
Essay on Politics: Topics, Tips, and Examples for Students

Defining What is Politics Essay
The process of decision-making that applies to members of a group or society is called politics. Arguably, political activities are the backbone of human society, and everything in our daily life is a form of it.
Understanding the essence of politics, reflecting on its internal elements, and critically analyzing them make society more politically aware and let them make more educated decisions. Constantly thinking and analyzing politics is critical for societal evolution.
Political thinkers often write academic papers that explore different political concepts, policies, and events. The essay about politics may examine a wide range of topics such as government systems, political ideologies, social justice, public policies, international relations, etc.
After selecting a specific research topic, a writer should conduct extensive research, gather relevant information, and prepare a logical and well-supported argument. The paper should be clear and organized, complying with academic language and standards. A writer should demonstrate a deep understanding of the subject, an ability to evaluate and remain non-biased to different viewpoints, and a capacity to draw conclusions.
Now that we are on the same page about the question 'what is politics essay' and understand its importance, let's take a deeper dive into how to build a compelling political essay, explore the most relevant political argumentative essay topics, and finally, examine the political essay examples written by the best essay writing service team.
Politics Essay Example for Students
If you are still unsure how to structure your essay or how to present your statement, don't worry. Our team of experts has prepared an excellent essay example for you. Feel free to explore and examine it. Use it to guide you through the writing process and help you understand what a successful essay looks like.
How to Write a Political Essay: Tips + Guide
A well-written essay is easy to read and digest. You probably remember reading papers full of big words and complex ideas that no one bothered to explain. We all agree that such essays are easily forgotten and not influential, even though they might contain a very important message.
If you are writing an essay on politics, acknowledge that you are on a critical mission to easily convey complicated concepts. Hence, what you are trying to say should be your main goal. Our guide on how to write a political essay will help you succeed.

Conduct Research for Your Politics Essay
After choosing a topic for the essay, take enough time for preparation. Even if you are familiar with the matter, conducting thorough research is wiser. Political issues are complex and multifaceted; comprehensive research will help you understand the topic better and offer a more nuanced analysis.
Research can help you identify different viewpoints and arguments around the topic, which can be beneficial for building more impartial and persuasive essays on politics. Sometimes in the hit of the moment, opposing sides are not able to see the common ground; your goal is to remain rational, speak to diverse audiences, and help them see the core of the problem and the ways to solve it.
In political papers, accuracy and credibility are vital. Researching the topic deeply will help you avoid factual errors or misrepresentations from any standpoint. It will allow you to gather reliable sources of information and create a trustworthy foundation for the entire paper.
If you want to stand out from the other students, get inspired by the list of hottest essay ideas and check out our political essay examples.
Need Professional Help on College Essays?
Essays designed to meet your specific requirements are a click away!
Brainstorm Political Essay Topics
The next step to writing a compelling politics essay is to polish your thoughts and find the right angle to the chosen topic.
Before you start writing, generate fresh ideas and organize your thoughts. There are different techniques to systematize the mess going on in your head, such as freewriting, mind mapping, or even as simple as listing ideas. This will open the doors to new angles and approaches to the topic.
When writing an essay about politics, ensure the topic is not too general. It's always better to narrow it down. It will simplify your job and help the audience better understand the core of the problem. Brainstorming can help you identify key points and arguments, which you can use to find a specific angle on the topic.
Brainstorming can also help you detect informational gaps that must be covered before the writing process. Ultimately, the brainstorming phase can bring a lot more clarity and structure to your essay.
We know how exhausting it is to come up with comparative politics essay topics. Let our research paper writing service team do all the hard work for you.
Create Your Politics Essay Thesis Statement
Thesis statements, in general, serve as a starting point of the roadmap for the reader. A political essay thesis statement outlines the main ideas and arguments presented in the body paragraphs and creates a general sense of the content of the paper.

Creating a thesis statement for essays about politics in the initial stages of writing can help you stay focused and on track throughout the working process. You can use it as an aim and constantly check your arguments and evidence against it. The question is whether they are relevant and supportive of the statement.
Get creative when creating a statement. This is the first sentence readers will see, and it should be compelling and clear.
The following is a great example of a clear and persuasive thesis statement:
'The lack of transparency and accountability has made the World Trade Organization one of the most controversial economic entities. Despite the influence, its effectiveness in promoting free trade and economic growth in developing countries has decreased.'
Provide Facts in Your Essay about Politic
It's a no-brainer that everything you will write in your essay should be supported by strong evidence. The credibility of your argument will be questioned every step of the way, especially when you are writing about sensitive subjects such as essays on government influence on economic troubles.
Provide facts and use them as supporting evidence in your politics essay. They will help you establish credibility and accuracy and take your paper out of the realm of speculation and mere opinions.
Facts will make your essay on political parties more persuasive, unbiased, and targeted to larger audiences. Remember, the goal is to bring the light to the core of the issue and find a solution, not to bring people even farther apart.
Speaking of facts, many students claim that when they say ' write my essay for me ' out loud, our writing team is the fastest to respond and deliver high-quality essays meeting their trickiest requirements.
Structure Your Political Essay
Your main goal is to communicate your ideas to many people. To succeed, you need to write an essay that is easy to read and understand. Creating a structure will help you present your ideas logically and lead the readers in the right direction.
Sometimes when writing about political essay topics, we get carried away. These issues can be very emotional and sensitive, and writers are not protected from becoming victims of their own writings. Having a structure will keep you on track, only focusing on providing supported arguments and relevant information.
Start with introducing the thesis statement and provide background information. Followed by the body paragraphs and discuss all the relevant facts and standpoints. Finish it up with a comprehensive conclusion, and state the main points of your essay once again.
The structure will also save you time. In the beginning, creating an outline for essays on politics will give you a general idea of what should be written, and you can track your progress against it.
Revise and Proofread Your Final Politics Essay
Once every opinion is on the paper and every argument is well-constructed, one final step should be taken. Revision!
We know nothing is better than finishing the homework and quickly submitting it, but we aim for an A+. Our political essay must be reviewed. You need to check if there is any error such as grammatical, spelling, or contextual.
Take some time off, relax, and start proofreading after a few minutes or hours. Having a fresh mind will help you review not only grammar but also the arguments. Check if something is missing from your essays about politics, and if you find gaps, provide additional information.
You had to spend a lot of time on them, don't give up now. Make sure they are in perfect condition.
Effective Political Essay Topics
We would be happy if our guide on how to write political essays helped you, but we are not stopping there. Below you will find a list of advanced and relevant political essay topics. Whether you are interested in global political topics or political science essay topics, we got you covered.
Once you select a topic, don't forget to check out our politics essay example! It will bring even more clarity, and you will be all ready to start writing your own paper.
Political Argumentative Essay Topics
Now that we know how to write a political analysis essay let's explore political argumentative essay topics:
- Should a political party take a stance on food politics and support policies promoting sustainable food systems?
- Should we label Winston Churchill as the most influential political figure of World War II?
- Does the focus on GDP growth in the political economy hinder the human development index?
- Is foreign influence a threat to national security?
- Is foreign aid the best practice for political campaigning?
- Does the electoral college work for an ideal political system?
- Are social movements making a real difference, or are they politically active for temporary change?
- Can global politics effectively address political conflicts in the modern world?
- Are opposing political parties playing positive roles in US international relations?
- To what extent should political influence be allowed in addressing economic concerns?
- Can representative democracy prevent civil wars in ethnically diverse countries?
- Should nuclear weapons be abolished for the sake of global relations?
- Is economic development more important than ethical issues for Caribbean politics?
- What role should neighboring nations play in preventing human rights abuse in totalitarian regimes?
- Should political decisions guide the resolution of conflicts in the South China Sea?
Political Socialization Essay Topics
Knowing how to write a political issue essay is one thing, but have you explored our list of political socialization essay topics?
- To what extent does a political party or an influential political figure shape the beliefs of young people?
- Does political influence shape attitudes toward environmental politics?
- How can individuals use their own learning process to navigate political conflicts in a polarized society?
- How do political strategies shape cultural globalization?
- Is gender bias used as a political instrument in political socialization?
- How can paying attention to rural communities improve political engagement?
- What is the role of Amnesty International in preventing the death penalty?
- What is the role of politically involved citizens in shaping minimum wage policies?
- How does a political party shape attitudes toward global warming?
- How does the federal system influence urban planning and attitudes toward urban development?
- What is the role of public opinion in shaping foreign policy, and how does it affect political decision making
- Did other countries' experiences affect policies on restricting immigration in the US?
- How can note-taking skills and practice tests improve political engagement?
- How do the cultural values of an independent country shape the attitudes toward national security?
- Does public opinion influence international intervention in helping countries reconcile after conflicts?
Political Science Essay Topics
If you are searching for political science essay topics, check our list below and write the most compelling essay about politic:
- Is environmental education a powerful political instrument?
- Can anarchist societies provide a viable alternative to traditional forms of governance?
- Pros and cons of deterrence theory in contemporary international relations
- Comparing the impact of the French Revolution and World War II on the political landscape of Europe
- The role of the ruling political party in shaping national policies on nuclear weapons
- Exploring the roots of where politics originate
- The impact of civil wars on the processes of democratization of the third-world countries
- The role of international organizations in promoting global health
- Does using the death penalty in the justice system affect international relations?
- Assessing the role of the World Trade Organization in shaping global trade policies
- The political and environmental implications of conventional agriculture
- The impact of the international court on political decision making
- Is philosophical anarchism relevant to contemporary political discourse?
- The emergence of global citizenship and its relationship with social movements
- The impact of other countries on international relations between the US and China
Final Words
See? Writing an essay about politic seems like a super challenging job, but in reality, all it takes is excellent guidance, a well-structured outline, and an eye for credible information.
If you are stressed out from juggling a hundred different course assignments and have no time to focus on your thesis, our dissertation writing services could relieve you! Our team of experts is ready to take over even the trickiest tasks on the tightest schedule. You just have to wish - ' write my essay ' out loud, and we will be on it!
Ready to Enrich Your Understanding of Politics?
Order our thought-provoking essay today and elevate your intellectual game!

Annie Lambert
specializes in creating authoritative content on marketing, business, and finance, with a versatile ability to handle any essay type and dissertations. With a Master’s degree in Business Administration and a passion for social issues, her writing not only educates but also inspires action. On EssayPro blog, Annie delivers detailed guides and thought-provoking discussions on pressing economic and social topics. When not writing, she’s a guest speaker at various business seminars.

is an expert in nursing and healthcare, with a strong background in history, law, and literature. Holding advanced degrees in nursing and public health, his analytical approach and comprehensive knowledge help students navigate complex topics. On EssayPro blog, Adam provides insightful articles on everything from historical analysis to the intricacies of healthcare policies. In his downtime, he enjoys historical documentaries and volunteering at local clinics.
Related Articles
.webp)
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.
US government and civics
Course: us government and civics > unit 5.
- Ideologies of political parties in the United States
Ideologies of political parties: lesson overview
- Ideologies of political parties
Dominant US ideologies and political parties
Other ideologies and parties, review questions, want to join the conversation.
- Upvote Button navigates to signup page
- Downvote Button navigates to signup page
- Flag Button navigates to signup page

6.1 Political Socialization: The Ways People Become Political
Learning outcomes.
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Define political socialization.
- Describe the main influences on a person’s political socialization.
- Analyze the ways social media has affected political socialization.
- Discuss the factors that determine which influences will have the greatest impact on a person’s political socialization.
Do you consider yourself to have a political identity? Do you belong to or identify with a political party? Do you have a political ideology, such as conservative, libertarian, liberal, or populist? Are you apolitical (indifferent to politics), or are you deeply engaged in political action? Whatever your answers are, there is a chance—but a rather small one—that you deliberately and thoughtfully made these choices at a single moment by analytically comparing the various alternatives. It’s more likely that your choices gradually emerged over time through a complex combination of environmental and social influences interacting with your own personal biological and psychological makeup.
It is not entirely clear how Greta Thunberg became a climate change activist, for example, although her father Svante was named after his grandfather, a Nobel Prize–winning scientist who identified the link between increases in atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) and higher global temperatures. 5 She grew up in Sweden, a country with a strong ethic of environmentalism (by some measures, it is ranked as the most environmentally friendly country in the world). 6 She reports learning about climate change by age eight and credits the American student activists who protested gun laws after the Parkland, Florida, school shootings with inspiring her to act. 7
The gradual process of developing values and beliefs, of people becoming who they are as adults, is socialization , and the slow development of who a person becomes as a political being is political socialization . 8 Through political socialization, people develop their political ideology in the broadest sense. This includes not only their values and attitudes regarding the role of citizens and the government, but also regarding issues such as social justice or climate change. Socialization also influences whether a person is likely to have any interest in politics at all.
Political socialization is neither premeditated nor preordained, although there is a growing body of evidence that indicates that there are genetic links to political predispositions. 9 As an infant, you did not choose who you would become as an adult. As you grew, you were subject to a wide variety of forces that shaped your personality. Some of these forces were present in your physical environment, such as your home (Was there lead paint on the walls?), your neighborhood (Was it safe?), 10 and your school (Was it a place you looked forward to going to?). 11 As your physical environment shapes your learning, it also influences your views and attitudes, even if you are unaware of these influences.
The line from your social and physical environment to your political personality may be indirect. If you grew up in a heavily policed neighborhood, attended a deteriorating school, and lacked safe drinking water, your attitudes about government are likely to differ from an otherwise identical individual who lived in a comfortable home with safe drinking water and attended a well-resourced school in an affluent neighborhood. Humans are complicated, and it would be unwise to conclude that all those growing up in privilege are identically socialized or that those raised lacking such privilege all have the same political personalities. Your social and physical environments do not determine your political personality, but they can have an important influence.
The Role of the Family
The family is usually considered the most important influence on both a person’s overall socialization and their political socialization . Families profoundly affect people’s views about religion, work, and education. 12 People gradually develop these preferences, attitudes, and behaviors as they grow from infants to adolescents to adults. The impact families have on people’s lives does not vanish when they become adults. It is likely to persist over their lifetimes. The influence need not always flow from the parents to the child. Greta Thunberg ’s activism led her parents to reconsider their own environmental attitudes, and research suggests that children often affect their parents’ views on the environment. 13
Your family is likely to exert a substantial influence on your political views. 14 In some political settings in which a child’s identity is defined by religion, ethnicity, and place, their political views may seem almost predetermined. In Bosnia-Herzegovina, for example, the three main groups tend to be divided by ethnicity and religion, which largely define their political affiliations. Ethnic Bosniaks tend to be Muslim, Croats tend to be Roman Catholic, and Serbs are mainly Orthodox Christians. These differing ethnic and religious groups largely determine individuals’ political affiliations: there is little political intermingling across ethnic and religious lines. 15
In most places around the world, if parents raise their children in a particular religious faith, those children are more likely than not to adopt that faith as they become adults (or, if the children are raised in no faith, they are less likely to have religious connections as adults). 16 The same is true for almost any other important facet of life: social attitudes, beliefs about the role of the family, and yes, political beliefs. This is not to say that beliefs are automatically transmitted: young people have agency and may accept, reject, or simply question what their parents believe. 17
THE CHANGING POLITICAL LANDSCAPE
The changing family.
Families play a key role in political socialization, and family structure is evolving in different ways around the world. One fundamental change is family size; fertility rates have dropped in virtually every country in the past century.
The People’s Republic of China (PRC) provides an extreme example. When the PRC was established in 1949, the government encouraged families to have children to create additional workers, and by the 1960s the typical Chinese family had six children. At that point political leaders became worried about rapid population growth, and so in 1980 they instituted a one-child policy strictly enforced through a combination of benefits and often-harsh penalties. The policy dramatically slowed population growth, and it substantially increased both the age of and the percentage of males in the population. Under this policy, a cultural preference for male children led to sex-selective abortions and female infanticide. Believing that they had gone too far, the Chinese government lifted the one-child policy in 2016. 18
What It Was Like to Grow Up under China’s One-Child Policy
In this TED talk, Chinese filmmaker Nanfu Wang describes her experiences as a child growing up under China’s one-child policy and as an adult making a documentary about people’s experiences under the policy.
Family structure involves not only how many children are in a family, but where they live when they effectively become adults. As of 2016, a higher percentage (52 percent) of 18-to-29-year-olds in the United States were living with their parents than at any time since 1900. 19 Among wealthy countries, the percentage of 15-to-29 year-olds living with their parents varied from about 80 percent in Italy to 30 percent in Canada. 20
Given what we already know about how family members can influence each other’s political attitudes and beliefs, it will be interesting to see how these changing family structures and living conditions impact political socialization .
Your parents’ political leanings and your broader family environment affect your political views. For example, who is expected to take responsibility for caring for parents as they age varies from country to country. In China, caring for one’s parents is a sacred duty; in Norway, it is more often seen as an obligation of the government. Germans and Italians are more than twice as likely as Americans to say that the government, rather than the family, has the main responsibility for caring for the elderly. 21
Note that these statements, like other generalizations, are not true for every person in every circumstance everywhere. Some children of devout worshippers become atheists, some people raised as capitalists become communists, and some of the children of political, social, and cultural liberals become ardent conservatives.
When making these generalizations, this chapter uses words like “generally” or “tend” to suggest that the statements are accurate for the bulk of the group or characteristic being discussed. For example, in the United States, about 7 out of 10 teenagers have political ideologies and partisan affiliations similar to their parents: liberal teens tend to have liberal parents, and conservative youth generally have conservative parents. Still, about one-third of US teenagers adopt different political ideologies from those they were raised with. 22
Bernie Sanders Says His Childhood Shaped His Political Views
In a 60 Minutes interview, Senator Bernie Sanders describes how his childhood experiences helped shape his political views.
The identities of a young person’s parent(s) affect that person’s political socialization . If parental engagement in politics is high and party identification is strong, children are more likely to adopt those attitudes and behaviors than if parental political engagement is low and their partisanship indifferent. 23 Family structure—whether a child is living with two parents or a single parent, and whether parents are married, divorced, or cohabitating, for example—raises complex issues for political socialization that are not well understood. 24 Moreover, the impact of the family on socialization is not limited to children. Family dynamics also impact the political socialization of adults. 25
Your living situation growing up largely determines what influences you will encounter as you mature. Your school can influence your political socialization, as different schools have differing teaching philosophies, student bodies, and political activities. Likewise, your place of worship may have a profound influence on who you become. When you are young, your parents or guardians probably choose your school and religion; however, as people grow older, many of them spend less time with their parents or guardians and more time with their peers, including friends at school, work, community, and play. You may change your language, clothing, and interests to fit in with those in your group. And as you grow older, you are increasingly able to make your own decisions.
It is less clear whether your peers will have a lasting impact on your political socialization. Like many things when you are growing up, your choice of peers is not entirely in your control. Most children don't pick where they live and where they attend primary school, and those two factors play a big part in determining the pool of people from which individuals can choose friends. In short, your parents’ life circumstances and choices shape who your peers are likely to be. Still, context is important. Before the advent of social media, parental decisions would almost entirely determine your pool of peers. Now, given internet access, young people can find their peer groups virtually anywhere.
Increasingly, young people rely on social media to learn about the world and connect with others. Political scientists are still trying to decipher what this means for political socialization. In the past, a young person’s peers tended to be local: other members of the clan, the village, or the church. Today, a young person’s peers can be almost anywhere in the world, assuming they understand the same language, and thus young people (and adults) can more easily choose their peers based on common interests and beliefs than they could in the past. To the extent that young people, and indeed all individuals, can choose their social networks rather than being placed in them by virtue of their location, it is more likely that peer networks will reinforce existing beliefs, attitudes, and behaviors rather than change them. The ability of individuals to choose their social networks leads to “echo chambers,” which Chapter 12: The Media will examine further.
Other Affiliations
Your family and peers greatly influence your political opinions, attitudes, values, and behaviors, but there are other important influences. How much these other influences affect a person’s political socialization depends, in part, on how important they are to the person’s identity and daily life.
What Does Being Indigenous Mean?
In this clip, Indigenous people in Canada explain what it means to them to be Indigenous.
Consider ethnicity. The dominant ethnic group within a country—the White British within the United Kingdom, for example—may not perceive their ethnicity as having much of an influence on their political socialization, but its impact is likely to be profound. Members of ethnic majorities may be more likely to assume that politics and government should favor their interests as a matter of course because they may (naively) believe that what is good for them is good for everyone. Ethnic minorities, in contrast, may be socialized to feel the sting of discrimination and to view the government as no friend. One’s ethnic identity is likely to be more salient if that identity signifies one as an outsider. 26
If you were raised in a devout family, that family’s religion may have an important influence on your political socialization. 27 In the United States, for example, those individuals identifying as evangelicals are much more likely than the rest of the population to favor socially conservative public policies such as prohibiting same sex marriage or curtailing abortion rights, and they are much more likely to support the Republican Party. At the opposite end of the spectrum, those raised as atheists are more likely to believe that governmental policy should not be based on religious principles. 28
Gender roles and gender identification can influence an individual’s political socialization. Socialization into “traditional” gender roles may discourage women from developing interest or participating in politics, while in countries with women in leadership positions, young women may be socialized to become more politically aware and active. 29 The impact of gender identification and sexual orientation on political socialization is not well understood, but it seems likely that the greater the importance a person places on these attributes and the more intense the formative experiences they have regarding these attributes, the greater the influence these attributes will have on that person’s political socialization. 30
Even though young people spend a lot of time in school, the impact of schooling on political socialization appears to be modest. Why? The schools children attend often reflect the choices and environment of their parents, so they have little independent influence on socialization. For example, if you come from a religious home and your family has the means to do so, your parents might choose to send you to religious school; this reinforces the influence of the family’s religion on socialization. More broadly, the schools young people attend are likely to reflect the conditions and values that already exist in their environment.
People are socialized as individuals, and they are socialized in groups, including their family, peers, and others in their social environments. As people are socialized, they become part of larger groupings of individuals with common characteristics. The next sections discuss these larger groupings.
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/introduction-political-science/pages/1-introduction
- Authors: Mark Carl Rom, Masaki Hidaka, Rachel Bzostek Walker
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Introduction to Political Science
- Publication date: May 18, 2022
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/introduction-political-science/pages/1-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/introduction-political-science/pages/6-1-political-socialization-the-ways-people-become-political
© Jan 3, 2024 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

Politics Essay Writing Guide

The analysis of political life is largely based on the written word. In both academic and ‘real world’ debates on politics, the examination of texts – books, journal articles, official reports, declarations etc. – is central and highly prized. All of the great political speeches in history began life on a blank page before a word was even uttered. In your studies as a politics student, it should not be surprising, therefore, that the practice of writing will occupy a major proportion of your time. This will involve you doing different types of writing, including shorter presentation outlines in seminars, book reviews, examination answers and larger dissertations. This guide is focused on the art of essay writing, although many of the recommendations expressed below will be relevant to the other forms of writing you will conduct. At the outset, it is important to underscore that there is no single ‘correct’ way to write a great politics essay but, rather, many potential avenues that could be selected. However, this guide contains a series of suggestions and tips that, if acted upon in an effective manner, may increase the likelihood of you achieving higher marks and enjoying the essay writing experience.
Related Papers
Writing Politics: Studies in Compositional Method
Michael Shapiro
Melissa E Lovell
Where They Belong: Political Content & Engagement Chapbook
Melissa Sipin
Adam Etinson
e-International Relations (online)
James R M Wakefield
Gregory A. McBrayer
afraz ahmad
Usamah Hussain
Ian Mabbett
RELATED PAPERS
mukti adi jaya
Advances in Pure Mathematics
Dr. Rehena Nasrin
The Japanese journal of ergonomics
Takashi Toriizuka
Antimicrobial stewardship & healthcare epidemiology
Bastienne Klein
Proceedings of Scandinavian GIS
Simonas Šaltenis
Vegetation History and Archaeobotany
Kevin Edwards
Data in Brief
Marco Cenni
Applied sciences
Zsofia Czinege
Journal of Applied and Industrial Mathematics
Alexander Kononov
Donato Sisto
Alzheimer's & Dementia
Jerome Braudeau
Prosiding Seminar Nasional Ekonomi dan Bisnis
Audito Anugrah
Ankit maurya
Rekomendasi Makan Malam
Archives of Oral Biology
Vinayak Joshi
Oncology Reports
Marianne Schmidt
Irrigation and Drainage
shahbaz khan
Invertebrate Systematics
Shane Ahyong
2020 IEEE Frontiers in Education Conference (FIE)
Mats Daniels
Applied Nursing Research
maryam niknamy
Journal of Urology
William Tinmouth
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
Department of Political Science

Senior Essays in Political Science
Introduction, summer research, the advising process, the one-term senior essays in conjunction with a seminar, the independent, one-term senior essay course (plsc 480), length and format of one-term senior essays, year-long senior essays, the intensive senior essay, the qualities of a good senior essay, an important note research on human subjects, submitting the essay, penalties for late submission, senior essay grades and grade submission.
- Senior Essay Prizes
One of the requirements of the Political Science major is the senior essay. The senior essay is an opportunity to go more deeply into a topic or puzzle than you ordinarily would on a final assignment for a course. At first, this may seem like a daunting task. This document is designed to allay some of that anxiety as well as familiarize you with things you need to know about the essay requirement.
Most Political Science majors write their senior essays in conjunction with a one-semester seminar. A small number of students write it in the independent, one-term senior essay course (PLSC 480), the year-long senior essay courses (PLSC 490 and 491), or the intensive senior essay courses (PLSC 490 and 493). More information can be found on these various options below
Whatever the venue in which you write your senior essay, you will have to develop a research topic, formulate specific questions that your essay will try to answer, and offer a strong motivation for the project – make the case to your readers that something valuable would be lost if your research questions were not answered. Your adviser will be your most important resource in helping you to develop the topic, questions, and motivation. There are also published guides that can help. A good one is:
• Wayne C. Booth, Gregory G. Colomb, and Joseph M. Williams. 2008. The Craft of Research. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
Another valuable resource is reference librarians, both in the Social Science library and elsewhere in the Yale library system. Many useful sources are now available on-line; the reference librarians will often be more up-to-date about how to access these resources than your adviser.
During part or all of the summer between their junior and senior years, some students choose to conduct research related to their eventual senior essay project. Some carry out research in the United States, others abroad. The Political Science Department distributes, on a competitive basis, Frank M. Patterson grants for such research (Patterson grants also support summer internships). Application deadlines are posted on our Undergraduate Funds Page . Yale supports summer undergraduate research through several other programs; the link to the “Grants and Fellowships Database” is on the website.
There are several settings you can enroll in for the writing of your essay, as described in the next sections. Common to all of them, however, is the need for a close working relationship with an adviser, be it the instructor of the senior seminar in which you write your essay or an adviser for your independent research. Of absolute importance is for you to make and appear at regular appointments, and to submit drafts of your ongoing work on time. This means that, at the outset, you need to make an agreement with your adviser about a schedule for meetings and preliminary drafts. You will find some suggestions about a schedule below. Do not wait for your adviser to bring up this matter or suggest a schedule. Having a set of deadlines can have an important effect on your time management and the ultimate quality of your essay.
If you are unsure about whom to recruit as an adviser and which seminar to take, use the Political Science website to get more information about our faculty and their interests . Although the ideal adviser is someone with whom you have taken courses and interacted in the past, many students have good experiences working with instructors with whom they have never worked before. Most importantly, you will want to select someone whose research and teaching interests overlap with your own. (It’s not that he/she has to have published on your topic, but you usually would not ask an international relations expert to advise you on an essay in, say, political philosophy.)
When thinking about the faculty adviser, keep in mind that the Department requires that this person be an instructor in Political Science. Such an instructor may, for example, be in the Sociology department, but teach a course that is cross-listed with Political Science. The objective behind this rule is to have students approach their topic as a Political Scientist would. Please feel free to turn to Yale instructors who have no connection to the Political Science Department for informal advice, but your formal adviser must be an instructor in the Department. If you have any questions about whether an instructor is qualified to advise you, please consult with the DUS.
When you are in the process of recruiting an adviser, give him or her the sense that you are hard-working, committed, and independent. Yale faculty are committed to research and enjoy guiding students through what is usually their first research experience. But keep in mind that Yale professors are also very busy people, with multiple responsibilities. Email is not the most effective way to initially contact a potential adviser; they receive dozens each day and yours may fall through the cracks. A better strategy is to visit the instructor during her or his office hours , describe your thoughts on the project, and explain why you hope to work with them. In advance of the meeting, review the information on the faculty member’s personal web page, so that you are familiar with their research and how their areas of expertise relate to your topic.
You should plan to meet with your adviser regularly over the course of the semester and we recommend that you meet at least once every three weeks. In many ways, the most crucial meetings will be the early ones, when she or he helps you to develop a topic and identify sources. Furthermore, many seniors incorporate primary materials into their essay, and/or analyze publically-available information in new and inventive ways. Your adviser can help you to develop an understanding of what the relevant primary materials might be for your chosen topic, and how to go about finding, assembling, and analyzing them. While your adviser can make suggestions on your research design and suggest relevant sources, it is your responsibility to conduct the research on your topic and gather the relevant literature. In addition, your adviser can provide written and oral commentary on your drafts and give you constructive criticism on your arguments and evidence. However, keep in mind that your adviser is not responsible for providing you with an answer to your research question; it is up to you to decide upon the argument you would like to make. Please know that the best senior essays at Yale make exceptionally creative arguments or depend on extensive and sometimes original data collection or field research.
We also recommend that you elect three deadlines to help pace your progress throughout the semester. The first should be for an essay proposal of 1-2 pages. Your proposal should identify a specific question, give a provisional answer to the question, and include a specific plan of research. The proposal deadline should fall around the third week of classes. The second and third deadlines should be for drafts of your essay. By “draft,” we mean a complete essay, including all elements (introduction, body, conclusion, full references, etc.). The first draft deadline should be approximately six weeks prior to the final essay deadline; the second should be around three weeks prior to the deadline.
If you are like most Yale students, your senior essay will be the longest paper you have written to date. It would be a big mistake to attempt to write it at the last minute. Remember that a bad process often results in a weak paper. The key to writing a strong senior essay is to start early, work steadily, and seek feedback well ahead of the final deadline. Start writing as soon as possible, even well before you really feel ready to do so. Often you will find that you are more ready than you suspect. Writing can also help you identify gaps in your research or argument. Also, it will be much easier for your adviser to give you useful feedback on an actual piece of writing than on an idea expressed verbally in a meeting.
This is the most common way that students write their essays. Ideally, you will write an essay in conjunction with a seminar on a topic about which you have done some prior coursework, and/or taught by an instructor with whom you have worked in the past. If you plan to write your senior essay in a seminar, review the course offerings for the full year and identify two or three potential seminars. Of course, the seminars being offered during the semester in which you plan to write the essay, and the availability of slots in these courses, may affect your choices and decisions. You may have good reasons to write your essay in one semester, but flexibility can also be an advantage. If the perfect course (for you) on African politics or the U.S. presidency is only offered in the fall, it may be worth it to change your plan and write your essay in the fall. If the ideal seminar isn’t being offered, we encourage you to broaden the list of seminars you would consider taking. Surely your interest can be sparked by a topic that is new to you at the beginning of the term and you can still write a satisfying one-term essay in this case.
Be sure to take advantage of the pre-registration process and apply for a slot in the seminars that interest you. Keep in mind that senior majors are accepted into seminars at higher rates than other students, especially when applying through pre-registration. Pre-registration is a great opportunity to make a case for yourself. In the form that the DUS provides to you, explain your background, previous coursework, and any relevant experiences you have had. You should also indicate that you would like to write your senior essay in his or her course. In other words, applying to a seminar is the first step in recruiting your adviser.
Once you have secured a slot in the seminar, be sure to meet with the instructor early, confirm his/her willingness to advise you on the essay, and have a full, substantive discussion about your topic and how to proceed. Again, office hours are a better setting for such discussions than classrooms crowded with students trying to get into that seminar. Please also have a discussion with your instructor early in the semester about his or her expectations for your senior essay and the course’s other assignments. Often, a term paper will be the final assignment in the seminar and your senior essay will be an extension of this paper. In fact, a senior essay differs from a term paper in that it is generally a bigger, more ambitious project. Whether you will produce a separate term paper as well as a senior essay is up to your instructor. In some seminars, the final project will not be a term paper; here again, it is up to your course instructor/essay adviser whether (if at all) your requirements in the course will be modified, in light of your work on the essay. What’s important is that you find out early in the term how the instructor wants to handle your course assignments.
Occasionally, students take a seminar with the intention of writing a senior essay and then, during the semester, change their minds. If you find yourself in this situation and would like to opt out, you should contact your instructor, the DUS, and the DUS Assistant.
Note: Seniors cannot take the course in which they write their senior essay Credit/D/Fail.
Some majors have a long-standing interest in a topic or a problem related to politics or public policy about which they want to write, but no seminar is offered that is related to their topic. Such students will frequently have worked with a faculty member in the past in a related course or project, and may have already taken the relevant seminars before their senior year. For these students, writing a senior essay in the context of the independent, one-term senior essay course (480a in the fall, 480b in the spring) is a good option. In order to pursue this option, they must recruit an adviser who is willing to work with them to develop a reading list and fulfill all of the other tasks involved in writing the essay. It is very important, if you want to fulfill your essay requirement this way, to approach a professor in the Department with your ideas and obtain her or his agreement to work with you before the term starts. For a fall essay, it would be best to do this in the spring of your junior year; for a spring essay, make arrangements during the fall of your senior year.
Please note that PLSC 480 counts as a course credit toward the total number of credits that a major is required to have. It does not, however, count as a seminar. Seniors writing their essays in this course also need to take a seminar during their senior year.
Whether you write your essay in a seminar or in PLSC 480, one-term senior essays should be double-spaced and at least 25 pages long using Times New Roman 12 and one-inch margins. This amounts to about 6,250 words, excluding long verbatim quotations, bibliography, tables and figures, or other appendices. You should include a title page with the title of your essay, your name, your adviser’s name, and the date. You must number the pages.
You are required to pay careful attention to footnoting or end-noting. You must have a bibliography or reference section. There is no single correct format for any of these, but you should choose a standard citation format and adhere consistently to it throughout.
You may want to consult your adviser to see if he or she has any specific requirements about the format. If you and your adviser agree that you may depart from the above requirements (other than length), you must indicate that in a note attached to the essay. If you and your adviser wish to reduce the minimum length, please contact the Director of Undergraduate Studies well in advance of submission for possible approval.
Some students elect to use the senior-essay requirement to take on a more extensive and substantial research project than could be carried out in a single semester. A small number of students write year-long senior essays. Many such students conduct related research during the summer between their junior and senior years. (This is by no means a requirement. See the section about sources of funding for summer research.) Year-long essays are expected to be substantially longer than a regular term paper. While there is no fixed length, the year-long senior essay is usually about 50-60 pages in length.
To write a year-long senior essay, students must apply during the spring term of their junior year. The application is usually due at the end of March. (Check the website for exact deadlines ). Students should submit to the DUS Office: (1) the yearlong senior essay prospectus form signed by the faculty adviser who has agreed to supervise the student’s essay, (2) a two-page statement of project, and (3) an up-to-date transcript. Normally a successful candidate will have at least an A- average in Political Science and a B+ average outside the major. It is expected that no more than fifteen students will be admitted.
Students who are admitted take two courses related to their essay. In the fall of their senior year, they take PLSC 490a, The Senior Colloquium, a course designed to hone their research skills. In this course, they develop a research prospectus for the senior essay, begin their research, and share their progress on a weekly basis with their instructor and their fellow classmates. (Note that 490a counts as a senior-year seminar.) In the spring, they take PLSC 491b, The Senior Essay, in which they work closely with their adviser to complete the essay. Please know that students receive a temporary grade of Satisfactory or Unsatisfactory in 490a. Once they have completed the senior essay, they receive a letter grade, which applies retroactively to 490a and to 491b.
During their junior year, a small number of students are accepted into a version of the major called the Intensive Major. To be accepted into this major, students need to apply in November of their junior year. (Check the website for exact deadlines ). During the spring of their junior year, Intensive Majors take PLSC 474b, Directed Reading and Research for Junior Intensive Majors. In the fall term of their senior year, they take PLSC 490a, The Senior Colloquium, and in the spring term they take PLSC 493b, Senior Essay for Intensive Majors. By taking PLSC490a/493b, Intensive Majors pursue a year-long independent study in partnership with their adviser. The intensive senior essay is similar to the year-long senior essay in scope and length.
There is no single standard or set of standards for what constitutes an excellent senior essay. For specific guidance, rely on your adviser. For a political science essay, of course, you should situate your essay within the best and most important literature on the politics of the question being examined (including political science literature), engage with the relevant ideas and controversies (both public and academic), bring to light important relevant evidence (with due research diligence), and engage the reader with an original, distinct, and hopefully even distinguished argument.
Rarely does an excellent essay rely exclusively on articles, especially journalistic ones, found on the internet with a search engine. Read and rely on a few scholarly books too, as well as academic journal articles. A good way to get leads on what those might be is to trace the published sources identified in footnotes of interesting books or articles you have already found. Be sure to consult your adviser about the quantity and quality of sources you are using.
Needless to say, good writing is an essential element to a good essay—that is to say an essay that is clear, engaging, and otherwise “a good read.” Strive for a captivating introduction, and a satisfying conclusion. Write, re-write, and re-write again, until the argument develops and flows from paragraph to paragraph, from beginning to end. You should, by all means, seek advice from resources in the Yale University Center for Teaching and learning (CTL) writing labs .
If you use a source for your essay, you must acknowledge it. It hardly needs saying that evidence of plagiarism can result in a failing grade for your senior essay and a delay of graduation. Plagiarism is the use of someone else’s work, words, or ideas as if they were your own. You must make clear in your written work where you have borrowed from others—whether data, opinions, questions, ideas, or specific language. This obligation holds whether the sources are published or unpublished. What counts as a source varies greatly, but the list certainly includes readings, lectures, Web sites, conversations, interviews, and other students’ papers. For more information see the Center for Teaching and Learning’s ‘What is Plagarism?’ page .
Ethical concerns incorporated in university rules require prior approval from Yale’s Human Subjects Committee for research involving gathering information from human subjects (a living person about whom an investigator gets identifiable private information through either a direct interaction with the person or through access to private data sources) in interviews, participant observation, experimental, medical and other personal records and potentially other kinds of research. Material gathered through such research cannot be included in your senior essay unless you received prior approval. Be sure to discuss this matter early with your adviser, and both of you should consult the Yale Human Research Protection Program and review the Educational Resources available on their website.
Upon completion of your essay, you must deliver a hard copy to your adviser. We recommend that you have your thesis bound, but this is not required. (If you choose to bind it, we recommend TYCO Printing, DocuPrint & Imaging, or Staples.) At the very least, it should be stapled. You may want to ask your instructor what he or she prefers.
You also need to email an electronic copy, in Word or PDF, to the DUS Office (send to undergrad.polisci@yale.edu ). You must include the entire essay (all text, tables, bibliography, etc.) in one electronic file. Please name the electronic version of your essay as follows: Last name_First name.
Note: You must submit a hard copy to your adviser, but we ask that you do not deliver a copy to the DUS Office as well. Instead, please send an electronic copy only to undergrad.polisci@yale.edu .
Your Senior Essay Prospectus form is due during Shopping Period of the semester in which you plan to write the essay. This form will outline your plans for completing the essay and, like all Political Science forms, it is available on the Political Science website ( http://www.yale.edu/polisci/undergrad/forms.html ). Please submit a hard copy of this form to the DUS Assistant in Rosenkranz Hall, Room 130. Check the Political Science website to see the exact date it is due ( http://www.yale.edu/polisci/undergrad/deadlines.html ).
NEW: the independent essay courses (PLSC 480, 490, 491, 493) now carry red permission keys. Students who enroll in PLSC 480 will not be able to seal their schedules until they have submitted the Senior Essay Prospectus form by the Department’s deadline. Once the DUS has signed your form, you will receive a green permission key and will be allowed to seal your schedule. Students who enroll in PLSC 490, 491, and 493 will automatically receive a green key before schedules are due.
Mid-way through the semester, the DUS Assistant will ask you to submit your tentative essay title. Please respond promptly. The title should give a clear idea of what your research is about. We need working titles early on to help the staff assign appropriate second readers to your essays. You are free to modify the title before final submission.
Please check the Undergraduate Program Deadlines Page to learn the date the senior essay is due and know that it is due no later than 4:00 p.m. on that day. By 4:00 p.m., you must give a hard copy to your adviser. You must also send an electronic copy to the DUS Office ( undergrad.polisci@yale.edu ). (Please do not deliver a hard copy to the DUS Office.)
We understand that in rare cases, unexpected or extenuating circumstances interfere with a student’s plans to complete his or her essay on time. Please know that extensions can only be granted by your residential college dean. Instructors cannot grant an extension unless the residential college dean has authorized one. In the event that you receive an extension, please submit a Dean’s Excuse to your adviser and the DUS Office that explains why the essay is late.
A late essay, for which there is no authorized extension, is penalized one half letter grade (e.g., A to A-) for each three days the essay is late.
Your faculty adviser will serve as the first reader of your senior essay, and will assign it a letter grade. The DUS will also appoint an anonymous second reader, who will assign a grade of Satisfactory or Unsatisfactory. (The second reader’s grade does not average into your final grade.) In the rare case of a failing grade from the first reader or an Unsatisfactory grade from the second reader, you will be asked to revise the essay and resubmit it.
Note that in order to graduate from Yale College, a student majoring in Political Science must achieve a passing grade on the senior essay.
If the essay is written for PLSC 480, the grade on the essay is the grade for the course. Instructors will be asked to report that grade to the DUS Office who will submit the grades on the Faculty Grading Submission site (FGS). If the essay is written in a seminar, the adviser will report the essay grade to the DUS Office and will calculate the grade for the seminar based on the essay and the other course requirements. Seminar instructors will be asked to submit their course grades on FGS. Please consult your adviser (not the DUS Office) for your final essay grade.
Your essay grade helps determine whether you will receive distinction in the major. To graduate with distinction in Political Science (as in all majors), you must receive an A or A- on your senior essay (as well as course grades of A or A- in 75% of your Political Science courses).
Senior Essay Prizes
Faculty advisers (and second readers) may nominate senior essays, whether written in the fall or spring semester or as year-long projects, for the following prizes:
- James Gordon Bennett Prize for the best senior essay in International Relations.
- Philo S. Bennett Prize for the best senior essay in Political Philosophy.
- Charles W. Clark Prize for the best senior essay in Comparative Government or Politics.
- Frank M. Patterson Prize for the best senior essay on the American Political System.
- Percival N. Clement Prize for the best senior essay in support of the principles of the American Constitution and its first ten amendments.
At the end of the academic year, all of the majors and all faculty members will be notified of the recipients of these prizes. In addition, these essays will be posted on the Department’s website. YOu can see previous years award winner and their essays on the Prizes Page .
What are your chances of acceptance?
Calculate for all schools, your chance of acceptance.
Your chancing factors
Extracurriculars.
Can I Talk About Politics on My College Applications?
What’s covered:, why is talking about politics not recommended, where can you mention politics in your application, how not to talk about politics in your application, how to effectively talk about politics in your application, where to get your essays edited.
For students interested in politics and government, you are told two conflicting pieces of information when it comes to college applications: talk about your interests and avoid politics. But if you avoid discussing politics, how will you show colleges what you are passionate about?
We are here to make sense of this sticky situation and hopefully release you from the double bind politics can create. This post will explain when you can talk about politics in your application and how you should, and shouldn’t, go about it.
The general advice to avoid politics in college applications stems from the idea that you don’t want to offend anyone with your application. Politics is a charged topic that many people have strict opinions on, and although admission officers are supposed to be unbiased, they are still human and no one wants to feel like their ideals are being challenged.
As a student, you have no idea who will read your application, so you have no way of knowing that person’s political beliefs. You might have liberal-leaning views on topics like gun reform and reproductive rights, but the admissions officer on the other side of your application might feel totally different. Even mentioning touchy subjects without discussing your opinion, like election losses or Supreme Court decisions, might trigger your readers and negatively impact how they perceive you.
It’s also recommended to avoid politics because institutions as a whole can have cultures that align with specific political ideologies. For example, liberal arts colleges are known for being more progressive and left-leaning, while some religious universities are aligned with more conservative values. It’s incredibly important to do your research before starting your application to gauge the culture of the school you are considering.
All that being said, don’t automatically assume you can write about how great the Democratic party is if you are applying to a liberal arts college. Just because a college has a reputation for a certain political affiliation does not mean each individual admissions officer identifies with that view.
With all the traps you can fall into, we normally recommend steering clear of the topic. However, if politics is an essential part of who you are, take these recommendations with a grain of salt and learn how to write about politics in an effective, non-offensive way.
There are two main places in your application where politics will come up: your activities and your essays. You will never be directly asked about your political beliefs or party affiliation, so it would only come up on your application if you write about it in these two sections.
In the activities section, you can include political extracurriculars you are involved with. If you were the president of the Young Democrats/Young Republicans club at your school or the social media manager for a state representative, you should include those activities with pride. Don’t worry about hiding them at the bottom of your application; if they were your most impressive and most important extracurriculars, give them the attention they deserve.
Essays are the other place you can discuss politics because it allows you to expand on your passions. You could use your involvement with politics in a variety of essays, including your personal statement, community involvement topics, and extracurricular topics. However, you might encounter a topic about political and global issues , and in this case, you are welcome to—and expected—to discuss politics.
Stating Your Beliefs Without Providing Context to Your Life
Your political beliefs didn’t just appear out of nowhere—they were shaped and have evolved over years of life experience. Colleges care way more about the life experiences that shaped you and led you to hold your views than what the views are themselves.
If you are talking about politics and just tell us what you believe without explaining why that’s the case, it could alienate your readers who disagree with your position. But, providing perspective on the experiences that shaped your opinion will make it easier for people with different beliefs to empathize and appreciate where you are coming from.
For example, writing about how you hate guns and think they should be banned in your essay might not go over well with your audience who holds a different view on guns. However, if you explain the mental strain of lockdown drills and the constant anxiety you feel because you grew up hearing about school shootings, your readers will be more understanding of why you have that view.
Describing a Politician’s Beliefs in Detail
When you are explaining the work you did on a campaign or as a politician’s assistant, don’t tell us what that politician’s political views are. Your college application is about you, not a politician, so no one needs to hear about their views on immigration, the work they’ve done to expand rights, or the bills they have sponsored and passed. Talk about the work you did, for example writing memos, sitting in on town hall meetings, and answering constituent questions.
The one exception to this is if you chose to work with a specific politician because of a specific issue they fight for that connects to you. If you volunteered with a politician working on expanding Green Card access because you come from a family of immigrants, then it’s okay. Just keep the focus largely on your background and connection to the topic, rather on the work the politician is doing.
Openly Trashing Other Viewpoints
This should be pretty self-explanatory, but don’t outwardly criticize and demonize opposing political beliefs. Going back to the points made before, you never know who will read your application and you don’t want to offend them. It goes back to the saying from kindergarten: if you don’t have something nice to say, don’t say it.
Lying About Your Stance
If you really want to attend a school where your political beliefs clash with the general culture of the school, don’t lie just to fit in. Students might be tempted to say their views align with the overall vibe of the school, but no good can come from lying on your application.
Even when a school has a reputation for leaning towards one political ideology or the other, admissions officers want to create a class of diverse perspectives, so you don’t need to conform perfectly to the average student to gain admission.
Focus on Your Involvement Rather than Your Beliefs
When it comes to describing political extracurriculars, either in the activities section or your essays, the focus should be on your involvement, achievements, and lessons learned.
When writing about your work with the Young Democrats, say how you “ Organized annual voter registration drives where over 150 students registered for the upcoming election, ” rather than how you were “ Part of a club that promoted Democratic perspectives on topics like abortion, immigration, and the economy. ”
Treat your political extracurriculars like any other—you wouldn’t describe each soccer drill in depth, instead you would explain how you demonstrate leadership by carefully picking drills based on each player’s weakness. Use your involvement with politics to highlight your character and accomplishments, but don’t dwell on the nitty-gritty details of your beliefs.
Be Open-Minded to Different Perspectives
People tend to be very polarized on certain political topics which makes it difficult to discuss issues rationally. Having an open mind and being willing to hear new perspectives is not only an invaluable skill for future politicians, but any productive citizen. You want to demonstrate in your application that although you might hold certain beliefs, you are always committed to learning and engaging in productive debate to expand your perspective.
Align With the School’s Culture (As Best You Can)
As we mentioned before, each college has its own unique culture that you should take into account when discussing politics. If you are applying to a school like BYU, a Mormon-sponsored institution, you should probably avoid taking a strong pro-LGBTQ stance in your application.
If politics are an important topic to you and you feel like the school you are applying to requires you to censor yourself, you should reconsider whether that school is a good fit for you. If you still want to attend, you can frame your political stances in a way to minimize the gap between your viewpoint and that of the school. You can also consider discussing a political issue that’s more economic than social, as economic issues tend to be less contentious.
Avoid Racism, Sexism, and Bigotism of Any Kind!
Racist, sexist, homophobic, or any other type of bigoted comments on your application are not okay and should never be included under any circumstances. Regardless of your personal views or those of the politician you worked for, avoid anything that could be perceived as offensive. Including anything along these lines is the easiest way for you to get your application immediately rejected.
To make sure that you’re talking about politics in a way that is respectful and productive, you will want to get your essays edited by others. That’s why we created our Peer Essay Review tool , where you can get a free review of your essay from another student. Since they don’t know you personally, they can be a more objective judge of whether your personality shines through, and whether you’ve fully answered the prompt.
If you want a college admissions expert to review your essay, advisors on CollegeVine have helped students refine their writing and submit successful applications to top schools. Find the right advisor for you to improve your chances of getting into your dream school!
Related CollegeVine Blog Posts

November 20, 2018
How Political Opinions Change
A clever experiment shows it's surprisingly easy to change someone’s political views, revealing how flexible we are
By Philip Pärnamets & Jay Van Bavel
Getty Images
Our political opinions and attitudes are an important part of who we are and how we construct our identities. Hence, if I ask your opinion on health care, you will not only share it with me, but you will likely resist any of my attempts to persuade you of another point of view. Likewise, it would be odd for me to ask if you are sure that what you said actually was your opinion. If anything seems certain to us, it is our own attitudes. But what if this weren’t necessarily the case?
In a recent experiment , we showed it is possible to trick people into changing their political views. In fact, we could get some people to adopt opinions that were directly opposite of their original ones. Our findings imply that we should rethink some of the ways we think about our own attitudes, and how they relate to the currently polarized political climate. When it comes to the actual political attitudes we hold, we are considerably more flexible than we think.
A powerful shaping factor about our social and political worlds is how they are structured by group belonging and identities . For instance, researchers have found that moral and emotion messages on contentious political topics, such as gun-control and climate change, spread more rapidly within rather than between ideologically like-minded networks. This echo-chamber problem seems to be made worse by the algorithms of social media companies who send us increasingly extreme content to fit our political preferences.
On supporting science journalism
If you're enjoying this article, consider supporting our award-winning journalism by subscribing . By purchasing a subscription you are helping to ensure the future of impactful stories about the discoveries and ideas shaping our world today.
We are also far more motivated to reason and argue to protect our own or our group’s views. Indeed, some researchers argue that our reasoning capabilities evolved to serve that very function . A recent study illustrates this very well: participants who were assigned to follow Twitter accounts that retweeted information containing opposing political views to their own with the hope of exposing them to new political views. But the exposure backfired—increased polarization in the participants. Simply tuning Republicans into MSNBC, or Democrats into Fox News, might only amplify conflict. What can we do to make people open their minds?
The trick, as strange as it may sound, is to make people believe the opposite opinion was their own to begin with.
The experiment relies on a phenomenon known as choice blindness. Choice blindness was discovered in 2005 by a team of Swedish researchers . They presented participants with two photos of faces and asked participants to choose the photo they thought was more attractive, and then handed participants that photo. Using a clever trick inspired by stage magic , when participants received the photo it had been switched to the person not chosen by the participant—the less attractive photo. Remarkably, most participants accepted this card as their own choice and then proceeded to give arguments for why they had chosen that face in the first place. This revealed a striking mismatch between our choices and our ability to rationalize outcomes. This same finding has since been replicated in various domains including taste for jam , financial decisions , and eye-witness testimony .
While it is remarkable that people can be fooled into picking an attractive photo or a sweet jam in the moment, we wondered whether it would be possible to use this false-feedback to alter political beliefs in a way that would stand the test of time.
In our experiment, we first gave false-feedback about their choices, but this time concerning actual political questions (e.g., climate taxes on consumer goods). Participants were then asked to state their views a second time that same day, and again one week later. The results were striking. Participants’ responses were shifted considerably in the direction of the manipulation. For instance, those who originally had favoured higher taxes were more likely to be undecided or even opposed to it.
These effects lasted up to a week later. The changes in their opinions were also larger when they were asked to give an argument—or rationalization—for their new opinion. It seems that giving people the opportunity to reason reinforced the false-feedback and led them further away from their initial attitude.
Why do attitudes shift in our experiment? The difference is that when faced with the false-feedback people are free from the motives that normally lead them to defend themselves or their ideas from external criticism. Instead they can consider the benefits of the alternative position.
To understand this, imagine that you have picked out a pair of pants to wear later in the evening. Your partner comes in and criticizes your choice, saying you should have picked the blue ones rather than the red ones. You will likely become defensive about your choice and defend it—maybe even becoming more entrenched in your choice of hot red pants.
Now imagine instead that your partner switches the pants while you are distracted, instead of arguing with you. You turn around and discover that you had picked the blue pants. In this case, you need to reconcile the physical evidence of your preference (the pants on your bed) with whatever inside your brain normally makes you choose the red pants. Perhaps you made a mistake or had a shift in opinion that slipped you mind. But now that the pants were placed in front of you, it would be easy to slip them on and continue getting ready for the party. As you catch yourself in the mirror, you decide that these pants are quite flattering after all.
The very same thing happens in our experiment, which suggests that people have a pretty high degree of flexibility about their political views once you strip away the things that normally make them defensive. Their results suggest that we need rethink what it means to hold an attitude. If we become aware that our political attitudes are not set in stone, it might become easier for us to seek out information that might change them.
There is no quick fix to the current polarization and inter-party conflict tearing apart this country and many others. But understanding and embracing the fluid nature of our beliefs, might reduce the temptation to grandstand about our political opinions. Instead humility might again find a place in our political lives.
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
Politics & Policy
Public’s positive economic ratings slip; inflation still widely viewed as major problem.
Today, 23% of U.S. adults say the economy is in excellent or good shape, and more than six-in-ten Americans (62%) see inflation as one of the top problems facing the nation.
Broad Public Support for Legal Abortion Persists 2 Years After Dobbs
In tight presidential race, voters are broadly critical of both biden and trump, changing partisan coalitions in a politically divided nation, sign up for our politics newsletter.
Our latest politics data every month
How Americans and Israelis view one another and the U.S. role in the Israel-Hamas war
Americans and Israelis now see one another’s leaders more negatively than in the recent past, and other key views have shifted as well.
More than half of Americans are following election news closely, and many are already worn out
More than half of Americans (58%) say they are following news about candidates for the 2024 presidential election very or fairly closely.
Majorities of both Republicans and Democrats remain fearful about the state of the country.
Americans have mixed views about how the news media cover Biden’s, Trump’s ages
Similar shares of U.S. adults believe news organizations are giving too much attention (32%) or too little attention (29%) to Biden’s age.
An Early Look at Black Voters’ Views on Biden, Trump and Election 2024
Black voters are more confident in Biden than Trump when it comes to having the qualities needed to serve another term.
Support for legal abortion is widespread in many places, especially in Europe
Majorities in most of the 27 places around the world surveyed in 2023 and 2024 say abortion should be legal in all or most cases.
Public Opinion on Abortion
Abortion has long been a contentious issue in the United States, and it is one that sharply divides Americans along partisan, ideological and religious lines.
Americans overwhelmingly say access to IVF is a good thing
Seven-in-ten Americans say in vitro fertilization access is a good thing. Just 8% say it is a bad thing, and 22% are unsure.
Views are split by political party, but support for legal abortion has risen modestly in both groups since before the 2022 Dobbs decision.
Americans are less likely than others around the world to feel close to people in their country or community
A median of 83% across 24 nations surveyed say they feel close to other people in their country, while 66% of Americans hold this view.
REFINE YOUR SELECTION
Research teams, signature reports.
Amid shifts in demographics and partisan allegiances, registered voters are now evenly split between the Democratic Party and the GOP.
Americans’ Dismal Views of the Nation’s Politics
Americans’ views of politics and elected officials are unrelentingly negative, with little hope of improvement on the horizon. 65% of Americans say they always or often feel exhausted when thinking about politics. By contrast, just 10% say they always or often feel hopeful about politics.
Beyond Red vs. Blue: The Political Typology
Pew Research Center’s political typology provides a roadmap to today’s fractured political landscape. It organizes the public into nine distinct groups, based on an analysis of their attitudes and values. Even in a polarized era, the 2021 survey reveals deep divisions in both partisan coalitions.
In a Politically Polarized Era, Sharp Divides in Both Partisan Coalitions
Partisanship remains the strongest factor dividing the American public. Yet there are substantial divisions within both parties on fundamental political values, views of current issues and the severity of the problems facing the nation.
Across the Table: Would you share your views of Donald Trump over dinner?
Tuning out: americans on the edge of politics, voters say those on the other side ‘don’t get’ them. here’s what they want them to know., political typology quiz.
1615 L St. NW, Suite 800 Washington, DC 20036 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
© 2024 Pew Research Center

Essay on Politics for Students and Children
500+ words essay on politics.
When we hear the term politics, we usually think of the government, politicians and political parties. For a country to have an organized government and work as per specific guidelines, we require a certain organization. This is where politics comes in, as it essentially forms the government. Every country, group and organization use politics to instrument various ways to organize their events, prospects and more.

Politics does not limit to those in power in the government. It is also about the ones who are in the run to achieve the same power. The candidates of the opposition party question the party on power during political debates . They intend to inform people and make them aware of their agenda and what the present government is doing. All this is done with the help of politics only.
Dirty Politics
Dirty politics refers to the kind of politics in which moves are made for the personal interest of a person or party. It ignores the overall development of a nation and hurts the essence of the country. If we look at it closely, there are various constituents of dirty politics.
The ministers of various political parties, in order to defame the opposition, spread fake news and give provocative speeches against them. This hampers with the harmony of the country and also degrades the essence of politics . They pass sexist remarks and instill hate in the hearts of people to watch their party win with a majority of seats.
Read 500 Words Essay on Corruption Here
Furthermore, the majority of politicians are corrupt. They abuse their power to advance their personal interests rather than that of the country. We see the news flooded with articles like ministers and their families involving in scams and illegal practices. The power they have makes them feel invincible which is why they get away with any crime.
Before coming into power, the government makes numerous promises to the public. They influence and manipulate them into thinking all their promises will be fulfilled. However, as soon as they gain power, they turn their back on the public. They work for their selfish motives and keep fooling people in every election. Out of all this, only the common suffers at the hands of lying and corrupt politicians.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
Lack of Educated Ministers
If we look at the scenario of Indian elections, any random person with enough power and money can contest the elections. They just need to be a citizen of the country and be at least 25 years old. There are a few clauses too which are very easy.
The strangest thing is that contesting for elections does not require any minimum education qualification. Thus, we see how so many uneducated and non-deserving candidates get into power and then misuse it endlessly. A country with uneducated ministers cannot develop or even be on the right path.
We need educated ministers badly in the government. They are the ones who can make the country progress as they will handle things better than the illiterate ones. The candidates must be well-qualified in order to take on a big responsibility as running an entire nation. In short, we need to save our country from corrupt and uneducated politicians who are no less than parasites eating away the development growth of the country and its resources. All of us must unite to break the wheel and work for the prosperous future of our country.
FAQs on Politics
Q.1 Why is the political system corrupt?
A.1 Political system is corrupt because the ministers in power exercise their authority to get away with all their crimes. They bribe everyone into working for their selfish motives making the whole system corrupt.
Q.2 Why does India need educated ministers?
A.2 India does not have a minimum educational qualification requirement for ministers. This is why the uneducated lot is corrupting the system and pushing the country to doom. We need educated ministers so they can help the country develop with their progressive thinking.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
student opinion
Should Athletes Speak Out On Social and Political Issues?
Do they have a responsibility to use their platform and influence to raise awareness? Or should they stick to sports?

By Jeremy Engle
Students in U.S. high schools can get free digital access to The New York Times until Sept. 1, 2021.
Are you a sports fan? Do you follow tennis? What was your reaction to Naomi Osaka’s U.S. Open title win in September and her use of masks to honor Black victims of violence?
The New York Times reported at the time:
Osaka, still just 22, is undoubtedly a great player already, and there was much for her to savor on many levels over the last three weeks. Much to ponder, as well, as she took on not only some of the toughest tennis players in the world but some of the thorniest social issues, as well. She handled the pressure on both fronts and returned to the fore in women’s tennis with Saturday’s gritty 1-6, 6-3, 6-3 victory. She wore seven masks with different names for each of her matches to honor Black victims of violence. She said it motivated her — “I wanted more people to say more names” — and she walked on court Saturday with a mask bearing the name of Tamir Rice, a 12-year-old boy shot and killed in Cleveland by a white police officer in 2014. “The point is to make people start talking,” Osaka said at the award ceremony.
If you watched the Open, what did you think of Osaka’s public display of activism? Did it make you more of a fan? Or did you feel it took away from your and other fans’ enjoyment of the game? Do you think the masks Osaka wore were an effective way to get people to start talking? (If you want to learn more about this moment, you can watch this short video profile on Osaka for Sports Illustrated’s 2020 Sportsperson of the Year.)
In “ Athletes, Speak Up ,” an essay for the Opinion section, Osaka writes about what inspired her:
“Shut up and dribble.” That’s what a news anchor suggested LeBron James do after he discussed racism, politics and the difficulties of being a Black public figure in America during an ESPN interview in 2018. LeBron, the activist, first caught my eye in 2012. He and his Miami Heat teammates posted photos of themselves in hoodies to protest the murder of Trayvon Martin , an unarmed Black teenager in Florida who was wearing a hoodie when he was fatally shot by George Zimmerman, a neighborhood watch volunteer. In 2014, Eric Garner , a Black man, died in Staten Island after police officers held him in a chokehold, a move banned by the police at the time and one that has since become illegal in New York State. Soon after, LeBron wore a T-shirt with the words “I can’t breathe” — Garner’s last words, which were captured on video as the officers strangled him — during a pregame warm-up. The rest of the league followed, but James was the focal point. Fast forward to this year and he is still in the cultural spotlight. LeBron has the loudest voice and the biggest platform, and he used them to protest systemic racism, inequality and police brutality, all while his game continued to flourish in the face of unprecedented protests, a world-changing pandemic and deeply personal hurts, including the tragic death of our mutual friend Kobe Bryant . LeBron is ferociously brave in his steadfast support of the Black community. He is unwavering, upfront and passionate. On the court or at the mic, he is simply unstoppable and an inspiration. He is dedicated to his craft, but equally dedicated to his community, even as he continues to fight against an established history of silencing athletes who speak out. Musicians sing and write about social movements, activism and equality all the time. Actors voice their opinions and often personally endorse political candidates, hosting fund-raisers and throwing parties. Business executives, authors and artists are almost expected both to have opinions about the latest news and to publicly defend their views. Yet when it comes to athletes, we are often met with criticism for expressing our opinions. Do people see us as no more than bodies — individuals who can achieve what’s physically impossible for nearly everyone else, and who entertain fans by pushing ourselves past our limits? Do they wonder if a collection of muscles, bones, blood and sweat might also be able to voice an opinion? Should sports just be sports, and politics just be politics?
Students, read the entire article, then tell us:
Do you think athletes should speak out on social and political issues? Or do you think they should stick to their sport? Are there limits to where and when they should express their views? Do you find that the activism of athletes interferes with your and other fans’ enjoyment of the game on the court?
What is your reaction to Osaka’s personal and passionate essay? Which of her arguments do you find most affecting and persuasive? Does it change how you view her or other activist athletes, like LeBron James? How would you respond to people who tell athletes: “Hit the ball. Sink the shot. Shut up and dribble”?
Osaka asks: “Do people see us as no more than bodies — individuals who can achieve what’s physically impossible for nearly everyone else, and who entertain fans by pushing ourselves past our limits?” How do you view athletes? Are you interested only in their physical prowess? Or are you interested in their life, opinions and views off the court?
The essay concludes:
Today, given the television coverage we receive and our prominence on social media, athletes have platforms that are larger and more visible than ever before. The way I see it, that also means that we have a greater responsibility to speak up. I will not shut up and dribble.
Do you agree that athletes have a responsibility to speak up? Do you think more favorably about athletes who take political stands? Do you think less of those who don’t? Do you think the political activism of athletes can make a difference?
Osaka cites many athlete activists, past and present, from Muhammad Ali to Colin Kaepernick to Megan Rapinoe. Which athletes and their activism are you most inspired by and why?
About Student Opinion
• Find all of our Student Opinion questions in this column . • Have an idea for a Student Opinion question? Tell us about it . • Learn more about how to use our free daily writing prompts for remote learning .
Students 13 and older in the United States and the United Kingdom, and 16 and older elsewhere, are invited to comment. All comments are moderated by the Learning Network staff, but please keep in mind that once your comment is accepted, it will be made public.
Jeremy Engle joined The Learning Network as a staff editor in 2018 after spending more than 20 years as a classroom humanities and documentary-making teacher, professional developer and curriculum designer working with students and teachers across the country. More about Jeremy Engle
You can Choose category
Political Science Essay Examples
Draw inspiration from your predecessors. Browse our free database of political science essays and research reports.
The complexity of our essay examples varies, but all have been checked for accuracy. Our database items have been written by the school, college, and university students.
Comprehensive database
The essay collection covers all political science topics and study fields.
Regular updates
If you haven't found the necessary example, repeat your search in several days.
Make your writing sparkle
We are glad to meet you on Politzilla.com, where you can learn from perfectly written political science essay examples. Besides, our resource features several helpful educational tools, lists of exam answers, homework solutions, professional academic assistance, and an extended multinational community.
This database will give you a second wind in creativity, enhance your writing skills, and facilitate the entire process of studying.
Most Searched Essay Topics
4,000 words
Latest Inquiries
India’s success in managing social divisions, the united nations: legitimacy sources, the most accurate political (development) model, evaluation of why we need the electoral college by ross, the impact of machiavelli’s “the prince” on european perceptions of power, the government and capitalism relationship, private sector human resource practice in federal civil service, discussion: freedom or governance, the complexity of the death penalty debate, the genesis of american governance, uganda: the democratic country, iran-united states relations and nuclear threat, the book “our global neighborhood” by the commission on global governance, how to increase voter turnout in the united states, international relations theories and states’ behaviors, globalization, economic integration, and humanitarian development, diplomacy: elements and application, the united arab emirates’ national security strategies, paper classifier.
We have grouped our enormous database by categories of papers to make the sample search easier and more efficient.
Our Clients Ask
How did you collect such a vast database, is the service 100% free, or will you ask me to pay for a subscription, what if i’d like to donate my writing, if there is no sample on the topic i need, can i ask for a custom-made one, what is the plagiarism level in your database papers, do you check the papers students donate.

6 ways to encourage political discussion on college campuses
Associate professor of education, University of Virginia
Disclosure statement
Rachel Wahl has received funding from the Spencer Foundation and the National Academy of Education
University of Virginia provides funding as a member of The Conversation US.
View all partners
With deep divisions on college campuses – most recently over the conflict in the Gaza Strip and Israel – many observers fear that universities are not places where students can discuss divisive issues with people who disagree with them. In my research and teaching, I have seen that students in fact want to have difficult conversations across divides, but they need support from faculty and other facilitators in order for these discussions to go well.
Since early 2017, I have been observing events on college campuses in which students are brought together with peers with whom they disagree to talk about politics. In these sessions, facilitators provide students with guiding questions that help them to understand their peers’ political views.
I conducted follow-up interviews with students a few weeks afterward and, when possible, three years later.
My aim is to understand what happens in these conversations. I want to know: Who learns what from whom? Who feels satisfied or frustrated, and why? And what does this all portend for America’s democracy?
The conversations I observed have taught me that six practices help to support a better experience for all students.
1. Set norms and expectations
When people talk about setting norms for conversation, they usually assume it is an effort to mandate speech rules. But norm-setting accomplishes something better than rule-following: It allows students to become sensitive to their own and others’ hopes and fears for the conversation.
In my experience, opening the session with questions such as “What do you most hope will happen in this conversation?” “What worries you most about the conversation?” “What are you willing to give to it?” and “What do you hope to get from it?” can show students that they already share more than they anticipate.
Moreover, this discussion leads naturally into the question of “How can we interact in a way that is most likely to realize our aims?” Students typically volunteer their own guidelines, such as assuming good faith, objecting to a person’s idea rather than attacking the person, honestly conveying when and why they feel hurt, and listening generously.
2. Allow students to tell their personal stories
Beginning with students’ personal stories lowers the barriers to entry, so that students who are not experts on politics can contribute. It allows students to feel heard about their direct experience. And it allows for what I have found to be the most profound outcome of dialogue: the shifts in how students feel about each other.
For example, consider the “ Can We Talk ” campus dialogue series, which brings together ideologically diverse students for two-hour sessions in which facilitators provide a series of questions for students to ask each other. The sessions began with questions such as, “How were politics discussed in the home in which you were raised?” and “What is your earliest political memory?” before moving on to questions about students’ substantive views on relevant issues.
The focus of these sessions, which I observed in the 2017-2018 academic year at colleges throughout Pennsylvania and New Jersey, is on cultivating students’ understanding of each other’s views and how they came to be.

If the dialogue is intended to focus on a specific issue, such as gun control , abortion or the war in Israel and Gaza , questions can be geared accordingly, such as “When did you first learn about this issue?” “How did it affect you at the time?” or “What about this issue draws you to this conversation?”
3. Encourage curiosity
Students are often afraid that they will end up validating views they oppose unless they try to discredit those views. But in follow-up interviews I conducted three years after their participation in a dialogue session, I found that those students who did eventually change their political views were prompted to do so through sincere and nonthreatening questions. “I remember one girl asked me, ‘If you say you believe this, then why did you vote like that?’ I’ve been asking myself that question ever since,” admitted one student, whose politics changed considerably in the years between our first and second interviews. It mattered most that she felt questioned, not attacked.
Questions can be encouraged throughout a conversation by reserving specific time for them in each round, as well as through directions such as “Think of one question you have always wanted to ask someone who thinks differently than you about this issue. Ask it now.”
4. Dig into disagreement
One risk of emphasizing personal experience at the start is that students hesitate to dig into their disagreements. They want to be supportive, and it’s hard to argue with personal experience. In my research, though, I found that students ended up with the deepest respect for each other when they gained understanding of the nature of their disagreements.
Clarifying what is at stake in their differences allowed students to see that their opposition was not caused by ignorance, malice or madness on the other side, but legitimate contrasts in views of what is good and possible.
After students have shared their views on issues and asked each other curiosity-oriented questions, they can be directed to ask each other questions such as “What is at the root of our disagreement?” and “What really matters to me, and to you, and is it the same thing? To the extent that it is not, why not?”

5. Collaborate on next steps
Students tend to feel most satisfied when they can work toward a more concrete aim. Most ambitiously, this can involve real cooperative projects.
For example, the Sorenson Institute , a political leadership institute at the University of Virginia, convenes dialogues that conclude with students putting together a proposal for the Virginia state Legislature on a specific topic such as gun control.
Even one-off conversations can conclude with what students might do differently on social media, on their campuses and in their families. When I followed up with them, I learned that many students had enacted these changes and found that people changed their own behavior in response. One student found that her uncle started reading and thinking about the articles she would send him. Another student discovered that peers in her political science class who had been dismissive of her in the past became respectful when she expressed her views and seemed to attend to them more sincerely.
Some students will flourish in these conversations, while others will struggle. In my research, I found that students whose rights are threatened by policy proposals of the other side understandably experience the most difficulty. However, these same students’ experiences can be improved by debriefing with a trusted mentor afterward.
For example, one student who identifies as queer felt shaken after a discussion with peers who opposed her marriage rights. But meeting with a professor afterward helped her to feel empowered by the conversation, equipped with new knowledge to help her fight for a more just society.
Listening to protest
Dialogue can deepen divides when it is presented as the only appropriate form of political communication, thereby silencing people who do not participate in these conversations. Students should be encouraged to also listen to messages conveyed through other means. For example, they can study protest movements – including ongoing, contemporary movements – and read the texts posted by activists who organize them.
It is important to convey to students that dialogue alone cannot solve all of what ails contemporary democracy. Protest, boycott and other forms of collective action matter, too.
- US higher education
- College students
- Political divide
- Higher ed attainment
- Political dialogue

Data Manager

Research Support Officer

Director, Social Policy

Head, School of Psychology

Senior Research Fellow - Women's Health Services
share this!
May 29, 2024
This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies . Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
Our political debates may not be as antagonistic as we think, study shows
by Laura Counts, University of California - Berkeley
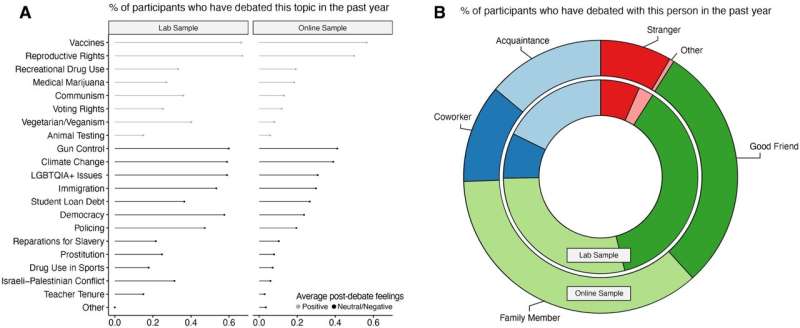
Spend any time scrolling through social media or news sites and it feels like America is a nation in constant argument. Off-hand remarks often spark fierce screaming matches. Partisanship is up, Gallup tells us, while trust in institutions is down.
However, a new study co-authored by Berkeley Haas Assistant Professor Erica R. Bailey suggests this perception may not accurately reflect the nature and frequency of political debates among everyday Americans. In three studies involving nearly 3,000 participants, researchers found most debates occur not with strangers on social media but rather among family and friends. Moreover, participants often felt positive after such discussions.
"We have these misperceptions because of algorithmic amplification of negative media and negative interactions on social media coupled with the fact that we tend to really remember negative information," says Bailey. "It creates this perception that we're all just out there fighting with strangers."
In fact, one study with a representative sample of nearly 2,000 Americans showed that people overestimate how frequently others engage in debates—and this misperception is especially pronounced for debates with strangers online. This false perception has psychological costs, the researchers say, fueling increased feelings of hopelessness about the future of America.
"Our findings suggest that Americans may experience a false reality about the landscape of debate which can unnecessarily undermine their hope about the future," the researchers wrote in the study, published in the journal Scientific Reports and co-authored by Michael W. White, Sheena S. Iyengar, and Modupe Akinola of Columbia Business School.
Difficult and nuanced conversations
Bailey says the genesis of the project was reflecting on her own experience. "When I think about who I talk about hot-button issues with, it's my colleagues and friends," she says. "Engaging online feels like a waste of time. Why would I have a difficult and nuanced conversation with someone I don't know or trust?"
Bailey, who studies authenticity, says online debates often feel artificial, with people less willing to openly share their personal experiences and more often just trying to make a point. But while we have a daily ringside seat to the most heated online debates, we lack line-of-sight into people's private kitchen-table conversations—and these are harder for researchers to observe, recreate, and measure.
Perceptions of 'typical' debates
In their first study, the researchers asked 282 participants to freely recall a recent debate they had witnessed or participated in. About half of the participants described debates they observed online, and recounted that these interactions skewed more negative than positive.
Interestingly, the respondents believed these instances were representative of typical debates, highlighting a perception that debates—particularly online—are generally seen as negative.
Personal experiences with debate
The second phase included two studies delving into personal debate experiences. The first involved 215 people in a behavioral science research lab, while the second included 526 individuals recruited online.
Participants in both groups were asked about the topics they debated over the past year, who they debated with, and how they felt afterward. They were also asked to choose from a list of twenty common topics—including climate change , gun control, gender identity issues, and reparations for slavery—which ones they had debated.
The results revealed that reproductive rights and vaccines were the most common topics, while other contentious issues, such as policing and immigration, were debated less frequently. Most of the topics were debated by less than half of participants. Contrary to the popular belief of hostile online interactions, participants said the majority of their debates occurred with family, friends, and other close contacts.
In terms of emotional impact, online participants reported that their average post-debate feeling was positive, suggesting that discussions, even on divisive topics, often ended on a constructive note. The lab participants' feelings were neutral, neither overwhelmingly positive nor negative.
"That was surprising to me, since I was not expecting for people to report feeling positive after a debate," Bailey says. "That suggests that at least on some topics, people are better at finding a compromise or at least ending on a positive note."
Measuring misperceptions and their impact
The third study was an investigation into how Americans perceive debates compared to their actual experiences. About 2,000 Americans in a nationally representative sample were randomly assigned to either self-report their own debate experiences or to predict how often others engage in debates.
The results were striking. Across almost all categories, people significantly overestimated the frequency of debates, especially online debates involving strangers (the exception was in-person debates with family members). In addition, this overestimation was strongly linked to a sense of hopelessness about the future of America.
Implications
The research highlights a critical gap between perception and reality. "Taken together, these findings suggest that the 'typical' debate seems substantively different than two strangers typing at one another from behind their computer screens," the researchers write. This misperception could be due to the visibility and virality of negative content on social media platforms, where extreme views often get amplified over moderate or conciliatory tones.
Second, the findings suggest that these misperceptions could be contributing to broader societal despair regarding the political climate and the future of democracy in America. By assuming that debates are overwhelmingly negative and frequent, people may feel a sense of futility about political engagement and discourse. (The researchers cautioned that this connection was largely correlational.)
Lastly, the research points to the need for interventions that not only make debates more productive but also adjust public perceptions about political debate. Educating the public about the actual dynamics of debates could help mitigate feelings of hopelessness and encourage more constructive and hopeful engagement with political processes.
Journal information: Scientific Reports
Provided by University of California - Berkeley
Explore further
Feedback to editors

New vestiges of the first life on Earth discovered in Saudi Arabia

Mussels downstream of wastewater treatment plant contain radium, study reports
3 hours ago

A new way to see viruses in action: Super-resolution microscopy provides a nano-scale look

Martian meteorites deliver a trove of information on red planet's structure

New imager acquires amplitude and phase information without digital processing
4 hours ago

AI helps scientists understand cosmic explosions

'Forever chemical' discovery can aid drinking water treatment

Mountain building linked to major extinction event half a billion years ago
5 hours ago
News from 'El Gordo': Study suggests dark matter may have collisional properties after all

Clues to mysterious disappearance of North America's large mammals 50,000 years ago found within ancient bone collagen
Relevant physicsforums posts, what's the opposite of subtlety, most underrated rock drummer, cover songs versus the original track, which ones are better, etymology of the word 'fart' in a handful of pie languages.
19 hours ago
Favorite Mashups - All Your Favorites in One Place
23 hours ago
Biographies, history, personal accounts
More from Art, Music, History, and Linguistics
Related Stories

Talking politics with strangers isn't as awful as you'd expect, research suggests
Apr 3, 2024

Study examines influence of social media on televised debate viewing
Apr 17, 2024
To win online debates, social networks worth a thousand words
May 16, 2019

Psychological research offers strategies for healthy political discussions among people with opposing views
May 13, 2024

Algorithm can predict debate winner
Jun 19, 2018
Viewers who tweet during presidential debates learn more about political issues
Aug 24, 2017
Recommended for you

Satellite data study shows 1.18 billion people are energy poor, finding no evidence of electricity usage from space
8 hours ago

A surprising result for a group's optimal path to cooperation
May 30, 2024

Misleading COVID-19 headlines from mainstream sources did more harm on Facebook than fake news, study finds
Most people trust accurate search results when the stakes are high, study finds

Who has the largest burial mound? Study examines differences among the upper classes of prehistoric societies

Study finds women are vulnerable in post-war peace processes
Let us know if there is a problem with our content.
Use this form if you have come across a typo, inaccuracy or would like to send an edit request for the content on this page. For general inquiries, please use our contact form . For general feedback, use the public comments section below (please adhere to guidelines ).
Please select the most appropriate category to facilitate processing of your request
Thank you for taking time to provide your feedback to the editors.
Your feedback is important to us. However, we do not guarantee individual replies due to the high volume of messages.
E-mail the story
Your email address is used only to let the recipient know who sent the email. Neither your address nor the recipient's address will be used for any other purpose. The information you enter will appear in your e-mail message and is not retained by Phys.org in any form.
Newsletter sign up
Get weekly and/or daily updates delivered to your inbox. You can unsubscribe at any time and we'll never share your details to third parties.
More information Privacy policy
Donate and enjoy an ad-free experience
We keep our content available to everyone. Consider supporting Science X's mission by getting a premium account.
E-mail newsletter

Civil Wars Apolitical Stance Is Making People Angry for the Wrong Reasons
- Alex Garland's apolitical stance on Civil War triggers criticism, but examining the film beyond politics is crucial.
- Civil War explores the emotional complexities of warfare without overt political commentary, focusing on the psychological impact.
- The murky political ambiguity in Civil War mirrors the chaotic nature of war and challenges viewers to rethink traditional political ideologies.
When a divisive film like Civil War comes along, it is worth appreciating, as the passionate discourse among the film community serves as a reminder that films are essential forms of media in a rapidly changing media and cultural climate. For a provocative filmmaker like Alex Garland , apathy is the enemy of artistic success. If his recently released dystopian war thriller failed to trigger anger and frustration among a cohort of critics, then something went awry. However, a large sector of negative criticism aimed at Civil War gravely misses the point of Garland's film. Even worse, many critics have refused to engage with the text of the film due to Garland's decision to take an apolitical stance on the film's subject. You're not supposed to be aware of Garland's politics, as the nature of the film's dystopian political climate is abstractly eerie . If anything, fixating on broad politics instead of the photojournalists on the battlefield who are coming into direct contact with the hellish backdrop of war is an absurd proposition.
The fanfare surrounding Civil War is two-pronged. The film's subject evokes a toxic political climate that has affected contemporary society. It's understood that the content of Garland's film could feasibly be from a future not too far from the present day. Being a Presidential Election year, any film concerned with the national divide will call attention to itself. From a cinematic perspective, Civil War represents a major leap in scale for the acclaimed independent studio, A24 . With a $50 million budget, Civil War is the studio's most expensive project to date. The studio, often celebrated as a luxury brand of films by cinephiles, is not known for grand, operatic war epics, but Garland, an A24 staple, keeps the film grounded. Civil War follows a team of reporters, veteran photojournalists Lee ( Kirsten Dunst ) and Joel ( Wagner Moura ), senior journalist Sammy ( Stephen McKinley Henderson ), and plucky newcomer Jessie ( Cailee Spaeney ), traveling across the United States during a rapidly escalating Second American Civil War tearing the nation to shreds.
A journey across a dystopian future America, following a team of military-embedded journalists as they race against time to reach DC before rebel factions descend upon the White House.
Release Date April 26, 2024
Director Alex Garland
Cast Jefferson White, Cailee Spaeny, Wagner Moura, Sonoya Mizuno, Nick Offerman, Kirsten Dunst
Genres Drama, Action
Alex Garland Does Not Wear His Politics on His Sleeve in 'Civil War'
The inherent nature of a civil war is that two parties are divided to such a degree that they are left with no other option besides disputing their differences through warfare. In such a divisive period, individuals are forced to take one side or the other. When viewers discovered that Alex Garland chose to tell the story from a neutral and apolitical perspective, some believed he was taking the easy way out — avoiding a hardline political statement to appease a mass audience. The writer-director's neutral voice drew the ire of critics, chalking up this decision as an act of cowardice by Garland. Critics' frustration with Garland not explicitly wearing his politics on his sleeve clouded them from engaging with the text . It's one thing to fail to connect with Garland's vision , but to suggest that Civil War is an empty reflection on the horrors of war and our turbulent political climate is unwarranted.
A film that brushes on thorny political topics is expected to be an active work of political commentary — think of Oliver Stone 's left-leaning confrontational rebukes of American foreign policy and the military-industrial complex in Platoon and JFK . In the case of explosive blockbusters that fetishize military combat and express unabashed jingoism, notably films by Michael Bay , they evoke the spirit of right-wing philosophy. There's nothing innately wrong with using the film medium to convey a message, but when a filmmaker solely relies on didactic storytelling, a film becomes less of an art form and more of a soapbox . In relation to Civil War , reprimanding Garland for not being explicitly political in his storytelling comes across as a misread of the purpose of film as an art form. Considering that the film's subject loosely parallels recent events, including civilian unrest in the streets, abuse of executive power, and the January 6th insurrection, one's personal politics interfering with the text interpretation is understandable, but it undermines Garland's vision.
'Civil War' Engages With the Emotional Complex of Living In an Apocalyptic Setting
In an interview with The Atlantic , Garland said that demanding a film be explicit in its political ideology is "unethical." Civil War operates as a comment on the psychological complex of polar extremism in everyday life , citing that his film "comes out of anger." The film is refreshingly devoid of hand-wringing and exhausting political theory. Instead, Garland focuses on the mood and tenor of a nation pulled apart. The abandoned parking lots, empty streets, and ravaged stadiums operate as liminal spaces for the characters and the audience. These familiar-looking places being afflicted by combat emphasize the jarring existence of a civil war. Despite Garland's "anger" comments, and the series of white-knuckled set pieces, the crown jewel scene being Jesse Plemons asking "What kind of American are you?", Civil War demonstrates an unexpected serenity against the backdrop of all-out conflict. The most resonant sequences occur when the principal characters camp out in the middle of the country at night. As gunfire echoes through the night, Lee and Jessie look for comfort amid the hellish reality. In a scene where Jessie buys Lee a dress at a local shop obliviously unaffected by the war, the film manages to reflect on the loss of simplistic innocence just through a shot of Lee gazing into a mirror.
War, as the most dangerous and barbaric form of competition, comes down to one regimented side versus another — like a sports match in that sense. Civil War , however, distorts which party is on what side , and it is ambivalent toward identifying the righteous side . Anecdotally speaking, as I was leaving my screening, a couple inquired about my thoughts on the film, and their main point of concern was that they couldn't comprehend the details of the war. This is another throughline in criticism of Civil War — no one knows who is fighting who. Anything that is hinted at, such as a unification between Texas and California, states with diametrically opposed political ideologies, left some viewers incredulous. Many critics have cited the vagueness of the machinations of the war as another sign of Garland's cowardice and lack of engagement with American politics. On a purely artistic level, the ominous nature of the fictionalized conflict feeds into the eeriness that surrounds the journalists' odyssey across the nation. Their adventure is not born out of the pursuit of social justice, but rather, to fuel their innate journalistic adrenaline by capturing harrowing snapshots of the war and obtaining an interview with the disgraced unnamed President ( Nick Offerman ).
The Political Ambiguity of 'Civil War' Feeds Into the Murkiness of War
On The Big Picture podcast , Garland found the ambiguity of the story practical, stating, "I think those things did not need to be explained because I don't meet people ... who really need that explained," concerning the specifics of the civil unrest. While it's tempting to read this as a cop-out on Garland's part, this rationale condenses the scope of the film. Along their journey, the group devolves from journalism to survivalism. Garland's commitment to framing the story from their perspective eases the pressure to communicate a grandiose political statement. When you're running for your life or caring for a colleague after they've been inflicted with gunshot wounds, you don't have time to preach profound ideology surrounding war.
Based on the historical precedent of a civil war within the United States, we imagine that a modern-day internal conflict would feature sides split between Democrats and Republicans , the two major parties that have never felt more divided. Alex Garland presupposes that maybe our clearly defined ideas of political ideology would collapse under the fatalistic pressure of a national revolt. In the throes of a war-torn America, our vision will likely be distorted, with the righteous and the evil blending with each other. "Extremism encourages extremism," Garland said on The Big Picture . From his worldview, this is how the events of the film transpired . By bemoaning the lack of explicit political hand-wringing in his film, we are headed toward a similar fate in real life. For people who want their politics valorized on screen, they'll have to look elsewhere, as Civil War approaches its dicey subject by attempting to mirror the psychological complex of a conflict that is too monumental to properly consume . Garland's passive voice implies indifference to provocation, but the divisive reception to his film suggests that the stubbornness of ideology was challenged.
Civil War is now available to rent on Prime Video in the U.S.
Rent on Prime


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Let's say you're applying to a school with progressive economic views, while you firmly believe in free markets. Consider these two essay options: Option 1: You believe in free markets because they have pulled billions out of terrible poverty in the developing world. Option 2: "Greed is good," baby!
The essay about politics may examine a wide range of topics such as government systems, political ideologies, social justice, public policies, international relations, etc. After selecting a specific research topic, a writer should conduct extensive research, gather relevant information, and prepare a logical and well-supported argument.
Founded in 1828 by supporters of Andrew Jackson, the Democratic Party is the world's oldest active political party. Although its platform has transformed many times over the years, today the core values of the Democratic Party align with liberal ideology. liberal ideology. The definition of liberalism has changed over time, but modern-day ...
Your family is likely to exert a substantial influence on your political views. 14 In some political settings in which a child's identity is defined by religion, ethnicity, and place, their political views may seem almost predetermined. In Bosnia-Herzegovina, for example, the three main groups tend to be divided by ethnicity and religion ...
The new survey of the public's views of democracy and the political system by Pew Research Center was conducted online Jan. 29-Feb. 13 among 4,656 adults. It was supplemented by a survey conducted March 7-14 among 1,466 adults on landlines and cellphones. Among the major findings: Mixed views of structural changes in the political system.
June 22, 2016. Partisanship and Political Animosity in 2016. 5. Views of parties' positions on issues, ideologies. Republicans and Democrats see little common ground between the two parties when it comes to issues, ideas and ideology. Majorities of partisans say the policy positions of the Republican and Democratic parties are very different ...
The University of Iowa. The stand in politics is a major form of current political theory, as it is of all political theory. intended for times of trouble. It possesses special characteristics, concerns, and connections. to aspects of political life. This essay contrasts the stand to other forms of theory and projects.
POLITICS ESSAY WRITING GUIDE Dr Matthew Eagleton-Pierce Lecturer in International Political Economy SOAS, University of London Email: [email protected] July 2015 The analysis of political life is largely based on the written word. In both academic and 'real world' debates on politics, the examination of texts - books, journal ...
Introduction. One of the requirements of the Political Science major is the senior essay. The senior essay is an opportunity to go more deeply into a topic or puzzle than you ordinarily would on a final assignment for a course. At first, this may seem like a daunting task. This document is designed to allay some of that anxiety as well as ...
Essays are the other place you can discuss politics because it allows you to expand on your passions. You could use your involvement with politics in a variety of essays, including your personal statement, community involvement topics, and extracurricular topics. ... If you still want to attend, you can frame your political stances in a way to ...
selection), essays that run together opposite points of view (no analysis), essays that are unclear, incoherent or boring, and essays that dont fully answer the question. The notes that follow are intended to help you avoid these pitfalls. Essay writing also helps you to acquire skills that are vital to most of the careers you may wish to follow.
For decades, political psychologists have explored why we are drawn to the views and values of one party over another. Examining data from more than 200 such studies from around the world, Jost and colleagues explored the relationship between political ideology and multiple categories of motivation, including dogmatism, personal need for order ...
Actually, this is something that me and my dad are always discussing. We have wildly different views; he agrees with most all right wing views and policies, while I agree with mostly left wing ideals.
These effects lasted up to a week later. The changes in their opinions were also larger when they were asked to give an argument—or rationalization—for their new opinion. It seems that giving ...
Data Essay (20) Video (13) Quiz (4) Press Release (3) Database (1) Regions & Countries. United States (250+) International (250+) ... Yet there are substantial divisions within both parties on fundamental political values, views of current issues and the severity of the problems facing the nation. Features. feature Oct 30, 2019.
500+ Words Essay on Politics. When we hear the term politics, we usually think of the government, politicians and political parties. For a country to have an organized government and work as per specific guidelines, we require a certain organization. This is where politics comes in, as it essentially forms the government.
In " Athletes, Speak Up ," an essay for the Opinion section, Osaka writes about what inspired her: "Shut up and dribble.". That's what a news anchor suggested LeBron James do after he ...
Political Science Essay Examples. Draw inspiration from your predecessors. Browse our free database of political science essays and research reports. The complexity of our essay examples varies, but all have been checked for accuracy. Our database items have been written by the school, college, and university students.
Political ideologies have two dimensions: (1) goals: how society should be organized; and (2) methods: the most appropriate way to achieve this goal. An ideology is a collection of ideas. Typically, each ideology contains certain ideas on what it considers to be the best form of government (e.g. autocracy or democracy ) and the best economic ...
Position Paper Topics. The argument or position essay is a standard type of writing exercise that almost everyone encounters at the high school or college level. This essay has two primary defining components: It has to be about an issue that people don't agree on. It focuses on disagreements about facts, definitions, causes, values, or solutions.
Views. 3916. My first political view was formed through my family. Although politics weren't really discussed with children, I eavesdropped in the conversations from time to time. I would hear how they liked one candidate over the other due to the issues they stood for. By overhearing my parents, I learned which issues were favored in my community.
The third reason is that my political stance was similar to Tony Blair, who served as the prime minister of the United Kingdom from 1997 to 2007. Tony has changed his stance over the years, but in the 1990's he started off in the same spot as me. Blair has conducted actions which are personally unacceptable, such as attacking Iraq numerous times.
Morsa Images via Getty Images. Students gain a better appreciation for opposing views when they probe what matters to them, and why. Kentaroo Tryman via Getty Images. Politics. US higher education ...
Mapping the Mind of a Large Language Model. Today we report a significant advance in understanding the inner workings of AI models. We have identified how millions of concepts are represented inside Claude Sonnet, one of our deployed large language models. This is the first ever detailed look inside a modern, production-grade large language model.
Topics and debate partners in lab and online samples. Figure presents the results of Studies 2a-2b which asked participants about their experience debating a series of issues over the past year.
Civil War. 9 /10. A journey across a dystopian future America, following a team of military-embedded journalists as they race against time to reach DC before rebel factions descend upon the White ...