What is Transformational Leadership? (Examples + How-To)

You're on a quest to become a better leader, and you've stumbled upon a term that keeps popping up: transformational leadership. You're in the right place to find out what it means, why it matters, and how it could change your life and the lives of those you lead.
Transformational Leadership is a leadership style where the leader inspires and motivates team members to exceed expectations, fosters an environment of trust and respect, and ultimately drives positive organizational change.
Don't just skim the surface; let's get into the nitty-gritty of transformational leadership. We'll uncover its roots, its impact, organizational effectiveness, and even its criticisms.

What is Transformational Leadership?
Transformational Leadership is a term that gets tossed around a lot, especially when people talk about great leaders who've made a real difference. But what does it actually mean?
Imagine you're in a boat and everyone's rowing. But there's a catch: You're not getting anywhere because everyone's rowing in different directions. A great transformational leader steps in and not only aligns everyone to row in the same direction but also makes them want to row harder and faster.
In simpler terms, a good transformational leaders' leader isn't just a boss; they're more like a mentor or coach.
Transformational Leadership is when you, the leader, motivate and inspire your team to exceed usual expectations and performance levels. You achieve this through various ways: communicating a compelling vision, fostering creativity, and building strong, respectful relationships with team members.
Importantly, transformational organizational leadership is not about directing or controlling. It's about nurturing growth—in both individuals and organizations.
The History of Transformational Leadership
You now know what transformational leadership is, but where did it come from? The concept of transformational leadership isn't as new as you might think; it has roots that date back to the late 20th century.
The term was first introduced in a presidential address by sociologist James V. Downton in 1973. But the concept really gained traction when James MacGregor Burns penned his seminal book "Leadership" in 1978.
Burns drew a line between transactional leaders , those who operate on an exchange basis like "do this for me, and I'll give you that," and transformational leaders , who ignite the internal motivations of their team members to exceed expectations.
Burns argued that effective transformational leaders create a more ethical and empowering environment.
The 1980s brought more meat to the bones of transformational leadership theory. Researchers like Bernard M. Bass expanded upon Burns' ideas.
Bass introduced the concept of Charismatic Leadership , which is a component of transformational leadership. He said that transformational leaders often have strong sense of charisma, but charisma alone isn't enough. You also need to empower your team, listen to them, and encourage their personal growth.
By now, you're starting to see how this leadership style has evolved over time. Knowing its history gives you a richer understanding of why it's so impactful today.
And as you'll find out, transformational leadership is not just a theory but a practice that has been embraced across diverse settings—from businesses to politics and education.
The Four 'I's of Transformational Leadership
You're probably thinking, "Okay, transformational leadership sounds great, but what makes it tick?" Experts usually break it down into four key components, often referred to as the Four 'I's.
First up is Idealized Influence . This is all about being a role model. You set high standards for ethical behavior and show dedication. When your team sees you walking the walk, they're more likely to trust you and follow your lead.
Second is Inspirational Motivation . Imagine you're a coach giving a halftime speech. You're uplifting your team, filling them with energy and enthusiasm for the tasks ahead. You set exciting visions for the future and show how everyone plays a vital part in reaching that vision.
The third 'I' stands for Intellectual Stimulation . Here, you're not just giving orders; you're encouraging your team to think creatively and solve problems. Imagine a teacher who doesn't just want the correct answer but challenges students to explain how they got there.
Last but not least, is Individualized Consideration . This means you're tuned into each team member's needs and potential for growth. It's like a gardener knowing exactly how much water, sunlight, and nutrients each type of plant in the garden needs. You provide coaching, give feedback, and open doors for individual consideration and opportunities that will help them grow.
Together, these four components make the transformational leadership style what it is—a holistic approach to guiding a team to reach and exceed their potential.
Transformational Leadership vs Other Leadership Styles
By now, you're getting a pretty good grip on what transformational leadership entails. But how does it stack up against other leadership styles? After all, it's not the only game in town.
You might have heard of Authoritarian Leadership , where the leader calls all the shots and expects the team to follow without question. It's like a strict parent dictating every move their child makes.
Transformational leadership, in contrast, gives room for creative thinking and individual growth. Instead of telling you what to do, a transformational leader guides you in discovering the best course of action for yourself.
Then there's Laissez-Faire Leadership , a style of organizational structure where the leader takes a hands-off approach. Picture a laid-back supervisor who lets the team figure things out on their own.
While this approach can foster independence, it often lacks the motivational spark that transformational leadership provides.
Don't forget about Transactional Leadership , which we touched on earlier. This management style is more about give-and-take. It's like a business deal: "You complete this task, you get a reward."
While transactional leadership can be effective, it doesn't aim to transform or inspire on a deeper level.
Transformational leadership has its own unique flavor. It combines the best of different worlds: it's motivating but not controlling, structured but not rigid, and inspirational without being unrealistic.
Examples of Transformational Leaders

1) Nelson Mandela
First, let's talk about Nelson Mandela. He led South Africa out of apartheid and into a new era of racial equality and democracy.
Mandela didn't just give orders; he inspired a nation. His leadership wasn't about transactions; it was about transformative change.
He exemplifies Idealized Influence , one of the Four 'I's we talked about earlier, by being a moral compass for his followers.
2) Oprah Winfrey
Next up is Oprah Winfrey. She broke multiple barriers in her career, and her impact extends beyond television to education and philanthropy.
Oprah is a fantastic example of Inspirational Motivation . She has the unique ability to connect with people, inspiring them to take action and make positive changes in their lives.
3) Steve Jobs
Steve Jobs, co-founder of Apple, transformed the way we interact with technology. He pushed for innovative designs and user-friendly interfaces, changing our relationship with computers, smartphones, and tablets.
Jobs exemplifies Intellectual Stimulation by encouraging his team to think differently and challenge the status quo.
4) Malala Yousafzai
Malala Yousafzai stood up for girls' education in Pakistan, despite facing life-threatening dangers. Her courage and advocacy have inspired a global movement.
Malala represents Inspirational Motivation and Idealized Influence by standing up for what she believes in and motivating others to do the same.
5) Richard Branson
The founder of the Virgin Group, Richard Branson, is known for his adventurous spirit and willingness to take risks. He has created a culture that fosters innovation and creativity across various industries, from music to air travel.
Branson illustrates Intellectual Stimulation by continually encouraging new ideas and approaches.
6) Angela Merkel
Angela Merkel, the Chancellor of Germany for over a decade, was a stabilizing force in European politics. She managed multiple crises, from the financial downturn to the refugee situation, with a balanced and humane approach.
Merkel shows Individualized Consideration by focusing on long-term solutions that consider the well-being of all parties involved.
7) Tony Dungy
Tony Dungy, former NFL coach, transformed the Indianapolis Colts into a Super Bowl-winning team. More importantly, he did it while emphasizing the importance of character and moral integrity.
Dungy is a prime example of Idealized Influence because he led by example, setting a standard for both sportsmanship and leadership.
The Psychology Behind Transformational Leadership

You might be wondering, "What's the secret sauce that makes transformational leadership so effective?" Well, it's not just about actions; it's also about the psychological impact on the team.
Firstly, this leadership style taps into Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs . Remember Maslow? He's the guy who said we have a pyramid of needs , from basic survival up to self-actualization. Transformational leaders aim for the top. They're not just offering you a paycheck (survival); they're helping you fulfill your potential ( self-actualization ).
Second, there's the concept of Emotional Intelligence , or EQ. Transformational leaders usually score high in EQ. They're tuned into their own emotions and can read the room, sensing the team's mood and adjusting their approach accordingly.
Lastly, let's talk about Intrinsic Motivation . This means you're doing something because you genuinely want to, not because you're getting a reward or avoiding a penalty. Transformational leaders excel at firing up this kind of motivation. They inspire you to give your best not for external rewards and punishments, but because you're committed to the vision and the team.
So, the psychology of transformational leadership is a mix of meeting higher-level needs, emotional intelligence, and intrinsic motivation. It's a compelling blend that not only gets results but also fosters a positive, engaged, and loyal team.
How to Cultivate Transformational Leadership Skills
By now, you've got a solid understanding of what transformational leadership is and why it works so well. You've even seen it in action through real-world examples and psychological frameworks. But here's the kicker: you can develop these skills, too. Let's break it down step by step.
First on the list is Self-Awareness . Before you can lead others, you need to know yourself . Take some time to reflect on your strengths and weaknesses. There are tools like the SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats) that can help. Knowing where you stand enables you to be a more effective leader.
Second, work on Communication Skills . Effective communication is more than just talking; it's about listening, too. If you can clearly articulate your vision and also pay attention to what others are saying, you're on the right track.
Last but not least, cultivate Empathy . This means putting yourself in someone else's shoes and understanding their perspective. Empathy allows you to connect on a deeper level, making it easier to inspire and motivate your team. It turns out, being a good leader is also about being a good human.
So there you have it—three achievable steps to hone your transformational leadership skills. And guess what? As you develop these skills, you'll not only become a better leader but also a better teammate, friend, and overall person.
Applications of Transformational Leadership
You've read about how transformational leadership works and how to cultivate the skills it requires. But where does this leadership style really shine? Let's unpack its applications in various fields, showing you that it's not a one-size-fits-all kind of deal.
In the Business World , transformational leadership helps companies adapt and innovate. Whether it's a tech startup or a century-old manufacturing firm, this leadership style can invigorate a company's culture. Leaders inspire employees to be proactive, solve problems creatively, and feel a stronger commitment to their roles.
Workplace Scenario: Improving Productivity in a Sales Team
- Identify the Issue : The sales team is not meeting its targets.
- Open Dialogue : The manager arranges a meeting to understand the challenges faced by the team. This is a form of Individualized Consideration .
- Clear Vision : The manager outlines a new sales strategy, which focuses on relationship-building with clients rather than just meeting quotas. This falls under Inspirational Motivation .
- Skill Development : The manager organizes training sessions to improve customer communication skills, tapping into Intellectual Stimulation .
- Celebrate Wins : Small victories, like landing a big client or successfully implementing a new sales tactic, are celebrated, reinforcing Idealized Influence .
Now, imagine a Healthcare Setting . Medical professionals often face high stress and life-or-death situations. A transformational leader in this space focuses on team well-being, encourages continued education, and fosters an environment where everyone feels valued. This can lead to improved patient care and job satisfaction.
Hospital Scenario: Reducing Stress and Improving Patient Care
- Identify the Issue : The nursing staff is stressed due to high patient load, leading to decreased patient satisfaction.
- Foster Team Cohesion : The head nurse organizes team-building activities aimed at reducing stress and improving collaboration. This is an application of Idealized Influence .
- Streamline Processes : The head nurse introduces a new roster system that distributes workload more evenly, embodying Inspirational Motivation .
- Education and Upskilling : Workshops are arranged to train nurses in stress management techniques and advanced patient care methods, encouraging Intellectual Stimulation .
- Personal Attention : The head nurse holds regular one-on-one meetings with each nurse to discuss challenges and offer solutions, showcasing Individualized Consideration .
Let's not forget Education . Teachers and administrators can significantly benefit from applying transformational leadership principles. By inspiring both educators and students to strive for higher standards and increased performance, learning environments become more enriching and productive.
Classroom Scenario: Boosting Student Engagement in History Class
- Identify the Issue : Students find history boring and are disengaged during class.
- Vision and Inspiration : The teacher decides to tie historical events to current social issues, making it more relatable and exciting. This is an example of Inspirational Motivation .
- Involve the Students : The teacher includes students in the lesson planning, asking them to pick current events that interest them. This exemplifies Individualized Consideration .
- Empower and Educate : The teacher breaks the class into small groups and asks them to research and present their chosen topic, fostering critical thinking and teamwork.
- Feedback Loop : After the presentations, the teacher praises individual and group efforts and gives constructive feedback, reinforcing Idealized Influence and Intellectual Stimulation .
And it doesn't stop there; transformational leadership can be applied in Non-Profits , Community Organizations , and even in Home Settings . It's that versatile. You see, this transformational leadership characteristics and style is more than just a management tactic; it's a strategy for enhancing collective effort and well-being, regardless of the context.
So there you have it—a broad look at where transformational leadership can be effectively applied. No matter the field, the core principles hold true: inspire, engage, and bring out the best in everyone.
Criticisms of Transformational Leadership
Alright, we've talked a lot about the good stuff, but nothing is perfect, right? Transformational leadership also has its fair share of challenges and criticisms. It's crucial to be aware of these to get a well-rounded understanding.
First off, there's the Hero Syndrome . Sometimes, transformational leaders are put on such a high pedestal that they become viewed as irreplaceable . This can lead to problems like lack of accountability or an over-reliance on a single individual for the group's success. It's vital to remember that even great leaders have limitations.
Then there's the issue of Manipulation . Because transformational leaders are so good at inspiring people, they could potentially use their influence for personal gain rather than the collective good. This could lead to ethical dilemmas, where the line between motivation and manipulation gets blurry.
Finally, let's talk about Sustainability . Can a leader keep up the high levels of enthusiasm and vision indefinitely? Burnout is a real concern. Additionally, once a leader has successfully transformed an organization or team, what comes next? Continuous transformation isn't always feasible or desirable.
So yes, while transformational leadership has numerous benefits, it also comes with its set of challenges. But don't fret; understanding these potential pitfalls prepares you to navigate them effectively.
The Future of Transformational Leadership
So, where is transformational leadership headed? In a world that's changing faster than ever, this style of leadership seems more relevant than ever. Let's explore some future trends and how they might shape or be shaped by transformational leadership.
First, we've got the Digital Age . Technology is revolutionizing how we work and communicate. Transformational leaders will need to adapt by fostering digital literacy and creating an environment where innovation thrives. Embracing tech tools can facilitate better communication, real-time feedback, and more efficient ways to inspire a remote workforce.
Second, there's an increasing focus on Diversity and Inclusion . Future transformational leaders will need to be well-versed in managing diverse teams . It's no longer just about being a great leader; it's about understanding different cultural perspectives and working towards inclusive growth. These leaders can act as bridges, uniting varied talents to achieve common goals.
Lastly, we have the Gig Economy . More people are opting for freelance or part-time roles . Traditional leadership models may struggle in such a setup, but transformational leaders could excel. They're skilled at quickly building rapport and aligning even short-term team members with a larger vision.
The world is evolving, and so are the challenges and opportunities that leaders face. The transformational leadership style, with its adaptability and focus on genuine connection, seems well-suited to navigate these changes. Whether you're an aspiring leader or already in a leadership role, understanding this future landscape empowers you to stay ahead of the curve.
From the very origins of transformational leadership, tracing back to James MacGregor Burns, all the way to its practical applications and future relevance, you've journeyed through a comprehensive understanding of this leadership style. You've even seen it in action across different settings like classrooms, workplaces, and hospitals.
While transformational leadership isn't the only game in town, its focus on genuine relationships, inspiration, and growth makes it incredibly relevant for today's challenges. It's a style that adapts well to change, making it a strong fit for our ever-evolving world.
Now, you're not just familiar with transformational leadership; you have the tools to implement it. Whether you’re an aspiring leader or already steering the ship, the principles you've learned can help you become more effective, empathetic, and yes, more transformational leader.
Related posts:
- 45+ Transformational Leaders (Examples + Quiz)
- Skinner’s Box Experiment (Behaviorism Study)
- 121+ Strengths Examples for Job Interviews
- Kurt Lewin Biography - Contributions To Psychology
- Fallacy of Composition (27 Examples + Definition)
Reference this article:
About The Author

Free Personality Test

Free Memory Test

Free IQ Test

PracticalPie.com is a participant in the Amazon Associates Program. As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
Follow Us On:
Youtube Facebook Instagram X/Twitter
Psychology Resources
Developmental
Personality
Relationships
Psychologists
Serial Killers
Psychology Tests
Personality Quiz
Memory Test
Depression test
Type A/B Personality Test
© PracticalPsychology. All rights reserved
Privacy Policy | Terms of Use

Bettmann/Getty Images
By Colin Baker Leaders Staff
Colin Baker
Leadership and Business Writer
Colin Baker is a business writer for Leaders Media. He has a background in as a television journalism, working as...
Learn about our editorial policy
Updated Jan 5, 2023
Reviewed by Hannah L. Miller
Hannah L. Miller
Senior Editor
Hannah L. Miller, MA, is the senior editor for Leaders Media. Since graduating with her Master of Arts in 2015,...
What Is Transformational Leadership?
What is transformational leadership, who developed the transformational leadership model, what are the 4 identifying factors of transformational leadership, top attributes of transformational leaders, benefits of practicing transformational leadership, 5 ways to be a transformational leader, best examples of transformational leaders, frequently asked questions about transformational leadership, transformational leaders are clear about the vision for their lives.
Leadership is not something that takes a “one-size-fits-all” approach. In fact, there are many different leadership styles people may choose to use, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. However, one particular leadership style—transformational leadership—is one of the most effective at bringing about lasting change.
You likely already know about several people who have practiced transformational leadership. For example, Henry Ford was a transformational leader who not only made the automobile more affordable through innovation but raised wages , cut down working hours, and provided health benefits.
Ford was not alone in his transformational leadership style. Others such as civil rights movement leader Martin Luther King Jr., advertising legend David Ogilvy, and technology magnate Steve Jobs , demonstrated the powerful effect transformational leadership has. Over time, leaders who guide their followers this way have become synonymous with innovation, progress, and modernity .
As you learn about transformational leadership, you’ll understand what skills and strengths you need to inspire others to change the world. You’ll also learn from some of the best examples of transformational leaders throughout history.
Key Takeaways
- People who follow transformational leaders report higher levels of well-being.
- Transformational leadership is a driving force behind many of the positive changes in the world.
- Transformational leaders need to have a positive vision of the future.
- Anyone can become a transformational leader.
- Servant leadership goes hand-in-hand with transformational leadership.
Transformational leadership is a leadership style that empowers people to accomplish positive change through big vision, inspiration, and a call to action. Leaders enable change by emotionally connecting with their audience and inspiring them to achieve something greater than themselves. By communicating a positive vision of the future , they motivate and encourage their followers to keep pushing forward. The end result is collective action that leads to innovation, massive transformation, and the betterment of society.
During the 1970s and 1980s, scholars began solidifying the transformational leadership theory. Sociologist James V. Downton coined the term “transformational leadership” in Rebel Leadership: Commitment and Charisma in the Revolutionary Process . Afterward, the idea attracted attention from James MacGregor Burns and Bernard M. Bass , two additional key players in the development of this leadership style.
Burns analyzed political figures such as Franklin D. Roosevelt and John F. Kennedy to identify the characteristics, traits, personalities, and goals of transformational leaders. One of his biggest contributions to the study was qualifying transformational leaders as people who also transform their followers into leaders. However, Bass focused more heavily on the impact transformational leaders have on their followers through The Four I’s listed below.
- Idealized Influence: The leader serves as a role model for others to follow . They also demonstrate established organizational values, setting an example so followers understand expectations. Leaders who have connected with followers through respect and trust can create this influence easily.
- Inspiring Leadership : A transformational leader can passionately communicate an exciting vision of the future, inspiring people to action . The leader can also encourage followers to keep pursuing the overall objective no matter what challenges or obstacles they may face.
- Intellectual Stimulation: Transformational leaders always support followers’ learning, growth, and development. They firmly believe that it is their duty to help others become the best version of themselves.
- Individualized Consideration: When a transformational leader acts, they don’t just do it to large groups. Instead, they work with individuals, showing concern for their progress as a person. These leaders act as a mentor or coach who is genuinely interested in working with each person in the group.
Over the last 50 years, leadership experts have identified several traits that transformational leaders share. The following list is just some of those leadership qualities , though leaders may exhibit other valuable traits and leadership skills.
A person practices transformational leadership when they:
- Clearly define a collective vision and shared mission .
- Unite people through a common cause.
- Emotionally connect with their followers.
- Lead with influence rather than authority.
- Ensure that team culture is ethical.
- Serve as an example for those they guide.
- Change their approach when circumstances necessitate it.
- Establish organizational values.
- Practice innovative leadership .
- Motivate and inspire others to take action.
- Eliminate self-interest and practice servant leadership .
- Create positive outcomes.
Transformational leadership isn’t just some buzzword employed by PR departments. It has real, lasting effects. Many people can benefit from this leadership style, including leaders themselves. The following are just some of the benefits.
- More Hope and Courage: At times, the world can be a depressing place. A transformational leader lifts up those around them, inspiring them to have hope and courage during the toughest moments. They motivate followers to act for the good of everyone.
- Real Change: Transformational leadership produces real change in the world. Just look at the incredible amount of good Martin Luther King Jr. did in such a short amount of time. A transformational leader like King is a changemaker. They usher in a new era of doing things differently.
- Strong Bonds Formed: Transformational leaders display high emotional intelligence and motivate people by emotionally resonating with them. This means that the bonds are typically very strong between them and their followers. Those who follow them respect and love them deeply.
- Improved Well-Being: Additionally, transformational leadership can have a positive impact on a person’s health and outlook. According to a survey of over 300 employees, workers who had a transformational leader reported that they experienced higher levels of well-being.
- More Feelings of Safety: When someone works with a transformational leader, they receive added support. This leads to what one recent study called an added feeling of “psychological safety” since followers could talk openly about mistakes without fear of receiving criticism or reprimands.
- Reduced Stress: Another benefit includes experiencing reduced stress. One study found that in an environment with transformational leadership, there was less conflict and lower stress, leading to more productivity and effectiveness.
1. Create a Positive Vision and Mission
Whether it’s for a business or simply for your own life, creating a vision and mission are two important aspects of the transformational leadership style. Be precise in your vision statement and communicate it with others. You can start with why , defining the purpose behind your vision so others will know why their work matters . As you center all your actions around your vision and mission, people will see your sincerity.
2. Inspire and Motivate Change
Transformational leaders prompt collective action by motivating people to bring about personal or organizational change . These types of leaders articulate a problem by resonating with the emotions of others who identify with it. The leader then paints an inspiring picture of what the future could look like, then presents a clear action plan. This is followed by an invitation to join the leader in enacting that change.
3. Practice Servant Leadership
Being a servant leader often coincides with being a transformational leader. This is because servant leadership is often the mentality and heart that motivates transformative experiences. Having a growth mindset and guiding positive change are top qualities shared by these leadership styles. Additionally, both build trusting communities around causes that serve others, rather than the leader.
4. Set an Example
Many people will only listen to a transformational leader if that leader practices what they preach. Ensure that you are living the philosophy you are sharing. Show people how to create the change you want them to create. It’s far easier for people to act when they have a blueprint they can follow. Otherwise, your message can come across as empty words.
5. Think of Solutions
Anyone can talk for hours about problems, but transformational leaders seek to solve them. It takes someone with a transformational mindset to come up with creative and effective solutions that will get results and change the world. People are naturally drawn to those who present solutions because they offer a remedy to a perceived ill.
Martin Luther King Jr.
“Not everybody can be famous but everybody can be great, because greatness is determined by service.”
Martin Luther King Jr. is one of the most influential leaders in American history. As a leader during the civil rights movement, MLK fought for the rights of people who had long been oppressed. His leadership provided a positive vision of the future, encouraging people to fight for a better tomorrow alongside him. King’s message was one of love and fair treatment for all, believing everyone could make a difference no matter their station in life.
Mother Teresa
“Small things done with great love will change the world.”
Mother Teresa devoted her life to caring for sick and impoverished people who were often overlooked. She won the Nobel Peace Prize in 1979 thanks to her selfless work all over the world. Mother Teresa believed that one could help the world by easing others’ suffering. She was willing to give up personal comfort to show kindness and compassion for unhoused people, addicts, the poverty-stricken, and more. In this, she provided an example others could follow, establishing a blueprint of how to help heal the world one person at a time.
Richard Branson
“There is no greater thing you can do with your life and your work than follow your passions—in a way that serves the world and you.”
Richard Branson is one of today’s most well-known transformational leaders. In 1972, he launched Virgin Records. Since then, the Virgin brand has been involved in exploring and evolving a wide variety of industries. One reason Branson is a well-loved leader is his charismatic, passionate personality that inspires customers and employees alike. Additionally, he is an environmentalist who is heavily involved in finding creative solutions for sustainable living.
Reed Hastings
“Be brutally honest about the short-term and optimistic and confident about the long-term.”
The CEO and co-founder of Netflix communicates and fulfills his company’s long-term vision of being the leading source of global entertainment. As a transformational leader, Reed Hastings saw room for improving DVD rentals by making movies and TV shows more accessible. Furthermore, Netflix continues to refine its streaming service and creates its own in-house content. As a result, the company continues to pave the way for online entertainment.
“When something is important enough, you do it even if the odds are not in your favor.”
Though no stranger to recent controversy, Elon Musk remains a leader with a clear vision for the future. Elon Musk’s leadership style is one that prioritizes solving problems no matter how significant they may appear. Whether it be more affordable space travel or popularizing electric vehicles, Musk doesn’t let the enormity of a problem keep him from tackling it. He has shown a determination to find solutions and make them a reality, inspiring many people to follow his every move.
What is the difference between transformational leadership and transactional leadership?
Transactional leadership is the opposite of transformational leadership. It’s a leadership style that uses the promise of rewards and the threat of punishment to motivate people. On the other hand, transformational leadership motivates through inspiration, positivity, and inner growth.
What are the downsides of transformational leadership?
While a transformational leader inspires changes by communicating big-picture ideas , they are typically less skilled with details and processes. Because of this, they often need logistical minds on the team who can carry out the planning and implementation of objectives.
Additionally, since transformational leaders generally have high levels of extroversion, charisma, and influence, they can potentially lead through unintentional manipulation. These leaders can benefit from having someone hold them accountable through insightful, balanced perspectives.
Who are the most famous transformational leaders?
There have been numerous transformational leaders throughout history. In addition to the ones listed above, people like Winston Churchill, Nelson Mandela, Abraham Lincoln, Jackie Robinson, Mahatma Gandhi, Thomas Jefferson, and Susan B. Anthony are great examples of transformational leaders.
What type of people are transformational leaders?
Transformational leaders are people with a big vision of changing the world for the better. They are innovators and artists—people who engage in first principles thinking . They also might be a little rebellious and willing to take risks. These leaders are not interested in the status quo and choose to strike out on their own to change things.
Anyone can incorporate this leadership style into the way they lead. All you need is a big vision, effective communication skills , and a desire to connect along with the strength to motivate and inspire others, even during tough times.
To practice transformational leadership, you need to have a strong sense of self and know who you are. Otherwise, you’ll struggle to communicate your vision, inspire others, or stick to your outlook on the future.
To create an uplifting vision, follow these steps:
- Start by asking deep questions about life and the world.
- Focus on one issue that is still afflicting the world.
- Create a vision statement.
- Make a plan for casting that vision to others.
- Reverse engineer that vision to make it a reality.
- Stay clear of distractions.
- Gain an understanding that your vision will grow and mature over time.
You can begin this journey of changing the world by reading the following article:
How to Create a Vision for Your Life: A Must for Leaders
Leaders Media has established sourcing guidelines and relies on relevant, and credible sources for the data, facts, and expert insights and analysis we reference. You can learn more about our mission, ethics, and how we cite sources in our editorial policy .
- “Mother Teresa.” Biography , 28 Apr. 2017, https://www.biography.com/religious-figure/mother-teresa.
- “Roosevelt: The Soldier of Freedom.” Google Books , https://books.google.com/books/about/Roosevelt_the_Soldier_of_Freedom.html?id=Q2UNeiY_ZvsC.
- Leadership Legacy Program . http://www.ila-net.org/LeadershipLegacy/bernie_bass.html.
- History.com Editors. (2020, April 29). Ford factory workers get 40-hour week . HISTORY. https://www.history.com/this-day-in-history/ford-factory-workers-get-40-hour-week
- “Transformational leadership and employee knowledge sharing: explore the mediating roles of psychological safety and team efficacy.” https://www.researchgate.net/publication/337107765_Transformational_leadership_and_employee_knowledge_sharing_explore_the_mediating_roles_of_psychological_safety_and_team_efficacy
- “THE INFLUENCE OF TRANSFORMATIONAL LEADERSHIP, INTERPERSONAL COMMUNICATION, AND ORGANIZATIONAL CONFLICT ON ORGANIZATIONAL EFFECTIVENESS.” https://www.researchgate.net/publication/342091626_THE_INFLUENCE_OF_TRANSFORMATIONAL_LEADERSHIP_INTERPERSONAL_COMMUNICATION_AND_ORGANIZATIONAL_CONFLICT_ON_ORGANIZATIONAL_EFFECTIVENESS
Search Leaders.com

Transformational Leadership Style: How to Inspire and Motivate
Chioma Ugochukwu
Harvard MME: President, Director of Distribution
BSc (Hons) Biological Science, Harvard University
Chioma Ugochukwu, currently studying Biological Science at Harvard University, serves as the president of the Harvard Foundation for the International Medical Relief of Children.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Saul Mcleod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul Mcleod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
On This Page:
People who have transformational leadership possess four attributes to varying degrees (Bass, Avolio, & Atwater, 1996).
They are idealized and charismatic (highly liked role models), demonstrate inspirational motivation (optimistic about goal attainment), are intellectually stimulating (encourage critical thinking and problem-solving), and are considerate (show empathy and purpose).

Transformational leadership inspires positive changes in those led and is invested in the success of every single member involved in the process.
Transformational leaders are full of energy, passion, and drive. It’s not a surprise that these qualities can be the things that can make or break an organization.
This kind of leadership is very popular—it can be seen in board rooms, hospitals, schools, and in the entertainment industry. Suddenly, as we look around, transformation seems to be everywhere.
What most people overlook is the time and effort required to fully understand and apply any leadership style, let alone one as dynamic and powerful as transformational leadership.
Transformational leadership style is characteristic of leaders who focus on supervision and organizational goals achieved through a system of rewards and punishments; maintenance of the organizational status quo.
What is transformational leadership?
- Transformational leadership is a leadership model that relies on a team’s encouragement to realize overall success. By raising a team’s morale and self-confidence, the team can then align itself to an overall vision or common purpose.
- This purpose, however, must be established early on for it to be effective. Transformational leadership, when properly applied, can take a struggling or stagnant team, and completely transform it into a productive and dynamic group of individuals.
- This starts by identifying the struggles and strengths of each individual member. Next, it is up to the leader to define a new common goal and guide the members of the team towards this new vision.
- Practically, transformational leadership is used to inspire team members to work together as a single unit, rather than many individual parts. For a stat so dynamic, it is no wonder that many researchers and experts had a hand in its development.
In their seminal work, Transformational Leadership , authors Bass and Riggio explained:
Transformational leaders…are those who stimulate and inspire followers to both achieve extraordinary outcomes and, in the process, develop their own leadership capacity. Transformational leaders help followers grow and develop into leaders by responding to individual followers’ needs by empowering them and by aligning the objectives and goals of the individual followers, the leader, the group, and the larger organization.
Origin and Development
Transformational leadership was started by James V. Downton in 1973. He was the first to coin the term. This was later added to by James Burns in 1978.
Burns was a leadership expert and biographer and proposed that it was only through the strength of the vision and personality that team members could be encouraged to follow.
After agreeing to follow, members then are inspired to change their expectations, perceptions, and are invited to a higher level of morality and motivation.
A few years later, Bernard Bass (1990) added even more to the concept. This is known as “Bass’s Transformational Leadership Theory”. Bass added ways to measure and rank the success of transformational leadership as well as the idea of leaders expressing authentic and focused energy to inspire the other team members to become more like them.
Bass felt that measuring the impact inspires more authentic community. He also explained the psychological mechanisms that are the basis of the theory. According to Bass, the followers of a leader must feel not only trust and admiration, but also loyalty and respect.
These emotions create an environment where the followers are willing to work harder than they originally thought they were capable. This is because transformational leaders offer followers something beyond self-gain—an inspirational mission and self-identity.
Even though it dates to the 70’s, Bass’s model looks much more like transformational leadership today. The basis of the transformational leadership style never changes, only the environment in which it must be applied. Therefore, it can apply in every industry, especially team-focused work environments.
Components of Transformational Leadership Style
Bass also suggested that there were four primary elements to transformational leadership style (also known as the “four I”s”): idealized influence, inspirational motivation, intellectual stimulation, and individual consideration.
Each of these four components is valuable to the leadership style and helps to transform its followers into better, more productive people. When these factors are combined, they help transformational leaders radically change the course of their following.
1. Idealized Influence / Charismatic
Idealized influence describes leaders who have charisma, are curious, and deliver messages with simplicity and tact. These leaders are exemplary role models and are readily trusted and respected by all members of the team.
Charisma is one of the essential pieces of this characteristic. Charisma is essential because it is how leaders can rally their followers around a shared vision. Charisma is most often expressed by their ability to listen actively to each team member and focus on the present moment.
Charismatic leaders give praise to individual members of the team with each success, and they are the first to take responsibility when things go wrong. They also provide constructive feedback to each individual team member. Intended influence is also represented through their curiosity.
Curiosity, not intelligence, is the driving force behind the success of these leaders. It is their job to find innovative solutions to problems and create new and dynamic paths for a team to follow.
Displays of charisma make others want to be more like that person, and as a role model, members will strive to mimic this leader.
2. Inspirational Motivation
Inspirational motivation describes leaders that are motivating and willing to commit to a vision. They encourage team members to also commit to this vision by raising team spirit, fostering community and a sense of purpose.
To do this, there must be simplicity in communication. This means their communication style must be best suited to the needs of the team. Leaders speak clearly and concisely to easily articulate their vision to the members.
This provides structure and order so that members can execute tasks without confusion. Leaders articulate a clear plan for the future and communicate expectations in the beginning before the work starts. Leaders must also express their messages with a sense of authority, in order for members to respect their thoughts and trust in their vision.
Along with this, leaders must be upbeat and positive, bringing energy to a room with their enthusiasm. As a visionary, transformational leaders use these skills to look toward future goals and have the foresight to see the small obstacles that may hinder this vision.
They recognize the smallest things that can turn into larger issues. Leaders have intuition towards the things that help to push their team and goals forward. These actions begin to instill trust in their followers and confidence in their leader.

3. Intellectual Stimulation
Intellectual stimulation describes leaders who encourage their members to think outside the box and be innovative. Stimulating followers promote critical thinking and problem-solving skills in order to improve the group or organization as a whole.
This challenges the normal beliefs of a group and encourages the team to perform better than they ever thought originally possible. Encouraging innovation involves each team member in the decision-making process and fosters a sense of importance and a stake in the organization’s over-all success.
The important thing about this is a leader must not criticize the thoughts or opinions of the members. Premature shutting down of ideas can create a climate of distrust and hurt.
Leaders must, therefore gently change the way followers problem-solve and brainstorm new and innovative ways to achieve their teams” goals. In short, leaders must recognize that there are many ways to achieve a goal, and no ordinary path to innovation.
Being a transformational leader requires risk-taking, creativity, curiosity, and openness to new ideas from each individual member.
4. Individual Consideration
Individual consideration is the degree to which a leader attends to each follower’s personal needs. Transformational leadership encourages members by focusing on the way each person effects the overall goal.
This means recognizing and valuing the motivations, desires, and needs of individual members. Upon recognizing the motivation behind the drive of the individual, leaders then provide opportunities for customized training.
This allows team members to grow and learn in an environment they feel comfortable in. Engaging individuals requires emotional intelligence.
Emotional intelligence includes showing genuine compassion, empathizing with the needs of individuals, and encouraging the on-going personal growth of individuals. When a leader takes into account the emotions of their followers, they then learn how to best engage with them.
Emotionally intelligent leaders connect with members, and build a bond based in trust. Leaders act as mentors, or a coach and are willing and open to listening to their followers’ concerns.
Examples of transformational leaders
Transformational leaders are all around us. Because of their marked positive impact on productivity and success, they are at the top of each of their individual industries.
Below are 5 examples of transformational leaders, their stories, and ways that you can begin to apply this leadership style to your own team.
Oprah Winfrey: Media Mogul
Oprah Winfrey was the host and producer of The Oprah Winfrey Show from 1986 to 2011. It is one of the highest rated talk shows in American history, so it is no surprise that Winfrey quickly became one of the richest women in the 20th century.
Winfrey was the continent’s first black multi-billionaire and was among Time Magazine’s most influential people for 6 years straight. Winfrey’s amazing communication skills, beginnings in poverty, and charismatic persona have enabled her to connect with people from every background and inspired people everywhere to dream big.
Amazon boss Jeff Bezos
In 1994, Jeff Bezos took the first step to creating the world’s first online bookstore. Bezos spearheaded the first initiative to create an online eBook reader, where digital eBooks could be stored in an eLibrary for later consumption.
This was introduced as the Kindle. Kindle sales, in addition to multiproduct sales, have contributed to Amazon’s current market value of 1.14 trillion as of April 2020.
Nike Corporation
Nike is one of the most famous footwear companies of the 20th century. With their slogan, “Just Do It,” it is one of the most obvious examples of transformational leadership and motivation.
Nike connected with customers through this focused marketing and created exclusive membership opportunities. By motivating its entire customer base to be the best, most healthy versions of themselves, Nike increased its product development cycle, quickly responding to changes in trends and customer feedback.
This resulted in Nike’s stock price increased from less than $50 to nearly 100 dollars in two years.
Netflix’s Reed Hastings
Reed Hastings founded Netflix in 1997, with a handful of team members. The subscription-based video streaming service offers popular movies and TV shows as well as original content.
When it first launched, despite its large competitor, Blockbuster, Hastings had a grand vision of Netflix replacing this company. He came up with the novel idea of user-friendly streaming that became the starting point of this dream’s actualization. Today, Netflix has nearly 200 million subscribers world-wide and is the largest online streaming service.
Apple’s Steve Jobs
Steve Jobs is one of the best examples of transformational leadership in the 21st century. From wearing pairs of the same clothing each day for increased productivity, to designing the break-through idea of the iCloud, Steve Jobs was the brain behind the success of Apple.
With Steve Jobs’ legacy guiding the company, the company shifted from product-based identification to more services and brand loyalty services. Apple is a 2 trillion-dollar company today, and in the next few years, this is only expected to expand.
What are the effects of transformational leadership?
Transformational leaders are those who inspire their members to achieve beyond their presumed potential. In the same way, these transformed members then go on to become leaders in their own right.
Transformational leaders’ personalized response empowers individuals and helps them to develop their potential. The effects of transformational leadership have a lasting and positive impact.
Research evidence from Psychology Today reported that teams led by transformational leaders have higher levels of performance and report overall high satisfaction than teams led by other styles.
Members develop positive psychological states and find greater meaning in their work. In addition, they also learn to think positively about themselves and the tasks that they are meant to complete.
This results in decreased burnout, social loafing, and increased individual motivation.
Leadership expert Ronald Riggio suggests that this is because of transformational leaders’ unflinching belief that each and every member brings unique talents and skills to a team, and that the voice of each member is important.
He also suggests that the leaders’ strong belief in the vision of the team has a significant impact on the overwhelmingly positive results of the leadership style. By creating a common goal, or vision, leaders enhance the quality of their relationships and create environments that are fair, respectful, and supportive.
It is important to recognize that while this leadership style is extremely effective, there are some team members who will not respond as favorably to transformational leadership. Leaders must adjust their efforts as needed in order to meet their goals.
Implications for managers
While it is important to look at the success and growth of companies and entrepreneurs, it is important to recognize that most of these companies and people did not start out successful.
It is important to recognize that these people and companies were mentored and guided by a transformational leader. The stories here show that this leadership style can help to transform you, your team, and your mission.
What can you do to become a more transformational leader? One of the critical ways to start is by having belief. You must believe in the vision and path you have created, so that you can inspire others to believe in your vision as well. Being charismatic, motivating, and focusing on each individual team member can help you accomplish this through transformative leadership.
Yukl (1994) draws some tips for transformational leadership:
- Develop a challenging and attractive vision, together with the employees.
- Tie the vision to a strategy for its achievement.
- Develop the vision, specify and translate it to actions.
- Express confidence, decisiveness and optimism about the vision and its implementation.
- Realize the vision through small planned steps and small successes in the path for its full implementation.
Bass, B. M. (1985) Leadership and Performance beyond Expectations. Free Press, New York.
Bass, B. M. (1990) From transactional to transformational leadership: Learning to share the vision. Organizational Dynamics 18, 19-31.
Bass, B. M. and Avolio, B. J. (1989). Manual for the Multifactor Leadership Questionnaire. Consulting Psychologists Press, Palo Alto.
Bass, B. M. and Avolio, B. J. (1994) Improving Organizational Effectiveness through Transformational Leadership. Sage Publications, Thousand Oaks, CA.
Bass, B. M., Avolio, B. J., & Atwater, L. (1996). The transformational and transactional leadership of men and women. Applied Psychology: An International Review, 45 , 5–34
Bass, B. M., & Riggio, R. E. (2006). Transformational leadership.
Burns, J. M. (1978). Leadership. NY: Harper & Row.
Downton, J. V. (1973). Rebel leadership: Commitment and charisma in a revolutionary process. New York: Free Press.
Yukl, G.(1999). An evaluation of conceptual weaknesses in transformational and charismatic leadership theories. Leadership Quarterly, 10, 285-305; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S1048-9843(99)00013-2
Further Information
- Leithwood, K., & Jantzi, D. (2005). Transformational leadership. The essentials of school leadership, 31-43.
- Bass, B. M. (1999). Two decades of research and development in transformational leadership. European journal of work and organizational psychology, 8(1), 9-32.
- Bass, B. M., & Avolio, B. J. (1993). Transformational leadership and organizational culture. Public administration quarterly, 112-121.
- Bass, B. M., & Steidlmeier, P. (1999). Ethics, character, and authentic transformational leadership behavior. The leadership quarterly, 10(2), 181-217.
Transformational leadership is a leadership style where leaders inspire, motivate, and stimulate their followers intellectually to work towards a shared and valued goal. These leaders encourage innovation, creativity, and personal development among their team members, fostering an environment of trust, respect, and admiration. They aim to transform their followers’ individual and collective consciousness to achieve organizational success.
Which leadership style can resemble transformational leadership because these leaders inspire enthusiasm in their teams and are energetic in motivating others to move forward?
Charismatic leadership style can closely resemble transformational leadership as charismatic leaders inspire enthusiasm and motivate others towards their goals. They use their personal charm and appeal to inspire, energize, and encourage their teams to move forward.
Related Articles

Personality
Exploring the MMPI-3 in a Transgender and Gender Diverse Sample

Are Developmental Trajectories of Personality and Socioeconomic Factors Related to Later Cognitive Function

Do Life Events Lead to Enduring Changes in Adult Attachment Styles?

Thin-Slicing Judgments In Psychology

Authoritarian Personality

Emotions , Personality
The Dark Side of Emotional Intelligence
Transformational Leadership Essay
Introduction.
In any organization, the focus is based on yielding high profits. The key to this lies in the leader, who in turn inspires the staff. Leadership in an organization is usually classified into different categories based on the style the leader uses.
Different leadership styles are used to attain desired goals, but Bass (2006) pointed out in his work that the secret to an organization that is effective in achieving its goals lies in the use of transformational leadership. A leader usually uses power and influence to exercise authority. In transformational leadership, however, the idea is to emphasize influence to manage the teams and bring them aboard to understand the leader’s vision.
What Is a Transformational Leader?
Transformational leadership can be defined as implementing new ideas through adopting a more flexible and universal method of influencing and continually ameliorating those around them. This type of leadership calls for the leader and the staff to improve one another’s motivation levels.
Motivational leaders bravely work towards making the staff realize the need for higher ideas and their vision for the organization’s future. Transformational leaders naturally role model their followers and pass their enthusiasm by clearly letting them visualize their ideas and what he is doing, and by outlining their genuine personal beliefs, he shows the followers that he has these values. Transformational leaders can achieve these results by possessing certain qualities and characteristics.
Transformational leaders understand their abilities and confidently stand firm on their beliefs. Confidence in their abilities keeps them motivated and helps them connect emotionally to the organization. They have high levels of self-determination, which helps them attain a sense of direction for the organization and, in turn, influence the followers, and together they propel the organization in the right course.
They possess self-drive, which helps them to visualize themselves as achievers who do not have to rely on luck to achieve good results. It is this understanding of self that helps them to transform those around them (Chammas, 2010).
Another characteristic of effective transformational leaders is seen in their ability to understand those around them and particularly those under them. Transformational leaders carefully understand and purposefully influence and motivate the staff to understand the goals. Together, they are working toward attaining that goal since he assists them in realizing its intended worth.
This requires the transformational leader to have the right communication skills to relay their vision to the point of winning the willingness of the followers such that they, too, are excited and have the drive to achieve the desired change. Transformational leader fully understands what they hope to achieve, and the process of carefully relaying the intent to the followers requires idealized influence, which ensures the followers are not resistant to the idea.
To do so, the leader must also be willing to actively involve them in chatting the way forward towards attaining the goal. After they agree on the right course of action, the transformational leader again provides inspirational motivation to keep them going and excite their minds to have the urge to achieve the task.
After the transformational leader purposefully develops the ideas and effectively influences the staff to yearn to attain the goal, it only marks the beginning of the process. The work of the transformational leader is to keep the staff focused on the vision continually, help them stick to the agreed course of action to attain the vision, and continually be actively involved in influencing more and more colleagues to support the vision.
The importance here is to make sure that the staff clearly understands the vision the leader has for the organization’s future and make sure that they will support the course and keep abreast with the importance of the task even in years to come. The staff should not just be involved in doing their assigned job but engage in the job because they realize the importance of the outcome of the job.
The last characteristic of transformation leadership is a combination of three qualities requiring the transformational leader to think outside the box. According to Chammas (2010), a transformational leader is not afraid to evaluate the organization’s traditions and make changes without interfering with its core business.
This requires that they come up with innovative and creative ways that align with their vision for the organization. In their pursuit of change, they are seen as ignoring the present and yearning for a better future. A factor that works with this is their willingness to embrace innovations and ideas.
The transformational leader encourages others to develop new methodologies and innovations that align with attaining the vision. They do so as to keep abreast with the changing times and to demonstrate that they understand that new challenges in the future need new solutions.
Therefore, they encourage suggestions and offer appraisals for the best ideas. The third point on the same is that the transformational leader takes up their role as the advisor and the guide of the team. Their role here is to assist the whole team through the operations. This requires that they understand that each individual has their own personal strengths and weaknesses in given areas.
The leader also considers the individual’s level and will to adjust to new ideas. By understanding the readiness levels, the leader can establish the right timing for implementing the new ideas so that the resistance is minimal. The ability to forge ahead and achieve a new, transformed organization depends on the transformational leader’s influence levels on the staff and developing them in the areas needed to achieve a new organization.
Transformational leadership has proven effective by far compared to other leadership styles. This is due to its influential nature that seeks to have both the leader and the follower develop each other, and together they work towards attaining a vision and, in turn, a new organization.
The benefits of adopting transformation leadership are clearly felt in the outcomes. Transformation leadership increases the influence at the topmost leadership level. This, according to Cox (2010), is because transformational leaders act as role models to other employees in the organization and hence are obeyed, and their method of dealing with people is respected. The result is an organization where there is solid unity between the leader and the employees, giving rise to an atmosphere of mutual trust and effective communication.
This means that the executive is given a hearing by other staff. Therefore the implementation of ideas is fast, and the environment at the workplace is not tense or hierarchical. This is because more emphasis is placed on developing each other instead of arguing about bureaucracy. The leader concentrates on guiding the staff through the vision instead of spending most of the time trying to unite opposing groups in an organization. Results are achieved quickly once all the staff are on board and working passionately.
Another benefit of transformational leadership is seen in how the leader oozes the charisma and excitement they have to perform their duty. The rest of the staff can read clearly the leader’s aspirations, and consequently, they follow in trying to achieve the vision too. The energy possessed by transformational leaders is said to be a major contributor to the other staff’s willingness to join in because they are inspired by their leader’s genuine vision of taking the organization to a whole new level.
A successful and effective organization is able to be realized through two important aspects; a leader who has a clearly defined vision for the organization and staff who have the will to assist and work together towards the realization of that goal. Transformational leaders are enthusiastic about their vision and through their ability to bring other staff on board, realizing the vision becomes very easy and hence a successful and effective organization (Cox, 2010).
A major benefit of transformational leadership is how it can guide the employees bit by bit in achieving a change in the organization. They do this by gradually explaining and influencing the employees and taking them through the step-by-step process of attaining the desired change.
They can visualize the changes the organization should hope to achieve, e.g., introducing a new product, new operating methods, new technology adjustments, etc. They then embark on a mission to carefully engage the employees to understand their feelings toward the desired change. According to Xenitelis (2010), they do this by employing tactical approaches to reveal their thoughts on the same and involve them directly in defining the desired change.
They then attempt to make that necessary adjustment to make the employees clearly understand why the change is important and what it hopes to achieve. After the necessary change is made to propel the vision, the transformational leader then guides the process and ensures that everyone is on board. The leader keeps a constant check by evaluating the process as it continues and hence makes the necessary changes.
This step-by-step engagement of the process proves very successful and is the most effective way for the organization to realize changes. It is also an effective way of avoiding resistance to change which is usually a major hindrance to organizational progress. Its effectiveness is seen especially when the organization wishes to launch a new product or desires to make a complete change in its operating processes (Xenitelis, 2010).
Employees in an organization led by a transformational leader always feel the challenge to keep their energies going because they are inspired by the leader. This fosters a feeling of taking one’s duties and responsibilities personally and yearning to perform one’s tasks to the best of their abilities. This sort of inspiration by the transformational leader encourages the employees to come up with new ways of doing things.
Creativity and innovativeness amongst the employees are encouraged, which, in turn, brings out the individual’s full potential while still addressing the issue of self-development. The benefits of such a working environment trickle down to the organization, which has employees with self-fulfillment and give their best, and their creative input is enjoyed; hence the organization’s effectiveness is realized (Stewart, 2006).
Bass, one of the pioneers of transformational leadership, pointed out that the application of this style of leadership helps the employees push their abilities to levels they never thought they could reach. In addition to transformational leadership uniting and ensuring people agree Bass pointed out that it fosters a working culture where moral force flourishes, and therefore the level of employee turnover is kept at a minimum.
Employees who understand that the organization they are working for encourages them to give their creativity and allows them to develop to levels they never thought they could achieve are likely to stick with the organization for long. The benefits of such a working culture are realized in the organization’s success in achieving its vision since the costs associated with employee turnover and retention are cut, as well as the benefits of developed and satisfied employees (Bass, 2006).
Transformational leadership brings forth culture and climate in an organization whereby success is bound to prosper. When a transformational leader takes into consideration the abilities and needs of each employee individually and shares their genuine vision clearly and elaborately, it brings forth a culture of honesty and receptiveness.
The employees feel that their input is respected and credit awarded for their ideas. This, in turn, gives rise to a working environment where there is job satisfaction, and consequently, due to the absence of commotion, the environment is stress-free.
The employees are always in high spirits, and their motivation to work hard is on top; hence they freely express their abilities to improve in certain areas, and the areas where they are strong are emphasized. An organization’s success is bound to be realized in such a stress-free working culture with high motivation levels. Job satisfaction is high and personal abilities are given consideration.
Transformational leadership is beneficial in that it can help an organization cut costs. Through the transformational leader’s ability to connect with the employees and give them a chance to understand the task at hand, including allowing their ideas and creativity, job satisfaction is achieved, which means employees do not feel the need to leave the organization hence the reduced employee turnover. This, in a major way, saves the organization high costs associated with losing employees and having to employ new ones.
In a transformational leadership organization, the employees are given a chance to concentrate on areas they are strong in; hence, the unnecessary costs of training the employees in unfamiliar areas are reduced. This also goes for the fact that the employees are given a chance to develop, and as they work harmoniously, they teach each other by sharing ideas. Hence, in-training employees is unnecessary in most cases (Stewart, 2006).
Transformational Leadership: Conclusion
In conclusion, effectiveness in an organization highly depends on the leader’s ability to have a vision, build consensus with the employees, and adjust his leadership style to fit the vision and guide the whole team toward the desired direction.
Transformational leadership considers all this by having the leader clearly understand the direction he wants to propel the organization, influencing the employees, and making them understand how important the change is. Then together, they engage in the process.
Transformational leadership combines the right employees and the right motives. It inspires creativity and motivation in achieving a smooth flow of processes which, in the long run, ensures an effective organization that delivers its results and is consistent in achieving the desired changes.
Reference List
Bass, M. and Riggio, E. (2006) Transformational Leadership. New York, Routledge.
Chammas, A. (2010) Leadership Characteristics for Organizational Transformation Success, Transformational Leadership , vol. 12, no. 6, pp. 16-27.
Cox, R. (2010) The Benefits of Transformational Leadership . Web.
Stewart, J. (2006) Transformational Leadership: An Evolving Concept Examined through the Works of Burns, Bass, Avolio, and Leithwood , Canadian Journal of Educational Administration and Policy. vol. 27, no. 56, pp. 1-19.
Xenitelis, M. (2010) Transformational Leadership , Management. vol. 43, no. 12, pp. 11 -17.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2019, February 7). Transformational Leadership Essay. https://ivypanda.com/essays/transformational-leadership/
"Transformational Leadership Essay." IvyPanda , 7 Feb. 2019, ivypanda.com/essays/transformational-leadership/.
IvyPanda . (2019) 'Transformational Leadership Essay'. 7 February.
IvyPanda . 2019. "Transformational Leadership Essay." February 7, 2019. https://ivypanda.com/essays/transformational-leadership/.
1. IvyPanda . "Transformational Leadership Essay." February 7, 2019. https://ivypanda.com/essays/transformational-leadership/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Transformational Leadership Essay." February 7, 2019. https://ivypanda.com/essays/transformational-leadership/.
- Transformational Leadership Theory and Personality
- Transformational Leadership and Management Skills
- "The Influence of the Transformational Leader" by Tucker and Russell
- Asia Pacific Breweries as an International Business
- Alain Limited' Management and Strategy
- Strategic Planning Essay
- The Field of Organizational Learning and Its Theories
- The Training Techniques of the Hudson Hotel in New York City
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
How Transformational Leadership Can Inspire Others
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Steven Gans, MD is board-certified in psychiatry and is an active supervisor, teacher, and mentor at Massachusetts General Hospital.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/steven-gans-1000-51582b7f23b6462f8713961deb74959f.jpg)
- Key Components
- Transformational Traits
- Transformational vs. Transactional
- Potential Pitfalls
Are You a Transformational Leader?
Transformational leadership is a leadership style that can inspire positive changes in those who follow. Transformational leaders are generally energetic, enthusiastic, and passionate. Not only are these leaders concerned and involved in the process, but they are also focused on helping every member of the group succeed.
Transformational leaders take control of situations by conveying a clear vision of the group's goals. These leaders have a marked passion for the work and an ability to make the rest of the group feel recharged and energized.
Transformational leaders focus on helping members of the group support one another and provide them with the support, guidance, and inspiration they need to work hard, perform well, and stay loyal to the group. The primary goals of transformational leadership are to inspire growth, promote loyalty, and instill confidence in group members.
This article discusses the characteristics of transformational leadership and its effects on groups.
History of Transformational Leadership
The concept of transformational leadership was initially introduced by leadership expert and presidential biographer James MacGregor Burns. According to Burns, transformational leadership can be seen when "leaders and followers make each other advance to a higher level of moral and motivation."
Through the strength of their vision and personality, transformational leaders are able to inspire followers to change expectations, perceptions, and motivations to work towards common goals.
Later, researcher Bernard M. Bass expanded upon Burns's original ideas to develop what is today referred to as Bass’s Transformational Leadership Theory. According to Bass, transformational leadership can be defined based on the impact that it has on followers. Transformational leaders, Bass suggested, garner trust, respect, and admiration from their followers.
Components of Transformational Leadership
Bass also suggested that there were four different components of transformational leadership. The four main elements of transformational leadership are:
- Intellectual stimulation: Transformational leaders not only challenge the status quo; they also encourage creativity among followers. The leader encourages followers to explore new ways of doing things and new opportunities to learn.
- Individualized consideration: Transformational leadership also involves supporting and encouraging individual followers. To foster supportive relationships, transformational leaders keep lines of communication open so that followers feel free to share ideas and so that leaders can offer immediate recognition of the unique contributions of each follower.
- Inspirational motivation: Transformational leaders have a clear vision that they can articulate to followers. These leaders can also help followers experience the same passion and motivation to fulfill these goals.
- Idealized influence: The transformational leader serves as a role model for followers. Because followers trust and respect the leader, they emulate this individual and internalize their ideals.
Groups led by this type of leader tend to be both successful and loyal. They give a lot to the team and care deeply about the group's ability to accomplish its goals. Turnover tends to be relatively low as transformational leaders can inspire a great deal of commitment in their followers.
Transformational Leadership Traits
So what are some typical signs of a transformational leader? Common characteristics of transformational leaders include:
- Able to encourage others to communicate and participate
- Active listening skills
- Adaptability
- Authenticity and genuineness
- Emotionally intelligent
- Inspirational
- Open-mindedness
- Proactive problem-solvers
- Self-awareness
- Willingness to take responsibility
- Willingness to take well-informed risks
While each leader is different, transformational leadership is characterized by a number of key traits. Five of the main qualities of a transformational leader are authenticity, self-awareness, humility, collaboration, and interdependence.
Examples of Transformational Leadership
Recognizable figures who are often cited as examples of transformational leadership include:
- Barack Obama : The former U.S. President was known for his transformational approach to running his administration, as well as his unifying, motivating, and hopeful communication style.
- Nelson Mandela : The former President of South Africa was famous for serving as a source of authentic inspiration.
- Oprah Winfrey : The media mogul is famous for her charismatic, visionary, and inspirational leadership style.
- Steve Jobs : Jobs was famous for his visionary leadership that transformed Apple into a leader in the technology industry.
Effects of Transformational Leadership
In their classic text, Transformational Leadership , authors Bass and Riggio explained that these leaders inspire people to achieve extraordinary results. Group members are not just encouraged to participate; they are also inspired to become leaders themselves.
Transformational leaders can accomplish this by being responsive and empowering. The individual's goals become better aligned with the purposes of the entire group so that each group member's success furthers the organization's goals.
Researchers have found that this style of leadership can have a positive effect on the group. Some of these effects include:
- Better performance : Those led by transformational individuals have better performance and are more satisfied than those in groups with different types of leaders.
- Better well-being : Employees who identified a higher level of transformational leadership in their employers also reported higher levels of well-being. The effect stayed significant even after researchers controlled for factors linked to well-being, such as job strain, education, and age.
- Sense of empowerment : This is attributed to the fact that transformational leaders believe that their followers can do their best, leading group members to feel inspired and empowered.
How to Become a More Transformational Leader
Becoming a more transformational leader may provide many benefits. Researchers believe that such results can help companies develop leadership training programs that can be used to teach transformational leadership skills.
Acquiring communication skills such as resolving workplace conflicts and recognizing employees' needs are important parts of transformational leadership. Such programs can serve as essential parts of health promotion efforts in the workplace to help improve employee well-being.
What can you do to become a more transformational leader? Leadership experts suggest that a robust and positive future vision plays a critical role. Not only is it essential to believe in this vision yourself, but you've also got to inspire others to buy into your vision as well.
You can also develop your transformational skills by being:
- Trustworthy
Transformational Leadership vs. Transactional Leadership
Transformational leadership is often contrasted with transactional leadership , which is a style that is essentially the opposite of transformational. In the transactional approach, leaders motivate their subordinates through the use of rewards and punishment.
While the transformational approach focuses on communication, inspiration, and positive reinforcement, transactional leaders supervise, monitor performance, and create routines to maximize efficiency. While the transactional approach can be effective in some situations, it does not foster loyalty, innovation, or creativity.
Motivates using rewards and punishments
Focused on compliance
Tends to focus on short-term goals
Uses extrinsic rewards (pay, promotions, etc.)
Motivates using enthusiasm and charismatic inspiration
Focused on commitment
More focused on long-term success
Uses intrinsic rewards (esteem, pride, etc.)
Potential Pitfalls of Transformational Leadership
While transformational leadership is often viewed as one of the best approaches to leadership, that doesn't mean that it is necessarily right for every situation. For example, when group members need more guidance and direction, it can be more effective to utilize a more transactional approach.
The transactional style can help improve group cohesion and commitment, but it can also contribute to burnout when group members feel constantly pressured to give up all of their time and effort to support the goals of the group.
In situations where a lot of creativity and innovation are important to success, a transformational style is often a beneficial approach. But if the focus is on achieving a prescribed set of short-term goals, taking a more transactional approach might lead to less chaos and better results.
Try our fast and free quiz to find out if you tend towards transformational leadership or one of the other styles.
The transformational style of leadership can be highly effective when used appropriately, but it might not necessarily be the best choice for every situation. In some cases, groups may require a more managerial or autocratic style that involves closer control and greater direction, particularly in situations where group member are unskilled and need a lot of oversight.
One way to improve your own leadership skills is to assess your own current leadership style and think about ways in which your strengths can benefit the group you are leading. By evaluating your own skills, you will be better able to play to your strengths and work on improving your areas of weakness.
Allen GP, Moore WM, Moser LR, Neill KK, Sambamoorthi U, Bell HS. The role of servant leadership and transformational leadership in academic pharmacy . Am J Pharm Educ . 2016;80(7):113. doi:10.5688/ajpe807113
Choi SL, Goh CF, Adam MB, Tan OK. Transformational leadership, empowerment, and job satisfaction: the mediating role of employee empowerment . Hum Resour Health . 2016;14(1):73. doi:10.1186/s12960-016-0171-2
Psychology Today. Are you a transformational leader ?
Jacobs C; Pfaff H; Lehner B, et al. The influence of transformational leadership on employee well-being: Results rrom a survey of companies in the information and communication technology sector in Germany. J Occup Environ Med . 2013;55(7):772-8. doi:10.1097/JOM.0b013e3182972ee5
Bass, B. M. & Riggio, R. E. Transformational Leadership . Mahwah, New Jersey: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Inc; 2008.
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
Transformational Leadership
- Living reference work entry
- First Online: 01 January 2016
- Cite this living reference work entry

- B. Parker Ellen III 2
2709 Accesses
1 Citations
Charismatic-inspirational leadership
Leadership that inspires and motivates followers to achieve outcomes beyond expectations and helps followers grow and develop by responding to their individual needs.
Introduction
The introduction of transformational leadership generally is credited to James MacGregor Burns ( 1978 ) who used the term to distinguish between those who led through the exchange of performance for rewards (i.e., transactional leaders) and those who led by inspiring followers to aim for and achieve ambitious goals (i.e., transformational leaders). This development in leadership thinking signaled the beginning of a shift to what has become known as new-genre perspectives that focus on more interpersonal, inspirational, and visionary leadership. Burns ( 1978 ) argued that transformational leaders develop followers as individuals and as future leaders by empowering them and responding to their needs. As a result, transformational leadership results in high...
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
Institutional subscriptions
Barling J (2013) The science of leadership: lessons from research for organizational leaders. Oxford University Press
Google Scholar
Bass BM (1985) Leadership and performance beyond expectations. Free Press/Collier Macmillan, New York: Free Press
Bass BM, Riggio RE (2006) Transformational leadership. Psychology Press (2nd ed.). Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum
Burns JM (1978) Leadership. Harper and Row, New York
Bono JE, Judge TA (2004) Personality and transformational and transactional leadership: a meta-analysis. J Appl Psychol 89(5):901–910
Article Google Scholar
Judge TA, Piccolo RF (2004) Transformational and transactional leadership: a meta-analytic test of their relative validity. J Appl Psychol 89(5):755–768
Van Knippenberg D, Sitkin SB (2013) A critical assessment of charismatic – transformational leadership research: back to the drawing board? Acad Manag Ann 7(1):1–60
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
D’Amore-McKim School of Business, Northeastern University, 112 Hayden Hall, 360 Huntington Avenue, Boston, MA, 02115-5000, USA
B. Parker Ellen III
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to B. Parker Ellen III .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Florida Atlantic University, Boca Raton, Florida, USA
Ali Farazmand
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2016 Springer International Publishing Switzerland
About this entry
Cite this entry.
Ellen, B.P. (2016). Transformational Leadership. In: Farazmand, A. (eds) Global Encyclopedia of Public Administration, Public Policy, and Governance. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-31816-5_1343-1
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-31816-5_1343-1
Received : 21 March 2016
Accepted : 23 April 2016
Published : 14 May 2016
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Online ISBN : 978-3-319-31816-5
eBook Packages : Springer Reference Economics and Finance Reference Module Humanities and Social Sciences Reference Module Business, Economics and Social Sciences
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research

- Calculators
- Swot Analysis
- Pestle Analysis
- Five Forces Analysis
- Organizational Structure
- Copywriting
- Research Topics
- Student Resources
Services We Provide

Resources We Provide

Login / Register

- Transforming Organizations with Transformational Leadership
- The Ultimate Guide to Top Leadership Theories
Transformational leadership is often viewed as one of the most successful approaches to leadership. The concept of transformational leadership was first devised in 1973 by James Downton and was further developed by James Burns and Bernard M. Bass in the subsequent years.
In the contemporary world, transformations at the organizational level have become the need of the hour. Ultimately, those who have the ability to drive outstanding transformations will redefine the very notion of success. Why we are emphasizing this is because transformational leadership is closely linked to the ideation of transformations within organizations.
To elaborate, the Transformational Theory of Leadership endorses a leadership wherein leaders go beyond their self-interests to bring major transformations to the floor for their organization to unlock new horizons of success. To make transformations possible, transformational leaders undertake effective change management and motivate their subordinates to participate in the change with great effectiveness. Transformational leaders have unique visions based on which they envisage organizational changes and do whatever it takes to make the transition successful. This style of leadership has its own unique place among various leadership theories relevant in contemporary times.
To delve deeper into this leadership style, let us shed light on some of the core fundamentals of transformational leadership.
Table of Contents
Key features of transformational leadership theory.
- Relevance of transformational leadership theory in modern workplace
A real-world example of a transformational leader
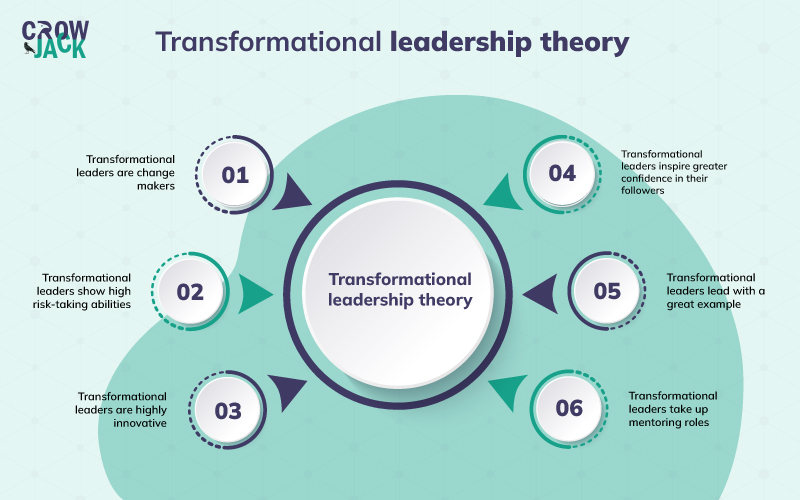
Transformational leaders are change-makers, have great risk-taking abilities, question the status quo of things, and effectively envisage the need for change and the impact on the other side of the transformation. They embrace the challenges of experimenting with difference change management models to determine the best strategies for transformations.
Transformational leaders as per the theory guide their subordinates through the change by clearly defining the need for the change, the vision, and values associated with the change, and the benefits of the change. They clearly define the mission and objectives that are linked to the change. They also empower their employees to acquire the skills and knowledge needed to facilitate the change and sustain it. Also, they encourage their subordinates to take initiative and decide for themselves.
The transformational leadership style is aimed at encouraging high innovation and creativity among the employees so that employees develop as change leaders in the future. Transformational leaders are innovators and they aim to cultivate similar attitudes among their team members. In fact, transformational leaders are more than happy to look beyond the traditional ways of doing things to boost efficiency with outside-the-box strategies
The Transformational Theory of Leadership also proposes that leaders need to lead from the front when it comes to talking and implementing changes within the organization. The theory focuses on the need for leaders to have an idealized influence on their followers by practicing what they preach to set fine standards.
The theory further states leaders should act as mentors and coaches for their employees and should appreciate even the smallest acts of creative intellect coming from the employees. Besides, leaders extend great support to employees who have similar characteristics and are inclined to the idea of transformations.
Relevance of the theory in the contemporary corporate world
In any organization, the need for transformational leadership may exist at different levels. To explain, transformations may be needed within the organizational structure, teams, operational processes, marketing strategies, product portfolio, and so on. Otherwise too, if we look at the external business environment in contemporary times, the enormous competition is pushing businesses to evolve constantly and incorporate positive changes.
This is where transformational leaders will prove to be the greatest assets for businesses. Transformational leaders have the ability to facilitate changes and keep all employees motivated and aligned to the process of change. With their great vision, transformational leaders can contribute with incredible business planning strategies linked to product development, business diversification , exploring new markets, and so on. With respect to business expansion, higher profitability, and diversification of revenue streams, transformational leadership has the potential to offer unparalleled competitive advantages.
Also, whenever employees will show resentment toward change or will begin to lose productivity amid new processes, transformational leaders are best suited to manage them. As per the transformational theory, leaders will help employees accept the change as well as participate in the change. When employees face productivity issues, leaders will contribute to their learning and adaptation by providing learning and training opportunities. They can lend perspective to their employees with their knack for innovation and creativity and reward innovation to keep the morale high.
Subsequently, they can have everyone on the same page when it comes to institutionalizing the change within the organization.
Also, by identifying the characteristics of transformational leadership, organizations can identify prospective leaders who have the capability to drive positive changes in the organization. In a fast-changing business environment, organizations can recognize exceptional and reliable leaders to be the face of change in the organization.
Reed Hastings leadership style analysis

Binge-watching is in vogue today and most millennials and Gen Z folks will tell you that ‘Netflix and Chill’ is one of their favorite interests to pursue. But was Netflix always a streaming platform or has it transformed its way to becoming the global hub of entertainment and binge-watching?
In case you don’t know, Netflix began its journey in 1997 as a small business that would rent DVDs to people via mail. It was founded by Reed Hastings and Marc Randolph in California and little did they know that Netflix will amass such exemplary success. However, as a truly transformational leader Reed Hastings always continued to believe that Netflix can be a big thing one day and today, owing to his transformational leadership, Netflix is the most beloved video streaming service in the world with a market capitalization of USD 174.8 billion.
Reed Hastings has never been shy of taking risks, proposing major changes in the company, and effectively leading these changes while keeping his teams motivated. What started as a DVD renting service in 1997 transformed in 2007 to become a streaming service after it became a profitable company in 2006. The first trial was started in Canada and in 2010, Netflix introduced its streaming services in the US as it embraced more positive changes under the transformational leadership of Reed Hastings. Through all these massive transitions, Reed Hastings ensured that he explained the need for change to his teams, defined the vision and value behind the change, and helped his employees to adapt to the change.
Further, in 2012, Netflix changed its strategy and started creating original content. In the subsequent year, the company transformed and innovated again to introduce Netflix subscriptions that would add to the revenues in a mammoth way. By the end of 2021, owing to the transformational leadership of Reed Hastings who is still the CEO of Netflix, the company had built a strong presence in more than 190 countries having amassed 209 million global subscribers.
In fact, the saga of transformations at Netflix still continues and the company is now looking forward to launching cloud gaming services. For that, Netflix has acquired Next Games, a Finland-based gaming company to pursue its ambitions of becoming the next gaming giant. The story of Netflix is quite intriguing and full of milestones that were set for some massive transformations. This is why Reed Hastings is one of the most exceptional examples of transformational leadership. With his strong vision, a knack for innovation, great mentorship, and progressive approach as a leader, he has led Netflix to become one of the most highly valued companies in the world. He was never reluctant to take risks, offer creative liberty to his employees and change the status quo to aim higher.
Are there any potential challenges with the Transformational Theory of Leadership?
While the Transformational Theory of Leadership is generally effective, some leaders might rely too heavily on charisma and vision, neglecting the importance of day-to-day management. Additionally, if followers' expectations are not met, their motivation may wane over time.
Can Transformational Leadership be combined with other leadership styles?
Yes, leaders often combine Transformational Leadership with other leadership styles to address various situations effectively. The combination of transformational and transactional leadership, known as the "transformational-transactional leadership continuum," allows leaders to balance inspiring followers with managing performance.
Previous Theory
Next Theory
Copyright © 2023 CrowJack. All Rights Reserved
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

Transformational Leadership: Theory and Reflections

Related Papers
Ananyo Chakravarty
Bernard Mees
There has been something rather evangelical going on in the part of management studies which concentrates on “leadership” in recent years. Since the 1980s, an obsession with heroes and charisma appears to have become characteristic of the field. If you are not doing “transformational” leadership study or are not devouring the associated literature, then you are not up with the cutting edge -- or at least that is the impression that many have of contemporary leadership studies. The field is unapologetically grounded in Carlyle and Weber, and is dominated by psychologists, business academics and those ever-present survey questionnaires. Innovation, entrepreneurship and change are the managerialist buzzwords most closely associated with the concept. Indeed the transformational approach to leadership has even been christened a new “paradigm” in leadership studies, an intellectual movement that represents a pronounced recalibration of the previous “world view” held by many leadership researchers.
Karolina Mobbs
The inspiration for that paper was the article Group Processes in the Movie, 'As it is in Heaven': Leadership that Enhances; Leadership that Stifles by Gila Ofer. In this article different aspects of the film As it is in Heaven by Kay Pollak are discussed in the context of analytical approach as well as recent research findings on the notion of leadership. In the film As it is in Heaven we contrast the model of stifle leadership presented by pastor Stig and the transformative model of leadership presented by Daniel, the former orchestra conductor. In other words two perspectives can be portrayed the scarcity versus abundance thinking – suspicious of others/fears competition versus cooperating with others/trust/building rapport (tightening bonds). The themes mentioned are among others gender differences in leadership, group matrics, ethical attention etc.
Jocelyn Chapman
… Management Administration & Leadership
Nicholas Allix
Deirdre Mulcahy
Manna Rafflesia
Avi Christian
Transformational leadership is a theory of leadership that has gained profound interest among scholars for decades. Compared to transactional leadership that emphasizes reward and punishment, transformational leadership style has focused more on the inner development of the followers. A leader with transformational leadership style would seek to stimulate his or her followers intellectually, so the transformation of the organization would start with the change of perception of the people. This article argues further that a Christian perspective could enrich the prominent theory of transformational leadership by placing Christ as the center of inspiration and God’s transformative power as the primary motivation to contribute toward the broader society. A Christian transformational leadership emphasizes God as the source of transformation and perceive the ability of the Christian leader to transforms the people as a horizontal expression of God’s transformative power experienced by th...
john malindretos , Charles Berendt , andreas christofi
Journal of Leadership Studies
Saurabh Prasad
RELATED PAPERS
Steven Sutantro
REVISTA DE EDUCACIÓN AMBIENTAL Y SOSTENIBILIDAD
Antonio Salvador
Phytopathology
Relaciones Internacionales
Maria Fernanda Camacho
Jean-Christophe LAPOUBLE
The Journal of Organic Chemistry
Ben Greatrex
Javier Alba-Tercedor
Journal of Solid State Electrochemistry
Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems
John Sinton
Analecta Veterinaria
guillermo horacio graziotti
Hydrobiologia
Daša Bastlová
The American Journal of Pathology
Valerie Askanas
Josipa Kern
IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing
Kon-Well Wang
Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Photonics, Optics and Laser Technology
Vlatko Lipovac
The Quarterly Journal of Economics
Imran Rasul
Papers on Philosophy, Psychology, Sociology and Pedagogy
Ana Proroković
Transmedia como estrategia de comunicación en el sector de la música. Caso específico: Coldplay
José Octavio Islas Carmona
Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets
Hanna Nekvasil
arXiv (Cornell University)
Rade Zivaljevic
Cuadernos del Centro de Estudios de Diseño y Comunicación
ANGÉLICA SIERRA FRANCO
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024

COMMENTS
Transformational Leadership is a leadership style where the leader inspires and motivates team members to exceed expectations, fosters an environment of trust and respect, and ultimately drives positive organizational change. Don't just skim the surface; let's get into the nitty-gritty of transformational leadership.
Transformational leadership is a driving force behind many of the positive changes in the world. Transformational leaders need to have a positive vision of the future. Anyone can become a transformational leader. Servant leadership goes hand-in-hand with transformational leadership.
Transformational leadership is a leadership style where leaders inspire, motivate, and stimulate their followers intellectually to work towards a shared and valued goal. These leaders encourage innovation, creativity, and personal development among their team members, fostering an environment of trust, respect, and admiration. They aim to transform their followers' individual and collective ...
Transformational leadership combines the right employees and the right motives. It inspires creativity and motivation in achieving a smooth flow of processes which, in the long run, ensures an effective organization that delivers its results and is consistent in achieving the desired changes.
Leadership models. Although almost every leadership researcher seems to propose a new or modified definition of the construct, leadership is generally operationalised in two ways: (1) leadership as a formal role or (2) leadership as a social influence (Yukl and Van Fleet Citation 1992).Most of the leadership research focuses on the latter, which it aims to understand through operationalisation ...
Transformational leaders focus on helping members of the group support one another and provide them with the support, guidance, and inspiration they need to work hard, perform well, and stay loyal to the group. The primary goals of transformational leadership are to inspire growth, promote loyalty, and instill confidence in group members.
each person has a sense of ownership. the group leader is the project owner. uses back-and-forth communication. uses top-down communication. motivated by personal growth. motivated by rewards and ...
With new leadership models showing very high correlations with transformational. leadership, we focus our review on the most studied leadership model of the last three. decades (Barling 2014) to ...
Transformational leadership is a theory of leadership where a leader works with teams or followers beyond their immediate self-interests to identify needed change, creating a vision to guide the change through influence, inspiration, and executing the change in tandem with committed members of a group; This change in self-interests elevates the ...
Transformational leadership is one of the most popular models, judging by the number of papers on this topic, and it has attracted global interest, expressed for example in numerous doctoral theses around the world. The concept has also been captured by political leaders anxious to reform their educational systems, in the light of international ...
Transformational leadership is a leadership theory based on the concept that a leader operates with team members or followers outside of their immediate self-interests to recognize necessary reform, create a vision to guide the change through influence, encouragement, and implementing the change in conjunction with dedicated members of a group. ...
Transformational Leadership B. Parker Ellen III D'Amore-McKim School of Business, Northeastern University, Boston, MA, USA Synonyms Charismatic-inspirational leadership Definition Leadership that inspires and motivates followers to achieve outcomes beyond expectations and helps followers grow and develop by responding to their individual ...
The transformational leadership style is aimed at encouraging high innovation and creativity among the employees so that employees develop as change leaders in the future. Transformational leaders are innovators and they aim to cultivate similar attitudes among their team members. In fact, transformational leaders are more than happy to look ...
Transformational leadership is concerned with vision, values, ethics, and relationships. It is a process of leadership in which the motives, needs, and humanity of followers is given full consideration. At the heart of the process is the visionary leader. Transformational leadership is making an impact on the church.
In reviewing these works, the authors focus on how transformational leadership influences the behaviour and practice of leaders in an effort to improve student achievement. The authors also examine limitations to the application of transformational leadership. Ultimately, the researchers determine that transformational leadership requires
Practicality, transformational leadership is a highly applicable and adaptable approach. Transformational leaders can effectively navigate the complexities of the ever-changing. educational ...
transformational and transformative leadership lies in the latter ' s view of leadership as an " everyday, everyone, everywhere, " relational process. In a time of transition
This study reviews nine qualitative works on the use of transformational leadership theory in education and identifies three major themes: 1.) globalization and multiculturalism, 2.) behaviour and ...
Transformational leadership has emerged as one of the most important approaches for understanding and influencing employee effectiveness. Inherent in this approach is the belief that transformational leaders inspire employees to greater levels of motivation and performance. Recent evidence has shown that this effect is accomplished by managing the meaning of work for employees, yet it is often ...
Transformational leadership in nursing has far-reaching implications for patient outcomes and care quality. By fostering a collaborative and patient-centered approach, empowering nursing staff, encouraging continuous learning, and promoting a culture of excellence, transformational leaders enhance the overall care experience for patients. ...
measured transformational leadership, the independent variable, by the leader's ability to motivate workers to be satisfied and productive, and by the leader's effectiveness in the organization.
Transformational leadership has surfaced as one of the most important leadership styles that foster higher levels of commitment in employees . It is defined as "a process through which leaders and followers raise one another to higher levels of morality and motivation" [ 12 ] (p. 20).
Transformational leadership is a leadership style that is often compared to and contrasted with transactional leadership. Where the latter tends to be more task-orientated and has a part to play in specific managerial contexts, transformational leadership focuses on the power of relationships to inspire others to achieve a shared vision, with longer lasting effects. The benefits of ...