
- Katrina Meteorology and Forecasting
- Katrina Impacts

Please enable JavaScript.
Coggle requires JavaScript to display documents.
HURRICANE SANDY (A-level geography case study) - Coggle Diagram
- 650,000 houses damaged/destroyed in NY+NJ
- 8.5 million businesses and homes without power
- 147 deaths (72 in US)
- NYC marathon cancelled
- $71 billion damage
- Flooded infrastructure further disrupted business
- 10m of beach lost in New Jersey making further erosion more likely
- International trade disruptions due to 18,000 cancelled flights
- Loss of income from cancelled events + reduced tourism
- Psychological damage to those whose friends/family died
- Responses + prep differed between countries (compared to Typhoon Haiyan)
- October 2012
- Most of the deaths were in the Caribbean (esp. Haiti)
- Winds 185km/h
- US is one of the richest countries in the world
- Rebuilding aimed to be more hurricane-proof
- International aid not needed so response faster
- 45,000 army personnel deployed in 7 states
- Many services etc. shut in advance
- 100,000s evacuated beforehand
- 0 Shopping Cart

Hurricane Katrina Case Study
Hurricane Katrina is tied with Hurricane Harvey (2017) as the costliest hurricane on record. Although not the strongest in recorded history, the hurricane caused an estimated $125 billion worth of damage. The category five hurricane is the joint eight strongest ever recorded, with sustained winds of 175 mph (280 km/h).
The hurricane began as a very low-pressure system over the Atlantic Ocean. The system strengthened, forming a hurricane that moved west, approaching the Florida coast on the evening of the 25th August 2005.
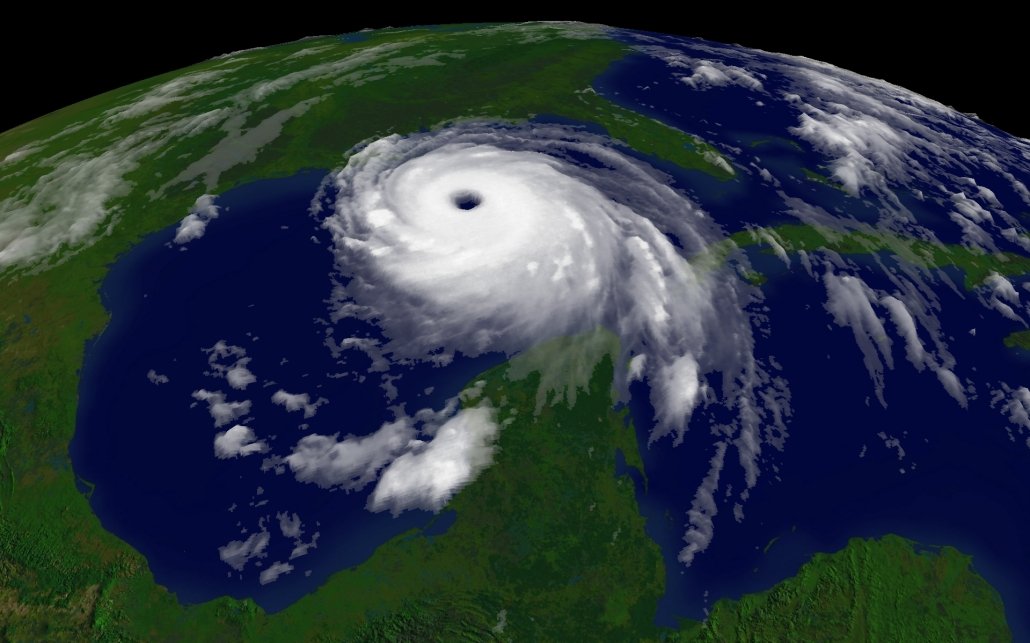
A satellite image of Hurricane Katrina.
Hurricane Katrina was an extremely destructive and deadly Category 5 hurricane. It made landfall on Florida and Louisiana, particularly the city of New Orleans and surrounding areas, in August 2005, causing catastrophic damage from central Florida to eastern Texas. Fatal flaws in flood engineering protection led to a significant loss of life in New Orleans. The levees, designed to cope with category three storm surges, failed to lead to catastrophic flooding and loss of life.
What were the impacts of Hurricane Katrina?
Hurricane Katrina was a category five tropical storm. The hurricane caused storm surges over six metres in height. The city of New Orleans was one of the worst affected areas. This is because it lies below sea level and is protected by levees. The levees protect the city from the Mississippi River and Lake Ponchartrain. However, these were unable to cope with the storm surge, and water flooded the city.
$105 billion was sought by The Bush Administration for repairs and reconstruction in the region. This funding did not include potential interruption of the oil supply, destruction of the Gulf Coast’s highway infrastructure, and exports of commodities such as grain.
Although the state made an evacuation order, many of the poorest people remained in New Orleans because they either wanted to protect their property or could not afford to leave.
The Superdome stadium was set up as a centre for people who could not escape the storm. There was a shortage of food, and the conditions were unhygienic.
Looting occurred throughout the city, and tensions were high as people felt unsafe. 1,200 people drowned in the floods, and 1 million people were made homeless. Oil facilities were damaged, and as a result, the price of petrol rose in the UK and USA.
80% of the city of New Orleans and large neighbouring parishes became flooded, and the floodwaters remained for weeks. Most of the transportation and communication networks servicing New Orleans were damaged or disabled by the flooding, and tens of thousands of people who had not evacuated the city before landfall became stranded with little access to food, shelter or basic necessities.
The storm surge caused substantial beach erosion , in some cases completely devastating coastal areas.
Katrina also produced massive tree loss along the Gulf Coast, particularly in Louisiana’s Pearl River Basin and among bottomland hardwood forests.
The storm caused oil spills from 44 facilities throughout southeastern Louisiana. This resulted in over 7 million US gallons (26,000 m 3 ) of oil being leaked. Some spills were only a few hundred gallons, and most were contained on-site, though some oil entered the ecosystem and residential areas.
Some New Orleans residents are no longer able to get home insurance to cover them from the impact of hurricanes.
What was the response to Hurricane Katrina?
The US Government was heavily criticised for its handling of the disaster. Despite many people being evacuated, it was a very slow process. The poorest and most vulnerable were left behind.
The government provided $50 billion in aid.
During the early stages of the recovery process, the UK government sent food aid.
The National Guard was mobilised to restore law and order in New Orleans.


Premium Resources
Please support internet geography.
If you've found the resources on this page useful please consider making a secure donation via PayPal to support the development of the site. The site is self-funded and your support is really appreciated.
Related Topics
Use the images below to explore related GeoTopics.
Hurricane Florence
Topic home, hurricane michael, share this:.
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window)
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
- Click to print (Opens in new window)
If you've found the resources on this site useful please consider making a secure donation via PayPal to support the development of the site. The site is self-funded and your support is really appreciated.
Search Internet Geography
Latest Blog Entries
Pin It on Pinterest
- Click to share
- Print Friendly

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Ian strengthened to a powerful Category 4 storm, bringing severe flooding to Cuba and the Florida Keys. At least 85 people have died in the states of Florida and North Carolina. More than 700 people were rescued from Charlotte and Lee Counties, the two worst hit areas in Floria.
Key Concepts. Unlike cold winter storms, hurricanes are strictly tropical storms with a warm core in the center. They are tropical cyclones. Hurricanes need warm tropical marine moisture to grow and sustain themselves. Hurricanes dissipate over land and over colder oceans.
Learn about and revise tropical cyclones and their causes and effects with GCSE Bitesize Geography (Edexcel).
Hurricane Katrina is the costliest natural disaster in the history of the United States. Among recorded Atlantic hurricanes, it was the sixth strongest overall but what made it deadly was where it hit and the physical and human geography of that region. .
Particularly, hurricane Katrina was one of the most devastating hurricanes faced by the US in the last century and is the costliest one ever to be recorded. Katrina made landfall along the Central Gulf Coast in Louisiana on Aug 29, 2005, as a Category-3 hurricane with a windspeed of 125 MPH.
Hurricane Sandy was the 10th and final hurricane of 2012, forming in the southwestern Caribbean Sea in late-October. Sandy made two initial landfalls in the Caribbean – in Jamaica on 24th October as a category 1 hurricane, and in eastern Cuba on 25th October as a category 3 hurricane (reaching peak intensity
Hurricane Katrina Case Study. Hurricane Katrina was a powerful and deadly storm. Katrina is the costliest storm and the third deadliest storm in U.S. history. Based on the size of the area impacted and the number of people affected, Katrina was one of the largest natural disasters in the history of the United States.
Primary effects. 650,000 houses damaged/destroyed in NY+NJ. 8.5 million businesses and homes without power. 147 deaths (72 in US) NYC marathon cancelled. $71 billion damage. Secondary effects. Flooded infrastructure further disrupted business. 10m of beach lost in New Jersey making further erosion more likely.
Hurricane Katrina was an extremely destructive and deadly Category 5 hurricane. It made landfall on Florida and Louisiana, particularly the city of New Orleans and surrounding areas, in August 2005, causing catastrophic damage from central Florida to eastern Texas.
Learn about and revise tropical storms and their causes and effects with GCSE Bitesize Geography (AQA).