The Ultimate Grant Writing Guide (and How to Find and Apply for Grants)
Securing grants requires strategic planning. Identifying relevant opportunities, building collaborations, and crafting a comprehensive grant proposal are crucial steps. Read our ultimate guide on grant writing, finding grants, and applying for grants to get the funding for your research.
Updated on February 22, 2024

Embarking on a journey of groundbreaking research and innovation always requires more than just passion and dedication, it demands financial support. In the academic and research domains, securing grants is a pivotal factor for transforming these ideas into tangible outcomes.
Grant awards not only offer the backing needed for ambitious projects but also stand as a testament to the importance and potential impact of your work. The process of identifying, pursuing, and securing grants, however, is riddled with nuances that necessitate careful exploration.
Whether you're a seasoned researcher or a budding academic, navigating this complex world of grants can be challenging, but we’re here to help. In this comprehensive guide, we'll walk you through the essential steps of applying for grants, providing expert tips and insights along the way.

Finding grant opportunities
Prior to diving into the application phase, the process of finding grants involves researching and identifying those that are relevant and realistic to your project. While the initial step may seem as simple as entering a few keywords into a search engine, the full search phase takes a more thorough investigation.
By focusing efforts solely on the grants that align with your goals, this pre-application preparation streamlines the process while also increasing the likelihood of meeting all the requirements. In fact, having a well thought out plan and a clear understanding of the grants you seek both simplifies the entire activity and sets you and your team up for success.
Apply these steps when searching for appropriate grant opportunities:
1. Determine your need
Before embarking on the grant-seeking journey, clearly articulate why you need the funds and how they will be utilized. Understanding your financial requirements is crucial for effective grant research.
2. Know when you need the money
Grants operate on specific timelines with set award dates. Align your grant-seeking efforts with these timelines to enhance your chances of success.
3. Search strategically
Build a checklist of your most important, non-negotiable search criteria for quickly weeding out grant options that absolutely do not fit your project. Then, utilize the following resources to identify potential grants:
- Online directories
- Small Business Administration (SBA)
- Foundations
4. Develop a tracking tool
After familiarizing yourself with the criteria of each grant, including paperwork, deadlines, and award amounts, make a spreadsheet or use a project management tool to stay organized. Share this with your team to ensure that everyone can contribute to the grant cycle.
Here are a few popular grant management tools to try:
- Jotform : spreadsheet template
- Airtable : table template
- Instrumentl : software
- Submit : software
Tips for Finding Research Grants
Consider large funding sources : Explore major agencies like NSF and NIH.
Reach out to experts : Consult experienced researchers and your institution's grant office.
Stay informed : Regularly check news in your field for novel funding sources.
Know agency requirements : Research and align your proposal with their requisites.
Ask questions : Use the available resources to get insights into the process.
Demonstrate expertise : Showcase your team's knowledge and background.
Neglect lesser-known sources : Cast a wide net to diversify opportunities.
Name drop reviewers : Prevent potential conflicts of interest.
Miss your chance : Find field-specific grant options.
Forget refinement : Improve proposal language, grammar, and clarity.
Ignore grant support services : Enhance the quality of your proposal.
Overlook co-investigators : Enhance your application by adding experience.
Grant collaboration
Now that you’ve taken the initial step of identifying potential grant opportunities, it’s time to find collaborators. The application process is lengthy and arduous. It requires a diverse set of skills. This phase is crucial for success.
With their valuable expertise and unique perspectives, these collaborators play instrumental roles in navigating the complexities of grant writing. While exploring the judiciousness that goes into building these partnerships, we will underscore why collaboration is both advantageous and indispensable to the pursuit of securing grants.
Why is collaboration important to the grant process?
Some grant funding agencies outline collaboration as an outright requirement for acceptable applications. However, the condition is more implied with others. Funders may simply favor or seek out applications that represent multidisciplinary and multinational projects.
To get an idea of the types of collaboration major funders prefer, try searching “collaborative research grants” to uncover countless possibilities, such as:
- National Endowment for the Humanities
- American Brain Tumor Association
For exploring grants specifically for international collaboration, check out this blog:
- 30+ Research Funding Agencies That Support International Collaboration
Either way, proposing an interdisciplinary research project substantially increases your funding opportunities. Teaming up with multiple collaborators who offer diverse backgrounds and skill sets enhances the robustness of your research project and increases credibility.
This is especially true for early career researchers, who can leverage collaboration with industry, international, or community partners to boost their research profile. The key lies in recognizing the multifaceted advantages of collaboration in the context of obtaining funding and maximizing the impact of your research efforts.
How can I find collaborators?
Before embarking on the search for a collaborative partner, it's essential to crystallize your objectives for the grant proposal and identify the type of support needed. Ask yourself these questions:
1)Which facet of the grant process do I need assistance with:
2) Is my knowledge lacking in a specific:
- Population?
3) Do I have access to the necessary:
Use these questions to compile a detailed list of your needs and prioritize them based on magnitude and ramification. These preliminary step ensure that search for an ideal collaborator is focused and effective.
Once you identify targeted criteria for the most appropriate partners, it’s time to make your approach. While a practical starting point involves reaching out to peers, mentors, and other colleagues with shared interests and research goals, we encourage you to go outside your comfort zone.
Beyond the first line of potential collaborators exists a world of opportunities to expand your network. Uncover partnership possibilities by engaging with speakers and attendees at events, workshops, webinars, and conferences related to grant writing or your field.
Also, consider joining online communities that facilitate connections among grant writers and researchers. These communities offer a space to exchange ideas and information. Sites like Collaboratory , NIH RePorter , and upwork provide channels for canvassing and engaging with feasible collaborators who are good fits for your project.
Like any other partnership, carefully weigh your vetted options before committing to a collaboration. Talk with individuals about their qualifications and experience, availability and work style, and terms for grant writing collaborations.
Transparency on both sides of this partnership is imperative to forging a positive work environment where goals, values, and expectations align for a strong grant proposal.
Putting together a winning grant proposal
It’s time to assemble the bulk of your grant application packet – the proposal itself. Each funder is unique in outlining the details for specific grants, but here are several elements fundamental to every proposal:
- Executive Summary
- Needs assessment
- Project description
- Evaluation plan
- Team introduction
- Sustainability plan
This list of multi-faceted components may seem daunting, but careful research and planning will make it manageable.
Start by reading about the grant funder to learn:
- What their mission and goals are,
- Which types of projects they have funded in the past, and
- How they evaluate and score applications.
Next, view sample applications to get a feel for the length, flow, and tone the evaluators are looking for. Many funders offer samples to peruse, like these from the NIH , while others are curated by online platforms , such as Grantstation.
Also, closely evaluate the grant application’s requirements. they vary between funding organizations and opportunities, and also from one grant cycle to the next. Take notes and make a checklist of these requirements to add to an Excel spreadsheet, Google smartsheet, or management system for organizing and tracking your grant process.
Finally, understand how you will submit the final grant application. Many funders use online portals with character or word limits for each section. Be aware of these limits beforehand. Simplify the editing process by first writing each section in a Word document to be copy and pasted into the corresponding submission fields.
If there is no online application platform, the funder will usually offer a comprehensive Request for Proposal (RFP) to guide the structure of your grant proposal. The RFP:
- Specifies page constraints
- Delineates specific sections
- Outlines additional attachments
- Provides other pertinent details
Components of a grant proposal
Cover letter.
Though not always explicitly requested, including a cover letter is a strategic maneuver that could be the factor determining whether or not grant funders engage with your proposal. It’s an opportunity to give your best first impression by grabbing the reviewer’s attention and compelling them to read further.
Cover letters are not the place for excessive emotion or detail, keep it brief and direct, stating your financial needs and purpose confidently from the outset. Also, try to clearly demonstrate the connection between your project and the funder’s mission to create additional value beyond the formal proposal.
Executive summary
Like an abstract for your research manuscript, the executive summary is a brief synopsis that encapsulates the overarching topics and key points of your grant proposal. It must set the tone for the main body of the proposal while providing enough information to stand alone if necessary.
Refer to How to Write an Executive Summary for a Grant Proposal for detailed guidance like:
- Give a clear and concise account of your identity, funding needs, and project roadmap.
- Write in an instructive manner aiming for an objective and persuasive tone
- Be convincing and pragmatic about your research team's ability.
- Follow the logical flow of main points in your proposal.
- Use subheadings and bulleted lists for clarity.
- Write the executive summary at the end of the proposal process.
- Reference detailed information explained in the proposal body.
- Address the funder directly.
- Provide excessive details about your project's accomplishments or management plans.
- Write in the first person.
- Disclose confidential information that could be accessed by competitors.
- Focus excessively on problems rather than proposed solutions.
- Deviate from the logical flow of the main proposal.
- Forget to align with evaluation criteria if specified
Project narrative
After the executive summary is the project narrative . This is the main body of your grant proposal and encompasses several distinct elements that work together to tell the story of your project and justify the need for funding.
Include these primary components:
Introduction of the project team
Briefly outline the names, positions, and credentials of the project’s directors, key personnel, contributors, and advisors in a format that clearly defines their roles and responsibilities. Showing your team’s capacity and ability to meet all deliverables builds confidence and trust with the reviewers.
Needs assessment or problem statement
A compelling needs assessment (or problem statement) clearly articulates a problem that must be urgently addressed. It also offers a well-defined project idea as a possible solution. This statement emphasizes the pressing situation and highlights existing gaps and their consequences to illustrate how your project will make a difference.
To begin, ask yourself these questions:
- What urgent need are we focusing on with this project?
- Which unique solution does our project offer to this urgent need?
- How will this project positively impact the world once completed?
Here are some helpful examples and templates.
Goals and objectives
Goals are broad statements that are fairly abstract and intangible. Objectives are more narrow statements that are concrete and measurable. For example :
- Goal : “To explore the impact of sleep deprivation on cognitive performance in college students.”
- Objective : “To compare cognitive test scores of students with less than six hours of sleep and those with 8 or more hours of sleep.”
Focus on outcomes, not processes, when crafting goals and objectives. Use the SMART acronym to align them with the proposal's mission while emphasizing their impact on the target audience.
Methods and strategies
It is vitally important to explain how you intend to use the grant funds to fulfill the project’s objectives. Detail the resources and activities that will be employed. Methods and strategies are the bridge between idea and action. They must prove to reviewers the plausibility of your project and the significance of their possible funding.
Here are some useful guidelines for writing your methods section that are outlined in " Winning Grants: Step by Step ."
- Firmly tie your methods to the proposed project's objectives and needs assessment.
- Clearly link them to the resources you are requesting in the proposal budget.
- Thoroughly explain why you chose these methods by including research, expert opinion, and your experience.
- Precisely list the facilities and capital equipment that you will use in the project.
- Carefully structure activities so that the program moves toward the desired results in a time-bound manner.
A comprehensive evaluation plan underscores the effectiveness and accountability of a project for both the funders and your team. An evaluation is used for tracking progress and success. The evaluation process shows how to determine the success of your project and measure the impact of the grant award by systematically gauging and analyzing each phase of your project as it compares to the set objectives.
Evaluations typically fall into two standard categories:
1. Formative evaluation : extending from project development through implementation, continuously provides feedback for necessary adjustments and improvements.
2. Summative evaluation : conducted post-project completion, critically assesses overall success and impact by compiling information on activities and outcomes.
Creating a conceptual model of your project is helpful when identifying these key evaluation points. Then, you must consider exactly who will do the evaluations, what specific skills and resources they need, how long it will take, and how much it will cost.
Sustainability
Presenting a solid plan that illustrates exactly how your project will continue to thrive after the grant money is gone builds the funder's confidence in the project’s longevity and significance. In this sustainability section, it is vital to demonstrate a diversified funding strategy for securing the long-term viability of your program.
There are three possible long term outcomes for projects with correlated sustainability options:
- Short term projects: Though only implemented once, will have ongoing maintenance costs, such as monitoring, training, and updates.
(E.g., digitizing records, cleaning up after an oil spill)
- Projects that will generate income at some point in the future: must be funded until your product or service can cover operating costs with an alternative plan in place for deficits.
(E.g., medical device, technology, farming method)
- Ongoing projects: will eventually need a continuous stream of funding from a government entity or large organization.
(E.g., space exploration, hurricane tracking)
Along with strategies for funding your program beyond the initial grant, reference your access to institutional infrastructure and resources that will reduce costs.
Also, submit multi-year budgets that reflect how sustainability factors are integrated into the project’s design.
The budget section of your grant proposal, comprising both a spreadsheet and a narrative, is the most influential component. It should be able to stand independently as a suitable representation of the entire endeavor. Providing a detailed plan to outline how grant funds will be utilized is crucial for illustrating cost-effectiveness and careful consideration of project expenses.
A comprehensive grant budget offers numerous benefits to both the grantor , or entity funding the grant, and the grantee , those receiving the funding, such as:
- Grantor : The budget facilitates objective evaluation and comparison between multiple proposals by conveying a project's story through responsible fund management and financial transparency.
- Grantee : The budget serves as a tracking tool for monitoring and adjusting expenses throughout the project and cultivates trust with funders by answering questions before they arise.
Because the grant proposal budget is all-encompassing and integral to your efforts for securing funding, it can seem overwhelming. Start by listing all anticipated expenditures within two broad categories, direct and indirect expenses , where:
- Direct : are essential for successful project implementation, are measurable project-associated costs, such as salaries, equipment, supplies, travel, and external consultants, and are itemized and detailed in various categories within the grant budget.
- Indirect : includes administrative costs not directly or exclusively tied to your project, but necessary for its completion, like rent, utilities, and insurance, think about lab or meeting spaces that are shared by multiple project teams, or Directors who oversee several ongoing projects.
After compiling your list, review sample budgets to understand the typical layout and complexity. Focus closely on the budget narratives , where you have the opportunity to justify each aspect of the spreadsheet to ensure clarity and validity.

While not always needed, the appendices consist of relevant supplementary materials that are clearly referenced within your grant application. These might include:
- Updated resumes that emphasize staff members' current positions and accomplishments.
- Letters of support from people or organizations that have authority in the field of your research, or community members that may benefit from the project.
- Visual aids like charts, graphs, and maps that contribute directly to your project’s story and are referred to previously in the application.
Finalizing your grant application
Now that your grant application is finished, make sure it's not just another document in the stack Aim for a grant proposal that captivates the evaluator. It should stand out not only for presenting an excellent project, but for being engaging and easily comprehended .
Keep the language simple. Avoid jargon. Prioritizing accuracy and conciseness. Opt for reader-friendly formatting with white space, headings, standard fonts, and illustrations to enhance readability.
Always take time for thorough proofreading and editing. You can even set your proposal aside for a few days before revisiting it for additional edits and improvements. At this stage, it is helpful to seek outside feedback from those familiar with the subject matter as well as novices to catch unnoticed mistakes and improve clarity.
If you want to be absolutely sure your grant proposal is polished, consider getting it edited by AJE .
How can AI help the grant process?
When used efficiently, AI is a powerful tool for streamlining and enhancing various aspects of the grant process.
- Use AI algorithms to review related studies and identify knowledge gaps.
- Employ AI for quick analysis of complex datasets to identify patterns and trends.
- Leverage AI algorithms to match your project with relevant grant opportunities.
- Apply Natural Language Processing for analyzing grant guidelines and tailoring proposals accordingly.
- Utilize AI-powered tools for efficient project planning and execution.
- Employ AI for tracking project progress and generating reports.
- Take advantage of AI tools for improving the clarity, coherence, and quality of your proposal.
- Rely solely on manual efforts that are less comprehensive and more time consuming.
- Overlook the fact that AI is designed to find patterns and trends within large datasets.
- Minimize AI’s ability to use set parameters for sifting through vast amounts of data quickly.
- Forget that the strength of AI lies in its capacity to follow your prompts without divergence.
- Neglect tools that assist with scheduling, resource allocation, and milestone tracking.
- Settle for software that is not intuitive with automated reminders and updates.
- Hesitate to use AI tools for improving grammar, spelling, and composition throughout the writing process.
Remember that AI provides a diverse array of tools; there is no universal solution. Identify the most suitable tool for your specific task. Also, like a screwdriver or a hammer, AI needs informed human direction and control to work effectively.
Looking for tips when writing your grant application?
Check out these resources:
- 4 Tips for Writing a Persuasive Grant Proposal
- Writing Effective Grant Applications
- 7 Tips for Writing an Effective Grant Proposal
- The best-kept secrets to winning grants
- The Best Grant Writing Books for Beginner Grant Writers
- Research Grant Proposal Funding: How I got $1 Million
Final thoughts
The bottom line – applying for grants is challenging. It requires passion, dedication, and a set of diverse skills rarely found within one human being.
Therefore, collaboration is key to a successful grant process . It encourages everyone’s strengths to shine. Be honest and ask yourself, “Which elements of this grant application do I really need help with?” Seek out experts in those areas.
Keep this guide on hand to reference as you work your way through this funding journey. Use the resources contained within. Seek out answers to all the questions that will inevitably arise throughout the process.
The grants are out there just waiting for the right project to present itself – one that shares the funder’s mission and is a benefit to our communities. Find grants that align with your project goals, tell your story through a compelling proposal, and get ready to make the world a better place with your research.

The AJE Team
See our "Privacy Policy"
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- PMC10250258

How to write a successful grant application: guidance provided by the European Society of Clinical Pharmacy
Anita e. weidmann.
1 Department of Clinical Pharmacy, Innsbruck University, Innsbruck, Austria
Cathal A. Cadogan
2 School of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences, Trinity College Dublin, Dublin, Ireland
Daniela Fialová
3 Department of Social and Clinical Pharmacy, Faculty of Pharmacy in Hradec Králové, Charles University, Hradec Králové, Czech Republic
4 Department of Geriatrics and Gerontology, 1st Faculty of Medicine, Charles University, Prague, Czech Republic
Ankie Hazen
5 Julius Centre for Health Sciences and Primary Care, University Medical Center Utrecht, Utrecht, The Netherlands
Martin Henman
6 Trinity College Dublin, Dublin, Ireland
Monika Lutters
7 Kantonsspital Aarau, Aarau, Switzerland
Betul Okuyan
8 Department of Clinical Pharmacy, Faculty of Pharmacy, Marmara University, Istanbul, Turkey
Vibhu Paudyal
9 University of Birmingham, Birmingham, United Kingdom
Francesca Wirth
10 Department of Pharmacy, University of Malta, Msida, Malta
Considering a rejection rate of 80–90%, the preparation of a research grant is often considered a daunting task since it is resource intensive and there is no guarantee of success, even for seasoned researchers. This commentary provides a summary of the key points a researcher needs to consider when writing a research grant proposal, outlining: (1) how to conceptualise the research idea; (2) how to find the right funding call; (3) the importance of planning; (4) how to write; (5) what to write, and (6) key questions for reflection during preparation. It attempts to explain the difficulties associated with finding calls in clinical pharmacy and advanced pharmacy practice, and how to overcome them. The commentary aims to assist all pharmacy practice and health services research colleagues new to the grant application process, as well as experienced researchers striving to improve their grant review scores. The guidance in this paper is part of ESCP’s commitment to stimulate “ innovative and high-quality research in all areas of clinical pharmacy ”.
Writing research grants is a central part of any good quality research. Once a detailed research proposal has been submitted, it is subjected to an expert peer review process. Such reviews are designed to reach a funding decision, with feedback provided to improve the study for this and any future submissions. Depending on the length of the proposal, complexity of the research and experience of the research team, a proposal can take between six to twelve months to write [ 1 ]. Ample time must be given to the writing of hypothesis/research aim, budgeting, discussion with colleagues and several rounds of feedback [ 2 ]. The draft research proposal should always be completed well before the deadline to allow for last minute delays. An application which is not fully developed should not be submitted since it will most likely be rejected [ 3 ].
Despite the large effort that goes into each grant application, success rates are low. Application success rates for Horizon 2020 were < 15% [ 4 ] and < 20% for the National Institute of Health (NIH) [ 5 – 8 ]. With these statistics in mind, it is evident that often repeated submissions are required before securing funding. Due to a paucity of specific clinical pharmacy grant awarding bodies, writing a grant application for a clinical pharmacy or pharmacy practice research project often involves multidisciplinary collaborations with other healthcare professions and focus on a specific patient population or condition. There is no guarantee of success when trying to secure funding for research. Even the most seasoned researchers will have applications rejected. The key is to never give up. This commentary provides useful pointers for the planning and execution of grant writing.
Conceptualising your research idea
Before writing a research grant proposal/application, consider what the research should achieve in the short, medium, and long term, and how the research goals will serve patients, science and society [ 9 , 10 ]. Practical implications of research, policy impact or positive impact on society and active patient/public involvement are highly valued by many research agencies as research should not be conducted “only for research”, serving the researchers’ interests. EU health policy and action strategies (CORDIS database) and other national strategies, such as national mental health strategy for grants within mental disorders, should be considered, as well as dissemination strategies, project deliverables, outcomes and lay public invitations to participate. The Science Community COMPASS has developed a useful “Message Box Tool” that can help in the identification of benefits and solutions, as well as the all-important “So What?” of the research [ 11 ]. Clearly determine what the lead researcher’s personal and professional strengths, expertise and past experiences are, and carefully select the research team to close these gaps [ 12 – 14 ].
How to find the right funding call
When trying to identify the right type of grant according to the research ambitions, one should be mindful that several types of grants exist, including small project grants (for equipment, imaging costs), personal fellowships (for salary costs, sometimes including project costs), project grants (for a combination of salary and project costs), programme grants (for comprehensive project costs and salary for several staff members), start-up grants and travel grants [ 15 ]. Types of grants include EU grants (e.g. Horizon, Norway Grant), commercial grants (e.g. healthcare agencies and insurance companies), New Health Program grants ideal for new, reimbursed clinical pharmacy service projects and national grants (e.g. FWF (Austria), ARRS (Slovenia), NKFIH (Hungary), NCN (Poland), FWO (Belgium), HRZZ (Croatia), GAČR (Czech Republic), SNSF (Switzerland), SSF (Sweden). It is worth remembering that early career researchers, normally within ten years of finishing a PhD, have a particular sub-category within most grants.
Many national agencies only have one “Pharmacy” category. This results in clinical pharmacy and advanced clinical pharmacy practice projects competing with pharmaceutical chemistry, pharmaceutical biology and pharmacy technology submissions, thereby reducing the success rate as these research areas can often be very advanced in most EU countries compared to clinical and advanced pharmacy practice. A second possible submission category is “Public Health”. Several essential factors can impact the grant selection, such as research field, budget capacity, leading researcher’s experience and bilateral grants. Examples of successful clinical pharmacy funded research studies can be found in the published literature [ 16 – 20 ].
Plan, plan, plan
One key element of successful grant writing is the ability to plan and organise time. In order to develop a realistic work plan and achieve milestones, it is imperative to note deadlines and to be well-informed about the details of what is required. The development of a table or Gantt Chart that notes milestones, outcomes and deliverables is useful [ 21 ].
All funders are quite specific about what they will and will not fund. Research your potential funders well in advance. It is vital to pay attention to the aims, ambitions and guidelines of the grant awarding bodies and focus your proposal accordingly. Submitting an application which does not adhere to the guidelines may lead to very early rejection. It is helpful to prepare the grant application in such a way that the reviewers can easily find the information they are looking for [ 15 , 22 ]. This includes checking the reviewers’ reports and adding “bolded” sentences into the application to allow immediate emphasis. Reviewers’ reports are often available on the agencies’ websites. It is extremely useful to read previously submitted and funded or rejected proposals to further help in the identification of what is required in each application. Most funding agencies publish a funded project list, and the ‘Centre for Open Science (COS) Database of Funded Research’ enables tracking of funding histories from leading agencies around the world [ 23 ]. Another useful recommendation is to talk to colleagues who have been successful when applying to that particular funder. Funding agency grant officers can provide advice on the suitability of the proposal and the application process.
It is important to pay particular attention to deadlines for the grant proposal and ensure that sufficient time is allocated for completion of all parts of the application, particularly those that are not fully within one’s own control, for example, gathering any required signatures/approvals. Funders will generally not review an application submitted beyond the deadline.
Lastly, it is important to obtain insight into the decision process of grants. Research applications are sent to several reviewers, who are either volunteers or receive a small compensation to judge the application on previously determined criteria. While the judging criteria may vary from funder to funder, the key considerations are:
- Is there a clear statement of the research aim(s)/research question(s)/research objective(s)?
- Is the proposed research “state-of-the-art” in its field and has all relevant literature been reviewed?
- Is the method likely to yield valid, reliable, trustworthy data to answer question 1.?
- If the answer to the second question is ’yes’, then what is the impact of financing this study on patient care, professional practice, society etc.?
- Is there sufficient confidence that the research team will deliver this study on time with expected quality outputs and on budget?
- Does the study provide value for money?
How to write
The key to good grant proposal writing is to be concise yet engaging. The use of colour and modern web-based tools such as #hashtags, webpage links, and links to YouTube presentations are becoming increasingly popular to improve the interest of a submission and facilitate a swift decision-making process. Ensure use of the exact section headings provided in the guidance, and use the keywords provided in the funding call documentation to reflect alignment with the funding bodies’ key interests. Attention to detail cannot be overstated; the quality and accuracy of the research proposal reflect the quality and accuracy of the research [ 24 ]. Try to adopt a clear, succinct, and simple writing style, making the grant easy to read. Having a clear focus can help to boost a grant to the top of a reviewer’s pile [ 25 , 26 ]. A clearly stated scientific question, hypothesis, and rationale are imperative. The reviewer should not have to work to understand the project [ 27 ]. Allow for plenty of time to incorporate feedback from trusted individuals with the appropriate expertise and consider having reviews for readability by non-experts.
What to write
Abstract, lay summary and background/rationale.
Take sufficient time to draft the scientific abstract and summary for the lay public. These should clearly state the long-term goal of the research, the aim and specific testable objectives, as well as the potential impact of the work. The research aim is a broad statement of research intent that sets out what the project hopes to achieve at the end. Research objectives are specific statements that define measurable outcomes of the project [ 28 , 29 ].
The lay summary is important for non-subject experts to quickly grasp the purpose and aims of the research. This is important in light of the increased emphasis on patient and public involvement in the design of the research. The abstract is often given little attention by the applicants, yet is essential. If reviewers have many applications to read, they may form a quick judgement when reading the abstract. The background should develop the argument for the study. It should flow and highlight the relevant literature and policy or society needs statements which support the argument, but at the same time must be balanced. It should focus on the need for the study at the local, national and international level, highlighting the knowledge gap the study addresses and what the proposed research adds. Ensure this section is well-referenced. The innovation section addresses the ‘‘So what?’’ question and should clearly explain how this research is important to develop an understanding in this field of practice and its potential impact. Will it change practice, or will it change the understanding of the disease process or its treatment? Will it generate new avenues for future scientific study? [ 30 ].
Hypothesis/aims and objectives
For the hypothesis, state the core idea of the grant in one or two sentences. It should be concise, and lead to testable specific aims. This section is fundamental; if it is unclear or poorly written, the reviewers may stop reading and reject the application. Do not attempt to make the aims overly complex. Well-written aims should be simply stated. Criteria such as PICO (population, intervention, comparison, outcomes) [ 31 ], and FINER (feasible, interesting, novel, ethical, relevant) [ 32 ], provide useful frameworks to help in writing aim(s), research question(s), objective(s) and hypotheses. Pay attention to the distinction between aim(s), research question(s), objective(s) and hypotheses. While it is tempting to want to claim that enormously complex problems can be solved in a single project, do not overreach. It is important to be realistic [ 25 ].
Experimental design, methods and expertise
The methodology is one of the most important parts of getting a grant proposal accepted. The reviewing board should be convinced that the relevant methodology is well within the research teams’ expertise. Any evidence of potential success, such as preliminary results or pilot studies strengthen the application significantly [ 33 ]. The methodology must relate directly to the aim. Structuring this section into specific activities/ set of activities that address each research question or objective should be considered. This clarifies how each question/ objective will be addressed. Each work-package should clearly define the title of the research question/objective to be addressed, the activities to be carried out including milestones and deliverables, and the overall duration of the proposed work-package. Deliverables should be presented in table format for ease of review. Each subsequent work-package should start once the previous one has been completed to provide a clear picture of timelines, milestones and deliverables which reflect stakeholder involvement and overall organisation of the proposed project. Using relevant EQUATOR Network reporting guidelines enhances the quality of detail included in the design [ 34 ]. Key elements of this methodology are detailed in Table 1 .
Summary of the key elements of the experimental design, methods and expertise
Proposed budget
The budget should be designed based on the needs of the project and the funding agency’s policies and instructions. Each aspect of the budget must be sufficiently justified to ensure accountability to the grant awarding body [ 35 ]. Costing and justification of the time of those involved, any equipment, consumables, travel, payment for participants, dissemination costs and other relevant costs are required. The funders will be looking for value for money and not necessarily a low-cost study. Ensure that the total budget is within the allocated funding frame.
Provide a breakdown of the key work packages and tasks to be completed, as well as an indication of the anticipated duration. Include a Gantt chart (A table detailing the most general project content milestones and activities) to demonstrate that all aspects of the proposal have been well thought through [ 21 ].
Critical appraisal, limitations, and impact of the proposed research
It is important to detail any strengths and limitations of the proposed project. Omitting these will present the reviewing board with sufficient grounds to reject the proposal [ 36 ]. Provide a clear statement about the short and long-term impact of the research [ 37 , 38 ]. The reviewers will pay particular attention to the differences the study can make and how potential impact aligns with the funding bodies goals as well as national policies. This statement is essential to make an informed decision whether or not to support the application. Useful diagrams summarise the different levels of impact [ 39 ].
Table 2 provides a summary of the key elements of project grants and key questions to ask oneself.
Summary of the key elements of project grants and key questions to ask oneself.
(Adapted from [ 5 ]: Koppelmann GH, Holloway JW. Successful grant writing. Paediatr Respir Rev. 2012; 13:63–66.)
Although the grant writing process is time-consuming and complex, support is widely available at each stage. It is important to involve colleagues and collaborators to improve the proposal as much as possible and invest time in the detailed planning and execution. Even if the grant is not awarded, do not be disheartened. Use the feedback for improvement and exercise resilience and persistence in pursuing your research ambition.
The guidance in this paper is part of ESCP’s commitment to stimulate “innovative and high-quality research in all areas of clinical pharmacy”. In a previous ESCP survey, it was found that few opportunities for collaboration (especially for grant applications) was one of the key barriers for members towards conducting research [ 40 ]. ESCP promotes networking, which is essential for multi-centre grant applications, both among ESCP members and with other organisations as it recognises the need for “multi-centre research in all areas of clinical pharmacy both within countries and between countries or differing healthcare delivery systems”. ESCP is planning to relaunch its own research grant which was paused during the pandemic, and it is also planning to provide ESCP members with information about the research grants offered by other organizations. ESCP is exploring partnering with other organisations to develop research proposals in areas of common interest and, in the near future, it will ask its members about their research priorities. Taken together, these initiatives will inform ESCP’s research strategy and help it to formulate policies to address the challenges its members face.
Acknowledgements
Research works of Assoc. Prof. Fialová were also supported by the institutional program Cooperation of the Faculty of Pharmacy, Charles University.
Open access funding provided by University of Innsbruck and Medical University of Innsbruck. This work was conducted without external funding.
Conflicts of interest
The authors have not disclosed any competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Reference management. Clean and simple.
How to write a grant proposal: a step-by-step guide

What is a grant proposal?
Why should you write a grant proposal, format of a grant proposal, how to write a grant proposal, step 1: decide what funding opportunity to apply for, and research the grant application process, step 2: plan and research your project, preliminary research for your grant proposal, questions to ask yourself as you plan your grant proposal, developing your grant proposal, step 3: write the first draft of your grant proposal, step 4: get feedback, and revise your grant proposal accordingly, step 5: prepare to submit your grant proposal, what happens after submitting the grant proposal, final thoughts, other useful sources for writing grant proposals, frequently asked questions about writing grant proposals, related articles.
You have a vision for a future research project, and want to share that idea with the world.
To achieve your vision, you need funding from a sponsoring organization, and consequently, you need to write a grant proposal.
Although visualizing your future research through grant writing is exciting, it can also feel daunting. How do you start writing a grant proposal? How do you increase your chances of success in winning a grant?
But, writing a proposal is not as hard as you think. That’s because the grant-writing process can be broken down into actionable steps.
This guide provides a step-by-step approach to grant-writing that includes researching the application process, planning your research project, and writing the proposal. It is written from extensive research into grant-writing, and our experiences of writing proposals as graduate students, postdocs, and faculty in the sciences.
A grant proposal is a document or collection of documents that outlines the strategy for a future research project and is submitted to a sponsoring organization with the specific goal of getting funding to support the research. For example, grants for large projects with multiple researchers may be used to purchase lab equipment, provide stipends for graduate and undergraduate researchers, fund conference travel, and support the salaries of research personnel.
As a graduate student, you might apply for a PhD scholarship, or postdoctoral fellowship, and may need to write a proposal as part of your application. As a faculty member of a university, you may need to provide evidence of having submitted grant applications to obtain a permanent position or promotion.
Reasons for writing a grant proposal include:
- To obtain financial support for graduate or postdoctoral studies;
- To travel to a field site, or to travel to meet with collaborators;
- To conduct preliminary research for a larger project;
- To obtain a visiting position at another institution;
- To support undergraduate student research as a faculty member;
- To obtain funding for a large collaborative project, which may be needed to retain employment at a university.
The experience of writing a proposal can be helpful, even if you fail to obtain funding. Benefits include:
- Improvement of your research and writing skills
- Enhancement of academic employment prospects, as fellowships and grants awarded and applied for can be listed on your academic CV
- Raising your profile as an independent academic researcher because writing proposals can help you become known to leaders in your field.
All sponsoring agencies have specific requirements for the format of a grant proposal. For example, for a PhD scholarship or postdoctoral fellowship, you may be required to include a description of your project, an academic CV, and letters of support from mentors or collaborators.
For a large research project with many collaborators, the collection of documents that need to be submitted may be extensive. Examples of documents that might be required include a cover letter, a project summary, a detailed description of the proposed research, a budget, a document justifying the budget, and the CVs of all research personnel.
Before writing your proposal, be sure to note the list of required documents.
Writing a grant proposal can be broken down into three major activities: researching the project (reading background materials, note-taking, preliminary work, etc.), writing the proposal (creating an outline, writing the first draft, revisions, formatting), and administrative tasks for the project (emails, phone calls, meetings, writing CVs and other supporting documents, etc.).
Below, we provide a step-by-step guide to writing a grant proposal:
- Decide what funding opportunity to apply for, and research the grant application process
- Plan and research your project
- Write the first draft of your grant proposal
- Get feedback, and revise your grant proposal accordingly
- Prepare to submit your grant proposal

- Start early. Begin by searching for funding opportunities and determining requirements. Some sponsoring organizations prioritize fundamental research, whereas others support applied research. Be sure your project fits the mission statement of the granting organization. Look at recently funded proposals and/or sample proposals on the agency website, if available. The Research or Grants Office at your institution may be able to help with finding grant opportunities.
- Make a spreadsheet of grant opportunities, with a link to the call for proposals page, the mission and aims of the agency, and the deadline for submission. Use the information that you have compiled in your spreadsheet to decide what to apply for.
- Once you have made your decision, carefully read the instructions in the call for proposals. Make a list of all the documents you need to apply, and note the formatting requirements and page limits. Know exactly what the funding agency requires of submitted proposals.
- Reach out to support staff at your university (for example, at your Research or Grants Office), potential mentors, or collaborators. For example, internal deadlines for submitting external grants are often earlier than the submission date. Make sure to learn about your institution’s internal processes, and obtain contact information for the relevant support staff.
- Applying for a grant or fellowship involves administrative work. Start preparing your CV and begin collecting supporting documents from collaborators, such as letters of support. If the application to the sponsoring agency is electronic, schedule time to set up an account, log into the system, download necessary forms and paperwork, etc. Don’t leave all of the administrative tasks until the end.
- Map out the important deadlines on your calendar. These might include video calls with collaborators, a date for the first draft to be complete, internal submission deadlines, and the funding agency deadline.
- Schedule time on your calendar for research, writing, and administrative tasks associated with the project. It’s wise to group similar tasks and block out time for them (a process known as ” time batching ”). Break down bigger tasks into smaller ones.

Now that you know what you are applying for, you can think about matching your proposed research to the aims of the agency. The work you propose needs to be innovative, specific, realizable, timely, and worthy of the sponsoring organization’s attention.
- Develop an awareness of the important problems and open questions in your field. Attend conferences and seminar talks and follow all of your field’s major journals.
- Read widely and deeply. Journal review articles are a helpful place to start. Reading papers from related but different subfields can generate ideas. Taking detailed notes as you read will help you recall the important findings and connect disparate concepts.
- Writing a grant proposal is a creative and imaginative endeavor. Write down all of your ideas. Freewriting is a practice where you write down all that comes to mind without filtering your ideas for feasibility or stopping to edit mistakes. By continuously writing your thoughts without judgment, the practice can help overcome procrastination and writer’s block. It can also unleash your creativity, and generate new ideas and associations. Mind mapping is another technique for brainstorming and generating connections between ideas.
- Establish a regular writing practice. Schedule time just for writing, and turn off all distractions during your focused work time. You can use your writing process to refine your thoughts and ideas.
- Use a reference manager to build a library of sources for your project. You can use a reference management tool to collect papers , store and organize references , and highlight and annotate PDFs . Establish a system for organizing your ideas by tagging papers with labels and using folders to store similar references.
To facilitate intelligent thinking and shape the overall direction of your project, try answering the following questions:
- What are the questions that the project will address? Am I excited and curious about their answers?
- Why are these questions important?
- What are the goals of the project? Are they SMART (Specific, Measurable, Actionable, Relevant, and Timely)?
- What is novel about my project? What is the gap in current knowledge?
- What methods will I use, and how feasible is my approach?
- Can the work be done over the proposed period, and with the budget I am requesting?
- Do I have relevant experience? For example, have I completed similar work funded by previous grants or written papers on my proposed topic?
- What pilot research or prior work can I use, or do I need to complete preliminary research before writing the proposal?
- Will the outcomes of my work be consequential? Will the granting agency be interested in the results?
- What solutions to open problems in my field will this project offer? Are there broader implications of my work?
- Who will the project involve? Do I need mentors, collaborators, or students to contribute to the proposed work? If so, what roles will they have?
- Who will read the proposal? For example, experts in the field will require details of methods, statistical analyses, etc., whereas non-experts may be more concerned with the big picture.
- What do I want the reviewers to feel, and take away from reading my proposal?
- What weaknesses does my proposed research have? What objections might reviewers raise, and how can I address them?
- Can I visualize a timeline for my project?
Create an actionable plan for your research project using the answers to these questions.
- Now is the time to collect preliminary data, conduct experiments, or do a preliminary study to motivate your research, and demonstrate that your proposed project is realistic.
- Use your plan to write a detailed outline of the proposal. An outline helps you to write a proposal that has a logical format and ensures your thought process is rational. It also provides a structure to support your writing.
- Follow the granting agency’s guidelines for titles, sections, and subsections to inform your outline.
At this stage, you should have identified the aims of your project, what questions your work will answer, and how they are relevant to the sponsoring agency’s call for proposals. Be able to explain the originality, importance, and achievability of your proposed work.

Now that you have done your research, you are ready to begin writing your proposal and start filling in the details of your outline. Build on the writing routine you have already started. Here are some tips:
- Follow the guidelines of the funding organization.
- Keep the proposal reviewers in mind as you write. Your audience may be a combination of specialists in your field and non-specialists. Make sure to address the novelty of your work, its significance, and its feasibility.
- Write clearly, concisely, and avoid repetition. Use topic sentences for each paragraph to emphasize key ideas. Concluding sentences of each paragraph should develop, clarify, or summarize the support for the declaration in the topic sentence. To make your writing engaging, vary sentence length.
- Avoid jargon, where possible. Follow sentences that have complex technical information with a summary in plain language.
- Don’t review all information on the topic, but include enough background information to convince reviewers that you are knowledgeable about it. Include preliminary data to convince reviewers you can do the work. Cite all relevant work.
- Make sure not to be overly ambitious. Don’t propose to do so much that reviewers doubt your ability to complete the project. Rather, a project with clear, narrowly-defined goals may prove favorable to reviewers.
- Accurately represent the scope of your project; don’t exaggerate its impacts. Avoid bias. Be forthright about the limitations of your research.
- Ensure to address potential objections and concerns that reviewers may have with the proposed work. Show that you have carefully thought about the project by explaining your rationale.
- Use diagrams and figures effectively. Make sure they are not too small or contain too much information or details.
After writing your first draft, read it carefully to gain an overview of the logic of your argument. Answer the following questions:
- Is your proposal concise, explicit, and specific?
- Have you included all necessary assumptions, data points, and evidence in your proposal?
- Do you need to make structural changes like moving or deleting paragraphs or including additional tables or figures to strengthen your rationale?
- Have you answered most of the questions posed in Step 2 above in your proposal?
- Follow the length requirements in the proposal guidelines. Don't feel compelled to include everything you know!
- Use formatting techniques to make your proposal easy on the eye. Follow rules for font, layout, margins, citation styles , etc. Avoid walls of text. Use bolding and italicizing to emphasize points.
- Comply with all style, organization, and reference list guidelines to make it easy to reviewers to quickly understand your argument. If you don’t, it’s at best a chore for the reviewers to read because it doesn’t make the most convincing case for you and your work. At worst, your proposal may be rejected by the sponsoring agency without review.
- Using a reference management tool like Paperpile will make citation creation and formatting in your grant proposal quick, easy and accurate.

Now take time away from your proposal, for at least a week or more. Ask trusted mentors or collaborators to read it, and give them adequate time to give critical feedback.
- At this stage, you can return to any remaining administrative work while you wait for feedback on the proposal, such as finalizing your budget or updating your CV.
- Revise the proposal based on the feedback you receive.
- Don’t be discouraged by critiques of your proposal or take them personally. Receiving and incorporating feedback with humility is essential to grow as a grant writer.

Now you are almost ready to submit. This is exciting! At this stage, you need to block out time to complete all final checks.
- Allow time for proofreading and final editing. Spelling and grammar mistakes can raise questions regarding the rigor of your research and leave a poor impression of your proposal on reviewers. Ensure that a unified narrative is threaded throughout all documents in the application.
- Finalize your documents by following a checklist. Make sure all documents are in place in the application, and all formatting and organizational requirements are met.
- Follow all internal and external procedures. Have login information for granting agency and institution portals to hand. Double-check any internal procedures required by your institution (applications for large grants often have a deadline for sign-off by your institution’s Research or Grants Office that is earlier than the funding agency deadline).
- To avoid technical issues with electronic portals, submit your proposal as early as you can.
- Breathe a sigh of relief when all the work is done, and take time to celebrate submitting the proposal! This is already a big achievement.
Now you wait! If the news is positive, congratulations!
But if your proposal is rejected, take heart in the fact that the process of writing it has been useful for your professional growth, and for developing your ideas.
Bear in mind that because grants are often highly competitive, acceptance rates for proposals are usually low. It is very typical to not be successful on the first try and to have to apply for the same grant multiple times.
Here are some tips to increase your chances of success on your next attempt:
- Remember that grant writing is often not a linear process. It is typical to have to use the reviews to revise and resubmit your proposal.
- Carefully read the reviews and incorporate the feedback into the next iteration of your proposal. Use the feedback to improve and refine your ideas.
- Don’t ignore the comments received from reviewers—be sure to address their objections in your next proposal. You may decide to include a section with a response to the reviewers, to show the sponsoring agency that you have carefully considered their comments.
- If you did not receive reviewer feedback, you can usually request it.
You learn about your field and grow intellectually from writing a proposal. The process of researching, writing, and revising a proposal refines your ideas and may create new directions for future projects. Professional opportunities exist for researchers who are willing to persevere with submitting grant applications.
➡️ Secrets to writing a winning grant
➡️ How to gain a competitive edge in grant writing
➡️ Ten simple rules for writing a postdoctoral fellowship
A grant proposal should include all the documents listed as required by the sponsoring organization. Check what documents the granting agency needs before you start writing the proposal.
Granting agencies have strict formatting requirements, with strict page limits and/or word counts. Check the maximum length required by the granting agency. It is okay for the proposal to be shorter than the maximum length.
Expect to spend many hours, even weeks, researching and writing a grant proposal. Consequently, it is important to start early! Block time in your calendar for research, writing, and administration tasks. Allow extra time at the end of the grant-writing process to edit, proofread, and meet presentation guidelines.
The most important part of a grant proposal is the description of the project. Make sure that the research you propose in your project narrative is new, important, and viable, and that it meets the goals of the sponsoring organization.
A grant proposal typically consists of a set of documents. Funding agencies have specific requirements for the formatting and organization of each document. Make sure to follow their guidelines exactly.
- About Grants
- How to Apply - Application Guide
- Write Application
Write Your Application
The following guidance may assist you in developing a strong application that allows reviewers to better evaluate the science and merit of your proposal. This page provides tips for demonstrating to reviewers and NIH staff the high quality of the personnel involved in your project and documenting resources and institutional support of the project. We provide information for new investigators and foreign applicants, as well.
Though the advice provided is relevant for all research grants, it is general in nature and geared toward the NIH Research Project (R01) . The tips should not replace your organization's internal guidance, specific advice provided by NIH program or grants management staff, or instructions found in the funding opportunity or application guide .
- Where to Find Instructions for Writing Your Application
What Peer Reviewers Look For
- Research Resources, Institutional Support and Available Expertise
- Cover Letter & Assignment Request Form
- Are You a New or Early Stage Investigator
Foreign Involvement: Institution and/or Investigator
Develop your budget, your research plan, additional elements required in a grant application, important writing tips, what to know before you start writing, where to find application instructions.
- In addition to form-by-form, field-by-field instructions you'll find guidance on formatting attachments (fonts, margins, etc., developing a budget, and more.
- Section IV. Application and Submission Information of each funding opportunity includes opportunity-specific instructions.
- Notices posted in the NIH Guide for Grants & Contracts may contain corrections, clarifications, or announcement of new policies.
If instructions in the application guide and funding opportunity conflict, the opportunity wins. If instructions in either the application guide or funding opportunity conflict with an NIH Guide notice (including a Notice of Special Interest), the notice wins.
Careful preparation and an understanding of how your application will be reviewed can help you build a solid application. During NIH’s peer review process , we convene a panel of non-Federal scientists to review your application. Although a number of factors contribute to whether your application will be funded, we place great emphasis on the review of scientific merit. The following sections describe the criteria reviewers employ to evaluate applications. Read them carefully for helpful hints on the information and content you should include in the application to garner a favorable evaluation.
Overall Impact
Reviewers will provide an overall impact score to reflect their assessment of the likelihood for the project to exert a sustained, powerful influence on the research field(s) involved, in consideration of the following review criteria, and additional review criteria (as applicable for the project proposed).
Scored Review Criteria
Reviewers will consider each of the review criteria below in the determination of scientific and technical merit, and give a separate score for each. An application does not need to be strong in all categories to be judged likely to have major scientific impact. For example, a project that by its nature is not innovative may be essential to advance a field.
Significance. Does the project address an important problem or a critical barrier to progress in the field? Is there a strong scientific premise for the project? If the aims of the project are achieved, how will scientific knowledge, technical capability, and/or clinical practice be improved? How will successful completion of the aims change the concepts, methods, technologies, treatments, services, or preventative interventions that drive this field?
Investigator(s). Are the PD/PIs, collaborators, and other researchers well suited to the project? If Early Stage Investigators or New Investigators, or in the early stages of independent careers, do they have appropriate experience and training? If established, have they demonstrated an ongoing record of accomplishments that have advanced their field(s)? If the project is collaborative or multi-PD/PI, do the investigators have complementary and integrated expertise; are their leadership approach, governance and organizational structure appropriate for the project?
Innovation. Does the application challenge and seek to shift current research or clinical practice paradigms by utilizing novel theoretical concepts, approaches or methodologies, instrumentation, or interventions? Are the concepts, approaches or methodologies, instrumentation, or interventions novel to one field of research or novel in a broad sense? Is a refinement, improvement, or new application of theoretical concepts, approaches or methodologies, instrumentation, or interventions proposed?
Approach. Are the overall strategy, methodology, and analyses well-reasoned and appropriate to accomplish the specific aims of the project? Have the investigators presented strategies to ensure a robust and unbiased approach, as appropriate for the work proposed? Are potential problems, alternative strategies, and benchmarks for success presented? If the project is in the early stages of development, will the strategy establish feasibility and will particularly risky aspects be managed? Have the investigators presented adequate plans to address relevant biological variables, such as sex, for studies in vertebrate animals or human subjects? If the project involves clinical research, are the plans for 1) protection of human subjects from research risks, and 2) inclusion (or exclusion) of individuals on the basis of sex/gender, race, and ethnicity, as well as the inclusion or exclusion of individuals of all ages (including children and older adults), justified in terms of the scientific goals and research strategy proposed? Environment. Will the scientific environment in which the work will be done contribute to the probability of success? Are the institutional support, equipment and other physical resources available to the investigators adequate for the project proposed? Will the project benefit from unique features of the scientific environment, subject populations, or collaborative arrangements?
Note that an application does not need to be strong in all categories to be judged likely to have major scientific impact. For example, a project that by its nature is not innovative may be essential to advance a field.
Learn more about how applications are scored.
Additional Review Criteria
As applicable for the project proposed, reviewers will evaluate the following additional items while determining scientific and technical merit and in providing an overall impact score, but will not give separate scores for these items.
- Protections for Human Subjects
- Inclusion of Women, Minorities, and Individuals Across the Lifespan
- Vertebrate Animals
- Resubmission
Be sure to address any of these additional review criteria that apply to your application, as reviewers will consider them when assigning overall impact/priority scores.
Additional Review Considerations
As applicable for the project proposed, reviewers will consider each of the following items, but will not give scores for these items and should not consider them in providing an overall impact score.
- Applications from Foreign Organizations
- Select Agent
- Resource Sharing Plans
- Authentication of Key Biological and/or Chemical Resources
- Budget and Period Support
Learn more about how applications are reviewed and scored on our peer review process page.
Research Resources, Institutional Support and Available Expertise
Sufficient information must be included to demonstrate to reviewers and NIH staff the high quality of the PD/PI, the co-investigators, available research resources, and the applicant institution and its support of the project.
Applicants should clearly state that they have the appropriate resources to conduct the research, such as adequate equipment and laboratory space. When possible, include letters of commitment for these resources.
- Understand the level of resources needed to compete.
- Conduct an organizational assessment.
- Determine what resources and support your organization has and what additional support you'll need.
- Consider whether the available equipment and facilities are adequate and whether the environment is conducive to the research.
Independence and Institutional Support
This is important for all investigators, but particularly for new and early stage investigators or those who are early in their independent careers:
- Provide reviewers evidence that you have the appropriate experience and training to lead and manage the research project.
- Letters of reference and institutional commitment are important.
- Mention any start-up funds, support for a technician, etc. This is a positive indicator of institutional commitment to the peer reviewers.
Collaborators and Consultants
Determine the expertise needed for your research study team (individuals, collaborating organizations, resources, etc.). Most scientific work requires collaboration among researchers, and NIH is dedicated to fostering such relationships.
- Include letters of commitment in your application that clearly spell out the roles of the collaborators. The grant application should contain a signed letter from each collaborator to the applicant that lists the contribution he or she intends to make and his or her commitment to the work. These letters are often the primary assurance the reviewers have that this work will in fact be done.
- For consultants, letters should include rate/charge for consulting services.
- The format, peer review and administration of applications submitted with multiple PIs do have some significant differences from the traditional single-PI application. Therefore, it is essential to consider all aspects of the funding mechanism before applying, regardless of the type of research proposal to be submitted.
- All applicants proposing team science efforts are strongly encouraged to contact their NIH program officials at the earliest possible date to discuss the appropriateness submitting with multiple-PIs for the support of their research.
Cover Letter & PHS Assignment Request Form
Although optional in most cases, the Cover Letter attachment on the SF424 (R&R) form and the PHS Assignment Request Form can be used to convey information to the Division of Receipt and Referral (DRR) in the Center for Scientific Review.
- Late applications
- Required agency approvals, if needed (e.g., approval to submit application with budget period(s) of $500k or more)
- Explanation of subaward budgets not active in all budget periods
- Intent to submit a video
- Anticipation of large-scale genomic data
- Proposed use of human fetal tissue from elective abortions
- A potentially appropriate institute or center assignment
- NIH Scientific Review Group (SRG) Roster Index
- Take advantage of the Assisted Referral Tool (ART)
- Reviewers that may have a conflict of interest and why they should not be considered to review your application
- Only NIH staff with a need to know are provided access to your assignment request and cover letter. Reviewers to not access to them.
Are You a New or Early Stage Investigator?
- Determine whether you qualify as a new investigator based on the NIH definition of new investigator . NIH offers funding opportunities tailored to new investigators, such as the NIH Director's New Innovator Award . More information on NIH programs designed for new investigators can be found on the New Investigators Program Web page.
- It is to your advantage to identify yourself as a new investigator because reviewers are instructed to give special consideration to new investigators. Reviewers will give greater consideration to the proposed approach, rather than the track record.
- First-time applicants may have less preliminary data and fewer publications than more seasoned investigators, and NIH reviewers understand this. Reviewers instead place more emphasis on how the investigator has demonstrated that he or she is truly independent of any former mentors, whether he or she has some of his or her own resources and institutional support, and whether he or she is able to independently lead the research.
- Foreign PD/PIs and those from foreign institutions should ensure their eligibility by checking the eligibility guidelines provided in every funding opportunity.
- Foreign PD/PI's and those from foreign institutions are highly encouraged to contact a NIH program officer as soon as possible in the planning and writing stages.
- Foreign applicants can learn more at our Information for Foreign Applicants and Grantees page.
This step will be one of your most time-consuming in the writing process.
- Know what type of budget will be required to submit with your application (found in your funding opportunity).
- Understand the various components of the budget, working with your institution’s central grants office and department administrator.
- Contact NIH program officials regarding allowability and other budgetary questions.
- For more information, see Develop Your Budget .
The research plan describes the proposed research, stating its significance and how it will be conducted. Remember, your application has two audiences: the majority of reviewers who will probably not be familiar with your techniques or field and a smaller number who will be familiar.
- To succeed in peer review, you must win over the assigned reviewers . They act as your advocates in guiding the review panel's discussion of your application.
- Write and organize your application so the primary reviewer can readily grasp and explain what you are proposing and advocate for your application.
- Appeal to the reviewers and the funding ICs by using language that stresses the significance of your proposed work.
The following elements need to be included in the grant application as appropriate. Unless stated, these elements do not influence the rating (priority score) of the application. However, the reviewers are asked to comment on the adequacy of the information provided for each element. Any concerns the reviewers identify may negatively affect and postpone the granting of an award.
- Bibliography & References Cited Provide a bibliography of any references cited in the Research Plan. Each reference must include the names of all authors (in the same sequence in which they appear in the publication; you can use “et al.” convention in place of listing all authors in a citation), the article and journal title, book title, volume number, page numbers, and year of publication. Make sure that only bibliographic citations are included. Be especially careful to follow scholarly practices in providing citations for source materials relied upon when preparing any section of the application.
- Office of Laboratory Animal Welfare
- PHS Policy Tutorial
- What Investigators Need to Know About the Use of Animals (PDF)
- Interactive training module: Vertebrate Animals Section (VAS) in Grant Applications
- NIAID's tutorial: Requirement for Grantees Using Research Animals
- Consortium/Contractual Arrangements Explain the programmatic, fiscal, and administrative arrangements to be made between the applicant organization and the consortium organization(s).
- Consultants and Collaborators Attach appropriate letters from all consultants and collaborators confirming their roles in the project. For consultants, letters should include rate/charge for consulting services.
- Facilities & Other Resources This information is used to assess the capability of the organizational resources available to perform the effort proposed. Identify the facilities to be used (Laboratory, Animal, Computer, Office, Clinical and Other). If appropriate, indicate their capacities, pertinent capabilities, relative proximity and extent of availability to the project. Describe only those resources that are directly applicable to the proposed work.
- Inclusion of Women, Minorities, and Individuals Across the Lifespan in Research Peer reviewers will also assess the adequacy of plans to include subjects from both genders, all racial and ethnic groups (and subgroups), and individuals across the lifespan, as appropriate, for the scientific goals of the research will be assessed. Plans for the recruitment and retention of subjects will also be evaluated. Check out the Inclusion Policies for Research Involving Human Subjects , which includes resources for Inclusion of Women and Minorities and Inclusion Across the Lifespan .
- Multiple PD/PI For applications designating multiple PDs/PIs , you must include a leadership plan.
- Other Plans(s) Applicants proposing to conduct research that will generate scientific data are subject to the NIH Data Management and Sharing (DMS) Policy and must attach a DMS Plan in this section. Note that applicants whose project also falls under NIH’s Genomic Data Sharing (GDS) Policy are expected to provide a single plan that covers the sharing of both scientific data and genomic data. See NIH’s DMS and GDS policies on the NIH Sharing website .
- Page Limits Follow the page limits specified for the attachments in your grant application, unless otherwise specified in the funding opportunity.
- Protection of Human Subjects from Research Risk Applicants must assure NIH that all human subjects are protected. Reviewers will assess the potential risk to human subjects in proposed research and evaluate what protections are in place to guard against any research-related risk. Awards cannot be made until assurances are on file with the Office for Human Research Protections (OHRP). Decision charts are presented that are helpful in thinking through relevant human subject protections issues (see http://www.hhs.gov/ohrp/policy/checklists/decisioncharts.html ).
- Resource Sharing Plan(s) This section includes the Model Organisms Sharing plan when applicable. See NIH’s Model Organisms Sharing Policy .
- Select Agents Identify any select agents to be used in the proposed research. Select agents are hazardous biological agents and toxins that HHS or USDA have identified as having the potential to pose a severe threat to public health and safety, to animal and plant health, or to animal and plant products. CDC maintains a list of HHS and USDA Select Agents and Toxins.
- Use of Internet Sites NIH instituted a policy that prohibits the use of World Wide Web addresses (URLs) in grant applications in the place of text describing the same material. This is because of the potential for providing a large amount of extra material from a Web site beyond what would fit in the page limit, and thereby giving an unfair advantage to some applicants and a large additional burden for reviewers.
You’ve planned, you’ve researched, you understand the application…now it’s time to write. A well-written, well formatted application is an important key to success. Remember the details when formatting attachments !
- Before you start writing the application, think about the budget and how it is related to your research plan. Remember that everything in the budget must be justified by the work you've proposed to do.
- Be realistic. Don't propose more work than can be reasonably done during the proposed project period. Make sure that the personnel have appropriate scientific expertise and training. Make sure that the budget is reasonable and well-justified.
Start with an outline, following the suggested organization of the application. The thought process of the application should be easy to follow.
Note: Upon submission, NIH Systems will automatically add: headers, footers (time stamping, tracking number, funding opportunity number, and page numbers). Therefore, do not include headers or footers.
- Write clear headings.
- Use sub-headings, short paragraphs, and other techniques to make the application as easy to navigate as possible. Be specific and informative, and avoid redundancies.
- Bookmark major sections.
- Use diagrams, figures and tables, and include appropriate legends, to assist the reviewers to understand complex information. These should complement the text and be appropriately inserted. Make sure the figures and labels are readable in the size they will appear in the application.
- Use bullets and numbered lists for effective organization. Indents and bold print add readability. Bolding highlights key concepts and allows reviewers to scan the pages and retrieve information quickly.
- Utilize white space effectively.
- Write a clear topic sentence for each paragraph with one main point or idea. This is key for readability.
- Make your points as direct as possible. Avoid jargon or excessive language.
- Write simple and clear sentences, keeping to about 20 words or less in each.
- Be consistent with terms, references and writing style.
- Use the active, rather than passive, voice. For example, write "We will develop an experiment, "not "An experiment will be developed."
- Spell out all acronyms on first reference.
- If writing is not your forte, seek help!
- Include enough background information to enable an intelligent reader to understand your proposed work.
- Support your idea with collaborators who have expertise that benefits the project.
- Have zero tolerance for typographical errors, misspellings, grammatical mistakes or sloppy formatting. A sloppy or disorganized application may lead the reviewers to conclude that your research may be conducted in the same manner.
- Remember the Details! There are format requirements , such as font size, margins, and spacing. Make sure you are familiar with them before submitting your application and label sections as directed. You don’t want your application delayed because any of these details are not incorporated.
- If more than one investigator is contributing to the writing, it would be helpful to have one editor not only review for punctuation errors, but ensure that the application has a consistent writing style.
- Request your colleagues or mentors review a first draft of your specific aims early in the process. This step can save lots of valuable time.
- Allow time for an internal review by collaborators, colleagues, mentors and make revisions/edits from that review. If possible, have both experts in your field and those who are less familiar with your science provide feedback.
- Ask those who are providing a review to use a critical eye and evaluate the application using the peer review criteria
- Allow sufficient time to put the completed application aside, and then read it from a fresh vantage point yourself. Also, try proofreading by reading the application aloud.
- Conduct your own review based on the NIH's five peer review criteria. How would you rate your own application?
- Prior to submission, look over the entire grant application one final time. Remember, you want a convincing proposal that is also formatted according to the application guidelines, punctuation error-free, clear to read, and is to the point!
This page last updated on: May 6, 2024
- Bookmark & Share
- E-mail Updates
- Help Downloading Files
- Privacy Notice
- Accessibility
- National Institutes of Health (NIH), 9000 Rockville Pike, Bethesda, Maryland 20892
- NIH... Turning Discovery Into Health

Grant Proposals (or Give me the money!)
What this handout is about.
This handout will help you write and revise grant proposals for research funding in all academic disciplines (sciences, social sciences, humanities, and the arts). It’s targeted primarily to graduate students and faculty, although it will also be helpful to undergraduate students who are seeking funding for research (e.g. for a senior thesis).
The grant writing process
A grant proposal or application is a document or set of documents that is submitted to an organization with the explicit intent of securing funding for a research project. Grant writing varies widely across the disciplines, and research intended for epistemological purposes (philosophy or the arts) rests on very different assumptions than research intended for practical applications (medicine or social policy research). Nonetheless, this handout attempts to provide a general introduction to grant writing across the disciplines.
Before you begin writing your proposal, you need to know what kind of research you will be doing and why. You may have a topic or experiment in mind, but taking the time to define what your ultimate purpose is can be essential to convincing others to fund that project. Although some scholars in the humanities and arts may not have thought about their projects in terms of research design, hypotheses, research questions, or results, reviewers and funding agencies expect you to frame your project in these terms. You may also find that thinking about your project in these terms reveals new aspects of it to you.
Writing successful grant applications is a long process that begins with an idea. Although many people think of grant writing as a linear process (from idea to proposal to award), it is a circular process. Many people start by defining their research question or questions. What knowledge or information will be gained as a direct result of your project? Why is undertaking your research important in a broader sense? You will need to explicitly communicate this purpose to the committee reviewing your application. This is easier when you know what you plan to achieve before you begin the writing process.
Diagram 1 below provides an overview of the grant writing process and may help you plan your proposal development.
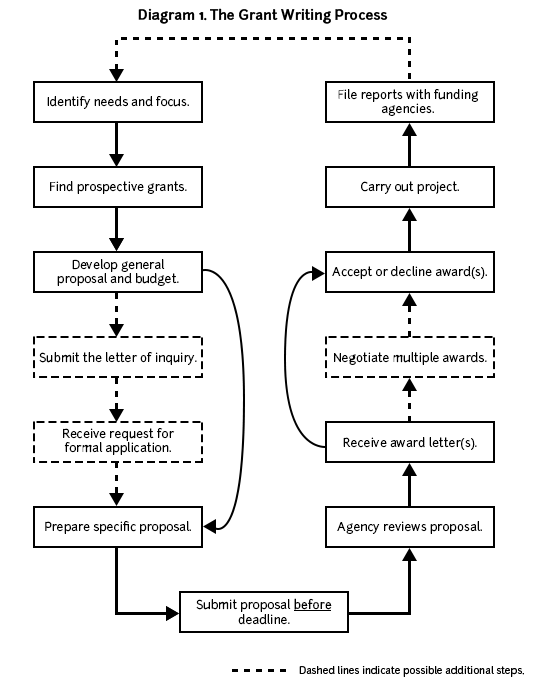
Applicants must write grant proposals, submit them, receive notice of acceptance or rejection, and then revise their proposals. Unsuccessful grant applicants must revise and resubmit their proposals during the next funding cycle. Successful grant applications and the resulting research lead to ideas for further research and new grant proposals.
Cultivating an ongoing, positive relationship with funding agencies may lead to additional grants down the road. Thus, make sure you file progress reports and final reports in a timely and professional manner. Although some successful grant applicants may fear that funding agencies will reject future proposals because they’ve already received “enough” funding, the truth is that money follows money. Individuals or projects awarded grants in the past are more competitive and thus more likely to receive funding in the future.
Some general tips
- Begin early.
- Apply early and often.
- Don’t forget to include a cover letter with your application.
- Answer all questions. (Pre-empt all unstated questions.)
- If rejected, revise your proposal and apply again.
- Give them what they want. Follow the application guidelines exactly.
- Be explicit and specific.
- Be realistic in designing the project.
- Make explicit the connections between your research questions and objectives, your objectives and methods, your methods and results, and your results and dissemination plan.
- Follow the application guidelines exactly. (We have repeated this tip because it is very, very important.)
Before you start writing
Identify your needs and focus.
First, identify your needs. Answering the following questions may help you:
- Are you undertaking preliminary or pilot research in order to develop a full-blown research agenda?
- Are you seeking funding for dissertation research? Pre-dissertation research? Postdoctoral research? Archival research? Experimental research? Fieldwork?
- Are you seeking a stipend so that you can write a dissertation or book? Polish a manuscript?
- Do you want a fellowship in residence at an institution that will offer some programmatic support or other resources to enhance your project?
- Do you want funding for a large research project that will last for several years and involve multiple staff members?
Next, think about the focus of your research/project. Answering the following questions may help you narrow it down:
- What is the topic? Why is this topic important?
- What are the research questions that you’re trying to answer? What relevance do your research questions have?
- What are your hypotheses?
- What are your research methods?
- Why is your research/project important? What is its significance?
- Do you plan on using quantitative methods? Qualitative methods? Both?
- Will you be undertaking experimental research? Clinical research?
Once you have identified your needs and focus, you can begin looking for prospective grants and funding agencies.
Finding prospective grants and funding agencies
Whether your proposal receives funding will rely in large part on whether your purpose and goals closely match the priorities of granting agencies. Locating possible grantors is a time consuming task, but in the long run it will yield the greatest benefits. Even if you have the most appealing research proposal in the world, if you don’t send it to the right institutions, then you’re unlikely to receive funding.
There are many sources of information about granting agencies and grant programs. Most universities and many schools within universities have Offices of Research, whose primary purpose is to support faculty and students in grant-seeking endeavors. These offices usually have libraries or resource centers to help people find prospective grants.
At UNC, the Research at Carolina office coordinates research support.
The Funding Information Portal offers a collection of databases and proposal development guidance.
The UNC School of Medicine and School of Public Health each have their own Office of Research.
Writing your proposal
The majority of grant programs recruit academic reviewers with knowledge of the disciplines and/or program areas of the grant. Thus, when writing your grant proposals, assume that you are addressing a colleague who is knowledgeable in the general area, but who does not necessarily know the details about your research questions.
Remember that most readers are lazy and will not respond well to a poorly organized, poorly written, or confusing proposal. Be sure to give readers what they want. Follow all the guidelines for the particular grant you are applying for. This may require you to reframe your project in a different light or language. Reframing your project to fit a specific grant’s requirements is a legitimate and necessary part of the process unless it will fundamentally change your project’s goals or outcomes.
Final decisions about which proposals are funded often come down to whether the proposal convinces the reviewer that the research project is well planned and feasible and whether the investigators are well qualified to execute it. Throughout the proposal, be as explicit as possible. Predict the questions that the reviewer may have and answer them. Przeworski and Salomon (1995) note that reviewers read with three questions in mind:
- What are we going to learn as a result of the proposed project that we do not know now? (goals, aims, and outcomes)
- Why is it worth knowing? (significance)
- How will we know that the conclusions are valid? (criteria for success) (2)
Be sure to answer these questions in your proposal. Keep in mind that reviewers may not read every word of your proposal. Your reviewer may only read the abstract, the sections on research design and methodology, the vitae, and the budget. Make these sections as clear and straightforward as possible.
The way you write your grant will tell the reviewers a lot about you (Reif-Lehrer 82). From reading your proposal, the reviewers will form an idea of who you are as a scholar, a researcher, and a person. They will decide whether you are creative, logical, analytical, up-to-date in the relevant literature of the field, and, most importantly, capable of executing the proposed project. Allow your discipline and its conventions to determine the general style of your writing, but allow your own voice and personality to come through. Be sure to clarify your project’s theoretical orientation.
Develop a general proposal and budget
Because most proposal writers seek funding from several different agencies or granting programs, it is a good idea to begin by developing a general grant proposal and budget. This general proposal is sometimes called a “white paper.” Your general proposal should explain your project to a general academic audience. Before you submit proposals to different grant programs, you will tailor a specific proposal to their guidelines and priorities.
Organizing your proposal
Although each funding agency will have its own (usually very specific) requirements, there are several elements of a proposal that are fairly standard, and they often come in the following order:
- Introduction (statement of the problem, purpose of research or goals, and significance of research)
Literature review
- Project narrative (methods, procedures, objectives, outcomes or deliverables, evaluation, and dissemination)
- Budget and budget justification
Format the proposal so that it is easy to read. Use headings to break the proposal up into sections. If it is long, include a table of contents with page numbers.
The title page usually includes a brief yet explicit title for the research project, the names of the principal investigator(s), the institutional affiliation of the applicants (the department and university), name and address of the granting agency, project dates, amount of funding requested, and signatures of university personnel authorizing the proposal (when necessary). Most funding agencies have specific requirements for the title page; make sure to follow them.
The abstract provides readers with their first impression of your project. To remind themselves of your proposal, readers may glance at your abstract when making their final recommendations, so it may also serve as their last impression of your project. The abstract should explain the key elements of your research project in the future tense. Most abstracts state: (1) the general purpose, (2) specific goals, (3) research design, (4) methods, and (5) significance (contribution and rationale). Be as explicit as possible in your abstract. Use statements such as, “The objective of this study is to …”
Introduction
The introduction should cover the key elements of your proposal, including a statement of the problem, the purpose of research, research goals or objectives, and significance of the research. The statement of problem should provide a background and rationale for the project and establish the need and relevance of the research. How is your project different from previous research on the same topic? Will you be using new methodologies or covering new theoretical territory? The research goals or objectives should identify the anticipated outcomes of the research and should match up to the needs identified in the statement of problem. List only the principle goal(s) or objective(s) of your research and save sub-objectives for the project narrative.
Many proposals require a literature review. Reviewers want to know whether you’ve done the necessary preliminary research to undertake your project. Literature reviews should be selective and critical, not exhaustive. Reviewers want to see your evaluation of pertinent works. For more information, see our handout on literature reviews .
Project narrative
The project narrative provides the meat of your proposal and may require several subsections. The project narrative should supply all the details of the project, including a detailed statement of problem, research objectives or goals, hypotheses, methods, procedures, outcomes or deliverables, and evaluation and dissemination of the research.
For the project narrative, pre-empt and/or answer all of the reviewers’ questions. Don’t leave them wondering about anything. For example, if you propose to conduct unstructured interviews with open-ended questions, be sure you’ve explained why this methodology is best suited to the specific research questions in your proposal. Or, if you’re using item response theory rather than classical test theory to verify the validity of your survey instrument, explain the advantages of this innovative methodology. Or, if you need to travel to Valdez, Alaska to access historical archives at the Valdez Museum, make it clear what documents you hope to find and why they are relevant to your historical novel on the ’98ers in the Alaskan Gold Rush.
Clearly and explicitly state the connections between your research objectives, research questions, hypotheses, methodologies, and outcomes. As the requirements for a strong project narrative vary widely by discipline, consult a discipline-specific guide to grant writing for some additional advice.
Explain staffing requirements in detail and make sure that staffing makes sense. Be very explicit about the skill sets of the personnel already in place (you will probably include their Curriculum Vitae as part of the proposal). Explain the necessary skill sets and functions of personnel you will recruit. To minimize expenses, phase out personnel who are not relevant to later phases of a project.
The budget spells out project costs and usually consists of a spreadsheet or table with the budget detailed as line items and a budget narrative (also known as a budget justification) that explains the various expenses. Even when proposal guidelines do not specifically mention a narrative, be sure to include a one or two page explanation of the budget. To see a sample budget, turn to Example #1 at the end of this handout.
Consider including an exhaustive budget for your project, even if it exceeds the normal grant size of a particular funding organization. Simply make it clear that you are seeking additional funding from other sources. This technique will make it easier for you to combine awards down the road should you have the good fortune of receiving multiple grants.
Make sure that all budget items meet the funding agency’s requirements. For example, all U.S. government agencies have strict requirements for airline travel. Be sure the cost of the airline travel in your budget meets their requirements. If a line item falls outside an agency’s requirements (e.g. some organizations will not cover equipment purchases or other capital expenses), explain in the budget justification that other grant sources will pay for the item.
Many universities require that indirect costs (overhead) be added to grants that they administer. Check with the appropriate offices to find out what the standard (or required) rates are for overhead. Pass a draft budget by the university officer in charge of grant administration for assistance with indirect costs and costs not directly associated with research (e.g. facilities use charges).
Furthermore, make sure you factor in the estimated taxes applicable for your case. Depending on the categories of expenses and your particular circumstances (whether you are a foreign national, for example), estimated tax rates may differ. You can consult respective departmental staff or university services, as well as professional tax assistants. For information on taxes on scholarships and fellowships, see https://cashier.unc.edu/student-tax-information/scholarships-fellowships/ .
Explain the timeframe for the research project in some detail. When will you begin and complete each step? It may be helpful to reviewers if you present a visual version of your timeline. For less complicated research, a table summarizing the timeline for the project will help reviewers understand and evaluate the planning and feasibility. See Example #2 at the end of this handout.
For multi-year research proposals with numerous procedures and a large staff, a time line diagram can help clarify the feasibility and planning of the study. See Example #3 at the end of this handout.
Revising your proposal
Strong grant proposals take a long time to develop. Start the process early and leave time to get feedback from several readers on different drafts. Seek out a variety of readers, both specialists in your research area and non-specialist colleagues. You may also want to request assistance from knowledgeable readers on specific areas of your proposal. For example, you may want to schedule a meeting with a statistician to help revise your methodology section. Don’t hesitate to seek out specialized assistance from the relevant research offices on your campus. At UNC, the Odum Institute provides a variety of services to graduate students and faculty in the social sciences.
In your revision and editing, ask your readers to give careful consideration to whether you’ve made explicit the connections between your research objectives and methodology. Here are some example questions:
- Have you presented a compelling case?
- Have you made your hypotheses explicit?
- Does your project seem feasible? Is it overly ambitious? Does it have other weaknesses?
- Have you stated the means that grantors can use to evaluate the success of your project after you’ve executed it?
If a granting agency lists particular criteria used for rating and evaluating proposals, be sure to share these with your own reviewers.
Example #1. Sample Budget
Jet travel $6,100 This estimate is based on the commercial high season rate for jet economy travel on Sabena Belgian Airlines. No U.S. carriers fly to Kigali, Rwanda. Sabena has student fare tickets available which will be significantly less expensive (approximately $2,000).
Maintenance allowance $22,788 Based on the Fulbright-Hays Maintenance Allowances published in the grant application guide.
Research assistant/translator $4,800 The research assistant/translator will be a native (and primary) speaker of Kinya-rwanda with at least a four-year university degree. They will accompany the primary investigator during life history interviews to provide assistance in comprehension. In addition, they will provide commentary, explanations, and observations to facilitate the primary investigator’s participant observation. During the first phase of the project in Kigali, the research assistant will work forty hours a week and occasional overtime as needed. During phases two and three in rural Rwanda, the assistant will stay with the investigator overnight in the field when necessary. The salary of $400 per month is based on the average pay rate for individuals with similar qualifications working for international NGO’s in Rwanda.
Transportation within country, phase one $1,200 The primary investigator and research assistant will need regular transportation within Kigali by bus and taxi. The average taxi fare in Kigali is $6-8 and bus fare is $.15. This figure is based on an average of $10 per day in transportation costs during the first project phase.
Transportation within country, phases two and three $12,000 Project personnel will also require regular transportation between rural field sites. If it is not possible to remain overnight, daily trips will be necessary. The average rental rate for a 4×4 vehicle in Rwanda is $130 per day. This estimate is based on an average of $50 per day in transportation costs for the second and third project phases. These costs could be reduced if an arrangement could be made with either a government ministry or international aid agency for transportation assistance.
Email $720 The rate for email service from RwandaTel (the only service provider in Rwanda) is $60 per month. Email access is vital for receiving news reports on Rwanda and the region as well as for staying in contact with dissertation committee members and advisors in the United States.
Audiocassette tapes $400 Audiocassette tapes will be necessary for recording life history interviews, musical performances, community events, story telling, and other pertinent data.
Photographic & slide film $100 Photographic and slide film will be necessary to document visual data such as landscape, environment, marriages, funerals, community events, etc.
Laptop computer $2,895 A laptop computer will be necessary for recording observations, thoughts, and analysis during research project. Price listed is a special offer to UNC students through the Carolina Computing Initiative.
NUD*IST 4.0 software $373.00 NUD*IST, “Nonnumerical, Unstructured Data, Indexing, Searching, and Theorizing,” is necessary for cataloging, indexing, and managing field notes both during and following the field research phase. The program will assist in cataloging themes that emerge during the life history interviews.
Administrative fee $100 Fee set by Fulbright-Hays for the sponsoring institution.
Example #2: Project Timeline in Table Format
Example #3: project timeline in chart format.
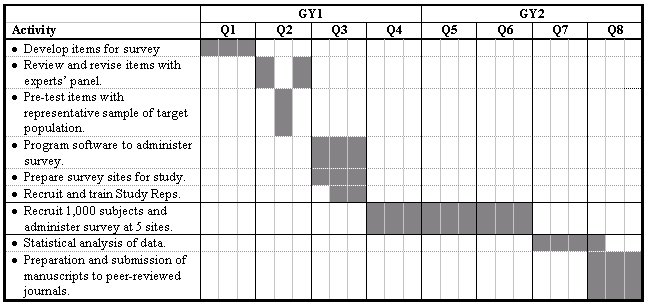
Some closing advice
Some of us may feel ashamed or embarrassed about asking for money or promoting ourselves. Often, these feelings have more to do with our own insecurities than with problems in the tone or style of our writing. If you’re having trouble because of these types of hang-ups, the most important thing to keep in mind is that it never hurts to ask. If you never ask for the money, they’ll never give you the money. Besides, the worst thing they can do is say no.
UNC resources for proposal writing
Research at Carolina http://research.unc.edu
The Odum Institute for Research in the Social Sciences https://odum.unc.edu/
UNC Medical School Office of Research https://www.med.unc.edu/oor
UNC School of Public Health Office of Research http://www.sph.unc.edu/research/
Works consulted
We consulted these works while writing this handout. This is not a comprehensive list of resources on the handout’s topic, and we encourage you to do your own research to find additional publications. Please do not use this list as a model for the format of your own reference list, as it may not match the citation style you are using. For guidance on formatting citations, please see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial . We revise these tips periodically and welcome feedback.
Holloway, Brian R. 2003. Proposal Writing Across the Disciplines. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey: Prentice Hall.
Levine, S. Joseph. “Guide for Writing a Funding Proposal.” http://www.learnerassociates.net/proposal/ .
Locke, Lawrence F., Waneen Wyrick Spirduso, and Stephen J. Silverman. 2014. Proposals That Work . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Przeworski, Adam, and Frank Salomon. 2012. “Some Candid Suggestions on the Art of Writing Proposals.” Social Science Research Council. https://s3.amazonaws.com/ssrc-cdn2/art-of-writing-proposals-dsd-e-56b50ef814f12.pdf .
Reif-Lehrer, Liane. 1989. Writing a Successful Grant Application . Boston: Jones and Bartlett Publishers.
Wiggins, Beverly. 2002. “Funding and Proposal Writing for Social Science Faculty and Graduate Student Research.” Chapel Hill: Howard W. Odum Institute for Research in Social Science. 2 Feb. 2004. http://www2.irss.unc.edu/irss/shortcourses/wigginshandouts/granthandout.pdf.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift
- Architecture and Design
- Asian and Pacific Studies
- Business and Economics
- Classical and Ancient Near Eastern Studies
- Computer Sciences
- Cultural Studies
- Engineering
- General Interest
- Geosciences
- Industrial Chemistry
- Islamic and Middle Eastern Studies
- Jewish Studies
- Library and Information Science, Book Studies
- Life Sciences
- Linguistics and Semiotics
- Literary Studies
- Materials Sciences
- Mathematics
- Social Sciences
- Sports and Recreation
- Theology and Religion
- Publish your article
- The role of authors
- Promoting your article
- Abstracting & indexing
- Publishing Ethics
- Why publish with De Gruyter
- How to publish with De Gruyter
- Our book series
- Our subject areas
- Your digital product at De Gruyter
- Contribute to our reference works
- Product information
- Tools & resources
- Product Information
- Promotional Materials
- Orders and Inquiries
- FAQ for Library Suppliers and Book Sellers
- Repository Policy
- Free access policy
- Open Access agreements
- Database portals
- For Authors
- Customer service
- People + Culture
- Journal Management
- How to join us
- Working at De Gruyter
- Mission & Vision
- De Gruyter Foundation
- De Gruyter Ebound
- Our Responsibility
- Partner publishers

Your purchase has been completed. Your documents are now available to view.
The Grant Writing Guide
A road map for scholars.
- X / Twitter
Please login or register with De Gruyter to order this product.
- Language: English
- Publisher: Princeton University Press
- Copyright year: 2023
- Main content: 240
- Other: 13 b/w illus.
- Keywords: Grant writing ; Institution ; Funding ; Principal investigator ; National Science Foundation ; Writing ; Adviser ; Action plan ; Grant (money) ; Red team ; Salary ; Finding ; Request for proposal ; Curriculum vitae ; Publishing ; Career ; Education policy ; Case study ; Mentorship ; Curriculum ; Manuscript ; Research fellow ; Programme (booklet) ; Funding of science ; Practicum ; Research Development ; Data management plan ; Guideline ; Research assistant ; Illustration ; Author ; Checklist ; Award ; Pension ; Reputation ; Development Workshop ; Proofreading ; Paragraph ; Proverb ; The Hidden Curriculum (book) ; Publication ; Institute of Education Sciences ; Learning ; Assistant professor ; Fundable ; Qualitative research ; Collaboration ; Project team ; Investment ; Teacher ; Institutional Fund ; Hewlett Foundation ; Writer ; Letter of intent ; Disaster ; Feeling ; Review article ; Gantt chart ; Handbook ; Op-ed ; Academic advising ; Newsletter ; Robert Wood Johnson Foundation ; Payment ; Narrative ; Call to action (marketing) ; Social proof ; Research program ; InterViews ; Geographic information system
- Published: January 10, 2023
- ISBN: 9780691231891
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- CAREER FEATURE
- 20 December 2019
Secrets to writing a winning grant
- Emily Sohn 0
Emily Sohn is a freelance journalist in Minneapolis, Minnesota.
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
When Kylie Ball begins a grant-writing workshop, she often alludes to the funding successes and failures that she has experienced in her career. “I say, ‘I’ve attracted more than $25 million in grant funding and have had more than 60 competitive grants funded. But I’ve also had probably twice as many rejected.’ A lot of early-career researchers often find those rejections really tough to take. But I actually think you learn so much from the rejected grants.”
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
24,99 € / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
185,98 € per year
only 3,65 € per issue
Rent or buy this article
Prices vary by article type
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Nature 577 , 133-135 (2020)
doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-019-03914-5
Related Articles

- Communication

I’m worried I’ve been contacted by a predatory publisher — how do I find out?
Career Feature 15 MAY 24

How I fled bombed Aleppo to continue my career in science
Career Feature 08 MAY 24

Illuminating ‘the ugly side of science’: fresh incentives for reporting negative results

US halts funding to controversial virus-hunting group: what researchers think
News 16 MAY 24

A DARPA-like agency could boost EU innovation — but cannot come at the expense of existing schemes
Editorial 14 MAY 24

US TikTok ban: how the looming restriction is affecting scientists on the app
News 09 MAY 24

‘Shrugging off failure is hard’: the $400-million grant setback that shaped the Smithsonian lead scientist’s career
Career Q&A 15 APR 24

How I harnessed media engagement to supercharge my research career
Career Column 09 APR 24
Research Associate - Metabolism
Houston, Texas (US)
Baylor College of Medicine (BCM)
Postdoc Fellowships
Train with world-renowned cancer researchers at NIH? Consider joining the Center for Cancer Research (CCR) at the National Cancer Institute
Bethesda, Maryland
NIH National Cancer Institute (NCI)
Faculty Recruitment, Westlake University School of Medicine
Faculty positions are open at four distinct ranks: Assistant Professor, Associate Professor, Full Professor, and Chair Professor.
Hangzhou, Zhejiang, China
Westlake University

PhD/master's Candidate
PhD/master's Candidate Graduate School of Frontier Science Initiative, Kanazawa University is seeking candidates for PhD and master's students i...
Kanazawa University
Senior Research Assistant in Human Immunology (wet lab)
Senior Research Scientist in Human Immunology, high-dimensional (40+) cytometry, ICS and automated robotic platforms.
Boston, Massachusetts (US)
Boston University Atomic Lab
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Check Out Our Brand-New 20 Minute Training on How to Make Money as a Grant Writer
Grant Writing 101: What is it & how do you get started?
Have you been thrown into the deep end working at a nonprofit organization and tasked to apply for grant funding for the first time? Maybe you've heard about the field, catching the buzz from a friend starting a grant writing side hustle . Or you've seen how others have pivoted their careers to launch grant writing consultant businesses.
However you found grant writing, we're glad you're here!
Grant writers are perceived to have superpowers—they know how to get free money!
Well, it's not quite that easy. There is no such thing as free money, and grant writing is a lot of hard work.
However, it is very learnable and an incredible skill set to have in your quiver. Even newcomers succeed with the right guidance and training under their belt.
This crash course in grant writing will cover everything you need to know to start approaching grant writing like a boss!
Grant Writing Essentials: Definitions & FAQs
- Grant Writing vs. Nonprofit Fundraising
The Grant Writing Process for Beginners
Understanding the grant fundraising landscape, why grant writing is such a valuable skill.
Curious about how to get into grant writing without prior experience? Check out this video to learn more.
Let’s start with the essentials: a few grant writing definitions and frequently asked questions.
What is grant writing?
Grant writing is the process of crafting a written proposal to receive grant funding from a grant making institution in order to fund a program or project.
Grant writing involves laying out your case for why the grant will do the most good for you (or your project or organization). A stellar grant proposal will clearly show the funder that your plan is the best possible choice for accomplishing your shared goals.
Think of grant writing like making a pitch to investors or lenders but to receive funding that you won’t need to pay back.
That begs the question…
What are grants?
A grant is a financial award to support a person, organization, project, or program. It is intended to achieve a specific goal or purpose. Nonprofits can use grants to complete projects, run programs, provide services, or continue running a smooth operation.
Great, now where is all of this money coming from?
Who provides grant funding?
Typically, grants are awarded to organizations from grant making institutions (also called grantors ). These include foundations, corporations, and government agencies.
Grantors provide grants to help further their goals in their communities (or around the country or world) and to support other organizations that do on-the-ground work. These goals are typically philanthropic or social in nature, but grants might also be offered for educational, scientific, or any other purpose.
Grants usually come with very specific guidelines for what the money can and can’t be used for, as well as rules for how the “winner” of the grant (or the grantee ) will report on its progress. When a grant has specific guidelines, we call these funds restricted . Restricted funding means they can only be used for the purposes laid out in the proposal and specified by the funder.
So, can anybody and everybody get grant money?
Who is eligible for grant funding?
Many different types of organizations are eligible to write proposals and apply for grant funding. Most notably, 501(c) nonprofit organizations that have IRS Letters of Determination (basically any type of legit nonprofit).
More specifically, these types of organizations are eligible for grants through grant writing:
- Nonprofits/public charities with IRS-recognized status
- Unincorporated community groups with fiscal sponsors
- Tribal organizations (and sometimes housing authorities)
- Faith-based organizations (which sometimes must provide direct social services depending on the grantor’s guidelines)
- Local governments
Exciting, right? Grants can do a lot of good for organizations of all sizes. But who’s doing the work?
Who does the actual grant writing and drafts the proposal?
All different kinds of folks! Each organization finds their sweet spot for getting the work done. Grant proposals can be written by:
- Employees of eligible organizations
- Volunteers lending their time
- Freelance grant writers providing a contract-based service
- Grant writing consultants who provide organizations with ongoing help through retainer contracts
Successful grant writing leads to positive impacts on real people and real communities. Grant writers put in the elbow grease because they care about charitable organizations and their missions. They want to see their communities thrive.
Is Grant Writing A Good Career For You?
Take the 3 minute personality quiz to find out!
How do you learn grant writing?
Grant writing is a set of specific skills and processes, so it can be taught and learned like any other subject.
There are a few different avenues you can explore to level up your grant writing skills.
- DIY Method: You can binge-watch YouTube content to pick up the bits and pieces of grant writing. This is certainly a cost-effective method! However, factoring in the stress of reinventing the wheel while riding the struggle bus of going it alone, you’re spending more time (and $$) in the long run to learn grant writing skills.
- Higher-Ed Programs: Several universities offer certifications in nonprofit management, but most do not focus solely on grant writing. For a semester or two, the curriculum will teach you the ins and outs of nonprofit organizations, which includes grant writing. These courses include a university certificate for formal education. The downside, however, is that university programs fall short of helping students bridge the gap between learning the material and actually applying it—in other words, getting paid tp use your newly acquired knowledge in the field.
- Online Courses: There’s a wide variety of online courses to help you learn how to become a grant writer. Online education is flexible for those who are looking to add grant writing as a new skill set on top of a full-time schedule (life, work, etc.) or level up their skills. Yes, even if you’re an in-house grant writer working with a nonprofit organization, professional training is applicable. You can check out a roundup of the best grant writing classes here.
Curious about how to break into grant writing without prior experience and with no added debt? The Global Grant Writers Collective is the only program of its kind to show you how to be a world-class grant writer while also building a flexible, fulfilling life you love.
Grant Writing vs. Non Profit Funding
We’ve covered all the basics, but there’s a bit more important context to understand as you launch your grant writing journey.
You know that grants provide funding to organizations to do good work in their communities, but how does this relate to the bigger concept of fundraising?
TL;DR — Grant Writing vs. Fundraising
Fundraising is how you raise money for your organization. Grant writing is one type of fundraising activity. Grant writing includes asking foundations or government entities for support while other fundraising activities usually target individual donors.
What is nonprofit fundraising?
Fundraising is generally defined as the process of soliciting financial support for a cause or project.
Central to the idea of fundraising is the collection of cash donations (although all kinds of assets can be donated). Donations can be collected immediately or over months or years, as is the case for long-term pledges of large donations to capital campaigns.
Fundraising is an essential way for most nonprofits to bring in revenue for their missions. Monies raised through general fundraising activities are often referred to as unrestricted funds and can be used for any expenses, such as staff salaries or rent. Donors can also require that their money be used in a specific (or restricted) way.
Who fundraises, and what do you need to do it?
Nonprofits are the most common group to fundraise. However, other groups like those adorable Girl Scouts selling their highly addictive cookies (our greatest weakness 😋) and people raising funds for mission trips are eligible for fundraising, too.
The only thing you technically need to fundraise is trust from your donors. But when you represent an organization, establishing trust means getting official with a 501(c)(3) designation and publishing an annual report.
Remember that fundraising isn’t so much about asking for money as it is about inviting others who have a passion for what you do to join you in your mission. Once you find them, you can do that work together—the beauty of fundraising!
How is grant writing different from fundraising?
As you can already tell, fundraising has a much broader definition than grant writing.
Fundraising can take many forms, and grant writing falls under that umbrella.
Fundraising usually refers to generating cash donations by:
- Building relationships with individual donors
- Holding fundraising events
- Making public appeals for donations and marketing your organization to the community
When you submit a proposal for a grant, it’s a one-on-one targeted pitch to a funder. You understand their past giving history. You’ve vetted them for mission alignment, and your project meets their goals for impact. The relationship between you and the funder is more formalized (though there is room for personal relationships over time).
With fundraising through individual donors, not through a grant, your approach is less formal. You likely don’t need a lengthy proposal, but that doesn’t mean you don’t have a plan. To fundraise from individual donors, you may be soliciting funds from individuals whose circumstances and philanthropic interests are largely unknown to you. Your approach can usually be applied to a wider audience, whereas grant writing targets one organization with specific guidelines.
In either case, relationship-building and strategies like prospect research are very important for nonprofits.
Then what do grant writing and fundraising have in common? In both cases, you need to do research, pursue leads, prepare talking points, evaluate opportunities, and cultivate relationships. The essence of both practices is the same. What is different is the target and approach.
With all the context out of the way, let’s get to the meat and potatoes. How do you actually write a grant proposal? What are the key steps to follow?
Here it is: our signature 7-step process for writing a winning grant. We’ll summarize the key points to understand for each step, but please check out our longer grant writing process explainer for a deep dive into the nitty gritty.
- Follow your North Star (the funding guidelines). A funder will provide guidelines for their grant that all applicants need to follow to be considered. Think of these as instructions. Guidelines can vary a lot from one grant to another, so it’s important to never take them for granted (see what we did there?). Download, print, read, and reread the guidelines.
- Prepare your narrative skeleton. Every grant should tell a story, but sitting down to write a prizewinning story on a blank page is a lot easier said than done. Give yourself an easier start by outlining your proposal based on the funding guidelines themselves. These are the questions you’ll have to answer, so bake them into your story from the very start. Simple bullet points will do here—no need to lock down full sentences just yet.
- Host a kick-off meeting. Gather everyone involved in the project to get on the same page. These are all the people who’ll provide you with the information you need for the grant as well as those who’ll be involved in running the project that it funds. Remember, everyone loves an organized meeting—send an agenda and your narrative skeleton in advance, then a summary of action items after, plus an invite to a progress check-in meeting.
- Finalize your grant budget. Next, you need to know how much the project you’re proposing will cost to complete—this budget will impact all other parts of your application. For example, funders often ask for a “budget narrative” that explains how you determined your final numbers. Some grants are structured to provide a percentage of your total costs rather than a flat sum. Grab a copy of our free grant budget template when you’re ready!
- Write your narrative fast and furiously. With your budget in hand, now’s the time to start putting pen to paper (or fingers to keys). Review your grant guidelines again, and start filling in your narrative skeleton with the details it needs to paint a compelling picture. We could go on and on with all the tips and hacks we’ve learned—check them out in Step 5 of our grant writing process guide.
- Prep your key attachments. Funders usually want more than just your perfectly written document. They often ask for additional attachments like separate budget documents, a resolution, and letters of support. Some attachments, like resolutions, can take a long time to get finalized, which is why understanding your guidelines early is so important so that you can get the ball rolling quickly.
- Review and submit your grant! Phew—you made it! But you’re not done yet. Reviewing and double-checking your proposal is a must, and it should be done by an independent reviewer who hasn’t been knee-deep in the process like you. Collect and discuss their feedback, make changes, review one last time, and then hit submit (ideally a day or two before the deadline). After the adrenaline wears off, take the afternoon off.
There’s no magic formula for writing a winning grant—your proposal should always be tailored to that unique grant and funder—but there are best practices and principles that give you a reliable roadmap to follow each time. Our 7-step grant writing process condenses a ton of them into one digestible process, but for an even closer look, join our free grant writing class!
Free Grant Writing Trainings
These how-to videos offer a smattering of webinar replays from our online grant writing training and feature topics such as working remotely, project management, fundraising, and how to utilize the Freedom of Information Act for federal funding.
Essential Grant Writing Tips for Newcomers
Once you’ve mastered the steps above, you’re probably wondering how to actually put rubber to the road and get started. Here are our top 5 recommendations:
- Find a real project to work on! Try identifying a real grant opportunity and approaching a nonprofit in your community. Or if that idea terrifies you—we get it—you can start slower with sample projects and training courses.
- Commit to excellence in project management. Grant writing is complicated, no way around it. Familiarize yourself with project management best practices and you can stay organized and energized.
- Fake it until you make it. Imposter syndrome is very real, and even experienced grant writers deal with it. But don’t let it hold you back. When you invest in your grant writing skills and get real-world practice, you have something worth sharing. Build some momentum and see how far you can go!
- Have a process mindset. When you pull the mask off the big hairy grant writing monster, you’ll find it’s really just a big stack of steps and processes—learnable steps and processes. Master these, and you’ll have a reliable framework for success.
- Don’t be stubborn (said with love). Trying to go it alone when learning grant writing leads to more mistakes and wasted time and money. Grant writing is a craft, after all, and there’s a lot to be gained from connecting with fellow grant writers.
P.S. Want more grant writing videos like this one? There’s more where that came from.
Check out our YouTube channel and give us a follow!
If you’re new to grant writing (or even considering turning it into a side hustle), it’s important to understand the big picture. Why do grants matter?
Grants make up a considerable chunk of nonprofits’ operating revenue.
According to Nonprofit Impact Matters , the nonprofit sector generates roughly 31.8% of its revenue from government sources (including both grants and paid contracts) and 2.9% from foundations in the form of grants.
It’s generally recommended that grant funding should provide 10-20% of a nonprofit’s total annual budget.
Funding from foundations is growing.
Total giving from foundations reached $105.21 billion in 2022, a 2.5% increase from the year before, and it’s part of a continued upward trend. Put another way, foundations provided 21% of total giving to nonprofits , or $1 of every $5 given to charity.
This is one of only a few areas that saw growth when adjusted for inflation. Family foundations (founded by families as a way to better manage their philanthropic activities) and corporate foundations have led the charge.
Grants are an important part of a safe revenue mix.
Nonprofits need to have diversified revenue streams so that they can rely on other ways to generate money when one shrinks or dries up.
Grants are an essential part of this equation, especially as a turbulent economy causes individual donors to rein in their spending. Case in point—the 2023 Giving USA Report found that giving from individuals declined 6.4% in 2022 (or 13.4%, when adjusted for inflation), a finding that sent shockwaves through the nonprofit world.
But when a nonprofit has a sturdy fundraising program, grant writing process, and an active grant opportunity pipeline, it becomes much easier to weather the storms and keep on doing the good work their communities need.
This leads us to a logical conclusion (which you might have already caught onto)...
Grant writing is an incredibly valuable skill because:
- It’s always in demand.
- It helps nonprofits secure the diverse funding they need to thrive.
- It drives on-the-ground good by funding projects and programs.
Competition for grants will only get tougher as giving from foundations grows and donor habits keep changing in the coming years.
The right unicorn of a grant writer can make a world of difference for nonprofit missions of all sizes and build the fulfilling career they want: a win-win!
Study up on grant writing best practices. Stretch your grant writing muscles by taking a free class or investing in more lessons, coaching, and community (like through the Global Grant Writers Collective ).
Whether you’re looking to win more funding for your nonprofit or break out into a new freelance field, anyone can succeed with grant writing with the right preparation and practice.
Want to learn more? We know you do. We recommend these additional resources:
- Can I Make Money as a Grant Writer?
- Three Possible Career Paths Through Grant Writing Training
- Why Start a Side Hustle Grant Writing?
- Grant Writing for Nonprofits: Our Top 10 Tips
- Tips for Writing Your First Draft of a Grant Narrative
- Top Mistakes Grant Applicants Make (And How to Avoid Them)
- A Review of the Top 10 Grant Databases
Free Grant Writing Class
Learn the 7-steps to write a winning grant application and amplify the impact you have on your community.
About the author...
Alexis Swenson serves as Unicorn Coach and Content Director for Learn Grant Writing. The product of small-town northwestern Minnesota, she is a self-declared “old soul” and grounded free spirit. She has secured over $2.7 million in grant funding in her career. Alexis writes to help people learn, laugh, and not be so hard on themselves.
Want To Learn More?
We made this video to answer your questions about how to build a career in grant writing without the fear of where you will find clients or the fear of failure. We cover the top three mistakes that keep people from making the leap from a soul-sucking job to something more meaningful.
Watch Video
Customized Training For You
Listen to the audiobook, take free grant writing class, free grant writing resources, take our career fit quiz, take our business diagnostic audit quiz.
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Introduction to Grant Writing

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
Introduction
Professional grant writers use clear, specific language to focus the reader’s attention, and to persuade the reader to fund their proposal. Learning to write successful grant proposals is no small task, but the writing process can become easier with practice and awareness of a few common missteps.
No doubt, the first step of successful grant writing is to plan the project, but the second step is following the directions of the granting organization (called, the grantmaker). In most cases, grantmakers require a(n): cover letter , executive summary , problem statements/need description , work schedule, budget, qualifications , conclusions , and appendices (or, supporting materials). Each section will have specific requirements and while keeping to a word limit is straightforward, being specific is less easy.
A Note on Following the Grantmaker’s Rules
Following directions helps the grantmaker read applications efficiently. Specificity of content will not only vary by grantmaker, but also by proposal sections. For example, a grantmaker may limit your application in general terms for background information on the contexts of your proposal:
“Please tell the grant committee in 2 to 3 pages about the support your institution or community will provide for your project if your proposal is granted the requested funds.”
Likewise, a grantmaker may explicitly limit your response to a section on the grant applicant’s qualifications by stating:
“In no more than 350 words, please summarize the grant applicant’s specific qualifications to manage the finances of the proposal. Discuss any financial experience (for example, certifications in accounting services), or other relevant office managerial duties that will help the applicant distribute funds and write regular quarterly financial reports.”
Keep in mind that many grantmakers will not read past the point of your departure from the application rules, no matter how worthy the project is or how neat and well designed the application package looks. So, while there is no guaranteed way to win a grantmaker’s funds, not following directions is a sure fire way of losing your chances at getting any funds. Ultimately, not following directions indicates carelessness—which is not a characteristic of a promising proposal.
How to write a successful research grant
Quick guide on how to approach your next research grant application.
15 October 2020
Supporting the scientists here at the Victor Chang Cardiac Research Institute, our Research Grants Officer, Naomi Arbon, knows exactly how daunting the grant writing process can be! Here, she's written a quick guide on how to approach your next research grant application.
Applying for grants is somewhat of an art form. Through your proposal, you have to convincingly convey to reviewers and funding agencies that your research is extremely important and it is vital to the advancement of science and society that it be carried out. In addition, the world of research grants is highly competitive and for every 'yes' you get you have to expect multiple 'no's, therefore, thick skin and a determination to not give up are prerequisites for the job!
Writing grants takes up an increasingly large portion of scientists time these days. Below are some suggestions for how to make that time count as best you can by creating a compelling case each time.
Tip #1: Detailed reading
Read the funding guidelines in-depth prior to making an application. Note what the applications will be scored on and ensure that you answer each of the assessment criteria succinctly and clearly. E.g. use the same language, use some of the key words from the scoring criteria as headings. This will make it easier for reviewers who are likely time poor and have a lot of grants to assess.
Tip #2: Tailor your writing style to the grant review panel
Who are your assessors? Do they come from a scientific or non-scientific background? Some grants, such as those from philanthropic organisations, may be reviewed by a more general audience. If you know they won’t be familiar with your area of research, it is best to tailor your writing style to a more lay audience, with the exception in some cases of the methods section, which often has to use more technical terms. If you know the grant applications are being reviewed by subject matter experts from your field, then it is generally fine to use jargon.
Tip #3: Research past recipients
Most funding agencies will list on their websites the types of projects or researchers they have supported in previous funding rounds. Look at this and use it as a guide for your project or Fellowship application. Does your project seem within their funding scope? If there is a grant range that you can apply for, look at the average of what has been provided previously. For Fellowships, is your track record on par with previously supported researchers? If not, use it as a marker as to what you need to work towards.
Tip #4: Give yourself time!
There is no doubt that researchers schedules are ridiculously busy and time is not something you get a lot of. It may be easier to plan for those grants that have annual deadlines than those ad hoc grants that arise. Ideally, start a draft six months before the deadline, put it aside and go back to it again with a fresh perspective. The more time you leave yourself the more time you will also have to get invaluable feedback from your peers.
Tip #5: Make sure your first page is impactful
The first page of any grant proposal is the most important. It needs to state the current research problem/ gap to address, how you will tackle it and why you and your team are the best placed to do so. You want the reviewer, who again will likely be reading lots of these late at night, to be intrigued from the start. Whenever possible, read as many previously successful applications as you can get your hands on. An example of a well-structured grant proposal is one that includes: a Project Title, the Research problem being addressed/ the health issue (always good to include stats in the first paragraph to emphasise the magnitude of the problem), Project Aims and Hypothesis, Background, Significance, Team, Methods, Timeline, Risks, Outputs and Expected Outcomes.
Tip #6: Take care and time with your budget
Ensure your budget is well thought out and covers all of the required project expenses. Don’t leave it till the last minute. Talk to people to cost things correctly and check the funding guidelines as to what are allowable costs and what are not. Use the correct salary scales. If you aren’t asking for salary, include your time and the time of any other staff working on the project as in kind.
Tip #7: Practice makes perfect
Writing a grant is hard work and requires a different writing style to that used for writing a research paper. Writing a great grant takes a lot of time and tends to come with experience. Don’t be discouraged by the unsuccessful applications. As cliché as it sounds, it really is all great experience and means you are one step closer to a yes!
Study and work in the institute
Learn more about our areas of research, donate to heart research, acknowledgement of country.
The Victor Chang Cardiac Research Institute acknowledges Traditional Owners of Country throughout Australia and recognises the continuing connection to lands, waters and communities. We pay our respect to Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander cultures; and to Elders past and present.
Grantwriting and Scientific Writing & Communication Resources
Return to postdoc services resources, on this page, grantwriting resources.
- Interested in finding funding? The Duke Office of Research Initiatives helps members of the Duke research community find grants, fellowships and other funding opportunities and collaborations. Through the Duke Office of Research Initiatives , postdocs can access funding search tools including COS PIVOT . PIVOT maintains a database of grants, fellowships, and other funding information from public and private, domestic and international sources. This service offers a wealth of information on biomedical and hard sciences, as well as social sciences, humanities & community outreach funding. This tool can help you make connections within Duke with its database of our faculty and postdocs.Creating a PIVOT COS email alert is an invaluable tool for researchers investigating funding options. Please note: You must use your Duke email address when creating your COS PIVOT account. ORS also provides help with other funding search tools, including Foundation Directory Online and internal funding opportunities . To search funding by discipline, eligibility (ie postdoc) and more: https://researchfunding.duke.edu/search-results
- The Duke Office of Campus Research Development provides toolkits focusing on either a specific federal funding agency or a specific funding program within a federal funding agency. These toolkits include templates and guidance documents to help write proposals. You can access any of the toolkits with your Duke NetID. OCRD also holds regular grant-writing workshops and info sessions .
- Duke Foundation Relations helps researchers understand how foundations work and how you might work with them, including a Guide to the Funding Process and a Grantwriter's Toolkit .
- myRESEARCHhome : Personalized Research Portal: This portal enables members of the research community to manage their research portfolio by consolidating tools and information in one place.
- myRESEARCHpath : Interactive Research Roadmap: This website helps members of the research community navigate the research ecosystem at Duke using an intuitive lifecycle-based interface.
- myRESEARCHnavigators : Expert help when you need it: This team of experts help researchers navigate the research ecosystem at Duke through services such as 1:1 consultations and a research ��‘hotline.’
- NIH F Award and K Award resources from myRESEARCHpath
Developing Your NIH K99/R00 and BWF Career Awards at the Scientific Interface: Postdocs often seek awards providing independent funding and financial support to facilitate the transition to faculty. The NIH Pathway to Independence Award (K99/R00) is a competitive award that supports postdoctoral researchers through the final years of their postdoctoral work and as they transition to independent scientists. Career Awards at the Scientific Interface (CASI) , offered by the Burroughs Wellcome Fund (BWF), presents an award that provides $560,000 over five years to bridge advanced postdoctoral training and the first three years of faculty service. Both awards are open to non-US citizens from all countries. In this Zoom session , Tammy Collins, Program Officer at BWF and Duke PhD graduate, gives an overview of the K99/R00 and CASI programs and give tips on when to apply, which center to apply to, an overview of specific aims & other aspects, and finally will compare and contrast the K99/R00 and the CASI award.
- The Duke Office of Research Initiatives hosts Write Winning NIH Grant Proposals and Write Winning NIH Career Development Award Proposals on an annual basis, typically in the summer. These sessions are led by Grant Writers’ Seminars & Workshops . All Duke research personnel involved in writing proposals for funding are invited to attend, though the sessions are geared towards faculty who are writing or planning to write NIH grant applications. Email [email protected] for more information.
- Facilities and Research Repository (boilerplate language) from myRESEARCHpath
- Effective Communication Series by Dr Joanna Downer, Duke School of Medicine Associate Dean for Research Development.
- Duke Graduate School Online Scientific Writing Course
- Duke Postdoctoral Services NIH F32 and K99 Grantsmanship Series
- Presenting Clinical and Translational Science (PCATS) Video Series : The PCATS series focuses on principles and techniques for developing and delivering effective scientific presentations.
- NIH Grantwriting YouTube Channel , including NIH Fundamentals, Apply for Grant Funding, and Advice for New and Early Career Scientists.
- NIH Samples of funded R01, R03, R15, R21, SBIR/STTR, K, and F applications.
- NIH Grantwriting Resources from NIH NIAID, including sample applications, application tips, and budget planning resources. Useful for anyone writing an NIH grant.
- NIH offers Virtual Grants Conferences each year, with archived sessions from previous conferences.
- NSF offers Virtual Grants Conferences each year, with archived sessions from previous conferences.
[Back to top]
Scientific Writing & Communication Resources
- The Science of Scientific Writing by noted Duke professor George Gopen
- Scientific Writing Resources by the Duke Medical Center Library and Archives
- Science Communication Resources from the Duke Graduate School
- Resources for Science Communication Self-Education from NC State University Leadership in Public Science
- Scientific Writing Resources compiled by Duquesne University
- Resources from the National Association of Science Writers
- Funding the research project
- Selecting an appropriate journal
- Best practices in writing scientific articles
- Post publication activities and driving visibility
- Becoming a peer reviewer
- Writing Pedagogy Opportunities for Postdocs : Postdocs across the disciplines are often tasked with assigning, responding to, or grading student writing. And because undergraduate institutions usually include the development of writing skills as a key goal of their undergraduate programs, new faculty are increasingly being expected to help students develop these skills. Because training in writing pedagogy is beneficial on the competitive academic job market, it is useful to have a way to document such training and to be able to speak effectively about one’s experience with and interest in student writing. The Thompson Writing Program Certificate of Accomplishment in Teaching Writing in the Disciplines provides a framework for acquiring basic knowledge of writing pedagogy and demonstrating that knowledge in job applications and during interviews. To allow participants to obtain the certificate in the way that best meets their needs and schedules, core workshops are offered at least once annually. While it will be possible to meet the certificate requirements in a single year, most students will complete the requirements over a two- or three-year period.
- Free Online Courses through Coursera for Duke : Coursera for Duke gives Duke students, staff, and faculty free access to 54 Duke-created Coursera courses and 3 specialization certificates. These co-curricular digital courses include Programming Fundamentals, English Composition, Statistics, Big Data, Healthcare Innovation and Entrepreneurship, Advertising and Society, Challenges of Global Health, Nanotechnology, and many more. The Duke community can enroll at any time and learn at their own pace, with no grade, and no additional academic pressure.
- Resources on Text Recycling (AKA "Self-Plagiarism") in Research Writing from a multi-institution, NSF-funded initiative investigating text recycling in STEM research led by Cary Moskovitz, PhD (Lead PI), Professor of the Practice and Director of Writing in the Disciplines, Duke University
Office of Postdoctoral Services - Resources
National Endowment for the Arts
- Grants for Arts Projects
- Challenge America
- Research Awards
- Partnership Agreement Grants
- Creative Writing
- Translation Projects
- Volunteer to be an NEA Panelist
- Manage Your Award
- Recent Grants
- Arts & Human Development Task Force
- Arts Education Partnership
- Blue Star Museums
- Citizens' Institute on Rural Design
- Creative Forces: NEA Military Healing Arts Network
- GSA's Art in Architecture
- Independent Film & Media Arts Field-Building Initiative
- Interagency Working Group on Arts, Health, & Civic Infrastructure
- International
- Mayors' Institute on City Design
- Musical Theater Songwriting Challenge
- National Folklife Network
- NEA Big Read
- NEA Research Labs
- Poetry Out Loud
- Save America's Treasures
- Shakespeare in American Communities
- Sound Health Network
- United We Stand
- American Artscape Magazine
- NEA Art Works Podcast
- National Endowment for the Arts Blog
- States and Regions
- Accessibility
- Arts & Artifacts Indemnity Program
- Arts and Health
- Arts Education
- Creative Placemaking
- Equity Action Plan
- Historically Black Colleges and Universities (HBCUs)
- Literary Arts
- Native Arts and Culture
- NEA Jazz Masters Fellowships
- National Heritage Fellowships
- National Medal of Arts
- Press Releases
- Upcoming Events
- NEA Chair's Page
- Leadership and Staff
- What Is the NEA
- Publications
- National Endowment for the Arts on COVID-19
- Open Government
- Freedom of Information Act (FOIA)
- Office of the Inspector General
- Civil Rights Office
- Appropriations History
- Make a Donation
CREATIVE WRITING FELLOWSHIPS
The National Endowment for the Arts Literature Fellowships program offers $25,000 grants in prose (fiction and creative nonfiction) and poetry to published creative writers that enable the recipients to set aside time for writing, research, travel, and general career advancement.
This program operates on a two-year cycle with fellowships in prose and poetry available in alternating years. In 2024 we will be accepting applications in poetry.
Learn more about past recipients of our literature fellowships in the Literary Arts Impact section.
If you have questions about your application, please contact the Literary Arts staff at 202-682-5034 or email [email protected]
Stay Connected to the National Endowment for the Arts
FundsforWriters
Tips and tools for serious writers to advance their careers!
Our free weekly newsletters reach
28,000 subscribers.
Grants are the free money everyone wants. Here you’ll find grants that cover a simple conference fee or a six-month retreat to write and get away from it all. Some pay for specifically designed projects and others exercise your ability to match writing with a social cause. No two are alike, so keep coming back to see what might suit your fancy.
These grants are legitimate. But like any market or contest, read the guidelines to make sure you fit the mold. While some of them are for big dreamers who face stiff competition, others provide new talent with opportunity. Find out why FundsforWriters is the specialist on grants available to freelance writers.
PLEASE NOTE : FundsforWriters is headquartered in the United States. We are familiar with grants in the US, Canada, the UK and sometimes Australia. However, we are NOT familiar with grant availability in Africa, the Far East, the Middle East, or the Caribbean. We are not an international grant provider. We do not directly give grants. If asked, we will not find you a list of grants without compensation for the service.
TO POST YOUR GRANT/FELLOWSHIP/SCHOLARSHIP/CROWDFUNDING: Email [email protected] with the link for consideration.
More Q&A on Grants
AWESOME GRANTS https://www.awesomefoundation.org/en/about_us The Awesome Foundation is a global community advancing the interest of awesome in the universe, $1000 at a time. Each fully autonomous chapter supports awesome projects through micro-grants, usually given out monthly. These micro-grants, $1000 or the local equivalent, come out of pockets of the chapter’s “trustees” and are given on a no-strings-attached basis to people and groups working on awesome projects.
RHODE ISLAND STATE COUNCIL ON THE ARTS https://arts.ri.gov/grants/general-operating-support-artists Deadline July 1, 2024. General Operating Support for Artists provides grants for artists to work toward larger, self-identified goals in their art practice. This funding is unrestricted, meaning artists can use the funds to support their goals however they need. Award Amount: $6,000 per year, for three years. Must line in Rhode Island.
THE IRELAND FUNDS MONACO https://irelandfunds.org/chapters/worldwide/monaco/bursaries/ Deadline October 2, 2024 . The Ireland Funds Monaco Bursaries were established to enable literary and academic writers born or living on the island of Ireland to pursue a current project during a one-month residency at The Princess Grace Irish Library in Monaco. The Bursaries are aimed at writers in each category who have already published some work of note and are currently engaged in a work-in-progress which would benefit in some regard from holding the award.
THE IRELAND ARTS COUNCIL MARKIEVICZ AWARD https://www.artscouncil.ie/Funds/Markievicz-Award/ Deadline June 6, 2024 . The Markievicz Award is a bursary scheme for artists. Up to 10 artists from all backgrounds, artform and arts practice areas will receive an award of €25,000. The award is designed to buy time and space for artists, working alone or in collaboration, to develop new work that reflects on the role of women in Ireland in the 20th century and beyond.
SUPPORT FOR AUSTRALIAN PUBLISHERS https://www.copyright.com.au/support-for-australian-publishers/ The Cultural Fund offers support for a small number of publishers’ commissions for work by First Nations and diverse writers. The publisher agrees to match the Cultural Fund’s contribution and all money must be paid to the authors. This does not replace royalties or an advance on royalties. Publishers must be Australian-based and books must be distributed nationally. Standard royalties must be paid to authors. Authors who self-publish their work are not eligible to apply.
SC INDIE GRANTS FOR SHORT FILMS https://www.indiegrants.org/indie-grants Deadline August 5, 2024. As part of Indie Grants prep, the South Carolina Film Commission will be holding a one-day INDIE FILM DEVELOPMENT workshop on Saturday, June 1, at Trident Technical College in North Charleston. Ideal for feature-films, webisodics, proof-of-concepts, docs and shorts, it will serve as a comprehensive primer on the mechanics of developing, creating, and selling content, especially in the independent film space.
ADVANCE GENDER EQUITY IN THE ARTS (AGE) GRANTS https://ageinthearts.org/age-grants/2024-2/ Deadline May 15, 2024 . Three awards of $10,000 each and six finalist awards of $1,000 each will be awarded to support emerging playwrights who identify as BIPOC, are 40+ years of age, and identify as a person of marginalized gender or gender-diverse. Must live and work in the United States or Puerto Rico and are able to submit a W9 if chosen as a Finalist or Recipient.
LEEWAY FOUNDATION https://www.leeway.org/grants/leeway_transformation_award/ Deadline May 15, 2024. Provides unrestricted annual awards of $15,000 to women, trans, and gender nonconforming artists and cultural producers living in Greater Philadelphia who create art for social change and have done so for the past five years or more, demonstrating a long-term commitment to social change work. Must have lived for the past two or more years in Greater Philadelphia: Bucks, Camden, Chester, Delaware, Montgomery, or Philadelphia County.
THE OLDER WRITERS GRANT https://speculativeliterature.org/grants-3/slf-older-writers-grant/ Deadline May 31, 2024 . This $1,000 grant, as with all SLF grants, is intended to help writers working with speculative literature, and this one is for writers fifty years of age and older. Include a short (500-1000 words) autobiographical statement describing your work thus far, including date of birth, and a bibliography of previously published work, if applicable. Applicants need not have prior publishing credits to apply. A writing sample: Up to 10 pages of poetry, 10 pages of drama, or 5,000 words of fiction or creative nonfiction.
THE SALTY QUILL SCHOLARSHIP FOR WRITERS RETREAT http://www.thesaltyquill.com/salty-quill-scholarships-1.html Fall scholarship applications will be available upon request after April 15th. The scholarship award is based primarily on your writing sample, with special attention given to writers with financial need. We hope to attract writers who would benefit from the kind of uninterrupted time and space achievable at McGee Island, alongside a supportive community of fellow writers, and those who otherwise could not afford to attend. Location McGee Island, Maine.
VIRGINIA CENTER FOR THE CREATIVE ARTS https://www.vcca.com/apply/financial-information/financial-assistance/ Writers, visual artists, and composers who request financial assistance on their residency applications can receive full or partial funding from a variety of sources. Virginia Center for the Creative Arts (VCCA), one of the leading artists communities in the world with locations in Amherst, Virginia, and Auvillar, France, hosts more than 400 visual artists, writers, and composers each year.
ANNUAL POET COTTAGE WRITER’S RESIDENCY https://poetcottage.com/the-residency/ Apply July 1-15, 2024 . To provide a refuge for writers who might not otherwise be able to afford to rent the cottage for a writing retreat of their own, Hollowdeck Press LLC sponsors the Annual Poet Cottage Writer’s Residency, offering a 10-day stay at Poet Cottage November 1-10th free of charge, an award worth over $2000. The Residency is open to writers of Creative Non-Fiction, Fiction, and Poetry. Winners are responsible for their own airfare, transportation, jeep rental, and food. Location Coral Bay, St John, USVI.
PORCHES WRITING RETREAT – Michael Kenneth Smith Fellowship https://www.porcheswritingretreat.com/ Deadline is in November . Location Virginia on the James River. Open to women 35 and older who have not yet published a novel.
PORCHES WRITING RETREAT – Michael Kenneth Smith Fellowship https://www.porcheswritingretreat.com/ Deadline June 15, 2024 . Location Virginia on the James River. A 10-night residency is available to a writer seriously committed to the short story. He or she should not yet have published a collection of short stories.
PORCHES WRITING RETREAT – Jane Barnes Creative Non-Fiction Fellowship https://www.porcheswritingretreat.com/ Deadline June 1, 2024 . Location Virginia on the James River. One week residency at Porches is available to a writer for essay, memoir, or creative non-fiction.
PORCHES WRITING RETREAT – Open Doors Poetry Fellowship https://www.porcheswritingretreat.com/ Deadline June 1, 2024 . Location Virginia on the James River. First time, new visitors with one published collection.
TENNESSEE ROLLING GRANTS https://tnartscommission.org/news/rolling-grants-remain-available-for-arts-activities/ Tennessee Arts Commission fiscal Year 2024 Rolling Grants remain available to cover a range of arts activities and arts services throughout the state between now and June 2024. Applicants are encouraged to apply for projects that range from a focus on serving an underrepresented population to professional development, arts learning, or engaging audiences in performances and hands-on artmaking.
ODYSSEY WORKSHOP SCHOLARSHIPS https://www.odysseyworkshop.org/2019-odyssey-writing-workshop-scholarship-opportunities/ Financial aid and scholarships are made available by supporters, alumni, various organizations, and Odyssey itself. Scholarships are awarded based on financial need, merit, or the specific criteria listed below. They range in size from several hundred dollars to over $4000.
CALIFORNIA ARTS SEEKING GRANT PANELISTS https://arts.ca.gov/grants/panels/ The California Arts Council has opened its call for applicants to serve on peer-review panels for the 2024 grant season. The state art agency is seeking arts and cultural practitioners from disparate communities statewide to volunteer for a critical role in the grant application process as grant review panelists. Individuals who complete their panel service will receive a $300 honorarium to subsidize them for their attendance at two to three virtual meetings and rank submission activities.
US WRITERS AID INITIATIVE https://pen.org/us-writers-aid-initiative/ Deadlines July 1, 2024, October 1, 2024. The U.S. Writers Aid Initiative is intended to assist fiction and nonfiction authors, poets, playwrights, translators, and journalists in addressing short-term financial emergencies. To be eligible, applicants must be professional writers based in the United States, and be able to demonstrate that this one-time grant will be meaningful in helping address a short-term emergency situation.
ENTRY FEES FOR POETS https://www.poetrybulletin.com/poetry-fee-support This group pays entry fees for poets attempting to submit their manuscripts to publishers that charge to submit. Submission fees for poetry chapbooks and full-length poetry manuscripts only. A maximum of three submissions per poet.
TEXAS TOURING ROSTER https://www.arts.texas.gov/artroster/roster/ Performing arts companies and artists from throughout the state apply to be included on the Texas Touring Roster. These artists must have a history of touring and must be willing to travel outside of their community to do a performance.
NJ ARTISTS IN EDUCATION https://www.nj.gov/state/njsca/dos_njsca_grants.html Practicing professional artists are placed in long-term residencies (20+ days) in schools across the state. Residencies are offered in all disciplines and at all grade levels. All NJ PreK-12 schools can apply for one-year residencies.
INDIANA ARTS PROJECT SUPPORT https://www.in.gov/arts/programs-and-services/funding/arts-project-support/#tab-225218-About_the_Program Arts Project Support (APS) provides funding to 501c3 nonprofits, units of government, and schools to support arts projects during July 1, 2024 – June 30, 2025. Eligible projects include a one-time art event, a single performance, an exhibition, an educational workshop, or series of related arts activities such as classes or training sessions that are open to the public whether free or for a fee. Applicants may request up to $4,000. WRITERS: Coordinate with these entities to design an event for you.
CASA UNO RESIDENCY https://mostlydance.com/1830-2 The ideal participant is an artist who wanting to be able to devote time to a project for three weeks in a beautiful nurturing environment in Costa Rica. Participants may be a writer, visual artist, photographer, filmmaker, storyteller, poet, composer, performer or dancer/choreographer. Artists who are going through career changes or developing a new aspect to their work are strongly encouraged to apply. There is no fee for the residency. The participating artist is responsible for travel to and from Costa Rica. (Thanks ErikaDreifus.com)
AUDIBLE EMERGING PLAYWRIGHTS FUND https://www.audible.com/ep/audible-theater The Fund specifically supports the creation of original dramatic work, written with audio in mind, but theatrical in spirit. Any applicant over the age of 18 may submit a Script. Typical response time is 6-8 months.
DGF EMERGENCY GRANT https://dramatistsguildfoundation.submittable.com/submit For dramatists (playwrights, composers, lyricists, librettists) to apply for emergency financial assistance from the Dramatists Guild Foundation. If you hold a minimum of $15,000 in your combined bank accounts, we kindly ask that you refrain from re-applying at this time.
DGF HOUSING ASSISTANCE GRANT https://dramatistsguildfoundation.submittable.com/submit The Dramatists Guild Foundation’s (DGF) Housing Assistance Grants are one-time awards that assist professional dramatists (playwrights, composers, lyricists, librettists) with housing expenses. DGF is committed to preventing eviction and displacement among theater writers and to help dramatists rebuild their lives during the pandemic recovery period. Theater writers should apply for immediate financial assistance with the following: outstanding mortgage and rent payments, sudden increases to rent prices, overdue utility bills, outstanding costs related to moving, or credit card debt related to any of the aforementioned reasons. If you hold a minimum of $15,000 in your combined bank accounts, we kindly ask that you refrain from applying at this time.
INEVITABLE FOUNDATION FELLOPSHIPS https://www.wgfoundation.org/fellowship-writing-programs-for-screenwriters-masterlist No deadline. Inevitable Foundation started the Screenwriting Fellowship to substantially increase the number of disabled screenwriters working in film and TV. The Fellowship is for disabled screenwriters working in the industry with ample talent and ambition. Fellows receive $25,000, which is meant to cover 4-6 months of living expenses, and the money is unrestricted—you can use it to cover living expenses and other project-related fees.
PATRICK HENRY HISTORY FELLOWSHIP https://www.washcoll.edu/learn-by-doing/starr/Fellowships/patrick_henry_fellowship/index.php The Center’s Patrick Henry History Fellowship includes a $45,000 stipend, health benefits, faculty privileges, a book allowance, and a nine-month residency (during the academic year) in a historic 18th-century house in Chestertown, Md. Applicants should have a significant project currently in progress — a book, film, oral history archive, podcast series, museum exhibition, or similar work. The project should address the history and/or legacy – broadly defined – of the U.S. founding era and/or the nation’s founding ideas.
PERSEPHONE MIEL FELLOWSHIPS https://pulitzercenter.org/grants-fellowships/opportunities-journalists/persephone-miel-fellowships The Persephone Miel Fellowship is designed to support journalists from outside the U.S. and Western Europe who are pursuing ambitious reporting projects and enable them to bring their work to a broader global audience. Grants are open to all journalists: writers, photographers, radio producers, and filmmakers; staff journalists as well as freelancers. We support veteran reporters who have been widely published, but also back younger applicants who are looking for help to jumpstart their careers. A diversity of voices— gender, ethnicities, backgrounds and nationalities—is important to us. The Pulitzer Center on Crisis Reporting will provide a grant of $5,000 for a reporting project on topics and regions of global importance, with an emphasis on issues that have gone unreported or underreported in the mainstream media.
WISCONSIN HUMANITIES https://wisconsinhumanities.org/grants/grants-for-humanities-programs/ An applicant must be a nonprofit organization. This includes historical societies, libraries, colleges, schools, civic organizations, or an ad hoc group with a nonprofit serving as fiscal sponsor. Grants are $2,000 to $10,000. Humanities programs should be reflective experiences that engage the public. Programs can take many forms including exhibitions, performances, community discussions, guest speakers, workshops, oral history projects, panels, town halls, films, and more.
FISHTRAP WRITER-IN-RESIDENCE – OREGON https://fishtrap.org/fishtrap-writer-in-residence/ Are you an experienced teaching artist looking to spend time immersed in the community and beauty of rural Wallowa County? Fishtrap Writers in Residence have the opportunity to get some creative work done and help inspire local writers of all ages through teaching in local schools, sharing a public reading, and offering your own Fishtrap writing workshop. Residence lasts from six to eight weeks during the months of April and May, and includes a stipend, travel allowance, and lodging. While you are here, Fishtrap will work with you to schedule up to eight hours a week of classroom time in Wallowa County schools. You will be asked to lead a one-day adult workshop as part of our local writing workshop series. You’ll also have the opportunity to hold a public reading event at Fishtrap’s new home in the historic Bowlby Building. The rest of the time is yours to use to write, be explore the county, and connect with the many local writers in the Fishtrap community. Since a Fishtrap Writer in Residence will be spending significant time in Wallowa County schools, proven teaching and classroom management experience, especially at the secondary level, is required. Location Enterprise, OR.
MISSISSIPPI ARTIST ROSTER https://arts.ms.gov/artist-roster/?view=mississippi The Mississippi Arts Commission’s Artist Roster is a listing of artists who have been accepted to the Teaching Artist Roster, the Mississippi Artist Roster, or both. Each artist or arts group applied and went through a thorough review by a panel of artists, presenters and educators. Grant funds are available to organizations for presenting Roster Artists (see Minigrants for Organizations). Individual artists may apply to be included in the Roster for a three-year term. Their fees are paid by the Mississippi Arts Commission.
NEW WRITING NORTH https://newwritingnorth.com/vacancies/ New Writing North are looking for experienced writer facilitators to run sessions with our North East Novelists group. The sessions should be focused on the practical craft of creative writing and suitable for novelists already published or under contract to publish, and who are already represented by an agent. Starting October 2023, there will be one session on the first Wednesday evening of every month, in a central Newcastle venue. We can offer a fee of £125 per session, and up to £50 to cover travel costs. If you are interested, please send a short pitch about yourself and the session to [email protected] .
GEORGIA WRITERS REGISTRY https://www.georgiawriters.org/georgia-writers-registry https://www.georgiawriters.org/literary-events-grant-of-georgia Once selected, you get the lucrative opportunity to be contacted by one of GWA’s local venues for a chance to host an event, workshop, or reading of your process and/or the work you’ve completed during your writing process. The quality of an applicant’s credentials will be evaluated by a peer review panel based on a writing sample and the listed criteria. Literary Event Grants of Georgia (LEGG) supports the writers’ fees for literary events in underserved communities across the state. Literary events include readings, workshops, presentations, and performances. They provide grants of $50-$250 for a literary event.
THE EMERGING PLAYWRIGHTS FUND https://www.audible.com/ep/audible-theater A program that invests in and nurtures self-identifying emerging playwrights, some of our most inventive, delightful, and provocative storytellers. Any applicant over the age of 18 may submit a Script. Submissions are accepted year-round. The Fund specifically supports the creation of original dramatic work, written with audio in mind, but theatrical in spirit. Contact: [email protected]
18TH STREET ARTS CENTER https://18thstreet.org/residency-program/ The Visiting Artist Residency Program accepts applications from working, professional artists who demonstrate a deep commitment to their practices. The program is open to artists of all generations, nationalities, and disciplines. Applicants are required to cover studio rental costs themselves. Although we primarily support visual artists, 18th Street Arts Center will consider applications from performing artists, writers, and filmmakers as well. Hosts artists from across the United States and from around the world.
OHIO ARTISTS WITH DISABILITIES GRANTS https://oac.ohio.gov/grants/10-grant-opportunities/40-artists-with-disabilities-access-program Deadlines November 1 and May 1 each year. The Artists with Disabilities Access Program (ADAP) provides funding that gives individual artists with disabilities the resources they need to further their artistic development. Creative expression by artists of all abilities is essential to building dynamic and diverse communities throughout Ohio. ADAP awards help artists with disabilities advance their artistic practices, making Ohio a more accessible and inclusive place to build an artistic career. Grants are awarded to individual artists at both the emerging artist level ($500) and professional artist level (up to $2,500), with no cash match required.
BLUEDOT LIVING https://bluedotliving.com/ Pitch Leslie Garrett, Editor at [email protected] . Seeking great solutions-focused climate stories to share about what’s happening in your community. Pays $175 for “dispatches”—reporting about a specific project/initiative in a community. Dispatches run 400-800 words. Features run 800-1,500 words, and we pay anywhere from $400-$750 depending on complexity/writer’s experience.
FATHERLY https://www.fatherly.com/ Pitch Tyler Santora, Health and Science Editor at [email protected] . Seeking science journalists to write for Fatherly about parenting and fitness. $250-300 per story, depending on amount of research needed. Email clips.
ATMOS https://atmos.earth/ https://brindle-caraway-75e.notion.site/Editorial-Guidelines-Home-0c1688d8986644a98cd3118dfb069c8e Standard writer’s rate is 50 cents/word. Kill fee is 50 percent. While all print stories are eventually published in one or more of the below topic categories, stories for the biannual printed edition of Atmos are commissioned based on the issue’s theme. Please see a list of previous issue themes online. If you are interested in pitching specifically for print, you may inquire as to the theme of the current issue. The ideal Atmos story exists at the intersection of climate and culture. That can mean a culture story with a climate twist, a climate story with a culture twist, or something directly in between.
THE WHITE PUBE CREATIVES GRANT – UK https://thewhitepube.co.uk/grants/ The White Pube Creatives Grant is a one-off £500 grant to be given out to a different working class creative practitioner based in the UK once every month. This grant has been set up to support creatives of all ages who are early in their careers and would benefit from this no-strings attached financial support to help them in whatever they like – be that money to cover time to make, or fund materials, equipment, research, subscriptions, development, travel, or even rent and bills.
THE AUTHORS’ FOUNDATION – UK https://www2.societyofauthors.org/grants/grants-for-work-in-progress/ Rolling deadline. The Authors’ Foundation and K Blundell Trust award grants to writers whose book project is for a commercial UK publisher. Grants are usually between £2,000-£3,500 and are a maximum of £6,000. You are eligible to apply if you have been commissioned by a commercial British or Irish publisher to write a full-length work of fiction, poetry, or nonfiction and need funding (in addition to any publisher’s advance) for important research, travel, or other general expenditure. -OR- You are without a contractual commitment with a publisher but have had at least one book published commercially by a British or Irish publisher, of which you are the sole author, and there is a strong likelihood that your next book will be published in Britain or Ireland.
FIRST JOBS FUND – UK https://journalistscharity.org.uk/how-we-help/first-jobs-fund/ The fund is only for new journalists who are struggling financially with essential costs. You’ll either be working full-time in journalism or about to start a new job with a firm offer of employment. If you’ve been a journalist for more than two years, the fund isn’t for you, but you might qualify for other forms of financial assistance from the charity. To be eligible for financial help from the charity you must be a journalist or former journalist in the UK, or work for a UK organisation overseas.
FINANCIAL ASSISTANCE – UK https://journalistscharity.org.uk/how-we-help/advice-financial-assistance/ If you’re a journalist, or former journalist and need financial help, you can apply for support quickly and easily using the online application form. To be eligible for financial help from the charity you must be a journalist or former journalist in the UK, or work for a UK organisation overseas.
PEGGY RAMSAY FOUNDATION – UK https://www.peggyramsayfoundation.org/grant-applications.html We give money to theatre writers in order to afford them the time and the space to write. You can be a writer who’s only had one play professionally produced, a writer who’s had dozens of successes or a writer who’s somewhere in between – if you’re struggling to pay the bills, then we can help. We only support writers resident in the British Isles.
WOMEN’S HISTORY NETWORK INDEPENDENT RESEARCHER GRANTS – UK https://womenshistorynetwork.org/womens-history-network-independent-researcher-grants-for-2023-24/ The Women’s History Network is offering a small grant of up to £750 to support the direct costs of those researching women’s history outside of academia. While applicants may be in possession of a degree or postgraduate qualification, the grants are intended to support research into women’s history by Independent scholars. We would therefore anticipate that the research would result in at least one tangible output (e.g. a publication, a museum exhibition, a podcast, etc) for a general audience.
GUILD OF FOOD WRITERS BENEVOLENT FUND https://www.gfw.co.uk/fellowship-fund/ A total sum of £2,000 is ring-fenced each year for the purpose of such Futures Fund grants. These are awarded to a member or members who make a suitable request. The member or members are required to make a written request of no more than 500 words, including an outline of the project and its merits, the amount required, what the money would be used for, including a breakdown of estimated costs, and any details of potential publication plans in order to justify the awarding of the grant. We are particularly keen to support projects for which there is no other funding (smaller applications for things like book purchases are also encouraged). The successful recipient or recipients should be willing to give back to the Guild in the form of a workshop, lecture, panel membership, website or newsletter contribution on the completion of their project. Members are represented across the UK regions, as well as overseas.
GRIST FELLOWSHIPS https://grist.org/fellowships/ The Grist Fellowship Program is a paid opportunity to hone your skills at a national news outlet and deepen your understanding of environmental issues. The experience is designed to give early-career journalists with a demonstrated interest in environmental issues the experience to succeed in climate and environmental media. We offer real-world experience at a fast-paced news site, training in a variety of skills key to a journalism career, and exposure to the leading sustainability thinkers and theories of our time. After a year of working full-time at Grist and gaining key skills in environmental journalism, fellows have gone on to outlets including The Atlantic, Capital B, The Verge, Wirecutter, Outside, Atlas Obscura, Greentech Media, and of course, Grist.
NORTH CAROLINA ARTIST SUPPORT GRANTS https://www.ncarts.org/grants-resources/grants/grants-artists/artist-support-grants Artist Support Grants is a program funded by the N.C. Arts Council to provide the opportunity for regional consortia of local arts councils to award project grants to artists in their regions. These grants support professional artists in any discipline and at any stage in their careers to pursue projects that further their artistic and professional development. Contact the granting local arts council for details. Grant amounts vary from region to region. Statewide, most grants are between $500 and $2,000.
STOCHASTIC LABS RESIDENCIES https://stochasticlabs.org/residencies/ Stochastic Labs awards fully sponsor residencies to exceptional engineers, artists, scientists, and entrepreneurs from around the world. Residencies are of variable length and include a private apartment at the mansion, co-working and/or dedicated work space, shop access (laser cutter, 3D printer etc), a monthly stipend and a budget for materials. Residents become part of Stochastic’s creative community, participating in weekly dinners and invitation events. Residents may apply as individuals or as teams. While applicants may be at any stage in their career, the selection is highly competitive. Stochastic Labs convenes leading creative minds in the SF bay area and beyond for conversations about the future of technology, science, entrepreneurship, and the arts (in a curious Victorian mansion in Berkeley, CA).
FICTION MEETS SCIENCE https://fictionmeetsscience.org/ccm/content/projects/invention/writers-in-residence/ Writing a work of fiction or creative non-fiction in which science and its practitioners play a major role entails a considerable amount of background research. Like writing any book, it also requires concentrated blocks of time free from the teaching, freelance, or other work that authors of literary fiction must often engage in to make ends meet. In this project, we award selected authors fellowships to work on science novels at the Hanse-Wissenschaftskolleg (HWK), an Institute for Advanced Study. We are considering authors of narrative non-fiction about science in various genres (memoir, biography, documentary, journalism, history, popular science), as well as novelists. Location Delmenhorst, Germany.
NEW ENGLAND FOUNDATION FOR THE ARTS NEST PROGRAM https://www.nefa.org/NEST Deadlines August 1, December 1 . The foundation invites applications from nonprofit organizations for its NEST (New England States Touring) program, which funds performances, readings, and screenings of work by regional, national, and international artists presented by New England-based nonprofit organizations. There are three distinct grant opportunities for New England nonprofit organizations: NEST 1, NEST 2, and NEST 3. Grants are available in amounts of up to 60% of the artists’ fees and range from $500 to $10,000. Requests below $500 will not be accepted. Applications with artist fees under $2,000 may request the full artist fee. Artists’ fees may include costs for creation of new work, travel, and per diem.
OF A CERTAIN AGE GRANT https://nwfilmforum.org/lynn-shelton-certain-age-grant-2/ A grant of $20,000 will be awarded to an individual woman, nonbinary, and/or transgender United States filmmaker, age 39 or older, who is working on their first narrative feature (at least 65 minutes) as a director. To be eligible, filmmakers must have “director” credit on at least one short film or feature documentary and desire to work in the narrative space. Filmmakers with “director” credit on a feature-length (70+ min) narrative film will not be considered.
NEBRASKA MINI GRANTS https://www.artscouncil.nebraska.gov/mini-grant/ Mini Grants are designed to provide quick access to funds supporting a variety of arts projects that use artists or arts activities as a key component. Examples of project types include exhibitions, performances, poetry readings, commissions and/or support of new work development, arts festivals, community murals, and cultural heritage projects. Limit $2,000. Open to groups and nonprofits, but can be used to sponsor individual artists for events. Deadline at least six weeks prior to the project start date.
NEBRASKA CREATIVE AGING ARTS PROGRAM https://www.artscouncil.nebraska.gov/apply/creative-aging/ This program provides grants to hire an artist to lead workshops at senior centers, assisted living facilities, libraries and nonprofit organizations serving older adults. Applicants select from a list of teaching artists trained in best practices of engaging older adults. Limit $3,000. Apply at https://www.artscouncil.nebraska.gov/artist-roster/join/ to join the teaching roster.
MASSACHUSETTS LOCAL CULTURAL COUNCIL PROGRAMS https://massculturalcouncil.org/communities/local-cultural-council-program/ The largest grassroots cultural funding network in the nation, the Local Cultural Council (LCC) Program enriches the cultural life of all cities and towns in Massachusetts. Use this link to find your local council nearest you in the state. https://massculturalcouncil.org/communities/local-cultural-council-program/find-your-lcc/
BROTHER THOMAS FELLOWSHIPS https://www.tbf.org/what-we-do/special-funds/br-thomas-fund The goal of the biennial Brother Thomas Fellowship program is to support and celebrate a diverse group of Greater Boston artists working at a high level of excellence in a range of disciplines—the visual, performing, literary, media and craft arts—and to enhance their ability to thrive and create new work. The Boston Foundation also hopes that fellowship winners will have greater access to a variety of markets, including galleries, residencies and commissions, and that the importance of artists to the vitality of Boston will be more broadly recognized. Each Brother Thomas Fellow receives an unrestricted award of $15,000—thus fulfilling the needs of artists and the wishes of the donor.
TEXAS TOURING ROSTER https://www.arts.texas.gov/ow/tcagrant/TXArtsPlan/TRC.htm The Texas Commission on the Arts maintains an approved roster of Texas-based touring companies and artists. In this program, the artist or artist’s management sets the fee and negotiates the booking. Applicants must have a history of touring and maintain a reasonable fee range. Roster artists are required to perform outside their community regularly. Touring artists offer performances as well as optional services that may include workshops, master classes, lecture-demonstrations, arts education components, residencies, or short performances.
MONTANA STRATEGIC INVESTMENT GRANTS https://art.mt.gov/sig Strategic Investment Grants (SIG) provide up to $1000 for expenses related to opportunities for professional development, market expansion, and art events. SIG enables artists and teachers to advance their professional careers and supports nonprofit organizations in the advancement of arts-related programs. Applications are due on the 15th of each month.
ATLANTIC CENTER FOR THE ARTS https://atlanticcenterforthearts.org/residencies/aair-application/ Atlantic Center for the Arts (ACA) is a non-profit multidisciplinary artist residency facility located in New Smyrna Beach, Florida. Review the Residency Schedule to select a Mentoring Artist you are interested in working with, review application requirements, and deadlines. Each Mentoring Artist determines the requirements and basic structure of their residency and selects up to six Associate Artists to participate in the residency program.
MONSON ARTS RESIDENCIES https://monsonarts.org/ Monson Arts’ residency program supports emerging and established artists and writers by providing them time and space to devote to their creative practices. During each of our two-week and four-week programs throughout the year, a cohort of five artists and five writers are invited to immerse themselves in small town life at the edge of Maine’s North Woods and focus intensely on their work within a creative and inspiring environment. They receive a private studio, private bedroom in shared housing, all meals, and $1,000 stipend ($500 for two-week programs). Open calls for residency applications currently take place three times throughout the year with deadlines on January 15, June 15, and September 15 .
MESA REFUGE https://mesarefuge.org/ Deadline June 1 (for the fall) and December 1 (for the following spring). Mesa Refuge welcomes a diverse group of writers—both emerging and established—who define and/or offer solutions to the pressing issues of our time. Particularly, it is our priority to support writers, activists and artists whose ideas are “on the edge”, taking on the pressing issues of our time including (but not limited to): nature, environment and climate crisis; economic, racial and gender equity; social justice and restorative justice; immigration; health care access; housing; and more. We especially want writers of nonfiction books, long-form journalism, audio and documentary film. Occasionally we accept poetry, fiction (Young Adult/Adult Literary), screenwriting and playwriting, photojournalism, personal memoirs (as a vehicle to tell a larger story) and graphic narrative. We tend not to accept academic writing. Location Point Reyes Station, CA,
SOMERSETT COUNTY ARTS – MARYLAND https://www.socoarts.org/individual-artist-grant The Somerset County Arts Council annually awards grants to talented individual artists. The purpose of these grants is to honor, support, and strengthen individual artists living and working in the area. Artists may apply for up to $1,000.
FIYA LIT MAG GRANTS https://fiyahlitmag.com/grants/ The FIYAH Literary Magazine Grant Series is intended to assist Black writers of speculative fiction in defraying costs associated with honing their craft. The series includes three $1,000 grants to be distributed annually based on a set of submission requirements. All grants with the exception of the Emergency Grant will be issued and awarded as part of Juneteenth every year. The emergency grant will be awarded twice a year in $500 amounts. Limited to prose only.
SOUTH ARTS EXPRESS GRANTS https://www.southarts.org/community-organization-grants/express-grants Deadline is 60 days before the event. South Arts believes that rural communities deserve great art, and can require specialized support to make that vision viable. Distributed on a first-come, first-serve basis, Express Grants support rural organizations and communities with expedited grants of up to $3,000. To be eligible for funding, applicants must program arts experiences featuring a Southern artist. Artist fee support is awarded for: film (documentary, fiction, experimental, and animation); performing arts (theater, music, opera, musical theater, and dance); literary arts (fiction, creative nonfiction, and poetry); traditional arts, and visual arts (crafts, drawing, experimental, painting, photography, sculpture, and mixed media). Projects must include both a public presentation (film screening, performance, reading, or exhibition) and an educational/community engagement component.
NEBRASKA MICRO GRANTS – ARTIST DEVELOPMENT https://www.artscouncil.nebraska.gov/apply/micro-grants/ https://www.artscouncil.nebraska.gov/wp-content/uploads/2022/10/Micro-Grant-Artist-Development-Guidelines-FINAL.pdf Micro Grants provide financial support to assist artists and community organizations applying for a grant for the first time. Artists may submit up to one application per fiscal year (June 30 – July 1). Limit $500. The Letter of Interest (LOI) must be received no less than six weeks prior to the start of the project or purchase of equipment. If invited to apply, applications must be submitted no later than four weeks prior to the project start date or purchase of equipment.
NEBRASKA CREATIVE AGING ARTS PROGRAMTS https://www.artscouncil.nebraska.gov/apply/creative-aging/ This program provides grants to hire an artist to lead workshops at senior centers, assisted living facilities, libraries and nonprofit organizations serving older adults. Applicants select from a list of teaching artists trained in best practices of engaging older adults. During a residency, artists will share their expertise through sequential arts lessons, helping participants hone their skills in a variety of disciplines. Programs will also foster intentional social engagement among participants, culminating with a special event to showcase their work with peers and the community. Submit at least six weeks prior to the event date.
OAK SPRING GARDEN FOUNDATION https://www.osgf.org/residencies/interdisciplinary-residency We offer five-week or two-week sessions of our Interdisciplinary Residency. The two-week Interdisciplinary Residency program is designed for parents, caregivers, or others for whom a five-week Residency is not possible. We encourage those who are able to apply to the five-week Interdisciplinary Residency to do so. The goal of this program is to provide individuals with the time and space to pursue their own creative projects alongside other Residents who may be examining plants, landscapes, gardens, and the natural world from different perspectives. Artists, conservation practitioners, researchers, scholars, scientists, and/or writers are encouraged to apply to our Interdisciplinary Residency Program. Residents selected for a five-week session receive a $2,000 individual grant, and Residents selected for a two-week session receive an $800 individual grant. Location Upperville, VA.
ARTS NEW ORLEANS SEEKING GRANT PANELISTS https://www.artsneworleans.org/panelist-nomination-form/ Arts New Orleans is looking for volunteers for its grants review panels for awards made possible with city and state funds. Our grant panels are comprised of community volunteers who are representative of the ethnic, demographic, and geographic diversity of the region. Panels also embody the artistic, community, and administrative expertise needed for application review. Meetings are usually held between May and August. Panelists who review grants made possible with city funds must reside in New Orleans. Panelists for grants made possible with state funds can reside in Orleans, Jefferson, and Plaquemines Parishes. Self-nominations are encouraged. Panelists will be compensated with a modest honorarium.
ASC FOUNDERS GRANTS https://artsandscience.org/founders-grants/ Distinct from other funding opportunities ASC provides for creative individuals, this award is intended to celebrate the commitment of Charlotte-Mecklenburg creatives to the community they call home and are intended to award their vision. As such, the applicants are not required to submit a budget or specify how they would leverage the resources. This is first and foremost an award celebrating the creative individual’s vision. ASC welcomes applications from Mecklenburg County based creative individuals who pursue their creative practice as their primary occupation. ASC will award up to five $50,000 Founders Grants.
FELLOWSHIP FOR PARENT WRITERS https://www.writerscolony.org/fellowships The Writers’ Colony is offering a unique fellowship opportunity for a one-week residency and a $500 stipend to provide time and space for a parent writer to focus on their work. The My Time fellowship is funded by the Sustainable Arts Foundation. Writers may submit work in any literary genre: poetry, fiction, plays, memoir, screenplays, or nonfiction.
GRUNEWALD GUILD RESIDENCIES https://grunewaldguild.com/artists-in-residence/ Residencies are available to individuals at all levels of artistic development who are prepared to work independently and whose artistic processes can be successfully supported by the Guild’s studio facilities. Although our spaces are primarily designed for visual artists, we welcome residents working in all creative disciplines, including writers, musicians, and performers. Our residency program is volunteer-based, and we provide artists with lodging, meals (with our programming), staple foods (non-program times), & studio space at no cost in exchange for part-time volunteer service to the Guild. Artists in residence commit to spending a minimum of 20 hours/week in the studio working on their own projects, as well as 15-20 hours/week in volunteer service to the Guild community. The residencies are usually 4-6 weeks. Location Leavenworth, WA.
MARYLAND GRANTS FOR ARTISTS https://msac.org/programs/grants-artists/grants-artists Must be an artist providing evidence of regular creative practice. Must produce or present projects or programs that are relevant to the community and accessible to the public. Must be Maryland residents (owning or renting residential real property in Maryland at the time of application submission and throughout the funded project or program) and must be 18 years of age or older. May not be enrolled in any matriculated high school, undergraduate or graduate degree program. Grants for Artists funds are intended to encourage artistic growth and sustained practice. Common expenses include but are not limited to: administrative costs, consultant fees, contractual services, daycare services, entry fees, equipment rental, exhibition costs, financial tools or planning, food, housing, insurance, studio or workspace costs, materials and supplies, marketing costs, medical costs, payment to technical crews, fabricators, or collaborators, professional memberships, performance costs, production costs, student loans, submission fees for grant or residency applications, travel and transportation, utilities, and website development. Rolling deadline. Grant amount $6,000.
POETRY BULLETIN SUBMISSION FEE SUPPORT https://www.poetrybulletin.com/poetry-fee-support Confidential, poet-to-poet support. Over $4,400 committed to this circle since March 2021, given to 70 poets so far. Submission fees for poetry chapbooks and full-length poetry manuscripts. A maximum of three submissions per poet, to share the funds with as many folks as possible. Designed for poets who cannot otherwise afford to submit their manuscripts to publishers; poets who face barriers of time, access, or energy; and poets who have historically been underrepresented.
TRILLIUM ARTS RESIDENCIES https://www.trilliumartsnc.org/artist-residencies Trillium Arts is an artist residency center where artists of many disciplines can find a creative home away from home, offering secluded space for rejuvenation in a beautiful, remote setting in the Blue Ridge Mountains. Our current facilities are best suited to the disciplines of literary arts, photography, visual arts and arts administration. June 8, 2023 deadline for residencies taking place during October & November 2023. The Application submission period is open for six weeks from April 20 – June 8, 2023. Rate for an independent artist is $600/week. Trillium Arts offers a limited number of work scholarships. The scholarship is an exchange of eight hours of work during the residency week for a 50 percent discount off the residency fee.
CRIME WRITERS ASSOCIATION BURSARIES https://thecwa.co.uk/member-benefits/bursaries The Crime Writers’ Association offers a range of bursaries for both new and existing members, to help those whose financial circumstances might prevent them from joining the CWA, renewing their membership or attending events. The bursaries are kindly provided by our members and other contributors to provide full or partial funding towards membership, CWA conference attendance or CrimeFest attendance. Some bursaries are targeted at helping authors from specific groups. They are all awarded in strict confidence to people who wouldn’t otherwise be able to afford the membership or activity. See the website for the 19 different bursary offers.
FLEISHHACKER FOUNDATION SMALL ARTS GRANT https://www.fleishhackerfoundation.org/small-arts Grants ranging from between $2,500 and $10,000 (generally closer to $5,000) will be awarded as general support to support small arts organizations engaged in the production and presentation of new work by Bay Area artists in the disciplines of dance, music, theater, visual arts, interdisciplinary arts, or film. General support grants are flexible and may be used for operations, staffing, facilities, health and safety compliance, artists’ compensation, rehearsals, performances, presentations, exhibitions, and other administrative, program, or production costs at the grantee’s discretion. Applicants must be arts and culture organizations incorporated as a 501(c)(3) nonprofit (including fiscal sponsors applying on behalf of a sponsored arts group or filmmaker). Organizations must be located and primarily offering programming in San Francisco, Alameda, Contra Costa, Marin, Sonoma, San Mateo, and/or Santa Clara counties and be able to demonstrate an artistic presence in the Bay Area for at least three years.
MAINE WRITERS AND PUBLISHERS ALLIANCE https://www.mainewriters.org/scholarships 1) Ashley Bryan Fellowships – Open to Maine residents who are emerging writers and who are Black, people of color, and/or members of one of the Wabanaki Nations or other Native peoples. Provides fellows with a Find Maine Writers membership, free workshops, and other benefits.
2) Bodwell Fellowship – Open to Maine residents who are emerging writers. Provides one Bodwell Fellow each year with a residency at Hewnoaks Artist Colony and a $500 award.
3) Christina Baker Kline Scholarships – Open to all Maine residents. Provides one-year of MWPA membership and attendance fees for two workshops.
4) Martin Dibner Memorial Fellowships – Open to all Maine residents who have not published a full-length book. Provides full funding to attend the MWPA’s autumn Harvest Writers Retreat or spring Black Fly Writers Retreat OR a multi-week workshop in the fall or spring.
DELAWARE ARTIST OPPORTUNITY GRANTS https://arts.delaware.gov/grants-for-artists/ Artist Opportunity Grants are awarded on a competitive basis to support unique professional and artistic development and presentation opportunities for artists. Examples include: materials to complete work for a specific show or program; the cost to rent a facility for a performance; study with a master for a specified period of time. Evaluation criteria include: anticipated impact on the artist’s work or career; financial feasibility and need; marketing plans; and uniqueness of the opportunity. Applicants can request up to 80 percent of the opportunity cost not to exceed $1,000. Quarterly deadlines: January 1, April 1, July 1, and October 1.
REIMAGINE RESIDENCIES https://janeaustens.house/reimagine-residencies/ Our Reimagine Residencies programme will run from Autumn 2022 – Winter 2023, and we’re on the lookout for emerging artists and creatives in all sorts of disciplines to take part – from art, design and drama to food, film and photography! We have six residencies available, to take place in 2023. Dates, times and projects are all flexible. We are open to in-person residencies here in Chawton, or virtual residencies that you complete from home, or a mixture of the two! Location Jane Austin House at Chawton Hampshire, UK.
JACK HAZARD FELLOWSHIPS https://www.newliteraryproject.org/jack-hazard-fellowship-apply Jack Hazard Fellows are fiction, creative nonfiction, and memoir writers who teach full-time in an accredited high school in the United States. We provide a $5,000 award that enables these creative writers who teach to focus on their writing for a summer.
MASS MOCA FULL FELLOWSHIPS https://www.assetsforartists.org/financial-aid/ The Studios at MASS MoCA will offer multiple full fellowships that do not have geographic or demographic limitations. This means that anyone who wishes to can apply for one of these fellowships, regardless of discipline. The fellowship funds all residency fees for up to four weeks in residence.
MASS MOCA FELLOWSHIP FOR BLACK OR INDIGENOUS ARTISTS AND WRITERS https://www.assetsforartists.org/financial-aid/ Recognizing the additional barriers faced by Black and Indigenous creators of all disciplines, the Studios shall award a number of additional fellowships to artists and writers working in any discipline who identify as Black or Indigenous. These fellowships fund all residency fees for up to four weeks in residence, and also include a stipend of $200 per week.
MASS MOCA MASSACHUSETTS FAMILY FELLOWSHIP https://www.assetsforartists.org/financial-aid/ At the Studios, we recognize the barriers parents of young children face when looking to attend artist residencies. Because of this, in 2023, we will award one family fellowship for a Massachusetts-based artist(s) and their kid(s) who are entering grades one through five at the time of the residency. The awarded artist (or artist-couple) will receive a fully funded two-week residency where they will have full run of a three-bedroom apartment, and the use of up to two studios on the MASS MoCA campus. The selected artist will receive a $1,000 stipend. We have also reserved slots in MASS MoCA’s “Camp Kidspace” to provide care and entertainment for the artists’ children on weekdays during their two-week residency.
WRITERS’ ACCESS SUPPORT STAFF TRAINING PROGRAM – THE WRITERS GUILD FOUNDATION https://www.wgfoundation.org/programs/writers-access-support-staff-training-program The program’s mission is to provide writers who are BIPOC, LGBTQ+, disabled writers, and writers over the age of 50, with tools and education to become a writers’ assistant and script coordinator, ultimately resulting in meaningful employment opportunities. Graduates of the program will be included in an ongoing list of trained writers’ assistants and script coordinators (WA/SCs) primarily from underrepresented groups, which will be made available to studios, networks and showrunners, in order to increase the pool of eligible hires in the movie/television industry. This program is free thanks to financial support from WarnerMedia. Current sessions are hosted online via Zoom. NOTE: The door just closed for the quarter ending in November. Sign up for the newsletter to be informed when this opportunity opens again.
FOLGER INSTITUTE ARTISTIC RESEARCH FELLOWSHIPS https://www.folger.edu/institute/artist-research-fellowship Folger Institute Artistic Research Fellowships are open to artists working in all media whose work would benefit from significant primary research. This includes, but is not limited to, visual artists, writers, dramaturgs, playwrights, performers, filmmakers, and composers. Artistic fellowships may be conducted either as a virtual fellowship for one month or as a residential fellowship at the Folger for one, two, or three months. Location Washington DC.
CALIFORNIA INVIDUAL ARTIST FELLOWSHIPS https://arts.ca.gov/grant_program/individual-artists-fellowship/ Applications for the Individual Artist Fellowship program will open for applications from California-based artists in early 2023. Through a network of regionally-based Administering Organizations (AOs), the Individual Artists Fellowship (IAF) program will continue to recognize, uplift, and celebrate the excellence of California artists practicing any art form.
STIWDIO MAELOR RESIDENCIES https://stiwdiomaelor.com/ Stiwdio Maelor offers selected artists and writers time and space out of their normal life to focus on the development of their work and explore the beautiful landscape of mid Wales. Residencies provide artists and writers the experience of working alongside other artists of different disciplines and at different stages in their careers.
NEBRASKA ARTS COUNCIL ARTIST ROSTER https://www.artscouncil.nebraska.gov/artist-roster/join/ Nebraska Arts Council’s Artist Roster helps nonprofit organizations and schools bring accomplished artists and performers into communities, giving people the chance to enjoy art to which they may not otherwise have access while ensuring artists get paid for their work. The roster is split between the Artists in Schools and Communities (AiS/C) program and the Nebraska Touring Program (NTP). Teaching artists in Nebraska and contiguous states may apply for the AiS/C Artist Roster. AiS/C artists may conduct programs in schools, non-profits, or other community settings. Programs may also target adult groups, engaging participants through lifelong learning and creative activities. The Nebraska Touring Program (NTP)/Exhibits Nebraska is designed to showcase artists residing in Nebraska, who provide a variety of high-quality touring performances and exhibits in various price ranges to all Nebraska communities throughout the year. It provides financial assistance to Nebraska’s non-profit sponsors as well as promotes resident Nebraska artists and groups with a record of professional achievement.
MARYLAND CREATIVITY GRANTS https://msac.org/programs/creativity-grants/creativity-grants-projects Intended to support specific arts projects, events, or programs, this option is available for independent artists, as well as organizations. Each application should focus on a proposal for one specific project or program. Funding amount $1,000 – $4,000.
MARYLAND PROFESSIONAL DEVELOPMENT GRANT https://www.msac.org/programs/professional-development/professional-development-opportunity-grant The Professional Development Opportunity Grant program encourages and supports relevant professional development opportunities for artists and arts organizations throughout Maryland. Up to $2,000.
VERMONT ARTISTS IN SCHOOLS https://www.vermontartscouncil.org/grants/schools/artists-in-schools Artists in Schools Grants support quality, multiday arts experiences in schools with Vermont teaching artists in residence and encourage collaborations between schools, youth, artists, and arts organizations. Residencies may take place during the school day or in a sequential, after-school setting. Grant funding supports multi-day projects typically between 3-10 days in length and support preK-12 teachers and students within a given school or district.
NORTHERN IRELAND SIAP TRAVEL AWARDS http://artscouncil-ni.org/funding/scheme/travel-awards These awards enable individual artists and established music groups (up to four members) to travel from Northern Ireland to develop their skills and expertise. Applicants must provide evidence that they have been invited by a host organisation in the country to which they intend to travel. Open to artists of all disciplines and in all types of working practice, who (a) Have made a contribution to artistic activities in Northern Ireland for a minimum period of one year within the last five years.
NEVADA PROJECT GRANTS https://www.nvartscouncil.org/wp-content/uploads/FY23-PROJECT-GRANT-FOR-ARTISTS-Guidelines-Final.pdf The PGA is awarded twice a year for projects that take place during a specified six-month period. Examples of eligible projects include art exhibitions, performances, readings, concerts, the creation of art, recording, filming, portfolio creation, and marketing/promotional activities related to an arts project. Must be a current Nevada resident and have been in residence for at least one year prior to the date of the grant application. Must be a U.S. citizen or have legal resident status. Up to $3,000 (no match required).
THE SHIRLEY HOLDEN HELBERG GRANTS FOR THE MATURE WOMAN http://www.nlapw.org/grants-and-scholarships/ Deadline September 30, 2023 . The National League of American Pen Women, Inc. awards three grants of $1,000 each in art, letters, and music to women 35 years of age or older who are not now nor ever have been a member of NLAPW. Entry period is in early fall of every odd year. (NOTE the year 2023 – this is every other year.)
GO ON GIRL BOOK CLUB SCHOLARSHIPS https://goongirl.org/scholarships/faq-s Each year, the GOG Scholarship Committee will grant at least two writing awards. One award is given to an Unpublished Writer and the other award is given to an Aspiring Writer who attends a Historically Black College or University (HBCU). The first place award winner in each category will receive $1,000. For the Unpublished Writer Award: applicant must be a U.S. citizen or resident alien, must have a strong connection to identify with the African Diaspora, must reside in the United States, must be unpublished and must not be self-published. For the Aspiring Writer Award: applicant must be a U.S. citizen or resident alien, must have a strong connection to identify with the African Diaspora, must be a full time student at a Historically Black College or University; and must have a grade point average of 2.5 or better.
SOCIETY OF AUTHORS GRANTS FUNDS – UK https://www2.societyofauthors.org/grants/grants-writers-in-need/ Applications are open to all professional authors who are resident in the UK or British subjects – including all types of writers, illustrators, literary translators, scriptwriters, poets, journalists and others – whose author-related activities make up a substantial amount of their annual income. You do not have to be a member of the Society of Authors to apply.
ARTIST SUPPORT GRANTS – CHARLOTTE AREA https://artsandscience.org/artist-support-grants/ Artist Support Grants fund professional development and artist development for emerging and established artists to enhance their skills and abilities to create work or to improve their business operations and capacity to bring their work to new audiences. ASC is accepting applications from creatives living in Mecklenburg, Cabarrus, Cleveland, Gaston, Lincoln and Rowan counties. The Artist Support Grants will support projects occurring between January 1, 2023 and December 31, 2023 but all funds should be expended by June 30, 2023. Artists may request up to $3,000. Applications selected for funding will receive the full award for which they are eligible.
MARYLAND CREATIVITY GRANTS https://msac.org/programs/creativity-grants Intended to support specific arts projects, events, or programs, this option is available for independent artists, as well as organizations. Each application should focus on a proposal for one specific project or program. Funding amount $1,000 – $4,000. Must be a Maryland resident.
MARYLAND EMERGENCY GRANTS https://msac.org/programs/special-requests/emergency-grant-independent-artists The purpose of the Emergency Grant is to support the needs of independent artists as they adjust to income losses as a result of an emergency. Funds up to $2,000. Must be a Maryland resident. Applicants must be independent artists, defined as artists who earn income from artistic activities and are not directly affiliated with an arts organization or program that provides any form of compensation.
JAN MICHALSKI FOUNDATION RESIDENCE FOR WRITERS https://fondation-janmichalski.com/en/residences Although open to all kinds of writing and all languages, the residency program does give priority to writers and translators. The residencies can vary in length and can be for either individuals or pairs of participants in the case of projects involving more than one discipline. Each year some forty authors from around the world, from the fledgling writer to the seasoned old hand, can count on a certain period of time they may dedicate to developing a writing project. A percentage of the residences is dedicated to nature writing, a form of fiction or creative non-fiction that raises awareness of nature, prepares for a sustainable way of living, and helps to better understand socio-environmental interconnections and the impact of human actions on nature. Two week-, one-, two-, three- or six-month stays are available. There are no age or nationality restrictions. Beginners are accepted. Residents’ travel costs to and from their home address will be covered by the Foundation. Residents are granted a monthly allowance of CHF 1200.
RHODE ISLAND OPPORTUNITY GRANTS https://risca.online/grants/opportunity-grant/ Open to artists over the age of 18 who live in Rhode Island. Amounts up to $1,000. Opportunity Grants provide Rhode Island artists funding for concrete opportunities that will support professional growth. This grant is available to artists working in all disciplines at any stage in their career.
SOUTHARTS EXPRESS GRANTS https://www.southarts.org/community-organization-grants/express-grants South Arts believes that rural communities deserve great art, and can require specialized support to make that vision viable. Distributed on a first-come, first-serve basis, Express Grants support rural organizations and communities with expedited grants of up to $2,000. To be eligible for funding, applicants must program arts experiences featuring a Southern artist. Express Grants can be used to support fees for presenting Southern guest film directors, visual and performing artists, or writers from inside or outside of the presenter’s state. Touring support is awarded for film (documentary, fiction, experimental and animation), performing arts (theater, music, opera, musical theater and dance), literary arts (fiction, creative nonfiction and poetry), traditional arts, and visual arts (crafts, drawing, experimental, painting, photography, sculpture and mixed media). Projects must include both a public presentation (film screening, performance, reading or exhibition) and an educational component.
CREATIVE AGING TENNESSEE GRANTS https://tnartscommission.org/grants/special-opportunities-creative-aging-tennessee-ii/ One-time non-matching funds for nonprofit arts, senior service or community organizations, and governmental entities to support sequential arts learning for seniors aged 60+ with the aim of reducing social isolation and loneliness and increasing creativity and artistic techniques. All projects must be implemented by teaching artists on the new TN Creative Aging Teaching Roster. Total funding for this project equals $75,000. Individual projects may request up to $3,000 for contractual fees for artists and supplies. Standard pay for teaching artists to deliver a series of sequential hour-long arts classes is $2,500.
LOUISIANA PROJECT GRANTS https://www.crt.state.la.us/Assets/OCD/arts/FY23-24/FY23%20Louisiana%20Project%20Grants%20Guidelines.pdf Applicants, both individuals and groups, can apply through one of the nine Regional Arts Councils in the state of Louisiana, applicable to where they live. Must be an ART project involving dance, design arts, folklife, literature, media, music, theatre, or visual arts for the purpose of performance, exhibit, presentation, series or workshop. Individuals and organizations lacking a 501(c)(3) federal tax-exempt status must arrange for a nonprofit organization with 501(c)(3) status to serve as a fiscal agent. Organizations serving as fiscal agents (the applicant) must be domiciled in the same region as the other organization or individual (sub-applicant). Grants are a minimum of $2,500 and as much as $7,500. A cash match demonstrates community involvement and commitment to the project.
LA BALDI RESIDENCY https://www.cultivateprojects.net/labaldi La Baldi Residency for welcomes individual and collaborative teams of artists, writers, and researchers. The multi-disciplinary residency is located in the historic village of Montegiovi, Italy, in southern Tuscany. The self-directed international residency is an opportunity to experiment, develop ideas and projects, dream, explore, rejuvenate, research, and investigate the land and culture of this special area. There are no dedicated traditional indoor studio facilities. They ask that applicants consider how they plan to embrace the outdoors as the primary workspace. One artist stay 550€/two weeks; 850€/one month. One artist and companion stay 700€/two weeks; 1000€/one month. Refundable security deposit 100€.
MACKINAC ISLAND ARTIST IN RESIDENCE https://www.mackinacparks.com/plan/artist-in-residence-program/ The Mackinac State Historic Parks Artist-In-Residence Program is designed to promote and encourage the creation of artistic works inspired by the history, natural wonders, and beauty of Mackinac Island. The residencies are available to artists in all mediums, including writers, composers, sculptures, and visual artists including photographers, among others. The two- and three-week residencies are available beginning in early June and continuing through early October. The resident artist is housed in the newly-remodeled second floor of the Mackinac Island Visitor’s Center, formerly the 1915 Mackinac Island Coast Guard Station. Applications accepted in January of each year.
SEED GRANTS – THE POLLINATION PROJECT https://thepollinationproject.org/ The Pollination Project seeks to unleash the goodness in every person. Through a daily practice of generosity and giving, The Pollination Project makes seed grants — 365 days a year — to social-change agents who seek to spread compassion in their communities and in the world for the benefit of all. The Purpose of a Pollination Project Seed Grant is to support passionate, committed people with an early-stage social change vision. It funds individuals and community groups, and you do not need to be a registered or established organization to apply. Grants $1,000 each and every day.
ART-TRAIN INDIVIDUAL ARTIST TRAINING – INDIANA https://springboardforthearts.org/art-train-training-artists/ The Art-Train Individual Artist Training is for artists who are interested in building on their existing skills to collaborate in and with their communities through their local agencies, non-profits, and arts councils. Artists will deepen practices around creative problem solving, equitable community engagement, and creating arts-based strategies to address recovery efforts. After taking a synchronous virtual training, artists receive one year of ongoing virtual support through an online resource library and optional bi-weekly group coaching rooms with Art-Train staff, experts and an expanding network of peers (every other Thursday).
FREE LEGAL ASSISTANCE FOR INDIANA ARTISTS https://indianalegalhelp.org/ Pro Bono Indiana’s (IndianaLegalHelp.org) Lawyers for the Arts project provides legal assistance at no cost to artists and small arts organizations in the state of Indiana. To obtain help, please call 812.402.6303 (Tuesdays and Thursdays from 9:00 am to 11:00 am CT).
PEGGY RAMSAY FOUNDATION – UK https://www.peggyramsayfoundation.org/ The Peggy Ramsay Foundation seeks to perpetuate Peggy Ramsay’s ideals, by directly helping dramatists at very different stages of experience in ways which we are determined to keep as quick and unbureaucratic as possible. We give money to theatre writers giving them the time and the space to write. You can be a writer who’s only had one play professionally produced, a writer who’s had dozens of successes or a writer who’s somewhere in between – if you’re struggling to pay the bills, then we can help. We only support writers resident in the British Isles.
ARVON https://www.arvon.org/writing-courses/grants/ Our grants help writers who are unable to afford our full course fees. For our residential courses, we offer two types of grants – Low Income Grant and Teachers Grant. If you couldn’t attend an Arvon week without some financial help, we encourage you to apply. Teachers Grants are a fixed amount of £200. With Low Income Grants, you can apply for any amount up to the full course fee, although most receive between £200 and £500. Last year we were able to help more than 90 percent of all writers who applied. You must be resident in the UK and able to demonstrate that you do not have the financial means to cover the full cost of an Arvon course.
CREATIVE SCOTLAND OPEN FUND FOR INDIVIDUAL ARTISTS https://www.creativescotland.com/funding/funding-programmes/open-fund/open-fund-for-individuals No deadline. The Open Fund will support a period of research, development, and delivery of creative activity for up to 24 months. We will ask you to tell us the start and end date for this activity and to describe the outcomes, benefits and impacts that you wish to achieve. This fund is designed to support creative activity such as a specific project, production or a period of research and development. It can support an individual’s time where this is related to specific creative outcomes. Open to freelance and self-employed artists and creative practitioners living in Scotland who are at least 18 years old. Must have a UK bank account. You can apply for between £500 and £100,000.
THE LITERARY CONSULTANCY – UK https://literaryconsultancy.co.uk/ TLC is the only editorial consultancy recognised by Arts Council England as a National Portfolio Organisation (NPO) for our wider work in the literary industry, and we offer a nationally-funded Free Reads programme designed to offer our core services, at no cost, to low-income writers. A range of partnerships and individual donations have helped us to further develop this scheme, which we now run as a Quality Writing for All campaign and includes campaigns, free event tickets, and additional support for writers facing barriers.
MONTANA OPPORTUNITY GRANTS https://www.humanitiesmontana.org/opportunity-grants/ Opportunity grants award up to $1,000 and do not require matching funds. Applications can be submitted any time, but at least four weeks prior to the supported project. We encourage proposals that engage Montanans in meaningful discussion about the human condition, strengthen cooperative relationships among communities and cultural organizations (museums, libraries, schools, tribal organizations, etc.), and enrich civic discourse among the state’s diverse cultures and across its geographical distances. Humanities Montana only awards opportunity grants to organizations, not individuals.
CRAIGARDAN RESIDENCY http://www.craigardan.org/writers-residency/ Craigardan now stewards 320 acres of field and forest, with a small-scale farm to provide food and hands-on experience for the community. Set within a working, educational farm, we provide creative residencies that span diverse artistic and knowledge disciplines in order to foster curiosity, inquiry, and collaboration. The Writer’s Residency is a year-round opportunity for writers to fully immerse themselves in an exquisite retreat environment conducive to working with no distraction. We invite applications from emerging and accomplished writers of all genres who would benefit from a focused amount of un-guided time to create a new work, complete a project, conduct research, or simply find inspiration amid the beauty of the Adirondack Mountains. Only one writer is accepted at a time. Writers live in a shared house. Housemates may include other writers, researchers, visual artists, culinary artists, or agriculturalists. The (highly subsidized) residency fee is $250 per week or $1,000 per month ($33/day). Location Elizabethtown, NY.
BOEHM MEDIA FELLOWSHIP https://ocimpact.com/boehm-media-fellowship/ The Boehm Media Fellowships provides opportunities for communication, media, and storytelling experts who are committed to social impact and sustainable solutions to poverty and injustice to participate as delegates at Opportunity Collaboration. We understand media to be a diverse and multidisciplinary field across sectors including but not limited to journalism, public relations and communications, social media, film, podcasts, radio, television, photography, media literacy and other mixed or new and emerging media channels and productions. We are seeking individuals who, on their own or through their organizational roles, utilize the media in creative and innovative ways to influence culture, collaborate with communities and interface with new paradigms and ideas to catalyze change. Financial need is a primary consideration.
CHARLES WALLACE INDIE TRUST SCHOLARSHIPS https://www.charleswallaceindiatrust.com/visiting-fellowships CWIT enables Indians in the early to mid-stages of their careers to spend time in the UK, helping them to achieve artistic, academic and professional ambitions and to broaden their international contacts.
TEXAS TOURING ROSTER https://www.arts.texas.gov/artroster/roster/ The Texas Touring Arts Program is designed to ensure that all Texans have the ability to enjoy performances by outstanding Texas-based companies and artists in their own communities. The Texas Commission on the Arts (TCA) provides grants to help with the costs of bringing in companies and artists from this roster for performances. Performing arts companies and artists from throughout the state apply to be included on the Texas Touring Roster. These artists must have a history of touring and must be willing to travel outside of their community to do a performance.
SC INDIE GRANTS https://www.indiegrants.org/ As part of their mission to support South Carolina’s production industry, the South Carolina Film Commission and Trident Technical College produce a series of grant and training programs through-out the year. Centered around the INDIE GRANTS, where top-notch production professionals and independent filmmakers make short films and Trident Technical College students work under them as hands-on technical training, these innovative programs also include technical and creative workshops, the South Carolina Young Filmmakers Project, special screenings, and other events. Providing professional development and training for South Carolina crew, production professionals, independent filmmakers, and students. The only one of its kind in the nation.
SC HUMANITIES MINI GRANTS https://schumanities.org/grants/howtoapply/#minigrants Monthly deadlines. Mini Grants are to support public humanities programs of modest cost. Awards are $2,000 or less. Mini Grants are reviewed monthly with deadlines on the first business day of the month.
CANADA COUNCIL FOR THE ARTS https://canadacouncil.ca/funding/grants/explore-and-create/research-and-creation The Research and Creation component of Explore and Create supports the initial stages of the creative process. Canadian artists, artistic groups and arts organizations can apply to develop and make creative works. Grants provide support for creative research, creation and project development.
NEW HAMPSHIRE CENTER FOR THE ARTS https://centerfortheartsnh.org/emergency-relief-fund The CFA Artists Emergency Relief Fund is a fund of last resort available to CFA members. Individuals are eligible to apply for these funds who can demonstrate their status as: A professional artist who has suffered a disaster which significantly interrupts or prevents them from making or performing their art form and earning a living, and for whom said disaster creates an emergency situation and need for immediate relief funds. The artist must be a permanent resident of the United States. Recipients of the CFA Relief funds are asked to “Pay it Back” or Pay it Forward” by performing or volunteering at a CFA event in the future. Awards up to $500. NOTE: This is in the CENTER FOR THE ARTS-LAKE SUNAPEE REGION.
ART LEADERS OF COLOR EMERGENCY FUND https://aacnetwork.org/ Arts Administrators of Color set up an Arts Leaders of Color Emergency Fund, which supports BIPOC (Black, Indigenous, People of Color) artists and arts administrators impacted by COVID-19 through $200 microgrants.
THE SHENANDOAH FELLOWSHIP FOR BIPOC EDITORS https://shenandoahliterary.org/submissions/ Selected fellows will receive a $1,000 honorarium and will curate a selection of published work in a genre of their choosing for a single issue of Shenandoah, working with the Shenandoah staff to guide the work to publication. We welcome writers and editors of all experience levels. No previous editorial experience is necessary, but we are looking for applicants who are passionate and informed about the literary community. We welcome candidates who identify as Black, Indigenous, and People of Color.
ARTS KANSAS CITY GRANTS https://artskc.org/inspirationgrantinformation/ ArtsKC Inspiration Grants are an investment in human capital, providing direct support to individual artists and arts professionals for projects and activities that have the potential to advance their careers and build their capacity for future work. These projects exemplify risk, growth, and change. Visual, music, theatre, literary, dance, and interdisciplinary projects are the primary focus of Inspiration Grants.
BARBARA DEMING MEMORIAL FUND https://demingfund.org/apply-pd-11.php Barbara Deming, Money for Women is the oldest ongoing feminist granting agency. Grants from the foundation give monetary support and encouragement to individual feminist writers and visual artists. Application period is January 1-31 each year. Gives small support grants ($500 – $1,500) to individual feminist women in the arts who are citizens with primary residence in the US and Canada. Does not award film, video, theatre, dance, music, or performance projects. Scripts and musical compositions are also not eligible. We do not award work that is or will be self-published.
THE HAVEN FOUNDATION http://www.thehavenfdn.org/guidelines/ In order to be eligible for assistance, an applicant must be a freelance qualified person. The Foundation defines the group as persons connected with the artistic or entertainment industries including, but not limited to authors, actors, singers, dancers, directors, producers, choreographers, musicians, artists, and screenwriters selling work or services by the hour, day, job, etc. rather than working on a regular salary basis for one employer. Must also be a professional, an individual who is committed to his/her industry or work, who has derived at least 40 percent of his/her annual income over the past three years from his/her personal production, performance or other work in the industry. The qualified person must have experienced a recent, unforeseen emergency or triggering event that has significantly and adversely affected the qualified person’s ability to produce, perform and market his/her work and, thus, creates the need for immediate relief funds and/or assistance. Must also be a legal US resident.
AUTHORS’ CONTINGENCY FUND https://societyofauthors.org/Grants/authors-contingency-fund Applications are open to all professional authors who are residents in the UK or British subjects – including all types of writers, illustrators, literary translators, scriptwriters, poets, journalists and others – for whom author-related activities make up a substantial amount of their annual income. Grants are likely to be up to £2,000 and designed to meet urgent need.
RAUSCHENBERG EMERGENCY GRANTS https://www.rauschenbergfoundation.org/programs/grants/rauschenberg-emergency-grants An emergency grant program that provides one-time grants of up to $5,000 for medical or dental emergencies. The grants are available to visual and media artists, and choreographers living anywhere in the United States or U.S. Territories.
DURHAM ARTS COUNCIL – NC http://www.durhamarts.org/artistinfo_emergingartists.html The council welcomes applications for its Emerging Artists Program. Through the program, grants of up to $1,500 will be awarded to developing or established professional artists in the North Carolina counties of Chatham, Durham, Granville, Orange, or Person in support of a project that is pivotal to advancing their careers. Disciplines eligible for consideration include craft, dance, drama, film and video, installation, literature, music, painting and drawing, photography, printmaking/mixed media, and sculpture.
WOODCOCK FUND https://www.writerstrust.com/programs/woodcock-fund-grant/ Emergency funding to professional Canadian writers in mid-project. Grants are $2,000 to $10,000. Must be a professional writer (minimum of two books published) facing an unforeseen financial need. Must be working on a project.
LIGHTHOUSE WORKS’ FELLOWSHIPS http://www.thelighthouseworks.org/fellowship-program/ The Lighthouse Works’ Fellowship is an artist-in-residence program that strives to support artists and writers working in the vanguard of their creative fields. The program accepts artists working in a wide range of disciplines, but we are best able to accommodate visual artists and writers. Fellowships are six weeks in length, occur year round and provide fellows with housing, food, studio space, a $250 travel allowance and a $1,500 stipend. Artistic excellence is the primary criterion for acceptance as a Lighthouse Works fellow. We are located in the Annex Building on Fishers Island, NY. The Annex is just west of Silver Eel Cove, where our ferry makes port, and north of the intersection of Hound Lane and Greenwood Road.
JENTEL RESIDENCIES http://jentelarts.org/applicants/ After reviewing the work samples, a panel of art and literary professionals rate and rank the applicants based on the development or promise of a personal vision or voice. Residents are responsible for transportation to and from Sheridan, Wyoming and for transporting or shipping personal items, materials and equipment needed for creative work. Residents also shop and prepare meals and purchase personal items. As part of the residency award, a $400 stipend helps to defray some of these expenses.
NORTH CAROLINA ARTIST SUPPORT GRANTS https://www.ncarts.org/invest-arts/grants-artists/artist-support-grants This program, funded by the NC Arts Council, provides the opportunity for regional consortia of local arts councils to award project grants to artists in their regions. These grants support professional artists in any discipline and at any stage in their careers to pursue projects that further their professional development. (See site to find your region of the state.)
NEW ORLEANS RESIDENCY SPACE FOR WRITERS AND ARTISTS https://forms.gle/hCty3QyLFzm6e4J38 In August, we repurposed our residency space as low-cost, short-term housing for writers and artists experiencing financial stress or housing instability. We are continuing this program for the foreseeable future and have space available, beginning in October. Cost: $300 per month. No deposit, no utilities, no application fee. Available beginning August 1, 2020. You will be asked about your preferred start date and length of stay (one to three months) when you apply. Ad-hoc changes after that will be accommodated as feasible. You must be a writer or artist experiencing financial stress or housing instability. Local (LA-based) applicants preferred; everyone is welcome.
NEW HAMPSHIRE COUNCIL ON DEVELOPMENTAL DISABILITIES https://www.nhddc.org/small_grants.php The New Hampshire Council on Developmental Disabilities offers small grants to individuals or groups to support disability-related activities and initiatives that help achieve the Council’s mission of “Dignity, Full Rights of Citizenship, Equal Opportunities, and Full Participation for All New Hampshire Citizens with Developmental Disabilities.”
HOSKING HOUSES TRUST https://hoskinghouses.co.uk/wp/how-to-apply/ We offer older women writers’ residencies in Church Cottage where they are able to pursue their own work in domestic peace without interruption. Many of these residencies also carry bursaries. Under our section Purposes and Policy we describe the criteria whereby we appoint writers, what we offer which includes bursaries, also duration of residencies and obligations in return. Tell us why you want a residency; do you need time and privacy or have you financial, personal, housing or medical needs or are you just tired? Applicants from outside the UK and Ireland are received but there must be a valid reason to justify a visit, such as study or attendance at a conference. Location Stratford-upon-Avon, Warwickshire, UK.
MARY C. CURTIS FELLOWSHIP http://www.wellstoneredwoods.org/mary-c-curtis-fellowship/ At Wellstone Center in the Redwoods we’ve mostly hosted writers working on books, fiction and memoir, but this can also be a good spot to make a big push on a book proposal. Two weeks of focus in a tranquil, beautiful corner of California has its plus sides especially for longtime adrenaline fiends used to powering through deadlines but not as used to unpacking a deeper perspective. Mary’s still working on her book, part memoir and part social history, new chapters keep presenting themselves all the time, and we’ll help spread the word when it appears. In 2020 we’re inaugurating a two-week fellowship in Mary’s name here at our small writers’ retreat center in Northern California, specifically for an African American journalist with a minimum of five years’ experience looking to spend two weeks intensively working on a proposal for a well-developed book project.
GREATER PITTSBURGH ARTS COUNCIL – PITTSBURGH, PA http://www.pittsburghartscouncil.org/programs/artist-services/emergency-fund Artists and creative workers living in Allegheny, Beaver, Butler, Fayette, Greene, Indiana, Lawrence, Washington, and Westmoreland counties are eligible to request up to $500.
PHILADELPHIA WRITERS EMERGENCY FUND – PHILADELPHIA, PA https://www.215festival.org/ This fund is for writers, booksellers, and individuals who work at independent presses that are based in the greater Philadelphia area. We define the greater Philadelphia area as Philadelphia County (PA), Delaware County (PA), Chester County (PA), Montgomery County (PA), Bucks County (PA), Burlington County (NJ), Camden County (NJ), Gloucester County (NJ), and New Castle County (DE).
AUTHORS LEAGUE FUND – US https://authorsleaguefund.org/ Since 1917, the Authors League Fund has helped professional authors, journalists, poets, and dramatists who find themselves in financial need because of medical or health-related problems, temporary loss of income, or other misfortune.
CLAYTON MEMORIAL MEDICAL FUND – OR, WA, ID, AK https://osfci.org/clayton/ The fund helps professional science fiction, fantasy, horror, and mystery writers living in the Pacific Northwest states of Oregon, Washington, Idaho, and Alaska deal with the financial burden of medical expenses.
THE PEN WRITERS FUND – US https://pen.org/writers-emergency-fund/ PEN America will distribute grants of $500 to $1,000 based on applications that demonstrate an inability to meet an acute financial need, especially one resulting from the impact of the COVID-19 outbreak. We have developed a new streamlined process for the duration of this crisis, and expect to be able to review and respond to applications within 10 days. To be eligible, applicants must be based in the United States, be a professional writer, and be able to demonstrate that this one-time grant will be meaningful in helping them to address an emergency situation. The fund is limited, and not every application can be supported.
SFWA EMERGENCY MEDICAL FUND http://www.sfwa.org/about/benevolent-funds/emergency-medical-fund/ The Emergency Medical Fund (EMF) was established to help genre writers pay medical expenses not otherwise covered by insurance. The fund is meant to cover only short-term (i.e. emergency situations that interfere with the ability to write). Requests must specify the recipient, a description of the circumstances, and the amount of support needed.
CARNEGIE FUND FOR AUTHORS – US https://www.carnegiefundforauthors.org/ The mission of Carnegie Fund for Authors is to award grants to published authors who are in need of emergency financial assistance as a result of illness or injury to self, spouse, or dependent child, or who has had some other misfortune that has placed the applicant in pressing and substantial pecuniary need. We accept applications from any American author who has written at least one book of reasonable length that has been published commercially and received reader acceptance.
CANADIAN COUNCIL FOR THE ARTS – RESEARCH AND CREATION GRANTS https://canadacouncil.ca/funding/grants/explore-and-create/research-and-creation The Research and Creation component of Explore and Create supports the initial stages of the creative process. Canadian artists, artistic groups, and arts organizations can apply to develop and make creative works. Grants provide support for creative research, creation, and project development. You may be eligible for Application Assistance to pay someone to help you with the application process if you are experiencing difficulty and self-identify as an artist who is Deaf, hard of hearing, has a disability or is living with a mental illness, or a First Nations, Inuit or Métis artist facing language, geographic or cultural barriers. This is a rolling deadline. Offers up to $25,000.
AWESOME FOUNDATION GRANTS https://www.awesomefoundation.org/en Have a crazy brilliant idea that needs funding? We award $1,000 grants every month. It couldn’t be simpler! Your idea is yours alone. We don’t want a stake in it. We just want to help you make it happen!
CHANGE, INC. No website. Emergency grants for artists in all disciplines needing help with rent, medical expenses, utility bills, fire damage, etc. Grants up to $1,000. Call the number below for complete instructions (via a clear, concise message) on how to apply for the grant. Change, Inc. P.O. Box 1818 Captiva, FL 33957 Phone: (212) 473-3742.
ELIZABETH GEORGE FOUNDATION http://www.elizabethgeorgeonline.com/foundation.htm Mystery writer Elizabeth George has a foundation that makes grants to unpublished fiction writers, poets, emerging playwrights, and organizations benefiting disadvantaged youth. These grants cover expenses in a number of areas. For further information, write and request a brochure: The Elizabeth George Foundation, PO Box 1429, Langley, WA 98260.
HATCHFUND http://www.hatchfund.org/ Unlike the other crowdfunding sites that take a 7-10 percent fee for using their platform, Hatchfund is free for artists. Once you reach your minimum goal, everything you raise is yours–we won’t take any fees. In order to do this, we do ask that donors make two additional donations–one is a minimum five percent donation to Hatchfund and the other is a five percent donation to help cover credit card processing costs. Both of these donations are also tax-deductible for donors. Our goal is to help artists successfully navigate the challenging world of online fundraising for their projects. Our expert team provides educational services, from fundraising 101 to case studies and best practices to project development and outreach support. A total of 75 percent of all artists who have turned to Hatchfund have succeeded in funding their projects.
FRACTURED ATLAS https://www.fracturedatlas.org/site/fiscal Fractured Atlas wants to help you raise money for your artistic work. As the country’s largest arts fiscal sponsor, we provide accessibility, efficiency, and affordability. There is a passionate community of philanthropic individuals, charitable foundations, and government institutions devoted to funding the arts. The catch is that many independent artists and small companies lack the 501(c)(3) tax status that makes them eligible to apply for grants and incentivizes individual gifts. With fiscal sponsorship, you can solicit tax-deductible donations and apply for grants without going through the onerous process of launching a 501(c)(3). The sponsored “project” might be a one-time collaboration or an independent artist or even an arts organization that does not have its own 501(c)(3) status. Our program is open and accessible to artists and arts organizations nationwide and in every artistic discipline. We won’t judge the artistic quality or merit of your work.
NATIONAL PARKS ARTIST-IN-RESIDENCE https://www.nps.gov/subjects/arts/air.htm Whether staying in a remote wilderness cabin at Denali National Park and Preserve in Alaska or contemplating history at Herbert Hoover National Historic Site in Iowa or working in a contemporary studio overlooking the stone-lined fields at Weir Farm National Historic Site in Connecticut, these programs provide artists with unique opportunities to create works of art in varied natural and cultural settings. There are programs for visual artists, writers, musicians, and other creative media. Programs vary, but residencies are typically two to four weeks in length, and most include lodging. Often artists are invited to participate in park programs by sharing their art with the public. Over 50 locations to consider.
CLAYTON MEMORIAL FUND https://osfci.org/clayton/ The fund helps professional science fiction, fantasy, horror, and mystery writers living in the Pacific Northwest states of Oregon, Washington, Idaho, and Alaska deal with the financial burden of medical expenses. We generally follow the standards of Science Fiction and Fantasy Writers of America (SFWA) for Active or Associate membership in determining professional status.
SOCIETY OF CHILDREN’S BOOK WRITERS AND ILLUSTRATORS https://www.scbwi.org/scbwi-emergency-fund/ The SCBWI Emergency Fund has been established to provide assistance to SCBWI members in times of emergency or hardship. The emergency or hardship could involve, for example, matters of health, family issues, or natural disasters that are in any way restricting or preventing an SCBWI member’s ability to work as an author or illustrator. There is a $1,500 cap on any given grant, and no member may receive the grant more than twice.
PEN AMERICA WRITERS’ EMERGENCY FUND https://pen.org/writers-emergency-fund/ The PEN America Writers’ Emergency Fund is a small grants program for professional—published or produced—writers in acute or unexpected financial crisis. Depending on the situation and level of need, grants are in the range of $2,000. Apart from exceptional circumstances, the Fund does not give repeat grants within a three-year period.
UNBOUND http://unbound.co.uk/ Unbound is a new way to connect authors and readers. Authors present a pitch, readers pledge, and when the goal is reached the book is written. It’s really that simple. Unbound gets involve with publication and distribution of the book as well, giving you a one-stop shop. Unbound is both a funding platform and a publisher, fulfilling all the normal publishing functions but also splitting a book’s net profit 50/50 with the author. Note that Unbound is UK located.
NOTE: Want to see more grants? Join our newsletters! FundsforWriters carries 3-10 grants per issue.
Yes, I want to know more about your newsletters!
Testimonials
I just got word that my residency fellowship in Taos, via the Wurlitzer Foundation, is set! I’ll be spending next summer there in a small adobe cottage writing full time. This opportunity-like many others that have made a big difference-came my way via your FundsforWriters newsletter, and I can’t thank you enough. ~Caroline Sposto
Hi Hope, I am sitting in a ferry terminal, waiting for the next boat to take me to the Turkeyland Cove Foundation Writer’s Retreat on Martha’s Vineyard Island. Am I excited? You bet I am! Why? Because this is the first time in my life that I have been offered the gift of time and space for an entire two weeks to focus on what I love to do most: WRITE! I was accepted months ago and “anticipation” has been my middle name. Thank you for your dedication to sharing the roller-coaster ride of writing. You are a gifted teacher and mentor. Laura Lee Perkins www.LauraLeePerkinsAuthor.com
- Caroline Sposto, Emerald Theatre Company
-laura kepner, safety harbor writers and poets, – with deep appreciation, laura lee perkins, – melanie steele, – reece w. manley.
Total Funds for Writers pays for itself almost immediately. Hope and her research skills are phenomenal. Thanks to TFFW I have sold four articles, all with clients who did this amazing thing called paying me. It’s quite delightful – money is querky but boy its fun stuff to have! If you haven’t signed up for TFFW, you’re just not serious about your career.

- Harvard Library
- Research Guides
- Harvard Graduate School of Design - Frances Loeb Library
Write and Cite
- From Research to Writing
- Academic Integrity
- Using Sources and AI
Getting Started
Research support, decoding the assignment, academic writing at the gsd, reading and notetaking, incorporating sources, finding your voice.
- Fair Use, Permissions, and Copyright
- Writing at the GSD
- FAQ: Writing Services
- Grants and Fellowships
On this page you will find resources offering an overview of the writing process to help you begin your writing journey. This page focuses on best practices for academic writing and stages of the writing process, and it includes helpful guides for the types of writing you might encounter at the GSD.
- Frances Loeb Library From the library homepage, you can access all kinds of resources and tools to help with your research.
- GSD Research Guides Start your research by utilizing our curated research guides.
- Manage Your Research Find GSD-approved tools to organize and store your research.
- Ask a Design Librarian If you have a research question and don't know who to ask, submit your question here and FLL library staff will find the answer.
- Research Consultations Meet with a GSD librarian to learn more about our collections, refine your research plan, and learn strategies for locating the sources you need.
Successful academic writing starts with identifying the explicit and implicit expectations of the assignment. If you don't understand the assignment, you may not only have trouble starting to write but might put effort into the wrong things. If you are still unsure how to proceed after following these steps, ask your instructor. And if you want support at any point in the writing process, including reading through the assignment, make an appointment with GSD's Writing Services at Frances Loeb Library.
Stated Expectations
Look for these elements in the assignment prompt:
- Is it asking for outside research?
- Are there course texts or materials you will need to include?
- Is there an approximate length requirement?
- Which skills does it want you to demonstrate? Look for the verbs
- Compare or contrast
Unstated Expectations
Some expectations of the assignment may not be mentioned in the prompt, so give some thought to the context of the assignment to figure these out.
- What kind of theoretical, practical, or disciplinary frameworks or procedures has the professor been modeling in class and assigning for homework? This writing assignment is probably in some way asking you to demonstrate understanding and proficiency in applying them.
- Who is your audience and what is the situation? You will adjust your use of industry terminology and the density of your writing depending on whether you are writing for your instructors or for a broader community. The assignment might not tell you that your writing will be persuasive or evaluative, but if you know your relationship to your audience, you can determine if you need to persuade them with evidence and analysis, help them make their own decision by providing pros and cons for a project, or energize them by helping them imagine the benefits and practicality of a design.
- Understanding Assignments UNC's Writing Center provides a detailed process for decoding assignments, including definitions of many key terms to watch for.
- Tips for Reading Assignment Prompts Harvard College Writing Center's brief overview of steps to take in understanding an assignment.
- Understanding Assignments Purdue OWL's succinct step-by-step guide for understanding assignment prompts.
- How to Read an Assignment Harvard College Writing Center's brief advice on what to do and avoid with examples.
You will have many kinds of writing assignments to complete while at the GSD. This resources created by fellow GSD students can help you identify key features and expectations of the most common forms of writing that you will encounter. Remember to ask your instructor if you have questions and to come to Writing Services for writing support.
- What is "Academic" Writing? This essay is useful for understanding style and method in academic writing.
- Harvard Faculty Explain Analytical Writing Faculty from Harvard College explain analytical writing in this project from the Harvard College Writing Center.
- Advice on Academic Writing This catalog of advice from the University of Toronto was created by writing instructors.
- Scholarly Pursuits (GSAS) This searchable booklet from Harvard GSAS is a comprehensive guide to writing dissertations, dissertation-fellowship applications, academic journal articles, and academic job documents.
- Strategies for Essay Writing This resource from Harvard College Writing Center offers strategies to begin a writing project.
On this page you will find resources to help you on the "front end" of your writing journey. Most of these documents and sites focus on reading and notetaking strategies to help you build a research agenda and argument. Also included are a series of resources from the GSD and Harvard for productivity and time management.
Questions to ask before you start reading:
1. how much time do i have for this text.
If you have more to read than you can realistically complete in the time you have, you will need to be strategic about how to proceed. Powering through as fast as you can for as long as you can will not be efficient or effective.
2. What do I most need from this text?
Knowing your purpose will help you determine how long you should spend on any one part of that text. If you are reading for class or for research, or if you are reading for background information or to explore an argument, you will use different reading strategies.
3. How can I find what I need from this text?
Once you know what you need, there are strategies for finding it quickly, like pre-reading, skimming, and scanning.
Determining your purpose
Your purpose will become clearer if you first situate the text within a larger context.
Reading for Class
Your professor had a reason for assigning the text, so first try to understand their intention. The professor might tell you their reason or provide reading questions to direct you. You can also infer the purpose from headings and groupings in the syllabus and from how the professor has approached prior readings in past lectures. Looking ahead to how you might use the text in future assignments or projects will also help you decide how much time to spend and what to focus on.

Reading for Research
For independent research, you will first need to decide if a text is even worth reading. Plan ahead by knowing what you need, like background information, theoretical underpinnings, similar arguments to engage with critically, or images and data. Check the source's date and author(s) to determine its relevance and authority. Keep your research goals in mind and try to stay focused on your immediate goals. If you discover a text that interests you but is not for this project, make a note to come back to it later. However, a source that excites your interest and changes your research goals or argument can be worth following now so long as you still have time to make that change.

Once you decide that a source is worth your time, you will apply your choice of reading strategy based on the type of information the text contains and how you plan to use it. For instance, if you want to use a graphic or obtain biographical information, a quick search would be enough. If you want to challenge the author’s argument, you will need to read more rigorously and slowly.
- << Previous: Using Sources and AI
- Next: Fair Use, Permissions, and Copyright >>
- Last Updated: May 16, 2024 11:08 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.harvard.edu/gsd/write
Harvard University Digital Accessibility Policy
7 Government Small Business Grants to Apply For in May 2024
Seeking funding is a right of passage for many small business owners. While there are endless private and government-backed loans to choose from, if you’re looking to evade strict repayment terms and steep interest rates, it could be worth considering government business grants.
Government business grants are financial awards issued by federal, state, or local authorities. There are thousands of grants up for grabs through government website portals, but since this type of financing is designed to support the public, their eligibility criteria tend to be quite specific.
If you’re interested in pursuing this type of finance, we round up some government grants small businesses can apply for in May, including their specialisms, funding limits, and deadlines. We also offer some advice for writing your application, to make sure your proposal is as competitive as possible.
In this guide:
Government Small Business Grants to Apply For in May 2024
Tips for perfecting your government grant application.
Get the latest tech news, straight to your inbox
Don't miss out on the top business tech news with Tech.co's weekly highlights reel
By signing up to receive our newsletter, you agree to our Privacy Policy . You can unsubscribe at any time.
There are thousands of government funds to apply for. If you want to cut through the noise, take a look at some of the most popular options below:
- Small Business Innovation Research (SBIR) program
- Small Business Technology Transfer (STTR) program
- Women-Owned Small Business (WOSB) Federal Contracting program
- 8(a) Business Development Program
- HUBZone Program
- Small State Business Credit Initiative (SSBCI)
- U.S. Department of Commerce Minority Business Development Agency (MBDA)

1. Small Business Innovation Research (SBIR) program
- For: Small businesses interested in carrying out innovation research
- Funding limit: Over $2 million
- Deadline: September 5, January 5, and April 5
The Small Business Innovation Research program was designed by the Small Business Administration to encourage US businesses to engage in Federal research and development. The competitive program is open to select small businesses and specifically encourages participation from women and socially or economically disadvantaged persons.
To be eligible for the SBIR program, your business must be for profit, be over 50% owned by permanent residents of the US, and have fewer than 500 employees. To apply for the grant, you need to register your business with SBIR, if you haven’t already, submit a proposal before one of the program’s tri-annual deadlines, and then respond to feedback and refine your concept if necessary.
Learn more about the SBIR grant, and how to apply here .
2. Small Business Technology Transfer (STTR) programs
- For: Small businesses that have paired up with a research institution
Like the SBIR, the Small Business Technology Transfer program is a government program focused on developing innovative solutions to pressing problems across the US. This type of funding aims to facilitate cooperative research and development efforts research between small business concerns and non-profit US research institutions, with the potential for commercialization of innovative technological solutions.
However, unlike the SBIR, this program requires the small business applicant to be teamed up with a non-profit research institution already, which typically takes the form of a university or Federal Laboratory. The STTR program is also focused on the transfer of technology from the research institution, rather than just the research alone.
Aside from being paired with a research institution, STTR’s eligibility criteria are nearly identical to SBIR’s.
Learn more about the STTR grant, and how to apply here .
3. Women-Owned Small Business (WOSB) Federal Contracting Program
- For: Women-owned businesses
- Funding limit: $4 million for service contracts and $6.5 million for manufacturing contracts
- Deadline: Rolling
The Women-Owned Small Business Federal Contracting Program was designed to build a level playing field for female business owners. The contracts are designated for specific industries where female-owned businesses are underrepresented. You can see which industries are eligible for the grant program here .
To be eligible for this program, you need to run a small business, have the business be at least 51% owned and controlled by US women, and have an economically disadvantaged woman manage the day-to-day operations and make long-term decisions.
Learn more about WOSB, and how to apply here.
4. 8(a) Business Development Program
- For: Socially and economically disadvantaged business owners
- Funding limit: $7 million for acquisitions assigned manufacturing NAICS codes and $4.5 million for all other acquisitions
The 8(a) program is a nine-year program created by the SBA to financially support firms owned and controlled by socially and economically disadvantaged individuals. It’s designed to span nine years and helps eligible businesses access new business paths from government contracting.
Since the creation of the program in 1970, it has helped disadvantaged businesses gain access to billions of dollars in funding. To be eligible for the government grant, you must run a small business, be at least 51% owned and controlled by US citizens who are socially and economically disadvantaged, have a personal net worth of under $805 thousand, and demonstrate good character.
Learn more about the 8(a) business development program, and how to apply here .
5. HUBZone Program
- For: Small businesses in historically under-utilized business zones
- Funding limit: $3.5 million for products and services, and $5.5 million per contract for manufacturing
The HUBZone program is a SBA initiative designed to promote economic development and job growth in historically underutilized business zones (HUBZones). The program does so by offering financial grants to business owners operating within these communities.
To be eligible for this business grant you need to run a small business, have the business be at least 51% owned and controlled by a Community Development Corporation, an agricultural cooperative, an Alaska Native corporation, a Native Hawaiian organization, or an Indian tribe, have its main office located in a HUBZone, and have at least 35% of it employees living in the HUBZone for at least 45 days before applying.
Learn more about the HUBZone program, and how to apply here .
6. Small State Business Credit Initiative (SSBCI)
- For: Small businesses run by socially and economically disadvantaged individuals
- Funding limit: $20 million
The Small State Business Credit Initiative is a federal program designed to support entrepreneurship across the US. The grant program is provided by the US Department of the Treasury and was expanded by President Biden’s American Rescue Plan Act in 2021, providing an extra $10 billion in funding to eligible businesses.
In addition to providing capital support to small businesses, SSBCI can also provide technical assistance to eligible businesses through its Technical Assistance (TA) Grant Program. The SSBCI is available to businesses owner-occupied small businesses with 500 employees or less, and is specifically tailored to small businesses owned and controlled by socially and economically disadvantaged (SEDI) owners and very small businesses with less than 10 employees.
Learn more about the SSBCI program, and apply here .
7. U.S. Department of Commerce Minority Business Development Agency (MBDA)
- For: Small businesses run by minorities
- Funding limit: Up to $350,000 for the first 10 months
The U.S. Department of Commerce Minority Business Development Agency (MBDA) is a Federal grants program designed to promote the growth of minority-owned businesses. The ultimate aim of the program is to provide minority business enterprises (MBEs) with access to funds, contracts, and market opportunities both in the US and globally.
To be eligible for MBDA assistance, a business must be owned or controlled by one or more socially or economically disadvantaged persons. The majority of business owners must also identify as racial minorities.
To apply for an MBDA business grant, you need to register your business with SAM.gov and Grants.gov if you haven’t already, align your proposal with the stated requirements, and submit your application before the deadline.
Learn more about the grant, and how to apply here .
Government grants offer a golden opportunity to businesses looking to grow or recover their business. However, due to the competitive nature of the financing, you need to ensure your grant proposal is polished and stands out from the crowd.
We understand that writing a grant application might seem like a daunting process, especially if you’re a first-timer. So, to give your proposal the best chance possible of succeeding, take heed of these pointers below.
- Give yourself enough time – You don’t want to be writing a grant application against the clock. Writing a proposal can take much longer than you expect, so to account for unexpected hold-ups we recommend giving yourself at least 45 days to complete your written application.
- Follow the instructions carefully – Don’t go off-piste when writing your application. Make sure you include all the information requested by the agency, and present it in the correct format.
- Be as concise and clear as possible – Ensure your application is written in clear, simple language, and use as many candid examples as possible to paint a clear image for your reader. If you use any graphs or imagery, make sure you label them clearly as well.
- Keep the audience in mind – The likelihood is that the reviewer won’t already be familiar with your business. To make sure you won’t gloss over necessary information write the proposal for an audience that’s hearing about your business for the first time.
- Develop a proofreading strategy – You don’t want to hamper your application’s success with silly mistakes like typos or grammatical errors. So, to ensure your proposal looks polished carefully proofread the application or outsource the service to a professional.
Stay informed on the top business tech stories with Tech.co's weekly highlights reel.
We're sorry this article didn't help you today – we welcome feedback, so if there's any way you feel we could improve our content, please email us at [email protected]
Written by:

7 Grants For Black-Owned Businesses to Apply For in 2024
Help your Black-owned business flourish in 2024 and beyond...

11 Small Business Grants and Loans to Apply For in 2024
Getting a financial boost could be easier than you think,...

Company Offering $10K for a 30 Day Phone Detox, Apply Now
If you think you've got what it takes to do a one-month...

9 Innovative Startups To Watch Out For in 2024
Discover the startups that have triumphed over adversity in...
- Introduction to Genomics
- Educational Resources
- Policy Issues in Genomics
- The Human Genome Project
- Funding Opportunities
- Funded Programs & Projects
- Division and Program Directors
- Scientific Program Analysts
- Contact by Research Area
- News & Events
- Research Areas
- Research investigators
- Research Projects
- Clinical Research
- Data Tools & Resources
- Genomics & Medicine
- Family Health History
- For Patients & Families
- For Health Professionals
- Jobs at NHGRI
- Training at NHGRI
- Funding for Research Training
- Professional Development Programs
- NHGRI Culture
- Social Media
- Broadcast Media
- Image Gallery
- Press Resources
- Organization
- NHGRI Director
- Mission & Vision
- Policies & Guidance
- Institute Advisors
- Strategic Vision
- Leadership Initiatives
- Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion
- Partner with NHGRI
- Staff Search
"The Human Genome Project is simply a bad idea"
The Human Genome Project was the most important biomedical research project of the 20th century. In many ways, it challenged some of the fundamental understandings of scientific inquiry that had stood for centuries. The completion of the project in 2003 and subsequent boom in the genomics field has had a profound impact not just on biology and medicine but also on ethics and society. The project also changed traditional understandings of how and why scientific research is conducted.
It was, however, not without its detractors.
Early in 1990, as the Human Genome Project was ramping up, there was an effort headed by Professor Martin Rechsteiner, Ph.D., from the University of Utah, School of Medicine, to stop funding for the nascent Human Genome Project. The effort came in the form of a letter writing campaign. In total, 55 individuals from 33 different academic institutions across the U.S. sent letters to then acting NIH Director, William Raub, Ph.D., each laying out a variety of arguments against the Human Genome Project.
At that time, Elke Jordan was the Deputy Director of the recently formed National Center for Human Genome Research (NCHGR), now National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI). As arguably the person who played the biggest role in keeping the Human Genome Project on track in those early days , Dr. Jordan responded to each of these letters, offering pointed rebuttals to the various arguments made against the project. As such, she kept copies of the majority of the letters and they comprise a small but important part of her collection of materials

Although the anti-Human Genome Project campaign was unsuccessful, the letters offer an interesting and important glimpse into the profound ways in which the Human Genome Project challenged the status quo of conducting scientific inquiry. The letters also highlight legitimate concerns at the time that were expressed by both the public and scientific community around the merits of what was expected to be a $3 billion dollar, 15-year-long endeavor: Would it be worth it? What would we learn? Would it actually lead to improvements in healthcare? These were just some of the questions generated by skeptics of the project.
The letter campaign also provides a snapshot of the relatively new scientific field of genomics. At the time, genomics was at a crossroads as scientists and clinicians debated the best course forward for the field. For those who objected to the Human Genome Project, the pursuit of the entire human genomic sequence was less desirable and useful than a more targeted approach to genome mapping and sequencing. By examining their arguments, we can see some of the fundamental questions about the role of genomics in healthcare, which it continues to influence over 20 years later.
“The human genome project: mediocre science, terrible science policy”

Caption: A copy of the first page of Martin Rechsteiner’s letter, which circulated and spurred the anti-Human Genome Project letter campaign. The first line of the letter reads “The human genome project: mediocre science, terrible science policy.”
"... most of the sequencing work will not be creative or innovative ..."

Caption: A copy of a letter sent from a University of Kentucky professor, Mary Sue Coleman, Ph.D., addressed to William Raub, Ph.D., the acting director of the NIH at the time. The above header is taken from a line in the letter: “The problem with this stems from the fact most of the sequencing work will not be creative or innovative and will not allow students of postdoctoral fellows to generate knowledge that will further their own careers.”
Mary Sue Coleman, Ph.D., a professor of biochemistry at the University of Kentucky Medical Center, argued that the Human Genome Project would not draw new professionals in science and medicine towards the field of genomics. Their argument stemmed from a belief, shared by many of the letter writers, that the majority of the work would be a merely technical and repetitive exercise, akin to pumping out endless lines of letters with “no interesting biological information.” According to the Coleman, the project “wouldn’t have much appeal for me or my colleagues.”
While it’s true that much of the work on the Human Genome Project was repetitive, the project interested and attracted more than just technicians. One of the most important legacies of the Human Genome Project is the role that interdisciplinary team science played in achieving the end goal. The Human Genome Project brought together a diverse cohort of professionals from both the private and public sector. This included not only biologists, geneticists and medical professionals, but also computer engineers, bioethicists, legal experts, mathematicians, statisticians and many others.
Many of the grantees of the Human Genome Project went on to do pathbreaking work in a diverse range of fields after the conclusion of the project. An important legacy of the Human Genome Project is to help legitimize large interdisciplinary team science.
"... Junk as far as we can tell ..."

Caption: A letter from Associate Professor Janet Stavnezer, Ph.D., of the University of Massachusetts Medical School, sent to William Raub, Ph.D. The header is taken from the sentence: “Most of the genome (about 95%) doesn’t encode proteins and is junk as far as we can tell. ”
A letter from Janet Stavnezer, Associate Professor at the University of Massachusetts Medical School, argued that sequencing the entire human genome wasn’t worth it because the majority of the genome was so-called “junk DNA.”
“Junk DNA” was a term that was widely used prior, during and after the Human Genome Project, including those who participated in and contributed to the project. The term describes portions of the genome that seemingly had no purpose as they didn’t code for proteins. Therefore, according to some, spending billions of dollars sequencing the genome, knowing already that most of it was “filler,” would be a waste of time and money.
Today, it remains a fact that an incredibly small percentage of the genome, only 2%, actually codes for proteins. After the Human Genome Project, however, our understanding of “junk DNA” has changed significantly. First, the scientific community retired this term and instead refer to these sections as “non-coding DNA.” We now know that some of these regions of the genome do indeed provide valuable functions in gene expression, among other things. There are still many non-coding regions of the genome whose functions are still unknown and that are being actively investigated today.
For more information on what we now refer to as “non-coding DNA,” please visit our Talking Glossary of Genomic and Genetic Terms .
Dr. Stavnezer recently commented to us about how her perception of the Human Genome Project has changed in the years since its completion: “The [Human] genome project has been very informative and has generated large amounts of data and has greatly increased our understanding of our and other species’ genomes. It has been a most important and wonderful project, and the scientists who foresaw that and made it happen have truly made a great contribution.”
"The 'Big Science Project' "

Caption: A letter from Samuel Cukierman, M.D., Ph.D., a professor in the Department of Biomedical Sciences at the University of California, Riverside. The header above the image comes from the sentence: “This is being called the ‘Big Science’ Project.”
Professor Samuel Cukeirman, M.D., Ph.D., from the University of California, Riverside’s Division of Biomedical Science, argued in their letter that the Human Genome Project, being an example of so-called “Big Science,” was both ineffective and “controversial.”
“Big Science” is a term used, often pejoratively, to describe a large-scale, centralized scientific project usually funded by a government or large bureaucratic entity. This is in contrast to what can be called “small science,” or inquiry driven by individual investigators, which is done in smaller labs with a small staff led by a principal investigator.
Historically, “big science” projects were viewed by many scientists as wasteful and inefficient. They argued that the most fruitful scientific research required a more independent and focused approach driven by a hypothesis, or central question. The Human Genome Project, by contrast, had no driving question but was motivated by a desire to explore an unknown part of the biological world.
Even Bruce Alberts, Ph.D., who would eventually serve on the Program Advisory Committee on the Human Genome Project, was outspoken in his criticisms of “big science” projects, even though he strongly supported the project. In the rebuttal letter that Dr. Jordan sent to each of the letter writers, she pointed this fact out in defense of the project.
Although the Human Genome Project bore many of the hallmarks of a “big science” project, the majority of the work of sequencing the genome was performed by individual labs that were funded largely by individual P01 and R01 grants.
"Flagrant Waste of Federal Research Funds"

Caption: A letter from a professor of neurobiology, John D. Hildebrand, from the University of Arizona. The header is taken from the sentence “I join the chorus of other scientists who believe that the Human Genome Project is a flagrant waste of Federal research funds.”
In all of the letters written opposing the Human Genome Project, the one argument made by everyone was the objection to the overall cost of the project. At the time, the projected cost was $3 billion and it was slated to take 15 years to complete.
John Hildebrand, Ph.D., at University of Arizona, wrote “[o]ur society cannot afford that kind of price tag on such an ill-considered initiative.” Many of the letter writers further argued that this money would be much better spent on funding smaller investigator-initiated projects.
While the total cost of the Human Genome Project is difficult to determine, most agree that its final price tag was close to the original estimate of $3 billion. It was, however, accomplished in a shorter timeframe, with the final draft sequence completed and announced in 2003, two years ahead of schedule.
The Human Genome Project certainly was an expensive endeavor. However, it’s important to provide some historical context when considering the cost and value. For example, one of the most important legacies of the project is the data sharing policy (as outlined in the Bermuda Principles ) of the genomic information generated. This kind of policy was made possible by the fact that the project was funded by the public. Researchers around the globe have been able to freely access this information to advance new pharmaceuticals and generate new technologies.
Additionally, a significant part of the budget was allocated to understanding the ethical and legal consequences of having human genomic information available to researchers. The Ethical, Social and Legal Implications (ELSI) Research Program was a congressionally mandated part of the Human Genome Project bud get and continues to be today.
"A Much More Sensible Beginning"

Caption: A letter from a Nobel Laureate and Professor of biology, Christian Anfinsen, Ph.D., from Johns Hopkins University. The header comes from the sentence “I do believe that the approach favored by individuals such as Dr. McKusick at Johns Hopkins University, aimed at locating and sequencing specific portions of the genome related to human disease, would make a much more sensible beginning.”
A number of letters made an argument that highlighted a division amongst genomicists and the focus of the genomics field that existed at the time, and to some extent still does. They argued that a more practical, and ultimately beneficial, approach to genome sequencing and mapping would be a more “targeted” approach. This targeted approach would seek to improve the existing genetic linkage by focusing on sequencing what one critic of the project called “medically important loc[i]” in the genome. They argued that this approach would yield more health benefits than sequencing the entire genome.
This was the type of approach that had led to researchers identifying specific genes for single-gene disorders such as cystic fibrosis and muscular dystrophy. There were many researchers in the field who believed that this approach was the best path forward. For example, a letter from Johns Hopkins University professor of biology and Nobel Laureate in chemistry, Christian B. Anfinsen cited the work of his colleague Dr. Victor McKusick, as a “more sensible beginning” for genome sequencing.
Today, these two approaches exist more harmoniously as both genomics and genetics continues to become more integrated in everyday human health care. The cost of genomic sequencing in the decades following the Human Genome Project has plummeted to a point where in the near future it will be possible for anyone to sequence their entire genome for an infinitesimally small amount compared to the cost of the Human Genome Project. The knowledge and information generated by the project has significantly improved our understanding of our genomes and genetic diseases in all of its complexity.
Other Resources
NHGRI History of Genomics Archive
NHGRI Human Genome Project Fact Sheet
Elke Jordan Oral History, NHGRI Oral History Collection
Anti-Human Genome Project Letter Campaign - Full Collection (PDF)
Last updated: May 6, 2024

Direct Links
JLU von A-Z
Informationen für
- Schülerinnen & Schüler
- Studieninteressierte
- Studierende
- Menschen mit Fluchthintergrund
- Unternehmen
- Jobs & Karriere
- Wissenschaftler/innen
- Promovierende
- Weiterbildungsangebote für JLU-Angehörige
- Lehrerfortbildung
- Wissenschaftliche Weiterbildung
- Ehemalige (Alumni)
- E-Campus ( Stud.IP , ILIAS , FlexNow , eVV )
Studium & Campus
- Vor dem Studium
- Studienangebot
- Bewerbung/Einschreibung
- Information/Beratung
- Vorlesungsverzeichnis
- Studien- und Prüfungsordnungen (MUG)
- Hochschulrechenzentrum
- Universitätsbibliothek
- Campusplan | Geschosspläne/JLUmaps
- Raumvergabe (ZLIS)
- Studierendenwerk/Mensen
- Corporate Design, Leitfäden, Logos
- Bildergalerie Pressestelle
- Formulare | Rundschreiben
- SAP & JustOS (JLU-Online-Shop)
- Rechtliche Grundlagen (MUG)
- Störungsmeldung
- Datenschutz
Karriere, Kultur, Sport, Marketing
- Allgemeiner Hochschulsport (ahs)
- Botanischer Garten
- Career Services
- Gender & JLU
- Hochschuldidaktik
- Justus' Kinderuni
- Sammlungen der JLU
- Universitätsorchester
- Uni-Shop/Merchandising
- E-Mail-Kontakt
- Telefonbuch
- Wegbeschreibung
- Call Justus
Information Event: Funding Opportunities of the DFG and VolkswagenStiftung for Postdocs
In this online informational event, you will have the opportunity to obtain in-depth information on the topic of acquiring third-party funding. Representatives of both the German Research Foundation (DFG) and VolkswagenStiftung will present comprehensive overviews of their funding programmes. Afterwards, we continue with a panel discussion on the topic of "Academic (Grant) Writing with AI".

Successful careers in academia are almost inseparably linked to the successful acquisition of third party funding . Finding, applying for and being given the "right" type of grant can be a tremendous boon the any researcher's career . But how does one navigate the sprawling landscape of academic funding? How does one determine which programme is suitable for the current or next step in their career?
To answer these questions — and related ones — we are hosting a digital informational event on June 26, 2024 from 1.00 pm to 3.45 pm .
In the first part of the event, representatives of the German Research Foundation (DFG) and the VolkswagenStiftung will present their institutions and research funding offers for postdocs , providing insights into how you can identify the right offer for your career station and successfully acquire funding for your own postdoc research project.
In the second part of the event we host a panel discussion on the role of AI in academia also with regard to grant writing. Together with panellists from the DFG, VolkswagenStiftung, Universität Marburg, HessenHub, and TwentyOne Skills we will discuss how artificial intelligence is transforming the landscape and practices of academic writing, what challenges this provides, and how the use of different AI models is viewed by the industry, universities, and funding institutions.
This event is part of the programme "Career Development for Postdoctoral Researchers", which is jointly organized by the three graduate institutions Giessen Graduate Centre for Social Sciences, Business, Economics and Law (GGS), International Giessen Graduate Centre for the Life Sciences (GGL) and MArburg University Research Academy (MARA) under the umbrella of the Research Campus Central Hessen.
The chief organizers of the event are Dr Christine Berger (MARA), Dr Sabine Otto (GGL), Dr Sina Weidenweber (THM), and Felix Wagner (GGS).
If you have any questions or remarks about the event and programme, contact us via email to [email protected] , [email protected] , or [email protected] .
Target Audience
Doctoral candidates, postdocs, junior research group leaders, junior professors, tenure-track professors from all disciplines (Philipps-Universität Marburg, Justus Liebig Universität Giessen, Technische Hochschule Mittelhessen — University of Applied Sciences, Research Campus of Central Hessen (FCMH), Goethe-Universität Frankfurt, Universität Kassel).
Registration
The event will be conducted online via Zoom .You may register via the application form linked below. Registered participants will receive the Zoom link in advance of the event, and we will also post access information shortly before the event on this site.
Click here to register via our digital registration form.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Securing grants requires strategic planning. Identifying relevant opportunities, building collaborations, and crafting a comprehensive grant proposal are crucial steps. Read our ultimate guide on grant writing, finding grants, and applying for grants to get the funding for your research.
How to Write a Successful Grant. Writing a grant application is a demanding process, especially in the current environment of historically low funding levels. 1 The current funding rate of the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute is 10%, compared with ≈30% funding rate in 2001. When preparing a grant application, the 5 criteria that reviewers will use to score the grant (ie ...
Include a sentence or two about what your organization does, and one research-based point that shows the need that your organization addresses. Limit your cover letter to one page with three or four paragraphs. Use the same date that you'll be sending the complete grant application to the funding source.
Writing research grants is a central part of any good quality research. Once a detailed research proposal has been submitted, it is subjected to an expert peer review process. Such reviews are designed to reach a funding decision, with feedback provided to improve the study for this and any future submissions.
1. Abstract. The abstract is a summary of your research proposal. It should be around 150 to 200 words and summarize your aims, the gap in literature, the methods you plan to use, and how long you might take. 2. Literature Review. The literature review is a review of the literature related to your field.
Step 2: Plan and research your project. Preliminary research for your grant proposal. Questions to ask yourself as you plan your grant proposal. Developing your grant proposal. Step 3: Write the first draft of your grant proposal. Step 4: Get feedback, and revise your grant proposal accordingly.
What to Know Before You Start Writing Where to Find Application Instructions. Application forms are posted with each funding opportunity. General application form instructions are found on the How to Apply - Application Guide page.. In addition to form-by-form, field-by-field instructions you'll find guidance on formatting attachments (fonts, margins, etc., developing a budget, and more.
A grant proposal or application is a document or set of documents that is submitted to an organization with the explicit intent of securing funding for a research project. Grant writing varies widely across the disciplines, and research intended for epistemological purposes (philosophy or the arts) rests on very different assumptions than ...
The Grant Writing Guide is an essential handbook for writing research grants, providing actionable strategies for professionals in every phase of their careers, from PhD students to seasoned researchers. This easy-to-use guide features writing samples, examples of how researchers use skills, helpful tips, and exercises. Drawing on interviews ...
The European Commission's Horizon 2020 programme is the European Union's largest-ever research and innovation programme, with nearly €80 billion (US$89 billion) in funding set aside between ...
Developing a grant application can feel daunting at first, but with practice and good support, becomes easier with experience. 1. Get Visible - The Sooner, the Better! It's a good idea to start building up your profile within academia early on. Make use of all the resources available to you to showcase yourself, your research, and your ...
A grant proposal must always complete two tasks: Clearly articulate the hypothesis of your research in its broadest strokes. Demonstrate that your goals in the research endeavor and the goals of the funding institution are symbiotic. Introduction/Abstract. As early in the proposal as possible, identify and explicitly state the question your ...
Grant Writing vs. Non Profit Funding. We've covered all the basics, but there's a bit more important context to understand as you launch your grant writing journey. ... In both cases, you need to do research, pursue leads, prepare talking points, evaluate opportunities, and cultivate relationships. The essence of both practices is the same ...
Make sure you and your collaborators are properly trained for the research. Closely examine grant applications from successful grantees. Read the instructions in the grant application kit (PHS 398), then read them again. Follow them to the letter. Have several experienced grantees critique your application.
It is organized according to the following stages of the writing process: I) project planning; II) researching funding opportunities; and III) writing and submitting the grant proposal. Note that the specific requirements of funding agencies vary significantly, and should always be consulted carefully before a grant proposal is begun.
"Time is a nonrenewable resource. Grants often provide time for you to think about these important issues." More specifically, grants allow researchers to pay for research assistants, postdocs, and other resources that distribute the workload and free up more time for the researchers to think about big ideas.
Tip #5: Make sure your first page is impactful. The first page of any grant proposal is the most important. It needs to state the current research problem/ gap to address, how you will tackle it and why you and your team are the best placed to do so. You want the reviewer, who again will likely be reading lots of these late at night, to be ...
All Duke research personnel involved in writing proposals for funding are invited to attend, though the sessions are geared towards faculty who are writing or planning to write NIH grant applications. Email [email protected] for more information. Facilities and Research Repository (boilerplate language) from myRESEARCHpath.
Writing your research grant application. Write a grant that is friendly to your reader and ensure that you always keep the priorities of the funding body in mind. Focus on your design, including timelines and methodologies. Focus on the merits/benefits of the research - it is essential to make a strong case for the importance of your research ...
The Literature Fellowships program awards grants in prose (fiction and creative nonfiction) and poetry to published creative writers that enable the recipients to set aside time for writing, research, travel, and general career advancement. Grants to individuals are only available in Literature. * Deadline: March 13, 2024.
Literary Grants. Since 1963, the PEN America Literary Awards, Grants, and Fellowships Program has honored many of the most outstanding voices in literature across diverse genres, including fiction, poetry, nonfiction, children's literature, translation, and drama. With the help of our partners, PEN America confers distinct grants each year to ...
Two grants of $1,500 each will be awarded to be used toward craft development (writing classes, retreats, conferences, travel), work-related materials (notebooks, laptops, software, research, etc.), childcare, bills, or any other financial obstacle.
NIAID is hosting a virtual grant writing webinar series called "Debuting Your Research Career: How to Plan for and Write Your First (or Next) NIH Grant Application." This monthly webinar series is free and open to pre- and post-doctoral fellows, clinician-scientists, and early-career investigators.
This page focuses on best practices for academic writing and stages of the writing process, and it includes helpful guides for the types of writing you might encounter at the GSD. From the library homepage, you can access all kinds of resources and tools to help with your research. Start your research by utilizing our curated research guides.
The Department of Anthropology offers graduate students funding through teaching assistantships, research assistantships, and teaching stand-alone courses. Continued funding is dependent on making satisfactory progress towards your degree and showing respectable performance in your assistantship. For 2023 - 2024, assistantships carry a ...
For: Small businesses interested in carrying out innovation research. Funding limit: Over $2 million. Deadline: September 5, January 5, and April 5. The Small Business Innovation Research program ...
This exploratory study addressed this research gap. Students from a Dutch university (N = 284) attended a three-week online module during which they were engaged in peer feedback on argumentative writing. At the end of the module, we measured students' perceptions of learning.
The completion of the Human Genome Project in 2003 and subsequent boom in the genomics field has had a profound impact not just on biology and medicine but also on ethics and society. The project also changed traditional understandings of how and why scientific research is conducted. It was, however, not without its detractors. Early in 1990, there was an effort to stop funding for the nascent ...
WASHINGTON, D.C.— Today, U.S. Senator Angus King (I-ME) is calling on the leaders of the Appropriations Committee to prioritize funding for traumatic brain injury (TBI) research in the FY2025 spending bill. In a letter to Defense Subcommittee Chairman Jon Tester (D-MT) and Ranking Member Susan Collins (R-ME), the Senator led a bipartisan group of his colleagues to urge the Appropriations ...
In this online informational event, you will have the opportunity to obtain in-depth information on the topic of acquiring third-party funding. Representatives of both the German Research Foundation (DFG) and VolkswagenStiftung will present comprehensive overviews of their funding programmes. Afterwards, we continue with a panel discussion on the topic of "Academic (Grant) Writing with AI".