind is, Albert Einstein once said that the measure of intelligence is the ability to change the mind. It is one of the most important characteristics of a good researcher because researching has to do with finding new fact which may sometimes require that the researchers alter previously valid facts.

The crux is that, a researcher must not be someone who hardly gives up on his beliefs, custom or knowledge. He has to be someone who is able to see things in different lights. He must understand that nothing is actually static and things change over time.
Researching may sometimes lead you to find out that even some of the things you consider fundamental knowledge are not actually fundamental; or maybe there are more to it. Thus, a researcher who is not open minded during researching is limited to alot of knowledge.
Recommended: How to remember what you have read faster
3. Motivation: A researcher must have the ability to motivate himself to work. He should not be easily discouraged. In the course of his research, he might come across some hostile respondents. This should not deter him from carrying on his research work.
Again, he might be met with opposition from his colleagues. Such oppositions should not serve as a source of discouragement to him. A researcher therefore, must have the ability to encourage and motivate himself to push on until he actualizes his aim.
Also see: Ways to Improve Your Reading Speed
4. Patience: One of the sterling attributes of a good researcher is patience. This quality is a follow-up attribute to being motivated. A researcher must exhibit a high degree of patience, both with his respondents and in the course of his research when the much needed result is not forthcoming, in addition to his being consistent with the effort he puts in.

5. Prudence: The quality of being prudent has to do with his ability to manage the resources at his disposal. Research is a capital intensive project and there are possibilities that one might not be well funded to carry out such project. The managerial skill and ability of the researcher becomes handy for a successful execution of the project.
Also, even if the resources are in abundance, he must be able to manage same so as to avoid waste and extravagant spendings. Therefore, a researcher must be able to effectively manage the resources at his disposal for optimum output.
Also see: Characteristics of fundamental human rights
6. Expertise: Though the aim of research is to add knowledge to already existing knowledge (as one ventures into new areas not yet explored), the researcher must have reasonable amount of knowledge in the field he intends carrying out his research.

It will amount to a ruse if an archaeologist embarks on a research in medicine. A researcher must therefore be an expert in the field of his research or must possess at least, reasonable amount of knowledge in the field he professes to carry out his research.
7. Unbiased in his Research: At the beginning of his research, a researcher must not have a preconceived notion or idea about the subject of his research. This is because the research may likely not be accurate as his leanings will mostly be towards his bias. If there exists such bias, the researcher should be liberal enough to accept findings that are against his held beliefs. This will aid him to present an accurate and unbiased research work.

Also see: Highest paying law firms in Nigeria
8. Interest: A researcher must show sufficient interest in the work he is doing. He should not be distracted. His interest should be focused on the work. This is quite different from being motivated. This is because it is the interest one has in a task that keeps him motivated.
If one is not interested in a research work, he cannot be motivated, even if all necessary things are in place to drive the project. A researcher has to build interest from within, in the field of his research to see him through the research work.
9. Amiable Personality: A researcher must have a friendly disposition. He should be easily approachable and should also have the ability to communicate with people in a friendly and coherent manner. A researcher that is unfriendly, gloomy and unapproachable may find it difficult extracting information from his respondents.
A researcher should also exhibit friendliness to whoever works with him (if he is in a team with other researchers). This act of friendliness reduces friction within the team and the team is most likely to finish up their task in record time.
Recommended: Advantages and Disadvantages of an unwritten constitution
10. The Ability to Work Under Pressure : A researcher must be able to work under pressure and unfavorable situations. The ability to carry out a task within little time frame and also work in conditions that are less favorable (for example, under a hostile boss) is a quality which the researcher should have to enable him carry out his task.

Limited time may be allocated to accomplish a research project such that if the researcher is unable to manage his time, the work will not be done. It is therefore a needed quality of the researcher to be able to persevere and work in unfriendly situations if he must accomplish his task on time.
11. Analytical in his research: A researcher should be analytical and should also be able to exhibit sound judgment. Proper analysis of issues is key to having a good research work. His ability to reason rationally and give sound judgment affects the quality of the research work.

Where the ability to give sound judgment is missing, there may be a misapplication of principles and rules. This might be fatal if such misapplication happens in a research work of great importance to health. Therefore, a researcher must have the natural ability to discern what is right between two factors brought before him.
Also see: Best side hustles for students to make money while in school
Conclusively, whether a research work is an academic or organizational work, the researcher must be able to consistently gather information that are needed for the task. Research has to do with the discovery of new information and only a well planned method of information gathering can aid in the actualizing of this aim.
The quality of a research work, its success and its usefulness is dependent on the level of diligence exhibited by the researcher. It is imperative that the researcher is one with good attributes to enable him scale the litmus test of acceptability of his work in the society.

Edeh Samuel Chukwuemeka, ACMC, is a lawyer and a certified mediator/conciliator in Nigeria. He is also a developer with knowledge in various programming languages. Samuel is determined to leverage his skills in technology, SEO, and legal practice to revolutionize the legal profession worldwide by creating web and mobile applications that simplify legal research. Sam is also passionate about educating and providing valuable information to people.
This Post Has One Comment
Easy to understand, simple and to the point thankyou
Comments are closed.
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
Research: What Companies Don’t Know About How Workers Use AI
- Jeremie Brecheisen

Three Gallup studies shed light on when and why AI is being used at work — and how employees and customers really feel about it.
Leaders who are exploring how AI might fit into their business operations must not only navigate a vast and ever-changing landscape of tools, but they must also facilitate a significant cultural shift within their organizations. But research shows that leaders do not fully understand their employees’ use of, and readiness for, AI. In addition, a significant number of Americans do not trust business’ use of AI. This article offers three recommendations for leaders to find the right balance of control and trust around AI, including measuring how their employees currently use AI, cultivating trust by empowering managers, and adopting a purpose-led AI strategy that is driven by the company’s purpose instead of a rules-heavy strategy that is driven by fear.
If you’re a leader who wants to shift your workforce toward using AI, you need to do more than manage the implementation of new technologies. You need to initiate a profound cultural shift. At the heart of this cultural shift is trust. Whether the use case for AI is brief and experimental or sweeping and significant, a level of trust must exist between leaders and employees for the initiative to have any hope of success.
- Jeremie Brecheisen is a partner and managing director of The Gallup CHRO Roundtable.
Partner Center
- Open access
- Published: 16 May 2024
Competency gap among graduating nursing students: what they have achieved and what is expected of them
- Majid Purabdollah 1 , 2 ,
- Vahid Zamanzadeh 2 , 3 ,
- Akram Ghahramanian 2 , 4 ,
- Leila Valizadeh 2 , 5 ,
- Saeid Mousavi 2 , 6 &
- Mostafa Ghasempour 2 , 4
BMC Medical Education volume 24 , Article number: 546 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
116 Accesses
Metrics details
Nurses’ professional competencies play a significant role in providing safe care to patients. Identifying the acquired and expected competencies in nursing education and the gaps between them can be a good guide for nursing education institutions to improve their educational practices.
In a descriptive-comparative study, students’ perception of acquired competencies and expected competencies from the perspective of the Iranian nursing faculties were collected with two equivalent questionnaires consisting of 85 items covering 17 competencies across 5 domains. A cluster sampling technique was employed on 721 final-year nursing students and 365 Iranian nursing faculties. The data were analyzed using descriptive statistics and independent t-tests.
The results of the study showed that the highest scores for students’ acquired competencies and nursing faculties’ expected competencies were work readiness and professional development, with mean of 3.54 (SD = 0.39) and 4.30 (SD = 0.45), respectively. Also, the lowest score for both groups was evidence-based nursing care with mean of 2.74 (SD = 0.55) and 3.74 (SD = 0.57), respectively. The comparison of competencies, as viewed by both groups of the students and the faculties, showed that the difference between the two groups’ mean scores was significant in all 5 core-competencies and 17 sub-core competencies ( P < .001). Evidence-based nursing care was the highest mean difference (mean diff = 1) and the professional nursing process with the lowest mean difference (mean diff = 0.70).
The results of the study highlight concerns about the gap between expected and achieved competencies in Iran. Further research is recommended to identify the reasons for the gap between the two and to plan how to reduce it. This will require greater collaboration between healthcare institutions and nursing schools.
Peer Review reports
Introduction| Background
Nursing competence refers to a set of knowledge, skills, and behaviors that are necessary to successfully perform roles or responsibilities [ 1 ]. It is crucial for ensuring the safe and high-quality care of patients [ 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 ]. However, evaluating nursing competence is challenging due to the complex, dynamic, and multi factorial nature of the clinical environment [ 3 ]. The introduction of nursing competencies and their assessment as a standard measure of clinical performance at the professional level has been highlighted by the Association of American Colleges of Nursing [ 6 , 7 ]. As a result, AACN (2020) introduces competence assessment as an emerging concept in nursing education [ 7 ].
On the other hand, the main responsibility of nursing education is to prepare graduates who have the necessary competencies to provide safe and quality care [ 3 ]. Although it is believed that it is impossible to teach everything to students, acquiring some competencies requires entering a real clinical setting and gaining work experience [ 8 ]. However, nursing students are expected to be competent to ensure patient safety and quality of care after graduation [ 9 ]. To the extent that the World Health Organization (WHO), while expressing concern about the low quality of nursing education worldwide, has recommended investing in nursing education and considers that the future to require nurses who are theoretically and clinically competent [ 5 ]. Despite efforts, the inadequate preparation of newly graduated nursing students and doubts about the competencies acquired in line with expectations to provide safe care for entering the nursing setting have become a global concern [ 10 , 11 , 12 , 13 ]. The results of studies in this field are different. The results of Amsalu et al. showed that the competence of newly graduated nursing students to provide quality and safe care was not satisfactory [ 14 ]. Some studies have also highlighted shortcomings in students’ “soft” skills, such as technical competency, critical thinking, communication, teamwork, helping roles, and professionalism [ 15 ]. Additionally, prior research has indicated that several nursing students have an unrealistic perception of their acquired competencies before entering the clinical setting and they report a high level of competence [ 2 ]. In other study, Hickerson et al. showed that the lack of preparation of nursing students is associated with an increase in patient errors and poor patient outcomes [ 16 ]. Some studies also discussed nursing competencies separately; Such as patient safety [ 17 ], clinical reasoning [ 18 ], interpersonal communication [ 19 ], and evidence-based care competence [ 20 ].
On the other hand, the growing need for safe nursing care and the advent of new educational technologies, the emergence of infectious diseases has increased the necessity of nursing competence. As a result, the nursing profession must be educated to excellence more than ever before [ 5 , 21 , 22 ]. Therefore, the self-assessment of students’ competence levels as well as the evaluation of nursing managers about the competencies expected from them is an essential criterion for all healthcare stakeholders, educators, and nursing policymakers to ensure the delivery of safe, and effective nursing care [ 9 , 23 , 24 ].
However, studies of nurse managers’ perceptions of the competence of newly graduated nursing students are limited and mostly conducted at the national level. Hence, further investigation is needed in this field [ 25 , 26 ]. Some other studies have been carried out according to the context and the needs of societies [ 3 , 26 , 27 , 28 ]. The results of some other studies in the field of students’ self-assessment of perceived competencies and managers’ and academic staff’s assessment of expected competency levels are different and sometimes contradictory, and there is the “academic-clinical gap” between expected and achieved competencies [ 25 , 29 , 30 ]. A review of the literature showed that this gap has existed for four decades, and the current literature shows that it has not changed much over time. The academe and practice settings have also been criticized for training nurses who are not sufficiently prepared to fully engage in patient care [ 1 ]. Hence, nursing managers must understand the expected competencies of newly graduated students, because they have a more complete insight into the healthcare system and the challenges facing the nursing profession. Exploration of these gaps can reveal necessities regarding the work readiness of nursing graduates and help them develop their competencies to enter the clinical setting [ 1 , 25 ].
Although research has been carried out on this topic in other countries, the educational system in those countries varies from that of Iran’s nursing education [ 31 , 32 ]. Iran’s nursing curriculum has tried to prepare nurses who have the necessary competencies to meet the care needs of society. Despite the importance of proficiency in nursing education, many nursing graduates often report feeling unprepared to fulfill expected competencies and they have deficiencies in applying their knowledge and experience in practice [ 33 ]. Firstly, the failure to define and identify the expected competencies in the nursing curriculum of Iran led to the absence of precise and efficient educational objectives. Therefore, it is acknowledged that the traditional nursing curriculum of Iran focuses more on lessons organization than competencies [ 34 ]. Secondly, insufficient attention has been given to the scheduling, location, and level of competencies in the nursing curriculum across different semesters [ 35 ]. Thirdly, the large volume of content instead of focusing on expected competencies caused nursing graduates challenged to manage complex situations [ 36 ]. Therefore, we should not expect competencies such as critical thinking, clinical judgment, problem-solving, decision-making, management, and leadership from nursing students and graduates in Iran [ 37 ]. Limited research has been conducted in this field in Iran. Studies have explored the cultural competence of nursing students [ 38 ] and psychiatric nurses [ 39 ]. Additionally, the competence priorities of nurses in acute care have been investigated [ 40 ], as well as the competency dimensions of nurses [ 41 ].
In Iran, after receiving the diploma, the students participate in a national exam called Konkur. Based on the results of this exam, they enter the field of nursing without conducting an aptitude test interview and evaluating individual and social characteristics. The 4-year nursing curriculum in Iran has 130 units including 22 general, 54 specific, 15 basic sciences, and 39 internship units. In each semester, several workshops are held according to the syllabus [ 42 ]. Instead of the expected competencies, a list of general competencies is specified as learning outcomes in the program. Accepted students based on their rank in the exam and their choice in public and Islamic Azad Universities (non-profit), are trained with a common curriculum. Islamic Azad Universities are not supported by government funding and are managed autonomously, this problem limits the access to specialized human resources and sufficient educational fields, and the lower salaries of faculty members in Azad Universities compared to the government system, students face serious challenges. Islamic Azad Universities must pay exorbitant fees to medical universities for training students in clinical departments and medical training centers, doubling these Universities’ financial problems. In some smaller cities, these financial constraints cause students to train in more limited fields of clinical training and not experience much of what they have learned in the classroom in practice and the real world of nursing. The evaluation of learners in the courses according to the curriculum is based on formative and summative evaluation with teacher-made tests, checklists, clinical assignments, conferences, and logbooks. The accreditation process of nursing schools includes two stages internal evaluation, which is done by surveying students, professors and managers of educational groups, and external accreditation is done by the nursing board. After completing all their courses, to graduate, students must participate in an exam called “Final”, which is held by each faculty without the supervision of an accreditation institution, the country’s assessment organization or the Ministry of Health, and obtain at least a score of 10 out of 20 to graduate.
Therefore, we conducted this comprehensive study as the first study in Iran to investigate the difference between the expected and perceived competence levels of final year nursing students. The study’s theoretical framework is based on Patricia Benner’s “From Novice to Expert” model [ 43 ].
Materials and methods
The present study had the following three objectives:
Determining self-perceived competency levels from the perspective of final year nursing students in Iran.
Determining expected levels of competency from the perspective of nursing faculties in Iran.
To determine the difference between the expected competencies from the perspective of nursing faculties and the achieved competencies from the perspective of final-year nursing students.
This study is a descriptive-comparative study.
First, we obtained a list of all nursing schools in the provinces of Iran from the Ministry of Health ( n = 31). From 208 Universities, 72 nursing schools were randomly selected using two-stage cluster sampling. Among the selected faculties, we chose 721 final-year nursing students and 365 nursing faculties who met the eligibility criteria for the study. Final-year nursing students who consented to participate in the study were selected. Full-time faculty members with at least 2 years of clinical experience and nurse managers with at least 5 years of clinical education experience were also included. In this study, nursing managers, in addition to their educational roles in colleges, also have managerial roles in the field of nursing. Some of these roles include nursing faculty management, nursing board member, curriculum development and review, planning and supervision of nursing education, evaluation, and continuous improvement of nursing education. The selection criteria were based on the significant role that managers play in nursing education and curriculum development [ 44 ]. Non-full-time faculty members and managers without clinical education experience were excluded from the study.
The instrument used in this study is a questionnaire developed and psychometrically tested in a doctoral nursing dissertation [ 45 ]. To design the tool, the competencies expected of undergraduate nursing students in Iran and worldwide were first identified through a scoping review using the methodology recommended by the Joanna Briggs Institute (JBI) and supported by the PAGER framework. Summative content analysis by Hsieh and Shannon (2005) was used for analysis, which included: counting and comparing keywords and content, followed by interpretation of textual meaning. In the second step, the results of the first step were used to create tool statements. Then the validity of the instrument was checked by face validity, content validity (determination of the ratio and index of content validity), and validity of known groups. Its reliability was also checked by internal consistency using Cronbach’s alpha method and stability using the test-retest method. The competency questionnaire comprises 85 items covering 17 competencies across 5 domains: “individualized care” (4 competencies with 21 items), “evidence-based nursing care” (2 competencies with 10 items), “professional nursing process” (3 competencies with 13 items), “nursing management” (2 competencies with 16 items), and “work readiness and professional development” (6 competencies with 25 items) [ 45 ]. “The Bondy Rating Scale was utilized to assess the competency items, with ratings ranging from 1 (Dependent) to 5 (Independent) on a 5-point Likert scale [ 46 ]. The first group (nursing students) was asked to indicate the extent to which they had acquired each competency. The second group (nursing faculties) was asked to specify the level to which they expected nursing students to achieve each competency.
Data collection
First, the researcher contacted the deans and managers of the selected nursing schools by email to obtain permission. After explaining the aims of the study and the sampling method, we obtained the telephone number of the representative of the group of final year nursing students and also the email of the faculty members. The representative of the student group was then asked to forward the link to the questionnaire to 10 students who were willing to participate in the research. Informed consent for students to participate in the online research was provided through the questionnaires, while nursing faculty members who met the eligibility criteria for the study received an informed consent form attached to the email questionnaire. The informed consent process clarified the study objectives and ensured anonymity of respondent participation in the research, voluntary agreement to participate and the right to revoke consent at any time. An electronic questionnaire was then sent to 900 final year nursing students and 664 nursing faculties (from 4 March 2023 to 11 July 2023). Reminder emails were sent to nursing faculty members three times at two-week intervals. The attrition rate in the student group was reported to be 0 (no incomplete questionnaires). However, four questionnaires from nursing faculty members were discarded because of incomplete responses. Of the 900 questionnaires sent to students and 664 sent to nursing faculties, 721 students and 365 nursing faculty members completed the questionnaire. The response rates were 79% and 66% respectively.
Data were analyzed using SPSS version 22. Frequencies and percentages were used to report categorical variables and mean and standard deviations were used for quantitative variables. The normality of the quantitative data was confirmed using the Shapiro-Wilk and Skewness tests. An independent t-test was used for differences between the two groups.
Data analysis revealed that out of 721 students, 441 (61.20%) was female. The mean and deviation of the students’ age was 22.50 (SD = 1.21). Most of the students 577 (80%) were in their final semester. Also, of the total 365 faculties, the majority were female 253 (69.31%) with a mean of age 44.06 (SD = 7.46) and an age range of 22–65. The academic rank of most nursing faculty members 156 (21.60%) was assistant professor (Table 1 ).
The results of the study showed that in both groups the highest scores achieved by the students and expected by the nursing faculty members were work readiness and professional development with a mean and standard deviation of 3.54 (0.39) and 4.30 (0.45) respectively. The lowest score for both groups was also evidence-based nursing care with a mean and standard deviation of 2.74 (0.55) for students and 3.74 (0.57) for nursing faculty members (Table 2 ).
Also, the result of the study showed that the highest expected competency score from the nursing faculty members’ point of view was the safety subscale. In other words, faculty members expected nursing students to acquire safety competencies at the highest level and to be able to provide safe care independently according to the rating scale (Mean = 4.51, SD = 0.45). The mean score of the competencies achieved by the students was not above 3.77 in any of the subscales and the highest level of competency achievement according to self-report of students was related to safety competencies (mean = 3.77, SD = 0.51), preventive health services (mean = 3.69, SD = 0.79), values and ethical codes (mean = 3.67, SD = 0.77), and procedural/clinical skills (mean = 3.67, SD = 0.71). The other competency subscales from the perspective of the two groups are presented in Table 3 , from highest to lowest score.
The analysis of core competencies achieved and expected from both students’ and nursing faculty members’ perspectives revealed that, firstly, there was a significant difference between the mean scores of the two groups in all five core competencies ( P < .001) and that the highest mean difference was related to evidence-based care with mean diff = 1 and the lowest mean difference was related to professional care process with mean diff = 0.70 (Table 4 ).
Table 5 indicates that there was a significant difference between the mean scores achieved by students and nursing faculty members in all 5 core competencies and 17 sub-core Competencies ( p < .001).
The study aimed to determine the difference between nursing students’ self-perceived level of competence and the level of competence expected of them by their nursing faculty members. The study results indicate that students scored highest in work readiness and professional development. However, they were not independent in this competency and required support. The National League for Nursing (NLN) recognizes nursing professional development as the goal of nursing education programs [ 47 ] However, Aguayo-Gonzalez [ 48 ] believes that the appropriate time for professional development is after entering a clinical setting. This theme includes personal characteristics, legality, clinical/ procedural skills, patient safety, preventive health services, and mentoring competence. Personality traits of nursing students are strong predictors of coping with nursing stress, as suggested by Imus [ 49 ]. These outcomes reflect changes in students’ individual characteristics during their nursing education. Personality changes, such as the need for patience and persistence in nursing care and understanding the nurse identity prepare students for the nursing profession, which is consistent with the studies of Neishabouri et al. [ 50 ]. Although the students demonstrated a higher level of competence in this theme, an examination of the items indicates that they can still not adapt to the challenges of bedside nursing and to use coping techniques. This presents a concerning issue that requires attention and resolution. Previous studies have shown that nursing education can be a very stressful experience [ 51 , 52 , 53 ].
Of course, there is no consensus on the definition of professionalism and the results of studies in this field are different. For example, Akhtar et al. (2013) identified common viewpoints about professionalism held by nursing faculty and students, and four viewpoints emerged humanists, portrayers, facilitators, and regulators [ 54 ]. The findings of another study showed that nursing students perceived vulnerability, symbolic representation, role modeling, discontent, and professional development are elements that show their professionalism [ 55 ]. The differences indicate that there may be numerous contextual variables that affect individuals’ perceptions of professionalism.
The legal aspects of nursing were the next item in this theme that students needed help with. The findings of studies regarding the legal competence of newly graduated nursing students are contradictory reported that only one-third of nurse managers were satisfied with the legal competence of newly graduated nursing students [ 56 , 57 ]. Whereas the other studies showed that legality was the highest acquired competence for newly graduated nursing students [ 58 , 59 ]. However, the results of this study indicated that legality may be a challenge for newly graduated nursing students. Benner [ 43 ] highlighted the significant change for new graduates in that they now have full legal and professional responsibility for the patient. Tong and Epeneter [ 60 ] also reported that facing an ethical dilemma is one of the most stressful factors for new graduates. Therefore, the inexperience of new graduates cannot reduce the standard of care that patients expect from them [ 60 ]. Legal disputes regarding the duties and responsibilities of nurses have increased with the expansion of their roles. This is also the case in Iran. Nurses are now held accountable by law for their actions and must be aware of their legal obligations. To provide safe healthcare services, it is essential to know of professional, ethical, and criminal laws related to nursing practice. The nursing profession is accountable for the quality of services delivered to patients from both professional and legal perspectives. Therefore, it is a valuable finding that nurse managers should support new graduates to better deal with ethical dilemmas. Strengthening ethical education in nursing schools necessitates integrating real cases and ethical dilemmas into the curriculum. Especially, Nursing laws are missing from Iran’s undergraduate nursing curriculum. By incorporating authentic case studies drawn from clinical practice, nursing schools provide students with opportunities to engage in critical reflection, ethical analysis, and moral deliberation. These real cases challenge students to apply ethical principles to complex and ambiguous situations, fostering the development of ethical competence and moral sensitivity. Furthermore, ethical reflection and debriefing sessions during clinical experiences enable students to discuss and process ethical challenges encountered in practice, promoting self-awareness, empathy, and professional growth. Overall, by combining theoretical instruction with practical application and the use of real cases, nursing schools can effectively prepare future nurses to navigate ethical dilemmas with integrity and compassion.
However, the theme of evidence-based nursing care was the lowest scoring, indicating that students need help with this theme. The findings from studies conducted in this field are varied. A limited number of studies reported that nursing students were competent to implement evidence-based care [ 61 ], while other researchers reported that nursing students’ attitudes toward evidence-based care to guide clinical decisions were largely negative [ 20 , 62 ]. The principal barriers to implementing evidence-based care are lack of authority to change patient care policy, slow dissemination of evidence and lack of time at the bedside to implement evidence [ 10 ], and lack of knowledge and awareness of the process of searching databases and evaluating research [ 63 ]. While the European Higher Education Area (EHEA) framework and the International Council of Nurses Code of Ethics introduce the ability to identify, critically appraise, and apply scientific information as expected learning outcomes for nursing students [ 64 , 65 ], the variation in findings highlights the complexity of the concept of competence and its assessment [ 23 ]. Evidence-Based Nursing (EBN) education for nursing students is most beneficial when it incorporates a multifaceted approach. Interactive workshops play a crucial role, providing students with opportunities to critically appraise research articles, identify evidence-based practices, and apply them to clinical scenarios. Simulation-based learning further enhances students’ skills by offering realistic clinical experiences in a safe environment. Additionally, clinical rotations offer invaluable opportunities for students to observe and participate in evidence-based practices under the guidance of experienced preceptors. Journal clubs foster a culture of critical thinking and ongoing learning, where students regularly review and discuss current research articles. Access to online resources such as databases and evidence-based practice guidelines allows students to stay updated on the latest evidence and best practices. To bridge the gap between clinical practice and academic theory, collaboration between nursing schools and healthcare institutions is essential. This collaboration can involve partnerships to create clinical learning environments that prioritize evidence-based practice, inter professional education activities to promote collaboration across disciplines, training and support for clinical preceptors, and continuing education opportunities for practicing nurses to strengthen their understanding and application of EBN [ 66 ]. By implementing these strategies, nursing education programs can effectively prepare students to become competent practitioners who integrate evidence-based principles into their clinical practice, ultimately improving patient outcomes.
The study’s findings regarding the second objective showed that nursing faculty members expected students to achieve the highest level of competence in work readiness and professional development, and the lowest in evidence-based nursing care competence. The results of the studies in this area revealed that there is a lack of clarity about the level of competence of newly graduated nursing students and that confusion about the competencies expected of them has become a major challenge [ 13 , 67 ]. Evidence of nurse managers’ perceptions of newly graduated nursing student’s competence is limited and rather fragmented. There is a clear need for rigorous empirical studies with comprehensive views of managers, highlighting the key role of managers in the evaluation of nurse competence [ 1 , 9 ]. Some findings also reported that nursing students lacked competence in primary and specialized care after entering a real clinical setting [ 68 ] and that nursing managers were dissatisfied with the competence of students [ 30 ].
The results of the present study on the third objective confirmed the gap between expected and achieved competence requirements. The highest average difference was related to evidence-based nursing care, and the lowest mean difference was related to the professional nursing process. The findings from studies in this field vary. For instance, Brown and Crookes [ 13 ] reported that newly graduated nursing students were not independent in at least 26 out of 30 competency domains. Similar studies have also indicated that nursing students need a structured program after graduation to be ready to enter clinical work [ 30 ]. It can be stated that the nursing profession does not have clear expectations of the competencies of newly graduated nursing students, and preparing them for entry into clinical practice is a major challenge for administrators [ 13 ]. These findings can be explained by the Duchscher transition shock [ 69 ]. It is necessary to support newly graduated nursing students to develop their competence and increase their self-confidence.
The interesting but worrying finding was the low expectations of faculty members and the low scores of students in the theme of evidence-based care. However, nursing students need to keep their competencies up to date to provide safe and high-quality care. The WHO also considers the core competencies of nurse educators to be the preparation of effective, efficient, and skilled nurses who can teach the evidence-based learning process and help students apply it clinically [ 44 ]. The teaching of evidence-based nursing care appears to vary across universities, and some clinical Faculties do not have sufficient knowledge to support students. In general, it can be stated that the results of the present study are in line with the context of Iran. Some of the problems identified include a lack of attention to students’ academic talent, a lack of a competency-based curriculum, a gap between theory and clinical practice, and challenges in teaching and evaluating the achieved competencies [ 42 ].
Strengths and limitations
The study was conducted on a national level with a sizable sample. It is one of the first studies in Iran to address the gap between students’ self-perceived competence levels and nursing faculty members’ expected competency levels. Nevertheless, one of the limitations of the study is the self-report nature of the questionnaire, which may lead to social desirability bias. In addition, the COVID-19 pandemic coinciding with the student’s first and second years could potentially impact their educational quality and competencies. The limitations established during the outbreak negatively affected the nursing education of students worldwide.
Acquiring nursing competencies is the final product of nursing education. The current study’s findings suggest the existence of an academic-practice gap, highlighting the need for educators, faculty members, and nursing managers to collaborate in bridging the potential gap between theory and practice. While nursing students were able to meet some expectations, such as value and ethical codes, there is still a distance between expectations and reality. Especially, evidence-based care was identified as one of the weaknesses of nursing students. It is recommended that future research investigates the best teaching strategies and more objective assessments of competencies. The findings of this study can be used as a guide for the revision of undergraduate nursing education curricula, as well as a guide for curriculum development based on the development of competencies expected of nursing students. Nursing managers can identify existing gaps and plan to fill them and use them for the professionalization of students. This requires the design of educational content and objective assessment tools to address these competencies at different levels throughout the academic semester. This significant issue necessitates enhanced cooperation between healthcare institutions and nursing schools. Enhancing nursing education requires the implementation of concrete pedagogical strategies to bridge the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical skills. Simulation-based learning emerges as a pivotal approach, offering students immersive experiences in realistic clinical scenarios using high-fidelity simulators [ 70 ]. Interprofessional education (IPE) is also instrumental, in fostering collaboration among healthcare professionals and promoting holistic patient care. Strengthening clinical preceptorship programs is essential, with a focus on providing preceptors with formal training and ongoing support to facilitate students’ clinical experiences and transition to professional practice [ 71 ]. Integrating evidence-based practice (EBP) principles throughout the curriculum cultivates critical thinking and inquiry skills among students, while technology-enhanced learning platforms offer innovative ways to engage students and support self-directed learning [ 72 ]. Diverse and comprehensive clinical experiences across various healthcare settings ensure students are prepared for the complexities of modern healthcare delivery. By implementing these practical suggestions, nursing education programs can effectively prepare students to become competent and compassionate healthcare professionals.
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Huston C, et al. The academic-practice gap: strategies for an enduring problem . In nursing forum . Wiley Online Library; 2018.
Meretoja R, Isoaho H, Leino-Kilpi H. Nurse competence scale: development and psychometric testing. J Adv Nurs. 2004;47(2):124–33.
Article Google Scholar
Järvinen T, et al. Nurse educators’ perceptions of factors related to the competence of graduating nursing students. Nurse Educ Today. 2021;101:104884.
Satu KU, et al. Competence areas of nursing students in Europe. Nurse Educ Today. 2013;33(6):625–32.
World Health Organization. State of the world’s nursing 2020: investing in education, jobs and leadership. 2020 [cited 12 June 2023; https://www.who.int/publications-detail-redirect/9789240003279 .
Lee W-H, Kim S, An J. Development and evaluation of korean nurses’ core competency scale (KNCCS) 2017.
American Association of Colleges of Nursing. The essentials: core competencies for professional nursing education… 2020 [cited 2023; https://www.aacnnursing.org/Portals/0/PDFs/Publications/Essentials-2021.pdf .
Gardulf A, et al. The Nurse Professional competence (NPC) scale: self-reported competence among nursing students on the point of graduation. Nurse Educ Today. 2016;36:165–71.
Kajander-Unkuri S, et al. The level of competence of graduating nursing students in 10 European countries-comparison between countries. Nurs Open. 2021;8(3):1048–62.
Labrague LJ et al. A Multicountry Study on Nursing Students’ Self-Perceived Competence and Barriers to Evidence‐Based Practice 2019. 16(3): pp. 236–246.
Visiers-Jiménez L, et al. Clinical learning environment and graduating nursing students’ competence: a multi-country cross-sectional study. Nurs Health Sci. 2021;23(2):398–410.
Herron EK. New graduate nurses’ preparation for recognition and prevention of failure to rescue: a qualitative study. J Clin Nurs. 2018;27(1–2):e390–401.
Google Scholar
Brown RA, Crookes PA. What are the ‘necessary’ skills for a newly graduating RN? Results of an Australian survey. BMC Nurs. 2016;15:23.
Amsalu B, et al. Clinical practice competence of Mettu University nursing students: a cross-sectional study. Adv Med Educ Pract. 2020;11:791–8.
Song Y, McCreary LL. New graduate nurses’ self-assessed competencies: an integrative review. Nurse Educ Pract. 2020;45:102801.
Hickerson KA, Taylor LA, Terhaar MF. The Preparation-Practice gap: an Integrative Literature Review. J Contin Educ Nurs. 2016;47(1):17–23.
Huang FF, et al. Self-reported confidence in patient safety competencies among Chinese nursing students: a multi-site cross-sectional survey. BMC Med Educ. 2020;20(1):32.
Hong S et al. A Cross-Sectional Study: What Contributes to Nursing Students’ Clinical Reasoning Competence? Int J Environ Res Public Health, 2021. 18(13).
Mcquitty DJPE, Counseling. Teaching interpersonal communication concepts to increase awareness and reduce health disparities: Presenter (s): DaKysha Moore, NCAT, United States 2023. 109: pp. 25–26.
Lam CK, Schubert CF, Herron EK. Evidence-based practice competence in nursing students preparing to transition to practice. Worldviews Evid Based Nurs. 2020;17(6):418–26.
Lake MA. What we know so far: COVID-19 current clinical knowledge and research. Clin Med (Lond). 2020;20(2):124–7.
Shustack L. Integrating Google Earth in Community Health nursing courses: preparing globally aware nurses. Nurse Educ. 2020;45(2):E11–2.
Zeleníková R, et al. Self-assessed competence of final-year nursing students. Nurs Open. 2023;10(7):4607–18.
Hyun A, Tower M, Turner C. Exploration of the expected and achieved competency levels of new graduate nurses. J Nurs Manag. 2020;28(6):1418–31.
Kukkonen P, et al. Nurse managers’ perceptions of the competence of newly graduated nurses: a scoping review. J Nurs Manag. 2020;28(1):4–16.
Nilsson J et al. Nurse professional competence (NPC) assessed among newly graduated nurses in higher educational institutions in Europe. 2019. 39(3): p. 159–67.
Kajander-Unkuri S et al. Students’ Self-assessed Competence Levels during Nursing Education Continuum - A Cross-sectional Survey. Int J Nurs Educ Scholarsh, 2020. 17(1).
Salminen L, et al. The competence of nurse educators and graduating nurse students. Nurse Educ Today. 2021;98:104769.
Numminen O, et al. Newly graduated nurses’ competence and individual and organizational factors: a multivariate analysis. J Nurs Scholarsh. 2015;47(5):446–57.
Södersved Källestedt ML, et al. Perceptions of managers regarding prerequisites for the development of professional competence of newly graduated nurses: a qualitative study. J Clin Nurs. 2020;29(23–24):4784–94.
Ezzati E, et al. Exploring the social accountability challenges of nursing education system in Iran. BMC Nurs. 2023;22(1):7.
Farsi Z, et al. Comparison of Iran’s nursing education with developed and developing countries: a review on descriptive-comparative studies. BMC Nurs. 2022;21(1):105.
Salem OA et al. Competency based nursing curriculum: establishing the standards for nursing competencies in higher education. 2018. 5(11): p. 1–8.
Noohi E, Ghorbani-Gharani L. and A.J.S.i.D.o.M.E. Abbaszadeh, A comparative study of the curriculum of undergraduate nursing education in Iran and selected renowned universities in the world 2015. 12(3): pp. 450–471.
Rassouli M, Zagheri Tafreshi M. J.J.o.c.e. Esmaeil. Challenges Clin Nurs Educ Iran Strategies. 2014;2(1):11–22.
Riazi S, et al. Understanding gaps and needs in the undergratue nursing curriculum in Iran: a prelude to design a competency-based curriculum model %J payesh (Health Monitor). Journal. 2020;19(2):145–58.
ADIB HM, Mazhariazad F. Nursing Bachelor’s Education program in Iran and UCLA: A comparative study 2019.
Farokhzadian J, et al. Using a model to design, implement, and evaluate a training program for improving cultural competence among undergraduate nursing students: a mixed methods study. BMC Nurs. 2022;21(1):85.
Sargazi O, et al. Improving the professional competency of psychiatric nurses: results of a stress inoculation training program. Psychiatry Res. 2018;270:682–7.
Faraji A, et al. Evaluation of clinical competence and its related factors among ICU nurses in Kermanshah-Iran: a cross-sectional study. Int J Nurs Sci. 2019;6(4):421–5.
Atashzadeh-Shoorideh F, et al. Essential dimensions of professional competency examination in Iran from academic and clinical nurses’ perspective: a mixed-method study. J Educ Health Promot. 2021;10:414.
Purabdollah M, et al. Comparison of the Iranian and scandinavian bachelor of nursing curriculum (Sweden): a scoping review. J Educ Health Promotion. 2023;12(1):389.
Benner P. J.B.o.s., technology and society, using the Dreyfus model of skill acquisition to describe and interpret skill acquisition and clinical judgment in nursing practice and education . 2004. 24(3): p. 188–99.
World Health Organization. Nurse educator core competencies. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization. 2016 [cited 23 June 2023; https://www.who.int/hrh/nursing_midwifery/nurse_educator050416.pdf .
Purabdollah M, et al. Competencies expected of undergraduate nursing students: a scoping review. Nurs Open. 2023;10(12):7487–508.
Bondy KN. Clinical evaluation of student performance: the effects of criteria on accuracy and reliability. Res Nurs Health. 1984;7(1):25–33.
NLf N. Outcomes for graduates of practical/vocational, diploma, associate degree, baccalaureate, master’s, practice doctorate, and research doctorate programs in nursing . New York 2010; 201]. https:api.semanticscholar.org/corpus ID: 68620057.
Aguayo-González M, Castelló-Badía M, Monereo-Font C. Critical incidents in nursing academics: discovering a new identity. Rev Bras Enferm. 2015;68(2):195–202. 219 – 27.
Scott Imus FJJNEP. Nurse anesthesia student’s personality characteristics and academic performance: A big five personality model perspective 2019. 9: pp. 47–55.
Neishabouri M, Ahmadi F, Kazemnejad A. Iranian nursing students’ perspectives on transition to professional identity: a qualitative study. Int Nurs Rev. 2017;64(3):428–36.
Zheng S, et al. New nurses’ experience during a two year transition period to clinical practice: a phenomenological study. Nurse Educ Today. 2023;121:105682.
Aryuwat P, et al. An integrative review of resilience among nursing students in the context of nursing education. Nurs Open. 2023;10(5):2793–818.
Ayaz-Alkaya S, Simones J. Nursing education stress and coping behaviors in Turkish and the United States nursing students: a descriptive study. Nurse Educ Pract. 2022;59:103292.
Akhtar-Danesh N, et al. Perceptions of professionalism among nursing faculty and nursing students. West J Nurs Res. 2013;35(2):248–71.
Keeling J, Templeman J. An exploratory study: student nurses’ perceptions of professionalism. Nurse Educ Pract. 2013;13(1):18–22.
Nilsson J, et al. Development and validation of a new tool measuring nurses self-reported professional competence–the nurse professional competence (NPC) scale. Nurse Educ Today. 2014;34(4):574–80.
Berkow S, et al. Assessing new graduate nurse performance. J Nurs Adm. 2008;38(11):468–74.
Lofmark A, Smide B, Wikblad K. Competence of newly-graduated nurses–a comparison of the perceptions of qualified nurses and students. J Adv Nurs. 2006;53(6):721–8.
Park E, Choi J. Attributes associated with person-centered care competence among undergraduate nursing students. Res Nurs Health. 2020;43(5):511–9.
Tong V, Epeneter BJ. A comparative study of newly licensed registered nurses’ stressors: 2003 and 2015. J Contin Educ Nurs. 2018;49(3):132–40.
Florin J, et al. Educational support for research utilization and capability beliefs regarding evidence-based practice skills: a national survey of senior nursing students. J Adv Nurs. 2012;68(4):888–97.
Reid J, et al. Enhancing utility and understanding of evidence based practice through undergraduate nurse education. BMC Nurs. 2017;16:58.
Phillips JM, Cullen D. Improving the adoption of evidence-based practice through RN-to-BSN education. J Contin Educ Nurs. 2014;45(10):467–72.
Stievano A, Tschudin V. The ICN code of ethics for nurses: a time for revision. Int Nurs Rev. 2019;66(2):154–6.
Ministry of Education and Research. Norwegian qualifications framework: levels and learning outcome descriptors… 2011 [cited 23 June 2023; https://www.regjeringen.no/contentassets/e579f913fa1d45c2bf2219afc726670b/nkr.pdf .
Chen Q, et al. Differences in evidence-based nursing practice competencies of clinical and academic nurses in China and opportunities for complementary collaborations: a cross‐sectional study. J Clin Nurs. 2023;32(13–14):3695–706.
Missen K, McKenna L, Beauchamp A. Registered nurses’ perceptions of new nursing graduates’ clinical competence: a systematic integrative review. Nurs Health Sci. 2016;18(2):143–53.
Leonardsen AL, et al. Nurses’ perspectives on technical skill requirements in primary and tertiary healthcare services. Nurs Open. 2020;7(5):1424–30.
Duchscher JE. B.J.J.o.a.n. Transition Shock: Initial Stage role Adaptation New Graduated Registered Nurses. 2009;65(5):1103–13.
Ajemba MN, Ikwe C, Iroanya JC. Effectiveness of simulation-based training in medical education: assessing the impact of simulation-based training on clinical skills acquisition and retention: a systematic review. World J Adv Res Reviews. 2024;21(1):1833–43.
Krystallidou D et al. Interprofessional education for healthcare professionals. A BEME realist review of what works, why, for whom and in what circumstances in undergraduate health sciences education: BEME Guide No. 83 Medical Teacher, 2024: pp. 1–18.
Sun Y, et al. Critical thinking abilities among newly graduated nurses: a cross-sectional survey study in China. Nurs Open. 2023;10(3):1383–92.
Download references
Acknowledgements
The authors extend their gratitude to all the nursing students and faculties who took part in this study.
This article is part of research approved with the financial support of the deputy of research and technology of Tabriz University of Medical Sciences.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Nursing, Khoy University of Medical Sciences, Khoy, Iran
Majid Purabdollah
Medical Education Research Center, Health Management and Safety Promotion Research Institute, Tabriz University of Medical Sciences, Tabriz, Iran
Majid Purabdollah, Vahid Zamanzadeh, Akram Ghahramanian, Leila Valizadeh, Saeid Mousavi & Mostafa Ghasempour
Department of Medical-Surgical Nursing, School of Nursing and Midwifery, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran
Vahid Zamanzadeh
Department of Medical Surgical Nursing, Faculty of Nursing and Midwifery, Tabriz University of Medical Sciences, Tabriz, Iran
Akram Ghahramanian & Mostafa Ghasempour
Department of Pediatric Nursing, School of Nursing and Midwifery, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran
Leila Valizadeh
Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, Assistant Professor of Biostatistics, School of Health, Tabriz University of Medical Sciences, Tabriz, Iran
Saeid Mousavi
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
M P: conceptualized the study, data collection, analysis and interpretation, drafting of manuscript; V Z: conceptualized the study, analysis and interpretation, drafting of manuscript; LV: conceptualized the study, data collection and analysis, manuscript revision; A Gh: conceptualized the study, data collection, analysis, and drafting of manuscript; S M: conceptualized the study, analysis, and drafting of manuscript; M Gh: data collection, analysis, and interpretation, drafting of manuscript; All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
All the participants voluntarily participated in this study and provided written informed consent. The study was approved by the ethics committee of the Tabriz University of Medical Sciences (Ethical Code: IR.TBZMED.REC.1400.791) and all methods were performed in accordance with relevant guidelines and regulations.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Purabdollah, M., Zamanzadeh, V., Ghahramanian, A. et al. Competency gap among graduating nursing students: what they have achieved and what is expected of them. BMC Med Educ 24 , 546 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-024-05532-w
Download citation
Received : 23 November 2023
Accepted : 07 May 2024
Published : 16 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-024-05532-w
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Nursing education
- Self-Assessment
- Nursing students
- Professional Competency Professional
BMC Medical Education
ISSN: 1472-6920
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
- General enquiries: [email protected]
- Open access
- Published: 13 May 2024
Sexual and reproductive health implementation research in humanitarian contexts: a scoping review
- Alexandra Norton 1 &
- Hannah Tappis 2
Reproductive Health volume 21 , Article number: 64 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
202 Accesses
6 Altmetric
Metrics details
Meeting the health needs of crisis-affected populations is a growing challenge, with 339 million people globally in need of humanitarian assistance in 2023. Given one in four people living in humanitarian contexts are women and girls of reproductive age, sexual and reproductive health care is considered as essential health service and minimum standard for humanitarian response. Despite growing calls for increased investment in implementation research in humanitarian settings, guidance on appropriate methods and analytical frameworks is limited.
A scoping review was conducted to examine the extent to which implementation research frameworks have been used to evaluate sexual and reproductive health interventions in humanitarian settings. Peer-reviewed papers published from 2013 to 2022 were identified through relevant systematic reviews and a literature search of Pubmed, Embase, PsycInfo, CINAHL and Global Health databases. Papers that presented primary quantitative or qualitative data pertaining to a sexual and reproductive health intervention in a humanitarian setting were included.
Seven thousand thirty-six unique records were screened for inclusion, and 69 papers met inclusion criteria. Of these, six papers explicitly described the use of an implementation research framework, three citing use of the Consolidated Framework for Implementation Research. Three additional papers referenced other types of frameworks used in their evaluation. Factors cited across all included studies as helping the intervention in their presence or hindering in their absence were synthesized into the following Consolidated Framework for Implementation Research domains: Characteristics of Systems, Outer Setting, Inner Setting, Characteristics of Individuals, Intervention Characteristics, and Process.
This review found a wide range of methodologies and only six of 69 studies using an implementation research framework, highlighting an opportunity for standardization to better inform the evidence for and delivery of sexual and reproductive health interventions in humanitarian settings. Increased use of implementation research frameworks such as a modified Consolidated Framework for Implementation Research could work toward both expanding the evidence base and increasing standardization.
Plain English summary
Three hundred thirty-nine million people globally were in need of humanitarian assistance in 2023, and meeting the health needs of crisis-affected populations is a growing challenge. One in four people living in humanitarian contexts are women and girls of reproductive age, and provision of sexual and reproductive health care is considered to be essential within a humanitarian response. Implementation research can help to better understand how real-world contexts affect health improvement efforts. Despite growing calls for increased investment in implementation research in humanitarian settings, guidance on how best to do so is limited. This scoping review was conducted to examine the extent to which implementation research frameworks have been used to evaluate sexual and reproductive health interventions in humanitarian settings. Of 69 papers that met inclusion criteria for the review, six of them explicitly described the use of an implementation research framework. Three used the Consolidated Framework for Implementation Research, a theory-based framework that can guide implementation research. Three additional papers referenced other types of frameworks used in their evaluation. This review summarizes how factors relevant to different aspects of implementation within the included papers could have been organized using the Consolidated Framework for Implementation Research. The findings from this review highlight an opportunity for standardization to better inform the evidence for and delivery of sexual and reproductive health interventions in humanitarian settings. Increased use of implementation research frameworks such as a modified Consolidated Framework for Implementation Research could work toward both expanding the evidence base and increasing standardization.
Peer Review reports
Over the past few decades, the field of public health implementation research (IR) has grown as a means by which the real-world conditions affecting health improvement efforts can be better understood. Peters et al. put forward the following broad definition of IR for health: “IR is the scientific inquiry into questions concerning implementation – the act of carrying an intention into effect, which in health research can be policies, programmes, or individual practices (collectively called interventions)” [ 1 ].
As IR emphasizes real-world circumstances, the context within which a health intervention is delivered is a core consideration. However, much IR implemented to date has focused on higher-resource settings, with many proposed frameworks developed with particular utility for a higher-income setting [ 2 ]. In recognition of IR’s potential to increase evidence across a range of settings, there have been numerous reviews of the use of IR in lower-resource settings as well as calls for broader use [ 3 , 4 ]. There have also been more focused efforts to modify various approaches and frameworks to strengthen the relevance of IR to low- and middle-income country settings (LMICs), such as the work by Means et al. to adapt a specific IR framework for increased utility in LMICs [ 2 ].
Within LMIC settings, the centrality of context to a health intervention’s impact is of particular relevance in humanitarian settings, which present a set of distinct implementation challenges [ 5 ]. Humanitarian responses to crisis situations operate with limited resources, under potential security concerns, and often under pressure to relieve acute suffering and need [ 6 ]. Given these factors, successful implementation of a particular health intervention may require different qualities than those that optimize intervention impact under more stable circumstances [ 7 ]. Despite increasing recognition of the need for expanded evidence of health interventions in humanitarian settings, the evidence base remains limited [ 8 ]. Furthermore, despite its potential utility, there is not standardized guidance on IR in humanitarian settings, nor are there widely endorsed recommendations for the frameworks best suited to analyze implementation in these settings.
Sexual and reproductive health (SRH) is a core aspect of the health sector response in humanitarian settings [ 9 ]. Yet, progress in addressing SRH needs has lagged far behind other services because of challenges related to culture and ideology, financing constraints, lack of data and competing priorities [ 10 ]. The Minimum Initial Service Package (MISP) for SRH in Crisis Situations is the international standard for the minimum set of SRH services that should be implemented in all crisis situations [ 11 ]. However, as in other areas of health, there is need for expanded evidence for planning and implementation of SRH interventions in humanitarian settings. Recent systematic reviews of SRH in humanitarian settings have focused on the effectiveness of interventions and service delivery strategies, as well as factors affecting utilization, but have not detailed whether IR frameworks were used [ 12 , 13 , 14 , 15 ]. There have also been recent reviews examining IR frameworks used in various settings and research areas, but none have explicitly focused on humanitarian settings [ 2 , 16 ].
Given the need for an expanded evidence base for SRH interventions in humanitarian settings and the potential for IR to be used to expand the available evidence, a scoping review was undertaken. This scoping review sought to identify IR approaches that have been used in the last ten years to evaluate SRH interventions in humanitarian settings.
This review also sought to shed light on whether there is a need for a common framework to guide research design, analysis, and reporting for SRH interventions in humanitarian settings and if so, if there are any established frameworks already in use that would be fit-for-purpose or could be tailored to meet this need.
The Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) extension for scoping reviews was utilized to guide the elements of this review [ 17 ]. The review protocol was retrospectively registered with the Open Science Framework ( https://osf.io/b5qtz ).
Search strategy
A two-fold search strategy was undertaken for this review, which covered the last 10 years (2013–2022). First, recent systematic reviews pertaining to research or evaluation of SRH interventions in humanitarian settings were identified through keyword searches on PubMed and Google Scholar. Four relevant systematic reviews were identified [ 12 , 13 , 14 , 15 ] Table 1 .
Second, a literature search mirroring these reviews was conducted to identify relevant papers published since the completion of searches for the most recent review (April 2017). Additional file 1 includes the search terms that were used in the literature search [see Additional file 1 ].
The literature search was conducted for papers published from April 2017 to December 2022 in the databases that were searched in one or more of the systematic reviews: PubMed, Embase, PsycInfo, CINAHL and Global Health. Searches were completed in January 2023 Table 2 .
Two reviewers screened each identified study for alignment with inclusion criteria. Studies in the four systematic reviews identified were considered potentially eligible if published during the last 10 years. These papers then underwent full-text review to confirm satisfaction of all inclusion criteria, as inclusion criteria were similar but not fully aligned across the four reviews.
Literature search results were exported into a citation manager (Covidence), duplicates were removed, and a step-wise screening process for inclusion was applied. First, all papers underwent title and abstract screening. The remaining papers after abstract screening then underwent full-text review to confirm satisfaction of all inclusion criteria. Title and abstract screening as well as full-text review was conducted independently by both authors; disagreements after full-text review were resolved by consensus.
Data extraction and synthesis
The following content areas were summarized in Microsoft Excel for each paper that met inclusion criteria: publication details including author, year, country, setting [rural, urban, camp, settlement], population [refugees, internally displaced persons, general crisis-affected], crisis type [armed conflict, natural disaster], crisis stage [acute, chronic], study design, research methods, SRH intervention, and intervention target population [specific beneficiaries of the intervention within the broader population]; the use of an IR framework; details regarding the IR framework, how it was used, and any rationale given for the framework used; factors cited as impacting SRH interventions, either positively or negatively; and other key findings deemed relevant to this review.
As the focus of this review was on the approach taken for SRH intervention research and evaluation, the quality of the studies themselves was not assessed.
Twenty papers underwent full-text review due to their inclusion in one or more of the four systematic reviews and meeting publication date inclusion criteria. The literature search identified 7,016 unique papers. After full-text screening, 69 met all inclusion criteria and were included in the review. Figure 1 illustrates the search strategy and screening process.
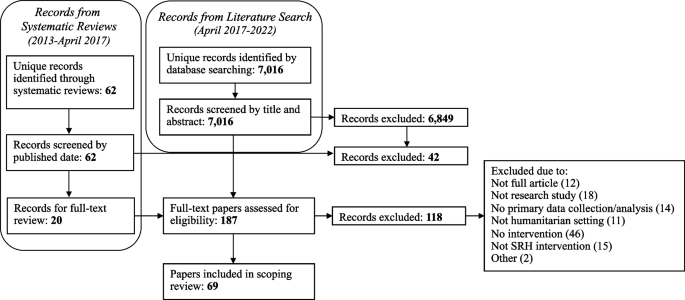
Flow chart of paper identification
Papers published in each of the 10 years of the review timeframe (2013–2022) were included. 29% of the papers originated from the first five years of the time frame considered for this review, with the remaining 71% papers coming from the second half. Characteristics of included publications, including geographic location, type of humanitarian crisis, and type of SRH intervention, are presented in Table 3 .
A wide range of study designs and methods were used across the papers, with both qualitative and quantitative studies well represented. Twenty-six papers were quantitative evaluations [ 18 , 19 , 20 , 21 , 22 , 23 , 24 , 25 , 26 , 27 , 28 , 29 , 30 , 31 , 32 , 33 , 34 , 35 , 36 , 37 , 38 , 39 , 40 , 41 , 42 , 43 ], 17 were qualitative [ 44 , 45 , 46 , 47 , 48 , 49 , 50 , 51 , 52 , 53 , 54 , 55 , 56 , 57 , 58 , 59 , 60 ], and 26 used mixed methods [ 61 , 62 , 63 , 64 , 65 , 66 , 67 , 68 , 69 , 70 , 71 , 72 , 73 , 74 , 75 , 76 , 77 , 78 , 79 , 80 , 81 , 82 , 83 , 84 , 85 , 86 ]. Within the quantitative evaluations, 15 were observational, while five were quasi-experimental, five were randomized controlled trials, and one was an economic evaluation. Study designs as classified by the authors of this review are summarized in Table 4 .
Six papers (9%) explicitly cited use of an IR framework. Three of these papers utilized the Consolidated Framework for Implementation Research (CFIR) [ 51 , 65 , 70 ]. The CFIR is a commonly used determinant framework that—in its originally proposed form in 2009—is comprised of five domains, each of which has constructs to further categorize factors that impact implementation. The CFIR domains were identified as core content areas influencing the effectiveness of implementation, and the constructs within each domain are intended to provide a range of options for researchers to select from to “guide diagnostic assessments of implementation context, evaluate implementation progress, and help explain findings.” [ 87 ] To allow for consistent terminology throughout this review, the original 2009 CFIR domains and constructs are used.
Guan et al. conducted a mixed methods study to assess the feasibility and effectiveness of a neonatal hepatitis B immunization program in a conflict-affected rural region of Myanmar. Guan et al. report mapping data onto the CFIR as a secondary analysis step. They describe that “CFIR was used as a comprehensive meta-theoretical framework to examine the implementation of the Hepatitis B Virus vaccination program,” and implementation themes from multiple study data sources (interviews, observations, examination of monitoring materials) were mapped onto CFIR constructs. They report their results in two phases – Pre-implementation training and community education, and Implementation – with both anchored in themes that they had mapped onto CFIR domains and constructs. All but six constructs were included in their analysis, with a majority summarized in a table and key themes explored further in the narrative text. They specify that most concerns were identified within the Outer Setting and Process domains, while elements identified within the Inner Setting domain provided strength to the intervention and helped mitigate against barriers [ 70 ].
Sarker et al. conducted a qualitative study to assess provision of maternal, newborn and child health services to Rohingya refugees residing in camps in Cox’s Bazar, Bangladesh. They cite using CFIR as a guide for thematic analysis, applying it after a process of inductive and deductive coding to index these codes into the CFIR domains. They utilized three of the five CFIR domains (Outer Setting, Inner Setting, and Process), stating that the remaining two domains (Intervention Characteristics and Characteristics of Individuals) were not relevant to their analysis. They then proposed two additional CFIR domains, Context and Security, for use in humanitarian contexts. In contrast to Guan et al., CFIR constructs are not used nor mentioned by Sarker et al., with content under each domain instead synthesized as challenges and potential solutions. Regarding the CFIR, Sarker et al. write, “The CFIR guided us for interpretative coding and creating the challenges and possible solutions into groups for further clarification of the issues related to program delivery in a humanitarian crisis setting.” [ 51 ]
Sami et al. conducted a mixed methods case study to assess the implementation of a package of neonatal interventions at health facilities within refugee and internally displaced persons camps in South Sudan. They reference use of the CFIR earlier in the study than Sarker et al., basing their guides for semi-structured focus group discussions on the CFIR framework. They similarly reference a general use of the CFIR framework as they conducted thematic analysis. Constructs are referenced once, but they do not specify whether their application of the CFIR framework included use of domains, constructs, or both. This may be in part because they then applied an additional framework, the World Health Organization (WHO) Health System Framework, to present their findings. They describe a nested approach to their use of these frameworks: “Exploring these [CFIR] constructs within the WHO Health Systems Framework can identify specific entry points to improve the implementation of newborn interventions at critical health system building blocks.” [ 65 ]
Three papers cite use of different IR frameworks. Bolan et al. utilized the Theoretical Domains Framework in their mixed methods feasibility study and pilot cluster randomized trial evaluating pilot use of the Safe Delivery App by maternal and newborn health workers providing basic emergency obstetric and newborn care in facilities in the conflict-affected Maniema province of the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC). They used the Theroetical Domains Framework in designing interview questions, and further used it as the coding framework for their analysis. Similar to the CFIR, the Theoretical Domains Framework is a determinant framework that consists of domains, each of which then includes constructs. Bolan et al. utilized the Theoretical Domains Framework at the construct level in interview question development and at the domain level in their analysis, mapping interview responses to eight of the 14 domains [ 83 ]. Berg et al. report using an “exploratory design guided by the principles of an evaluation framework” developed by the Medical Research Council to analyze the implementation process, mechanisms of impact, and outcomes of a three-pillar training intervention to improve maternal and neonatal healthcare in the conflict-affected South Kivu province of the DRC [ 67 , 88 ]. Select components of this evaluation framework were used to guide deductive analysis of focus group discussions and in-depth interviews [ 67 ]. In their study of health workers’ knowledge and attitudes toward newborn health interventions in South Sudan, before and after training and supply provision, Sami et al. report use of the Conceptual Framework of the Role of Attitudes in Evidence-Based Practice Implementation in their analysis process. The framework was used to group codes following initial inductive coding analysis of in-depth interviews [ 72 ].
Three other papers cite use of specific frameworks in their intervention evaluation [ 19 , 44 , 76 ]. As a characteristic of IR is the use of an explicit framework to guide the research, the use of the frameworks in these three papers meets the intention of IR and serves the purpose that an IR framework would have in strengthening the analytical rigor. Castle et al. cite use of their program’s theory of change as a framework for a mixed methods evaluation of the provision of family planning services and more specifically uptake of long-acting reversible contraception use in the DRC. They describe use of the theory of change to “enhance effectiveness of [long-acting reversible contraception] access and uptake.” [ 76 ] Thommesen et al. cite use of the AAAQ (Availability, Accessibility, Acceptability and Quality) framework in their qualitative study assessing midwifery services provided to pregnant women in Afghanistan. This framework is focused on the “underlying elements needed for attainment of optimum standard of health care,” but the authors used it in this paper to evaluate facilitators and barriers to women accessing midwifery services [ 44 ]. Jarrett et al. cite use of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s (CDC) Guidelines for Evaluating Public Health Surveillance Systems to explore the characteristics of a population mobility, mortality and birth surveillance system in South Kivu, DRC. Use of these CDC guidelines is cited as one of four study objectives, and commentary is included in the Results section pertaining to each criteria within these guidelines, although more detail regarding use of these guidelines or the authors’ experience with their use in the study is not provided [ 19 ].
Overall, 22 of the 69 papers either explicitly or implicitly identified IR as relevant to their work. Nineteen papers include a focus on feasibility (seven of which did not otherwise identify the importance of exploring questions concerning implementation), touching on a common outcome of interest in implementation research [ 89 ].
While a majority of papers did not explicitly or implicitly use an IR framework to evaluate their SRH intervention of focus, most identified factors that facilitated implementation when they were present or served as a barrier when absent. Sixty cite factors that served as facilitators and 49 cite factors that served as barriers, with just three not citing either. Fifty-nine distinct factors were identified across the papers.
Three of the six studies that explicitly used an IR framework used the CFIR, and the CFIR is the only IR framework that was used by multiple studies. As previously mentioned, Means et al. put forth an adaptation of the CFIR to increase its relevance in LMIC settings, proposing a sixth domain (Characteristics of Systems) and 11 additional constructs [ 2 ]. Using the expanded domains and constructs as proposed by Means et al., the 59 factors cited by papers in this review were thematically grouped into the six domains: Characteristics of Systems, Outer Setting, Inner Setting, Characteristics of Individuals, Intervention Characteristics, and Process. Within each domain, alignment with CFIR constructs was assessed for, and alignment was found with 29 constructs: eight of Means et al.’s 11 constructs, and 21 of the 39 standard CFIR constructs. Three factors did not align with any construct (all fitting within the Outer Setting domain), and 14 aligned with a construct label but not the associated definition. Table 5 synthesizes the mapping of factors affecting SRH intervention implementation to CFIR domains and constructs, with the construct appearing in italics if it is considered to align with that factor by label but not by definition.
Table 6 lists the CFIR constructs that were not found to have alignment with any factor cited by the papers in this review.
This scoping review sought to assess how IR frameworks have been used to bolster the evidence base for SRH interventions in humanitarian settings, and it revealed that IR frameworks, or an explicit IR approach, are rarely used. All four of the systematic reviews identified with a focus on SRH in humanitarian settings articulate the need for more research examining the effectiveness of SRH interventions in humanitarian settings, with two specifically citing a need for implementation research/science [ 12 , 13 ]. The distribution of papers across the timeframe included in this review does suggest that more research on SRH interventions for crisis-affected populations is taking place, as a majority of relevant papers were published in the second half of the review period. The papers included a wide range of methodologies, which reflect the differing research questions and contexts being evaluated. However, it also invites the question of whether there should be more standardization of outcomes measured or frameworks used to guide analysis and to facilitate increased comparison, synthesis and application across settings.
Three of the six papers that used an IR framework utilized the CFIR. Guan et al. used the CFIR at both a domain and construct level, Sarker et al. used the CFIR at the domain level, and Sami et al. did not specify which CFIR elements were used in informing the focus group discussion guide [ 51 , 65 , 70 ]. It is challenging to draw strong conclusions about the applicability of CFIR in humanitarian settings based on the minimal use of CFIR and IR frameworks within the papers reviewed, although Guan et al. provides a helpful model for how analysis can be structured around CFIR domains and constructs. It is worth considering that the minimal use of IR frameworks, and more specifically CFIR constructs, could be in part because that level of prescriptive categorization does not allow for enough fluidity in humanitarian settings. It also raises questions about the appropriate degree of standardization to pursue for research done in these settings.
The mapping of factors affecting SRH intervention implementation provides an example of how a modified CFIR framework could be used for IR in humanitarian contexts. This mapping exercise found factors that mapped to all five of the original CFIR domains as well as the sixth domain proposed by Means et al. All factors fit well within the definition for the selected domain, indicating an appropriate degree of fit between these existing domains and the factors identified as impacting SRH interventions in humanitarian settings. On a construct level, however, the findings were more variable, with one-quarter of factors not fully aligning with any construct. Furthermore, over 40% of the CFIR constructs (including the additional constructs from Means et al.) were not found to align with any factors cited by the papers in this review, also demonstrating some disconnect between the parameters posed by the CFIR constructs and the factors cited as relevant in a humanitarian context.
It is worth noting that while the CFIR as proposed in 2009 was used in this assessment, as well as in the included papers which used the CFIR, an update was published in 2022. Following a review of CFIR use since its publication, the authors provide updates to construct names and definitions to “make the framework more applicable across a range of innovations and settings.” New constructs and subconstructs were also added, for a total of 48 constructs and 19 subconstructs across the five domains [ 90 ]. A CFIR Outcomes Addendum was also published in 2022, based on recommendations for the CFIR to add outcomes and intended to be used as a complement to the CFIR determinants framework [ 91 ]. These expansions to the CFIR framework may improve applicability of the CFIR in humanitarian settings. Several constructs added to the Outer Setting domain could be of particular utility – critical incidents, local attitudes, and local conditions, each of which could help account for unique challenges faced in contexts of crisis. Sub-constructs added within the Inner Setting domain that seek to clarify structural characteristics and available resources would also be of high utility based on mapping of the factors identified in this review to the original CFIR constructs. As outcomes were not formally included in the CFIR until the 2022 addendum, a separate assessment of implementation outcomes was not undertaken in this review. However, analysis of the factors cited by papers in this review as affecting implementation was derived from the full text of the papers and thus captures content relevant to implementation determinants that is contained within the outcomes.
Given the demonstrated need for additional flexibility within an IR framework for humanitarian contexts, while not a focus of this review, it is worth considering whether a different framework could provide a better fit than the CFIR. Other frameworks have differing points of emphasis that would create different opportunities for flexibility but that do not seem to resolve the challenges experienced in applying the CFIR to a humanitarian context. As one example, the EPIS (Exploration, Preparation, Implementation, Sustainment) Framework considers the impact of inner and outer context on each of four implementation phases; while the constructs within this framework are broader than the CFIR, an emphasis on the intervention characteristics is missing, a domain where stronger alignment within the CFIR is also needed [ 92 ]. Alternatively, the PRISM (Practical, Robust Implementation and Sustainability Model) framework is a determinant and evaluation framework that adds consideration of context factors to the RE-AIM (Reach, Effectiveness, Adoption, Implementation, Maintenance) outcomes framework. It has a stronger emphasis on intervention aspects, with sub-domains to account for both organization and patient perspectives within the intervention. While PRISM does include aspects of context, external environment considerations are less robust and intentionally less comprehensive in scope, which would not provide the degree of alignment possible between the Characteristics of Systems and Outer Setting CFIR domains for the considerations unique to humanitarian environments [ 93 ].
Reflecting on their experience with the CFIR, Sarker et al. indicate that it can be a “great asset” in both evaluating current work and developing future interventions. They also encourage future research of humanitarian health interventions to utilize the CFIR [ 51 ]. The other papers that used the CFIR do not specifically reflect on their experience utilizing it, referring more generally to having felt that it was a useful tool [ 65 , 70 ]. On their use of an evaluation framework, Berg et al. reflected that it lent useful structure and helped to identify aspects affecting implementation that otherwise would have gone un-noticed [ 67 ]. The remaining studies that utilized an IR framework did not specifically comment on their experience with its use [ 72 , 83 ]. While a formal IR framework was not engaged by other studies, a number cite a desire for IR to contribute further detail to their findings [ 21 , 37 ].
In their recommendations for strengthening the evidence base for humanitarian health interventions, Ager et al. speak to the need for “methodologic innovation” to develop methodologies with particular applicability in humanitarian settings [ 7 ]. As IR is not yet routinized for SRH interventions, this could be opportune timing for the use of a standardized IR framework to gauge its utility. Using an IR framework to assess factors influencing implementation of the MISP in initial stages of a humanitarian response, and interventions to support more comprehensive SRH service delivery in protracted crises, could lend further rigor and standardization to SRH evaluations, as well as inform strategies to improve MISP implementation over time. Based on categorizing factors identified by these papers as relevant for intervention evaluation, there does seem to be utility to a modified CFIR approach. Given the paucity of formal IR framework use within SRH literature, it would be worth conducting similar scoping exercises to assess for explicit use of IR frameworks within the evidence base for other health service delivery areas in humanitarian settings. In the interim, the recommended approach from this review for future IR on humanitarian health interventions would be a modified CFIR approach with domain-level standardization and flexibility for constructs that may standardize over time with more use. This would enable use of a common analytical framework and vocabulary at the domain level for stakeholders to describe interventions and the factors influencing the effectiveness of implementation, with constructs available to use and customize as most appropriate for specific contexts and interventions.
This review had a number of limitations. As this was a scoping review and a two-part search strategy was used, the papers summarized here may not be comprehensive of those written pertaining to SRH interventions over the past 10 years. Papers from 2013 to 2017 that would have met this scoping review’s inclusion criteria may have been omitted due to being excluded from the systematic reviews. The review was limited to papers available in English. Furthermore, this review did not assess the quality of the papers included or seek to assess the methodology used beyond examination of the use of an IR framework. It does, however, serve as a first step in assessing the extent to which calls for implementation research have been addressed, and identify entry points for strengthening the science and practice of SRH research in humanitarian settings.
With one in 23 people worldwide in need of humanitarian assistance, and financing required for response plans at an all-time high, the need for evidence to guide resource allocation and programming for SRH in humanitarian settings is as important as ever [ 94 ]. Recent research agenda setting initiatives and strategies to advance health in humanitarian settings call for increased investment in implementation research—with priorities ranging from research on effective strategies for expanding access to a full range of contraceptive options to integrating mental health and psychosocial support into SRH programming to capturing accurate and actionable data on maternal and perinatal mortality in a wide range of acute and protracted emergency contexts [ 95 , 96 ]. To truly advance guidance in these areas, implementation research will need to be conducted across diverse humanitarian settings, with clear and consistent documentation of both intervention characteristics and outcomes, as well as contextual and programmatic factors affecting implementation.
Conclusions
Implementation research has potential to increase impact of health interventions particularly in crisis-affected settings where flexibility, adaptability and context-responsive approaches are highlighted as cornerstones of effective programming. There remains significant opportunity for standardization of research in the humanitarian space, with one such opportunity occurring through increased utilization of IR frameworks such as a modified CFIR approach. Investing in more robust sexual and reproductive health research in humanitarian contexts can enrich insights available to guide programming and increase transferability of learning across settings.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
Availability, Accessibility, Acceptability and Quality
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
Consolidated Framework for Implementation Research
Democratic Republic of the Congo
Exploration, Preparation, Implementation, Sustainment
- Implementation research
Low and middle income country
Minimum Initial Service Package
Practical, Robust Implementation and Sustainability Model
Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses
Reach, Effectiveness, Adoption, Implementation, Maintenance
- Sexual and reproductive health
World Health Organization
Peters DH, et al. Implementation research: what it is and how to do it. RESEARCH METHODS. 2013;347:7.
Means AR, et al. Evaluating and optimizing the consolidated framework for implementation research (CFIR) for use in low- and middle-income countries: a systematic review. Implement Sci. 2020;15(1):17.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Alonge O, et al. How is implementation research applied to advance health in low-income and middle-income countries? BMJ Glob Health. 2019;4(2):e001257.
Ridde V, Pérez D, Robert E. Using implementation science theories and frameworks in global health. BMJ Glob Health. 2020;5(4):e002269.
Gaffey MF, et al. Delivering health and nutrition interventions for women and children in different conflict contexts: a framework for decision making on what, when, and how. Lancet (London, England). 2021;397(10273):543–54.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Singh NS, et al. Delivering health interventions to women, children, and adolescents in conflict settings: what have we learned from ten country case studies? The Lancet. 2021;397(10273):533–42.
Article Google Scholar
Ager A, et al. Strengthening the evidence base for health programming in humanitarian crises. Science. 2014;345(6202):1290–2.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Blanchet K, et al. Evidence on public health interventions in humanitarian crises. The Lancet. 2017;390(10109):2287–96.
Sphere A. The Sphere Handbook | Standards for quality humanitarian response. 2018.
Google Scholar
Barot S. In a State of Crisis: Meeting the Sexual and Reproductive Health Needs of Women in Humanitarian Situations. Guttmacher Policy Rev. 2017;20:7.
Crisis, I.-A.W.G.f.R.H.i., Minimum Initial Service Package. 2020: https://www.unfpa.org/resources/minimum-initial-service-package-misp-srh-crisis-situations .
Casey SE. Evaluations of reproductive health programs in humanitarian settings: a systematic review. Confl Heal. 2015;9(1):S1.
Singh NS, et al. A long way to go: a systematic review to assess the utilisation of sexual and reproductive health services during humanitarian crises. BMJ Glob Health. 2018;3(2):e000682.
Singh NS, et al. Evaluating the effectiveness of sexual and reproductive health services during humanitarian crises: A systematic review. PLoS ONE. 2018;13(7):e0199300.
Warren E, et al. Systematic review of the evidence on the effectiveness of sexual and reproductive health interventions in humanitarian crises. BMJ Open. 2015;5(12):e008226.
Dadich A, Piper A, Coates D. Implementation science in maternity care: a scoping review. Implement Sci. 2021;16(1):16.
Tricco AC, et al. PRISMA Extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR): Checklist and Explanation. Ann Intern Med. 2018;169(7):467–73.
Devine A, et al. Strategies for the prevention of perinatal hepatitis B transmission in a marginalized population on the Thailand-Myanmar border: a cost-effectiveness analysis. BMC Infect Dis. 2017;17(1):552.
Jarrett P, et al. Evaluation of a population mobility, mortality, and birth surveillance system in South Kivu. Democratic Republic of the Congo Disasters. 2020;44(2):390–407.
PubMed Google Scholar
Logie CH, et al. A Psycho-Educational HIV/STI Prevention Intervention for Internally Displaced Women in Leogane, Haiti: Results from a Non-Randomized Cohort Pilot Study. PLoS ONE. 2014;9(2):e89836.
O’Laughlin KN, et al. A cohort study to assess a communication intervention to improve linkage to HIV care in Nakivale Refugee Settlement. Uganda Glob Public Health. 2021;16(12):1848–55.
Adam I. The influence of maternal health education on the place of delivery in conflict settings of Darfur. Sudan Conflict and Health. 2015;9:31.
Adam IF, et al. Relationship between implementing interpersonal communication and mass education campaigns in emergency settings and use of reproductive healthcare services: evidence from Darfur, Sudan. BMJ Open. 2015;5(9):e008285.
Edmond K, et al. Mobile outreach health services for mothers and children in conflict-affected and remote areas: a population-based study from Afghanistan. Arch Dis Child. 2020;105(1):18–25.
Nasir S, et al. Dissemination and implementation of the e-MCHHandbook, UNRWA’s newly released maternal and child health mobile application: a cross-sectional study. BMJ Open. 2020;10(3):e034885.
O’Laughlin KN, et al. Feasibility and acceptability of home-based HIV testing among refugees: a pilot study in Nakivale refugee settlement in southwestern Uganda. BMC Infect Dis. 2018;18(1):332.
Adam I. Evidence from cluster surveys on the association between home-based counseling and use of family planning in conflict-affected Darfur. Int J Gynecol Obstet. 2016;133(2):221–5.
Casey S, et al. Availability of long-acting and permanent family-planning methods leads to increase in use in conflict-affected northern Uganda: Evidence from cross-sectional baseline and endline cluster surveys. Glob Public Health. 2013;8(3):284–97.
Corna F, et al. Supporting maternal mental health of Rohingya refugee women during the perinatal period to promote child health and wellbeing: a field study in Cox’s Bazar. Intervention, the Journal of Mental Health & Psychosocial Support in Conflict Affected Areas. 2019;17(2):160–8.
Glass N, et al. Effectiveness of the Communities Care programme on change in social norms associated with gender-based violence (GBV) with residents in intervention compared with control districts in Mogadishu, Somalia. BMJ Open. 2019;9(3):e023819.
James LE, et al. Development and Testing of a Community-Based Intervention to Address Intimate Partner Violence among Rohingya and Syrian Refugees: A Social Norms-Based Mental Health-Integrated Approach. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18(21):11674.
Le Roux E, et al. Engaging with faith groups to prevent VAWG in conflict-affected communities: results from two community surveys in the DRC. BMC Int Health Hum Rights. 2020;20(1):27.
Morris CN, et al. When political solutions for acute conflict in Yemen seem distant, demand for reproductive health services is immediate: a programme model for resilient family planning and post-abortion care services. Sex Reprod Health Matters. 2019;27(2):1610279.
Anibueze AU, et al. Impact of counseling visual multimedia on use of family planning methods among displaced Nigerian families. Health Promot Int. 2022;37(3):daac060.
Doocy S, et al. Cash-based assistance and the nutrition status of pregnant and lactating women in the Somalia food crisis: A comparison of two transfer modalities. PLoS ONE. 2020;15(4):e0230989.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Draiko CV, et al. The effect of umbilical cord cleansing with chlorhexidine gel on neonatal mortality among the community births in South Sudan: a quasi-experimental study. Pan Afr Med J. 2021;38:78.
Edmond KM, et al. Can community health worker home visiting improve care-seeking and maternal and newborn care practices in fragile states such as Afghanistan? A population-based intervention study. BMC Med. 2018;16(1):106.
Edmond KM, et al. Conditional cash transfers to improve use of health facilities by mothers and newborns in conflict affected countries, a prospective population based intervention study from Afghanistan. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2019;19(1):193.
Bakesiima R, et al. Effect of peer counselling on acceptance of modern contraceptives among female refugee adolescents in northern Uganda: A randomised controlled trial. PLoS ONE. 2021;16(9):e0256479.
Greene MC, et al. Evaluation of an integrated intervention to reduce psychological distress and intimate partner violence in refugees: Results from the Nguvu cluster randomized feasibility trial. PLoS ONE. 2021;16(6):e0252982.
Gupta J, et al. Gender norms and economic empowerment intervention to reduce intimate partner violence against women in rural Côte d’Ivoire: a randomized controlled pilot study. BMC Int Health Hum Rights. 2013;13(1):46.
Hossain M, et al. Working with men to prevent intimate partner violence in a conflict-affected setting: a pilot cluster randomized controlled trial in rural Côte d’Ivoire. BMC Public Health. 2014;14(1):339.
Vaillant J, et al. Engaging men to transform inequitable gender attitudes and prevent intimate partner violence: a cluster randomised controlled trial in North and South Kivu, Democratic Republic of Congo. BMJ Glob Health. 2020;5(5):e002223.
Thommesen T, et al. “The midwife helped me … otherwise I could have died”: women’s experience of professional midwifery services in rural Afghanistan - a qualitative study in the provinces Kunar and Laghman. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2020;20(1):140.
Awasom-Fru A, et al. Doctors’ experiences providing sexual and reproductive health care at Catholic Hospitals in the conflict-affected North-West region of Cameroon: a qualitative study. Reprod Health. 2022;19(1):126.
Kabakian-Khasholian T, Makhoul J, Ghusayni A. “A person who does not have money does not enter”: a qualitative study on refugee women’s experiences of respectful maternity care. BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth. 2022;22(1):748.
Lilleston P, et al. Evaluation of a mobile approach to gender-based violence service delivery among Syrian refugees in Lebanon. Health Policy Plan. 2018;33(7):767–76.
Mugo NS, et al. Barriers Faced by the Health Workers to Deliver Maternal Care Services and Their Perceptions of the Factors Preventing Their Clients from Receiving the Services: A Qualitative Study in South Sudan. Matern Child Health J. 2018;22(11):1598–606.
Persson M, et al. A qualitative study on health care providers’ experiences of providing comprehensive abortion care in Cox’s Bazar, Bangladesh. Conflict and Health. 2021;15(1):6.
Phanwichatkul T, et al. The perceptions and practices of Thai health professionals providing maternity care for migrant Burmese women: An ethnographic study. Women Birth. 2022;35(4):e356–68.
Sarker M, et al. Effective maternal, newborn and child health programming among Rohingya refugees in Cox’s Bazar, Bangladesh: Implementation challenges and potential solutions. PLoS ONE. 2020;15(3):e0230732.
Tousaw E, et al. “Without this program, women can lose their lives”: migrant women’s experiences with the Safe Abortion Referral Programme in Chiang Mai. Thailand Reprod Health Matters. 2017;25(51):58–68.
Tousaw E, et al. “It is just like having a period with back pain”: exploring women’s experiences with community-based distribution of misoprostol for early abortion on the Thailand-Burma border. Contraception. 2018;97(2):122–9.
West L, et al. Factors in use of family planning services by Syrian women in a refugee camp in Jordan. Journal of Family Planning and Reproductive Health Care. 2017;43(2):96–102.
O’Connell KA, et al. Meeting the Sexual and Reproductive Health Needs of Internally Displaced Persons in Ethiopia’s Somali Region: A Qualitative Process Evaluation. Glob Health Sci Pract. 2022;10(5):e2100818.
Orya E, et al. Strengthening close to community provision of maternal health services in fragile settings: an exploration of the changing roles of TBAs in Sierra Leone and Somaliland. BMC Health Serv Res. 2017;17(1):460.
Perera SM, et al. Barriers to seeking post-abortion care in Paktika Province, Afghanistan: a qualitative study of clients and community members. BMC Womens Health. 2021;21(1):390.
Tanabe M, et al. Piloting community-based medical care for survivors of sexual assault in conflict-affected Karen State of eastern Burma. Confl Heal. 2013;7(1):12.
Tran NT, et al. Clinical outreach refresher trainings in crisis settings (S-CORT): clinical management of sexual violence survivors and manual vacuum aspiration in Burkina Faso, Nepal, and South Sudan. Reprod Health Matters. 2017;25(51):103–13.
Yankah E, et al. Feasibility and acceptability of mobile phone platforms to deliver interventions to address gender-based violence among Syrian adolescent girls and young women in Izmir. Turkey Vulnerable Children and Youth Studies. 2020;15(2):133–43.
Muuo S, et al. Barriers and facilitators to care-seeking among survivors of gender-based violence in the Dadaab refugee complex. Sex Reprod Health Matters. 2020;28(1):1722404.
Amsalu R, et al. Essential newborn care practice at four primary health facilities in conflict affected areas of Bossaso, Somalia: a cross-sectional study. Conflict and Health. 2019;13(13):27.
Myers A, et al. Facilitators and barriers in implementing the Minimum Initial Services Package (MISP) for reproductive health in Nepal post-earthquake. Conflict and Health. 2018;12:35.
Santo L.C.d, et al. Feasibility and acceptability of a video library tool to support community health worker counseling in rural Afghan districts: a cross-sectional assessment. Conflict and Health. 2020;14:56.
Sami S, et al. Understanding health systems to improve community and facility level newborn care among displaced populations in South Sudan: a mixed methods case study. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2018;18(1):325.
Amsalu R, et al. Effectiveness of clinical training on improving essential newborn care practices in Bossaso, Somalia: a pre and postintervention study. BMC Pediatr. 2020;20(1):215.
Berg M, Mwambali SN, Bogren M. Implementation of a three-pillar training intervention to improve maternal and neonatal healthcare in the Democratic Republic Of Congo: a process evaluation study in an urban health zone. Glob Health Action. 2022;15(1):2019391.
Castillo M, et al. Turning Disaster into an Opportunity for Quality Improvement in Essential Intrapartum and Newborn Care Services in the Philippines: Pre- to Posttraining Assessments. Biomed Res Int. 2016;2016:1–9.
Foster AM, Arnott G, Hobstetter M. Community-based distribution of misoprostol for early abortion: evaluation of a program along the Thailand-Burma border. Contraception. 2017;96(4):242–7.
Guan TH, et al. Implementation of a neonatal hepatitis B immunization program in rural Karenni State, Myanmar: A mixed-methods study. PLoS ONE. 2021;16(12):e0261470.
Logie, C.H., et al., Mixed-methods findings from the Ngutulu Kagwero (agents of change) participatory comic pilot study on post-rape clinical care and sexual violence prevention with refugee youth in a humanitarian setting in Uganda. Global Public Health, 2022((Logie C.H., [email protected]) Factor-Inwentash Faculty of Social Work, University of Toronto, Toronto, Canada(Logie C.H., [email protected]) Women’s College Research Institute, Women’s College Hospital, Toronto, Canada(Logie C.H., carmen.l).
Sami S, et al. “You have to take action”: changing knowledge and attitudes towards newborn care practices during crisis in South Sudan. Reprod Health Matters. 2017;25(51):124–39.
Smith JR, et al. Clinical care for sexual assault survivors multimedia training: a mixed-methods study of effect on healthcare providers’ attitudes, knowledge, confidence, and practice in humanitarian settings. Confl Heal. 2013;7(1):14.
Stevens A, et al. Folate supplementation to prevent birth abnormalities: evaluating a community-based participatory action plan for refugees and migrant workers on the Thailand-Myanmar border. Public Health. 2018;161:83–9.
Nguyen Toan T, et al. Strengthening healthcare providers’ capacity for safe abortion and postabortion care services in humanitarian settings: lessons learned from the clinical outreach refresher training model (S-CORT) in Uganda, Nigeria, and the Democratic Republic of Congo. Conflict and Health. 2021;15(1):20.
Castle S, et al. Successful programmatic approaches to facilitating IUD uptake: CARE’s experience in DRC. BMC Womens Health. 2019;19(1):104.
Deitch J, et al. “They Love Their Patients”: Client Perceptions of Quality of Postabortion Care in North and South Kivu, the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Global health, science and practice. 2019;7(Suppl 2):S285–98.
Ferreyra C, et al. Evaluation of a community-based HIV test and start program in a conflict affected rural area of Yambio County, South Sudan. PLoS ONE. 2021;16(7):e0254331.
Ho LS, Wheeler E. Using Program Data to Improve Access to Family Planning and Enhance the Method Mix in Conflict-Affected Areas of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Glob Health Sci Pract. 2018;6(1):161–77.
Klabbers RE, et al. Health Worker Perspectives on Barriers and Facilitators of Assisted Partner Notification for HIV for Refugees and Ugandan Nationals: A Mixed Methods Study in West Nile Uganda. AIDS Behav. 2021;25(10):3206–22.
Turner C, et al. Neonatal Intensive Care in a Karen Refugee Camp: A 4 Year Descriptive Study. PLoS ONE. 2013;8(8):e72721.
Vries Id, et al. Key lessons from a mixed-method evaluation of a postnatal home visit programme in the humanitarian setting of Gaza. Eastern Mediterr Health J. 2021;27(6):546–52.
Bolan NE, et al. mLearning in the Democratic Republic of the Congo: A Mixed-Methods Feasibility and Pilot Cluster Randomized Trial Using the Safe Delivery App. Global health, science and practice. 2018;6(4):693–710.
Khan MN, et al. Evaluating feasibility and acceptability of a local psycho-educational intervention for pregnant women with common mental problems affected by armed conflict in Swat, Pakistan: A parallel randomized controlled feasibility trial. Int J Soc Psychiatry. 2017;63(8):724–35.
Hynes M, et al. Using a quality improvement approach to improve maternal and neonatal care in North Kivu, Democratic Republic of Congo. Reprod Health Matters. 2017;25(51):140–50.
Gibbs A, et al. The impacts of combined social and economic empowerment training on intimate partner violence, depression, gender norms and livelihoods among women: an individually randomised controlled trial and qualitative study in Afghanistan. BMJ Glob Health. 2020;5(3):e001946.
Damschroder L, et al. Fostering implementation of health services research findings into practice: a consolidated framework for advancing implementation science. Implementation science: IS; 2009.
Moore GF, et al. Process evaluation of complex interventions: Medical Research Council guidance. BMJ. 2015;350:h1258.
Proctor E, et al. Outcomes for Implementation Research: Conceptual Distinctions, Measurement Challenges, and Research Agenda. Adm Policy Ment Health. 2011;38(2):65–76.
Damschroder LJ, et al. The updated Consolidated Framework for Implementation Research based on user feedback. Implement Sci. 2022;17(1):75.
Damschroder LJ, et al. Conceptualizing outcomes for use with the Consolidated Framework for Implementation Research (CFIR): the CFIR Outcomes Addendum. Implement Sci. 2022;17(1):7.
Aarons GA, Hurlburt M, Horwitz SM. Advancing a Conceptual Model of Evidence-Based Practice Implementation in Public Service Sectors. Administration and Policy in Mental Health and Mental Health Services Research. 2011;38(1):4–23.
Feldstein AC, Glasgow RE. A Practical, Robust Implementation and Sustainability Model (PRISM) for Integrating Research Findings into Practice. The Joint Commission Journal on Quality and Patient Safety. 2008;34(4):228–43.
OCHA. Global Humanitarian Overview 2023. 2022 [cited 2023 8/3/2023]; Available from: https://humanitarianaction.info/node/13073/article/glance-0 . Accessed 8 Mar 2023.
Kobeissi L, et al. Setting research priorities for sexual, reproductive, maternal, newborn, child and adolescent health in humanitarian settings. Confl Heal. 2021;15(1):16.
Save the, C., et al. Roadmap to Accelerate Progress for Every Newborn in Humanitarian Settings 2020 – 2024. 2020. p. 52.
Inter-Agency Working Group on Reproductive Health in, C. Inter-Agency Field Manual on Reproductive Health in Humanitarian Settings. 2018.
Download references
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
The authors received no funding for this study.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Duke University School of Medicine, 40 Duke Medicine Circle, Durham, NC, 27710, USA
Alexandra Norton
Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, 615 N. Wolfe St, Baltimore, MD, 21205, USA
Hannah Tappis
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
AN and HT designed the scoping review. AN conducted the literature search. AN and HT screened records for inclusion. AN extracted data from included studies. Both authors contributed to synthesis of results. AN drafted the manuscript and both authors contributed to editorial changes.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Alexandra Norton .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate, consent for publication, competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1.
. Literature search terms: Exact search terms used in literature search, with additional detail on the methodology to determine search terms and definitions used for each component of the search
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Norton, A., Tappis, H. Sexual and reproductive health implementation research in humanitarian contexts: a scoping review. Reprod Health 21 , 64 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12978-024-01793-2
Download citation
Received : 06 November 2023
Accepted : 12 April 2024
Published : 13 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12978-024-01793-2
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Humanitarian settings
Reproductive Health
ISSN: 1742-4755
- General enquiries: [email protected]
- MEMBER LOGIN
- MEDIA RELATIONS
Military Stress

- ASSESSMENTS
- DOCUMENTARIES

The Good, Bad and Ugly of Stress
- April 19, 2023

Managing that stress, therefore, is an essential element of maintaining a healthy lifestyle. Learning how to manage it can go a long way to improving our mental and physical well-being as well as minimizing health-related issues brought on by stress or anxiety.
What is Stress? It’s critical we recognize what stress looks like, take steps to build resilience, and know where to go for help. Firstly, you have to decide if it is stress or anxiety you feel. Stress is the physical or mental response to an external cause, such as having a lot of work or having an illness. The stressor may be a one-time or short-term occurrence, or it can repeatedly happen over a long time. It can wear you out, leave you jittery, and is harmful to your health, manifesting as anxiety, confusion, poor concentration, and decreased performance.
Stress becomes a problem when it starts to take over your life. According to the Mayo Clinic, symptoms of stress may include: Upset stomach, Headaches Exhaustion and difficulty sleeping, Irritability and heightened reactions, Restlessness and difficulty focusing Weakened immune system Increased risk of anxiety disorder and depression Anxiety, on the other hand, is how your body reacts to stress. Anxiety can be normal such as in public speaking or taking an exam. If anxiety begins to interfere with your life, it could then affect your health in the same way as stress. You may experience problems with sleeping or with your immune, digestive, cardiovascular, and reproductive systems. You also may be at higher risk for developing a mental illness such as an anxiety disorder or depression.
Coping with Stress and Anxiety
Learning what causes or triggers your stress or anxiety and deciding which coping techniques work best for you to reduce your anxiety may take trial and error to discover what works best for you. Here are some tips:
Eliminate stress where you can — a great place to begin is to learn how to say “no” more often. Avoid people who stress you out, and pare down your to-do list. Once you learn how to manage your time more effectively, your stress level will go down.
Accept there are events you can’t control — there are many things in life that are beyond our control. Instead of stressing about what you can’t control, focus on what you can control. This way, your energy can be way more effective.
Think positive thoughts — Negative thoughts lead to negative behavior while being optimistic and positive helps offset difficult situations. Always try to think positively by looking for the upside in every situation. Think about all the things you appreciate in your life, including your own positive qualities.
Add relaxation techniques to your everyday routine. Relaxation promotes overall health and gives you a chance to step away and clear your head. It doesn’t have to be a big time commitment; it can be accomplished with deep breathing exercises, meditation, or even yoga.
Stay healthy and fit. A well-balanced diet and staying active ensures your body is better prepared to fight stress. Exercise relaxes your body and mind while improving your mood. In fact, physical exercise has been proven to play a key role in preventing and reducing the effects of stress.
Get a good night’s rest — getting enough rest is vital. Getting a good night’s sleep will give your body time to recover from stressful events and set you up to face any new challenges.
The Upside of Stress
Although the mere mention of the word stress can conjure up mental images of unpaid bills, work deadlines, or tense family situations, some studies have determined that stress can also be positive.
Psychologists identify this type of stress when we feel excited, and there is no threat or fear. The pulse quickens, and hormones burgeon. Both good and bad stress result in your body releasing hormones, such as adrenaline and cortisol, that trigger common signs of stress: butterflies in the stomach, racing heart, and sweaty palms. Ultimately, what distinguishes good stress from bad is how you react or feel about the experience. We feel this positive type of stress when we ride a roller coaster, for example, compete for a promotion, or go on a first date. There are many triggers for this good stress, and it keeps us feeling alive and excited about life.
Unfortunately, we don’t live in a perfect world — one where we could live stress-free, but if we learn and practice ways to lower our stress levels and focus our energies on what really matters to us, we can overcome the temptations of unhealthy coping mechanisms. These may include alcohol or substance abuse, overeating or eating too little, self-harm, anger or violence, and strained relationships.
We are all unique, and taking the time to try many different things and figure out what combination of skills works for you is well worth doing. Reach out for support. Confide in family and friends, or turn to someone professional. Expressing how you feel can be cathartic. Also, it’s important to express your feelings instead of bottling them up because that can only add to your stress.
If you’re experiencing depression or anxiety, if you’re unable to sleep or enjoy life, or if you’re turning to alcohol or drugs to cope with stress, it’s time to ask for help. Reach out to your doctor or therapist; the National Suicide Prevention Lifeline at 1-800-273-8255; The Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration Helpline at 1-800-662-HELP, or The American Institute for Stress.
By Sue Quigley
Original post Hernando Sun
Photo by Gerd Altmann
More Articles

Post-Traumatic Growth Finding Hope in Adversity

New research reveals stress hormones trigger white blood cells to create pathways for cancer metastasis.

Workplace Stress and Painkiller Dependency: A Hidden Crisis

How to thrive under stress, according to a former Navy SEAL and FBI Agent

7 Ways to Ease Work Stress — Including the Desktop Decoration That Can Dial Down Tension Fast

Combating Workplace Stress with Online Therapy: A Modern Solution for Busy Professionals

Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder and Traumatic Brain Injury, TESI Statistical Analysis. Operations Iraqi and Enduring Freedom.

What Are the Signs of PTSD? 4 Ways to Tell

How Stress-Dumping Can Threaten a Relationship

Northamptonshire Mind revolutionises mental health support with innovative Alpha-Stim partnership
Feeling good about feeling bad, or how guilt can make you better
It’s a complex emotion that can be a tool for growth if you go beyond using it for self-flagellation.
I’ve long since rendered the verdict on myself: I’m guilty. Yes, guilty as charged, guilty in the first degree, guilty on all counts. All my life I’ve felt every inch the guilty party. I’ve even managed to feel guilty about feeling guilty.
It’s amply documented that guilt, especially if excessive and left to persist unchecked, can produce problems ranging from the physical, such as headaches, indigestion and muscle tension, to the mental, chiefly stress, anxiety and depression .
But research also increasingly shows that guilt is a complex, multifaceted emotion, long miscast as little more than nagging neurosis and even masochism. Despite its reputation, guilt — once properly harnessed and leveraged — can be more positive than negative and therefore more tonic than toxic.
Yes, guilt can be good for you, which is why at long last, I’ve come to feel good about, well, sometimes feeling bad.
“We’ve only recently come to understand that guilt — historically perceived strictly as a distressing emotion — can be constructive,” says Will Bynum, an associate professor of family medicine and community health at the Duke University School of Medicine, who has studied guilt as well as its cousin, shame . “We now have a new concept of guilt as a potential source for growth. It can point us toward actions we can take to improve our lives.”
Could’ve, should’ve, would’ve
The American Psychological Association defines guilt as “a self-conscious emotion characterized by a painful appraisal of having done (or thought) something that is wrong and often by a readiness to take action designed to undo or mitigate this wrong.”
It’s a feeling of could’ve, should’ve, would’ve that’s often termed a “self-aware” emotion. It’s a twinge in our guts, a voice whispering warnings in our heads — it’s the reminder that we have a conscience.
Almost everyone at some point — except, say, psychopaths and sociopaths — feels the pang of guilt. In one study , 68 percent of participants reported having felt guilty at some point.
In the best case, guilt signals that we’ve come up short of the standards of behavior that we set for ourselves, as well as those of our culture and society.
“Guilt is a moral emotion,” says June Tangney, a professor of psychology at George Mason University and author of the book “ Shame and Guilt .” Her research on guilt is regarded as seminal and is widely cited. “Recognizing your guilt can be healthy for your relationships. Your guilt about your behavior focuses you on the person you harmed and directs you toward how you can do better in the future.”
Upset stomach, electric skin
Guilt is often experienced not only psychologically but also physically in the moment.
In a 2021 study, researchers interviewed Canadian adults and then showed them videos related to their interview responses and designed to induce guilt. For example, the researchers wrote, “before a video about starving children in need of donations, a participant would see ‘You donate less than the average Canadian.’”
Researchers found that guilt affected the autonomic nervous system, raising electrical activity in the skin, upsetting gastric rhythms in the stomach and lowering swallowing rates.
We humans have no difficulty finding satisfactory rationales for our guilt. A 2022 study identified 1,515 reasons that 604 German adults gave for feeling guilty in a survey.
Telling lies or withholding information or the truth topped the list, followed by spending too little time with or inadequately taking care of family members . Women proved more likely to feel guilty about family issues and the well-being of others, whereas men felt guilt more often about misbehavior and relationship problems.
The researchers said the disparity might reflect gender differences in Germany, where women “on average, spend 52.4% more time per day on unpaid care work … than men.” But they also equivocated, adding that “such differences should also not be overinterpreted or overemphasized.”
Nature and nurture
I’ve personally never lacked for reasons to feel guilty.
Growing up, I felt guilty because my mother had been stricken with spinal meningitis in infancy that left her profoundly deaf. I felt bad for her. It seemed unjust that I could hear. All through boyhood, guilt also gnawed at me for misbehaving in school, getting poor grades and being insufficiently athletic.
Into my mid-30s, I faulted myself — altogether justifiably, mind you — for my failures to work harder, earn or save enough money, establish my independence sooner and take my family responsibilities more seriously.
As in my case, guilt typically emerges early in our lives.
“Guilt comes from both nature and nurture,” says Michael Lewis, developmental psychologist and professor emeritus at the Rutgers Robert Wood Johnson Medical School, who has researched emotions in infancy and childhood.
“It has to do with the standards your parents expect you to meet as a child, and how they then respond to your missing the mark,” Lewis said. “If they encourage you to take responsibility for your failures, you’re given an opportunity to learn from the experience and improve.”
Trading remorse for relief
Of what, exactly, do I, at age 72, still feel guilty today? Much. But if I’ve learned anything (and, for the record, my wife seriously doubts it), it’s that feeling bad can occasionally be good for you.
My lifelong guilt trip has evolved into a guilty pleasure of sorts. Guilt fuels me with fresh incentive to do and be better. It forces me to recognize my mistakes, fulfill my obligations and apologize to those I’ve wronged. My guilt insistently steers me toward virtue.
I now see guilt as inherently instructive, tangible proof that I’ve learned from my misdeeds.
But this attitude is far from easy to achieve. Guilt affects us for good or for ill depending on how we experience and manage it. The trick to replacing remorse with relief, really, is to learn how to distinguish between the healthy guilt that can help you and the unhealthy kind. But how do we best acknowledge, address and channel our guilt?
Healthy guilt is realistic and justified, a self-correction that promotes personal development, whereas unhealthy guilt is distorted and festers, eating into our self-respect and stunting our growth.
To get better at managing guilt, for starters, accept responsibility for your guilt rather than try to deny its existence. Research says to give yourself credit for holding yourself accountable. Learn from your mistakes, make amends accordingly and, above all, forgive yourself.
“Anticipate your guilt,” advises Roy F. Baumeister, professor of psychology at the University of Queensland in Australia, president of the International Positive Psychology Association and author of numerous landmark studies about guilt .
“Thinking ahead about guilt works even better than later acknowledging it,” Baumeister says. “If you get an inkling you’re about to do wrong to someone and will feel guilty about it afterwards, just stop yourself. The sooner you see the guilt coming, the better prepared you’ll be to prevent it.”
Get Well+Being tips straight to your inbox

Read more from Well+Being
Well+Being shares news and advice for living well every day. Sign up for our newsletter to get tips directly in your inbox.
Diabetes, air pollution and alcohol consumption could be the biggest risk factors for dementia .
Dairy vs. plant milk : Which is better?
Why is my gas so smelly ? Gender, diet and plane rides can play a role.
Quitting can be a superpower that helps your mental health. Here’s how to quit smarter .
Our relationships with pets can be strong and uncomplicated.


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Qualities of Good Research 1. Good research is anchored on a sound research question. A sound research question is one of the most important characteristics of good research. In fact, formulating one is embedded in the curricula of research-heavy programs like engineering and physics degrees and careers.In 2010, Farrugia et al. proposed that developing a research question is the most important ...
Fundamental Criteria: General Research Quality. Various researchers have put forward criteria for evaluating qualitative research, which have been summarized in Table 3.Also, the criteria outlined in Table 4 effectively deliver the various approaches to evaluate and assess the quality of qualitative work. The entries in Table 4 are based on Tracy's "Eight big‐tent criteria for excellent ...
Becoming a good researcher requires time, dedication, key skills and attributes, and a lot of hard work! (Image by cookie_studio on Freepik) Year after year, people with different personalities and backgrounds step into the field of research eager to develop the key qualities of a good researcher, only to find themselves faced with anxiety and self-doubt.
Curiosity can fuel a researcher's passion for their work. 3. Perseverance: "Talent is quite common; it is not intelligence that is scarce, but perseverance.". - Doris Lessing. Researchers should also possess perseverance — the grit and determination to keep going, even in the face of setbacks and obstacles.
Theory and Methodology. Good research follows from a reasonable starting point, a theoretical concept or perspective. Quantitative research uses a positivist perspective in which evidence is objectively and systematically obtained to prove a causal model or hypothesis; what works is the focus. 3 Alternatively, qualitative approaches focus on how and why something works, to build understanding ...
makes for good qualitative research'' (Tracy, 2010, p. 837) To decide what represents good qualitative research is highly debatable. There are numerous methods that are contained within qualitative research and that are estab-lished on diverse philosophical perspectives. Bryman et al., (2008, p. 262) suggest that ''It is widely assumed that
In this editorial, we attempt to answer what characterizes research quality before we first examine how to achieve and subsequently evidence research of high quality. 2. What research quality is. 2.1. What research quality historically is. Research assessment plays an essential role in academic appointments, in annual performance reviews, in ...
good qualitative research and one of the most common omissions in qualitative articles. If the sample is representing the themes around an issue using theoretical sampling, cases will be collected until issues are felt to be 'theoretically saturated'; i.e. no new relevant data seem to emerge (Strauss & Corbin, 1990).
Organization and planning. Acquire knowledge of research methodology. Critical and positive attitude towards difficulties and failure. Prioritization of objectives and time management. The importance of a good mentor. Establishment of a network of collaborators and teamwork. Maintain a balance between clinical and research activity.
INTRODUCTION. Scientific research is usually initiated by posing evidenced-based research questions which are then explicitly restated as hypotheses.1,2 The hypotheses provide directions to guide the study, solutions, explanations, and expected results.3,4 Both research questions and hypotheses are essentially formulated based on conventional theories and real-world processes, which allow the ...
Answer: Good quality research is one that provides robust and ethical evidence. A good research must revolve around a novel question and must be based on a feasible study plan. It must make a significant contribution to scientific development by addressing an unanswered question or by solving a problem or difficulty that existed in the real world.
The truly good researcher perseveres. They accept this disappointment, learn from the failure, reevaluate their experiment, and keep moving forward. 4. Collaboration. Teamwork makes the dream work. Contrary to the common perception of the solitary genius in their lab, research is an extremely collaborative process.
A good research is doable and replicable in future. It must be based on a logical rationale and tied to theory. It must generate new questions or hypotheses for incremental work in future. It must directly or indirectly address some real world problem. It must clearly state the variables of the experiment.
This is a great way to open the door for your work to reach potential benefits in a wider audience. 7. Communication Skills. Good quality research also factors in the ability of the researcher to communicate the findings clearly and effectively. Communication is yet another important quality of academic research.
Critical thinking refers to a person's ability to think rationally and analyze and interpret information and make connections. This skill is important in research because it allows individuals to better gather and evaluate data and establish significance. Common critical thinking skills include: Open-mindedness. Inference.
Check out the 10 qualities of a good researcher:-. 1. Inquisitiveness: The Craving for Knowledge. Think of a good researcher as that friend who's always full of questions. They're the eternal curious cats of the academic world, forever wondering, forever seeking, and forever hungry for knowledge.
Importance of quality research. Quality research helps us better understand complex problems. It enables us to make decisions based on facts and evidence. And it empowers us to solve real-world issues. Without quality research, we can't advance knowledge or identify trends and patterns.
Writing about the 10 Qualities of a Good Researcher represents a great responsibility since it is not simple to assemble in a concise manner all the important qualities of a good researcher. Knowing the difficulties lying ahead, I would like to suggest the following qualities: interest, motivation, inquisitiveness, commitment, sacrifice ...
This research work described the basics and systematic steps to follow in writing a good scientific thesis/article. ... the systematic approaches in writing research, the characteristics of a good ...
Example: Research aim. To examine contributory factors to muscle retention in a group of elderly people. Example: Research objectives. To assess the relationship between sedentary habits and muscle atrophy among the participants. To determine the impact of dietary factors, particularly protein consumption, on the muscular health of the ...
Characteristics of Good Research. 1. The purpose of the research should be clearly defined (aims and. objectives). 2. The need and significance of the topic of research must be stated. 3. Research ...
9 Qualities of Research. Good research generates dependable data. It is conducted by professionals and can be used reliably for decision-making. It is thus of crucial importance that research should be made acceptable to the audience for which research should possess some desirable qualities in terms of. 9 qualities of research are;
11. Analytical in his research: A researcher should be analytical and should also be able to exhibit sound judgment. Proper analysis of issues is key to having a good research work. His ability to reason rationally and give sound judgment affects the quality of the research work. qualities of a good researcher.
Three Gallup studies shed light on when and why AI is being used at work — and how employees and customers really feel about it. Leaders who are exploring how AI might fit into their business ...
Background Nurses' professional competencies play a significant role in providing safe care to patients. Identifying the acquired and expected competencies in nursing education and the gaps between them can be a good guide for nursing education institutions to improve their educational practices. Methods In a descriptive-comparative study, students' perception of acquired competencies and ...
Background Meeting the health needs of crisis-affected populations is a growing challenge, with 339 million people globally in need of humanitarian assistance in 2023. Given one in four people living in humanitarian contexts are women and girls of reproductive age, sexual and reproductive health care is considered as essential health service and minimum standard for humanitarian response ...
Getting a good night's sleep will give your body time to recover from stressful events and set you up to face any new challenges. The Upside of Stress. Although the mere mention of the word stress can conjure up mental images of unpaid bills, work deadlines, or tense family situations, some studies have determined that stress can also be ...
I've long since rendered the verdict on myself: I'm guilty. Yes, guilty as charged, guilty in the first degree, guilty on all counts. All my life I've felt every inch the guilty party. I ...