- Research Paper Guides
- Research Paper Topics

Environmental Research Topics: 235 Ideas for Students
- Speech Topics
- Basics of Essay Writing
- Essay Topics
- Other Essays
- Main Academic Essays
- Basics of Research Paper Writing
- Miscellaneous
- Chicago/ Turabian
- Data & Statistics
- Methodology
- Admission Writing Tips
- Admission Advice
- Other Guides
- Student Life
- Studying Tips
- Understanding Plagiarism
- Academic Writing Tips
- Basics of Dissertation & Thesis Writing
- Essay Guides
- Formatting Guides
- Basics of Research Process
- Admission Guides
- Dissertation & Thesis Guides

Table of contents
Use our free Readability checker
Are you looking for environmental research paper topics? With ongoing debates about global warming, air pollution, and other issues, there is no shortage of exciting topics to craft a research paper around. Whether you’re studying ecology, geology, or marine biology, developing the perfect environmental research topic to get your science research assignment off the ground can be challenging. Stop worrying – we got you covered. Continue reading to learn about 235 different ideas on environmental research topics. In this article, we will discuss environmental topics and show you how to choose an interesting research topic for your subject. We will also provide a list of various environmental topics from our research paper services . In addition, we will present you with environmental science research topics, discuss other ideas about the environment for research papers, and offer our final thoughts on these topics for research papers.
What Are Environmental Topics?
Environmental topics provide an analysis of environmental issues and their effect on people, culture, nature, or a particular place, often interdisciplinary, drawing from sciences, politics, economics, sociology, and public policy. Topics about environmental science may include environmental justice, engineering and communication, regulation, economics, and health. Environment research topics may focus on environmental sustainability, impact assessment, management systems, and resources. In addition, these areas for research papers offer a few opportunities to explore our relationship with the environment and consider how human activities influence it through climate change, pollution, or other factors such as natural resource usage as well as biodiversity loss.
What Makes a Good Environmental Research Topic?
When choosing an environmental research topic, it is essential to consider what makes good environmental topics. Below is an expert list outlining what your topic should be like:
- It should be interesting and relevant to your study field.
- It's essential to consider the topic's potential implications on environment-related policies. Think about the possible positive or negative effects this topic could have when implemented in terms of protecting our environment.
- A good topic should be specific enough to provide a focus for your research paper and allow you to explore a particular issue in depth.
- The research topic should be feasible and manageable to ensure that you can find the necessary information and resources.
- Environmental sciences research topics should be current and relevant to ecological developments.
How to Choose Environmental Science Topics?
When choosing research topics for environmental science, it is essential to research the available information and determine its relevance. It all depends on whether the research topic is feasible and has the potential for exploration. Environmental issue topics should be well-defined and interesting to the researcher. The reason is that the researcher should be able to provide solutions or make suggestions on improvement strategies. You can follow the below steps when choosing environmental science topics for research:
Step 1: Identify topics that are relevant to your research context. Step 2: Develop a list of research areas by extracting critical concepts from the available literature.
Step 3: Select interesting and feasible topics by considering the methods available for analysis.
Step 4: Analyze these topics to identify the gaps in current research and formulate questions for further investigation. Step 5: Review the available literature to gain insights about the chosen topic and develop a research proposal.
Step 6: Consult experts in this field to get feedback and refine the proposed research.
Don’t have time for writing your environmental research paper? Count on StudyCrumb. Send us a ‘ write a research paper for me ’ message and get professional assistance in a timely manner.
List of Environment Research Paper Topics
Environmental topics for a research paper can be overwhelming to navigate due to the vast number of issues you can discuss in your article. To help narrow down your research paper search, below is a list of environmental research topics that include climate change, renewable energy, ecology, pollution, sustainability, endangered species, ecosystems, nature, and water management. You can choose one of them as a guide to writing an excellent essay
Environmental Research Topics on Climate Change
Climate change is one of the most pressing issues that humanity is currently facing due to increased temperature levels. Climate change is amongst the most debated environmental research topics among researchers, policymakers, and governments. Here are critical areas related to climate change that you can use for your environmental science research paper topics:
- Causes and effects of climate change.
- Climate change adaptation strategies.
- Climate change impact on rural communities.
- Role of renewable energy sources in mitigating climate change.
- Carbon dioxide emission policies.
- Global warming and its impact on ocean acidification.
- Social effects of climate change.
- Permafrost melting and its implications.
- Role of international organizations in climate change.
- Climate change and forest fire: examining the role of climate change on wildfire season, frequency, and burned area.
Environmental Science Research Topics on Renewable Energy
Renewable energy is essential due to its potential to reduce ecological damage from burning fossil fuels and provides valuable topics in environmental science. You can use renewable energy technologies as a cleaner alternative for generating electricity and heating. In addition, renewable energy is crucial for cooling homes and factories in the world. The following are environmental science topics for research paper on renewable energy:
- Renewable energy types, sources, and their impact on the environment.
- Economic benefits of renewable energy.
- Research on new technologies in renewable energy.
- Role of renewable energy in protecting businesses from legal actions.
- Hydropower and its role in renewable energy.
- Chemical batteries for renewable energy storage.
- Green microgrids in optimizing renewable energy usage.
- Ocean energy and its effects on the environment.
- Geothermal drilling and its consequences.
- Biomass resources and their use in renewable energy.
Environment Research Topics on Ecology
Ecology studies how living organisms interact with each other and their environment. Also, it is an important area of research for understanding how the environment affects the function of various species and ecosystems. It also gives a background for one of the best environment research paper topics. Below are topics for environmental research paper on ecology:
- Biodiversity conservation strategies.
- Impact of pollution on ecosystems.
- Ecological research on saving endangered species from extinction.
- Role of environment in migrations patterns of animals.
- Habitat fragmentation effects on the environment.
- Ecological implications of climate change.
- Ecology and pest control strategies.
- Ecological effects of deforestation.
- Ecology and conservation of marine life.
- Ecological consequences of urbanization.
Research Topics in Environmental Science About Pollution
Pollution is an issue at the forefront of scientific research. As one of the environmental science paper topics, it offers insights into how pollution destroys the environment and its negative impact on human and animal health. Stated below are hot environmental science research topics on pollution which you can use for your article:
- Air pollution: causes & effects.
- Water pollution and its consequences for people and other living organisms.
- Issue of urban & industrial pollution.
- Noise pollution and environment-related health risks.
- Marine plastic pollution in oceans.
- Radiological waste disposal policies.
- Nuclear energy, radiation & health impacts.
- Sustainable waste management solutions.
- Impact of pollution on biodiversity.
- Soil pollution and its effects on agriculture.
Environmental Topics for Research Papers on Sustainability
One of the many topics for environmental research papers is sustainability. Sustainability is an important topic to explore, as it involves finding a way for humans to reduce their ecological footprint and ensure that the environment can recover from our activities. Stated below are environmental topics for research paper on sustainability which you can explore:
- Strategies for sustainable development.
- Renewable energy sources and their effects.
- Environmental sustainability and its economic benefits.
- Sustainable energy sources and their effects.
- Implications of sustainable agriculture on the environment.
- Ecological impacts of sustainable forestry.
- Social implications of renewable energy use.
- Strategies for mitigating ecological impact from unsustainable development.
- Psychological effects of ecological awareness on sustainable practices.
- Influence of ecological sustainability on economic growth.
Environmental Topics to Write About Endangered Species
Endangered species are one of the environmental topics of great importance to research and find solutions for their conservation. Poaching, habitat destruction, and climate change negatively impact endangered species. Also, human activities have put other species at risk of extinction by competing for resources as well as introducing invasive species. Below is a list of cool environment topics to write about endangered species:
- Endangered species conservation.
- Causes & effects of habitat fragmentation.
- Wildlife conservation strategies.
- Climate change impacts on endangered species.
- Illegal wildlife trade and trafficking.
- Marine protected areas for conserving marine life.
- Ecological restoration and reintroduction programs.
- Endangered species in developing nations.
- Human rights & animal welfare laws .
- Captive breeding for conservation purposes.
Environmental Research Paper Topics on Ecosystems
Ecosystems are fascinating to explore in environmental paper topics because they contain a variety of living organisms and are a complex web of interactions between species, the environment, and humans. The subject provides environmental issues topics for research paper essential in exploring the dynamics of ecosystems and their importance. Below is a list of topics for environmental science research paper:
- Ecosystem services & their value.
- Climate change impacts on ecosystems.
- Hydrological cycle & effects on ecosystems.
- Ecological restoration & biodiversity conservation.
- Invasive species & their impact on native species.
- Biodiversity hotspots: areas of high endemism.
- Soil degradation & its impact on ecosystems.
- Sustainable forestry practices.
- Ecological restoration of wetlands.
Environmental Topics About Nature
Nature is a broad topic that includes ecological conservation, protection, and sustainability issues. Environmental research topics about nature allow us to explore areas that focus on preserving and conserving the environment. Research papers about nature can provide insight into utilizing nature as a resource, both from a practical and ecological aspect. Below is a list of environment topics that you can explore in your essays:
- Nature conservation & preservation strategies.
- Climate change effects on natural environments.
- Natural resource management strategies.
- Policies for natural resources management.
- Impact of human development on wildlands.
- Sustainable use of natural resources.
- Role of ethics in nature conservation.
- De-extinction: pros & cons of bringing back extinct species.
- Protected areas & conservation of rare species.
Environmental Issues Topics on Water Management
Water management is an issue that has a significant impact on the environment. Exploring a topic related to water management can provide experts, among others, with insights into environmental science issues and their implications. When it's time to write your project related to water management, you can explore the following topics for environmental issues:
- Water pollution & its control.
- Groundwater management strategies.
- Climate change impact on water resources.
- Integrated water resources management.
- Wetland conservation & restoration projects.
- Industrial effluents role in water pollution.
- Desalination technologies for freshwater production.
- Urbanization impact on groundwater resources.
- Inland & coastal water management strategies.
- Wastewater treatment & reuse technologies.
Environmental Science Topics in Different Areas
Environmental science studies ecological processes and their interactions with living organisms. Exploring environmental science related topics can provide valuable insights into environmental science issues, their ecological implications, and conservation efforts. In addition, these topics can also be explored in different areas, providing a comprehensive understanding of how different factors impact the environment. This section delves into various environmental science topics for projects related to law, justice, policy, economics, biology, chemistry, and health science.
Environmental Law Research Topics
Environmental law governs environmental processes and their interactions with living organisms. Delving into environmental law can uncover invaluable information on environment paper topics, ranging from legal matters and their consequences to preservation initiatives. Students can use the following environmental issue topics for research papers for their essays:
- Climate change liability & lawsuits.
- Strategies for conservation and protection under environmental law.
- Consequences of non-compliance with regulations on the environment.
- Impact of trade agreements on environment protection.
- Regulatory strategies for hazardous waste disposal.
- Strategies for enforcement and compliance with environment-related laws.
- International environment treaties and their implications.
- Effects of climate change legislation on the environment.
- Corporate environmental policies and regulations and their effects.
- Role of law in mitigating environment-related issues.
Environmental Justice Research Topics
Environmental justice seeks to ensure equitable treatment and meaningful involvement of all people in ecological protection, regardless of their race, sex, or economic status. Environment topics related to justice can provide valuable insights into ecological issues and their impacts. Listed below are justice-related Environmental topics to research:
- Implications of unequal access to resources.
- Disproportionate impacts of climate change on vulnerable populations.
- Consequences of marginalization of marginalized communities from environmental processes.
- Links between poverty and environment degradation.
- Effects of non-participation in environment-related decision-making.
- Policies to ensure access to clean air and water.
- Impact of social inequality on environment protection.
- Intersection between gender, race, and environment justice.
- Ecological consequences of corporate negligence of marginalized communities.
- Disproportionate implications of climate change on vulnerable populations.
Environmental Policy Research Paper Topics
Environmental policy is a set of laws, rules, and regulations created to protect the environment as well as its resources. Studying environment-related policies provides an area for students to explore a range of subjects related to the environment, ranging from local to global. Below are potential environmental sciences research topics for your reference.
- Environmental policy initiatives' implications on global climate change.
- Effectiveness of carbon taxes for air pollution control.
- Land use and development impact on the environment.
- Water quality in the united states, focusing on natural resource governance.
- Educational initiative's impact on public opinion and policy outcomes.
- Social aspects of policy making and implementation on the environment.
- Promoting sustainability from a global perspective.
- Potential for justice initiatives in promoting equitable and effective management.
- Rise of green economy its impact.
- Environment policies and their potential for success.
Environmental Economics Research Topics
Environmental economics seeks to understand environmental issues from an economic perspective. Examining environmental studies topics can offer insights into ecological conservation and sustainability while connecting protection efforts with economic interests and helping inform policies. The following are creative topics about environmental science related to economics:
- Economic impacts of regulating the environment.
- Strategies for environmentally sustainable economic growth.
- Consequences of non-compliance with environment-related regulations.
- Environment conservation and protection using economic incentives.
- Taxes and subsidies and their implications on the environment.
- Economic implications of climate change legislation.
- The private sector role in environment conservation and protection.
- Green finance role in mitigating ecological issues.
- Economics of pollution control and management.
- Conservation and protection of the environment in the face of economic interests.
>> Learn more: Economics Research Topics
Environmental Biology Research Topics
Environmental biology is a field of science that focuses on understanding the interactions between living organisms and their environment. It covers environmental biology topics such as biodiversity, conservation, pollution, management, health, and sustainability. The following are environment research paper topics related to biology:
- Biodiversity conservation in managing the environment.
- Role of biotechnology in reducing air pollution.
- Environment degradation and its consequences on wildlife.
- Role of microorganisms in maintaining soil fertility.
- Ecological consequences of over-exploitation of natural resources.
- Habitat fragmentation and its role in species conservation.
- Education's role in environment conservation.
- Environment degradation and its effects on food security.
- Invasive species and their impacts on ecosystem.
Keep in mind that we have a whole blog on biological topics if you need more ideas in this field.
Environmental Chemistry Research Topics
Environmental chemistry research is a complex interdisciplinary field aiming to understand the behavior of a chemical process within an environment. It involves researching the impact of pollutants in the air, soil, water, and other ecological media. Possible research topics about the environment related to this field include:
- Effect of agricultural chemicals on water systems.
- Air pollution control strategies and their effectiveness.
- Climate change impacts on aquatic ecosystems.
- Sources and implications of persistent organic pollutants.
- Air quality monitoring for urban areas.
- Water quality monitoring in coastal areas.
- Characterization and fate of toxic compounds in soil and groundwater.
- Impact of hazardous chemical waste on the environment.
- Monitoring and remediation of contaminated sites.
- The roles of environmental chemistry in climate change research.
Need more ideas? There is one more blog with chemistry research topics on our platform.
Environmental Health Science Research Topics
Environmental health is a diverse field focusing on the natural environment as well as its effects on human health. It is an interdisciplinary field that offers environment topics for research, such as environmental epidemiology, toxicology, and ecology, in addition to risk assessment. Provided below is a list of topics for an environmental science project that is suitable for your research paper:
- Air pollution effects on human health.
- Climate change effects on health.
- Water pollution and public health.
- Noise pollution effects on well-being.
- Mental health effects of environment-related toxins.
- Human health effects of natural disasters.
- Urbanization's effect on human health.
- Sustainable development and public health.
- Role of social media in promoting environmental health and awareness.
- Biodiversity preservation and its impact on human health.
Other Ideas & Topics About Environment for Research Papers
Ecological crisis is a key issue that has continuously affected planet earth. People are becoming more aware of environmental problems as well as their impact on health, well-being, and quality of life. As such, ecological fields for research are becoming ever more critical. This section will explore interesting environmental topics related to current ecological issues, controversial, interesting topics, easy research questions for projects, as well as unique research areas which students might study. These environmental issue project ideas below will help you develop interesting fields for research papers.
Current Issues in Environmental Science
Current ecological issues are a hot topic that has become increasingly important. They provide outstanding environmental issues to write about due to their impact on the environment and human health. The following are environmental issue topics for paper writing that are currently in discussion:
- Global warming and how to prevent its impact.
- Sustainable energy and its role in protecting the environment.
- Water conservation practices.
- Renewable energy role in global ecological protection.
- Carbon footprint and climate change.
- Ozone layer depletion and its effects on human health.
- Plastic pollution and its impact.
- Land degradation and soil erosion.
- Energy industry activities effects on ecological health.
- Air pollution and its impact on human health.
- Deforestation and its consequences.
- Effect of agricultural practices on ecological health.
- Overuse and exploitation of natural resources.
- Industrial waste impact on health.
- Green technology role in ecological protection.
Controversial Environmental Topics for Research Paper
Environmental controversies constitute a significant challenge facing society today. From climate change to air and water pollution, the effects of human activity on our natural environment are increasingly becoming a focus of public debate and research. Research papers on environmental controversial topics can help inform the public as well as policymakers about the potential impacts of human activities on the environment. The following are examples of environmental controversy topics for research paper:
- Climate change: is human activity a primary cause of global warming.
- Deforestation: are current logging practices sustainable in the long term.
- Air pollution: what are the health impacts of air pollution.
- Water pollution: how is water pollution impacting biodiversity and ecosystems.
- Geothermal energy: what potential impacts does geothermal energy extraction have on the environment.
- Renewable energy: are wind and solar energy carbon-neutral.
- Arctic drilling: is drilling for oil in the arctic ocean a viable option given current climate conditions.
- Nuclear power: what health risks are associated with nuclear power plants.
- Biodiversity loss: what steps can you take to protect biodiversity from human activities.
- Endangered species: how protecting endangered species can impact conservation efforts and how they live.
- GMO foods: are genetically modified organisms safe for human consumption? how does GMO food affect humans.
- Pesticides: how does pesticide use affect our health and the environment.
- Ocean acidification: how is ocean acidification impacting marine ecosystems.
- Waste management: what are the most effective ways to manage waste and reduce pollution.
- Resource exploitation: how does the exploitation of natural resources impact local communities.
Interesting Environmental Research Topics
In the context of environmental subjects, research topics explore the effects of human activities on the environment as well as the potential solutions to the identified problems. In addition to providing insight into ecological protection and conservation, research areas in this category cover social issues related to environmentalism and ecological justice. Below are interesting environmental science topics to consider when looking for a research topic in the future:
- Effects of environment-related toxins on human health.
- Climate change effects on coastal habitats.
- Agricultural activities impacts on the environment.
- Groundwater contamination and its effects on water quality.
- Pollution from factories and its impact on the environment.
- Waste management strategies and their impacts.
- Consequences of water contamination on local wildlife.
- Impacts of mining.
- Deforestation effects on ecosystems and species diversity.
- Industrial fishing practices effects.
- Sustainable forestry practices and their impact on ecosystems.
- Nuclear energy production and its consequences.
- Reducing emissions from vehicles and their effects on air quality.
- Landfills implications on the environment.
- Implications of plastic pollution.
Easy Environmental Research Questions for Projects
When it comes to environmental science topics for project work, there are plenty of easy options. Research projects in this category can explore ecological issues as well as their consequences or potential solutions to these problems. The following is a list of the top fifteen most accessible environment project topics for your research project.
- Air pollution levels impact on urban areas.
- Agricultural practices effects on the environment.
- Developing strategies for sustainable development.
- Causes of water contamination.
- Factors contributing to global warming.
- Natural disasters effects on the environment.
- Land use changes effects on the environment.
- Energy consumption impacts on the environment.
- Climate change effects on the environment.
- Industrialization and its consequences.
- Impact of plastic pollution.
- Health risks associated with air pollution.
- Deforestation impacts on the environment.
- Soil erosion and its effects on the environment.
- Causes and consequences of species extinction.
Unique Environmental Research Topics for Students
As environmental issues become increasingly complex, research fields for students become more varied. Unique environmental research topics for college students can range from local ecological concerns to global ones. The following are fifteen unique environmental science research topics for high school students and college students:
- Climate change impact on water quality.
- Acid rain and its effects.
- Urbanization's effect on biodiversity.
- Effects of offshore drilling.
- Ocean acidification and its impact.
- Impact of privatization on natural resources.
- Effectiveness of renewable energy sources.
- Relationship between energy consumption and the environment.
- Potential impacts regarding genetic engineering on biodiversity.
- Toxic waste disposal and its impacts.
- Environment-related policies impact on water quality.
- Deforestation and its effects on soil quality.
- Causes and consequences of ozone layer depletion.
- Relationship between pollution and public health issues.
Final Thoughts on Environmental Topics for Research Papers
This article has provided 235 environmental science research topics for research papers as well as project work that high school and college students can use. Topics range from local issues, such as assessing air pollution levels in an urban area, to global concerns, like examining the ecological effects of plastic pollution. Whether its health risks are associated with air pollution in an environment or the impacts of industrialization, research can help shape your understanding of how to protect as well as preserve our planet. It is up to the students to identify good environmental research topics that are interesting and relevant to them and to delve deeper to understand the earth better.
Get in touch with our academic writing service and receive expert help. Let us know your topic, pay for research paper and get an excellent result in no time.

Joe Eckel is an expert on Dissertations writing. He makes sure that each student gets precious insights on composing A-grade academic writing.
You may also like


Research Topics & Ideas: Environment
100+ Environmental Science Research Topics & Ideas

Finding and choosing a strong research topic is the critical first step when it comes to crafting a high-quality dissertation, thesis or research project. Here, we’ll explore a variety research ideas and topic thought-starters related to various environmental science disciplines, including ecology, oceanography, hydrology, geology, soil science, environmental chemistry, environmental economics, and environmental ethics.
NB – This is just the start…
The topic ideation and evaluation process has multiple steps . In this post, we’ll kickstart the process by sharing some research topic ideas within the environmental sciences. This is the starting point though. To develop a well-defined research topic, you’ll need to identify a clear and convincing research gap , along with a well-justified plan of action to fill that gap.
If you’re new to the oftentimes perplexing world of research, or if this is your first time undertaking a formal academic research project, be sure to check out our free dissertation mini-course. Also be sure to also sign up for our free webinar that explores how to develop a high-quality research topic from scratch.
Overview: Environmental Topics
- Ecology /ecological science
- Atmospheric science
- Oceanography
- Soil science
- Environmental chemistry
- Environmental economics
- Environmental ethics
- Examples of dissertations and theses
Topics & Ideas: Ecological Science
- The impact of land-use change on species diversity and ecosystem functioning in agricultural landscapes
- The role of disturbances such as fire and drought in shaping arid ecosystems
- The impact of climate change on the distribution of migratory marine species
- Investigating the role of mutualistic plant-insect relationships in maintaining ecosystem stability
- The effects of invasive plant species on ecosystem structure and function
- The impact of habitat fragmentation caused by road construction on species diversity and population dynamics in the tropics
- The role of ecosystem services in urban areas and their economic value to a developing nation
- The effectiveness of different grassland restoration techniques in degraded ecosystems
- The impact of land-use change through agriculture and urbanisation on soil microbial communities in a temperate environment
- The role of microbial diversity in ecosystem health and nutrient cycling in an African savannah
Topics & Ideas: Atmospheric Science
- The impact of climate change on atmospheric circulation patterns above tropical rainforests
- The role of atmospheric aerosols in cloud formation and precipitation above cities with high pollution levels
- The impact of agricultural land-use change on global atmospheric composition
- Investigating the role of atmospheric convection in severe weather events in the tropics
- The impact of urbanisation on regional and global atmospheric ozone levels
- The impact of sea surface temperature on atmospheric circulation and tropical cyclones
- The impact of solar flares on the Earth’s atmospheric composition
- The impact of climate change on atmospheric turbulence and air transportation safety
- The impact of stratospheric ozone depletion on atmospheric circulation and climate change
- The role of atmospheric rivers in global water supply and sea-ice formation

Topics & Ideas: Oceanography
- The impact of ocean acidification on kelp forests and biogeochemical cycles
- The role of ocean currents in distributing heat and regulating desert rain
- The impact of carbon monoxide pollution on ocean chemistry and biogeochemical cycles
- Investigating the role of ocean mixing in regulating coastal climates
- The impact of sea level rise on the resource availability of low-income coastal communities
- The impact of ocean warming on the distribution and migration patterns of marine mammals
- The impact of ocean deoxygenation on biogeochemical cycles in the arctic
- The role of ocean-atmosphere interactions in regulating rainfall in arid regions
- The impact of ocean eddies on global ocean circulation and plankton distribution
- The role of ocean-ice interactions in regulating the Earth’s climate and sea level

Tops & Ideas: Hydrology
- The impact of agricultural land-use change on water resources and hydrologic cycles in temperate regions
- The impact of agricultural groundwater availability on irrigation practices in the global south
- The impact of rising sea-surface temperatures on global precipitation patterns and water availability
- Investigating the role of wetlands in regulating water resources for riparian forests
- The impact of tropical ranches on river and stream ecosystems and water quality
- The impact of urbanisation on regional and local hydrologic cycles and water resources for agriculture
- The role of snow cover and mountain hydrology in regulating regional agricultural water resources
- The impact of drought on food security in arid and semi-arid regions
- The role of groundwater recharge in sustaining water resources in arid and semi-arid environments
- The impact of sea level rise on coastal hydrology and the quality of water resources

Topics & Ideas: Geology
- The impact of tectonic activity on the East African rift valley
- The role of mineral deposits in shaping ancient human societies
- The impact of sea-level rise on coastal geomorphology and shoreline evolution
- Investigating the role of erosion in shaping the landscape and impacting desertification
- The impact of mining on soil stability and landslide potential
- The impact of volcanic activity on incoming solar radiation and climate
- The role of geothermal energy in decarbonising the energy mix of megacities
- The impact of Earth’s magnetic field on geological processes and solar wind
- The impact of plate tectonics on the evolution of mammals
- The role of the distribution of mineral resources in shaping human societies and economies, with emphasis on sustainability
Topics & Ideas: Soil Science
- The impact of dam building on soil quality and fertility
- The role of soil organic matter in regulating nutrient cycles in agricultural land
- The impact of climate change on soil erosion and soil organic carbon storage in peatlands
- Investigating the role of above-below-ground interactions in nutrient cycling and soil health
- The impact of deforestation on soil degradation and soil fertility
- The role of soil texture and structure in regulating water and nutrient availability in boreal forests
- The impact of sustainable land management practices on soil health and soil organic matter
- The impact of wetland modification on soil structure and function
- The role of soil-atmosphere exchange and carbon sequestration in regulating regional and global climate
- The impact of salinization on soil health and crop productivity in coastal communities
Topics & Ideas: Environmental Chemistry
- The impact of cobalt mining on water quality and the fate of contaminants in the environment
- The role of atmospheric chemistry in shaping air quality and climate change
- The impact of soil chemistry on nutrient availability and plant growth in wheat monoculture
- Investigating the fate and transport of heavy metal contaminants in the environment
- The impact of climate change on biochemical cycling in tropical rainforests
- The impact of various types of land-use change on biochemical cycling
- The role of soil microbes in mediating contaminant degradation in the environment
- The impact of chemical and oil spills on freshwater and soil chemistry
- The role of atmospheric nitrogen deposition in shaping water and soil chemistry
- The impact of over-irrigation on the cycling and fate of persistent organic pollutants in the environment
Topics & Ideas: Environmental Economics
- The impact of climate change on the economies of developing nations
- The role of market-based mechanisms in promoting sustainable use of forest resources
- The impact of environmental regulations on economic growth and competitiveness
- Investigating the economic benefits and costs of ecosystem services for African countries
- The impact of renewable energy policies on regional and global energy markets
- The role of water markets in promoting sustainable water use in southern Africa
- The impact of land-use change in rural areas on regional and global economies
- The impact of environmental disasters on local and national economies
- The role of green technologies and innovation in shaping the zero-carbon transition and the knock-on effects for local economies
- The impact of environmental and natural resource policies on income distribution and poverty of rural communities
Topics & Ideas: Environmental Ethics
- The ethical foundations of environmentalism and the environmental movement regarding renewable energy
- The role of values and ethics in shaping environmental policy and decision-making in the mining industry
- The impact of cultural and religious beliefs on environmental attitudes and behaviours in first world countries
- Investigating the ethics of biodiversity conservation and the protection of endangered species in palm oil plantations
- The ethical implications of sea-level rise for future generations and vulnerable coastal populations
- The role of ethical considerations in shaping sustainable use of natural forest resources
- The impact of environmental justice on marginalized communities and environmental policies in Asia
- The ethical implications of environmental risks and decision-making under uncertainty
- The role of ethics in shaping the transition to a low-carbon, sustainable future for the construction industry
- The impact of environmental values on consumer behaviour and the marketplace: a case study of the ‘bring your own shopping bag’ policy
Examples: Real Dissertation & Thesis Topics
While the ideas we’ve presented above are a decent starting point for finding a research topic, they are fairly generic and non-specific. So, it helps to look at actual dissertations and theses to see how this all comes together.
Below, we’ve included a selection of research projects from various environmental science-related degree programs to help refine your thinking. These are actual dissertations and theses, written as part of Master’s and PhD-level programs, so they can provide some useful insight as to what a research topic looks like in practice.
- The physiology of microorganisms in enhanced biological phosphorous removal (Saunders, 2014)
- The influence of the coastal front on heavy rainfall events along the east coast (Henson, 2019)
- Forage production and diversification for climate-smart tropical and temperate silvopastures (Dibala, 2019)
- Advancing spectral induced polarization for near surface geophysical characterization (Wang, 2021)
- Assessment of Chromophoric Dissolved Organic Matter and Thamnocephalus platyurus as Tools to Monitor Cyanobacterial Bloom Development and Toxicity (Hipsher, 2019)
- Evaluating the Removal of Microcystin Variants with Powdered Activated Carbon (Juang, 2020)
- The effect of hydrological restoration on nutrient concentrations, macroinvertebrate communities, and amphibian populations in Lake Erie coastal wetlands (Berg, 2019)
- Utilizing hydrologic soil grouping to estimate corn nitrogen rate recommendations (Bean, 2019)
- Fungal Function in House Dust and Dust from the International Space Station (Bope, 2021)
- Assessing Vulnerability and the Potential for Ecosystem-based Adaptation (EbA) in Sudan’s Blue Nile Basin (Mohamed, 2022)
- A Microbial Water Quality Analysis of the Recreational Zones in the Los Angeles River of Elysian Valley, CA (Nguyen, 2019)
- Dry Season Water Quality Study on Three Recreational Sites in the San Gabriel Mountains (Vallejo, 2019)
- Wastewater Treatment Plan for Unix Packaging Adjustment of the Potential Hydrogen (PH) Evaluation of Enzymatic Activity After the Addition of Cycle Disgestase Enzyme (Miessi, 2020)
- Laying the Genetic Foundation for the Conservation of Longhorn Fairy Shrimp (Kyle, 2021).
Looking at these titles, you can probably pick up that the research topics here are quite specific and narrowly-focused , compared to the generic ones presented earlier. To create a top-notch research topic, you will need to be precise and target a specific context with specific variables of interest . In other words, you’ll need to identify a clear, well-justified research gap.
Need more help?
If you’re still feeling a bit unsure about how to find a research topic for your environmental science dissertation or research project, be sure to check out our private coaching services below, as well as our Research Topic Kickstarter .
Need a helping hand?
11 Comments
research topics on climate change and environment
I wish to learn things in a more advanced but simple way and with the hopes that I am in the right place.
Thank so much for the research topics. It really helped
the guides were really helpful
Research topics on environmental geology
Thanks for the research topics….I need a research topic on Geography
hi I need research questions ideas
Implications of climate variability on wildlife conservation on the west coast of Cameroon
I want the research on environmental planning and management
I want a topic on environmental sustainability
It good coaching
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
Are you seeking one-on-one college counseling and/or essay support? Limited spots are now available. Click here to learn more.
50 Best Environmental Science Research Topics
May 31, 2023
Environmental science is a varied discipline that encompasses a variety of subjects, including ecology, atmospheric science, and geology among others. Professionals within this field can pursue many occupations from lab technicians and agricultural engineers to park rangers and environmental lawyers. However, what unites these careers is their focus on how the natural world and the human world interact and impact the surrounding environment. There is also one other significant commonality among environmental science careers: virtually all of them either engage in or rely on research on environmental science topics to ensure their work is accurate and up to date.
In this post, we’ll outline some of the best environmental science research topics to help you explore disciplines within environmental science and kickstart your own research. If you are considering majoring in environmental science or perhaps just need help brainstorming for a research paper, this post will give you a broad sense of timely environmental science research topics.
What makes a research topic good?
Before we dive into specific environmental science research topics, let’s first cover the basics: what qualities make for a viable research topic. Research is the process of collecting information to make discoveries and reach new conclusions. We often think of research as something that occurs in academic or scientific settings. However, everyone engages in informal research in everyday life, from reading product reviews to investigating statistics for admitted students at prospective colleges . While we all conduct research in our day-to-day lives, formal academic research is necessary to advance discoveries and scholarly discourses. Therefore, in this setting, good research hinges on a topic in which there are unanswered questions or ongoing debates. In other words, meaningful research focuses on topics where you can say something new.
However, identifying an interesting research topic is only the first step in the research process. Research topics tend to be broad in scope. Strong research is dependent on developing a specific research question, meaning the query your project will seek to answer. While there are no comprehensive guidelines for research questions, most scholars agree that research questions should be:
1) Specific
Research questions need to clearly identify and define the focus of your research. Without sufficient detail, your research will likely be too broad or imprecise in focus to yield meaningful insights. For example, you might initially be interested in addressing this question: How should governments address the effects of climate change? While that is a worthwhile question to investigate, it’s not clear enough to facilitate meaningful research. What level of government is this question referring to? And what specific effects of global warming will this research focus on? You would need to revise this question to provide a clearer focus for your research. A revised version of this question might look like this: How can state government officials in Florida best mitigate the effects of sea-level rise?
2) Narrow
Our interest in a given topic often starts quite broad. However, it is difficult to produce meaningful, thorough research on a broad topic. For that reason, it is important that research questions be narrow in scope, focusing on a specific issue or subtopic. For example, one of the more timely environmental science topics is renewable energy. A student who is just learning about this topic might wish to write a research paper on the following question: Which form of renewable energy is best? However, that would be a difficult question to answer in one paper given the various ways in which an energy source could be “best.” Instead, this student might narrow their focus, assessing renewable energy sources through a more specific lens: Which form of renewable energy is best for job creation?
3) Complex
As we previously discussed, good research leads to new discoveries. These lines of inquiry typically require a complicated and open-ended research question. A question that can be answered with just a “yes” or “no” (or a quick Google search) is likely indicative of a topic in which additional research is unnecessary (i.e. there is no ongoing debate) or a topic that is not well defined. For example, the following question would likely be too simple for academic research: What is environmental justice? You can look up a definition of environmental justice online. You would need to ask a more complex question to sustain a meaningful research project. Instead, you might conduct research on the following query: Which environmental issue(s) disproportionately impact impoverished communities in the Pacific Northwest? This question is narrower and more specific, while also requiring more complex thought and analysis to answer.
4) Debatable
Again, strong research provides new answers and information, which means that they must be situated within topics or discourses where there is ongoing debate. If a research question can only lead to one natural conclusion, that may indicate that it has already been sufficiently addressed in prior research or that the question is leading. For example, Are invasive species bad? is not a very debatable question (the answer is in the term “invasive species”!). A paper that focused on this question would essentially define and provide examples of invasive species (i.e. information that is already well documented). Instead, a researcher might investigate the effects of a specific invasive species. For example: How have Burmese pythons impacted ecosystems in the Everglades, and what mitigation strategies are most effective to reduce Burmese python populations?
Therefore, research topics, including environmental science topics, are those about which there are ample questions yet to be definitively answered. Taking time to develop a thoughtful research question will provide the necessary focus and structure to facilitate meaningful research.
10 Great Environmental Science Research Topics (With Explanations!)
Now that we have a basic understanding of what qualities can make or break a research topic, we can return to our focus on environmental science topics. Although “great” research topics are somewhat subjective, we believe the following topics provide excellent foundations for research due to ongoing debates in these areas, as well as the urgency of the challenges they seek to address.
1) Climate Change Adaptation and Mitigation
Although climate change is now a well-known concept , there is still much to be learned about how humans can best mitigate and adapt to its effects. Mitigation involves reducing the severity of climate change. However, there are a variety of ways mitigation can occur, from switching to electric vehicles to enforcing carbon taxes on corporations that produce the highest carbon emission levels. Many of these environmental science topics intersect with issues of public policy and economics, making them very nuanced and versatile.
In comparison, climate change adaptation considers how humans can adjust to life in an evolving climate where issues such as food insecurity, floods, droughts, and other severe weather events are more frequent. Research on climate change adaptation is particularly fascinating due to the various levels at which it occurs, from federal down to local governments, to help communities anticipate and adjust to the effects of climate change.
Both climate change mitigation and adaptation represent excellent environmental science research topics as there is still much to be learned to address this issue and its varied effects.
2) Renewable Energy
Renewable energy is another fairly mainstream topic in which there is much to learn and research. Although scientists have identified many forms of sustainable energy, such as wind, solar, and hydroelectric power, questions remain about how to best implement these energy sources. How can politicians, world leaders, and communities advance renewable energy through public policy? What impact will renewable energy have on local and national economies? And how can we minimize the environmental impact of renewable energy technologies? While we have identified alternatives to fossil fuels, questions persist about the best way to utilize these technologies, making renewable energy one of the best environmental science topics to research.
3) Conservation
Conservation is a broad topic within environmental science, focusing on issues such as preserving environments and protecting endangered species. However, conservation efforts are more challenging than ever in the face of a growing world population and climate change. In fact, some scientists theorize that we are currently in the middle of a sixth mass extinction event. While these issues might seem dire, we need scientists to conduct research on conservation efforts for specific species, as well as entire ecosystems, to help combat these challenges and preserve the planet’s biodiversity.
4) Deforestation
The Save the Rainforest movement of the 1980s and 90s introduced many people to the issue of deforestation. Today, the problems associated with deforestation, such as reduced biodiversity and soil erosion, are fairly common knowledge. However, these challenges persist due, in part, to construction and agricultural development projects. While we know the effects of deforestation, it is more difficult to identify and implement feasible solutions. This is particularly true in developing countries where deforestation is often more prevalent due to political, environmental, and economic factors. Environmental science research can help reduce deforestation by identifying strategies to help countries sustainably manage their natural resources.
Environmental Science Topics (Continued)
5) urban ecology.
When we think of “the environment,” our brains often conjure up images of majestic mountain ranges and lush green forests. However, less “natural” environments also warrant study: this is where urban ecology comes in. Urban ecology is the study of how organisms interact with one another and their environment in urban settings. Through urban ecology, researchers can address topics such as how greenspaces in cities can reduce air pollution, or how local governments can adopt more effective waste management practices. As one of the newer environmental science topics, urban ecology represents an exciting research area that can help humans live more sustainably.
6) Environmental Justice
While environmental issues such as climate change impact people on a global scale, not all communities are affected equally. For example, wealthy nations tend to contribute more to greenhouse-gas emissions. However, less developed nations are disproportionately bearing the brunt of climate change . Studies within the field of environmental justice seek to understand how issues such as race, national origin, and income impact the degree to which people experience hardships from environmental issues. Researchers in this field not only document these inequities, but also identify ways in which environmental justice can be achieved. As a result, their work helps communities have access to clean, safe environments in which they can thrive.
7) Water Management
Water is, of course, necessary for life, which is why water management is so important within environmental science research topics. Water management research ensures that water resources are appropriately identified and maintained to meet demand. However, climate change has heightened the need for water management research, due to the occurrence of more severe droughts and wildfires. As a result, water management research is necessary to ensure water is clean and accessible.
8) Pollution and Bioremediation
Another impact of the increase in human population and development is heightened air, water, and soil pollution. Environmental scientists study pollutants to understand how they work and where they originate. Through their research, they can identify solutions to help address pollution, such as bioremediation, which is the use of microorganisms to consume and break down pollutants. Collectively, research on pollution and bioremediation helps us restore environments so they are sufficient for human, animal, and plant life.
9) Disease Ecology
While environmental science topics impact the health of humans, we don’t always think of this discipline as intersecting with medicine. But, believe it or not, they can sometimes overlap! Disease ecology examines how ecological processes and interactions impact disease evolution. For example, malaria is a disease that is highly dependent on ecological variables, such as temperature and precipitation. Both of these factors can help or hinder the breeding of mosquitoes and, therefore, the transmission of malaria. The risk of infectious diseases is likely to increase due to climate change , making disease ecology an important research topic.
10) Ecosystems Ecology
If nothing else, the aforementioned topics and their related debates showcase just how interconnected the world is. None of us live in a vacuum: our environment affects us just as we affect it. That makes ecosystems ecology, which examines how ecosystems operate and interact, an evergreen research topic within environmental science.
40 More Environmental Science Research Topics
Still haven’t stumbled upon the right environmental science research topic? The following ideas may help spark some inspiration:
- The effects of agricultural land use on biodiversity and ecosystems.
- The impact of invasive plant species on ecosystems.
- How wildfires and droughts shape ecosystems.
- The role of fire ecology in addressing wildfire threats.
- The impact of coral bleaching on biodiversity.
- Ways to minimize the environmental impact of clean energies.
- The effects of climate change on ocean currents and migration patterns of marine species.
Environmental Justice and Public Policy
- Opportunities to equalize the benefits of greenspaces for impoverished and marginalized communities.
- The impact of natural disasters on human migration patterns.
- The role of national parks and nature reserves in human health.
- How to address inequalities in the impact of air pollution.
- How to prevent and address the looming climate refugee crisis.
- Environmentally and economically sustainable alternatives to deforestation in less developed countries.
- Effects of environmental policies and regulations on impoverished communities.
- The role of pollutants in endocrine disruption.
- The effects of climate change on the emergence of infectious diseases.
AP Environmental Science Research Topics (Continued)
Soil science.
- Effects of climate change on soil erosion.
- The role of land management in maintaining soil health.
- Agricultural effects of salinization in coastal areas.
- The effects of climate change on agriculture.
Urban Ecology
- How road construction impacts biodiversity and ecosystems.
- The effects of urbanization and city planning on water cycles.
- Impacts of noise pollution on human health.
- The role of city planning in reducing light pollution.
Pollution and Bioremediation
- The role of bioremediation in removing “forever” chemicals from the environment.
- Impacts of air pollution on maternal health.
- How to improve plastic recycling processes.
- Individual measures to reduce consumption and creation of microplastics.
- Environmental impacts of and alternatives to fracking.
Environmental Law and Ethics
- Ethical implications of human intervention in the preservation of endangered species.
- The efficacy and impact of single-use plastic laws.
- Effects of religious and cultural values in environmental beliefs.
- The ethics of climate change policy for future generations.
- Ethical implications of international environmental regulations for less developed countries.
- The impact and efficacy of corporate carbon taxes.
- Ethical and environmental implications of fast fashion.
- The ethics and efficacy of green consumerism.
- Impacts of the hospitality and travel industries on pollution and emissions.
- The ethical implications of greenwashing in marketing.
- Effects of “Right to Repair” laws on pollution.
Final Thoughts: Environmental Science Research Topics
Environmental science is a diverse and very important area of study that impacts all aspects of life on Earth. If you’ve found a topic you’d like to pursue, it’s time to hit the books (or online databases)! Begin reading broadly on your chosen topic so you can define a specific research question. If you’re unsure where to begin, contact a research librarian who can connect you with pertinent resources. As you familiarize yourself with the discourse surrounding your topic, consider what questions spring to mind. Those questions may represent gaps around which you can craft a research question.
Interested in conducting academic research? Check out the following resources for information on research opportunities and programs:
- Research Opportunities for High School Students
- Colleges with the Best Undergraduate Research Programs
- College Success
- High School Success
Emily Smith
Emily earned a BA in English and Communication Studies from UNC Chapel Hill and an MA in English from Wake Forest University. While at UNC and Wake Forest, she served as a tutor and graduate assistant in each school’s writing center, where she worked with undergraduate and graduate students from all academic backgrounds. She also worked as an editorial intern for the Wake Forest University Press as well as a visiting lecturer in the Department of English at WFU, and currently works as a writing center director in western North Carolina.
- 2-Year Colleges
- Application Strategies
- Best Colleges by Major
- Best Colleges by State
- Big Picture
- Career & Personality Assessment
- College Essay
- College Search/Knowledge
- Costs & Financial Aid
- Data Visualizations
- Dental School Admissions
- Extracurricular Activities
- Graduate School Admissions
- High Schools
- Homeschool Resources
- Law School Admissions
- Medical School Admissions
- Navigating the Admissions Process
- Online Learning
- Outdoor Adventure
- Private High School Spotlight
- Research Programs
- Summer Program Spotlight
- Summer Programs
- Teacher Tools
- Test Prep Provider Spotlight
“Innovative and invaluable…use this book as your college lifeline.”
— Lynn O'Shaughnessy
Nationally Recognized College Expert
College Planning in Your Inbox
Join our information-packed monthly newsletter.
Environmental Research Paper Topics

100 Environmental Research Paper Topics
Embarking on a research journey in environmental studies is an exciting endeavor. It offers an opportunity to delve into diverse environmental issues, examine various practices, and contribute to the development of more sustainable and eco-friendly systems. To help you get started, we have compiled a comprehensive list of environmental research paper topics. These topics are divided into ten categories, each featuring ten unique topics.
Academic Writing, Editing, Proofreading, And Problem Solving Services
Get 10% off with 24start discount code.
- Climate Change
- The impact of climate change on biodiversity.
- Climate change and its effects on human health.
- The role of renewable energy in mitigating climate change.
- Climate change and its impact on agriculture.
- The role of international cooperation in addressing climate change.
- Climate change and its effects on water resources.
- The impact of climate change on the world’s oceans.
- Climate change and its effects on migration patterns.
- The role of carbon capture technology in mitigating climate change.
- Climate change and its impact on natural disasters.
- The impact of plastic pollution on marine life.
- Air pollution and its effects on human health.
- The role of government regulations in controlling industrial pollution.
- The impact of agricultural practices on soil pollution.
- The effects of noise pollution on wildlife.
- The role of technology in reducing air pollution.
- The impact of pollution on urban environments.
- The effects of light pollution on nocturnal animals.
- The role of recycling in reducing waste pollution.
- The impact of pollution on freshwater ecosystems.
Conservation
- The role of protected areas in biodiversity conservation.
- The impact of deforestation on wildlife conservation.
- The role of community involvement in conservation efforts.
- The impact of climate change on conservation strategies.
- The role of ecotourism in wildlife conservation.
- The impact of invasive species on conservation efforts.
- The role of legislation in protecting endangered species.
- The impact of poaching on wildlife conservation.
- The role of scientific research in conservation planning.
- The impact of urbanization on habitat conservation.
- Sustainable Development
- The role of renewable energy in sustainable development.
- The impact of sustainable agriculture on food security.
- The role of green building in sustainable development.
- The impact of sustainable transport on urban development.
- The role of education in promoting sustainable development.
- The impact of sustainable development on economic growth.
- The role of government policies in promoting sustainable development.
- The impact of sustainable development on poverty reduction.
- The role of corporate social responsibility in sustainable development.
- The impact of sustainable development on quality of life.
- Environmental Policy
- The role of international treaties in environmental protection.
- The impact of environmental policies on business practices.
- The role of environmental impact assessments in policy making.
- The impact of environmental policies on urban planning.
- The role of public participation in environmental policy making.
- The impact of environmental policies on energy production.
- The role of environmental justice in policy making.
- The impact of environmental policies on waste management.
- The role of science in environmental policy making.
- The impact of environmental policies on water resources management.
Environmental Education
- The role of environmental education in promoting sustainable behaviors.
- The impact of environmental education on students’ attitudes towards the environment.
- The role of outdoor education in promoting environmental awareness.
- The impact of environmental education on community engagement.
- The role of environmental education in curriculum development.
- The impact of environmental education on conservation efforts.
- The role of environmental education in promoting recycling behaviors.
- The impact of environmental education on students’ understanding of climate change.
- The role of environmental education in promoting water conservation.
- The impact of environmental education on students’ attitudes towards wildlife.
Environmental Health
- The impact of air pollution on respiratory health.
- The role of clean water in promoting environmental health.
- The impact of chemical pollutants on human health.
- The role of environmental health in disease prevention.
- The impact of climate change on environmental health.
- The role of environmental health in urban planning.
- The impact of noise pollution on human health.
- The role of environmental health in disaster management.
- The impact of environmental health on community wellbeing.
- The role of environmental health in public health policy.
- Environmental Justice
- The impact of environmental justice on community development.
- The impact of environmental justice on health disparities.
- The role of environmental justice in urban planning.
- The impact of environmental justice on indigenous rights.
- The role of environmental justice in climate change mitigation.
- The impact of environmental justice on waste management.
- The role of environmental justice in conservation efforts.
- The impact of environmental justice on access to clean water.
- The role of environmental justice in promoting sustainable development.
Environmental Technology
- The role of renewable energy technology in reducing carbon emissions.
- The impact of green building technology on energy efficiency.
- The role of technology in promoting sustainable agriculture.
- The impact of technology on waste management.
- The role of technology in promoting water conservation.
- The impact of technology on environmental monitoring.
- The role of technology in promoting sustainable transport.
- The impact of technology on environmental education.
- The role of technology in promoting biodiversity conservation.
- The impact of technology on environmental health.
- Environmental Ethics
- The role of environmental ethics in conservation efforts.
- The impact of environmental ethics on business practices.
- The role of environmental ethics in policy making.
- The impact of environmental ethics on sustainable development.
- The role of environmental ethics in environmental education.
- The impact of environmental ethics on animal rights.
- The role of environmental ethics in climate change mitigation.
- The impact of environmental ethics on resource management.
- The role of environmental ethics in promoting environmental justice.
- The impact of environmental ethics on community development.
This comprehensive list of environmental research paper topics provides a starting point for your research journey. Whether your interest lies in climate change, pollution, conservation, sustainable development, environmental policy, environmental education, environmental health, environmental justice, environmental technology, or environmental ethics, there is a topic for you. Remember, the key to a successful research paper is choosing a topic that you are passionate about and willing to explore in depth.
Browse 1200 more Environmental Research Paper Topics in:
- Global Warming
- Air Pollution
- Noise Pollution
- Water Pollution
- Environmental Law
- Environmental Economics
- Environmental Issues
Environmental Studies Research Guide

Environmental studies is an interdisciplinary field that explores the relationship between humans and the environment. It integrates knowledge from natural sciences, social sciences, and humanities to understand environmental issues and develop sustainable solutions. The field is driven by the recognition that addressing environmental challenges requires a holistic understanding of the environment that includes both natural and human elements.
The natural sciences component of environmental studies includes disciplines such as biology, chemistry, and geology. These disciplines provide essential knowledge about the natural world, such as the functioning of ecosystems, the chemistry of pollutants, and the processes that shape the Earth’s surface. This knowledge is crucial for understanding environmental issues such as climate change, pollution, and biodiversity loss.
The social sciences component includes disciplines such as economics, sociology, and political science. These disciplines provide insights into human behavior, economic systems, and political structures, which are critical for understanding how human activities impact the environment and how societies can transition to more sustainable practices.
The humanities component, which includes disciplines such as philosophy, history, and literature, provides insights into human values, historical perspectives, and cultural narratives about the environment. This component enriches our understanding of environmental issues by highlighting the ethical dimensions, historical contexts, and cultural diversity of human-environment relationships.
Research is a vital part of environmental studies. It generates new knowledge, informs policy-making, and promotes public awareness about environmental issues. Research topics in environmental studies are diverse and interdisciplinary, ranging from the study of environmental processes and systems to the analysis of environmental policies and the exploration of human attitudes towards the environment.
How to Choose Environmental Research Paper Topics
Choosing a topic for your environmental research paper is a critical step in your research process. The topic you choose will guide your research, shape your argument, and influence your writing. Here are some factors to consider and steps to follow when choosing an environmental research paper topic.
- Consider Your Interests: The first step in choosing a research paper topic is to consider your interests. Research is a time-consuming process, and it can be challenging if you’re not genuinely interested in the topic. Do you have a passion for climate change issues? Are you interested in conservation efforts? Are you intrigued by the role of technology in environmental protection? Reflect on your interests and choose a topic that you are excited to explore.
- Understand the Assignment Requirements: Before you settle on a topic, make sure you understand the assignment requirements. Does your professor want an argumentative paper or a research report? How long should the paper be? Is there a specific format you need to follow? Understanding the assignment requirements will help you choose a topic that fits the scope of the assignment.
- Conduct Preliminary Research: Once you have a general idea of what you’re interested in, conduct some preliminary research. This will help you understand the current state of research in your area of interest and identify gaps in the literature that you can address. Preliminary research can also help you narrow down a broad topic to a more specific one.
- Evaluate the Scope of the Topic: The scope of your topic is an important consideration. If your topic is too broad, you may have difficulty covering all aspects of it in your paper. On the other hand, if your topic is too narrow, you may struggle to find enough information to support your argument. Aim for a topic that is specific enough to be manageable but broad enough to have sufficient resources.
- Consider the Availability of Resources: Before finalizing your topic, consider the availability of resources. Are there enough scholarly sources related to your topic? Can you access these sources? If resources are limited, you may need to choose a different topic or broaden your current one.
- Reflect on the Relevance and Impact of the Topic: Consider the relevance and impact of your topic. Is the topic relevant to current environmental issues? Does it have the potential to contribute to the field of environmental studies? Choosing a relevant and impactful topic can make your research more meaningful and engaging.
- Seek Feedback: Once you have a potential topic in mind, seek feedback. Discuss your topic with your professor, classmates, or anyone familiar with environmental studies. They can provide valuable insights, suggest resources, and help you refine your topic.
- Formulate a Research Question: Finally, formulate a research question. A good research question is clear, focused, complex, and arguable. It provides a direction for your research and a framework for your argument.
Remember, choosing a research paper topic is not a one-time event. It’s a dynamic process that involves exploration, reflection, and refinement. Don’t be afraid to change your topic if your research takes you in a different direction. The goal is to choose a topic that you are passionate about, meets the assignment requirements, has sufficient resources, and has the potential to contribute to environmental studies.
How to Write an Environment Research Paper
Writing an environmental research paper is a significant academic endeavor. It requires a clear understanding of the topic, thorough research, critical thinking, and effective writing skills. Here are some steps to guide you through the process of writing an environment research paper.
- Understand the Assignment: Before you start writing, make sure you understand the assignment. What is the purpose of the paper? What is the required length? What format should you use? Understanding the assignment will help you plan your research and writing process effectively.
- Choose a Topic: Choose a topic that interests you and fits the assignment requirements. A good topic is one that you are passionate about, is relevant to your course, and has sufficient resources. Refer to the previous section for detailed advice on choosing a topic.
- Conduct Preliminary Research: Conduct preliminary research to familiarize yourself with your topic and identify gaps in the literature. Use reliable sources such as scholarly articles, books, and reputable websites. Preliminary research will help you refine your topic and formulate a research question.
- Formulate a Thesis Statement: Based on your preliminary research, formulate a thesis statement. A thesis statement is a clear, concise statement that expresses the main argument or focus of your paper. It should be specific, arguable, and capable of being supported by evidence.
- Create an Outline: Create an outline for your paper. An outline is a plan that organizes your ideas and evidence. It typically includes an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion. Each body paragraph should focus on a single point or argument that supports your thesis.
- Conduct In-depth Research: Once you have an outline, conduct in-depth research. Find evidence that supports your thesis and fits into your outline. Be sure to evaluate the credibility of your sources and take notes as you read.
- Write a Draft: Start writing a draft of your paper. Begin with the body paragraphs, as they form the core of your argument. Each paragraph should have a clear topic sentence, evidence to support the topic sentence, and a concluding sentence that ties the evidence back to your thesis.
- Write the Introduction and Conclusion: After writing the body paragraphs, write the introduction and conclusion. The introduction should grab the reader’s attention, provide background information, and present the thesis statement. The conclusion should summarize your main points, restate the thesis in new words, and provide a closing thought or implication.
- Revise Your Draft: Revise your draft to improve its content and clarity. Check that your thesis is clear and arguable, your arguments are logical and supported by evidence, and your conclusion effectively wraps up your paper. Also, check for coherence, transitions, and sentence variety.
- Edit and Proofread: Edit and proofread your paper to correct grammar, spelling, punctuation, and formatting errors. Consider reading your paper aloud or having someone else review it to catch errors you may have missed.
- Cite Your Sources: Finally, cite your sources. Proper citation is crucial to avoid plagiarism and give credit to the original authors. Be sure to follow the citation style specified by your professor, such as APA, MLA, Chicago, or Harvard.
Writing an environmental research paper is a process that requires time, effort, and patience. But with careful planning, diligent research, and thoughtful writing, you can produce a paper that is informative, engaging, and academically rigorous.
Custom Research Paper Writing Services
In the academic journey, students often find themselves in need of professional assistance, whether it’s due to a lack of time, a complex topic, or the need for a high-quality paper to secure good grades. This is where iResearchNet steps in. We offer a range of writing services designed to help students excel in their academic endeavors, particularly when it comes to writing an environmental research paper.
- Expert Degree-Holding Writers: At iResearchNet, we have a team of expert degree-holding writers who are well-versed in various academic disciplines, including environmental studies. Our writers are not just experts in their respective fields, but they are also skilled in academic writing, research, and critical analysis. They understand the intricacies of writing a research paper and are committed to producing high-quality, original work.
- Custom Written Works: We understand that every research paper is unique, with its own set of requirements and expectations. That’s why we offer custom written works. Our writers will work closely with you to understand your assignment requirements, research goals, and writing style to produce a paper that meets your specific needs.
- In-Depth Research: A good research paper is grounded in thorough and rigorous research. Our writers are skilled researchers who know how to find reliable sources, evaluate them critically, and use them effectively to support your arguments. They are adept at conducting in-depth research to provide a comprehensive and insightful analysis of your chosen topic.
- Custom Formatting: Formatting is a crucial aspect of academic writing that contributes to the readability and professionalism of your paper. At iResearchNet, we offer custom formatting services. Whether your paper requires APA, MLA, Chicago/Turabian, or Harvard style, our writers are well-versed in these formatting styles and will ensure that your paper adheres to the appropriate guidelines.
- Top Quality: Quality is our top priority at iResearchNet. We strive to provide top-quality writing services that meet and exceed your expectations. Our writers, editors, and quality assurance team work together to ensure that every paper we deliver is of the highest quality, free of errors, and meets your assignment requirements.
- Customized Solutions: We understand that every student has unique needs and challenges. That’s why we offer customized solutions. Whether you need help with choosing a topic, conducting research, writing a paper, or editing and proofreading, we can provide a service that fits your needs.
- Flexible Pricing: We believe that high-quality writing services should be accessible to all students. That’s why we offer flexible pricing options that cater to different budgets. We strive to provide a balance between affordability and high-quality services.
- Short Deadlines: We understand that time is of the essence when it comes to academic assignments. That’s why we offer services that cater to short deadlines. Whether you need a paper in a week or in as little as 3 hours, our writers are up to the task. They are skilled at working under pressure and delivering high-quality work within tight deadlines.
- Timely Delivery: At iResearchNet, we understand the importance of submitting your assignments on time. That’s why we guarantee timely delivery of our services. Once you place an order with us, you can rest assured that your paper will be completed and delivered to you within the agreed timeframe.
- 24/7 Support: We believe in providing continuous support to our clients. Our customer support team is available 24/7 to answer your questions, address your concerns, and provide assistance whenever you need it. Whether you have a question about our services, need help with placing an order, or want to provide feedback, we are just a call or a click away.
- Absolute Privacy: We respect your privacy and are committed to protecting it. All your personal informationand transaction details are kept confidential. We have stringent privacy policies in place to ensure that your data is secure and not shared with third parties.
- Easy Order Tracking: With our easy order tracking system, you can keep track of your order’s progress. You can check the status of your order, communicate with your writer, provide additional instructions, and request updates whenever you want.
- Money Back Guarantee: Your satisfaction is our top priority. If you’re not satisfied with the work we deliver, we offer a money-back guarantee. We will do our best to resolve any issues, but if you’re still not satisfied, we will refund your money.
At iResearchNet, we are committed to helping you succeed in your academic journey. We understand the challenges of writing a research paper, and we are here to support you every step of the way. Whether you need help with choosing a topic, conducting research, writing a paper, or editing and proofreading, we have the expertise and resources to help. With our team of expert writers, commitment to quality, and range of services, we are confident that we can help you write a research paper that you can be proud of. Trust iResearchNet with your environmental research paper, and let us help you achieve your academic goals.
Unleash Your Potential with iResearchNet
Are you ready to take your academic journey to the next level? With iResearchNet, you have a reliable partner that’s committed to helping you achieve your academic goals. Whether you’re working on an environmental research paper or any other academic assignment, our team of expert writers is ready to assist you.
Writing a research paper is no small feat. It requires time, effort, and a deep understanding of the topic. But you don’t have to do it alone. With iResearchNet, you have access to a team of professional writers who are experts in various academic disciplines, including environmental studies. They can help you choose a compelling topic, conduct in-depth research, and write a high-quality paper that meets your professor’s requirements.
But our services don’t stop at writing. We also offer editing and proofreading services to ensure that your paper is free of errors and ready for submission. Our custom formatting services ensure that your paper adheres to the required citation style, enhancing its professionalism and credibility.
We understand that as a student, you’re juggling multiple responsibilities and deadlines. That’s why we offer flexible pricing and short deadlines to accommodate your needs. And with our 24/7 customer support, you can reach out to us anytime, anywhere.
At iResearchNet, we value your privacy and guarantee the confidentiality of your personal information. We also believe in the quality of our services, which is why we offer a money-back guarantee. If you’re not satisfied with our work, we’ll do our best to rectify the issue or give you a refund.
So, why wait? Take the first step towards academic success. Place an order with iResearchNet today and let us help you write an outstanding environmental research paper. With iResearchNet, you’re not just getting a paper; you’re gaining a partner in your academic journey. Let’s succeed together!
ORDER HIGH QUALITY CUSTOM PAPER


- Customer Reviews
- Extended Essays
- IB Internal Assessment
- Theory of Knowledge
- Literature Review
- Dissertations
- Essay Writing
- Research Writing
- Assignment Help
- Capstone Projects
- College Application
- Online Class
Research Paper Topics on Environment: 30+ Ideas for Inspiration
by Antony W
July 6, 2022

Are you looking for the best research paper topics on environment? You’ve come to the right place.
Whether you wish to write a research paper that raises environmental awareness or you want to explore solutions to save the plant and preserve the environment, you’ll find the topic ideas shared in this guide incredibly useful.
Of course, finding the right topic for your paper by brainstorming can take a lot of time. Add the research process involved and you might spend more time on the assignment than you should.
These topic ideas cut the brainstorming time by almost half, so you can spend less time thinking about what to write about and more time exploring a topic you love.
Professional Writing Help
Stuck with your environment research paper assignment and need help to get it done? Hire our research paper writing help for just $19.9.page and get the assignment written fast.
What Are Environmental Research Topics?
Environmental research paper topics are ideas that relate to the biological, chemical, and physical aspect of our ecosystem.
The focus area includes natural landmarks, human activities, weather, and living organisms.
When it comes to writing a research paper on environment, many students will focus primarily on conservation or prevention.
It’s equally important to focus on other areas related to the environment, such as climate change, sustainability, environmental justice, endangered species, paleoecology, and wildlife ecology.
Research Paper Topics on Environment
The following is a list of research paper topics on environment that are worth looking at.
Keep in mind that these are just ideas, which can help you brainstorm and build an interest around environmental conservation.
1. Climate Change Research Paper Topics
- What is the relationship between ozone depletion and climate change?
- What exactly is the distinction between climate change and global warming?
- Investigate the reasons why some people do not believe in climate change.
- Which regions are the most affected by increasing sea levels?
- Discuss how hydraulic fracturing impacts the environment.
- What effect do melting glaciers have on the environment?
- Investigate which natural disasters are associated with climate change.
- What effect does an overabundance of CO2 have on the environment?
- What relationship exists between tree planting and climate change?
- How has the weather in your area changed over the last 20 years?
- Investigate the impact of deforestation on the climate.
- Discuss the primary causes of climate change.
- What are the most serious agricultural issues brought on by climate change?
Related: Psychology Research Paper Topic Ideas
2. Ecology Research Paper Topics
- What factors influence the number of creatures in a community?
- What kinds of interactions may creatures have with their surroundings?
- What is the relationship between water management and environmental concerns?
- What is the impact of human garbage on marine ecosystems?
- What are the most serious environmental threats today?
- What can people do to save pandas from becoming extinct?
3. Living Environment Research Paper Topics
- What impact will the extermination of honey bees have on the world?
- A comparison of photosynthesis in different plants
- How germs enter into food that humans eat
- What impact do invading species have on the environment?
- A comparison of the dust observed in various locations
- How amphibians interact with their surroundings
- Is the soil composition consistent throughout?
- Talk about the variety of trees in your neighborhood.
- Discuss the weed diversity in your town.
- What is the relationship between the earth and a live organism?
- A comparison of the roots of several plants
- The role of the environment in asthma attacks
4. Interesting Topics Environmental Research
- Will hybrid vehicles aid in the reduction of pollutants in the atmosphere?
- Is ocean acidification a major environmental issue?
- What effect do rising CO2 concentrations have on the atmosphere?
- Describe the connection between industrialization and acid rain.
- The truth about global warming and the misconceptions that accompany it
- What role do minor water sources play in the environment?
- What effects does climate change have on human health?
- Why should the world transition from fossil fuels to hydrogen?
- What role pesticides and wastes have in soil contamination
- Are industrial facilities near water resources a major source of human disease?
- What role does paleoecology play in environmental research?
Also Read: Business Research Paper Topics
The Benefits of Conducting a Research on Environment
It’s not the first time you’ve seen environmental preservation campaigns, and it definitely won’t be the last.
There’s a need to enhance sustainability and make the world a better place for the future generation.
The drive to save the planet and make our environments better than it already is makes research study in this area interesting.
Here are some of the reasons why it makes a lot of sense to conduct research studies on environment.
1. Protect the Environment
By engaging in research on environment, you’ll identify safe ideas and practices that can help to reduce or completely eliminate negative effect of human activities on the environment.
For example, learning about the ins and outs of natural phenomenon such as wildfire will enable you to come up with suggestions of preventative measures to optimize the use of natural resource to make the environment as humanly safe as possible.
2. Graduate with a Degree
You have to complete a research paper project to graduate and earn a degree in your area of environmental studies.
As such, you should to take this project seriously by choosing a topic that you find interesting to explore, provided it’s within the scope of your field of study.
3. Contribute to Existing Research
Taking part in studying and giving recommendations for environmental preservation gives you the opportunity to contribute to existing research.
By examining existing research , you can identify the weaknesses (or gaps) in existing studies, and then offer objective contribution that can fill these gaps and make the environment better than it already is.
Now that you have some research paper topics on environment, it shouldn’t take you long to get started with writing.
If you feel like you have a ton of assignments waiting for you, you can take advantage of the research paper writing service by Help for Assessment.
Our team will help you to:
- Choose a research paper topic
- Conduct research for your paper from relevant sources
- Formulate a research issue
- Structure your research paper based on current academic standards and
- Help you with writing from start to finish
We’ll work within your deadline to help you get the research paper written, proofread, edited, and submitted on time.
About the author
Antony W is a professional writer and coach at Help for Assessment. He spends countless hours every day researching and writing great content filled with expert advice on how to write engaging essays, research papers, and assignments.
Top 100 Environmental Science Project Topics
Table of contents
- 1 Climate Change
- 2 Renewable Energy
- 3 Urban Ecology
- 4 Land and Water Use
- 5 Pollution
- 6 Environmental Science Topics for College Students
- 7 Energy Resources and Consumption
- 8 Population
- 9 Noise and Light Pollution
- 10.1 Conclusion
With the environment and global warming in its current predicament, it’s no surprise that environmental science job opportunities will be on the rise in the very near future.
With the environment and global warming in its current predicament, it’s no surprise that environmental science job opportunities will be on the rise in the very near future. Therefore, so are the numbers of students pursuing studies in this field. The last four decades have seen huge changes in the rate of global warming and so more than ever before, we need people to study topics in environmental science.
For anyone majoring in environmental science, anyone needing to write environmental studies project topics for a science course, or essay writer who is working on topical essays this comprehensive article will talk you through the top ten project topics to pursue. For each project topic, we’ll give you ten ideas.
Climate Change
There’ll always be an environment, but it’s looking more and more likely that it won’t be like our current one in the future. With this in mind, here are the top ten environmental project topics for college students on climate change:
- Is global warming a natural phenomenon?
- The politicization of global warming.
- How do eddy covariance towers work?
- Planetary tilt – does it affect global warming?
- The differences between climate change and the greenhouse effect.
- Why is carbon dioxide a greenhouse gas?
- How do changes to weather patterns affect the Earth’s climate?
- The concept of polar amplification.
- The barriers to climate change responses.
- The “heat island” effect.

Renewable Energy
Our advances through the industrial revolution and the use of fossil fuels are now coming back to bite us. Here are ten environmental topics for project on renewable energy:
- The pros and cons of hydropower.
- Solar energy and pollution.
- Solar energy to help the economy.
- Geothermal energy: an unlikely major energy source?
- The problems caused by renewable energies.
- Understanding geothermal energy.
- Are hydrogen fuel cells a viable alternative?
- The advantages and disadvantages of solar power.
- Transporting geothermal energy: a study.
- The challenges of large-scale biomass energy use.
Urban Ecology
Urban ecology is an important consideration for environmental science projects for college students who are eager to pay for essay to receive high grades for assignments. When we study the environment, we tend to think of green spaces and rural lands, but urban ecology is important too. As such, here are ten environmental science project ideas on this topic:
- How do unequal urban planning and greenspace distribution affect temperatures in a city?
- How does urbanization affect surrounding rural areas?
- How is the local climate affected by buildings and pavements?
- What is the urban heat island effect?
- How are water sources affected by urbanization?
- How has human development affected our green spaces?
- How is social identity linked to urbanization?
- What impact does transport have on rural locations?
- How can the natural environment be integrated into urban planning and design projects?
- What is water harvesting?

Land and Water Use
When humans use natural resources, they also disrupt natural ecosystems. This is an important area of study as we try to claw back and save some of the world’s resources from being entirely depleted. Here are ten interesting environment related topics for project on this subject:
- How have overfishing and non-sustainable fishing methods affected our oceans?
- How does using water for irrigation affect natural ecosystems?
- The impacts of different societies’ ecological footprints in terms of waste production and resource demands.
- How can we mitigate deforestation?
- An analysis of The Green Revolution.
- The impact of salt application to streams.
- How does using an ANN (artificial neural network) for rainfall-runoff affect ecosystems?
- How do land-use changes impact urban runoff?
- Relationships between water quality, land use and land use change.
- Land use effects on lake water quality.
Pollution is one of the planet and humanity’s worst enemies. Agriculture, transportation, and industry can cause horrific environmental catastrophes. Check out the possible environment science project topics on pollution:
- The impact of pollution on health care.
- The effects of environmental pollution and water pollution on marine life.
- The effects of air pollution on the food chain.
- How environmental pollution affects Arctic.
- The health hazards associated with waste accumulation and water pollution.
- How do human activities change the world’s oceans?
- Conservation and how it helps to reduce air pollution.
- The difficulty of establishing direct links between health problems, air pollution, and air quality.
- Environmental policy regarding air pollution and acid rain.
- The effect of acid rain in urban and natural areas.
Environmental Science Topics for College Students
Environmental studies at college is all about studying in-depth biological, chemical, and physical processes on Earth. Environmental sciences also incorporates social, cultural, and political processes that have an impact. When studying Environmental Science at college level, a project need to seek out ways to present complex relationships in a simple way. Here are some ideal environmental science projects for college students:
- Genetically Modified (GM) foods and their impact on the environment.
- The global impact of radiation and nuclear accidents.
- The role of the UNEP in environmental conservation.
- The impact of freak weather incidents.
- Micro-plastics in drinking water – why and how have they got there?
- The Nagasaki and Hiroshima bombings – what have we learned about nuclear bombs and the effects on the ecosystem?
- The impact of Coronavirus and maintaining the ecosystem.
- The role of the media in conservation campaigns.
- Tourism and the impact of human activities on a local and global level.
- How has the US departure from the Paris Climate Agreement changed things?
Energy Resources and Consumption
Lots of environmental studies project topics goes into looking at energy resources and consumption, which makes this a great project topic. There is already a lot of information out there, which makes this easy to research.
- What is the relationship between energy efficiency and energy conservation?
- What are the economic, social, and environmental costs of solar energy?
- Was coal pivotal in industrialization?
- The impact of fracking on the environment.
- Compare and contrast the processes of extracting oil and mining coal.
- How is ethanol produced as a biofuel?
- Nuclear energy is a viable clean energy. Discuss.
- The environmental effects of a nuclear conflict explored.
- What is plant biomass?
- The challenges of converting to large-scale biomass energy.
You can't write a list environment project topics about environmental science, without mentioning population, environmental health, and the changes we've seen over the years. A lot of environment research focuses on population and its effects. Here are some ideas:
- Population growth and its effects on GDP.
- Factors that control population growth and the effect of density.
- An exploration of population momentum.
- The importance of studying population ecology.
- The effect of human migration on populations.
- The effects of overpopulation.
- The effects of global warming on the global population.
- Is sustainable development possible in a growing population?
- What would happen if the demand for natural resources became greater than the supply?
- How serious is the world population explosion?
Noise and Light Pollution
Though lots of people don’t consider light and noise as pollutants, the reality is that they are. Noise levels and light levels can affect organisms. Here are some interesting topics for science projects on noise and light pollution:
- How is local wildlife affected by airport noise?
- What happens if orcas aren’t able to use echolocation due to freight noise?
- Migrating birds and the confusion from bright lights.
- The effect of bright lights in resorts and sea turtles emerging from nests.
- How bright city lights affect nocturnal animals.
- The disruption of nocturnal activity in frogs and toads due to artificial light glare.
- Artificial lights and the effects on migratory birds.
- Light pollution and the effects on plants.
- Changes in animal behavior due to noise pollution.
- Noise pollution and the effects on mating frogs.
Conservation Biology
With as many as 2,000 species becoming extinct each year, we’re experiencing a serious problem. Conservation biology is a huge topic of interest when you need to " write my essay " and want to succeed with this task. Here are some ideas for exploration:
- How has human behavior ramped up endangered species extinction rates?
- How do humans threaten endangered species?
- What will the effects of a loss in biodiversity be for humans?
- If honeybees become extinct, what other changes would we see?
- Why is the decline in pollinating insects so dangerous?
- What happens if we lose endangered species?
- What is the Holocene extinction event?
- The collapse of the world’s coral reef ecosystems.
- The threat of acidification in our oceans.
- How can environmental policy help threats to biodiversity?
It's clear to say that there is a huge variety in topics in environmental science. For anyone looking for an environmental science project topic, we hope this extensive list has helped narrow down your ideas. Whether you're looking for environmental research topics for college students or high school, there is something for everyone here.
Readers also enjoyed

WHY WAIT? PLACE AN ORDER RIGHT NOW!
Just fill out the form, press the button, and have no worries!
We use cookies to give you the best experience possible. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Int J Environ Res Public Health

The Relationship between Environmental Awareness, Habitat Quality, and Community Residents’ Pro-Environmental Behavior—Mediated Effects Model Analysis Based on Social Capital
Associated data.
Not applicable.
Pro-environmental behavior can promote the optimization of the living environment and sustainable social development. This paper constructs a theoretical analysis framework of “environmental consciousness, habitat environment-social capital- pro-environmental behavior”. By using structural equation modeling and 1005 instances of microscopic research data, we analyzed the influence of environmental awareness and habitat environment on the pro-environmental behavior of community residents. The results of the analysis were combined with the Bootstrap method to verify the mediating role of social capital dimensions in the influence of environmental awareness and habitat quality on the pro-environmental behavior of community residents. The results show that: Firstly, environmental awareness, habitat quality, and social capital have positive effects on the pro-environmental behavior of community residents. Secondly, environmental awareness and habitat quality have positive effects on the five dimensions of social capital. Thirdly, among the five dimensions of social capital, four dimensions of social trust, social norms, sense of community belonging, and community voluntarism play a partially mediating role between environmental awareness, habitat quality, and pro-environmental behavior. This paper enriches the research on the influence of environmental awareness and habitat environment on pro-environmental behavior, reveals the mediating effect of each dimension of social capital, and broadens the horizon for the study of pro-environmental behavior. The results of the study can provide a reference for decision making to promote the implementation of pro-environmental behavior among community residents.
1. Introduction
Pro-environmental behavior, also known as environmentally friendly behavior or environmental protection behavior, is a socially altruistic behavior of community residents who have a positive attitude and behavioral tendency to care about the environment [ 1 ]. The concept of pro-environmental behavior is based on the relationship of “Individuals have an impact on the environment”. The elements that influence environmentally friendly behavior can be divided into four categories.
The first type of influencing factors are cognitive factors, namely people’s environmental awareness [ 2 ], environmental knowledge [ 3 ], and so on. At the same time, it also includes the personality traits of individuals. The agreeableness and openness in personality traits are considered to be the two personality traits most related to the pro environmental behavior [ 4 ].
The second influencing factor is the emotional factor, which can be divided into two parts in an irrational perspective. On the one hand, this kind of research focused on the influence of individual emotions on the willingness to practice pro environmental behavior [ 5 ]. On the other hand, it focused on the influence of the emotional connection between individuals and specific things on the implementation of pro environmental behavior. Some scholars have found that human feelings about the current place of residence will affect individuals’ behavior in public life. At the same time, human beings connect with the environment through the place where they live, and then have a place attachment to the place where they live [ 6 ].
The third kind of influencing factor is social psychological factor, which includes ethics, environmental attitude, and environmental values. Moral norm refers to the moral cognition that individuals embody when they make certain behavioral decisions [ 7 ]. The social pressures they bring have an impact on individuals’ pro-environment behavior [ 8 ]. Environmental attitude refers to an individual’s subjective evaluation of a behavior, which presents both positive and negative aspects. Numerous empirical studies have shown that environmental behavior attitudes have a significant positive effect on individuals practicing pro-environmental behavior [ 1 ]. Environmental values are the guiding principles that individuals have developed, and this guiding principle, as an intrinsic element, profoundly influences pro-environmental behavior [ 9 ].
The fourth influencing factor is the situational factor. Excluding cognitive, emotional, psychosocial, and other elements, the academic community also pointed out that situational factors have an important impact on pro-environmental behavior. The availability of convenient transportation facilities [ 10 ], the availability of facilities to recycle waste [ 11 ], the availability of energy-efficient commodities for sale, and the availability of suitable prices [ 12 ] all affect an individual’s willingness and motivation to engage in pro-environmental behavior.
In summary, residents’ pro-environmental behavior is a behavior driven by the joint action of their own emotional factors and the external environment [ 13 ], which is the performance of both internal and external factors. The mechanism of the interaction between internal motivational factors and external influences, which is the key factor in establishing a long-term mechanism for environmental protection, has been little explored by scholars. This study aims to investigate the multiple effects of environmental awareness as an internal personal psychological factor, habitat quality as an external contextual factor, and social capital as a social environmental factor on pro-environmental behavior.
From the perspective of residents’ own emotional factors, their internal recognition and support of pro-environmental awareness as independent-minded individuals is the psychological basis for the implementation of pro-environmental behaviors [ 14 ]. Environmental consciousness can be applied to residents’ own behavior through their evaluation and judgment of external objective things, which is also a necessary condition to ensure the long-term implementation of pro-environmental behavior [ 14 ]. From the perspective of external factors, the community residents’ behavior will be affected by the external situational factors, namely habitat environment [ 15 ]. The evaluation of the quality of the habitat environment is the subjective feelings and psychological perceptions of residents regarding the community environment and the changes in this environment, which can influence people’s specific environmental behaviors in a certain contextual environment [ 16 ]. At the same time, social capital as one of the social environmental factors can also have some influence on residents’ pro-environmental behaviors [ 17 ]. For example, when individual cognition and moral beliefs are consistent with group norms, individuals will identify with the group and be influenced by it. If the group is related to the protection of the environment, its members are more likely to engage in pro-environmental behavior [ 18 ]. Thus, social capital in the social environment may be a factor that attracts members to participate and act, and can positively influence pro-environmental behavior.
1.1. Theoretical Assumptions and Analysis
1.1.1. the direct influence of environmental awareness on pro-environmental behavior.
According to “Social Cognitive Theory”, the vast majority of individual behaviors are goal-oriented. This means that when individuals have a higher level of cognition, the quality of personal behavior will be correspondingly higher, and vice versa [ 19 ]. Similarly, environmental awareness has a very important role in influencing the pro-environmental behavior of community residents. Individuals with higher levels of environmental concern are more inclined toward pro-environmental behavior [ 20 , 21 ]. That is to say, if residents have a higher level of environmental concern, their willingness to engage in pro-environmental behavior will be stronger [ 22 ]. In addition, environmental concern also has a positive effect on individuals’ willingness to pay green [ 23 ]. Furthermore, the more environmentally knowledgeable residents are, the more knowledgeable and skilled they are to implement pro-environmental behaviors, thus promoting them to implement pro-environmental behaviors consciously will be easier [ 24 ]. Finally, establishing correct environmental values not only can effectively reduce the negative impact of their own behavior on the environment [ 25 ], but also can motivate them to take corresponding measures to implement environmental protection and improve their behavior. On the contrary, low environmental awareness inhibits residents’ knowledge about the environment to a certain extent, restricts their participation enthusiasm, and hinders the implementation of pro-environmental behaviors in general [ 26 ].
1.1.2. Direct Impact of Habitat Quality on Pro-Environmental Behavior
Contextual factors such as the quality of human habitat also have an impact on pro-environmental behavior [ 27 ]. The affluence theory of economic development suggests that the affluence of a region is positively related to environmental responsibility and the pro-environmental behavior of local residents. The environment is not only a public good, but also a “scarce good”. Therefore, as economic growth increases the demand for environmental improvement, people will consume the “scarce goods” after necessary consumption [ 28 ]. “Low-cost Theory “suggests that people are more likely to behave in an environmentally manner in situations where they have lower costs of action. The term “cost” here refers to a broad sense of “cost”, i.e., not only economic costs, but also non-economic costs, such as the convenience of the living environment and difficulty of implementation.
Based on the above theoretical analysis and research, it can be determined that the quality of the habitat environment can have an impact on pro-environmental behavior in the following aspects. First, the quality of environmental hygiene can have an impact on residents’ pro-environmental behavior. Specifically, in the process of living, residents will regard the environmental health condition of the community as an external environmental signal, and based on the interpretation of this signal, they will formulate community behavior rules, i.e., whether or not the behavior is acceptable, and make their self-behavior choices accordingly [ 21 ]. Likewise, the convenience, comfort, and safety of the infrastructure can influence the willingness and motivation of residents to participate in environmental actions. A clear example is Switzerland, where a virtuous cycle of waste recycling has been developed, with clear responsibilities and division of labor, both for sorting, collection, and reuse. The reason for the high level of waste recycling behavior among Swiss community residents is that these areas already provide convenient waste recycling facilities, and all the residents have to do is to choose the right bins to put their waste in, a practice that increases the convenience of pro-environmental behavior [ 29 ]. Similarly, community environmental management has a greater impact on pro-environmental behavior. There will be more positive pro-environmental behavior in residents when the quality of residential environment management is higher and where there is a certain quality of life guarantee for the residents of the able residential area [ 30 ].

1.2. The Intermediary Role of Social Capital
1.2.1. the mediating role of social capital between environmental awareness and pro-environmental behavior.
Residents’ environmental awareness has an influential role in the formation of social capital. Residents’ awareness of environmental issues affects their social participation, which in turn strengthens understanding, familiarity, and identification among community members, and creates a dense network of social relationships through continuous interaction [ 31 ]. Through communication, coordination, and interaction, residents in a social network can determine how to cooperate with each other in a mutually beneficial way [ 32 ]. The process of mutual agreement on goals and values lays the foundation for the cultivation of social trust [ 33 ], the core element of social capital. In the process of participation, the rules of “mutual aid” and “reciprocity” are formed [ 13 ], and a sense of community is established in real life and in a particular environment. As residents develop a sense of belonging and cohesion in the community, social capital can be formed in spaces where community members can interact.
At the same time, the formation of social capital can guide the collective action of community members, on this basis, become a factor to guide individual action in the community [ 34 ], and also promote the community to organize itself for voluntary services [ 32 ]. Pro-environmental behavior can be seen as an “Altruistic Behavior”, when people pay for the environment as a “Quasi-Public Good”, they tend to have a sense of “contribution”, because the positive externalities of environmental protection are often greater for the public domain than for the private domain [ 35 ]. This tends to create a sense of “empowerment”, and thus is more likely to promote the positive effects of social capital on environmental behavior [ 31 ].
1.2.2. The Mediating Role of Social Capital between Habitat Quality and Pro-Environmental Behavior
The quality of habitat affects the formation of social capital. The quality of habitat indirectly reflects the economic status of the region and is the deep soil for cultivating the social capital of the residents [ 30 ]. If an area has a high level of economic development, then the improvement of environmental health, infrastructure, and environmental management can achieve a greater degree for community residents’ recognition of the quality of their living environment. In order to maintain the status quo, people consciously or unconsciously form organizations and reach a consensus, forming an atmosphere and force that can protect the status quo. In other words, when residents perceive a high-quality living environment, they will have positive feelings and influences on the development of social capital.
The development of social capital influences the implementation of pro-environmental behaviors. Community residents’ satisfaction with the quality of their habitat is implicitly internalized in their emotions toward the community. Emotions about the community lead residents to invest resources in their community and to engage in a range of beneficial behaviors for the development of the community [ 36 ]. It is also believed that residents are more willing to help others or to participate in community activities when they are satisfied with their living experience. Community residents are often able to form an environmental organization on environmental issues, and the development of environmental organizations is more mature, thus helping to guide people to become involved in environmental issues [ 37 ]. At the same time, good environmental management helps to resolve community frictions, thus enhancing the cohesiveness and solidarity of community residents.
Research proves that social capital can be an effective resource pool for collective community action through the long-term interaction of community residents or organizations [ 38 ]. At the same time, social capital as a “soft environment” can also improve the efficiency of social operation, become a catalyst for social vitality, and the habitat environment is the spatial carrier for the formation of social capital. The two are mutually coupled to promote the optimization of habitat. Under the influence of the social atmosphere, where residents advocate for environmental protection and effective interpersonal interaction, the habitat environment has more effective impacts on the pro-environmental behavior of individuals [ 30 ]. Social capital promotes residents’ participation in environmental governance, as well as promotes synergistic cooperation and benign interaction among environmental stakeholders based on trust in environmental governance, which plays a role in resolving people’s conflicts in environmental resource allocation and eases social conflicts [ 32 ]. Thus, social capital is considered as a more efficient and humane tool for organization and coordination in environmental governance. As mentioned earlier, habitat quality has positive implications for social capital, which in turn has an impact on pro-environmental behavior. Therefore, this study predicts that better habitat environment will lead to higher levels of social capital among residents, which in turn will promote their pro-environmental behavior.
1.3. Objectives and Hypotheses
This study intends to construct a structural relationship model of “environmental awareness, habitat quality-social capital- pro-environmental behavior” ( Figure 1 ) to investigate the relationship between environmental awareness, habitat quality, social capital, and pro-environmental behavior. In this study, we explore the mediating mechanism through which environmental awareness, habitat quality, and social capital influence the pro-environmental behaviors of community residents.

Theoretical framework diagram.
Based on previously reviewed research, the following hypotheses were proposed ( Figure 1 ).
Environmental awareness has a direct impact on the dimensions of social capital.
Environmental awareness has a direct impact on Social network.
Environmental awareness has a direct impact on Social trust plays.
Environmental awareness has a direct impact on Social norms refer.
Environmental awareness has a direct impact on Community belonging.
Environmental awareness has a direct impact on Community voluntarism.
Habitat quality has a direct impact on the dimensions of social capital.
Habitat quality has a direct impact on Social network.
Habitat quality has a direct impact on Social trust plays.
Habitat quality has a direct impact on Social norms refer.
Habitat quality has a direct impact on Community belonging.
Habitat quality has a direct impact on Community voluntarism .
Environmental awareness has a direct impact on pro-environmental behavior.
Habitat quality has a direct impact on pro-environmental behavior.
Social capital has a direct impact on pro-environmental behavior.
Social network has a direct impact on pro-environmental behavior.
Social trust has a direct impact on pro-environmental behavior.
Social norms refer has a direct impact on pro-environmental behavior.
Community belonging has a direct impact on pro-environmental behavior.
Community voluntarism has a direct impact on pro-environmental behavior.
Social capital has a mediating effect between the influence of environmental awareness and pro-environmental behavior.
Social network has a mediating effect between the influence of environmental awareness and pro-environmental behavior.
Social trust has a mediating effect between the influence of environmental awareness and pro-environmental behavior.
Social norms refer has a mediating effect between the influence of environmental awareness and pro-environmental behavior.
Community belonging has a mediating effect between the influence of environmental awareness and pro-environmental behavior.
Community voluntarism has a mediating effect between the influence of environmental awareness and pro-environmental behavior.
Social capital has a mediating effect between the effects of habitat quality and pro-environmental behavior.
Social network has a mediating effect between the effects of habitat quality and pro-environmental behavior.
Social trust has a mediating effect between the effects of habitat quality and pro-environmental behavior.
Social norms have a mediating effect between the effects of habitat quality and pro-environmental behavior.
Community belonging has a mediating effect between the effects of habitat quality and pro-environmental behavior .
Community voluntarism has a mediating effect between the effects of habitat quality and pro-environmental behavior.
2. Data and Methodology
2.1. methodology.
This study applied AMOS 21.0 to examine and analyze the mechanisms underlying the influence of environmental awareness, habitat quality, and social capital on pro-environmental behavior. Each latent variable was measured via multiple entries in the scale. To further validate the mediating effects and influence mechanisms of social capital, the Bootstrap method was used to validate the mediating effects of each of the five dimensions of social capital.
2.2. Variable Selection
Based on the mature scales at home and abroad, the environmental awareness, habitat quality, social capital, and pro-environmental behavior scales were designed by combining the research objectives and by using the Likert 5-point scale.
2.2.1. Independent Variable: Environmental Awareness
Environmental awareness refers to the intention of individuals to promote a series of environmental actions motivated by psychological factors and emotional forces [ 20 ]. In conjunction with the purpose of the study, the environmental awareness of community residents was divided into three dimensions: environmental concern, environmental knowledge, and environmental values [ 4 ]. Firstly, environmental concern is the degree of residents’ tendency to recognize environmental problems and to support the solutions to these problems [ 39 ]. Secondly, environmental knowledge refers to the specific knowledge mainly related to the protection of the environment, which is mainly reflected in the three aspects of system, action and utility [ 3 ]. Thirdly, environmental values are residents’ emotions, perceptions, and behavioral intentions toward environmental protection issues [ 9 ] ( Table 1 ).
Environmental awareness evaluation indicators.
| Dimensionality | Indicators |
|---|---|
| Environmental Concern | |
| Environmental Knowledge | |
| Environmental Values |
2.2.2. Independent Variable: Habitat Quality
Habitat quality refers to the degree to which the environment is suitable for human living [ 40 ]. The comprehensive evaluation indexes of habitat quality can be divided into three aspects: environmental health conditions, infrastructure conditions, and environmental management conditions [ 41 ]. Firstly, environmental health conditions mainly includes the satisfactory outdoor air quality, water quality, and greening degree [ 42 ]. Secondly, infrastructure conditions refer to the municipal utilities within the community, including community greening conditions, environmental health conditions, municipal facilities deployment, and disaster prevention support facilities [ 41 , 42 ]. Thirdly, environmental management conditions include greening management, safety and disaster prevention management, and municipal facility management [ 41 , 42 ] ( Table 2 ).
Habitat quality evaluation indicators.
| Design Level | Indicators |
|---|---|
| Environmental health condition | |
| Infrastructure conditions | |
| Environmental Management Status |
2.2.3. Mediating Variable: Social Capital
Social capital is an important factor that effectively motivates individuals to actively participate in cooperative behavior [ 17 ]. The social capital discussed in this study refers to the social capital of community residents, which is analyzed in five dimensions: social network, social trust, social norms, sense of community belonging, and community voluntarism. Firstly, social network refers to a kind of “local social relationship network”, which is an individual social network that includes neighborhood relationships and interactions formed by community residents via community participation [ 43 ]. Secondly, social trust refers to a special trust relationship formed by the community residents in the process of long-term interaction [ 17 ]. Thirdly, social norms refer to the behavioral norms of community residents in maintaining generally acceptable community order, promoting the collective actions of community members, and in maximizing the collective welfare of community members [ 17 ]. Fourthly, community belonging refers to the emotional attachment of community residents to their communities [ 44 ]. Fifth, community voluntarism refers to the willingness of residents to volunteer in the community, and thus to help other residents without compensation for performing these helpful acts ( Table 3 ).
Social capital evaluation indicators.
| Design Level | Indicators |
|---|---|
| Social Networks | |
| Social Trust | |
| Social Norms | |
| Sense of Community Belonging | |
| Community volunteerism |
2.2.4. Dependent Variable: Pro-Environmental Behavior
Pro-environmental behavior is a conscious behavior that reflects the subject’s sense of personal and social responsibility, as well as environmental values in order to be able to solve environmental problems [ 45 ]. According to Sivek and Hungerford, the attributes of pro-environmental behavior determine it as a behavior that allows for the sustainable and controlled exploitation of natural resources [ 45 ]. According to Stern, pro-environmental behavior can be considered as an activity that aims to protect the ecological environment [ 41 ]. Hungerford and Sia et al., organized pro-environmental behavior into four dimensions: ecological management, consumption behavior, persuasive behavior, and citizenship behavior [ 42 ]. Among them, ecological management is a series of practical actions taken to maintain and protect the ecology or improve the environment; consumption behavior uses green consumption-oriented means to protect the environment; persuasive behavior means persuading or encouraging others to engage in positive environmental protection behavior through the subject’s words; civic behavior means taking the initiative to perform one’s civic duties and to pay attention to, and explore and discuss how to solve environmental issues ( Table 4 ).
Pro-environmental behavior evaluation indicators.
| Dimensionality | Indicators |
|---|---|
| Ecological Management | |
| Consumer Behavior | |
| Persuasive behavior | |
| Civic Behavior |
2.3. Study Area and Data Acquisition
Jinan is the capital city of Shandong Province and one of the 15 sub-provincial cities in China, with a per capita gross regional product of ¥110,119.00 in 2020 (the national per capita GDP was ¥71,999.60). The resident population of Jinan is 9,202,400, and the urbanization rate of the resident population reaches 77.00% (13.11% higher than the national average of 63.89%). Therefore, the study and discussion of Jinan city as a case area can be a reference value for exploring the pro-environmental behavior of residents in other large and medium-sized cities.
The empirical research data for this study were mainly obtained from the questionnaire. The study combines random sampling and stratified sampling to investigate the research. First, four districts in Jinan, namely, Lixia, Licheng, Changqing, and Zhangqiu, were selected according to the regional economic development status to conduct the survey. Among them, the economic development level of Lixia district is the highest in Jinan city, the economic development level of Licheng district and Zhangqiu district is in the middle, and the economic development level of Changqing district is relatively weak. Secondly, four residential areas were randomly selected in each district. Again, 50–80 residents were randomly selected in each sample residential area according to a certain proportion, and the questionnaire survey was conducted in a one-on-one question-and-answer format, and each questionnaire was guaranteed to be completed by one of the members of each household.
The data collection was divided into two stages: pre-survey and formal survey. A total of 150 questionnaires were collected in the pre-survey stage from July to September 2021, some of the items were improved after the reliability analysis, and the questionnaire questions were modified in a colloquial way to ensure the effectiveness of the questionnaire. A total of 1150 questionnaires were formally placed in the formal survey stage from September to December 2021, and 1005 questionnaires were effectively answered. The results of the descriptive statistics of the sample are shown in Table 5 .
Descriptive statistics of the sample.
| Basic Information | Classification | Frequency | Percentage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | Male | 543 | 54 |
| Female | 462 | 46 | |
| Age | 16–20 years old | 91 | 9.1 |
| 21–30 years old | 272 | 27.1 | |
| 31–40 years old | 192 | 19.1 | |
| 41–50 years old | 202 | 20.1 | |
| 51–60 years old | 141 | 14 | |
| 61 years old and above | 107 | 10.6 | |
| Current place of residence | Lixia District | 262 | 26.0 |
| Licheng District | 304 | 30.2 | |
| Changqing District | 212 | 21.1 | |
| Zhangqiu District | 268 | 26.7 | |
| Average monthly income | Under RMB 4500 | 111 | 11 |
| RMB 4500–5500 | 272 | 27.1 | |
| RMB 5500–6500 | 322 | 32 | |
| RMB 6500–7500 | 181 | 18 | |
| RMB 7500 and above | 119 | 11.8 | |
| Highest level of education | Junior high school and below | 119 | 11.8 |
| High school, junior college, technical school | 213 | 21.2 | |
| University specialists | 336 | 33.4 | |
| Undergraduate | 228 | 22.7 | |
| Graduate student and above | 109 | 10.8 | |
| Current Occupation | Students | 101 | 10 |
| Government units, institutions | 162 | 16.1 | |
| State-owned enterprises | 151 | 15 | |
| Private enterprises, foreign-funded enterprises | 262 | 26.1 | |
| Individual business people, personal studio | 192 | 19.1 | |
| Retirees and others | 117 | 11.6 |
3. Empirical Tests and Results
3.1. structural equation model testing, 3.1.1. reliability and validity tests.
Four latent variables were set in this study’s scale, which was measured using 56 measurement questions. The overall Cronbach’s alpha for the environmental awareness variable was 0.846, and the Cronbach’s alpha for environmental concern, environmental knowledge, and environmental evaluation were 0.794, 0.831, and 0.807, respectively. The overall Cronbach’s alpha for the living environment variable was 0.884, the overall Cronbach’s alpha for the social capital variable was 0.887, and the Cronbach’s alpha for social network, social trust, social norms, community belonging, and community voluntarism were 0.869, 0.889, and 0.861, respectively. The overall Cronbach’s alpha for pro-environmental behavior variables was 0.826, and the Cronbach’s alpha for the four dimensions of pro-environmental behavior, ecological management, consumer behavior, persuasive behavior, and civic behavior, were 0.892, 0.796, 0.889, and 0.789, respectively. The coefficient values for each variable and each dimension were greater than 0.7; thus the reliability of the questionnaire in this study was good. In addition, the CITC values (corrected item total correlation) between the observed variables and their latent variables were greater than the standard value of 0.5, thus indicating that the survey options for each latent variable were well set, i.e., the questionnaire reliability was good.
3.1.2. Structural Equation Model Fitting Index
According to the study hypothesis, with the help of AMOS 24.0 data analysis software, the X 2 /df value was 1.985, which is less than 3; the RMSEA was 0.031, which is less than the standard level of 0.08, indicating a good fit. gfi = 0.960, agfi = 0.949, nfi = 0.957, ifi = 0.978, cfi = 0.978, and tli= 0.974, all goodness-of-fit indicators, met the general criteria, indicating that the model developed in this study was valid and a good fit to the recovered data.
In addition, the KMO test values for the four latent variables were 0.824, 0.858, 0.884, and 0.862, which were all greater than the general criterion of 0.70, and the Bartlett’s sphericity test results also showed that the significance probability values were all 0.000 ( p < 0.01), so the null hypothesis of Bartlett’s sphericity test could also be rejected and the validity structure could be considered as being good.
3.2. Structural Equation Model Results
In this study, structural equation model path analysis was performed using AMOS 21.0 software, which led to the structural equation model path coefficient values and C.R. values ( Table 6 ).
| Research Hypothesis Path | Standardization Factor | Standard Error | t | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Environmental Awareness | → | Social Networks | 0.003 | 0.155 | 0.035 | 0.972 |
| Environmental Awareness | → | Social Trust | 0.198 | 0.145 | 2.905 | 0.004 |
| Environmental Awareness | → | Social Norms | 0.419 | 0.143 | 5.62 | *** |
| Environmental Awareness | → | Sense of Community Belonging | 0.208 | 0.139 | 3.156 | 0.002 |
| Environmental Awareness | → | Community volunteerism | 0.298 | 0.127 | 4.258 | *** |
| Habitat Quality | → | Social Networks | 0.503 | 0.109 | 6.589 | *** |
| Habitat Quality | → | Social Trust | 0.496 | 0.101 | 7.2 | *** |
| Habitat Quality | → | Social Norms | 0.284 | 0.09 | 4.136 | *** |
| Habitat Quality | → | Sense of Community Belonging | 0.561 | 0.1 | 8.198 | *** |
| Habitat Quality | → | Community volunteerism | 0.447 | 0.086 | 6.488 | *** |
| Environmental Awareness | → | Pro-environmental behavior | 0.246 | 0.072 | 2.785 | 0.005 |
| Habitat Quality | → | Pro-environmental behavior | 0.285 | 0.061 | 2.615 | 0.009 |
| Social Networks | → | Pro-environmental behavior | 0.019 | 0.016 | 0.464 | 0.643 |
| Social Trust | → | Pro-environmental behavior | 0.134 | 0.019 | 2.69 | 0.007 |
| Social Norms | → | Pro-environmental behavior | 0.102 | 0.022 | 2.01 | 0.044 |
| Sense of Community Belonging | → | Pro-environmental behavior | 0.156 | 0.022 | 2.685 | 0.007 |
| Community volunteerism | → | Pro-environmental behavior | 0.19 | 0.025 | 3.376 | *** |
Note: *** indicates p < 0.001; “→” indicates the influence path.
3.2.1. The Influence of Environmental Awareness on the Dimensions of Social Capital
The standardized path coefficient value for the influence of environmental awareness on social network was 0.003 (t-value = 0.035, p = 0.972 > 0.05), indicating that environmental awareness did not play a significant role in influencing social network ( Table 6 ). These results did not support H.1a.
The standardized path coefficient value for the influence of environmental awareness on social trust was 0.198 (t-value = 2.905, p = 0.004 < 0.01), indicating a significant positive effect of environmental awareness on social trust. These results supported H.1b. The standardized path coefficient value for the influence of environmental awareness on social norms was 0.419 (t-value = 5.62, p = 0.000 < 0.001), indicating a significant positive effect of environmental awareness on social norms. These results supported H.1c. The standardized path coefficient value for the influence of environmental awareness on community belonging was 0.208 (t-value = 3.156, p = 0.002 < 0.01), indicating a significant positive effect of environmental awareness on community belonging. These results supported H.1d. The standardized path coefficient value for the influence of environmental awareness on community voluntarism was 0.298 (t-value = 4.258, p = 0.000 < 0.001), indicating that environmental awareness has a significant positive effect on community voluntarism. These results supported H.1e ( Table 6 ).
3.2.2. The Impact of Habitat Quality on the Dimensions of Social Capital
The standardized path coefficient value for the influence of habitat quality on social networks was 0.503 (t-value = 6.589, p = 0.000 < 0.001), indicating a significant positive effect of habitat quality on social networks. These results did not support H.2a. The standardized path coefficient value for the influence of habitat quality on social trust was 0.496 (t-value = 7.2, p = 0.000 < 0.001), indicating a significant positive effect of habitat quality on social trust. These results supported H.2b.The standardized path coefficient value for the influence of habitat quality on social norms was 0.284 (t-value = 4.136, p = 0.000 < 0.001), indicating that habitat quality has a significant positive effect on social norms. These results supported H.2c.The standardized path coefficient value for the influence of habitat quality sense of community belonging was 0.561 (t-value = 8.198, p = 0.000 < 0.001), indicating a significant positive effect of habitat quality on community belonging. These results supported H.2d. The standardized path coefficient value for the influence of habitat quality community voluntarism was 0.447 (t-value = 6.488, p = 0.000 < 0.001), indicating a significant positive effect of habitat quality on community voluntarism. These results supported H.2e ( Table 6 ).
3.2.3. The Influence of Environmental Awareness on Pro-Environmental Behavior
The standardized path coefficient value for the influence of environmental awareness on pro-environmental behavior was 0.246 (t-value = 2.785, p = 0.005 < 0.01), which can prove that environmental awareness has a significant positive effect on pro-environmental behavior, i.e., environmental awareness can significantly and positively predict pro-environmental behavior. These results supported H.3 ( Table 6 ).
3.2.4. The Influence of Habitat Quality on Pro-Environmental Behavior
The standardized path coefficient value for the influence of habitat quality on pro-environmental behavior was 0.285 (t-value = 2.615, p = 0.009 < 0.01). That indicates a significant positive effect of habitat quality on pro-environmental behavior. These results supported H.4 ( Table 6 ).
3.2.5. The Influence of Social Capital on Pro-Environmental Behavior
The standardized path coefficient value for the influence of social network on pro-environmental behavior was 0.019 (t-value = 0.464, p = 0.643 > 0.05), indicating that the effect of social network on pro-environmental behavior did not pass the significance test, namely, the effect of social networks on pro-environmental behaviors. These results did not support H.5a ( Table 6 ).
The standardized path coefficient value for the influence of social trust on pro-environmental behavior was 0.134 (t-value = 2.69, p = 0.007 < 0.01), indicating a significant positive effect of social trust on pro-environmental behavior. The standardized path coefficient value for the influence of social norms on pro-environmental behavior was 0.102 (t-value = 2.01, p = 0.044 < 0.05), indicating a significant positive effect of social norms on significant positive effect. The standardized path coefficient value for the influence of community affiliation on pro-environmental behavior was 0.156 (t-value = 2.685, p = 0.007 < 0.01), this shows that community affiliation has a significant and positive impact on environmental behavior. These results supported H.5d. The standardized path coefficient value for the influence of community voluntarism on pro-environmental behavior was 0.19 (t-value = 3.376, p = 0.000 < 0.001), indicating that community voluntarism has a significant positive effect on pro-environmental behavior. These results supported H.5e ( Table 6 ).
3.2.6. The Mediating Effect of Social Capital
In order to verify whether there was a mediating effect of social capital in the influence path of environmental awareness and habitat environmental quality on pro-environmental behavior, the Bootstrap method in AMOS 21.0 software (IBM, New York, USA) was used to test the mediating effect, and then the mediating effect of each dimension of social capital in the influence mechanism of environmental awareness and habitat environmental quality on pro-environmental behavior was explored. The main analysis results are shown in Table 7 .
Bootstrap method-mediated effect test results.
| Intermediary Effect Hypothesis | Effect Value | Standard Error | Lower 95% Confidence Interval | Upper 95% Confidence Interval | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Environmental Awareness—Social Network—Pro-Environmental Behavior | 0.001 | 0.006 | −0.01 | 0.012 | 0.86 |
| Environmental awareness—Social trust—Pro-environmental behavior | 0.026 | 0.017 | 0.002 | 0.072 | 0.031 |
| Environmental Awareness—Social Norms—Pro-Environmental Behavior | 0.043 | 0.025 | 0.001 | 0.102 | 0.048 |
| Environmental awareness—sense of community belonging—pro-environmental behavior | 0.032 | 0.017 | 0.005 | 0.076 | 0.012 |
| Environmental Awareness—Community Voluntarism—Pro-Environmental Behavior | 0.057 | 0.027 | 0.015 | 0.124 | 0.004 |
| Habitat Quality—Social Network—Pro-Environmental Behavior | 0.01 | 0.024 | −0.036 | 0.063 | 0.677 |
| Habitat Quality—Social Trust—Pro-Environmental Behavior | 0.066 | 0.031 | 0.014 | 0.138 | 0.016 |
| Habitat Quality—Social Norms—Pro-Environmental Behavior | 0.029 | 0.018 | 0.001 | 0.075 | 0.044 |
| Habitat Quality—Community Belonging—Pro-Environmental Behavior | 0.087 | 0.038 | 0.012 | 0.169 | 0.017 |
| Habitat Quality—Community Voluntarism—Pro-Environmental Behavior | 0.085 | 0.034 | 0.031 | 0.172 | 0.001 |
Since neither environmental awareness on social networks nor social networks on pro-environmental behaviors played a significant role, the basic prerequisites of the mediating effect test were not satisfied, so no further mediating effect test was needed. However, in this study, the mediating effect was also tested in order to truly show the results. The results showed that the p -value of the mediating effect was greater than the standard 0.05, indicating that the mediating effect was not valid.
- (1) Social capital has a mediating effect between the influence of environmental awareness on pro-environmental behavior.
Firstly, the [environmental awareness—social trust—pro-environmental behavior] effect value of 0.026, with 95% confidence upper and lower intervals of [0.002–0.072], does not contain 0, and the p -value is less than the significance level of 0.05, indicating the presence of a mediating effect. These results supported H.6b. Secondly, the [environmental awareness—social norms—pro-environmental behavior] effect value of 0.043, with a 95% confidence interval above and below [0.001–0.102] does not contain 0, and the p -value is less than the significance level of 0.05, indicating the existence of a mediating effect. These results supported H.6c. Thirdly, the [environmental awareness—community belongingness—pro-environmental behavior] effect value of 0.032, with 95% confidence upper and lower intervals of [0.005–0.076] does not contain 0, and the p -value is less than the significance level of 0.05, indicating the existence of a mediating effect. These results supported H.6d.Fourthly, the effect value for [environmental awareness—community voluntarism—pro-environmental behavior] was 0.057, with an upper and lower 95% confidence interval of [0.015–0.124] not containing 0, and a p -value of less than the significance level of 0.05, indicating the presence of a mediating effect. These results supported H.6e.
- (2) Social capital has a mediating effect between the effects of habitat quality on pro-environmental behavior.
Firstly, the [habitat quality—social trust—pro-environmental behavior] effect value of 0.066, with 95% confidence upper and lower intervals of [0.014–0.138], does not contain 0, and the p -value is less than the significance level of 0.05, indicating the presence of a mediating effect. These results supported H.7b. Secondly, the [habitat quality—social norms—pro-environmental behavior] effect value of 0.029, with a 95% confidence interval above and below [0.001–0.075], does not contain 0, and the p -value is less than the significance level of 0.05, indicating the existence of a mediating effect. These results supported H.7c. Thirdly, the [habitat quality—community belongingness—pro-environmental behavior] effect value of 0.087, with a 95% confidence interval above and below [0.012–0.169], does not contain 0, and the p -value is less than the significant level of 0.05, indicating the existence of a mediating effect. These results supported H.7d. Fourthly, the effect value of [habitat quality—community voluntarism—pro-environmental behavior] is 0.085, the upper and lower 95% confidence interval of [0.031–0.172] does not contain 0, and the p -value is less than the significant level 0.05, indicating the existence of a mediating effect. These results supported H.7e. Habitat quality firstly acts directly on pro-environmental behavior, and secondly, it indirectly influences pro-environmental behavior with social trust, social norms, sense of community belonging, and community voluntarism. That is, social trust, social norms, community belongingness, and community voluntarism partially mediate the effect between habitat quality and pro-environmental behavior.
4. Discussion
This study focuses on the pro-environmental behavior of community residents, and constructs an analytical framework of “environmental awareness, habitat environment-social capital-pro-environmental behavior” from multiple perspectives, including external social environmental factors, situational factors, and internal social psychological factors. Using structural equation modeling, we analyzed the influence of environmental awareness and habitat on pro-environmental behavior. Based on this, we further verified the mediating effect of social capital dimensions in the influence mechanism of environmental awareness and habitat environment on pro-environmental behavior using the Bootstrap method. The main findings are as follows.
Regarding H1, environmental awareness has a significant effect on social trust, social norms, community belongingness, and community voluntarism in social capital. Among them, environmental awareness had the most significant effect on social norms, followed by community voluntarism, community belongingness, and social trust. Environmental awareness has no significant impact on social networks, which are not consistent with the results of Steg, L. et al., (2009) [ 46 ]. This may be due to the fact of that social networks are relatively stable social relationships formed by the interaction between residents, and in the complex social environment of “differential pattern” and vernacular relationship, the social network formed by the residents’ social interaction activities with their neighbors, relatives, and friends in their daily lives has a broad meaning. This network is usually fixed and will not change with changes in environmental awareness.
Regarding H2, the quality of the habitat environment has a direct effect on social capital and the most significant effect on the sense of community belonging, followed by social networks, social trust, and community voluntarism. However, the quality of the habitat environment has the least effect on social norms. This corroborates John A. K.’s view that the physical urban environment affects social capital formation [ 47 ]. The importance of habitat has also been confirmed by traditional Chinese cultural concepts. For example, in the Chinese idiom of “Anju Leye”, “Anju” is the basic condition for people to live and produce, and it is placed written first, indicating its importance: “Only when people live in peace can they live in happiness”.
Regarding H3, environmental awareness can significantly and positively predict pro-environmental behavior. This is consistent with the view put forward by Kang, M. et al., (2009) [ 48 ], which indicates that environmental awareness is one of the important driving factors affecting environment-friendly behavior. The mechanism of the effect may be as follows: first, the more community residents are inclined toward naturalistic concepts, the more likely they are to adopt daily environmental protection behaviors; second, community residents with more environmental knowledge will be more likely to understand the relationship between daily behaviors and environmental protection, and will also acquire more knowledge related to pro-environmental behaviors, thus driving people to adopt pro-environmental behaviors in their daily lives; third, when community residents have strong environmental values, they usually feel a high level of emotional attachment to the environment, develop a sense of closeness to the natural environment, take the initiative to connect with the natural world around them, and believe that they are closely related to the natural world around them. When this sense of connection to the environment increases, residents often increase their level of pro-environmental behavior [ 49 ].
Regarding H4, there was a significant positive effect of habitat quality on pro-environmental behavior. This conclusion is consistent with the view of Han, H. et al., (2017) [ 50 ] that the living environment is an external stimulus. When residents perceive the high-quality living environment, they will naturally restrict their own behavior, generate the mentality of environmental protection and make pro environmental behavior. The reason for this is that at high levels of habitat quality, residents choose to conform to environmental characteristics and self-regulate their own environmental behaviors [ 30 ], thus adopting pro-environmental behaviors; while at low levels of habitat quality, residents do not perceive external pressures on their inappropriate environmental behaviors and view them as normal and acceptable, thus inhibiting pro-environmental behaviors. In addition, a low level of habitat quality makes residents feel that pro-environmental behavior is difficult and ineffective, and therefore they will give up their personal efforts and choose to conform to the external environment, thus triggering inappropriate environmental behavior. On the other hand, high levels of habitat quality improve residents’ assessment of the effectiveness of their behaviors, thus leading them to adopt environmental behaviors [ 51 ].
Regarding H5, it shows that social trust, social norms, community belongingness, and community voluntarism in social capital can significantly promote residents’ pro-environmental behavior. The research conclusion confirms the opinion of Polyzou, E. et al., (2011) [ 52 ]. That is to say, the formation of social capital can guide the collective action of community members, and on this basis become a factor guiding individual action in the community, and also promote the pro-environmental behavior of community residents. Among them, the relationship between the effect size of each dimension of social capital is as follows: community voluntarism > community belongingness > social trust > social norms. The reason may be that if the degree of social capital is higher, community residents will be more active in complying with social norms, take the initiative to discipline their individual behavior, promote collective cooperation, and will monitor specific actions. When residents’ cognitive and moral beliefs are consistent with group norms, they identify with the group, making pro-environmental behavior a collective action of individuals with a common perspective (i.e., opinion-based group). In this process, residents have a stronger sense of emotional attachment to their community and are able to participate in community volunteerism, and help other residents for free, or are willing to help other residents for free, showing more positive pro-environmental behavior. Thus, increased awareness of environmental protection can produce good pro-environmental behaviors.
Regarding H6, the research results show that when the residents of a community are more environmentally conscious this motivates them to interact effectively on environmental issues, thus forming a collective environmental consciousness. Based on rational human assumption, individuals are more likely to display “free-rider” behaviors when making decisions, and enter into a collective action dilemma. This research result confirms the view of Putnam, R. D. et al., (1997) [ 53 ] that social capital is an important factor to encourage individuals to actively participate in cooperation and avoid the dilemma of collective action. Social capital is considered to be an important factor to motivate individuals to actively participate in cooperation and to avoid collective action dilemmas. When an awareness of group behavior is established, and under the influence of the mediating effect of social capital, it will have a positive impact on the pro-environmental behaviors of community residents. Therefore, while environmental awareness directly influences residents’ pro-environmental behaviors, it also indirectly influences their pro-environmental behaviors through the role of residents’ social capital. Therefore, the influence of environmental consciousness on pro-environmental behavior can be conveyed through environmental consciousness, and the logical relationship between the three is “environmental consciousness → social capital (social trust, social norms, community belonging, and community voluntarism) → pro-environmental behavior”.
Regarding H7, the mechanism of action may be that environmental awareness influences changes in residents’ social capital, which in turn promotes residents’ pro-environmental behavior. This research result is consistent with Petzold, J. et al., (2015) [ 54 ] and Hua, Y. et al., (2020) [ 54 , 55 ]. That is, satisfaction with the quality of the human environment will motivate community residents to interact effectively on environmental issues and be more willing to interact and communicate with each other. Based on the social exchange theory of reciprocity, in a peaceful community environment, residents will actively work for the well-being of their community, and the resulting emotional ties will stimulate the residents’ sense of community, which will increase their own social capital stock. In other words, social capital, as a collection of resources based on neighborhood interaction, trust, common ideas, and relationship networks, can promote residents’ spontaneous adoption of environmental sustainability protection behaviors and promote the construction of an environmental governance system with the joint participation of social organizations and residents.
In terms of samples, this study selected community residents in Jinan, Shandong Province. Jinan is one of the 15 sub-provincial cities in China, with a permanent population of 9.2024 million people. Therefore, the research conclusions drawn from Jinan City as a case area have certain reference value for exploring the problem of the pro-environment behavior of residents in large and medium-sized cities across the country. A more comprehensive studies in more places would further verify the generalization of the results found in this study. Therefore, more in-depth research needs to explore how to further refine the research framework and increase the number of completed spatial samples and questionnaires. Subsequently, in a future study, we will consider dividing pro-environmental behavior into multiple dimensions to explore the underlying mechanisms influencing the pro-environmental behavior of community residents in greater depth.
5. Conclusions
This study empirically analyzes the mechanism of environmental awareness and habitat quality on pro-environmental behavior, and identifies the important mediating effect of social capital. In other words, the social capital of community residents is influenced by the perception of individual environmental awareness and habitat quality; after taking on this influence, individuals will continue to act on their pro-environmental behavior. This study confirmed the multiple effects of environmental awareness as an internal personal psychological factor, habitat quality as an external contextual factor, and social capital as a social environmental factor on pro-environmental behavior.
For community residents, residents’ awareness of environmental issues affects their trust in society, their level of participation, etc., and makes it easy to build a sense of community with a particular environment in real life. Habitat is the spatial carrier of social capital formation, and with the satisfaction that community residents have with the habitat, they will implicitly internalize their sense of belonging to the community. As residents’ sense of belonging to the community and sense of community grows, social capital can be formed in spaces where community members can interact, and social capital is a “soft environment” that can improve the efficiency of social functioning and stimulate social vitality. This leads to civic behaviors that contribute to community development, which in turn promotes pro-environmental behaviors among community residents.
Based on this, the implementation of pro-environmental behaviors by community residents can be promoted from the following three aspects. One is to raise the environmental awareness of residents. Public education can be conducted in public places and government agencies on the current state of environmental protection, knowledge of protection, and significance and future development prospects, so that residents can understand the local environment, raise expectations for the achievement of group goals, and portray a better vision of collective efforts. The content of education should be relevant, practical, and actionable, so that residents can understand what they can do to have a beneficial impact on the environment. It is also important to expand residents’ knowledge of the environment, especially the knowledge and skills that can guide them in their daily environmental behavior. The second is to improve the quality of the habitat. The higher the quality of residents’ habitat environment, the greater the positive impact on pro-environmental behavior. Nowadays, local governments pay more attention to community hardware facilities, but relatively less investment in software facilities. Therefore, on top of focusing on hard environment construction, it is more important to pay attention to community human environment construction, to create a good cultural atmosphere for residents, and to create external conditions that are conducive to the implementation of pro-environmental behaviors. If these scenarios are described more specifically, contextual factors such as setting up convenient waste recycling bins for residents to separate garbage, and establishing an effective management system for residents to separate domestic waste are essential. These contextual factors will be an effective support for community residents to implement pro-environmental behaviors. The third is to cultivate the social capital of the population. To foster the concepts of altruism and social norms, we can actively carry out various popular education activities. To strengthen residents’ sense of belonging and identity to the area, communities can be guided to normalize various cultural and sports activities that stimulate the inner emotions. To enhance residents’ sense of dependence on the community, better community environmental and health conditions can be created, as well as better infrastructure conditions and community management conditions, so that the community can best meet the real needs of residents and become a warm community. In order to strengthen residents’ emotions towards the community, diversified community activities should be held and the public spaces for activities should be built. In addition, a platform for interaction to strengthen residents’ ties, reinforce collective memory, and eliminate barriers and strangeness should be provided.
Funding Statement
This research was funded by Social Science Planning and Research Project of Shandong, China (Grant NO. 22DGLJ32).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, W.S. and L.M.; methodology, W.S. and L.M.; software, W.S.; validation, L.M.; formal analysis, W.S.; investigation, W.S.; resources, W.S.; data curation, W.S.; writing—original draft preparation, W.S. and L.M.; writing—review and editing, W.S., C.J. and L.M.; visualization, W.S. and L.M.; supervision, W.S. and L.M.; project administration, W.S.; funding acquisition, W.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed consent statement.
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of interest.
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.

An official website of the United States government
Here’s how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock A locked padlock ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
JavaScript appears to be disabled on this computer. Please click here to see any active alerts .
Environmental Topics
Epa environmental topics.
EPA's environmental topics guides you to the most popular pages in your topic of interest.
Find EPA Articles and News Releases related to popular topics.
Search the A-Z Topic Index for specific terms.
- Kreyòl ayisyen

- Criteria (NAAQS) Air Pollutants
- Particulate Matter (PM)
- Greenhouse Gas (GHG) Emissions

Chemicals, Pesticides, and Toxics
- Chemicals under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA)
- Formaldehyde
- Managing Chemical Risks
- Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS)
Chemicals, Pesticides, and Toxics Topics

Environmental Information by Location
- Cleanups in My Community
- Environmental Justice in Your Community
- Radon Zones: Maps and Supporting Documents by State
- Toxic Chemical Releases
More Location-Specific Info

Greener Living
- Energy and the Environment
- Greener Products and Services
- Reduce, Reuse, Recycle
- Sustainability
Greener Living Topics

- Children's Health Protection
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- Endocrine Disruption
- Human Health Risk Assessment
- Pesticides and Food: Healthy, Sensible Food Practices
Health Topics

Land, Waste, and Cleanup
- Household Hazardous Waste (HHW)
- Learn About Hazardous Waste
Land, Waste, and Cleanup Topics

- Citizen Science for Environmental Protection
- Climate Change Indicators
- Environmental Measurements and Modeling
- EPA Science Models and Research Tools (SMaRT) Search
- Research at EPA
- Research Grants
More Science Topics

- Drinking Water Basics
- Lakes and Rivers
- Local Water Quality Reports
- National Aquatic Resource Surveys
- Wastewater Treatment
Water Topics

More Environmental Topics
- Climate Change
- Children's Health
- Environmental Justice
- Pesticides
EPA Articles and News Releases
Recent EPA Perspectives Articles:

Activating the Building Blocks of Sustainability
One thing I’ve learned through my work with local communities is that they love celebrating what makes them unique. I love learning what they are most proud of and helping them turn their greatest assets into actions that matter for their community.
- Date: July 1, 2024
- By: Chip Gurkin

Urban Golf and the Partnerships for Progress
In many ways golf is more than just a game. There’s a special place, right down the street from our Region 3 office in Center City Philadelphia, that is reimaging how kids can experience greenspaces.
- Date: May 3, 2024
- By: Hunter Pates

For Local Communities, the Sky is the Limit
Local Foods, Local Places' community-driven approach unleashes local creative minds to envision innovative paths to overcome the complex legacies of social and environmental problems and inequities.
- Date: April 18, 2024
- By: John Foster
Recent EPA News Releases:
EPA Invites Public Comment on Review that Shows Progress and Need for More Data After Historic Hudson River PCB Cleanup
EPA to hold a virtual informational meeting on August 21; Public can comment on draft report until October 8
EPA News Release: EPA Invites Public Comment on Review that Shows Progress and Need for More Data After Historic Hudson River PCB Cleanup
- Release Date: July 10, 2024
EPA Selects Neighborhood House in Milwaukee to Receive $100,000 to Support Educational Projects
EPA News Release: EPA Selects Neighborhood House in Milwaukee to Receive $100,000 to Support Educational Projects
- Release Date: July 9, 2024
Biden-Harris Administration Establishes Four Stormwater Centers of Excellence with $5 Million in Grants under Investing in America Agenda
EPA News Release: Biden-Harris Administration Establishes Four Stormwater Centers of Excellence with $5 Million in Grants under Investing in America Agenda
EPA Selects Mississippi State University Extension to receive $100,000 in funding to support Environmental Education in Jackson and across Mississippi
EPA News Release: EPA Selects Mississippi State University Extension to receive $100,000 in funding to support Environmental Education in Jackson and across Mississippi
Environmental research paper topics
Climate change research paper topics, conservation biology research paper topics, sustainable development research paper topics, renewable energy research paper topics, biodiversity conservation research paper topics, pollution control research paper topics, green technology research paper topics, oceanography research paper topics, environmental ethics research paper topics.
- Modern environmental issues research paper topics
Writing Metier has also been doing deep research to ensure that if a customer asks our writers to write about this topic, the paper will be based on up-to-date facts and information.
Research paper topics on Environmental Science and Sustainability
I’ll provide you with ten research paper topics and RQs ideas for each of the abovementioned categories related to ESS . Let’s start with the first one.
Global warming, deforestation, and the effectiveness of renewable energy sources have become widely discussed topics among environmentalists. The number of studies devoted to these areas of science has also increased, drawing more public attention.
- Research Question: How is climate change affecting biodiversity in different ecosystems?
- Overview: Analyze the effects of temperature changes, extreme weather events, and altered habitats on species diversity and ecosystem health.
- Research Question: What are the most effective sustainable agriculture practices for reducing environmental impact?
- Overview: Investigate methods such as crop rotation, organic farming, and agroforestry, and their effects on soil health, water use, and biodiversity.
- Research Question: How can renewable energy sources be optimized to replace fossil fuels?
- Overview: Explore advancements in solar, wind, hydro, and geothermal energy technologies, focusing on efficiency, cost, and environmental benefits.
- Research Question: What are the main causes of deforestation, and how effective are reforestation efforts in mitigating its impact?
- Overview: Examine deforestation drivers such as agriculture and logging, and assess reforestation projects’ success in restoring ecosystems and carbon sequestration.
- Research Question: What are the sources and impacts of plastic pollution on marine environments, and what solutions exist?
- Overview: Study the extent of plastic pollution, its effects on marine life and ecosystems, and potential mitigation strategies such as biodegradable plastics and cleanup initiatives.
- Research Question: How does urbanization affect local and global environments, and what sustainable urban planning practices can mitigate these effects?
- Overview: Investigate the environmental consequences of urban sprawl, including habitat destruction and pollution, and explore sustainable urban planning solutions like green spaces and public transport.
- Research Question: What are the main causes of water scarcity, and how can sustainable water management practices address this issue?
- Overview: Analyze factors contributing to water scarcity, such as overuse and climate change, and evaluate water management practices like conservation, desalination, and watershed management.
- Research Question: How do wetlands contribute to ecosystem services, and what threats do they face?
- Overview: Examine the ecological functions of wetlands, such as water filtration and habitat provision, and discuss threats like drainage and pollution, along with conservation strategies.
- Research Question: What are the main sources of air pollution, and how does it affect public health?
- Overview: Study the pollutants’ sources, such as transportation and industry, their health impacts, including respiratory diseases, and policies aimed at reducing air pollution.
- Research Question: What are the most effective methods for managing waste sustainably?
- Overview: Explore waste reduction, recycling, composting, and waste-to-energy technologies, assessing their environmental and economic benefits.
Global warming has become one of the most devastating threats to Earth’s existence. Ice glaciers are melting in Antarctica at an alarming rate, which, in turn, may cause irreversible damage to Earth’s fauna and flora.
- Research Question: How is climate change affecting the polar ice caps, and what are the implications for global sea levels?
- Overview: Investigate the rate of ice melt in the Arctic and Antarctic, the contributing factors, and the projected impacts on sea level rise and coastal communities.
- Research Question: How is climate change influencing the frequency and intensity of extreme weather events?
- Overview: Analyze the links between global warming and events such as hurricanes, droughts, and heatwaves, and their implications for ecosystems and human societies.
- Research Question: What are the effects of ocean acidification on marine ecosystems?
- Overview: Explore the causes of ocean acidification, its impact on marine species, particularly those with calcium carbonate shells, and potential mitigation strategies.
- Research Question: How does climate change impact global food security, and what adaptation strategies can be employed?
- Overview: Examine the effects of changing climate conditions on agricultural productivity, food distribution, and the potential adaptation strategies to ensure food security.
- Research Question: How can forest conservation and reforestation contribute to climate change mitigation?
- Overview: Investigate the carbon sequestration capabilities of forests, the impact of deforestation, and the benefits of reforestation and afforestation efforts.
- Research Question: How effective are international agreements, such as the Paris Agreement, in addressing climate change?
- Overview: Analyze the goals and commitments of major international climate agreements, their implementation, and their effectiveness in reducing global greenhouse gas emissions.
- Research Question: What are the health impacts of climate change, and how can public health systems adapt?
- Overview: Study the direct and indirect health effects of climate change, including heat-related illnesses, vector-borne diseases, and mental health issues, and discuss adaptation strategies.
- Research Question: How can the adoption of renewable energy sources help mitigate climate change?
- Overview: Explore the potential of renewable energy technologies such as solar, wind, and geothermal to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and their integration into energy systems.
- Research Question: What are the economic implications of climate change for different sectors and regions?
- Overview: Analyze the economic costs of climate change, including impacts on agriculture, infrastructure, and healthcare, and discuss strategies for economic resilience and adaptation.
- Research Question: How can effective communication strategies improve public understanding and action on climate change?
- Overview: Investigate the role of media, education, and policy in shaping public perception of climate change, and explore methods to enhance climate literacy and motivate action.
Understanding the underlying causes that accelerate climate change has become critical these days. The more accurate and profound research on the topic, the more insights about the potential causes and solutions to the problem.
Breathe Easy! We’re Handling Your Paper
- Polished Papers : Styled right, glitch-free
- Ask Away : Direct chat with your writer
- Free Goodies : Revisions, title page, and bib
- Fair Prices : Plus a money-back guarantee
- All Human : No AI, just real experts
- Private & Secure : Your details, our secret
Bye-Bye, Burnout!
Slash 15% OFF using the coupon code: BLG15WM

Many animals are on the brink of extinction, and many are considered to be in the vulnerable group list. Conserving and protecting nature and other animal lives is not only to ensure diverse life forms on Earth but also to ensure our guaranteed future. Without animals and plants, the Earth would also become inhabitable to us.
- Research Question: How do wildlife corridors mitigate the effects of habitat fragmentation on biodiversity?
- Overview: Explore the impacts of habitat fragmentation on wildlife populations and ecosystems, and evaluate the effectiveness of wildlife corridors in promoting genetic diversity and species migration.
- Research Question: What are the key components of successful endangered species recovery programs?
- Overview: Investigate various recovery programs, focusing on habitat restoration, captive breeding, and legal protections, and assess their success in increasing endangered species populations.
- Research Question: How can genetic tools be used to inform conservation strategies for threatened species?
- Overview: Examine the applications of genetic diversity analysis, population structure studies, and genetic rescue techniques in conserving genetic variability and reducing inbreeding in small populations.
- Research Question: What role do marine protected areas play in conserving marine biodiversity?
- Overview: Analyze the effectiveness of MPAs in protecting marine ecosystems, preserving fish stocks, and enhancing biodiversity, and discuss challenges in their implementation and management.
- Research Question: How can the spread of invasive species be controlled to protect native biodiversity?
- Overview: Investigate the ecological impacts of invasive species on native ecosystems, and evaluate various management strategies such as biological control , habitat restoration, and public awareness campaigns.
- Research Question: How can conservation strategies be adapted to address the impacts of climate change on biodiversity?
- Overview: Explore the effects of climate change on species distribution, habitat suitability, and ecosystem resilience, and discuss adaptive management approaches to enhance conservation efforts.
- Research Question: What are the benefits and challenges of community-based conservation approaches?
- Overview: Examine the role of local communities in biodiversity conservation, focusing on participatory management, traditional ecological knowledge, and the integration of socio-economic benefits with conservation goals.
- Research Question: How does rewilding contribute to ecosystem restoration and biodiversity conservation?
- Overview: Investigate the principles and practices of rewilding, including the reintroduction of keystone species and the restoration of natural processes, and assess its effectiveness in rebuilding resilient ecosystems.
- Research Question: How are biodiversity hotspots identified, and why are they important for conservation efforts?
- Overview: Explore the criteria used to designate biodiversity hotspots, their significance in global conservation strategies, and the challenges in protecting these critical areas.
- Research Question: What are the key conservation policies and legislations that support biodiversity protection, and how effective are they?
- Overview: Analyze major international, national, and local conservation policies and legislations, such as the Endangered Species Act and CITES, and evaluate their impact on biodiversity conservation.
Thus, conservation biology and research on this aspect require extra attention from experts and other members of society, including students.
Economics is growing ever-increasingly, causing more and more damage to surrounding nature. Creating eco-friendly buildings and factories is the only possible solution to decrease the toxic gas emissions into the environment.
- Research Question: How can urban planning incorporate sustainable development principles to create livable cities?
- Overview: Explore strategies for integrating green spaces, sustainable transportation, energy-efficient buildings, and waste management systems in urban planning to enhance quality of life and reduce environmental impact.
- Research Question: What role do renewable energy sources play in promoting sustainable development?
- Overview: Investigate the benefits and challenges of transitioning to renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, and hydro, and their contributions to reducing carbon emissions and fostering economic growth.
- Research Question: How can sustainable agriculture practices improve food security and environmental health?
- Overview: Examine methods such as crop rotation, agroforestry, organic farming, and precision agriculture, focusing on their impact on soil health, biodiversity, and productivity.
- Research Question: What are the key principles of a circular economy, and how can they be applied to waste management?
- Overview: Discuss the concepts of reduce, reuse, and recycle within a circular economy framework, and explore successful case studies in waste reduction and resource efficiency.
- Research Question: How are countries progressing towards the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)?
- Overview: Analyze the strategies and policies implemented by various countries to achieve SDGs, focusing on areas such as poverty reduction, clean water, and education, and assess their effectiveness.
- Research Question: How can sustainable tourism practices benefit both the environment and local communities?
- Overview: Investigate approaches to sustainable tourism, including eco-tourism, community-based tourism, and green certifications, and their impact on conservation efforts and economic development.
- Research Question: How do corporate social responsibility initiatives contribute to sustainable development?
- Overview: Explore the role of CSR in promoting sustainable business practices, reducing environmental footprints, and enhancing social well-being , with examples from various industries.
- Research Question: What are the best practices for sustainable water management to address water scarcity?
- Overview: Examine techniques for water conservation, such as efficient irrigation, rainwater harvesting, and wastewater treatment, and their role in ensuring sustainable water use.
- Research Question: What challenges and opportunities exist for sustainable development in developing countries?
- Overview: Analyze the socio-economic and environmental barriers to sustainable development in developing regions, and explore initiatives that promote economic growth while preserving natural resources.
- Research Question: How can communities build climate resilience through sustainable development practices?
- Overview: Investigate strategies for enhancing resilience to climate change impacts, such as sustainable infrastructure, ecosystem-based adaptation, and community engagement, and their benefits for long-term sustainability.
Finding more sustainable energy sources and building more sustainable buildings and infrastructures may ensure our existence on Earth.
As we know, natural resources, such as gas, oil, and coal, are not infinite; sooner or later, we will have to find other energy sources. Modern societies have started using more renewable energy sources such as wind, sun, water, etc. Unlike traditional energy sources, creating energy from these sources is far safer.
- Research Question: What are the latest technological advancements in solar energy, and how do they improve efficiency and affordability?
- Overview: Explore innovations in photovoltaic cells, solar panel materials, and energy storage solutions that enhance the efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and scalability of solar energy systems.
- Research Question: How can wind energy potential be maximized, and what are the challenges associated with wind power generation?
- Overview: Investigate the factors affecting wind energy efficiency, such as turbine design, site selection, and grid integration, and discuss the environmental and social impacts of wind farms.
- Research Question: How does hydropower development impact aquatic ecosystems, and what mitigation strategies can be employed?
- Overview: Examine the ecological effects of dams and hydroelectric plants on river systems, fish populations, and water quality, and explore methods to minimize environmental disruption.
- Research Question: What are the benefits and drawbacks of bioenergy as a renewable energy source, and how can its sustainability be ensured?
- Overview: Analyze the production of bioenergy from biomass, including biofuels and biogas, and discuss the environmental, social, and economic implications of large-scale bioenergy use.
- Research Question: How can geothermal energy be effectively harnessed for sustainable power generation?
- Overview: Explore the technologies used in geothermal energy extraction, including ground source heat pumps and enhanced geothermal systems, and assess their potential and limitations.
- Research Question: What policies and incentives are most effective in promoting the adoption of renewable energy?
- Overview: Investigate government policies, subsidies, and market mechanisms that support renewable energy development, and evaluate their impact on accelerating the transition to clean energy.
- Research Question: How can hybrid renewable energy systems improve reliability and efficiency in power generation?
- Overview: Examine the integration of multiple renewable energy sources, such as solar-wind or solar-geothermal hybrids, and discuss their advantages in enhancing energy stability and efficiency.
- Research Question: What are the latest advancements in energy storage technologies for renewable energy, and how do they address intermittency issues?
- Overview: Explore various energy storage methods, including batteries, pumped hydro storage, and thermal storage, and their role in ensuring a stable and reliable renewable energy supply.
- Research Question: What is the potential of ocean energy sources like tidal and wave power, and what are the technical and environmental challenges?
- Overview: Investigate the technologies used to harness tidal and wave energy, their potential contributions to the energy mix, and the environmental impacts and logistical challenges involved.
- Research Question: How do community-based renewable energy projects contribute to local sustainability and energy independence?
- Overview: Analyze the benefits and challenges of community-led renewable energy initiatives, focusing on local engagement, economic development, and the creation of resilient energy systems.
Another important issue in implementing renewable energy sources into extensive usage is raising awareness among people to make them start using those sustainable energy sources. It is only possible to imagine modern life with electricity and its benefits; thus, employing much more eco-friendly energy sources will benefit Earth and us.
How many animals are on the verge of extinction, and how many are almost extinct? According to science, the extinction of certain animals is a natural phenomenon; however, these days, the extinction rate exceeds all the previous ones. More and more animals are disappearing because of human consumerism behavior.
- Research Question: How can genetic diversity be preserved in endangered species populations?
- Overview: Explore methods such as captive breeding, genetic rescue, and habitat management to maintain and enhance genetic diversity in small and fragmented populations.
- Research Question: What are the effects of habitat destruction on biodiversity, and how can these impacts be mitigated?
- Overview: Investigate the consequences of habitat loss and fragmentation on species richness and ecosystem function, and discuss strategies for habitat restoration and conservation.
- Research Question: How effective are protected areas in conserving biodiversity, and what factors influence their success?
- Overview: Examine the design, management, and effectiveness of protected areas, and assess their role in safeguarding ecosystems and species.
- Research Question: What are the threats to pollinators, and how can their habitats be conserved to ensure ecosystem services?
- Overview: Explore the decline of pollinator populations, the factors contributing to their decline, and conservation strategies such as habitat restoration and sustainable agricultural practices.
- Research Question: How do community-based conservation initiatives contribute to biodiversity conservation?
- Overview: Investigate the role of local communities in conservation efforts, focusing on participatory approaches, traditional knowledge, and the integration of conservation and livelihood goals.
- Research Question: How does climate change affect biodiversity, and what adaptive strategies can be employed to mitigate these impacts?
- Overview: Analyze the effects of climate change on species distribution, migration patterns, and ecosystem dynamics, and discuss adaptive management practices to enhance resilience.
- Research Question: What are the impacts of invasive species on native biodiversity, and how can they be effectively managed?
- Overview: Explore the ecological and economic impacts of invasive species, and evaluate management strategies such as biological control , habitat restoration, and public awareness campaigns.
- Research Question: What are the key challenges in conserving marine biodiversity, and how can they be addressed?
- Overview: Investigate threats to marine ecosystems, such as overfishing, pollution, and climate change, and discuss conservation strategies like marine protected areas, sustainable fisheries, and habitat restoration.
- Research Question: How effective are biodiversity offsetting and conservation banking in mitigating the impacts of development on biodiversity?
- Overview: Examine the principles and practices of biodiversity offsetting and conservation banking, their implementation, and their effectiveness in achieving conservation goals.
- Research Question: How can restoration ecology contribute to biodiversity recovery in degraded ecosystems?
- Overview: Explore techniques and strategies for restoring degraded habitats, including reforestation, wetland restoration, and invasive species removal, and assess their success in promoting biodiversity recovery.
Accordingly, studying some methods to find the most effective ones for biodiversity conservation is stupendous. Currently, many research papers are exploring the methods and ways to protect biodiversity on Earth. They provide some insights into what ordinary people can do not to cause even more damage to nature.
Air pollution, soil pollution, noise pollution, water pollution, and many other types of pollution are added to the list, but all of the mentioned need to be solved completely. The devastating causes of these types of pollution become evident in every facet of modern human life, ranging from animal extinction to fatal diseases.
- Research Question: What are the most effective strategies for mitigating air pollution in urban areas?
- Overview: Explore various air pollution control methods such as emission reductions, the use of renewable energy, implementation of green spaces, and policies aimed at reducing vehicular and industrial emissions.
- Research Question: How can industrial and agricultural practices be modified to prevent water pollution?
- Overview: Investigate the sources of water pollution from industrial and agricultural activities and examine techniques such as waste treatment, sustainable farming practices, and policy interventions to prevent contamination.
- Research Question: What are the most effective approaches for managing plastic waste to reduce environmental pollution?
- Overview: Analyze the challenges of plastic waste management, including recycling, biodegradation, and alternative materials, and evaluate the effectiveness of these approaches in reducing plastic pollution.
- Research Question: How can soil contamination be effectively remediated to restore ecosystem health?
- Overview: Examine the causes and effects of soil contamination, and explore remediation techniques such as phytoremediation, bioremediation, and soil washing to restore contaminated lands.
- Research Question: What are the environmental impacts of heavy metals, and how can their pollution be controlled?
- Overview: Investigate the sources and effects of heavy metal pollution on ecosystems and human health, and evaluate control measures such as pollution prevention, treatment technologies, and regulatory policies.
- Research Question: What are the effective measures for controlling noise pollution in urban environments?
- Overview: Explore the sources and impacts of noise pollution, and discuss control measures such as urban planning, noise barriers, and policies to reduce noise from transportation and industrial activities.
- Research Question: How can greenhouse gas emissions be effectively reduced to mitigate climate change?
- Overview: Examine strategies for reducing greenhouse gas emissions, including the transition to renewable energy, energy efficiency improvements, carbon capture and storage, and policy frameworks like carbon pricing.
- Research Question: What are the impacts of chemical pollution on aquatic ecosystems, and how can it be controlled?
- Overview: Analyze the sources and effects of chemical pollutants, such as pesticides and pharmaceuticals, on water bodies, and explore methods for controlling and mitigating their impact.
- Research Question: What pollution control technologies can be implemented in manufacturing industries to minimize environmental impact?
- Overview: Investigate various pollution control technologies used in manufacturing, such as scrubbers, filters, and waste treatment processes, and assess their effectiveness in reducing industrial pollution.
- Research Question: How can urban waste management systems be improved to reduce environmental pollution?
- Overview: Explore the challenges and solutions for urban waste management, including recycling programs, waste-to-energy technologies, and policies aimed at reducing waste generation and improving disposal practices.
Pollution control, especially in developing countries, has become a problem that cannot be delayed anymore. The earlier the effective measures are taken, the less the irreversible damage will be.

Green technology focuses on developing equipment , products, and systems that are entirely eco-friendly. Such technology aims to decrease the damaging impact on nature caused by aggressive human activities. Green technologies suggest using renewable energy sources, less harmful products (such as paper bags instead of plastic ones), etc.
- Research Question: What are the latest advancements in solar panel technology to improve efficiency and reduce costs?
- Overview: Investigate new materials, designs, and manufacturing techniques for photovoltaic cells that enhance solar energy conversion efficiency and decrease production costs.
- Research Question: How do electric vehicles contribute to sustainable transportation, and what are the challenges in their widespread adoption?
- Overview: Explore the environmental benefits of electric vehicles (EVs), the development of charging infrastructure, battery technology advancements, and barriers to EV adoption.
- Research Question: What are the most effective green building technologies for reducing energy consumption and environmental impact?
- Overview: Examine sustainable building practices, including energy-efficient HVAC systems, green roofs, sustainable materials, and smart building management systems.
- Research Question: How have recent advancements in wind turbine design improved energy production and efficiency?
- Overview: Explore innovations in turbine blade design, materials, and aerodynamics that enhance wind energy capture, as well as advancements in offshore wind technology.
- Research Question: What are the latest developments in bioenergy and biomass conversion technologies for sustainable energy production?
- Overview: Investigate methods for converting biomass into biofuels and biogas, including anaerobic digestion, pyrolysis, and fermentation, and their potential to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
- Research Question: How does smart grid technology facilitate the integration of renewable energy sources into the power grid?
- Overview: Examine the role of smart grids in managing energy flow, enhancing grid stability, and optimizing the use of renewable energy through real-time data and advanced control systems.
- Research Question: What are the most promising methods for producing green hydrogen, and what are their potential applications?
- Overview: Explore techniques for producing hydrogen using renewable energy sources, such as electrolysis powered by solar and wind, and discuss applications in transportation, industry, and energy storage.
- Research Question: How effective are carbon capture and storage technologies in reducing carbon emissions, and what are the challenges in their implementation?
- Overview: Investigate the principles and methods of CCS, including post-combustion, pre-combustion, and oxy-fuel combustion, and assess their feasibility and scalability.
- Research Question: What are the latest sustainable technologies for water purification, and how do they address water scarcity issues?
- Overview: Examine advancements in water purification methods such as membrane filtration, solar distillation, and biofiltration, focusing on their efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and environmental impact.
- Research Question: How can green computing practices and energy-efficient data centers reduce the environmental footprint of IT operations?
- Overview: Explore strategies for reducing energy consumption in data centers, including server virtualization, advanced cooling techniques, and the use of renewable energy sources for powering IT infrastructure.
Oceans bear historical secrets tracing back millions of years ago. Getting deeper into understanding the oceans may give clues to many questions considered to be unanswerable.
- Research Question: How is climate change affecting the patterns and strength of ocean currents?
- Overview: Investigate the influence of global warming on major ocean currents like the Gulf Stream and the Antarctic Circumpolar Current, and their implications for global climate and marine ecosystems.
- Research Question: What are the sources and impacts of marine pollution on marine organisms and ecosystems?
- Overview: Examine pollutants such as plastics, oil spills, heavy metals, and agricultural runoff, and their effects on marine biodiversity, food webs, and ecosystem health.
- Research Question: What are the main causes of coral reef degradation, and what conservation strategies are most effective?
- Overview: Analyze factors such as ocean acidification, warming waters, overfishing, and pollution that contribute to coral reef decline, and explore restoration and protection efforts.
- Research Question: What have recent deep-sea exploration missions revealed about biodiversity in the deep ocean?
- Overview: Discuss the discoveries made by deep-sea submersibles and ROVs, including new species, unique ecosystems, and the adaptations of deep-sea organisms to extreme environments.
- Research Question: How is ocean acidification affecting marine ecosystems, particularly calcifying organisms?
- Overview: Investigate the causes of ocean acidification, its impact on shell-forming species like mollusks and corals, and the broader implications for marine food webs and ecosystems.
- Research Question: What are the contributing factors to sea level rise, and how is it impacting coastal erosion and human settlements?
- Overview: Explore the effects of melting ice caps and thermal expansion on sea levels, the resulting coastal erosion, and the adaptation strategies for affected communities.
- Research Question: How effective are marine protected areas in conserving marine biodiversity?
- Overview: Evaluate the design, management, and enforcement of MPAs, and assess their success in protecting habitats, restoring fish populations, and preserving marine biodiversity.
- Research Question: What are the sources and ecological impacts of microplastics in marine environments?
- Overview: Examine the distribution and accumulation of microplastics in the ocean, their effects on marine organisms, and potential mitigation strategies.
- Research Question: How do oceans contribute to carbon sequestration, and what is their role in mitigating climate change?
- Overview: Investigate the processes of carbon uptake and storage in oceanic systems, including biological and physical pumps, and their importance in the global carbon cycle.
- Research Question: What are the ecological consequences of overfishing, and what measures can be implemented to ensure sustainable fisheries?
- Overview: Analyze the impacts of overfishing on marine species and ecosystems, and explore management strategies such as quotas, marine reserves, and sustainable fishing practices.
Currently, more researchers are interested in revealing the secrets that oceans try to conceal.
What are environmental ethics when new policies are made? Animal rights protection in the modern world, climate change mitigation, and adaptation are the most commonly debated topics when discussing environmental ethics. As mentioned earlier, those and many other similar issues should be effectively addressed when conducting any environmental research.
- Research Question: Who holds the ethical responsibility for addressing climate change, and how should this responsibility be distributed?
- Overview: Examine the roles of individuals, corporations, and governments in mitigating climate change, and discuss ethical frameworks for distributing responsibility and accountability.
- Research Question: How do environmental ethics intersect with animal rights, and what are the implications for conservation practices?
- Overview: Explore ethical considerations regarding the treatment of animals within conservation efforts, including the balance between species preservation and individual animal welfare.
- Research Question: What ethical principles should guide sustainable development to ensure fairness to future generations?
- Overview: Investigate the concept of intergenerational justice, focusing on how current environmental policies and practices impact the well-being and resources available to future generations.
- Research Question: How can environmental justice be achieved to ensure equitable access to a healthy environment for all communities?
- Overview: Analyze the disproportionate environmental burdens faced by marginalized communities and discuss strategies for promoting environmental equity and justice.
- Research Question: What are the ethical implications of using geoengineering technologies to combat climate change?
- Overview: Examine the potential benefits and risks of geoengineering methods such as solar radiation management and carbon dioxide removal, and discuss the moral considerations surrounding their deployment.
- Research Question: What ethical obligations do corporations have to minimize their environmental impact, and how can these obligations be enforced?
- Overview: Explore the concept of corporate environmental responsibility, focusing on ethical practices, corporate social responsibility (CSR) initiatives, and regulatory frameworks.
- Research Question: How do indigenous environmental ethics contribute to contemporary conservation practices?
- Overview: Investigate the principles of indigenous environmental ethics, their emphasis on harmony with nature, and the integration of traditional ecological knowledge into modern conservation efforts.
- Research Question: What are the ethical considerations in prioritizing certain species or ecosystems for conservation?
- Overview: Discuss the moral dilemmas involved in conservation prioritization, including species triage, ecosystem services, and the intrinsic value of biodiversity.
- Research Question: How should water resources be ethically allocated to balance human needs and ecological sustainability?
- Overview: Examine the ethical principles guiding water rights and allocation, focusing on issues such as access to clean water, ecosystem preservation, and the rights of indigenous communities.
- Research Question: What ethical responsibilities do consumers have in reducing their environmental impact through sustainable consumption?
- Overview: Explore the role of ethical consumerism in promoting sustainability, including the impact of lifestyle choices, eco-labeling, and the promotion of sustainable products and practices.
Modern environmental issues and sustainable economy topics
Time to also check the latest trends and problems related to environmental issues and sustainable economy. Select the topic that suits you better!
- Research Question: How is the development of green hydrogen technology contributing to sustainable energy systems?
- Overview: Explore advancements in green hydrogen production, storage, and applications in various industries, and assess its potential to decarbonize energy systems.
- Research Question: What are the latest innovations in carbon capture and utilization technologies, and how do they impact greenhouse gas emissions?
- Overview: Investigate recent developments in CCU technologies, their effectiveness in reducing carbon emissions, and their economic and environmental benefits.
- Research Question: How are regenerative agriculture practices being adopted to enhance soil health and combat climate change?
- Overview: Examine the principles of regenerative agriculture, including cover cropping, no-till farming, and agroforestry, and their impact on soil carbon sequestration and biodiversity.
- Research Question: How are smart grid technologies facilitating the integration of renewable energy sources?
- Overview: Explore the role of smart grids in managing energy flow, enhancing grid stability, and optimizing renewable energy usage through real-time data and advanced control systems.
- Research Question: What is the role of sustainable finance and green bonds in promoting environmental sustainability?
- Overview: Investigate the growth of sustainable finance markets, the issuance of green bonds, and their impact on funding renewable energy projects and sustainable development initiatives.
- Research Question: How are circular economy initiatives being implemented to reduce waste and promote resource efficiency?
- Overview: Analyze the principles of the circular economy, focusing on recent case studies of waste reduction, recycling, and product lifecycle management in various industries.
- Research Question: What advancements in electric mobility and infrastructure are driving the transition to sustainable transportation?
- Overview: Explore developments in electric vehicle technology, charging infrastructure, and policy incentives, and assess their impact on reducing transportation-related emissions.
- Research Question: How are smart city technologies contributing to sustainable urban development?
- Overview: Examine the integration of IoT, data analytics, and green infrastructure in urban planning to improve energy efficiency, reduce pollution, and enhance quality of life in cities.
- Research Question: What are the latest trends in using nature-based solutions to enhance climate resilience?
- Overview: Investigate the implementation of nature-based solutions such as reforestation, wetland restoration, and green infrastructure to mitigate climate impacts and protect ecosystems.
- Research Question: How are sustainable aquaculture practices being developed to meet growing food demands while protecting marine ecosystems?
- Overview: Explore innovations in aquaculture, including integrated multi-trophic aquaculture (IMTA), recirculating aquaculture systems (RAS), and their environmental benefits.
- Research Question: How is blockchain technology enhancing supply chain transparency and sustainability?
- Overview: Examine the use of blockchain to track and verify sustainable practices in supply chains, reduce fraud, and ensure the ethical sourcing of materials.
- Research Question: What are the latest advancements in designing climate-resilient infrastructure?
- Overview: Investigate new materials, construction techniques, and planning strategies that enhance the resilience of infrastructure to extreme weather events and climate change.
- Research Question: How are waste-to-energy technologies contributing to sustainable waste management?
- Overview: Explore recent advancements in converting waste into energy, including anaerobic digestion, pyrolysis, and gasification, and their role in reducing landfill use and generating renewable energy.
- Research Question: How are companies incorporating ESG criteria into their business strategies to promote sustainability?
- Overview: Analyze the integration of ESG factors into corporate decision-making, investor behavior, and the impact on long-term sustainability and financial performance.
- Research Question: What is the role of microgrids in enhancing energy security and sustainability?
- Overview: Investigate the development of microgrids, their applications in remote and urban areas, and their benefits in providing reliable, sustainable, and resilient energy solutions.
The topics mentioned above may sound complicated and too difficult to handle, but by trusting professional writers, you can engage in your other tasks with peace of mind. We guarantee not only free-of-mistake content but also uniqueness. We always create research papers from scratch based on updated information.
Need a Dope Paper Written? We've Got Your Back!
So, if you are looking for a reputable and reliable writing service, you are highly recommended to check our services.
Select ESS RP Topics Wisely
Being in the market for a long time, our academic writing service is considered one of the top. We offer high-quality papers free of any mistakes and unique content. Top-notch services are available for affordable prices, so you do not need to worry about the high prices with us.
Free topic suggestions
Laura Orta is an avid author on Writing Metier's blog. Before embarking on her writing career, she practiced media law in one of the local media. Aside from writing, she works as a private tutor to help students with their academic needs. Laura and her husband share their home near the ocean in northern Portugal with two extraordinary boys and a lifetime collection of books.
Similar posts
100+ ib extended essay topic ideas for your ease.
One of the very important requirements of an IB diploma is the extended essay. This really helps bring up the total score. And one problem students face here is gathering ideas for their IB extended essay. Here is some guiding information that can help with extended essay topics.
100+ IT and Computer Science research paper topic ideas
This comprehensive guide offers over 100 research paper topics across various subfields of Computer Science, including artificial intelligence, cloud computing, cybersecurity, IoT, robotics, quantum mechanics, data science, information technology, operating systems, and virtual reality. Each topic includes a research question and brief overview, providing a valuable resource for students and researchers seeking inspiration and direction for their projects in the rapidly evolving field of Computer Science.
150 Health and Medicine Research paper topics
In this article, we present 150 research paper topics that cover a wide range of areas, including public health, medical technology, mental health, and more
150+ Political and International Relations Topics for Research Paper
The right research paper topic in political and international relations is crucial for student success. Topics ensure motivation and align and ultimately make grades positively.
200+ History Research Paper Topics with Research Questions
In exploring the vast expanse of history, students can explore the complex interplay of events, cultures, and influential figures that have shaped today’s world. From the transformative impact of the Silk Road in fostering unparalleled cultural exchanges to the revolutionary advent of the printing press that ignited the spread of knowledge across Europe, research topics abound. Additionally, the intricate process of decolonization in Africa post-World War II provides a rich tableau for examining the struggles and triumphs of nations in pursuit of self-governance.
200 Term Paper Topics in Different Fields
Our extensive collection of term paper topics, meticulously curated to cater to diverse interests and fields of study. From the intricacies of argumentative essays to the innovative realms of experimental research, discover the perfect topic to ignite your curiosity and challenge your academic prowess.
We rely on cookies to give you the best experince on our website. By browsing, you agree to it. Read more
- My Shodhganga
- Receive email updates
- Edit Profile
Shodhganga : a reservoir of Indian theses @ INFLIBNET
- Shodhganga@INFLIBNET
- Shri Jagdishprasad Jhabarmal Tibarewala University
- Faculty of Education
| Title: | A study of environmental awareness and environmental ethics among the secondary and higher secondary school students of greater Mumbai |
| Researcher: | Balachandran, Sumathi |
| Guide(s): | |
| Keywords: | Education Environmental awareness |
| Upload Date: | 25-Oct-2013 |
| University: | Shri Jagdishprasad Jhabarmal Tibarewala University |
| Completed Date: | 08-08-2013 |
| Abstract: | The principal of this thesis is newlineThe origin of life on the earth was divided and controlled by a set of environmental conditions. Through these past millions of years, for sustenance of life environment has played a major role, and it will continue to be so for all times. newlineIn 1972, the Stockholm conference on human environment, at Rio de Janeiro, in 1992, the earth summit was held, in 2007 the Copenhagen climate council was founded, the Montreal protocol, the earth summit 2011 to the earth summit 2012 shows that the International community is very much concerned about environment. All the above conferences felt that in order to solve the environmental crisis it is better to have environmental oriented education to create environmental conscious citizen. newlineHence, the purpose of conducting this study was to find out the level of awareness of environment and environmental ethics among the Secondary school and Higher secondary school students of greater Mumbai. newlineThe objective of the study was to understand the awareness of environment and the level of environmental ethics among the Secondary school students based on gender and education at Maharashtra state board and CBSE board and also among the Higher secondary school students based on gender and discipline i.e. Arts, Commerce and Science students. newlineIn this study Data was collected using the questionnaire method. The sample size consists of 265 students from English medium secondary school belonging to S.S.C board, 277 students from CBSE board and from the higher secondary school 251 students from Arts faculty, 252 students from Commerce faculty and 294 students from Science faculty from the region of greater Mumbai by using stratified random sampling technique. newlineThe data was analysed in two ways, descriptive analysis and inferential analysis. Techniques used for descriptive analysis were mean, SD,mode,kurtosis,skewness,medium, etc. ANOVA,t- testand Pearson s correlation were used for inferential analysis. |
| Pagination: | xvii, 221p. |
| URI: | |
| Appears in Departments: | |
| File | Description | Size | Format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Attached File | 17.53 kB | Adobe PDF | ||
| 12.32 kB | Adobe PDF | |||
| 12.23 kB | Adobe PDF | |||
| 17.7 kB | Adobe PDF | |||
| 17.66 kB | Adobe PDF | |||
| 19.06 kB | Adobe PDF | |||
| 10.62 kB | Adobe PDF | |||
| 14.69 kB | Adobe PDF | |||
| 122.45 kB | Adobe PDF | |||
| 174.52 kB | Adobe PDF | |||
| 473.92 kB | Adobe PDF | |||
| 16.56 MB | Adobe PDF | |||
| 125.67 kB | Adobe PDF | |||
| 11.64 kB | Adobe PDF | |||
| 12.57 kB | Adobe PDF | |||
| 13.74 kB | Adobe PDF | |||
| 25.81 kB | Adobe PDF | |||
| 11.53 kB | Adobe PDF |
Items in Shodhganga are licensed under Creative Commons Licence Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-SA 4.0).

Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Open access
- Published: 05 July 2024
Exploring the ecological security evaluation of water resources in the Yangtze River Basin under the background of ecological sustainable development
- Jie-Rong Zhou 1 na1 ,
- Xiao-Qing Li 1 na1 ,
- Xin Yu 1 , 2 ,
- Tian-Cheng Zhao 1 &
- Wen-Xi Ruan 3
Scientific Reports volume 14 , Article number: 15475 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
165 Accesses
1 Altmetric
Metrics details
- Environmental social sciences
The Yangtze River (hereafter referred to as the YZR), the largest river in China, is of paramount importance for ensuring water resource security. The Yangtze River Basin (hereafter referred to as the YRB) is one of the most densely populated areas in China, and complex human activities have a significant impact on the ecological security of water resources. Therefore, this paper employs theories related to ecological population evolution and the Driving Force-Pressure-State-Impact-Response (DPSIR) model to construct an indicator system for the ecological security of water resources in the YRB. The report evaluates the ecological security status of water resources in each province of the YRB from 2010 to 2019, clarifies the development trend of its water resource ecological security, and proposes corresponding strategies for regional ecological security and coordinated economic development. According to the results of the ecological population evolution competition model, the overall indicator of the ecological security of water resources in the YRB continues to improve, with the safety level increasing annually. Maintaining sound management of water resources in the YRB is crucial for sustainable socioeconomic development. To further promote the ecological security of water resources in the YRB and the coordinated development of the regional economy, this paper proposes policy suggestions such as promoting the continuous advancement of sustainable development projects, actively adjusting industrial structure, continuously enhancing public environmental awareness, and actively participating in international ecological construction and seeking cooperation among multiple departments.
Similar content being viewed by others
Global impacts of heat and water stress on food production and severe food insecurity
Threat of low-frequency high-intensity floods to global cropland and crop yields
Projected loss of brown macroalgae and seagrasses with global environmental change
Introduction.
Water is the primary resource for sustaining living organisms and also an important contributor to the ecological environment and the global economy. However, the current status of water resources is facing formidable challenges owing to rapid global population growth, sustained economic development, and extreme climatic conditions triggered by climate change. According to reports from the World Economic Forum and the United Nations, currently, over 2 billion people worldwide inhabit water-scarce regions, a figure projected to increase to as much as 3.5 billion by the year 2025. Approximately a quarter of the global population is confronting a “water stress” crisis, with water scarcity issues gradually becoming commonplace, defying prior expectations 1 . The report assessed the water risks in almost 200 countries and regions. Seventeen regions and countries around the world consume more than 80% of the available water supply, putting them at risk of experiencing severe water scarcity. The scarcity, uneven distribution, and deteriorating environmental quality of water resources have emerged as significant impediments to human sustainable development and societal progress, posing severe threats to water resource security across various regions. Consequently, there is an urgent imperative to engage in interdisciplinary research and foster collaborative innovation to devise scientifically sound water resource management strategies, thereby advancing the societal attainment of sustainable development goals.
Water resources are a strategic asset for ensuring economic and social development. Water is not only a fundamental element for human survival but also a crucial guarantee for economic and social development. If industry is the foundation of the national economy, then water is its “lifeblood”, essential for the development of all industries. As the largest river in China, the YZR originates from the Qinghai‒Tibet Plateau, traverses three major economic zones, and finally flows into the East China Sea. The YZR the world’s third-longest river and also has the widest basin area in China, accounting for approximately 36% of the country's total water resources. Thus, it is one of China’s most critical rivers. The YZR runs through eleven regions, including an autonomous region, eight provinces, and two municipalities directly under the central government, namely, Qinghai Province, the Tibet Autonomous Region, Yunnan Province, Sichuan Province, Hunan Province, Hubei Province, Jiangxi Province, Anhui Province, Jiangsu Province, Chongqing Municipality, and Shanghai Municipality. Due to the complex terrain and low population density in the Tibet Autonomous Region, human activities in the area have a relatively minor impact on water resource ecological security. Considering the integrity of administrative divisions, this paper selects ten provinces (municipalities), namely, Qinghai, Yunnan, Sichuan, Hunan, Hubei, Jiangxi, Anhui, Jiangsu, Chongqing, and Shanghai, as the research area, representing the YRB as the research object. The YRB currently has hundreds of millions of residents, meaning that the supply and demand of water resources in the basin are crucial for people’s livelihoods and industrial and agricultural production. As one of the most economically developed regions in China, the YRB has important economic centres and industrial bases. The rational utilization and management of water resources are crucial for the economic development of this region. Assessing the security of water resources in the YRB is the foundation for ensuring high-quality development in this area. To actively address the challenges posed by water security issues and achieve sustainable development, it is essential to prioritize and resolve water security challenges 2 .
By investigating research progress on water resource security both domestically and internationally, it has been found that the majority of studies primarily focus on the ecological system aspect, while a minority are based on the social attributes of water resources. Particularly within the realm of human–water relationships 3 , research examining the impact of socioeconomic factors on water resource ecological security from temporal and spatial perspectives is relatively limited. This study introduces the Lotka–Volterra biological concept to explore the competitive or symbiotic relationships between two populations concerning ecological resources within the same temporal and spatial context. Here, we assume that the changes in socioeconomic factors have an impact on the ecological security of water resources, and at the same time, the continuous improvement of water resource ecological security is also a sign of the advancement of socioeconomic development. The two mutually influence each other. Meanwhile, the water resource ecosystem possesses a certain degree of resilience, meaning that it can recover to a certain level through natural restoration or human intervention after being damaged to a certain extent. Building upon this foundation, the DPSIR model is employed to establish a symbiotic assessment index system for socioeconomic factors and water resources. The entropy weight method was utilized to calculate the weights of the indicators. Furthermore, the Lotka–Volterra coexistence model was employed to conduct an in-depth evaluation of the ecological security of water resources in the YRB from 2010 to 2019. The results indicate that during the period of 2010–2015, the ecological security status of water resources in the YRB was highly sensitive and even approached a dangerous state. However, with national governance and policy adjustments, the ecological security of water resources in the YRB has shown a trend of orderly recovery, currently stabilizing at a state of security or near-security. Nevertheless, challenges still exist in the management of water resource ecological security. It is vital not only to maintain and protect the YRB but also to further research and safeguard other water source areas. In summary, future efforts to govern and maintain the ecological security of water resources will be arduous, requiring the collaborative participation and governance of multiple stakeholders. Establishing a sound management system and calling for concerted efforts from the entire society to protect the YZR are crucial. Active participation in comprehensive ecological security protection projects in the YRB is essential. This lays the groundwork for constructing a healthier and more sustainable water resource ecological security management system.
Research progress at domestic and abroad
Interspecific competition model foundation—logistic model.
The logistic curve, also known as the “S-shaped curve, ” is a graphical representation of the growth pattern of a population 4 . This logistic growth model was constructed by Verhulst 5 . The logistic model describes the development of many phenomena in nature, showing continuous growth within a certain period 6 . Generally, in the initial stages of species development, the population grows rapidly. After a certain period, the growth rate reaches its peak. Due to internal factors, the rate gradually slows until it no longer increases, reaching a stable state at the limit. This process of changing population size is referred to as a finite growth process, namely, the logistic growth process. According to the research results of scholars such as Haibo et al. 7 , Lingyun and Jun 8 , and Tao 9 , the basic interspecies competition model, the logistic model, is represented by the following equation:
The constant \({\upgamma } > 0\) in the equation represents the self-intrinsic growth rate of the population, indicating the maximum growth rate of a single population without external environmental limitations. This variable reflects the difference between the average birth rate and the average death rate of individuals in a population who are not subjected to external inhibitory effects. This constant reveals the intrinsic growth characteristics of a species population. The parameter K reflects the abundance of available resources within an ecosystem. When the population size K of a species equals K, the population will no longer grow. Therefore, the K value represents the maximum number of individuals of a species that the ecosystem environment can accommodate, also known as the carrying capacity.
According to the logistic equation, we can observe that the relative growth rate of a population is proportional to the remaining resource capacity in the ecological system environment. When the remaining resources are abundant, the relative growth rate of the species population is high. This phenomenon, where the rate of population growth slows as population density gradually increases, is known as density-dependent regulation. As the ecological system capacity K approaches infinity, the growth rate of the population approaches exponential growth, and this change in the population growth curve is known as the logistic curve.
Lotka–Volterra ecological model
In 1925, Lotka introduced a significant model in his research titled “Elements of Physical Biology”, the predator‒prey interaction model. This model quantitatively elucidates the interactions between organisms 10 . In 1926, Volterra, in his study “Variazionie fluttuazioni del numero d’individui in specie animali conviventi,” described the population dynamics of two interacting species in the biological realm 11 . These contributions laid the theoretical foundation for interspecific competition models and significantly influenced the development of modern ecological competition theories.
The interactions between species can be classified into three main types: competitive relationships, predator–prey relationships, and mutualistic cooperation relationships 12 . The Lotka–Volterra model was initially developed to describe predator‒prey relationships. However, with the increasingly widespread application of differential equation theory, this ecological model has evolved to encompass a broader range of applicability.
- DPSIR model
In 1993, the research group OECD innovatively proposed the DPSIR model, which is the “driving force-pressure-state-influence-response” model based on previous research models and has since been widely promoted in policy-making and research. Combining the characteristics of both the DSR (Driving Force-State-Response) and PSR frameworks, the DPSIR model effectively reflects causal relationships within systems, integrating elements such as resources, development, environment, and human health. As a result, it is considered a suitable method for evaluating watershed ecological security.
Consistent with the PSR framework, the DPSIR model organizes information and relevant indicators based on causal relationships with the aim of establishing a chain of causality: driving force (D)-pressure (P)-state (S)-impact (I)-response (R). In this context, “Driving Force (D)” primarily refers to potential factors reflecting changes in the health of the water cycle system, such as socioeconomic and population growth. “Pressure (P)” mainly refers to the impacts on the structure and functioning of the water cycle system, such as the utilization of water resources. “State (S)” represents changes in the water cycle system resulting from the combined effects of driving forces and pressures, serving as the starting point for impact and response analysis. “Impact (I)” reflects the effects of the hydrological cycle system on human health and social development. “Response (R)” refers to the feedback provided by the water cycle system to driving forces and pressures.
This model describes the causal chain between activities conducted by humans and the water environment, illustrating the mutually constraining and influencing processes between the two. It can encompass elements such as society, economy, and environment to indicate the threats posed by social, economic, and human activities to watershed ecological security. It can also utilize response indicators to demonstrate the feedback of the environment to society resulting from human activities and their impacts, as shown in Fig. 1 13 .

DPSIR model framework.
Overview of water resource ecological security
Water resources are a vital strategic asset for sustainable development and a key factor influencing human survival and socioeconomic development. The security of water resources is intricately linked to national economies and social stability 14 , 15 , 16 , 17 , 18 . As the population and economy grow rapidly, as well as due to the influence of climate change, water scarcity and deterioration of the water environment have become increasingly prevalent, posing a critical constraint to human survival and development 19 . Currently, research on water resource ecological security issues primarily revolves around the following three aspects.
The first aspect involves the evaluation of the water resources carrying capacity (hereafter referred to as the WRCC) and vulnerability.
Regarding the WRCC, some studies consider that the WRCC implies the need for water resources to sustain a healthy societal system 20 . Other researchers argue that the WRCC is the maximum threshold for sustaining human activities 21 .
In terms of calculation methods, various quantification methods for the WRCC have gradually emerged. For example, Qu and Fan 22 considered the available water volume in water demand, national economic sectors and the ecological environment. They employed the traditional trend approach to obtain the population and development scales of industry and agriculture. Zhou Fulei adopted the entropy weight method, an objective weight determination method, to determine the weights of each evaluation indicator, utilized the analytic hierarchy process (AHP) to adjust the weights, constructed composite weights, and then used the TOPSIS model to evaluate the water resources carrying capacity of Qingdao city from 2015 to 2021 23 . Ma et al. 24 and Xiong et al. 25 analysed and evaluated the WRCC using the entropy weight method and provided suggestions for regional sustainable development. Wang et al. 26 , under the traditional TOPSIS model, used an improved structural entropy weighting method to determine the weights of evaluation indicators. They then constructed a grey-weighted TOPSIS model using a grey correlation matrix to specifically evaluate the current state of the agricultural WRCC in Anhui Province. Zhang X and Duan X combined the weights obtained from the entropy and CRITIC methods using the geometric mean method. They applied these combined weights to a model integrating grey relational analysis (GRA), the technique for order preference by similarity to an ideal solution (TOPSIS), and the coupling coordination degree model (CCDM) to calculate the evaluation value of the water resource carrying capacity 27 . Zhang and Tan 28 and Fu et al. 29 separately used optimization models and projection tracking models to evaluate the WRCC in their study areas and conducted comprehensive assessments of the regional WRCC. Gong and Jin 30 , Meng et al. 31 , Wang et al. 32 , and Gao et al. 33 applied fuzzy comprehensive evaluation methods to assess the influencing factors of the WRCC by establishing a fuzzy comprehensive evaluation matrix. On this basis, they analysed the factors affecting the WRCC and evaluated and predicted the future carrying capacity of water resources in the study area. Additionally, other methods have been employed, such as multidimensional regulation 34 , neural network genetic algorithms 35 , 36 , multi-index evaluation models 37 , and nonparametric analysis models 38 .
Ait-Aoudia and Berezowska-Azzag 39 conducted an assessment of the WRCC to analyse the balance between domestic demand and water supply. To assess the WRCC of specific regions, the assessment factors were determined by evaluating the relevant factors of water usage and availability. The conceptual framework for assessing the capacity of water resources was developed based on the supply–demand relationship. Yan et al. 40 focused on the previous decade’s regional water resource data of Anhui Province in China. They constructed a framework for the Driving Force-Pressure-State-Impact-Response Management (DPSIRM) model and conducted a comprehensive evaluation of the WRCC using the entropy weight method and variable weight theory. Based on the derived comprehensive evaluation values and incorporating the modified Gray–Markov combined forecasting, they made predictions about the local WRCC for the coming years. In 2020, Zhengqian 41 discussed the concept and research methods of regional WRCC. The research methodology has evolved from a singular and static approach to a dynamic, multilevel, and comprehensive study with various indicators. Jiajun et al. 42 , starting from a systemic perspective, studied the coordinated development relationships among China’s economy, social development, ecological environment, and water resources. They applied the WRCC Comprehensive Evaluation Model, calculating the comprehensive evaluation index for specific years based on relevant data. This allowed them to describe the WRCC status of provinces and regions in China, providing a comprehensive analysis and evaluation of China’s WRCC. Ren et al. 43 introduced the concept of biological metabolism to the regional WRCC and proposed the theory of regional water resource metabolism. Additionally, they established an evaluation indicator system for the WRCC considering regional water resource characteristics, socioeconomic systems, and sustainable development principles.
Raskin et al. 44 assessed the extent of water resource security by using the proportion of water extraction relative to the total water resources, defined as the water resource vulnerability index. Rui 45 constructed a water resource vulnerability model based on the theory of mutation series. They utilized the principles of mutation series to redefine grading standards and assessed the vulnerability status of water resources in Shanxi Province from 2004 to 2016. The aim was to offer technical assistance for the scientific management of water resources.
The second aspect involves the measurement of the sustainable utilization and efficiency of regional water resources.
Over the last few years, numerous domestic researchers have actively conducted research on the sustainable utilization of water resources, focusing primarily on two aspects:
First, research on evaluation indicator systems for the sustainable utilization of water resources should be conducted. Li Zhijun, Xiang Yang, and others addressed the lack of connection between water resource ecology and socioeconomic development in traditional water resource ecological footprint methods. They introduced the water resource ecological benefit ratio and analysed the water resource security and sustainable development status through an improved water resource energy value ecological footprint method 46 . Zhang et al. 47 established a fuzzy comprehensive evaluation model based on entropy weight, providing recommendations for the sustainable utilization of water resources in Guangxi Province. Liu Miliang, aiming for sustainable development, quantitatively analysed the current situation and influencing factors. Based on the DPSIR model, they established an evaluation system for the sustainable utilization of water resources 48 .
Second, in terms of evaluation methods and research on the sustainable utilization of water resources, Yunling et al. 49 constructed an evaluation indicator system for the WRCC to assess the comprehensive water resource carrying status in Hebei Province. Xuexiu et al. 50 , based on both domestic and international research on water resource pressure theory, analysed the connotation of water resource pressure, introduced commonly used methods for water resource pressure evaluation, and provided a comprehensive overview and comparative analysis of water resource pressure evaluation methods from aspects such as calculation principles, processes, and applications. Guohua et al. 51 established an entropy-based fuzzy comprehensive evaluation model of water resource allocation harmony and evaluated the water resource allocation status of various districts and counties in Xi’an city. Shiklomanov 52 used indicators such as available water resources, industrial and agricultural water usage, and household water consumption to assess water resource security.
The SBM-DEA model was used by Deng et al. 53 to appraise the efficiency of water resource utilization across nearly all provinces in China. They proposed factors influencing water resource utilization efficiency, including the added value of the agricultural sector, per capita water usage, the output-to-pollution ratio of polluting units, and import–export dependency. Yaguai and Lingyan 54 employed a two-stage model combining superefficiency DEA and Tobit to assess water resource efficiency in China from 2004 to 2014. They analysed regional differences and influencing factors. Mei et al. 55 separately used stochastic frontier analysis and data envelopment analysis to measure the absolute and relative efficiencies of water resource utilization in 14 cities in Liaoning Province. They employed a kernel density estimation model to analyse the dynamic evolution patterns of water resource utilization efficiency. Xiong et al. 56 adopted an iterative correction approach to modify and apply water resource utilization efficiency evaluation models based on single assessment methods such as entropy, mean square deviation, and deviation methods.
The third aspect involves investigating the relationship between water resource security and other societal systems.
Shanshan et al. 57 laid the foundation for the rational construction of an urbanization and water resource indicator system. Through the establishment of a dynamic coupled model, they conducted an analytical study on the harmonized development trends between the urbanization system and the water resource system in Beijing. Wei 58 utilized a coordination degree model to explore the coupling relationship between the quality of new urbanization and water resource security in Guangdong Province. Caizhi and Xiaodong 59 combining coupled scheduling models with exploratory spatial data analysis and conducted an analysis of the security conditions and spatial correlations among water resources, energy, and food in China. Additionally, Xia et al. 60 employed the Mann–Kendal test method to study the degrees of matching between water resources and socioeconomic development in six major geographical regions of China.
A review of the relevant literature reveals that scholars have explored the issues of water resource ecological security and regional socioeconomic development from various perspectives and fields, which is one of the urgent problems to be addressed in the current process of social development. These research findings not only have learning and reference significance but also provide insights for the writing of this paper.
Summarizing the achievements of previous research, the essence of water resource security evaluation mainly includes three aspects: ensuring water quantity, sustainability, and water quality. Evaluation methods include principal component analysis, fuzzy comprehensive evaluation methods, analytic hierarchy processes, and system dynamics modelling methods, among others, among which the analytic hierarchy process has certain advantages in addressing multilevel problems and is widely used in constructing multilevel analysis models. Therefore, this paper introduces the Lotka–Volterra biological concept and continues to explore this topic further. It can effectively combine the relationships between indicators and weights and study the competition or symbiotic relationship between two populations competing for ecological resources in the same time and space context 61 . Drawing from the DPSIR model, this study devises a comprehensive evaluation framework to assess the interdependence of socioeconomic factors and water resources. Through the application of the entropy weight method, this study determines the relative importance of various indices within this framework. Employing the Lotka–Volterra symbiotic model, this research scrutinizes and quantifies the ecological security status of water resources in the YRB from 2010 to 2019. The overarching objective is to furnish technical insights that can catalyse efforts to enhance the ecological security of regional water resources.
Methodology
- Lotka–Volterra symbiosis model
In the 1940s, A. J. Lotka and V. Volterra jointly introduced the Lotka–Volterra model 62 , which serves as a method for studying the relationships between biological populations. Its basic form is as follows:
In the given equation, \({\text{N}}_{1} \left( {\text{t}} \right), {\text{N}}_{2} \left( {\text{t}} \right)\) denote the populations of species \({\text{S}}_{1}\) and \({\text{S}}_{2}\) , respectively. \({\text{K}}_{1}\) and \({\text{K}}_{2}\) represent the carrying capacities of populations \({\text{S}}_{1}\) and \({\text{S}}_{2}\) in their respective environments. \({\text{r}}_{1}\) and \({\text{r}}_{2}\) represent the growth rates of populations \({\text{S}}_{1}\) and \({\text{S}}_{2}\) , respectively. \(\alpha\) denotes the competitive intensity coefficient of species \({\text{S}}_{2}\) on species \({\text{S}}_{1}\) , while \(\beta\) represents the competitive intensity coefficient of species \({\text{S}}_{1}\) on species \({\text{S}}_{2}\) .
By replacing the socioeconomic relationships within the entire YRB with the provinces within the basin, the Lotka–Volterra model is introduced into the regional water resource ecological security assessment. This allows for the construction of a symbiotic model between socioeconomic factors and water resources within the YRB. The specific formula is as follows:
In the equation, \({\text{F}}\left( {\text{k}} \right)\) denotes the comprehensive socioeconomic development status, \({\text{E}}\left( {\text{k}} \right)\) signifies the comprehensive development status of water resources, \({\text{C}}\) represents the ecological environment, \({\text{r}}_{{\text{F}}}\) signifies the socioeconomic growth rate, \({\text{r}}_{{\text{E}}}\) represents the growth rate of water resources, \(\alpha\) denotes the coefficient of water resources’ impact on the socioeconomy, and \(\beta\) denotes the coefficient of the impact of the socioeconomy on water resources. Therefore, solving for the coefficients \(\alpha\) and \(\beta\) in the model is essential for examining the interaction between the socioeconomy and water resources. The specific steps for solving the equation are as follows.
Discretizing Eqs. ( 4 ), ( 5 ) yields:
The solution is:
Different values of \(\alpha\) and \(\beta\) correspond to different symbiotic relationships between the socioeconomy and water resources, as illustrated in Fig. 2 .

Symbiotic model between the socioeconomic and water resources in the YRB.
Construction of the DPSIR model and indicator system
To construct a water resource ecological security index system for the 10 provinces in the YRB, this paper is based on the research of relevant scholars and introduces the DPSIR model to evaluate water resource ecological security. This model was proposed to describe the concept of environmental systems and the structure of complex cause-and-effect relationships by the European Environment Agency (EEA) in 1999. It is mainly applied in assessments of ecological security, regional sustainable development, and water resource ecological security.
The establishment of the DPSIR model in this paper is illustrated in Fig. 3 .

DPSIR model.
Generally, the driver (D) in the socioeconomic system tends to improve the environmental and resource states (S), while the economic pressure (P) tends to disrupt the resource and environmental states (S). The states of resources and the environment contribute essential production materials to the socioeconomic system. Simultaneously, drivers (D) and pressures (P) reflect two different aspects of socioeconomic development. Therefore, these factors can indicate the level of socioeconomic development. Based on these definitions, the following indicators are selected to assess the DPSIR model for water resource ecological security. The weights of various indicators calculated through the entropy weight method are presented in Table 1 . A more significant role played by the corresponding indicator in the comprehensive assessment of regional ecological security will have a greater weight.
On this basis, the socioeconomic stress index \({\text{S}}_{{\text{F}}} \left( {\text{k}} \right)\) and water resource stress index \({\text{S}}_{{\text{E}}} \left( {\text{k}} \right)\) are defined as follows:
The comprehensive index between socioeconomic and water resources, also called the symbiosis index \({\text{S}}\left( {\text{k}} \right)\) , is calculated as follows:
According to Eq. ( 14 ), \({\text{S}}\left( {\text{k}} \right) \in \left[ { - \sqrt 2 ,\sqrt 2 } \right]\) , a larger value of A indicates that the symbiotic state between the socioeconomy and water resources is better; conversely, a smaller value of A indicates that the symbiotic state between the two is worse.
The water resources force index can illustrate the direction of the socioeconomic impact on water resources, and the symbiotic index can illustrate the magnitude of the socioeconomic impact on water resources. Therefore, these two indices serve as the basis for evaluating the water resource security status. Formula ( 14 ) implies that the symbiotic index \({\text{S}}\left( {\text{k}} \right)\) falls within the range of \(\left[ { - \sqrt 2 ,\sqrt 2 } \right]\) . A larger numerical value indicates a better symbiotic relationship between the two subsystems, while a smaller value suggests a poorer symbiotic relationship. However, the relationship between the symbiotic index and regional ecological security is not straightforward. Regional ecological security must be judged according to specific criteria grounded in both the measure of symbiosis \({\text{S}}\left( {\text{k}} \right)\) and the ecological force index \({\text{S}}_{{\text{E}}} \left( {\text{k}} \right)\) . This approach comprehensively characterizes the ecological security of the YRB urban agglomeration. In our study, a two-dimensional symbiotic model of socioeconomic–natural ecology is employed to depict the evolution of ecological security under dual-characteristic indices.
Within this model, ecological security is divided into six regions that progress in a sequential manner, conforming to the progressive law of ecological security evolution. In the safe zone, the socioeconomic and natural ecological systems mutually benefit, and both experience robust development. In the subsafe zone, although the natural ecological system is still in a growing state, this occurs at the expense of socioeconomic development, leading to an unstable ecological security status. If the socioeconomic system continues to suffer damage, it falls into the sensitive zone, where the harm to the socioeconomic system outweighs the benefits to the natural ecological system. If this condition persists, both systems enter a state of competition, resulting in harm to both, and they are situated in the danger zone. In unfavourable zones, the socioeconomic system gains weak benefits, while the natural economy suffers damage. If humanity recognizes this situation and takes measures to improve the environment, it may transition from the unfavourable zone to the cautious zone, leading to an improvement in ecological security and potential entry into the safe zone. For ease of analysis and based on the relevant literature 63 , following expert discussions, this study classifies ecological security into six categories corresponding to six ecological security early warning levels, as shown in Table 2 .
Discrimination of water resource ecological security levels
The YZR originates from the Qinghai‒Tibet Plateau, considered the “Roof of the World,” traversing three major economic regions before ultimately flowing into the East China Sea. For our study area, we selected the eight provinces and two municipalities through which the YZR flows. These regions are Shanghai, Jiangsu, Anhui, Jiangxi, Hubei, Hunan, Chongqing, Sichuan, Yunnan, and Qinghai. In the subsequent text, they will be referred to collectively as the YRB. The data for this study primarily originate from statistical yearbooks, water resource bulletins, and development reports spanning the years 2010 to 2019.
According to the criteria for water resource security status presented in Table 2 , the corresponding information is summarized in Table 3 for the years 2011 to 2018, indicating the water resource security status in the YRB during this period. It is observed that from 2011 to 2018, the water resources security status in the YRB initially experienced a decline but later recovered to a secure level. In recent years, the country has not only emphasized economic development but also placed significant importance on environmental protection. Rapid industrial development in earlier years led to an exacerbation of water pollution issues. However, the government promptly recognized this problem and implemented a series of measures to address water pollution. Stringent controls were also imposed on industrial water usage. Consequently, the water resource status quickly returned to a level considered safe.
The water resource security evaluation values obtained using the entropy method range from 0 to 1. Ideally, a value closer to 1 indicates a better water resource security situation, while a value closer to 0 suggests a poorer water resource security situation.
After standardizing the processed data, we can plug them into Eq. ( 15 ) to sequentially obtain the basic indices for socioeconomic, ecological environment, and water resource security in the YRB. The specific process involves substituting the basic indices for socioeconomic, ecological environment, and water resource ecological security into Eqs. ( 12 )–( 14 ). This approach yields comprehensive indices, including the socioeconomic stress index, water resource stress index, and symbiotic degree index. These indices serve as the basis for evaluating the water resource security status in the assessment region, with the water resource stress index and symbiotic degree index being the key indicators.
In the equation, f i represents the comprehensive level of water resource ecological security, \({\text{x}}_{{\text{i}}}^{\prime }\) signifies the standardized values obtained from the original data, and \({\text{w}}_{{\text{i}}}\) denotes the weights assigned to each indicator. When the value of f i falls between 0 and 1, the closer the value is to 1, the better the ecological security of water resources. In contrast, it shows a poorer ecological security status. Similarly, according to this equation, the classification of water resource ecological security can be divided into six categories: 0–0.16 denotes a dangerous state, 0.16–0.32 indicates a deteriorating state, 0.32–0.48 signifies a sensitive state, 0.48–0.64 represents a vigilant state, 0.64–0.8 implies a subsecure state, and 0.8–1.0 corresponds to a safe state. Different levels of water resource ecological security entail varying relationships with the national economy and society. For specific characteristics corresponding to each security level, please refer to Table 4 .
Informed consent statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Evaluation of water resource ecological security levels in the Yangtze River Basin
Overall, the evaluation values of water resource security in the YRB from 2010 to 2019 showed a fluctuating upwards trend (refer to Table 5 ). From 2010 to 2013, the evaluation values fluctuated between 0.2 and 0.4, reaching the lowest level at Grade V. In 2011, the evaluation value was only 0.2201, indicating that during this period, the water resources in the YRB were in an unsafe state, resulting in water scarcity. These results indicate that economic and social development are not being met on a sustainable basis at the watershed scale. In 2014, the water resource security evaluation value for the YRB reached 0.4243, classified as Grade III. Subsequently, there was a significant upwards trend, with the evaluation value reaching 0.6746 in 2017, which was classified as Grade II, indicating a relatively secure state. These results suggest that the water resources of the YRB appeared to be more secure than they were before, and the YRB could essentially fulfil the requirements for sustainable economic and social development at the national level. This upwards trend continued, reaching 0.7215 in 2019. From 2010 to 2019, the water resource security status in the YRB improved from Grade V to Grade II, demonstrating significant improvement. However, it has not yet reached Grade I, indicating that there is still room for improvement in the future.
The DPSIR model was used to analyse the reasons for the improvement in the ecological security of water resources in the YRB based on five criteria. Table 5 shows that the evaluation values for driving forces significantly increased from 2010 to 2019, while the values for pressure and response slightly increased, and those for state and impact fluctuated, resulting in a slight overall improvement. Specifically, the evaluation values for driving forces fluctuated from 0.0543 to 0.2370, indicating the significant contributions of indicators such as per capita GDP, the proportion of primary industry, population density, and the urbanization rate to the enhancement of water resource security. The assurance provided by economic and social development for water resource security is evident. The evaluation value for pressure fluctuated from 0.0403 to 0.1149, suggesting a reduction in pressure on water resources from economic development, agricultural and industrial production, and residents' lifestyles, leading to a decrease in basin water pollution and an alleviation of water quality deterioration. The response increased from 0.0527 to 0.1665, indicating relatively significant growth. These results suggest that measures taken by the government and society to address water resource issues have been effective, resulting in improvements in both the quantity and quality of water resources and an enhancement of water resource security levels. The evaluation value for impact fluctuated from 0.0261 to 0.0349, indicating a standardized industrial wastewater discharge volume and an improvement in water resource security conditions. The evaluation value for state initially decreased from 0.1633 to a minimum of 0.0656 before increasing to approximately 0.17. These results suggest that, considering indicators such as per capita sewage discharge and per capita water consumption, the status of water resources initially declined but gradually improved after governance measures were implemented.
In summary, from 2010 to 2019, the improvement in water resource security in the YRB can be attributed mainly to the enhancement of driving forces and response indicators. Economic and social development has provided ample assurance for water resource security, while water resources have imposed constraints on economic and social development to a certain extent. In the YRB, the current governance of water resources has reached a relatively high level, making it challenging to achieve significant breakthroughs in the future. The efficiency of water use in the existing industrial structure is difficult to substantially improve. Therefore, adjusting the industrial structure to enhance water resource security is a future research focus. These findings align with the conclusions of other domestic scholars. For instance, a study by Xiaotao and Fa-wen 64 revealed that water consumption per unit of production energy and agricultural production in the YRB contributed the same proportion of GDP. They argued that future water conservation efforts should focus on adjusting industrial structures and developing water-saving technologies. Another study by Wang Hao revealed that the water resource utilization efficiency in the YRB was second only to that in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region 65 . These authors suggested that the potential for mitigating the contradiction between water supply and demand through deep water conservation is limited.
According to the above methods and steps, further calculations were conducted to determine the water resource ecological security status of each province in the YRB from 2010 to 2019, as shown in Tables 6 and 7 . Information gleaned from Tables 6 and 7 suggests that the overall improvement in the water resource ecological security status of each province in the YRB from 2010 to 2019 was significant. There was a discernible improvement from 2014 to 2015, with a clear boundary line. Before 2015, the water resources in most areas were relatively sensitive, and some regions even experienced deterioration. However, after 2015, almost all areas reached subsafe or safe states.
Calculation results of the water resource security status of each province in the YRB from 2010 to 2019.
Trends in water resource ecological security in the Yangtze River Basin
According to Eq. ( 15 ), and by empirically examining the ecological status of water resources in the YRB from 2010 to 2019, the comprehensive levels of the ecological environment, socioeconomic development, and water resources in ten provinces of the YRB were obtained, as shown in Fig. 4 .

Development of the basic indices in the YRB.
The information gleaned from Table 4 suggests that the economic development in the YRB from 2010 to 2019 showed a positive trend, increasing from 0.09 to 0.35. This increase is attributed to the favourable current economic development environment and robust support from national directives. Policies such as the 2013 “Guiding Opinions on Building China’s New Economic Support Belt Based on the Yangtze River”, the 2018 speech at the Symposium on Deepening the Development of the YZR Economic Belt, the “Development Plan for the Huaihe River Ecological Economic Belt”, and the 2019 “Outline of the Development Plan for the Regional Integration of the Yangtze River Delta” have played crucial roles in driving industrial restructuring and achieving quality economic development in the YRB.
The ecological environment comprehensive level in the YRB exhibited a fluctuating development trend from 2010 to 2019, resembling an “M” shape, increasing from 0.24 to 0.37 with a relatively small amplitude. Ecological civilization construction, as a fundamental national policy, has provided important guidance for the economic development of the YRB. This development includes intensified efforts in the treatment of industrial pollutants and urban wastewater, along with increased levels of regional afforestation and greenery. Notably, significant improvements were observed in indicators such as per capita park green space, the urban green space ratio, and the harmless disposal of waste in the YRB in 2015.
The comprehensive level of water resources in the YRB increased slightly from 0.19 to 0.20 from 2010 to 2019. Although there was an upwards trend, the magnitude of the increase was minimal, indicating an unfavourable water resource status in the YRB. The primary factor in this slight increase is the accelerated consumption of water resources. As a part of the ecological environment, a decrease in the comprehensive level of water resources is also an important factor restricting the overall improvement of the ecological environment. In future development, the YRB should leverage favourable national policies to promote breakthrough development in the regional economy. Simultaneously, efforts should be intensified towards the protection and management of regional water resources and the ecological environment, striving to enhance the comprehensive level of water resources and the ecological environment.
Based on the previously calculated comprehensive socioeconomic, ecological environment, and water resource levels, the stress indices for socioeconomic and water resources, as well as the symbiotic index for the YRB during the years 2010–2019, were computed, and the results are presented in Fig. 5 .

Development status of comprehensive indices in the YRB.
Figure 5 clearly shows that, except for the years 2012, 2014, and 2016, the impact of water resources on the socioeconomy remained consistently positive, indicating that during this period, water resources positively contributed to economic growth. The water resources force index has been consistently positive in recent years, signifying the promotion by socioeconomic development, with a relatively minor hindrance from socioeconomic development during this period. The symbiotic index values between the two factors were 1.05, 1.24, 1.40, 1.26, and 1.07 in the years 2011, 2013, 2015, 2017, and 2018, respectively, reaching an optimal state of mutual benefit and symbiosis. However, a slight decline was observed in subsequent years, suggesting the need for further improvement.
Spatial pattern analysis of water resource ecological security in the Yangtze River Basin
Using the ArcGIS10.4 tool, which is provided by the Environmental Systems Research Institute, Inc (commonly known as ESRI), several representative years were selected to visualize the ecological security status of water resources in the YRB. The computational results are visualized in Figs. 6 , 7 and 8 .
Ecological security status of water resources in the YRB in 2011(map were generated with software ArcMap10.4 http://www.esri.com/ ).
According to the division standards for administrative regions along the YZR in 2014, the YRB studied in this paper can be categorized into three main regions: the upper, middle, and lower reaches. The upper reach includes three provinces: Qinghai, Sichuan, and Yunnan. The middle reach comprises four provinces and municipalities: Chongqing, Hunan, Hubei, and Jiangxi. The lower reach consists of three provinces and municipalities: Anhui, Jiangsu, and Shanghai.
Figures 6 , 7 and 8 show that from 2011 to 2019, the overall ecological security status of water resources in the YRB transitioned from “deteriorating,” “sensitive,” and “vigilant” states to “subsecure” and “safe” states. The range of comprehensive evaluation values for water resource ecological security (hereafter referred to as evaluation values) increased from 0.16–0.64 to 0.64–1.
As illustrated in Fig. 6 , notable disparities were present in the distribution of the ecological security status of water resources among provinces and municipalities in the YRB, with the ecological security status of water resources in the upper and lower reaches of the YZR notably superior to that in the middle reaches. The data indicate that the water resource utilization efficiency levels in the upper and lower reaches of the YZR were greater than that in the middle reaches in 2011, exhibiting a pattern of high efficiency at both ends and lower efficiency in the middle. Regions with high comprehensive water resource utilization efficiency are mainly concentrated in the upper and lower reaches of the YZR.
Although the upstream regions have limited economic strength, they also have relatively fewer water-intensive industries. Meanwhile, these regions actively respond to green development policies and prioritize energy conservation and environmental protection industries. Underdeveloped regions can also achieve higher water resource efficiency by controlling total water consumption and improving the output of water per unit used.
The areas with low comprehensive utilization efficiency of water resources are primarily concentrated in the middle reaches of the YZR, where the proportions of traditional industries such as steel, chemicals, and nonferrous metals are relatively large, leading to high industrial water consumption and consequently the lowest efficiency in water resource utilization. Provinces such as Hunan and Hubei, with large populations and rapid economic development, exhibit high demands for water resources, resulting in increased regional water resource consumption and persistently high per capita sewage discharge indicators.
The downstream regions of the YZR boast strong economic progress, with high levels of industrial technological innovation and governance capabilities. This region exhibits the highest level of economic development, which can drive improvements in the utilization efficiency of water resources. Consequently, Shanghai and Jiangsu provinces have the highest water resource utilization efficiency. As a result, the ecological security status of water resources in Shanghai has improved rapidly.
As shown in Fig. 7 , in 2015, the overall ecological security status of water resources notably improved in the YRB. The fundamental reason for this improvement is that in recent years, regions across the basin have recognized the importance of the ecological environment for overall development. They have gradually undertaken regional industrial restructuring and upgrading and accelerated urbanization and simultaneously emphasized the preservation of water resources and the environment. The three major regions exhibit regional disparities in water resource utilization efficiency due to differences in geographical environment, economic foundation, and industrial structure. In terms of the total water consumption of each province and municipality, agricultural water usage accounts for more than half of the total water consumption, which is significantly greater than the water usage in the industrial, domestic, and ecological sectors. However, compared to other industries' output values, the overall water resource utilization efficiency in agriculture is lower. Therefore, regions with greater proportions of primary industry output tend to have lower water resource utilization efficiency.
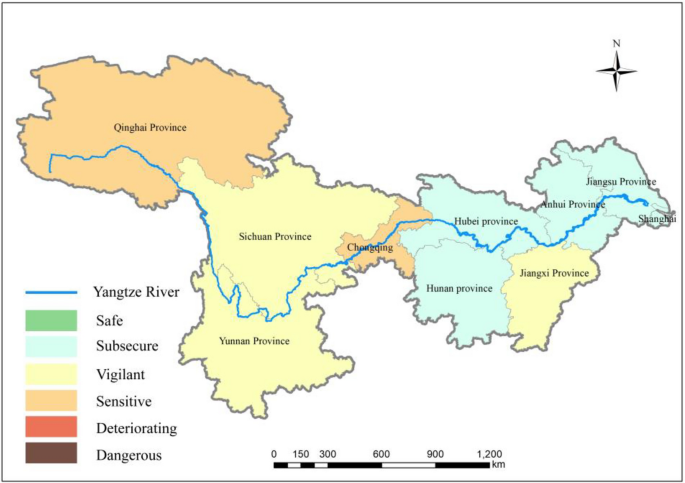
Ecological security status of water resources in the YRB in 2015(map were generated with software ArcMap10.4 http://www.esri.com/ ).
The industrialization level in the upstream regions is relatively low, with relatively outdated production technologies. As industrialization progresses, the negative impact on water resources' ecological security is gradually increasing. The industrialization in the middle and lower reaches of the YZR has reached relatively high levels. Control measures have been gradually implemented to manage the resource consumption and environmental pollution generated during the industrial development process. With advancements in technology, the negative impact on water resource ecological security is gradually diminishing. Among these provinces, Hunan Province and Hubei Province in the middle reaches of the YZR experienced the greatest increases in water resource ecological security status, transitioning from “deteriorating” to “subsecure.” The regions in the middle reaches emphasize considering the resource and environmental carrying capacity to ensure the coordination between water resource allocation and regional sustainable development, achieving rational distribution and efficient utilization of water resources within the region.
The lower reaches of the YZR are characterized by developed economies, advanced technologies, and high levels of both urbanization efficiency and water resource efficiency, maintaining harmonious development. This region exhibits the strongest economic development and hosts the highly integrated YZR Delta urban agglomeration. With a solid foundation in secondary and tertiary industries, high levels of technological innovation, and openness, the overall ecological security status of water resources in this region is at a relatively high level.
Across the provinces and municipalities in the YRB, efforts have been intensified to control the discharge of pollutants such as phosphorus, leading to reduced pollutant emissions and improved water quality. Moreover, improvements in water resource allocation have been made, reducing the risks associated with pollution factors through increased water volume and dilution effects, thereby ensuring the supply and safety of drinking water downstream of Shanghai. The stable proportion of GDP in the YZR Economic Belt indicates a balanced relationship between economic development and the ecological protection of water resources. While maintaining economic growth, downstream cities also prioritize environmental protection and water resource management.
Figure 8 clearly shows that the overall ecological security status of water resources in the YRB has been developing at an accelerated pace, trending towards overall coordinated development by 2019, with mutual promotion between socioeconomic and water resources. This trend can be attributed to various factors. This positive influence is exemplified in agricultural water use efficiency, which has improved in recent years due to various factors, such as changes in agricultural production methods, organizational structures, cropping patterns, and water-saving practices. As a result, the negative impact of the proportion of the output value of the primary industry on water resource efficiency has been mitigated.

Ecological security status of water resources in the YRB in 2019(map were generated with software ArcMap10.4 http://www.esri.com/ ).
However, despite efforts, China still faces serious water pollution issues, with poor water environmental quality and significant pollution discharge loads from industrial, agricultural, and domestic sources. These factors pose severe challenges to the ecological security of water resources. To address these challenges, China has formulated a series of plans aimed at strengthening water pollution prevention and control and ensuring national water resource ecological security. These plans were officially announced and implemented after 2015.
Based on the analysis results, each province and city in the YRB should embrace a people-centred approach to new urbanization and the scientific development concept of water resource protection and utilization. While focusing on promoting new urbanization construction, efforts should be intensified to enhance ecological environmental protection and explore new paths for coordinated regional economic development and resource utilization. Provinces and cities should rely on the golden waterway of the YZR to establish cross-regional and cross-provincial basin cooperation mechanisms and long-term mechanisms, actively promoting coordinated development among the three major regions of the YRB.
Against the backdrop of the global environmental crisis, the Lancang-Mekong River, as Asia’s largest transboundary river, also faces certain water security issues. Specifically, the “status” of water resources is relatively low, as manifested by the polluted state of the water quality of the river. Additionally, factors such as the uneven distribution of precipitation within the year and the weakness of storage facilities such as wetlands and reservoirs contribute to seasonal water shortages and serious water disasters in the basin. Moreover, the response levels of basin countries are limited, and there is room for improvement in the level of water resource management. Countries in the Lancang-Mekong River Basin are in a stage of rapid economic and social development, and population growth, economic activities, and changes in land use (such as urbanization) will have direct or indirect impacts on water resources in the basin. The Ganges River Basin faces similar ecological and environmental problems. In recent years, India’s economic prosperity and urbanization process have had significant impacts on the Ganges River Basin. Soil erosion and insufficient drinking water under population pressure have plagued the people of the Ganges River Basin. Additionally, the serious problem of surface water pollution caused by the discharge of industrial and domestic wastewater has led to a certain degree of land salinization.
Climate change, land use, human consumption of water resources, and government management of water resources are all factors that can directly or indirectly affect the water security situation in a region. Given that the Lancang-Mekong River spans China and five Southeast Asian countries, its water resource ecological security is particularly influenced by socioeconomic factors. Therefore, we believe that the methods we propose are equally applicable to the evaluation of water resource ecological security in this basin. By introducing the Lotka–Volterra symbiotic model and using the DPSIR model to construct a system of evaluation indicators for the symbiosis between socioeconomic factors and water resources in the study area, this system will help us to thoroughly assess the water resource ecological security of the Lancang-Mekong River Basin and provide a scientific basis for the implementation of region-specific water security strategies. These approaches are highly important for promoting regional sustainable development and maintaining basin ecological security.
Research has revealed that over a decade ago, the water resource ecological security status in the YRB initially fell within a relatively poor range. However, with close attention from the government and the implementation of various regulations, as well as active participation from the public in protecting the YZR, the water resource ecological security status in the YRB has improved rapidly. It is now generally maintained at levels of safety or near safety, with prospects for further improvement in the future. Comprehensive analysis of data from 2010 to 2019 revealed continuous trends in improvement in water resource security. To further enhance water resource security, we propose the following recommendations:
The industrial structure should be adjusted to achieve sustainable utilization of water resources. Governments should strongly support the green economy and environmental protection industries by providing tax incentives for enterprises, encouraging them to invest in water resource management and protection projects. By establishing corresponding financial funds and reward mechanisms, more social forces can be guided to participate, achieving a mutually beneficial outcome for water resource security and economic development. The Chinese government has called for all citizens to actively respond to carbon peak and carbon neutrality strategies and has formulated specific and feasible emission reduction plans. Enterprises are encouraged to adopt clean production technologies to improve resource utilization efficiency and achieve carbon emission reduction goals. There should be a focus on strengthening sewage resource utilization, integrating atypical water sources into unified water resource allocation, and encouraging locations with the necessary conditions to fully utilize unconventional water sources. Water-deficient cities should actively expand the scale and scope of recycled water utilization. The principles of demand-driven supply, water quality division, and local utilization should be followed to promote the use of recycled water in industrial production, municipal miscellaneous use, land greening, ecological replenishment, and other areas.
Focusing on agricultural water use and preventing water source pollution. As one of the main rice-producing regions in China, to further enhance water resource security in the YRB, agricultural measures should be taken. With respect to water conservation, water-saving irrigation techniques combined with smart irrigation systems should be adopted to achieve precise irrigation and improve water resource utilization efficiency. Moreover, enhancing rainwater collection and utilization by establishing rainwater collection systems and storing water for agricultural irrigation can effectively utilize rainwater resources and alleviate irrigation pressure during the dry season.
Agricultural pesticide use is also an issue that cannot be ignored. Excessive use and improper handling of pesticides can often lead to serious water pollution, posing a threat to the water resource security of the YRB. To address this issue, we need to strengthen pesticide use management, promote scientific pesticide application techniques, reduce excessive pesticide use, raise farmers' environmental awareness to prevent pesticide waste from being directly discharged into water bodies, and strengthen water quality monitoring and treatment to promptly detect and address pesticide pollution problems.
Improve people’s education level and strengthen environmental awareness. As people's living standards and education levels improve, concerns about ecological water security have increased, and higher demands are being placed on water safety and quality. The incomplete assessment and mismanagement of water resources, coupled with wasteful practices, have led to water resources becoming uncontrollable variables. Recognizing, measuring, and expressing the value of water and incorporating it into decision-making processes are particularly important against the backdrop of increasingly scarce water resources, population growth, and the pressures of climate change. It is essential to achieve sustainable and equitable water resource management and meet the development goals of the United Nations' 2030 Agenda.
Actively participate in international ecological construction. According to Maximo Torero of the FAO, strengthening water resource protection and management requires enhanced cooperation among countries, the integration of various stakeholders' interests, multipronged approaches, and the consideration of social, economic, and environmental factors. It also involves a focus on technology, legal frameworks, and overall policy environments. We recommend that governments actively engage in international cooperation projects, sharing experiences and technologies in managing water resources in the YRB while drawing lessons from successful ecological initiatives in other countries. Such cross-border collaboration can foster global ecological sustainability, address global environmental issues collectively, share innovative technologies and research achievements, and achieve global governance of ecological environments.
Data availability
Our data is sourced from the provincial data in the China Statistical Yearbooks from 2011 to 2019 published by the National Bureau of Statistics of China ( https://www.stats.gov.cn/sj/ndsj/ ), as well as the Water Resources Bulletins ( http://www.mwr.gov.cn/sj/tjgb/szygb/ ). Figures 6 , 7 , and 8 were created by us using ArcGIS 10.4 software, which is provided by the Environmental Systems Research Institute, Inc. (commonly known as ESRI). Our vector boundary data and the Yangtze River data are sourced from the National Catalogue Service For Geographic Information ( www.webmap.cn ), using the 1:1,000,000 public version of basic geographic information data (2021). The tiled data is processed according to GB/T 13989-2012 “National Fundamental Scale Topographic Map Tiling and Numbering”.
Lun, C. The state of the world’s water resources is alarming Water challenges are exceptionally serious. Ecol. Econ. 6 , 526 (2012).
Google Scholar
Zunwen, Q. & Xiaqing, N. Spatial and temporal evolution and drivers of coordinated development of urbanization efficiency and water resources efficiency in the Yangtze River economic belt. Resource. Env. Yangtze Basin 2023 , 2237–2253 (2023).
Li-hong, M., Ying-fei, S. & You-cun, L. Evaluation of water resources security pattern of urban agglomeration in the middle reaches of the Yangtze river from the perspective of man-water relationship. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2022 , 50 (2022).
Yinmeng, C. Analysis and numerical simulation ofenvironmentalpollution logisties population growth system Master thesis, Donghua University (2022).
Verhulst, P. F. Notice sur la loi que la population suit dans son accroissement. Correspond. Math. Phys. 10 , 113–121 (1838).
Yi, L., Yuanhua, J. & Changfeng, S. Study on selforganization evolution mechanism of regional transport structure—analysis based on Logistic Model. Tech. Econ. Manage. 4 , 856 (2011).
Haibo, C., Yujing, L. & Fang, C. Law of R&D investment and strategic thinking in China based on Logistic curve model. Sci. Technol. Manage. Res. 30 , 25–27 (2010).
Zhou, L. & Jun, Z. Evolution mechanism of regional logistics ecosystem based on composite Logistic development mechanism. Ecol. Econ. 30 , 142–145 (2014).
Tao, Z. Study on urban spatial evolution based on Logistic model. Ecol. Econ. 31 , 155–158 (2015).
Zichen, N. Research on enterprise co-opetition relationship based on multi-patent subject Lotka-Volterra model. Northeast Normal Univ. 2020 , 523 (2020).
Holst, D. R. & Weiss, J. ASEAN and China: Export rivals or partners in regional growth?. World Econ. 27 , 1255–1274. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-9701.2004.00649.x (2004).
Article Google Scholar
Qian, Y. The extension and application of Lotka-Volterra model. Jiangxi Univ. Financ. Econ. 2022 , 56 (2022).
Jinhao, Q., Fuqiang, W., Subing, L., Heng, Z. & Honglu, Z. Prediction of water cycle health status in Zhengzhou City based on DPSIR model and entropy weight fuzzy comprehensive evaluation. Water Resourc. Power 41 , 45–48. https://doi.org/10.20040/j.cnki.1000-7709.2023.20222176 (2023).
Jianhua, W., Fan, H. & Guohua, H. Some understandings on water resources carrying capacity need to be clarified. China Water Resourc. 2020 , 5 (2020).
Zhen, Z., Chunxia, C. & Bo, H. Research progress and trend of ’ double evaluation ’ in the context of reconstruction of territorial spatial planning system. Planner 36 , 5–9 (2020).
Li, B., Wang, X., Wei, T., Zeng, Y. & Zhang, B. Analysis of sustainable utilization of water resources in karst region based on the ecological footprint model—Liupanshui city case. J. Water Supply Res. Technol. 67 , 575 (2018).
Chaoyang, D., Huaping, Z. & Jingjie, Y. Research on the mechanism of sustainable water resources system. Adv. Water Sci. 24 , 8 (2013).
Mei, G., Zhen-Cheng, X. U. & Xiao-Chun, P. Progress in water security. Water Resourc. Protect. 2007 , 545 (2007).
Chuheng, H. et al. Evaluation and influencing factors analysis of water resources security in Guangdong Province based on entropy method and analytic hierarchy process. J. Water Resourc. Water Eng. 2019 , 128790 (2019).
Ofoezie, I. E. Human health and sustainable water resources development in Nigeria: Schistosomiasis inartificial lakes. Nat. Resourc. Forum 26 , 150–160 (2010).
Sun, H., Guo, H., Li, L. & Chen, B. System analysis on water resources supporting alternatives for Chaidamu Basin. Chin. J. Enviroment. 21 , 16–21 (2000).
Yaoguang, Q. & Shengyue, F. Analysis, calculation and countermeasures of water resources carrying capacity in Heihe River Basin. J. Desert Res. 20 , 1–8 (2000).
Fulei, Z. & Zhijun, L. Evaluation of water resources carrying capacity in Qingdao city based on AHP-TOPSlS model. Tech. Supervis. Water Resourc. 2024 , 218–222 (2024).
Ma, L., Zhao, J. H., Hong, M. & Chen, L. L. Application of set pair analysis model based on entropy weight for comprehensive evaluation of water resources carrying capacity. Mech. Eng. Intell. Syst. 195–196 , 764–769 (2012).
Xiong, H. G., Fu, J. H. & Wang, K. L. Evaluation of water resource carrying capacity of Qitai Oasis in Xinjiang by entropy method. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 20 , 1382–1387 (2012).
Wang, C., Li, Z. J., Chen, H. F. & Wang, M. B. Comprehensive evaluation of agricultural water resources’ carrying capacity in Anhui Province based on an improved TOPSIS model. Sustainability 15 , 13297. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151813297 (2023).
Xingwang, Z. & Xuechun, D. Evaluating water resource carrying capacity in Pearl River-West River economic Belt based on portfolio weights and GRA-TOPSIS-CCDM. Ecol. Indic. 161 , 111962 (2024).
Zhang, Q. & Tan, B. In 2011 Second International Conference on Mechanic Automation and Control Engineering (2011).
Fu, Q., Jiang, Q. & Wang, Z. Comprehensive Evaluation of Regional Agricultural Water and Land Resources Carrying Capacity Based on DPSIR Concept Framework and PP Model. (Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, 2012).
Gong, L. & Jin, C. L. Fuzzy comprehensive evaluation for carrying capacity of regional water resources. Water Resourc. Manage. 23 , 2505–2513. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-008-9393-y (2009).
Meng, L. H., Chen, Y. N., Li, W. H. & Zhao, R. F. Fuzzy comprehensive evaluation model for water resources carrying capacity in Tarim River Basin, Xinjiang, China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 19 , 89–95. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-009-0089-x (2009).
Wang, Y. J., Yang, G. & Xu, H. L. In International Conference of Environment Materials and Environment Management 488 (2010).
Gao, Y., Zhang, S., Xu, G. W., Su, H. M. & Zhang, Y. In 2nd International Conference on Energy, Environment and Sustainable Development (EESD 2012) 2701–2704 (2013).
Xiaolin, S. Research on evaluation and regulation of regional water resources carrying capacity in Taiyuan City. In Zhengzhou University (2021).
Xing, C., Zihan, S., Qin, X., Ruijia, L. & Jing, C. Research and analysis on monthly water consumption prediction methods in Shaanxi Province. Adv. Sci. Technol. Water Resourc. 2020 , 1–10 (2024).
Hongye, N., Cuimei, L., Hao, W., Yan, H. & Zhuo, Z. Prediction model of water demand in Yinchuan City based on ClWOA-BP and Grey confidence interval. Yellow River 46 , 75–78 (2024).
Jing, H. Evaluation of Water Security in the Lancang-Mekong River Basin Master thesis. In Yunnan Normal University (2023).
Yang, G. Evaluation method of groundwater resources utilization efficiency based on fuzzy probability. Water Conserv. Sci. Technol. Econ. 28 , 8–12 (2022).
Ait-Aoudia, M. N. & Berezowska-Azzag, E. Water resources carrying capacity assessment: The case of Algeria’s capital city. Habitat Int. 58 , 51–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.habitatint.2016.09.006 (2016).
Yan, L., Jiao, D. & Yongshi, Z. Evaluation of regional water resources carrying capacity in China based on variable weight model and grey-markov model: A case study of Anhui province. Sci. Rep. 13 , 1 (2023).
Zhenggan, C. Discussion on the concept and research method of regional water resources carrying capacity. Jushe 65 , 183–200 (2020).
Jiajun, L., Suocheng, D. & Zehong, L. Study on comprehensive evaluation of water resources carrying capacity in China. J. Nat. Resourc. 26 , 258–269 (2011).
Ren, C., Guo, P., Li, M. & Li, R. An innovative method for water resources carrying capacity research e Metabolic theory of regional water resources. J. Environ. Manage. 167 , 139–146 (2020).
Raskin, P., Gleick, P., Kirshen, P., Pontius, G. & Strzepek, K. Comprehensive assessment of the freshwater resources of the world. Water futures: Assessment of long-range patterns and problems. Stockholm Sweden Stockholm Env. Inst. 1997 , 856 (1997).
Rui, Z. Vulnerability assessment of water resources in Shanxi Province based on catastrophe progression method. Water Resourc. Power 37 , 29–32 (2019).
Zhijun, L. & Yang, X. Comprehensive evaluation of water resources security in Xi’an based on lmproved emergy ecological footprint. J. Yangtze River Sci. Res. Inst. 2024 , 1–8 (2024).
Zhang, J., Deng, X., Zhai, L. & Hou, M. Fuzzy comprehensive evaluation of water resources sustainable utilization based on entropy weight in Guangxi. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 25 , 385–389 (2018).
Miliang, L. Comprehensive evaluation of urban water resources carrying capacity and analysis of influencing factors. Water Conserv. Sci. Technol. Econ. 30 , 106–111 (2024).
Yunling, L., Xuning, G., Dongyang, G. & Xiaohong, W. Research and application of water resources carrying capacity evaluation method. Adv. Geogr. Sci. 36 , 8 (2017).
Xuexiu, J. et al. Review of regional water resources pressure analysis and evaluation methods. J. Nat. Resourc. 9 , 1783 (2016).
Guohua, H., Ni, W., Warehouse, T. B. & Jiwei, Z. Establishment and application of fuzzy comprehensive evaluation model of water resources allocation harmony based on entropy weight. J. Northwest A&F Univ. Nat. Sci. Ed. 44 , 7 (2016).
Shiklomanov, I. A. et al. World water resources at the beginning of the 21st century. Int. Hydrol. 2003 , 13 (2003).
Deng, G., Li, L. & Song, Y. Provincial water use efficiency measurement and factor analysis in China: Based on SBM-DEA model. Ecol. Indic. 69 , 12–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2016.03.052 (2016).
Yahao, Y. & Lingyan, L. Analysis of regional differences and influencing factors of water resources efficiency in China. Econ. Geogr. 37 , 8 (2017).
Mei, G., Huige, W. & Benliang, Q. Study on the utilization efficiency of water resources and its spatial correlation pattern in Liaoning Province under the background of a new round of revitalization of Northeast China. Resourc. Sci. 38 , 14 (2016).
Kaohsiung, H. W., Yuanyuan, G. & Xinyi, X. Evaluation model of water resources utilization efficiency based on iterative correction and its application. J. Hydraul. Eng. 44 , 478–488. https://doi.org/10.13243/j.cnki.slxb.2013.04.003 (2013).
Shanshan, L., Hailiang, M. & Yaru, H. Dynamic coupling analysis of urbanization and water resources system in Beijing. Yangtze River 49 , 60–74. https://doi.org/10.16232/j.cnki.1001-4179.2018.01.012 (2018).
Wei, Z. Coupling analysis of new urbanization quality and water resources security in Guangdong Province. Yangtze River 50 , 7 (2019).
Caizhi, S. & Xiaodong, Y. Safety assessment and spatial correlation analysis of water resources-energy-food coupling system in China. Water Resourc. Protect. 34 , 1–8 (2018).
Xia, Z. et al. Dynamic analysis of the matching degree between water resources and economic and social development in China. Yangtze River 49 , 68–73. https://doi.org/10.16232/j.cnki.1001-4179.2018.23.012 (2018).
Yanxia, W., Heng, L. & Zhikang, L. Study on ecological security measurement of Yangtze River economic belt. Acta Ecol. Sin. 40 , 15 (2020).
Zhiguang, Z. The symbiotic coupling measurement model and criterion of forestry ecological security. China Popul. Resourc. Env. 24 , 10 (2014).
Yuze, Z., Jianlan, R., Kai, L. & Yu, C. Ecological security early warning measurement and spatial-temporal pattern in Shandong Province. Econ. Geogr. 7 , 110233 (2015).
Xiaotao, Z. & Fa-wen, Y. Analysis on the matching status of economic development and water resources in the Yellow River Basin. China Popul. Resourc. Env. 27 , 2742 (2012).
Hao, W. & Yong, Z. A preliminary study on the strategy of yellow river treatment in the new period. J. Hydraul. Eng. 18 , 109856 (2018).
Download references
This research was supported by the Project of Social Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (No. 22TQC005).
Author information
These authors contributed equally: Jie-Rong Zhou and Xiao-Qing Li.
Authors and Affiliations
Nanjing Xiaozhuang University, Nanjing, 211171, Jiangsu, China
Jie-Rong Zhou, Xiao-Qing Li, Xin Yu & Tian-Cheng Zhao
School of Information Management, Nanjing University, Nanjing, 210023, Jiangsu, China
Wageningen University and Research, 6700 AA, Wageningen, The Netherlands
Wen-Xi Ruan
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Conceptualization, J.Z. and X.Y.; methodology, J.Z. and X.L.; software, W.R.; writing—original draft preparation, X.L. and X.Y.; writing—review and editing, X.L., X.Y. and J.Z.; visualization, T.Z.; supervision, X.Y.; project administration, X.Y.; funding acquisition, X.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Xin Yu .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Zhou, JR., Li, XQ., Yu, X. et al. Exploring the ecological security evaluation of water resources in the Yangtze River Basin under the background of ecological sustainable development. Sci Rep 14 , 15475 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-65781-z
Download citation
Received : 03 April 2024
Accepted : 24 June 2024
Published : 05 July 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-65781-z
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Water resource ecological security
- Yangtze River Basin
- Evaluation system
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines . If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Sign up for the Nature Briefing: Anthropocene newsletter — what matters in anthropocene research, free to your inbox weekly.
Information
- Author Services
Initiatives
You are accessing a machine-readable page. In order to be human-readable, please install an RSS reader.
All articles published by MDPI are made immediately available worldwide under an open access license. No special permission is required to reuse all or part of the article published by MDPI, including figures and tables. For articles published under an open access Creative Common CC BY license, any part of the article may be reused without permission provided that the original article is clearly cited. For more information, please refer to https://www.mdpi.com/openaccess .
Feature papers represent the most advanced research with significant potential for high impact in the field. A Feature Paper should be a substantial original Article that involves several techniques or approaches, provides an outlook for future research directions and describes possible research applications.
Feature papers are submitted upon individual invitation or recommendation by the scientific editors and must receive positive feedback from the reviewers.
Editor’s Choice articles are based on recommendations by the scientific editors of MDPI journals from around the world. Editors select a small number of articles recently published in the journal that they believe will be particularly interesting to readers, or important in the respective research area. The aim is to provide a snapshot of some of the most exciting work published in the various research areas of the journal.
Original Submission Date Received: .
- Active Journals
- Find a Journal
- Proceedings Series
- For Authors
- For Reviewers
- For Editors
- For Librarians
- For Publishers
- For Societies
- For Conference Organizers
- Open Access Policy
- Institutional Open Access Program
- Special Issues Guidelines
- Editorial Process
- Research and Publication Ethics
- Article Processing Charges
- Testimonials
- Preprints.org
- SciProfiles
- Encyclopedia

Article Menu

- Subscribe SciFeed
- Recommended Articles
- Google Scholar
- on Google Scholar
- Table of Contents
Find support for a specific problem in the support section of our website.
Please let us know what you think of our products and services.
Visit our dedicated information section to learn more about MDPI.
JSmol Viewer
The impact of regional carbon emission reduction on corporate esg performance in china.

1. Introduction
2. institutional background, 2.1. chinese carbon emission reduction history, 2.2. analysis of the relationship between carbon emission reduction and esg performance of local firms in chinese provinces, 2.3. the impact of the covid-19 pandemic on carbon emissions in china, 3. literature review, theoretical analysis, and hypothesis development, 3.1. regional carbon emission reduction and esg performance of local enterprises, 3.2. the channel mechanisms of regional carbon emission reduction in the esg performance of local enterprises: green credit, 3.3. the channel mechanisms of regional carbon emission reduction in the esg performance of local enterprises: media coverage, 3.4. the channel mechanisms of regional carbon emission reduction in the esg performance of local enterprises: green investors, 4. research design, 4.1. sample and data, 4.2. variable definitions, 4.2.1. carbon emission reduction, 4.2.2. corporate esg performance, 4.2.3. control variables, 4.3. empirical models, 5. empirical results and analysis, 5.1. descriptive statistics, 5.2. baseline regression analysis, 5.3. robustness check, 5.3.1. instrumental variable approach, 5.3.2. propensity score matching, 5.3.3. excluding the three biggest provinces in terms of population, 5.3.4. alternative measures of corporate esg performance, 5.3.5. alternative measures of regional carbon emissions reduction, 5.3.6. lagging the explanatory variable, 5.3.7. excluding the impact of the covid-19 pandemic.
| Variables | (1) ESG | (2) ESG | (3) WindESG | (4) ESG | (5) ESG | (6) ESG |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.360 *** | 0.261 *** | 0.693 *** | 0.294 *** | 0.270 *** | ||
| (3.813) | (2.760) | (5.666) | (3.272) | (3.225) | ||
| 0.055 ** | ||||||
| (2.112) | ||||||
| 2.072 *** | 2.136 *** | −0.516 | 1.855 *** | 1.563 *** | 1.977 *** | |
| (4.902) | (4.923) | (−1.248) | (4.748) | (3.684) | (4.573) | |
| Control variables | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | |
| YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | |
| N | 21,680 | 23,057 | 12,852 | 30,349 | 26,238 | 23,560 |
| adj. R | 0.360 | 0.367 | 0.203 | 0.374 | 0.390 | 0.262 |
5.4. Mechanism Analysis
5.4.1. the green credit mechanism, 5.4.2. the media coverage mechanism, 5.4.3. the green investor mechanism, 5.5. heterogeneity analysis, 5.5.1. impact of environmental regulation, 5.5.2. impact of industry nature, 5.5.3. impact of digitization.
| Variables | Environmental Regulation | Industry Nature | Digitization | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) Lenient ESG | (2) Stringent ESG | (3) Non-Heavy-Polluting ESG | (4) Heavy-Polluting ESG | (5) Low ESG | (6) High ESG | |
| 0.079 | 0.314 *** | 0.167 | 0.476 *** | 0.335 *** | 0.128 | |
| (0.545) | (3.226) | (1.492) | (3.715) | (3.720) | (0.902) | |
| 3.033 *** | 1.309 *** | 1.709 ** | 2.675 *** | 2.634 *** | 1.137 ** | |
| (6.273) | (2.700) | (3.845) | (3.961) | (5.281) | (2.111) | |
| Control variables | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | |
| YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | |
| N | 15,264 | 15,085 | 21,401 | 8945 | 14,824 | 14,824 |
| adj. R | 0.444 | 0.271 | 0.410 | 0.290 | 0.322 | 0.414 |
6. Further Analysis
6.1. the spillover effects of regional residents’ carbon emission reduction, 6.2. economic consequence check, 7. discussion, 8. conclusions, author contributions, institutional review board statement, informed consent statement, data availability statement, conflicts of interest.
- Baldini, M.; Maso, L.D.; Liberatore, G.; Mazzi, F.; Terzani, S. Role of country-and firm-level determinants in environmental, social, and governance disclosure. J. Bus. Ethics 2018 , 150 , 79–98. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Martiny, A.; Testa, F.; Taglialatela, J.; Iraldo, F. Determinants of Environmental Social and Governance (ESG) Performance: A Systematic Literature Review. J. Clean. Prod. 2024 , 456 , 142213. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Yan, J.; Huang, Y.; Liao, X. Help or hindrance? The impact of female executives on corporate ESG performance in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2024 , 437 , 140614. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Li, Y.; Gong, M.; Zhang, X.Y.; Koh, L. The impact of environmental, social, and governance disclosure on firm value: The role of CEO power. Br. Account. Rev. 2018 , 50 , 60–75. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Fang, M.; Nie, H.; Shen, X. Can enterprise digitization improve ESG performance? Econ. Model. 2023 , 118 , 106101. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Deng, X.; Li, W.; Ren, X. More sustainable, more productive: Evidence from ESG ratings and total factor productivity among listed Chinese firms. Financ. Res. Lett. 2023 , 51 , 103439. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Tsang, A.; Frost, T.; Cao, H. Environmental, social, and governance (ESG) disclosure: A literature review. Br. Account. Rev. 2023 , 55 , 101149. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Shen, H.; Lin, H.; Han, W.; Wu, H. ESG in China: A review of practice and research, and future research avenues. China J. Account. Res. 2023 , 4 , 100325. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Wang, K.; Chen, X.; Wang, C. The impact of sustainable development planning in resource-based cities on corporate ESG—Evidence from China. Energy Econ. 2023 , 127 , 107087. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- He, Y.; Zhao, X.; Zheng, H. How does the environmental protection tax law affect firm ESG? Evidence from the Chinese stock markets. Energy Econ. 2023 , 127 , 107067. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Wang, Y.; Shen, N. Environmental regulation and environmental productivity: The case of China. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016 , 62 , 758–766. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Li, J.; Lian, G.; Xu, A. How do ESG affect the spillover of green innovation among peer firms? Mechanism discussion and performance study. J. Bus. Res. 2023 , 158 , 113648. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Broadstock, D.C.; Chan, K.; Cheng, L.T.; Wang, X. The role of ESG performance during times of financial crisis: Evidence from COVID-19 in China. Financ. Res. Lett. 2021 , 38 , 101716. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ PubMed ]
- Zhong, S.; Hou, J.; Li, J.; Gao, W. Exploring the relationship of ESG score and firm value using fsQCA method: Cases of the Chinese manufacturing enterprises. Front. Psychol. 2022 , 13 , 1019469. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ PubMed ]
- Qiang, S.; Gang, C.; Dawei, H. Environmental cooperation system, ESG performance and corporate green innovation: Empirical evidence from China. Front. Psychol. 2023 , 14 , 1096419. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Zhu, N.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, S.; Yan, J. Tax incentives and environmental, social, and governance performance: Empirical evidence from China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023 , 30 , 54899–54913. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ PubMed ]
- Bai, F.; Shang, M.; Huang, Y. Corporate culture and ESG performance: Empirical evidence from China. J. Clean. Prod. 2024 , 437 , 140732. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Letta, M.; Tol, R.S. Weather, climate and total factor productivity. Environ. Resour. Econ. 2019 , 73 , 283–305. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Li, C.; Tang, W.; Liang, F.; Wang, Z. The impact of climate change on corporate ESG performance: The role of resource misallocation in enterprises. J. Clean. Prod. 2024 , 445 , 141263. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Ji, Q.; Quan, X.; Yin, H.; Yuan, Q. Gambling preferences and stock price crash risk: Evidence from China. J. Bank. Financ. 2021 , 128 , 106158. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Ding, X.; Ren, Y.; Tan, W.; Wu, H. Does carbon emission of firms matter for Bank loans decision? Evidence from China. Int. Rev. Financ. Anal. 2023 , 86 , 102556. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Safiullah, M.; Kabir, M.N.; Miah, M.D. Carbon emissions and credit ratings. Energy Econ. 2021 , 100 , 105330. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Hu, Y.; Monroy, C.R. Chinese energy and climate policies after Durban: Save the Kyoto Protocol. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2012 , 16 , 3243–3250. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, S. Preventing carbon emission retaliatory rebound post-COVID-19 requires expanding free trade and improving energy efficiency. Sci. Total Environ. 2020 , 746 , 141158. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ PubMed ]
- Han, P.; Cai, Q.; Oda, T.; Zeng, N.; Shan, Y.; Lin, X.; Liu, D. Assessing the recent impact of COVID-19 on carbon emissions from China using domestic economic data. Sci. Total Environ. 2021 , 750 , 141688. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ PubMed ]
- Wang, Q.; Li, S.; Li, R.; Jiang, F. Underestimated impact of the COVID-19 on carbon emission reduction in developing countries—A novel assessment based on scenario analysis. Environ. Res. 2022 , 204 , 111990. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ PubMed ]
- Le Quéré, C.; Jackson, R.B.; Jones, M.W.; Smith, A.J.P.; Abernethy, S.; Andrew, R.M.; De-Gol, A.J.; Willis, D.R.; Shan, Y.; Canadell, J.G.; et al. Temporary reduction in daily global CO2 emissions during the COVID-19 forced confinement. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2020 , 10 , 647–653. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Peters, G.P.; Marland, G.; Le Quéré, C.; Boden, T.; Canadell, J.G.; Raupach, M.R. Rapid growth in CO2 emissions after the 2008–2009 global financial crisis. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2012 , 2 , 2–4. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Freeman, R.B. Unionism comes to the public sector. J. Econ. Lit. 1986 , 3 , 41–86. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Huynh, T.D.; Xia, Y. Climate Change News Risk and Corporate Bond Returns. J. Financ. Quant. Anal. 2021 , 56 , 1985–2009. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Bannier, C.E.; Bofinger, Y.; Rock, B. Corporate social responsibility and credit risk. Financ. Res. Lett. 2022 , 44 , 102052. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Leins, S. ‘Responsible investment’: ESG and the post-crisis ethical order. Econ. Soc. 2020 , 49 , 71–91. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Wong, S.L. The impact of female representation and ethnic diversity in committees on environmental, social and governance performance in Malaysia. Soc. Bus. Rev. 2024 , 19 , 207–229. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Huang, M.; Li, M.; Li, X. Do non-local CEOs affect environmental, social and governance performance? Manag. Decis. 2023 , 61 , 2354–2373. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- He, F.; Guo, X.; Yue, P. Media coverage and corporate ESG performance: Evidence from China. Int. Rev. Financ. Anal. 2024 , 91 , 103003. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Jiang, Y.; Wang, C.; Li, S.; Wan, J. Do institutional investors’ corporate site visits improve ESG performance? Evidence from China. Pac.-Basin Financ. J. 2022 , 76 , 101884. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Cheng, J.; Yi, J.; Dai, S.; Xiong, Y. Can low-carbon city construction facilitate green growth? Evidence from China’s pilot low-carbon city initiative. J. Clean. Prod. 2019 , 231 , 1158–1170. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Sovacool, B.K.; Blyth, P.L. Energy and environmental attitudes in the green state of Denmark: Implications for energy democracy, low carbon transitions, and energy literacy. Environ. Sci. Policy 2015 , 54 , 304–315. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Homroy, S. GHG emissions and firm performance: The role of CEO gender socialization. J. Bank. Financ. 2023 , 148 , 106721. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Barahona, N.; Gallego, F.A.; Montero, J.P. Vintage-specific driving restrictions. Rev. Econ. Stud. 2020 , 87 , 1646–1682. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Tina Dacin, M.; Goodstein, J.; Richard Scott, W. Institutional theory and institutional change: Introduction to the special research forum. Acad. Manag. J. 2002 , 45 , 45–56. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Shu, H.; Tan, W. Does carbon control policy risk affect corporate ESG performance? Econ. Model. 2023 , 120 , 106148. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Elster, J. Social norms and economic theory. J. Econ. Perspect. 1989 , 3 , 99–117. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- John, K.; Knyazeva, A.; Knyazeva, D. Does geography matter? Firm location and corporate payout policy. J. Financ. Econ. 2011 , 101 , 533–551. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Coval, J.D.; Moskowitz, T.J. Home bias at home: Local equity preference in domestic portfolios. J. Financ. 1999 , 54 , 2045–2073. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Kaustia, M.; Rantala, V. Social learning and corporate peer effects. J. Financ. Econ. 2015 , 117 , 653–669. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Wang, Y.; Lei, X.; Long, R.; Zhao, J. Green credit, financial constraint, and capital investment: Evidence from China’s energy-intensive enterprises. Environ. Manag. 2020 , 66 , 1059–1071. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Fazzari, S.M.; Petersen, B.C. Working capital and fixed investment: New evidence on financing constraints. RAND J. Econ. 1993 , 24 , 328–342. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Yu, C.; Wu, X.; Zhang, D.; Chen, S.; Zhao, J. Demand for green finance: Resolving financing constraints on green innovation in China. Energy Policy 2021 , 153 , 112255. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Hu, G.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y. Can the green credit policy stimulate green innovation in heavily polluting enterprises? Evidence from a quasi-natural experiment in China. Energy Econ. 2021 , 98 , 105134. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Wang, Y.C.; Feng, Z.Y.; Huang, H.W. Corporate carbon dioxide emissions and the cost of debt financing: Evidence from the global tourism industry. Int. J. Tour. Res. 2021 , 23 , 56–69. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Fan, L.; Yang, K.; Liu, L. New media environment, environmental information disclosure and firm valuation: Evidence from high-polluting enterprises in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020 , 277 , 123253. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Bednar, M.K.; Boivie, S.; Prince, N.R. Burr under the saddle: How media coverage influences strategic change. Organ. Sci. 2013 , 24 , 910–925. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Saxton, G.D.; Ren, C.; Guo, C. Responding to diffused stakeholders on social media: Connective power and firm reactions to CSR-related Twitter messages. J. Bus. Ethics 2021 , 172 , 229–252. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Gibson, R.; Glossner, S.; Krueger, P.; Matos, P.; Steffen, T. Responsible Institutional Investing around the World (No. 20-13) ; Swiss Finance Institute: Zürich, Switzerland, 2020. [ Google Scholar ]
- Zhang, L.; Xie, Y.; Xu, D. Green Investor Holdings and Corporate Green Technological Innovation. Sustainability 2024 , 16 , 4292. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Sangiorgi, I.; Schopohl, L. Why do institutional investors buy green bonds: Evidence from a survey of European asset managers. Int. Rev. Financ. Anal. 2021 , 75 , 101738. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Porter, M.E.; Kramer, M.R. Creating shared value: How to reinvent capitalism—And unleash a wave of innovation and growth. In Managing Sustainable Business: An Executive Education Case and Textbook ; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 323–346. Available online: http://hbr.org/2011/01/the-big-idea-creating-shared-value/ar/pr (accessed on 3 June 2024).
- Piñeiro-Chousa, J.; López-Cabarcos, M.Á.; Caby, J.; Šević, A. The influence of investor sentiment on the green bond market. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2021 , 162 , 120351. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Bharath, S.T.; Jayaraman, S.; Nagar, V. Exit as governance: An empirical analysis. J. Financ. 2013 , 68 , 2515–2547. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Xu, J.; Guan, Y.; Oldfield, J.; Guan, D.; Shan, Y. China carbon emission accounts 2020–2021. Appl. Energy 2024 , 360 , 122837. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Hu, Y.; Zheng, J. How does green credit affect carbon emissions in China? A theoretical analysis framework and empirical study. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022 , 29 , 59712–59726. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
Click here to enlarge figure
| Type | Variable | Symbol | Definition |
|---|---|---|---|
| Explained variable | Corporate ESG performance | According to the Hua Zheng ESG rating, the ESG index has nine levels: the lowest level is 1, and the highest level is 9 | |
| Explanatory variables | Regional carbon emission reduction | Carbon emission reduction level per unit regional gross domestic product | |
| Dummy variable, assigned a value of 1 if carbon emission intensity decreases and 0 otherwise (this variable is used for robustness testing) | |||
| Province-level control variables | Human capital | Enrollment in higher education institutions/total population | |
| Transportation infrastructure level | The natural logarithm of freight volume | ||
| Energy structure | Regional electricity consumption/national electricity consumption | ||
| Level of informatization | Total postal and telecommunications services volume/regional gross domestic product | ||
| Firm-level control variables | Corporate size | The natural logarithm of the total number of assets | |
| Corporate age | The natural logarithm of years that the company has been in existence | ||
| Company performance | Net profit/operating income | ||
| Operating revenue growth rate | (Current operating income − previous operating income)/previous operating income | ||
| Board size | The natural logarithm of the number of directors | ||
| Equity checks and balances | The combined shareholdings of the second to fifth largest shareholders/the shareholding of the largest shareholder | ||
| Proportion of independent directors | Number of independent directors/total number of board of directors | ||
| Management expense ratio | Operating expenses/operating revenue | ||
| Dual positions | Dummy variable, which equals 1 if the CEO also serves as chairman and 0 otherwise | ||
| Institutional investor shareholding ratio | The total number of shares held by institutional investors/the total outstanding shares of the company | ||
| Property rights nature | Assign a value of 1 to state-owned enterprises and a value of 0 to non-state-owned enterprises based on the nature of the actual controlling entity | ||
| Year fixed effects | Year dummy variables | ||
| Industry fixed effects | Industry dummy variables |
| Variables | N | Mean | SD | Min | Median | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30,349 | 5.758 | 0.874 | 3.250 | 5.500 | 7.750 | |
| 390 | −0.090 | 0.181 | −1.140 | −0.042 | 0.173 | |
| 390 | 0.877 | 0.329 | 0.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | |
| 30,349 | 0.020 | 0.005 | 0.012 | 0.020 | 0.036 | |
| 30,349 | 11.940 | 0.834 | 9.907 | 12.170 | 12.940 | |
| 30,349 | 0.051 | 0.030 | 0.011 | 0.038 | 0.097 | |
| 30,349 | 0.064 | 0.046 | 0.017 | 0.046 | 0.195 | |
| 30,349 | 22.220 | 1.284 | 19.940 | 22.040 | 26.210 | |
| 30,349 | 2.880 | 0.336 | 1.792 | 2.944 | 3.497 | |
| 30,349 | 0.067 | 0.121 | −0.550 | 0.072 | 0.358 | |
| 30,349 | 0.178 | 0.399 | −0.540 | 0.114 | 2.486 | |
| 30,349 | 2.132 | 0.198 | 1.609 | 2.197 | 2.708 | |
| 30,349 | 0.348 | 0.284 | 0.009 | 0.263 | 0.994 | |
| 30,349 | 0.375 | 0.053 | 0.333 | 0.357 | 0.571 | |
| 30,349 | 0.086 | 0.066 | 0.008 | 0.070 | 0.395 | |
| 30,349 | 0.266 | 0.442 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 1.000 | |
| 30,349 | 0.398 | 0.234 | 0.002 | 0.407 | 0.883 | |
| 30,349 | 0.394 | 0.489 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 1.000 |
| Variables | (1) ESG | (2) ESG | (3) ESG |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.238 ** | 0.247 *** | 0.297 *** | |
| (2.503) | (2.823) | (3.475) | |
| −2.391 | −8.062 *** | ||
| (−0.752) | (−2.980) | ||
| −0.076 *** | −0.067 *** | ||
| (−3.423) | (−3.579) | ||
| −0.227 | 0.111 | ||
| (−0.424) | (0.243) | ||
| −0.861 ** | −1.044 *** | ||
| (−2.080) | (−2.872) | ||
| 0.187 *** | 0.184 *** | ||
| (20.923) | (20.526) | ||
| −0.040 | −0.034 | ||
| (−1.250) | (−1.077) | ||
| 1.150 *** | 1.161 *** | ||
| (19.751) | (20.112) | ||
| −0.092 *** | −0.093 *** | ||
| (−8.803) | (−8.847) | ||
| 0.077 | 0.078 | ||
| (1.397) | (1.409) | ||
| 0.001 | 0.005 | ||
| (0.042) | (0.167) | ||
| 0.335 * | 0.316 * | ||
| (1.919) | (1.817) | ||
| −0.021 | −0.073 | ||
| (−0.146) | (−0.516) | ||
| −0.004 | −0.003 | ||
| (−0.231) | (−0.183) | ||
| 0.176 *** | 0.177 *** | ||
| (4.745) | (4.781) | ||
| 0.212 *** | 0.205 *** | ||
| (8.455) | (8.127) | ||
| 6.363 *** | 0.964 *** | 1.970 *** | |
| (19.879) | (3.132) | (5.030) | |
| YES | YES | YES | |
| YES | YES | YES | |
| N | 30,349 | 30,349 | 30,349 |
| adj. R | 0.247 | 0.372 | 0.374 |
| Variables | (1) 1st Stage CER | (2) 2nd Stage ESG |
|---|---|---|
| 0.293 *** | ||
| (3.058) | ||
| −19.774 *** | ||
| (−20.167) | ||
| 0.021 *** | ||
| (5.326) | ||
| −3.818 *** | 1.969 *** | |
| (−25.163) | (5.048) | |
| Control variables | YES | YES |
| YES | YES | |
| YES | YES | |
| N | 30,349 | 30,349 |
| adj. R | 0.855 | 0.377 |
| Variables | Entire Sample | Financing Costs | Credit Availability | Implementation of the “Green Credit Guidelines” | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) ESG | (2) Low ESG | (3) High ESG | (4) Low ESG | (5) High ESG | (6) Pre- ESG | (7) Post- ESG | |
| 0.283 *** | 0.158 | 0.400 *** | 0.143 | 0.371 *** | 0.122 | 0.302 *** | |
| (20.202) | (1.559) | (3.565) | (1.284) | (3.188) | (1.277) | (2.705) | |
| 0.522 *** | 1.764 *** | 1.786 *** | 1.424 *** | 1.445 ** | 2.043 *** | 1.825 *** | |
| (7.488) | (3.499) | (3.581) | (2.818) | (2.472) | (3.216) | (4.273) | |
| Control variables | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | |
| YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | |
| N | 30,349 | 15,164 | 15,164 | 11,005 | 11,004 | 6129 | 24,220 |
| adj. R | 0.323 | 0.402 | 0.370 | 0.353 | 0.368 | 0.220 | 0.401 |
| Variables | Entire Sample | Number of Securities Analysts | |
|---|---|---|---|
| (1) ESG | (2) Low ESG | (3) High ESG | |
| 0.223 *** | 0.345 *** | 0.160 | |
| (3.778) | (3.307) | (0.996) | |
| −4.922 *** | 2.562 *** | 0.503 | |
| (−10.538) | (5.156) | (0.801) | |
| Control variables | YES | YES | YES |
| YES | YES | YES | |
| YES | YES | YES | |
| N | 21,422 | 14,083 | 7559 |
| adj. R | 0.337 | 0.328 | 0.339 |
| Variables | Entire Sample | Executives with Environmental Employment Backgrounds | |
|---|---|---|---|
| (1) ESG | (2) Without ESG | (3) Have ESG | |
| 0.163 ** | 0.291 *** | 0.218 | |
| (2.297) | (2.635) | (1.132) | |
| −5.257 *** | 1.562 *** | 1.888 *** | |
| (−22.588) | (3.023) | (2.704) | |
| Control variables | YES | YES | YES |
| YES | YES | YES | |
| YES | YES | YES | |
| N | 25,742 | 18,999 | 6743 |
| adj. R | 0.346 | 0.394 | 0.391 |
| Variables | (1) ESG |
|---|---|
| 0.016 *** | |
| (3.041) | |
| 1.884 *** | |
| (4.827) | |
| Control variables | YES |
| YES | |
| YES | |
| 30,349 | |
| 0.374 |
| Variables | Regional Carbon Emission Reduction | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) High TobinQ | (2) Low TobinQ | (3) High NCSKEW | (4) Low NCSKEW | (5) High DUVOL | (6) Low DUVOL | |
| 0.033 *** | 0.020 | −0.023 *** | −0.009 | −0.014 *** | −0.001 | |
| (1.486) | (−2.926) | (−1.227) | (−2.776) | (−0.100) | ||
| 10.211 *** | 9.878 *** | −0.261 | 0.361 | 0.222 | 0.468 ** | |
| (10.106) | (14.952) | (−0.905) | (1.280) | (1.133) | (2.470) | |
| Control variables | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | |
| YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | |
| 12,525 | 12,683 | 10,953 | 12,683 | 10,953 | ||
| 0.379 | 0.053 | 0.057 | 0.063 | 0.068 | ||
| The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
Share and Cite
Chen, X.; Wang, J. The Impact of Regional Carbon Emission Reduction on Corporate ESG Performance in China. Sustainability 2024 , 16 , 5802. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16135802
Chen X, Wang J. The Impact of Regional Carbon Emission Reduction on Corporate ESG Performance in China. Sustainability . 2024; 16(13):5802. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16135802
Chen, Xiaoqiu, and Jinxiang Wang. 2024. "The Impact of Regional Carbon Emission Reduction on Corporate ESG Performance in China" Sustainability 16, no. 13: 5802. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16135802
Article Metrics
Article access statistics, further information, mdpi initiatives, follow mdpi.

Subscribe to receive issue release notifications and newsletters from MDPI journals
Suggestions or feedback?
MIT News | Massachusetts Institute of Technology
- Machine learning
- Social justice
- Black holes
- Classes and programs
Departments
- Aeronautics and Astronautics
- Brain and Cognitive Sciences
- Architecture
- Political Science
- Mechanical Engineering
Centers, Labs, & Programs
- Abdul Latif Jameel Poverty Action Lab (J-PAL)
- Picower Institute for Learning and Memory
- Lincoln Laboratory
- School of Architecture + Planning
- School of Engineering
- School of Humanities, Arts, and Social Sciences
- Sloan School of Management
- School of Science
- MIT Schwarzman College of Computing
How to increase the rate of plastics recycling
Press contact :.

Previous image Next image
While recycling systems and bottle deposits have become increasingly widespread in the U.S., actual rates of recycling are “abysmal,” according to a team of MIT researchers who studied the rates for recycling of PET, the plastic commonly used in beverage bottles. However, their findings suggest some ways to change this.
The present rate of recycling for PET, or polyethylene terephthalate, bottles nationwide is about 24 percent and has remained stagnant for a decade, the researchers say. But their study indicates that with a nationwide bottle deposit program, the rates could increase to 82 percent, with nearly two-thirds of all PET bottles being recycled into new bottles, at a net cost of just a penny a bottle when demand is robust. At the same time, they say, policies would be needed to ensure a sufficient demand for the recycled material.
The findings are being published today in the Journal of Industrial Ecology , in a paper by MIT professor of materials science and engineering Elsa Olivetti, graduate students Basuhi Ravi and Karan Bhuwalka, and research scientist Richard Roth.
The team looked at PET bottle collection and recycling rates in different states as well as other nations with and without bottle deposit policies, and with or without curbside recycling programs, as well as the inputs and outputs of various recycling companies and methods. The researchers say this study is the first to look in detail at the interplay between public policies and the end-to-end realities of the packaging production and recycling market.
They found that bottle deposit programs are highly effective in the areas where they are in place, but at present there is not nearly enough collection of used bottles to meet the targets set by the packaging industry. Their analysis suggests that a uniform nationwide bottle deposit policy could achieve the levels of recycling that have been mandated by proposed legislation and corporate commitments.
The recycling of PET is highly successful in terms of quality, with new products made from all-recycled material virtually matching the qualities of virgin material. And brands have shown that new bottles can be safely made with 100 percent postconsumer waste. But the team found that collection of the material is a crucial bottleneck that leaves processing plants unable to meet their needs. However, with the right policies in place, “one can be optimistic,” says Olivetti, who is the Jerry McAfee Professor in Engineering and the associate dean of the School of Engineering.
“A message that we have found in a number of cases in the recycling space is that if you do the right work to support policies that think about both the demand but also the supply,” then significant improvements are possible, she says. “You have to think about the response and the behavior of multiple actors in the system holistically to be viable,” she says. “We are optimistic, but there are many ways to be pessimistic if we’re not thinking about that in a holistic way.”
For example, the study found that it is important to consider the needs of existing municipal waste-recovery facilities. While expanded bottle deposit programs are essential to increase recycling rates and provide the feedstock to companies recycling PET into new products, the current facilities that process material from curbside recycling programs will lose revenue from PET bottles, which are a relatively high-value product compared to the other materials in the recycled waste stream. These companies would lose a source of their income if the bottles are collected through deposit programs, leaving them with only the lower-value mixed plastics.
The researchers developed economic models based on rates of collection found in the states with deposit programs, recycled-content requirements, and other policies, and used these models to extrapolate to the nation as a whole. Overall, they found that the supply needs of packaging producers could be met through a nationwide bottle deposit system with a 10-cent deposit per bottle — at a net cost of about 1 cent per bottle produced when demand is strong. This need not be a federal program, but rather one where the implementation would be left up to the individual states, Olivetti says.
Other countries have been much more successful in implementing deposit systems that result in very high participation rates. Several European countries manage to collect more than 90 percent of PET bottles for recycling, for example. But in the U.S., less than 29 percent are collected, and after losses in the recycling chain about 24 percent actually get recycled, the researchers found. Whereas 73 percent of Americans have access to curbside recycling, presently only 10 states have bottle deposit systems in place.
Yet the demand is there so far. “There is a market for this material,” says Olivetti. While bottles collected through mixed-waste collection can still be recycled to some extent, those collected through deposit systems tend to be much cleaner and require less processing, and so are more economical to recycle into new bottles, or into textiles.
To be effective, policies need to not just focus on increasing rates of recycling, but on the whole cycle of supply and demand and the different players involved, Olivetti says. Safeguards would need to be in place to protect existing recycling facilities from the lost revenues they would suffer as a result of bottle deposits, perhaps in the form of subsidies funded by fees on the bottle producers, to avoid putting these essential parts of the processing chain out of business. And other policies may be needed to ensure the continued market for the material that gets collected, including recycled content requirements and extended producer responsibility regulations, the team found.
At this stage, it’s important to focus on the specific waste streams that can most effectively be recycled, and PET, along with many metals, clearly fit that category. “When we start to think about mixed plastic streams, that’s much more challenging from an environmental perspective,” she says. “Recycling systems need to be pursuing extended producers’ responsibility, or specifically thinking about materials designed more effectively toward recycled content,” she says.
It's also important to address “what the right metrics are to design for sustainably managed materials streams,” she says. “It could be energy use, could be circularity [for example, making old bottles into new bottles], could be around waste reduction, and making sure those are all aligned. That’s another kind of policy coordination that’s needed.”
Share this news article on:
Related links.
- Elsa Olivetti
- Basuhi Ravi
- Karan Bhuwalka
- Richard Roth
- Department of Materials Science and Engineering
Related Topics
- Materials science and engineering
- Sustainability
- Singapore-MIT Alliance for Research and Technology (SMART)
- Cleaner industry
- Technology and society
- Environment
Related Articles

Elsa Olivetti appointed associate dean of engineering
Rescuing small plastics from the waste stream

Merging science and systems thinking to make materials more sustainable

Making buildings from industrial waste
Previous item Next item
More MIT News

Empowering future innovators through a social impact lens
Read full story →

Researchers study differences in attitudes toward Covid-19 vaccines between women and men in Africa

A new way to miniaturize cell production for cancer treatment

Investigating the past to see technology’s future

“They can see themselves shaping the world they live in”

A new strategy to cope with emotional stress
- More news on MIT News homepage →
Massachusetts Institute of Technology 77 Massachusetts Avenue, Cambridge, MA, USA
- Map (opens in new window)
- Events (opens in new window)
- People (opens in new window)
- Careers (opens in new window)
- Accessibility
- Social Media Hub
- MIT on Facebook
- MIT on YouTube
- MIT on Instagram
ASLA Professional Practice Networks’ Blog
Call for papers: critical research needs for landscape & environmental design .
by Christine Colley, RLA, ASLA

Transportation Research Board 104th Annual Meeting January 5 – 9, 2025, Washington, D.C.
Call for Papers: Topics of Critical Research Needs for Landscape and Environmental Design Sponsoring Committee: Standing Technical Committee on Landscape and Environmental Design (AKD40)
This Call for Papers invites researchers and practitioners to develop papers to be considered for publication and/or presentation at the 2025 TRB Annual Meeting .
The Standing Technical Committee on Landscape and Environmental Design (AKD40) is concerned with design parameters that relate to protecting, conserving, restoring, and enhancing safe, sustainable, and livable transportation systems, facilities, and their associated environments. The Committee promotes research to advance design principles and practices that enhance safety, and traveler experiences; scenic, aesthetic, and visual quality; harmonious integration of facilities within their natural, cultural, and social environments; sustainable solutions and systems; and the quality of life for transportation system users and surrounding communities.
The following areas were identified by the AKD40 Committee as being critical areas of research:
- Seek out and support research on Sustainable Design and Maintenance of Green Infrastructure to Improve System Resiliency.
- Promote the Design of Complete Streets: Inclusive Design for Active Living and Sustainable and Healthy Modal Choices in Transportation.
- Support efforts to design and manage roadsides and transportation corridors that are productive, restorative, and sustainable as environmental and economic assets using innovative approaches to keep roadside ecology, climate resilience and energy concerns at the forefront.
- Create solutions to mitigate the decline in pollinator insects and other threatened species and support the potential for the roadside environment to encourage the well-being of these species.
AKD40 Keywords
Landscape, Environment, Vegetation, Context, Visual, Roadside, Median, Corridor, Prescribed fire, Complete Streets, Beautification, Water Conservation, Encampment, Pedestrian, Aesthetics, Worker Safety, Erosion Control, Revegetation, Resiliency, Livability, Green Infrastructure, Streetscape, Urban Design, Trees, Multi-Modal, Sustainable Design and Pollinator.
The deadline for submissions is August 1, 2024.
Authors interested in submitting papers are advised to check the Instructions for Authors page and read the Submission Requirements . Authors submitting papers in response to this Call for Papers should submit full papers for peer review to the Transportation Research Board online . When submitting please indicate the Call for Papers title if you want your paper to be associated with a call. Note that this will not affect your chances of acceptance. Please contact the Call for Papers organizer if you need additional information.
A Note for Paper Authors
It is critical that you check the Instructions for Authors page and read the Submission Requirements . After you submit there are no second chances, so be very careful with your paper submission. If you are unsure, hit “Save and Submit Later” until your paper is ready for review.
The paper submission website will close when it is no longer August 1 anywhere in the world.
For a recap of a presentation from the 2024 TRB Annual Meeting, see Transporting SITES to Washington .
Christine Colley, RLA, ASLA, is Associate Landscape Architect at the New York State Department of Transportation, Committee Member of the TRB Standing Committee on Landscape and Environmental Design (AKD40) , and is The Field editor for ASLA’s Transportation Professional Practice Network (PPN) .
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to print (Opens in new window)
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Discover more from the field.
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
To help narrow down your research paper search, below is a list of environmental research topics that include climate change, renewable energy, ecology, pollution, sustainability, endangered species, ecosystems, nature, and water management. You can choose one of them as a guide to writing an excellent essay.
Abstract In the United States, there are substantial barriers to youth nature access and environmental education (EE). These barriers may lead to racial, geographic, and socioeconomic disparities in both nature contact and environmental awareness. This study investigated the impacts of a Photovoice EE intervention on the environmental perceptions, STEM-capacity, and environmental awareness of ...
Explore the latest full-text research PDFs, articles, conference papers, preprints and more on ENVIRONMENTAL AWARENESS. Find methods information, sources, references or conduct a literature review ...
A mega list of research topic ideas in environmental sciences, including ecology, oceanography, hydrology, geology, soil science and more.
In this post, we'll outline some of the best environmental science research topics to help you explore disciplines within environmental science and kickstart your own research. If you are considering majoring in environmental science or perhaps just need help brainstorming for a research paper, this post will give you a broad sense of timely environmental science research topics.
Environmental degradation is one of the main topics in the 21st century (1). Based on 50 years of research, environmental issues have been prioritized and need immediate action (2).
To better understand the research-implementation spaces where those environmental education outcomes occur, are measured, and are reported, we undertook a systematic review of research on environmental education's contributions to conservation and environmental quality outcomes.
This comprehensive guide on environmental research paper topics is designed to assist students and researchers in the field of environmental science. It provides a broad range of potential research topics, expert advice on selecting a topic and writing a research paper, and information about the custom writing services offered by iResearchNet.
Whether you're majoring in environmental science or hoping to write a compelling research paper, here are some of the most interesting environmental science topics you can pursue right now.
Recently, sustainable development practices have increased attention as climate change and environmental impacts have increased. Interventions to encourage sustainability awareness are developing, so fostering them through education is crucial. Evidence-based studies conducted in this field have suggested the use of different digital tools to promote environmental learning gains and to foster ...
Whether you wish to write a research paper that raises environmental awareness or you want to explore solutions to save the plant and preserve the environment, you'll find the topic ideas shared in this guide incredibly useful.
Read our list of best environmental science project topics for anyone majoring or needing to write an environmental research paper for a science course.
This paper enriches the research on the influence of environmental awareness and habitat environment on pro-environmental behavior, reveals the mediating effect of each dimension of social capital, and broadens the horizon for the study of pro-environmental behavior.
Learn about environmental issues and how to take action with the US EPA's resources on research, basics, and specific terms.
Feature papers represent the most advanced research with significant potential for high impact in the field. ... which is now one of the most important topics of environmental research. ... Gholipoor, S.; Adinevand, M. A survey of the relationship between environmental awareness, attitude and pro-environmental behavior of female students at Qom ...
A study on assessment of environmental awareness among teacher trainees in teacher training institutes. International Journal of Research in Social Sciences 2 (3): [312-321].
To study the extend of awareness of students to environmental educationTo study the extend of a. reness of students to social issues related to environmental pollution.To offer a few. uggestions to get over the problems related to environmental p. To throw light on salient features of environmental education.
Discover 100+ research paper topics on environmental issues and sustainable economy trends. Green tech, smart grids, circular economy & more.
The citizen's awareness and its pro-environmental actions play crucial role in making the environmental policy successful. The study on behaviour and attitude desegregated the process of decision making and discovered importance and influence of attitude by 'others' in promoting pro-environmental behaviours.
This descriptive-correlational study sought to measure the level of awareness and practices of 100 Science students in a public secondary school in Zambales, Philippines. Findings revealed that the Science students are very aware on environmental concepts and state of environment; and very aware in environmental issues and problems.
Environmental research topics are subjects and ideas related to ecosystems and biology. Scientists and activists may conduct this research to raise awareness or find solutions to preserve the environment and the organisms in it. Learning about these topics can help you brainstorm ideas for research or build an interest in environmental conservation. In this article, we define environmental ...
Shodhganga : a reservoir of Indian theses @ INFLIBNET The Shodhganga@INFLIBNET Centre provides a platform for research students to deposit their Ph.D. theses and make it available to the entire scholarly community in open access.
To further promote the ecological security of water resources in the YRB and the coordinated development of the regional economy, this paper proposes policy suggestions such as promoting the ...
Abstract The increasing population and changing lifestyles of the people will contribute tremendously towards increasing environmental issues at global, regional and local level. Today, people are not aware with regard to environmental problems and how it will badly impact on our environment. Environmental education plays significant role in the development of environmental awareness. In the ...
This study determined the level of environmental a wareness, and. practices, and attitudes of the selected students of the University Of Northern. Philippines (UNP) in terms of seve n ...
Laughlin is lead author of a paper ... journal of the American Association for the Advancement of Science that publishes important original scientific research. ... Environmental Awareness;
The integrated planning of central and local emission reduction tasks is crucial for achieving sustainable economic development, and corporate ESG performance aligns with the principles of sustainable development, having become a prominent topic in academic research. This paper empirically investigates the impact of regional carbon emission reductions on the ESG performance of local ...
A nationwide bottle deposit program could increase recycling of PET plastic to 82 percent, with nearly two-thirds of all PET bottles being recycled into new bottles, at a net cost of just a penny a bottle when demand is robust, MIT researchers report. At the same time, policies would be needed to ensure a sufficient demand for the recycled material.
Call for Papers: Topics of Critical Research Needs for Landscape and Environmental Design Sponsoring Committee: Standing Technical Committee on Landscape and Environmental Design (AKD40) This Call for Papers invites researchers and practitioners to develop papers to be considered for publication and/or presentation at the 2025 TRB Annual Meeting.
topics of environment ally sound nature to assess the awareness of the studen ts and each topic has five sensitive type questions of local environmental issues and also global issues with the ...