What is The Null Hypothesis & When Do You Reject The Null Hypothesis
Julia Simkus
Editor at Simply Psychology
BA (Hons) Psychology, Princeton University
Julia Simkus is a graduate of Princeton University with a Bachelor of Arts in Psychology. She is currently studying for a Master's Degree in Counseling for Mental Health and Wellness in September 2023. Julia's research has been published in peer reviewed journals.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Saul McLeod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul McLeod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc
Associate Editor for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MSc Psychology of Education
Olivia Guy-Evans is a writer and associate editor for Simply Psychology. She has previously worked in healthcare and educational sectors.
On This Page:
A null hypothesis is a statistical concept suggesting no significant difference or relationship between measured variables. It’s the default assumption unless empirical evidence proves otherwise.
The null hypothesis states no relationship exists between the two variables being studied (i.e., one variable does not affect the other).
The null hypothesis is the statement that a researcher or an investigator wants to disprove.
Testing the null hypothesis can tell you whether your results are due to the effects of manipulating the dependent variable or due to random chance.

How to Write a Null Hypothesis
Null hypotheses (H0) start as research questions that the investigator rephrases as statements indicating no effect or relationship between the independent and dependent variables.
It is a default position that your research aims to challenge or confirm.
For example, if studying the impact of exercise on weight loss, your null hypothesis might be:
There is no significant difference in weight loss between individuals who exercise daily and those who do not.
Examples of Null Hypotheses
When do we reject the null hypothesis .
We reject the null hypothesis when the data provide strong enough evidence to conclude that it is likely incorrect. This often occurs when the p-value (probability of observing the data given the null hypothesis is true) is below a predetermined significance level.
If the collected data does not meet the expectation of the null hypothesis, a researcher can conclude that the data lacks sufficient evidence to back up the null hypothesis, and thus the null hypothesis is rejected.
Rejecting the null hypothesis means that a relationship does exist between a set of variables and the effect is statistically significant ( p > 0.05).
If the data collected from the random sample is not statistically significance , then the null hypothesis will be accepted, and the researchers can conclude that there is no relationship between the variables.
You need to perform a statistical test on your data in order to evaluate how consistent it is with the null hypothesis. A p-value is one statistical measurement used to validate a hypothesis against observed data.
Calculating the p-value is a critical part of null-hypothesis significance testing because it quantifies how strongly the sample data contradicts the null hypothesis.
The level of statistical significance is often expressed as a p -value between 0 and 1. The smaller the p-value, the stronger the evidence that you should reject the null hypothesis.
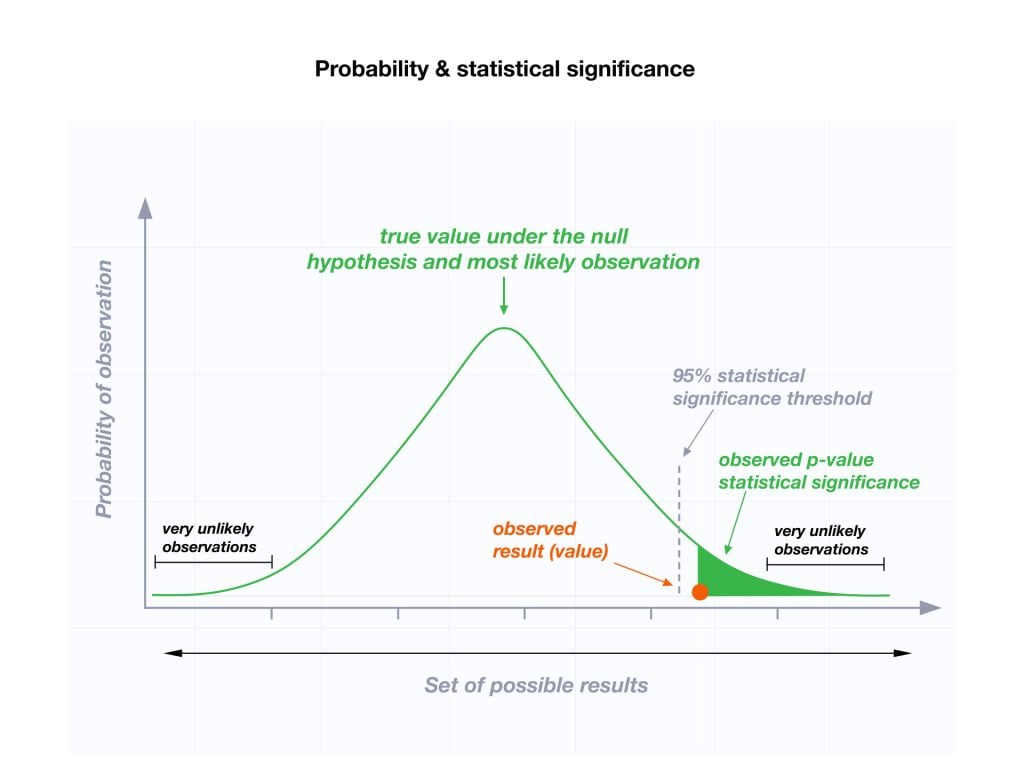
Usually, a researcher uses a confidence level of 95% or 99% (p-value of 0.05 or 0.01) as general guidelines to decide if you should reject or keep the null.
When your p-value is less than or equal to your significance level, you reject the null hypothesis.
In other words, smaller p-values are taken as stronger evidence against the null hypothesis. Conversely, when the p-value is greater than your significance level, you fail to reject the null hypothesis.
In this case, the sample data provides insufficient data to conclude that the effect exists in the population.
Because you can never know with complete certainty whether there is an effect in the population, your inferences about a population will sometimes be incorrect.
When you incorrectly reject the null hypothesis, it’s called a type I error. When you incorrectly fail to reject it, it’s called a type II error.
Why Do We Never Accept The Null Hypothesis?
The reason we do not say “accept the null” is because we are always assuming the null hypothesis is true and then conducting a study to see if there is evidence against it. And, even if we don’t find evidence against it, a null hypothesis is not accepted.
A lack of evidence only means that you haven’t proven that something exists. It does not prove that something doesn’t exist.
It is risky to conclude that the null hypothesis is true merely because we did not find evidence to reject it. It is always possible that researchers elsewhere have disproved the null hypothesis, so we cannot accept it as true, but instead, we state that we failed to reject the null.
One can either reject the null hypothesis, or fail to reject it, but can never accept it.
Why Do We Use The Null Hypothesis?
We can never prove with 100% certainty that a hypothesis is true; We can only collect evidence that supports a theory. However, testing a hypothesis can set the stage for rejecting or accepting this hypothesis within a certain confidence level.
The null hypothesis is useful because it can tell us whether the results of our study are due to random chance or the manipulation of a variable (with a certain level of confidence).
A null hypothesis is rejected if the measured data is significantly unlikely to have occurred and a null hypothesis is accepted if the observed outcome is consistent with the position held by the null hypothesis.
Rejecting the null hypothesis sets the stage for further experimentation to see if a relationship between two variables exists.
Hypothesis testing is a critical part of the scientific method as it helps decide whether the results of a research study support a particular theory about a given population. Hypothesis testing is a systematic way of backing up researchers’ predictions with statistical analysis.
It helps provide sufficient statistical evidence that either favors or rejects a certain hypothesis about the population parameter.
Purpose of a Null Hypothesis
- The primary purpose of the null hypothesis is to disprove an assumption.
- Whether rejected or accepted, the null hypothesis can help further progress a theory in many scientific cases.
- A null hypothesis can be used to ascertain how consistent the outcomes of multiple studies are.
Do you always need both a Null Hypothesis and an Alternative Hypothesis?
The null (H0) and alternative (Ha or H1) hypotheses are two competing claims that describe the effect of the independent variable on the dependent variable. They are mutually exclusive, which means that only one of the two hypotheses can be true.
While the null hypothesis states that there is no effect in the population, an alternative hypothesis states that there is statistical significance between two variables.
The goal of hypothesis testing is to make inferences about a population based on a sample. In order to undertake hypothesis testing, you must express your research hypothesis as a null and alternative hypothesis. Both hypotheses are required to cover every possible outcome of the study.
What is the difference between a null hypothesis and an alternative hypothesis?
The alternative hypothesis is the complement to the null hypothesis. The null hypothesis states that there is no effect or no relationship between variables, while the alternative hypothesis claims that there is an effect or relationship in the population.
It is the claim that you expect or hope will be true. The null hypothesis and the alternative hypothesis are always mutually exclusive, meaning that only one can be true at a time.
What are some problems with the null hypothesis?
One major problem with the null hypothesis is that researchers typically will assume that accepting the null is a failure of the experiment. However, accepting or rejecting any hypothesis is a positive result. Even if the null is not refuted, the researchers will still learn something new.
Why can a null hypothesis not be accepted?
We can either reject or fail to reject a null hypothesis, but never accept it. If your test fails to detect an effect, this is not proof that the effect doesn’t exist. It just means that your sample did not have enough evidence to conclude that it exists.
We can’t accept a null hypothesis because a lack of evidence does not prove something that does not exist. Instead, we fail to reject it.
Failing to reject the null indicates that the sample did not provide sufficient enough evidence to conclude that an effect exists.
If the p-value is greater than the significance level, then you fail to reject the null hypothesis.
Is a null hypothesis directional or non-directional?
A hypothesis test can either contain an alternative directional hypothesis or a non-directional alternative hypothesis. A directional hypothesis is one that contains the less than (“<“) or greater than (“>”) sign.
A nondirectional hypothesis contains the not equal sign (“≠”). However, a null hypothesis is neither directional nor non-directional.
A null hypothesis is a prediction that there will be no change, relationship, or difference between two variables.
The directional hypothesis or nondirectional hypothesis would then be considered alternative hypotheses to the null hypothesis.
Gill, J. (1999). The insignificance of null hypothesis significance testing. Political research quarterly , 52 (3), 647-674.
Krueger, J. (2001). Null hypothesis significance testing: On the survival of a flawed method. American Psychologist , 56 (1), 16.
Masson, M. E. (2011). A tutorial on a practical Bayesian alternative to null-hypothesis significance testing. Behavior research methods , 43 , 679-690.
Nickerson, R. S. (2000). Null hypothesis significance testing: a review of an old and continuing controversy. Psychological methods , 5 (2), 241.
Rozeboom, W. W. (1960). The fallacy of the null-hypothesis significance test. Psychological bulletin , 57 (5), 416.


User Preferences
Content preview.
Arcu felis bibendum ut tristique et egestas quis:
- Ut enim ad minim veniam, quis nostrud exercitation ullamco laboris
- Duis aute irure dolor in reprehenderit in voluptate
- Excepteur sint occaecat cupidatat non proident
Keyboard Shortcuts
6a.1 - introduction to hypothesis testing, basic terms section .
The first step in hypothesis testing is to set up two competing hypotheses. The hypotheses are the most important aspect. If the hypotheses are incorrect, your conclusion will also be incorrect.
The two hypotheses are named the null hypothesis and the alternative hypothesis.
The goal of hypothesis testing is to see if there is enough evidence against the null hypothesis. In other words, to see if there is enough evidence to reject the null hypothesis. If there is not enough evidence, then we fail to reject the null hypothesis.
Consider the following example where we set up these hypotheses.
Example 6-1 Section
A man, Mr. Orangejuice, goes to trial and is tried for the murder of his ex-wife. He is either guilty or innocent. Set up the null and alternative hypotheses for this example.
Putting this in a hypothesis testing framework, the hypotheses being tested are:
- The man is guilty
- The man is innocent
Let's set up the null and alternative hypotheses.
\(H_0\colon \) Mr. Orangejuice is innocent
\(H_a\colon \) Mr. Orangejuice is guilty
Remember that we assume the null hypothesis is true and try to see if we have evidence against the null. Therefore, it makes sense in this example to assume the man is innocent and test to see if there is evidence that he is guilty.
The Logic of Hypothesis Testing Section
We want to know the answer to a research question. We determine our null and alternative hypotheses. Now it is time to make a decision.
The decision is either going to be...
- reject the null hypothesis or...
- fail to reject the null hypothesis.
Consider the following table. The table shows the decision/conclusion of the hypothesis test and the unknown "reality", or truth. We do not know if the null is true or if it is false. If the null is false and we reject it, then we made the correct decision. If the null hypothesis is true and we fail to reject it, then we made the correct decision.
So what happens when we do not make the correct decision?
When doing hypothesis testing, two types of mistakes may be made and we call them Type I error and Type II error. If we reject the null hypothesis when it is true, then we made a type I error. If the null hypothesis is false and we failed to reject it, we made another error called a Type II error.
Types of errors
The “reality”, or truth, about the null hypothesis is unknown and therefore we do not know if we have made the correct decision or if we committed an error. We can, however, define the likelihood of these events.
\(\alpha\) and \(\beta\) are probabilities of committing an error so we want these values to be low. However, we cannot decrease both. As \(\alpha\) decreases, \(\beta\) increases.
Example 6-1 Cont'd... Section
A man, Mr. Orangejuice, goes to trial and is tried for the murder of his ex-wife. He is either guilty or not guilty. We found before that...
- \( H_0\colon \) Mr. Orangejuice is innocent
- \( H_a\colon \) Mr. Orangejuice is guilty
Interpret Type I error, \(\alpha \), Type II error, \(\beta \).
As you can see here, the Type I error (putting an innocent man in jail) is the more serious error. Ethically, it is more serious to put an innocent man in jail than to let a guilty man go free. So to minimize the probability of a type I error we would choose a smaller significance level.
Try it! Section
An inspector has to choose between certifying a building as safe or saying that the building is not safe. There are two hypotheses:
- Building is safe
- Building is not safe
Set up the null and alternative hypotheses. Interpret Type I and Type II error.
\( H_0\colon\) Building is not safe vs \(H_a\colon \) Building is safe
Power and \(\beta \) are complements of each other. Therefore, they have an inverse relationship, i.e. as one increases, the other decreases.
- Science, Tech, Math ›
- Chemistry ›
- Scientific Method ›
Null Hypothesis Examples
ThoughtCo / Hilary Allison
- Scientific Method
- Chemical Laws
- Periodic Table
- Projects & Experiments
- Biochemistry
- Physical Chemistry
- Medical Chemistry
- Chemistry In Everyday Life
- Famous Chemists
- Activities for Kids
- Abbreviations & Acronyms
- Weather & Climate
- Ph.D., Biomedical Sciences, University of Tennessee at Knoxville
- B.A., Physics and Mathematics, Hastings College
In statistical analysis, the null hypothesis assumes there is no meaningful relationship between two variables. Testing the null hypothesis can tell you whether your results are due to the effect of manipulating a dependent variable or due to chance. It's often used in conjunction with an alternative hypothesis, which assumes there is, in fact, a relationship between two variables.
The null hypothesis is among the easiest hypothesis to test using statistical analysis, making it perhaps the most valuable hypothesis for the scientific method. By evaluating a null hypothesis in addition to another hypothesis, researchers can support their conclusions with a higher level of confidence. Below are examples of how you might formulate a null hypothesis to fit certain questions.
What Is the Null Hypothesis?
The null hypothesis states there is no relationship between the measured phenomenon (the dependent variable ) and the independent variable , which is the variable an experimenter typically controls or changes. You do not need to believe that the null hypothesis is true to test it. On the contrary, you will likely suspect there is a relationship between a set of variables. One way to prove that this is the case is to reject the null hypothesis. Rejecting a hypothesis does not mean an experiment was "bad" or that it didn't produce results. In fact, it is often one of the first steps toward further inquiry.
To distinguish it from other hypotheses , the null hypothesis is written as H 0 (which is read as “H-nought,” "H-null," or "H-zero"). A significance test is used to determine the likelihood that the results supporting the null hypothesis are not due to chance. A confidence level of 95% or 99% is common. Keep in mind, even if the confidence level is high, there is still a small chance the null hypothesis is not true, perhaps because the experimenter did not account for a critical factor or because of chance. This is one reason why it's important to repeat experiments.
Examples of the Null Hypothesis
To write a null hypothesis, first start by asking a question. Rephrase that question in a form that assumes no relationship between the variables. In other words, assume a treatment has no effect. Write your hypothesis in a way that reflects this.
Other Types of Hypotheses
In addition to the null hypothesis, the alternative hypothesis is also a staple in traditional significance tests . It's essentially the opposite of the null hypothesis because it assumes the claim in question is true. For the first item in the table above, for example, an alternative hypothesis might be "Age does have an effect on mathematical ability."
Key Takeaways
- In hypothesis testing, the null hypothesis assumes no relationship between two variables, providing a baseline for statistical analysis.
- Rejecting the null hypothesis suggests there is evidence of a relationship between variables.
- By formulating a null hypothesis, researchers can systematically test assumptions and draw more reliable conclusions from their experiments.
- What Are Examples of a Hypothesis?
- Random Error vs. Systematic Error
- Six Steps of the Scientific Method
- What Is a Hypothesis? (Science)
- Scientific Method Flow Chart
- What Are the Elements of a Good Hypothesis?
- Scientific Method Vocabulary Terms
- Understanding Simple vs Controlled Experiments
- The Role of a Controlled Variable in an Experiment
- What Is an Experimental Constant?
- What Is a Testable Hypothesis?
- Scientific Hypothesis Examples
- What Is the Difference Between a Control Variable and Control Group?
- DRY MIX Experiment Variables Acronym
- What Is a Controlled Experiment?
- Scientific Variable

COMMENTS
When writing the conclusion of a hypothesis test, we typically include: Whether we reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis. The significance level. A short explanation in the context of the hypothesis test. For example, we would write: We reject the null hypothesis at the 5% significance level.
The null hypothesis in statistics states that there is no difference between groups or no relationship between variables. It is one of two mutually exclusive hypotheses about a population in a hypothesis test. When your sample contains sufficient evidence, you can reject the null and conclude that the effect is statistically significant.
The null hypothesis states that there is no effect or no relationship between variables, while the alternative hypothesis claims that there is an effect or relationship in the population. It is the claim that you expect or hope will be true.
The null and alternative hypotheses are two competing claims that researchers weigh evidence for and against using a statistical test: Null hypothesis (H0): There’s no effect in the population. Alternative hypothesis (Ha or H1): There’s an effect in the population.
This tutorial explains how to write a null hypothesis, including several step-by-step examples.
The null hypothesis and the alternative hypothesis are types of conjectures used in statistical tests to make statistical inferences, which are formal methods of reaching conclusions and separating scientific claims from statistical noise.
State your research hypothesis as a null hypothesis and alternate hypothesis (H o) and (H a or H 1). Collect data in a way designed to test the hypothesis. Perform an appropriate statistical test. Decide whether to reject or fail to reject your null hypothesis. Present the findings in your results and discussion section.
Basic Terms. The first step in hypothesis testing is to set up two competing hypotheses. The hypotheses are the most important aspect. If the hypotheses are incorrect, your conclusion will also be incorrect. The two hypotheses are named the null hypothesis and the alternative hypothesis. Null hypothesis.
By evaluating a null hypothesis in addition to another hypothesis, researchers can support their conclusions with a higher level of confidence. Below are examples of how you might formulate a null hypothesis to fit certain questions.
The null hypothesis is written as H 0, while the alternative hypothesis is H 1 or H a. H 0 : The number of lectures attended by first-year students has no effect on their final exam scores. H 1 : The number of lectures attended by first-year students has a positive effect on their final exam scores.