- Aller au menu
- Aller au menu mobile
- Aller au contenu
- Emplois et concours Emplois et concours
- Salle de presse Salle de presse
- Archives et traités Archives et traités
- Augmenter la taille de la police
- Réduire la taille de la police
- Ajouter notre fil RSS

Présentation du Zimbabwé
- Partager sur Twitter
- Partager sur Facebook
- Partager sur Linkedin
Présentation du pays
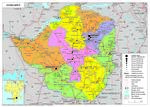
Données générales
Nom officiel : République du Zimbabwe Nature du régime : République (régime présidentiel) Chef de l’Etat et du Gouvernement : M. Emmerson MNANGAGWA (depuis le 24/11/2017)
Données géographiques
Superficie : 390.580 km² Capitale : Harare Villes principales : Bulawayo, Chitungwiza, Mutare, Epworth, Gweru Langues officielles : anglais, shona, ndebele Fête nationale : 18 avril (Indépendance : 18 avril 1980)
Données démographiques
Population (2021) : 15, 092 millions Croissance démographique (2021) : 1,5 % Espérance de vie (2020) : 62 Taux d’alphabétisation de la population âgée de 15 à 24 ans : 90,4 % Religions : chrétiens : ≈ 67 % (dont anglicans, catholiques, méthodistes, pentecôtistes et apostoliques) ; autres religions et animistes : ≈ 30 % Indice de développement humain (PNUD, 2019) : 150e sur 189 pays
Éléments d’actualité
Politique intérieure.
Après l’indépendance le 18 avril 1980, Robert Mugabe, leader de la guérilla anticolonialiste de l’Union nationale africaine du Zimbabwe (ZANU), est élu Premier ministre, puis devient chef de l’Etat du Zimbabwe à partir de 1987 sur modification de la Constitution. Le 21 novembre 2017, le président Mugabe démissionne après trente-sept ans de présidence, dans un contexte de fortes tensions et de scissions au sein de la ZANU-PF entre les prétendants à la succession.
Le 24 novembre 2017, l’ancien vice-président et ministre de la Défense, Emmerson D. Mnangagwa, est désigné président par intérim par la ZANU-PF, puis élu président de la République lors des élections du 30 juillet 2018. Ces élections générales (présidentielles, législatives et locales) sont marquées par une très forte participation (85 %). Le Président Mnangagwa (ZANU-PF) est proclamé vainqueur dès le 1er tour avec 50,67 % des voix, contre 44,3 % voix pour son opposant Nelson Chamisa (Alliance MDC). A l’Assemblée nationale (270 sièges), la ZANU-PF remporte 180 sièges contre 87 pour l’Alliance MDC, 1 siège pour le National Patriotic Front (NPF), 1 indépendant, et 1 siège pour le MDC-T (faction de l’Alliance MDC présidée par Mme Thokozani Khuphe). Au Sénat (80 sièges), la ZANU-PF obtient également la majorité avec 35 sièges. L’Alliance MDC obtient 24 sièges à l’alliance MDC, le MDC-T, 1 siège.
Les prochaines élections générales auront lieu en 2023.
Politique étrangère
La diplomatie zimbabwéenne repose notamment sur la solidarité avec les frères d’armes, notamment les anciens membres de la Ligne de Front, qui se retrouvent au sein de la Communauté pour le développement de l’Afrique australe (SADC).Le Zimbabwe est aussi membre de l’Union africaine et du Marché commun de l’Afrique australe et orientale (COMESA). Dans les enceintes internationales et sur le plan bilatéral, le Zimbabwe s’oppose en revanche aux pays ayant pris des sanctions à son encontre à la suite des violations des droits de l’Homme commises lors de la réforme agraire de 2001 et des élections de 2002 et 2008 (Etats-Unis, Canada, Australie, Nouvelle-Zélande, Commonwealth). Le Zimbabwe n’a pas ratifié le Statut de Rome de la Cour pénale internationale (CPI).
L’Union européenne a adopté plusieurs « mesures restrictives » contre les individus et les acteurs privés jugés responsables des violations. Certains évènements (tenue d’un référendum constitutionnel en 2013, organisation d’élections générales en 2013 et 2018) ont toutefois conduit l’Union à encourager l’effort de redressement et d’ouverture du Zimbabwe et à initier, depuis 2013, une politique de réengagement. Cette politique s’est notamment traduite par un allègement des mesures restrictives (fin de l’interdiction de voyager en Europe et du gel des avoirs) qui ne sont plus effectives que pour l’entreprise d’armement Zimbabwe Defence Industries (renouvelé en février 2022). L’embargo sur les armes (et le matériel utilisable pour la répression) est maintenu. Les « mesures appropriées » prises au titre de l’article 96 de Cotonou sont arrivées à expiration le 1er novembre 2014 et n’ont pas été reconduites permettant l’intensification de la coopération européenne concentrée sur la santé, le développement agricole et la bonne gouvernance (le 11e Fonds européen de développement a alloué 234M€ au Zimbabwé sur la période 2014-2020). En 2009, le Zimbabwe a signé un accord de partenariat économique (APE), ratifié et entré en vigueur en mai 2012, qui lui octroie un accès exempts des droits de douane et de quotas au marché de l’UE.
Conformément aux lignes directrices adoptées par le l’Union Européenne en février 2021, l’Union Européenne demeure disponible pour réviser à tout moment l’ensemble de ses politiques au Zimbabwe en fonction des mesures prises par les autorités locales et de l’évolution de la situation sur le terrain. De leur côté, les membres de la SADC ont appelé à la levée des sanctions pesant sur le Zimbabwe.
Outre les pays européens, le Zimbabwe entretient notamment des relations avec le Royaume-Uni, l’Afrique du Sud, les Etats-Unis, la Chine et la Russie.
Situation économique
Dans les années 1980, le Zimbabwe est l’une des économies les plus développées et les plus riches du continent africain. L’Etat dispose de multiples atouts : puissance agricole (en particulier la culture du tabac) et industrielle, richesse en minerais (pierres et métaux précieux, nickel, minerai de fer), services publics performants. A la fin des années 1990, le programme de réforme mis en place par la présidence Mugabe entraîne néanmoins une chute drastique de la production dont les conséquences sur la croissance sont accentuées par les sanctions internationales. Le pays accumule également des arriérés de paiements importants vis-à-vis des Institutions Financières Internationales (IFIs), des créanciers du club de Paris et des autres créanciers comme la Chine.
Depuis octobre 2018, le pays fait face à une grave crise de change et de confiance dans la monnaie domestique qui a durement affecté le pouvoir d’achat des ménages. En 2019, le PIB s’est fortement contracté de 8,3%. L’inflation a atteint des niveaux à trois chiffres et la monnaie s’est fortement dépréciée. Les effets de la crise ont été encore exacerbés par la survenue de chocs externes : le passage des cyclones Idaï et Kenneth en 2019, les épisodes de sécheresse qui ont entrainé une chute de la production agricole et hydroélectrique (qui représente environ la moitié de l’énergie produite localement), la crise de la Covid-19 qui a accentué la récession et creusé le déficit public. La pénurie de devises limite également la capacité du pays à importer, notamment pour satisfaire ses besoins en électricité.
En 2021, le Zimbabwe est toutefois la 2e économie d’Afrique australe en termes de PIB derrière l’Afrique du Sud (26 Mds USD) et la 15e du continent. L’économie a rebondi, tirée par la reprise de l’agriculture et de l’industrie et par la stabilisation relative des prix (60,7% d’inflation fin 2021 contre 838% en juillet 2020) et des taux de change.
La crise a également joué comme un facteur aggravant des conditions sociales dans le pays : taux de pauvreté autour de 57%, insécurité alimentaire persistante, blocage des services publics. Le Zimbabwe était 150e sur 189 pays au dernier classement IDH.
Mise à jour : 12 mai 2023
Informations complémentaires
- Images France / Zimbabwé
- Traités bilatéraux
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.
Art of Africa
Course: art of africa > unit 6, great zimbabwe.
- Great Zimbabwe National Monument (UNESCO/NHK)
Conical tower
Wealth and trade, want to join the conversation.
- Upvote Button navigates to signup page
- Downvote Button navigates to signup page
- Flag Button navigates to signup page

The World Bank in Zimbabwe
The World Bank’s lending program in Zimbabwe is inactive due to arrears and the role is now limited to technical assistance and analytical work through Trust Funds.
Zimbabwe has strong foundations for accelerating future economic growth and improving living standards. Private sector-led growth is critical to maximize the country’s potential. For decades after independence, Zimbabwe was one of the countries with the highest living standards in Africa—buttressed by a skilled workforce and infrastructure superior to most countries. Notwithstanding its economic decline since 1995, it continues to boast several sectors that are still competitive or could—in the short to medium term—be competitive regionally and globally. The recently completed Country Private Sector Diagnostic finds Zimbabwe highly competitive in several value chains in agriculture and agribusiness industries, including sugar, cotton, horticulture, and meat and dairy. Furthermore, tourism and mining of energy transition minerals –including ample lithium reserves – hold significant potential in the short term.
To realize this potential fully, Zimbabwe needs to find new ways to capitalize on existing and emerging opportunities for the private sector to drive economic growth and harness the country’s comparative advantages, including its relatively strong human capital, comparable to that of upper-middle-income economies in Sub-Saharan Africa, and its abundant mineral and natural resources.
Economic context
Zimbabwe’s economic development continues to be hampered by several challenges. Real GDP is estimated to have grown by 5.5% in 2023, after a 6.5% growth in 2022, due to an expansion in agriculture, mining, and remittances-induced services growth. Nevertheless, macroeconomic volatility fueled by monetary instability and substantial exchange rate distortions keeps Zimbabwe’s economic activity below its potential.
Inflationary pressures remain high in 2024 as local currency depreciation intensifies. In February 2024, annual inflation increased for the fourth consecutive month, reflecting the sharp depreciation of the local currency at both the official and parallel foreign exchange markets. Annual inflation increased from 26.5% in December 2023 to 47.6% in February 2024. The official exchange rate depreciated by 788% in 2023, with the parallel market premium estimated at 30% as of February 2024.
Fiscal pressures increased in 2023 ahead of national elections and the transfer of the Reserve Bank of Zimbabwe’s (RBZ) external liabilities to the treasury. The government increased civil servants’ salaries in foreign and local currency. The Treasury took over the servicing of debt of $1.8 billion in external liabilities from RBZ. Meanwhile, some of the revenue proposals in the 2024 budget have been reversed, casting doubt on the credibility of the budget. Nevertheless, the implemented taxes, like the sugar tax, have led to increased prices. The current account surplus narrowed in 2023 as remittances from non-governmental organizations contracted.
Real GDP growth is projected to slow further to 3.3% in 2024, partly reflecting the impact of structural bottlenecks, macroeconomic instability (high inflation and severe exchange rate volatility), an El Niño-related drought, and lower commodity prices. El-Nino-induced drought will affect most rain-fed crops and may intensify electricity supply shortages. Nevertheless, continued increases in remittances will help to stimulate growth in services (wholesale and retail trade) and construction. Inflationary pressures will intensify in 2024, given drought conditions and domestic tax increases. The fiscal deficit will increase in 2024, driven by high-interest payments on external debt, drought mitigation-related spending, wage pressures, and the reversal of several budget revenue measures. The fiscal deficit is projected to reach 2.5% of GDP in 2024 before slowing to under 2% in the medium term. The current account surplus is expected to shrink further, reflecting increased imports in the face of drought conditions and lower commodity prices.
Key Developmental Challenges
Although extreme poverty has declined since its peak in 2020, it remains high in the context of cyclical agricultural production and elevated food prices. Persistent inflation, high dependence on low-productivity agriculture, slow structural transformation, and intermittent shocks like drought, natural disasters, and the COVID-19 pandemic have contributed to the high rate of poverty and vulnerability in Zimbabwe. High, unsustainable debt and arrears to international financial institutions (IFIs) limit fiscal space and growth potential.
Last Updated: Apr 09, 2024
World Bank Group (WBG) assistance to Zimbabwe totaled $1.6 billion between 1980 and 2000. While Zimbabwe is in arrears, the WBG has remained fully engaged through financing from the global trust funds and the Country’s Multi-Donor Trust Fund, the Zimbabwe Reconstruction Fund (ZIMREF), renamed the Zimbabwe Socio-Economic Transformation (ZISET) Fund. ZIMREF (established in 2014) raised $52 million and has supported the World Bank’s primary engagement in Zimbabwe.
ZISET, with a closing date of March 2028, will support Zimbabwe under two pillars: (1) ensuring socio-economic stability and (2) building resilience. Three thematic arears will guide the implementation.
1. Promoting private sector-led growth will prioritize the growth and the jobs agenda. Activities include addressing bottlenecks in the business environment (e.g., licensing) and in enabling sectors (renewable energy, digital) to strengthen the regulatory environment and institutional capacities.
2. Enhancing real sector competitiveness and investment, seeks to increase competitiveness of high-growth potential sub-sectors like horticulture and tourism and promote investment in specific agricultural value chains with high competitiveness and revealed comparative advantages.
3. Establishment of building blocks of a social registry system and an immediate focus on the design and implementation of the social impact mitigation program to complement critical subsidy reform.
ZISET is supplemented by other trust funds which fund sector-specific activities. The Health Emergency Preparedness and Response Trust Fund (HEPRT), and the Energy Sector Management Assistance Program (ESMAP) Trust Funds provided a grant of $6.6 million to the Zimbabwe COVID-19 Emergency Response Project (ZCERP) to deploy and manage COVID-19 vaccines and to strengthen related health system capacity. Additional financing ($15 million) funded by the Global Financing Facility (GFF) for essential health services was approved and incorporated into ZCERP. The Health Sector Development Project funded by the GFF (additional financing of $25 million) recently closed in March 2024.
Following Cyclone Idai in March 2019, the WBG provided an exceptional allocation of $72 million from the Crisis Response Window of the International Development Association (IDA) for the Zimbabwe Idai Recovery Project (ZIRP), which aimed to address stages of the early recovery and medium-term disaster recovery for people affected by the cyclone. The ZIRP responded to Cyclone Idai’s disproportionate effects on eastern Zimbabwe’s poorest and most vulnerable. It maintained a strong focus on poverty reduction by integrating local financial stabilization into its activities through the provision of otherwise costly food and social services, the restoration and generation of livelihoods, as well as sustainable infrastructure and resilience to future disasters. The project closed in June 2023.
The International Finance Corporation (IFC) provides technical assistance to various activities, including expanding access to agricultural sector finance and enhancing Victoria Falls's competitiveness as a tourism destination, through the Zimbabwe Destination Development Program (ZDDP). The ZDDP focused on strategic air access, destination management, marketing, policy, and SME support in Victoria Falls, the country’s primary tourism destination. In 2023, Victoria Falls increased its air capacity by 5% over 2019, 15% ahead of the sub-Saharan average.
Through Advisory Services and analytical work, the WBG has developed key diagnostics to contribute to the development agenda. Recent products include:
· Zimbabwe Country Economic Memorandum
· Zimbabwe Poverty Assessment ,
· Zimbabwe Economic Update
· Country Climate Development Report
· Country Private Sector Diagnostic
· Zimbabwe Gender assessment
· Gender-Based Violence (GBV) assessment.
· Mapping and Valuing Ecosystem Services in Zimbabwe
Investment climate reform programs led by IFC have also yielded significant policy, legislative, and regulatory reforms, including such foundational laws as a new Companies Act, an Insolvency Law, and laws to create a Commercial Court. This analytical work has advanced the understanding of policy and institution gaps and set blueprints for progress. Many WBG recommendations – including on private sector development, public sector systems, and human capital – have been included in the government’s National Development Strategy (NDS1).
Analytical work in Zimbabwe’s agricultural sector has been focused on policy dialogue, production enhancement, and climate resilience. Ongoing policy dialogue has focused on strategic policy actions and climate investments designed to fortify the resilience of the agri-food sector against environmental challenges. To enhance productive capacity and market resilience, a sectoral deep dive note was produced on five critical agricultural value chains—sugar, maize, horticulture (with an emphasis on macadamia), cotton, and livestock (with a focus on dairy). The culmination of these sector-specific analyses led to the creation of a comprehensive Guide Note on drafting agricultural investment prospectuses. This tool led to the development of an Agriculture Investment Factsheet and detailed Investment Prospectus by the Ministry of Agriculture, which will serve as a cornerstone to attract investment and foster sector growth.
In response to the devastating loss of nearly 300,000 cattle to feed scarcity and tick-borne diseases, World Bank technical assistance pivoted towards fostering resilient and responsible livestock development. This includes championing One Health approaches and exploring innovative avenues like insect-based food and feed solutions. Zimbabwe is at the forefront of pioneering work on insects for food, feed, and fertilizer, with pilot projects in the Tongogara refugee camp and cyclone-impacted regions of Manicaland through ZIRP. This emerging field contributes to a circular economy and offers a sustainable pathway to bolstering food security and livelihoods in the face of environmental challenges.
Despite a challenging operating context, the Zimbabwe Reconstruction Fund (ZIMREF) has been pivotal in supporting legislative reforms and early reform implementation.
- Financial Management: ZIMREF helped to strengthen the public procurement framework, improve the coverage and reporting of internal and external audits, and improve Parliamentary and civil society oversight. Forty-six government funds started using Public Financial Management Systems (PFMS) against a target of 10. The Integrated Financial Management System (IFMIS) was successfully rolled out to 63 districts by setting up district kiosks.
- Poverty Monitoring: ZIMREF assisted the Government in monitoring poverty outcomes and their integration into national strategy and planning documents. This included financing of the 2017 Poverty, Income, Consumption and Expenditure Survey (PICES), release of the 2017 poverty report, and publication of poverty microdata for 2017 and 2019.
- Human Capital: ZIMREF has also supported the establishment of a basic social protection Management Information System (MIS), which is the basis for a social registry system.
- Water Supply: ZIMREF strengthened the Zimbabwe National Water Authority and the regulatory framework in the sector increased access to piped water for 34,810 people (74% more people than the target) and provided installations of new water connections for 1,265 households in three growth points (Guruve, Lupane, and Zimunya).
- Climate Change: ZIMREF helped develop Zimbabwe’s climate policies, its pipeline of climate adaptation, and its mainstreaming of climate changes in investment planning.
The Zimbabwe Idai Recovery Project (ZIRP) closed in June 2023, meeting or exceeding all planned recovery and reconstruction targets. The project achieved the following:
- 661,692 people, including 3,611 Internally Displaced People (IDP), were provided with integrated health services, and coverage in hard-to-reach areas was extended through the training of 2,843 Village Health Workers (VHWs).
- Food assistance interventions reached 239,324 beneficiaries within the affected communities.
- 12,111 GBV survivors benefited from the Project, receiving survivor-centered health services and comprehensive legal and psychosocial support.
- 47km of community roads were rehabilitated as well as seven cyclone damaged community schools, three community health facilities and one agro-market all using revised design and build back better standards.
- 482 water systems and 3,789 sanitation facilities were rehabilitated and restored, reaching 44,106 households.
- 88,516 cyclone-affected students were supported with education supplies
- Six irrigation schemes were rehabilitated with substantial advisory and extension support services provided to over 10,000 farmers.
- Two new community radio stations were established to disseminate early warning information in the two affected districts, Chimanimani and Chipinge
The Health Sector Development Project has increased coverage and quality of an integrated package of Reproductive, Maternal, Neonatal, Child, Adolescent health and nutrition (RMNCAH-N) services and also has accelerated progress in the National COVID-19 Response, providing technical assistance and dialogue at the national level on response and vaccine deployment. The project has achieved the following:
- Provided more than 1 million women antenatal care services, consisting of at least one visit a year to a supported facility.
- At least 92% of births (for those who booked) have been attended by skilled health personnel in participating rural districts, benefiting an estimated 1.5 million women.
- Improved the quality of care at health facilities in terms of structure and process, with average scores (awarded by patients) ranging between 80% and 85% to compare favorably with previous averages that fell below 70%. At least 54% of the health facilities registered an increase in quality scores since the previous quarter at the end of December 2022.
- From its inception in 2014 to date, over 81,000 women were enrolled into an urban voucher component of the RBF program, which played a critical role in strengthening the urban health systems and improving access to maternity services for the urban poor in Harare and Bulawayo Metropolitan Provinces.
- The Urban Voucher initiative was scaled up to cover 35 health facilities in Harare and Bulawayo which has helped to improve access to more vulnerable women and children with increasing urban poverty levels exacerbated by the COVID-19 Pandemic.
- The Results Based Financing (RBF) Program’s impact evaluation confirmed the approach resulted in faster rates of improvements in key maternal and child health indicators, for example, a 13% improvement in the in-facility delivery rate and a 12% improvement in postnatal care in RBF districts, compared to those that have not yet started the approach.
The World Bank Group works with a variety of partners in Zimbabwe. The Zimbabwe Socio-Economic Transformation Trust Fund is supported by the United Kingdom (FCDO), Canada and Norway.
CORDAID implements the health projects while UNOPS working with eight other UN Agencies implemented the Zimbabwe Idai Recovery Project.
The African Development Bank supports the country portfolio through the Kariba Dam Rehabilitation Project that is implemented through Zambia.
History of the Bank's work in Zimbabwe
- Annual Report 2022
Zimbabwe: Commitments by Fiscal Year (in millions of dollars)*
Around the bank group.
Find out what the Bank Group's branches are doing in Zimbabwe.

STAY CONNECTED
Africa’s Pulse
Short term economic prospects for the continent, its current development challenges.

CPIA Africa
The 2023 Africa Country Policy and Institutional Assessment (CPIA) report covers the period January to December 2022. The overall average score for Sub-Saharan Africa’s IDA-eligible countries remained unchanged in 2022 ...

IDA Impact in Africa
With IDA’s help, hundreds of millions of people have escaped poverty—through the creation of jobs, access to clean water, schools, roads, nutrition, electricity, and more.

Fake IFC Loan Applications
World Bank Group warns of an online scam offering loans from the International Finance Corporation.

World Bank Africa Multimedia
Watch, listen and click through the latest videos, podcasts and slideshows highlighting the World Bank’s work in Sub-Saharan Africa.
Additional Resources
- Annual Report 2018
Country Office Contacts
This site uses cookies to optimize functionality and give you the best possible experience. If you continue to navigate this website beyond this page, cookies will be placed on your browser. To learn more about cookies, click here .
- The Culture Of Zimbabwe

The landlocked southern African nation of Zimbabwe hosts a population of 14,030,368 individuals. The country has a rich tradition and culture that reflects the ethnic diversity of its population.
7. Ethnicity, Language, and Religion of Zimbabwe
The Shona and the Ndebele are the largest ethnic groups residing in the country. English, Shona, and Ndebele are the official languages of Zimbabwe. Around 13 minority languages have also been given the official status. Most Zimbabweans adhere to Christianity with the majority being Protestant Christians.
6. Cuisine of Zimbabwe
Cornmeal is a staple of the Zimbabwean diet. It is used to make the porridge-like bota which is flavored with peanut butter or butter and had for breakfast. Sadza is also prepared from cornmeal and consumed for lunch or dinner. It is also similar to bota but thicker. Sadza is served with vegetables, meat, and beans. Meat can be stewed, roasted, grilled, or sundried. Boerewors, a type of pork or beef sausage, is eaten frequently. Chicken and rice meals are also widely consumed. Braaied (barbecued) meat is popular during celebrations. The influence of the British colonization can still be observed in the culinary habits of the Zimbabweans. They have tea at midday and the 4 o'clock tea as well. Occasionally, they also have tea after dinner.
5. Clothing in Zimbabwe
Today, most Zimbabweans wear modern, western-style clothing. Traditional clothes are worn on a daily-basis by only a small section of the population. Such dresses vary between ethnic groups. Usually, the dresses have bright colors and tribal patterns. Elaborate tribal headgears are often worn. Bright and showy beaded ornaments also accompany such dresses.
4. Literature and the Arts in Zimbabwe
Although Zimbabwe has a rich and age-old heritage of oral literature, written literary works were absent for most of the country’s ancient history. It only developed after colonization of the land by the Europeans and the spread of the modern form of education in the country. The oral literature comprised of folk tales and legends, war stories and poems, heroic epics, historical accounts, etc. Many of the early writers of Zimbabwe made great efforts to produce the oral literature in the published form to preserve the country’s history and culture for the future generations. Today, Zimbabwean writers and poets explore various literary genres and produce publications that are often praised internationally.
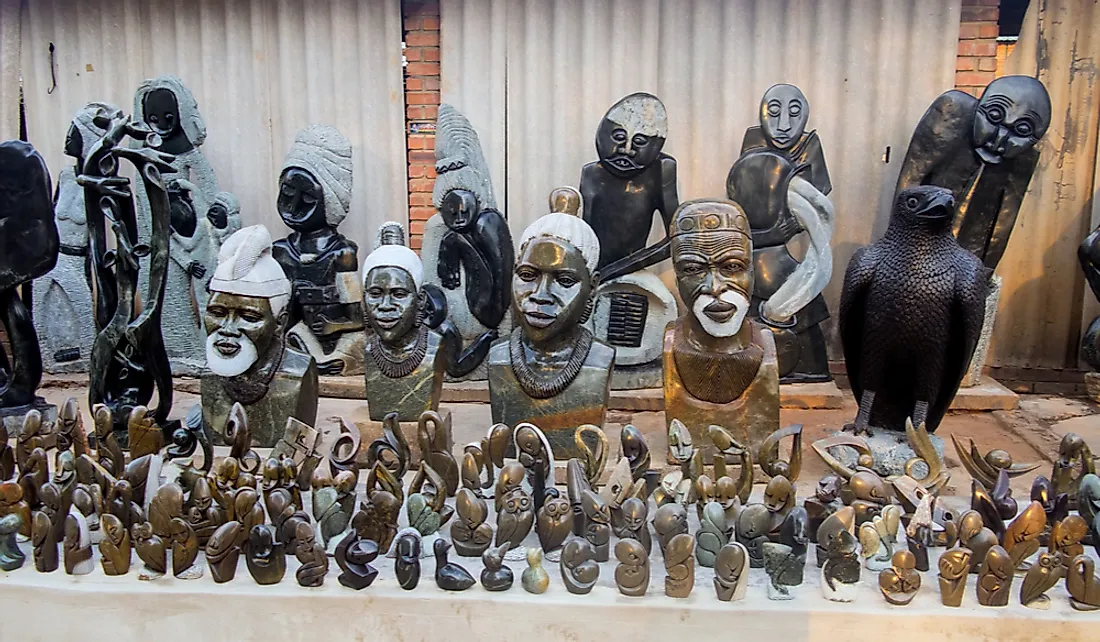
Traditional crafts in Zimbabwe include basketry, carving, jewelry, pottery, etc. Stools carved from a single piece of wood and woven baskets with symmetrical patterns are among the most famous handicrafts of the country. The sculptures made by the Shona people have earned worldwide fame. These sculptures are made of soapstone or other harder igneous rocks.
3. Performance Arts in Zimbabwe
The music scene of Zimbabwe is rich and varied. It ranges from folk music to pop and rock. Music has played a very significant role in the history of the country. Some of the traditional instruments used to produce the folk music of the country include hosho, ngoma drums, and mbira. Music has always been an integral part of the religious rites of the Zimbabweans and often used to call on ancestral spirits. Music also played an important role in portraying the people’s desire for freedom from colonial rule. Zimbabwean jazz, sungura, Tuku music, Chimurenga music, etc., are some of the most popular musical genres in Zimbabwe.
2. Sports in Zimbabwe
Football is the most popular sport in the country. It is played both professionally and informally in the cities and villages throughout the nation. The national football team of Zimbabwe has won several international championships like the Southern Africa championship. Rugby and cricket are also popular sports played in Zimbabwe. The national rugby and cricket teams are quite successful. Other games played in the country include volleyball, netball, water polo, chess, cycling, squash, swimming, horse racing, kayaking, etc.
1. Life in the Zimbabwean Society
Although the Constitution of the country grants equal rights to both men and women, gender-based discrimination in the country is not uncommon. There are complaints that the law of the country is often more in favor of men than women, especially in areas of inheritance, marriage, and the conditions of part-time work. Although a significant section of the women in urban areas receive education and enter the workforce, those in rural areas are still confined to the traditional roles. Although both men and women take part in agricultural activities in the villages, women are also expected to perform the household chores and take care of the children. In urban areas, a significant percentage of women participate in the workforce. However, men predominate in the political and administrative fields.
Marriages in Zimbabwe are based on both individual choice and family arrangements. However, the former is growing in popularity. Polygamous marriages are not uncommon but are gradually decreasing in number due to the higher costs of maintaining more wives and children. Most ethnic groups are associated with patrilocal residence where the bride moves in with the husband’s family. Matrilocal residence can be seen in the case of the Tonga people. In urban areas, nuclear families are more common. Brideprice is usually paid by the groom to the bride’s family in exchange of their daughter. Divorces are not encouraged and often viewed as a stigma, especially for women.
Households vary in size from extended in rural areas to nuclear in the urban areas. In polygynous families, each wife lives with her children in a small dwelling within a large compound owned by the husband. Men usually rule the household. The eldest person in the family is also highly respected and his or her words are regarded as wise. A woman gathers respect as she ages and through her children. Inheritance is patrilineal in most cases and the property passes from the father to the sons.
Children are the primary responsibility of the mother. Other female relatives including older sisters also participate in childcare. Since children in the large Zimbabwean households are rarely alone, they learn social values, customs, and rituals from their family and community members from an early age. Gender-based tasks are taught to the girls and boys from the age of about seven or eight.
Education is valued but quality education is more easily accessible in urban than in rural areas. Also, fewer girls than boys receive the opportunity to complete school.
More in Society

Age Of Consent Around The World
"Hell Is Other People," What Did Sartre Mean By That?

The Largest Megachurches In The US


The Biggest Stadiums In The World

How to be Happy According To Aristotle

What is the Ideal World According to Famous Philosophers?

The 10 Largest Soccer Stadiums In The World

Understanding Stoicism and Its Philosophy for a Better Life
Got any suggestions?
We want to hear from you! Send us a message and help improve Slidesgo
Top searches
Trending searches

26 templates

102 templates

15 templates
49 templates
cyber security
9 templates

386 templates
Zimbabwe Minitheme
It seems that you like this template, zimbabwe minitheme presentation, free google slides theme, powerpoint template, and canva presentation template.
Have you heard of the awesomely captivating country of Zimbabwe? It's a landlocked gem located in southern Africa, surrounded by stunning neighbors like South Africa, Zambia, Botswana, and Mozambique! Promote this beautiful country with this lovely template. We have the minitheme template about Zimbabwe that's going to make you go, "Wow!" Packed with magical pictures of heavenly landscapes and a creative icon pack, it is the perfect tool to make your presentation stand out and impress your audience.
Features of this template
- 100% editable and easy to modify
- 20 different slides to impress your audience
- Contains easy-to-edit graphics such as graphs, maps, tables, timelines and mockups
- Includes 500+ icons and Flaticon’s extension for customizing your slides
- Designed to be used in Google Slides, Canva, and Microsoft PowerPoint
- 16:9 widescreen format suitable for all types of screens
- Includes information about fonts, colors, and credits of the resources used
How can I use the template?
Am I free to use the templates?
How to attribute?
Attribution required If you are a free user, you must attribute Slidesgo by keeping the slide where the credits appear. How to attribute?
Related posts on our blog.

How to Add, Duplicate, Move, Delete or Hide Slides in Google Slides

How to Change Layouts in PowerPoint

How to Change the Slide Size in Google Slides
Related presentations.

Premium template
Unlock this template and gain unlimited access

Home PowerPoint Templates Maps Editable Zimbabwe PowerPoint Map
Editable Zimbabwe PowerPoint Map
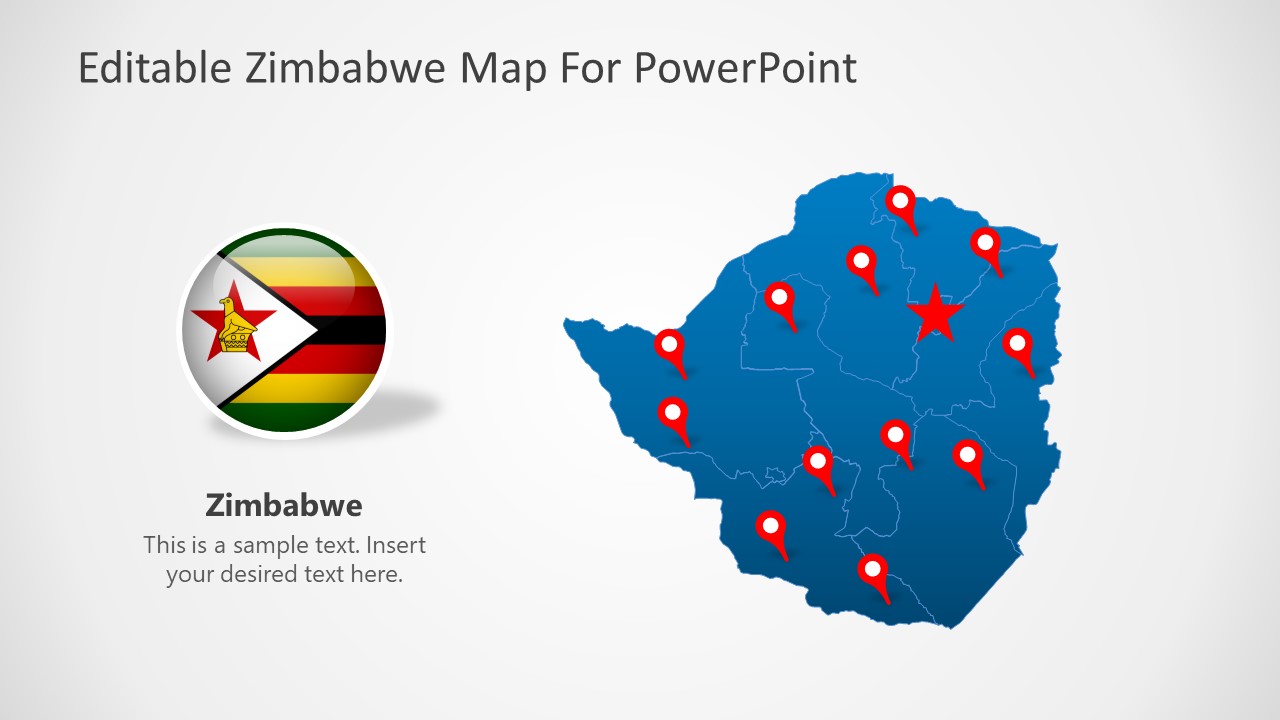
The Editable Zimbabwe PowerPoint Map enables the users to present the highlighted features of Zimbabwe. It is a land-locked country located in southeastern Africa, and it is known for its waterfalls and National parks. This PPT template shows various map layouts for presenting on any subject relevant to Zimbabwe. Users can edit the location pins, markers, and text areas to prepare custom presentations.
The flag of Zimbabwe is displayed on the first slide of the template, placed along with the blue-colored country map. The map shows several adjustable location pins and star icons to highlight a specific region on the map. The second slide focuses on the location of Zimbabwe within Africa and displays it on the World-map. The following two slides contain the country flag and map in two color variations, i.e., blue and grey. Presenters can generally use these slides to discuss the history or cultural distribution within the country. Nextly, the fifth slide contains numerous location markers; hence a thematic map can be constructed using this layout. Lastly, the ending slide carries the labeled Zimbabwe map to show the location of Harare, the Capital city. Tourist attractions such as the resorts are a big specialty of this city.
The increasing tourism trends and the exploration tendency of Zimbabwe are the counting factors for its economic growth. Tourism agencies, researchers, or analysts can utilize the Editable Zimbabwe PowerPoint Map to prepare interactive reports about Zimbabwe. Also, educationists can visually present geographic details of different cities within the country.
Each layout component is 100% editable, and users can quickly move the locator objects over the maps. The user can alter the background color and other color schemes accordingly. Moreover, text boxes are placed on each slide to mention the relevant information. Presenters can easily customize this template using PowerPoint, Keynote, and Google Slides. So, download this template and engage your audience by using high-resolution graphics of these template slides.
You must be logged in to download this file.
Favorite Add to Collection
Details (6 slides)

Supported Versions:
Subscribe today and get immediate access to download our PowerPoint templates.
Related PowerPoint Templates
Editable Croatia Map Template for PowerPoint
Editable Gabon PowerPoint Map
Editable Equatorial Guinea PowerPoint Map

Business Slide Deck Presentation Template
- My View My View
- Following Following
- Saved Saved
Zimbabwe targets small deficits, lower inflation in budget speech
- Medium Text
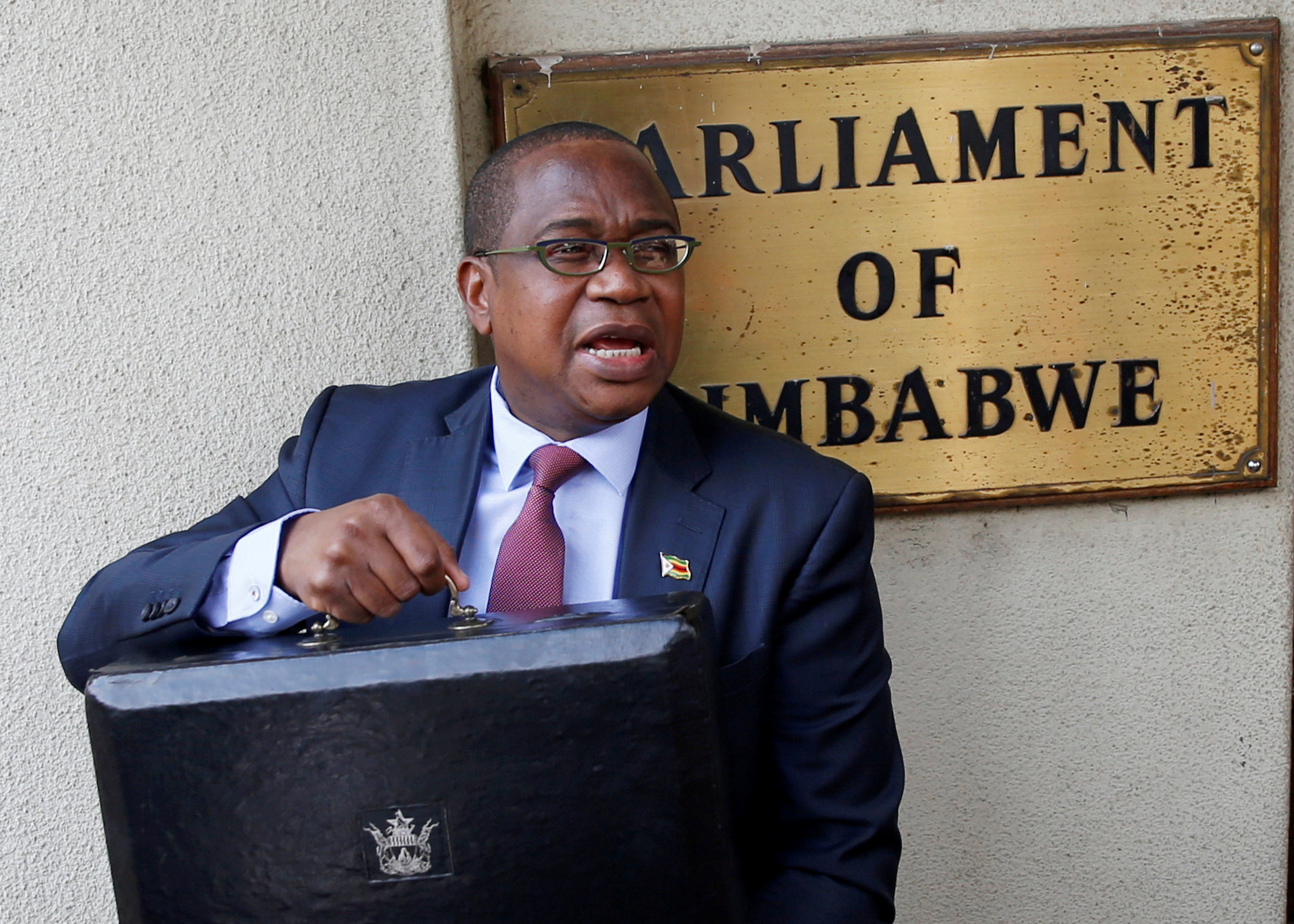

- Zimbabwe trying to restore investor confidence
- Targets 1.5%/GDP budget deficit in 2022
- Aims for 5.5% growth, 32.6% average inflation
Sign up here.
Editing by Alexander Winning, Barbara Lewis and Giles Elgood
Our Standards: The Thomson Reuters Trust Principles. New Tab , opens new tab

World Chevron
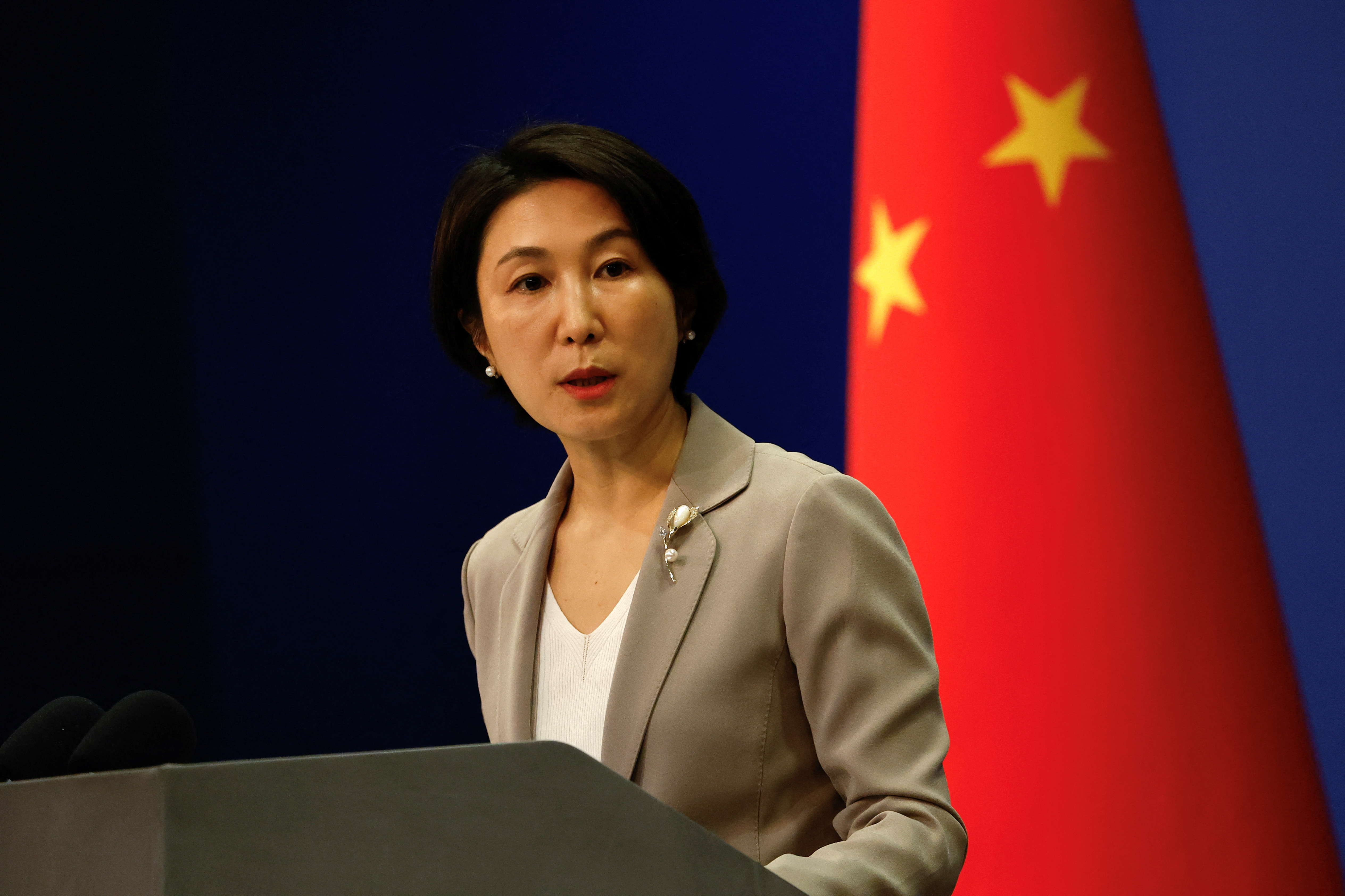

China says all efforts should be recognised in Russia-Ukraine peace measures
China believes all efforts should be recognised in supporting peace measures around the Russia-Ukraine war, a spokesperson for the Chinese foreign ministry said on Monday.

MyFreeSlides

Zimbabwe Google Slides and Powerpoint Template
Zimbabwe google slides themes and powerpoint template.
This Trendy Country PowerPoint Template is a nice and captivating presentation for multipurpose uses, you are free to use for school, colleges, corporal meeting presentations. Also, can be used by teachers, businessman, employees, startups to show professional look in their presentation. You can use it to present the Nation’s demographical, cultural and geographical topics along with their Flags icons which can be used as various Powerpoint Presentations.
Companies or startups can also easily use these Free google slides themes to market, Report and demonstrate their new product’s launch and the services they provide in a specific country or their growth in international markets. This Powerpoint template can also be used to create projects of school, colleges on History, Geography or report on the country.
The Free Zimbabwe Powerpoint template features:
1. Intro and History slide : Start your presentation by adding the introduction about the country, it’s history and evolution that is how are the people evolve in the country their tradition, culture, religion, dressing sense, etc. Add an image to enhance the quality of your presentation. 2. Famous Personalities : Include the names of some of the famous persons, explorers, reformers, noble people, democrats, elite members, etc. 3. Geography and Climate : Add points regarding the climatic conditions, geographical locations – latitudes & longitudes, etc. You can always use various Icons and shapes to make a presentation more interactive. 4. Government and policies : This free learning presentation can be used to include the running political party and its policies. Also, add few points regarding the economy and expenditure on different fields of the country that is education, sports, poverty, cleanliness, and environment, welfare for people, scientific research and technological improvement, defense and military, etc. 5. Extras : Powerpoint world map template slide to show the location, fun facts about the country, medical improvements, demographic slides, about (add population, capital, city details etc), Quotation slide, Title slide, etc.
Copy in Google Slide
Download as PPT
Contribute: Spread a Word!
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Tumblr (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window)
Discover more from MyFreeSlides
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading

Featured Resource
Why hiv prevention, we are not on track..
Despite progress in several countries, we are still not on track to end the AIDS epidemic by 2030. In 2022, about 4000 adults and children acquired HIV each day — a total of 1.3 million new HIV infections. Lifesaving antiretroviral therapy can also prevent HIV by suppressing the virus in a person’s blood to an untransmissible level, but 9.2 million people living with AIDS did not receive ART in 2022.
Intensive effort is needed to reach the global target of fewer than 370,000 new HIV infections annually by 2025.
Accelerating progress in HIV prevention is particularly important in the GPC focus countries where three out of four new HIV infections occur.
Learn About the GPC
1.3 million new HIV infections
39 million people living with hiv, 630,000 people died of aids related illnesses, global search.

Assess HIV prevention efforts in your country
The Global HIV Prevention Coalition and partners in HIV prevention have developed tools to facilitate country-led planning of prevention programmes. Tools are available for use in GPC and non-GPC countries for each of the thematic “pillars” of HIV prevention.
Upcoming Events
South-to-south learning network webinar: sexual and reproductive health and prevention of mother-to-child transmission, south-to-south learning network webinar: hiv prevention self-assessment tools, global key populations hiv prevention pre-conference.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Zimbabwe lies almost entirely over 1,000 feet (300 metres) above sea level.Its principal physical feature is the broad ridge running 400 miles from southwest to northeast across the entire country, from Plumtree near the Botswana frontier through Gweru (formerly Gwelo) and Marondera (formerly Marandellas) to the Inyanga Mountains, which separate Zimbabwe from Mozambique.
Le Zimbabwe ou Zimbabwé, en forme longue la république du Zimbabwe, est un pays situé en Afrique australe. Enclavé entre les fleuves Zambèze et Limpopo, le pays est entouré par l'Afrique du Sud au sud, le Botswana à l'ouest, le Mozambique à l'est et la Zambie au nord. La capitale, Harare, est située dans le nord-est et possède le statut de ville-province.
Dans les enceintes internationales et sur le plan bilatéral, le Zimbabwe s'oppose en revanche aux pays ayant pris des sanctions à son encontre à la suite des violations des droits de l'Homme commises lors de la réforme agraire de 2001 et des élections de 2002 et 2008 (Etats-Unis, Canada, Australie, Nouvelle-Zélande, Commonwealth).
General information. Zimbabwe is a land locked country in Southern Africa. It has dramatic landscape and diverse wildlife within its parks, reserves and safari areas. It has many attractions including the Victoria falls, Lake Kariba, Chinhoyi caves, Great Zimbabwe ruins and Hwange National Park.
Great Zimbabwe has been described as "one of the most dramatic architectural landscapes in sub-Saharan Africa.". [1] It is the largest stone complex in Africa built before the modern era, aside from the monumental architecture of ancient Egypt. The ruins that survive are a four-hour drive south of Zimbabwe's present-day capital of Harare.
INTRODUCTION AND BACKGROUND. The diverse agro-climatic conditions in Zimbabwe enable farmers to grow a variety of food and cash crops, over 23 types of food and cash crops are grown with white maize being the main staple food, we also have a well developed livestock sector. The performance of the agricultural sector determines the overall level ...
Until roughly 2,000 years ago, what would become Zimbabwe was populated by ancestors of the San people. Bantu inhabitants of the region arrived and developed ceramic production in the area. A series of trading empires emerged, including the Kingdom of Mapungubwe and Kingdom of Zimbabwe.In the 1880s, the British South Africa Company began its activities in the region, leading to the colonial ...
Economic context. Zimbabwe's economic development continues to be hampered by several challenges. Real GDP is estimated to have grown by 5.5% in 2023, after a 6.5% growth in 2022, due to an expansion in agriculture, mining, and remittances-induced services growth. Nevertheless, macroeconomic volatility fueled by monetary instability and ...
Zimbabwe's next step towards Vision 2030 is the Five year National Development Strategy of 2021-2025 (NDS1). The NDS1 is the successor to the TSP and will be underpinned by 5 annual National ...
The landlocked southern African nation of Zimbabwe hosts a population of 14,030,368 individuals. The country has a rich tradition and culture that reflects the ethnic diversity of its population. 7. Ethnicity, Language, and Religion of Zimbabwe. The Shona and the Ndebele are the largest ethnic groups residing in the country.
Presentation Outline Vision 2030 The National Development Strategy 1 ... The graph on the next slide shows Zimbabwe economic blue prints and corresponding growth rates from 1980 to 2020. 3. ... g de-industriali zation and informalisa tion Moving the economy up the Value Chain and Structural
The CCA findings also noted that Zimbabwe made remarkable progress in the first decade of independence with quantum improvements in social wellbeing, while registering a decline in some socio-economic indicators, largely due to prolonged periods of economic recession, political challenges, and recurrent climate-induced humanitarian crises. ...
Free Google Slides theme, PowerPoint template, and Canva presentation template. Have you heard of the awesomely captivating country of Zimbabwe? It's a landlocked gem located in southern Africa, surrounded by stunning neighbors like South Africa, Zambia, Botswana, and Mozambique! Promote this beautiful country with this lovely template.
This Humanitarian Response Plan will continue to deliver the support necessary to Zimbabweans who have endured multiple shocks impacting the lives of many in both rural and urban communities. Indeed, indications suggest that another poor harvest in 2020 is forecast leaving the most vulnerable people especially in rural areas in need of assistance.
Editable Zimbabwe PowerPoint Map. The Editable Zimbabwe PowerPoint Map enables the users to present the highlighted features of Zimbabwe. It is a land-locked country located in southeastern Africa, and it is known for its waterfalls and National parks. This PPT template shows various map layouts for presenting on any subject relevant to Zimbabwe.
Zimbabwe Finance Minister Mthuli Ncube arrives to present the 2020 National Budget at Parliament Building in Harare, Zimbabwe, November 14, 2019. ... a finance ministry presentation showed.
This Powerpoint template can also be used to create projects of school, colleges on History, Geography or report on the country. The Free Zimbabwe Powerpoint template features: 1. Intro and History slide: Start your presentation by adding the introduction about the country, it's history and evolution that is how are the people evolve in the ...
Zimbabwe including the People's Republic of China, the Russian Federation and the Republic of India, for their support to our vaccination programme. Citizens are assured that the efficacy of the vaccines we have rolled out has been duly considered and approved by the Medicines Control Authority of Zimbabwe. I,
Download this professionally designed Zimbabwe Map PowerPoint template and present your well-researched information without much trouble. It doesn't matter what industry you belong to - if your business is linked to the African nation, then this set would be of a great help to you. One can use these high-quality maps to depict any information ...
• The Zimbabwe Economic Development Conference (ZEDCON), held over the period 10-12 August, 2022, in Victoria Falls; • The inaugural Infrastructure Summit and Expo, convened by the National Economic Consultative Forum (NECF) and held from 8-9 September, 2022, in Victoria Falls; 2 Rodrik, D., 2015.
the Republic of Zimbabwe for the 2021 Financial Year and to make Provisions for matters ancillary and incidental to this purpose. INTRODUCTION 2. Mr Speaker Sir, let me start by thanking the President - His Excellency, Dr. E.D. Mnangagwa, and the Honourable Vice Presidents, Dr. C.G.D.N. Chiwenga and Cde K.C.D. Mohadi,
We are not on track.. Despite progress in several countries, we are still not on track to end the AIDS epidemic by 2030. In 2022, about 4000 adults and children acquired HIV each day — a total of 1.3 million new HIV infections.