
How To Write The Results/Findings Chapter
For quantitative studies (dissertations & theses).
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Expert Reviewed By: Kerryn Warren (PhD) | July 2021
So, you’ve completed your quantitative data analysis and it’s time to report on your findings. But where do you start? In this post, we’ll walk you through the results chapter (also called the findings or analysis chapter), step by step, so that you can craft this section of your dissertation or thesis with confidence. If you’re looking for information regarding the results chapter for qualitative studies, you can find that here .
Overview: Quantitative Results Chapter
- What exactly the results chapter is
- What you need to include in your chapter
- How to structure the chapter
- Tips and tricks for writing a top-notch chapter
- Free results chapter template
What exactly is the results chapter?
The results chapter (also referred to as the findings or analysis chapter) is one of the most important chapters of your dissertation or thesis because it shows the reader what you’ve found in terms of the quantitative data you’ve collected. It presents the data using a clear text narrative, supported by tables, graphs and charts. In doing so, it also highlights any potential issues (such as outliers or unusual findings) you’ve come across.
But how’s that different from the discussion chapter?
Well, in the results chapter, you only present your statistical findings. Only the numbers, so to speak – no more, no less. Contrasted to this, in the discussion chapter , you interpret your findings and link them to prior research (i.e. your literature review), as well as your research objectives and research questions . In other words, the results chapter presents and describes the data, while the discussion chapter interprets the data.
Let’s look at an example.
In your results chapter, you may have a plot that shows how respondents to a survey responded: the numbers of respondents per category, for instance. You may also state whether this supports a hypothesis by using a p-value from a statistical test. But it is only in the discussion chapter where you will say why this is relevant or how it compares with the literature or the broader picture. So, in your results chapter, make sure that you don’t present anything other than the hard facts – this is not the place for subjectivity.
It’s worth mentioning that some universities prefer you to combine the results and discussion chapters. Even so, it is good practice to separate the results and discussion elements within the chapter, as this ensures your findings are fully described. Typically, though, the results and discussion chapters are split up in quantitative studies. If you’re unsure, chat with your research supervisor or chair to find out what their preference is.

What should you include in the results chapter?
Following your analysis, it’s likely you’ll have far more data than are necessary to include in your chapter. In all likelihood, you’ll have a mountain of SPSS or R output data, and it’s your job to decide what’s most relevant. You’ll need to cut through the noise and focus on the data that matters.
This doesn’t mean that those analyses were a waste of time – on the contrary, those analyses ensure that you have a good understanding of your dataset and how to interpret it. However, that doesn’t mean your reader or examiner needs to see the 165 histograms you created! Relevance is key.
How do I decide what’s relevant?
At this point, it can be difficult to strike a balance between what is and isn’t important. But the most important thing is to ensure your results reflect and align with the purpose of your study . So, you need to revisit your research aims, objectives and research questions and use these as a litmus test for relevance. Make sure that you refer back to these constantly when writing up your chapter so that you stay on track.

As a general guide, your results chapter will typically include the following:
- Some demographic data about your sample
- Reliability tests (if you used measurement scales)
- Descriptive statistics
- Inferential statistics (if your research objectives and questions require these)
- Hypothesis tests (again, if your research objectives and questions require these)
We’ll discuss each of these points in more detail in the next section.
Importantly, your results chapter needs to lay the foundation for your discussion chapter . This means that, in your results chapter, you need to include all the data that you will use as the basis for your interpretation in the discussion chapter.
For example, if you plan to highlight the strong relationship between Variable X and Variable Y in your discussion chapter, you need to present the respective analysis in your results chapter – perhaps a correlation or regression analysis.
Need a helping hand?
How do I write the results chapter?
There are multiple steps involved in writing up the results chapter for your quantitative research. The exact number of steps applicable to you will vary from study to study and will depend on the nature of the research aims, objectives and research questions . However, we’ll outline the generic steps below.
Step 1 – Revisit your research questions
The first step in writing your results chapter is to revisit your research objectives and research questions . These will be (or at least, should be!) the driving force behind your results and discussion chapters, so you need to review them and then ask yourself which statistical analyses and tests (from your mountain of data) would specifically help you address these . For each research objective and research question, list the specific piece (or pieces) of analysis that address it.
At this stage, it’s also useful to think about the key points that you want to raise in your discussion chapter and note these down so that you have a clear reminder of which data points and analyses you want to highlight in the results chapter. Again, list your points and then list the specific piece of analysis that addresses each point.
Next, you should draw up a rough outline of how you plan to structure your chapter . Which analyses and statistical tests will you present and in what order? We’ll discuss the “standard structure” in more detail later, but it’s worth mentioning now that it’s always useful to draw up a rough outline before you start writing (this advice applies to any chapter).
Step 2 – Craft an overview introduction
As with all chapters in your dissertation or thesis, you should start your quantitative results chapter by providing a brief overview of what you’ll do in the chapter and why . For example, you’d explain that you will start by presenting demographic data to understand the representativeness of the sample, before moving onto X, Y and Z.
This section shouldn’t be lengthy – a paragraph or two maximum. Also, it’s a good idea to weave the research questions into this section so that there’s a golden thread that runs through the document.

Step 3 – Present the sample demographic data
The first set of data that you’ll present is an overview of the sample demographics – in other words, the demographics of your respondents.
For example:
- What age range are they?
- How is gender distributed?
- How is ethnicity distributed?
- What areas do the participants live in?
The purpose of this is to assess how representative the sample is of the broader population. This is important for the sake of the generalisability of the results. If your sample is not representative of the population, you will not be able to generalise your findings. This is not necessarily the end of the world, but it is a limitation you’ll need to acknowledge.
Of course, to make this representativeness assessment, you’ll need to have a clear view of the demographics of the population. So, make sure that you design your survey to capture the correct demographic information that you will compare your sample to.
But what if I’m not interested in generalisability?
Well, even if your purpose is not necessarily to extrapolate your findings to the broader population, understanding your sample will allow you to interpret your findings appropriately, considering who responded. In other words, it will help you contextualise your findings . For example, if 80% of your sample was aged over 65, this may be a significant contextual factor to consider when interpreting the data. Therefore, it’s important to understand and present the demographic data.
Step 4 – Review composite measures and the data “shape”.
Before you undertake any statistical analysis, you’ll need to do some checks to ensure that your data are suitable for the analysis methods and techniques you plan to use. If you try to analyse data that doesn’t meet the assumptions of a specific statistical technique, your results will be largely meaningless. Therefore, you may need to show that the methods and techniques you’ll use are “allowed”.
Most commonly, there are two areas you need to pay attention to:
#1: Composite measures
The first is when you have multiple scale-based measures that combine to capture one construct – this is called a composite measure . For example, you may have four Likert scale-based measures that (should) all measure the same thing, but in different ways. In other words, in a survey, these four scales should all receive similar ratings. This is called “ internal consistency ”.
Internal consistency is not guaranteed though (especially if you developed the measures yourself), so you need to assess the reliability of each composite measure using a test. Typically, Cronbach’s Alpha is a common test used to assess internal consistency – i.e., to show that the items you’re combining are more or less saying the same thing. A high alpha score means that your measure is internally consistent. A low alpha score means you may need to consider scrapping one or more of the measures.
#2: Data shape
The second matter that you should address early on in your results chapter is data shape. In other words, you need to assess whether the data in your set are symmetrical (i.e. normally distributed) or not, as this will directly impact what type of analyses you can use. For many common inferential tests such as T-tests or ANOVAs (we’ll discuss these a bit later), your data needs to be normally distributed. If it’s not, you’ll need to adjust your strategy and use alternative tests.
To assess the shape of the data, you’ll usually assess a variety of descriptive statistics (such as the mean, median and skewness), which is what we’ll look at next.

Step 5 – Present the descriptive statistics
Now that you’ve laid the foundation by discussing the representativeness of your sample, as well as the reliability of your measures and the shape of your data, you can get started with the actual statistical analysis. The first step is to present the descriptive statistics for your variables.
For scaled data, this usually includes statistics such as:
- The mean – this is simply the mathematical average of a range of numbers.
- The median – this is the midpoint in a range of numbers when the numbers are arranged in order.
- The mode – this is the most commonly repeated number in the data set.
- Standard deviation – this metric indicates how dispersed a range of numbers is. In other words, how close all the numbers are to the mean (the average).
- Skewness – this indicates how symmetrical a range of numbers is. In other words, do they tend to cluster into a smooth bell curve shape in the middle of the graph (this is called a normal or parametric distribution), or do they lean to the left or right (this is called a non-normal or non-parametric distribution).
- Kurtosis – this metric indicates whether the data are heavily or lightly-tailed, relative to the normal distribution. In other words, how peaked or flat the distribution is.
A large table that indicates all the above for multiple variables can be a very effective way to present your data economically. You can also use colour coding to help make the data more easily digestible.
For categorical data, where you show the percentage of people who chose or fit into a category, for instance, you can either just plain describe the percentages or numbers of people who responded to something or use graphs and charts (such as bar graphs and pie charts) to present your data in this section of the chapter.
When using figures, make sure that you label them simply and clearly , so that your reader can easily understand them. There’s nothing more frustrating than a graph that’s missing axis labels! Keep in mind that although you’ll be presenting charts and graphs, your text content needs to present a clear narrative that can stand on its own. In other words, don’t rely purely on your figures and tables to convey your key points: highlight the crucial trends and values in the text. Figures and tables should complement the writing, not carry it .
Depending on your research aims, objectives and research questions, you may stop your analysis at this point (i.e. descriptive statistics). However, if your study requires inferential statistics, then it’s time to deep dive into those .

Step 6 – Present the inferential statistics
Inferential statistics are used to make generalisations about a population , whereas descriptive statistics focus purely on the sample . Inferential statistical techniques, broadly speaking, can be broken down into two groups .
First, there are those that compare measurements between groups , such as t-tests (which measure differences between two groups) and ANOVAs (which measure differences between multiple groups). Second, there are techniques that assess the relationships between variables , such as correlation analysis and regression analysis. Within each of these, some tests can be used for normally distributed (parametric) data and some tests are designed specifically for use on non-parametric data.
There are a seemingly endless number of tests that you can use to crunch your data, so it’s easy to run down a rabbit hole and end up with piles of test data. Ultimately, the most important thing is to make sure that you adopt the tests and techniques that allow you to achieve your research objectives and answer your research questions .
In this section of the results chapter, you should try to make use of figures and visual components as effectively as possible. For example, if you present a correlation table, use colour coding to highlight the significance of the correlation values, or scatterplots to visually demonstrate what the trend is. The easier you make it for your reader to digest your findings, the more effectively you’ll be able to make your arguments in the next chapter.

Step 7 – Test your hypotheses
If your study requires it, the next stage is hypothesis testing. A hypothesis is a statement , often indicating a difference between groups or relationship between variables, that can be supported or rejected by a statistical test. However, not all studies will involve hypotheses (again, it depends on the research objectives), so don’t feel like you “must” present and test hypotheses just because you’re undertaking quantitative research.
The basic process for hypothesis testing is as follows:
- Specify your null hypothesis (for example, “The chemical psilocybin has no effect on time perception).
- Specify your alternative hypothesis (e.g., “The chemical psilocybin has an effect on time perception)
- Set your significance level (this is usually 0.05)
- Calculate your statistics and find your p-value (e.g., p=0.01)
- Draw your conclusions (e.g., “The chemical psilocybin does have an effect on time perception”)
Finally, if the aim of your study is to develop and test a conceptual framework , this is the time to present it, following the testing of your hypotheses. While you don’t need to develop or discuss these findings further in the results chapter, indicating whether the tests (and their p-values) support or reject the hypotheses is crucial.
Step 8 – Provide a chapter summary
To wrap up your results chapter and transition to the discussion chapter, you should provide a brief summary of the key findings . “Brief” is the keyword here – much like the chapter introduction, this shouldn’t be lengthy – a paragraph or two maximum. Highlight the findings most relevant to your research objectives and research questions, and wrap it up.
Some final thoughts, tips and tricks
Now that you’ve got the essentials down, here are a few tips and tricks to make your quantitative results chapter shine:
- When writing your results chapter, report your findings in the past tense . You’re talking about what you’ve found in your data, not what you are currently looking for or trying to find.
- Structure your results chapter systematically and sequentially . If you had two experiments where findings from the one generated inputs into the other, report on them in order.
- Make your own tables and graphs rather than copying and pasting them from statistical analysis programmes like SPSS. Check out the DataIsBeautiful reddit for some inspiration.
- Once you’re done writing, review your work to make sure that you have provided enough information to answer your research questions , but also that you didn’t include superfluous information.
If you’ve got any questions about writing up the quantitative results chapter, please leave a comment below. If you’d like 1-on-1 assistance with your quantitative analysis and discussion, check out our hands-on coaching service , or book a free consultation with a friendly coach.

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
You Might Also Like:

Thank you. I will try my best to write my results.
Awesome content 👏🏾
this was great explaination
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
3.1 What is Quantitative Research?
Quantitative research is a research method that uses numerical data and statistical analysis to study phenomena. 1 Quantitative research plays an important role in scientific inquiry by providing a rigorous, objective, systematic process using numerical data to test relationships and examine cause-and-effect associations between variables. 1, 2 The goal is to make generalisations about a population (extrapolate findings from the sample to the general population). 2 The data and variables are predetermined and measured as consistently and accurately as possible, and statistical analysis is used to evaluate the outcomes. 2 Quantitative research is based on the scientific method, wherein deductive reductionist reasoning is used to formulate hypotheses about a particular phenomenon.
An Introduction to Research Methods for Undergraduate Health Profession Students Copyright © 2023 by Faith Alele and Bunmi Malau-Aduli is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.

Quantitative and Qualitative Research
- I NEED TO . . .
What is Quantitative Research?
- What is Qualitative Research?
- Quantitative vs Qualitative
- Step 1: Accessing CINAHL
- Step 2: Create a Keyword Search
- Step 3: Create a Subject Heading Search
- Step 4: Repeat Steps 1-3 for Second Concept
- Step 5: Repeat Steps 1-3 for Quantitative Terms
- Step 6: Combining All Searches
- Step 7: Adding Limiters
- Step 8: Save Your Search!
- What Kind of Article is This?
- More Research Help This link opens in a new window
Quantitative methodology is the dominant research framework in the social sciences. It refers to a set of strategies, techniques and assumptions used to study psychological, social and economic processes through the exploration of numeric patterns . Quantitative research gathers a range of numeric data. Some of the numeric data is intrinsically quantitative (e.g. personal income), while in other cases the numeric structure is imposed (e.g. ‘On a scale from 1 to 10, how depressed did you feel last week?’). The collection of quantitative information allows researchers to conduct simple to extremely sophisticated statistical analyses that aggregate the data (e.g. averages, percentages), show relationships among the data (e.g. ‘Students with lower grade point averages tend to score lower on a depression scale’) or compare across aggregated data (e.g. the USA has a higher gross domestic product than Spain). Quantitative research includes methodologies such as questionnaires, structured observations or experiments and stands in contrast to qualitative research. Qualitative research involves the collection and analysis of narratives and/or open-ended observations through methodologies such as interviews, focus groups or ethnographies.
Coghlan, D., Brydon-Miller, M. (2014). The SAGE encyclopedia of action research (Vols. 1-2). London, : SAGE Publications Ltd doi: 10.4135/9781446294406
What is the purpose of quantitative research?
The purpose of quantitative research is to generate knowledge and create understanding about the social world. Quantitative research is used by social scientists, including communication researchers, to observe phenomena or occurrences affecting individuals. Social scientists are concerned with the study of people. Quantitative research is a way to learn about a particular group of people, known as a sample population. Using scientific inquiry, quantitative research relies on data that are observed or measured to examine questions about the sample population.
Allen, M. (2017). The SAGE encyclopedia of communication research methods (Vols. 1-4). Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, Inc doi: 10.4135/9781483381411
How do I know if the study is a quantitative design? What type of quantitative study is it?
Quantitative Research Designs: Descriptive non-experimental, Quasi-experimental or Experimental?
Studies do not always explicitly state what kind of research design is being used. You will need to know how to decipher which design type is used. The following video will help you determine the quantitative design type.
- << Previous: I NEED TO . . .
- Next: What is Qualitative Research? >>
- Last Updated: May 13, 2024 12:01 PM
- URL: https://libguides.uta.edu/quantitative_and_qualitative_research
University of Texas Arlington Libraries 702 Planetarium Place · Arlington, TX 76019 · 817-272-3000
- Internet Privacy
- Accessibility
- Problems with a guide? Contact Us.

- Chapter Four: Quantitative Methods (Part 3 - Making Sense of Your Study)
After you have designed your study, collected your data, and analyzed it, you have to figure out what it means and communicate that to potential interested audiences. This section of the chapter is about how to make sense of your study, in terms of data interpretation, data write-up, and data presentation, as seen in the above diagram.
- Chapter One: Introduction
- Chapter Two: Understanding the distinctions among research methods
- Chapter Three: Ethical research, writing, and creative work
- Chapter Four: Quantitative Methods (Part 1)
- Chapter Four: Quantitative Methods (Part 2 - Doing Your Study)
- Chapter Five: Qualitative Methods (Part 1)
- Chapter Five: Qualitative Data (Part 2)
- Chapter Six: Critical / Rhetorical Methods (Part 1)
- Chapter Six: Critical / Rhetorical Methods (Part 2)
- Chapter Seven: Presenting Your Results
Data Interpretation
Once you have run your statistics, you have to figure out what your findings mean or interpret your data. To do this, you need to tie back your findings to your research questions and/or hypotheses, think about how your findings relate to what you discovered beforehand about the already existing literature, and determine how your findings take the literature or current theory in the field further. Your interpretation of the data you collected will be found in the last section of your paper, what is commonly called the "discussion" section.
Remember Your RQs/Hs
Your research questions and hypotheses, once developed, should guide your study throughout the research process. As you are choosing your research design, choosing how to operationalize your variables, and choosing/conducting your statistical tests, you should always keep your RQs and Hs in mind.
What were you wanting to discover by your study? What were you wanting to test? Make sure you answer these questions clearly for the reader of your study in both the results and discussion section of the paper. (Specific guidelines for these sections will be covered later in this chapter, including the common practice of placing the data as you present it with each research question in the results section.)
Tie Findings to Your Literature Review
As you have seen in chapter 3 and the Appendix, and will see in chapter 7, the literature review is what you use to set up your quantitative study and to show why there is a need for your study. It should start out broad, with the context for your study, and lead into showing what still needs to be known and studied about your topic area, justifying your focus in the study. It will be brought in again in the last section of the paper you write, i.e., the discussion section.
Your paper is like an hourglass – starting out broad and narrowing down in the middle with your actual study and findings, and then moving to broad implications for the larger context of your study near the end.
Think about Relationship of Findings to Theory
One of the things you will write about in your discussion or last section of your paper is the implications of what you found. These implications are both practical and theoretical. Practical implications are how the research can provide practical applications to real-world people and issues. Theoretical implications are how the research takes the current academic literature further, specifically, in relationship to theory-building.
Did any of the research you reviewed for your literature review mention a theory your findings could expand upon? If so, you should think about how your findings related to this theory. If not, then think about the theories you have already studied in your communication classes. Would any of them provide a possible explanation of what you found? Would your findings help expand that theory to a different context, the context you studied? Does a theory need to be developed in the area of your research? If so, then what aspects of that theory could your findings help explain?
Data Write-Up
All quantitative studies, when written, have four parts. The first part is the introduction and literature review, the second part is the methods section, the third section is the results or findings, and the fourth section is the discussion section. This portion of this chapter will explain what elements you will need to include in each of these sections.
Literature Review
The beginning of your paper and first few pages sets the tone for your study. It tells the reader what the context of your study is and what other people who are also interested in your topic have studied about your topic.
There are many ways to organize a literature review, as can be seen in the following website. Literature Reviews — The Writing Center at UNC-Chapel Hill
After you have done a thorough literature search on your topic, then you have to organize your literature into topics of some kind. Your main goal is to show what has been done and what still needs to be done, to show the need for your study, so at the end of each section of your literature review, you should identify what still needs to be known about that particular area.
For quantitative research, you should do your literature review before coming up with your research questions/hypotheses. Your questions and hypotheses should flow from the literature. This is different from the other two research methods discussed in this book, which do not rely so heavily on a literature review to situation the study before conducting it.
In the methods section, you should tell your reader how you conducted your study, from start to finish, explaining why you made the choices you did along the way. A reader should be able to replicate your study from the descriptions you provide in this section of your write-up. Common headings in the methods section include a description of the participants, procedures, and analysis.
Participants
For the participants' subheading of the methods section, you should minimally report the demographics of your sample in terms of biological sex (frequencies/percentages), age (range of ages and mean), and ethnicity (frequencies/percentages). If you collected data on other demographics, such as socioeconomic status, religious affiliation, type of occupation, etc., then you can report data for that also in the participants' sub-section.
For the procedures sub-section, you report everything you did to collect your data: how you recruited your participants, including what type of sampling you used (probability or non-probability) and informed consent procedures; how you operationalized your variables (including your survey questions, which often are explained in the methods section briefly while the whole survey can be found in an appendix of your paper); the validity and reliability of your survey instrument or methods you used; and what type of study design you had (experimental, quasi-experimental, or non-experimental). For each one of these design issues, in this sub-section of the methods part, you need to explain why you made the decisions you did in order to answer your research questions or test your hypotheses.
In this section, you explain how you converted your data for analysis and how you analyzed your data. You need to explain what statistics you chose to run for each of your research questions/hypotheses and why.
In this section of your paper, you organize the results by your research questions/hypotheses. For each research question/hypothesis, you should present any descriptive statistic results first and then your inferential statistics results. You do not make any interpretation of what your results mean or why you think you got the results you did. You merely report your results.
Reporting Significant Results
For each of the inferential statistics, there is a typical template you can follow when reporting significant results: reporting the test statistic value, the degrees of freedom 3 , and the probability level. Examples follow for each of the statistics we have talked about in this text.
T-test results
"T-tests results show there was a significant difference found between men and women on their levels of self-esteem, t (df) = t value, p < .05, with men's self-esteem being higher (or lower) (men's mean & standard deviation) than women's self-esteem (women's mean & standard deviation)."
ANOVA results
"ANOVA results indicate there was a significant difference found between [levels of independent variable] on [dependent variable], F (df) = F value, p < .05."
If doing a factorial ANOVA, you would report the above sentence for all of your independent variables (main effects), as well as for the interaction (interaction effect), with language something like: "ANOVA results indicate a significant main effect for [independent variable] on [dependent variable], F (df) = F value, p < .05. .... ANOVA results indicate a significant interaction effect between [independent variables] on [dependent variable], F (df) = F value, p < .05."
See example YouTube tutorial for writing up a two-way ANOVA at the following website.
Factorial Design (Part C): Writing Up Results
Chi-square results
For goodness of fit results, your write-up would look something like: "Using a chi-square goodness of fit test, there was a significant difference found between observed and expected values of [variable], χ2 (df) = chi-square value, p < .05." For test of independence results, it would like like: "Using a chi-square test of independence, there was a significant interaction between [your two variables], χ2 (df) = chi-square value, p < .05."
Correlation results
"Using Pearson's [or Spearman's] correlation coefficient, there was a significant relationship found between [two variables], r (df) = r value, p < .05." If there are a lot of significant correlation results, these results are often presented in a table form.
For more information on these types of tables, see the following website: Correlation Tables .
Regression results
Reporting regression results is more complicated, but generally, you want to inform the reader about how much variance is accounted by the regression model, the significance level of the model, and the significance of the predictor variable. For example:
A regression analysis, predicting GPA scores from GRE scores, was statistically significant, F (1,8) = 10.34, p < .05.
Coefficientsa
The regression equation is: Ŷ = .411 * .005X. For every one unit increase in GRE score, there is a corresponding increase in GPA of .005 (Walen-Frederick, n.d., p. 4).
For more write-up help on regression and other statistics, see the following website location:
Multiple Regression (pp. 217-220)
Reporting Non-Significant Results
You can follow a similar template when reporting non-significant results for all of the above inferential statistics. It is the same as provided in the above examples, except the word "non-significant" replaces the word "significant," and the p values are adjusted to indicate p > .05.
Many times readers of articles do not read the whole article, especially if they are afraid of the statistical sections. When this happens, they often read the discussion section, which makes this a very important section in your writing. You should include the following elements in your discussion section: (a) a summary of your findings, (b) implications, (c) limitations, and (d) future research ideas.

Summary of Findings
You should summarize the answers to your research questions or what you found when testing your hypotheses in this sub-section of the discussion section. You should not report any statistical data here, but just put your results into narrative form. What did you find out that you did not know before doing your study? Answer that question in this sub- section.
Implications
You need to indicate why your study was important, both theoretically and practically. For the theoretical implications, you should relate what you found to the already existing literature, as discussed earlier when the "hourglass" format was mentioned as a way of conceptualizing your whole paper. If your study added anything to the existing theory on a particular topic, you talk about this here as well.
For practical implications, you need to identify for the reader how this study can help people in their real-world experiences related to your topic. You do not want your study to just be important to academic researchers, but also to other professionals and persons interested in your topic.
Limitations
As you get through conducting your study, you are going to realize there are things you wish you had done differently. Rather than hide these things from the reader, it is better to forthrightly state these for the reader. Explain why your study is limited and what you wish you had done in this sub-section.
Future Research
The limitations sub-section usually is tied directly to the future research sub-section, as your limitations mean that future research should be done to deal with these limitations. There may also be other things that could be studied, however, as a result of what you have found. What would other people say are the "gaps" your study left unstudied on your topic? These should be identified, with some suggestions on how they might be studied.
Other Aspects of the Paper
There are other parts of the academic paper you should include in your final write-up. We have provided useful resources for you to consider when including these aspects as part of your paper. For an example paper that uses the required APA format for a research paper write-up, see the following source: Varying Definitions of Online Communication .
Abstract & Titles.
Research Abstracts General Format
Tables, References, & Other Materials.
APA Tables and Figures 1 Reference List: Basic Rules
Data Presentation
You will probably be called upon to present your data in other venues besides in writing. Two of the most common venues are oral presentations such as in class or at conferences, and poster presentations, such as what you might find at conferences. You might also be called upon to not write an academic write-up of your study, but rather to provide an executive summary of the results of your study to the "powers that be," who do not have time to read more than 5 pages or so of a summary. There are good resources for doing all of these online, so we have provided these here.
Oral Presentations
Oral Presentations Delivering Presentations
Poster Presentations
Executive Summary
Executive Summaries Complete the Report Good & Poor Examples of Executive Summaries with the following link: http://unilearning.uow.edu.au/report/4bi1.html
Congratulations! You have learned a great deal about how to go about using quantitative methods for your future research projects. You have learned how to design a quantitative study, conduct a quantitative study, and write about a quantitative study. You have some good resources you can take with you when you leave this class. Now, you just have to apply what you have learned to projects that will come your way in the future.
Remember, just because you may not like one method the best does not mean you should not use it. Your research questions/hypotheses should ALWAYS drive your choice of which method you use. And remember also that you can do quantitative methods!
[NOTE: References are not provided for the websites cited in the text, even though if this was an actual research article, they would need to be cited.]
Baker, E., Baker, W., & Tedesco, J. C. (2007). Organizations respond to phishing: Exploring the public relations tackle box. Communication Research Reports, 24 (4), 327-339.
Benoit, W. L., & Hansen, G. J. (2004). Presidential debate watching, issue knowledge, character evaluation, and vote choice. Human Communication Research, 30 (1), 121-144.
Chatham, A. (1991). Home vs. public schooling: What about relationships in adolescence? Doctoral dissertation, University of Oklahoma.
Cousineau, T. M., Rancourt, D., and Green, T. C. (2006). Web chatter before and after the women's health initiative results: A content analysis of on-line menopause message boards. Journal of Health Communication, 11 (2), 133-147.
Derlega, V., Winstead, B. A., Mathews, A., and Braitman, A. L. (2008). Why does someone reveal highly personal information?: Attributions for and against self-disclosure in close relationships. Communication Research Reports, 25 , 115-130.
Fischer, J., & Corcoran, K. (2007). Measures for clinical practice and research: A sourcebook (volumes 1 & 2) . New York: Oxford University Press.
Guay, S., Boisvert, J.-M., & Freeston, M. H. (2003). Validity of three measures of communication for predicting relationship adjustment and stability among a sample of young couples. Psychological Assessment , 15(3), 392-398.
Holbert, R. L., Tschida, D. A., Dixon, M., Cherry, K., Steuber, K., & Airne, D. (2005). The West Wing and depictions of the American Presidency: Expanding the domains of framing in political communication. Communication Quarterly, 53 (4), 505-522.
Jensen, J. D. (2008). Scientific uncertainty in news coverage of cancer research: Effects of hedging on scientists' and journalists' credibility. Human Communication Research, 34 , 347- 369.
Keyton, J. (2011). Communicating research: Asking questions, finding answers . New York: McGraw Hill.
Lenhart, A., Ling, R., Campbell, S., & Purcell, K. (2010, Apr. 10). Teens and mobile phones . Report from the Pew Internet and American Life Project, retrieved from http://www.pewinternet.org/Reports/2010/Teens-and-Mobile-Phones.aspx .
Maddy, T. (2008). Tests: A comprehensive reference for assessments in psychology, education, and business . Austin, TX: Pro-Ed.
McCollum Jr., J. F., & Bryant, J. (2003). Pacing in children's television programming. Mass Communication and Society, 6 (2), 115-136.
Medved, C. E., Brogan, S. M., McClanahan, A. M., Morris, J. F., & Shepherd, G. J. (2006). Family and work socializing communication: Messages, gender, and ideological implications. Journal of Family Communication, 6 (3), 161-180.
Moyer-Gusé, E., & Nabi, R. L. (2010). Explaining the effects of narrative in an entertainment television program: Overcoming resistance to persuasion. Human Communication Research, 36 , 26-52.
Nabi, R. L. (2009). Cosmetic surgery makeover programs and intentions to undergo cosmetic enhancements: A consideration of three models of media effects. Human Communication Research, 35 , 1-27.
Pearson, J. C., DeWitt, L., Child, J. T., Kahl Jr., D. H., and Dandamudi, V. (2007). Facing the fear: An analysis of speech-anxiety content in public-speaking textbooks. Communication Research Reports, 24 (2), 159-168.
Rubin. R. B., Rubin, A. M., Graham, E., Perse, E. M., & Seibold, D. (2009). Communication research measures II: A sourcebook . New York: Routledge.
Serota, K. B., Levine, T. R., and Boster, F. J. (2010). The prevalence of lying in America: Three studies of reported deception. Human Communication Research, 36 , 1-24.
Sheldon, P. (2008). The relationship between unwillingness-to-communicate and students' facebook use. Journal of Media Psychology, 20 (2), 67–75.
Trochim, W. M. K. (2006). Reliability and validity. Research methods data base , retrieved from http://www.socialresearchmethods.net/kb/relandval.php .
Walen-Frederick, H. (n.d.). Help sheet for reading SPSS printouts . Retrieved from http://www.scribd.com/doc/51982223/help-sheet-for-reading-spss-printouts .
Weaver, A. J., & Wilson, B. J. (2009). The role of graphic and sanitized violence in the enjoyment of television dramas. Human Communication Research, 35 (3), 442-463.
Weber, K., Corrigan, M., Fornash, B., & Neupauer, N. C. (2003). The effect of interest on recall: An experiment. Communication Research Reports, 20 (2), 116-123.
Witt, P. L., & Schrodt, P. (2006). The influence of instructional technology use and teacher immediacy on student affect for teacher and course. Communication Reports, 19 (1), 1-15.
3 Degrees of freedom (df) relate to your sample size and to the number of groups being compared. SPSS always computes the df for your statistics. For more information on degrees of freedom, see the following web-based resources: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wsvfasNpU2s and http://www.creative-wisdom.com/pub/df/index.htm .
Back to Previous Spot
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- J Korean Med Sci
- v.37(16); 2022 Apr 25

A Practical Guide to Writing Quantitative and Qualitative Research Questions and Hypotheses in Scholarly Articles
Edward barroga.
1 Department of General Education, Graduate School of Nursing Science, St. Luke’s International University, Tokyo, Japan.
Glafera Janet Matanguihan
2 Department of Biological Sciences, Messiah University, Mechanicsburg, PA, USA.
The development of research questions and the subsequent hypotheses are prerequisites to defining the main research purpose and specific objectives of a study. Consequently, these objectives determine the study design and research outcome. The development of research questions is a process based on knowledge of current trends, cutting-edge studies, and technological advances in the research field. Excellent research questions are focused and require a comprehensive literature search and in-depth understanding of the problem being investigated. Initially, research questions may be written as descriptive questions which could be developed into inferential questions. These questions must be specific and concise to provide a clear foundation for developing hypotheses. Hypotheses are more formal predictions about the research outcomes. These specify the possible results that may or may not be expected regarding the relationship between groups. Thus, research questions and hypotheses clarify the main purpose and specific objectives of the study, which in turn dictate the design of the study, its direction, and outcome. Studies developed from good research questions and hypotheses will have trustworthy outcomes with wide-ranging social and health implications.
INTRODUCTION
Scientific research is usually initiated by posing evidenced-based research questions which are then explicitly restated as hypotheses. 1 , 2 The hypotheses provide directions to guide the study, solutions, explanations, and expected results. 3 , 4 Both research questions and hypotheses are essentially formulated based on conventional theories and real-world processes, which allow the inception of novel studies and the ethical testing of ideas. 5 , 6
It is crucial to have knowledge of both quantitative and qualitative research 2 as both types of research involve writing research questions and hypotheses. 7 However, these crucial elements of research are sometimes overlooked; if not overlooked, then framed without the forethought and meticulous attention it needs. Planning and careful consideration are needed when developing quantitative or qualitative research, particularly when conceptualizing research questions and hypotheses. 4
There is a continuing need to support researchers in the creation of innovative research questions and hypotheses, as well as for journal articles that carefully review these elements. 1 When research questions and hypotheses are not carefully thought of, unethical studies and poor outcomes usually ensue. Carefully formulated research questions and hypotheses define well-founded objectives, which in turn determine the appropriate design, course, and outcome of the study. This article then aims to discuss in detail the various aspects of crafting research questions and hypotheses, with the goal of guiding researchers as they develop their own. Examples from the authors and peer-reviewed scientific articles in the healthcare field are provided to illustrate key points.
DEFINITIONS AND RELATIONSHIP OF RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
A research question is what a study aims to answer after data analysis and interpretation. The answer is written in length in the discussion section of the paper. Thus, the research question gives a preview of the different parts and variables of the study meant to address the problem posed in the research question. 1 An excellent research question clarifies the research writing while facilitating understanding of the research topic, objective, scope, and limitations of the study. 5
On the other hand, a research hypothesis is an educated statement of an expected outcome. This statement is based on background research and current knowledge. 8 , 9 The research hypothesis makes a specific prediction about a new phenomenon 10 or a formal statement on the expected relationship between an independent variable and a dependent variable. 3 , 11 It provides a tentative answer to the research question to be tested or explored. 4
Hypotheses employ reasoning to predict a theory-based outcome. 10 These can also be developed from theories by focusing on components of theories that have not yet been observed. 10 The validity of hypotheses is often based on the testability of the prediction made in a reproducible experiment. 8
Conversely, hypotheses can also be rephrased as research questions. Several hypotheses based on existing theories and knowledge may be needed to answer a research question. Developing ethical research questions and hypotheses creates a research design that has logical relationships among variables. These relationships serve as a solid foundation for the conduct of the study. 4 , 11 Haphazardly constructed research questions can result in poorly formulated hypotheses and improper study designs, leading to unreliable results. Thus, the formulations of relevant research questions and verifiable hypotheses are crucial when beginning research. 12
CHARACTERISTICS OF GOOD RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
Excellent research questions are specific and focused. These integrate collective data and observations to confirm or refute the subsequent hypotheses. Well-constructed hypotheses are based on previous reports and verify the research context. These are realistic, in-depth, sufficiently complex, and reproducible. More importantly, these hypotheses can be addressed and tested. 13
There are several characteristics of well-developed hypotheses. Good hypotheses are 1) empirically testable 7 , 10 , 11 , 13 ; 2) backed by preliminary evidence 9 ; 3) testable by ethical research 7 , 9 ; 4) based on original ideas 9 ; 5) have evidenced-based logical reasoning 10 ; and 6) can be predicted. 11 Good hypotheses can infer ethical and positive implications, indicating the presence of a relationship or effect relevant to the research theme. 7 , 11 These are initially developed from a general theory and branch into specific hypotheses by deductive reasoning. In the absence of a theory to base the hypotheses, inductive reasoning based on specific observations or findings form more general hypotheses. 10
TYPES OF RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
Research questions and hypotheses are developed according to the type of research, which can be broadly classified into quantitative and qualitative research. We provide a summary of the types of research questions and hypotheses under quantitative and qualitative research categories in Table 1 .
Research questions in quantitative research
In quantitative research, research questions inquire about the relationships among variables being investigated and are usually framed at the start of the study. These are precise and typically linked to the subject population, dependent and independent variables, and research design. 1 Research questions may also attempt to describe the behavior of a population in relation to one or more variables, or describe the characteristics of variables to be measured ( descriptive research questions ). 1 , 5 , 14 These questions may also aim to discover differences between groups within the context of an outcome variable ( comparative research questions ), 1 , 5 , 14 or elucidate trends and interactions among variables ( relationship research questions ). 1 , 5 We provide examples of descriptive, comparative, and relationship research questions in quantitative research in Table 2 .
Hypotheses in quantitative research
In quantitative research, hypotheses predict the expected relationships among variables. 15 Relationships among variables that can be predicted include 1) between a single dependent variable and a single independent variable ( simple hypothesis ) or 2) between two or more independent and dependent variables ( complex hypothesis ). 4 , 11 Hypotheses may also specify the expected direction to be followed and imply an intellectual commitment to a particular outcome ( directional hypothesis ) 4 . On the other hand, hypotheses may not predict the exact direction and are used in the absence of a theory, or when findings contradict previous studies ( non-directional hypothesis ). 4 In addition, hypotheses can 1) define interdependency between variables ( associative hypothesis ), 4 2) propose an effect on the dependent variable from manipulation of the independent variable ( causal hypothesis ), 4 3) state a negative relationship between two variables ( null hypothesis ), 4 , 11 , 15 4) replace the working hypothesis if rejected ( alternative hypothesis ), 15 explain the relationship of phenomena to possibly generate a theory ( working hypothesis ), 11 5) involve quantifiable variables that can be tested statistically ( statistical hypothesis ), 11 6) or express a relationship whose interlinks can be verified logically ( logical hypothesis ). 11 We provide examples of simple, complex, directional, non-directional, associative, causal, null, alternative, working, statistical, and logical hypotheses in quantitative research, as well as the definition of quantitative hypothesis-testing research in Table 3 .
Research questions in qualitative research
Unlike research questions in quantitative research, research questions in qualitative research are usually continuously reviewed and reformulated. The central question and associated subquestions are stated more than the hypotheses. 15 The central question broadly explores a complex set of factors surrounding the central phenomenon, aiming to present the varied perspectives of participants. 15
There are varied goals for which qualitative research questions are developed. These questions can function in several ways, such as to 1) identify and describe existing conditions ( contextual research question s); 2) describe a phenomenon ( descriptive research questions ); 3) assess the effectiveness of existing methods, protocols, theories, or procedures ( evaluation research questions ); 4) examine a phenomenon or analyze the reasons or relationships between subjects or phenomena ( explanatory research questions ); or 5) focus on unknown aspects of a particular topic ( exploratory research questions ). 5 In addition, some qualitative research questions provide new ideas for the development of theories and actions ( generative research questions ) or advance specific ideologies of a position ( ideological research questions ). 1 Other qualitative research questions may build on a body of existing literature and become working guidelines ( ethnographic research questions ). Research questions may also be broadly stated without specific reference to the existing literature or a typology of questions ( phenomenological research questions ), may be directed towards generating a theory of some process ( grounded theory questions ), or may address a description of the case and the emerging themes ( qualitative case study questions ). 15 We provide examples of contextual, descriptive, evaluation, explanatory, exploratory, generative, ideological, ethnographic, phenomenological, grounded theory, and qualitative case study research questions in qualitative research in Table 4 , and the definition of qualitative hypothesis-generating research in Table 5 .
Qualitative studies usually pose at least one central research question and several subquestions starting with How or What . These research questions use exploratory verbs such as explore or describe . These also focus on one central phenomenon of interest, and may mention the participants and research site. 15
Hypotheses in qualitative research
Hypotheses in qualitative research are stated in the form of a clear statement concerning the problem to be investigated. Unlike in quantitative research where hypotheses are usually developed to be tested, qualitative research can lead to both hypothesis-testing and hypothesis-generating outcomes. 2 When studies require both quantitative and qualitative research questions, this suggests an integrative process between both research methods wherein a single mixed-methods research question can be developed. 1
FRAMEWORKS FOR DEVELOPING RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
Research questions followed by hypotheses should be developed before the start of the study. 1 , 12 , 14 It is crucial to develop feasible research questions on a topic that is interesting to both the researcher and the scientific community. This can be achieved by a meticulous review of previous and current studies to establish a novel topic. Specific areas are subsequently focused on to generate ethical research questions. The relevance of the research questions is evaluated in terms of clarity of the resulting data, specificity of the methodology, objectivity of the outcome, depth of the research, and impact of the study. 1 , 5 These aspects constitute the FINER criteria (i.e., Feasible, Interesting, Novel, Ethical, and Relevant). 1 Clarity and effectiveness are achieved if research questions meet the FINER criteria. In addition to the FINER criteria, Ratan et al. described focus, complexity, novelty, feasibility, and measurability for evaluating the effectiveness of research questions. 14
The PICOT and PEO frameworks are also used when developing research questions. 1 The following elements are addressed in these frameworks, PICOT: P-population/patients/problem, I-intervention or indicator being studied, C-comparison group, O-outcome of interest, and T-timeframe of the study; PEO: P-population being studied, E-exposure to preexisting conditions, and O-outcome of interest. 1 Research questions are also considered good if these meet the “FINERMAPS” framework: Feasible, Interesting, Novel, Ethical, Relevant, Manageable, Appropriate, Potential value/publishable, and Systematic. 14
As we indicated earlier, research questions and hypotheses that are not carefully formulated result in unethical studies or poor outcomes. To illustrate this, we provide some examples of ambiguous research question and hypotheses that result in unclear and weak research objectives in quantitative research ( Table 6 ) 16 and qualitative research ( Table 7 ) 17 , and how to transform these ambiguous research question(s) and hypothesis(es) into clear and good statements.
a These statements were composed for comparison and illustrative purposes only.
b These statements are direct quotes from Higashihara and Horiuchi. 16
a This statement is a direct quote from Shimoda et al. 17
The other statements were composed for comparison and illustrative purposes only.
CONSTRUCTING RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
To construct effective research questions and hypotheses, it is very important to 1) clarify the background and 2) identify the research problem at the outset of the research, within a specific timeframe. 9 Then, 3) review or conduct preliminary research to collect all available knowledge about the possible research questions by studying theories and previous studies. 18 Afterwards, 4) construct research questions to investigate the research problem. Identify variables to be accessed from the research questions 4 and make operational definitions of constructs from the research problem and questions. Thereafter, 5) construct specific deductive or inductive predictions in the form of hypotheses. 4 Finally, 6) state the study aims . This general flow for constructing effective research questions and hypotheses prior to conducting research is shown in Fig. 1 .

Research questions are used more frequently in qualitative research than objectives or hypotheses. 3 These questions seek to discover, understand, explore or describe experiences by asking “What” or “How.” The questions are open-ended to elicit a description rather than to relate variables or compare groups. The questions are continually reviewed, reformulated, and changed during the qualitative study. 3 Research questions are also used more frequently in survey projects than hypotheses in experiments in quantitative research to compare variables and their relationships.
Hypotheses are constructed based on the variables identified and as an if-then statement, following the template, ‘If a specific action is taken, then a certain outcome is expected.’ At this stage, some ideas regarding expectations from the research to be conducted must be drawn. 18 Then, the variables to be manipulated (independent) and influenced (dependent) are defined. 4 Thereafter, the hypothesis is stated and refined, and reproducible data tailored to the hypothesis are identified, collected, and analyzed. 4 The hypotheses must be testable and specific, 18 and should describe the variables and their relationships, the specific group being studied, and the predicted research outcome. 18 Hypotheses construction involves a testable proposition to be deduced from theory, and independent and dependent variables to be separated and measured separately. 3 Therefore, good hypotheses must be based on good research questions constructed at the start of a study or trial. 12
In summary, research questions are constructed after establishing the background of the study. Hypotheses are then developed based on the research questions. Thus, it is crucial to have excellent research questions to generate superior hypotheses. In turn, these would determine the research objectives and the design of the study, and ultimately, the outcome of the research. 12 Algorithms for building research questions and hypotheses are shown in Fig. 2 for quantitative research and in Fig. 3 for qualitative research.

EXAMPLES OF RESEARCH QUESTIONS FROM PUBLISHED ARTICLES
- EXAMPLE 1. Descriptive research question (quantitative research)
- - Presents research variables to be assessed (distinct phenotypes and subphenotypes)
- “BACKGROUND: Since COVID-19 was identified, its clinical and biological heterogeneity has been recognized. Identifying COVID-19 phenotypes might help guide basic, clinical, and translational research efforts.
- RESEARCH QUESTION: Does the clinical spectrum of patients with COVID-19 contain distinct phenotypes and subphenotypes? ” 19
- EXAMPLE 2. Relationship research question (quantitative research)
- - Shows interactions between dependent variable (static postural control) and independent variable (peripheral visual field loss)
- “Background: Integration of visual, vestibular, and proprioceptive sensations contributes to postural control. People with peripheral visual field loss have serious postural instability. However, the directional specificity of postural stability and sensory reweighting caused by gradual peripheral visual field loss remain unclear.
- Research question: What are the effects of peripheral visual field loss on static postural control ?” 20
- EXAMPLE 3. Comparative research question (quantitative research)
- - Clarifies the difference among groups with an outcome variable (patients enrolled in COMPERA with moderate PH or severe PH in COPD) and another group without the outcome variable (patients with idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension (IPAH))
- “BACKGROUND: Pulmonary hypertension (PH) in COPD is a poorly investigated clinical condition.
- RESEARCH QUESTION: Which factors determine the outcome of PH in COPD?
- STUDY DESIGN AND METHODS: We analyzed the characteristics and outcome of patients enrolled in the Comparative, Prospective Registry of Newly Initiated Therapies for Pulmonary Hypertension (COMPERA) with moderate or severe PH in COPD as defined during the 6th PH World Symposium who received medical therapy for PH and compared them with patients with idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension (IPAH) .” 21
- EXAMPLE 4. Exploratory research question (qualitative research)
- - Explores areas that have not been fully investigated (perspectives of families and children who receive care in clinic-based child obesity treatment) to have a deeper understanding of the research problem
- “Problem: Interventions for children with obesity lead to only modest improvements in BMI and long-term outcomes, and data are limited on the perspectives of families of children with obesity in clinic-based treatment. This scoping review seeks to answer the question: What is known about the perspectives of families and children who receive care in clinic-based child obesity treatment? This review aims to explore the scope of perspectives reported by families of children with obesity who have received individualized outpatient clinic-based obesity treatment.” 22
- EXAMPLE 5. Relationship research question (quantitative research)
- - Defines interactions between dependent variable (use of ankle strategies) and independent variable (changes in muscle tone)
- “Background: To maintain an upright standing posture against external disturbances, the human body mainly employs two types of postural control strategies: “ankle strategy” and “hip strategy.” While it has been reported that the magnitude of the disturbance alters the use of postural control strategies, it has not been elucidated how the level of muscle tone, one of the crucial parameters of bodily function, determines the use of each strategy. We have previously confirmed using forward dynamics simulations of human musculoskeletal models that an increased muscle tone promotes the use of ankle strategies. The objective of the present study was to experimentally evaluate a hypothesis: an increased muscle tone promotes the use of ankle strategies. Research question: Do changes in the muscle tone affect the use of ankle strategies ?” 23
EXAMPLES OF HYPOTHESES IN PUBLISHED ARTICLES
- EXAMPLE 1. Working hypothesis (quantitative research)
- - A hypothesis that is initially accepted for further research to produce a feasible theory
- “As fever may have benefit in shortening the duration of viral illness, it is plausible to hypothesize that the antipyretic efficacy of ibuprofen may be hindering the benefits of a fever response when taken during the early stages of COVID-19 illness .” 24
- “In conclusion, it is plausible to hypothesize that the antipyretic efficacy of ibuprofen may be hindering the benefits of a fever response . The difference in perceived safety of these agents in COVID-19 illness could be related to the more potent efficacy to reduce fever with ibuprofen compared to acetaminophen. Compelling data on the benefit of fever warrant further research and review to determine when to treat or withhold ibuprofen for early stage fever for COVID-19 and other related viral illnesses .” 24
- EXAMPLE 2. Exploratory hypothesis (qualitative research)
- - Explores particular areas deeper to clarify subjective experience and develop a formal hypothesis potentially testable in a future quantitative approach
- “We hypothesized that when thinking about a past experience of help-seeking, a self distancing prompt would cause increased help-seeking intentions and more favorable help-seeking outcome expectations .” 25
- “Conclusion
- Although a priori hypotheses were not supported, further research is warranted as results indicate the potential for using self-distancing approaches to increasing help-seeking among some people with depressive symptomatology.” 25
- EXAMPLE 3. Hypothesis-generating research to establish a framework for hypothesis testing (qualitative research)
- “We hypothesize that compassionate care is beneficial for patients (better outcomes), healthcare systems and payers (lower costs), and healthcare providers (lower burnout). ” 26
- Compassionomics is the branch of knowledge and scientific study of the effects of compassionate healthcare. Our main hypotheses are that compassionate healthcare is beneficial for (1) patients, by improving clinical outcomes, (2) healthcare systems and payers, by supporting financial sustainability, and (3) HCPs, by lowering burnout and promoting resilience and well-being. The purpose of this paper is to establish a scientific framework for testing the hypotheses above . If these hypotheses are confirmed through rigorous research, compassionomics will belong in the science of evidence-based medicine, with major implications for all healthcare domains.” 26
- EXAMPLE 4. Statistical hypothesis (quantitative research)
- - An assumption is made about the relationship among several population characteristics ( gender differences in sociodemographic and clinical characteristics of adults with ADHD ). Validity is tested by statistical experiment or analysis ( chi-square test, Students t-test, and logistic regression analysis)
- “Our research investigated gender differences in sociodemographic and clinical characteristics of adults with ADHD in a Japanese clinical sample. Due to unique Japanese cultural ideals and expectations of women's behavior that are in opposition to ADHD symptoms, we hypothesized that women with ADHD experience more difficulties and present more dysfunctions than men . We tested the following hypotheses: first, women with ADHD have more comorbidities than men with ADHD; second, women with ADHD experience more social hardships than men, such as having less full-time employment and being more likely to be divorced.” 27
- “Statistical Analysis
- ( text omitted ) Between-gender comparisons were made using the chi-squared test for categorical variables and Students t-test for continuous variables…( text omitted ). A logistic regression analysis was performed for employment status, marital status, and comorbidity to evaluate the independent effects of gender on these dependent variables.” 27
EXAMPLES OF HYPOTHESIS AS WRITTEN IN PUBLISHED ARTICLES IN RELATION TO OTHER PARTS
- EXAMPLE 1. Background, hypotheses, and aims are provided
- “Pregnant women need skilled care during pregnancy and childbirth, but that skilled care is often delayed in some countries …( text omitted ). The focused antenatal care (FANC) model of WHO recommends that nurses provide information or counseling to all pregnant women …( text omitted ). Job aids are visual support materials that provide the right kind of information using graphics and words in a simple and yet effective manner. When nurses are not highly trained or have many work details to attend to, these job aids can serve as a content reminder for the nurses and can be used for educating their patients (Jennings, Yebadokpo, Affo, & Agbogbe, 2010) ( text omitted ). Importantly, additional evidence is needed to confirm how job aids can further improve the quality of ANC counseling by health workers in maternal care …( text omitted )” 28
- “ This has led us to hypothesize that the quality of ANC counseling would be better if supported by job aids. Consequently, a better quality of ANC counseling is expected to produce higher levels of awareness concerning the danger signs of pregnancy and a more favorable impression of the caring behavior of nurses .” 28
- “This study aimed to examine the differences in the responses of pregnant women to a job aid-supported intervention during ANC visit in terms of 1) their understanding of the danger signs of pregnancy and 2) their impression of the caring behaviors of nurses to pregnant women in rural Tanzania.” 28
- EXAMPLE 2. Background, hypotheses, and aims are provided
- “We conducted a two-arm randomized controlled trial (RCT) to evaluate and compare changes in salivary cortisol and oxytocin levels of first-time pregnant women between experimental and control groups. The women in the experimental group touched and held an infant for 30 min (experimental intervention protocol), whereas those in the control group watched a DVD movie of an infant (control intervention protocol). The primary outcome was salivary cortisol level and the secondary outcome was salivary oxytocin level.” 29
- “ We hypothesize that at 30 min after touching and holding an infant, the salivary cortisol level will significantly decrease and the salivary oxytocin level will increase in the experimental group compared with the control group .” 29
- EXAMPLE 3. Background, aim, and hypothesis are provided
- “In countries where the maternal mortality ratio remains high, antenatal education to increase Birth Preparedness and Complication Readiness (BPCR) is considered one of the top priorities [1]. BPCR includes birth plans during the antenatal period, such as the birthplace, birth attendant, transportation, health facility for complications, expenses, and birth materials, as well as family coordination to achieve such birth plans. In Tanzania, although increasing, only about half of all pregnant women attend an antenatal clinic more than four times [4]. Moreover, the information provided during antenatal care (ANC) is insufficient. In the resource-poor settings, antenatal group education is a potential approach because of the limited time for individual counseling at antenatal clinics.” 30
- “This study aimed to evaluate an antenatal group education program among pregnant women and their families with respect to birth-preparedness and maternal and infant outcomes in rural villages of Tanzania.” 30
- “ The study hypothesis was if Tanzanian pregnant women and their families received a family-oriented antenatal group education, they would (1) have a higher level of BPCR, (2) attend antenatal clinic four or more times, (3) give birth in a health facility, (4) have less complications of women at birth, and (5) have less complications and deaths of infants than those who did not receive the education .” 30
Research questions and hypotheses are crucial components to any type of research, whether quantitative or qualitative. These questions should be developed at the very beginning of the study. Excellent research questions lead to superior hypotheses, which, like a compass, set the direction of research, and can often determine the successful conduct of the study. Many research studies have floundered because the development of research questions and subsequent hypotheses was not given the thought and meticulous attention needed. The development of research questions and hypotheses is an iterative process based on extensive knowledge of the literature and insightful grasp of the knowledge gap. Focused, concise, and specific research questions provide a strong foundation for constructing hypotheses which serve as formal predictions about the research outcomes. Research questions and hypotheses are crucial elements of research that should not be overlooked. They should be carefully thought of and constructed when planning research. This avoids unethical studies and poor outcomes by defining well-founded objectives that determine the design, course, and outcome of the study.
Disclosure: The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Author Contributions:
- Conceptualization: Barroga E, Matanguihan GJ.
- Methodology: Barroga E, Matanguihan GJ.
- Writing - original draft: Barroga E, Matanguihan GJ.
- Writing - review & editing: Barroga E, Matanguihan GJ.
Quantitative Research Methods
- First Online: 26 October 2016
Cite this chapter

- Yvette C. Latunde 2
1513 Accesses
This chapter distinguishes between quantitative and other types of research, while providing specific free resources for accessing pre-collected data. It identifies philosophical assumptions related to quantitative research in parental involvement. It also examines issues and limitations in measuring parental involvement using quantitative research, and provides examples of important quantitative research into parental involvement. Lastly, this chapter identifies questions about the impact of quantitative research in parental involvement and the importance of quantitative research.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Durable hardcover edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Babbie, E. R. (2010). The practice of social research (12th ed.). Belmont, CA: Wadsworth Cengage.
Google Scholar
Balnaves, M., & Caputi, P. (2001). Introduction to quantitative research methods: An investigative approach . London, UK: Sage.
Book Google Scholar
California Department of Education. (2013). Time to eat survey results. Retrieved from http://www.cde.ca.gov/ls/nu/sn/documents/timetoeatsurvey.pdf
Creswell, J. W. (2012). Qualitative inquiry and research design: Choosing among five approaches (3rd ed.). Los Angeles, CA: Sage.
Gale, T. (2008). Meta-analysis. International Encyclopedia of the Social Sciences. Retrieved from http://www.encyclopedia.com/topic/Meta-analysis.aspx
Haase, R. (2011). Power analysis of research in counselor education. Counselor Education and Supervision, 14 (2), 124–132.
Article Google Scholar
Handcock, G., Mueller, R., & Handcock, G. R. (2010). The reviewer’s guide to quantitative methods in the social sciences . Howick Place, London: Routledge.
Hill, N. E., & Tyson, D. F. (2009). Parental involvement in middle school: A meta-analytic assessment of the strategies that promote academic achievement. Developmental Psychology, 45 (3), 740–763.
Jeynes, W. (2005). A meta-analysis of the relation of parental involvement to urban elementary school student academic achievement. Urban Education, 40 (3), 237–269.
Jeynes, W. (2007). The relationship between parental involvement and urban secondary school academic achievement: A meta-analysis. Urban Education, 42 (1), 82–110.
Kim, S. W., & Hill, N. E. (2015). Including fathers in the picture: A meta-analysis of parental involvement and students’ academic achievement. Journal of Educational Psychology, 107 (4), 919–934.
McGowan, H.M. (2011). Planning a comparative experiment in educational settings. Journal of Statistics Education , 19(2), 1–19. Retrieved from http://www.amstat.org/publications/jse/v19n2/mcgowan.pdf
National Center for Education Statistics. (2015). National household education surveys. Parent and family involvement in education survey: Early childhood participation survey. Retrieved from http://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/ED556344.pdf
National Head Start Association. (2015). The head start impact study Retrieved from https://www.nhsa.org/files/resources/head_start_impact_study_2015.pdf
Pennsylvania State University. (n.d.). Probability, theory, and mathematical statistics: Test for homogeneity. Retrieved from https://onlinecourses.science.psu.edu/stat414/node/311
Sousa, D. A. (2015). How the brain learns mathematics (2nd ed.). Thousand Oaks, CA: Corwin Press.
Torbeyns, J., Schneider, M., Ziqiang, X., & Seigler, R. S. (2015). Bringing the gap: Fraction understanding is central to mathematics achievement in students from three different countries. Learning and Instruction, 37 , 5–13.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Teacher Education, Azusa Pacific University, Azusa, California, USA
Yvette C. Latunde
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Copyright information
© 2017 The Author(s)
About this chapter
Latunde, Y.C. (2017). Quantitative Research Methods. In: Research in Parental Involvement. Palgrave Macmillan, New York. https://doi.org/10.1057/978-1-137-59146-3_5
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1057/978-1-137-59146-3_5
Published : 26 October 2016
Publisher Name : Palgrave Macmillan, New York
Print ISBN : 978-1-137-59145-6
Online ISBN : 978-1-137-59146-3
eBook Packages : Education Education (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research

Part II: Data Analysis Methods in Quantitative Research
Data analysis methods in quantitative research.
We started this module with levels of measurement as a way to categorize our data. Data analysis is directed toward answering the original research question and achieving the study purpose (or aim). Now, we are going to delve into two main statistical analyses to describe our data and make inferences about our data:
Descriptive Statistics and Inferential Statistics.
Descriptive Statistics:
Before you panic, we will not be going into statistical analyses very deeply. We want to simply get a good overview of some of the types of general statistical analyses so that it makes some sense to us when we read results in published research articles.
Descriptive statistics summarize or describe the characteristics of a data set. This is a method of simply organizing and describing our data. Why? Because data that are not organized in some fashion are super difficult to interpret.
Let’s say our sample is golden retrievers (population “canines”). Our descriptive statistics tell us more about the same.
- 37% of our sample is male, 43% female
- The mean age is 4 years
- Mode is 6 years
- Median age is 5.5 years

Let’s explore some of the types of descriptive statistics.
Frequency Distributions : A frequency distribution describes the number of observations for each possible value of a measured variable. The numbers are arranged from lowest to highest and features a count of how many times each value occurred.
For example, if 18 students have pet dogs, dog ownership has a frequency of 18.
We might see what other types of pets that students have. Maybe cats, fish, and hamsters. We find that 2 students have hamsters, 9 have fish, 1 has a cat.
You can see that it is very difficult to interpret the various pets into any meaningful interpretation, yes?
Now, let’s take those same pets and place them in a frequency distribution table.
As we can now see, this is much easier to interpret.
Let’s say that we want to know how many books our sample population of students have read in the last year. We collect our data and find this:
We can then take that table and plot it out on a frequency distribution graph. This makes it much easier to see how the numbers are disbursed. Easier on the eyes, yes?
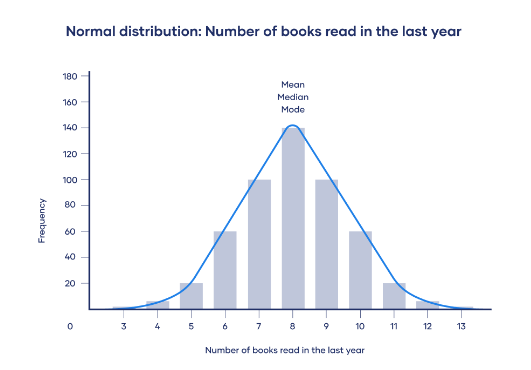
Here’s another example of symmetrical, positive skew, and negative skew:
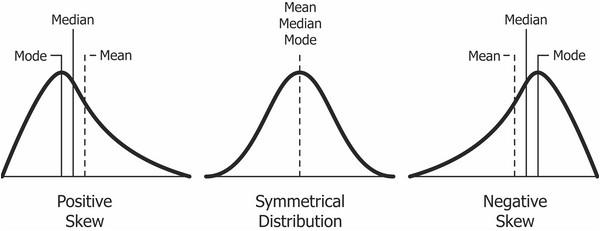
Correlation : Relationships between two research variables are called correlations . Remember, correlation is not cause-and-effect. Correlations simply measure the extent of relationship between two variables. To measure correlation in descriptive statistics, the statistical analysis called Pearson’s correlation coefficient I is often used. You do not need to know how to calculate this for this course. But, do remember that analysis test because you will often see this in published research articles. There really are no set guidelines on what measurement constitutes a “strong” or “weak” correlation, as it really depends on the variables being measured.
However, possible values for correlation coefficients range from -1.00 through .00 to +1.00. A value of +1 means that the two variables are positively correlated, as one variable goes up, the other goes up. A value of r = 0 means that the two variables are not linearly related.
Often, the data will be presented on a scatter plot. Here, we can view the data and there appears to be a straight line (linear) trend between height and weight. The association (or correlation) is positive. That means, that there is a weight increase with height. The Pearson correlation coefficient in this case was r = 0.56.
A type I error is made by rejecting a null hypothesis that is true. This means that there was no difference but the researcher concluded that the hypothesis was true.
A type II error is made by accepting that the null hypothesis is true when, in fact, it was false. Meaning there was actually a difference but the researcher did not think their hypothesis was supported.
Hypothesis Testing Procedures : In a general sense, the overall testing of a hypothesis has a systematic methodology. Remember, a hypothesis is an educated guess about the outcome. If we guess wrong, we might set up the tests incorrectly and might get results that are invalid. Sometimes, this is super difficult to get right. The main purpose of statistics is to test a hypothesis.
- Selecting a statistical test. Lots of factors go into this, including levels of measurement of the variables.
- Specifying the level of significance. Usually 0.05 is chosen.
- Computing a test statistic. Lots of software programs to help with this.
- Determining degrees of freedom ( df ). This refers to the number of observations free to vary about a parameter. Computing this is easy (but you don’t need to know how for this course).
- Comparing the test statistic to a theoretical value. Theoretical values exist for all test statistics, which is compared to the study statistics to help establish significance.
Some of the common inferential statistics you will see include:
Comparison tests: Comparison tests look for differences among group means. They can be used to test the effect of a categorical variable on the mean value of some other characteristic.
T-tests are used when comparing the means of precisely two groups (e.g., the average heights of men and women). ANOVA and MANOVA tests are used when comparing the means of more than two groups (e.g., the average heights of children, teenagers, and adults).
- t -tests (compares differences in two groups) – either paired t-test (example: What is the effect of two different test prep programs on the average exam scores for students from the same class?) or independent t-test (example: What is the difference in average exam scores for students from two different schools?)
- analysis of variance (ANOVA, which compares differences in three or more groups) (example: What is the difference in average pain levels among post-surgical patients given three different painkillers?) or MANOVA (compares differences in three or more groups, and 2 or more outcomes) (example: What is the effect of flower species on petal length, petal width, and stem length?)
Correlation tests: Correlation tests check whether variables are related without hypothesizing a cause-and-effect relationship.
- Pearson r (measures the strength and direction of the relationship between two variables) (example: How are latitude and temperature related?)
Nonparametric tests: Non-parametric tests don’t make as many assumptions about the data, and are useful when one or more of the common statistical assumptions are violated. However, the inferences they make aren’t as strong as with parametric tests.
- chi-squared ( X 2 ) test (measures differences in proportions). Chi-square tests are often used to test hypotheses. The chi-square statistic compares the size of any discrepancies between the expected results and the actual results, given the size of the sample and the number of variables in the relationship. For example, the results of tossing a fair coin meet these criteria. We can apply a chi-square test to determine which type of candy is most popular and make sure that our shelves are well stocked. Or maybe you’re a scientist studying the offspring of cats to determine the likelihood of certain genetic traits being passed to a litter of kittens.
Inferential Versus Descriptive Statistics Summary Table
Statistical Significance Versus Clinical Significance
Finally, when it comes to statistical significance in hypothesis testing, the normal probability value in nursing is <0.05. A p=value (probability) is a statistical measurement used to validate a hypothesis against measured data in the study. Meaning, it measures the likelihood that the results were actually observed due to the intervention, or if the results were just due by chance. The p-value, in measuring the probability of obtaining the observed results, assumes the null hypothesis is true.
The lower the p-value, the greater the statistical significance of the observed difference.
In the example earlier about our diabetic patients receiving online diet education, let’s say we had p = 0.05. Would that be a statistically significant result?
If you answered yes, you are correct!
What if our result was p = 0.8?
Not significant. Good job!
That’s pretty straightforward, right? Below 0.05, significant. Over 0.05 not significant.
Could we have significance clinically even if we do not have statistically significant results? Yes. Let’s explore this a bit.
Statistical hypothesis testing provides little information for interpretation purposes. It’s pretty mathematical and we can still get it wrong. Additionally, attaining statistical significance does not really state whether a finding is clinically meaningful. With a large enough sample, even a small very tiny relationship may be statistically significant. But, clinical significance is the practical importance of research. Meaning, we need to ask what the palpable effects may be on the lives of patients or healthcare decisions.
Remember, hypothesis testing cannot prove. It also cannot tell us much other than “yeah, it’s probably likely that there would be some change with this intervention”. Hypothesis testing tells us the likelihood that the outcome was due to an intervention or influence and not just by chance. Also, as nurses and clinicians, we are not concerned with a group of people – we are concerned at the individual, holistic level. The goal of evidence-based practice is to use best evidence for decisions about specific individual needs.
Additionally, begin your Discussion section. What are the implications to practice? Is there little evidence or a lot? Would you recommend additional studies? If so, what type of study would you recommend, and why?
- Were all the important results discussed?
- Did the researchers discuss any study limitations and their possible effects on the credibility of the findings? In discussing limitations, were key threats to the study’s validity and possible biases reviewed? Did the interpretations take limitations into account?
- What types of evidence were offered in support of the interpretation, and was that evidence persuasive? Were results interpreted in light of findings from other studies?
- Did the researchers make any unjustifiable causal inferences? Were alternative explanations for the findings considered? Were the rationales for rejecting these alternatives convincing?
- Did the interpretation consider the precision of the results and/or the magnitude of effects?
- Did the researchers draw any unwarranted conclusions about the generalizability of the results?
- Did the researchers discuss the study’s implications for clinical practice or future nursing research? Did they make specific recommendations?
- If yes, are the stated implications appropriate, given the study’s limitations and the magnitude of the effects as well as evidence from other studies? Are there important implications that the report neglected to include?
- Did the researchers mention or assess clinical significance? Did they make a distinction between statistical and clinical significance?
- If clinical significance was examined, was it assessed in terms of group-level information (e.g., effect sizes) or individual-level results? How was clinical significance operationalized?
References & Attribution
“ Green check mark ” by rawpixel licensed CC0 .
“ Magnifying glass ” by rawpixel licensed CC0
“ Orange flame ” by rawpixel licensed CC0 .
Polit, D. & Beck, C. (2021). Lippincott CoursePoint Enhanced for Polit’s Essentials of Nursing Research (10th ed.). Wolters Kluwer Health
Vaid, N. K. (2019) Statistical performance measures. Medium. https://neeraj-kumar-vaid.medium.com/statistical-performance-measures-12bad66694b7
Evidence-Based Practice & Research Methodologies Copyright © by Tracy Fawns is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

Quantitative strategies, Wall Street-caliber research, and insightful market analysis since 1998.
ZGC Overseas Science Park helps open a new chapter for all-round cooperation between China-Serbia with innovation exchanges and communication
Wuhan - May 30, 2024 —
Serbia was China's first free trade partner in Central and Eastern Europe and one of the first countries that responded to the BRI. Under the strategic leadership of the heads of state of both countries, China and Serbia have witnessed closer economic and trade ties and strengthening scientific and technological exchanges over the past few years.
Under the guidance of the Ministry of Science and Technology, the Beijing Municipal Science and Technology Commission, Administrative Commission of Zhongguancun Science Park and Zhongguancun Development Group, Zhongguancun Overseas Science Park (“ZGC Overseas Science Park”) organized and took domestic enterprises to the 66th International Fair of Technics and Technical Achievements from May 20 to 24 for promoting scientific and technological cooperation between China and Serbia.
On the morning of May 20, local time, a delegation led by Mr. Pan Jinfeng, Chairman of Zhongguancun Development Group, visited the Ministry of Science, Technological Development and Innovation of the Republic of Serbia and discussed with Minister Jelena Begović in Belgrade on strategic cooperation between Zhongguancun Development Group and BIO4 Campus in the fields of biomedicine and biotechnology. Pan said, ZGC Group looks forward to strengthening cooperation with BIO4 Campus, exchanging experience in park planning, construction, operation and management, leveraging respective talent and research resources and strengths to build a world-class big health industrial ecosystem spanning the Earth’s eastern and western hemispheres, and contributing to scientific and technological innovation cooperation, people's health and well-being, and friendship of China and Serbia. The delegation also visited the office of BGI Genomics in Belgrade and the Chinese Embassy in Serbia, having in-depth discussions with those involved on strengthening international exchanges and cooperation concerning the “dual circulation” and building a global innovation ecosystem.

On May 21, a Memorandum of Understanding was entered by and among the Beijing Municipal Science and Technology Commission, Administrative Commission of Zhongguancun Science Park, Zhongguancun Development Group, the Ministry of Science, Technological Development and Innovation of the Republic of Serbia and BIO4 Campus at the fair. According to the MOU, the four parties will further work with each other to create a sister park relationship, promote practical cooperation in biomedicine and biotechnology between BIO4 Campus and Z-Park at all levels; facilitate all-round cooperation between high-tech enterprises, academic institutions, and research centers from Serbia and Beijing, set up incubators, enable knowledge sharing and exchanges; share experience in science and technology and development, build innovation clusters of emerging technologies; carry out practical exchanges in technology promotion, technology transfer and high-end talent training, and support China-Serbia technological exchanges and cooperation.
There were 22 enterprises participating the fair as organized by ZGC Overseas Science Park. The latest technological achievements from China were displayed in a creative, novel, interactive and high-tech manner. This showcased that China created an innovation environment, fostered innovation-oriented enterprises and made breakthroughs in cutting-edge technologies for collaborative innovation and in-depth international capacity cooperation.
In the space technology area, China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation showcased the progress in Serbia aid cooperation on remote sensing satellites, and used Egypt Satellite 2 as an example to describe the ATI facilities and joint training service, and detailed China's space station, Chang’e-5 and other major national aerospace initiatives, demonstrating the strength of China’s aerospace industry.

In the AI area, Beijing RealAI Intelligent Technology Co., Ltd. showed the AI “Invisibility cloak", generative AI content detection platform, and the solutions to AI abuses and misuses and to endogenous and derivative risks in the AI security field. Beijing VAS Medical Technology Co., Ltd. presented the robotic system for high-precision, minimally invasive vascular interventions. Developed under the guidance of the company, the system was the first of its kind in China entered the clinical trial phases and obtained the NMPA registration certificate for “Vascular Intervention Auxiliary System (Robot)”. As the first one completed multi-center clinical trial in China, the system is at the forefront of the world.

In the biomedicine area, products of BGI Genomics from Huo-Yan laboratory model that provided a complete pathogen detection solution and its standard system to sequencer T20 that set a new global single-unit throughput record for gene sequencer, and DNA storage model were shown. These reflected China’s latest achievements in infectious disease prevention and control, virus detection and gene sequencing.
In the popular autonomous driving area, Beijing iDriverPlus Technology Co., Ltd. showcased its VIGGO autonomous scrubber and sweeper. As an autonomous driving solution provider integrating “software, hardware and cloud”, iDriverPlus has always been specialized in intelligent mobility, smart life, and specialized applications. VIGGO under the company is the brand that started mass production of autonomous sweeper in China. Since the launch of the first product, VIGGO series has served over 3,000 customers in over 100 domestic cities, cleaning hundreds of millions of square meters in total.

In keeping pace with the times, China and Serbia have been stepping up cooperation on science and technology for mutual benefits and win-win results. With advancement in modernization, both countries will need more cooperation in infrastructure construction, economy and trade than before. In frontier fields of emerging industries, such as digitalization and informatization, high-end manufacturing, and biomedicine, there is an urgent need for more outstanding Chinese enterprises to seize opportunities and open up possibilities.

The Chinese exhibitors who attended the fair as organized by ZGC Overseas Science Park showcased their products that represented the latest technological achievements of China in a creative, novel, interactive and high-tech manner, showing that China has created an innovation environment, fostered innovation-oriented enterprises and made breakthroughs in cutting-edge technologies for collaborative innovation and in-depth international capacity cooperation.
Contact Info: Name: Hu Wei Email: Send Email Organization: Wuhan Waimai Culture Communication Co., Ltd Website: http://www.waimaicb.com
Release ID: 89131406
Should you detect any errors, issues, or discrepancies with the content contained within this press release, or if you need assistance with a press release takedown, we kindly request that you inform us immediately by contacting [email protected] (it is important to note that this email is the authorized channel for such matters, sending multiple emails to multiple addresses does not necessarily help expedite your request). Our expert team will be available to promptly respond and take necessary steps within the next 8 hours to resolve any identified issues or guide you through the removal process. We value the trust placed in us by our readers and remain dedicated to providing accurate and reliable information.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Revised on June 22, 2023. Quantitative research is the process of collecting and analyzing numerical data. It can be used to find patterns and averages, make predictions, test causal relationships, and generalize results to wider populations. Quantitative research is the opposite of qualitative research, which involves collecting and analyzing ...
Quantitative . Research Methods. T. his chapter focuses on research designs commonly used when conducting . quantitative research studies. The general purpose of quantitative research is to investigate a particular topic or activity through the measurement of variables in quantifiable terms. Quantitative approaches to conducting educational ...
The results chapter (also referred to as the findings or analysis chapter) is one of the most important chapters of your dissertation or thesis because it shows the reader what you've found in terms of the quantitative data you've collected. It presents the data using a clear text narrative, supported by tables, graphs and charts.
Quantitative research is 'Explaining phenomena by collecting numeri-cal data that are analysed using mathematically based methods (in particular statistics).'. Let's go through this definition step by step. The first element is explain-ing phenomena. This is a key element of all research, be it quantitative or qualitative.
Mixed-methods research is a flexible approach, where the research design is determined by what we want to find out rather than by any predetermined epistemological position. In mixed-methods research, qualitative or quantitative components can predominate, or both can have equal status. 1.4. Units and variables.
PDF | Chapter excerpt from "Quantitative Research Methods (5th Ed)" by Johnathan Mun, Ph.D. ISBN:... | Find, read and cite all the research you need on ResearchGate
Quantitative research methods are concerned with the planning, design, and implementation of strategies to collect and analyze data. Descartes, the seventeenth-century philosopher, suggested that how the results are achieved is often more important than the results themselves, as the journey taken along the research path is a journey of discovery. . High-quality quantitative research is ...
Introduction. Quantitative research, in contrast to qualitative research, deals with data that are numerical or that can be converted into numbers. The basic methods used to investigate numerical data are called 'statistics'. Statistical techniques are concerned with the organisation, analysis, interpretation and presentation of numerical data.
Quantitative research is a research method that uses numerical data and statistical analysis to study phenomena. 1 Quantitative research plays an important role in scientific inquiry by providing a rigorous, objective, systematic process using numerical data to test relationships and examine cause-and-effect associations between variables.
Chapter 2 | Foundational Concepts for Quantitative Research 15 A variable is a characteristic that can vary from one case to another. Each case has a value for each variable, capturing the nature or extent of that characteristic for that case. In contrast to a variable, a constant is a characteristic that has the same value for all cases being studied, often due to restrictions on which cases ...
These parts can also be used as a checklist when working through the steps of your study. Specifically, part 1 focuses on planning a quantitative study (collecting data), part two explains the steps involved in doing a quantitative study, and part three discusses how to make sense of your results (organizing and analyzing data). Research Methods.
Social scientists are concerned with the study of people. Quantitative research is a way to learn about a particular group of people, known as a sample population. Using scientific inquiry, quantitative research relies on data that are observed or measured to examine questions about the sample population. Allen, M. (2017). The SAGE encyclopedia ...
This chapter begins the exploration of quantitative studies in detail. Chapters 6 through 13 address the design of studies, along with how to develop measurement procedures to collect data and how subsequently to analyze the data collected. The methods introduced relate directly to the comparison-based, objectives-based, and decision-facilitation approaches to evaluation described in Chap. 2.
Key Concepts in Quantitative Research. In this module, we are going to explore the nuances of quantitative research, including the main types of quantitative research, more exploration into variables (including confounding and extraneous variables), and causation. Content includes: Objectives: Discuss the flaws, proof, and rigor in research.
Chapter Two: Understanding the distinctions among research methods. Chapter Three: Ethical research, writing, and creative work. Chapter Four: Quantitative Methods. Chapter Four: Quantitative Methods (Part 1) Chapter Five: Qualitative Methods. Chapter Six: Critical / Rhetorical Methods. Chapter Seven: Presenting Your Results.
Quantitative research is the process of collecting and analyzing numerical data to describe, predict, or control variables of interest. This type of research helps in testing the causal relationships between variables, making predictions, and generalizing results to wider populations. The purpose of quantitative research is to test a predefined ...
quantitative research is all about. Below is a table that differentiates between qualitative and quantitative research. Arabian Journal of Business and Management Review (Kuwait Chapter)
INTRODUCTION. Scientific research is usually initiated by posing evidenced-based research questions which are then explicitly restated as hypotheses.1,2 The hypotheses provide directions to guide the study, solutions, explanations, and expected results.3,4 Both research questions and hypotheses are essentially formulated based on conventional theories and real-world processes, which allow the ...
Instruments. This section should include the instruments you plan on using to measure the variables in the research questions. (a) the source or developers of the instrument. (b) validity and reliability information. •. (c) information on how it was normed. •. (d) other salient information (e.g., number of. items in each scale, subscales ...
Y.C. Latunde, Research in Parental Involvement , DOI10.1057/978-1-137-59146-3_5 Chapter 5: Quantitative Research Methods INTRODUCTION All research starts with a phenomenon or issuethat a researcher wants to explainor understand. That phenomenon is addressed in the form of well-crafted research questions.
THE PROBLEM AND ITS BACKGROUND CHAPTER 1 -A hypothesis is a prediction of the possible outcomes of a study (Fraenkel & Wallen, 2009) -Hypotheses are statements in quantitative research in which the investigator makes a prediction about the outcome of a relationship among attributes or characteristics (Creswell, 2012). Hypothesis
When thinking of research in general, and how researchers can make inferences from their sample population and generalize it to the general population we are referring to inferential statistics. We are making inferences, or predictions, based on probabilities. Inferential statistics are used to test research hypotheses.
ZGC Overseas Science Park helps open a new chapter for all-round cooperation between China-Serbia with innovation exchanges and communication. Quantitative strategies, Wall Street-caliber research, and insightful market analysis since 1998. ... leveraging respective talent and research resources and strengths to build a world-class big health ...