- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
- QuestionPro

- Solutions Industries Gaming Automotive Sports and events Education Government Travel & Hospitality Financial Services Healthcare Cannabis Technology Use Case NPS+ Communities Audience Contactless surveys Mobile LivePolls Member Experience GDPR Positive People Science 360 Feedback Surveys
- Resources Blog eBooks Survey Templates Case Studies Training Help center
Home Market Research

Participant observation: What it is, types & uses

Participant observation has been widely used in disciplines such as anthropology, sociology, communication studies, political science, social psychology, and even in market research.
To help you get a broad overview of this methodology, in this article we have compiled its most important characteristics, its importance, and some of the types of participant observation that you can put into practice for your next study.
LEARN ABOUT: Behavioral Research
What is participant observation?
Participant observation is a qualitative research methodology in which the researcher studies a group not only through observation, but also by participating in its activities.
In this qualitative observation methodology, the researcher immerses himself in the daily activities of the participants in order to record the behavior in as many scenarios as possible.
Thanks to the immersion in the study place, the researchers can observe the daily life of the people: their exchanges with each other, their formal and informal conversations, habits, etc.
It offers researchers the opportunity to collect honest and intimate information about people. However, this information is filtered through the perspective of researchers who, by using this method, run the risk of losing their objectivity and altering with their presence the behavior of the groups they study.
LEARN ABOUT: Research Process Steps
Importance of participant observation
Participant observation is a method that helps you see and understand what people are doing and compare it with what they say. In this way, you help researchers know if the people with whom you are conducting a study act differently from what they are described.
It also allows the researcher to better understand what is happening in a given group and its cultural environment, giving greater credibility to their interpretations of the observation.
In addition, it allows the researcher to collect qualitative data through various types of interviews and quantitative data through surveys and different quantitative observation techniques.
Characteristics of participant observation
Participant observation has historically been associated with a form of field research in which the researcher resides for long periods of time in a small community.
Today, this methodology is used in a wide variety of settings and for widely varying periods of time, from a single interaction to many years. But it is usually characterized by the following points:
- The long-term nature of the interaction between the researcher and the participants as part of the fieldwork process.
- A wide range of relationship dynamics that it studies, such as differences in status between the two parties, differences in power and educational differences, as well as degrees of formality. Differences in power can have their origin in gender, social class, health and other aspects.
- The variety of settings, from close interpersonal interactions to observing public gatherings and actual participation in social events.
- In many cases, research takes place in settings unfamiliar to the researcher, which will make her presentation and interaction with others especially sensitive.
- There may be different ethical codes between the groups studied and those of the researcher’s country or institution of origin. They may also differ from the ethical principles followed by the host government, non-governmental organizations in the area, or agencies funding the research .
- The changing nature of the researcher’s roles and relationships with the studied group over time.
- The use of technology to document observations, including mapping, photography, and video and audio recording.
LEARN ABOUT: Social Communication Questionnaire
Types of participant observation
Now that you know what this method is and what its most common characteristics are, we will introduce you to the types that exist.
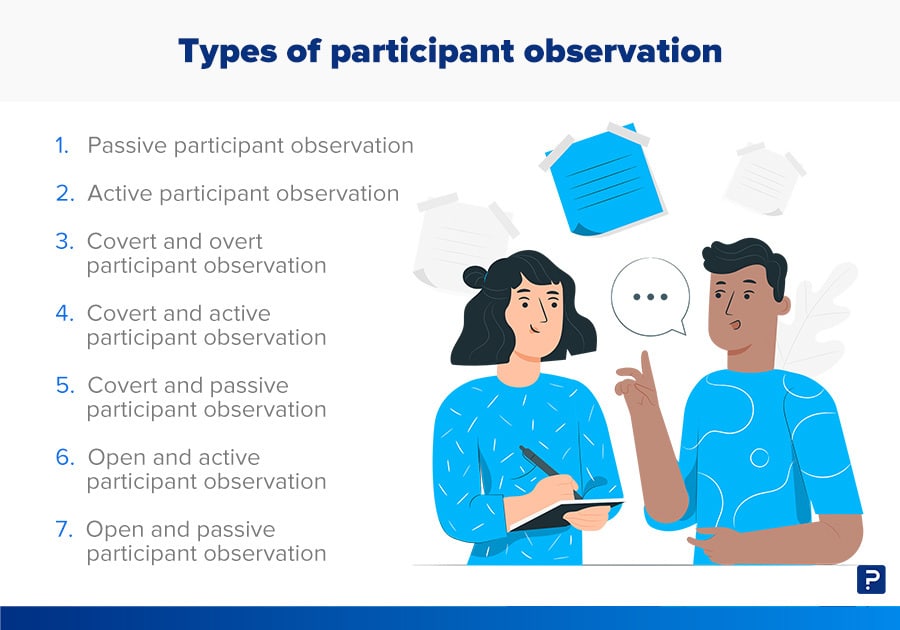
Passive participant observation
Researchers observe and record the behaviors of their subjects in their own environment without conversing or interacting with them in any way.
Many of the studies that use this form of participant observation are studies in which researchers observe people’s behavior and communications in public places, such as restaurants, coffee shops, transportation hubs, and even on the Internet through innovative methods such as netnography .
Active participant observation
In this way, researchers converse with their subjects and participate in the daily life of the groups they study, including their activities, c ustoms, rituals, routines, etc.
The degree of commitment of researchers to these groups varies. Some researchers limit their interactions to interviews, while others engage in all aspects of their subjects’ lives.
Examples of this form of participant observation are studies in which researchers lived for long periods of time among different ethnic, cultural, or religious communities.
Covert and overt
In covert participant observation, researchers do not make their presence known to their subjects and, if they do, they do not identify themselves as investigators, whereas in open participant observation they do.
However, even when the investigation is open, investigators often do not inform the people they meet in the course of their investigation of the specific purpose of the investigation, nor do they inform everyone they meet that they are researchers, as this could unnecessarily interrupt conversations and events being observed.
Covert and active
Covert and active participant observation has several advantages. In this type of participant observation, researchers can have access to a group that they would not otherwise have the opportunity to observe, and they can experience the practices of the group as they are experienced by the members of the group.
Generally, researchers can alter group behavior by their presence, but in this form of participant observation, groups would not consciously change their behavior in response to the researcher’s presence because they are not aware of being observed.
Covert and passive
In the case of covert and passive participant observation, researchers are not likely to alter the behaviors of their subjects, since the researchers do not actively engage with their subjects and because the subjects are also not aware that they are being observed.
However, since observation is passive, researchers do not have the opportunity to experience the lives of their subjects for themselves.
Open and active
If observation is open and active, people can participate in and experience their subjects’ activities as their subjects would, but they run the risk of both changing the behavior of their subjects through their interactions with them, and that their subjects change their behavior by themselves knowing that they are being studied.
Open and passive
As in the case of covert and passive participant observation, researchers do not run the risk that their presence alters the behavior of the groups they study through their interactions with them.
However, the guinea pig effect is a problem for this form of observation, unlike the case of covert and passive participant observation, because the participants are aware that they are being studied. Furthermore, researchers cannot experience the world as it is as subjects would.
As you can see, participant observation is a research method that provides valuable information about the social and cultural relationships of a group or community over time.
Uncover the insights that matter the most. Use QuestionPro’s market research platform to uncover complex insights that can propel your business to the forefront of your industry.
MORE LIKE THIS

The Best Email Survey Tool to Boost Your Feedback Game
May 7, 2024

Top 10 Employee Engagement Survey Tools

Top 20 Employee Engagement Software Solutions
May 3, 2024

15 Best Customer Experience Software of 2024
May 2, 2024
Other categories
- Academic Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assessments
- Brand Awareness
- Case Studies
- Communities
- Consumer Insights
- Customer effort score
- Customer Engagement
- Customer Experience
- Customer Loyalty
- Customer Research
- Customer Satisfaction
- Employee Benefits
- Employee Engagement
- Employee Retention
- Friday Five
- General Data Protection Regulation
- Insights Hub
- Life@QuestionPro
- Market Research
- Mobile diaries
- Mobile Surveys
- New Features
- Online Communities
- Question Types
- Questionnaire
- QuestionPro Products
- Release Notes
- Research Tools and Apps
- Revenue at Risk
- Survey Templates
- Training Tips
- Uncategorized
- Video Learning Series
- What’s Coming Up
- Workforce Intelligence

Chapter 13. Participant Observation
Introduction.
Although there are many possible forms of data collection in the qualitative researcher’s toolkit, the two predominant forms are interviewing and observing. This chapter and the following chapter explore observational data collection. While most observers also include interviewing, many interviewers do not also include observation. It takes some special skills and a certain confidence to be a successful observer. There is also a rich tradition of what I am going to call “deep ethnography” that will be covered in chapter 14. In this chapter, we tackle the basics of observational data collection.

What is Participant Observation?
While interviewing helps us understand how people make sense of their worlds, observing them helps us understand how they act and behave. Sometimes, these actions and behaviors belie what people think or say about their beliefs and values and practices. For example, a person can tell you they would never racially discriminate, but observing how they actually interact with racialized others might undercut those statements. This is not always about dishonesty. Most of us tend to act differently than we think we do or think we should. That is part of being human. If you are interested in what people say and believe , interviewing is a useful technique for data collection. If you are interested in how people act and behave , observing them is essential. And if you want to know both, particularly how thinking/believing and acting/behaving complement or contradict each other, then a combination of interviewing and observing is ideal.
There are a variety of terms we use for observational data collection, from ethnography to fieldwork to participant observation . Many researchers use these terms fairly interchangeably, but here I will separately define them. The subject of this chapter is observation in general, or participant observation, to highlight the fact that observers can also be participants. The subject of chapter 14 will be deep ethnography , a particularly immersive form of study that is attractive for a certain subset of qualitative researchers. Both participant observation and deep ethnography are forms of fieldwork in which the researcher leaves their office and goes into a natural setting to record observations that take place in that setting. [1]
Participant observation (PO) is a field approach to gathering data in which the researcher enters a specific site for purposes of engagement or observation. Participation and observation can be conceptualized as a continuum, and any given study can fall somewhere on that line between full participation (researcher is a member of the community or organization being studied) and observation (researcher pretends to be a fly on the wall surreptitiously but mostly by permission, recording what happens). Participant observation forms the heart of ethnographic research, an approach, if you remember, that seeks to understand and write about a particular culture or subculture. We’ll discuss what I am calling deep ethnography in the next chapter, where researchers often embed themselves for months if not years or even decades with a particular group to be able to fully capture “what it’s like.” But there are lighter versions of PO that can form the basis of a research study or that can supplement or work with other forms of data collection, such as interviews or archival research. This chapter will focus on these lighter versions, although note that much of what is said here can also apply to deep ethnography (chapter 14).
PO methods of gathering data present some special considerations—How involved is the researcher? How close is she to the subjects or site being studied? And how might her own social location—identity, position—affect the study? These are actually great questions for any kind of qualitative data collection but particularly apt when the researcher “enters the field,” so to speak. It is helpful to visualize where one falls on a continuum or series of continua (figure 13.1).
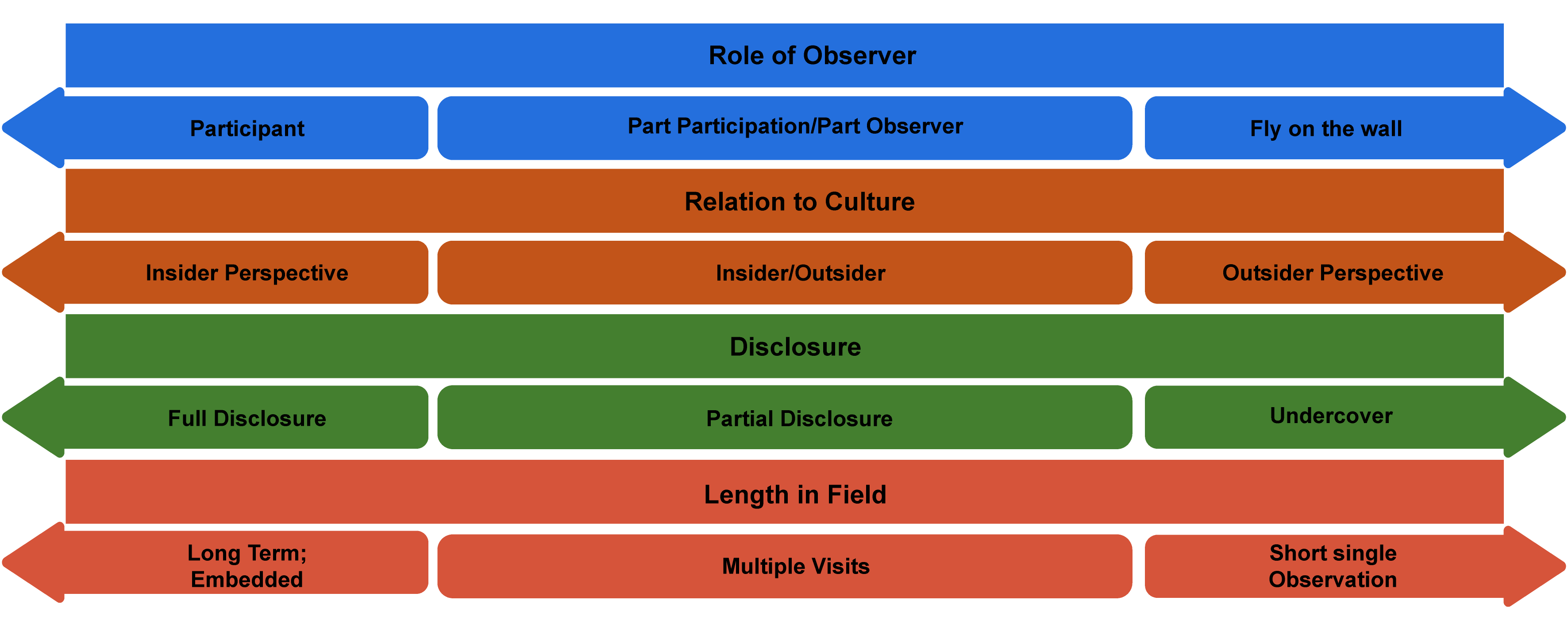
Let’s take a few examples and see how these continua work. Think about each of the following scenarios, and map them onto the possibilities of figure 13.1:
- a nursing student during COVID doing research on patient/doctor interactions in the ICU
- a graduate student accompanying a police officer during her rounds one day in a part of the city the graduate student has never visited
- a professor raised Amish who goes back to her hometown to conduct research on Amish marriage practices for one month
- (What if the sociologist was also a member of the OCF board and camping crew?)
Depending on how the researcher answers those questions and where they stand on the P.O. continuum, various techniques will be more or less effective. For example, in cases where the researcher is a participant, writing reflective fieldnotes at the end of the day may be the primary form of data collected. After all, if the researcher is fully participating, they probably don’t have the time or ability to pull out a notepad and ask people questions. On the other side, when a researcher is more of an observer, this is exactly what they might do, so long as the people they are interrogating are able to answer while they are going about their business. The more an observer, the more likely the researcher will engage in relatively structured interviews (using techniques discussed in chapters 11 and 12); the more a participant, the more likely casual conversations or “unstructured interviews” will form the core of the data collected. [2]
Observation and Qualitative Traditions
Observational techniques are used whenever the researcher wants to document actual behaviors and practices as they happen (not as they are explained or recorded historically). Many traditions of inquiry employ observational data collection, but not all traditions employ them in the same way. Chapter 14 will cover one very specific tradition: ethnography. Because the word ethnography is sometimes used for all fieldwork, I am calling the subject of chapter 14 deep ethnography, those studies that take as their focus the documentation through the description of a culture or subculture. Deeply immersive, this tradition of ethnography typically entails several months or even years in the field. But there are plenty of other uses of observation that are less burdensome to the researcher.
Grounded Theory, in which theories emerge from a rigorous and systematic process of induction, is amenable to both interviewing and observing forms of data collection, and some of the best Grounded Theory works employ a deft combination of both. Often closely aligned with Grounded Theory in sociology is the tradition of symbolic interactionism (SI). Interviews and observations in combination are necessary to properly address the SI question, What common understandings give meaning to people’s interactions ? Gary Alan Fine’s body of work fruitfully combines interviews and observations to build theory in response to this SI question. His Authors of the Storm: Meteorologists and the Culture of Prediction is based on field observation and interviews at the Storm Prediction Center in Oklahoma; the National Weather Service in Washington, DC; and a few regional weather forecasting outlets in the Midwest. Using what he heard and what he observed, he builds a theory of weather forecasting based on social and cultural factors that take place inside local offices. In Morel Tales: The Culture of Mushrooming , Fine investigates the world of mushroom hunters through participant observation and interviews, eventually building a theory of “naturework” to describe how the meanings people hold about the world are constructed and are socially organized—our understanding of “nature” is based on human nature, if you will.
Phenomenology typically foregrounds interviewing, as the purpose of this tradition is to gather people’s understandings and meanings about a phenomenon. However, it is quite common for phenomenological interviewing to be supplemented with some observational data, especially as a check on the “reality” of the situations being described by those interviewed. In my own work, for example, I supplemented primary interviews with working-class college students with some participant observational work on the campus in which they were studying. This helped me gather information on the general silence about class on campus, which made the salience of class in the interviews even more striking ( Hurst 2010a ).
Critical theories such as standpoint approaches, feminist theory, and Critical Race Theory are often multimethod in design. Interviews, observations (possibly participation), and archival/historical data are all employed to gather an understanding of how a group of persons experiences a particular setting or institution or phenomenon and how things can be made more just . In Making Elite Lawyers , Robert Granfield ( 1992 ) drew on both classroom observations and in-depth interviews with students to document the conservatizing effects of the Harvard legal education on working-class students, female students, and students of color. In this case, stories recounted by students were amplified by searing examples of discrimination and bias observed by Granfield and reported in full detail through his fieldnotes.
Entry Access and Issues
Managing your entry into a field site is one of the most important and nerve-wracking aspects of doing ethnographic research. Unlike interviews, which can be conducted in neutral settings, the field is an actual place with its own rules and customs that you are seeking to explore. How you “gain access” will depend on what kind of field you are entering. If your field site is a physical location with walls and a front desk (such as an office building or an elementary school), you will need permission from someone in the organization to enter and to conduct your study. Negotiating this might take weeks or even months. If your field site is a public site (such as a public dog park or city sidewalks), there is no “official” gatekeeper, but you will still probably need to find a person present at the site who can vouch for you (e.g., other dog owners or people hanging out on their stoops). [3] And if your field site is semipublic, as in a shopping mall, you might have to weigh the pros and cons of gaining “official” permission, as this might impede your progress or be difficult to ascertain whose permission to request. If you recall, many of the ethical dilemmas discussed in chapter 7 were about just such issues.
Even with official (or unofficial) permission to enter the site, however, your quest to gain access is not done. You will still need to gain the trust and permission of the people you encounter at that site. If you are a mere observer in a public setting, you probably do not need each person you observe to sign a consent form, but if you are a participant in an event or enterprise who is also taking notes and asking people questions, you probably do. Each study is unique here, so I recommend talking through the ethics of permission and consent seeking with a faculty mentor.
A separate but related issue from permission is how you will introduce yourself and your presence. How you introduce yourself to people in the field will depend very much on what level of participation you have chosen as well as whether you are an insider or outsider. Sometimes your presence will go unremarked, whereas other times you may stick out like a very sore thumb. Lareau ( 2021 ) advises that you be “vague but accurate” when explaining your presence. You don’t want to use academic jargon (unless your field is the academy!) that would be off-putting to the people you meet. Nor do you want to deceive anyone. “Hi, I’m Allison, and I am here to observe how students use career services” is accurate and simple and more effective than “I am here to study how race, class, and gender affect college students’ interactions with career services personnel.”
Researcher Note
Something that surprised me and that I still think about a lot is how to explain to respondents what I’m doing and why and how to help them feel comfortable with field work. When I was planning fieldwork for my dissertation, I was thinking of it from a researcher’s perspective and not from a respondent’s perspective. It wasn’t until I got into the field that I started to realize what a strange thing I was planning to spend my time on and asking others to allow me to do. Like, can I follow you around and write notes? This varied a bit by site—it was easier to ask to sit in on meetings, for example—but asking people to let me spend a lot of time with them was awkward for me and for them. I ended up asking if I could shadow them, a verb that seemed to make clear what I hoped to be able to do. But even this didn’t get around issues like respondents’ self-consciousness or my own. For example, respondents sometimes told me that their lives were “boring” and that they felt embarrassed to have someone else shadow them when they weren’t “doing anything.” Similarly, I would feel uncomfortable in social settings where I knew only one person. Taking field notes is not something to do at a party, and when introduced as a researcher, people would sometimes ask, “So are you researching me right now?” The answer to that is always yes. I figured out ways of taking notes that worked (I often sent myself text messages with jotted notes) and how to get more comfortable explaining what I wanted to be able to do (wanting to see the campus from the respondent’s perspective, for example), but it is still something I work to improve.
—Elizabeth M. Lee, Associate Professor of Sociology at Saint Joseph’s University, author of Class and Campus Life and coauthor of Geographies of Campus Inequality
Reflexivity in Fieldwork
As always, being aware of who you are, how you are likely to be read by others in the field, and how your own experiences and understandings of the world are likely to affect your reading of others in the field are all very important to conducting successful research. When Annette Lareau ( 2021 ) was managing a team of graduate student researchers in her study of parents and children, she noticed that her middle-class graduate students took in stride the fact that children called adults by their first names, while her working-class-origin graduate students “were shocked by what they considered the rudeness and disrespect middle-class children showed toward their parents and other adults” ( 151 ). This “finding” emerged from particular fieldnotes taken by particular research assistants. Having graduate students with different class backgrounds turned out to be useful. Being reflexive in this case meant interrogating one’s own expectations about how children should act toward adults. Creating thick descriptions in the fieldnotes (e.g., describing how children name adults) is important, but thinking about one’s response to those descriptions is equally so. Without reflection, it is possible that important aspects never even make it into the fieldnotes because they seem “unremarkable.”
The Data of Observational Work: Fieldnotes
In interview data collection, recordings of interviews are transcribed into the data of the study. This is not possible for much PO work because (1) aural recordings of observations aren’t possible and (2) conversations that take place on-site are not easily recorded. Instead, the participant observer takes notes, either during the fieldwork or at the day’s end. These notes, called “fieldnotes,” are then the primary form of data for PO work.
Writing fieldnotes takes a lot of time. Because fieldnotes are your primary form of data, you cannot be stingy with the time it takes. Most practitioners suggest it takes at least the same amount of time to write up notes as it takes to be in the field, and many suggest it takes double the time. If you spend three hours at a meeting of the organization you are observing, it is a good idea to set aside five to six hours to write out your fieldnotes. Different researchers use different strategies about how and when to do this. Somewhat obviously, the earlier you can write down your notes, the more likely they are to be accurate. Writing them down at the end of the day is thus the default practice. However, if you are plainly exhausted, spending several hours trying to recall important details may be counterproductive. Writing fieldnotes the next morning, when you are refreshed and alert, may work better.
Reseaarcher Note
How do you take fieldnotes ? Any advice for those wanting to conduct an ethnographic study?
Fieldnotes are so important, especially for qualitative researchers. A little advice when considering how you approach fieldnotes: Record as much as possible! Sometimes I write down fieldnotes, and I often audio-record them as well to transcribe later. Sometimes the space to speak what I observed is helpful and allows me to be able to go a little more in-depth or to talk out something that I might not quite have the words for just yet. Within my fieldnote, I include feelings and think about the following questions: How do I feel before data collection? How did I feel when I was engaging/watching? How do I feel after data collection? What was going on for me before this particular data collection? What did I notice about how folks were engaging? How were participants feeling, and how do I know this? Is there anything that seems different than other data collections? What might be going on in the world that might be impacting the participants? As a qualitative researcher, it’s also important to remember our own influences on the research—our feelings or current world news may impact how we observe or what we might capture in fieldnotes.
—Kim McAloney, PhD, College Student Services Administration Ecampus coordinator and instructor
What should be included in those fieldnotes? The obvious answer is “everything you observed and heard relevant to your research question.” The difficulty is that you often don’t know what is relevant to your research question when you begin, as your research question itself can develop and transform during the course of your observations. For example, let us say you begin a study of second-grade classrooms with the idea that you will observe gender dynamics between both teacher and students and students and students. But after five weeks of observation, you realize you are taking a lot of notes about how teachers validate certain attention-seeking behaviors among some students while ignoring those of others. For example, when Daisy (White female) interrupts a discussion on frogs to tell everyone she has a frog named Ribbit, the teacher smiles and asks her to tell the students what Ribbit is like. In contrast, when Solomon (Black male) interrupts a discussion on the planets to tell everyone his big brother is called Jupiter by their stepfather, the teacher frowns and shushes him. These notes spark interest in how teachers favor and develop some students over others and the role of gender, race, and class in these teacher practices. You then begin to be much more careful in recording these observations, and you are a little less attentive to the gender dynamics among students. But note that had you not been fairly thorough in the first place, these crucial insights about teacher favoritism might never have been made.
Here are some suggestions for things to include in your fieldnotes as you begin: (1) descriptions of the physical setting; (2) people in the site: who they are and how they interact with one another (what roles they are taking on); and (3) things overheard: conversations, exchanges, questions. While you should develop your own personal system for organizing these fieldnotes (computer vs. printed journal, for example), at a minimum, each set of fieldnotes should include the date, time in the field, persons observed, and location specifics. You might also add keywords to each set so that you can search by names of participants, dates, and locations. Lareau ( 2021:167 ) recommends covering the following key issues, which mnemonically spell out WRITE— W : who, what, when, where, how; R: reaction (responses to the action in question and the response to the response); I: inaction (silence or nonverbal response to an action); T: timing (how slowly or quickly someone is speaking); and E: emotions (nonverbal signs of emotion and/or stoicism).
In addition to the observational fieldnotes, if you have time, it is a good practice to write reflective memos in which you ask yourself what you have learned (either about the study or about your abilities in the field). If you don’t have time to do this for every set of fieldnotes, at least get in the practice of memoing at certain key junctures, perhaps after reading through a certain number of fieldnotes (e.g., every third day of fieldnotes, you set aside two hours to read through the notes and memo). These memos can then be appended to relevant fieldnotes. You will be grateful for them when it comes time to analyze your data, as they are a preliminary by-the-seat-of-your-pants analysis. They also help steer you toward the study you want to pursue rather than allow you to wallow in unfocused data.
Ethics of Fieldwork
Because most fieldwork requires multiple and intense interactions (even if merely observational) with real living people as they go about their business, there are potentially more ethical choices to be made. In addition to the ethics of gaining entry and permission discussed above, there are issues of accurate representation, of respecting privacy, of adequate financial compensation, and sometimes of financial and other forms of assistance (when observing/interacting with low-income persons or other marginalized populations). In other words, the ethical decision of fieldwork is never concluded by obtaining a signature on a consent form. Read this brief selection from Pascale’s ( 2021 ) methods description (observation plus interviews) to see how many ethical decisions she made:
Throughout I kept detailed ethnographic field and interview records, which included written notes, recorded notes, and photographs. I asked everyone who was willing to sit for a formal interview to speak only for themselves and offered each of them a prepaid Visa Card worth $25–40. I also offered everyone the opportunity to keep the card and erase the tape completely at any time they were dissatisfied with the interview in any way. No one asked for the tape to be erased; rather, people remarked on the interview being a really good experience because they felt heard. Each interview was professionally transcribed and for the most part the excerpts in this book are literal transcriptions. In a few places, the excerpta have been edited to reduce colloquial features of speech (e.g., you know, like, um) and some recursive elements common to spoken language. A few excerpts were placed into standard English for clarity. I made this choice for the benefit of readers who might otherwise find the insights and ideas harder to parse in the original. However, I have to acknowledge this as an act of class-based violence. I tried to keep the original phrasing whenever possible. ( 235 )
Summary Checklist for Successful Participant Observation
The following are ten suggestions for being successful in the field, slightly paraphrased from Patton ( 2002:331 ). Here, I take those ten suggestions and turn them into an extended “checklist” to use when designing and conducting fieldwork.
- Consider all possible approaches to your field and your position relative to that field (see figure 13.2). Choose wisely and purposely. If you have access to a particular site or are part of a particular culture, consider the advantages (and disadvantages) of pursuing research in that area. Clarify the amount of disclosure you are willing to share with those you are observing, and justify that decision.
- Take thorough and descriptive field notes. Consider how you will record them. Where your research is located will affect what kinds of field notes you can take and when, but do not fail to write them! Commit to a regular recording time. Your field notes will probably be the primary data source you collect, so your study’s success will depend on thick descriptions and analytical memos you write to yourself about what you are observing.
- Permit yourself to be flexible. Consider alternative lines of inquiry as you proceed. You might enter the field expecting to find something only to have your attention grabbed by something else entirely. This is perfectly fine (and, in some traditions, absolutely crucial for excellent results). When you do see your attention shift to an emerging new focus, take a step back, look at your original research design, and make careful decisions about what might need revising to adapt to these new circumstances.
- Include triangulated data as a means of checking your observations. If you are that ICU nurse watching patient/doctor interactions, you might want to add a few interviews with patients to verify your interpretation of the interaction. Or perhaps pull some public data on the number of arrests for jaywalking if you are the student accompanying police on their rounds to find out if the large number of arrests you witnessed was typical.
- Respect the people you are witnessing and recording, and allow them to speak for themselves whenever possible. Using direct quotes (recorded in your field notes or as supplementary recorded interviews) is another way to check the validity of the analyses of your observations. When designing your research, think about how you can ensure the voices of those you are interested in get included.
- Choose your informants wisely. Who are they relative to the field you are exploring? What are the limitations (ethical and strategic) in using those particular informants, guides, and gatekeepers? Limit your reliance on them to the extent possible.
- Consider all the stages of fieldwork, and have appropriate plans for each. Recognize that different talents are required at different stages of the data-collection process. In the beginning, you will probably spend a great deal of time building trust and rapport and will have less time to focus on what is actually occurring. That’s normal. Later, however, you will want to be more focused on and disciplined in collecting data while also still attending to maintaining relationships necessary for your study’s success. Sometimes, especially when you have been invited to the site, those granting access to you will ask for feedback. Be strategic about when giving that feedback is appropriate. Consider how to extricate yourself from the site and the participants when your study is coming to an end. Have an ethical exit plan.
- Allow yourself to be immersed in the scene you are observing. This is true even if you are observing a site as an outsider just one time. Make an effort to see things through the eyes of the participants while at the same time maintaining an analytical stance. This is a tricky balance to do, of course, and is more of an art than a science. Practice it. Read about how others have achieved it.
- Create a practice of separating your descriptive notes from your analytical observations. This may be as clear as dividing a sheet of paper into two columns, one for description only and the other for questions or interpretation (as we saw in chapter 11 on interviewing), or it may mean separating out the time you dedicate to descriptions from the time you reread and think deeply about those detailed descriptions. However you decide to do it, recognize that these are two separate activities, both of which are essential to your study’s success.
- As always with qualitative research, be reflective and reflexive. Do not forget how your own experience and social location may affect both your interpretation of what you observe and the very things you observe themselves (e.g., where a patient says more forgiving things about an observably rude doctor because they read you, a nursing student, as likely to report any negative comments back to the doctor). Keep a research journal!
Further Readings
Emerson, Robert M., Rachel I. Fretz, and Linda L. Shaw. 2011. Writing Ethnographic Fieldnotes . 2nd ed. University of Chicago Press. Excellent guide that uses actual unfinished fieldnote to illustrate various options for composing, reviewing, and incorporating fieldnote into publications.
Lareau, Annette. 2021. Listening to People: A Practical Guide to Interviewing, Participant Observation, Data Analysis, and Writing It All Up . Chicago: University of Chicago Press. Includes actual fieldnote from various studies with a really helpful accompanying discussion about how to improve them!
Wolfinger, Nicholas H. 2002. “On Writing Fieldnotes: Collection Strategies and Background Expectancies.” Qualitative Research 2(1):85–95. Uses fieldnote from various sources to show how the researcher’s expectations and preexisting knowledge affect what gets written about; offers strategies for taking useful fieldnote.
- Note that leaving one’s office to interview someone in a coffee shop would not be considered fieldwork because the coffee shop is not an element of the study. If one sat down in a coffee shop and recorded observations, then this would be fieldwork. ↵
- This is one reason why I have chosen to discuss deep ethnography in a separate chapter (chapter 14). ↵
- This person is sometimes referred to as the [pb_glossary id="389"]informant [/pb_glossary](and more on these characters in chapter 14). ↵
Methodological tradition of inquiry that holds the view that all social interaction is dependent on shared views of the world and each other, characterized through people’s use of language and non-verbal communication. Through interactions, society comes to be. The goal of the researcher in this tradition is to trace that construction, as in the case of documenting how gender is “done” or performed, demonstrating the fluidity of the concept (and how it is constantly being made and remade through daily interactions).
Used primarily in ethnography , as in the goal of fieldnotes is to produce a thick description of what is both observed directly (actions, actors, setting, etc.) and the meanings and interpretations being made by those actors at the time. In this way, the observed cultural and social relationships are contextualized for future interpretation. The opposite of a thick description is a thin description, in which observations are recorded without any social context or cues to help explain them. The term was coined by anthropologist Clifford Geertz (see chapter 14 ).
Reflective summaries of findings that emerge during analysis of qualitative data; they can include reminders to oneself for future analyses or considerations, reinterpretations or generations of codes, or brainstorms and concept mapping.
Introduction to Qualitative Research Methods Copyright © 2023 by Allison Hurst is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Observation Method in Psychology: Naturalistic, Participant and Controlled
Saul Mcleod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul Mcleod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc
Associate Editor for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MSc Psychology of Education
Olivia Guy-Evans is a writer and associate editor for Simply Psychology. She has previously worked in healthcare and educational sectors.
On This Page:
The observation method in psychology involves directly and systematically witnessing and recording measurable behaviors, actions, and responses in natural or contrived settings without attempting to intervene or manipulate what is being observed.
Used to describe phenomena, generate hypotheses, or validate self-reports, psychological observation can be either controlled or naturalistic with varying degrees of structure imposed by the researcher.
There are different types of observational methods, and distinctions need to be made between:
1. Controlled Observations 2. Naturalistic Observations 3. Participant Observations
In addition to the above categories, observations can also be either overt/disclosed (the participants know they are being studied) or covert/undisclosed (the researcher keeps their real identity a secret from the research subjects, acting as a genuine member of the group).
In general, conducting observational research is relatively inexpensive, but it remains highly time-consuming and resource-intensive in data processing and analysis.
The considerable investments needed in terms of coder time commitments for training, maintaining reliability, preventing drift, and coding complex dynamic interactions place practical barriers on observers with limited resources.
Controlled Observation
Controlled observation is a research method for studying behavior in a carefully controlled and structured environment.
The researcher sets specific conditions, variables, and procedures to systematically observe and measure behavior, allowing for greater control and comparison of different conditions or groups.
The researcher decides where the observation will occur, at what time, with which participants, and in what circumstances, and uses a standardized procedure. Participants are randomly allocated to each independent variable group.
Rather than writing a detailed description of all behavior observed, it is often easier to code behavior according to a previously agreed scale using a behavior schedule (i.e., conducting a structured observation).
The researcher systematically classifies the behavior they observe into distinct categories. Coding might involve numbers or letters to describe a characteristic or the use of a scale to measure behavior intensity.
The categories on the schedule are coded so that the data collected can be easily counted and turned into statistics.
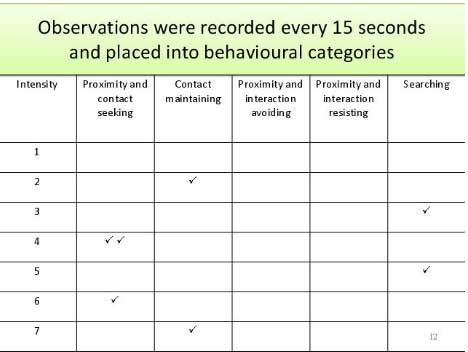
For example, Mary Ainsworth used a behavior schedule to study how infants responded to brief periods of separation from their mothers. During the Strange Situation procedure, the infant’s interaction behaviors directed toward the mother were measured, e.g.,
- Proximity and contact-seeking
- Contact maintaining
- Avoidance of proximity and contact
- Resistance to contact and comforting
The observer noted down the behavior displayed during 15-second intervals and scored the behavior for intensity on a scale of 1 to 7.
Sometimes participants’ behavior is observed through a two-way mirror, or they are secretly filmed. Albert Bandura used this method to study aggression in children (the Bobo doll studies ).
A lot of research has been carried out in sleep laboratories as well. Here, electrodes are attached to the scalp of participants. What is observed are the changes in electrical activity in the brain during sleep ( the machine is called an EEG ).
Controlled observations are usually overt as the researcher explains the research aim to the group so the participants know they are being observed.
Controlled observations are also usually non-participant as the researcher avoids direct contact with the group and keeps a distance (e.g., observing behind a two-way mirror).
- Controlled observations can be easily replicated by other researchers by using the same observation schedule. This means it is easy to test for reliability .
- The data obtained from structured observations is easier and quicker to analyze as it is quantitative (i.e., numerical) – making this a less time-consuming method compared to naturalistic observations.
- Controlled observations are fairly quick to conduct which means that many observations can take place within a short amount of time. This means a large sample can be obtained, resulting in the findings being representative and having the ability to be generalized to a large population.
Limitations
- Controlled observations can lack validity due to the Hawthorne effect /demand characteristics. When participants know they are being watched, they may act differently.
Naturalistic Observation
Naturalistic observation is a research method in which the researcher studies behavior in its natural setting without intervention or manipulation.
It involves observing and recording behavior as it naturally occurs, providing insights into real-life behaviors and interactions in their natural context.
Naturalistic observation is a research method commonly used by psychologists and other social scientists.
This technique involves observing and studying the spontaneous behavior of participants in natural surroundings. The researcher simply records what they see in whatever way they can.
In unstructured observations, the researcher records all relevant behavior with a coding system. There may be too much to record, and the behaviors recorded may not necessarily be the most important, so the approach is usually used as a pilot study to see what type of behaviors would be recorded.
Compared with controlled observations, it is like the difference between studying wild animals in a zoo and studying them in their natural habitat.
With regard to human subjects, Margaret Mead used this method to research the way of life of different tribes living on islands in the South Pacific. Kathy Sylva used it to study children at play by observing their behavior in a playgroup in Oxfordshire.
Collecting Naturalistic Behavioral Data
Technological advances are enabling new, unobtrusive ways of collecting naturalistic behavioral data.
The Electronically Activated Recorder (EAR) is a digital recording device participants can wear to periodically sample ambient sounds, allowing representative sampling of daily experiences (Mehl et al., 2012).
Studies program EARs to record 30-50 second sound snippets multiple times per hour. Although coding the recordings requires extensive resources, EARs can capture spontaneous behaviors like arguments or laughter.
EARs minimize participant reactivity since sampling occurs outside of awareness. This reduces the Hawthorne effect, where people change behavior when observed.
The SenseCam is another wearable device that passively captures images documenting daily activities. Though primarily used in memory research currently (Smith et al., 2014), systematic sampling of environments and behaviors via the SenseCam could enable innovative psychological studies in the future.
- By being able to observe the flow of behavior in its own setting, studies have greater ecological validity.
- Like case studies , naturalistic observation is often used to generate new ideas. Because it gives the researcher the opportunity to study the total situation, it often suggests avenues of inquiry not thought of before.
- The ability to capture actual behaviors as they unfold in real-time, analyze sequential patterns of interactions, measure base rates of behaviors, and examine socially undesirable or complex behaviors that people may not self-report accurately.
- These observations are often conducted on a micro (small) scale and may lack a representative sample (biased in relation to age, gender, social class, or ethnicity). This may result in the findings lacking the ability to generalize to wider society.
- Natural observations are less reliable as other variables cannot be controlled. This makes it difficult for another researcher to repeat the study in exactly the same way.
- Highly time-consuming and resource-intensive during the data coding phase (e.g., training coders, maintaining inter-rater reliability, preventing judgment drift).
- With observations, we do not have manipulations of variables (or control over extraneous variables), meaning cause-and-effect relationships cannot be established.
Participant Observation
Participant observation is a variant of the above (natural observations) but here, the researcher joins in and becomes part of the group they are studying to get a deeper insight into their lives.
If it were research on animals , we would now not only be studying them in their natural habitat but be living alongside them as well!
Leon Festinger used this approach in a famous study into a religious cult that believed that the end of the world was about to occur. He joined the cult and studied how they reacted when the prophecy did not come true.
Participant observations can be either covert or overt. Covert is where the study is carried out “undercover.” The researcher’s real identity and purpose are kept concealed from the group being studied.
The researcher takes a false identity and role, usually posing as a genuine member of the group.
On the other hand, overt is where the researcher reveals his or her true identity and purpose to the group and asks permission to observe.
- It can be difficult to get time/privacy for recording. For example, researchers can’t take notes openly with covert observations as this would blow their cover. This means they must wait until they are alone and rely on their memory. This is a problem as they may forget details and are unlikely to remember direct quotations.
- If the researcher becomes too involved, they may lose objectivity and become biased. There is always the danger that we will “see” what we expect (or want) to see. This problem is because they could selectively report information instead of noting everything they observe. Thus reducing the validity of their data.
Recording of Data
With controlled/structured observation studies, an important decision the researcher has to make is how to classify and record the data. Usually, this will involve a method of sampling.
In most coding systems, codes or ratings are made either per behavioral event or per specified time interval (Bakeman & Quera, 2011).
The three main sampling methods are:
Event-based coding involves identifying and segmenting interactions into meaningful events rather than timed units.
For example, parent-child interactions may be segmented into control or teaching events to code. Interval recording involves dividing interactions into fixed time intervals (e.g., 6-15 seconds) and coding behaviors within each interval (Bakeman & Quera, 2011).
Event recording allows counting event frequency and sequencing while also potentially capturing event duration through timed-event recording. This provides information on time spent on behaviors.
Coding Systems
The coding system should focus on behaviors, patterns, individual characteristics, or relationship qualities that are relevant to the theory guiding the study (Wampler & Harper, 2014).
Codes vary in how much inference is required, from concrete observable behaviors like frequency of eye contact to more abstract concepts like degree of rapport between a therapist and client (Hill & Lambert, 2004). More inference may reduce reliability.
Macroanalytic coding systems
Macroanalytic coding systems involve rating or summarizing behaviors using larger coding units and broader categories that reflect patterns across longer periods of interaction rather than coding small or discrete behavioral acts.
For example, a macroanalytic coding system may rate the overall degree of therapist warmth or level of client engagement globally for an entire therapy session, requiring the coders to summarize and infer these constructs across the interaction rather than coding smaller behavioral units.
These systems require observers to make more inferences (more time-consuming) but can better capture contextual factors, stability over time, and the interdependent nature of behaviors (Carlson & Grotevant, 1987).
Microanalytic coding systems
Microanalytic coding systems involve rating behaviors using smaller, more discrete coding units and categories.
For example, a microanalytic system may code each instance of eye contact or head nodding during a therapy session. These systems code specific, molecular behaviors as they occur moment-to-moment rather than summarizing actions over longer periods.
Microanalytic systems require less inference from coders and allow for analysis of behavioral contingencies and sequential interactions between therapist and client. However, they are more time-consuming and expensive to implement than macroanalytic approaches.
Mesoanalytic coding systems
Mesoanalytic coding systems attempt to balance macro- and micro-analytic approaches.
In contrast to macroanalytic systems that summarize behaviors in larger chunks, mesoanalytic systems use medium-sized coding units that target more specific behaviors or interaction sequences (Bakeman & Quera, 2017).
For example, a mesoanalytic system may code each instance of a particular type of therapist statement or client emotional expression. However, mesoanalytic systems still use larger units than microanalytic approaches coding every speech onset/offset.
The goal of balancing specificity and feasibility makes mesoanalytic systems well-suited for many research questions (Morris et al., 2014). Mesoanalytic codes can preserve some sequential information while remaining efficient enough for studies with adequate but limited resources.
For instance, a mesoanalytic couple interaction coding system could target key behavior patterns like validation sequences without coding turn-by-turn speech.
In this way, mesoanalytic coding allows reasonable reliability and specificity without requiring extensive training or observation. The mid-level focus offers a pragmatic compromise between depth and breadth in analyzing interactions.
Preventing Coder Drift
Coder drift results in a measurement error caused by gradual shifts in how observations get rated according to operational definitions, especially when behavioral codes are not clearly specified.
This type of error creeps in when coders fail to regularly review what precise observations constitute or do not constitute the behaviors being measured.
Preventing drift refers to taking active steps to maintain consistency and minimize changes or deviations in how coders rate or evaluate behaviors over time. Specifically, some key ways to prevent coder drift include:
- Operationalize codes : It is essential that code definitions unambiguously distinguish what interactions represent instances of each coded behavior.
- Ongoing training : Returning to those operational definitions through ongoing training serves to recalibrate coder interpretations and reinforce accurate recognition. Having regular “check-in” sessions where coders practice coding the same interactions allows monitoring that they continue applying codes reliably without gradual shifts in interpretation.
- Using reference videos : Coders periodically coding the same “gold standard” reference videos anchors their judgments and calibrate against original training. Without periodic anchoring to original specifications, coder decisions tend to drift from initial measurement reliability.
- Assessing inter-rater reliability : Statistical tracking that coders maintain high levels of agreement over the course of a study, not just at the start, flags any declines indicating drift. Sustaining inter-rater agreement requires mitigating this common tendency for observer judgment change during intensive, long-term coding tasks.
- Recalibrating through discussion : Having meetings for coders to discuss disagreements openly explores reasons judgment shifts may be occurring over time. Consensus on the application of codes is restored.
- Adjusting unclear codes : If reliability issues persist, revisiting and refining ambiguous code definitions or anchors can eliminate inconsistencies arising from coder confusion.
Essentially, the goal of preventing coder drift is maintaining standardization and minimizing unintentional biases that may slowly alter how observational data gets rated over periods of extensive coding.
Through the upkeep of skills, continuing calibration to benchmarks, and monitoring consistency, researchers can notice and correct for any creeping changes in coder decision-making over time.
Reducing Observer Bias
Observational research is prone to observer biases resulting from coders’ subjective perspectives shaping the interpretation of complex interactions (Burghardt et al., 2012). When coding, personal expectations may unconsciously influence judgments. However, rigorous methods exist to reduce such bias.
Coding Manual
A detailed coding manual minimizes subjectivity by clearly defining what behaviors and interaction dynamics observers should code (Bakeman & Quera, 2011).
High-quality manuals have strong theoretical and empirical grounding, laying out explicit coding procedures and providing rich behavioral examples to anchor code definitions (Lindahl, 2001).
Clear delineation of the frequency, intensity, duration, and type of behaviors constituting each code facilitates reliable judgments and reduces ambiguity for coders. Application risks inconsistency across raters without clarity on how codes translate to observable interaction.
Coder Training
Competent coders require both interpersonal perceptiveness and scientific rigor (Wampler & Harper, 2014). Training thoroughly reviews the theoretical basis for coded constructs and teaches the coding system itself.
Multiple “gold standard” criterion videos demonstrate code ranges that trainees independently apply. Coders then meet weekly to establish reliability of 80% or higher agreement both among themselves and with master criterion coding (Hill & Lambert, 2004).
Ongoing training manages coder drift over time. Revisions to unclear codes may also improve reliability. Both careful selection and investment in rigorous training increase quality control.
Blind Methods
To prevent bias, coders should remain unaware of specific study predictions or participant details (Burghardt et al., 2012). Separate data gathering versus coding teams helps maintain blinding.
Coders should be unaware of study details or participant identities that could bias coding (Burghardt et al., 2012).
Separate teams collecting data versus coding data can reduce bias.
In addition, scheduling procedures can prevent coders from rating data collected directly from participants with whom they have had personal contact. Maintaining coder independence and blinding enhances objectivity.

Bakeman, R., & Quera, V. (2017). Sequential analysis and observational methods for the behavioral sciences. Cambridge University Press.
Burghardt, G. M., Bartmess-LeVasseur, J. N., Browning, S. A., Morrison, K. E., Stec, C. L., Zachau, C. E., & Freeberg, T. M. (2012). Minimizing observer bias in behavioral studies: A review and recommendations. Ethology, 118 (6), 511-517.
Hill, C. E., & Lambert, M. J. (2004). Methodological issues in studying psychotherapy processes and outcomes. In M. J. Lambert (Ed.), Bergin and Garfield’s handbook of psychotherapy and behavior change (5th ed., pp. 84–135). Wiley.
Lindahl, K. M. (2001). Methodological issues in family observational research. In P. K. Kerig & K. M. Lindahl (Eds.), Family observational coding systems: Resources for systemic research (pp. 23–32). Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Mehl, M. R., Robbins, M. L., & Deters, F. G. (2012). Naturalistic observation of health-relevant social processes: The electronically activated recorder methodology in psychosomatics. Psychosomatic Medicine, 74 (4), 410–417.
Morris, A. S., Robinson, L. R., & Eisenberg, N. (2014). Applying a multimethod perspective to the study of developmental psychology. In H. T. Reis & C. M. Judd (Eds.), Handbook of research methods in social and personality psychology (2nd ed., pp. 103–123). Cambridge University Press.
Smith, J. A., Maxwell, S. D., & Johnson, G. (2014). The microstructure of everyday life: Analyzing the complex choreography of daily routines through the automatic capture and processing of wearable sensor data. In B. K. Wiederhold & G. Riva (Eds.), Annual Review of Cybertherapy and Telemedicine 2014: Positive Change with Technology (Vol. 199, pp. 62-64). IOS Press.
Traniello, J. F., & Bakker, T. C. (2015). The integrative study of behavioral interactions across the sciences. In T. K. Shackelford & R. D. Hansen (Eds.), The evolution of sexuality (pp. 119-147). Springer.
Wampler, K. S., & Harper, A. (2014). Observational methods in couple and family assessment. In H. T. Reis & C. M. Judd (Eds.), Handbook of research methods in social and personality psychology (2nd ed., pp. 490–502). Cambridge University Press.
Research Methodologies Guide
- Action Research
- Bibliometrics
- Case Studies
- Content Analysis
- Digital Scholarship This link opens in a new window
- Documentary
- Ethnography
- Focus Groups
- Grounded Theory
- Life Histories/Autobiographies
- Longitudinal
Participant Observation
- Qualitative Research (General)
- Quasi-Experimental Design
- Usability Studies
Participant Observation is
"A method of research in anthropology which involves extended immersion in a culture and participation in its day-to-day activities" (Calhoun, 2002).
This type of research methodology is used in circumstances where an individual wants to observe a group to which they do not belong without altering the behavior of the group because of their involvement. Because of this, before observations can be noted as being "natural," the observer must immerse themselves in the culture or group they are observing. The extent to which the observers' participation affects their results has been debated over time.
For more information on participant observation, review the resources below:
Where to Start
Below are listed a few tools and online guides that can help you start your Participant Observation research. These include free online resources and resources available only through ISU Library.
- Participation Observation Field Guide [pdf] From Duke University, a thorough overview of participant observation.
- Participant Observation by Danny L. Jorgensen Call Number: H62 .J625 1989 While providing an introduction to basic principles and strategies, this volume also explores the philosophy and methodology underlying the actual practice of participant observation. Taking a thoroughly practical approach to the methods of participant observation, Jorgensen illustrates these methods with both classic and current research studies.
Online Resources
- Participant Observation definition From the Social Research Glossary, A thorough explanation, with links to the definitions of terms used and to other people's writings on the subject.
- Participant Observation and Field Notes A guide to participant observation from the Ethnographic Action Research training handbook.
- How to... Use Ethnographic Methods and Participant Observation From Emerald, a journal publisher, in their Research Zone for practicing authors.
- Ethical Challenges in Participant Observation: A Reflection on Ethnographic Fieldwork An article by Jun Li from The Qualitative Report.
- Participant observation--Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Wikipedia can be a useful place to start your research- check the citations at the bottom of the article for more information.
- << Previous: Longitudinal
- Next: Qualitative Research (General) >>
- Last Updated: Dec 19, 2023 2:12 PM
- URL: https://instr.iastate.libguides.com/researchmethods
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Methodology
- What Is Participant Observation? | Definition & Examples
What Is Participant Observation? | Definition & Examples
Published on 10 March 2023 by Tegan George .
Participant observation is a research method where the researcher immerses themself in a particular social setting or group, observing the behaviours, interactions, and practices of the participants. This can be a valuable method for any research project that seeks to understand the experiences of individuals or groups in a particular social context.
In participant observation, the researcher is called a participant-observer , meaning that they participate in the group’s activities while also observing the group’s behaviour and interactions. There is flexibility in the level of participation, ranging from non-participatory (the weakest) to complete participation (the strongest but most intensive.) The goal here is to gain a deep understanding of the group’s culture, beliefs, and practices from an ‘insider’ perspective.
You immerse yourself in this subculture by spending time at skateparks, attending skateboarding events, and engaging with skateboarders. Perhaps you may even learn to skateboard yourself, in order to better understand the experiences of your study participants.
As you observe, you take notes on the behaviour, language, norms, and values you witness and also conduct informal unstructured interviews with individual skateboarders to gain further insight into their thoughts and lived experiences.
Typically used in fields like anthropology, sociology, and other social sciences, this method is often used to gather rich and detailed data about social groups or phenomena through ethnographies or other qualitative research .
Table of contents
When to use participant observation, examples of participant observation, how to analyse data from participant observation, advantages and disadvantages of participant observations, other types of research bias, frequently asked questions.
Participant observation is a type of observational study . Like most observational studies, these are primarily qualitative in nature, used to conduct both explanatory research and exploratory research . Participant observation is also often used in conjunction with other types of research, like interviews and surveys .
This type of study is especially well suited for studying social phenomena that are difficult to observe or measure through other methods. As the researcher observes, they typically take detailed notes about their observations and interactions with the group. These are then analysed to identify patterns and themes using thematic analysis or a similar method.
A participant observation could be a good fit for your research if:
- You are studying subcultures or groups with unique practices or beliefs. Participant observation fosters a deep and intimate understanding of the beliefs, values, and practices of your group or subculture of interest from an insider’s perspective. This can be especially useful when studying marginalised groups or groups that are resistant to observation.
- You are studying complex social interactions . Participant observation can be a powerful tool for studying the complex social interactions that occur within a particular group or community. By immersing yourself in the group and observing these interactions firsthand, you can gain a much more nuanced understanding of how these interactions flow.
- You are studying behaviours or practices that may be difficult to self-report . In some cases, participants may be unwilling or unable to accurately report their own behaviours or practices. Participant observation allows researchers to observe these behaviours directly, allowing for more accuracy in the data collection phase.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Participant observation is a common research method in social sciences, with findings often published in research reports used to inform policymakers or other stakeholders.
Over the course of several months, you observe and take notes on the social interactions, customs, and beliefs of the community members, conducting informal interviews with individual residents to gain further insight into their experiences and perspectives. Through your observations, you gain a deep understanding of the community’s culture, including its values, traditions, and social hierarchy.
Participant observations are often also used in sociology to study social groups and related phenomena, like group formation, stratification, or conflict resolution.
Through this participant observation, you soon see that the group is highly stratified, with certain individuals occupying positions of social power and others being marginalised or even largely excluded. You also observe patterns of conformity within the group, alongside complex interpersonal dynamics.
Data analysis in participant observation typically involves a step-by-step process of immersion, categorisation, and interpretation.
- After finishing up your observations, you read through your field notes or transcripts multiple times in the immersion phase. This helps you reflect on what you studied, and is well paired with conducting data cleansing to ensure everything is clear and correct prior to proceeding.
- You then create categories or themes to organise the data. This helps with identifying patterns, behaviours, and interactions relevant to your research question or study aims. In turn, these categories help you to form a coding system that labels or ‘tags’ the aspects of the data that you want to focus on. These can be specific behaviours, emotions, or social interactions – whatever helps you to identify connections between different elements of your data.
- Next, your data can be analysed using a variety of qualitative research methods, such as thematic analysis , grounded theory, or discourse analysis using the coded categories you created. This helps you interpret the data and develop further theories. You may also want to use triangulation , comparing data from multiple sources or methods, to bolster the reliability and validity of your findings.
- Lastly, it’s always a good research practice to seek feedback on your findings from other researchers in your field of study, as well as members of the group you studied. This helps to ensure the accuracy and reliability of your analysis and can mitigate some potential research biases .
Participant observations are a strong fit for some research projects, but with their advantages come their share of disadvantages as well.
Advantages of participant observations
- Participant observations allow you to generate rich and nuanced qualitative data – particularly useful when seeking to develop a deep understanding of a particular social context or experience. By immersing yourself in the group, you can gain an unrivaled insider perspective on the group’s beliefs, values, and practices.
- Participant observation is a flexible research method that can be adapted to fit a variety of research questions and contexts. Metrics like level of participation in the group, the length of the observation period, and the types of data collected all can be adjusted based on research goals and timeline.
- Participant observation is often used in combination with other research methods, such as interviews or surveys , to provide a more complete picture of the phenomenon being studied. This triangulation can help to improve the reliability and validity of the research findings, as participant observations are not particularly strong as a standalone method.
Disadvantages of participant observations
- Like many observational studies, participant observations are at high risk for many research biases , particularly on the side of the researcher. Because participant observation involves the researcher immersing themselves in the group being studied, there is a risk that their own biases could influence the data they collect, leading to observer bias . Likewise, the presence of a researcher in the group being studied can potentially influence the behaviour of the participants. This can lead to inaccurate or biased data if participants alter their behaviour in response to the researcher’s presence, leading to a Hawthorne effect or social desirability bias .
- Participant observations can be very expensive, time-consuming, and challenging to carry out. They often require a long period of time to build trust and gather sufficient data, with the data usually collected in an intensive, in-person manner. Some participant observations take generations to complete, which can make it difficult to conduct studies with limited time or resources.
- Participant observation can raise ethical concerns , requiring measured ethical consideration on the part of the researcher with regard to informed consent, privacy, and confidentiality. The researcher must take care to protect the privacy and autonomy of the participants and ensure that they are not placed at undue risk by the research.
Cognitive bias
- Confirmation bias
- Baader–Meinhof phenomenon
- Availability heuristic
- Halo effect
- Hindsight bias
- Ingroup bias
- Outgroup bias
- Perception bias
- Framing effect
- Self-serving bias
- Affect heuristic
- Representativeness heuristic
- Anchoring heuristic
- Primacy bias
- Optimism bias
Selection bias
- Sampling bias
- Ascertainment bias
- Attrition bias
- Self-selection bias
- Survivorship bias
- Nonresponse bias
- Undercoverage bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Observer bias
- Omitted variable bias
- Publication bias
- Conformity bias
- Pygmalion effect
- Recall bias
- Social desirability bias
- Placebo effect
- Actor-observer bias
- Ceiling effect
- Ecological fallacy
- Affinity bias
Ethical considerations in participant observation involve:
- Obtaining informed consent from all participants
- Protecting their privacy and confidentiality
- Ensuring that they are not placed at undue risk by the research, and
- Respecting their autonomy and agency as participants
Researchers should also consider the potential impact of their research on the community being studied and take steps to minimize any negative after-effects.
Participant observation is a type of qualitative research method . It involves active participation on the part of the researcher in the group being studied, usually over a longer period of time.
Other qualitative research methods, such as interviews or focus groups , do not involve the same level of immersion in the research and can be conducted in a less intense manner.
In participant observation , the researcher plays an active role in the social phenomenon, group, or social context being studied. They may move into the community, attend events or activities, or even take on specific roles within the group— fully joining the community over the course of the study. However, the researcher also maintains an observer role here, taking notes on the behavior and interactions of the participants to draw conclusions and guide further research.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
George, T. (2023, March 10). What Is Participant Observation? | Definition & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 6 May 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/research-methods/participant-observations/
Is this article helpful?
Tegan George
Other students also liked, ethical considerations in research | types & examples, what is qualitative research | methods & examples, what is an observational study | guide & examples.
Just one more step to your free trial.
.surveysparrow.com
Already using SurveySparrow? Login
By clicking on "Get Started", I agree to the Privacy Policy and Terms of Service .
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
Enterprise Survey Software
Enterprise Survey Software to thrive in your business ecosystem
NPS® Software
Turn customers into promoters
Offline Survey
Real-time data collection, on the move. Go internet-independent.
360 Assessment
Conduct omnidirectional employee assessments. Increase productivity, grow together.
Reputation Management
Turn your existing customers into raving promoters by monitoring online reviews.
Ticket Management
Build loyalty and advocacy by delivering personalized support experiences that matter.
Chatbot for Website
Collect feedback smartly from your website visitors with the engaging Chatbot for website.
Swift, easy, secure. Scalable for your organization.
Executive Dashboard
Customer journey map, craft beautiful surveys, share surveys, gain rich insights, recurring surveys, white label surveys, embedded surveys, conversational forms, mobile-first surveys, audience management, smart surveys, video surveys, secure surveys, api, webhooks, integrations, survey themes, accept payments, custom workflows, all features, customer experience, employee experience, product experience, marketing experience, sales experience, hospitality & travel, market research, saas startup programs, wall of love, success stories, sparrowcast, nps® benchmarks, learning centre, apps & integrations, testimonials.
Our surveys come with superpowers ⚡
Blog Best Of
Participant Observation 101: Definition, Types, Uses, Examples
Kate williams.
13 February 2024
Table Of Contents
What is participant observation?
- The 6 types of participant observation
Where is participant observation used?
5 top participant observation examples.
If you’re planning to use participant observation in research, or just want to brush up on the basics, you’ve come to the right place.
Here’s what we’ll cover in this blog:
- Participant observation: definition
- 6 types of participant observation
- 5 participant observation examples
“But then you must’ve some idea who’s behind it all.”
This line is from ‘Harry Potter: The Chamber of Secrets’. In short, Harry and Ron turn into Goyle and Crabbe (thanks to Hermione’s Polyjuice potion) to see Draco and find out if he’s the heir of Salazar Slytherin. Spoiler if you haven’t read the book: he wasn’t.
But why on earth are we discussing Harry Potter and this scene? Well, because it is a great fictional example of the participant observation method .
Participant observation is a research method where the researcher observes a target audience or group and their day-to-day activities.
The goal of the participant observation method is to study as wide a range of behaviors as possible in a natural, organic setting. As a result, participant observation studies play a vital role in fields that study human behavior – including sociology, psychology, cultural anthropology, and ethnography.
In business, participant observation is defined as qualitative research , and it is helpful for building and marketing better products. You can use it in combination with survey tools like SurveySparrow to collect and visualize the results of your research in real-time.
You can access 1000+ templates and survey tools that will scale up your research by signing up below. Bonus: you will also get complete access to all of our features for 14 days.
Market Research Survey Template
What are the 6 types of participant observation, #1. passive participant observation.
In the passive participant observation method, the researchers observe and record participant behavior without actively involving themselves in the situation. They don’t interact or converse with the participants, and the observation is often done without the participants’ knowledge.
Example : Observing people in public places, like parks, cafés, malls, transport hubs, and even social media. Stuff taken directly out of a detective’s book, won’t you agree?
- Pros: It brings rich data without being intrusive or disturbing the participant’s normal routine.
- Cons : It can potentially violate a person’s privacy because they are not able to give informed consent.
#2. Active participant observation
In the active form of participant observation, the researchers speak with the participants and immerse themselves in their lives. With this, the researcher finds information about their activities, habits, interests, and even goals. Some researchers limit their participation to interviewing the subjects, while others immerse themselves in experiencing the life of their target group.
Example : Research that goes on for a long period – like an anthropologist living in an indigenous community to study a set of their customs and culture.
- Pros : The researcher can get access to rare nuggets of information from living as part of the target group.
- Cons: Reactivity, or change of behavior by the participants because they know they are under observation, can affect the findings.
#3. Covert-active participant observation
Covert participant observation is when the researcher goes undercover. In other words, the researchers assume the identity of their target group. They conceal their true identity for the duration of the study, and the target group is unaware that they are being studied. In the active form of this participant observation method, the researchers experience all practices as experienced by everyone in the group.
Example : This 2009 study of football hooliganism was based on covert active research on Blackpool FC supporters during the 90s.
- Pros : Gaining access to closed groups is easier as the researcher doesn’t need to get permission.
- Cons: The researcher is under constant pressure to maintain their alternate identity and record data at the same time.
#4. Covert-passive participant observation
In the passive form of covert research, the investigator does not attempt to deceive or mislead participants. Traditionally, the most common example of this type of covert research has involved observation of activity in public places such as shopping malls, parks, restaurants, etc., or virtual communities and forums.
Example: A researcher observes and monitors online interactions of other members in a subreddit, but chooses not to contribute or provide a public explanation of their research.
- Pros : This method is helpful for observation in places which people inhabit for short periods, and where social interactions are minimal.
- Cons: Due to the time constraints, this method may offer only limited information on certain topics.
#5. Overt-active participant observation
In the overt observation type, the researcher becomes a full member of their target group…but the group knows they are doing research. The active form of overt observation lets the researcher take part in the group’s daily activities.
Example: Many ethnographic studies, like this study of an elite high school in Concord, New Hampshire , use overt-active observation.
- Pros : This is the most ethical type of observation because participants can give their informed consent, and deception isn’t necessary.
- Cons: The researcher can still unwittingly influence what’s happening in the group.
#6. Overt-passive participant observation
Here, the target group knows about the researcher. However, the researcher plays no part in their activities. He’s just a silent observer, observing the practices followed by all participants. So, no participant feels his presence.
Example: When a researcher joins employees for meetings but doesn’t interfere in any way.
- Pros : This method can be combined with 1:1 interviews and surveys to get more insight on the perspectives of different people involved.
- Cons: Even when the researcher is not actively interacting, the subjects might still alter their behavior because they know a person is observing them.
The use of participant observation as a qualitative research method lies in multiple sectors and industries. However, there are 4 main areas that use participation observation. Let’s talk about them:
#1. Market research
Organizations of all shapes and sizes use participant observation for conducting market research. They share a targeted market research survey with people, and the survey organizers analyze the responses to find relevant patterns. Read how you can create the perfect market research survey that gets the job done.
In fact, the organizer doesn’t directly involve himself in the audience’s shoes. They observe and record subject behaviors through their responses to the survey. Yes, you guessed it right! Passive participation observation is how things are done here.
#2. Sociological research
Almost all the discussed participant observation methods (types) are used extensively in sociological research. Here, human behaviors and cultures are studied based on their social interactions. The researchers use this observation method for participating in activities and performing critical analysis based on their communication with them.
Sociological research using participant observation can be short or even long-term research, where there’s free will to find relevant patterns over an extended period.
#3. Campaigns & events
“I don’t know which way the result is gonna swing. Oh god, I’m so nervous!”
Are you this guy before the results of a campaign are announced?
Well, come on… don’t get all tensed up. Know your audience beforehand using participant observation, and you’ll have a fair idea of which way the tide is going. Political campaigns, organizational events, college elections. You name it. This qualitative research method is the way to do it.
#4. Mental health
The Covid-19 pandemic was a big wake-up call that mental health is just as important as physical. There were lots of cases of employee dissatisfaction leading to deteriorated mental well-being. Organizations, globally, have done a fantastic job of raising mental health awareness, and participant observation played (and still plays) a significant role in that.
There were many cases of HR teams engaging with employees and participating in activities to understand their satisfaction levels. Similarly, interactions with people suffering from mental health issues helped find the root cause. Both of these participant observation methods focused on direct interactions with the target group and stepping into their shoes to find the problem areas. It worked!
Top published participant observation examples are the best way to recognize the importance of this research method even more. So with no further ado, time to let the cat out of the bag.
#1. The ethnography of an elite high school
Most of the ethnographic work we see is around minority communities and the poor. However, this qualitative research example mentioned above gained immense attention as it focused on finding a scientific description of students’ culture and customs from an elite high school.
The researcher, Shamus Khan, used the open and active participant observation method to get a job at the school, move into an apartment on the campus, and observe the daily routines of students. While this observation went on, the researcher took part in most activities of the target group and interviewed them on his questions relating to the research.
Once he had got the answers, he found relevant patterns that led to many revelations about the cultures followed and habits developed in an elite school. All of those findings are here in this book .
#2. Observing social activism & migrants
One of the best places for participant observation usage is to study what’s causing social activism to rise and a specific group of people to migrate.
In most cases, like in this case , too, they performed the observation discreetly, where the researcher stayed covert but kept interacting with all participants. As a result, the what, why, how, and when are answered well this way.
#3. Top athlete’s behavior
People always look upon top athletes as ideals, and role models to follow. For instance, they wish to know their routine, diet, and training. More research is always ongoing on that front, and most of them use participant observation for it.
So a researcher conducts covert observation on them to learn about their behavior and entire routine. The participating observer becomes involved with an athlete as a student interested in the sport. This way, he doesn’t have to participate in the game. Hence they can observe and ask athletes about their curiosities (questions).
The other way is when athletes know you’re the observer, and they’re willing to give answers. You can take part with them actively in a ‘day in the life of…’ manner and fire away your questions to understand what makes them a top player.
Then, there are ‘investigations’ being conducted on players to find how they are in real life, away from the sport. For this, the observer stays covert, spending time spotting differences in behavior both on and off the pitch. To achieve that, the observer should gain the athlete’s group trust to get more accurate information, and that takes time.
#4. Studying regional challenges
Lora-Wainwright studied the challenge of the severe population in rural China from 2009 until 2013 using participant observation. The main agenda of her research was to find how people there coped with it, knowing its detrimental effect on their health.
For this, she observed three villages that were coping with large-scale industrial pollution. Notably, Lora focused on finding how people responded after knowing the risk of cancer from this pollution, how they organized themselves to protest, and how they coped with it every day, as polluted water was hampering people’s health in these villages.
Moreover, her focus was also on the Chinese government’s inability to curb this pollution and its industrialization agenda. She has written a book about it, currently under revision, but this podcast summarizes all her findings. Check it out.

#5. Understanding an industry
Conducting market research is a great way to do it, and we’ve already talked about how participant observation is used there. But it’s done in a fun way, too!
For instance, Helen Sampson boarded her first cargo ship as she wanted to understand a great deal about how the shipping industry worked. She had her doubts about the journey, but the seafarers welcomed her well. They all knew she was here for research. Yet, they helped her, took part in her interviews, and gave her quality insights into the industry and the cargo ship.
It was one helluva ride for her, and this research won Thinking Allowed’s first ethnography award in 2014. You’ll find the summary of this research at the end of the show.
Wrapping Up
Any product, service, or offering becomes a resounding success when it clicks with its intended market. Otherwise, it loses its shine and ends on a low. For that to not happen, market research is critical, and even more crucial is deciding how the research will be conducted.
Here, we’ve given a strong case for participant observation. And although there are other qualitative methods, too, this one gets our support.
At SurveySparrow, we’ve helped conduct many market research surveys in multiple sectors that collected crucial data. We would love to help you with it too. Get in touch with us and let us know your requirements, and we’ll contact you ASAP.
Or, you can go ahead and try it out first. It’s free!
Please enter a valid Email ID.
14-Day Free Trial • No Credit Card Required • No Strings Attached
Content Marketer at SurveySparrow
You Might Also Like
20 ways to successfully implement virtual employee engagement in 2024, how to make a poll on google forms a complete guide, customer is king but customer service is the god | great customer service, cherry-picked blog posts. the best of the best..
Leave us your email, we wont spam. Promise!
Start your free trial today
No Credit Card Required. 14-Day Free Trial
Request a Demo
Want to learn more about SurveySparrow? We'll be in touch soon!
14-Day Free Trial • No Credit card required • 40% more completion rate
Hi there, we use cookies to offer you a better browsing experience and to analyze site traffic. By continuing to use our website, you consent to the use of these cookies. Learn More
Qualitative Research: Participant Observation
- First Online: 23 November 2016
Cite this chapter

- Patric Finkbeiner 2
1149 Accesses
The first phase of this ESD consists of the qualitative methods for gathering data.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
- Durable hardcover edition
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
This checklist is based on major predictors found in literature.
Almost completely subjective, this approach amounts to a nearly live-in method. It is applied to gain generalizations about living styles (Collins 1991).
He observed the natives of the Trobriand Islands in the South Pacific from 1915 to 1918.
Main article about her research: Coming of Age in Samoa which was foreworded by Franz Boas, the so-called founding father of American anthropology.
Daimler as well as Porsche, part of VW Group, have their headquarters in Stuttgart. BMW and Audi operate major subsidiaries in this region.
Owner–master–mechanic ( German : Geselle similar to: “fellow of a guild”)—trainee (applicant for being a fellow of the guild).
All names used are fictive names and do not have a direct link to the observation.
Chris is a fictive name; names cannot be attributed to any observed participant.
In all workshops observed.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Stuttgart, Germany
Patric Finkbeiner
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Patric Finkbeiner .
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2017 Springer International Publishing AG
About this chapter
Finkbeiner, P. (2017). Qualitative Research: Participant Observation. In: Social Media for Knowledge Sharing in Automotive Repair. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-48544-7_5
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-48544-7_5
Published : 23 November 2016
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-319-48543-0
Online ISBN : 978-3-319-48544-7
eBook Packages : Engineering Engineering (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
ReviseSociology
A level sociology revision – education, families, research methods, crime and deviance and more!
Participant Observation in Social Research
Participant Observation is a qualitative research method in which the researcher joins in with the group under investigation. This post explores the theoretical, practical and ethical advantages and disadvantages of participant observation
Table of Contents
Last Updated on October 12, 2022 by
Participant Observation is where the researcher joins in with the group being studied and observes their behaviour. This post covers the theoretical, practical and ethical strengths and limitations of using overt and covert participant observation in social research.
It has been written primarily for students studying the research methods aspect of A-level sociology.

Participant observation is closely related to the ethnographic method (or ‘ethnography’), which consists of an in-depth study of the way of life of a group of people.
Ethnography is traditionally associated with anthropology , wherein the anthropologist visits a (usually) foreign land, gains access to a group (for example a tribe or village), and spends several years living with them with the aim of uncovering their culture. The ethnographic method involves watching what participants do, listening to them, engaging in probing conversations, and joining them in day to day tasks as necessary; it also involves investigating any cultural artefacts such as art work and any written work if it exists, as well as analysing what religious rituals and popular stories can tell us about the culture. Ethnographic research has traditionally involved taking copious field notes, and the resulting ‘monographs’ which are produced can take several months, if not a year or more to write up.
To cut a long winded definition short, ethnography is basically the same as participant observation, but includes the writing up of a detailed account of one’s findings:
Ethnography = participant observation + a detailed written account of one’s findings.
Participant Observation and the use of other methods
Most participant observers (or ‘ethnographers’) will combine their observations with other methods – most obviously unstructured interviews, and some will combine them with more formal questionnaire based research, normally towards the end of their study period, meaning many of these studies are actually mixed-methods studies. Nonetheless, Participant Observation is still technically classified, for the purposes of A-level sociology as a ‘qualitative’ method.
Overt and Covert Observation
An important distinction in Participation/ Ethnography is between covert and over observation.
- Overt Observation – this is where the group being studied know they are being observed.
- Covert Observation – this where the group being studied does not know they are being observed, or where the research goes ‘undercover’.
These both have their strengths and limitations – overt research is obviously more ethical because of the lack of deception, and it allows the researcher to ask probing questions and use other research methods. Covert research may be the only way to gain access to deviant groups, it may enable you to gain fuller ‘immersion’ into the host culture and avoids the ‘Hawthorne Effect’. However, ethically it involves deception and can be very stressful for the researcher.
The Strengths of Participant Observation
Theoretical advantages.
The most significant strength of both types of participant observation is the high degree of validity the method achieves. There are at least five reasons for this:

You can observe what people do, not what they say they do – In contrast to most other methods, participant observation allows the researcher to see what people do rather than what people say they do.
Participant Observation takes place in natural settings – this should mean respondents act more naturally than in a laboratory, or during a more formal interview. This should mean the Hawthorne effect will be less, especially with covert research. You also get more of a feel for respondents’ actions in context, which might otherwise seem out of place if in an artificial research environment.
Digging deep and gaining insight – the length of time ethnographers spend with a community means that close bonds that can be established, thus enabling the researcher to dig deeper than with other methods and find out things which may be hidden to all other means of enquiry.
Verstehen/empathetic understanding– participant observation allows the researcher to fully join the group and to see things through the eyes (and actions) of the people in group. Joining in allows the researcher to gain empathy through personal experiences. This closeness to people’s reality means that participant observation can give uniquely personal, authentic data.
Flexibility and generating new ideas – when completing questionnaires researchers begin with pre-set questions. Even before starting to collect the data, therefore, the researchers have decided what’s important. The problem with this is what if the questions the researcher thinks are important are not the same as the ones the subject thinks are important. By contrast, participant observation is much more flexible. It allows the researcher to enter the situation with an open mind and as new situations are encountered they can be followed up.
Practical Advantages
There are few practical advantages with this method, but participant observation might be the only methods for gaining access to certain groups. For example, a researcher using questionnaires to research street gangs is likely to be seen as an authority figure and unlikely to be accepted.
Ethical Advantages
Interpretivists prefer this method because it is respondent led – it allows respondents to speak for themselves and thus avoids a master-client relationship which you get with more quantitative methods.
The Limitations of Participant Observation
Theoretical disadvantages.
One theoretical disadvantage is the low degree of reliability. It would be almost impossible for another researcher to repeat given that a participant observation study relies on the personal skills and characteristics of the lone researcher.
Another theoretical disadvantage is the low degree of representativeness. Sociologists who use quantitative research methods study large, carefully selected, representative samples that provide a sound basis for making generalisations, In contrast, the groups used in participant observation studies are usually unrepresentative, because they are accessed through snowball sampling and thus haphazardly selected.
Critics also question how valid participant observation really is. They argue the method lacks objectivity. It can be very difficult for the researcher to avoid subjectivity and forming biased views of the group being studied. Also researchers decide what is significant and worth recording and what’s not, therefore, it depends on the values of the researcher. In extreme cases, researchers might ‘go native’, where they become sympathatic with the respondents and omit any negative analysis of their way of life.
A further threat to validity is the Hawthorne Effect, where people act differently because they know they are being observed, although participant observers would counter this by saying that people can’t keep up an act over long time periods: they will eventually relax and be themselves.
Also, the methods lack a concept of social structures such as class, gender or ethnicity. By focussing on the participants own interpretation of events, the researcher tends to ignore the wider social structures, which means giving only a partial explanation.
Practical Disadvantages
Firstly, this method tends to be time consuming and expensive in relation to the relatively small amount of respondents. It can take time to gain trust and build rapport, and so for this reason, it may take several days, weeks or even months, before the respondents really start to relax in the presence of the researcher.
Participant Observation also requires observational and interpersonal skills that not everyone possesses – you have to be able to get on with people and understand when to take a back seat and when to probe for information.
Gaining access can also be a problem – many people will not want to be researched this way, and where covert research is concerned, researchers are limited by their own characteristics. Not everyone can pass as a Hells Angel if covert observation is being used!
Ethical Disadvantages
Ethical problems are mainly limited to Covert Participant Observation, in which respondents are deceived and thus cannot give informed consent to participate in the research.
Legality can also be an issue in covert research where researchers working with deviant groups may have to do illegal acts to maintain their cover.
Some advantages of Overt compared to Covert Observation
Students often think that Covert Observation is superior to Over Observation, however there are five reasons why Overt might be a better choice of research method:
1. You can ask awkward, probing questions
2. You can combine it with other methods
3. You can take on the role of the ‘professional stranger’ – respondents might tell you things because they know you are not ‘one of them’
4. It is less stressful and risky for the researcher
5. It is easier to do follow up studies.
Related Posts
Some recent examples of PO studies within sociology
Learning to Labour by Paul Willis – A Summary
Please click here to return to the homepage – ReviseSociology.com
Bryman (2016) Social Research Methods
Chapman et al (2016) Sociology AQA A-level Year 1 and AS Student Book
Share this:
- Share on Tumblr
10 thoughts on “Participant Observation in Social Research”
Thanks for your comment I will take that under consideration!
More explanations about the factors that affect validity and reliability in studies would be very useful
Thanks, and you are most welcome!
Very very helpful. #lifesaviour
- Pingback: The strengths and limitations of covert participant observation | ReviseSociology
- Pingback: Some (Relatively) Recent Examples of Participant Observation Studies | ReviseSociology
- Pingback: How I would’ve answered A level sociology paper 3: crime and deviance with theory and methods, June 2017 | ReviseSociology
- Pingback: Participant Observation – Essay Plan | ReviseSociology
- Pingback: Learning to Labour by Paul Willis – Summary and Evaluation of Research Methods | ReviseSociology
- Pingback: Methods in Context Essay Template | ReviseSociology
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Discover more from ReviseSociology
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Continue reading


Participant Observation

Meet Dr Mwenza Blell , a biosocial medical anthropologist who has done quantitative, qualitative, and mixed methods work, including ethnographic research and participant observation.
Meet Profesor Suzanne Moffatt , who primarily uses qualitative research methods, including participant observation.
Participant observation is the study of individuals, communities or groups in ‘the field’ to gain an understanding of their lived experience. As Boccagni and Schrooten (2018: 212) note, participant observation is “an embodied and extended presence in the social world of those being studied. Social life as it is being lived, rather than only as it is reported by informants (often in ephemeral, artificial or ad-hoc settings), is its fundamental concern.” Closely observing patterns, norms, attitudes and practices can enable the researcher to become immersed within the group and therefore gain a deeper understanding of the phenomena being studied. Participant observation is widely used in many disciplines such as sociology, cultural anthropology and human geography. Other research areas that use participant observation include healthcare and gerontology (Graham, 2017), creative arts practice (Lainé, 2015) and migration studies (Boccagni and Schrooten, 2018).
Participant observation and ethnography are terms often used interchangeably however hold two distinct traditions. While ethnography is a broad methodological approach, participant observation is a distinct method that can be utilised within ethnographic study. Other related research methods include direct observation, which typically requires less interaction between the ‘observer’ and the ‘observed’ and is used within fields such as psychology (Hintze, 2019) and public health (Catchpole et al, 2019).
Participant observation often requires a level of organisation and record-taking within the field. Typically, the researcher generates material ‘in the moment’ with a view to systematically organising and analysing it at a later date. This can be done by taking notes, photographs and sound, asking questions and collecting objects. The length of time one needs to spend in the field varies according to the research context and can take between days, months or years.
There is significant skill involved in engaging with participants and groups naturally and authentically whist sensitively collecting relevant data. With this in mind, there are many ethical considerations when using participant observation such as the impact of the researcher-participant relationship, maintaining informed consent and protecting the anonymity of participants (Kawulich, 2005).
- Agata Jalosinska – Doctoral Researcher, Open Lab
- Dr Bruce Davenport, Research Associate, School of Arts and Cultures
- Dr Clifton Evers – Senior Lecturer in Media and Cultural Studies
- Gemma Molyneux – Doctoral Researcher, Sociology
- Dr Menelaos Gkartzios – Reader in Planning & Rural Development
- Dr Mwenza Blell – Rutherford Fellow & NUAcT Fellow
- Dr Sarah Winkler-Reid – Lecturer in Social Anthropology
An in-depth guide to participant observation by SAGE can be found here .
- Boccagni, P., and Schrooten, M., (2018). Participant Observation in Migration Studies: An Overview and Some Emerging Issues. In: R. Zapata-Barrero and E. Yalaz. Eds. Qualitative Research in European Migration Studies , New York: Springer. Ch.12.
- Catchpole, K., Neyens, D.M., Abernathy, J., Allison, D., Joseph, A., and Reeves, S.T., (2019). Framework for direct observation of performance and safety in healthcare, BMJ Qual Saf , 26(12), pp.1015-1021.
- Graham, M.E., (2017) Arts-Inspired Participant Observation in Ethnographic Fieldwork: Researching the Experience of Movement in Long-Term Care. In: SAGE Research Methods Cases. https://www.doi.org/10.4135/9781526422644 .
- Hintze, J.M., (2019). Psychometrics of Direct Observation, School Psychology Review , 34(40), pp.507-519.
- Lainé, A., (2015) ‘Participatory Art and Participant Observation: Exploring Social Relationships through Interdisciplinary Practices’, Transvaluation Symposium 2015, Sweden.
- Kawulich, B., (2005) Participant Observation as a Data Collection Method, Forum: Qualitative Social Research , 6(2), Art.43.

What Is Participant Observation Research?
Understanding an Important Qualitative Research Method
Zero Creatives / Getty Images
- Research, Samples, and Statistics
- Key Concepts
- Major Sociologists
- News & Issues
- Recommended Reading
- Archaeology
The participant observation method, also known as ethnographic research , is when a sociologist actually becomes a part of the group they are studying in order to collect data and understand a social phenomenon or problem. During participant observation, the researcher works to play two separate roles at the same time: subjective participant and objective observer. Sometimes, though not always, the group is aware that the sociologist is studying them.
The goal of participant observation is to gain a deep understanding and familiarity with a certain group of individuals, their values, beliefs, and way of life. Often the group in focus is a subculture of a greater society, like a religious, occupational, or particular community group. To conduct participant observation, the researcher often lives within the group, becomes a part of it, and lives as a group member for an extended period of time, allowing them access to the intimate details and goings-on of the group and their community.
This research method was pioneered by anthropologists Bronislaw Malinowski and Franz Boas but was adopted as a primary research method by many sociologists affiliated with the Chicago School of Sociology in the early twentieth century . Today, participant observation, or ethnography, is a primary research method practiced by qualitative sociologists around the world.
Subjective Versus Objective Participation
Participant observation requires the researcher to be a subjective participant in the sense that they use knowledge gained through personal involvement with the research subjects to interact with and gain further access to the group. This component supplies a dimension of information that is lacking in survey data . Participant observation research also requires the researcher to aim to be an objective observer and record everything that he or she has seen, not letting feelings and emotions influence their observations and findings.
Yet, most researchers recognize that true objectivity is an ideal, not an actuality, given that the way in which we see the world and people in it is always shaped by our previous experiences and our positionality in the social structure relative to others. As such, a good participant observer will also maintain a critical self-reflexivity that allows her to recognize the way she herself might influence the field of research and the data she collects.
Strengths and Weaknesses
The strengths of participant observation include the depth of knowledge that it allows the researcher to obtain and the perspective of knowledge of social problems and phenomena generated from the level of the everyday lives of those experiencing them. Many consider this an egalitarian research method because it centers the experiences, perspectives, and knowledge of those studied. This type of research has been the source of some of the most striking and valuable studies in sociology.
Some drawbacks or weaknesses of this method are that it is very time-consuming, with researchers spending months or years living in the place of study. Because of this, participant observation can yield a vast amount of data that might be overwhelming to comb through and analyze. And, researchers must be careful to remain somewhat detached as observers, especially as time passes and they become an accepted part of the group, adopting its habits, ways of life, and perspectives. Questions about objectivity and ethics were raised about sociologist Alice Goffman's research methods because some interpreted passages from her book " On the Run " as an admission of involvement in a murder conspiracy.
Students wishing to conduct participant observation research should consult two excellent books on the subject: " Writing Ethnographic Fieldnotes " by Emerson et al., and " Analyzing Social Settings ", by Lofland and Lofland.
- What Is Ethnography?
- An Overview of Qualitative Research Methods
- Anthropology vs. Sociology: What's the Difference?
- How to Understand Interpretive Sociology
- Understanding Secondary Data and How to Use It in Research
- Definition of Idiographic and Nomothetic
- Defining Unobtrusive Measures in Sociology Experiments
- An Introduction to Cultural Anthropology
- Macro- and Microsociology
- Biography of Patricia Hill Collins, Esteemed Sociologist
- How to Conduct a Sociology Research Interview
- A Biography of Erving Goffman
- What Is Naturalistic Observation? Definition and Examples
- Immersion Definition: Cultural, Language, and Virtual
- Definition of Aggregate and Social Aggregate
- Applied and Clinical Sociology
Breadcrumbs
Participant Observation
Participant observation methodology.
Participant observation (PO) is a research methodology where the researcher is immersed in the day-to-day activities of the participants. The objective is usually to record conduct under the widest range of possible settings. In this way, PO differs from naturalistic observation, because the latter does not involve interaction between the researcher and participants. PO was historically associated with a form of research in which the researcher resides for extended periods of time in a small community. Currently, PO is used in a wide variety of settings, and over varied periods of time, from single interactions to many years.
The methodology has several inherent characteristics that may lead to ethical issues if not properly understood. These include the following.
- The often long term nature of the interface between researcher and participants
- The wide range of relationship dynamics, such as status differences between the two parties, power differences and educational differences, as well as degrees of formality. Power differentials may be rooted in gender, class, health and other aspects
- The variety of settings, from close interpersonal interactions to observation of public meetings and actual participation in social events
- In many cases, the research will be taking place in settings that are unfamiliar to the researcher, making her/his presentation of self and interaction with others especially sensitive
- The ethical codes of the groups under study may well be different from those of the researcher’s home country/home institution. They may also be different from the ethical principles followed by the host government, non-governmental organizations in the area, or funding agencies for the research
- The potentially changing nature of the researcher’s roles and relationships over time
- The use of technology to document observations, including mapping, photography, video- and audio-recording
Ethical Conduct
To conduct PO ethically, it is important that researchers reflect on the general principles of Tri-council Policy Statement: Ethical Conduct for Research Involving Humans (TCPS) and how they can best be implemented in the context of PO. In completing the ethics protocol, they should consider the following.
Methodology: Researchers should fully explain the setting(s) for PO, what potential interactions are involved, how data will be gathered, the kinds of issues that might be discussed more formally, and detail as much as possible the anticipated process. It is fine to acknowledge the limitations of predicting ahead of time what will happen during the research, but details that can be anticipated should be stated
Participants: Describe the people and reflect on potential ethical issues that may arise in the context of the research. It is acceptable to disregard issues of sample size and inclusion/exclusion criteria unless these are relevant to your methods. The researcher should also explain how s/he plans to enter the field and make people more familiar with his/her presence and the nature of the research project
Potential harms: The researcher should expand as much as possible on the extent and variety of potential harm to participants, recognizing that these will primarily involve social, legal or psychological harms, depending on the nature of the research and the vulnerability of the group. The repercussions of breaching confidentiality may be greatly tied to risk of harm
Privacy and confidentiality: The researcher should provide information about how he/she will safeguard data once collected and treat sensitive information. This should be in line with data security requirements outlined in other University policies and guidelines. If there is a foreseeable risk that information may be requested by third parties, the researcher should discuss how s/he would respond to such a request
Informed consent: The researcher should elaborate on the appropriateness of a particular informed consent process (written or verbal) for the setting/group studied and should include means of informing the community/group/individuals of the researcher’s identity, purpose, topic of research and method; appropriateness of seeking consent from group leaders or spokespersons; informal/formal means of obtaining informed consent, relative to what is appropriate in the given setting. It is important to clearly explain ethical dilemmas that might arise, or limitations to ideal procedures in given contexts

VPRI Contact
Dean sharpe.

Other Resources
Tri-council Policy Statement: Ethical Conduct for Research Involving Humans >
Back To Top

You are invited to provide feedback about the services and support you recently received from VPRI. You need valid UTORid credentials to access the feedback form.


Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Non-Experimental Research
32 Observational Research
Learning objectives.
- List the various types of observational research methods and distinguish between each.
- Describe the strengths and weakness of each observational research method.
What Is Observational Research?
The term observational research is used to refer to several different types of non-experimental studies in which behavior is systematically observed and recorded. The goal of observational research is to describe a variable or set of variables. More generally, the goal is to obtain a snapshot of specific characteristics of an individual, group, or setting. As described previously, observational research is non-experimental because nothing is manipulated or controlled, and as such we cannot arrive at causal conclusions using this approach. The data that are collected in observational research studies are often qualitative in nature but they may also be quantitative or both (mixed-methods). There are several different types of observational methods that will be described below.
Naturalistic Observation
Naturalistic observation is an observational method that involves observing people’s behavior in the environment in which it typically occurs. Thus naturalistic observation is a type of field research (as opposed to a type of laboratory research). Jane Goodall’s famous research on chimpanzees is a classic example of naturalistic observation. Dr. Goodall spent three decades observing chimpanzees in their natural environment in East Africa. She examined such things as chimpanzee’s social structure, mating patterns, gender roles, family structure, and care of offspring by observing them in the wild. However, naturalistic observation could more simply involve observing shoppers in a grocery store, children on a school playground, or psychiatric inpatients in their wards. Researchers engaged in naturalistic observation usually make their observations as unobtrusively as possible so that participants are not aware that they are being studied. Such an approach is called disguised naturalistic observation . Ethically, this method is considered to be acceptable if the participants remain anonymous and the behavior occurs in a public setting where people would not normally have an expectation of privacy. Grocery shoppers putting items into their shopping carts, for example, are engaged in public behavior that is easily observable by store employees and other shoppers. For this reason, most researchers would consider it ethically acceptable to observe them for a study. On the other hand, one of the arguments against the ethicality of the naturalistic observation of “bathroom behavior” discussed earlier in the book is that people have a reasonable expectation of privacy even in a public restroom and that this expectation was violated.
In cases where it is not ethical or practical to conduct disguised naturalistic observation, researchers can conduct undisguised naturalistic observation where the participants are made aware of the researcher presence and monitoring of their behavior. However, one concern with undisguised naturalistic observation is reactivity. Reactivity refers to when a measure changes participants’ behavior. In the case of undisguised naturalistic observation, the concern with reactivity is that when people know they are being observed and studied, they may act differently than they normally would. This type of reactivity is known as the Hawthorne effect . For instance, you may act much differently in a bar if you know that someone is observing you and recording your behaviors and this would invalidate the study. So disguised observation is less reactive and therefore can have higher validity because people are not aware that their behaviors are being observed and recorded. However, we now know that people often become used to being observed and with time they begin to behave naturally in the researcher’s presence. In other words, over time people habituate to being observed. Think about reality shows like Big Brother or Survivor where people are constantly being observed and recorded. While they may be on their best behavior at first, in a fairly short amount of time they are flirting, having sex, wearing next to nothing, screaming at each other, and occasionally behaving in ways that are embarrassing.
Participant Observation
Another approach to data collection in observational research is participant observation. In participant observation , researchers become active participants in the group or situation they are studying. Participant observation is very similar to naturalistic observation in that it involves observing people’s behavior in the environment in which it typically occurs. As with naturalistic observation, the data that are collected can include interviews (usually unstructured), notes based on their observations and interactions, documents, photographs, and other artifacts. The only difference between naturalistic observation and participant observation is that researchers engaged in participant observation become active members of the group or situations they are studying. The basic rationale for participant observation is that there may be important information that is only accessible to, or can be interpreted only by, someone who is an active participant in the group or situation. Like naturalistic observation, participant observation can be either disguised or undisguised. In disguised participant observation , the researchers pretend to be members of the social group they are observing and conceal their true identity as researchers.
In a famous example of disguised participant observation, Leon Festinger and his colleagues infiltrated a doomsday cult known as the Seekers, whose members believed that the apocalypse would occur on December 21, 1954. Interested in studying how members of the group would cope psychologically when the prophecy inevitably failed, they carefully recorded the events and reactions of the cult members in the days before and after the supposed end of the world. Unsurprisingly, the cult members did not give up their belief but instead convinced themselves that it was their faith and efforts that saved the world from destruction. Festinger and his colleagues later published a book about this experience, which they used to illustrate the theory of cognitive dissonance (Festinger, Riecken, & Schachter, 1956) [1] .
In contrast with undisguised participant observation , the researchers become a part of the group they are studying and they disclose their true identity as researchers to the group under investigation. Once again there are important ethical issues to consider with disguised participant observation. First no informed consent can be obtained and second deception is being used. The researcher is deceiving the participants by intentionally withholding information about their motivations for being a part of the social group they are studying. But sometimes disguised participation is the only way to access a protective group (like a cult). Further, disguised participant observation is less prone to reactivity than undisguised participant observation.
Rosenhan’s study (1973) [2] of the experience of people in a psychiatric ward would be considered disguised participant observation because Rosenhan and his pseudopatients were admitted into psychiatric hospitals on the pretense of being patients so that they could observe the way that psychiatric patients are treated by staff. The staff and other patients were unaware of their true identities as researchers.
Another example of participant observation comes from a study by sociologist Amy Wilkins on a university-based religious organization that emphasized how happy its members were (Wilkins, 2008) [3] . Wilkins spent 12 months attending and participating in the group’s meetings and social events, and she interviewed several group members. In her study, Wilkins identified several ways in which the group “enforced” happiness—for example, by continually talking about happiness, discouraging the expression of negative emotions, and using happiness as a way to distinguish themselves from other groups.
One of the primary benefits of participant observation is that the researchers are in a much better position to understand the viewpoint and experiences of the people they are studying when they are a part of the social group. The primary limitation with this approach is that the mere presence of the observer could affect the behavior of the people being observed. While this is also a concern with naturalistic observation, additional concerns arise when researchers become active members of the social group they are studying because that they may change the social dynamics and/or influence the behavior of the people they are studying. Similarly, if the researcher acts as a participant observer there can be concerns with biases resulting from developing relationships with the participants. Concretely, the researcher may become less objective resulting in more experimenter bias.
Structured Observation
Another observational method is structured observation . Here the investigator makes careful observations of one or more specific behaviors in a particular setting that is more structured than the settings used in naturalistic or participant observation. Often the setting in which the observations are made is not the natural setting. Instead, the researcher may observe people in the laboratory environment. Alternatively, the researcher may observe people in a natural setting (like a classroom setting) that they have structured some way, for instance by introducing some specific task participants are to engage in or by introducing a specific social situation or manipulation.
Structured observation is very similar to naturalistic observation and participant observation in that in all three cases researchers are observing naturally occurring behavior; however, the emphasis in structured observation is on gathering quantitative rather than qualitative data. Researchers using this approach are interested in a limited set of behaviors. This allows them to quantify the behaviors they are observing. In other words, structured observation is less global than naturalistic or participant observation because the researcher engaged in structured observations is interested in a small number of specific behaviors. Therefore, rather than recording everything that happens, the researcher only focuses on very specific behaviors of interest.
Researchers Robert Levine and Ara Norenzayan used structured observation to study differences in the “pace of life” across countries (Levine & Norenzayan, 1999) [4] . One of their measures involved observing pedestrians in a large city to see how long it took them to walk 60 feet. They found that people in some countries walked reliably faster than people in other countries. For example, people in Canada and Sweden covered 60 feet in just under 13 seconds on average, while people in Brazil and Romania took close to 17 seconds. When structured observation takes place in the complex and even chaotic “real world,” the questions of when, where, and under what conditions the observations will be made, and who exactly will be observed are important to consider. Levine and Norenzayan described their sampling process as follows:
“Male and female walking speed over a distance of 60 feet was measured in at least two locations in main downtown areas in each city. Measurements were taken during main business hours on clear summer days. All locations were flat, unobstructed, had broad sidewalks, and were sufficiently uncrowded to allow pedestrians to move at potentially maximum speeds. To control for the effects of socializing, only pedestrians walking alone were used. Children, individuals with obvious physical handicaps, and window-shoppers were not timed. Thirty-five men and 35 women were timed in most cities.” (p. 186).
Precise specification of the sampling process in this way makes data collection manageable for the observers, and it also provides some control over important extraneous variables. For example, by making their observations on clear summer days in all countries, Levine and Norenzayan controlled for effects of the weather on people’s walking speeds. In Levine and Norenzayan’s study, measurement was relatively straightforward. They simply measured out a 60-foot distance along a city sidewalk and then used a stopwatch to time participants as they walked over that distance.
As another example, researchers Robert Kraut and Robert Johnston wanted to study bowlers’ reactions to their shots, both when they were facing the pins and then when they turned toward their companions (Kraut & Johnston, 1979) [5] . But what “reactions” should they observe? Based on previous research and their own pilot testing, Kraut and Johnston created a list of reactions that included “closed smile,” “open smile,” “laugh,” “neutral face,” “look down,” “look away,” and “face cover” (covering one’s face with one’s hands). The observers committed this list to memory and then practiced by coding the reactions of bowlers who had been videotaped. During the actual study, the observers spoke into an audio recorder, describing the reactions they observed. Among the most interesting results of this study was that bowlers rarely smiled while they still faced the pins. They were much more likely to smile after they turned toward their companions, suggesting that smiling is not purely an expression of happiness but also a form of social communication.
In yet another example (this one in a laboratory environment), Dov Cohen and his colleagues had observers rate the emotional reactions of participants who had just been deliberately bumped and insulted by a confederate after they dropped off a completed questionnaire at the end of a hallway. The confederate was posing as someone who worked in the same building and who was frustrated by having to close a file drawer twice in order to permit the participants to walk past them (first to drop off the questionnaire at the end of the hallway and once again on their way back to the room where they believed the study they signed up for was taking place). The two observers were positioned at different ends of the hallway so that they could read the participants’ body language and hear anything they might say. Interestingly, the researchers hypothesized that participants from the southern United States, which is one of several places in the world that has a “culture of honor,” would react with more aggression than participants from the northern United States, a prediction that was in fact supported by the observational data (Cohen, Nisbett, Bowdle, & Schwarz, 1996) [6] .
When the observations require a judgment on the part of the observers—as in the studies by Kraut and Johnston and Cohen and his colleagues—a process referred to as coding is typically required . Coding generally requires clearly defining a set of target behaviors. The observers then categorize participants individually in terms of which behavior they have engaged in and the number of times they engaged in each behavior. The observers might even record the duration of each behavior. The target behaviors must be defined in such a way that guides different observers to code them in the same way. This difficulty with coding illustrates the issue of interrater reliability, as mentioned in Chapter 4. Researchers are expected to demonstrate the interrater reliability of their coding procedure by having multiple raters code the same behaviors independently and then showing that the different observers are in close agreement. Kraut and Johnston, for example, video recorded a subset of their participants’ reactions and had two observers independently code them. The two observers showed that they agreed on the reactions that were exhibited 97% of the time, indicating good interrater reliability.
One of the primary benefits of structured observation is that it is far more efficient than naturalistic and participant observation. Since the researchers are focused on specific behaviors this reduces time and expense. Also, often times the environment is structured to encourage the behaviors of interest which again means that researchers do not have to invest as much time in waiting for the behaviors of interest to naturally occur. Finally, researchers using this approach can clearly exert greater control over the environment. However, when researchers exert more control over the environment it may make the environment less natural which decreases external validity. It is less clear for instance whether structured observations made in a laboratory environment will generalize to a real world environment. Furthermore, since researchers engaged in structured observation are often not disguised there may be more concerns with reactivity.
Case Studies
A case study is an in-depth examination of an individual. Sometimes case studies are also completed on social units (e.g., a cult) and events (e.g., a natural disaster). Most commonly in psychology, however, case studies provide a detailed description and analysis of an individual. Often the individual has a rare or unusual condition or disorder or has damage to a specific region of the brain.
Like many observational research methods, case studies tend to be more qualitative in nature. Case study methods involve an in-depth, and often a longitudinal examination of an individual. Depending on the focus of the case study, individuals may or may not be observed in their natural setting. If the natural setting is not what is of interest, then the individual may be brought into a therapist’s office or a researcher’s lab for study. Also, the bulk of the case study report will focus on in-depth descriptions of the person rather than on statistical analyses. With that said some quantitative data may also be included in the write-up of a case study. For instance, an individual’s depression score may be compared to normative scores or their score before and after treatment may be compared. As with other qualitative methods, a variety of different methods and tools can be used to collect information on the case. For instance, interviews, naturalistic observation, structured observation, psychological testing (e.g., IQ test), and/or physiological measurements (e.g., brain scans) may be used to collect information on the individual.
HM is one of the most notorious case studies in psychology. HM suffered from intractable and very severe epilepsy. A surgeon localized HM’s epilepsy to his medial temporal lobe and in 1953 he removed large sections of his hippocampus in an attempt to stop the seizures. The treatment was a success, in that it resolved his epilepsy and his IQ and personality were unaffected. However, the doctors soon realized that HM exhibited a strange form of amnesia, called anterograde amnesia. HM was able to carry out a conversation and he could remember short strings of letters, digits, and words. Basically, his short term memory was preserved. However, HM could not commit new events to memory. He lost the ability to transfer information from his short-term memory to his long term memory, something memory researchers call consolidation. So while he could carry on a conversation with someone, he would completely forget the conversation after it ended. This was an extremely important case study for memory researchers because it suggested that there’s a dissociation between short-term memory and long-term memory, it suggested that these were two different abilities sub-served by different areas of the brain. It also suggested that the temporal lobes are particularly important for consolidating new information (i.e., for transferring information from short-term memory to long-term memory).

The history of psychology is filled with influential cases studies, such as Sigmund Freud’s description of “Anna O.” (see Note 6.1 “The Case of “Anna O.””) and John Watson and Rosalie Rayner’s description of Little Albert (Watson & Rayner, 1920) [7] , who allegedly learned to fear a white rat—along with other furry objects—when the researchers repeatedly made a loud noise every time the rat approached him.
The Case of “Anna O.”
Sigmund Freud used the case of a young woman he called “Anna O.” to illustrate many principles of his theory of psychoanalysis (Freud, 1961) [8] . (Her real name was Bertha Pappenheim, and she was an early feminist who went on to make important contributions to the field of social work.) Anna had come to Freud’s colleague Josef Breuer around 1880 with a variety of odd physical and psychological symptoms. One of them was that for several weeks she was unable to drink any fluids. According to Freud,
She would take up the glass of water that she longed for, but as soon as it touched her lips she would push it away like someone suffering from hydrophobia.…She lived only on fruit, such as melons, etc., so as to lessen her tormenting thirst. (p. 9)
But according to Freud, a breakthrough came one day while Anna was under hypnosis.
[S]he grumbled about her English “lady-companion,” whom she did not care for, and went on to describe, with every sign of disgust, how she had once gone into this lady’s room and how her little dog—horrid creature!—had drunk out of a glass there. The patient had said nothing, as she had wanted to be polite. After giving further energetic expression to the anger she had held back, she asked for something to drink, drank a large quantity of water without any difficulty, and awoke from her hypnosis with the glass at her lips; and thereupon the disturbance vanished, never to return. (p.9)
Freud’s interpretation was that Anna had repressed the memory of this incident along with the emotion that it triggered and that this was what had caused her inability to drink. Furthermore, he believed that her recollection of the incident, along with her expression of the emotion she had repressed, caused the symptom to go away.
As an illustration of Freud’s theory, the case study of Anna O. is quite effective. As evidence for the theory, however, it is essentially worthless. The description provides no way of knowing whether Anna had really repressed the memory of the dog drinking from the glass, whether this repression had caused her inability to drink, or whether recalling this “trauma” relieved the symptom. It is also unclear from this case study how typical or atypical Anna’s experience was.

Case studies are useful because they provide a level of detailed analysis not found in many other research methods and greater insights may be gained from this more detailed analysis. As a result of the case study, the researcher may gain a sharpened understanding of what might become important to look at more extensively in future more controlled research. Case studies are also often the only way to study rare conditions because it may be impossible to find a large enough sample of individuals with the condition to use quantitative methods. Although at first glance a case study of a rare individual might seem to tell us little about ourselves, they often do provide insights into normal behavior. The case of HM provided important insights into the role of the hippocampus in memory consolidation.
However, it is important to note that while case studies can provide insights into certain areas and variables to study, and can be useful in helping develop theories, they should never be used as evidence for theories. In other words, case studies can be used as inspiration to formulate theories and hypotheses, but those hypotheses and theories then need to be formally tested using more rigorous quantitative methods. The reason case studies shouldn’t be used to provide support for theories is that they suffer from problems with both internal and external validity. Case studies lack the proper controls that true experiments contain. As such, they suffer from problems with internal validity, so they cannot be used to determine causation. For instance, during HM’s surgery, the surgeon may have accidentally lesioned another area of HM’s brain (a possibility suggested by the dissection of HM’s brain following his death) and that lesion may have contributed to his inability to consolidate new information. The fact is, with case studies we cannot rule out these sorts of alternative explanations. So, as with all observational methods, case studies do not permit determination of causation. In addition, because case studies are often of a single individual, and typically an abnormal individual, researchers cannot generalize their conclusions to other individuals. Recall that with most research designs there is a trade-off between internal and external validity. With case studies, however, there are problems with both internal validity and external validity. So there are limits both to the ability to determine causation and to generalize the results. A final limitation of case studies is that ample opportunity exists for the theoretical biases of the researcher to color or bias the case description. Indeed, there have been accusations that the woman who studied HM destroyed a lot of her data that were not published and she has been called into question for destroying contradictory data that didn’t support her theory about how memories are consolidated. There is a fascinating New York Times article that describes some of the controversies that ensued after HM’s death and analysis of his brain that can be found at: https://www.nytimes.com/2016/08/07/magazine/the-brain-that-couldnt-remember.html?_r=0
Archival Research
Another approach that is often considered observational research involves analyzing archival data that have already been collected for some other purpose. An example is a study by Brett Pelham and his colleagues on “implicit egotism”—the tendency for people to prefer people, places, and things that are similar to themselves (Pelham, Carvallo, & Jones, 2005) [9] . In one study, they examined Social Security records to show that women with the names Virginia, Georgia, Louise, and Florence were especially likely to have moved to the states of Virginia, Georgia, Louisiana, and Florida, respectively.
As with naturalistic observation, measurement can be more or less straightforward when working with archival data. For example, counting the number of people named Virginia who live in various states based on Social Security records is relatively straightforward. But consider a study by Christopher Peterson and his colleagues on the relationship between optimism and health using data that had been collected many years before for a study on adult development (Peterson, Seligman, & Vaillant, 1988) [10] . In the 1940s, healthy male college students had completed an open-ended questionnaire about difficult wartime experiences. In the late 1980s, Peterson and his colleagues reviewed the men’s questionnaire responses to obtain a measure of explanatory style—their habitual ways of explaining bad events that happen to them. More pessimistic people tend to blame themselves and expect long-term negative consequences that affect many aspects of their lives, while more optimistic people tend to blame outside forces and expect limited negative consequences. To obtain a measure of explanatory style for each participant, the researchers used a procedure in which all negative events mentioned in the questionnaire responses, and any causal explanations for them were identified and written on index cards. These were given to a separate group of raters who rated each explanation in terms of three separate dimensions of optimism-pessimism. These ratings were then averaged to produce an explanatory style score for each participant. The researchers then assessed the statistical relationship between the men’s explanatory style as undergraduate students and archival measures of their health at approximately 60 years of age. The primary result was that the more optimistic the men were as undergraduate students, the healthier they were as older men. Pearson’s r was +.25.
This method is an example of content analysis —a family of systematic approaches to measurement using complex archival data. Just as structured observation requires specifying the behaviors of interest and then noting them as they occur, content analysis requires specifying keywords, phrases, or ideas and then finding all occurrences of them in the data. These occurrences can then be counted, timed (e.g., the amount of time devoted to entertainment topics on the nightly news show), or analyzed in a variety of other ways.
Media Attributions
- What happens when you remove the hippocampus? – Sam Kean by TED-Ed licensed under a standard YouTube License
- Pappenheim 1882 by unknown is in the Public Domain .
- Festinger, L., Riecken, H., & Schachter, S. (1956). When prophecy fails: A social and psychological study of a modern group that predicted the destruction of the world. University of Minnesota Press. ↵
- Rosenhan, D. L. (1973). On being sane in insane places. Science, 179 , 250–258. ↵
- Wilkins, A. (2008). “Happier than Non-Christians”: Collective emotions and symbolic boundaries among evangelical Christians. Social Psychology Quarterly, 71 , 281–301. ↵
- Levine, R. V., & Norenzayan, A. (1999). The pace of life in 31 countries. Journal of Cross-Cultural Psychology, 30 , 178–205. ↵
- Kraut, R. E., & Johnston, R. E. (1979). Social and emotional messages of smiling: An ethological approach. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 37 , 1539–1553. ↵
- Cohen, D., Nisbett, R. E., Bowdle, B. F., & Schwarz, N. (1996). Insult, aggression, and the southern culture of honor: An "experimental ethnography." Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 70 (5), 945-960. ↵
- Watson, J. B., & Rayner, R. (1920). Conditioned emotional reactions. Journal of Experimental Psychology, 3 , 1–14. ↵
- Freud, S. (1961). Five lectures on psycho-analysis . New York, NY: Norton. ↵
- Pelham, B. W., Carvallo, M., & Jones, J. T. (2005). Implicit egotism. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 14 , 106–110. ↵
- Peterson, C., Seligman, M. E. P., & Vaillant, G. E. (1988). Pessimistic explanatory style is a risk factor for physical illness: A thirty-five year longitudinal study. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 55 , 23–27. ↵
Research that is non-experimental because it focuses on recording systemic observations of behavior in a natural or laboratory setting without manipulating anything.
An observational method that involves observing people’s behavior in the environment in which it typically occurs.
When researchers engage in naturalistic observation by making their observations as unobtrusively as possible so that participants are not aware that they are being studied.
Where the participants are made aware of the researcher presence and monitoring of their behavior.
Refers to when a measure changes participants’ behavior.
In the case of undisguised naturalistic observation, it is a type of reactivity when people know they are being observed and studied, they may act differently than they normally would.
Researchers become active participants in the group or situation they are studying.
Researchers pretend to be members of the social group they are observing and conceal their true identity as researchers.
Researchers become a part of the group they are studying and they disclose their true identity as researchers to the group under investigation.
When a researcher makes careful observations of one or more specific behaviors in a particular setting that is more structured than the settings used in naturalistic or participant observation.
A part of structured observation whereby the observers use a clearly defined set of guidelines to "code" behaviors—assigning specific behaviors they are observing to a category—and count the number of times or the duration that the behavior occurs.
An in-depth examination of an individual.
A family of systematic approaches to measurement using qualitative methods to analyze complex archival data.
Research Methods in Psychology Copyright © 2019 by Rajiv S. Jhangiani, I-Chant A. Chiang, Carrie Cuttler, & Dana C. Leighton is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
What is Qualitative Observation? Definition, Types, Examples
Appinio Research · 03.05.2024 · 30min read

Have you ever wondered how researchers gain deep insights into human behavior and social interactions? Qualitative observation offers a fascinating window into the complexities of everyday life, allowing researchers to immerse themselves in natural settings and observe people in their element. From bustling city streets to quiet coffee shops, qualitative observation captures the nuances, subtleties, and context-specific dynamics that shape human experiences. In this guide, we'll explore the definition, purpose, methods, and applications of qualitative observation, providing practical insights and tips for conducting meaningful research and understanding the world around us. Whether you're a student delving into the realm of social sciences or a curious individual eager to explore the intricacies of human behavior, this guide will equip you with the knowledge and skills to navigate the fascinating terrain of qualitative observation with confidence and clarity.
What is Qualitative Observation?
Qualitative observation is a research method used to gather detailed insights into human behavior, experiences, and interactions through direct observation in natural settings. Unlike quantitative methods that rely on numerical data and statistical analysis , qualitative observation focuses on capturing the richness, complexity, and context of social phenomena through descriptive and interpretive means.
The primary purpose of qualitative observation is to deepen understanding and generate insights into the subjective experiences, perspectives, and behaviors of individuals and groups within their natural environments. By immersing researchers in the context of the study, qualitative observation facilitates the exploration of social dynamics, cultural norms, and contextual factors that shape human behavior.
Importance of Qualitative Observation in Research
- Richness of Insights : Qualitative observation allows researchers to explore the depth and complexity of human behavior and interactions in real-world settings, providing rich and detailed insights that may not be captured through quantitative methods alone.
- Contextual Understanding : By immersing researchers in the natural environments of participants, qualitative observation enables the exploration of behavior within its social, cultural, and environmental contexts. This contextual understanding is essential for interpreting and making sense of human actions and interactions.
- Theory Development : Qualitative observation contributes to theory development by generating new hypotheses, concepts , and frameworks grounded in empirical evidence and real-world observations. It allows researchers to uncover patterns , themes, and relationships that inform theoretical perspectives and models.
- Informing Practice : In addition to its role in academic research, qualitative observation has practical applications in various fields, including education, healthcare , business, and social services. It informs decision-making, program development, and policy formulation by providing insights into people's needs, preferences , and experiences.
- Enhanced Validity : Qualitative observation enhances the validity and credibility of research findings by complementing quantitative data with rich, contextualized insights. Triangulation of data sources and methods increases the robustness of research conclusions and reduces the risk of bias or misinterpretation.
- Personal Development : Beyond its role in academic and professional contexts, qualitative observation offers opportunities for personal growth and development. Engaging in observation and reflection fosters empathy, cultural competence, and critical thinking skills, enhancing researchers' capacity to navigate diverse social contexts and understand human behavior.
Qualitative observation is not only a valuable research method but also a powerful tool for understanding and navigating the complexities of human behavior and social interactions in everyday life. Its emphasis on context, depth, and interpretation makes it a versatile and indispensable approach in both research and practice.
Understanding Qualitative Observation
Qualitative observation serves as a fundamental research method across various disciplines, providing rich insights into human behavior, social interactions, and cultural dynamics. To effectively utilize qualitative observation, it's crucial to understand its underlying principles and the different types of observation methods available.
Qualitative Observation Principles
Qualitative observation operates on several fundamental principles that shape the approach to data collection , analysis, and interpretation:
- Subjectivity vs. Objectivity : Unlike quantitative methods that aim for objectivity and generalizability, qualitative observation acknowledges the subjective nature of human experiences. Researchers recognize their role as active participants in the research process, influencing the interpretation of data through their perspectives and biases.
- Contextual Understanding : Qualitative observation emphasizes the importance of understanding behavior within its social, cultural, and environmental contexts. By immersing themselves in the natural settings of participants, researchers gain a deeper appreciation for the factors that shape human actions and interactions.
- Holistic Perspective : Qualitative observation adopts a holistic approach to studying phenomena, focusing on the interconnectedness of various elements within a given context. Researchers seek to capture the complexity and nuance of human experiences, considering multiple layers of meaning and interpretation.
- Inductive Reasoning : Qualitative observation often employs inductive reasoning, allowing patterns and themes to emerge from the data rather than imposing preconceived hypotheses or theories. This open-ended approach enables researchers to explore new insights and perspectives that may challenge existing paradigms.
Types of Qualitative Observation
Qualitative observation encompasses a diverse range of methods, each offering unique advantages and considerations for data collection and analysis:
- Participant Observation : In participant observation, researchers immerse themselves in the natural settings of participants, actively engaging in social interactions and activities. By becoming part of the environment under study, researchers gain insider perspectives and access to rich, contextualized data. This method is particularly well-suited for studying cultural practices, group dynamics, and everyday behaviors.
- Naturalistic Observation : Naturalistic observation involves observing people in their natural environments without intervention or manipulation by the researcher. Researchers adopt a passive role, simply observing and documenting behaviors as they naturally occur. This method provides authentic insights into real-world behaviors and interactions, free from artificial constraints or biases.
- Structured Observation : Structured observation involves defining specific behaviors, events, or criteria for observation in advance. Researchers develop structured protocols or checklists to guide data collection, ensuring consistency and reliability across observations. While less flexible than participant and naturalistic observation, this method allows for standardized data collection and comparison across different contexts or groups.
Each type of qualitative observation offers distinct advantages and challenges, and researchers must carefully consider the appropriateness of each method based on their research goals, context, and ethical considerations.
Qualitative observation is an invaluable tool for gaining deep insights into human behavior and social interactions. With Appinio , conducting qualitative research becomes a seamless and efficient process, allowing researchers to collect real-time consumer insights in minutes without the hassle. By leveraging our intuitive platform and global reach, researchers can unlock a wealth of qualitative data to inform their decision-making and drive business success. Say goodbye to lengthy research processes and hello to actionable insights at your fingertips.
Ready to experience the power of Appinio for yourself? Book a demo today and discover how our platform can revolutionize your qualitative research endeavors!
Book a Demo
How to Prepare for Qualitative Observation?
Before embarking on qualitative observation, thorough planning and preparation are essential to ensure the success and ethical integrity of your study.
1. Define Research Objectives
Defining clear and specific research objectives is the cornerstone of any qualitative observation study. Your research objectives serve as guiding principles that shape your study's scope, focus, and direction.
- Identify Research Questions : Start by identifying the key questions you want to address through your qualitative observation. What phenomena are you interested in exploring? What specific aspects of human behavior or social interactions do you want to investigate?
- Clarify Purpose and Scope : Clearly articulate the purpose and scope of your study. What do you hope to achieve through your observation? Are you aiming to generate new insights, test existing theories, or explore a particular phenomenon in depth?
- Consider Practical Constraints : Take into account any practical constraints or limitations that may impact your research objectives, such as time, resources, and access to participants or observation settings. Set realistic goals that align with the available resources and logistical considerations.
2. Select Observation Methods
Once you've defined your research objectives, the next step is to select the most appropriate observation methods to achieve your goals. Qualitative observation offers a variety of techniques, each with its own strengths and considerations.
- Research Objectives : Choose observation methods that align with your research objectives and questions. Consider whether you need to immerse yourself in the environment as a participant, observe behaviors from a distance, or use structured protocols for data collection.
- Context and Setting : Take into account the specific context and setting of your study. Are you observing individuals in a naturalistic environment, such as a public space or workplace, or are you conducting observations within a controlled setting, such as a laboratory or simulated environment?
- Ethical Considerations : Consider the ethical implications of different observation methods, particularly in terms of privacy, consent, and potential risks to participants. Ensure that your chosen methods adhere to ethical guidelines and respect the rights and dignity of participants.
3. Identify Observation Settings
Identifying the appropriate observation settings is crucial for ensuring the validity and relevance of your observations. The observation setting should provide access to the phenomena of interest while allowing for naturalistic and unobtrusive observation.
- Access and Permissions : Obtain necessary permissions and access to the observation settings, whether they are public spaces, private institutions, or community settings. Seek cooperation from relevant stakeholders, such as facility managers, organizational leaders, or community members.
- Naturalistic Environments : Whenever possible, choose observation settings that reflect the natural environments where the phenomena of interest naturally occur. This could include public spaces, workplaces, classrooms, homes, or other community settings.
- Variety and Diversity : Consider the importance of sampling diverse observation settings to capture a range of experiences, perspectives, and contexts. Avoid over-reliance on a single setting or context, as this may limit the generalizability and richness of your observations.
4. Establish Ethical Guidelines
Given the potential impact on participants' privacy, autonomy, and well-being, ethical considerations are paramount in qualitative observation research. Establishing clear ethical guidelines helps ensure the ethical conduct of your study and protect the rights of participants.
- Informed Consent : Obtain informed consent from participants before initiating any observation activities. Clearly explain the purpose, procedures, risks, and benefits of the study, and allow participants to make an informed decision about their participation.
- Confidentiality and Anonymity : Protect participants' privacy and anonymity by keeping their identities and personal information confidential. Avoid using identifying information in your observations or reporting unless participants explicitly consent.
- Respect for Autonomy : Respect the autonomy and agency of participants throughout the research process. Allow participants to withdraw from the study at any time without consequence and ensure that their decisions are respected without coercion or undue influence.
- Minimization of Harm : Take proactive measures to minimize any potential harm or discomfort to participants arising from the observation process. Be attentive to signs of distress or discomfort and take appropriate steps to address them, including providing support or discontinuing the observation if necessary.
By carefully planning and preparing for qualitative observation, you can lay the foundation for a rigorous, ethical, and insightful study that contributes valuable insights to your field of inquiry.
How to Conduct Qualitative Observation?
Once you've completed the planning phase, it's time to immerse yourself in the field and start collecting data through qualitative observation. Let's take a look at the essential aspects of conducting qualitative observation.
Immersion in the Environment
Immersing yourself in the observation environment is crucial for gaining a deep understanding of the context, culture, and dynamics at play. To effectively immerse yourself:
- Engage with the Environment : Actively participate in the activities and interactions occurring within the observation setting. Immerse yourself in the daily routines, rituals, and social dynamics to gain insider perspectives and insights.
- Observe Unobtrusively : While actively engaging with the environment, strive to maintain a balance between active participation and unobtrusive observation. Avoid drawing undue attention to yourself or disrupting the natural flow of interactions.
- Build Trust and Familiarity : Take the time to build trust and familiarity with the participants and stakeholders in the observation setting. Be approachable, respectful, and non-judgmental in your interactions, allowing participants to feel comfortable and open in your presence.
Building Rapport with Participants
Establishing rapport with participants is essential for gaining their cooperation and obtaining rich, meaningful data. To build rapport effectively:
- Demonstrate Genuine Interest : Show genuine curiosity and interest in the participants' lives, experiences, and perspectives. Listen actively, ask open-ended questions , and express empathy and understanding.
- Respect Cultural Sensitivities : Be mindful of cultural norms, values, and sensitivities that may influence your interactions with participants. Respect their cultural practices, traditions, and beliefs, and avoid imposing your own cultural biases or assumptions.
- Be Transparent and Ethical : Be transparent about the purpose and objectives of your study, as well as the role of participants in the observation process. Ensure that participants understand their rights, including the option to withdraw from the study at any time.
Recording Observations
During observation sessions, recording detailed and accurate observations is essential for capturing the richness and complexity of human behavior and interactions. To record observations effectively:
- Use Multiple Data Collection Methods : Employ a combination of data collection methods , such as field notes, audio recordings, video recordings, photographs, or sketches, to capture different aspects of the observation setting.
- Document Contextual Details : Record not only what is happening but also the context, nuances, and subtleties of interactions. Note the physical environment, social dynamics, non-verbal cues, and emotional expressions that contribute to the overall context of the observation.
- Maintain Objectivity and Neutrality : Strive to maintain objectivity and neutrality in your observations, avoiding personal biases or interpretations. Record observations objectively without filtering or distorting the data to fit preconceived notions or expectations.
Managing Observer Bias
Observer bias refers to the tendency of researchers to interpret observations in a way that aligns with their preconceived beliefs or expectations. To manage observer bias effectively:
- Reflect on Personal Biases : Reflect on your own biases, assumptions, and perspectives that may influence your observations and interpretations. Be aware of how your background, experiences, and beliefs shape your perceptions of the observation setting and participants.
- Seek Diverse Perspectives : Involve multiple observers or researchers in the observation process to mitigate individual biases and enhance the reliability and validity of the observations. Compare and discuss observations to identify and address any discrepancies or biases.
- Triangulate Data Sources : Triangulate your observations with other data sources, such as interviews, surveys , or existing literature, to corroborate findings and minimize the impact of observer bias. Use multiple perspectives and sources of evidence to validate your interpretations.
By immersing yourself in the observation environment, building rapport with participants, recording detailed observations, and managing observer bias, you can conduct qualitative observation effectively and ethically, generating valuable insights into human behavior and social interactions.
Qualitative Observation Examples
Examples of qualitative observation abound in various contexts, offering valuable insights into human behavior, social interactions, and cultural dynamics. Here are a few illustrative examples to showcase the diverse applications and approaches of qualitative observation:
Ethnographic Studies
Ethnographic studies involve immersive, long-term observation of a specific group or community within its natural environment. For example, an ethnographer might live in a tribal community for an extended period, observing their daily routines, rituals, and social interactions. Through participant observation, interviews , and field notes, ethnographers gain deep insights into the cultural beliefs, practices, and norms of the community.
Classroom Observations
In education, qualitative observation plays a crucial role in understanding classroom dynamics, teaching practices, and student behaviors. Researchers may observe classroom activities, interactions between teachers and students, and instructional strategies to identify effective teaching methods and areas for improvement. By capturing the complexity of the learning environment, qualitative observation informs educational policy, curriculum development, and teacher training initiatives.
Workplace Observations
Qualitative observation is also valuable in studying organizational behavior and dynamics within the workplace. Researchers may observe employee interactions, communication patterns, and leadership styles to understand organizational culture, team dynamics, and factors influencing employee satisfaction and productivity. Workplace observations inform management practices, employee training programs, and organizational development strategies to foster a positive work environment and enhance performance.
Clinical Observations
In healthcare settings , qualitative observation studies patient-provider interactions, healthcare delivery processes, and patient experiences. Clinicians and researchers may observe medical consultations, treatment procedures, and patient interactions to identify barriers to effective care, communication challenges, and opportunities for patient-centered interventions. Clinical observations contribute to improving healthcare quality, patient satisfaction , and health outcomes.
Urban Planning and Design
In urban planning and design, qualitative observation helps researchers understand the built environment's impact on human behavior and well-being. Urban planners may observe pedestrian movement patterns, public space utilization, and community interactions to inform the design of cities, neighborhoods, and public infrastructure. Qualitative observation contributes to creating inclusive, accessible, and sustainable urban environments that enhance the quality of life for residents.
These examples demonstrate the versatility and significance of qualitative observation in generating insights, informing decision-making, and addressing complex social phenomena across diverse fields and contexts. Whether studying cultural practices in remote villages, classroom dynamics in schools, or patient experiences in healthcare settings, qualitative observation offers a powerful lens through which to explore the intricacies of human behavior and society.
How to Analyze Qualitative Data from Observation?
Analyzing qualitative data from observation involves systematically organizing, interpreting, and making sense of the rich and nuanced information gathered during the observation process.
Data Coding and Categorization
Data coding and categorization are fundamental processes in qualitative data analysis , enabling researchers to organize and structure the raw data into meaningful units for analysis. To effectively code and categorize qualitative data:
- Open Coding : Begin by engaging in open coding, where you systematically review and categorize the data into initial codes or categories based on recurring patterns, themes, or concepts. This process involves breaking down the data into smaller units and identifying key concepts or ideas.
- Axial Coding : Once you have generated initial codes, use axial coding to establish relationships and connections between codes. Look for patterns, associations, and linkages between different codes, grouping them into broader categories or themes.
- Selective Coding : Finally, engage in selective coding to refine and prioritize the most salient and significant codes or themes that capture the essence of the data. Selective coding involves identifying core themes or concepts that emerge as central to the phenomenon under study and integrating them into a coherent narrative.
Identifying Patterns and Themes
Identifying patterns and themes is a central aspect of qualitative data analysis , allowing researchers to uncover underlying meanings, insights, and relationships within the data. To identify patterns and themes effectively:
- Thematic Analysis : Conduct thematic analysis to systematically identify and explore recurring patterns, themes, or concepts within the data. This involves reviewing the coded data, looking for commonalities, variations, and outliers, and organizing them into meaningful clusters or themes.
- Constant Comparison : Engage in continuous comparison , where you continually compare and contrast different segments of the data to identify similarities and differences. This iterative process allows themes to emerge organically from the data rather than imposing preconceived categories or frameworks.
- Contextual Interpretation : Interpret the identified patterns and themes within the broader context of the observation setting, participants' experiences, and relevant theoretical frameworks. Consider the socio-cultural, historical, and environmental factors that may influence the emergence and significance of the themes.
Integrating Qualitative and Quantitative Data (if applicable)
In some research studies, it may be appropriate to integrate qualitative observation data with quantitative data from other sources to gain a comprehensive understanding of the phenomenon under study. To integrate qualitative and quantitative data effectively:
- Mixed Methods Approach : Adopt a mixed methods approach, where qualitative observation data are triangulated with quantitative data collected through surveys, experiments , or secondary sources. This integration allows for a more holistic and nuanced analysis of the research problem, providing multiple perspectives and insights.
- Complementary Analysis : Analyze qualitative and quantitative data separately to identify unique insights and patterns within each dataset. Then, integrate the findings through comparison, contrast, or synthesis to identify convergent or divergent themes and trends.
- Data Transformation : Transform qualitative observation data into quantitative metrics or variables for comparative analysis with quantitative data. This may involve quantifying qualitative codes or themes into numerical scores or categories for statistical analysis.
Ensuring Data Trustworthiness and Reliability
Ensuring the trustworthiness and reliability of qualitative data is essential for establishing the validity and credibility of the research findings. To ensure data trustworthiness and reliability:
- Credibility : Enhance credibility by employing rigorous data collection and analysis techniques, maintaining detailed documentation of the research process, and engaging in member checking, where participants review and validate the findings to ensure accuracy and authenticity.
- Transferability : Enhance transferability by providing rich, detailed descriptions of the observation setting, participants, and data collection procedures, allowing readers to assess the applicability of the findings to other contexts or populations.
- Dependability : Enhance dependability by ensuring transparency and consistency in the research process, including clear documentation of data collection methods, coding procedures, and analytical decisions. Engage in peer debriefing and external audits to verify the reliability of the findings.
- Confirmability : Enhance confirmability by maintaining reflexivity throughout the research process, acknowledging and addressing personal biases or assumptions that may influence the interpretation of the data. Use transparent and systematic approaches to data analysis, allowing for independent verification by other researchers.
By systematically analyzing qualitative data from observation, researchers can uncover meaningful patterns, themes, and insights that provide rich insights into human behavior, social interactions, and cultural dynamics. By ensuring the trustworthiness and reliability of the data, researchers can generate robust and credible findings that contribute to the body of knowledge in their respective fields.
How to Report Qualitative Observation Findings?
Reporting findings from qualitative observation is a critical step in the research process. It enables researchers to communicate their insights, interpretations, and conclusions to the broader academic community and stakeholders. We'll explore the key considerations for effectively reporting findings from qualitative observation studies.
1. Choose the Right Format
Choosing the proper format for reporting your qualitative observation findings depends on various factors, including the nature of the research, the preferences of the target audience, and the intended impact of the study. Popular formats include:
- Research Papers : Academic journals are a common platform for reporting qualitative observation findings. Research papers typically follow a standardized structure, including an abstract, introduction, methods, results, discussion, and conclusion sections. Choose a journal that specializes in qualitative research and aligns with the scope and focus of your study.
- Reports : Reports provide a more comprehensive and detailed overview of the research findings, including background information, methods, results, and implications. Reports may be distributed to stakeholders, funding agencies, or organizational partners interested in the study outcomes.
- Presentations : Presentations offer an opportunity to disseminate key findings and insights to a broader audience in a concise and engaging format. Consider presenting your findings at academic conferences, professional meetings, or community forums to share your research with peers and stakeholders.
2. Structure the Narrative
Structuring the narrative of your qualitative observation report is essential for guiding readers through the research process and facilitating understanding and interpretation of the findings. When structuring the narrative, make sure to include these elements:
- Introduction : Provide an overview of the research problem, objectives, and significance of the study. Briefly summarize the research design , methods, and approach to qualitative observation.
- Methods : Describe the methods used to conduct qualitative observation, including the observation setting, participants , data collection procedures, and ethical considerations. Provide sufficient detail to allow readers to assess the rigor and credibility of the study.
- Results : Present the key findings and insights derived from qualitative observation. Organize the results thematically, highlighting recurring patterns, themes, or categories that emerged from the data. Use illustrative examples and quotes to support your interpretations.
- Discussion : Interpret and discuss the implications of the findings in relation to the research objectives, theoretical frameworks, and existing literature. Explore the significance of the findings, their practical implications, and areas for further research.
- Conclusion : Summarize the study's main findings and conclusions, emphasizing their relevance and contributions to the field. Reflect on the research's strengths and limitations and offer recommendations for future research or practice.
3. Incorporate Quotes and Examples
Incorporating quotes and examples from the qualitative observation data adds depth, richness, and authenticity to your report, helping to illustrate key themes, insights, and interpretations.
- Selecting Representative Quotes : Choose quotes that capture the essence of participants' experiences, perspectives, and emotions. Select quotes that are vivid, compelling, and representative of the broader themes or patterns identified in the data.
- Providing Contextual Information : Provide contextual information to accompany the quotes, including details about the participant, the observation setting, and the specific context in which the quote was obtained. This helps readers understand the significance and relevance of the quote within the broader narrative of the study.
- Interpreting Quotes : Interpret and analyze the quotes within the discussion section of your report, providing insights into their meanings, implications, and contributions to the overall findings. Avoid simply presenting quotes without analysis or interpretation, as this may limit the depth of understanding for readers.
4. Address Limitations and Future Directions
Every research study, including qualitative observation, has its limitations and areas for improvement. Acknowledging and addressing these limitations is essential for maintaining transparency and credibility in your reporting.
- Limitations : Identify and discuss any limitations or challenges encountered during the research process, such as sample size constraints, data collection biases, or contextual constraints. Be honest and transparent about the limitations of the study and their potential impact on the validity and generalizability of the findings.
- Future Directions : Based on your study's findings, suggest potential avenues for future research or areas for further exploration. Consider unanswered questions, emerging themes, or areas of controversy that warrant further investigation. Offer recommendations for methodological improvements or alternative approaches to address the limitations identified.
By carefully choosing a suitable format, structuring the narrative effectively, incorporating quotes and examples, and addressing limitations and future directions, you can create a compelling and informative report that effectively communicates the findings of your qualitative observation study to the broader academic community and stakeholders.
Conclusion for Qualitative Observation
Qualitative observation is a powerful tool for understanding the richness and complexity of human behavior and social interactions. By immersing researchers in natural settings and allowing them to observe people in their everyday environments, qualitative observation offers unique insights that complement quantitative methods. From uncovering cultural norms and social dynamics to informing policy decisions and program development, qualitative observation has diverse applications across various fields, including academia, healthcare, business, and social services. Embracing the principles of subjectivity, contextuality, and inductive reasoning, qualitative observation empowers researchers to explore the depth and nuance of human experiences, ultimately contributing to our collective understanding of the world around us. Furthermore, as we continue to navigate an increasingly interconnected and diverse world, the importance of qualitative observation only grows. Its emphasis on context, perspective, and interpretation enables researchers to bridge disciplinary boundaries, engage with diverse communities, and address complex social issues. By fostering empathy, cultural competence, and critical thinking skills, qualitative observation not only advances knowledge and scholarship but also promotes social justice, equity, and inclusion.
How to Conduct Qualitative Research in Minutes?
Introducing Appinio , the real-time market research platform revolutionizing qualitative observation. With Appinio, conducting your own market research is not only quick but also incredibly easy and intuitive. By leveraging Appinio's powerful platform, you can unlock real-time consumer insights and make informed, data-driven decisions for your business with ease. Say hello to a new era of market research that is exciting, intuitive, and seamlessly integrated into everyday decision-making.
Here's why you should consider using Appinio for your qualitative research needs:
- From Questions to Insights in Minutes: With Appinio, you can go from formulating your research questions to gaining actionable insights in a matter of minutes. Say goodbye to long wait times and cumbersome research processes.
- Intuitive Platform for Everyone: You don't need a PhD in research to use Appinio. Our platform is designed to be user-friendly and accessible to anyone, regardless of their level of expertise in market research.
- Global Reach and Targeting: Define your target group with precision from over 1200 characteristics and survey respondents in over 90 countries. Whether you're interested in local or global insights, Appinio has you covered.
Get free access to the platform!
Join the loop 💌
Be the first to hear about new updates, product news, and data insights. We'll send it all straight to your inbox.
Get the latest market research news straight to your inbox! 💌
Wait, there's more

07.05.2024 | 29min read
Interval Scale: Definition, Characteristics, Examples
03.05.2024 | 29min read

02.05.2024 | 32min read
What is a Perceptual Map and How to Make One? (+ Template)

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Participant observation is a research method where the researcher immerses themself in a particular social setting or group, observing the behaviors, interactions, and practices of the participants. This can be a valuable method for any research project that seeks to understand the experiences of individuals or groups in a particular social ...
Participant observation is one type of data collection method by practitioner-scholars typically used in qualitative research and ethnography.This type of methodology is employed in many disciplines, particularly anthropology (incl. cultural anthropology and ethnology), sociology (incl. sociology of culture and cultural criminology), communication studies, human geography, and social psychology.
Participant observation is a qualitative research methodology in which the researcher studies a group not only through observation, but also by participating in its activities. In this qualitative observation methodology, the researcher immerses himself in the daily activities of the participants in order to record the behavior in as many ...
from being there. And when you have to be there, participant observation is the method of choice. DIRECT OBSERVATION VERSUS PARTICIPANT OBSERVATION "An observer is under the bed. A participant observer is in it." —spoken by John Whiting, age 80-something, to an undergraduate class when he was a guest lecturer at UC Irvine
Both participant observation and deep ethnography are forms of fieldwork in which the researcher leaves their office and goes into a natural setting to record observations that take place in that setting. [1] Participant observation (PO) is a field approach to gathering data in which the researcher enters a specific site for purposes of ...
Naturalistic observation is a research method in which the researcher studies behavior in its natural setting without intervention or manipulation. It involves observing and recording behavior as it naturally occurs, providing insights into real-life behaviors and interactions in their natural context. ... Participant observation is a variant ...
Participant observation is considered a st aple in anthropological studies, especially in ethnographic studies, and has been used as a data collection. method for over a cent ury. As DeWALT and ...
"Participant observation is the central research method of ethnography. It requires a researcher to engage with people in as many different situations as possible to look at what people actually do as well as what they say they do (as in interviews or documents) in their everyday lives" - from EAR Training Handbook
Participant observation is a method of social inquiry which, "… aims to generate practical and theoretical truths about human life grounded in the realities of daily existence" (Jorgensen 1989, p. 14).Requiring active engagement in the day-to-day lives of research subjects for extended periods of time, it is often used in ethnographic research, particularly in fields such as anthropology ...
Participant Observation is. "A method of research in anthropology which involves extended immersion in a culture and participation in its day-to-day activities" (Calhoun, 2002). This type of research methodology is used in circumstances where an individual wants to observe a group to which they do not belong without altering the behavior of the ...
This paper explores the validity of qualitative observational research methods, specifically participant observation. Through an exploration of the relevant literature and a critical review of a ...
Participant observation is a research method where the researcher immerses themself in a particular social setting or group, observing the behaviours, interactions, and practices of the participants. This can be a valuable method for any research project that seeks to understand the experiences of individuals or groups in a particular social ...
Participant observation is a research method where the researcher observes a target audience or group and their day-to-day activities. The goal of the participant observation method is to study as wide a range of behaviors as possible in a natural, organic setting. As a result, participant observation studies play a vital role in fields that ...
Participant observation forms part of the phenomenological approach. This approach is about studying the personal experience and gathering data from the perspective of the researched individual (s). In the context of epistemology, phenomenological research is founded on personal knowledge and is thus considered subjective (Lester 1999, p. 2).
Participant Observation is where the researcher joins in with the group being studied and observes their behaviour. This post covers the theoretical, practical and ethical strengths and limitations of using overt and covert participant observation in social research. It has been written primarily for students studying the research methods ...
Observation in qualitative research "is one of the oldest and most fundamental research methods approaches. This approach involves collecting data using one's senses, especially looking and listening in a systematic and meaningful way" (McKechnie, 2008, p. 573).Similarly, Adler and Adler (1994) characterized observations as the "fundamental base of all research methods" in the social ...
Meet Profesor Suzanne Moffatt, who primarily uses qualitative research methods, including participant observation. Participant observation is the study of individuals, communities or groups in 'the field' to gain an understanding of their lived experience. As Boccagni and Schrooten (2018: 212) note, participant observation is "an embodied ...
The participant observation method, also known as ethnographic research, is when a sociologist actually becomes a part of the group they are studying in order to collect data and understand a social phenomenon or problem.During participant observation, the researcher works to play two separate roles at the same time: subjective participant and objective observer.
Participant observation (PO) is a research methodology where the researcher is immersed in the day-to-day activities of the participants. The objective is usually to record conduct under the widest range of possible settings. In this way, PO differs from naturalistic observation, because the latter does not involve interaction between the ...
Community-based participant-observation purposefully combines participant-observation and community-based participatory research. While participant-observation is the core method of ethnography and foundational to cultural anthropology, community-based participatory research initially emerged from health and related applied sciences to align researchers' and communities' agendas through ...
Naturalistic observation is an observational method that involves observing people's behavior in the environment in which it typically occurs. Thus naturalistic observation is a type of field research (as opposed to a type of laboratory research). Jane Goodall's famous research on chimpanzees is a classic example of naturalistic observation ...
Participant observation is a qualitative research method in which the researcher observes members of the group or community being researched and participates with them in their activities. This ...
Qualitative observation is a research method used to gather detailed insights into human behavior, experiences, and interactions through direct observation in natural settings. ... Participant Observation: In participant observation, researchers immerse themselves in the natural settings of participants, actively engaging in social interactions ...