This is the Difference Between a Hypothesis and a Theory
What to Know A hypothesis is an assumption made before any research has been done. It is formed so that it can be tested to see if it might be true. A theory is a principle formed to explain the things already shown in data. Because of the rigors of experiment and control, it is much more likely that a theory will be true than a hypothesis.
As anyone who has worked in a laboratory or out in the field can tell you, science is about process: that of observing, making inferences about those observations, and then performing tests to see if the truth value of those inferences holds up. The scientific method is designed to be a rigorous procedure for acquiring knowledge about the world around us.

In scientific reasoning, a hypothesis is constructed before any applicable research has been done. A theory, on the other hand, is supported by evidence: it's a principle formed as an attempt to explain things that have already been substantiated by data.
Toward that end, science employs a particular vocabulary for describing how ideas are proposed, tested, and supported or disproven. And that's where we see the difference between a hypothesis and a theory .
A hypothesis is an assumption, something proposed for the sake of argument so that it can be tested to see if it might be true.
In the scientific method, the hypothesis is constructed before any applicable research has been done, apart from a basic background review. You ask a question, read up on what has been studied before, and then form a hypothesis.

What is a Hypothesis?
A hypothesis is usually tentative, an assumption or suggestion made strictly for the objective of being tested.
When a character which has been lost in a breed, reappears after a great number of generations, the most probable hypothesis is, not that the offspring suddenly takes after an ancestor some hundred generations distant, but that in each successive generation there has been a tendency to reproduce the character in question, which at last, under unknown favourable conditions, gains an ascendancy. Charles Darwin, On the Origin of Species , 1859 According to one widely reported hypothesis , cell-phone transmissions were disrupting the bees' navigational abilities. (Few experts took the cell-phone conjecture seriously; as one scientist said to me, "If that were the case, Dave Hackenberg's hives would have been dead a long time ago.") Elizabeth Kolbert, The New Yorker , 6 Aug. 2007
What is a Theory?
A theory , in contrast, is a principle that has been formed as an attempt to explain things that have already been substantiated by data. It is used in the names of a number of principles accepted in the scientific community, such as the Big Bang Theory . Because of the rigors of experimentation and control, its likelihood as truth is much higher than that of a hypothesis.
It is evident, on our theory , that coasts merely fringed by reefs cannot have subsided to any perceptible amount; and therefore they must, since the growth of their corals, either have remained stationary or have been upheaved. Now, it is remarkable how generally it can be shown, by the presence of upraised organic remains, that the fringed islands have been elevated: and so far, this is indirect evidence in favour of our theory . Charles Darwin, The Voyage of the Beagle , 1839 An example of a fundamental principle in physics, first proposed by Galileo in 1632 and extended by Einstein in 1905, is the following: All observers traveling at constant velocity relative to one another, should witness identical laws of nature. From this principle, Einstein derived his theory of special relativity. Alan Lightman, Harper's , December 2011
Non-Scientific Use
In non-scientific use, however, hypothesis and theory are often used interchangeably to mean simply an idea, speculation, or hunch (though theory is more common in this regard):
The theory of the teacher with all these immigrant kids was that if you spoke English loudly enough they would eventually understand. E. L. Doctorow, Loon Lake , 1979 Chicago is famous for asking questions for which there can be no boilerplate answers. Example: given the probability that the federal tax code, nondairy creamer, Dennis Rodman and the art of mime all came from outer space, name something else that has extraterrestrial origins and defend your hypothesis . John McCormick, Newsweek , 5 Apr. 1999 In his mind's eye, Miller saw his case suddenly taking form: Richard Bailey had Helen Brach killed because she was threatening to sue him over the horses she had purchased. It was, he realized, only a theory , but it was one he felt certain he could, in time, prove. Full of urgency, a man with a mission now that he had a hypothesis to guide him, he issued new orders to his troops: Find out everything you can about Richard Bailey and his crowd. Howard Blum, Vanity Fair , January 1995
And sometimes one term is used as a genus, or a means for defining the other:
Laplace's popular version of his astronomy, the Système du monde , was famous for introducing what came to be known as the nebular hypothesis , the theory that the solar system was formed by the condensation, through gradual cooling, of the gaseous atmosphere (the nebulae) surrounding the sun. Louis Menand, The Metaphysical Club , 2001 Researchers use this information to support the gateway drug theory — the hypothesis that using one intoxicating substance leads to future use of another. Jordy Byrd, The Pacific Northwest Inlander , 6 May 2015 Fox, the business and economics columnist for Time magazine, tells the story of the professors who enabled those abuses under the banner of the financial theory known as the efficient market hypothesis . Paul Krugman, The New York Times Book Review , 9 Aug. 2009
Incorrect Interpretations of "Theory"
Since this casual use does away with the distinctions upheld by the scientific community, hypothesis and theory are prone to being wrongly interpreted even when they are encountered in scientific contexts—or at least, contexts that allude to scientific study without making the critical distinction that scientists employ when weighing hypotheses and theories.
The most common occurrence is when theory is interpreted—and sometimes even gleefully seized upon—to mean something having less truth value than other scientific principles. (The word law applies to principles so firmly established that they are almost never questioned, such as the law of gravity.)
This mistake is one of projection: since we use theory in general use to mean something lightly speculated, then it's implied that scientists must be talking about the same level of uncertainty when they use theory to refer to their well-tested and reasoned principles.
The distinction has come to the forefront particularly on occasions when the content of science curricula in schools has been challenged—notably, when a school board in Georgia put stickers on textbooks stating that evolution was "a theory, not a fact, regarding the origin of living things." As Kenneth R. Miller, a cell biologist at Brown University, has said , a theory "doesn’t mean a hunch or a guess. A theory is a system of explanations that ties together a whole bunch of facts. It not only explains those facts, but predicts what you ought to find from other observations and experiments.”
While theories are never completely infallible, they form the basis of scientific reasoning because, as Miller said "to the best of our ability, we’ve tested them, and they’ve held up."
More Differences Explained
- Epidemic vs. Pandemic
- Diagnosis vs. Prognosis
- Treatment vs. Cure
Word of the Day
See Definitions and Examples »
Get Word of the Day daily email!
Games & Quizzes

Commonly Confused
'canceled' or 'cancelled', is it 'home in' or 'hone in', the difference between 'race' and 'ethnicity', homophones, homographs, and homonyms, on 'biweekly' and 'bimonthly', grammar & usage, primary and caucus: what is the difference, words commonly mispronounced, merriam-webster’s great big list of words you love to hate, more commonly misspelled words, commonly misspelled words, 12 words for signs of spring, 12 more bird names that sound like insults (and sometimes are), 13 unusually long english words, the words of the week - apr. 26, 9 superb owl words.
Hypothesis vs. Theory
A hypothesis is either a suggested explanation for an observable phenomenon, or a reasoned prediction of a possible causal correlation among multiple phenomena. In science , a theory is a tested, well-substantiated, unifying explanation for a set of verified, proven factors. A theory is always backed by evidence; a hypothesis is only a suggested possible outcome, and is testable and falsifiable.
Comparison chart
Examples of theory and hypothesis.
Theory: Einstein's theory of relativity is a theory because it has been tested and verified innumerable times, with results consistently verifying Einstein's conclusion. However, simply because Einstein's conclusion has become a theory does not mean testing of this theory has stopped; all science is ongoing. See also the Big Bang theory , germ theory , and climate change .
Hypothesis: One might think that a prisoner who learns a work skill while in prison will be less likely to commit a crime when released. This is a hypothesis, an "educated guess." The scientific method can be used to test this hypothesis, to either prove it is false or prove that it warrants further study. (Note: Simply because a hypothesis is not found to be false does not mean it is true all or even most of the time. If it is consistently true after considerable time and research, it may be on its way to becoming a theory.)
This video further explains the difference between a theory and a hypothesis:
Common Misconception
People often tend to say "theory" when what they're actually talking about is a hypothesis. For instance, "Migraines are caused by drinking coffee after 2 p.m. — well, it's just a theory, not a rule."
This is actually a logically reasoned proposal based on an observation — say 2 instances of drinking coffee after 2 p.m. caused a migraine — but even if this were true, the migraine could have actually been caused by some other factors.
Because this observation is merely a reasoned possibility, it is testable and can be falsified — which makes it a hypothesis, not a theory.
- What is a Scientific Hypothesis? - LiveScience
- Wikipedia:Scientific theory
Related Comparisons

Share this comparison via:
If you read this far, you should follow us:
"Hypothesis vs Theory." Diffen.com. Diffen LLC, n.d. Web. 24 Apr 2024. < >
Comments: Hypothesis vs Theory
Anonymous comments (2).
October 11, 2013, 1:11pm "In science, a theory is a well-substantiated, unifying explanation for a set of verified, proven hypotheses." But there's no such thing as "proven hypotheses". Hypotheses can be tested/falsified, they can't be "proven". That's just not how science works. Logical deductions based on axioms can be proven, but not scientific hypotheses. On top of that I find it somewhat strange to claim that a theory doesn't have to be testable, if it's built up from hypotheses, which DO have to be testable... — 80.✗.✗.139
May 6, 2014, 11:45pm "Evolution is a theory, not a fact, regarding the origin of living things." this statement is poorly formed because it implies that a thing is a theory until it gets proven and then it is somehow promoted to fact. this is just a misunderstanding of what the words mean, and of how science progresses generally. to say that a theory is inherently dubious because "it isn't a fact" is pretty much a meaningless statement. no expression which qualified as a mere fact could do a very good job of explaining the complicated process by which species have arisen on Earth over the last billion years. in fact, if you claimed that you could come up with such a single fact, now THAT would be dubious! everything we observe in nature supports the theory of evolution, and nothing we observe contradicts it. when you can say this about a theory, it's a pretty fair bet that the theory is correct. — 71.✗.✗.151
- Accuracy vs Precision
- Deductive vs Inductive
- Subjective vs Objective
- Subconscious vs Unconscious mind
- Qualitative vs Quantitative
- Creationism vs Evolution
Edit or create new comparisons in your area of expertise.
Stay connected
© All rights reserved.
“Theory” vs. “Hypothesis”: What Is The Difference?
Chances are you’ve heard of the TV show The Big Bang Theory . Lots of people love this lighthearted sitcom for its quirky characters and their relationships, but others haven’t even given the series a chance for one reason: they don’t like science and assume the show is boring.
However, it only takes a few seconds with Sheldon and Penny to disprove this assumption and realize that this theory ab0ut The Big Bang Theory is wrong—it isn’t a scientific snoozefest.
But wait: is it a theory or a hypothesis about the show that leads people astray? And would the actual big bang theory— the one that refers to the beginning of the universe—mean the same thing as a big bang hypothesis ?
Let’s take a closer look at theory and hypothesis to nail down what they mean.
What does theory mean?
As a noun, a theory is a group of tested general propositions “commonly regarded as correct, that can be used as principles of explanation and prediction for a class of phenomena .” This is what is known as a scientific theory , which by definition is “an understanding that is based on already tested data or results .” Einstein’s theory of relativity and the theory of evolution are both examples of such tested propositions .
Theory is also defined as a proposed explanation you might make about your own life and observations, and it’s one “whose status is still conjectural and subject to experimentation .” For example: I’ve got my own theories about why he’s missing his deadlines all the time. This example refers to an idea that has not yet been proven.
There are other uses of the word theory as well.
- In this example, theory is “a body of principles or theorems belonging to one subject.” It can be a branch of science or art that deals with its principles or methods .
- For example: when she started to follow a new parenting theory based on a trendy book, it caused a conflict with her mother, who kept offering differing opinions .
First recorded in 1590–1600, theory originates from the Late Latin theōria , which stems from the Greek theōría. Synonyms for theory include approach , assumption , doctrine , ideology , method , philosophy , speculation , thesis , and understanding .
What does hypothesis mean?
Hypothesis is a noun that means “a proposition , or set of propositions, set forth as an explanation” that describe “some specified group of phenomena.” Sounds familiar to theory , no?
But, unlike a theory , a scientific hypothesis is made before testing is done and isn’t based on results. Instead, it is the basis for further investigation . For example: her working hypothesis is that this new drug also has an unintended effect on the heart, and she is curious what the clinical trials will show .
Hypothesis also refers to “a proposition assumed as a premise in an argument,” or “mere assumption or guess.” For example:
- She decided to drink more water for a week to test out her hypothesis that dehydration was causing her terrible headaches.
- After a night of her spouse’s maddening snoring, she came up with the hypothesis that sleeping on his back was exacerbating the problem.
Hypothesis was first recorded around 1590–1600 and originates from the Greek word hypóthesis (“basis, supposition”). Synonyms for hypothesis include: assumption , conclusion , conjecture , guess , inference , premise , theorem , and thesis .
How to use each
Although theory in terms of science is used to express something based on extensive research and experimentation, typically in everyday life, theory is used more casually to express an educated guess.
So in casual language, theory and hypothesis are more likely to be used interchangeably to express an idea or speculation .
In most everyday uses, theory and hypothesis convey the same meaning. For example:
- Her opinion is just a theory , of course. She’s just guessing.
- Her opinion is just a hypothesis , of course. She’s just guessing.
It’s important to remember that a scientific theory is different. It is based on tested results that support or substantiate it, whereas a hypothesis is formed before the research.
For example:
- His hypothesis for the class science project is that this brand of plant food is better than the rest for helping grass grow.
- After testing his hypothesis , he developed a new theory based on the experiment results: plant food B is actually more effective than plant food A in helping grass grow.
In these examples, theory “doesn’t mean a hunch or a guess,” according to Kenneth R. Miller, a cell biologist at Brown University. “A theory is a system of explanations that ties together a whole bunch of facts. It not only explains those facts, but predicts what you ought to find from other observations and experiments.”
So if you have a concept that is based on substantiated research, it’s a theory .
But if you’re working off of an assumption that you still need to test, it’s a hypothesis .
So remember, first comes a hypothesis , then comes theory . Now who’s ready for a Big Bang Theory marathon?
Now that you’ve theorized and hypothesized through this whole article … keep testing your judgment (Or is it judgement?). Find out the correct spelling here!
Or find out the difference between these two common issues below!
WATCH: "Lethologica" vs. "Lethonomia": What's The Difference?
Go Behind The Words!
- By clicking "Sign Up", you are accepting Dictionary.com Terms & Conditions and Privacy policies.
- Comments This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
Commonly Confused

Trending Words
[ neb -y uh -l uh s ]
- Phone This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.

- Science Notes Posts
- Contact Science Notes
- Todd Helmenstine Biography
- Anne Helmenstine Biography
- Free Printable Periodic Tables (PDF and PNG)
- Periodic Table Wallpapers
- Interactive Periodic Table
- Periodic Table Posters
- How to Grow Crystals
- Chemistry Projects
- Fire and Flames Projects
- Holiday Science
- Chemistry Problems With Answers
- Physics Problems
- Unit Conversion Example Problems
- Chemistry Worksheets
- Biology Worksheets
- Periodic Table Worksheets
- Physical Science Worksheets
- Science Lab Worksheets
- My Amazon Books
Scientific Theory Definition and Examples

A scientific theory is a well-established explanation of some aspect of the natural world. Theories come from scientific data and multiple experiments. While it is not possible to prove a theory, a single contrary result using the scientific method can disprove it. In other words, a theory is testable and falsifiable.
Examples of Scientific Theories
There are many scientific theory in different disciplines:
- Astronomy : theory of stellar nucleosynthesis , theory of stellar evolution
- Biology : cell theory, theory of evolution, germ theory, dual inheritance theory
- Chemistry : atomic theory, Bronsted Lowry acid-base theory , kinetic molecular theory of gases , Lewis acid-base theory , molecular theory, valence bond theory
- Geology : climate change theory, plate tectonics theory
- Physics : Big Bang theory, perturbation theory, theory of relativity, quantum field theory
Criteria for a Theory
In order for an explanation of the natural world to be a theory, it meets certain criteria:
- A theory is falsifiable. At some point, a theory withstands testing and experimentation using the scientific method.
- A theory is supported by lots of independent evidence.
- A theory explains existing experimental results and predicts outcomes of new experiments at least as well as other theories.
Difference Between a Scientific Theory and Theory
Usually, a scientific theory is just called a theory. However, a theory in science means something different from the way most people use the word. For example, if frogs rain down from the sky, a person might observe the frogs and say, “I have a theory about why that happened.” While that theory might be an explanation, it is not based on multiple observations and experiments. It might not be testable and falsifiable. It’s not a scientific theory (although it could eventually become one).
Value of Disproven Theories
Even though some theories are incorrect, they often retain value.
For example, Arrhenius acid-base theory does not explain the behavior of chemicals lacking hydrogen that behave as acids. The Bronsted Lowry and Lewis theories do a better job of explaining this behavior. Yet, the Arrhenius theory predicts the behavior of most acids and is easier for people to understand.
Another example is the theory of Newtonian mechanics. The theory of relativity is much more inclusive than Newtonian mechanics, which breaks down in certain frames of reference or at speeds close to the speed of light . But, Newtonian mechanics is much simpler to understand and its equations apply to everyday behavior.
Difference Between a Scientific Theory and a Scientific Law
The scientific method leads to the formulation of both scientific theories and laws . Both theories and laws are falsifiable. Both theories and laws help with making predictions about the natural world. However, there is a key difference.
A theory explains why or how something works, while a law describes what happens without explaining it. Often, you see laws written in the form of equations or formulas.
Theories and laws are related, but theories never become laws or vice versa.
Theory vs Hypothesis
A hypothesis is a proposition that is tested via an experiment. A theory results from many, many tested hypotheses.
Theory vs Fact
Theories depend on facts, but the two words mean different things. A fact is an irrefutable piece of evidence or data. Facts never change. A theory, on the other hand, may be modified or disproven.
Difference Between a Theory and a Model
Both theories and models allow a scientist to form a hypothesis and make predictions about future outcomes. However, a theory both describes and explains, while a model only describes. For example, a model of the solar system shows the arrangement of planets and asteroids in a plane around the Sun, but it does not explain how or why they got into their positions.
- Frigg, Roman (2006). “ Scientific Representation and the Semantic View of Theories .” Theoria . 55 (2): 183–206.
- Halvorson, Hans (2012). “What Scientific Theories Could Not Be.” Philosophy of Science . 79 (2): 183–206. doi: 10.1086/664745
- McComas, William F. (December 30, 2013). The Language of Science Education: An Expanded Glossary of Key Terms and Concepts in Science Teaching and Learning . Springer Science & Business Media. ISBN 978-94-6209-497-0.
- National Academy of Sciences (US) (1999). Science and Creationism: A View from the National Academy of Sciences (2nd ed.). National Academies Press. doi: 10.17226/6024 ISBN 978-0-309-06406-4.
- Suppe, Frederick (1998). “Understanding Scientific Theories: An Assessment of Developments, 1969–1998.” Philosophy of Science . 67: S102–S115. doi: 10.1086/392812
Related Posts

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

1.2: Theories, Hypotheses and Models
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 19359
For the purpose of this textbook (and science in general), we introduce a distinction in what we mean by “theory”, “hypothesis”, and by “model”. We will consider a “theory” to be a set of statements (or an equation) that gives us a broad description, applicable to several phenomena and that allows us to make verifiable predictions. For example, Chloë’s Theory ( \(t \propto \sqrt{h}\) ) can be considered a theory. Specifically, we do not use the word theory in the context of “I have a theory about this...”
A “hypothesis” is a consequence of the theory that one can test. From Chloë’s Theory, we have the hypothesis that an object will take \(\sqrt{2}\) times longer to fall from \(1\:\text{m}\) than from \(2\:\text{m}\) . We can formulate the hypothesis based on the theory and then test that hypothesis. If the hypothesis is found to be invalidated by experiment, then either the theory is incorrect, or the hypothesis is not consistent with the theory.
A “model” is a situation-specific description of a phenomenon based on a theory , that allows us to make a specific prediction. Using the example from the previous section, our theory would be that the fall time of an object is proportional to the square root of the drop height, and a model would be applying that theory to describe a tennis ball falling by \(4.2\) m. From the model, we can form a testable hypothesis of how long it will take the tennis ball to fall that distance. It is important to note that a model will almost always be an approximation of the theory applied to describe a particular phenomenon. For example, if Chloë’s Theory is only valid in vacuum, and we use it to model the time that it take for an object to fall at the surface of the Earth, we may find that our model disagrees with experiment. We would not necessarily conclude that the theory is invalidated, if our model did not adequately apply the theory to describe the phenomenon (e.g. by forgetting to include the effect of air drag).
This textbook will introduce the theories from Classical Physics, which were mostly established and tested between the seventeenth and nineteenth centuries. We will take it as given that readers of this textbook are not likely to perform experiments that challenge those well-established theories. The main challenge will be, given a theory, to define a model that describes a particular situation, and then to test that model. This introductory physics course is thus focused on thinking of “doing physics” as the task of correctly modeling a situation.
Emma's Thoughts
What’s the difference between a model and a theory?
“Model” and “Theory” are sometimes used interchangeably among scientists. In physics, it is particularly important to distinguish between these two terms. A model provides an immediate understanding of something based on a theory.
For example, if you would like to model the launch of your toy rocket into space, you might run a computer simulation of the launch based on various theories of propulsion that you have learned. In this case, the model is the computer simulation, which describes what will happen to the rocket. This model depends on various theories that have been extensively tested such as Newton’s Laws of motion, Fluid dynamics, etc.
- “Model”: Your homemade rocket computer simulation
- “Theory”: Newton’s Laws of motion, Fluid dynamics
With this analogy, we can quickly see that the “model” and “theory” are not interchangeable. If they were, we would be saying that all of Newton’s Laws of Motion depend on the success of your piddly toy rocket computer simulation!
Exercise \(\PageIndex{2}\)
Models cannot be scientifically tested, only theories can be tested.

Home » Education » Difference Between Hypothesis and Theory
Difference Between Hypothesis and Theory
Main difference – hypothesis vs theory.
Hypothesis and theory are two words that are often used in the field of science and research. Although these two words have somewhat similar meanings, there is a fundamental difference between hypothesis and theory. Hypothesis is a suggested explanation to explain some phenomenon, and is based on limited data. Theory, on the other hand, is a set of ideas that is intended to explain facts or events; they are based on concrete evidence. This is the main difference between hypothesis and theory.
This article explains,
1. What is a Hypothesis? – Definitions and Features
2. What is a Theory? – Definitions and Features

What is a Hypothesis
A hypothesis is a proposed explanation based on some evidence. According to the Oxford dictionary, hypothesis is “a supposition or proposed explanation made on the basis of limited evidence as a starting point for further investigation” and Merriam-Webster dictionary defines it as “an idea or theory that is not proven but that leads to further study or discussion.”
However, a hypothesis is not scientifically tested or proven; it is a logical assumption based on the available evidence. A hypothesis can be accurate or inaccurate. Once the hypothesis is scientifically tested and proven, it becomes a theory.

The hypothesis of Andreas Cellarius, showing the planetary motions in eccentric and epicyclical orbits.
What is a Theory
Theory is an idea or set of ideas that is intended to explain facts or events. A theory is formulated after in-depth research analysis. It is always proven scientifically with evidence. The Oxford dictionary defines theory as “supposition or a system of ideas intended to explain something, especially one based on general principles independent of the thing to be explained.”
As mentioned above, a theory is usually formulated from a hypothesis. Once a hypothesis is tested and proven, it is accepted as a theory. Copernicus’ Heliocentric theory, Darwin’s theory of evolution, quantum theory, special relativity theory, are examples of are some important scientific theories.
A theory can be used to understand, explain and make predictions over a concept. However, theories can be proven to be wrong as well, depending on the proof. However, theoretical knowledge is important in understanding different concepts and situations.

Special Theory of Relativity
Definition
Hypothesis is a proposed explanation for some phenomenon based on limited evidence.
Theory is an idea or set of ideas that is intended to explain facts or events.
Testing and Proof
Hypothesis is not scientifically tested or proven.
Theory is scientifically tested and proven.
Hypothesis is based on limited data.
Theory is based on a wide range of data.
Interdependence
Hypothesis can lead to a theory.
Theory can be formulated through a hypothesis.
Image Courtesy:
“Cellarius Harmonia Macrocosmica – Hypothesis Ptolemaica” By Andreas Cellarius – (Public Domain) via Commons Wikimedia
“World line” By SVG version: K. Aainsqatsi at en.wikipediaOriginal PNG version: Stib at en.wikipedia – Transferred from en.wikipedia.(Original text : self-made) (CC BY-SA 3.0) via Commons Wikimedia
About the Author: Hasa
Hasanthi is a seasoned content writer and editor with over 8 years of experience. Armed with a BA degree in English and a knack for digital marketing, she explores her passions for literature, history, culture, and food through her engaging and informative writing.
You May Also Like These
- Key Differences
Know the Differences & Comparisons
Difference Between Hypothesis and Theory
The term ‘hypothesis’ is often contrasted with the term theory which implies an idea, typically proven, which aims at explaining facts and events. Both hypothesis and theory are important components of developing an approach, but these are not same. There exist a fine line of difference between hypothesis and theory, discussed in this article, have a look.
Content: Hypothesis Vs Theory
Comparison chart, definition of hypothesis.
An unproven statement or a mere assumption to be proved or disproved, about a factor, on which the researcher is interested, is called a hypothesis. It is a tentative statement, which is concerned with the relationship between two or more phenomena, as specified by the theoretical framework. The hypothesis has to go through a test, to determine its validity.
In other words, the hypothesis is a predictive statement, which can be objectively verified and tested through scientific methods, and relates the independent factor to the dependent one. To a researcher, a hypothesis is more like a question which he intends to resolve. The salient features of hypothesis are:
- It must be clear and precise or else the reliability of the inferences drawn will be questioned.
- It can be put to the test.
- If the hypothesis is relational, it should state the relationship between independent and dependent variables.
- The hypothesis should be open and responsive to testing within the stipulated time.
- It should be limited in scope and must be clearly defined.
Definition of Theory
An idea or a broad range of ideas that are assumed to be true, which aims at explaining cause and effect relationship between multiple observed phenomena. It is based on hypothesis, which after a thorough analysis and continuous testing and confirmation through observation and experiments, becomes a theory. As it is backed by evidence, it is scientifically proven.
Just like hypothesis, theories can also be accepted or rejected. As more and more information is gathered on the subject, theories are modified accordingly, to increase the accuracy of prediction over time.
Key Differences Between Hypothesis and Theory
The points given below are vital, so far as the difference between hypothesis and theory is concerned:
- Hypothesis refers to a supposition, based on few pieces of evidence, as an inception of further research or investigation. A theory is a well-affirmed explanation of natural phenomena, which is frequently validated through experimentation and observation.
- While the hypothesis is based on a little amount of data, the theory is based on a wide set of data.
- The hypothesis is an unproven statement; that can be tested. On the other hand, the theory is a scientifically tested and proven explanation of fact or event.
- Hypothesis relies on suggestions, prediction, possibility or projects whereas a theory is supported by evidence and is verified.
- The hypothesis may or may not be proved true, so the result is uncertain. On the contrary, the theory is one, that is assumed to be true and so its result is certain.
- Hypothesis and theory are two levels of the scientific method, i.e. theory follows hypothesis and the basis for research is hypothesis whose outcome is a theory.
Both hypothesis and theory are testable and falsifiable. When a hypothesis is proved true, by passing all critical tests and analysis, it becomes a theory. So, the hypothesis is very different from theory, as the former is something unproven but the latter is a proven and tested statement.
You Might Also Like:

BELLENS MOTEBEJANE says
July 15, 2019 at 2:31 pm
AMAIZING !WHAT ARE THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN THEORY AND LAW?
February 17, 2022 at 3:47 am
Thanks, I’m finally clear on this for the first time in my life of 65 years
Curtis Le Gendre says
September 14, 2022 at 8:02 am
Great Information
Kenneth says
November 19, 2022 at 2:10 am
I was looking for some takes on this topic, and I found your article quite informative. It has given me a fresh perspective on the topic tackled. Thanks!
Stefanie Banis says
February 9, 2024 at 6:35 pm
Very informative! Thank you! I understand the difference much better now!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Hypothesis, Model, Theory, and Law
Dorling Kindersley / Getty Images
- Physics Laws, Concepts, and Principles
- Quantum Physics
- Important Physicists
- Thermodynamics
- Cosmology & Astrophysics
- Weather & Climate
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/AZJFaceShot-56a72b155f9b58b7d0e783fa.jpg)
- M.S., Mathematics Education, Indiana University
- B.A., Physics, Wabash College
In common usage, the words hypothesis, model, theory, and law have different interpretations and are at times used without precision, but in science they have very exact meanings.
Perhaps the most difficult and intriguing step is the development of a specific, testable hypothesis. A useful hypothesis enables predictions by applying deductive reasoning, often in the form of mathematical analysis. It is a limited statement regarding the cause and effect in a specific situation, which can be tested by experimentation and observation or by statistical analysis of the probabilities from the data obtained. The outcome of the test hypothesis should be currently unknown, so that the results can provide useful data regarding the validity of the hypothesis.
Sometimes a hypothesis is developed that must wait for new knowledge or technology to be testable. The concept of atoms was proposed by the ancient Greeks , who had no means of testing it. Centuries later, when more knowledge became available, the hypothesis gained support and was eventually accepted by the scientific community, though it has had to be amended many times over the year. Atoms are not indivisible, as the Greeks supposed.
A model is used for situations when it is known that the hypothesis has a limitation on its validity. The Bohr model of the atom , for example, depicts electrons circling the atomic nucleus in a fashion similar to planets in the solar system. This model is useful in determining the energies of the quantum states of the electron in the simple hydrogen atom, but it is by no means represents the true nature of the atom. Scientists (and science students) often use such idealized models to get an initial grasp on analyzing complex situations.
Theory and Law
A scientific theory or law represents a hypothesis (or group of related hypotheses) which has been confirmed through repeated testing, almost always conducted over a span of many years. Generally, a theory is an explanation for a set of related phenomena, like the theory of evolution or the big bang theory .
The word "law" is often invoked in reference to a specific mathematical equation that relates the different elements within a theory. Pascal's Law refers an equation that describes differences in pressure based on height. In the overall theory of universal gravitation developed by Sir Isaac Newton , the key equation that describes the gravitational attraction between two objects is called the law of gravity .
These days, physicists rarely apply the word "law" to their ideas. In part, this is because so many of the previous "laws of nature" were found to be not so much laws as guidelines, that work well within certain parameters but not within others.
Scientific Paradigms
Once a scientific theory is established, it is very hard to get the scientific community to discard it. In physics, the concept of ether as a medium for light wave transmission ran into serious opposition in the late 1800s, but it was not disregarded until the early 1900s, when Albert Einstein proposed alternate explanations for the wave nature of light that did not rely upon a medium for transmission.
The science philosopher Thomas Kuhn developed the term scientific paradigm to explain the working set of theories under which science operates. He did extensive work on the scientific revolutions that take place when one paradigm is overturned in favor of a new set of theories. His work suggests that the very nature of science changes when these paradigms are significantly different. The nature of physics prior to relativity and quantum mechanics is fundamentally different from that after their discovery, just as biology prior to Darwin’s Theory of Evolution is fundamentally different from the biology that followed it. The very nature of the inquiry changes.
One consequence of the scientific method is to try to maintain consistency in the inquiry when these revolutions occur and to avoid attempts to overthrow existing paradigms on ideological grounds.
Occam’s Razor
One principle of note in regards to the scientific method is Occam’s Razor (alternately spelled Ockham's Razor), which is named after the 14th century English logician and Franciscan friar William of Ockham. Occam did not create the concept—the work of Thomas Aquinas and even Aristotle referred to some form of it. The name was first attributed to him (to our knowledge) in the 1800s, indicating that he must have espoused the philosophy enough that his name became associated with it.
The Razor is often stated in Latin as:
entia non sunt multiplicanda praeter necessitatem
or, translated to English:
entities should not be multiplied beyond necessity
Occam's Razor indicates that the most simple explanation that fits the available data is the one which is preferable. Assuming that two hypotheses presented have equal predictive power, the one which makes the fewest assumptions and hypothetical entities takes precedence. This appeal to simplicity has been adopted by most of science, and is invoked in this popular quote by Albert Einstein:
Everything should be made as simple as possible, but not simpler.
It is significant to note that Occam's Razor does not prove that the simpler hypothesis is, indeed, the true explanation of how nature behaves. Scientific principles should be as simple as possible, but that's no proof that nature itself is simple.
However, it is generally the case that when a more complex system is at work there is some element of the evidence which doesn't fit the simpler hypothesis, so Occam's Razor is rarely wrong as it deals only with hypotheses of purely equal predictive power. The predictive power is more important than the simplicity.
Edited by Anne Marie Helmenstine, Ph.D.
- Scientific Hypothesis, Model, Theory, and Law
- Theory Definition in Science
- The Basics of Physics in Scientific Study
- A Brief History of Atomic Theory
- Einstein's Theory of Relativity
- What Is a Paradigm Shift?
- Wave Particle Duality and How It Works
- Scientific Method
- Oversimplification and Exaggeration Fallacies
- Hypothesis Definition (Science)
- Kinetic Molecular Theory of Gases
- Understanding Cosmology and Its Impact
- The History of Gravity
- Tips on Winning the Debate on Evolution
- The Copenhagen Interpretation of Quantum Mechanics
- Geological Thinking: Method of Multiple Working Hypotheses

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

1.3: Hypothesis, Theories, and Laws
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 105252
Learning Objectives
- Describe the difference between hypothesis, theory as scientific terms.
- Describe the difference between a theory and scientific law.
Although all of us have taken science classes throughout the course of our study, many people have incorrect or misleading ideas about some of the most important and basic principles in science. We have all heard of hypotheses, theories, and laws, but what do they really mean? Before you read this section, think about what you have learned about these terms before. What do these terms mean to you? What do you read contradicts what you thought? What do you read supports what you thought?
What is a Fact?
A fact is a basic statement establish by experiment or observation. All facts are true under the specific conditions of the observation.
What is a Hypothesis?
One of the most common terms used in science classes is a "hypothesis". The word can have many different definitions, depending on the context in which it is being used:
- "An educated guess" - because it provides a suggested solution based on evidence to be a scientific hypothesis
- Prediction - if you have ever carried out a science experiment, you probably made this type of hypothesis, in which you predicted the outcome of your experiment.
- Tentative or Proposed explanation - hypotheses can be suggestions about why something is observed, but in order for it to be scientific, we must be able to test the explanation to see if it works, if it is able to correctly predict what will happen in a situation, such as: if my hypothesis is correct, we should see ___ result when we perform ___ test.
A hypothesis is very tentative; it can be easily changed.
What is a Theory?
The United States National Academy of Sciences describes what a theory is as follows:
"Some scientific explanations are so well established that no new evidence is likely to alter them. The explanation becomes a scientific theory. In everyday language a theory means a hunch or speculation. Not so in science. In science, the word theory refers to a comprehensive explanation of an important feature of nature supported by facts gathered over time. Theories also allow scientists to make predictions about as yet unobserved phenomena."
"A scientific theory is a well-substantiated explanation of some aspect of the natural world, based on a body of facts that have been repeatedly confirmed through observation and experimentation. Such fact-supported theories are not "guesses" but reliable accounts of the real world. The theory of biological evolution is more than "just a theory." It is as factual an explanation of the universe as the atomic theory of matter (stating that everything is made of atoms) or the germ theory of disease (which states that many diseases are caused by germs). Our understanding of gravity is still a work in progress. But the phenomenon of gravity, like evolution, is an accepted fact."
Not some key features of theories that are important to understand from this description:
- Theories are explanations of natural phenomenon. They aren't predictions (although we may use theories to make predictions). They are explanations why we observe something.
- Theories aren't likely to change. They have so much support and are able to explain satisfactorily so many observations, that they are not likely to change. Theories can, indeed, be facts. Theories can change, but it is a long and difficult process. In order for a theory to change, there must be many observations or evidence that the theory cannot explain.
- Theories are not guesses. The phrase "just a theory" has no room in science. To be a scientific theory carries a lot of weight; it is not just one person's idea about something
Theories aren't likely to change.
What is a Law?
Scientific laws are similar to scientific theories in that they are principles that can be used to predict the behavior of the natural world. Both scientific laws and scientific theories are typically well-supported by observations and/or experimental evidence. Usually scientific laws refer to rules for how nature will behave under certain conditions, frequently written as an equation. Scientific theories are more overarching explanations of how nature works and why it exhibits certain characteristics. As a comparison, theories explain why we observe what we do and laws describe what happens.
For example, around the year 1800, Jacques Charles and other scientists were working with gases to, among other reasons, improve the design of the hot air balloon. These scientists found, after many, many tests, that certain patterns existed in the observations on gas behavior. If the temperature of the gas is increased, the volume of the gas increased. This is known as a natural law. A law is a relationship that exists between variables in a group of data. Laws describe the patterns we see in large amounts of data, but do not describe why the patterns exist.
What is a Belief?
A statement that is not scientifically provable. Beliefs may or may not be incorrect; they just are outside the realm of science to explore.
Laws vs. Theories
A common misconception is that scientific theories are rudimentary ideas that will eventually graduate into scientific laws when enough data and evidence has been accumulated. A theory does not change into a scientific law with the accumulation of new or better evidence. Remember, theories are explanations and laws are patterns we see in large amounts of data, frequently written as an equation. A theory will always remain a theory; a law will always remain a law.
Video \(\PageIndex{1}\): What’s the difference between a scientific law and theory?
- A hypothesis is a tentative explanation that can be tested by further investigation.
- A theory is a well-supported explanation of observations.
- A scientific law is a statement that summarizes the relationship between variables.
- An experiment is a controlled method of testing a hypothesis.
Contributors and Attributions
Marisa Alviar-Agnew ( Sacramento City College )
Henry Agnew (UC Davis)
- Privacy Policy

Home » What is a Hypothesis – Types, Examples and Writing Guide
What is a Hypothesis – Types, Examples and Writing Guide
Table of Contents

Definition:
Hypothesis is an educated guess or proposed explanation for a phenomenon, based on some initial observations or data. It is a tentative statement that can be tested and potentially proven or disproven through further investigation and experimentation.
Hypothesis is often used in scientific research to guide the design of experiments and the collection and analysis of data. It is an essential element of the scientific method, as it allows researchers to make predictions about the outcome of their experiments and to test those predictions to determine their accuracy.
Types of Hypothesis
Types of Hypothesis are as follows:
Research Hypothesis
A research hypothesis is a statement that predicts a relationship between variables. It is usually formulated as a specific statement that can be tested through research, and it is often used in scientific research to guide the design of experiments.
Null Hypothesis
The null hypothesis is a statement that assumes there is no significant difference or relationship between variables. It is often used as a starting point for testing the research hypothesis, and if the results of the study reject the null hypothesis, it suggests that there is a significant difference or relationship between variables.
Alternative Hypothesis
An alternative hypothesis is a statement that assumes there is a significant difference or relationship between variables. It is often used as an alternative to the null hypothesis and is tested against the null hypothesis to determine which statement is more accurate.
Directional Hypothesis
A directional hypothesis is a statement that predicts the direction of the relationship between variables. For example, a researcher might predict that increasing the amount of exercise will result in a decrease in body weight.
Non-directional Hypothesis
A non-directional hypothesis is a statement that predicts the relationship between variables but does not specify the direction. For example, a researcher might predict that there is a relationship between the amount of exercise and body weight, but they do not specify whether increasing or decreasing exercise will affect body weight.
Statistical Hypothesis
A statistical hypothesis is a statement that assumes a particular statistical model or distribution for the data. It is often used in statistical analysis to test the significance of a particular result.
Composite Hypothesis
A composite hypothesis is a statement that assumes more than one condition or outcome. It can be divided into several sub-hypotheses, each of which represents a different possible outcome.
Empirical Hypothesis
An empirical hypothesis is a statement that is based on observed phenomena or data. It is often used in scientific research to develop theories or models that explain the observed phenomena.
Simple Hypothesis
A simple hypothesis is a statement that assumes only one outcome or condition. It is often used in scientific research to test a single variable or factor.
Complex Hypothesis
A complex hypothesis is a statement that assumes multiple outcomes or conditions. It is often used in scientific research to test the effects of multiple variables or factors on a particular outcome.
Applications of Hypothesis
Hypotheses are used in various fields to guide research and make predictions about the outcomes of experiments or observations. Here are some examples of how hypotheses are applied in different fields:
- Science : In scientific research, hypotheses are used to test the validity of theories and models that explain natural phenomena. For example, a hypothesis might be formulated to test the effects of a particular variable on a natural system, such as the effects of climate change on an ecosystem.
- Medicine : In medical research, hypotheses are used to test the effectiveness of treatments and therapies for specific conditions. For example, a hypothesis might be formulated to test the effects of a new drug on a particular disease.
- Psychology : In psychology, hypotheses are used to test theories and models of human behavior and cognition. For example, a hypothesis might be formulated to test the effects of a particular stimulus on the brain or behavior.
- Sociology : In sociology, hypotheses are used to test theories and models of social phenomena, such as the effects of social structures or institutions on human behavior. For example, a hypothesis might be formulated to test the effects of income inequality on crime rates.
- Business : In business research, hypotheses are used to test the validity of theories and models that explain business phenomena, such as consumer behavior or market trends. For example, a hypothesis might be formulated to test the effects of a new marketing campaign on consumer buying behavior.
- Engineering : In engineering, hypotheses are used to test the effectiveness of new technologies or designs. For example, a hypothesis might be formulated to test the efficiency of a new solar panel design.

How to write a Hypothesis
Here are the steps to follow when writing a hypothesis:
Identify the Research Question
The first step is to identify the research question that you want to answer through your study. This question should be clear, specific, and focused. It should be something that can be investigated empirically and that has some relevance or significance in the field.
Conduct a Literature Review
Before writing your hypothesis, it’s essential to conduct a thorough literature review to understand what is already known about the topic. This will help you to identify the research gap and formulate a hypothesis that builds on existing knowledge.
Determine the Variables
The next step is to identify the variables involved in the research question. A variable is any characteristic or factor that can vary or change. There are two types of variables: independent and dependent. The independent variable is the one that is manipulated or changed by the researcher, while the dependent variable is the one that is measured or observed as a result of the independent variable.
Formulate the Hypothesis
Based on the research question and the variables involved, you can now formulate your hypothesis. A hypothesis should be a clear and concise statement that predicts the relationship between the variables. It should be testable through empirical research and based on existing theory or evidence.
Write the Null Hypothesis
The null hypothesis is the opposite of the alternative hypothesis, which is the hypothesis that you are testing. The null hypothesis states that there is no significant difference or relationship between the variables. It is important to write the null hypothesis because it allows you to compare your results with what would be expected by chance.
Refine the Hypothesis
After formulating the hypothesis, it’s important to refine it and make it more precise. This may involve clarifying the variables, specifying the direction of the relationship, or making the hypothesis more testable.
Examples of Hypothesis
Here are a few examples of hypotheses in different fields:
- Psychology : “Increased exposure to violent video games leads to increased aggressive behavior in adolescents.”
- Biology : “Higher levels of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere will lead to increased plant growth.”
- Sociology : “Individuals who grow up in households with higher socioeconomic status will have higher levels of education and income as adults.”
- Education : “Implementing a new teaching method will result in higher student achievement scores.”
- Marketing : “Customers who receive a personalized email will be more likely to make a purchase than those who receive a generic email.”
- Physics : “An increase in temperature will cause an increase in the volume of a gas, assuming all other variables remain constant.”
- Medicine : “Consuming a diet high in saturated fats will increase the risk of developing heart disease.”
Purpose of Hypothesis
The purpose of a hypothesis is to provide a testable explanation for an observed phenomenon or a prediction of a future outcome based on existing knowledge or theories. A hypothesis is an essential part of the scientific method and helps to guide the research process by providing a clear focus for investigation. It enables scientists to design experiments or studies to gather evidence and data that can support or refute the proposed explanation or prediction.
The formulation of a hypothesis is based on existing knowledge, observations, and theories, and it should be specific, testable, and falsifiable. A specific hypothesis helps to define the research question, which is important in the research process as it guides the selection of an appropriate research design and methodology. Testability of the hypothesis means that it can be proven or disproven through empirical data collection and analysis. Falsifiability means that the hypothesis should be formulated in such a way that it can be proven wrong if it is incorrect.
In addition to guiding the research process, the testing of hypotheses can lead to new discoveries and advancements in scientific knowledge. When a hypothesis is supported by the data, it can be used to develop new theories or models to explain the observed phenomenon. When a hypothesis is not supported by the data, it can help to refine existing theories or prompt the development of new hypotheses to explain the phenomenon.
When to use Hypothesis
Here are some common situations in which hypotheses are used:
- In scientific research , hypotheses are used to guide the design of experiments and to help researchers make predictions about the outcomes of those experiments.
- In social science research , hypotheses are used to test theories about human behavior, social relationships, and other phenomena.
- I n business , hypotheses can be used to guide decisions about marketing, product development, and other areas. For example, a hypothesis might be that a new product will sell well in a particular market, and this hypothesis can be tested through market research.
Characteristics of Hypothesis
Here are some common characteristics of a hypothesis:
- Testable : A hypothesis must be able to be tested through observation or experimentation. This means that it must be possible to collect data that will either support or refute the hypothesis.
- Falsifiable : A hypothesis must be able to be proven false if it is not supported by the data. If a hypothesis cannot be falsified, then it is not a scientific hypothesis.
- Clear and concise : A hypothesis should be stated in a clear and concise manner so that it can be easily understood and tested.
- Based on existing knowledge : A hypothesis should be based on existing knowledge and research in the field. It should not be based on personal beliefs or opinions.
- Specific : A hypothesis should be specific in terms of the variables being tested and the predicted outcome. This will help to ensure that the research is focused and well-designed.
- Tentative: A hypothesis is a tentative statement or assumption that requires further testing and evidence to be confirmed or refuted. It is not a final conclusion or assertion.
- Relevant : A hypothesis should be relevant to the research question or problem being studied. It should address a gap in knowledge or provide a new perspective on the issue.
Advantages of Hypothesis
Hypotheses have several advantages in scientific research and experimentation:
- Guides research: A hypothesis provides a clear and specific direction for research. It helps to focus the research question, select appropriate methods and variables, and interpret the results.
- Predictive powe r: A hypothesis makes predictions about the outcome of research, which can be tested through experimentation. This allows researchers to evaluate the validity of the hypothesis and make new discoveries.
- Facilitates communication: A hypothesis provides a common language and framework for scientists to communicate with one another about their research. This helps to facilitate the exchange of ideas and promotes collaboration.
- Efficient use of resources: A hypothesis helps researchers to use their time, resources, and funding efficiently by directing them towards specific research questions and methods that are most likely to yield results.
- Provides a basis for further research: A hypothesis that is supported by data provides a basis for further research and exploration. It can lead to new hypotheses, theories, and discoveries.
- Increases objectivity: A hypothesis can help to increase objectivity in research by providing a clear and specific framework for testing and interpreting results. This can reduce bias and increase the reliability of research findings.
Limitations of Hypothesis
Some Limitations of the Hypothesis are as follows:
- Limited to observable phenomena: Hypotheses are limited to observable phenomena and cannot account for unobservable or intangible factors. This means that some research questions may not be amenable to hypothesis testing.
- May be inaccurate or incomplete: Hypotheses are based on existing knowledge and research, which may be incomplete or inaccurate. This can lead to flawed hypotheses and erroneous conclusions.
- May be biased: Hypotheses may be biased by the researcher’s own beliefs, values, or assumptions. This can lead to selective interpretation of data and a lack of objectivity in research.
- Cannot prove causation: A hypothesis can only show a correlation between variables, but it cannot prove causation. This requires further experimentation and analysis.
- Limited to specific contexts: Hypotheses are limited to specific contexts and may not be generalizable to other situations or populations. This means that results may not be applicable in other contexts or may require further testing.
- May be affected by chance : Hypotheses may be affected by chance or random variation, which can obscure or distort the true relationship between variables.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples

Institutional Review Board – Application Sample...

Evaluating Research – Process, Examples and...

Hypothesis vs. Theory: A Simple Guide to Tell Them Apart
By: Author ESLBUZZ
Posted on Last updated: July 27, 2023
Sharing is caring!
Hypothesis and theory are no stranger to those who conduct studies and work in science. These two terms are often used interchangeably by non-researchers, but they have distinct meanings in the scientific community. Understanding the difference between a hypothesis and a theory is essential for anyone interested in scientific research or critical thinking.
In this article, we will explore the differences between hypothesis and theory and provide examples to help you understand how they are used in scientific research. We will also discuss the importance of these terms in the scientific method and how they contribute to our understanding of the natural world. Whether you are a student, a researcher, or simply someone interested in science, this article will provide valuable insights into the world of scientific research.
To help illustrate the differences between hypothesis and theory, we will provide a comparison table that summarizes the key differences between these two terms and examples of how scientists use hypotheses and theories to explain natural phenomena and make predictions about future events. By the end of this article, you will have a clear understanding of the differences between hypothesis and theory and how they are used in scientific research.
Hypothesis vs. Theory

Hypothesis vs. Theory: Definitions
Understanding hypothesis.
A hypothesis is an educated guess or assumption that is made before conducting research. It is a tentative explanation for a phenomenon or observation that is based on limited evidence or prior knowledge. In other words, a hypothesis is a statement that proposes a relationship between two or more variables, which can be tested through further investigation.
Characteristics of Hypothesis
Hypotheses have certain characteristics that set them apart from other types of statements. These characteristics include:
- Testable: A hypothesis must be testable through empirical research. This means that it must be possible to collect data that can either support or refute the hypothesis.
- Specific: A hypothesis must be specific in its predictions. It should clearly state what is expected to happen and under what conditions.
- Falsifiable: A hypothesis must be falsifiable, which means that it must be possible to disprove the hypothesis if it is not supported by the evidence.
- Parsimonious: A hypothesis should be simple and straightforward. It should not include unnecessary assumptions or variables.
Examples of Hypothesis
Here are some examples of hypotheses:
- If a plant is exposed to sunlight, then it will grow faster than a plant that is not exposed to sunlight.
- If a person consumes more calories than they burn, then they will gain weight.
- If students are given more time to study for an exam, then they will perform better on the exam.
In summary, a hypothesis is an educated guess or assumption that is made before conducting research. It is testable, specific, falsifiable, and parsimonious. Examples of hypotheses include statements that propose a relationship between two or more variables, which can be tested through further investigation.
Understanding Theory
Definition of Theory
In scientific terms, a theory is a well-substantiated explanation of some aspect of the natural world that is based on empirical evidence. It is a collection of ideas that have been tested and confirmed through observation and experimentation. A theory is a framework that explains how and why things work in a certain way. It is a set of principles that can be used to make predictions about future events.
Characteristics of Theory
A theory has several characteristics that distinguish it from other scientific concepts such as hypotheses or laws. Some of the key characteristics of a theory are:
- A theory is based on empirical evidence and is supported by multiple lines of evidence.
- A theory is constantly evolving and can be modified or refined as new evidence emerges.
- A theory is generally accepted as true by the scientific community and is widely used to make predictions and guide research.
- A theory is not a guess or a hunch, but a well-substantiated explanation that has been rigorously tested.
Examples of Theory
There are many examples of well-established theories in science. Here are a few examples:
In summary, a theory is a well-substantiated explanation of some aspect of the natural world that is based on empirical evidence. It is a framework that explains how and why things work in a certain way and is constantly evolving as new evidence emerges. Theories are widely accepted as true by the scientific community and are used to make predictions and guide research.
Hypothesis vs. Theory: The Distinctions
As a writer, it is important to understand the differences between a hypothesis and a theory. These two scientific terms are often used interchangeably, but they have drastically different meanings in the world of science. In this section, we will explore the process of formulation, level of proof, and usage in the scientific community.
Process of Formulation
A hypothesis is an educated guess or assumption made before any research has been done. It is formed so that it can be tested to see if it might be true. Hypotheses are often based on observations or previous research and can be either proven or disproven through experimentation.
On the other hand, a theory is a well-established principle that is formed to explain the things already shown in data. Theories are based on a large body of evidence and have been extensively tested and proven through experimentation. The formulation of a theory requires a lot of research, experimentation, and analysis.
Level of Proof
The level of proof required for a hypothesis and a theory is vastly different. A hypothesis requires a certain level of proof to be considered valid, but it can still be disproven through experimentation. In contrast, a theory has been extensively tested and proven through experimentation, and therefore requires a much higher level of proof to be disproven.
Usage in Scientific Community
In the scientific community, hypotheses and theories play different roles. Hypotheses are used to generate predictions and testable explanations for phenomena, while theories are used to explain and predict a wide range of phenomena. Hypotheses are usually the starting point for research, while theories are the end result of extensive research and experimentation.
To summarize, a hypothesis is an educated guess or assumption made before any research has been done, while a theory is a well-established principle that is formed to explain the things already shown in data. Hypotheses require a certain level of proof to be considered valid, while theories require a much higher level of proof. In the scientific community, hypotheses are used to generate predictions and testable explanations for phenomena, while theories are used to explain and predict a wide range of phenomena.
Hypothesis vs. Theory: Common Misconceptions
When it comes to scientific research, there are several misconceptions about the differences between hypothesis and theory. In this section, we’ll explore some of the most common misconceptions and clarify the differences between these two scientific terms.
Misconception #1: Hypotheses are less important than theories
One common misconception is that hypotheses are less important than theories. This is not true. A hypothesis is the foundation of scientific research, as it is a proposed explanation for an observation or phenomenon. Without a hypothesis, there can be no scientific investigation.
Misconception #2: Hypotheses are guesses
Another common misconception is that hypotheses are guesses. While a hypothesis is an educated guess, it is not a random or arbitrary guess. A hypothesis is based on prior knowledge, observations, and data. It is a proposed explanation that can be tested through experimentation.
Misconception #3: Theories are proven facts
Many people believe that theories are proven facts. This is not true. A theory is a well-substantiated explanation for a set of observations or phenomena. It is based on a large body of evidence and has been repeatedly tested and confirmed through experimentation. However, theories are not absolute truths and are subject to revision or rejection based on new evidence.
Misconception #4: Hypotheses become theories
Some people believe that hypotheses become theories once they are proven. This is not true. A hypothesis can be supported or rejected by experimental evidence, but it does not become a theory. A theory is a broader explanation that encompasses many hypotheses and has been extensively tested and confirmed.
Misconception #5: Theories are more certain than hypotheses
Another common misconception is that theories are more certain than hypotheses. While theories are based on a large body of evidence and have been extensively tested, they are not absolute truths. Theories are subject to revision or rejection based on new evidence, just like hypotheses.
In summary, hypotheses and theories are both important components of scientific research. Hypotheses are proposed explanations that can be tested through experimentation, while theories are well-substantiated explanations that have been extensively tested and confirmed. While there are many misconceptions about the differences between hypotheses vs. theory, understanding these differences is crucial for conducting scientific research.
In conclusion, while the terms “hypothesis” and “theory” are often used interchangeably, they have distinct differences in the scientific method. A hypothesis is an assumption made before any research has been done, formed so that it can be tested to see if it might be true. On the other hand, a theory is a principle formed to explain the things already shown in data.
One way to differentiate between a hypothesis and a theory is to consider the level of evidence supporting each. A hypothesis is a proposed explanation for a phenomenon, but it is not yet supported by sufficient evidence. In contrast, a theory is a well-established explanation for a phenomenon that has been supported by a large body of evidence.
Another way to differentiate between a hypothesis and a theory is to consider their role in the scientific method. A hypothesis is an initial step in the scientific method, where a researcher formulates a testable prediction about a phenomenon. A theory, on the other hand, is the end result of the scientific method, where a researcher has tested and confirmed a hypothesis over time.
It is important to note that a hypothesis can eventually become a theory if it is repeatedly tested and supported by evidence. However, a theory can never become a hypothesis, as it is already a well-established explanation for a phenomenon.
In summary, understanding the differences between hypothesis and theory is crucial for conducting and interpreting scientific research. By using these terms correctly, researchers can communicate their ideas clearly and accurately, contributing to the advancement of scientific knowledge.
Frequently Asked Questions
How can you distinguish between hypothesis and theory?
A hypothesis is an educated guess or a proposed explanation for an observation or phenomenon. It is a tentative explanation that can be tested through experiments and observations. On the other hand, a theory is a well-established explanation that has been supported by a large body of evidence. The main difference between a hypothesis and a theory is that a hypothesis is a proposed explanation that needs to be tested, while a theory is a well-supported explanation that has been tested and confirmed by multiple lines of evidence.
What is the difference between a theory and a hypothesis in biology?
In biology, a hypothesis is a proposed explanation for a biological phenomenon that can be tested through experiments and observations. For example, a biologist might propose a hypothesis to explain why a particular species of bird has a particular beak shape. A theory in biology, on the other hand, is a well-established explanation that has been supported by a large body of evidence. For example, the theory of evolution is a well-established explanation for the diversity of life on Earth.
What is an example of a theory statement?
A theory statement is a statement that summarizes a well-established explanation for a phenomenon. For example, the theory of relativity is a statement that summarizes Einstein’s well-established explanation for the behavior of objects in space and time.
How are hypotheses and theories similar and different?
Both hypotheses and theories are proposed explanations for phenomena. However, while hypotheses are tentative and need to be tested, theories are well-established and have been supported by a large body of evidence. In addition, hypotheses are often specific to a particular observation or phenomenon, while theories are more general and can explain a wide range of phenomena.
What are some examples of the differences between a hypothesis and a theory?
An example of a hypothesis might be that a particular drug will cure a particular disease. An example of a theory might be the theory of plate tectonics, which explains the movement of the Earth’s crust. The main difference between these two examples is that the first is a tentative explanation that needs to be tested, while the second is a well-established explanation that has been supported by a large body of evidence.
"}},{"@type":"Question","name":"What is the difference between a theory and a hypothesis in biology?","acceptedAnswer":{"@type":"Answer","text":"
"}},{"@type":"Question","name":"What is an example of a theory statement?","acceptedAnswer":{"@type":"Answer","text":"
A theory statement is a statement that summarizes a well-established explanation for a phenomenon. For example, the theory of relativity is a statement that summarizes Einstein's well-established explanation for the behavior of objects in space and time.
"}},{"@type":"Question","name":"How are hypotheses and theories similar and different?","acceptedAnswer":{"@type":"Answer","text":"
"}},{"@type":"Question","name":"Which of these statements best distinguishes between hypotheses and theories?","acceptedAnswer":{"@type":"Answer","text":"
The best way to distinguish between hypotheses and theories is to remember that hypotheses are tentative explanations that need to be tested, while theories are well-established explanations that have been supported by a large body of evidence.
"}},{"@type":"Question","name":"What are some examples of the differences between a hypothesis and a theory?","acceptedAnswer":{"@type":"Answer","text":"
An example of a hypothesis might be that a particular drug will cure a particular disease. An example of a theory might be the theory of plate tectonics, which explains the movement of the Earth's crust. The main difference between these two examples is that the first is a tentative explanation that needs to be tested, while the second is a well-established explanation that has been supported by a large body of evidence.
- Recent Posts
- Ed Words: Expand Your Vocabulary and Improve Your Writing! - April 15, 2024
- List of Ethnicities and Their Cultures from Around the World - April 2, 2024
- Mastering English Writing: Essential Transitional Words for Body Paragraphs - March 25, 2024
Related posts:
- Difference between Would Rather, Prefer and Had Better
- COME and GO: How to Use Come vs. Go Correctly
- LIKE and ALIKE: Useful Difference between Like and Alike
- BY vs. UNTIL: How to Use By and Until Correctly
Research Hypothesis In Psychology: Types, & Examples
Saul Mcleod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul Mcleod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc
Associate Editor for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MSc Psychology of Education
Olivia Guy-Evans is a writer and associate editor for Simply Psychology. She has previously worked in healthcare and educational sectors.
On This Page:
A research hypothesis, in its plural form “hypotheses,” is a specific, testable prediction about the anticipated results of a study, established at its outset. It is a key component of the scientific method .
Hypotheses connect theory to data and guide the research process towards expanding scientific understanding
Some key points about hypotheses:
- A hypothesis expresses an expected pattern or relationship. It connects the variables under investigation.
- It is stated in clear, precise terms before any data collection or analysis occurs. This makes the hypothesis testable.
- A hypothesis must be falsifiable. It should be possible, even if unlikely in practice, to collect data that disconfirms rather than supports the hypothesis.
- Hypotheses guide research. Scientists design studies to explicitly evaluate hypotheses about how nature works.
- For a hypothesis to be valid, it must be testable against empirical evidence. The evidence can then confirm or disprove the testable predictions.
- Hypotheses are informed by background knowledge and observation, but go beyond what is already known to propose an explanation of how or why something occurs.
Predictions typically arise from a thorough knowledge of the research literature, curiosity about real-world problems or implications, and integrating this to advance theory. They build on existing literature while providing new insight.
Types of Research Hypotheses
Alternative hypothesis.
The research hypothesis is often called the alternative or experimental hypothesis in experimental research.
It typically suggests a potential relationship between two key variables: the independent variable, which the researcher manipulates, and the dependent variable, which is measured based on those changes.
The alternative hypothesis states a relationship exists between the two variables being studied (one variable affects the other).
A hypothesis is a testable statement or prediction about the relationship between two or more variables. It is a key component of the scientific method. Some key points about hypotheses:
- Important hypotheses lead to predictions that can be tested empirically. The evidence can then confirm or disprove the testable predictions.
In summary, a hypothesis is a precise, testable statement of what researchers expect to happen in a study and why. Hypotheses connect theory to data and guide the research process towards expanding scientific understanding.
An experimental hypothesis predicts what change(s) will occur in the dependent variable when the independent variable is manipulated.
It states that the results are not due to chance and are significant in supporting the theory being investigated.
The alternative hypothesis can be directional, indicating a specific direction of the effect, or non-directional, suggesting a difference without specifying its nature. It’s what researchers aim to support or demonstrate through their study.
Null Hypothesis
The null hypothesis states no relationship exists between the two variables being studied (one variable does not affect the other). There will be no changes in the dependent variable due to manipulating the independent variable.
It states results are due to chance and are not significant in supporting the idea being investigated.
The null hypothesis, positing no effect or relationship, is a foundational contrast to the research hypothesis in scientific inquiry. It establishes a baseline for statistical testing, promoting objectivity by initiating research from a neutral stance.
Many statistical methods are tailored to test the null hypothesis, determining the likelihood of observed results if no true effect exists.
This dual-hypothesis approach provides clarity, ensuring that research intentions are explicit, and fosters consistency across scientific studies, enhancing the standardization and interpretability of research outcomes.
Nondirectional Hypothesis
A non-directional hypothesis, also known as a two-tailed hypothesis, predicts that there is a difference or relationship between two variables but does not specify the direction of this relationship.
It merely indicates that a change or effect will occur without predicting which group will have higher or lower values.
For example, “There is a difference in performance between Group A and Group B” is a non-directional hypothesis.
Directional Hypothesis
A directional (one-tailed) hypothesis predicts the nature of the effect of the independent variable on the dependent variable. It predicts in which direction the change will take place. (i.e., greater, smaller, less, more)
It specifies whether one variable is greater, lesser, or different from another, rather than just indicating that there’s a difference without specifying its nature.
For example, “Exercise increases weight loss” is a directional hypothesis.
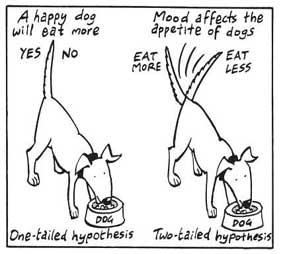
Falsifiability
The Falsification Principle, proposed by Karl Popper , is a way of demarcating science from non-science. It suggests that for a theory or hypothesis to be considered scientific, it must be testable and irrefutable.
Falsifiability emphasizes that scientific claims shouldn’t just be confirmable but should also have the potential to be proven wrong.
It means that there should exist some potential evidence or experiment that could prove the proposition false.
However many confirming instances exist for a theory, it only takes one counter observation to falsify it. For example, the hypothesis that “all swans are white,” can be falsified by observing a black swan.
For Popper, science should attempt to disprove a theory rather than attempt to continually provide evidence to support a research hypothesis.
Can a Hypothesis be Proven?
Hypotheses make probabilistic predictions. They state the expected outcome if a particular relationship exists. However, a study result supporting a hypothesis does not definitively prove it is true.
All studies have limitations. There may be unknown confounding factors or issues that limit the certainty of conclusions. Additional studies may yield different results.
In science, hypotheses can realistically only be supported with some degree of confidence, not proven. The process of science is to incrementally accumulate evidence for and against hypothesized relationships in an ongoing pursuit of better models and explanations that best fit the empirical data. But hypotheses remain open to revision and rejection if that is where the evidence leads.
- Disproving a hypothesis is definitive. Solid disconfirmatory evidence will falsify a hypothesis and require altering or discarding it based on the evidence.
- However, confirming evidence is always open to revision. Other explanations may account for the same results, and additional or contradictory evidence may emerge over time.
We can never 100% prove the alternative hypothesis. Instead, we see if we can disprove, or reject the null hypothesis.
If we reject the null hypothesis, this doesn’t mean that our alternative hypothesis is correct but does support the alternative/experimental hypothesis.
Upon analysis of the results, an alternative hypothesis can be rejected or supported, but it can never be proven to be correct. We must avoid any reference to results proving a theory as this implies 100% certainty, and there is always a chance that evidence may exist which could refute a theory.
How to Write a Hypothesis
- Identify variables . The researcher manipulates the independent variable and the dependent variable is the measured outcome.
- Operationalized the variables being investigated . Operationalization of a hypothesis refers to the process of making the variables physically measurable or testable, e.g. if you are about to study aggression, you might count the number of punches given by participants.
- Decide on a direction for your prediction . If there is evidence in the literature to support a specific effect of the independent variable on the dependent variable, write a directional (one-tailed) hypothesis. If there are limited or ambiguous findings in the literature regarding the effect of the independent variable on the dependent variable, write a non-directional (two-tailed) hypothesis.
- Make it Testable : Ensure your hypothesis can be tested through experimentation or observation. It should be possible to prove it false (principle of falsifiability).
- Clear & concise language . A strong hypothesis is concise (typically one to two sentences long), and formulated using clear and straightforward language, ensuring it’s easily understood and testable.
Consider a hypothesis many teachers might subscribe to: students work better on Monday morning than on Friday afternoon (IV=Day, DV= Standard of work).
Now, if we decide to study this by giving the same group of students a lesson on a Monday morning and a Friday afternoon and then measuring their immediate recall of the material covered in each session, we would end up with the following:
- The alternative hypothesis states that students will recall significantly more information on a Monday morning than on a Friday afternoon.
- The null hypothesis states that there will be no significant difference in the amount recalled on a Monday morning compared to a Friday afternoon. Any difference will be due to chance or confounding factors.
More Examples
- Memory : Participants exposed to classical music during study sessions will recall more items from a list than those who studied in silence.
- Social Psychology : Individuals who frequently engage in social media use will report higher levels of perceived social isolation compared to those who use it infrequently.
- Developmental Psychology : Children who engage in regular imaginative play have better problem-solving skills than those who don’t.
- Clinical Psychology : Cognitive-behavioral therapy will be more effective in reducing symptoms of anxiety over a 6-month period compared to traditional talk therapy.
- Cognitive Psychology : Individuals who multitask between various electronic devices will have shorter attention spans on focused tasks than those who single-task.
- Health Psychology : Patients who practice mindfulness meditation will experience lower levels of chronic pain compared to those who don’t meditate.
- Organizational Psychology : Employees in open-plan offices will report higher levels of stress than those in private offices.
- Behavioral Psychology : Rats rewarded with food after pressing a lever will press it more frequently than rats who receive no reward.
- Maths Notes Class 12
- NCERT Solutions Class 12
- RD Sharma Solutions Class 12
- Maths Formulas Class 12
- Maths Previous Year Paper Class 12
- Class 12 Syllabus
- Class 12 Revision Notes
- Physics Notes Class 12
- Chemistry Notes Class 12
- Biology Notes Class 12
- Null Hypothesis
- Hypothesis Testing Formula
- Difference Between Hypothesis And Theory
- Real-life Applications of Hypothesis Testing
- Permutation Hypothesis Test in R Programming
- Bayes' Theorem
- Hypothesis in Machine Learning
- Current Best Hypothesis Search
- Understanding Hypothesis Testing
- Hypothesis Testing in R Programming
- Jobathon | Stats | Question 10
- Jobathon | Stats | Question 17
- Testing | Question 1
- Difference between Null and Alternate Hypothesis
- ML | Find S Algorithm
- Python - Pearson's Chi-Square Test
- Libraries in Python
- How to Connect Python with SQL Database?
- Reading Rows from a CSV File in Python
- Data Communication - Definition, Components, Types, Channels
- Logic Gates - Definition, Types, Uses
- What is an IP Address?
- SQL HAVING Clause with Examples
- Sorting Algorithms in Python
- Business Studies
Hypothesis is a testable statement that explains what is happening or observed. It proposes the relation between the various participating variables. Hypothesis is also called Theory, Thesis, Guess, Assumption, or Suggestion. Hypothesis creates a structure that guides the search for knowledge.
In this article, we will learn what is hypothesis, its characteristics, types, and examples. We will also learn how hypothesis helps in scientific research.

What is Hypothesis?
A hypothesis is a suggested idea or plan that has little proof, meant to lead to more study. It’s mainly a smart guess or suggested answer to a problem that can be checked through study and trial. In science work, we make guesses called hypotheses to try and figure out what will happen in tests or watching. These are not sure things but rather ideas that can be proved or disproved based on real-life proofs. A good theory is clear and can be tested and found wrong if the proof doesn’t support it.
Hypothesis Meaning
A hypothesis is a proposed statement that is testable and is given for something that happens or observed.
- It is made using what we already know and have seen, and it’s the basis for scientific research.
- A clear guess tells us what we think will happen in an experiment or study.
- It’s a testable clue that can be proven true or wrong with real-life facts and checking it out carefully.
- It usually looks like a “if-then” rule, showing the expected cause and effect relationship between what’s being studied.
Characteristics of Hypothesis
Here are some key characteristics of a hypothesis:
- Testable: An idea (hypothesis) should be made so it can be tested and proven true through doing experiments or watching. It should show a clear connection between things.
- Specific: It needs to be easy and on target, talking about a certain part or connection between things in a study.
- Falsifiable: A good guess should be able to show it’s wrong. This means there must be a chance for proof or seeing something that goes against the guess.
- Logical and Rational: It should be based on things we know now or have seen, giving a reasonable reason that fits with what we already know.
- Predictive: A guess often tells what to expect from an experiment or observation. It gives a guide for what someone might see if the guess is right.
- Concise: It should be short and clear, showing the suggested link or explanation simply without extra confusion.
- Grounded in Research: A guess is usually made from before studies, ideas or watching things. It comes from a deep understanding of what is already known in that area.
- Flexible: A guess helps in the research but it needs to change or fix when new information comes up.
- Relevant: It should be related to the question or problem being studied, helping to direct what the research is about.
- Empirical: Hypotheses come from observations and can be tested using methods based on real-world experiences.
Sources of Hypothesis
Hypotheses can come from different places based on what you’re studying and the kind of research. Here are some common sources from which hypotheses may originate:
- Existing Theories: Often, guesses come from well-known science ideas. These ideas may show connections between things or occurrences that scientists can look into more.
- Observation and Experience: Watching something happen or having personal experiences can lead to guesses. We notice odd things or repeat events in everyday life and experiments. This can make us think of guesses called hypotheses.
- Previous Research: Using old studies or discoveries can help come up with new ideas. Scientists might try to expand or question current findings, making guesses that further study old results.
- Literature Review: Looking at books and research in a subject can help make guesses. Noticing missing parts or mismatches in previous studies might make researchers think up guesses to deal with these spots.
- Problem Statement or Research Question: Often, ideas come from questions or problems in the study. Making clear what needs to be looked into can help create ideas that tackle certain parts of the issue.
- Analogies or Comparisons: Making comparisons between similar things or finding connections from related areas can lead to theories. Understanding from other fields could create new guesses in a different situation.
- Hunches and Speculation: Sometimes, scientists might get a gut feeling or make guesses that help create ideas to test. Though these may not have proof at first, they can be a beginning for looking deeper.
- Technology and Innovations: New technology or tools might make guesses by letting us look at things that were hard to study before.
- Personal Interest and Curiosity: People’s curiosity and personal interests in a topic can help create guesses. Scientists could make guesses based on their own likes or love for a subject.
Types of Hypothesis
Here are some common types of hypotheses:
Simple Hypothesis
Complex hypothesis, directional hypothesis.
- Non-directional Hypothesis
Null Hypothesis (H0)
Alternative hypothesis (h1 or ha), statistical hypothesis, research hypothesis, associative hypothesis, causal hypothesis.
Simple Hypothesis guesses a connection between two things. It says that there is a connection or difference between variables, but it doesn’t tell us which way the relationship goes.
Complex Hypothesis tells us what will happen when more than two things are connected. It looks at how different things interact and may be linked together.
Directional Hypothesis says how one thing is related to another. For example, it guesses that one thing will help or hurt another thing.
Non-Directional Hypothesis
Non-Directional Hypothesis are the one that don’t say how the relationship between things will be. They just say that there is a connection, without telling which way it goes.
Null hypothesis is a statement that says there’s no connection or difference between different things. It implies that any seen impacts are because of luck or random changes in the information.
Alternative Hypothesis is different from the null hypothesis and shows that there’s a big connection or gap between variables. Scientists want to say no to the null hypothesis and choose the alternative one.
Statistical Hypotheis are used in math testing and include making ideas about what groups or bits of them look like. You aim to get information or test certain things using these top-level, common words only.
Research Hypothesis comes from the research question and tells what link is expected between things or factors. It leads the study and chooses where to look more closely.
Associative Hypotheis guesses that there is a link or connection between things without really saying it caused them. It means that when one thing changes, it is connected to another thing changing.
Causal Hypothesis are different from other ideas because they say that one thing causes another. This means there’s a cause and effect relationship between variables involved in the situation. They say that when one thing changes, it directly makes another thing change.
Hypothesis Examples
Following are the examples of hypotheses based on their types:
Simple Hypothesis Example
- Studying more can help you do better on tests.
- Getting more sun makes people have higher amounts of vitamin D.
Complex Hypothesis Example
- How rich you are, how easy it is to get education and healthcare greatly affects the number of years people live.
- A new medicine’s success relies on the amount used, how old a person is who takes it and their genes.
Directional Hypothesis Example
- Drinking more sweet drinks is linked to a higher body weight score.
- Too much stress makes people less productive at work.
Non-directional Hypothesis Example
- Drinking caffeine can affect how well you sleep.
- People often like different kinds of music based on their gender.
- The average test scores of Group A and Group B are not much different.
- There is no connection between using a certain fertilizer and how much it helps crops grow.
Alternative Hypothesis (Ha)
- Patients on Diet A have much different cholesterol levels than those following Diet B.
- Exposure to a certain type of light can change how plants grow compared to normal sunlight.
- The average smarts score of kids in a certain school area is 100.
- The usual time it takes to finish a job using Method A is the same as with Method B.
- Having more kids go to early learning classes helps them do better in school when they get older.
- Using specific ways of talking affects how much customers get involved in marketing activities.
- Regular exercise helps to lower the chances of heart disease.
- Going to school more can help people make more money.
- Playing violent video games makes teens more likely to act aggressively.
- Less clean air directly impacts breathing health in city populations.
Functions of Hypothesis
Hypotheses have many important jobs in the process of scientific research. Here are the key functions of hypotheses:
- Guiding Research: Hypotheses give a clear and exact way for research. They act like guides, showing the predicted connections or results that scientists want to study.
- Formulating Research Questions: Research questions often create guesses. They assist in changing big questions into particular, checkable things. They guide what the study should be focused on.
- Setting Clear Objectives: Hypotheses set the goals of a study by saying what connections between variables should be found. They set the targets that scientists try to reach with their studies.
- Testing Predictions: Theories guess what will happen in experiments or observations. By doing tests in a planned way, scientists can check if what they see matches the guesses made by their ideas.
- Providing Structure: Theories give structure to the study process by arranging thoughts and ideas. They aid scientists in thinking about connections between things and plan experiments to match.
- Focusing Investigations: Hypotheses help scientists focus on certain parts of their study question by clearly saying what they expect links or results to be. This focus makes the study work better.
- Facilitating Communication: Theories help scientists talk to each other effectively. Clearly made guesses help scientists to tell others what they plan, how they will do it and the results expected. This explains things well with colleagues in a wide range of audiences.
- Generating Testable Statements: A good guess can be checked, which means it can be looked at carefully or tested by doing experiments. This feature makes sure that guesses add to the real information used in science knowledge.
- Promoting Objectivity: Guesses give a clear reason for study that helps guide the process while reducing personal bias. They motivate scientists to use facts and data as proofs or disprovals for their proposed answers.
- Driving Scientific Progress: Making, trying out and adjusting ideas is a cycle. Even if a guess is proven right or wrong, the information learned helps to grow knowledge in one specific area.
How Hypothesis help in Scientific Research?
Researchers use hypotheses to put down their thoughts directing how the experiment would take place. Following are the steps that are involved in the scientific method:
- Initiating Investigations: Hypotheses are the beginning of science research. They come from watching, knowing what’s already known or asking questions. This makes scientists make certain explanations that need to be checked with tests.
- Formulating Research Questions: Ideas usually come from bigger questions in study. They help scientists make these questions more exact and testable, guiding the study’s main point.
- Setting Clear Objectives: Hypotheses set the goals of a study by stating what we think will happen between different things. They set the goals that scientists want to reach by doing their studies.
- Designing Experiments and Studies: Assumptions help plan experiments and watchful studies. They assist scientists in knowing what factors to measure, the techniques they will use and gather data for a proposed reason.
- Testing Predictions: Ideas guess what will happen in experiments or observations. By checking these guesses carefully, scientists can see if the seen results match up with what was predicted in each hypothesis.
- Analysis and Interpretation of Data: Hypotheses give us a way to study and make sense of information. Researchers look at what they found and see if it matches the guesses made in their theories. They decide if the proof backs up or disagrees with these suggested reasons why things are happening as expected.
- Encouraging Objectivity: Hypotheses help make things fair by making sure scientists use facts and information to either agree or disagree with their suggested reasons. They lessen personal preferences by needing proof from experience.
- Iterative Process: People either agree or disagree with guesses, but they still help the ongoing process of science. Findings from testing ideas make us ask new questions, improve those ideas and do more tests. It keeps going on in the work of science to keep learning things.
People Also View:
Mathematics Maths Formulas Branches of Mathematics
Summary – Hypothesis
A hypothesis is a testable statement serving as an initial explanation for phenomena, based on observations, theories, or existing knowledge. It acts as a guiding light for scientific research, proposing potential relationships between variables that can be empirically tested through experiments and observations. The hypothesis must be specific, testable, falsifiable, and grounded in prior research or observation, laying out a predictive, if-then scenario that details a cause-and-effect relationship. It originates from various sources including existing theories, observations, previous research, and even personal curiosity, leading to different types, such as simple, complex, directional, non-directional, null, and alternative hypotheses, each serving distinct roles in research methodology. The hypothesis not only guides the research process by shaping objectives and designing experiments but also facilitates objective analysis and interpretation of data, ultimately driving scientific progress through a cycle of testing, validation, and refinement.
FAQs on Hypothesis
What is a hypothesis.
A guess is a possible explanation or forecast that can be checked by doing research and experiments.
What are Components of a Hypothesis?
The components of a Hypothesis are Independent Variable, Dependent Variable, Relationship between Variables, Directionality etc.
What makes a Good Hypothesis?
Testability, Falsifiability, Clarity and Precision, Relevance are some parameters that makes a Good Hypothesis
Can a Hypothesis be Proven True?
You cannot prove conclusively that most hypotheses are true because it’s generally impossible to examine all possible cases for exceptions that would disprove them.
How are Hypotheses Tested?
Hypothesis testing is used to assess the plausibility of a hypothesis by using sample data
Can Hypotheses change during Research?
Yes, you can change or improve your ideas based on new information discovered during the research process.
What is the Role of a Hypothesis in Scientific Research?
Hypotheses are used to support scientific research and bring about advancements in knowledge.
Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.

- Geeks Premier League 2023
- Maths-Class-12
- Geeks Premier League
- Mathematics
- School Learning

Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A hypothesis is an assumption made before any research has been done. It is formed so that it can be tested to see if it might be true. A theory is a principle formed to explain the things already shown in data. Because of the rigors of experiment and control, it is much more likely that a theory will be true than a hypothesis.
A hypothesis is either a suggested explanation for an observable phenomenon, or a reasoned prediction of a possible causal correlation among multiple phenomena. In science, a theory is a tested, well-substantiated, unifying explanation for a set of verified, proven factors. A theory is always backed by evidence; a hypothesis is only a suggested possible outcome, and is testable and falsifiable.
How to use each. Although theory in terms of science is used to express something based on extensive research and experimentation, typically in everyday life, theory is used more casually to express an educated guess. So in casual language, theory and hypothesis are more likely to be used interchangeably to express an idea or speculation.
Theory vs. Hypothesis: Basics of the Scientific Method. Written by MasterClass. Last updated: Jun 7, 2021 • 2 min read. Though you may hear the terms "theory" and "hypothesis" used interchangeably, these two scientific terms have drastically different meanings in the world of science.
Theory vs Hypothesis. A hypothesis is a proposition that is tested via an experiment. A theory results from many, many tested hypotheses. Theory vs Fact. Theories depend on facts, but the two words mean different things. A fact is an irrefutable piece of evidence or data. Facts never change. A theory, on the other hand, may be modified or ...
A theory is valid as long as there is no evidence to dispute it. Therefore, theories can be disproven. Basically, if evidence accumulates to support a hypothesis, then the hypothesis can become accepted as a good explanation of a phenomenon. One definition of a theory is to say that it's an accepted hypothesis.
Hypothesis vs. Theory: The Definition What Does Hypothesis Mean? A hypothesis is a proposed explanation for a phenomenon or a scientific question that can be tested through experimentation or observation. It is an essential part of the scientific method, which involves formulating a hypothesis, conducting experiments to test it, and analyzing ...
A "hypothesis" is a consequence of the theory that one can test. From Chloë's Theory, we have the hypothesis that an object will take 2-√ 2 times longer to fall from 1m 1 m than from 2 m 2 m. We can formulate the hypothesis based on the theory and then test that hypothesis. If the hypothesis is found to be invalidated by experiment ...
Hypothesis & theory have one main difference. Use these definitions & examples to explore how these terms differ from each other and similar science terms. ... Definition of Hypothesis. In the scientific process, a hypothesis is "a statement that makes generalizations about a set of facts, usually forming a basis for possible experiments ...
scientific hypothesis, an idea that proposes a tentative explanation about a phenomenon or a narrow set of phenomena observed in the natural world.The two primary features of a scientific hypothesis are falsifiability and testability, which are reflected in an "If…then" statement summarizing the idea and in the ability to be supported or refuted through observation and experimentation.
Key takeaways. Both a theory and hypothesis have a place in the scientific method and their primary difference is when they occur in this type of research. Scientists, researchers and psychologists commonly use theories to guide their studies and develop hypotheses. A theory requires evidence to prove, while a hypothesis guides research and ...
Hypothesis is a suggested explanation to explain some phenomenon, and is based on limited data. Theory, on the other hand, is a set of ideas that is intended to explain facts or events; they are based on concrete evidence. This is the main difference between hypothesis and theory. This article explains, 1. What is a Hypothesis?
Marisa Alviar-Agnew ( Sacramento City College) Henry Agnew (UC Davis) 1.6: Hypothesis, Theories, and Laws is shared under a CK-12 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by Marisa Alviar-Agnew & Henry Agnew. Although many have taken science classes throughout the course of their studies, people often have incorrect or misleading ideas ...
A theory is a well-affirmed explanation of natural phenomena, which is frequently validated through experimentation and observation. While the hypothesis is based on a little amount of data, the theory is based on a wide set of data. The hypothesis is an unproven statement; that can be tested.
A scientific theory or law represents a hypothesis (or group of related hypotheses) which has been confirmed through repeated testing, almost always conducted over a span of many years. Generally, a theory is an explanation for a set of related phenomena, like the theory of evolution or the big bang theory.
scientific theory, systematic ideational structure of broad scope, conceived by the human imagination, that encompasses a family of empirical (experiential) laws regarding regularities existing in objects and events, both observed and posited. A scientific theory is a structure suggested by these laws and is devised to explain them in a scientifically rational manner.
Henry Agnew (UC Davis) 1.3: Hypothesis, Theories, and Laws is shared under a CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by LibreTexts. Although all of us have taken science classes throughout the course of our study, many people have incorrect or misleading ideas about some of the most important and basic principles in ...
Definition: Hypothesis is an educated guess or proposed explanation for a phenomenon, based on some initial observations or data. It is a tentative statement that can be tested and potentially proven or disproven through further investigation and experimentation. Hypothesis is often used in scientific research to guide the design of experiments ...
A hypothesis is an educated guess or a proposed explanation for an observation or phenomenon. It is a tentative explanation that can be tested through experiments and observations. On the other hand, a theory is a well-established explanation that has been supported by a large body of evidence.
A research hypothesis, in its plural form "hypotheses," is a specific, testable prediction about the anticipated results of a study, established at its outset. It is a key component of the scientific method. Hypotheses connect theory to data and guide the research process towards expanding scientific understanding.
Hypothesis. Hypothesis is a testable statement that explains what is happening or observed. It proposes the relation between the various participating variables. Hypothesis is also called Theory, Thesis, Guess, Assumption, or Suggestion. Hypothesis creates a structure that guides the search for knowledge.