- English Grammar
- Grammar Exercises
- Reported Speech Exercises For Class 9

Reported Speech Exercises with Answers for Class 9
Reported speech is a grammatical component that is used to communicate what has been said by someone to another person. Knowing for sure how to use the direct and reported speech can be achieved only with continuous practice, just like it is with every other English grammar topic.

Are you a Class 9 student? Looking for a chance to assess your understanding of reported speech? If you are, here are some exercises that will help you practise and improve your knowledge of reported speech.
Read the following sentences and change them into reported speech
- Suman said, “I get up early every morning.”
- The maths teacher said, “three multiplied by three is nine.”
- The tourist said, “India is a very beautiful country.”
- Tina said, “It is hot outside.”
- The teacher said, “The Sepoy Mutiny took place in 1857.”
- Ira said, “I saw an elephant in the zoo.”
- Peter said, “I can do this work.”
- Uma said to her mother, “I have passed the exam”.
- Ajay said to Lucy, “I will go to Bangalore tomorrow.”
- Lewis said, “my mother is sleeping.”
- Tamal said to Naira, “When are you leaving?”
- “Where do you live?” the old man asked Timothy.
- The teacher asked Arjun, “Why are you talking?”
- Olena said to Andrew, “Bring me my rifle.”
- “Call the first convict,” said the jury.
- “Please call the ambulance,” said the woman.
- Betty said to me, “I will cook today’s dinner.”
- The teacher said to me, “You are very intelligent.”
- My mother said to me, “Please wait here till I come back.”
- The coach said to David, “Bravo! You have played well.”
- Ramen said, “Alas! My kitten passed away.”
- Bruce said, “I may go to the party.”
- Miss Davis said to the student, “Did you listen to me?”
- The lady said, “Let me come in.”
- Granny said to me, “May God bless you.”
- The policeman said to us, “Where are you going?”
- The boy shouted, “Let me go.”
- Shilpa said, “Alas! I am undone.”
- “I know his address,” said Rupert
- Punit said, “My mother is writing letters.”
- Rishav said to Roshni, “Have you ever been to the Taj Mahal?”
- Anu said to Shivina, “Please lend me a pencil.”
- Logan said, “When are you coming home?”
- Rory said to her colleagues, “We have successfully achieved our goal.”
- The teacher said to the students, “Make sure you hand over your papers before 12 p.m.”
- My mom said, “Everything is going to be fine.”
- Luke said, “I will cook for you tomorrow.”
- Manisha said, “I think I will have a shot at it next year.”
- Soumia said, “I am wearing a black dress for Achu’s reception.”
- The manager said, “All the rooms have been allocated according to your choices.”
- My grandmother said, “I have some work to do.”
- Lakshmi said, “I am a tailor.”
- Madhav said, “The cricket team did their best.”
- Dhoni said, “Can you help me with the luggage?”
- My parents said, “We loved the passion fruit dessert.”
- Danny said, “I am starting work from tomorrow.”
- The police officer said, “We are investigating the matter.”
- Emily said to Richard, “You are raising your voice.”
- Josh said, “I love shrimp.”
- Naomi said, “Was Farsana present yesterday?”
- Suman said that she got up early every morning.
- The maths teacher said that three multiplied by three is nine
- The tourist said that India was a very beautiful country.
- Tina said that it was hot outside.
- The teacher said that the Sepoy Mutiny took place in 1857.
- Ira said that she saw/had seen an elephant in the zoo.
- Peter said that he could do that work.
- Uma told her mother that she had passed the exam.
- Ajay informed Lucy that he would go to Bangalore the next day.
- Lewis said that his mother was sleeping
- Tamal asked Naira when she was leaving.
- The old man asked Timothy where he lived.
- The teacher asked Arjun why he was talking.
- Olena ordered Andrew to bring her rifle.
- The jury ordered to call the first convict.
- The woman requested to call an ambulance.
- Betty said to me that she would cook that day’s dinner.
- The teacher told me that I was intelligent.
- My mother requested me to wait there till she returned.
- The coach applauded David, saying that he had played well.
- Ramen exclaimed sadly that his kitten had passed away.
- Bruce said that he might go to the party.
- Miss Davis asked the student if he was listening to her.
- The lady asked to let her come in.
- Granny prayed that God might bless me.
- The policeman enquired where we were going.
- The boy shouted to them to let him go.
- Shilpa exclaimed sadly that she was undone.
- Rupert said that he knows/knew his address.
- Punit said that his mother was writing letters.
- Rishav asked Roshni if she had ever been to the Taj Mahal.
- Anu requested Shivina to lend her a pencil.
- Logan asked when I was coming home.
- Rory said to her colleagues that they have successfully achieved their goal.
- The teacher told the students to make sure that they handed over their papers before 12:00 p.m.
- My mom said that everything was going to be fine.
- Luke said that he would cook for me the next day.
- Manisha said that she thought she would have a shot at it the next year.
- Soumia said that she was wearing a black dress for Achu’s reception.
- The manager said that all the rooms have been allocated according to their choices.
- My grandmother said that she had some work to do.
- Lakshmi said that she was a tailor.
- Madhav said that the cricket team did/had done their best.
- Dhoni asked if I could help him with the luggage.
- My parents said that they loved the passion fruit dessert.
- Danny said that he was starting work from the next day.
- The police officer said that they were investigating the matter.
- Emily said to Richard that he was raising his voice.
- Josh said that he loved shrimp.
- Naomi asked if Farsana was present the previous day.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is direct narration.
When the actual words/sentences spoken by the speaker are quoted in a speech, it’s called direct speech/narration.
What is indirect speech?
When the quoted speech is reported in the form of a narrative without changing the meaning of the actual quotation/words by the speaker, it’s called indirect speech. Indirect speech is also known as reported speech.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- Reported Speech

What is Reported Speech?

Reported speech, also known as indirect speech, is a way of conveying what someone else has said without quoting their exact words. Instead of using quotation marks , the speaker paraphrases or summarises the original statement. This transformation often involves changes in pronouns, tenses, and time expressions to fit the context of the reporting. Understanding reported speech is crucial for effective communication , as it allows you to relay information accurately and fluently in both spoken and written English.
Reported Speech - How Does it Work?
Indirect speech or Reported speech is just a way of expressing your intent in questions, statements or other phrases, without essentially quoting them outrightly as the way it is done in indirect speech.
Reported Speech Rules
To understand Reported Speech Grammar and Reported Verbs, you need to first understand reported speech rules and how it works. Here are some types of reported speech:
Reported Statements
Reported speech is used when someone says a sentence, like, "I'm going to the movie tonight". Later, we want to tell a 3rd person what the first person is doing.
It works like this:
We use a reporting verb i.e 'say' or 'tell'. In the present tense, just put in 'he says.
Direct Speech: I like burgers.
Reported Speech: He says (that) he likes burgers.
You don't need to change the tense, but you do need to switch the 'person' from 'I' to 'he’. You also need to change words like 'my' and 'your'.
But, in case the reporting verb is in the past tense, then change the tenses in the reported speech itself.
Reported Questions
Reported questions to go like
Direct Speech: Where do you reside?
We make the change to reported speech by-
It is similar to reported statements. The tense changes are exact, and we keep the question’s word. But we need to change the grammar of that normal sentence into positive. For eg:
Reported Speech: He asked me where I resided.
The direct speech question is in the present simple tense. We make a present simple question with 'do' or 'does'. For that, I need to take that away. Then change the verb to the past simple.
Direct Speech: Where is Jolly?
Reported Speech: He asked me where Jolly was.
The direct question is the present simple of 'be'. We change the question form of the present simple of being by changing the position of the subject and the verb. So, change them back before putting the verb into the past simple.
Reported Speech Examples with Answers
Reported Requests
The reported speech goes a long way. What if a person asks you to do something politely or make a request? It’s called a reported request. For example
Direct Speech: Close the door, please / Could you close the door please? / Would you mind closing the door, please?
All these requests mean the same, so we don't need to report every word there when we tell a 3rd person about it.
We can simply use 'ask me + to + infinitive':
Reported Speech: They asked me to close the door.
Direct Speech: Please be punctual.
Reported Speech: They asked us to be punctual.
Reported Orders
And lastly, how about when someone doesn't ask that politely? This is known as an 'order' in English, which is when someone tells you to do something pretty much directly. This is called a reported order. For example
Direct Speech: Stand up right now!
We make this into a reported speech in the same way as that for a request. Just use 'tell' rather than 'ask':
Reported Speech: She told me to stand up right now.
Time Expressions within the Ambit of Reported Speech
Sometimes when we want to change the direct speech into reported speech, we will have to change the time expressions too. We don't necessarily always have to do that. However, It depends on when we heard the speech in indirect form and when we said the speech in reported form.
For Example,
It's Sunday. Kiran Ma’am says "I'm leaving today".
If You tell someone on Sunday, You will say "Kiran Ma’am said she was leaving today".
If you tell someone on Tuesday, You will say "Kiran Ma’am said she was leaving yesterday".
If you tell someone on Friday, you will say "Kiran Ma’am said she was leaving on Sunday ".
If you tell someone a month later, you will say "Kiran Ma’am said she was leaving that day".
So, technically there's no easy way to convert. You need to put in real effort and have to think about it when the direct speech is said.
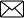
Conversions of Direct Speech to Reported Speech
Now let us check our understanding through this table.
This is all about reported speech. English grammar is a tricky thing given both the rules and practice. Reading these rules solely will not help you to get a strong grasp of them. You also have to practice reported speech sentences in practical life to know how and when they can be used.
Change of Pronouns
Change of adverbs time and place, change of modal verbs, test your knowledge of reported speech with reported speech exercises.
Exercise 1: Convert the following sentences from direct speech to reported speech.
Direct: "I am going to the market now," said John.
Reported: __________________________
Direct: "We will finish the project tomorrow," the team leader said.
Direct: "Can you help me with my homework?" Sarah asked Tom.
Direct: "She is studying French," said her teacher.
Direct: "I must complete this assignment by tonight," the student mentioned.
Exercise 2: Correct the error in the following reported speech sentences.
He said that he will go to the party the next day.
Correction: __________________________
She told me that she can come to the meeting.
They said that they are going to visit their grandparents.
The teacher told us that we must complete the homework by tomorrow.
He said that he might will arrive late.
Exercise 3: Convert the following sentences from reported speech to direct speech.
Reported: She said that she had finished her work.
Direct: __________________________
Reported: He told me that he would help me later.
Reported: They mentioned that they were planning a trip.
Reported: The doctor said that the patient needed rest.
Reported: She said that she could not attend the party.
Find out if you got them right from the answers below.
John said that he was going to the market then.
The team leader said that they would finish the project the next day.
Sarah asked Tom if he could help her with her homework.
Her teacher said that she was studying French.
The student mentioned that he/she had to complete the assignment by that night.
He said that he would go to the party the next day.
She told me that she could come to the meeting.
They said that they were going to visit their grandparents.
The teacher told us that we had to complete the homework by the next day.
He said that he might arrive late.
"I have finished my work," she said.
"I will help you later," he told me.
"We are planning a trip," they mentioned.
"The patient needs rest," the doctor said.
"I cannot attend the party," she said.
Takeaways from this Page
Understanding the reported speech requires understanding how pronouns shift based on the speaker and context.
Recognising the necessary tense changes when converting from direct to reported speech is crucial for accurate communication.
Knowing how adverbs of time and place change in reported speech ensures clarity in conveying when and where something occurred.
Familiarity with how modal verbs like "will" change to "would" helps maintain the intended meaning when reporting statements.
FAQs on Reported Speech
1. How do you convert present tenses to reported speech?
To convert present tenses to reported speech, follow these rules:
Present Simple changes to Past Simple.
Present Continuous changes to Past Continuous.
Present Perfect changes to Past Perfect.
Present Perfect Continuous changes to Past Perfect Continuous.
"I do yoga every morning." → She said that she did yoga every morning.
"My friend is watching a movie." → She said that her friend was watching a movie.
"I have been to the USA." → She told me that she had been to the USA.
2. How do you convert past tenses to reported speech?
To convert past tenses to reported speech, follow these rules:
Past Simple changes to Past Perfect.
Past Continuous changes to Past Perfect Continuous.
Past Perfect and Past Perfect Continuous remain unchanged.
"He arrived on Friday." → He said that he had arrived on Friday.
"I was playing cricket." → He said that he had been playing cricket.
"She had worked hard." → She said that she had worked hard.
3. What are the rules for converting future tenses to reported speech?
When converting future tenses to reported speech:
Future Simple (will) changes to would.
Future Continuous (will be) changes to would be.
Future Perfect (will have) changes to would have.
Future Perfect Continuous (will have been) changes to would have been.
"I will be attending the wedding." → She said that she would be attending the wedding.
4. How do you convert sentences with 'can' and 'can't' to reported speech?
'Can' changes to 'could'.
'Can't' changes to 'couldn't'.
"I can help you." → She said that she could help me.
"I can't come to the party." → He said that he couldn't come to the party.
5. How do you convert sentences with 'will' and 'won't' to reported speech?
'Will' changes to 'would'.
'Won't' changes to 'wouldn't'.
"I will call you tomorrow." → She said that she would call me the next day.
"I won't attend the meeting." → He said that he wouldn't attend the meeting.
6. What are some examples of reported requests?
Reported requests typically use the verb "ask" followed by an infinitive.
Direct: "Please open the window."
Reported: She asked me to open the window.
Direct: "Could you help me with this?"
Reported: He asked me to help him with that.
7. What are some examples of reported orders?
Reported orders often use the verb "tell" followed by an infinitive.
Direct: "Sit down."
Reported: The teacher told the student to sit down.
Direct: "Don't touch that."
Reported: He told me not to touch that.
8. How do time expressions change in reported speech?
Time expressions change as follows:
Today → That day
Tomorrow → The next day
Yesterday → The day before
Next week → The following week
Last week → The previous week
9. Does the past perfect tense change in reported speech?
No, the past perfect tense remains the same in reported speech.
"She had left early." → He said that she had left early.
10. What happens to pronouns in reported speech?
Pronouns in reported speech usually change based on the speaker and listener.
"I am going to the store." → He said that he was going to the store.
"You should see this." → She told me that I should see that.

Question and Answer forum for K12 Students

Reported Speech Exercises for Class 9 CBSE With Answers
Reported speech is when we express or say things that have already been said by somebody else.
Basic English Grammar rules can be tricky. In this article, we’ll get you started with the basics of sentence structure, punctuation, parts of speech, and more.
We also providing Extra Questions for Class 9 English Chapter wise.
Reported Speech Exercises for Class 9 CBSE With Answers Pdf
When we say things that have been said, we use two ways of expressing it. The first is direct speech when we express what the speaker said as it is and the second is indirect speech where we express what was said in our words.
Examples: If you ask your friend Pradeep, ‘Did you take my book?’, the reply could be ‘Your book is with Jai.’ Now, we can report this statement in two ways:
- Pradeep told me, ‘Your book is with Jai’.
- Pradeep told me that my book is with Jai.

Rules For Reported Speech While changing direct speech into reported speech or vice versa, the following change:
- the reporting verb
- the pronouns
- the situations
- report using present and future tenses
- modal verbs
- word order with who, which, and what

Changes in reporting verb:
- Affirmative sentences: said, told (object), asserted, replied, assured, informed, responded, whispered, alleged, believed, assumed, though.
- Interrogative sentences: asked, inquired, wanted to know, enquired When we report.
- Imperative sentences: ordered, begged, pleaded, implored, advised, demanded.
Change of pronouns:
- Direct speech: Surabhi said, “I am reading.”
- Indirect speech: Surabhi said that she was reading.
- A first-person and second-person generally change to a third person (depending upon the object to reporting verb).
Change of tenses:
In general, the present tense becomes past tense; past and perfect tenses become the past perfect tense.
Change Of Situations: Examples:
- Surabhi said, “I read this book last week.” (direct speech)
- Surabhi said that she had read that book the previous week, (indirect speech)
If the speaker talks about a universal truth, the tense is unchanged.
In case of questions and answers: Examples:
- Surabhi asked, “Have you read this book?” (Direct Speech)
- Surabhi asked if/whether I had read that book. (Indirect Speech)
- Surabhi asked, “Where is the book?” (Direct Speech)
- Surabhi asked where the book was. (Indirect Speech)
(a) yes/no questions – use if/whether (b) wh-questions – use the wh-word
Word Order:
- Surabhi asked, “What’s the matter?”
- Surabhi asked what the matter was. (what + the matter + was)
- Surabhi asked what was the matter, (what + was + the matter)
Can Be Either:
- who/which/what + complement + be or
- who/which/what + be + complement
Reported speech using present and future tenses: Examples:
- Surabhi said, “The sun rises in the east.” (Direct Speech)
- Surabhi said that the sun rises in the east. (Indirect Speech)
- Surabhi said, “I will read this book.” (Direct Speech)
- Surabhi said that she will read that book. (Indirect Speech)
If the original speaker’s present and future are still present and future, the tense remains unchanged. In case of modal verbs:
would, should, could, might, ought to, and must remain unchanged. Example:
- Surabhi said, “I can solve this sum.” (Direct Speech)
- Surabhi said that she could solve that sum. (Indirect Speech)
In our daily lives, we use reported speech in many forms. We use reported speech to report statements, questions, requests or even commands. There are certain things we need to keep in mind when we report each of them.
- When we report statements, we have to make sure what changes need to be made in the pronoun, tense or temporal-spatial expression.
- When we transform questions into reported speech, we have to check whether or not to change the tense, pronoun as well as place and time expression.
- Upon changing, we have to ensure that the question is an indirect question.
- We also have to make use of words such as where, when, how, if, whether etc.
- In transforming requests and commands into reported speech, tenses are not relevant.
- We only have to ensure that there are changes in the pronoun and the place and time expression.
Reported Speech Exercises Solved Example for Class 9 CBSE
Diagnostic Test 18

The child called out to his mother to (a) ……………………… . The mother replied that (b) ……………………… . She asked her son if (c) ……………………… . Her son replied in the affirmative. He added that (d) ……………………… . The mother then wanted to know what (e) ……………………… . The child informed her (f) ……………………… . Answer: (a) come and look as the house across the road was on fire. (b) she couldn’t go then as she was cooking. (c) the Fire Brigade was there. (d) they had just arrived and the men were jumping down from the engine. (e) the people of the house were doing. (f) that some of them were standing in the street holding an umbrella and others were throwing valuables down from the window into it.

45,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today
Meet top uk universities from the comfort of your home, here’s your new year gift, one app for all your, study abroad needs, start your journey, track your progress, grow with the community and so much more.

Verification Code
An OTP has been sent to your registered mobile no. Please verify

Thanks for your comment !
Our team will review it before it's shown to our readers.

- Reported Speech /
Reported Speech Exercises For Class 9 [PDF Available]
- Updated on
- May 7, 2024

Reported speech exercises for class 9: In this vast realm of English Grammar , reported speech , commonly known as indirect speech, plays an important role in conveying information relayed from another person. However, for class 9 students, grasping the nuances of reported speech is essential for effective communication and comprehension. The blog article below aims to provide class 9 students with engaging exercises to solidify their preparation.
This Blog Includes:
Definition of reported speech, reported speech rules to know, quiz for reported speech exercises for class 9, exercise 1: change direct speech to reported speech, exercise 2: choose the correct reported speech, exercise 3: create reported speech, exercise 4: fill in the blanks with the appropriate reported speech, exercise 5: convert sentences to indirect speech, exercise 6: change into reported speech, exercise 7: convert sentences to indirect speech, exercise 8: complete the sentences to reported speech.
Oxford Learner’s Dictionary definition of reported speech is “ A report of what somebody has said that does not use their exact words.”
As per the Macmillan Dictionary, the words that you use to report what someone else has said are known are reported speech.
MUST READ! Reported Speech: Definition, Rules, Usage with Examples, Tips, Exercises for Students
Here are some common rules for changing direct speech to reported speech:
➡️ We use conjunctions like ‘if’, and ‘whether’ after the reporting verb in reported speech
➡️ The reporting verb’s tense is never altered.
➡️ The verb of reporting varies according to sense: it can be told, inquired, asked, etc.
➡️ First and foremost, we do not use inverted commas in reported speech which must be clear from the example given above.
Also Read: Useful Idioms for IELTS Exams That Will Boost Your Score
Here’s a quiz on reported speech for students. Each question presents a direct speech statement, and you need to rewrite it in reported speech. Choose the correct option for each question.
Question 1: Direct Speech: “I love playing the guitar.”
a) He loves playing the guitar. b) I love playing the guitar. c) He loved playing the guitar. d) I loved playing the guitar.
Question 2: Direct Speech: “We are going to the park tomorrow.”
a) They are going to the park tomorrow. b) We were going to the park tomorrow. c) They were going to the park tomorrow. d) We go to the park tomorrow.
Question 3: Direct Speech: “She said, ‘I have already finished my homework.'”
a) She said that she already finished her homework. b) She said that she had already finished her homework. c) She says that she finished her homework already. d) She said that she has already finished her homework.
Question 4: Direct Speech: “The teacher exclaimed, ‘What a wonderful painting!'”
a) The teacher exclaimed that it was a wonderful painting. b) The teacher exclaimed what a wonderful painting it was. c) The teacher exclaimed that what a wonderful painting. d) The teacher exclaimed a wonderful painting.
Question 5: Direct Speech: “I will call you later.”
a) He said that he will call you later. b) He said that he would call you later. c) He says that he will call you later. d) He says that he would call you later.
Question 6: Direct Speech: “They said, ‘We haven’t received the email.'”
a) They said that they haven’t received the email. b) They said that they didn’t receive the email. c) They said that they hadn’t received the email. d) They say that they haven’t received the email.
Question 7: Direct Speech: “Tom said, ‘I can swim.'”
a) Tom said that he could swim. b) Tom says that he could swim. c) Tom said that he can swim. d) Tom says that he can swim.
- b) I love playing the guitar.
- a) They are going to the park tomorrow.
- b) She said that she had already finished her homework.
- b) The teacher exclaimed what a wonderful painting it was.
- b) He said that he would call you later.
- c) They said that they hadn’t received the email.
- a) Tom said that he could swim.
Also Read: 50 Examples of Direct and Indirect Speech Interrogative Sentences
Following are some useful reported speech exercises for class 9. Convert the following sentences from direct speech to reported speech:
Direct Speech : She said, “I am going to the store.”
Reported Speech : She said that she was going to the store.
Direct Speech : He said, “I will finish the project by Friday.”
Reported Speech : He said that he would finish the project by Friday.
Direct Speech : “We have completed our homework,” they said.
Reported Speech : They said that they had completed their homework.
Direct Speech : “They are coming to the party,” she said.
Reported Speech : She said that they were coming to the party.
Direct Speech : “I can speak French,” he said.
Reported Speech : He said that he could speak French.
Read the following sentences and choose the correct reported speech option:
Direct Speech : “I saw Sarah yesterday,” Tom said.
a) Tom said he had seen Sarah yesterday.
b) Tom said he sees Sarah yesterday.
Correct Answer: a) Tom said he had seen Sarah yesterday.
Direct Speech : “I’m going to the cinema tonight,” she said.
a) She said she was going to the cinema that night.
b) She said she is going to the cinema tonight.
Correct Answer: a) She said she was going to the cinema that night.
Direct Speech : “We will travel to Paris next week,” they said.
a) They said they will travel to Paris next week.
b) They said they would travel to Paris the following week.
Correct Answer: b) They said they would travel to Paris the following week.
Direct Speech : “I have finished my work,” he said.
a) He said he has finished his work.
b) He said he had finished his work.
Correct Answer: b) He said he had finished his work.
Direct Speech : “I’m cooking dinner right now,” she said.
a) She said she was cooking dinner right then.
b) She said she is cooking dinner right now.
Correct Answer: a) She said she was cooking dinner right then.
Must Read: Subject-Verb Agreement: Definition, 12 Rules & Examples
Form reported speech for the following direct speech sentences:
Direct Speech : “She will be here soon,” he said.
Reported Speech : He mentioned that she would be there soon.
Direct Speech : “I don’t like seafood,” she said.
Reported Speech : She expressed that she didn’t like seafood.
Direct Speech : “They were studying in the library,” he said.
Reported Speech : He mentioned that they had been studying in the library.
Direct Speech : “I am working on a new project,” she said.
Reported Speech : She mentioned that she was working on a new project.
Direct Speech : “We have completed the assignment,” they said.
Reported Speech : They confirmed that they had completed the assignment.
Also Read: Tenses Rules: Charts, Examples, Types [PDF Available]
Practise the following direct sentences to appropriate report speech.
She said, “I have been to Paris before.”
Reported Speech : She mentioned that she had been to Paris before.
“We will come early,” they said.
Reported Speech : They said that they would come early.
“He’s writing a novel,” she said.
Reported Speech : She mentioned that he was writing a novel.
“I won’t be able to attend the meeting,” he said.
Reported Speech : He said that he wouldn’t be able to attend the meeting.
“We were watching a movie,” they said.
Reported Speech : They mentioned that they had been watching a movie.
Also Read: Adjective: Definition, Usage, Example, Forms, Types
Change the following sentences into indirect speech:
- He said, “Honesty is the best policy.”
- He said, “The sun rises in the east.”
- Rakesh said, “I am an early riser.”
- She said, “God is omnipresent.”
- The teacher said, “The First World War started in 1914.”
Exploring the Types of Reported Speech: A Complete Guide
Read the following sentences and convert them into reported speech.
- Rahul said, “I get up early every morning.”
- Andrew said, “I can do this work.”
- Priya said, “It is hot outside.”
- Raj said to Marie, “I will go to London tomorrow.”
- Archie said to me, “I will cook today’s dinner.”
Check Your Answers:
- Rahul said that he got up early every morning.
- Andrew said that he could do that work.
- Priya said that it was hot outside.
- Raj informed Marie that he would go to London the next day.
- Archie said to me that he would cook that day’s dinner.
Must Read: Reported Speech For Class 10: Exciting Exercises with Answers [PDF]
Convert the following direct speech sentences into indirect speech.
- Direct Speech: “I love playing basketball,” said Sarah.
- Direct Speech: “We are going to visit Paris next month,” said Tom.
- Direct Speech: “She has already finished her homework,” said Jack.
- Direct Speech: “They will arrive at 9 o’clock,” said the receptionist.
- Direct Speech: “I have never been to Japan,” said Emily.
- Sarah said that she loved playing basketball.
- Tom said that they were going to visit Paris the following month.
- Jack said that she had already finished her homework.
- The receptionist said that they would arrive at 9 o’clock.
- Emily said that she had never been to Japan.
Reported speech exercises help reinforce understanding of how to report what someone else has said. They aid in learning how to shift verb tenses, pronouns, time expressions, and other changes when reporting speech.
When converting direct speech to reported speech, pay attention to the changes in verb tenses, pronouns, time expressions, and other relevant modifications based on the context and the tense used in the original sentence.
Common changes include the shift of tenses (present to past, future to conditional), pronoun changes, changes in time expressions (today to that day, tomorrow to the next day), and changes in modal verbs (can to could, will to would, etc.).
We hope this blog has provided you with all the necessary information on reported speech exercises for class 9. To advance your grammar knowledge and read more informative blogs, check out our Learn English page and don’t forget to follow Leverage Edu .
Vaishnavi Shukla
Vaishnavi has 2+ years of experience in SEO and Content Marketing. She is highly proficient in English, possessing exceptional language skills and a deep understanding of English grammar and communication. Currently working on Ed Tech, Finance, Lifestyle, and other niches. All her works are infused with love for writing!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Contact no. *

Leaving already?
8 Universities with higher ROI than IITs and IIMs
Grab this one-time opportunity to download this ebook
Connect With Us
45,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. take the first step today..

Resend OTP in

Need help with?
Study abroad.
UK, Canada, US & More
IELTS, GRE, GMAT & More
Scholarship, Loans & Forex
Country Preference
New Zealand
Which English test are you planning to take?
Which academic test are you planning to take.
Not Sure yet
When are you planning to take the exam?
Already booked my exam slot
Within 2 Months
Want to learn about the test
Which Degree do you wish to pursue?
When do you want to start studying abroad.
January 2025
September 2025
What is your budget to study abroad?

How would you describe this article ?
Please rate this article
We would like to hear more.
Have something on your mind?
Reported Speech
Perfect english grammar.

Reported Statements
Here's how it works:
We use a 'reporting verb' like 'say' or 'tell'. ( Click here for more about using 'say' and 'tell' .) If this verb is in the present tense, it's easy. We just put 'she says' and then the sentence:
- Direct speech: I like ice cream.
- Reported speech: She says (that) she likes ice cream.
We don't need to change the tense, though probably we do need to change the 'person' from 'I' to 'she', for example. We also may need to change words like 'my' and 'your'. (As I'm sure you know, often, we can choose if we want to use 'that' or not in English. I've put it in brackets () to show that it's optional. It's exactly the same if you use 'that' or if you don't use 'that'.)
But , if the reporting verb is in the past tense, then usually we change the tenses in the reported speech:
- Reported speech: She said (that) she liked ice cream.
* doesn't change.
- Direct speech: The sky is blue.
- Reported speech: She said (that) the sky is/was blue.
Click here for a mixed tense exercise about practise reported statements. Click here for a list of all the reported speech exercises.
Reported Questions
So now you have no problem with making reported speech from positive and negative sentences. But how about questions?
- Direct speech: Where do you live?
- Reported speech: She asked me where I lived.
- Direct speech: Where is Julie?
- Reported speech: She asked me where Julie was.
- Direct speech: Do you like chocolate?
- Reported speech: She asked me if I liked chocolate.
Click here to practise reported 'wh' questions. Click here to practise reported 'yes / no' questions. Reported Requests
There's more! What if someone asks you to do something (in a polite way)? For example:
- Direct speech: Close the window, please
- Or: Could you close the window please?
- Or: Would you mind closing the window please?
- Reported speech: She asked me to close the window.
- Direct speech: Please don't be late.
- Reported speech: She asked us not to be late.
Reported Orders
- Direct speech: Sit down!
- Reported speech: She told me to sit down.
- Click here for an exercise to practise reported requests and orders.
- Click here for an exercise about using 'say' and 'tell'.
- Click here for a list of all the reported speech exercises.

Hello! I'm Seonaid! I'm here to help you understand grammar and speak correct, fluent English.

Perfectyourenglish.com
English Grammar Lessons And Worksheets
- Class 9 worksheets
Reported Speech Worksheet for Class 9 CBSE
by Manjusha Nambiar · Published February 1, 2024 · Updated April 6, 2024
When we report questions, the question word (who, what, which etc.) is retained in the reported speech.
Note that a reported question has the same word order as a statement. That means the subject goes before the auxiliary verb.
- The teacher said, ‘What are you doing?’
- The teacher asked what I was doing. (NOT The Teacher asked that what I was doing.) (NOT The teacher asked what was I doing.)
In order to report Yes/No questions , we use the conjunction if or whether.
- ‘Would you like a cup of coffee?’ she asked.
- She asked if / whether I would like a cup of coffee.
Reporting commands
In order to report a command, we use a reporting verb like asked, told, requested, warned, advised, begged, urged, commanded, ordered etc.
- Direct speech: ‘Help me, please,’ she cried.
- Indirect speech: She begged them to help her.
Reported speech worksheet
Sentences are given in the direct speech. Change them into the indirect / reported speech.
1. ‘Leave me alone,’ she said.
2. ‘I don’t know what I am supposed to do,’ he said.
3. ‘How are we going to overcome this difficulty?’ they said.
4. Mother said, ‘Have you applied for that job?’
5. ‘Please wait for me,’ said the girl.
6. ‘It doesn’t work,’ she said.
7. ‘I can drive any car,’ she said.
8. Sam said, ‘I haven’t heard anything from them yet.’
9. ‘Close the doors and windows before you leave,’ said the woman.
10. ‘Should I wait any longer?’ he asked.
11. ‘Whose bag is this?’ he asked.
12. ‘I will wait outside,’ he said.
13. ‘Have you brought your lunch?’ she asked.
14. ‘Take this file with you when you go to work,’ she said to me.
15. ‘Be careful when you cross the road,’ said the mother to the children.
16. ‘Please wait a minute,’ the receptionist said to me.
17. ‘I don’t want to go,’ Maya said to me.
18. ‘Why are you crying?’ mother said to me.
19. ‘Do you know Rahul’s address?’ Rohit asked me.
20. ‘Submit your work before Monday,’ the teacher said to the students.
1. She requested / told me / us to leave her alone.
2. He said that he didn’t know what he was supposed to do.
3. They wondered how they were going to overcome that difficulty.
4. Mother asked if / whether I had applied for that job.
5. The girl requested me to wait for her.
6. She said that it didn’t work.
7. She said that she could drive any car.
8. Sam said that he hadn’t heard anything from them yet.
9. The woman told us to close the doors and windows before we left.
10. He asked if / whether he should / had to wait any longer.
11. He asked whose bag that was.
12. He said that he would wait outside.
13. She asked me if / whether I had brought my lunch.
14. She told me to take that file with me when I went to work.
15. The mother warned / advised the children to be careful when they cross the road.
16. The receptionist asked / requested me to wait a minute.
17. Maya told me that she didn’t want to go.
18. Mother asked me why I was crying.
19. Rohit asked me if / whether I knew Rahul’s address.
20. The teacher told / instructed the students to submit their work before Monday.
Related posts:
- Reported Speech Worksheet For Class 10 | Reporting Questions
- Reported Speech Worksheet for Class 10 KSEEB SSLC
- Direct And Indirect Speech Worksheet For Class 10
- Reported Speech Worksheet for Class 9
- Reported Speech Worksheet for Class 10 CBSE
- Direct And Indirect Speech Worksheet For Class 8 CBSE
- Reported Speech Worksheet For Classes 9 And 10
- Reported Speech Worksheet For Class 10
Tags: reported speech worksheet for class 9
Manjusha Nambiar
Hi, I am Manjusha. This is my blog where I give English grammar lessons and worksheets.
- Next story In The Modern World, A University Education Is Essential In Order To Get A Rewarding Job
- Previous story Gerund or Infinitive Worksheet for Class 8
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Explore perfectyourenglish.com
Useful links
- English Grammar
Learn English with me
If you need one-on-one private tuition, please send an email to [email protected]
- A word a day
- B2 First (Cambridge English)
- Bank PO English
- CBSE Grammar Worksheets
- Class 10 worksheets
- Class 11 Worksheets
- Class 2 Worksheets
- Class 3 worksheets
- Class 4 worksheets
- Class 5 worksheets
- Class 6 worksheets
- Class 7 worksheets
- Class 8 worksheets
- Class 9 and 10 worksheets
- Grammar exercises
- Karnataka Board English
- Kerala Syllabus English
- Maharashtra Syllabus English
- Phrasal verbs
- PSC Coaching
- Reading comprehension
- Sample Letters
- Tamil Nadu Board English
- Test Preparation
- Uncategorized
- Vocabulary exercises
Never Miss an Update!
Enter your email address to receive our lessons in your inbox:
Delivered by FeedBurner
Sites in our network
NCERT Guides
Learn Maths Online | Free NCERT Maths Solutions

Recent Posts
- Local Shops Have Closed Because of Online Shopping | IELTS Essay Sample
- Letter to the Editor about Incorrect Information in an Article
- Number of Films Produced in Five Countries | IELTS Report Sample
- Advertisement for a Baby Sitter | IELTS Letter Sample
- Cars That Burn Fossil Fuels Should Be Banned
Reported Speech - English Grammar for Class 9 - Class 9 - Notes, Videos & Tests
Part of the course, reported speech study material.

Videos for Reported Speech - English Grammar for Class 9 | Class 9
Notes for reported speech - english grammar for class 9, online test for reported speech - english grammar for class 9, extra questions for reported speech - english grammar for class 9, other chapters in english grammar for class 9, frequently asked questions on class 9 preparation.
- What are the questions asked in Class 9 examinations? As per the CBSE exam pattern for Class 9 2021, the type of questions asked in the examination are Very Short Answer (VSA) type, Short Answer(SA) type, and Long Answer (LA) type. There will be CBSE internal marks for Class 9 2022 of 20 marks for both the terms.
Top Courses for Class 9

Importance of Reported Speech Class 9
Reported speech notes free pdf download, important questions for reported speech, reported speech practice questions, welcome back, create your account for free.
Forgot Password
Change country.

- Andhra Pradesh
- Chhattisgarh
- West Bengal
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Jammu & Kashmir
- NCERT Books 2022-23
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Notes
- NCERT Exemplar Books
- NCERT Exemplar Solution
- States UT Book
- School Kits & Lab Manual
- NCERT Books 2021-22
- NCERT Books 2020-21
- NCERT Book 2019-2020
- NCERT Book 2015-2016
- RD Sharma Solution
- TS Grewal Solution
- TR Jain Solution
- Selina Solution
- Frank Solution
- Lakhmir Singh and Manjit Kaur Solution
- I.E.Irodov solutions
- ICSE - Goyal Brothers Park
- ICSE - Dorothy M. Noronhe
- Micheal Vaz Solution
- S.S. Krotov Solution
- Evergreen Science
- KC Sinha Solution
- ICSE - ISC Jayanti Sengupta, Oxford
- ICSE Focus on History
- ICSE GeoGraphy Voyage
- ICSE Hindi Solution
- ICSE Treasure Trove Solution
- Thomas & Finney Solution
- SL Loney Solution
- SB Mathur Solution
- P Bahadur Solution
- Narendra Awasthi Solution
- MS Chauhan Solution
- LA Sena Solution
- Integral Calculus Amit Agarwal Solution
- IA Maron Solution
- Hall & Knight Solution
- Errorless Solution
- Pradeep's KL Gogia Solution
- OP Tandon Solutions
- Sample Papers
- Previous Year Question Paper
- Important Question
- Value Based Questions
- CBSE Syllabus
- CBSE MCQs PDF
- Assertion & Reason
- New Revision Notes
- Revision Notes
- Question Bank
- Marks Wise Question
- Toppers Answer Sheets
- Exam Paper Aalysis
- Concept Map
- CBSE Text Book
- Additional Practice Questions
- Vocational Book
- CBSE - Concept
- KVS NCERT CBSE Worksheets
- Formula Class Wise
- Formula Chapter Wise
- Toppers Notes
- Most Repeated Question
- Diagram Based Question
- Study Planner
- JEE Previous Year Paper
- JEE Mock Test
- JEE Crash Course
- JEE Sample Papers
- JEE Toppers Notes
- JEE Formula
- JEE Important Question
- JEE Mind Map
- JEE Integer-Numerical Type Question
- JEE Study Planner
- Important Info
- SRM-JEEE Previous Year Paper
- SRM-JEEE Mock Test
- VITEEE Previous Year Paper
- VITEEE Mock Test
- BITSAT Previous Year Paper
- BITSAT Mock Test
- Manipal Previous Year Paper
- Manipal Engineering Mock Test
- AP EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- AP EAMCET Mock Test
- COMEDK Previous Year Paper
- COMEDK Mock Test
- GUJCET Previous Year Paper
- GUJCET Mock Test
- KCET Previous Year Paper
- KCET Mock Test
- KEAM Previous Year Paper
- KEAM Mock Test
- MHT CET Previous Year Paper
- MHT CET Mock Test
- TS EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- TS EAMCET Mock Test
- WBJEE Previous Year Paper
- WBJEE Mock Test
- AMU Previous Year Paper
- AMU Mock Test
- CUSAT Previous Year Paper
- CUSAT Mock Test
- AEEE Previous Year Paper
- AEEE Mock Test
- UPSEE Previous Year Paper
- UPSEE Mock Test
- CGPET Previous Year Paper
- BCECE Previous Year Paper
- JCECE Previous Year Paper
- Crash Course
- Previous Year Paper
- NCERT Based Short Notes
- NCERT Based Tests
- NEET Sample Paper
- Previous Year Papers
- Quantitative Aptitude
- Numerical Aptitude Data Interpretation
- General Knowledge
- Mathematics
- Agriculture
- Accountancy
- Business Studies
- Political science
- Enviromental Studies
- Mass Media Communication
- Teaching Aptitude
- Verbal Ability & Reading Comprehension
- Logical Reasoning & Data Interpretation
- CAT Mock Test
- CAT Important Question
- CAT Vocabulary
- CAT English Grammar
- MBA General Knowledge
- CAT Mind Map
- CAT Study Planner
- CMAT Mock Test
- SRCC GBO Mock Test
- SRCC GBO PYQs
- XAT Mock Test
- SNAP Mock Test
- IIFT Mock Test
- MAT Mock Test
- CUET PG Mock Test
- CUET PG PYQs
- MAH CET Mock Test
- MAH CET PYQs
- NAVODAYA VIDYALAYA
- SAINIK SCHOOL (AISSEE)
- Mechanical Engineering
- Electrical Engineering
- Electronics & Communication Engineering
- Civil Engineering
- Computer Science Engineering
- CBSE Board News
- Scholarship Olympiad
- School Admissions
- Entrance Exams
- All Board Updates
- Miscellaneous
- State Wise Books
- Engineering Exam
Reported Speech Class 9 Notes English (Handwritten Short & Revision Notes)
Reported Speech is one of the most important chapters in English which every student should study if they want to score good marks in their examination. Keeping in mind, Selfstudys.com has decided to solve this issue of the students. Reported Speech Class 9 Notes not only help the students to understand the concepts better but also boosts their confidence.
Reported Speech Class 9 Notes are created as per the latest pattern of the Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE) to ensure that the student covers each and every topic and does not miss any important topic. Class 9 Reported Speech Notes are written in a well-detailed manner which clears every doubt of the students and helps them to score good marks in their examinations.
All the students are advised to study from Reported Speech Class 9 Notes on a weekly basis to create a strong foundation of all the topics and memorise them in a way so that you remember them for a longer period of time.
About Reported Speech Class 9 Notes PDF
All the students can have access to Class 9 Reported Speech Notes at the official website of selfstudys i.e. selfstudys.com. Reported Speech Class 9 Notes are created by the highly qualified subject matter experts who have their expertise in the field of education.
Students can access Reported Speech Class 9 Notes absolutely free of cost. These Notes are a success mantra for all the students who want to improve their marks and score well in their examinations.
These Notes can be easily downloaded in the PDF Format and can be accessed 24×7. The Notes of Class 9 Reported Speech are also mobile-friendly.
Students using Reported Speech Notes can also identify their strong and weak areas and can work on them to improve their scores.
What Are Reported Speech Class 9 Notes and Why Are They Famous Among the Students?
Class 9 Reported Speech Notes are important study materials which consist of the important definitions, HOTS (High Order Thinking Skills) questions, key points etc. Class 9 Reported Speech helps to increase the accuracy of the students and is completely free of cost. This makes Reported Speech Class 9 Notes famous among the students.
Our highly qualified subject matter experts at selfstudys who have their expertise in the educational industry have created Reported Speech Class 9 Notes. Also, they are familiar with the most common questions which often get repeated in the examinations.
How to Download Reported Speech Class 9 Notes?
Downloading Class 9 Reported Speech Notes is not a very difficult task if you are aware of the right steps. The steps to download Reported Speech Class 9 Notes is as follows:
- Visit the official website of selfstudys i.e. selfstudys.com.
- After going to the official website, you need to click on the three lines which you will see on the upper left side. After clicking on the three lines, you need to click on the ‘CBSE’ option.
- After clicking on the ‘CBSE’ option, click on the option of ‘New Revision Notes’.
- After clicking on the option of ‘New Revision Notes’, you will be redirected on the page where you have to select the class and the subject for which you want to download the Notes.
- And you are done! Now you can access Reported Speech Class 9 Notes.
What are the Benefits of Reported Speech Class 9 Notes?
There are numerous benefits of Reported Speech Class 9 Notes. Some of the most important of them includes:
- You will cover each and every topic: If you are studying from Reported Speech Class 9 Notes, it can be said that you will cover each and every topic and will not miss even a single topic. The subject matter experts at selfstudys have made sure to cover each topic in a well-explained manner.
- Increases focus: Reported Speech Class 9 Notes are written in a way which keeps the students interested in their studies which can increase focus. The students can go through Class 9 Reported Speech Notes thoroughly to score good marks in their exams.
- Easy Language: Class 9 Reported Speech Notes are written in an easy to understand language to ensure that the students do not find any term difficult while studying them. As they are written in an easy language, the students will be able to memorise them fast.
- Increases Learning Capacity: Reported Speech Class 9 Notes not only boosts the confidence of the students but also increases the learning capacity of all the students. By this, they are able to memorise the concepts fast. This helps them to do effective preparation and score well in their examinations.
- A great source of revision: One of the biggest benefits of Reported Speech Class 9 Notes is that it can be a great source of revision. As these Notes consist of each and every piece of information, students reading them after completing their exam preparation will not only stick the information in their mind but will also remember them for a longer period of time.
Revision Tips to Study from Reported Speech Class 9 Notes
There are various revision tips which students should follow to study from Reported Speech Class 9 Notes. Some of them are:
- Note down your mistakes: While studying from Reported Speech Class 9 Notes, it is advisable for all the students to make a list of their mistakes and then work on them. Students can improve their preparation level by noting down their mistakes and working on them.
- Practise Study Materials: All the students are advised to practise from the study materials for example: previous year question paper, Mock tests and more. By practising them regularly, a student gets to know about the pattern of the examination, weightage per question, marking scheme etc.
- Blurting: Another great way which students can choose to do is by the blurting method. In this technique, a student has to read Reported Speech Class 9 Notes repeatedly to memorise them. After following the blurting method, make sure that you test yourself by writing down the topics which you remembered so far during the revision time.
- Take short breaks between your exam preparation: Students are always advised to take short breaks between their exam preparation as it will ensure effective learning. Taking short breaks while studying Reported Speech Class 9 Notes also improves memory and recalling power. So, make sure to follow this revision tip while doing exam preparation.
- Pomodoro Technique: Another important revision tip which is advisable for all the students is to follow the pomodoro technique as it helps to reduce distractions and improves the concentration of the students. This technique can be used by all the students to increase their accuracy and concentration when they are using Reported Speech Class 9 Notes.
How to Prepare for Annual Exam from Reported Speech Class 9 Notes?
There are various tips which students should follow to prepare from Reported Speech Class 9 Notes. The tips are:
- Start reading or rewriting your Notes: The first tip which students should follow is that they should start reading their Reported Speech Notes repeatedly. After reading, they can write them to stick in their memory and remember them for a longer period of time. There are also various ways which you can use to rewrite them.
- Start studying in advance: It is always advisable for all the students to start studying for their examinations in advance from Reported Speech Class 9 Notes. If they study at the last moment, they will not be able to study effectively and chances of getting stressed and anxious will also increase. Studying in advance also helps to create a strong base of each and every concept.
- Always take food breaks in between your exam preparation: Students are advised to take short food breaks of 15-20 minutes in between their exam preparation to revive their energy levels and also to improve their memory.
- Get a good night’s sleep: All the students are advised to get a good night’s sleep as it will help the students to improve their brain function which will automatically improve the learning power of all the students.
What are the Advantages of Having Reported Speech Class 9 Notes?
There are various Advantages of Class 9 Reported Speech Notes. Some of the most important of them are:
- Boost in Confidence: By studying from Reported Speech Class 9 Notes, a student can boost their confidence as they will find out that they are aware of the majority of the topics and will do well in the final examinations. This will not only enhance their self-confidence but will also motivate them to do better in exams.
- Forces the student to level up: Reported Speech Class 9 Notes are written in a way which includes various HOTS (High Order Thinking Skills) questions which will force the students to think at a higher level.
- Access to Detailed Explanations: The subject matter experts at selfstudys have created these Notes in a detailed way which will help the students to increase their conceptual knowledge and also build a strong foundation of all the concepts in their minds.
- As per the latest syllabus: Reported Speech Class 9 Notes are created as per the latest syllabus to ensure that the student covers each and every topic and does not miss even a single topic.
- Diagrammatically Explained Resources: Apart from the easy theoretical language which is used in explaining the students through the Notes, various diagrams, tables etc. are also used to help the students understand all the concepts in a better way.
- Mobile Friendly: One of the biggest advantages of Reported Speech English Grammar Class 9 Notes is that they can be easily accessed on mobile phones. One does not need a laptop or PC to access them.

- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Maths
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths
- CBSE Syllabus 2023-24
- Social Media Channels
- Login Customize Your Notification Preferences

One Last Step...

- Second click on the toggle icon

Provide prime members with unlimited access to all study materials in PDF format.
Allow prime members to attempt MCQ tests multiple times to enhance their learning and understanding.
Provide prime users with access to exclusive PDF study materials that are not available to regular users.


100 Reported Speech Examples: How To Change Direct Speech Into Indirect Speech
Reported speech, also known as indirect speech, is a way of communicating what someone else has said without quoting their exact words. For example, if your friend said, “ I am going to the store ,” in reported speech, you might convey this as, “ My friend said he was going to the store. ” Reported speech is common in both spoken and written language, especially in storytelling, news reporting, and everyday conversations.
Reported speech can be quite challenging for English language learners because in order to change direct speech into reported speech, one must change the perspective and tense of what was said by the original speaker or writer. In this guide, we will explain in detail how to change direct speech into indirect speech and provide lots of examples of reported speech to help you understand. Here are the key aspects of converting direct speech into reported speech.
Reported Speech: Changing Pronouns
Pronouns are usually changed to match the perspective of the person reporting the speech. For example, “I” in direct speech may become “he” or “she” in reported speech, depending on the context. Here are some example sentences:
- Direct : “I am going to the park.” Reported : He said he was going to the park .
- Direct : “You should try the new restaurant.” Reported : She said that I should try the new restaurant.
- Direct : “We will win the game.” Reported : They said that they would win the game.
- Direct : “She loves her new job.” Reported : He said that she loves her new job.
- Direct : “He can’t come to the party.” Reported : She said that he couldn’t come to the party.
- Direct : “It belongs to me.” Reported : He said that it belonged to him .
- Direct : “They are moving to a new city.” Reported : She said that they were moving to a new city.
- Direct : “You are doing a great job.” Reported : He told me that I was doing a great job.
- Direct : “I don’t like this movie.” Reported : She said that she didn’t like that movie.
- Direct : “We have finished our work.” Reported : They said that they had finished their work.
- Direct : “You will need to sign here.” Reported : He said that I would need to sign there.
- Direct : “She can solve the problem.” Reported : He said that she could solve the problem.
- Direct : “He was not at home yesterday.” Reported : She said that he had not been at home the day before.
- Direct : “It is my responsibility.” Reported : He said that it was his responsibility.
- Direct : “We are planning a surprise.” Reported : They said that they were planning a surprise.
Reported Speech: Reporting Verbs
In reported speech, various reporting verbs are used depending on the nature of the statement or the intention behind the communication. These verbs are essential for conveying the original tone, intent, or action of the speaker. Here are some examples demonstrating the use of different reporting verbs in reported speech:
- Direct: “I will help you,” she promised . Reported: She promised that she would help me.
- Direct: “You should study harder,” he advised . Reported: He advised that I should study harder.
- Direct: “I didn’t take your book,” he denied . Reported: He denied taking my book .
- Direct: “Let’s go to the cinema,” she suggested . Reported: She suggested going to the cinema .
- Direct: “I love this song,” he confessed . Reported: He confessed that he loved that song.
- Direct: “I haven’t seen her today,” she claimed . Reported: She claimed that she hadn’t seen her that day.
- Direct: “I will finish the project,” he assured . Reported: He assured me that he would finish the project.
- Direct: “I’m not feeling well,” she complained . Reported: She complained of not feeling well.
- Direct: “This is how you do it,” he explained . Reported: He explained how to do it.
- Direct: “I saw him yesterday,” she stated . Reported: She stated that she had seen him the day before.
- Direct: “Please open the window,” he requested . Reported: He requested that I open the window.
- Direct: “I can win this race,” he boasted . Reported: He boasted that he could win the race.
- Direct: “I’m moving to London,” she announced . Reported: She announced that she was moving to London.
- Direct: “I didn’t understand the instructions,” he admitted . Reported: He admitted that he didn’t understand the instructions.
- Direct: “I’ll call you tonight,” she promised . Reported: She promised to call me that night.
Reported Speech: Tense Shifts
When converting direct speech into reported speech, the verb tense is often shifted back one step in time. This is known as the “backshift” of tenses. It’s essential to adjust the tense to reflect the time elapsed between the original speech and the reporting. Here are some examples to illustrate how different tenses in direct speech are transformed in reported speech:
- Direct: “I am eating.” Reported: He said he was eating.
- Direct: “They will go to the park.” Reported: She mentioned they would go to the park.
- Direct: “We have finished our homework.” Reported: They told me they had finished their homework.
- Direct: “I do my exercises every morning.” Reported: He explained that he did his exercises every morning.
- Direct: “She is going to start a new job.” Reported: He heard she was going to start a new job.
- Direct: “I can solve this problem.” Reported: She said she could solve that problem.
- Direct: “We are visiting Paris next week.” Reported: They said they were visiting Paris the following week.
- Direct: “I will be waiting outside.” Reported: He stated he would be waiting outside.
- Direct: “They have been studying for hours.” Reported: She mentioned they had been studying for hours.
- Direct: “I can’t understand this chapter.” Reported: He complained that he couldn’t understand that chapter.
- Direct: “We were planning a surprise.” Reported: They told me they had been planning a surprise.
- Direct: “She has to complete her assignment.” Reported: He said she had to complete her assignment.
- Direct: “I will have finished the project by Monday.” Reported: She stated she would have finished the project by Monday.
- Direct: “They are going to hold a meeting.” Reported: She heard they were going to hold a meeting.
- Direct: “I must leave.” Reported: He said he had to leave.
Reported Speech: Changing Time and Place References
When converting direct speech into reported speech, references to time and place often need to be adjusted to fit the context of the reported speech. This is because the time and place relative to the speaker may have changed from the original statement to the time of reporting. Here are some examples to illustrate how time and place references change:
- Direct: “I will see you tomorrow .” Reported: He said he would see me the next day .
- Direct: “We went to the park yesterday .” Reported: They said they went to the park the day before .
- Direct: “I have been working here since Monday .” Reported: She mentioned she had been working there since Monday .
- Direct: “Let’s meet here at noon.” Reported: He suggested meeting there at noon.
- Direct: “I bought this last week .” Reported: She said she had bought it the previous week .
- Direct: “I will finish this by tomorrow .” Reported: He stated he would finish it by the next day .
- Direct: “She will move to New York next month .” Reported: He heard she would move to New York the following month .
- Direct: “They were at the festival this morning .” Reported: She said they were at the festival that morning .
- Direct: “I saw him here yesterday.” Reported: She mentioned she saw him there the day before.
- Direct: “We will return in a week .” Reported: They said they would return in a week .
- Direct: “I have an appointment today .” Reported: He said he had an appointment that day .
- Direct: “The event starts next Friday .” Reported: She mentioned the event starts the following Friday .
- Direct: “I lived in Berlin two years ago .” Reported: He stated he had lived in Berlin two years before .
- Direct: “I will call you tonight .” Reported: She said she would call me that night .
- Direct: “I was at the office yesterday .” Reported: He mentioned he was at the office the day before .
Reported Speech: Question Format
When converting questions from direct speech into reported speech, the format changes significantly. Unlike statements, questions require rephrasing into a statement format and often involve the use of introductory verbs like ‘asked’ or ‘inquired’. Here are some examples to demonstrate how questions in direct speech are converted into statements in reported speech:
- Direct: “Are you coming to the party?” Reported: She asked if I was coming to the party.
- Direct: “What time is the meeting?” Reported: He inquired what time the meeting was.
- Direct: “Why did you leave early?” Reported: They wanted to know why I had left early.
- Direct: “Can you help me with this?” Reported: She asked if I could help her with that.
- Direct: “Where did you buy this?” Reported: He wondered where I had bought that.
- Direct: “Who is going to the concert?” Reported: They asked who was going to the concert.
- Direct: “How do you solve this problem?” Reported: She questioned how to solve that problem.
- Direct: “Is this the right way to the station?” Reported: He inquired whether it was the right way to the station.
- Direct: “Do you know her name?” Reported: They asked if I knew her name.
- Direct: “Why are they moving out?” Reported: She wondered why they were moving out.
- Direct: “Have you seen my keys?” Reported: He asked if I had seen his keys.
- Direct: “What were they talking about?” Reported: She wanted to know what they had been talking about.
- Direct: “When will you return?” Reported: He asked when I would return.
- Direct: “Can she drive a manual car?” Reported: They inquired if she could drive a manual car.
- Direct: “How long have you been waiting?” Reported: She asked how long I had been waiting.
Reported Speech: Omitting Quotation Marks
In reported speech, quotation marks are not used, differentiating it from direct speech which requires them to enclose the spoken words. Reported speech summarizes or paraphrases what someone said without the need for exact wording. Here are examples showing how direct speech with quotation marks is transformed into reported speech without them:
- Direct: “I am feeling tired,” she said. Reported: She said she was feeling tired.
- Direct: “We will win the game,” he exclaimed. Reported: He exclaimed that they would win the game.
- Direct: “I don’t like apples,” the boy declared. Reported: The boy declared that he didn’t like apples.
- Direct: “You should visit Paris,” she suggested. Reported: She suggested that I should visit Paris.
- Direct: “I will be late,” he warned. Reported: He warned that he would be late.
- Direct: “I can’t believe you did that,” she expressed in surprise. Reported: She expressed her surprise that I had done that.
- Direct: “I need help with this task,” he admitted. Reported: He admitted that he needed help with the task.
- Direct: “I have never been to Italy,” she confessed. Reported: She confessed that she had never been to Italy.
- Direct: “We saw a movie last night,” they mentioned. Reported: They mentioned that they saw a movie the night before.
- Direct: “I am learning to play the piano,” he revealed. Reported: He revealed that he was learning to play the piano.
- Direct: “You must finish your homework,” she instructed. Reported: She instructed that I must finish my homework.
- Direct: “I will call you tomorrow,” he promised. Reported: He promised that he would call me the next day.
- Direct: “I have finished my assignment,” she announced. Reported: She announced that she had finished her assignment.
- Direct: “I cannot attend the meeting,” he apologized. Reported: He apologized for not being able to attend the meeting.
- Direct: “I don’t remember where I put it,” she confessed. Reported: She confessed that she didn’t remember where she put it.
Reported Speech Quiz
Thanks for reading! I hope you found these reported speech examples useful. Before you go, why not try this Reported Speech Quiz and see if you can change indirect speech into reported speech?

What is Reported Speech and how to use it? with Examples
Published by
Olivia Drake
Reported speech and indirect speech are two terms that refer to the same concept, which is the act of expressing what someone else has said.
On this page:
Reported speech is different from direct speech because it does not use the speaker’s exact words. Instead, the reporting verb is used to introduce the reported speech, and the tense and pronouns are changed to reflect the shift in perspective. There are two main types of reported speech: statements and questions.
1. Reported Statements: In reported statements, the reporting verb is usually “said.” The tense in the reported speech changes from the present simple to the past simple, and any pronouns referring to the speaker or listener are changed to reflect the shift in perspective. For example, “I am going to the store,” becomes “He said that he was going to the store.”
2. Reported Questions: In reported questions, the reporting verb is usually “asked.” The tense in the reported speech changes from the present simple to the past simple, and the word order changes from a question to a statement. For example, “What time is it?” becomes “She asked what time it was.”
It’s important to note that the tense shift in reported speech depends on the context and the time of the reported speech. Here are a few more examples:
- Direct speech: “I will call you later.”Reported speech: He said that he would call me later.
- Direct speech: “Did you finish your homework?”Reported speech: She asked if I had finished my homework.
- Direct speech: “I love pizza.”Reported speech: They said that they loved pizza.
When do we use reported speech?
Reported speech is used to report what someone else has said, thought, or written. It is often used in situations where you want to relate what someone else has said without quoting them directly.
Reported speech can be used in a variety of contexts, such as in news reports, academic writing, and everyday conversation. Some common situations where reported speech is used include:
News reports: Journalists often use reported speech to quote what someone said in an interview or press conference.
Business and professional communication: In professional settings, reported speech can be used to summarize what was discussed in a meeting or to report feedback from a customer.
Conversational English: In everyday conversations, reported speech is used to relate what someone else said. For example, “She told me that she was running late.”
Narration: In written narratives or storytelling, reported speech can be used to convey what a character said or thought.
How to make reported speech?
1. Change the pronouns and adverbs of time and place: In reported speech, you need to change the pronouns, adverbs of time and place to reflect the new speaker or point of view. Here’s an example:
Direct speech: “I’m going to the store now,” she said. Reported speech: She said she was going to the store then.
In this example, the pronoun “I” is changed to “she” and the adverb “now” is changed to “then.”
2. Change the tense: In reported speech, you usually need to change the tense of the verb to reflect the change from direct to indirect speech. Here’s an example:
Direct speech: “I will meet you at the park tomorrow,” he said. Reported speech: He said he would meet me at the park the next day.
In this example, the present tense “will” is changed to the past tense “would.”
3. Change reporting verbs: In reported speech, you can use different reporting verbs such as “say,” “tell,” “ask,” or “inquire” depending on the context of the speech. Here’s an example:
Direct speech: “Did you finish your homework?” she asked. Reported speech: She asked if I had finished my homework.
In this example, the reporting verb “asked” is changed to “said” and “did” is changed to “had.”
Overall, when making reported speech, it’s important to pay attention to the verb tense and the changes in pronouns, adverbs, and reporting verbs to convey the original speaker’s message accurately.
How do I change the pronouns and adverbs in reported speech?
1. Changing Pronouns: In reported speech, the pronouns in the original statement must be changed to reflect the perspective of the new speaker. Generally, the first person pronouns (I, me, my, mine, we, us, our, ours) are changed according to the subject of the reporting verb, while the second and third person pronouns (you, your, yours, he, him, his, she, her, hers, it, its, they, them, their, theirs) are changed according to the object of the reporting verb. For example:
Direct speech: “I love chocolate.” Reported speech: She said she loved chocolate.
Direct speech: “You should study harder.” Reported speech: He advised me to study harder.
Direct speech: “She is reading a book.” Reported speech: They noticed that she was reading a book.
2. Changing Adverbs: In reported speech, the adverbs and adverbial phrases that indicate time or place may need to be changed to reflect the perspective of the new speaker. For example:
Direct speech: “I’m going to the cinema tonight.” Reported speech: She said she was going to the cinema that night.
Direct speech: “He is here.” Reported speech: She said he was there.
Note that the adverb “now” usually changes to “then” or is omitted altogether in reported speech, depending on the context.
It’s important to keep in mind that the changes made to pronouns and adverbs in reported speech depend on the context and the perspective of the new speaker. With practice, you can become more comfortable with making these changes in reported speech.
How do I change the tense in reported speech?
In reported speech, the tense of the reported verb usually changes to reflect the change from direct to indirect speech. Here are some guidelines on how to change the tense in reported speech:
Present simple in direct speech changes to past simple in reported speech. For example: Direct speech: “I like pizza.” Reported speech: She said she liked pizza.
Present continuous in direct speech changes to past continuous in reported speech. For example: Direct speech: “I am studying for my exam.” Reported speech: He said he was studying for his exam.
Present perfect in direct speech changes to past perfect in reported speech. For example: Direct speech: “I have finished my work.” Reported speech: She said she had finished her work.
Past simple in direct speech changes to past perfect in reported speech. For example: Direct speech: “I visited my grandparents last weekend.” Reported speech: She said she had visited her grandparents the previous weekend.
Will in direct speech changes to would in reported speech. For example: Direct speech: “I will help you with your project.” Reported speech: He said he would help me with my project.
Can in direct speech changes to could in reported speech. For example: Direct speech: “I can speak French.” Reported speech: She said she could speak French.
Remember that the tense changes in reported speech depend on the tense of the verb in the direct speech, and the tense you use in reported speech should match the time frame of the new speaker’s perspective. With practice, you can become more comfortable with changing the tense in reported speech.
Do I always need to use a reporting verb in reported speech?
No, you do not always need to use a reporting verb in reported speech. However, using a reporting verb can help to clarify who is speaking and add more context to the reported speech.
In some cases, the reported speech can be introduced by phrases such as “I heard that” or “It seems that” without using a reporting verb. For example:
Direct speech: “I’m going to the cinema tonight.” Reported speech with a reporting verb: She said she was going to the cinema tonight. Reported speech without a reporting verb: It seems that she’s going to the cinema tonight.
However, it’s important to note that using a reporting verb can help to make the reported speech more formal and accurate. When using reported speech in academic writing or journalism, it’s generally recommended to use a reporting verb to make the reporting more clear and credible.
Some common reporting verbs include say, tell, explain, ask, suggest, and advise. For example:
Direct speech: “I think we should invest in renewable energy.” Reported speech with a reporting verb: She suggested that they invest in renewable energy.
Overall, while using a reporting verb is not always required, it can be helpful to make the reported speech more clear and accurate
How to use reported speech to report questions and commands?
1. Reporting Questions: When reporting questions, you need to use an introductory phrase such as “asked” or “wondered” followed by the question word (if applicable), subject, and verb. You also need to change the word order to make it a statement. Here’s an example:
Direct speech: “What time is the meeting?” Reported speech: She asked what time the meeting was.
Note that the question mark is not used in reported speech.
2. Reporting Commands: When reporting commands, you need to use an introductory phrase such as “ordered” or “told” followed by the person, to + infinitive, and any additional information. Here’s an example:
Direct speech: “Clean your room!” Reported speech: She ordered me to clean my room.
Note that the exclamation mark is not used in reported speech.
In both cases, the tense of the reported verb should be changed accordingly. For example, present simple changes to past simple, and future changes to conditional. Here are some examples:
Direct speech: “Will you go to the party with me?”Reported speech: She asked if I would go to the party with her. Direct speech: “Please bring me a glass of water.”Reported speech: She requested that I bring her a glass of water.
Remember that when using reported speech to report questions and commands, the introductory phrases and verb tenses are important to convey the intended meaning accurately.
How to make questions in reported speech?
To make questions in reported speech, you need to use an introductory phrase such as “asked” or “wondered” followed by the question word (if applicable), subject, and verb. You also need to change the word order to make it a statement. Here are the steps to make questions in reported speech:
Identify the reporting verb: The first step is to identify the reporting verb in the sentence. Common reporting verbs used to report questions include “asked,” “inquired,” “wondered,” and “wanted to know.”
Change the tense and pronouns: Next, you need to change the tense and pronouns in the sentence to reflect the shift from direct to reported speech. The tense of the verb is usually shifted back one tense (e.g. from present simple to past simple) in reported speech. The pronouns should also be changed as necessary to reflect the shift in perspective from the original speaker to the reporting speaker.
Use an appropriate question word: If the original question contained a question word (e.g. who, what, where, when, why, how), you should use the same question word in the reported question. If the original question did not contain a question word, you can use “if” or “whether” to introduce the reported question.
Change the word order: In reported speech, the word order of the question changes from the inverted form to a normal statement form. The subject usually comes before the verb, unless the original question started with a question word.
Here are some examples of reported questions:
Direct speech: “Did you finish your homework?”Reported speech: He wanted to know if I had finished my homework. Direct speech: “Where are you going?”Reported speech: She wondered where I was going.
Remember that when making questions in reported speech, the introductory phrases and verb tenses are important to convey the intended meaning accurately.
Here you can find more examples of direct and indirect questions
What is the difference between reported speech an indirect speech?
In reported or indirect speech, you are retelling or reporting what someone said using your own words. The tense of the reported speech is usually shifted back one tense from the tense used in the original statement. For example, if someone said, “I am going to the store,” in reported speech you would say, “He/she said that he/she was going to the store.”
The main difference between reported speech and indirect speech is that reported speech usually refers to spoken language, while indirect speech can refer to both spoken and written language. Additionally, indirect speech is a broader term that includes reported speech as well as other ways of expressing what someone else has said, such as paraphrasing or summarizing.
Examples of direct speech to reported
- Direct speech: “I am hungry,” she said. Reported speech: She said she was hungry.
- Direct speech: “Can you pass the salt, please?” he asked. Reported speech: He asked her to pass the salt.
- Direct speech: “I will meet you at the cinema,” he said. Reported speech: He said he would meet her at the cinema.
- Direct speech: “I have been working on this project for hours,” she said. Reported speech: She said she had been working on the project for hours.
- Direct speech: “What time does the train leave?” he asked. Reported speech: He asked what time the train left.
- Direct speech: “I love playing the piano,” she said. Reported speech: She said she loved playing the piano.
- Direct speech: “I am going to the grocery store,” he said. Reported speech: He said he was going to the grocery store.
- Direct speech: “Did you finish your homework?” the teacher asked. Reported speech: The teacher asked if he had finished his homework.
- Direct speech: “I want to go to the beach,” she said. Reported speech: She said she wanted to go to the beach.
- Direct speech: “Do you need help with that?” he asked. Reported speech: He asked if she needed help with that.
- Direct speech: “I can’t come to the party,” he said. Reported speech: He said he couldn’t come to the party.
- Direct speech: “Please don’t leave me,” she said. Reported speech: She begged him not to leave her.
- Direct speech: “I have never been to London before,” he said. Reported speech: He said he had never been to London before.
- Direct speech: “Where did you put my phone?” she asked. Reported speech: She asked where she had put her phone.
- Direct speech: “I’m sorry for being late,” he said. Reported speech: He apologized for being late.
- Direct speech: “I need some help with this math problem,” she said. Reported speech: She said she needed some help with the math problem.
- Direct speech: “I am going to study abroad next year,” he said. Reported speech: He said he was going to study abroad the following year.
- Direct speech: “Can you give me a ride to the airport?” she asked. Reported speech: She asked him to give her a ride to the airport.
- Direct speech: “I don’t know how to fix this,” he said. Reported speech: He said he didn’t know how to fix it.
- Direct speech: “I hate it when it rains,” she said. Reported speech: She said she hated it when it rained.
If you've read this far, you likely found value in our content. We measure the quality of our articles in various ways, and one significant metric is the number of shares. If you appreciated this piece, please spread the word.
Leave a reply cancel reply, i’m olivia.
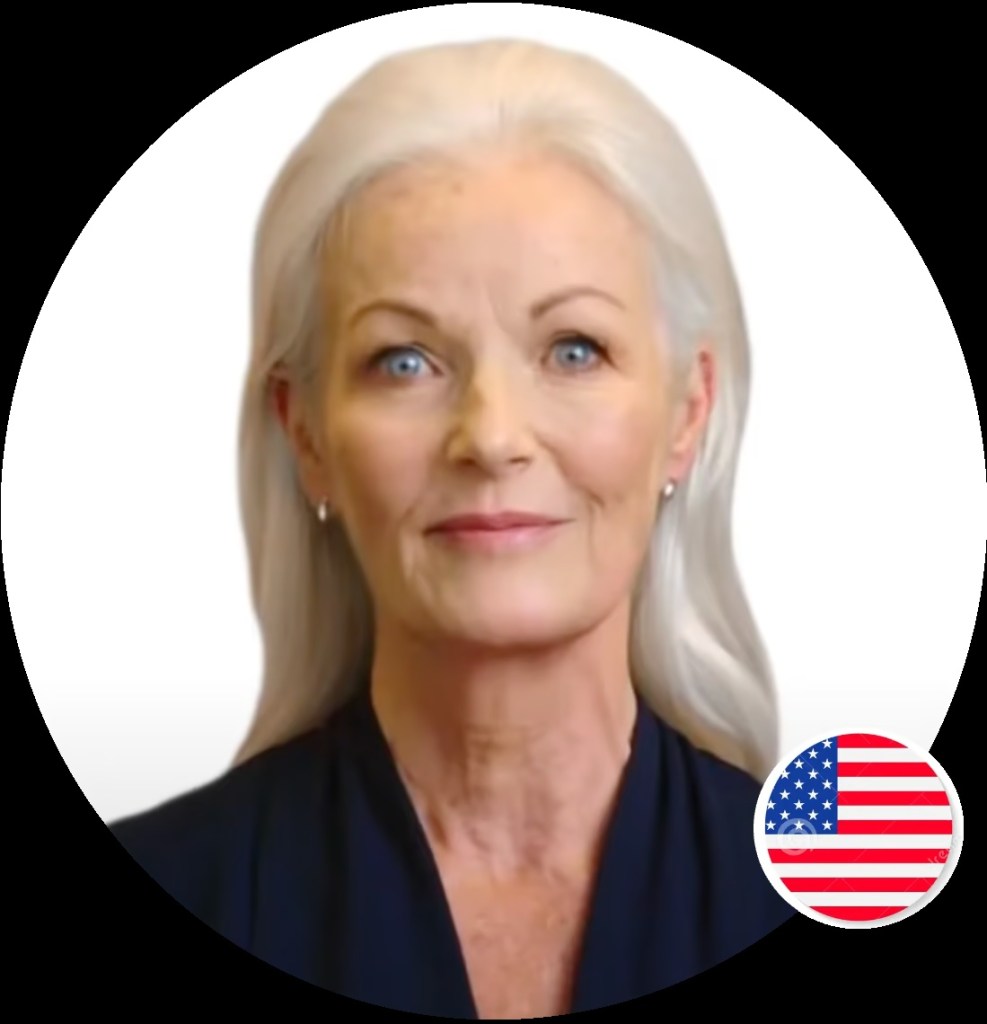

Welcome to my virtual classroom! Join me on a journey of language and learning, where we explore the wonders of English together. Let’s discover the joy of words and education!
Let’s connect
Join the fun!
Stay updated with our latest tutorials and ideas by joining our newsletter.
Type your email…
Recent posts
Modal verbs in conditional sentences with examples, questions in future perfect continuous tense with examples, questions in future perfect tense with examples, questions in future continuous tense with examples, questions in future indefinite (simple) tense with examples, questions in past perfect continuous tense with examples, discover more from fluent english grammar.
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Continue reading
Online Education Reported Speech Exercises for Class 9 CBSE With Answers

This grammar section explains Online Education English Grammar in a clear and simple way. There are example sentences to show how the language is used. You can also visit the most accurate and elaborate NCERT Solutions for Class 9 English . Every question of the textbook has been answered here. https://ncertmcq.com/reported-speech-exercises-for-class-9/
Online Education Reported Speech Exercises for Class 9 CBSE With Answers Pdf
Reported Speech Class 9
Type 1. Statements Steps to be kept in mind for changing direct speech into indirect (statements).
Step 1. The reporting verb is changed as under. (a) We ‘say’ something but we ‘tell’ somebody. Says to …………………………… tells. (b) Says …………………………… says. (c) Said to …………………………… told/asserted/stated/informed. (d) Said …………………………… said.
Step 2. Inverted commas are dropped and the conjunction ‘that’ is used.

Note. These words refer to the speaker. So they change according to who the speaker is.
Reported Speech Class 9 Exercise With Answers
Step 4. If the reporting verb is in the present or future tense, the tense of the reported speech does not change. Meera says to Mini, “Your teacher has praised you.” Meera tells mini that her teacher has praised her.
Reported Speech Exercises For Class 9
Step 5. Words denoting nearness of time and place are generally changed into words denoting distance.
Note. There are two situations where even if the reporting verb is in the past tense, the verb of the reported speech remains unchanged.
1. If the reported speech expresses a universal truth or a habitual fact.
- The teacher said, “Two and two make four.” The teacher said that two and two make four.
- Ramesh said to the tourist, “Summers in India are usually very hot.” Ramesh informed the tourist that summers in India are usually very hot.
2. The reported speech describes a situation which still exists when the speech is reported.
- The stationmaster said, “Due to heavy rains, the trains are running late”.
- The stationmaster said that due to heavy rains, the trains are running late.
Reported Speech Worksheet For Class 9 Pdf
Type 2. Questions
A. If the reported speech is a question, the following changes are made. The reporting verb is changed into ‘asked/required’.
B. The inverted commas are removed and If/whether is used. The question mark is removed and a full stop is placed. No conjunction is used while reporting wh-questions. The direct form is changed to indirect question form. Place the subject before verb in the reported question.
- I said to Meera, “When are your parents coming?” I asked Meera when her parents were coming.
- Ramesh said to me, “Are you reading this book?” Ramesh asked me if/whether I was reading that book.
- He said, “Will you come with me?” He asked if/whether I would go with him.
Reported Speech Class 9 Exercise
Type 3. Commands and Requests
If reporting commands and requests, the indirect speech is introduced by some verbs expressing commands or requests and the imperative mood is changed into the infinitive.
Step 1. The reporting say (said) is changed to order(ed)/request(ed)/advise(d)/command(ed)/ encourage(ed) /shout(ed)/forbid (forbade), proposed, etc.
Step 2. The verb of the reported speech is changed into an infinitive and inverted commas are removed.
Step 3. Do not is changed to ‘not to’.
- He said to his sister, “Please speak slowly.” He requested his sister to speak slowly.
- The teacher said, “Keep quiet.” The teacher ordered to keep quiet.
- He said to me, “Don’t tease the animal.” He advised me not to tease the animal.
- She said to me, “Let us go for a picnic”. She proposed (or suggested) to me that we should go for a picnic.
Class 9 Reported Speech Exercises
Type 4. Exclamations and wishes Step 1. The reporting verb said is changed to exclaimed, wished, prayed, etc. Step 2. The exclamatory form is changed into the statement form and the mark of exclamation is replaced by a full stop. Step 3. The reporting verb is joined with reported speech with ‘that’. Step 4. All interjections are omitted and suitable adverbs or other expressive words are used.
- They said, “Hurrah! We have won the match.” They exclaimed with joy that they had won the match.
- She said, “Alas! He is no more.” A She exclaimed with sorrow that he was no more.
- He said, “Good-bye friends.” He bade good-bye to his friends.
Reported Speech Solved Examples Exercises for Class 9 CBSE
Change the following from direct to indirect speech.
Reported Speech Class 9 Worksheet
Question 1. The doctor said to me, “The climate of this city won’t suit you.” Answer: The doctor told me that the climate of that city wouldn’t suit me.
Question 2. Priya says, “The Earth is round.” Answer: Priya says that the Earth is round.
Question 3. My brother said to his friend, “I am very sleepy.” Answer: My brother told his friend that he was very sleepy.
Question 4. She said, “I have passed the exams.” ‘ Answer: She said that she had passed the exams.
Question 5. My friend said, “Have you ever been to London?” Answer: My friend asked me if I had ever been to London.
Question 6. The policeman said to us, “Where are you going?” Answer: The policeman enquired where we were going.
Question 7. My friend said to me, “Can you solve the problem?” Answer: My friend asked me if/whether I could solve the problem.
Question 8. My mother said to the stranger, “What is the purpose of your coming?” Answer: My mother asked the stranger what was the purpose of his coming.
Question 9. The teacher said to the students, “Complete your work.” [ Answer: The teacher ordered the students to complete their work. ,
Question 10. The Principal said to the parents, “Please sit inside the hall.” | Answer: The Principal requested the parents to sit inside the hall. j
Question 11. Sunil said to his friend, “Don’t forget to recharge your mobile.” i Answer: Sunil reminded his friend not to forget to recharge his mobile.
Question 12. My sister said to me, “Consult a doctor regarding your eyesight.” Answer: My sister advised me to consult a doctor regarding my eyesight. |
Question 13. She said, “May God bless her with a child!” Answer: She said that God might bless her with a child!
Question 14. He said, “What a terrible night it is!” Answer: He exclaimed that it was a terrible night.
Question 15. He said, “Alas! I perish by the people I made. Answer: He confessed with regret that he was perished by the people he had made.
Question 16. He said, “Alas! what a fool I am. Answer: He exclaimed with grief/regret that he was a great fool.
Change the narration of the following sentences from direct to indirect.
Question 17. The saint said, “Go to the Himalayas for meditation.” Answer: The saint ordered to go to the Himalayas for meditation.
Question 18. Sita said to Praveen, “I will return your money tomorrow.” Answer: Sita told Praveen that she would return his money the next day.
Question 19. The news said, “A strong earthquake has hit Japan.” Answer: The news said that a strong earthquake has hit Japan. . ”
Question 20. My uncle said to Sheela, “I have a surprise for you.” Answer: My uncle told Sheela that he had a surprise for her.
Question 21. She said, “Do you want to stay abroad?” Answer: She asked if he wanted to stay abroad.
Question 22. The Met Department announced, “It may rain tomorrow.” Answer: The Met. Department announced that it might rain the next day.
Question 23. I/He said, “How I wish they would come”. Answer: He exclaimed that he wished they would come.
Question 24. Ashu said to his friend, “Are you willing to share your books with me?” Answer: Ashu asked his friend if he was willing to share his books with him.
Question 25. The Major said to the jawans, “Start marching left.” Answer: The major ordered the Jawans to start marching left.
Question 26. Sheetal said to her mother, “Have you ever thought about yourself in life?” Answer: Sheetal asked her mother if she had ever thought about herself in life.
Read the following dialogues and report in indirect narration.
Question 27. Mother : Where were you? Daughter ‘ : I was on the terrace playing. Mother : Please do not go without prior permission. Daughter : This was the first time ever that I went on the terrace. Mother : Remember, do not go there alone. Answer: Mother asked her daughter where she had been. The daughter replied that she had been on the terrace playing. The mother then requested her not to go without prior permission. The daughter apologised saying that that had been the first time ever that she had gone on the terrace. The mother warned her saying not to go there alone.
Question 28. Master : How are you feeling now? Worker : I am feeling batter but I am not completely fine. Master : Do you need more rest? Worker : It is okey. I will report tomorrow. Answer: Master asked his worker how was he feeling then. The worker replied that he was feeling better but was not completely fine. The master further asked him if he needed more rest. The worker replied that that was okey and that he would report the next day.
Question 29. Rajesh : Where are you going, Rohan? Rohan : I am going to the temple to offer flowers. Rajesh : Do you worship everyday and go to the temple? Rohan : Yes, I go to the temple everyday to worship Lord Shiva. Answer: Rajesh asked Rohan where was he going. Rohan replied that he was going to the temple to offer flowers. Rajesh then asked him if he worshipped every day and went to the temple. Rohan replied in the affirmative and said that he went to the temple every day to worship Lord Shivai
Question 30. Teacher : I want all students to quietly do the work. Students : Will you allow us to go for games after this? Teacher : First, all of you have to finish your work. Students : We promise that we will finish our work first. Answer: Teacher instructed the students that she wanted them to quietly do the work. The students asked if she would allow them to go for games after that. The teacher insisted that first, all of them had to finish their work. The students then promised her that they would finish their work first.
Question 31. Father : Why did you go to the market today? Son : I had to buy some material to do my project. Father : Who gave you the project? Son : My science teacher gave the project. Father : Do you need any money for it? Ans. Father asked his son why had he gone to the market that day. Son replied that he had to buy some material to do his project. Father then asked him who had given the project. Son replied that his science teacher had given the project. Father then asked his son if he needed any money for that.
Question 32. Customer : You have a variety of frozen stuff. Shopkeeper : You can buy as much as you like. Customer : Why don’t you keep fresh vegetables? Shopkeeper : Things have become very expensive these days. Customer : You should start keeping good stuff otherwise I shall stop buying from you. Answer: Customer told the shopkeeper that he had a variety of frozen stuff. Shopkeeper replied that he could buy as much as he liked. The customer then asked the shopkeeper why he didn’t keep fresh vegetables. The shopkeeper replied that things had become very expensive those days. The customer warned him that he should start keeping good stuff otherwise, he (customer) would stop buying from him.
Question 33. Doctor : What did you eat yesterday? Patient : I could hardly eat anything as I was having stomachache. Doctor : Are you still having it? Patient : At this moment, I am having fever and feeling weak. Doctor : You most take rest. Answer: Doctor asked the patient what had he eaten the previous day. The patient repled that he could hardly eat anything as he had been having stomachache. Doctor then asked him if he was still having that. The patient replied that at that moment, he was having fever and was feeling weak. The doctor advised him to take rest.
Question 34. Employee : Please grant me two weeks’ leave. Boss : Why do you need it for such a long time? Employee : I have to visit my ailing mother. Boss : Okey, I shall grant you leave but do not overstay your leave. Answer: The employee requested his boss to grant him two weeks’ leave. The boss asked him why he needed leave for such a long time. The employee replied that he had to visit his ailing mother. The boss agreed to grant him leave but instructed him not to overstay his leave.
Question 35. Kanika : Have you seen the animation film released recently? Keshav : I am not allowed to watch films. Kanika : How is this possible in present times? Keshav : My parents are very strict. Answer: Kanika asked Keshav if he had seen the animation film released recently. Keshav replied that he was not allowed to watch films. Kanika further asked how that was possible in present times. Keshav informed that his parents were/are very strict.
Question 36. Hameed : Did you visit the national museum? Shano : How can I as there is nobody to accompany me? Hameed : Do not worry. Shano : I am not worrying but I am the only one who has not seen it. Answer: Hameed asked Shano if she had visited the national museum. Shano replied how she could as there was nobody to accompany her. Hameed told her not to worry. Shano replied taht she was not worrying but she was the only one who had not seen that.
Read the following dialogues and complete the report appropriately.
Question 37. Preeti : Where did you spend your holidays? Naman : I went to many hills stations. ‘ Preeti : Which one did you like the most? Naman : Honestly speaking. I liked all as I am very fond of hills. Preeti asked Naman (a) ………………………….. his holidays. Naman replied, (b) ………………………….. to many hill stations. Preeti then asked him (c) the most. Naman said that honestly speaking (d) ………………………….. of hills. Answer: (a) where he had spent his holidays. (b) that he had gone to many hill stations. (c) which one he had liked. „ (d) he liked all as he was very fond.
Question 38. Archna : Do you know swimming? Rudra : Yes, I do. Archna : Can you teacher me how to swim? Rudra : Yes, I will. Come to my swimming club tomorrow. Archna asked Rudra (a) ………………………….. swimming. Rudra replied in the affirmative. Then, Archna further asked him (b) ………………………….. how to swim. Rudra replied that he (c) ………………………….. he also asked Archna (d) ………………………….. club (e) …………………………. . Answer: (a) if he knew (b) if he could teach her (c) would (d) to go to his swimming (e) the next day.
Question 39. Father : How was the paper? Son : It was easy. I could solve all the problems. Father : Start preparing for the economics paper. You do not have much time left Son : Yes father, I shall immediately start. The father asked his son (a) ………………………….. Son replied that (b) ………………………….. He (c) ………………………….. all the problems. Father further advised him (d) ………………………….. economics paper. He (e) ………………………….. much time left. Son agreed with his father and said that he (f) ………………………….. start. Answer: (a) how the paper had been (b) that had been easy (c) could solve (d) to start preparing for the (e) did not have (f) would immediately
Question 40. Inspector : Were you sleeping when the robbers entered the bank? Guard : No, Sir. The bank had closed and I had just gone to relieve myself. Inspector : What did you see when you came back? Guard : The iron grill lock was broken and the bank looked ransacked but the robbers could not take away anything as I had returned quickly. Inspector : Yes, I can see that not much damage has been done but you have to be more careful in future. Inspector asked the guard (a) ………………………….. entered the bank. Guard replied in the negative and said that the bank had been closed and (b) ………………………….. Inspector further asked him (c) ………………………….. The guard replied that (d) ………………………….. and the bank had looked ransacked, but the robbers (e) ………………………….. as he (f) ………………………….. Inspector said that he (g) ………………………….. but also warned him (h) …………………………. . Answer: (a) if he had been sleeping when the robbers had (b) he had just gone to relieve himself (c) what he had seen when he had come back (d) the iron grill lock had been broken (e) could not take away anything (f) had returned quickly (g) could see that not much damage had been done (h) that he had to be more careful in future.
Question 41. You have learnt how to report questions from direct to indirect speech. Here is a paragraph with direct speech questions. Read them carefully and report into indirect speech. Rewrite the paragraph in the space given below. [NCERT Workbook]
Once an old man asked a young boy, “Who do you think are the most intelligent people?” The young man said in return, “Who do you think so?” The old man said, “How can sons and daughters be intelligent without learning from their parents?” The young man said, “How did you as a parent learn?”
The old man said, “Why are you hijacking my question by asking me back?” The young man said, “Didn’t you know that you as a parent, now have learnt all the things an your own?” The old man said, “How do you say that we all learnt from others?” The young man said, “Why do you ask me about how to operate electronic gadget all the time?” The old man said, “Why can’t I ask you because I have paid for the gadget you use?” Answer: Once an old man asked a young boy who he thought were the most intelligent people. The young man asked why he thought so. The old man further asked how sons and daughters could be intelligent without learning from their parents. The young man asked how he had learnt as a parent. The old man asked why he was hijacking his questions by asking him back.
The young man said if he hadn’t known that he as a parent, then had learnt all the things on his own. The old man said how he learnt that they all learnt from others. The young man said why he asked him how to operate electronic gadget all the time. The old man replied why he couldn’t ask him because he had paid for the gadgets he used.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Reported speech is the form in which one can convey a message said by oneself or someone else, mostly in the past. It can also be said to be the third person view of what someone has said. In this form of speech, you need not use quotation marks as you are not quoting the exact words spoken by the speaker, but just conveying the message. Q2.
Reported speech Exercises for Class 9: In this article, you will be able to brush up your knowledge of reported speech and also work on the exercise to check your understanding of the topic. ... Punit said that his mother was writing letters. Rishav asked Roshni if she had ever been to the Taj Mahal.
Reported Speech Solved Examples Exercises for Class 9 CBSE. Change the following from direct to indirect speech. Type 1. Question 1. The doctor said to me, "The climate of this city won't suit you." Answer: The doctor told me that the climate of that city wouldn't suit me. Question 2. Priya says, "The Earth is round." Answer:
Reported speech is used when someone says a sentence, like, "I'm going to the movie tonight". Later, we want to tell a 3rd person what the first person is doing. It works like this: We use a reporting verb i.e 'say' or 'tell'. In the present tense, just put in 'he says. Direct Speech: I like burgers.
Class 9 English Grammar Reported Speech (Direct and Indirect) Exercise with Answer. Reported Speech - Reported speech refers to recording the speaker's speech, whether it is done directly by recording the speaker's words or indirectly by recording the speaker's words but changing them. For example. Direct speech - Priya said, "I'd ...
In transforming requests and commands into reported speech, tenses are not relevant. We only have to ensure that there are changes in the pronoun and the place and time expression. Reported Speech Exercises Solved Example for Class 9 CBSE. Diagnostic Test 18. Look at the comic strip and complete the passage given below.
Quiz for Reported Speech Exercises for Class 9. Here's a quiz on reported speech for students. Each question presents a direct speech statement, and you need to rewrite it in reported speech. Choose the correct option for each question. Question 1: Direct Speech: "I love playing the guitar." a) He loves playing the guitar.
Direct speech: I like ice cream. Reported speech: She said (that) she liked ice cream. She said (that) she liked ice cream. She said (that) she was living in London. She said (that) she had bought a car OR She said (that) she bought a car. She said (that) she had been walking along the street.
Direct speech: 'Help me, please,' she cried. Indirect speech: She begged them to help her. Reported speech worksheet. Sentences are given in the direct speech. Change them into the indirect / reported speech. 1. 'Leave me alone,' she said. 2. 'I don't know what I am supposed to do,' he said. 3.
Online Test for Reported Speech - English Grammar for Class 9. After completing the Reported Speech it becomes important for students to evaluate themselves how much they have learned from the chapter. Here comes the role of chapter-wise Tests of Reported Speech. EduRev provides you with three to four tests for each chapter.
Direct : The master said to the servant, "Fetch me a glass of water.". Indirect : The master ordered the servant to fetch him a glass of water. Direct : I said to him, "Please bring me a glass of water.". Indirect : I requested him to bring me a glass of water. Direct : I said to my friend, "Please lend me your book.".
Students can access Reported Speech Class 9 Notes absolutely free of cost. These Notes are a success mantra for all the students who want to improve their marks and score well in their examinations. These Notes can be easily downloaded in the PDF Format and can be accessed 24×7. The Notes of Class 9 Reported Speech are also mobile-friendly.
Learn to use reported speech and direct speech correctly in English with this lesson and quiz! 📝 *GET THE FREE LESSON PDF* _here_ 👉🏼 https://bit.ly/PDFRe...
Direct: "I will help you," she promised. Reported: She promised that she would help me. Direct: "You should study harder," he advised. Reported: He advised that I should study harder. Direct: "I didn't take your book," he denied. Reported: He denied taking my book. Direct: "Let's go to the cinema," she suggested.
CBSE Class 9 English Workbook Solutions Unit 7 Reported Speech. Question 1. Read the conversation between a young boy and his mother. The boy is determined to go to camp, despite his mother's refusal to let him (from George Layfon's short story "The Holiday"). It wasn't fair.
Reported speech: She said she was going to the store then. In this example, the pronoun "I" is changed to "she" and the adverb "now" is changed to "then.". 2. Change the tense: In reported speech, you usually need to change the tense of the verb to reflect the change from direct to indirect speech. Here's an example:
Step 1. The reporting verb said is changed to exclaimed, wished, prayed, etc. Step 2. The exclamatory form is changed into the statement form and the mark of exclamation is replaced by a full stop. Step 3. The reporting verb is joined with reported speech with 'that'.
Hello Students,Today we will learn 7 Rules in Reported Speech/ Indirect SpeechClass 8Class 9Class 10You can find the notes and many more study material of th...