- Engineering Mathematics
- Discrete Mathematics
- Operating System
- Computer Networks
- Digital Logic and Design
- C Programming
- Data Structures
- Theory of Computation
- Compiler Design
- Computer Org and Architecture

Presentation Layer in OSI model
Prerequisite : OSI Model
Introduction : Presentation Layer is the 6th layer in the Open System Interconnection (OSI) model. This layer is also known as Translation layer, as this layer serves as a data translator for the network. The data which this layer receives from the Application Layer is extracted and manipulated here as per the required format to transmit over the network. The main responsibility of this layer is to provide or define the data format and encryption. The presentation layer is also called as Syntax layer since it is responsible for maintaining the proper syntax of the data which it either receives or transmits to other layer(s).
Functions of Presentation Layer :
The presentation layer, being the 6th layer in the OSI model, performs several types of functions, which are described below-
- Presentation layer format and encrypts data to be sent across the network.
- This layer takes care that the data is sent in such a way that the receiver will understand the information (data) and will be able to use the data efficiently and effectively.
- This layer manages the abstract data structures and allows high-level data structures (example- banking records), which are to be defined or exchanged.
- This layer carries out the encryption at the transmitter and decryption at the receiver.
- This layer carries out data compression to reduce the bandwidth of the data to be transmitted (the primary goal of data compression is to reduce the number of bits which is to be transmitted).
- This layer is responsible for interoperability (ability of computers to exchange and make use of information) between encoding methods as different computers use different encoding methods.
- This layer basically deals with the presentation part of the data.
- Presentation layer, carries out the data compression (number of bits reduction while transmission), which in return improves the data throughput.
- This layer also deals with the issues of string representation.
- The presentation layer is also responsible for integrating all the formats into a standardized format for efficient and effective communication.
- This layer encodes the message from the user-dependent format to the common format and vice-versa for communication between dissimilar systems.
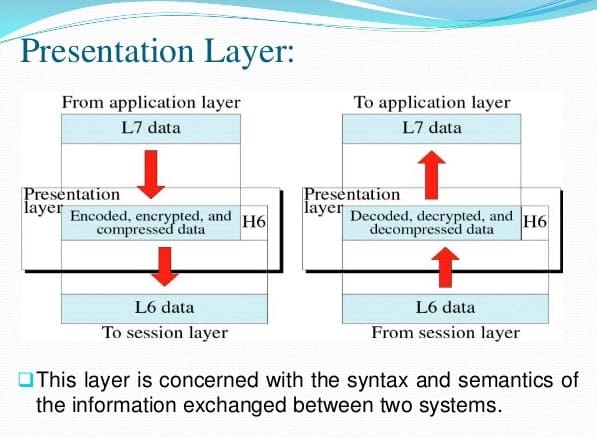
- This layer deals with the syntax and semantics of the messages.
- This layer also ensures that the messages which are to be presented to the upper as well as the lower layer should be standardized as well as in an accurate format too.
- Presentation layer is also responsible for translation, formatting, and delivery of information for processing or display.
- This layer also performs serialization (process of translating a data structure or an object into a format that can be stored or transmitted easily).
Features of Presentation Layer in the OSI model: Presentation layer, being the 6th layer in the OSI model, plays a vital role while communication is taking place between two devices in a network.
List of features which are provided by the presentation layer are:
- Presentation layer could apply certain sophisticated compression techniques, so fewer bytes of data are required to represent the information when it is sent over the network.
- If two or more devices are communicating over an encrypted connection, then this presentation layer is responsible for adding encryption on the sender’s end as well as the decoding the encryption on the receiver’s end so that it can represent the application layer with unencrypted, readable data.
- This layer formats and encrypts data to be sent over a network, providing freedom from compatibility problems.
- This presentation layer also negotiates the Transfer Syntax.
- This presentation layer is also responsible for compressing data it receives from the application layer before delivering it to the session layer (which is the 5th layer in the OSI model) and thus improves the speed as well as the efficiency of communication by minimizing the amount of the data to be transferred.
Working of Presentation Layer in the OSI model : Presentation layer in the OSI model, as a translator, converts the data sent by the application layer of the transmitting node into an acceptable and compatible data format based on the applicable network protocol and architecture. Upon arrival at the receiving computer, the presentation layer translates data into an acceptable format usable by the application layer. Basically, in other words, this layer takes care of any issues occurring when transmitted data must be viewed in a format different from the original format. Being the functional part of the OSI mode, the presentation layer performs a multitude (large number of) data conversion algorithms and character translation functions. Mainly, this layer is responsible for managing two network characteristics: protocol (set of rules) and architecture.
Presentation Layer Protocols : Presentation layer being the 6th layer, but the most important layer in the OSI model performs several types of functionalities, which makes sure that data which is being transferred or received should be accurate or clear to all the devices which are there in a closed network. Presentation Layer, for performing translations or other specified functions, needs to use certain protocols which are defined below –
- Apple Filing Protocol (AFP): Apple Filing Protocol is the proprietary network protocol (communications protocol) that offers services to macOS or the classic macOS. This is basically the network file control protocol specifically designed for Mac-based platforms.
- Lightweight Presentation Protocol (LPP): Lightweight Presentation Protocol is that protocol which is used to provide ISO presentation services on the top of TCP/IP based protocol stacks.
- NetWare Core Protocol (NCP): NetWare Core Protocol is the network protocol which is used to access file, print, directory, clock synchronization, messaging, remote command execution and other network service functions.
- Network Data Representation (NDR): Network Data Representation is basically the implementation of the presentation layer in the OSI model, which provides or defines various primitive data types, constructed data types and also several types of data representations.
- External Data Representation (XDR): External Data Representation (XDR) is the standard for the description and encoding of data. It is useful for transferring data between computer architectures and has been used to communicate data between very diverse machines. Converting from local representation to XDR is called encoding, whereas converting XDR into local representation is called decoding.
- Secure Socket Layer (SSL): The Secure Socket Layer protocol provides security to the data that is being transferred between the web browser and the server. SSL encrypts the link between a web server and a browser, which ensures that all data passed between them remains private and free from attacks.

Similar Reads
Please login to comment..., improve your coding skills with practice.
What kind of Experience do you want to share?
Layer 6 Presentation Layer
De/Encryption, Encoding, String representation
The presentation layer (data presentation layer, data provision level) sets the system-dependent representation of the data (for example, ASCII, EBCDIC) into an independent form, enabling the syntactically correct data exchange between different systems. Also, functions such as data compression and encryption are guaranteed that data to be sent by the application layer of a system that can be read by the application layer of another system to the layer 6. The presentation layer. If necessary, the presentation layer acts as a translator between different data formats, by making an understandable for both systems data format, the ASN.1 (Abstract Syntax Notation One) used.
OSI Layer 6 - Presentation Layer
The presentation layer is responsible for the delivery and formatting of information to the application layer for further processing or display. It relieves the application layer of concern regarding syntactical differences in data representation within the end-user systems. An example of a presentation service would be the conversion of an EBCDIC-coded text computer file to an ASCII-coded file. The presentation layer is the lowest layer at which application programmers consider data structure and presentation, instead of simply sending data in the form of datagrams or packets between hosts. This layer deals with issues of string representation - whether they use the Pascal method (an integer length field followed by the specified amount of bytes) or the C/C++ method (null-terminated strings, e.g. "thisisastring\0"). The idea is that the application layer should be able to point at the data to be moved, and the presentation layer will deal with the rest. Serialization of complex data structures into flat byte-strings (using mechanisms such as TLV or XML) can be thought of as the key functionality of the presentation layer. Encryption is typically done at this level too, although it can be done on the application, session, transport, or network layers, each having its own advantages and disadvantages. Decryption is also handled at the presentation layer. For example, when logging on to bank account sites the presentation layer will decrypt the data as it is received.[1] Another example is representing structure, which is normally standardized at this level, often by using XML. As well as simple pieces of data, like strings, more complicated things are standardized in this layer. Two common examples are 'objects' in object-oriented programming, and the exact way that streaming video is transmitted. In many widely used applications and protocols, no distinction is made between the presentation and application layers. For example, HyperText Transfer Protocol (HTTP), generally regarded as an application-layer protocol, has presentation-layer aspects such as the ability to identify character encoding for proper conversion, which is then done in the application layer. Within the service layering semantics of the OSI network architecture, the presentation layer responds to service requests from the application layer and issues service requests to the session layer. In the OSI model: the presentation layer ensures the information that the application layer of one system sends out is readable by the application layer of another system. For example, a PC program communicates with another computer, one using extended binary coded decimal interchange code (EBCDIC) and the other using ASCII to represent the same characters. If necessary, the presentation layer might be able to translate between multiple data formats by using a common format. Wikipedia
- Data conversion
- Character code translation
- Compression
- Encryption and Decryption
The Presentation OSI Layer is usually composed of 2 sublayers that are:
CASE common application service element
Sase specific application service element, layer 7 application layer, layer 6 presentation layer, layer 5 session layer, layer 4 transport layer, layer 3 network layer, layer 2 data link layer, layer 1 physical layer.
Service Impact Notice: Due to the ongoing hurricane, our operations may be affected. Our primary concern is the safety of our team members. As a result, response times may be delayed, and live chat will be temporarily unavailable. We appreciate your understanding and patience during this time. Please feel free to email us, and we will get back to you as soon as possible.
- +1 855.488.5327
- [email protected]
- Mon - Fri: 9:00am - 5:00pm ET

An Overview of SIEM Tools: Essential for Modern Cybersecurity

Introduction to CompTIA Data+: What You Need to Know Before Taking the Exam
The Four Stages of the Computing Cycle: How Computers Process Data
- Live Webinars
- What Is the Presentation Layer in the OSI Model?
The Presentation Layer is the sixth layer of the OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) model. It plays a crucial role in translating and formatting data between the application layer and the network. Often referred to as the “translator” of the OSI model, the Presentation Layer is responsible for data encoding, encryption, compression, and formatting. This layer ensures that data sent from one device is in a format that the receiving device’s application can interpret and use, even if the two systems use different data formats.
Definition: Presentation Layer
The Presentation Layer in the OSI model is responsible for translating data between the application and network layers, ensuring compatibility between different systems. It handles tasks such as data encryption, compression, encoding, and conversion to ensure that the data is in the correct format and can be understood by both the sender and the receiver.
Key Functions of the Presentation Layer
The Presentation Layer provides several key services that ensure data is presented in a way that can be understood by the receiving application:
- Data Translation: The Presentation Layer translates data between the formats used by the application layer and the underlying network layer. This ensures that data from different platforms can be exchanged and understood.
- Data Encryption and Decryption: For secure communication, the Presentation Layer encrypts data before it is transmitted across the network and decrypts it upon arrival, ensuring privacy and confidentiality.
- Data Compression and Decompression: To optimize bandwidth usage, the Presentation Layer compresses data before sending it over the network and decompresses it when it is received.
- Character Encoding: It converts data from one character encoding set to another, for example, ASCII to EBCDIC or Unicode, to ensure that both systems can correctly interpret text data.
- Syntax Handling: The Presentation Layer handles syntax conversion, ensuring that different systems using varying data structures can successfully communicate.
Data Translation in the Presentation Layer
One of the fundamental roles of the Presentation Layer is data translation . Since applications may use different data formats (such as numbers, characters, or file formats), the Presentation Layer translates this data into a standardized format that the receiving application can interpret.
For instance, consider two systems where one uses Big Endian byte ordering (the most significant byte is stored first) and the other uses Little Endian ordering (the least significant byte is stored first). The Presentation Layer converts data between these formats to ensure it is interpreted correctly by the receiver.
Similarly, image formats (e.g., JPEG, PNG) or file formats (e.g., PDF, DOC) may be encoded differently on various systems. The Presentation Layer ensures that these formats are properly translated between sender and receiver to maintain data integrity.
Data Encryption and Decryption
The encryption and decryption of data are essential for securing sensitive information in transit. The Presentation Layer provides the functionality needed to encrypt data before it is sent over the network and decrypt it upon receipt.
For example, in a secure banking transaction over the internet, the data transferred between the user and the bank’s server must be encrypted to prevent eavesdropping or unauthorized access. Secure Socket Layer (SSL) and Transport Layer Security (TLS) protocols operate at this level to secure communications.
Encryption involves converting readable data (plaintext) into an unreadable format (ciphertext) using an encryption key. When the data reaches its destination, the Presentation Layer uses a decryption key to convert the ciphertext back into plaintext, making it readable again.
Data Compression and Decompression
Data compression is a technique used by the Presentation Layer to reduce the size of the data being transmitted, thereby optimizing bandwidth usage and speeding up data transfer. By compressing data, the layer ensures that more information can be sent across the network in less time.
For instance, when transferring large files such as images, videos, or software, compression algorithms like ZIP or GZIP are applied to minimize file size. At the receiving end, the data is decompressed by the Presentation Layer to restore it to its original size.
Compression helps improve network performance by reducing congestion and making the most of available bandwidth, especially in scenarios where bandwidth is limited or expensive.
Character Encoding and Syntax Conversion
Character encoding is another key responsibility of the Presentation Layer. Since different systems may use different encoding standards, such as ASCII , Unicode , or EBCDIC , the Presentation Layer ensures that the data is properly converted so that it can be correctly interpreted by the receiver.
For example, if a sender uses ASCII encoding for a text file but the receiver uses Unicode, the Presentation Layer converts the ASCII-encoded characters into Unicode format to ensure that the text is correctly displayed on the receiving end.
Similarly, the Presentation Layer handles syntax conversion , ensuring that the data structures or data types used by the sending application are properly converted into a format that the receiving application can process. This is particularly important when exchanging data between systems that may use different file formats, data representations, or programming languages.
Protocols Operating at the Presentation Layer
Several protocols and formats operate at the Presentation Layer, helping to manage data translation, encryption, and compression. Some of the most widely used include:
- SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) / TLS (Transport Layer Security): These protocols provide encryption and secure data transmission over the internet, commonly used in web browsers and secure online transactions.
- JPEG, PNG, GIF: These image formats are handled at the Presentation Layer to ensure that images are properly encoded and displayed.
- MIME (Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions): MIME is used to encode binary data for transmission in email attachments. It converts binary data into a text-based format that can be sent through email systems.
- XDR (External Data Representation): XDR is a standard for the description and encoding of data that is used for data exchange between different platforms.
- ASCII and EBCDIC: Character encoding standards that are often converted by the Presentation Layer to ensure cross-platform compatibility.
Role of the Presentation Layer in the OSI Model
The Presentation Layer serves as the intermediary between the Application Layer (which is closest to the end user) and the lower layers that manage network functionality. It translates, encrypts, compresses, and formats data so that it can be successfully transmitted and understood by different systems.
While the Transport Layer ensures reliable delivery of data, the Presentation Layer focuses on ensuring that the data itself is in the correct format and structure for the receiving system. Without the Presentation Layer, data could become corrupted, unreadable, or incompatible between systems with different architectures or formats.
Use Cases of the Presentation Layer
The Presentation Layer plays a vital role in many everyday network activities and services. Some of the most common use cases include:
- Secure Web Browsing: When a user visits a secure website (e.g., one using HTTPS), the Presentation Layer ensures that all data exchanged between the browser and server is encrypted via SSL/TLS protocols.
- File Compression for Transmission: Before sending large files over a network, the Presentation Layer compresses the data to optimize bandwidth usage, ensuring faster transmission speeds.
- Email Attachments: When attaching files to emails, the Presentation Layer encodes the file data using MIME, ensuring it can be correctly transmitted and decoded by the recipient’s email client.
- Multimedia Applications: In multimedia applications such as video streaming or image sharing, the Presentation Layer handles the compression and formatting of video, audio, and image files to ensure they are displayed correctly on the receiver’s device.
- Cross-Platform Data Sharing: The Presentation Layer enables different systems (e.g., a Windows machine and a Unix server) to share data by converting it into a format that is compatible with both systems.
Benefits of the Presentation Layer
The Presentation Layer provides numerous benefits that are essential to network communication:
- Data Compatibility: It ensures that data exchanged between different systems is compatible, regardless of differences in data formats or encoding schemes.
- Data Security: Through encryption and decryption, the Presentation Layer protects sensitive information during transmission, ensuring confidentiality and security.
- Bandwidth Optimization: Data compression reduces file sizes, allowing for more efficient use of bandwidth and faster transmission times.
- Cross-Platform Communication: It handles character encoding and syntax conversion, enabling different systems with varying architectures to communicate seamlessly.
- Ensures Data Integrity: By translating and formatting data, the Presentation Layer helps prevent data corruption or misinterpretation between sender and receiver.
Challenges of the Presentation Layer
Despite its benefits, the Presentation Layer faces several challenges:
- Complexity in Data Translation: Handling multiple data formats and character encodings can add complexity, especially when ensuring compatibility across different systems and applications.
- Processing Overhead: Encryption, compression, and decompression processes can introduce overhead, increasing the time it takes to process and transmit data.
- Security Vulnerabilities: While the Presentation Layer manages encryption, any flaws in its implementation (e.g., outdated SSL/TLS versions) can leave data vulnerable to attacks.
Frequently Asked Questions Related to the Presentation Layer
What is the role of the presentation layer in the osi model.
The Presentation Layer is responsible for translating, encrypting, and formatting data to ensure it can be properly interpreted by the receiving application. It handles data compression, encryption, and syntax conversion to enable communication between different systems.
How does the Presentation Layer handle data encryption and decryption?
The Presentation Layer encrypts data before it is sent across a network to ensure secure transmission. Upon arrival, the layer decrypts the data so that the receiving application can read it. Encryption protocols like SSL/TLS operate at this layer to ensure data privacy.
What are the key functions of the Presentation Layer?
The key functions of the Presentation Layer include data translation, encryption/decryption, data compression, and character encoding conversion. It ensures that data from the application layer is properly formatted before being transmitted over the network.
Which protocols operate at the Presentation Layer?
Common protocols and formats that operate at the Presentation Layer include SSL/TLS for encryption, JPEG and PNG for image compression, and MIME for encoding email attachments. These protocols ensure that data is properly formatted and secure during transmission.
How does data compression work at the Presentation Layer?
The Presentation Layer compresses data before it is transmitted to reduce file sizes and optimize bandwidth usage. Upon reaching the destination, the data is decompressed to its original format. This helps speed up data transmission and improve network performance.
Related Blogs on the OSI Model
- What is the OSI Model?
- What Is the Physical Layer in the OSI Model?
- What Is the Data Link Layer in the OSI Model?
- What Is the Network Layer in the OSI Model?
- What Is the Transport Layer in the OSI Model?
- What Is the Session Layer in the OSI Model?
- What Is the Application Layer in the OSI Model?
Click the Copy to Clipboard button and paste into your web page to automatically add this blog content to your website
Content Copyright(c) 2024, ITU Online, LLC. Permission is granted to embed but not copy content in this blog. ITU Online, LLC reserves the right to modify or remove this content at any time.

Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
$ 699.00 Original price was: $699.00. $ 349.00 Current price is: $349.00.

$ 199.00 Original price was: $199.00. $ 129.00 Current price is: $129.00.

$ 49.99 Original price was: $49.99. $ 16.99 Current price is: $16.99. / month with a 10-day free trial

Start for only $1. Unlock endless learning opportunities with over 2,600 hours of IT training at our lowest price ever. Plus, get all new and updated online courses for free while your subscription remains active.
Cancel at your convenience. This exceptional deal on IT training provides you access to high-quality IT education at the lowest monthly subscription rate in the market. Boost your IT skills and join our journey towards a smarter tomorrow.

- Monday - Friday: 9am - 5pm ET
- Office: +1 855.488.5327
SHOPPING CART

Information
- IT Glossary
- Quick Byte Answers
- Our Instructors
- Privacy Policy
- Career Paths
Business Solutions
- Reseller Opportunities
- Team Training
- Affiliate Opportunities
- Student Login
ENDING THIS WEEKEND: Train for LIFE at our lowest price. Buy once and never have to pay for IT Training Again.
The OSI Model – The 7 Layers of Networking Explained in Plain English

By Chloe Tucker
This article explains the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model and the 7 layers of networking, in plain English.
The OSI model is a conceptual framework that is used to describe how a network functions. In plain English, the OSI model helped standardize the way computer systems send information to each other.
Learning networking is a bit like learning a language - there are lots of standards and then some exceptions. Therefore, it’s important to really understand that the OSI model is not a set of rules. It is a tool for understanding how networks function.
Once you learn the OSI model, you will be able to further understand and appreciate this glorious entity we call the Internet, as well as be able to troubleshoot networking issues with greater fluency and ease.
All hail the Internet!
Prerequisites
You don’t need any prior programming or networking experience to understand this article. However, you will need:
- Basic familiarity with common networking terms (explained below)
- A curiosity about how things work :)
Learning Objectives
Over the course of this article, you will learn:
- What the OSI model is
- The purpose of each of the 7 layers
- The problems that can happen at each of the 7 layers
- The difference between TCP/IP model and the OSI model
Common Networking Terms
Here are some common networking terms that you should be familiar with to get the most out of this article. I’ll use these terms when I talk about OSI layers next.
A node is a physical electronic device hooked up to a network, for example a computer, printer, router, and so on. If set up properly, a node is capable of sending and/or receiving information over a network.
Nodes may be set up adjacent to one other, wherein Node A can connect directly to Node B, or there may be an intermediate node, like a switch or a router, set up between Node A and Node B.
Typically, routers connect networks to the Internet and switches operate within a network to facilitate intra-network communication. Learn more about hub vs. switch vs. router.
Here's an example:
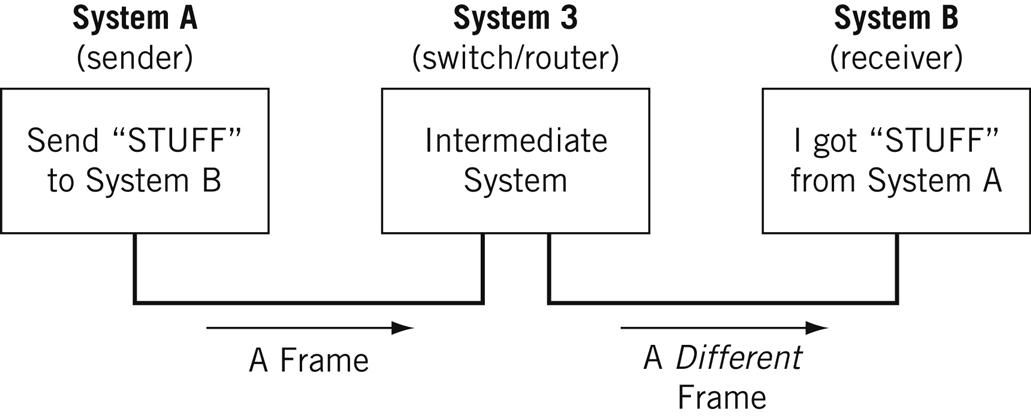
For the nitpicky among us (yep, I see you), host is another term that you will encounter in networking. I will define a host as a type of node that requires an IP address. All hosts are nodes, but not all nodes are hosts. Please Tweet angrily at me if you disagree.
Links connect nodes on a network. Links can be wired, like Ethernet, or cable-free, like WiFi.
Links to can either be point-to-point, where Node A is connected to Node B, or multipoint, where Node A is connected to Node B and Node C.
When we’re talking about information being transmitted, this may also be described as a one-to-one vs. a one-to-many relationship.
A protocol is a mutually agreed upon set of rules that allows two nodes on a network to exchange data.
“A protocol defines the rules governing the syntax (what can be communicated), semantics (how it can be communicated), and synchronization (when and at what speed it can be communicated) of the communications procedure. Protocols can be implemented on hardware, software, or a combination of both. Protocols can be created by anyone, but the most widely adopted protocols are based on standards.” - The Illustrated Network.
Both wired and cable-free links can have protocols.
While anyone can create a protocol, the most widely adopted protocols are often based on standards published by Internet organizations such as the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF).
A network is a general term for a group of computers, printers, or any other device that wants to share data.
Network types include LAN, HAN, CAN, MAN, WAN, BAN, or VPN. Think I’m just randomly rhyming things with the word can ? I can ’t say I am - these are all real network types. Learn more here .
Topology describes how nodes and links fit together in a network configuration, often depicted in a diagram. Here are some common network topology types:
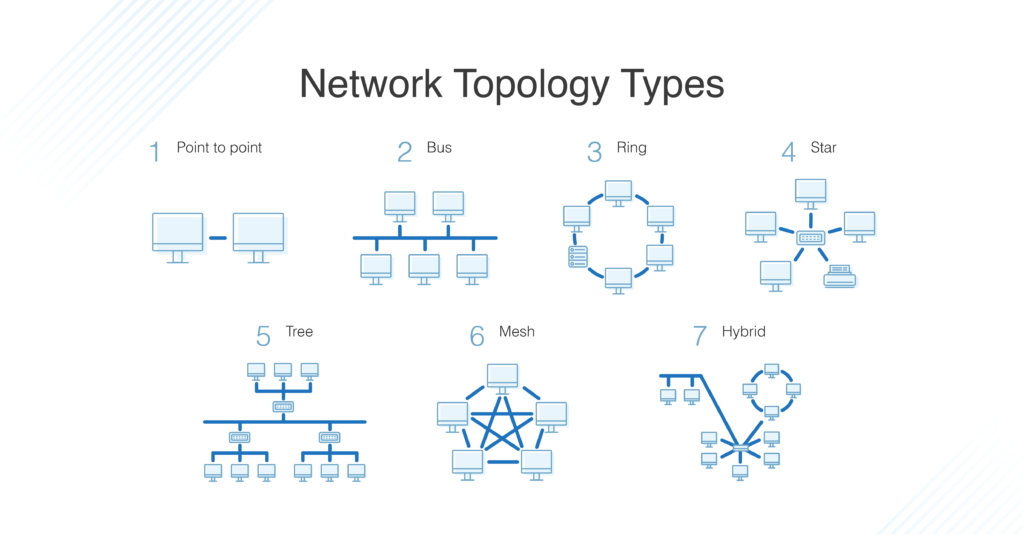
A network consists of nodes, links between nodes, and protocols that govern data transmission between nodes.
At whatever scale and complexity networks get to, you will understand what’s happening in all computer networks by learning the OSI model and 7 layers of networking.
What is the OSI Model?
The OSI model consists of 7 layers of networking.
First, what’s a layer?

No, a layer - not a lair . Here there are no dragons.
A layer is a way of categorizing and grouping functionality and behavior on and of a network.
In the OSI model, layers are organized from the most tangible and most physical, to less tangible and less physical but closer to the end user.
Each layer abstracts lower level functionality away until by the time you get to the highest layer. All the details and inner workings of all the other layers are hidden from the end user.
How to remember all the names of the layers? Easy.
- Please | Physical Layer
- Do | Data Link Layer
- Not | Network Layer
- Tell (the) | Transport Layer
- Secret | Session Layer
- Password (to) | Presentation Layer
- Anyone | Application Layer
Keep in mind that while certain technologies, like protocols, may logically “belong to” one layer more than another, not all technologies fit neatly into a single layer in the OSI model. For example, Ethernet, 802.11 (Wifi) and the Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) procedure operate on >1 layer.
The OSI is a model and a tool, not a set of rules.
OSI Layer 1
Layer 1 is the physical layer . There’s a lot of technology in Layer 1 - everything from physical network devices, cabling, to how the cables hook up to the devices. Plus if we don’t need cables, what the signal type and transmission methods are (for example, wireless broadband).
Instead of listing every type of technology in Layer 1, I’ve created broader categories for these technologies. I encourage readers to learn more about each of these categories:
- Nodes (devices) and networking hardware components. Devices include hubs, repeaters, routers, computers, printers, and so on. Hardware components that live inside of these devices include antennas, amplifiers, Network Interface Cards (NICs), and more.
- Device interface mechanics. How and where does a cable connect to a device (cable connector and device socket)? What is the size and shape of the connector, and how many pins does it have? What dictates when a pin is active or inactive?
- Functional and procedural logic. What is the function of each pin in the connector - send or receive? What procedural logic dictates the sequence of events so a node can start to communicate with another node on Layer 2?
- Cabling protocols and specifications. Ethernet (CAT), USB, Digital Subscriber Line (DSL) , and more. Specifications include maximum cable length, modulation techniques, radio specifications, line coding, and bits synchronization (more on that below).
- Cable types. Options include shielded or unshielded twisted pair, untwisted pair, coaxial and so on. Learn more about cable types here .
- Signal type. Baseband is a single bit stream at a time, like a railway track - one-way only. Broadband consists of multiple bit streams at the same time, like a bi-directional highway.
- Signal transmission method (may be wired or cable-free). Options include electrical (Ethernet), light (optical networks, fiber optics), radio waves (802.11 WiFi, a/b/g/n/ac/ax variants or Bluetooth). If cable-free, then also consider frequency: 2.5 GHz vs. 5 GHz. If it’s cabled, consider voltage. If cabled and Ethernet, also consider networking standards like 100BASE-T and related standards.
The data unit on Layer 1 is the bit.
A bit the smallest unit of transmittable digital information. Bits are binary, so either a 0 or a 1. Bytes, consisting of 8 bits, are used to represent single characters, like a letter, numeral, or symbol.
Bits are sent to and from hardware devices in accordance with the supported data rate (transmission rate, in number of bits per second or millisecond) and are synchronized so the number of bits sent and received per unit of time remains consistent (this is called bit synchronization). The way bits are transmitted depends on the signal transmission method.
Nodes can send, receive, or send and receive bits. If they can only do one, then the node uses a simplex mode. If they can do both, then the node uses a duplex mode. If a node can send and receive at the same time, it’s full-duplex – if not, it’s just half-duplex.
The original Ethernet was half-duplex. Full-duplex Ethernet is an option now, given the right equipment.
How to Troubleshoot OSI Layer 1 Problems
Here are some Layer 1 problems to watch out for:
- Defunct cables, for example damaged wires or broken connectors
- Broken hardware network devices, for example damaged circuits
- Stuff being unplugged (...we’ve all been there)
If there are issues in Layer 1, anything beyond Layer 1 will not function properly.
Layer 1 contains the infrastructure that makes communication on networks possible.
It defines the electrical, mechanical, procedural, and functional specifications for activating, maintaining, and deactivating physical links between network devices. - Source
Fun fact: deep-sea communications cables transmit data around the world. This map will blow your mind: https://www.submarinecablemap.com/
And because you made it this far, here’s a koala:

OSI Layer 2
Layer 2 is the data link layer . Layer 2 defines how data is formatted for transmission, how much data can flow between nodes, for how long, and what to do when errors are detected in this flow.
In more official tech terms:
- Line discipline. Who should talk for how long? How long should nodes be able to transit information for?
- Flow control. How much data should be transmitted?
- Error control - detection and correction . All data transmission methods have potential for errors, from electrical spikes to dirty connectors. Once Layer 2 technologies tell network administrators about an issue on Layer 2 or Layer 1, the system administrator can correct for those errors on subsequent layers. Layer 2 is mostly concerned with error detection, not error correction. ( Source )
There are two distinct sublayers within Layer 2:
- Media Access Control (MAC): the MAC sublayer handles the assignment of a hardware identification number, called a MAC address, that uniquely identifies each device on a network. No two devices should have the same MAC address. The MAC address is assigned at the point of manufacturing. It is automatically recognized by most networks. MAC addresses live on Network Interface Cards (NICs). Switches keep track of all MAC addresses on a network. Learn more about MAC addresses on PC Mag and in this article . Learn more about network switches here .
- Logical Link Control (LLC): the LLC sublayer handles framing addressing and flow control. The speed depends on the link between nodes, for example Ethernet or Wifi.
The data unit on Layer 2 is a frame .
Each frame contains a frame header, body, and a frame trailer:
- Header: typically includes MAC addresses for the source and destination nodes.
- Body: consists of the bits being transmitted.
- Trailer: includes error detection information. When errors are detected, and depending on the implementation or configuration of a network or protocol, frames may be discarded or the error may be reported up to higher layers for further error correction. Examples of error detection mechanisms: Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC) and Frame Check Sequence (FCS). Learn more about error detection techniques here .
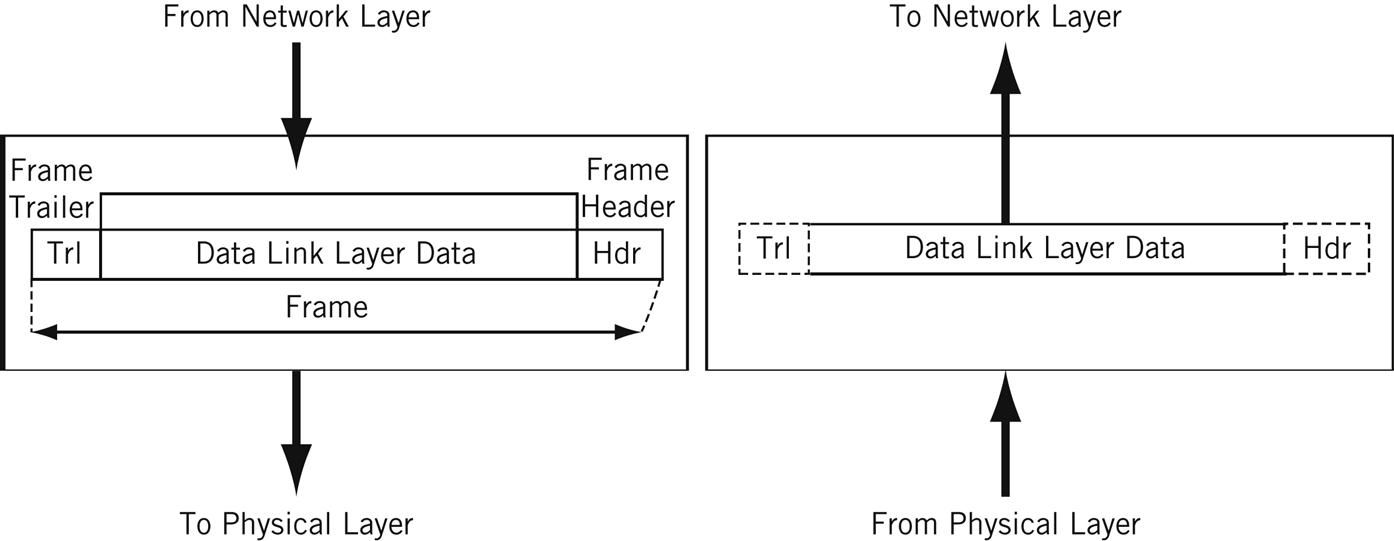
Typically there is a maximum frame size limit, called an Maximum Transmission Unit, MTU. Jumbo frames exceed the standard MTU, learn more about jumbo frames here .
How to Troubleshoot OSI Layer 2 Problems
Here are some Layer 2 problems to watch out for:
- All the problems that can occur on Layer 1
- Unsuccessful connections (sessions) between two nodes
- Sessions that are successfully established but intermittently fail
- Frame collisions
The Data Link Layer allows nodes to communicate with each other within a local area network. The foundations of line discipline, flow control, and error control are established in this layer.
OSI Layer 3
Layer 3 is the network layer . This is where we send information between and across networks through the use of routers. Instead of just node-to-node communication, we can now do network-to-network communication.
Routers are the workhorse of Layer 3 - we couldn’t have Layer 3 without them. They move data packets across multiple networks.
Not only do they connect to Internet Service Providers (ISPs) to provide access to the Internet, they also keep track of what’s on its network (remember that switches keep track of all MAC addresses on a network), what other networks it’s connected to, and the different paths for routing data packets across these networks.
Routers store all of this addressing and routing information in routing tables.
Here’s a simple example of a routing table:

The data unit on Layer 3 is the data packet . Typically, each data packet contains a frame plus an IP address information wrapper. In other words, frames are encapsulated by Layer 3 addressing information.
The data being transmitted in a packet is also sometimes called the payload . While each packet has everything it needs to get to its destination, whether or not it makes it there is another story.
Layer 3 transmissions are connectionless, or best effort - they don't do anything but send the traffic where it’s supposed to go. More on data transport protocols on Layer 4.
Once a node is connected to the Internet, it is assigned an Internet Protocol (IP) address, which looks either like 172.16. 254.1 (IPv4 address convention) or like 2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334 (IPv6 address convention). Routers use IP addresses in their routing tables.
IP addresses are associated with the physical node’s MAC address via the Address Resolution Protocol (ARP), which resolves MAC addresses with the node’s corresponding IP address.
ARP is conventionally considered part of Layer 2, but since IP addresses don’t exist until Layer 3, it’s also part of Layer 3.
How to Troubleshoot OSI Layer 3 Problems
Here are some Layer 3 problems to watch out for:
- All the problems that can crop up on previous layers :)
- Faulty or non-functional router or other node
- IP address is incorrectly configured
Many answers to Layer 3 questions will require the use of command-line tools like ping , trace , show ip route , or show ip protocols . Learn more about troubleshooting on layer 1-3 here .
The Network Layer allows nodes to connect to the Internet and send information across different networks.
OSI Layer 4
Layer 4 is the transport layer . This where we dive into the nitty gritty specifics of the connection between two nodes and how information is transmitted between them. It builds on the functions of Layer 2 - line discipline, flow control, and error control.
This layer is also responsible for data packet segmentation, or how data packets are broken up and sent over the network.
Unlike the previous layer, Layer 4 also has an understanding of the whole message, not just the contents of each individual data packet. With this understanding, Layer 4 is able to manage network congestion by not sending all the packets at once.
The data units of Layer 4 go by a few names. For TCP, the data unit is a packet. For UDP, a packet is referred to as a datagram. I’ll just use the term data packet here for the sake of simplicity.
Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and User Datagram Protocol (UDP) are two of the most well-known protocols in Layer 4.
TCP, a connection-oriented protocol, prioritizes data quality over speed.
TCP explicitly establishes a connection with the destination node and requires a handshake between the source and destination nodes when data is transmitted. The handshake confirms that data was received. If the destination node does not receive all of the data, TCP will ask for a retry.
TCP also ensures that packets are delivered or reassembled in the correct order. Learn more about TCP here .
UDP, a connectionless protocol, prioritizes speed over data quality. UDP does not require a handshake, which is why it’s called connectionless.
Because UDP doesn’t have to wait for this acknowledgement, it can send data at a faster rate, but not all of the data may be successfully transmitted and we’d never know.
If information is split up into multiple datagrams, unless those datagrams contain a sequence number, UDP does not ensure that packets are reassembled in the correct order. Learn more about UDP here .
TCP and UDP both send data to specific ports on a network device, which has an IP address. The combination of the IP address and the port number is called a socket.
Learn more about sockets here .
Learn more about the differences and similarities between these two protocols here .
How to Troubleshoot OSI Layer 4 Problems
Here are some Layer 4 problems to watch out for:
- Blocked ports - check your Access Control Lists (ACL) & firewalls
- Quality of Service (QoS) settings. QoS is a feature of routers/switches that can prioritize traffic, and they can really muck things up. Learn more about QoS here .
The Transport Layer provides end-to-end transmission of a message by segmenting a message into multiple data packets; the layer supports connection-oriented and connectionless communication.
OSI Layer 5
Layer 5 is the session layer . This layer establishes, maintains, and terminates sessions.
A session is a mutually agreed upon connection that is established between two network applications. Not two nodes! Nope, we’ve moved on from nodes. They were so Layer 4.
Just kidding, we still have nodes, but Layer 5 doesn’t need to retain the concept of a node because that’s been abstracted out (taken care of) by previous layers.
So a session is a connection that is established between two specific end-user applications. There are two important concepts to consider here:
- Client and server model: the application requesting the information is called the client, and the application that has the requested information is called the server.
- Request and response model: while a session is being established and during a session, there is a constant back-and-forth of requests for information and responses containing that information or “hey, I don’t have what you’re requesting.”
Sessions may be open for a very short amount of time or a long amount of time. They may fail sometimes, too.
Depending on the protocol in question, various failure resolution processes may kick in. Depending on the applications/protocols/hardware in use, sessions may support simplex, half-duplex, or full-duplex modes.
Examples of protocols on Layer 5 include Network Basic Input Output System (NetBIOS) and Remote Procedure Call Protocol (RPC), and many others.
From here on out (layer 5 and up), networks are focused on ways of making connections to end-user applications and displaying data to the user.

How to Troubleshoot OSI Layer 5 Problems
Here are some Layer 5 problems to watch out for:
- Servers are unavailable
- Servers are incorrectly configured, for example Apache or PHP configs
- Session failure - disconnect, timeout, and so on.
The Session Layer initiates, maintains, and terminates connections between two end-user applications. It responds to requests from the presentation layer and issues requests to the transport layer.
OSI Layer 6
Layer 6 is the presentation layer . This layer is responsible for data formatting, such as character encoding and conversions, and data encryption.
The operating system that hosts the end-user application is typically involved in Layer 6 processes. This functionality is not always implemented in a network protocol.
Layer 6 makes sure that end-user applications operating on Layer 7 can successfully consume data and, of course, eventually display it.
There are three data formatting methods to be aware of:
- American Standard Code for Information Interchange (ASCII): this 7-bit encoding technique is the most widely used standard for character encoding. One superset is ISO-8859-1, which provides most of the characters necessary for languages spoken in Western Europe.
- Extended Binary-Coded Decimal Interchange Code (EBDCIC): designed by IBM for mainframe usage. This encoding is incompatible with other character encoding methods.
- Unicode: character encodings can be done with 32-, 16-, or 8-bit characters and attempts to accommodate every known, written alphabet.
Learn more about character encoding methods in this article , and also here .
Encryption: SSL or TLS encryption protocols live on Layer 6. These encryption protocols help ensure that transmitted data is less vulnerable to malicious actors by providing authentication and data encryption for nodes operating on a network. TLS is the successor to SSL.
How to Troubleshoot OSI Layer 6 Problems
Here are some Layer 6 problems to watch out for:
- Non-existent or corrupted drivers
- Incorrect OS user access level
The Presentation Layer formats and encrypts data.
OSI Layer 7
Layer 7 is the application layer .
True to its name, this is the layer that is ultimately responsible for supporting services used by end-user applications. Applications include software programs that are installed on the operating system, like Internet browsers (for example, Firefox) or word processing programs (for example, Microsoft Word).
Applications can perform specialized network functions under the hood and require specialized services that fall under the umbrella of Layer 7.
Electronic mail programs, for example, are specifically created to run over a network and utilize networking functionality, such as email protocols, which fall under Layer 7.
Applications will also control end-user interaction, such as security checks (for example, MFA), identification of two participants, initiation of an exchange of information, and so on.
Protocols that operate on this level include File Transfer Protocol (FTP), Secure Shell (SSH), Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP), Internet Message Access Protocol (IMAP), Domain Name Service (DNS), and Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP).
While each of these protocols serve different functions and operate differently, on a high level they all facilitate the communication of information. ( Source )
How to Troubleshoot OSI Layer 7 Problems
Here are some Layer 7 problems to watch out for:
- All issues on previous layers
- Incorrectly configured software applications
- User error (... we’ve all been there)
The Application Layer owns the services and functions that end-user applications need to work. It does not include the applications themselves.
Our Layer 1 koala is all grown up.

Learning check - can you apply makeup to a koala?
Don’t have a koala?
Well - answer these questions instead. It’s the next best thing, I promise.
- What is the OSI model?
- What are each of the layers?
- How could I use this information to troubleshoot networking issues?
Congratulations - you’ve taken one step farther to understanding the glorious entity we call the Internet.
Learning Resources
Many, very smart people have written entire books about the OSI model or entire books about specific layers. I encourage readers to check out any O’Reilly-published books about the subject or about network engineering in general.
Here are some resources I used when writing this article:
- The Illustrated Network, 2nd Edition
- Protocol Data Unit (PDU): https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/difference-between-segments-packets-and-frames/
- Troubleshooting Along the OSI Model: https://www.pearsonitcertification.com/articles/article.aspx?p=1730891
- The OSI Model Demystified: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HEEnLZV2wGI
- OSI Model for Dummies: https://www.dummies.com/programming/networking/layers-in-the-osi-model-of-a-computer-network/
Chloe Tucker is an artist and computer science enthusiast based in Portland, Oregon. As a former educator, she's continuously searching for the intersection of learning and teaching, or technology and art. Reach out to her on Twitter @_chloetucker and check out her website at chloe.dev .
If you read this far, thank the author to show them you care. Say Thanks
Learn to code for free. freeCodeCamp's open source curriculum has helped more than 40,000 people get jobs as developers. Get started
Presentation Layer
Last Edited
What is the Presentation Layer?
Presentation Layer is the Layer 6 of the seven-layer Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) reference model . The presentation layer structures data that is passed down from the application layer into a format suitable for network transmission. This layer is responsible for data encryption, data compression, character set conversion, interpretation of graphics commands, and so on. The network redirector also functions at this layer.
Presentation Layer functions
- Translation: Before being transmitted, information in the form of characters and numbers should be changed to bit streams. Layer 6 is responsible for interoperability between encoding methods as different computers use different encoding methods. It translates data between the formats the network requires and the format the computer.
- Encryption: Encryption at the transmitter and decryption at the receiver
- Compression: Data compression to reduce the bandwidth of the data to be transmitted. The primary role of data compression is to reduce the number of bits to be transmitted. Multimedia files, such as audio and video, are bigger than text files and compression is more important.
Role of Presentation Layer in the OSI Model
This layer is not always used in network communications because its functions are not always necessary. Translation is only needed if different types of machines need to talk with each other. Encryption is optional in communication. If the information is public there is no need to encrypt and decrypt info. Compression is also optional. If files are small there is no need for compression.
Explaining Layer 6 in video
Most real-world protocol suites, such as TCP/IP , do not use separate presentation layer protocols. This layer is mostly an abstraction in real-world networking.
An example of a program that loosely adheres to layer 6 of OSI is the tool that manages the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) — although it’s technically considered an application-layer protocol per the TCP/IP model.
However, HTTP includes presentation layer services within it. HTTP works when the requesting device forwards user requests passed to the web browser onto a web server elsewhere in the network.
It receives a return message from the web server that includes a multipurpose internet mail extensions (MIME) header. The MIME header indicates the type of file – text, video, or audio – that has been received so that an appropriate player utility can be used to present the file to the user.
In short, the presentation layer
Makes sure that data which is being transferred or received should be accurate or clear to all the devices which are there, in a closed network.
- ensures proper formatting and delivery to and from the application layer;
- performs data encryption; and
- manages serialization of data objects.
The OSI Model’s 7 Layers, Explained
The seven layers in the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model each serve a specific function and work together to create an efficient network communication system.
The Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model is a framework in network communication that simplifies complex network interactions into a structured format.
What Is the OSI Model?
The Open Systems Interconnection model is a framework in network communication designed to simplify complex network interactions into a structured format. This architecture has seven layers, each of which serves a specific function. All seven layers work together to create a robust and efficient network communication system.
Each of its seven layers has a distinct role, ensuring efficient data transfer from one device to another . The OSI model is essential for understanding how data is transmitted in a network and is also a practical guide for network protocol design and problem solving.
learn more about cybersecurity An Introduction to Microsegmentation in Network Security
The OSI model, developed by the International Organization for Standardization , outlines the essential functions of networking and telecommunications systems for practical application. It plays a crucial role in telecommunications, where vendors use it to define the features and capabilities of their products and services.
This approach allows for a detailed explanation of different aspects of network communication, including transport protocols, addressing schemes and data packaging methods. As a result, the OSI model resolves the complexities of network communication and fosters a more integrated and coherent digital world .
The 7 Layers of the OSI Model
Each layer of the OSI model serves a specific function, yet they work in harmony to create a robust and efficient network communication system. Understanding these layers provides valuable insights into the complexities of network design and operation, showcasing the intricate nature of modern digital communication.
Layer 7: Application Layer
Functionality: The Application Layer is the closest to the end user. It facilitates user interaction with networked systems, providing interfaces and protocols for web browsers, email clients and other applications.
Key protocols: Protocols like HTTP, FTP and SMTP operate at this layer, enabling services such as web browsing, file transfers and email communications.
Layer 6: Presentation Layer
Role: The Presentation Layer acts as a translator, converting data formats from the application layer into a network-compatible format and vice versa. It ensures that data sent from one system is readable by another.
Data formatting: This layer is responsible for data encryption and compression, playing a significant role in maintaining data privacy and efficient transmission.
Layer 5: Session Layer
Managing sessions: It establishes, manages and terminates sessions between applications. This layer ensures that sessions are maintained for the duration of the communication.
Coordination: The Session Layer coordinates communication between systems, managing dialogues and synchronizing data exchange.
Layer 4: Transport Layer
Data segmentation and control: The Transport Layer is crucial for segmenting data into smaller packets. It ensures end-to-end data integrity and delivery, managing flow control, error correction and sequencing.
Protocols: TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) and UDP (User Datagram Protocol) are key protocols in this layer, differing in their approach to data transmission.
Layer 3: Network Layer
Routing and addressing: This layer is responsible for logical addressing and routing data packets across different networks. It determines the best path for data to travel from source to destination.
Internet protocol: The Internet Protocol (IP), fundamental for internet data exchange, operates at this layer.
Layer 2: Data Link Layer
Framing and MAC addressing: The Data Link Layer frames data into packets. It handles physical addressing through MAC addresses, ensuring that data is directed to the correct hardware.
Error detection: This layer is also involved in error detection and handling, improving overall data transmission reliability.
Layer 1: Physical Layer
Physical transmission: The Physical Layer deals with the physical aspects of data transmission, including cable types, electrical signals and data rates.
Hardware components: It involves hardware components like cables, switches and network interface cards, forming the foundation of network communication.
How Data Flows in the OSI Model
Understanding this data flow process is crucial for professionals, as it aids in diagnosing and troubleshooting network issues, designing efficient network solutions and ensuring robust data security and management.
Encapsulation Process
When data is sent, it begins at the Application Layer and moves down through the layers. At each stage, it is encapsulated with the necessary headers, trailers, and other control information relevant to that layer. For instance, at the Transport Layer, data is segmented and encapsulated with port numbers, while at the Network Layer, IP addresses are added.
Each layer plays a role in preparing the data for transmission. The Presentation Layer may encrypt the data for security, while the Data Link Layer ensures it is formatted into frames suitable for physical transmission.
Data Transmission Across the Network
The Physical Layer transmits the raw bits over a physical medium, such as a cable or wireless network. This transmission is the actual movement of data across the network. In cases where data must move across different networks, the Network Layer’s routing functionalities become crucial. It ensures that data packets find the most efficient path to their destination.
Decapsulation Process
Upon reaching the destination, the data moves up the OSI model, with each layer removing its respective encapsulation. The Data Link Layer, for instance, removes framing, and the Transport Layer checks for transmission errors and reassembles the data segments. Once the data reaches the Application Layer, it is in its original format and ready to be used by the receiving application, whether it’s an email client, a web browser or any other networked software.
Seamless Data Flow
The OSI model ensures that each layer only communicates with its immediate upper and lower layers, creating a seamless flow. This layered approach means changes in one layer’s protocols or functionalities can occur without disrupting the entire network.
OSI Model Advantages
The OSI model is a cornerstone in network architecture for several reasons:
Simplification of network design
The OSI model’s layered approach breaks down complex network processes, making design and operation more manageable. Each layer focuses on a specific aspect of communication, allowing for independent development and easier troubleshooting.
Standardization and interoperability
It establishes universal standards for network communication, enabling different technologies to interact seamlessly. This interoperability is crucial for the efficient functioning of diverse network devices and applications.
Flexibility and Scalability
Adaptable to technological advancements, the OSI model allows individual layers to evolve without overhauling the entire system. This scalability makes it suitable for various network sizes and types.
Enhanced Security
Security measures are integrated at multiple layers, providing a robust defense against threats. Each layer can address specific security concerns, leading to comprehensive network protection.
Real-World Applications of the OSI Model
The OSI model’s influence extends well beyond theoretical concepts, playing a crucial role in various practical aspects of networking:
Network Design and Protocol Development
Network professionals use the OSI model as a blueprint for structuring and developing robust networks. It guides the creation of new protocols, ensuring seamless integration and functionality across different network layers.
Efficient Troubleshooting and Management
In troubleshooting, the OSI model provides a systematic approach for identifying issues, from physical connectivity to application-level errors. It also aids in network maintenance and performance optimization, addressing each layer to enhance overall efficiency.
Cybersecurity Strategy
The model is foundational in crafting layered security strategies . By implementing security measures at different layers, it offers comprehensive protection against various cyber threats. Understanding the OSI layers is key in detecting and mitigating attacks targeting specific network segments.
Educational and Training Tool
It serves as an essential framework in networking education, helping students and professionals alike understand complex network operations. The OSI model is a cornerstone in training programs , emphasizing the intricacies of network architecture and security.
safety first When and How to Run a Phishing Simulation
OSI Model vs. TCP/IP Model
While the OSI model offers a detailed conceptual framework, the TCP/IP model is recognized for its practical application in today’s internet-driven world.
Structural Differences
OSI model : Introduced as a comprehensive, protocol-independent framework, the OSI model details seven distinct layers, offering a more granular approach to network communication.
TCP/IP model : Developed earlier by the U.S. Department of Defense, the TCP/IP model consists of four layers (Application, Transport, Internet and Network Access), combining certain OSI layers.
Theoretical vs. Practical Approach
OSI model : Developed as a theoretical and universal networking model, it’s used more for educational purposes to explain how networks operate.
TCP/IP model : This model is designed around specific standard protocols, focusing on solving practical communication issues. It leaves sequencing and acknowledgment functions to the transport layer, differing from the OSI approach.
Adoption and Use
OSI model: While not widely implemented in its entirety, the OSI model’s clear layer separation is influential in protocol design and network education; simpler applications in the OSI framework may not utilize all seven layers, with only the first three layers (Physical, Data Link, and Network) being mandatory for basic data communication.
TCP/IP model : The dominant model used in most network architectures today, especially in internet-related communications. In TCP/IP, most applications engage all layers for communication.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is the osi model important.
The OSI model is crucial for standardizing network communication and ensuring interoperability between various devices and systems. It simplifies network design and troubleshooting and serves as a fundamental educational tool in networking.
What are the 7 layers of the OSI model?
Layer 1: Physical Layer — Transmits raw data.
Layer 2: Data Link Layer — Manages direct links and framing.
Layer 3: Network Layer — Handles addressing and routing.
Layer 4: Transport Layer — Ensures reliable data transfer.
Layer 5: Session Layer — Manages connections.
Layer 6: Presentation Layer — Translates data formats.
Layer 7: Application Layer — Interfaces with applications.
Recent Cybersecurity Articles


COMMENTS
Presentation layer in the OSI model, as a translator, converts the data sent by the application layer of the transmitting node into an acceptable and compatible data format based on the applicable network protocol and architecture.
The presentation layer (data presentation layer, data provision level) sets the system-dependent representation of the data (for example, ASCII, EBCDIC) into an independent form, enabling the syntactically correct data exchange between different systems.
The presentation layer is the sixth layer within the open systems interconnection (OSI) model. It is located next to the application layer and translates data to transmit from or send to the application layer. It does this by converting, compressing, encrypting, and serializing data into different forms that can be more easily transmitted ...
Within the service layering semantics of the OSI network architecture, the presentation layer responds to service requests from the application layer and issues service requests to the session layer through a unique presentation service access point (PSAP).
The Presentation Layer in the OSI model is responsible for translating data between the application and network layers, ensuring compatibility between different systems.
The presentation layer resides at Layer 6 of the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) communications model and ensures that communications that pass through it are in the appropriate form for the recipient application.
This article explains the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model and the 7 layers of networking, in plain English. The OSI model is a conceptual framework that is used to describe how a network functions.
What is the Presentation Layer? Presentation Layer is the Layer 6 of the seven-layer Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) reference model. The presentation layer structures data that is passed down from the application layer into a format suitable for network transmission.
Layer 6 in the OSI model - the presentation layer - translates, compresses, and encrypts data across networks. In this article, we’ll explain what the presentation layer is, how it works, and its functions and protocols.
Layer 6: Presentation Layer. Role: The Presentation Layer acts as a translator, converting data formats from the application layer into a network-compatible format and vice versa. It ensures that data sent from one system is readable by another.