How To Present Your Market Research Results And Reports In An Efficient Way

Table of Contents
1) What Is A Market Research Report?
2) Market Research Reports Examples
3) Why Do You Need Market Research Reports
4) How To Make A Market Research Report?
5) Types Of Market Research Reports
6) Challenges & Mistakes Market Research Reports
Market research analyses are the go-to solution for many professionals, and for good reason: they save time, offer fresh insights, and provide clarity on your business. In turn, market research reports will help you to refine and polish your strategy. Plus, a well-crafted report will give your work more credibility while adding weight to any marketing recommendations you offer a client or executive.
But, while this is the case, today’s business world still lacks a way to present market-based research results efficiently. The static, antiquated nature of PowerPoint makes it a bad choice for presenting research discoveries, yet it is still widely used to present results.
Fortunately, things are moving in the right direction. There are online data visualization tools that make it easy and fast to build powerful market research dashboards. They come in handy to manage the outcomes, but also the most important aspect of any analysis: the presentation of said outcomes, without which it becomes hard to make accurate, sound decisions.
Here, we consider the benefits of conducting research analyses while looking at how to write and present market research reports, exploring their value, and, ultimately, getting the very most from your research results by using professional market research software .
Let’s get started.

What Is a Market Research Report?
A market research report is an online reporting tool used to analyze the public perception or viability of a company, product, or service. These reports contain valuable and digestible information like customer survey responses and social, economic, and geographical insights.
On a typical market research results example, you can interact with valuable trends and gain insight into consumer behavior and visualizations that will empower you to conduct effective competitor analysis. Rather than adding streams of tenuous data to a static spreadsheet, a full market research report template brings the outcomes of market-driven research to life, giving users a data analysis tool to create actionable strategies from a range of consumer-driven insights.
With digital market analysis reports, you can make your business more intelligent more efficient, and, ultimately, meet the needs of your target audience head-on. This, in turn, will accelerate your commercial success significantly.
Your Chance: Want to test a market research reporting software? Explore our 14-day free trial & benefit from interactive research reports!
How To Present Your Results: 4 Essential Market Research Report Templates
When it comes to sharing rafts of invaluable information, research dashboards are invaluable.
Any market analysis report example worth its salt will allow everyone to get a firm grip on their results and discoveries on a single page with ease. These dynamic online dashboards also boast interactive features that empower the user to drill down deep into specific pockets of information while changing demographic parameters, including gender, age, and region, filtering the results swiftly to focus on the most relevant insights for the task at hand.
These four market research report examples are different but equally essential and cover key elements required for market survey report success. You can also modify each and use it as a client dashboard .
While there are numerous types of dashboards that you can choose from to adjust and optimize your results, we have selected the top 3 that will tell you more about the story behind them. Let’s take a closer look.
1. Market Research Report: Brand Analysis
Our first example shares the results of a brand study. To do so, a survey has been performed on a sample of 1333 people, information that we can see in detail on the left side of the board, summarizing the gender, age groups, and geolocation.
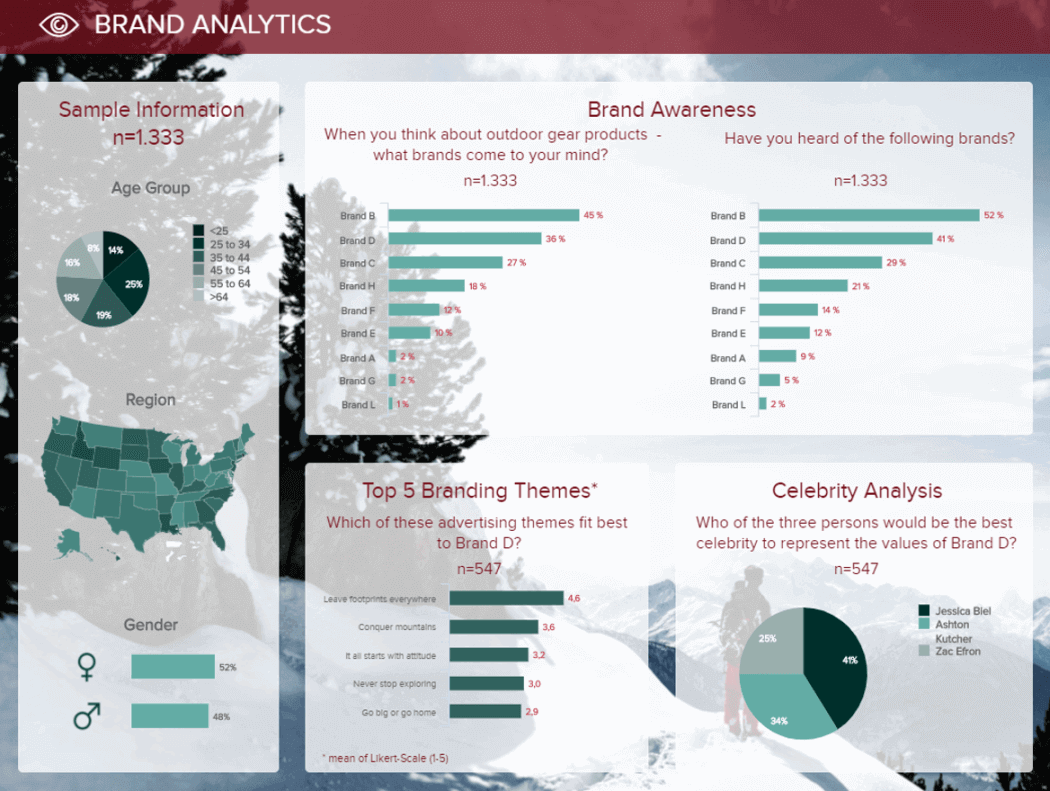
**click to enlarge**
At the dashboard's center, we can see the market-driven research discoveries concerning first brand awareness with and without help, as well as themes and celebrity suggestions, to know which image the audience associates with the brand.
Such dashboards are extremely convenient to share the most important information in a snapshot. Besides being interactive (but it cannot be seen on an image), it is even easier to filter the results according to certain criteria without producing dozens of PowerPoint slides. For instance, I could easily filter the report by choosing only the female answers, only the people aged between 25 and 34, or only the 25-34 males if that is my target audience.
Primary KPIs:
a) Unaided Brand Awareness
The first market research KPI in this most powerful report example comes in the form of unaided brand awareness. Presented in a logical line-style chart, this particular market study report sample KPI is invaluable, as it will give you a clear-cut insight into how people affiliate your brand within their niche.
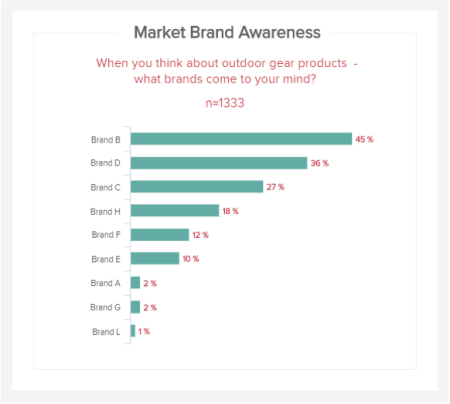
As you can see from our example, based on a specific survey question, you can see how your brand stacks up against your competitors regarding awareness. Based on these outcomes, you can formulate strategies to help you stand out more in your sector and, ultimately, expand your audience.
b) Aided Brand Awareness
This market survey report sample KPI focuses on aided brand awareness. A visualization that offers a great deal of insight into which brands come to mind in certain niches or categories, here, you will find out which campaigns and messaging your target consumers are paying attention to and engaging with.

By gaining access to this level of insight, you can conduct effective competitor research and gain valuable inspiration for your products, promotional campaigns, and marketing messages.
c) Brand image
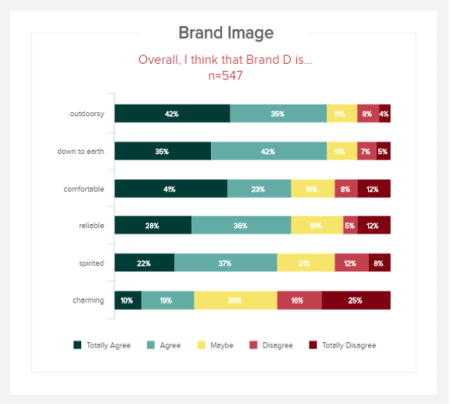
When it comes to research reporting, understanding how others perceive your brand is one of the most golden pieces of information you could acquire. If you know how people feel about your brand image, you can take informed and very specific actions that will enhance the way people view and interact with your business.
By asking a focused question, this visual of KPIs will give you a definitive idea of whether respondents agree, disagree, or are undecided on particular descriptions or perceptions related to your brand image. If you’re looking to present yourself and your message in a certain way (reliable, charming, spirited, etc.), you can see how you stack up against the competition and find out if you need to tweak your imagery or tone of voice - invaluable information for any modern business.
d) Celebrity analysis
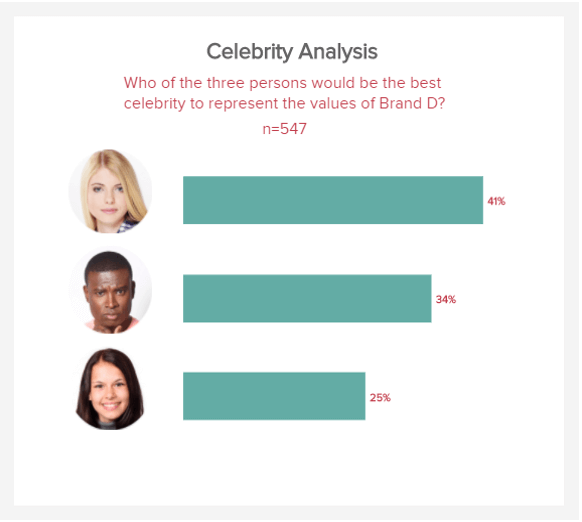
This indicator is a powerful part of our research KPI dashboard on top, as it will give you a direct insight into the celebrities, influencers, or public figures that your most valued consumers consider when thinking about (or interacting with) your brand.
Displayed in a digestible bar chart-style format, this useful metric will not only give you a solid idea of how your brand messaging is perceived by consumers (depending on the type of celebrity they associate with your brand) but also guide you on which celebrities or influencers you should contact.
By working with the right influencers in your niche, you will boost the impact and reach of your marketing campaigns significantly, improving your commercial awareness in the process. And this is the KPI that will make it happen.
2. Market Research Results On Customer Satisfaction
Here, we have some of the most important data a company should care about: their already-existing customers and their perception of their relationship with the brand. It is crucial when we know that it is five times more expensive to acquire a new consumer than to retain one.
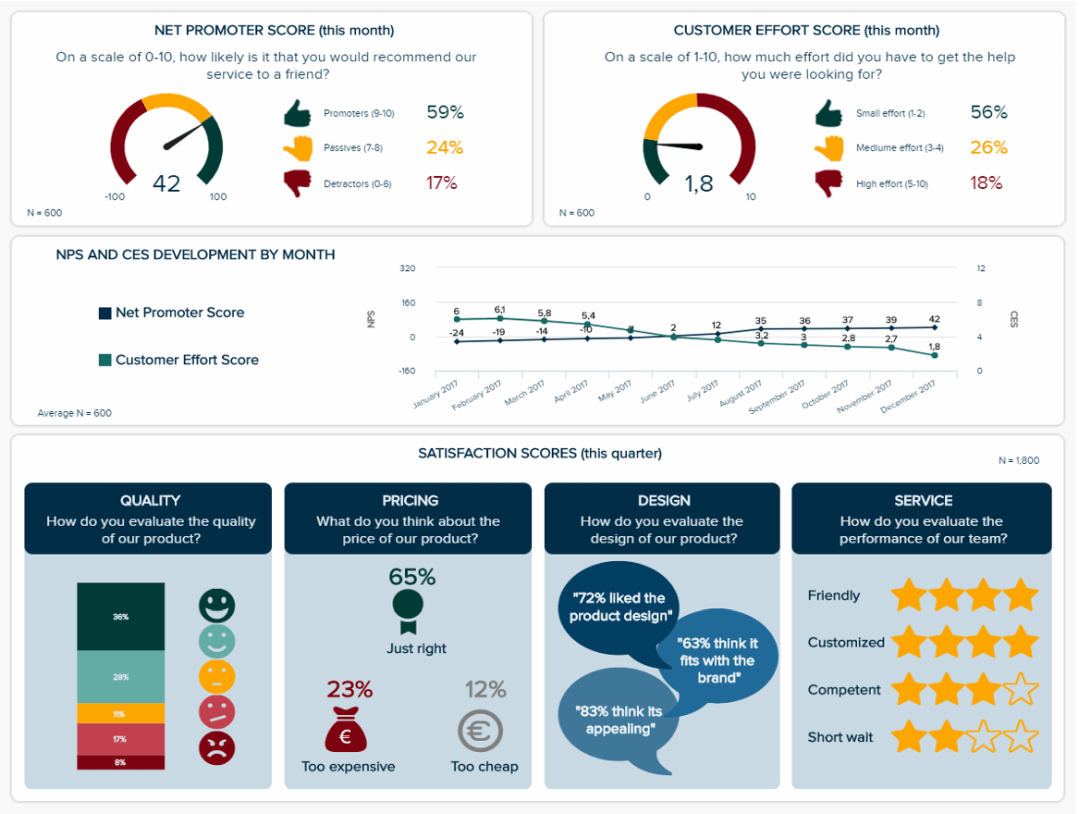
This is why tracking metrics like the customer effort score or the net promoter score (how likely consumers are to recommend your products and services) is essential, especially over time. You need to improve these scores to have happy customers who will always have a much bigger impact on their friends and relatives than any of your amazing ad campaigns. Looking at other satisfaction indicators like the quality, pricing, and design, or the service they received is also a best practice: you want a global view of your performance regarding customer satisfaction metrics .
Such research results reports are a great tool for managers who do not have much time and hence need to use them effectively. Thanks to these dashboards, they can control data for long-running projects anytime.
Primary KPIs :
a) Net Promoter Score (NPS)
Another pivotal part of any informative research presentation is your NPS score, which will tell you how likely a customer is to recommend your brand to their peers.
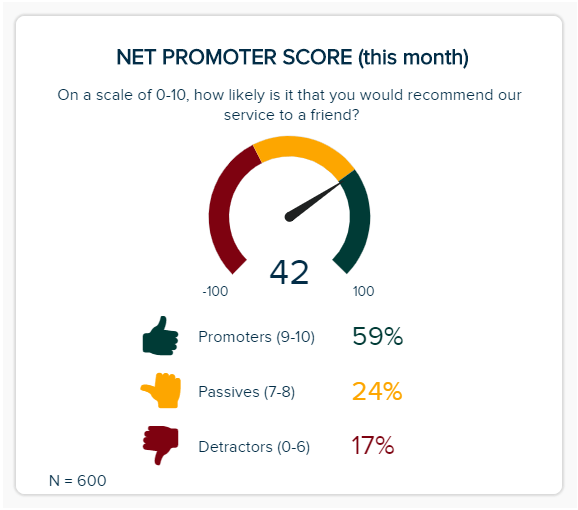
Centered on overall customer satisfaction, your NPS Score can cover the functions and output of many departments, including marketing, sales, and customer service, but also serve as a building block for a call center dashboard . When you’re considering how to present your research effectively, this balanced KPI offers a masterclass. It’s logical, it has a cohesive color scheme, and it offers access to vital information at a swift glance. With an NPS Score, customers are split into three categories: promoters (those scoring your service 9 or 10), passives (those scoring your service 7 or 8), and detractors (those scoring your service 0 to 6). The aim of the game is to gain more promoters. By gaining an accurate snapshot of your NPS Score, you can create intelligent strategies that will boost your results over time.
b) Customer Satisfaction Score (CSAT)
The next in our examples of market research reports KPIs comes in the form of the CSAT. The vast majority of consumers that have a bad experience will not return. Honing in on your CSAT is essential if you want to keep your audience happy and encourage long-term consumer loyalty.
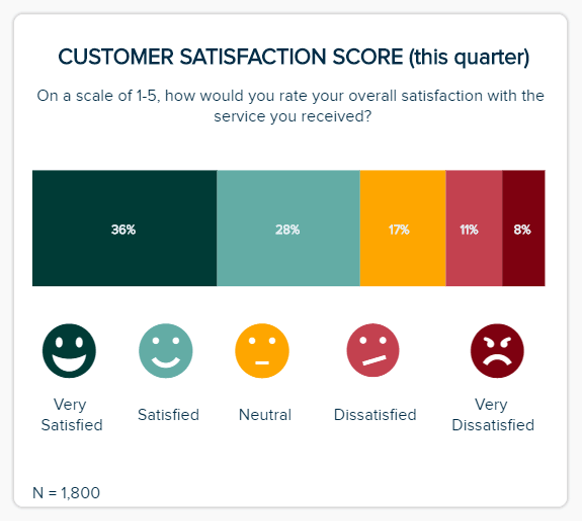
This magnificent, full report KPI will show how satisfied customers are with specific elements of your products or services. Getting to grips with these scores will allow you to pinpoint very specific issues while capitalizing on your existing strengths. As a result, you can take measures to improve your CSAT score while sharing positive testimonials on your social media platforms and website to build trust.
c) Customer Effort Score (CES)
When it comes to presenting research findings, keeping track of your CES Score is essential. The CES Score KPI will give you instant access to information on how easy or difficult your audience can interact with or discover your company based on a simple scale of one to ten.
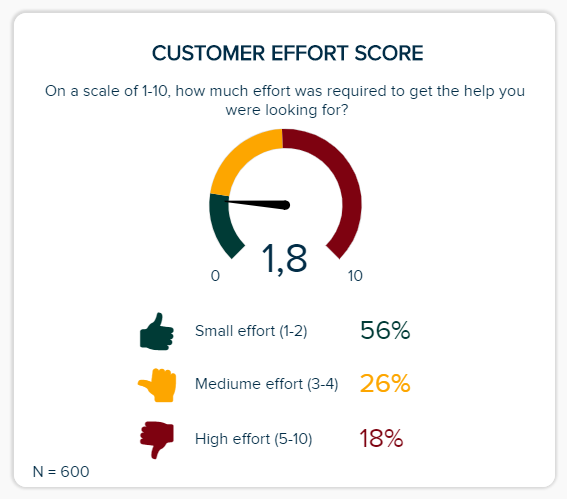
By getting a clear-cut gauge of how your customers find engagement with your brand, you can iron out any weaknesses in your user experience (UX) offerings while spotting any friction, bottlenecks, or misleading messaging. In doing so, you can boost your CES score, satisfy your audience, and boost your bottom line.
3. Market Research Results On Product Innovation
This final market-driven research example report focuses on the product itself and its innovation. It is a useful report for future product development and market potential, as well as pricing decisions.
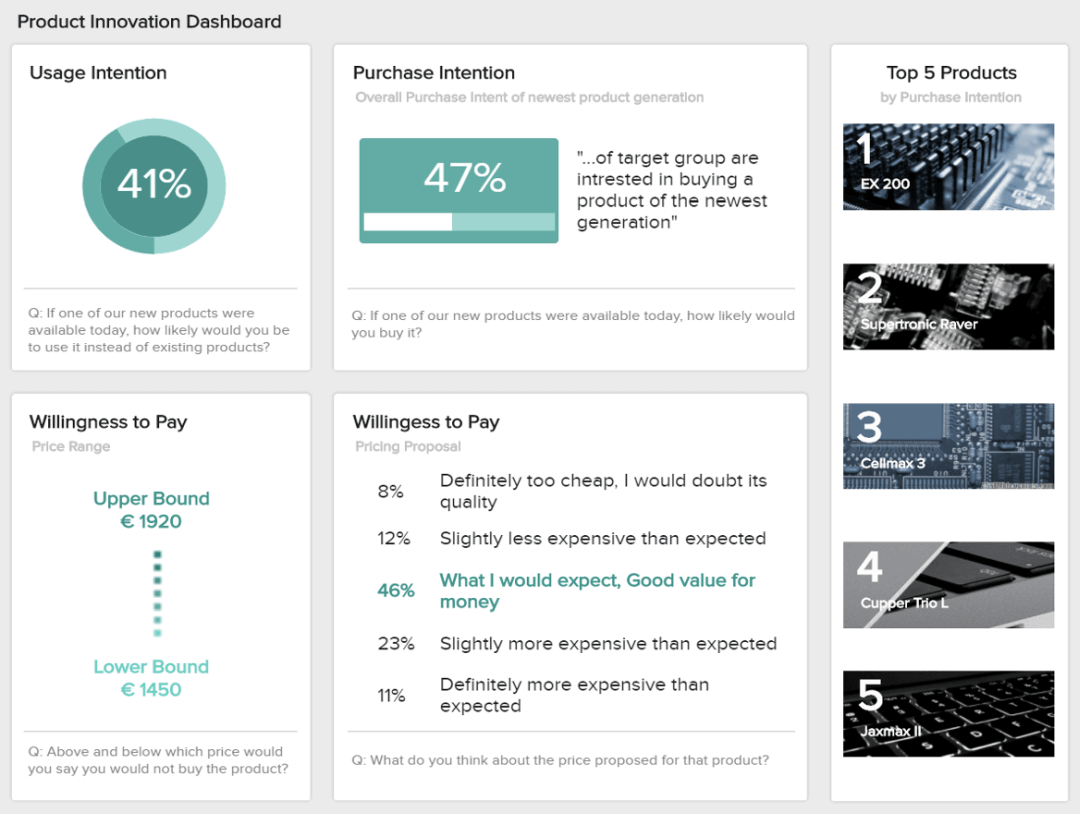
Using the same sample of surveyed people as for the first market-focused analytical report , they answer questions about their potential usage and purchase of the said product. It is good primary feedback on how the market would receive the new product you would launch. Then comes the willingness to pay, which helps set a price range that will not be too cheap to be trusted nor too expensive for what it is. That will be the main information for your pricing strategy.
a) Usage Intention
The first of our product innovation KPI-based examples comes in the form of usage intention. When you’re considering how to write a market research report, including metrics centered on consumer intent is critical.
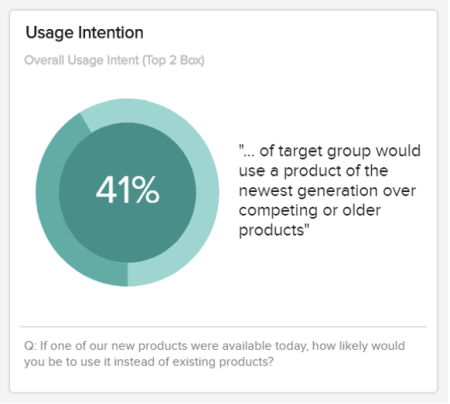
This simple yet effective visualization will allow you to understand not only how users see your product but also whether they prefer previous models or competitor versions . While you shouldn’t base all of your product-based research on this KPI, it is very valuable, and you should use it to your advantage frequently.
b) Purchase Intention
Another aspect to consider when looking at how to present market research data is your audience’s willingness or motivation to purchase your product. Offering percentage-based information, this effective KPI provides a wealth of at-a-glance information to help you make accurate forecasts centered on your product and service offerings.
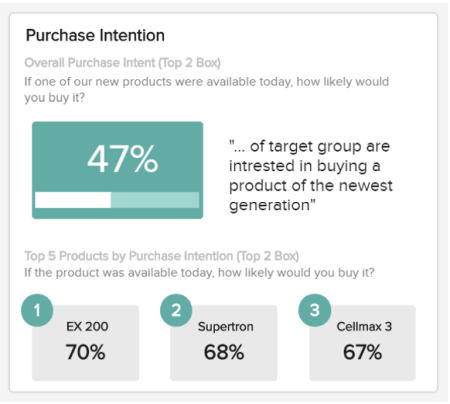
Analyzing this information regularly will give you the confidence and direction to develop strategies that will steer you to a more prosperous future, meeting the ever-changing needs of your audience on an ongoing basis.
c) Willingness To Pay (WPS)
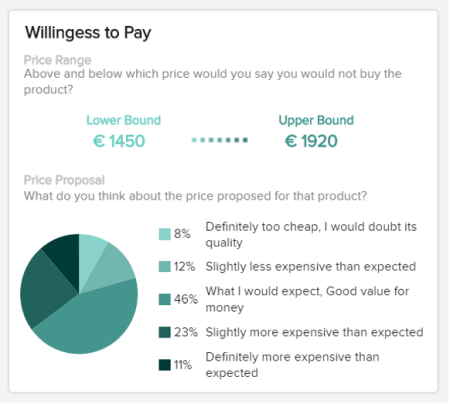
Our final market research example KPI is based on how willing customers are to pay for a particular service or product based on a specific set of parameters. This dynamic visualization, represented in an easy-to-follow pie chart, will allow you to realign the value of your product (USPs, functions, etc.) while setting price points that are most likely to result in conversions. This is a market research presentation template that every modern organization should use to its advantage.
4. Market Research Report On Customer Demographics
This particular example of market research report, generated with a modern dashboard creator , is a powerful tool, as it displays a cohesive mix of key demographic information in one intuitive space.
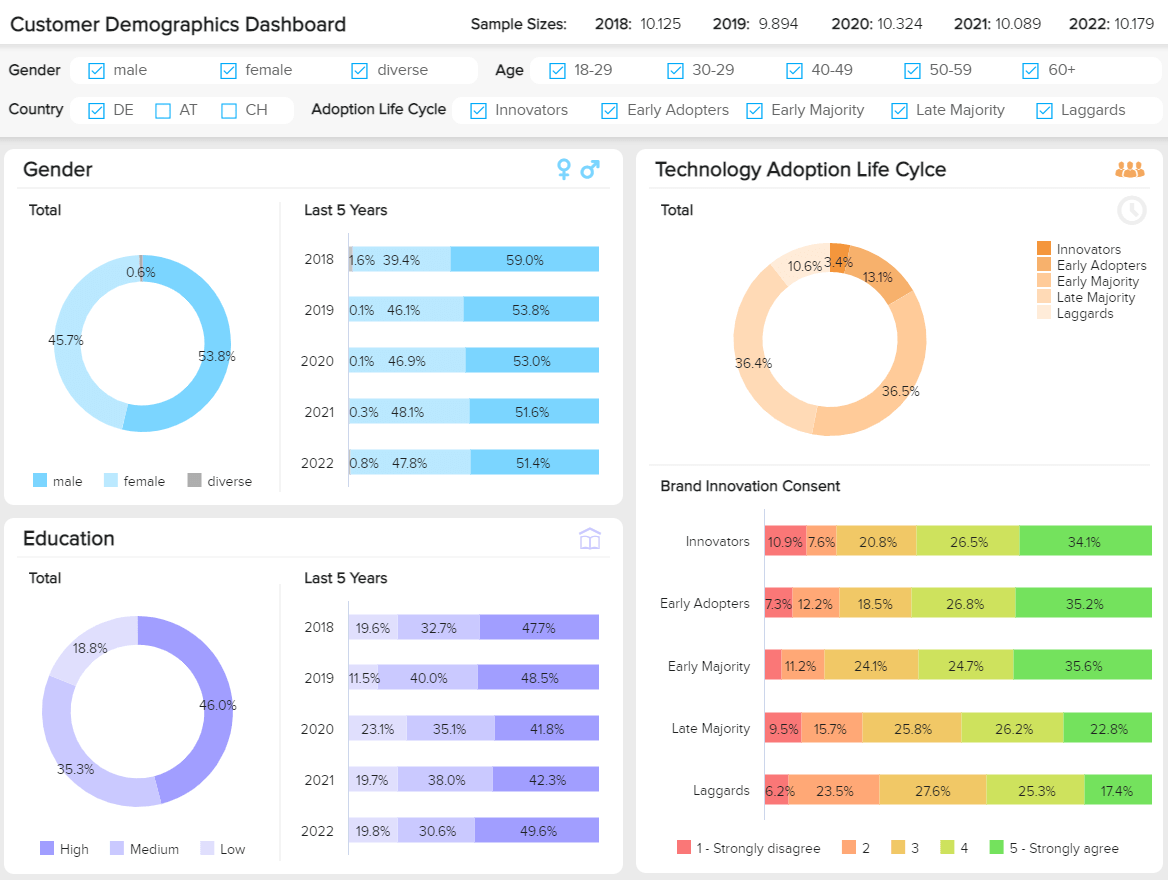
By breaking down these deep pockets of consumer-centric information, you can gain the power to develop more impactful customer communications while personalizing every aspect of your target audience’s journey across every channel or touchpoint. As a result, you can transform theoretical insights into actionable strategies that will result in significant commercial growth.
Every section of this responsive marketing research report works in unison to build a profile of your core audience in a way that will guide your company’s consumer-facing strategies with confidence. With in-depth visuals based on gender, education level, and tech adoption, you have everything you need to speak directly to your audience at your fingertips.
Let’s look at the key performance indicators (KPIs) of this invaluable market research report example in more detail.
a) Customer By Gender
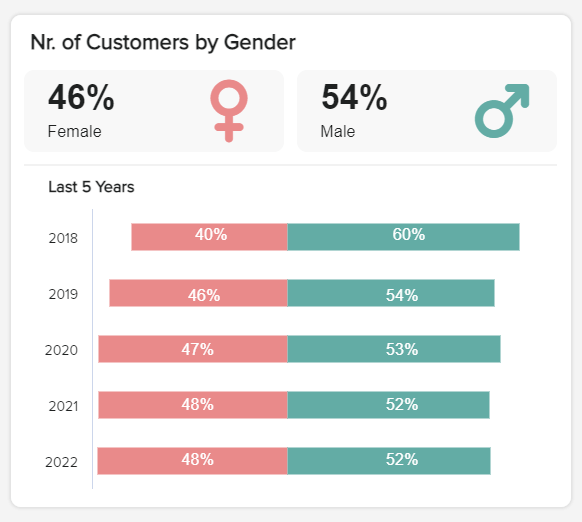
This KPI is highly visual and offers a clear-cut representation of your company’s gender share over time. By gaining access to this vital information, you can deliver a more personalized experience to specific audience segments while ensuring your messaging is fair, engaging, and inclusive.
b) Customers by education level
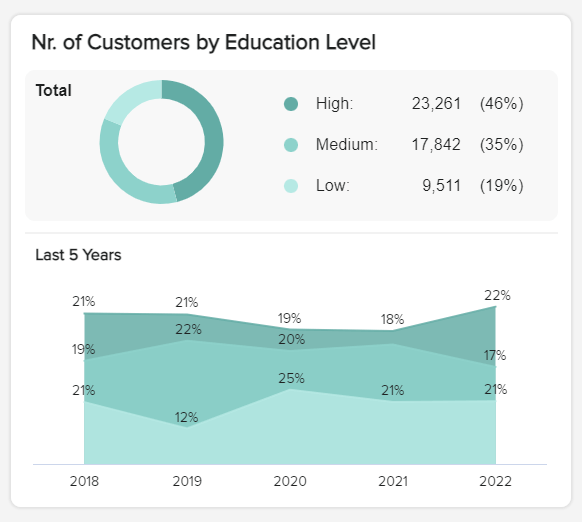
The next market analysis report template is a KPI that provides a logical breakdown of your customers’ level of education. By using this as a demographic marker, you can refine your products to suit the needs of your audience while crafting your content in a way that truly resonates with different customer groups.
c) Customers by technology adoption
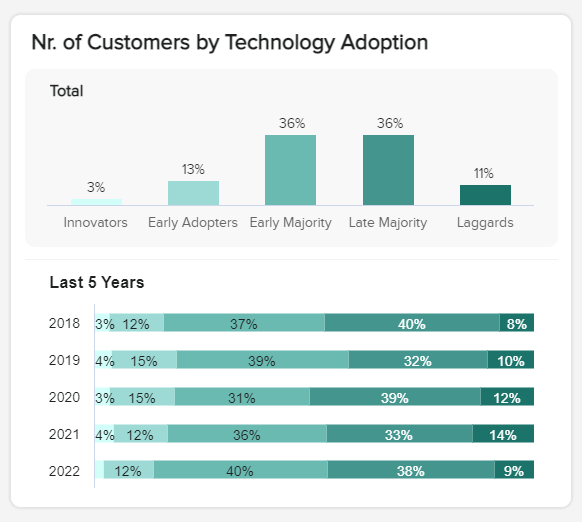
Particularly valuable if you’re a company that sells tech goods or services, this linear KPI will show you where your customers are in terms of technological know-how or usage. By getting to grips with this information over time, you can develop your products or services in a way that offers direct value to your consumers while making your launches or promotions as successful as possible.
d) Customer age groups
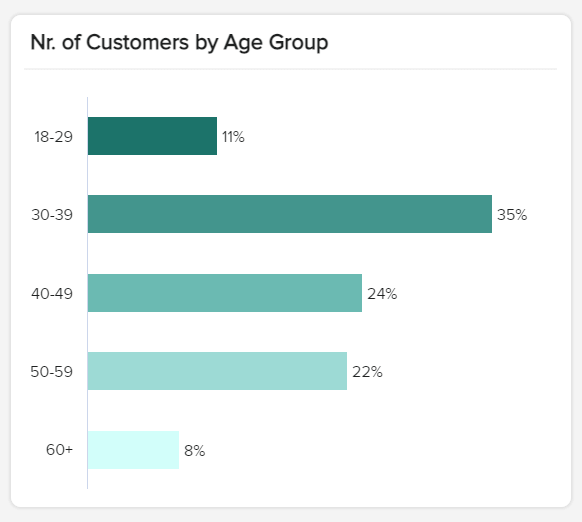
By understanding your customers’ age distribution in detail, you can gain a deep understanding of their preferences. And that’s exactly what this market research report sample KPI does. Presented in a bar chart format, this KPI will give you a full breakdown of your customers’ age ranges, allowing you to build detailed buyer personas and segment your audience effectively.
Why Do You Need Market Research Reports?
As the adage goes, “Look before you leap“ – which is exactly what a research report is here for. As the headlights of a car, they will show you the pitfalls and fast lanes on your road to success: likes and dislikes of a specific market segment in a certain geographical area, their expectations, and readiness. Among other things, a research report will let you:
- Get a holistic view of the market : learn more about the target market and understand the various factors involved in the buying decisions. A broader view of the market lets you benchmark other companies you do not focus on. This, in turn, will empower you to gather the industry data that counts most. This brings us to our next point.
- Curate industry information with momentum: Whether you’re looking to rebrand, improve on an existing service, or launch a new product, time is of the essence. By working with the best market research reports created with modern BI reporting tools , you can visualize your discoveries and data, formatting them in a way that not only unearths hidden insights but also tells a story - a narrative that will gain a deeper level of understanding into your niche or industry. The features and functionality of a market analysis report will help you grasp the information that is most valuable to your organization, pushing you ahead of the pack in the process.
- Validate internal research: Doing the internal analysis is one thing, but double-checking with a third party also greatly helps avoid getting blinded by your own data.
- Use actionable data and make informed decisions: Once you understand consumer behavior as well as the market, your competitors, and the issues that will affect the industry in the future, you are better armed to position your brand. Combining all of it with the quantitative data collected will allow you to more successful product development. To learn more about different methods, we suggest you read our guide on data analysis techniques .
- Strategic planning: When you want to map out big-picture organizational goals, launch a new product development, plan a geographic market expansion, or even a merger and acquisition – all of this strategic thinking needs solid foundations to fulfill the variety of challenges that come along.
- Consistency across the board: Collecting, presenting, and analyzing your results in a way that’s smarter, more interactive, and more cohesive will ensure your customer communications, marketing campaigns, user journey, and offerings meet your audience’s needs consistently across the board. The result? Faster growth, increased customer loyalty, and more profit.
- Better communication: The right market research analysis template (or templates) will empower everyone in the company with access to valuable information - the kind that is relevant and comprehensible. When everyone is moving to the beat of the same drum, they will collaborate more effectively and, ultimately, push the venture forward thanks to powerful online data analysis techniques.
- Centralization: Building on the last point, using a powerful market research report template in the form of a business intelligence dashboard will make presenting your findings to external stakeholders and clients far more effective, as you can showcase a wealth of metrics, information, insights, and invaluable feedback from one centralized, highly visual interactive screen.
- Brand reputation: In the digital age, brand reputation is everything. By making vital improvements in all of the key areas above, you will meet your customers’ needs head-on with consistency while finding innovative ways to stand out from your competitors. These are the key ingredients of long-term success.
How To Present Market Research Analysis Results?

Here we look at how you should present your research reports, considering the steps it takes to connect with the outcomes you need to succeed:
- Collect your data
As with any reporting process, you first and foremost need to collect the data you’ll use to conduct your studies. Businesses conduct research studies to analyze their brand awareness, identity, and influence in the market. For product development and pricing decisions, among many others. That said, there are many ways to collect information for a market research report. Among some of the most popular ones, we find:
- Surveys: Probably the most common way to collect research data, surveys can come in the form of open or closed questions that can be answered anonymously. They are the cheapest and fastest way to collect insights about your customers and business.
- Interviews : These are face-to-face discussions that allow the researcher to analyze responses as well as the body language of the interviewees. This method is often used to define buyer personas by analyzing the subject's budget, job title, lifestyle, wants, and needs, among other things.
- Focus groups : This method involves a group of people discussing a topic with a mediator. It is often used to evaluate a new product or new feature or to answer a specific question that the researcher might have.
- Observation-based research : In this type of research, the researcher or business sits back and watches customers interact with the product without any instructions or help. It allows us to identify pain points as well as strong features.
- Market segmentation : This study allows you to identify and analyze potential market segments to target. Businesses use it to expand into new markets and audiences.
These are just a few of the many ways in which you can gather your information. The important point is to keep the research objective as straightforward as possible. Supporting yourself with professional BI solutions to clean, manage, and present your insights is probably the smartest choice.
2. Hone in on your research:
When looking at how to source consumer research in a presentation, you should focus on two areas: primary and secondary research. Primary research comes from your internal data, monitoring existing organizational practices, the effectiveness of sales, and the tools used for communication, for instance. Primary research also assesses market competition by evaluating the company plans of the competitors. Secondary research focuses on existing data collected by a third party, information used to perform benchmarking and market analysis. Such metrics help in deciding which market segments are the ones the company should focus its efforts on or where the brand is standing in the minds of consumers. Before you start the reporting process, you should set your goals, segmenting your research into primary and secondary segments to get to grips with the kind of information you need to work with to achieve effective results.
3. Segment your customers:
To give your market research efforts more context, you should segment your customers into different groups according to the preferences outlined in the survey or feedback results or by examining behavioral or demographic data.
If you segment your customers, you can tailor your market research and analysis reports to display only the information, charts, or graphics that will provide actionable insights into their wants, needs, or industry-based pain points.
- Identify your stakeholders:
Once you’ve drilled down into your results and segmented your consumer groups, it’s important to consider the key stakeholders within the organization that will benefit from your information the most.
By looking at both internal and external stakeholders, you will give your results a path to effective presentation, gaining the tools to understand which areas of feedback or data are most valuable, as well as most redundant. As a consequence, you will ensure your results are concise and meet the exact information needs of every stakeholder involved in the process.
- Set your KPIs:
First, remember that your reports should be concise and accurate - straight to the point without omitting any essential information. Work to ensure your insights are clean and organized, with participants grouped into relevant categories (demographics, profession, industry, education, etc.). Once you’ve organized your research, set your goals, and cleaned your data, you should set your KPIs to ensure your report is populated with the right visualizations to get the job done. Explore our full library of interactive KPI examples for inspiration.
- Include competitor’s analysis
Whether you are doing product innovation research, customer demographics, pricing, or any other, including some level of insights about competitors in your reports is always recommended as it can help your business or client better understand where they stand in the market. That being said, competitor analysis is not as easy as picking a list of companies in the same industry and listing them. Your main competitor can be just a company's division in an entirely different industry. For example, Apple Music competes with Spotify even though Apple is a technology company. Therefore, it is important to carefully analyze competitors from a general but detailed level.
Providing this kind of information in your reports can also help you find areas that competitors are not exploiting or that are weaker and use them to your advantage to become a market leader.
- Produce your summary:
To complement your previous efforts, writing an executive summary of one or two pages that will explain the general idea of the report is advisable. Then come the usual body parts:
- An introduction providing background information, target audience, and objectives;
- The qualitative research describes the participants in the research and why they are relevant to the business;
- The survey research outlines the questions asked and answered;
- A summary of the insights and metrics used to draw the conclusions, the research methods chosen, and why;
- A presentation of the findings based on your research and an in-depth explanation of these conclusions.
- Use a mix of visualizations:
When presenting your results and discoveries, you should aim to use a balanced mix of text, graphs, charts, and interactive visualizations.
Using your summary as a guide, you should decide which type of visualization will present each specific piece of market research data most effectively (often, the easier to understand and more accessible, the better).
Doing so will allow you to create a story that will put your research information into a living, breathing context, providing a level of insight you need to transform industry, competitor, or consumer info or feedback into actionable strategies and initiatives.
- Be careful not to mislead
Expanding on the point above, using a mix of visuals can prove highly valuable in presenting your results in an engaging and understandable way. That being said, when not used correctly, graphs and charts can also become misleading. This is a popular practice in the media, news, and politics, where designers tweak the visuals to manipulate the masses into believing a certain conclusion. This is a very unethical practice that can also happen by mistake when you don’t pick the right chart or are not using it in the correct way. Therefore, it is important to outline the message you are trying to convey and pick the chart type that will best suit those needs.
Additionally, you should also be careful with the data you choose to display, as it can also become misleading. This can happen if you, for example, cherry-pick data, which means only showing insights that prove a conclusion instead of the bigger picture. Or confusing correlation with causation, which means assuming that because two events happened simultaneously, one caused the other.
Being aware of these practices is of utmost importance as objectivity is crucial when it comes to dealing with data analytics, especially if you are presenting results to clients. Our guides on misleading statistics and misleading data visualizations can help you learn more about this important topic.
- Use professional dashboards:
To optimize your market research discoveries, you must work with a dynamic business dashboard . Not only are modern dashboards presentable and customizable, but they will offer you past, predictive, and real-time insights that are accurate, interactive, and yield long-lasting results.
All market research reports companies or businesses gathering industry or consumer-based information will benefit from professional dashboards, as they offer a highly powerful means of presenting your data in a way everyone can understand. And when that happens, everyone wins.
Did you know? The interactive nature of modern dashboards like datapine also offers the ability to quickly filter specific pockets of information with ease, offering swift access to invaluable insights.
- Prioritize interactivity
The times when reports were static are long gone. Today, to extract the maximum value out of your research data, you need to be able to explore the information and answer any critical questions that arise during the presentation of results. To do so, modern reporting tools provide multiple interactivity features to help you bring your research results to life.
For instance, a drill-down filter lets you go into lower levels of hierarchical data without generating another graph. For example, imagine you surveyed customers from 10 different countries. In your report, you have a chart displaying the number of customers by country, but you want to analyze a specific country in detail. A drill down filter would enable you to click on a specific country and display data by city on that same chart. Even better, a global filter would allow you to filter the entire report to show only results for that specific country.
Through the use of interactive filters, such as the one we just mentioned, you’ll not only make the presentation of results more efficient and profound, but you’ll also avoid generating pages-long reports to display static results. All your information will be displayed in a single interactive page that can be filtered and explored upon need.
- Customize the reports
This is a tip that is valuable for any kind of research report, especially when it comes to agencies that are reporting to external clients. Customizing the report to match your client’s colors, logo, font, and overall branding will help them grasp the data better, thanks to a familiar environment. This is an invaluable tip as often your audience will not feel comfortable dealing with data and might find it hard to understand or intimidating. Therefore, providing a familiar look that is also interactive and easier to understand will keep them engaged and collaborative throughout the process.
Plus, customizing the overall appearance of the report will also make your agency look more professional, adding extra value to your service.
- Know your design essentials
When you’re presenting your market research reports sample to internal or external stakeholders, having a firm grasp on fundamental design principles will make your metrics and insights far more persuasive and compelling.
By arranging your metrics in a balanced and logical format, you can guide users toward key pockets of information exactly when needed. In turn, this will improve decision-making and navigation, making your reports as impactful as possible.
For essential tips, read our 23 dashboard design principles & best practices to enhance your analytics process.
- Think of security and privacy
Cyberattacks are increasing at a concerning pace, making security a huge priority for organizations of all sizes today. The costs of having your sensitive information leaked are not only financial but also reputational, as customers might not trust you again if their data ends up in the wrong hands. Given that market research analysis is often performed by agencies that handle data from clients, security and privacy should be a top priority.
To ensure the required security and privacy, it is necessary to invest in the right tools to present your research results. For instance, tools such as datapine offer enterprise-level security protocols that ensure your information is encrypted and protected at all times. Plus, the tool also offers additional security features, such as being able to share your reports through a password-protected URL or to set viewer rights to ensure only the right people can access and manipulate the data.
- Keep on improving & evolving
Each time you gather or gain new marketing research reports or market research analysis report intel, you should aim to refine your existing dashboards to reflect the ever-changing landscape around you.
If you update your reports and dashboards according to the new research you conduct and new insights you connect with, you will squeeze maximum value from your metrics, enjoying consistent development in the process.
Types of Market Research Reports: Primary & Secondary Research
With so many market research examples and such little time, knowing how to best present your insights under pressure can prove tricky.
To squeeze every last drop of value from your market research efforts and empower everyone with access to the right information, you should arrange your information into two main groups: primary research and secondary research.
A. Primary research
Primary research is based on acquiring direct or first-hand information related to your industry or sector and the customers linked to it.
Exploratory primary research is an initial form of information collection where your team might set out to identify potential issues, opportunities, and pain points related to your business or industry. This type of research is usually carried out in the form of general surveys or open-ended consumer Q&As, which nowadays are often performed online rather than offline .
Specific primary research is definitive, with information gathered based on the issues, information, opportunities, or pain points your business has already uncovered. When doing this kind of research, you can drill down into a specific segment of your customers and seek answers to the opportunities, issues, or pain points in question.
When you’re conducting primary research to feed into your market research reporting efforts, it’s important to find reliable information sources. The most effective primary research sources include:
- Consumer-based statistical data
- Social media content
- Polls and Q&A
- Trend-based insights
- Competitor research
- First-hand interviews
B. Secondary research
Secondary research refers to every strand of relevant data or public records you have to gain a deeper insight into your market and target consumers. These sources include trend reports, market stats, industry-centric content, and sales insights you have at your disposal. Secondary research is an effective way of gathering valuable intelligence about your competitors.
You can gather very precise, insightful secondary market research insights from:
- Public records and resources like Census data, governmental reports, or labor stats
- Commercial resources like Gartner, Statista, or Forrester
- Articles, documentaries, and interview transcripts
Another essential branch of both primary and secondary research is internal intelligence. When it comes to efficient market research reporting examples that will benefit your organization, looking inward is a powerful move.
Existing sales, demographic, or marketing performance insights will lead you to valuable conclusions. Curating internal information will ensure your market research discoveries are well-rounded while helping you connect with the information that will ultimately give you a panoramic view of your target market.
By understanding both types of research and how they can offer value to your business, you can carefully choose the right informational sources, gather a wide range of intelligence related to your specific niche, and, ultimately, choose the right market research report sample for your specific needs.
If you tailor your market research report format to the type of research you conduct, you will present your visualizations in a way that provides the right people with the right insights, rather than throwing bundles of facts and figures on the wall, hoping that some of them stick.
Taking ample time to explore a range of primary and secondary sources will give your discoveries genuine context. By doing so, you will have a wealth of actionable consumer and competitor insights at your disposal at every stage of your organization’s development (a priceless weapon in an increasingly competitive digital age).
Dynamic market research is the cornerstone of business development, and a dashboard builder is the vessel that brings these all-important insights to life. Once you get into that mindset, you will ensure that your research results always deliver maximum value.
Common Challenges & Mistakes Of Market Research Reporting & Analysis
We’ve explored different types of market research analysis examples and considered how to conduct effective research. Now, it’s time to look at the key mistakes of market research reporting. Let’s start with the mistakes.
The mistakes
One of the biggest mistakes that stunt the success of a company’s market research efforts is strategy. Without taking the time to gather an adequate mix of insights from various sources and define your key aims or goals, your processes will become disjointed. You will also suffer from a severe lack of organizational vision.
For your market research-centric strategy to work, everyone within the company must be on the same page. Your core aims and objectives must align throughout the business, and everyone must be clear on their specific role. If you try to craft a collaborative strategy and decide on your informational sources from the very start of your journey, your strategy will deliver true growth and intelligence.
- Measurement
Another classic market research mistake is measurement – or, more accurately, a lack of precise measurement. When embarking on market intelligence gathering processes, many companies fail to select the right KPIs and set the correct benchmarks for the task at hand. Without clearly defined goals, many organizations end up with a market analysis report format that offers little or no value in terms of decision-making or market insights.
To drive growth with your market research efforts, you must set clearly defined KPIs that align with your specific goals, aims, and desired outcomes.
- Competition
A common mistake among many new or scaling companies is failing to explore and examine the competition. This will leave you with gaping informational blindspots. To truly benefit from market research, you must gather valuable nuggets of information from every key source available. Rather than solely looking at your consumers and the wider market (which is incredibly important), you should take the time to see what approach your direct competitors have adopted while getting to grips with the content and communications.
One of the most effective ways of doing so (and avoiding such a monumental market research mistake) is by signing up for your competitors’ mailing lists, downloading their apps, and examining their social media content. This will give you inspiration for your own efforts while allowing you to exploit any gaps in the market that your competitors are failing to fill.
The challenges
- Informational quality
We may have an almost infinite wealth of informational insights at our fingertips, but when it comes to market research, knowing which information to trust can prove an uphill struggle.
When working with metrics, many companies risk connecting with inaccurate insights or leading to a fruitless informational rabbit hole, wasting valuable time and resources in the process. To avoid such a mishap, working with a trusted modern market research and analysis sample is the only way forward.
- Senior buy-in
Another pressing market research challenge that stunts organizational growth is the simple case of senior buy-in. While almost every senior decision-maker knows that market research is an essential component of a successful commercial strategy, many are reluctant to invest an ample amount of time or money in the pursuit.
The best way to overcome such a challenge is by building a case that defines exactly how your market research strategies will offer a healthy ROI to every key aspect of the organization, from marketing and sales to customer experience (CX) and beyond.
- Response rates
Low interview, focus group, or poll response rates can have a serious impact on the success and value of your market research strategy. Even with adequate senior buy-in, you can’t always guarantee that you will get enough responses from early-round interviews or poll requests. If you don’t, your market research discoveries run the risk of being shallow or offering little in the way of actionable insight.
To overcome this common challenge, you can improve the incentive you offer your market research prospects while networking across various platforms to discover new contact opportunities. Changing the tone of voice of your ads or emails will also help boost your consumer or client response rates.
Bringing Your Reports a Step Further
Even if it is still widespread for market-style research results presentation, using PowerPoint at this stage is a hassle and presents many downsides and complications. When busy managers or short-on-time top executives grab a report, they want a quick overview that gives them an idea of the results and the big picture that addresses the objectives: they need a dashboard. This can be applied to all areas of a business that need fast and interactive data visualizations to support their decision-making.
We all know that a picture conveys more information than simple text or figures, so managing to bring it all together on an actionable dashboard will convey your message more efficiently. Besides, market research dashboards have the incredible advantage of always being up-to-date since they work with real-time insights: the synchronization/updating nightmare of dozens of PowerPoint slides doesn’t exist for you anymore. This is particularly helpful for tracking studies performed over time that recurrently need their data to be updated with more recent ones.
In today’s fast-paced business environment, companies must identify and grab new opportunities as they arise while staying away from threats and adapting quickly. In order to always be a step further and make the right decisions, it is critical to perform market research studies to get the information needed and make important decisions with confidence.
We’ve asked the question, “What is a market research report?”, and examined the dynamics of a modern market research report example, and one thing’s for sure: a visual market research report is the best way to understand your customer and thus increase their satisfaction by meeting their expectations head-on.
From looking at a sample of a market research report, it’s also clear that modern dashboards help you see what is influencing your business with clarity, understand where your brand is situated in the market, and gauge the temperature of your niche or industry before a product or service launch. Once all the studies are done, you must present them efficiently to ensure everyone in the business can make the right decisions that result in real progress. Market research reports are your key allies in the matter.
To start presenting your results with efficient, interactive, dynamic research reports and win on tomorrow’s commercial battlefield, try our dashboard reporting software and test every feature with our 14-day free trial !
Get science-backed answers as you write with Paperpal's Research feature
How to Write a Conclusion for Research Papers (with Examples)

The conclusion of a research paper is a crucial section that plays a significant role in the overall impact and effectiveness of your research paper. However, this is also the section that typically receives less attention compared to the introduction and the body of the paper. The conclusion serves to provide a concise summary of the key findings, their significance, their implications, and a sense of closure to the study. Discussing how can the findings be applied in real-world scenarios or inform policy, practice, or decision-making is especially valuable to practitioners and policymakers. The research paper conclusion also provides researchers with clear insights and valuable information for their own work, which they can then build on and contribute to the advancement of knowledge in the field.
The research paper conclusion should explain the significance of your findings within the broader context of your field. It restates how your results contribute to the existing body of knowledge and whether they confirm or challenge existing theories or hypotheses. Also, by identifying unanswered questions or areas requiring further investigation, your awareness of the broader research landscape can be demonstrated.
Remember to tailor the research paper conclusion to the specific needs and interests of your intended audience, which may include researchers, practitioners, policymakers, or a combination of these.
Table of Contents
What is a conclusion in a research paper, summarizing conclusion, editorial conclusion, externalizing conclusion, importance of a good research paper conclusion, how to write a conclusion for your research paper, research paper conclusion examples.
- How to write a research paper conclusion with Paperpal?
Frequently Asked Questions
A conclusion in a research paper is the final section where you summarize and wrap up your research, presenting the key findings and insights derived from your study. The research paper conclusion is not the place to introduce new information or data that was not discussed in the main body of the paper. When working on how to conclude a research paper, remember to stick to summarizing and interpreting existing content. The research paper conclusion serves the following purposes: 1
- Warn readers of the possible consequences of not attending to the problem.
- Recommend specific course(s) of action.
- Restate key ideas to drive home the ultimate point of your research paper.
- Provide a “take-home” message that you want the readers to remember about your study.

Types of conclusions for research papers
In research papers, the conclusion provides closure to the reader. The type of research paper conclusion you choose depends on the nature of your study, your goals, and your target audience. I provide you with three common types of conclusions:
A summarizing conclusion is the most common type of conclusion in research papers. It involves summarizing the main points, reiterating the research question, and restating the significance of the findings. This common type of research paper conclusion is used across different disciplines.
An editorial conclusion is less common but can be used in research papers that are focused on proposing or advocating for a particular viewpoint or policy. It involves presenting a strong editorial or opinion based on the research findings and offering recommendations or calls to action.
An externalizing conclusion is a type of conclusion that extends the research beyond the scope of the paper by suggesting potential future research directions or discussing the broader implications of the findings. This type of conclusion is often used in more theoretical or exploratory research papers.
Align your conclusion’s tone with the rest of your research paper. Start Writing with Paperpal Now!
The conclusion in a research paper serves several important purposes:
- Offers Implications and Recommendations : Your research paper conclusion is an excellent place to discuss the broader implications of your research and suggest potential areas for further study. It’s also an opportunity to offer practical recommendations based on your findings.
- Provides Closure : A good research paper conclusion provides a sense of closure to your paper. It should leave the reader with a feeling that they have reached the end of a well-structured and thought-provoking research project.
- Leaves a Lasting Impression : Writing a well-crafted research paper conclusion leaves a lasting impression on your readers. It’s your final opportunity to leave them with a new idea, a call to action, or a memorable quote.

Writing a strong conclusion for your research paper is essential to leave a lasting impression on your readers. Here’s a step-by-step process to help you create and know what to put in the conclusion of a research paper: 2
- Research Statement : Begin your research paper conclusion by restating your research statement. This reminds the reader of the main point you’ve been trying to prove throughout your paper. Keep it concise and clear.
- Key Points : Summarize the main arguments and key points you’ve made in your paper. Avoid introducing new information in the research paper conclusion. Instead, provide a concise overview of what you’ve discussed in the body of your paper.
- Address the Research Questions : If your research paper is based on specific research questions or hypotheses, briefly address whether you’ve answered them or achieved your research goals. Discuss the significance of your findings in this context.
- Significance : Highlight the importance of your research and its relevance in the broader context. Explain why your findings matter and how they contribute to the existing knowledge in your field.
- Implications : Explore the practical or theoretical implications of your research. How might your findings impact future research, policy, or real-world applications? Consider the “so what?” question.
- Future Research : Offer suggestions for future research in your area. What questions or aspects remain unanswered or warrant further investigation? This shows that your work opens the door for future exploration.
- Closing Thought : Conclude your research paper conclusion with a thought-provoking or memorable statement. This can leave a lasting impression on your readers and wrap up your paper effectively. Avoid introducing new information or arguments here.
- Proofread and Revise : Carefully proofread your conclusion for grammar, spelling, and clarity. Ensure that your ideas flow smoothly and that your conclusion is coherent and well-structured.
Write your research paper conclusion 2x faster with Paperpal. Try it now!
Remember that a well-crafted research paper conclusion is a reflection of the strength of your research and your ability to communicate its significance effectively. It should leave a lasting impression on your readers and tie together all the threads of your paper. Now you know how to start the conclusion of a research paper and what elements to include to make it impactful, let’s look at a research paper conclusion sample.

How to write a research paper conclusion with Paperpal?
A research paper conclusion is not just a summary of your study, but a synthesis of the key findings that ties the research together and places it in a broader context. A research paper conclusion should be concise, typically around one paragraph in length. However, some complex topics may require a longer conclusion to ensure the reader is left with a clear understanding of the study’s significance. Paperpal, an AI writing assistant trusted by over 800,000 academics globally, can help you write a well-structured conclusion for your research paper.
- Sign Up or Log In: Create a new Paperpal account or login with your details.
- Navigate to Features : Once logged in, head over to the features’ side navigation pane. Click on Templates and you’ll find a suite of generative AI features to help you write better, faster.
- Generate an outline: Under Templates, select ‘Outlines’. Choose ‘Research article’ as your document type.
- Select your section: Since you’re focusing on the conclusion, select this section when prompted.
- Choose your field of study: Identifying your field of study allows Paperpal to provide more targeted suggestions, ensuring the relevance of your conclusion to your specific area of research.
- Provide a brief description of your study: Enter details about your research topic and findings. This information helps Paperpal generate a tailored outline that aligns with your paper’s content.
- Generate the conclusion outline: After entering all necessary details, click on ‘generate’. Paperpal will then create a structured outline for your conclusion, to help you start writing and build upon the outline.
- Write your conclusion: Use the generated outline to build your conclusion. The outline serves as a guide, ensuring you cover all critical aspects of a strong conclusion, from summarizing key findings to highlighting the research’s implications.
- Refine and enhance: Paperpal’s ‘Make Academic’ feature can be particularly useful in the final stages. Select any paragraph of your conclusion and use this feature to elevate the academic tone, ensuring your writing is aligned to the academic journal standards.
By following these steps, Paperpal not only simplifies the process of writing a research paper conclusion but also ensures it is impactful, concise, and aligned with academic standards. Sign up with Paperpal today and write your research paper conclusion 2x faster .
The research paper conclusion is a crucial part of your paper as it provides the final opportunity to leave a strong impression on your readers. In the research paper conclusion, summarize the main points of your research paper by restating your research statement, highlighting the most important findings, addressing the research questions or objectives, explaining the broader context of the study, discussing the significance of your findings, providing recommendations if applicable, and emphasizing the takeaway message. The main purpose of the conclusion is to remind the reader of the main point or argument of your paper and to provide a clear and concise summary of the key findings and their implications. All these elements should feature on your list of what to put in the conclusion of a research paper to create a strong final statement for your work.
A strong conclusion is a critical component of a research paper, as it provides an opportunity to wrap up your arguments, reiterate your main points, and leave a lasting impression on your readers. Here are the key elements of a strong research paper conclusion: 1. Conciseness : A research paper conclusion should be concise and to the point. It should not introduce new information or ideas that were not discussed in the body of the paper. 2. Summarization : The research paper conclusion should be comprehensive enough to give the reader a clear understanding of the research’s main contributions. 3 . Relevance : Ensure that the information included in the research paper conclusion is directly relevant to the research paper’s main topic and objectives; avoid unnecessary details. 4 . Connection to the Introduction : A well-structured research paper conclusion often revisits the key points made in the introduction and shows how the research has addressed the initial questions or objectives. 5. Emphasis : Highlight the significance and implications of your research. Why is your study important? What are the broader implications or applications of your findings? 6 . Call to Action : Include a call to action or a recommendation for future research or action based on your findings.
The length of a research paper conclusion can vary depending on several factors, including the overall length of the paper, the complexity of the research, and the specific journal requirements. While there is no strict rule for the length of a conclusion, but it’s generally advisable to keep it relatively short. A typical research paper conclusion might be around 5-10% of the paper’s total length. For example, if your paper is 10 pages long, the conclusion might be roughly half a page to one page in length.
In general, you do not need to include citations in the research paper conclusion. Citations are typically reserved for the body of the paper to support your arguments and provide evidence for your claims. However, there may be some exceptions to this rule: 1. If you are drawing a direct quote or paraphrasing a specific source in your research paper conclusion, you should include a citation to give proper credit to the original author. 2. If your conclusion refers to or discusses specific research, data, or sources that are crucial to the overall argument, citations can be included to reinforce your conclusion’s validity.
The conclusion of a research paper serves several important purposes: 1. Summarize the Key Points 2. Reinforce the Main Argument 3. Provide Closure 4. Offer Insights or Implications 5. Engage the Reader. 6. Reflect on Limitations
Remember that the primary purpose of the research paper conclusion is to leave a lasting impression on the reader, reinforcing the key points and providing closure to your research. It’s often the last part of the paper that the reader will see, so it should be strong and well-crafted.
- Makar, G., Foltz, C., Lendner, M., & Vaccaro, A. R. (2018). How to write effective discussion and conclusion sections. Clinical spine surgery, 31(8), 345-346.
- Bunton, D. (2005). The structure of PhD conclusion chapters. Journal of English for academic purposes , 4 (3), 207-224.
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 21+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed.
Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
- 5 Reasons for Rejection After Peer Review
- Ethical Research Practices For Research with Human Subjects
7 Ways to Improve Your Academic Writing Process
- Paraphrasing in Academic Writing: Answering Top Author Queries
Preflight For Editorial Desk: The Perfect Hybrid (AI + Human) Assistance Against Compromised Manuscripts
You may also like, phd qualifying exam: tips for success , ai in education: it’s time to change the..., is it ethical to use ai-generated abstracts without..., what are journal guidelines on using generative ai..., quillbot review: features, pricing, and free alternatives, what is an academic paper types and elements , should you use ai tools like chatgpt for..., 9 steps to publish a research paper, what are the different types of research papers, how to make translating academic papers less challenging.
- Privacy Policy
Buy Me a Coffee

Home » Research Paper Conclusion – Writing Guide and Examples
Research Paper Conclusion – Writing Guide and Examples
Table of Contents

Research Paper Conclusion
Definition:
A research paper conclusion is the final section of a research paper that summarizes the key findings, significance, and implications of the research. It is the writer’s opportunity to synthesize the information presented in the paper, draw conclusions, and make recommendations for future research or actions.
The conclusion should provide a clear and concise summary of the research paper, reiterating the research question or problem, the main results, and the significance of the findings. It should also discuss the limitations of the study and suggest areas for further research.
Parts of Research Paper Conclusion
The parts of a research paper conclusion typically include:
Restatement of the Thesis
The conclusion should begin by restating the thesis statement from the introduction in a different way. This helps to remind the reader of the main argument or purpose of the research.
Summary of Key Findings
The conclusion should summarize the main findings of the research, highlighting the most important results and conclusions. This section should be brief and to the point.
Implications and Significance
In this section, the researcher should explain the implications and significance of the research findings. This may include discussing the potential impact on the field or industry, highlighting new insights or knowledge gained, or pointing out areas for future research.
Limitations and Recommendations
It is important to acknowledge any limitations or weaknesses of the research and to make recommendations for how these could be addressed in future studies. This shows that the researcher is aware of the potential limitations of their work and is committed to improving the quality of research in their field.
Concluding Statement
The conclusion should end with a strong concluding statement that leaves a lasting impression on the reader. This could be a call to action, a recommendation for further research, or a final thought on the topic.
How to Write Research Paper Conclusion
Here are some steps you can follow to write an effective research paper conclusion:
- Restate the research problem or question: Begin by restating the research problem or question that you aimed to answer in your research. This will remind the reader of the purpose of your study.
- Summarize the main points: Summarize the key findings and results of your research. This can be done by highlighting the most important aspects of your research and the evidence that supports them.
- Discuss the implications: Discuss the implications of your findings for the research area and any potential applications of your research. You should also mention any limitations of your research that may affect the interpretation of your findings.
- Provide a conclusion : Provide a concise conclusion that summarizes the main points of your paper and emphasizes the significance of your research. This should be a strong and clear statement that leaves a lasting impression on the reader.
- Offer suggestions for future research: Lastly, offer suggestions for future research that could build on your findings and contribute to further advancements in the field.
Remember that the conclusion should be brief and to the point, while still effectively summarizing the key findings and implications of your research.
Example of Research Paper Conclusion
Here’s an example of a research paper conclusion:
Conclusion :
In conclusion, our study aimed to investigate the relationship between social media use and mental health among college students. Our findings suggest that there is a significant association between social media use and increased levels of anxiety and depression among college students. This highlights the need for increased awareness and education about the potential negative effects of social media use on mental health, particularly among college students.
Despite the limitations of our study, such as the small sample size and self-reported data, our findings have important implications for future research and practice. Future studies should aim to replicate our findings in larger, more diverse samples, and investigate the potential mechanisms underlying the association between social media use and mental health. In addition, interventions should be developed to promote healthy social media use among college students, such as mindfulness-based approaches and social media detox programs.
Overall, our study contributes to the growing body of research on the impact of social media on mental health, and highlights the importance of addressing this issue in the context of higher education. By raising awareness and promoting healthy social media use among college students, we can help to reduce the negative impact of social media on mental health and improve the well-being of young adults.
Purpose of Research Paper Conclusion
The purpose of a research paper conclusion is to provide a summary and synthesis of the key findings, significance, and implications of the research presented in the paper. The conclusion serves as the final opportunity for the writer to convey their message and leave a lasting impression on the reader.
The conclusion should restate the research problem or question, summarize the main results of the research, and explain their significance. It should also acknowledge the limitations of the study and suggest areas for future research or action.
Overall, the purpose of the conclusion is to provide a sense of closure to the research paper and to emphasize the importance of the research and its potential impact. It should leave the reader with a clear understanding of the main findings and why they matter. The conclusion serves as the writer’s opportunity to showcase their contribution to the field and to inspire further research and action.
When to Write Research Paper Conclusion
The conclusion of a research paper should be written after the body of the paper has been completed. It should not be written until the writer has thoroughly analyzed and interpreted their findings and has written a complete and cohesive discussion of the research.
Before writing the conclusion, the writer should review their research paper and consider the key points that they want to convey to the reader. They should also review the research question, hypotheses, and methodology to ensure that they have addressed all of the necessary components of the research.
Once the writer has a clear understanding of the main findings and their significance, they can begin writing the conclusion. The conclusion should be written in a clear and concise manner, and should reiterate the main points of the research while also providing insights and recommendations for future research or action.
Characteristics of Research Paper Conclusion
The characteristics of a research paper conclusion include:
- Clear and concise: The conclusion should be written in a clear and concise manner, summarizing the key findings and their significance.
- Comprehensive: The conclusion should address all of the main points of the research paper, including the research question or problem, the methodology, the main results, and their implications.
- Future-oriented : The conclusion should provide insights and recommendations for future research or action, based on the findings of the research.
- Impressive : The conclusion should leave a lasting impression on the reader, emphasizing the importance of the research and its potential impact.
- Objective : The conclusion should be based on the evidence presented in the research paper, and should avoid personal biases or opinions.
- Unique : The conclusion should be unique to the research paper and should not simply repeat information from the introduction or body of the paper.
Advantages of Research Paper Conclusion
The advantages of a research paper conclusion include:
- Summarizing the key findings : The conclusion provides a summary of the main findings of the research, making it easier for the reader to understand the key points of the study.
- Emphasizing the significance of the research: The conclusion emphasizes the importance of the research and its potential impact, making it more likely that readers will take the research seriously and consider its implications.
- Providing recommendations for future research or action : The conclusion suggests practical recommendations for future research or action, based on the findings of the study.
- Providing closure to the research paper : The conclusion provides a sense of closure to the research paper, tying together the different sections of the paper and leaving a lasting impression on the reader.
- Demonstrating the writer’s contribution to the field : The conclusion provides the writer with an opportunity to showcase their contribution to the field and to inspire further research and action.
Limitations of Research Paper Conclusion
While the conclusion of a research paper has many advantages, it also has some limitations that should be considered, including:
- I nability to address all aspects of the research: Due to the limited space available in the conclusion, it may not be possible to address all aspects of the research in detail.
- Subjectivity : While the conclusion should be objective, it may be influenced by the writer’s personal biases or opinions.
- Lack of new information: The conclusion should not introduce new information that has not been discussed in the body of the research paper.
- Lack of generalizability: The conclusions drawn from the research may not be applicable to other contexts or populations, limiting the generalizability of the study.
- Misinterpretation by the reader: The reader may misinterpret the conclusions drawn from the research, leading to a misunderstanding of the findings.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

How to Cite Research Paper – All Formats and...

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Paper Format – Types, Examples and...

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples
- How to Cite
- Language & Lit
- Rhyme & Rhythm
- The Rewrite
- Search Glass
How to Write a Conclusion on a Marketing Research Paper
Writing a marketing research paper is a challenging undertaking that requires a great deal of time and preparation. Writing the conclusion to a marketing research paper is relatively straightforward because you've already done all the hard work. A good conclusion summarizes the main argument of your paper and points to the strengths and limitations of your research. A successful conclusion answers the "so what?" question and paves the road for future studies pertaining to your topic. With a nudge in the right direction, you'll write a conclusion that will bring your paper to an effective close.
Summarize the main argument of your paper without repeating too much. Point out why the argument is significant to the research and issue at hand to bring them to a concluding point.
Explain the strengths and limitations of your research and arguments to suggest what future work is required.
Explain the importance of your work and the significance it has to the real world. Answer the question: "How are my arguments and research useful?"
Demonstrate how all the ideas and research you put forth in the paper work together without having to present new information.
Echo the introduction without repeating it word for word to tie the paper together neatly. Explain how the insights and information found in the body of the paper reinforce the ideas suggested by the thesis in the introduction.
End the conclusion with something you want your readers to think about by issuing a challenge to your readers pertaining to how the information presented in the paper can influence their lives.
- Do not present new information in your conclusion; instead, structure your conclusion to reinforce and validate the arguments and research already presented.
- Don't write more than one concluding paragraph. Exercise brevity by writing to the point without exaggerating the content of your paper.
- LEO: Strategies for Writing a Conclusion; Randa Holewa et. al.; February 2004
- ACC: Tips for Writing a Strong Conclusion; Barry Hamilton; October 2005
Based in Victoria, British Columbia, Sebastian Malysa began his writing career in 2010. His work focuses on the general arts and appears on Answerbag and eHow. He has won a number of academic awards, most notably the CTV Award for best proposed documentary film. He holds a Master of Arts in contemporary disability theater from the University of Victoria.
Market Research: A How-To Guide and Template
Discover the different types of market research, how to conduct your own market research, and use a free template to help you along the way.

MARKET RESEARCH KIT
5 Research and Planning Templates + a Free Guide on How to Use Them in Your Market Research

Updated: 02/21/24
Published: 02/21/24
Today's consumers have a lot of power. As a business, you must have a deep understanding of who your buyers are and what influences their purchase decisions.
Enter: Market Research.
![conclusion for a market research → Download Now: Market Research Templates [Free Kit]](https://no-cache.hubspot.com/cta/default/53/6ba52ce7-bb69-4b63-965b-4ea21ba905da.png)
Whether you're new to market research or not, I created this guide to help you conduct a thorough study of your market, target audience, competition, and more. Let’s dive in.
Table of Contents
What is market research?
Primary vs. secondary research, types of market research, how to do market research, market research report template, market research examples.
Market research is the process of gathering information about your target market and customers to verify the success of a new product, help your team iterate on an existing product, or understand brand perception to ensure your team is effectively communicating your company's value effectively.
Market research can answer various questions about the state of an industry. But if you ask me, it's hardly a crystal ball that marketers can rely on for insights on their customers.
Market researchers investigate several areas of the market, and it can take weeks or even months to paint an accurate picture of the business landscape.
However, researching just one of those areas can make you more intuitive to who your buyers are and how to deliver value that no other business is offering them right now.
How? Consider these two things:
- Your competitors also have experienced individuals in the industry and a customer base. It‘s very possible that your immediate resources are, in many ways, equal to those of your competition’s immediate resources. Seeking a larger sample size for answers can provide a better edge.
- Your customers don't represent the attitudes of an entire market. They represent the attitudes of the part of the market that is already drawn to your brand.
The market research services market is growing rapidly, which signifies a strong interest in market research as we enter 2024. The market is expected to grow from roughly $75 billion in 2021 to $90.79 billion in 2025 .
.png)
Free Market Research Kit
- SWOT Analysis Template
- Survey Template
- Focus Group Template
You're all set!
Click this link to access this resource at any time.
Why do market research?
Market research allows you to meet your buyer where they are.
As our world becomes louder and demands more of our attention, this proves invaluable.
By understanding your buyer's problems, pain points, and desired solutions, you can aptly craft your product or service to naturally appeal to them.
Market research also provides insight into the following:
- Where your target audience and current customers conduct their product or service research
- Which of your competitors your target audience looks to for information, options, or purchases
- What's trending in your industry and in the eyes of your buyer
- Who makes up your market and what their challenges are
- What influences purchases and conversions among your target audience
- Consumer attitudes about a particular topic, pain, product, or brand
- Whether there‘s demand for the business initiatives you’re investing in
- Unaddressed or underserved customer needs that can be flipped into selling opportunity
- Attitudes about pricing for a particular product or service
Ultimately, market research allows you to get information from a larger sample size of your target audience, eliminating bias and assumptions so that you can get to the heart of consumer attitudes.
As a result, you can make better business decisions.
To give you an idea of how extensive market research can get , consider that it can either be qualitative or quantitative in nature — depending on the studies you conduct and what you're trying to learn about your industry.
Qualitative research is concerned with public opinion, and explores how the market feels about the products currently available in that market.
Quantitative research is concerned with data, and looks for relevant trends in the information that's gathered from public records.
That said, there are two main types of market research that your business can conduct to collect actionable information on your products: primary research and secondary research.
Primary Research
Primary research is the pursuit of first-hand information about your market and the customers within your market.
It's useful when segmenting your market and establishing your buyer personas.
Primary market research tends to fall into one of two buckets:
- Exploratory Primary Research: This kind of primary market research normally takes place as a first step — before any specific research has been performed — and may involve open-ended interviews or surveys with small numbers of people.
- Specific Primary Research: This type of research often follows exploratory research. In specific research, you take a smaller or more precise segment of your audience and ask questions aimed at solving a suspected problem.
Secondary Research
Secondary research is all the data and public records you have at your disposal to draw conclusions from (e.g. trend reports, market statistics, industry content, and sales data you already have on your business).
Secondary research is particularly useful for analyzing your competitors . The main buckets your secondary market research will fall into include:
- Public Sources: These sources are your first and most-accessible layer of material when conducting secondary market research. They're often free to find and review — like government statistics (e.g., from the U.S. Census Bureau ).
- Commercial Sources: These sources often come in the form of pay-to-access market reports, consisting of industry insight compiled by a research agency like Pew , Gartner , or Forrester .
- Internal Sources: This is the market data your organization already has like average revenue per sale, customer retention rates, and other historical data that can help you draw conclusions on buyer needs.
- Focus Groups
- Product/ Service Use Research
- Observation-Based Research
- Buyer Persona Research
- Market Segmentation Research
- Pricing Research
- Competitive Analysis Research
- Customer Satisfaction and Loyalty Research
- Brand Awareness Research
- Campaign Research
1. Interviews
Interviews allow for face-to-face discussions so you can allow for a natural flow of conversation. Your interviewees can answer questions about themselves to help you design your buyer personas and shape your entire marketing strategy.
2. Focus Groups
Focus groups provide you with a handful of carefully-selected people that can test out your product and provide feedback. This type of market research can give you ideas for product differentiation.
3. Product/Service Use Research
Product or service use research offers insight into how and why your audience uses your product or service. This type of market research also gives you an idea of the product or service's usability for your target audience.
4. Observation-Based Research
Observation-based research allows you to sit back and watch the ways in which your target audience members go about using your product or service, what works well in terms of UX , and which aspects of it could be improved.
5. Buyer Persona Research
Buyer persona research gives you a realistic look at who makes up your target audience, what their challenges are, why they want your product or service, and what they need from your business or brand.
6. Market Segmentation Research
Market segmentation research allows you to categorize your target audience into different groups (or segments) based on specific and defining characteristics. This way, you can determine effective ways to meet their needs.
7. Pricing Research
Pricing research helps you define your pricing strategy . It gives you an idea of what similar products or services in your market sell for and what your target audience is willing to pay.
8. Competitive Analysis
Competitive analyses give you a deep understanding of the competition in your market and industry. You can learn about what's doing well in your industry and how you can separate yourself from the competition .
9. Customer Satisfaction and Loyalty Research
Customer satisfaction and loyalty research gives you a look into how you can get current customers to return for more business and what will motivate them to do so (e.g., loyalty programs , rewards, remarkable customer service).
10. Brand Awareness Research
Brand awareness research tells you what your target audience knows about and recognizes from your brand. It tells you about the associations people make when they think about your business.
11. Campaign Research
Campaign research entails looking into your past campaigns and analyzing their success among your target audience and current customers. The goal is to use these learnings to inform future campaigns.
- Define your buyer persona.
- Identify a persona group to engage.
- Prepare research questions for your market research participants.
- List your primary competitors.
- Summarize your findings.
1. Define your buyer persona.
You have to understand who your customers are and how customers in your industry make buying decisions.
This is where your buyer personas come in handy. Buyer personas — sometimes referred to as marketing personas — are fictional, generalized representations of your ideal customers.
Use a free tool to create a buyer persona that your entire company can use to market, sell, and serve better.

Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.
![conclusion for a market research SWOT Analysis: How To Do One [With Template & Examples]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/marketingplan_20.webp)
SWOT Analysis: How To Do One [With Template & Examples]

20+ Tools & Resources for Conducting Market Research

TAM SAM SOM: What Do They Mean & How Do You Calculate Them?
![conclusion for a market research How to Run a Competitor Analysis [Free Guide]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/Google%20Drive%20Integration/how%20to%20do%20a%20competitor%20analysis_122022.jpeg)
How to Run a Competitor Analysis [Free Guide]
![conclusion for a market research 5 Challenges Marketers Face in Understanding Audiences [New Data + Market Researcher Tips]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/challenges%20marketers%20face%20in%20understanding%20the%20customer%20.png)
5 Challenges Marketers Face in Understanding Audiences [New Data + Market Researcher Tips]

Causal Research: The Complete Guide

Total Addressable Market (TAM): What It Is & How You Can Calculate It

What Is Market Share & How Do You Calculate It?
![conclusion for a market research 3 Ways Data Privacy Changes Benefit Marketers [New Data]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/how-data-privacy-benefits-marketers_1.webp)
3 Ways Data Privacy Changes Benefit Marketers [New Data]

What is a Competitive Analysis — and How Do You Conduct One?
Free Guide & Templates to Help Your Market Research
Marketing software that helps you drive revenue, save time and resources, and measure and optimize your investments — all on one easy-to-use platform
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
How to Write a Conclusion for a Research Paper

3-minute read
- 29th August 2023
If you’re writing a research paper, the conclusion is your opportunity to summarize your findings and leave a lasting impression on your readers. In this post, we’ll take you through how to write an effective conclusion for a research paper and how you can:
· Reword your thesis statement
· Highlight the significance of your research
· Discuss limitations
· Connect to the introduction
· End with a thought-provoking statement
Rewording Your Thesis Statement
Begin your conclusion by restating your thesis statement in a way that is slightly different from the wording used in the introduction. Avoid presenting new information or evidence in your conclusion. Just summarize the main points and arguments of your essay and keep this part as concise as possible. Remember that you’ve already covered the in-depth analyses and investigations in the main body paragraphs of your essay, so it’s not necessary to restate these details in the conclusion.
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
Highlighting the Significance of Your Research
The conclusion is a good place to emphasize the implications of your research . Avoid ambiguous or vague language such as “I think” or “maybe,” which could weaken your position. Clearly explain why your research is significant and how it contributes to the broader field of study.
Here’s an example from a (fictional) study on the impact of social media on mental health:
Discussing Limitations
Although it’s important to emphasize the significance of your study, you can also use the conclusion to briefly address any limitations you discovered while conducting your research, such as time constraints or a shortage of resources. Doing this demonstrates a balanced and honest approach to your research.
Connecting to the Introduction
In your conclusion, you can circle back to your introduction , perhaps by referring to a quote or anecdote you discussed earlier. If you end your paper on a similar note to how you began it, you will create a sense of cohesion for the reader and remind them of the meaning and significance of your research.
Ending With a Thought-Provoking Statement
Consider ending your paper with a thought-provoking and memorable statement that relates to the impact of your research questions or hypothesis. This statement can be a call to action, a philosophical question, or a prediction for the future (positive or negative). Here’s an example that uses the same topic as above (social media and mental health):
Expert Proofreading Services
Ensure that your essay ends on a high note by having our experts proofread your research paper. Our team has experience with a wide variety of academic fields and subjects and can help make your paper stand out from the crowd – get started today and see the difference it can make in your work.
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
2-minute read
How to Cite the CDC in APA
If you’re writing about health issues, you might need to reference the Centers for Disease...
5-minute read
Six Product Description Generator Tools for Your Product Copy
Introduction If you’re involved with ecommerce, you’re likely familiar with the often painstaking process of...
What Is a Content Editor?
Are you interested in learning more about the role of a content editor and the...
4-minute read
The Benefits of Using an Online Proofreading Service
Proofreading is important to ensure your writing is clear and concise for your readers. Whether...
6 Online AI Presentation Maker Tools
Creating presentations can be time-consuming and frustrating. Trying to construct a visually appealing and informative...
What Is Market Research?
No matter your industry, conducting market research helps you keep up to date with shifting...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.
How to write a strong conclusion for your research paper
Last updated
17 February 2024
Reviewed by
Writing a research paper is a chance to share your knowledge and hypothesis. It's an opportunity to demonstrate your many hours of research and prove your ability to write convincingly.
Ideally, by the end of your research paper, you'll have brought your readers on a journey to reach the conclusions you've pre-determined. However, if you don't stick the landing with a good conclusion, you'll risk losing your reader’s trust.
Writing a strong conclusion for your research paper involves a few important steps, including restating the thesis and summing up everything properly.
Find out what to include and what to avoid, so you can effectively demonstrate your understanding of the topic and prove your expertise.
- Why is a good conclusion important?
A good conclusion can cement your paper in the reader’s mind. Making a strong impression in your introduction can draw your readers in, but it's the conclusion that will inspire them.
- What to include in a research paper conclusion
There are a few specifics you should include in your research paper conclusion. Offer your readers some sense of urgency or consequence by pointing out why they should care about the topic you have covered. Discuss any common problems associated with your topic and provide suggestions as to how these problems can be solved or addressed.
The conclusion should include a restatement of your initial thesis. Thesis statements are strengthened after you’ve presented supporting evidence (as you will have done in the paper), so make a point to reintroduce it at the end.
Finally, recap the main points of your research paper, highlighting the key takeaways you want readers to remember. If you've made multiple points throughout the paper, refer to the ones with the strongest supporting evidence.
- Steps for writing a research paper conclusion
Many writers find the conclusion the most challenging part of any research project . By following these three steps, you'll be prepared to write a conclusion that is effective and concise.
- Step 1: Restate the problem
Always begin by restating the research problem in the conclusion of a research paper. This serves to remind the reader of your hypothesis and refresh them on the main point of the paper.
When restating the problem, take care to avoid using exactly the same words you employed earlier in the paper.
- Step 2: Sum up the paper
After you've restated the problem, sum up the paper by revealing your overall findings. The method for this differs slightly, depending on whether you're crafting an argumentative paper or an empirical paper.
Argumentative paper: Restate your thesis and arguments
Argumentative papers involve introducing a thesis statement early on. In crafting the conclusion for an argumentative paper, always restate the thesis, outlining the way you've developed it throughout the entire paper.
It might be appropriate to mention any counterarguments in the conclusion, so you can demonstrate how your thesis is correct or how the data best supports your main points.
Empirical paper: Summarize research findings
Empirical papers break down a series of research questions. In your conclusion, discuss the findings your research revealed, including any information that surprised you.
Be clear about the conclusions you reached, and explain whether or not you expected to arrive at these particular ones.
- Step 3: Discuss the implications of your research
Argumentative papers and empirical papers also differ in this part of a research paper conclusion. Here are some tips on crafting conclusions for argumentative and empirical papers.
Argumentative paper: Powerful closing statement
In an argumentative paper, you'll have spent a great deal of time expressing the opinions you formed after doing a significant amount of research. Make a strong closing statement in your argumentative paper's conclusion to share the significance of your work.
You can outline the next steps through a bold call to action, or restate how powerful your ideas turned out to be.
Empirical paper: Directions for future research
Empirical papers are broader in scope. They usually cover a variety of aspects and can include several points of view.
To write a good conclusion for an empirical paper, suggest the type of research that could be done in the future, including methods for further investigation or outlining ways other researchers might proceed.
If you feel your research had any limitations, even if they were outside your control, you could mention these in your conclusion.
After you finish outlining your conclusion, ask someone to read it and offer feedback. In any research project you're especially close to, it can be hard to identify problem areas. Having a close friend or someone whose opinion you value read the research paper and provide honest feedback can be invaluable. Take note of any suggested edits and consider incorporating them into your paper if they make sense.
- Things to avoid in a research paper conclusion
Keep these aspects to avoid in mind as you're writing your conclusion and refer to them after you've created an outline.
Dry summary
Writing a memorable, succinct conclusion is arguably more important than a strong introduction. Take care to avoid just rephrasing your main points, and don't fall into the trap of repeating dry facts or citations.
You can provide a new perspective for your readers to think about or contextualize your research. Either way, make the conclusion vibrant and interesting, rather than a rote recitation of your research paper’s highlights.
Clichéd or generic phrasing
Your research paper conclusion should feel fresh and inspiring. Avoid generic phrases like "to sum up" or "in conclusion." These phrases tend to be overused, especially in an academic context and might turn your readers off.
The conclusion also isn't the time to introduce colloquial phrases or informal language. Retain a professional, confident tone consistent throughout your paper’s conclusion so it feels exciting and bold.
New data or evidence
While you should present strong data throughout your paper, the conclusion isn't the place to introduce new evidence. This is because readers are engaged in actively learning as they read through the body of your paper.
By the time they reach the conclusion, they will have formed an opinion one way or the other (hopefully in your favor!). Introducing new evidence in the conclusion will only serve to surprise or frustrate your reader.
Ignoring contradictory evidence
If your research reveals contradictory evidence, don't ignore it in the conclusion. This will damage your credibility as an expert and might even serve to highlight the contradictions.
Be as transparent as possible and admit to any shortcomings in your research, but don't dwell on them for too long.
Ambiguous or unclear resolutions
The point of a research paper conclusion is to provide closure and bring all your ideas together. You should wrap up any arguments you introduced in the paper and tie up any loose ends, while demonstrating why your research and data are strong.
Use direct language in your conclusion and avoid ambiguity. Even if some of the data and sources you cite are inconclusive or contradictory, note this in your conclusion to come across as confident and trustworthy.
- Examples of research paper conclusions
Your research paper should provide a compelling close to the paper as a whole, highlighting your research and hard work. While the conclusion should represent your unique style, these examples offer a starting point:
Ultimately, the data we examined all point to the same conclusion: Encouraging a good work-life balance improves employee productivity and benefits the company overall. The research suggests that when employees feel their personal lives are valued and respected by their employers, they are more likely to be productive when at work. In addition, company turnover tends to be reduced when employees have a balance between their personal and professional lives. While additional research is required to establish ways companies can support employees in creating a stronger work-life balance, it's clear the need is there.
Social media is a primary method of communication among young people. As we've seen in the data presented, most young people in high school use a variety of social media applications at least every hour, including Instagram and Facebook. While social media is an avenue for connection with peers, research increasingly suggests that social media use correlates with body image issues. Young girls with lower self-esteem tend to use social media more often than those who don't log onto social media apps every day. As new applications continue to gain popularity, and as more high school students are given smartphones, more research will be required to measure the effects of prolonged social media use.
What are the different kinds of research paper conclusions?
There are no formal types of research paper conclusions. Ultimately, the conclusion depends on the outline of your paper and the type of research you’re presenting. While some experts note that research papers can end with a new perspective or commentary, most papers should conclude with a combination of both. The most important aspect of a good research paper conclusion is that it accurately represents the body of the paper.
Can I present new arguments in my research paper conclusion?
Research paper conclusions are not the place to introduce new data or arguments. The body of your paper is where you should share research and insights, where the reader is actively absorbing the content. By the time a reader reaches the conclusion of the research paper, they should have formed their opinion. Introducing new arguments in the conclusion can take a reader by surprise, and not in a positive way. It might also serve to frustrate readers.
How long should a research paper conclusion be?
There's no set length for a research paper conclusion. However, it's a good idea not to run on too long, since conclusions are supposed to be succinct. A good rule of thumb is to keep your conclusion around 5 to 10 percent of the paper's total length. If your paper is 10 pages, try to keep your conclusion under one page.
What should I include in a research paper conclusion?
A good research paper conclusion should always include a sense of urgency, so the reader can see how and why the topic should matter to them. You can also note some recommended actions to help fix the problem and some obstacles they might encounter. A conclusion should also remind the reader of the thesis statement, along with the main points you covered in the paper. At the end of the conclusion, add a powerful closing statement that helps cement the paper in the mind of the reader.
Get started today
Go from raw data to valuable insights with a flexible research platform
Editor’s picks
Last updated: 21 December 2023
Last updated: 16 December 2023
Last updated: 6 October 2023
Last updated: 25 November 2023
Last updated: 12 May 2023
Last updated: 15 February 2024
Last updated: 11 March 2024
Last updated: 12 December 2023
Last updated: 18 May 2023
Last updated: 6 March 2024
Last updated: 10 April 2023
Last updated: 20 December 2023
Latest articles
Related topics, log in or sign up.
Get started for free
EXCLUSIVE SUMMIT OFFER Join foundr+ and get Ecommerce Kickstarter program free!
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
A magazine for young entrepreneurs
The best advice in entrepreneurship
Subscribe for exclusive access, the complete guide to market research: what it is, why you need it, and how to do it.

Written by Mary Kate Miller | June 1, 2021
Comments -->

Get real-time frameworks, tools, and inspiration to start and build your business. Subscribe here
Market research is a cornerstone of all successful, strategic businesses. It can also be daunting for entrepreneurs looking to launch a startup or start a side hustle . What is market research, anyway? And how do you…do it?
We’ll walk you through absolutely everything you need to know about the market research process so that by the end of this guide, you’ll be an expert in market research too. And what’s more important: you’ll have actionable steps you can take to start collecting your own market research.
What Is Market Research?
Market research is the organized process of gathering information about your target customers and market. Market research can help you better understand customer behavior and competitor strengths and weaknesses, as well as provide insight for the best strategies in launching new businesses and products. There are different ways to approach market research, including primary and secondary research and qualitative and quantitative research. The strongest approaches will include a combination of all four.
“Virtually every business can benefit from conducting some market research,” says Niles Koenigsberg of Real FiG Advertising + Marketing . “Market research can help you piece together your [business’s] strengths and weaknesses, along with your prospective opportunities, so that you can understand where your unique differentiators may lie.” Well-honed market research will help your brand stand out from the competition and help you see what you need to do to lead the market. It can also do so much more.
The Purposes of Market Research
Why do market research? It can help you…
- Pinpoint your target market, create buyer personas, and develop a more holistic understanding of your customer base and market.
- Understand current market conditions to evaluate risks and anticipate how your product or service will perform.
- Validate a concept prior to launch.
- Identify gaps in the market that your competitors have created or overlooked.
- Solve problems that have been left unresolved by the existing product/brand offerings.
- Identify opportunities and solutions for new products or services.
- Develop killer marketing strategies .
What Are the Benefits of Market Research?
Strong market research can help your business in many ways. It can…
- Strengthen your market position.
- Help you identify your strengths and weaknesses.
- Help you identify your competitors’ strengths and weaknesses.
- Minimize risk.
- Center your customers’ experience from the get-go.
- Help you create a dynamic strategy based on market conditions and customer needs/demands.

What Are the Basic Methods of Market Research?
The basic methods of market research include surveys, personal interviews, customer observation, and the review of secondary research. In addition to these basic methods, a forward-thinking market research approach incorporates data from the digital landscape like social media analysis, SEO research, gathering feedback via forums, and more. Throughout this guide, we will cover each of the methods commonly used in market research to give you a comprehensive overview.
Primary vs. Secondary Market Research
Primary and secondary are the two main types of market research you can do. The latter relies on research conducted by others. Primary research, on the other hand, refers to the fact-finding efforts you conduct on your own.
This approach is limited, however. It’s likely that the research objectives of these secondary data points differ from your own, and it can be difficult to confirm the veracity of their findings.
Primary Market Research
Primary research is more labor intensive, but it generally yields data that is exponentially more actionable. It can be conducted through interviews, surveys, online research, and your own data collection. Every new business should engage in primary market research prior to launch. It will help you validate that your idea has traction, and it will give you the information you need to help minimize financial risk.
You can hire an agency to conduct this research on your behalf. This brings the benefit of expertise, as you’ll likely work with a market research analyst. The downside is that hiring an agency can be expensive—too expensive for many burgeoning entrepreneurs. That brings us to the second approach. You can also do the market research yourself, which substantially reduces the financial burden of starting a new business .
Secondary Market Research
Secondary research includes resources like government databases and industry-specific data and publications. It can be beneficial to start your market research with secondary sources because it’s widely available and often free-to-access. This information will help you gain a broad overview of the market conditions for your new business.
Identify Your Goals and Your Audience
Before you begin conducting interviews or sending out surveys, you need to set your market research goals. At the end of your market research process, you want to have a clear idea of who your target market is—including demographic information like age, gender, and where they live—but you also want to start with a rough idea of who your audience might be and what you’re trying to achieve with market research.
You can pinpoint your objectives by asking yourself a series of guiding questions:
- What are you hoping to discover through your research?
- Who are you hoping to serve better because of your findings?
- What do you think your market is?
- Who are your competitors?
- Are you testing the reception of a new product category or do you want to see if your product or service solves the problem left by a current gap in the market?
- Are you just…testing the waters to get a sense of how people would react to a new brand?
Once you’ve narrowed down the “what” of your market research goals, you’re ready to move onto how you can best achieve them. Think of it like algebra. Many math problems start with “solve for x.” Once you know what you’re looking for, you can get to work trying to find it. It’s a heck of a lot easier to solve a problem when you know you’re looking for “x” than if you were to say “I’m gonna throw some numbers out there and see if I find a variable.”

How to Do Market Research
This guide outlines every component of a comprehensive market research effort. Take into consideration the goals you have established for your market research, as they will influence which of these elements you’ll want to include in your market research strategy.
Secondary Data
Secondary data allows you to utilize pre-existing data to garner a sense of market conditions and opportunities. You can rely on published market studies, white papers, and public competitive information to start your market research journey.
Secondary data, while useful, is limited and cannot substitute your own primary data. It’s best used for quantitative data that can provide background to your more specific inquiries.
Find Your Customers Online
Once you’ve identified your target market, you can use online gathering spaces and forums to gain insights and give yourself a competitive advantage. Rebecca McCusker of The Creative Content Shop recommends internet recon as a vital tool for gaining a sense of customer needs and sentiment. “Read their posts and comments on forums, YouTube video comments, Facebook group [comments], and even Amazon/Goodreads book comments to get in their heads and see what people are saying.”
If you’re interested in engaging with your target demographic online, there are some general rules you should follow. First, secure the consent of any group moderators to ensure that you are acting within the group guidelines. Failure to do so could result in your eviction from the group.
Not all comments have the same research value. “Focus on the comments and posts with the most comments and highest engagement,” says McCusker. These high-engagement posts can give you a sense of what is already connecting and gaining traction within the group.
Social media can also be a great avenue for finding interview subjects. “LinkedIn is very useful if your [target customer] has a very specific job or works in a very specific industry or sector. It’s amazing the amount of people that will be willing to help,” explains Miguel González, a marketing executive at Dealers League . “My advice here is BE BRAVE, go to LinkedIn, or even to people you know and ask them, do quick interviews and ask real people that belong to that market and segment and get your buyer persona information first hand.”
Market research interviews can provide direct feedback on your brand, product, or service and give you a better understanding of consumer pain points and interests.
When organizing your market research interviews, you want to pay special attention to the sample group you’re selecting, as it will directly impact the information you receive. According to Tanya Zhang, the co-founder of Nimble Made , you want to first determine whether you want to choose a representative sample—for example, interviewing people who match each of the buyer persona/customer profiles you’ve developed—or a random sample.
“A sampling of your usual persona styles, for example, can validate details that you’ve already established about your product, while a random sampling may [help you] discover a new way people may use your product,” Zhang says.
Market Surveys
Market surveys solicit customer inclinations regarding your potential product or service through a series of open-ended questions. This direct outreach to your target audience can provide information on your customers’ preferences, attitudes, buying potential, and more.
Every expert we asked voiced unanimous support for market surveys as a powerful tool for market research. With the advent of various survey tools with accessible pricing—or free use—it’s never been easier to assemble, disseminate, and gather market surveys. While it should also be noted that surveys shouldn’t replace customer interviews , they can be used to supplement customer interviews to give you feedback from a broader audience.
Who to Include in Market Surveys
- Current customers
- Past customers
- Your existing audience (such as social media/newsletter audiences)
Example Questions to Include in Market Surveys
While the exact questions will vary for each business, here are some common, helpful questions that you may want to consider for your market survey. Demographic Questions: the questions that help you understand, demographically, who your target customers are:
- “What is your age?”
- “Where do you live?”
- “What is your gender identity?”
- “What is your household income?”
- “What is your household size?”
- “What do you do for a living?”
- “What is your highest level of education?”
Product-Based Questions: Whether you’re seeking feedback for an existing brand or an entirely new one, these questions will help you get a sense of how people feel about your business, product, or service:
- “How well does/would our product/service meet your needs?”
- “How does our product/service compare to similar products/services that you use?”
- “How long have you been a customer?” or “What is the likelihood that you would be a customer of our brand?
Personal/Informative Questions: the deeper questions that help you understand how your audience thinks and what they care about.
- “What are your biggest challenges?”
- “What’s most important to you?”
- “What do you do for fun (hobbies, interests, activities)?”
- “Where do you seek new information when researching a new product?”
- “How do you like to make purchases?”
- “What is your preferred method for interacting with a brand?”
Survey Tools
Online survey tools make it easy to distribute surveys and collect responses. The best part is that there are many free tools available. If you’re making your own online survey, you may want to consider SurveyMonkey, Typeform, Google Forms, or Zoho Survey.
Competitive Analysis
A competitive analysis is a breakdown of how your business stacks up against the competition. There are many different ways to conduct this analysis. One of the most popular methods is a SWOT analysis, which stands for “strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.” This type of analysis is helpful because it gives you a more robust understanding of why a customer might choose a competitor over your business. Seeing how you stack up against the competition can give you the direction you need to carve out your place as a market leader.
Social Media Analysis
Social media has fundamentally changed the market research landscape, making it easier than ever to engage with a wide swath of consumers. Follow your current or potential competitors on social media to see what they’re posting and how their audience is engaging with it. Social media can also give you a lower cost opportunity for testing different messaging and brand positioning.
SEO Analysis and Opportunities
SEO analysis can help you identify the digital competition for getting the word out about your brand, product, or service. You won’t want to overlook this valuable information. Search listening tools offer a novel approach to understanding the market and generating the content strategy that will drive business. Tools like Google Trends and Awario can streamline this process.
Ready to Kick Your Business Into High Gear?
Now that you’ve completed the guide to market research you know you’re ready to put on your researcher hat to give your business the best start. Still not sure how actually… launch the thing? Our free mini-course can run you through the essentials for starting your side hustle .

About Mary Kate Miller
Mary Kate Miller writes about small business, real estate, and finance. In addition to writing for Foundr, her work has been published by The Washington Post, Teen Vogue, Bustle, and more. She lives in Chicago.
Related Posts

How to Get More Views on Snapchat with These 12 Tactics

12 Instagram Growth Hacks For More Engaged Followers (Without Running Ads)

Create Viral Infographics That Boost Your Organic Traffic
How to Create a Video Sales Letter (Tips and Tricks from a 7-Figure Copywriter)

How to Write a Sales Email That Converts in 2024

What Is a Media Kit: How to Make One in 2024 (With Examples)

Namestorming: How to Choose a Brand Name in 20 Minutes or Less

10 Ways to Increase Brand Awareness without Increasing Your Budget

What Is a Content Creator? A Deep Dive Into This Evolving Industry

Content Creator vs Influencer: What’s the Difference?

How Much Do YouTube Ads Cost? A Beginner’s Pricing Breakdown

How to Get Podcast Sponsors Before Airing an Episode

How Founders Can Overcome Their Sales Fears with AJ Cassata

How to Grow Your YouTube Channel & Gain Subscribers Quickly

How to Write Good Instagram Captions That Hook Your Audience
FREE TRAINING FROM LEGIT FOUNDERS
Actionable Strategies for Starting & Growing Any Business.

- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- 9. The Conclusion
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Applying Critical Thinking
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
The conclusion is intended to help the reader understand why your research should matter to them after they have finished reading the paper. A conclusion is not merely a summary of the main topics covered or a re-statement of your research problem, but a synthesis of key points derived from the findings of your study and, if applicable, where you recommend new areas for future research. For most college-level research papers, two or three well-developed paragraphs is sufficient for a conclusion, although in some cases, more paragraphs may be required in describing the key findings and their significance.
Conclusions. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Conclusions. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University.
Importance of a Good Conclusion
A well-written conclusion provides you with important opportunities to demonstrate to the reader your understanding of the research problem. These include:
- Presenting the last word on the issues you raised in your paper . Just as the introduction gives a first impression to your reader, the conclusion offers a chance to leave a lasting impression. Do this, for example, by highlighting key findings in your analysis that advance new understanding about the research problem, that are unusual or unexpected, or that have important implications applied to practice.
- Summarizing your thoughts and conveying the larger significance of your study . The conclusion is an opportunity to succinctly re-emphasize your answer to the "So What?" question by placing the study within the context of how your research advances past research about the topic.
- Identifying how a gap in the literature has been addressed . The conclusion can be where you describe how a previously identified gap in the literature [first identified in your literature review section] has been addressed by your research and why this contribution is significant.
- Demonstrating the importance of your ideas . Don't be shy. The conclusion offers an opportunity to elaborate on the impact and significance of your findings. This is particularly important if your study approached examining the research problem from an unusual or innovative perspective.
- Introducing possible new or expanded ways of thinking about the research problem . This does not refer to introducing new information [which should be avoided], but to offer new insight and creative approaches for framing or contextualizing the research problem based on the results of your study.
Bunton, David. “The Structure of PhD Conclusion Chapters.” Journal of English for Academic Purposes 4 (July 2005): 207–224; Conclusions. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Kretchmer, Paul. Twelve Steps to Writing an Effective Conclusion. San Francisco Edit, 2003-2008; Conclusions. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Assan, Joseph. "Writing the Conclusion Chapter: The Good, the Bad and the Missing." Liverpool: Development Studies Association (2009): 1-8.
Structure and Writing Style
I. General Rules
The general function of your paper's conclusion is to restate the main argument . It reminds the reader of the strengths of your main argument(s) and reiterates the most important evidence supporting those argument(s). Do this by clearly summarizing the context, background, and necessity of pursuing the research problem you investigated in relation to an issue, controversy, or a gap found in the literature. However, make sure that your conclusion is not simply a repetitive summary of the findings. This reduces the impact of the argument(s) you have developed in your paper.
When writing the conclusion to your paper, follow these general rules:
- Present your conclusions in clear, concise language. Re-state the purpose of your study, then describe how your findings differ or support those of other studies and why [i.e., what were the unique, new, or crucial contributions your study made to the overall research about your topic?].
- Do not simply reiterate your findings or the discussion of your results. Provide a synthesis of arguments presented in the paper to show how these converge to address the research problem and the overall objectives of your study.
- Indicate opportunities for future research if you haven't already done so in the discussion section of your paper. Highlighting the need for further research provides the reader with evidence that you have an in-depth awareness of the research problem but that further investigations should take place beyond the scope of your investigation.
Consider the following points to help ensure your conclusion is presented well:
- If the argument or purpose of your paper is complex, you may need to summarize the argument for your reader.
- If, prior to your conclusion, you have not yet explained the significance of your findings or if you are proceeding inductively, use the end of your paper to describe your main points and explain their significance.
- Move from a detailed to a general level of consideration that returns the topic to the context provided by the introduction or within a new context that emerges from the data [this is opposite of the introduction, which begins with general discussion of the context and ends with a detailed description of the research problem].
The conclusion also provides a place for you to persuasively and succinctly restate the research problem, given that the reader has now been presented with all the information about the topic . Depending on the discipline you are writing in, the concluding paragraph may contain your reflections on the evidence presented. However, the nature of being introspective about the research you have conducted will depend on the topic and whether your professor wants you to express your observations in this way. If asked to think introspectively about the topics, do not delve into idle speculation. Being introspective means looking within yourself as an author to try and understand an issue more deeply, not to guess at possible outcomes or make up scenarios not supported by the evidence.
II. Developing a Compelling Conclusion
Although an effective conclusion needs to be clear and succinct, it does not need to be written passively or lack a compelling narrative. Strategies to help you move beyond merely summarizing the key points of your research paper may include any of the following:
- If your essay deals with a critical, contemporary problem, warn readers of the possible consequences of not attending to the problem proactively.
- Recommend a specific course or courses of action that, if adopted, could address a specific problem in practice or in the development of new knowledge leading to positive change.
- Cite a relevant quotation or expert opinion already noted in your paper in order to lend authority and support to the conclusion(s) you have reached [a good source would be from your literature review].
- Explain the consequences of your research in a way that elicits action or demonstrates urgency in seeking change.
- Restate a key statistic, fact, or visual image to emphasize the most important finding of your paper.
- If your discipline encourages personal reflection, illustrate your concluding point by drawing from your own life experiences.
- Return to an anecdote, an example, or a quotation that you presented in your introduction, but add further insight derived from the findings of your study; use your interpretation of results from your study to recast it in new or important ways.
- Provide a "take-home" message in the form of a succinct, declarative statement that you want the reader to remember about your study.
III. Problems to Avoid
Failure to be concise Your conclusion section should be concise and to the point. Conclusions that are too lengthy often have unnecessary information in them. The conclusion is not the place for details about your methodology or results. Although you should give a summary of what was learned from your research, this summary should be relatively brief, since the emphasis in the conclusion is on the implications, evaluations, insights, and other forms of analysis that you make. Strategies for writing concisely can be found here .
Failure to comment on larger, more significant issues In the introduction, your task was to move from the general [the field of study] to the specific [the research problem]. However, in the conclusion, your task is to move from a specific discussion [your research problem] back to a general discussion framed around the implications and significance of your findings [i.e., how your research contributes new understanding or fills an important gap in the literature]. In short, the conclusion is where you should place your research within a larger context [visualize your paper as an hourglass--start with a broad introduction and review of the literature, move to the specific analysis and discussion, conclude with a broad summary of the study's implications and significance].
Failure to reveal problems and negative results Negative aspects of the research process should never be ignored. These are problems, deficiencies, or challenges encountered during your study. They should be summarized as a way of qualifying your overall conclusions. If you encountered negative or unintended results [i.e., findings that are validated outside the research context in which they were generated], you must report them in the results section and discuss their implications in the discussion section of your paper. In the conclusion, use negative results as an opportunity to explain their possible significance and/or how they may form the basis for future research.
Failure to provide a clear summary of what was learned In order to be able to discuss how your research fits within your field of study [and possibly the world at large], you need to summarize briefly and succinctly how it contributes to new knowledge or a new understanding about the research problem. This element of your conclusion may be only a few sentences long.
Failure to match the objectives of your research Often research objectives in the social and behavioral sciences change while the research is being carried out. This is not a problem unless you forget to go back and refine the original objectives in your introduction. As these changes emerge they must be documented so that they accurately reflect what you were trying to accomplish in your research [not what you thought you might accomplish when you began].
Resist the urge to apologize If you've immersed yourself in studying the research problem, you presumably should know a good deal about it [perhaps even more than your professor!]. Nevertheless, by the time you have finished writing, you may be having some doubts about what you have produced. Repress those doubts! Don't undermine your authority as a researcher by saying something like, "This is just one approach to examining this problem; there may be other, much better approaches that...." The overall tone of your conclusion should convey confidence to the reader about the study's validity and realiability.
Assan, Joseph. "Writing the Conclusion Chapter: The Good, the Bad and the Missing." Liverpool: Development Studies Association (2009): 1-8; Concluding Paragraphs. College Writing Center at Meramec. St. Louis Community College; Conclusions. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Conclusions. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Freedman, Leora and Jerry Plotnick. Introductions and Conclusions. The Lab Report. University College Writing Centre. University of Toronto; Leibensperger, Summer. Draft Your Conclusion. Academic Center, the University of Houston-Victoria, 2003; Make Your Last Words Count. The Writer’s Handbook. Writing Center. University of Wisconsin Madison; Miquel, Fuster-Marquez and Carmen Gregori-Signes. “Chapter Six: ‘Last but Not Least:’ Writing the Conclusion of Your Paper.” In Writing an Applied Linguistics Thesis or Dissertation: A Guide to Presenting Empirical Research . John Bitchener, editor. (Basingstoke,UK: Palgrave Macmillan, 2010), pp. 93-105; Tips for Writing a Good Conclusion. Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Kretchmer, Paul. Twelve Steps to Writing an Effective Conclusion. San Francisco Edit, 2003-2008; Writing Conclusions. Writing Tutorial Services, Center for Innovative Teaching and Learning. Indiana University; Writing: Considering Structure and Organization. Institute for Writing Rhetoric. Dartmouth College.
Writing Tip
Don't Belabor the Obvious!
Avoid phrases like "in conclusion...," "in summary...," or "in closing...." These phrases can be useful, even welcome, in oral presentations. But readers can see by the tell-tale section heading and number of pages remaining that they are reaching the end of your paper. You'll irritate your readers if you belabor the obvious.
Assan, Joseph. "Writing the Conclusion Chapter: The Good, the Bad and the Missing." Liverpool: Development Studies Association (2009): 1-8.
Another Writing Tip
New Insight, Not New Information!
Don't surprise the reader with new information in your conclusion that was never referenced anywhere else in the paper. This why the conclusion rarely has citations to sources. If you have new information to present, add it to the discussion or other appropriate section of the paper. Note that, although no new information is introduced, the conclusion, along with the discussion section, is where you offer your most "original" contributions in the paper; the conclusion is where you describe the value of your research, demonstrate that you understand the material that you’ve presented, and position your findings within the larger context of scholarship on the topic, including describing how your research contributes new insights to that scholarship.
Assan, Joseph. "Writing the Conclusion Chapter: The Good, the Bad and the Missing." Liverpool: Development Studies Association (2009): 1-8; Conclusions. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina.
- << Previous: Limitations of the Study
- Next: Appendices >>
- Last Updated: Apr 22, 2024 9:12 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide

- Join the AMA
- Find learning by topic
- Free learning resources for members
- Certification
- Training for teams
- Why learn with the AMA?
- Marketing News
- Academic Journals
- Guides & eBooks
- Marketing Job Board
- Academic Job Board
- AMA Foundation
- Diversity, Equity and Inclusion
- Collegiate Resources
- Awards and Scholarships
- Sponsorship Opportunities
- Strategic Partnerships
We noticed that you are using Internet Explorer 11 or older that is not support any longer. Please consider using an alternative such as Microsoft Edge, Chrome, or Firefox.
Market Research Conclusion Prioritization Tool
Use this tool to evaluate a series of research conclusions and find which conclusions will be helpful in gaining a better market position.
- Estimated time required: 2 hours
- Skills required: Microsoft Excel (advanced)
Get Full Access to This Resource With AMA Membership

Market Research Playbook
This tool can be used alone, but it’s also part of the comprehensive Market Research Playbook. It provides step-by-step planning guidance while also helping you utilize more than 25 downloadable tools from the popular AMA Marketer’s Toolkit library.
This tool is powered by Demand Metric .
By continuing to use this site, you accept the use of cookies, pixels and other technology that allows us to understand our users better and offer you tailored content. You can learn more about our privacy policy here

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
10.2 Steps in the Marketing Research Process
Learning objective.
- Describe the basic steps in the marketing research process and the purpose of each step.
The basic steps used to conduct marketing research are shown in Figure 10.6 “Steps in the Marketing Research Process” . Next, we discuss each step.
Figure 10.6 Steps in the Marketing Research Process
Step 1: Define the Problem (or Opportunity)
There’s a saying in marketing research that a problem half defined is a problem half solved. Defining the “problem” of the research sounds simple, doesn’t it? Suppose your product is tutoring other students in a subject you’re a whiz at. You have been tutoring for a while, and people have begun to realize you’re darned good at it. Then, suddenly, your business drops off. Or it explodes, and you can’t cope with the number of students you’re being asked help. If the business has exploded, should you try to expand your services? Perhaps you should subcontract with some other “whiz” students. You would send them students to be tutored, and they would give you a cut of their pay for each student you referred to them.
Both of these scenarios would be a problem for you, wouldn’t they? They are problems insofar as they cause you headaches. But are they really the problem? Or are they the symptoms of something bigger? For example, maybe your business has dropped off because your school is experiencing financial trouble and has lowered the number of scholarships given to incoming freshmen. Consequently, there are fewer total students on campus who need your services. Conversely, if you’re swamped with people who want you to tutor them, perhaps your school awarded more scholarships than usual, so there are a greater number of students who need your services. Alternately, perhaps you ran an ad in your school’s college newspaper, and that led to the influx of students wanting you to tutor them.
Businesses are in the same boat you are as a tutor. They take a look at symptoms and try to drill down to the potential causes. If you approach a marketing research company with either scenario—either too much or too little business—the firm will seek more information from you such as the following:
- In what semester(s) did your tutoring revenues fall (or rise)?
- In what subject areas did your tutoring revenues fall (or rise)?
- In what sales channels did revenues fall (or rise): Were there fewer (or more) referrals from professors or other students? Did the ad you ran result in fewer (or more) referrals this month than in the past months?
- Among what demographic groups did your revenues fall (or rise)—women or men, people with certain majors, or first-year, second-, third-, or fourth-year students?
The key is to look at all potential causes so as to narrow the parameters of the study to the information you actually need to make a good decision about how to fix your business if revenues have dropped or whether or not to expand it if your revenues have exploded.
The next task for the researcher is to put into writing the research objective. The research objective is the goal(s) the research is supposed to accomplish. The marketing research objective for your tutoring business might read as follows:
To survey college professors who teach 100- and 200-level math courses to determine why the number of students referred for tutoring dropped in the second semester.
This is admittedly a simple example designed to help you understand the basic concept. If you take a marketing research course, you will learn that research objectives get a lot more complicated than this. The following is an example:
“To gather information from a sample representative of the U.S. population among those who are ‘very likely’ to purchase an automobile within the next 6 months, which assesses preferences (measured on a 1–5 scale ranging from ‘very likely to buy’ to ‘not likely at all to buy’) for the model diesel at three different price levels. Such data would serve as input into a forecasting model that would forecast unit sales, by geographic regions of the country, for each combination of the model’s different prices and fuel configurations (Burns & Bush, 2010).”
Now do you understand why defining the problem is complicated and half the battle? Many a marketing research effort is doomed from the start because the problem was improperly defined. Coke’s ill-fated decision to change the formula of Coca-Cola in 1985 is a case in point: Pepsi had been creeping up on Coke in terms of market share over the years as well as running a successful promotional campaign called the “Pepsi Challenge,” in which consumers were encouraged to do a blind taste test to see if they agreed that Pepsi was better. Coke spent four years researching “the problem.” Indeed, people seemed to like the taste of Pepsi better in blind taste tests. Thus, the formula for Coke was changed. But the outcry among the public was so great that the new formula didn’t last long—a matter of months—before the old formula was reinstated. Some marketing experts believe Coke incorrectly defined the problem as “How can we beat Pepsi in taste tests?” instead of “How can we gain market share against Pepsi?” (Burns & Bush, 2010)
New Coke Is It! 1985
(click to see video)
This video documents the Coca-Cola Company’s ill-fated launch of New Coke in 1985.
1985 Pepsi Commercial—“They Changed My Coke”
This video shows how Pepsi tried to capitalize on the blunder.
Step 2: Design the Research
The next step in the marketing research process is to do a research design. The research design is your “plan of attack.” It outlines what data you are going to gather and from whom, how and when you will collect the data, and how you will analyze it once it’s been obtained. Let’s look at the data you’re going to gather first.
There are two basic types of data you can gather. The first is primary data. Primary data is information you collect yourself, using hands-on tools such as interviews or surveys, specifically for the research project you’re conducting. Secondary data is data that has already been collected by someone else, or data you have already collected for another purpose. Collecting primary data is more time consuming, work intensive, and expensive than collecting secondary data. Consequently, you should always try to collect secondary data first to solve your research problem, if you can. A great deal of research on a wide variety of topics already exists. If this research contains the answer to your question, there is no need for you to replicate it. Why reinvent the wheel?
Sources of Secondary Data
Your company’s internal records are a source of secondary data. So are any data you collect as part of your marketing intelligence gathering efforts. You can also purchase syndicated research. Syndicated research is primary data that marketing research firms collect on a regular basis and sell to other companies. J.D. Power & Associates is a provider of syndicated research. The company conducts independent, unbiased surveys of customer satisfaction, product quality, and buyer behavior for various industries. The company is best known for its research in the automobile sector. One of the best-known sellers of syndicated research is the Nielsen Company, which produces the Nielsen ratings. The Nielsen ratings measure the size of television, radio, and newspaper audiences in various markets. You have probably read or heard about TV shows that get the highest (Nielsen) ratings. (Arbitron does the same thing for radio ratings.) Nielsen, along with its main competitor, Information Resources, Inc. (IRI), also sells businesses scanner-based research . Scanner-based research is information collected by scanners at checkout stands in stores. Each week Nielsen and IRI collect information on the millions of purchases made at stores. The companies then compile the information and sell it to firms in various industries that subscribe to their services. The Nielsen Company has also recently teamed up with Facebook to collect marketing research information. Via Facebook, users will see surveys in some of the spaces in which they used to see online ads (Rappeport, Gelles, 2009).
By contrast, MarketResearch.com is an example of a marketing research aggregator. A marketing research aggregator is a marketing research company that doesn’t conduct its own research and sell it. Instead, it buys research reports from other marketing research companies and then sells the reports in their entirety or in pieces to other firms. Check out MarketResearch.com’s Web site. As you will see there are a huge number of studies in every category imaginable that you can buy for relatively small amounts of money.
Figure 10.7
Market research aggregators buy research reports from other marketing research companies and then resell them in part or in whole to other companies so they don’t have to gather primary data.
Source: http://www.marketresearch.com .
Your local library is a good place to gather free secondary data. It has searchable databases as well as handbooks, dictionaries, and books, some of which you can access online. Government agencies also collect and report information on demographics, economic and employment data, health information, and balance-of-trade statistics, among a lot of other information. The U.S. Census Bureau collects census data every ten years to gather information about who lives where. Basic demographic information about sex, age, race, and types of housing in which people live in each U.S. state, metropolitan area, and rural area is gathered so that population shifts can be tracked for various purposes, including determining the number of legislators each state should have in the U.S. House of Representatives. For the U.S. government, this is primary data. For marketing managers it is an important source of secondary data.
The Survey Research Center at the University of Michigan also conducts periodic surveys and publishes information about trends in the United States. One research study the center continually conducts is called the “Changing Lives of American Families” ( http://www.isr.umich.edu/home/news/research-update/2007-01.pdf ). This is important research data for marketing managers monitoring consumer trends in the marketplace. The World Bank and the United Nations are two international organizations that collect a great deal of information. Their Web sites contain many free research studies and data related to global markets. Table 10.1 “Examples of Primary Data Sources versus Secondary Data Sources” shows some examples of primary versus secondary data sources.
Table 10.1 Examples of Primary Data Sources versus Secondary Data Sources
Gauging the Quality of Secondary Data
When you are gathering secondary information, it’s always good to be a little skeptical of it. Sometimes studies are commissioned to produce the result a client wants to hear—or wants the public to hear. For example, throughout the twentieth century, numerous studies found that smoking was good for people’s health. The problem was the studies were commissioned by the tobacco industry. Web research can also pose certain hazards. There are many biased sites that try to fool people that they are providing good data. Often the data is favorable to the products they are trying to sell. Beware of product reviews as well. Unscrupulous sellers sometimes get online and create bogus ratings for products. See below for questions you can ask to help gauge the credibility of secondary information.
Gauging the Credibility of Secondary Data: Questions to Ask
- Who gathered this information?
- For what purpose?
- What does the person or organization that gathered the information have to gain by doing so?
- Was the information gathered and reported in a systematic manner?
- Is the source of the information accepted as an authority by other experts in the field?
- Does the article provide objective evidence to support the position presented?
Types of Research Design
Now let’s look specifically at the types of research designs that are utilized. By understanding different types of research designs, a researcher can solve a client’s problems more quickly and efficiently without jumping through more hoops than necessary. Research designs fall into one of the following three categories:
- Exploratory research design
- Descriptive research design
- Causal research design (experiments)
An exploratory research design is useful when you are initially investigating a problem but you haven’t defined it well enough to do an in-depth study of it. Perhaps via your regular market intelligence, you have spotted what appears to be a new opportunity in the marketplace. You would then do exploratory research to investigate it further and “get your feet wet,” as the saying goes. Exploratory research is less structured than other types of research, and secondary data is often utilized.
One form of exploratory research is qualitative research. Qualitative research is any form of research that includes gathering data that is not quantitative, and often involves exploring questions such as why as much as what or how much . Different forms, such as depth interviews and focus group interviews, are common in marketing research.
The depth interview —engaging in detailed, one-on-one, question-and-answer sessions with potential buyers—is an exploratory research technique. However, unlike surveys, the people being interviewed aren’t asked a series of standard questions. Instead the interviewer is armed with some general topics and asks questions that are open ended, meaning that they allow the interviewee to elaborate. “How did you feel about the product after you purchased it?” is an example of a question that might be asked. A depth interview also allows a researcher to ask logical follow-up questions such as “Can you tell me what you mean when you say you felt uncomfortable using the service?” or “Can you give me some examples?” to help dig further and shed additional light on the research problem. Depth interviews can be conducted in person or over the phone. The interviewer either takes notes or records the interview.
Focus groups and case studies are often utilized for exploratory research as well. A focus group is a group of potential buyers who are brought together to discuss a marketing research topic with one another. A moderator is used to focus the discussion, the sessions are recorded, and the main points of consensus are later summarized by the market researcher. Textbook publishers often gather groups of professors at educational conferences to participate in focus groups. However, focus groups can also be conducted on the telephone, in online chat rooms, or both, using meeting software like WebEx. The basic steps of conducting a focus group are outlined below.
The Basic Steps of Conducting a Focus Group
- Establish the objectives of the focus group. What is its purpose?
- Identify the people who will participate in the focus group. What makes them qualified to participate? How many of them will you need and what they will be paid?
- Obtain contact information for the participants and send out invitations (usually e-mails are most efficient).
- Develop a list of questions.
- Choose a facilitator.
- Choose a location in which to hold the focus group and the method by which it will be recorded.
- Conduct the focus group. If the focus group is not conducted electronically, include name tags for the participants, pens and notepads, any materials the participants need to see, and refreshments. Record participants’ responses.
- Summarize the notes from the focus group and write a report for management.
A case study looks at how another company solved the problem that’s being researched. Sometimes multiple cases, or companies, are used in a study. Case studies nonetheless have a mixed reputation. Some researchers believe it’s hard to generalize, or apply, the results of a case study to other companies. Nonetheless, collecting information about companies that encountered the same problems your firm is facing can give you a certain amount of insight about what direction you should take. In fact, one way to begin a research project is to carefully study a successful product or service.
Two other types of qualitative data used for exploratory research are ethnographies and projective techniques. In an ethnography , researchers interview, observe, and often videotape people while they work, live, shop, and play. The Walt Disney Company has recently begun using ethnographers to uncover the likes and dislikes of boys aged six to fourteen, a financially attractive market segment for Disney, but one in which the company has been losing market share. The ethnographers visit the homes of boys, observe the things they have in their rooms to get a sense of their hobbies, and accompany them and their mothers when they shop to see where they go, what the boys are interested in, and what they ultimately buy. (The children get seventy-five dollars out of the deal, incidentally.) (Barnes, 2009)
Projective techniques are used to reveal information research respondents might not reveal by being asked directly. Asking a person to complete sentences such as the following is one technique:
People who buy Coach handbags __________.
(Will he or she reply with “are cool,” “are affluent,” or “are pretentious,” for example?)
KFC’s grilled chicken is ______.
Or the person might be asked to finish a story that presents a certain scenario. Word associations are also used to discern people’s underlying attitudes toward goods and services. Using a word-association technique, a market researcher asks a person to say or write the first word that comes to his or her mind in response to another word. If the initial word is “fast food,” what word does the person associate it with or respond with? Is it “McDonald’s”? If many people reply that way, and you’re conducting research for Burger King, that could indicate Burger King has a problem. However, if the research is being conducted for Wendy’s, which recently began running an advertising campaign to the effect that Wendy’s offerings are “better than fast food,” it could indicate that the campaign is working.
Completing cartoons is yet another type of projective technique. It’s similar to finishing a sentence or story, only with the pictures. People are asked to look at a cartoon such as the one shown in Figure 10.8 “Example of a Cartoon-Completion Projective Technique” . One of the characters in the picture will have made a statement, and the person is asked to fill in the empty cartoon “bubble” with how they think the second character will respond.
Figure 10.8 Example of a Cartoon-Completion Projective Technique

In some cases, your research might end with exploratory research. Perhaps you have discovered your organization lacks the resources needed to produce the product. In other cases, you might decide you need more in-depth, quantitative research such as descriptive research or causal research, which are discussed next. Most marketing research professionals advise using both types of research, if it’s feasible. On the one hand, the qualitative-type research used in exploratory research is often considered too “lightweight.” Remember earlier in the chapter when we discussed telephone answering machines and the hit TV sitcom Seinfeld ? Both product ideas were initially rejected by focus groups. On the other hand, relying solely on quantitative information often results in market research that lacks ideas.
The Stone Wheel—What One Focus Group Said
Watch the video to see a funny spoof on the usefulness—or lack of usefulness—of focus groups.
Descriptive Research
Anything that can be observed and counted falls into the category of descriptive research design. A study using a descriptive research design involves gathering hard numbers, often via surveys, to describe or measure a phenomenon so as to answer the questions of who , what , where , when , and how . “On a scale of 1–5, how satisfied were you with your service?” is a question that illustrates the information a descriptive research design is supposed to capture.
Physiological measurements also fall into the category of descriptive design. Physiological measurements measure people’s involuntary physical responses to marketing stimuli, such as an advertisement. Elsewhere, we explained that researchers have gone so far as to scan the brains of consumers to see what they really think about products versus what they say about them. Eye tracking is another cutting-edge type of physiological measurement. It involves recording the movements of a person’s eyes when they look at some sort of stimulus, such as a banner ad or a Web page. The Walt Disney Company has a research facility in Austin, Texas, that it uses to take physical measurements of viewers when they see Disney programs and advertisements. The facility measures three types of responses: people’s heart rates, skin changes, and eye movements (eye tracking) (Spangler, 2009).
Figure 10.9

A woman shows off her headgear for an eye-tracking study. The gear’s not exactly a fashion statement but . . .
lawrencegs – Google Glass – CC BY 2.0.
A strictly descriptive research design instrument—a survey, for example—can tell you how satisfied your customers are. It can’t, however, tell you why. Nor can an eye-tracking study tell you why people’s eyes tend to dwell on certain types of banner ads—only that they do. To answer “why” questions an exploratory research design or causal research design is needed (Wagner, 2007).
Causal Research
Causal research design examines cause-and-effect relationships. Using a causal research design allows researchers to answer “what if” types of questions. In other words, if a firm changes X (say, a product’s price, design, placement, or advertising), what will happen to Y (say, sales or customer loyalty)? To conduct causal research, the researcher designs an experiment that “controls,” or holds constant, all of a product’s marketing elements except one (or using advanced techniques of research, a few elements can be studied at the same time). The one variable is changed, and the effect is then measured. Sometimes the experiments are conducted in a laboratory using a simulated setting designed to replicate the conditions buyers would experience. Or the experiments may be conducted in a virtual computer setting.
You might think setting up an experiment in a virtual world such as the online game Second Life would be a viable way to conduct controlled marketing research. Some companies have tried to use Second Life for this purpose, but the results have been somewhat mixed as to whether or not it is a good medium for marketing research. The German marketing research firm Komjuniti was one of the first “real-world” companies to set up an “island” in Second Life upon which it could conduct marketing research. However, with so many other attractive fantasy islands in which to play, the company found it difficult to get Second Life residents, or players, to voluntarily visit the island and stay long enough so meaningful research could be conducted. (Plus, the “residents,” or players, in Second Life have been known to protest corporations invading their world. When the German firm Komjuniti created an island in Second Life to conduct marketing research, the residents showed up waving signs and threatening to boycott the island.) (Wagner, 2007)
Why is being able to control the setting so important? Let’s say you are an American flag manufacturer and you are working with Walmart to conduct an experiment to see where in its stores American flags should be placed so as to increase their sales. Then the terrorist attacks of 9/11 occur. In the days afterward, sales skyrocketed—people bought flags no matter where they were displayed. Obviously, the terrorist attacks in the United States would have skewed the experiment’s data.
An experiment conducted in a natural setting such as a store is referred to as a field experiment . Companies sometimes do field experiments either because it is more convenient or because they want to see if buyers will behave the same way in the “real world” as in a laboratory or on a computer. The place the experiment is conducted or the demographic group of people the experiment is administered to is considered the test market . Before a large company rolls out a product to the entire marketplace, it will often place the offering in a test market to see how well it will be received. For example, to compete with MillerCoors’ sixty-four-calorie beer MGD 64, Anheuser-Busch recently began testing its Select 55 beer in certain cities around the country (McWilliams, 2009).
Figure 10.10
Select 55 beer: Coming soon to a test market near you? (If you’re on a diet, you have to hope so!)
Martine – Le champagne – CC BY-NC 2.0.
Many companies use experiments to test all of their marketing communications. For example, the online discount retailer O.co (formerly called Overstock.com) carefully tests all of its marketing offers and tracks the results of each one. One study the company conducted combined twenty-six different variables related to offers e-mailed to several thousand customers. The study resulted in a decision to send a group of e-mails to different segments. The company then tracked the results of the sales generated to see if they were in line with the earlier experiment it had conducted that led it to make the offer.
Step 3: Design the Data-Collection Forms
If the behavior of buyers is being formally observed, and a number of different researchers are conducting observations, the data obviously need to be recorded on a standardized data-collection form that’s either paper or electronic. Otherwise, the data collected will not be comparable. The items on the form could include a shopper’s sex; his or her approximate age; whether the person seemed hurried, moderately hurried, or unhurried; and whether or not he or she read the label on products, used coupons, and so forth.
The same is true when it comes to surveying people with questionnaires. Surveying people is one of the most commonly used techniques to collect quantitative data. Surveys are popular because they can be easily administered to large numbers of people fairly quickly. However, to produce the best results, the questionnaire for the survey needs to be carefully designed.
Questionnaire Design
Most questionnaires follow a similar format: They begin with an introduction describing what the study is for, followed by instructions for completing the questionnaire and, if necessary, returning it to the market researcher. The first few questions that appear on the questionnaire are usually basic, warm-up type of questions the respondent can readily answer, such as the respondent’s age, level of education, place of residence, and so forth. The warm-up questions are then followed by a logical progression of more detailed, in-depth questions that get to the heart of the question being researched. Lastly, the questionnaire wraps up with a statement that thanks the respondent for participating in the survey and information and explains when and how they will be paid for participating. To see some examples of questionnaires and how they are laid out, click on the following link: http://cas.uah.edu/wrenb/mkt343/Project/Sample%20Questionnaires.htm .
How the questions themselves are worded is extremely important. It’s human nature for respondents to want to provide the “correct” answers to the person administering the survey, so as to seem agreeable. Therefore, there is always a hazard that people will try to tell you what you want to hear on a survey. Consequently, care needs to be taken that the survey questions are written in an unbiased, neutral way. In other words, they shouldn’t lead a person taking the questionnaire to answer a question one way or another by virtue of the way you have worded it. The following is an example of a leading question.
Don’t you agree that teachers should be paid more ?
The questions also need to be clear and unambiguous. Consider the following question:
Which brand of toothpaste do you use ?
The question sounds clear enough, but is it really? What if the respondent recently switched brands? What if she uses Crest at home, but while away from home or traveling, she uses Colgate’s Wisp portable toothpaste-and-brush product? How will the respondent answer the question? Rewording the question as follows so it’s more specific will help make the question clearer:
Which brand of toothpaste have you used at home in the past six months? If you have used more than one brand, please list each of them 1 .
Sensitive questions have to be asked carefully. For example, asking a respondent, “Do you consider yourself a light, moderate, or heavy drinker?” can be tricky. Few people want to admit to being heavy drinkers. You can “soften” the question by including a range of answers, as the following example shows:
How many alcoholic beverages do you consume in a week ?
- __0–5 alcoholic beverages
- __5–10 alcoholic beverages
- __10–15 alcoholic beverages
Many people don’t like to answer questions about their income levels. Asking them to specify income ranges rather than divulge their actual incomes can help.
Other research question “don’ts” include using jargon and acronyms that could confuse people. “How often do you IM?” is an example. Also, don’t muddy the waters by asking two questions in the same question, something researchers refer to as a double-barreled question . “Do you think parents should spend more time with their children and/or their teachers?” is an example of a double-barreled question.
Open-ended questions , or questions that ask respondents to elaborate, can be included. However, they are harder to tabulate than closed-ended questions , or questions that limit a respondent’s answers. Multiple-choice and yes-and-no questions are examples of closed-ended questions.
Testing the Questionnaire
You have probably heard the phrase “garbage in, garbage out.” If the questions are bad, the information gathered will be bad, too. One way to make sure you don’t end up with garbage is to test the questionnaire before sending it out to find out if there are any problems with it. Is there enough space for people to elaborate on open-ended questions? Is the font readable? To test the questionnaire, marketing research professionals first administer it to a number of respondents face to face. This gives the respondents the chance to ask the researcher about questions or instructions that are unclear or don’t make sense to them. The researcher then administers the questionnaire to a small subset of respondents in the actual way the survey is going to be disseminated, whether it’s delivered via phone, in person, by mail, or online.
Getting people to participate and complete questionnaires can be difficult. If the questionnaire is too long or hard to read, many people won’t complete it. So, by all means, eliminate any questions that aren’t necessary. Of course, including some sort of monetary incentive for completing the survey can increase the number of completed questionnaires a market researcher will receive.
Step 4: Specify the Sample
Once you have created your questionnaire or other marketing study, how do you figure out who should participate in it? Obviously, you can’t survey or observe all potential buyers in the marketplace. Instead, you must choose a sample. A sample is a subset of potential buyers that are representative of your entire target market, or population being studied. Sometimes market researchers refer to the population as the universe to reflect the fact that it includes the entire target market, whether it consists of a million people, a hundred thousand, a few hundred, or a dozen. “All unmarried people over the age of eighteen who purchased Dirt Devil steam cleaners in the United States during 2011” is an example of a population that has been defined.
Obviously, the population has to be defined correctly. Otherwise, you will be studying the wrong group of people. Not defining the population correctly can result in flawed research, or sampling error. A sampling error is any type of marketing research mistake that results because a sample was utilized. One criticism of Internet surveys is that the people who take these surveys don’t really represent the overall population. On average, Internet survey takers tend to be more educated and tech savvy. Consequently, if they solely constitute your population, even if you screen them for certain criteria, the data you collect could end up being skewed.
The next step is to put together the sampling frame , which is the list from which the sample is drawn. The sampling frame can be put together using a directory, customer list, or membership roster (Wrenn et. al., 2007). Keep in mind that the sampling frame won’t perfectly match the population. Some people will be included on the list who shouldn’t be. Other people who should be included will be inadvertently omitted. It’s no different than if you were to conduct a survey of, say, 25 percent of your friends, using friends’ names you have in your cell phone. Most of your friends’ names are likely to be programmed into your phone, but not all of them. As a result, a certain degree of sampling error always occurs.
There are two main categories of samples in terms of how they are drawn: probability samples and nonprobability samples. A probability sample is one in which each would-be participant has a known and equal chance of being selected. The chance is known because the total number of people in the sampling frame is known. For example, if every other person from the sampling frame were chosen, each person would have a 50 percent chance of being selected.
A nonprobability sample is any type of sample that’s not drawn in a systematic way. So the chances of each would-be participant being selected can’t be known. A convenience sample is one type of nonprobability sample. It is a sample a researcher draws because it’s readily available and convenient to do so. Surveying people on the street as they pass by is an example of a convenience sample. The question is, are these people representative of the target market?
For example, suppose a grocery store needed to quickly conduct some research on shoppers to get ready for an upcoming promotion. Now suppose that the researcher assigned to the project showed up between the hours of 10 a.m. and 12 p.m. on a weekday and surveyed as many shoppers as possible. The problem is that the shoppers wouldn’t be representative of the store’s entire target market. What about commuters who stop at the store before and after work? Their views wouldn’t be represented. Neither would people who work the night shift or shop at odd hours. As a result, there would be a lot of room for sampling error in this study. For this reason, studies that use nonprobability samples aren’t considered as accurate as studies that use probability samples. Nonprobability samples are more often used in exploratory research.
Lastly, the size of the sample has an effect on the amount of sampling error. Larger samples generally produce more accurate results. The larger your sample is, the more data you will have, which will give you a more complete picture of what you’re studying. However, the more people surveyed or studied, the more costly the research becomes.
Statistics can be used to determine a sample’s optimal size. If you take a marketing research or statistics class, you will learn more about how to determine the optimal size.
Of course, if you hire a marketing research company, much of this work will be taken care of for you. Many marketing research companies, like ResearchNow, maintain panels of prescreened people they draw upon for samples. In addition, the marketing research firm will be responsible for collecting the data or contracting with a company that specializes in data collection. Data collection is discussed next.
Step 5: Collect the Data
As we have explained, primary marketing research data can be gathered in a number of ways. Surveys, taking physical measurements, and observing people are just three of the ways we discussed. If you’re observing customers as part of gathering the data, keep in mind that if shoppers are aware of the fact, it can have an effect on their behavior. For example, if a customer shopping for feminine hygiene products in a supermarket aisle realizes she is being watched, she could become embarrassed and leave the aisle, which would adversely affect your data. To get around problems such as these, some companies set up cameras or two-way mirrors to observe customers. Organizations also hire mystery shoppers to work around the problem. A mystery shopper is someone who is paid to shop at a firm’s establishment or one of its competitors to observe the level of service, cleanliness of the facility, and so forth, and report his or her findings to the firm.
Make Extra Money as a Mystery Shopper
Watch the YouTube video to get an idea of how mystery shopping works.
Survey data can be collected in many different ways and combinations of ways. The following are the basic methods used:
- Face-to-face (can be computer aided)
- Telephone (can be computer aided or completely automated)
- Mail and hand delivery
- E-mail and the Web
A face-to-face survey is, of course, administered by a person. The surveys are conducted in public places such as in shopping malls, on the street, or in people’s homes if they have agreed to it. In years past, it was common for researchers in the United States to knock on people’s doors to gather survey data. However, randomly collected door-to-door interviews are less common today, partly because people are afraid of crime and are reluctant to give information to strangers (McDaniel & Gates, 1998).
Nonetheless, “beating the streets” is still a legitimate way questionnaire data is collected. When the U.S. Census Bureau collects data on the nation’s population, it hand delivers questionnaires to rural households that do not have street-name and house-number addresses. And Census Bureau workers personally survey the homeless to collect information about their numbers. Face-to-face surveys are also commonly used in third world countries to collect information from people who cannot read or lack phones and computers.
A plus of face-to-face surveys is that they allow researchers to ask lengthier, more complex questions because the people being surveyed can see and read the questionnaires. The same is true when a computer is utilized. For example, the researcher might ask the respondent to look at a list of ten retail stores and rank the stores from best to worst. The same question wouldn’t work so well over the telephone because the person couldn’t see the list. The question would have to be rewritten. Another drawback with telephone surveys is that even though federal and state “do not call” laws generally don’t prohibit companies from gathering survey information over the phone, people often screen such calls using answering machines and caller ID.
Probably the biggest drawback of both surveys conducted face-to-face and administered over the phone by a person is that they are labor intensive and therefore costly. Mailing out questionnaires is costly, too, and the response rates can be rather low. Think about why that might be so: if you receive a questionnaire in the mail, it is easy to throw it in the trash; it’s harder to tell a market researcher who approaches you on the street that you don’t want to be interviewed.
By contrast, gathering survey data collected by a computer, either over the telephone or on the Internet, can be very cost-effective and in some cases free. SurveyMonkey and Zoomerang are two Web sites that will allow you to create online questionnaires, e-mail them to up to one hundred people for free, and view the responses in real time as they come in. For larger surveys, you have to pay a subscription price of a few hundred dollars. But that still can be extremely cost-effective. The two Web sites also have a host of other features such as online-survey templates you can use to create your questionnaire, a way to set up automatic reminders sent to people who haven’t yet completed their surveys, and tools you can use to create graphics to put in your final research report. To see how easy it is to put together a survey in SurveyMonkey, click on the following link: http://help.surveymonkey.com/app/tutorials/detail/a_id/423 .
Like a face-to-face survey, an Internet survey can enable you to show buyers different visuals such as ads, pictures, and videos of products and their packaging. Web surveys are also fast, which is a major plus. Whereas face-to-face and mailed surveys often take weeks to collect, you can conduct a Web survey in a matter of days or even hours. And, of course, because the information is electronically gathered it can be automatically tabulated. You can also potentially reach a broader geographic group than you could if you had to personally interview people. The Zoomerang Web site allows you to create surveys in forty different languages.
Another plus for Web and computer surveys (and electronic phone surveys) is that there is less room for human error because the surveys are administered electronically. For instance, there’s no risk that the interviewer will ask a question wrong or use a tone of voice that could mislead the respondents. Respondents are also likely to feel more comfortable inputting the information into a computer if a question is sensitive than they would divulging the information to another person face-to-face or over the phone. Given all of these advantages, it’s not surprising that the Internet is quickly becoming the top way to collect primary data. However, like mail surveys, surveys sent to people over the Internet are easy to ignore.
Lastly, before the data collection process begins, the surveyors and observers need to be trained to look for the same things, ask questions the same way, and so forth. If they are using rankings or rating scales, they need to be “on the same page,” so to speak, as to what constitutes a high ranking or a low ranking. As an analogy, you have probably had some teachers grade your college papers harder than others. The goal of training is to avoid a wide disparity between how different observers and interviewers record the data.
Figure 10.11

Training people so they know what constitutes different ratings when they are collecting data will improve the quality of the information gathered in a marketing research study.
Ricardo Rodriquez – Satisfaction survey – CC BY-NC-ND 2.0.
For example, if an observation form asks the observers to describe whether a shopper’s behavior is hurried, moderately hurried, or unhurried, they should be given an idea of what defines each rating. Does it depend on how much time the person spends in the store or in the individual aisles? How fast they walk? In other words, the criteria and ratings need to be spelled out.
Collecting International Marketing Research Data
Gathering marketing research data in foreign countries poses special challenges. However, that doesn’t stop firms from doing so. Marketing research companies are located all across the globe, in fact. Eight of the ten largest marketing research companies in the world are headquartered in the United States. However, five of these eight firms earn more of their revenues abroad than they do in the United States. There’s a reason for this: many U.S. markets were saturated, or tapped out, long ago in terms of the amount that they can grow. Coke is an example. As you learned earlier in the book, most of the Coca-Cola Company’s revenues are earned in markets abroad. To be sure, the United States is still a huge market when it comes to the revenues marketing research firms generate by conducting research in the country: in terms of their spending, American consumers fuel the world’s economic engine. Still, emerging countries with growing middle classes, such as China, India, and Brazil, are hot new markets companies want to tap.
What kind of challenges do firms face when trying to conduct marketing research abroad? As we explained, face-to-face surveys are commonly used in third world countries to collect information from people who cannot read or lack phones and computers. However, face-to-face surveys are also common in Europe, despite the fact that phones and computers are readily available. In-home surveys are also common in parts of Europe. By contrast, in some countries, including many Asian countries, it’s considered taboo or rude to try to gather information from strangers either face-to-face or over the phone. In many Muslim countries, women are forbidden to talk to strangers.
And how do you figure out whom to research in foreign countries? That in itself is a problem. In the United States, researchers often ask if they can talk to the heads of households to conduct marketing research. But in countries in which domestic servants or employees are common, the heads of households aren’t necessarily the principal shoppers; their domestic employees are (Malhotra).
Translating surveys is also an issue. Have you ever watched the TV comedians Jay Leno and David Letterman make fun of the English translations found on ethnic menus and products? Research tools such as surveys can suffer from the same problem. Hiring someone who is bilingual to translate a survey into another language can be a disaster if the person isn’t a native speaker of the language to which the survey is being translated.
One way companies try to deal with translation problems is by using back translation. When back translation is used, a native speaker translates the survey into the foreign language and then translates it back again to the original language to determine if there were gaps in meaning—that is, if anything was lost in translation. And it’s not just the language that’s an issue. If the research involves any visual images, they, too, could be a point of confusion. Certain colors, shapes, and symbols can have negative connotations in other countries. For example, the color white represents purity in many Western cultures, but in China, it is the color of death and mourning (Zouhali-Worrall, 2008). Also, look back at the cartoon-completion exercise in Figure 10.8 “Example of a Cartoon-Completion Projective Technique” . What would women in Muslim countries who aren’t allowed to converse with male sellers think of it? Chances are, the cartoon wouldn’t provide you with the information you’re seeking if Muslim women in some countries were asked to complete it.
One way marketing research companies are dealing with the complexities of global research is by merging with or acquiring marketing research companies abroad. The Nielsen Company is the largest marketing research company in the world. The firm operates in more than a hundred countries and employs more than forty thousand people. Many of its expansions have been the result of acquisitions and mergers.
Step 6: Analyze the Data
Step 6 involves analyzing the data to ensure it’s as accurate as possible. If the research is collected by hand using a pen and pencil, it’s entered into a computer. Or respondents might have already entered the information directly into a computer. For example, when Toyota goes to an event such as a car show, the automaker’s marketing personnel ask would-be buyers to complete questionnaires directly on computers. Companies are also beginning to experiment with software that can be used to collect data using mobile phones.
Once all the data is collected, the researchers begin the data cleaning , which is the process of removing data that have accidentally been duplicated (entered twice into the computer) or correcting data that have obviously been recorded wrong. A program such as Microsoft Excel or a statistical program such as Predictive Analytics Software (PASW, which was formerly known as SPSS) is then used to tabulate, or calculate, the basic results of the research, such as the total number of participants and how collectively they answered various questions. The programs can also be used to calculate averages, such as the average age of respondents, their average satisfaction, and so forth. The same can done for percentages, and other values you learned about, or will learn about, in a statistics course, such as the standard deviation, mean, and median for each question.
The information generated by the programs can be used to draw conclusions, such as what all customers might like or not like about an offering based on what the sample group liked or did not like. The information can also be used to spot differences among groups of people. For example, the research might show that people in one area of the country like the product better than people in another area. Trends to predict what might happen in the future can also be spotted.
If there are any open-ended questions respondents have elaborated upon—for example, “Explain why you like the current brand you use better than any other brand”—the answers to each are pasted together, one on top of another, so researchers can compare and summarize the information. As we have explained, qualitative information such as this can give you a fuller picture of the results of the research.
Part of analyzing the data is to see if it seems sound. Does the way in which the research was conducted seem sound? Was the sample size large enough? Are the conclusions that become apparent from it reasonable?
The two most commonly used criteria used to test the soundness of a study are (1) validity and (2) reliability. A study is valid if it actually tested what it was designed to test. For example, did the experiment you ran in Second Life test what it was designed to test? Did it reflect what could really happen in the real world? If not, the research isn’t valid. If you were to repeat the study, and get the same results (or nearly the same results), the research is said to be reliable . If you get a drastically different result if you repeat the study, it’s not reliable. The data collected, or at least some it, can also be compared to, or reconciled with, similar data from other sources either gathered by your firm or by another organization to see if the information seems on target.
Stage 7: Write the Research Report and Present Its Findings
If you end up becoming a marketing professional and conducting a research study after you graduate, hopefully you will do a great job putting the study together. You will have defined the problem correctly, chosen the right sample, collected the data accurately, analyzed it, and your findings will be sound. At that point, you will be required to write the research report and perhaps present it to an audience of decision makers. You will do so via a written report and, in some cases, a slide or PowerPoint presentation based on your written report.
The six basic elements of a research report are as follows.
- Title Page . The title page explains what the report is about, when it was conducted and by whom, and who requested it.
- Table of Contents . The table of contents outlines the major parts of the report, as well as any graphs and charts, and the page numbers on which they can be found.
- Executive Summary . The executive summary summarizes all the details in the report in a very quick way. Many people who receive the report—both executives and nonexecutives—won’t have time to read the entire report. Instead, they will rely on the executive summary to quickly get an idea of the study’s results and what to do about those results.
Methodology and Limitations . The methodology section of the report explains the technical details of how the research was designed and conducted. The section explains, for example, how the data was collected and by whom, the size of the sample, how it was chosen, and whom or what it consisted of (e.g., the number of women versus men or children versus adults). It also includes information about the statistical techniques used to analyze the data.
Every study has errors—sampling errors, interviewer errors, and so forth. The methodology section should explain these details, so decision makers can consider their overall impact. The margin of error is the overall tendency of the study to be off kilter—that is, how far it could have gone wrong in either direction. Remember how newscasters present the presidential polls before an election? They always say, “This candidate is ahead 48 to 44 percent, plus or minus 2 percent.” That “plus or minus” is the margin of error. The larger the margin of error is, the less likely the results of the study are accurate. The margin of error needs to be included in the methodology section.
- Findings . The findings section is a longer, fleshed-out version of the executive summary that goes into more detail about the statistics uncovered by the research that bolster the study’s findings. If you have related research or secondary data on hand that back up the findings, it can be included to help show the study did what it was designed to do.
- Recommendations . The recommendations section should outline the course of action you think should be taken based on the findings of the research and the purpose of the project. For example, if you conducted a global market research study to identify new locations for stores, make a recommendation for the locations (Mersdorf, 2009).
As we have said, these are the basic sections of a marketing research report. However, additional sections can be added as needed. For example, you might need to add a section on the competition and each firm’s market share. If you’re trying to decide on different supply chain options, you will need to include a section on that topic.
As you write the research report, keep your audience in mind. Don’t use technical jargon decision makers and other people reading the report won’t understand. If technical terms must be used, explain them. Also, proofread the document to ferret out any grammatical errors and typos, and ask a couple of other people to proofread behind you to catch any mistakes you might have missed. If your research report is riddled with errors, its credibility will be undermined, even if the findings and recommendations you make are extremely accurate.
Many research reports are presented via PowerPoint. If you’re asked to create a slideshow presentation from the report, don’t try to include every detail in the report on the slides. The information will be too long and tedious for people attending the presentation to read through. And if they do go to the trouble of reading all the information, they probably won’t be listening to the speaker who is making the presentation.
Instead of including all the information from the study in the slides, boil each section of the report down to key points and add some “talking points” only the presenter will see. After or during the presentation, you can give the attendees the longer, paper version of the report so they can read the details at a convenient time, if they choose to.
Key Takeaway
Step 1 in the marketing research process is to define the problem. Businesses take a look at what they believe are symptoms and try to drill down to the potential causes so as to precisely define the problem. The next task for the researcher is to put into writing the research objective, or goal, the research is supposed to accomplish. Step 2 in the process is to design the research. The research design is the “plan of attack.” It outlines what data you are going to gather, from whom, how, and when, and how you’re going to analyze it once it has been obtained. Step 3 is to design the data-collection forms, which need to be standardized so the information gathered on each is comparable. Surveys are a popular way to gather data because they can be easily administered to large numbers of people fairly quickly. However, to produce the best results, survey questionnaires need to be carefully designed and pretested before they are used. Step 4 is drawing the sample, or a subset of potential buyers who are representative of your entire target market. If the sample is not correctly selected, the research will be flawed. Step 5 is to actually collect the data, whether it’s collected by a person face-to-face, over the phone, or with the help of computers or the Internet. The data-collection process is often different in foreign countries. Step 6 is to analyze the data collected for any obvious errors, tabulate the data, and then draw conclusions from it based on the results. The last step in the process, Step 7, is writing the research report and presenting the findings to decision makers.
Review Questions
- Explain why it’s important to carefully define the problem or opportunity a marketing research study is designed to investigate.
- Describe the different types of problems that can occur when marketing research professionals develop questions for surveys.
- How does a probability sample differ from a nonprobability sample?
- What makes a marketing research study valid? What makes a marketing research study reliable?
- What sections should be included in a marketing research report? What is each section designed to do?
1 “Questionnaire Design,” QuickMBA , http://www.quickmba.com/marketing/research/qdesign (accessed December 14, 2009).
Barnes, B., “Disney Expert Uses Science to Draw Boy Viewers,” New York Times , April 15, 2009, http://www.nytimes.com/2009/04/14/arts/television/14boys.html?pagewanted=1&_r=1 (accessed December 14, 2009).
Burns A. and Ronald Bush, Marketing Research , 6th ed. (Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall, 2010), 85.
Malhotra, N., Marketing Research: An Applied Approach , 6th ed. (Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall), 764.
McDaniel, C. D. and Roger H. Gates, Marketing Research Essentials , 2nd ed. (Cincinnati: South-Western College Publishing, 1998), 61.
McWilliams, J., “A-B Puts Super-Low-Calorie Beer in Ring with Miller,” St. Louis Post-Dispatch , August 16, 2009, http://www.stltoday.com/business/next-matchup-light-weights-a-b-puts-super-low-calorie/article_47511bfe-18ca-5979-bdb9-0526c97d4edf.html (accessed April 13, 2012).
Mersdorf, S., “How to Organize Your Next Survey Report,” Cvent , August 24, 2009, http://survey.cvent.com/blog/cvent-survey/0/0/how-to-organize-your-next-survey-report (accessed December 14, 2009).
Rappeport A. and David Gelles, “Facebook to Form Alliance with Nielsen,” Financial Times , September 23, 2009, 16.
Spangler, T., “Disney Lab Tracks Feelings,” Multichannel News 30, no. 30 (August 3, 2009): 26.
Wagner, J., “Marketing in Second Life Doesn’t Work…Here Is Why!” GigaOM , April 4, 2007, http://gigaom.com/2007/04/04/3-reasons-why-marketing-in-second-life-doesnt-work (accessed December 14, 2009).
Wrenn, B., Robert E. Stevens, and David L. Loudon, Marketing Research: Text and Cases , 2nd ed. (Binghamton, NY: Haworth Press, 2007), 180.
Zouhali-Worrall, M., “Found in Translation: Avoiding Multilingual Gaffes,” CNNMoney.com , July 14, 2008, http://money.cnn.com/2008/07/07/smallbusiness/language_translation.fsb/index.htm (accessed December 14, 2009).
Principles of Marketing Copyright © 2015 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Marketing (The Brian Tracy Success Library) by Brian Tracy
Get full access to Marketing (The Brian Tracy Success Library) and 60K+ other titles, with a free 10-day trial of O'Reilly.
There are also live events, courses curated by job role, and more.
Summary and Conclusion
MARKETING IS the most exciting of all business sports. It is the heartbeat of every successful business. It is continually changing in response to the explosion of information, the expansion of technology, and the aggressiveness of competition, at all levels and everywhere.
All business strategy is marketing strategy. Your ability to think clearly and well about the very best marketing strategies, and to continually change and upgrade your activities, is the key to the future of your business.
Fortunately, like all business skills, marketing can be learned by practice, experimentation, and continually making mistakes. The key is to test, test, test. And whatever marketing strategy is working for you today, no matter how ...
Get Marketing (The Brian Tracy Success Library) now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.
Don’t leave empty-handed
Get Mark Richards’s Software Architecture Patterns ebook to better understand how to design components—and how they should interact.
It’s yours, free.

Check it out now on O’Reilly
Dive in for free with a 10-day trial of the O’Reilly learning platform—then explore all the other resources our members count on to build skills and solve problems every day.

BUS203: Principles of Marketing
The Marketing Plan
Read this chapter, which discusses marketing planning roles, the parts and functions of the marketing plan, forecasting, and the structure of a marketing plan audit. It also discusses PEST Analysis and other external factors that affect marketing decisions. This chapter reviews other concepts we've discussed so far. Key takeaways include the steps in the forecasting process. You will be able to identify types of forecasting methods and their advantages and disadvantages and discuss the methods used to improve the accuracy of forecasts. Lastly, you will apply marketing planning processes to ongoing business settings and identify the role of the marketing audit. Answer the discussion questions at the end of the chapter.
Functions of the Marketing Plan
In the conclusion, repeat the highlights. Summarize the target market, the offer, and the communication plan. Your conclusion should remind the reader of all the reasons why your plan is the best choice.
Of course, the written plan is itself a marketing tool. You want it to convince someone to invest in your ideas, so you want to write it down on paper in a compelling way. Figure 16.9 "Tips for Writing an Effective Marketing Plan" offers some tips for effectively doing so. Also, keep in mind that a marketing plan is created at a single point in time. The market, though, is dynamic. A good marketing plan includes how the organization should respond to various scenarios if the market changes. In addition, the plan should include "triggers" detailing what should happen under the scenarios. For example, it might specify that when a certain percentage of market share is reached, then the price of the product will be reduced (or increased). Or the plan might specify the minimum amount of the product that must be sold by a certain point in time – say, six months after the product is launched – and what should happen if the mark isn't reached. Also, it should once again be noted that the marketing plan is a communication device. For that reason, the outline of a marketing plan may look somewhat different from the order in which the tasks in the outline are actually completed.
Figure 16.9 Tips for Writing an Effective Marketing Plan

- PrivateProxy >
How to Do Market Research Using Proxies
Web scraping is a popular strategy for any small business right now. You can pick up tonnes of valuable global data without lifting a finger. You get the fun of learning all about your competitors and buyer preferences, all with some impressive protection. So, how can web scraping help you, and why should you use proxies for market research?
Data-Driven Marketing Research Solutions
Data-driven solutions are all about tailoring your approach to handle that plethora of amazing online data. You need something hands-free and efficient – something that can detect everything you need to know with minimal effort. Traditional approaches, such as market research and customer surveys aren’t completely obsolete. The issue is you can end up targeting the wrong people and wasting a lot of time. So, what’s the solution?
Using Web Scraping For Marketing Research
The easiest way to locate that valuable market data is with a web scraping tool. This lets you go even deeper into websites and draw out everything need. Your scraping tool will find detailed data on all your specific requests, and then download the results into an accessible spreadsheet. You’re then primed for your next ad campaign, product launch, or other initiative.
Strategies For Marketing Research
One strategy is to use scraping for customer data analysis. Social media platforms are perfect for this. You get to learn about visitors, their preferences, and how they interact with your brand. It helps you get a clear picture of the demographics you’re actually engaging with – not just the ones you want to be engaging with.
Another option is to go for competitor data. Start creating a detailed spreadsheet about a company’s current product line. Look at the different versions of a product, pricing options, and more. You can see where bigger businesses focus their attention and what works for them. It might not be exactly what you need to do, but it can point you in the right direction.
The Legality of Web Scraping
While all of this is still legal, it does go against the terms of service on some sites. Global websites have been known to catch users in the act and ban their IP – so watch out. That is where the best proxies for market research come in.
Using Proxies For Marketing Research.
A proxy is the perfect barrier between your personal computer and the website you want to target. You can think of this as a cloak disguising your IP address as you remain hidden. You get to work remotely, often while multitasking, and all with complete anonymity. The question is, do you want to start with a traditional datacenter proxy or opt for a residential proxy ?
Proxy Options For Marketing Research
The first option is a datacenter proxy . This is where many newbie web crawlers start because these IPs are so common and affordable. You can also use these to operate multiple profiles for easy customer engagement.
Alternatively, you might prefer to use a static residential proxy . This is a way to get an authentic residential IP address from a server and bypass all those pesky blocks. They are pretty reliable and can reward you with some impressive data hoards. However, you may have to pay more for the privilege.
To summarize, the best proxies for market research can make a massive difference. You get the anonymity and security to bypass website blocks while collecting all the business data you need. You’re then left with a valuable resource that helps you understand your target market and competitors. From there, your business is sure to grow.
Frequently Asked Questions
Please read our Documentation if you have questions that are not listed below.
Manual Web Scraping V Bot Web Scraping. Which is best?
Manual data collection is time-consuming. You can copy and paste results into a spreadsheet, but you have to be prepared to put the time and effort in for the best results. A bot works behind the scenes while you handle other tasks. It's more costly, but a big help in the long run.
Are Mobile IPs a good idea?
This is a third option for those who aren't keen on datacenter proxies. The problem is that they aren't as easy to obtain and can be far too expensive. You're better off with a more traditional approach right now.
Should you use a rotating proxy for market research?
A datacenter rotating proxy is popular because it can help you stay undetected for longer. However, static proxies can offer a more reliable connection for data transfer on larger projects. Go with what suits you best.
Top 5 posts
- How to Avoid Captcha and ReCaptcha: 10 Best Ways
- How to Fix Spotify Proxy Settings and Unblock Access to the App
- What is a Proxy Server Ports, Port Number & Proxy Address?
- 7 Ways To Fix Proxy Server Isn’t Responding Error
- How to Get Around Being Blocked on OnlyFans
Get 100% Clean DC & Residential Proxies
Related articles.
How to Scrape Best Buy With Proxy
Best Buy is a large consumer electronics retail company. In addition to its online store, it has over 1000 retail stores across the US and Canada. It sells a wide range of electronics and home appliances, from power cables and webcams up to high-end home theaters.
What is a Residential VPN?
The modern Internet forces us to be more and more attentive to the security and privacy topics of online activities. This trend is becoming more popular, both for regular users and businesses. One of the solutions to this problem lies in using special tools like VPNs or proxies to increase your privacy online. In this article, we will look at the business IP, residential IP, VPN proxy, and residential VPN tools for your online privacy.
How to Scrape Zillow
Zillow platform is a website designed to ensure an enhanced user experience for renters, buyers, and sellers of real estate at every stage of the deal. They empower people with information so they can find the best home.
8 Best & Cheapest Residential Proxies
The residential server category ranks highest in the hierarchy of all private proxies. With such an IP, you ‘borrow’ a legitimate online user's IP, and your scraping or gaming bot becomes undetectable by the geo-sensitive anti-bot programs on the intended websites. There is a cost associated with this degree of anonymity, so the best residential proxies among all the private proxy services are the most expensive. This article will compare the top residential IPs available. Knowing about its features will help you determine which proxy best meets your needs.
How to Use Residential Proxies
At Private Proxy, you can purchase a residential type of proxy with IP addresses that belong to real households. This IP is assigned by the regular ISPs, so in the end, your address will look completely legitimate and clean. In this guide, we will talk about all of the basic settings and learn how to use residential proxies.
How to Set Proxy in BlueStacks
What is BlueStacks?
Do you remember the times when mobile and computer apps were like spacecrafts that started together, but landed on the neighboring planets? You couldn’t automatically use contacts from the Android-based messenger in your PC or launch your favorite mobile game on a bigger screen, because it was made for Android.
Early Examples of EU Digital Product Passports in Action

As the world's circularity rate plummets to a mere 7.2% , the severity of unsustainable business practices looms large. A staggering 90% of product materials end up as waste, wreaking havoc on our environment. In a bid to address this pressing sustainability crisis, the European Union (EU) is pushing for the adoption of Digital Product Passports (DPPs) for most goods imported into and within the EU by 2030. Industries with high environmental impact, like batteries and textiles, will be mandated to use DPPs by 2026/2027.
A DPP is a digital copy of a physical product that contains various sustainability- and quality-related information throughout a product’s supply chain journey. This includes everything from material sources and workplace conditions to product recyclability and repairability. While DPPs are still in the pilot stage, a few early case studies have already showcased the potential of this technology.
Tesla and Audi Battery Passports
The battery industry is the prime target for DPP use, especially as EV sales are expected to increase significantly in the coming years . Questions arise about the origins of battery materials/components and battery recycling , necessitating a battery Lifecycle Assessment (LCA) that primes automakers for a Battery Digital Passport.
To address these EV challenges, the Global Battery Alliance (GBA) revealed its Battery Passport Proofs of Concept (PoC) for Tesla and Audi at the World Economic Forum in Davos in early 2023. The Battery Passports provide Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) information, including partial carbon footprint reporting, materials sourcing locations, and human rights performance.
For instance, the DPP was able to trace 100% of the cobalt used in Tesla’s EV batteries back to the Kamoto Copper Company in the Democratic Republic of Congo. While this only represents 1% of the battery materials for Tesla’s Chinese-made EV batteries, the ultimate goal is to source all materials in the future. In two similar pilot studies, Audi's Battery Passports accounted for 10% and 13.6% of total battery materials, respectively, from Hungarian and Chinese-made cells. Audi’s two Battery Passport case studies yielded a higher materials traceability percentage due to the GBA tracing lithium sourcing in addition to cobalt. These examples highlight the potential of DPPs to enhance supply chain transparency, reduce environmental impact, and improve consumer trust.
Figure 1: DPP for EV Batteries—Audi Showcasing Battery Information, Materials, ESG Specifications, and Related Data
(Source: Global Battery Alliance)

By 2027, ABI Research forecasts that 5.22 million Battery Digital Transports will ship in Western Europe, the same number of Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs) expected to be sold that year. While batteries are the biggest focus for DPPs, other industries are also being evaluated.
Edenica Building Leverages Materials Passports
Accounting for roughly 40% of raw materials consumption worldwide, the construction industry is another high priority for European DPP utilization. While not an EU member, the United Kingdom is home to a notable DPP example. The 12-story Edenica building development in London is setting a precedent for Materials Passports for commercial real estate companies across Europe. In collaboration with the engineering and environmental consultancy firm Waterman Group, solution provider Circuland has piloted a Materials Passport for the property. The DPP tracks geometry, location, material information, and other key data for structural components (floor slabs, steel frame, concrete floor, etc.). Historical data on construction materials helps real estate operators reuse resources during and after the end of their usage. With the Edenica building expected to last more than 120 years, documenting materials and components with a digital product passport will ensure significant rates of product reuse.
Chart 1: Total Number of New Buildings in the EU as Digital Passport Regulations Evolve
(Source: ABI Research)

Burton Snowboards Leverages a Digital Product Passport Platform from Avery Dennison
Companies that use textiles in manufacturing will be on the shortlist of businesses required to use DPPs by 2027. To help retailers prepare for the upcoming EU legislation, Avery Dennison recently launched a DPP-as-a-Service (DPPaaS) platform. Outdoors-focused apparel company Burton Snowboards is the first customer of Avery Dennison's DPPaaS platform. Burton Snowboards is provided with the hardware, software, digital ID technology, physical labels, and consultancy required to track the sustainability of products. The cloud-based atma.io platform centralizes supply chain data that helps Burton Snowboards understand where it can eliminate waste and how it can promote greater circularity. Customers in Burton Snowboards’ Innsbruck, Austria store, for example, will one day be able to scan a QR code on a shelfed product to reveal insight into its supply chain journey and how it can be reused. Resultingly, the DPP solution empowers the company to put its sustainability commitments in the spotlight and expand its customer base.
Figure 2: Demonstration of DPPaaS for Burton Snowboards
(Source: Avery Dennison)

Each company highlighted in this article has gained a competitive advantage early. Not only are they well-suited for the upcoming digital product passport mandates set by the EU, but their supply chain digitalization journeys are accelerating faster than those of other brands in their industry. These companies can demonstrate to their consumers and investors how they tackle climate change. Through End-to-End (E2E) supply chain visibility and sustainability reporting, stakeholders can hold these companies accountable for their green claims.
For a far more detailed analysis of how DPPs are influencing EU businesses, download ABI Research’s Digital Product Passports: Tech-Driven Sustainability and Traceability for EV Batteries, Construction Materials, and Pilot Use Cases report.

Related Blog Posts

As the EU Mandates Digital Product Passports, Here’s What Supply Chain Leaders Should Know

Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) – Creating Sustainable Products

4 Market Research Case Studies Highlighting Our Technology Intelligence Expertise

Top 14 Carbon Accounting Software Solutions
Related services.
- Circularity Technologies & Programs
Cyber & Digital Security
Industrial & manufacturing, sustainable technologies, all other services.
- Resource Center
- Journalist Inquiry
- ABI Research News
- Management Team
- Office Locations
©2024 Allied Business Intelligence, Inc. All Rights Reserved
Advertisement
Marketing Crash Investigation: Pret a Manger and Krispy Kreme’s subprime subscriptions
- Facebook Messenger
By The Drum, Crash Investigation Team
April 23, 2024 | 6 min read
Listen to article 4 min
The Drum draws on major research carried out by EY – which was recently unveiled at Possible Miami – to gain insights into subscription struggles at Pret a Manger and Krispy Kreme.

/ Photo by No Revisions on Unsplash
The subscriptions & slip-ups:
The introduction of subscription models in retail and food service industries is a strategic move aimed at enhancing customer loyalty and ensuring a steady revenue stream. However, the recent debacles surrounding the Krispy Kreme and Pret a Manger apps demonstrate that even well-intended initiatives can falter disastrously if not executed correctly. Here we examine the unfolding controversies and the lessons that can be learned.
The promise of subscriptions
The subscription model has revolutionized industries by providing customers with convenience and value, while offering businesses predictable recurring income. Krispy Kreme and Pret A Manger, sister companies under the JAB Holding Company, ventured into this model, anticipating a boost in customer engagement and sales consistency. Pret’s Coffee Subscription, for instance, offers unlimited hot drinks for a monthly fee, and Krispy Kreme recently introduced a similar scheme for doughnuts.
The downfall begins
However, what was supposed to be a smooth rollout turned chaotic. Technical glitches and operational mishaps plagued both companies, frustrating customers and tarnishing brand reputations, culminating in a lot of negative press. The subscription model, which relies heavily on an app’s functionality, stumbled due to underestimating the technical challenges involved. Customers experienced app crashes, incorrect billing, and issues with redeeming subscriptions, which led to widespread dissatisfaction.
According to reports from The Telegraph, both companies faced backlash as customers took to social media to vent their frustrations, revealing the scale of the operational shortcomings. The chaos was not limited to customer experiences; it also exposed flaws in internal communications and staff preparedness, with employees struggling to handle the surge in subscription redemptions and technical queries.
Key lessons: the crucial nature of loyalty schemes
The Drum turned to a study EY has conducted on loyalty strategies – which it recently unveiled at Possible Miami – to gain insights into what apparently has gone wrong.
There are several critical areas where Krispy Kreme and Pret faltered. First and foremost is the underestimation of the infrastructure needed to support such a subscription model. EY emphasizes the importance of robust technical solutions that can handle increased loads and complex data interactions. In this instance, both brands likely failed to align their IT capabilities with the ambitious scale of their subscription offerings.
Secondly, EY points out the significance of customer experience management in loyalty programs. Any loyalty scheme’s success heavily depends on the seamless integration of technology, staff training, and clear communication. Missteps in any of these areas can lead to customer dissatisfaction, which is particularly damaging in a social media-driven market where negative experiences are quickly amplified.
Consumer trust and brand damage
The backlash from these operational issues extends beyond immediate customer irritation. EY’s presentation underscores the long-term implications of failing at loyalty programs. Trust, once broken, is challenging to rebuild. For consumer-facing businesses like Pret and Krispy Kreme, the impact of such failures can translate into a loss of loyal customers and a tarnished brand image that dissuades potential new customers.
Moreover, the financial repercussions can be significant. While subscriptions are intended to smooth out revenue fluctuations, the costs associated with rectifying these failures – through refunds, additional customer service resources, and potential legal challenges – can negate the anticipated benefits.
Recovery and rebuilding
Recovering from such a setback requires a multifaceted approach. Companies must address the immediate technical issues and ensure that their app platforms are robust and reliable. Equally important is retraining staff and revising internal communication protocols to better manage customer expectations and responses.
Proactively engaging with affected customers is also crucial. Offering compensation, such as extended free subscription periods or direct apologies, can help mitigate some of the immediate damage to customer relationships.
The road ahead
For Krispy Kreme and Pret, the path forward involves not only addressing the current crisis but also taking proactive steps to ensure such issues do not recur. This might include investing in advanced technology infrastructures, revising operational procedures, and continuously monitoring the execution of their subscription models.
Furthermore, these experiences offer lessons for other companies in the consumer sector considering subscription models. The key takeaway from EY’s insights is the critical importance of planning, testing, and readiness – elements that must be thoroughly evaluated and implemented to avoid the pitfalls experienced by Krispy Kreme and Pret.
The unfolding situation with Krispy Kreme and Pret a Manger serves as a cautionary tale for all consumer-facing businesses. Loyalty schemes and subscription models, while potentially lucrative, require meticulous planning and robust execution. Companies must ensure they are not only attracting customers with promises but are also fully prepared to deliver on them consistently. As these companies navigate their recovery, the broader industry watches and learns, hopefully leading to better implementation strategies in the future.
In conclusion, while Krispy Kreme and Pret’s intention to innovate customer engagement through subscriptions was commendable, the execution was flawed, underscoring the delicate balance required in the design and deployment of new customer loyalty schemes. The lessons drawn from their experiences will shape how businesses approach similar strategies in the future, with an increased focus.
More from Brand Strategy
Industry insights.
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
Majority of workers who quit a job in 2021 cite low pay, no opportunities for advancement, feeling disrespected

The COVID-19 pandemic set off nearly unprecedented churn in the U.S. labor market. Widespread job losses in the early months of the pandemic gave way to tight labor markets in 2021, driven in part by what’s come to be known as the Great Resignation . The nation’s “quit rate” reached a 20-year high last November.
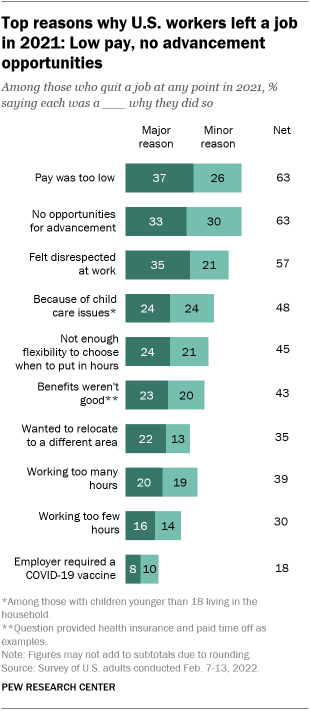
A new Pew Research Center survey finds that low pay, a lack of opportunities for advancement and feeling disrespected at work are the top reasons why Americans quit their jobs last year. The survey also finds that those who quit and are now employed elsewhere are more likely than not to say their current job has better pay, more opportunities for advancement and more work-life balance and flexibility.
Majorities of workers who quit a job in 2021 say low pay (63%), no opportunities for advancement (63%) and feeling disrespected at work (57%) were reasons why they quit, according to the Feb. 7-13 survey. At least a third say each of these were major reasons why they left.
Roughly half say child care issues were a reason they quit a job (48% among those with a child younger than 18 in the household). A similar share point to a lack of flexibility to choose when they put in their hours (45%) or not having good benefits such as health insurance and paid time off (43%). Roughly a quarter say each of these was a major reason.
Pew Research Center conducted this analysis to better understand the experiences of Americans who quit a job in 2021. This analysis is based on 6,627 non-retired U.S. adults, including 965 who say they left a job by choice last year. The data was collected as a part of a larger survey conducted Feb. 7-13, 2022. Everyone who took part is a member of the Center’s American Trends Panel (ATP), an online survey panel that is recruited through national, random sampling of residential addresses. This way, nearly all U.S. adults have a chance of selection. The survey is weighted to be representative of the U.S. adult population by gender, race, ethnicity, partisan affiliation, education and other categories. Read more about the ATP’s methodology .
Here are the questions used for this analysis, along with responses, and its methodology.
About four-in-ten adults who quit a job last year (39%) say a reason was that they were working too many hours, while three-in-ten cite working too few hours. About a third (35%) cite wanting to relocate to a different area, while relatively few (18%) cite their employer requiring a COVID-19 vaccine as a reason.
When asked separately whether their reasons for quitting a job were related to the coronavirus outbreak, 31% say they were. Those without a four-year college degree (34%) are more likely than those with a bachelor’s degree or more education (21%) to say the pandemic played a role in their decision.
For the most part, men and women offer similar reasons for having quit a job in the past year. But there are significant differences by educational attainment.
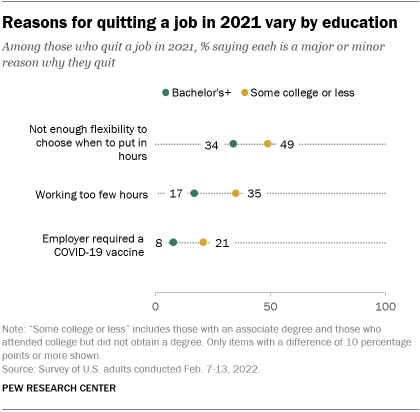
Among adults who quit a job in 2021, those without a four-year college degree are more likely than those with at least a bachelor’s degree to point to several reasons. These include not having enough flexibility to decide when they put in their hours (49% of non-college graduates vs. 34% of college graduates), having to work too few hours (35% vs. 17%) and their employer requiring a COVID-19 vaccine (21% vs. 8%).
There are also notable differences by race and ethnicity. Non-White adults who quit a job last year are more likely than their White counterparts to say the reasons include not having enough flexibility (52% vs. 38%), wanting to relocate to a different area (41% vs. 30%), working too few hours (37% vs. 24%) or their employer requiring that they have a COVID-19 vaccine (27% vs. 10%). The non-White category includes those who identify as Black, Asian, Hispanic, some other race or multiple races. These groups could not be analyzed separately due to sample size limitations.
Many of those who switched jobs see improvements
A majority of those who quit a job in 2021 and are not retired say they are now employed, either full-time (55%) or part-time (23%). Of those, 61% say it was at least somewhat easy for them to find their current job, with 33% saying it was very easy. One-in-five say it was very or somewhat difficult, and 19% say it was neither easy nor difficult.
For the most part, workers who quit a job last year and are now employed somewhere else see their current work situation as an improvement over their most recent job. At least half of these workers say that compared with their last job, they are now earning more money (56%), have more opportunities for advancement (53%), have an easier time balancing work and family responsibilities (53%) and have more flexibility to choose when they put in their work hours (50%).
Still, sizable shares say things are either worse or unchanged in these areas compared with their last job. Fewer than half of workers who quit a job last year (42%) say they now have better benefits, such as health insurance and paid time off, while a similar share (36%) says it’s about the same. About one-in-five (22%) now say their current benefits are worse than at their last job.
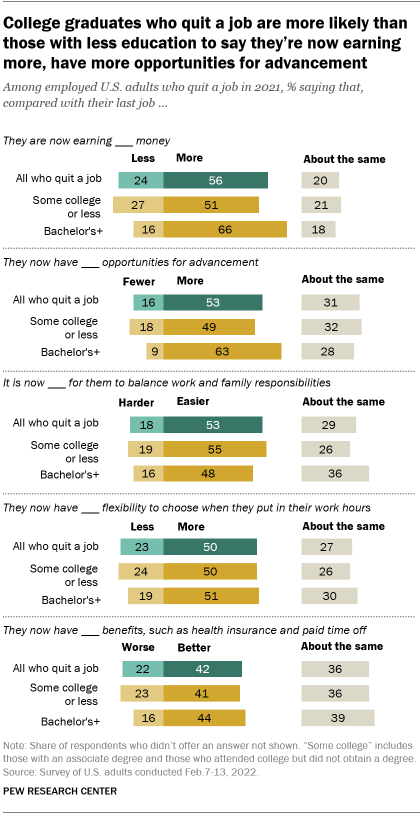
College graduates are more likely than those with less education to say that compared with their last job, they are now earning more (66% vs. 51%) and have more opportunities for advancement (63% vs. 49%). In turn, those with less education are more likely than college graduates to say they are earning less in their current job (27% vs. 16%) and that they have fewer opportunities for advancement (18% vs. 9%).
Employed men and women who quit a job in 2021 offer similar assessments of how their current job compares with their last one. One notable exception is when it comes to balancing work and family responsibilities: Six-in-ten men say their current job makes it easier for them to balance work and family – higher than the share of women who say the same (48%).
Some 53% of employed adults who quit a job in 2021 say they have changed their field of work or occupation at some point in the past year. Workers younger than age 30 and those without a postgraduate degree are especially likely to say they have made this type of change.
Younger adults and those with lower incomes were more likely to quit a job in 2021
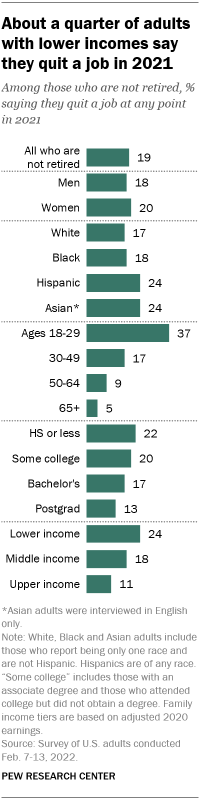
Overall, about one-in-five non-retired U.S. adults (19%) – including similar shares of men (18%) and women (20%) – say they quit a job at some point in 2021, meaning they left by choice and not because they were fired, laid off or because a temporary job had ended.
Adults younger than 30 are far more likely than older adults to have voluntarily left their job last year: 37% of young adults say they did this, compared with 17% of those ages 30 to 49, 9% of those ages 50 to 64 and 5% of those ages 65 and older.
Experiences also vary by income, education, race and ethnicity. About a quarter of adults with lower incomes (24%) say they quit a job in 2021, compared with 18% of middle-income adults and 11% of those with upper incomes.
Across educational attainment, those with a postgraduate degree are the least likely to say they quit a job at some point in 2021: 13% say this, compared with 17% of those with a bachelor’s degree, 20% of those with some college and 22% of those with a high school diploma or less education.
About a quarter of non-retired Hispanic and Asian adults (24% each) report quitting a job last year; 18% of Black adults and 17% of White adults say the same.
Note: Here are the questions used for this analysis, along with responses, and its methodology.
- Business & Workplace
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- COVID-19 & the Economy
- Income & Wages

Kim Parker is director of social trends research at Pew Research Center

Juliana Menasce Horowitz is an associate director of research at Pew Research Center
A look at small businesses in the U.S.
Majorities of adults see decline of union membership as bad for the u.s. and working people, a look at black-owned businesses in the u.s., from businesses and banks to colleges and churches: americans’ views of u.s. institutions, 2023 saw some of the biggest, hardest-fought labor disputes in recent decades, most popular.
1615 L St. NW, Suite 800 Washington, DC 20036 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Age & Generations
- Economy & Work
- Family & Relationships
- Gender & LGBTQ
- Immigration & Migration
- International Affairs
- Internet & Technology
- Methodological Research
- News Habits & Media
- Non-U.S. Governments
- Other Topics
- Politics & Policy
- Race & Ethnicity
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
Copyright 2024 Pew Research Center
Terms & Conditions
Privacy Policy
Cookie Settings
Reprints, Permissions & Use Policy
- Sports Page
- Cayuga County
- Livingston County
- Ontario County
- Schuyler County
- Seneca County
- Steuben County
- Tompkins County
- Wayne County
- Yates County
- Now Streaming

How to score the best office rental deals in Hong Kong
- April 23, 2024 10:16 AM / Updated: April 23, 2024 10:16 AM
With its vibrant economy and bustling business environment, Hong Kong is a prime destination for entrepreneurs and established corporations.
However, the city’s competitive real estate market can make finding the perfect office space at an affordable rate daunting. In this blog post, we’ll delve into the strategies and tips for scoring the best office for rent in Hong Kong , ensuring you find a space that meets your needs without breaking the bank.
Understanding the Hong Kong Office Rental Market
Before diving into the tips for securing the best office rental deals, it’s crucial to understand the dynamics of the Hong Kong office rental market. Hong Kong is known for its limited supply of office space, high demand, and sky-high rental prices.
The Central Business District remains the most sought-after location, with prestigious addresses commanding premium rents. Additionally, factors such as lease terms, size, and amenities can significantly impact rental rates.
Tips for Scoring the Best Deals
Research, research, research.
The key to securing the best office rental deal in Hong Kong begins with thorough research. Utilize online platforms, real estate agencies, and networking connections to gather information on available office spaces, rental rates, and market trends. Understanding the market will empower you to negotiate effectively and identify hidden gems.
Flexibility is Key
Flexibility in your office space requirements can open doors to better deals. Consider alternative locations within Hong Kong, explore co-working spaces, or opt for shared offices to reduce costs. Additionally, be open to negotiating lease terms such as lease duration, rent escalations, and tenant improvements to secure a favorable deal.
Engage a Reliable Real Estate Agent
Partnering with a reputable real estate agent who specializes in commercial leasing can streamline your search and negotiation process. A knowledgeable agent can provide valuable insights, access to exclusive listings, and negotiate on your behalf to secure the best possible deal.
Timing is Everything
Timing plays a crucial role in securing the best office rental deals in Hong Kong. Keep an eye on market trends, lease expirations, and economic indicators to identify favorable conditions for negotiation. Off-peak seasons or economic downturns may present opportunities for lower rental rates and favorable lease terms.
Negotiate Wisely
Effective negotiation skills are paramount when securing the best office rental deals. Come prepared with market research, understand your leverage points, and be clear about your budget and requirements. Negotiate not only on rental rates but also on lease terms, incentives, and amenities to maximize value.
Factor in Additional Costs
When evaluating office rental deals, consider the total cost of occupancy beyond the base rent. Factor in additional costs such as maintenance fees, utilities, property taxes, and common area charges to accurately assess the space’s affordability.
Seek Professional Advice
When navigating the complexities of the Hong Kong office rental market, seeking professional advice from legal advisors and financial experts can provide valuable guidance and ensure that you make informed decisions.
Securing the best office rental deals in Hong Kong requires a combination of research, flexibility, negotiation skills, and market savvy. By understanding the dynamics of the market, being proactive in your approach, and leveraging the expertise of professionals, you can find an office space that meets your needs at a competitive rate. With these tips in mind, you’ll be well-equipped to navigate the competitive real estate landscape of Hong Kong and secure the perfect office space for your business.
This content is brought to you by the FingerLakes1.com Team. Support our mission by visiting www.patreon.com/fl1 or learn how you send us your local content here .
- Open access
- Published: 08 November 2023
Policies to prevent zoonotic spillover: a systematic scoping review of evaluative evidence
- Chloe Clifford Astbury 1 , 2 , 3 ,
- Kirsten M. Lee 1 , 2 ,
- Ryan Mcleod 1 ,
- Raphael Aguiar 2 ,
- Asma Atique 1 ,
- Marilen Balolong 4 ,
- Janielle Clarke 1 ,
- Anastassia Demeshko 1 ,
- Ronald Labonté 5 ,
- Arne Ruckert 5 ,
- Priyanka Sibal 6 ,
- Kathleen Chelsea Togño 4 ,
- A. M. Viens 1 , 3 ,
- Mary Wiktorowicz 1 , 2 ,
- Marc K. Yambayamba 7 ,
- Amy Yau 8 &
- Tarra L. Penney 1 , 2 , 3
Globalization and Health volume 19 , Article number: 82 ( 2023 ) Cite this article
2931 Accesses
24 Altmetric
Metrics details
Emerging infectious diseases of zoonotic origin present a critical threat to global population health. As accelerating globalisation makes epidemics and pandemics more difficult to contain, there is a need for effective preventive interventions that reduce the risk of zoonotic spillover events. Public policies can play a key role in preventing spillover events. The aim of this review is to identify and describe evaluations of public policies that target the determinants of zoonotic spillover. Our approach is informed by a One Health perspective, acknowledging the inter-connectedness of human, animal and environmental health.
In this systematic scoping review, we searched Medline, SCOPUS, Web of Science and Global Health in May 2021 using search terms combining animal health and the animal-human interface, public policy, prevention and zoonoses. We screened titles and abstracts, extracted data and reported our process in line with PRISMA-ScR guidelines. We also searched relevant organisations’ websites for evaluations published in the grey literature. All evaluations of public policies aiming to prevent zoonotic spillover events were eligible for inclusion. We summarised key data from each study, mapping policies along the spillover pathway.
Our review found 95 publications evaluating 111 policies. We identified 27 unique policy options including habitat protection; trade regulations; border control and quarantine procedures; farm and market biosecurity measures; public information campaigns; and vaccination programmes, as well as multi-component programmes. These were implemented by many sectors, highlighting the cross-sectoral nature of zoonotic spillover prevention. Reports emphasised the importance of surveillance data in both guiding prevention efforts and enabling policy evaluation, as well as the importance of industry and private sector actors in implementing many of these policies. Thoughtful engagement with stakeholders ranging from subsistence hunters and farmers to industrial animal agriculture operations is key for policy success in this area.
This review outlines the state of the evaluative evidence around policies to prevent zoonotic spillover in order to guide policy decision-making and focus research efforts. Since we found that most of the existing policy evaluations target ‘downstream’ determinants, additional research could focus on evaluating policies targeting ‘upstream’ determinants of zoonotic spillover, such as land use change, and policies impacting infection intensity and pathogen shedding in animal populations, such as those targeting animal welfare.
The increasing incidence of zoonotic emerging infectious diseases (EIDs) has been attributed to behavioural practices and ecological and socioeconomic change, and is predicted to continue in the coming years [ 1 ]. Higher levels of anthropogenic activity, including agricultural intensification, urbanisation and other forms of land use change, have led to increased interactions between wildlife, humans and livestock, increasing the risk of cross-species transmission [ 2 , 3 , 4 ]. Meanwhile, accelerating rates of globalisation and urbanisation, leading to increased global movement of people and goods and more dense human settlements, have made outbreaks of disease in human populations more difficult to contain [ 5 ]. In response, a call has been issued by leading organisations and experts, including the United Nations Environment Programme, the International Livestock Research Institute and the Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services, to complement reactive policy responses with policies that prevent zoonotic EIDs [ 1 , 6 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 ]. This approach, sometimes called deep prevention, would need to target upstream drivers to reduce the risk of outbreaks occuring [ 11 ].
Zoonotic spillover, defined as the transmission of a pathogen from an animal to a human, depends on the alignment of ecological, epidemiological and behavioural factors [ 12 ]. Zoonotic pathogens must be transmitted across a spillover pathway (Fig. 1 ) in order to induce infections in humans [ 12 , 13 ]. This involves meeting a series of conditions including appropriate density and distribution of reservoir hosts, pathogen prevalence, infection intensity and human exposure [ 12 ]. Across this pathway, a number of drivers of zoonotic spillover have been identified, including changes in wildlife and livestock populations [ 14 ]; deforestation, urbanisation and other forms of land use change [ 15 , 16 ]; bushmeat consumption [ 17 , 18 , 19 ]; and a variety of human practices including hunting, farming, animal husbandry, mining, keeping of exotic pets and trade [ 8 , 9 , 20 , 21 , 22 ]. These large-scale changes have repeatedly given rise to spillover events [ 2 , 15 , 23 ], sometimes involving pathogens with epidemic or pandemic potential [ 24 ].
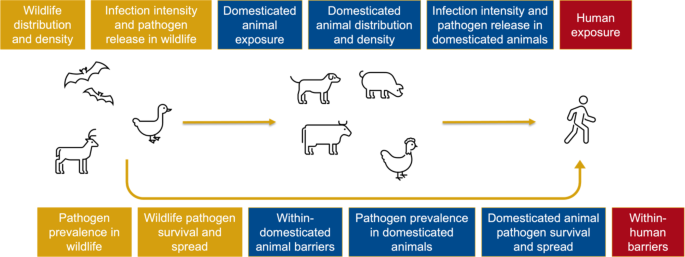
Spillover pathway adapted from Plowright et al. [ 12 , 13 ]
The responsibility for addressing zoonotic disease frequently spans multiple sectors of governance due to its relevance for both animals and humans. A One Health perspective, which recognises the health of humans, animals and the environment as being closely linked and inter-dependent [ 25 ], can be useful in understanding the spillover pathway and drivers of spillover events, as well as informing policy and governance approaches to address this cross-sectoral problem. At the international level, the World Health Organization, the Food and Agriculture Organization, the World Organisation for Animal Health and the United Nations Environment Programme have endorsed a One Health approach to policymaking to respond to zoonotic infectious diseases, emphasising collaboration between agencies [ 26 ].
Operationalising a One Health approach to policy
While One Health is a promising approach to preventing zoonotic EIDs, operationalising this concept remains a challenge. Evaluative evidence exists around the effectiveness of interventions to prevent spillover events [ 13 , 27 , 28 , 29 ], however these have often been implemented as short- to medium-term programmes or academic investigations [ 8 ]. In some cases, zoonoses have re-emerged after successful programmes have ended [ 29 ]. As a result, experts have argued for the incorporation of successful interventions into policy frameworks, providing interventions with the sustainability required for long-term disease control [ 8 , 10 ].
Operationalising a One Health approach to policy involves understanding the policy options, identifying the stakeholders involved and developing insights into how to successfully implement and evaluate these policies. Although the longevity and scope of government actions may make policy an effective vehicle for prevention of emerging diseases, implementing policy is a complex process involving numerous actors with competing views and interests [ 30 ]. This context presents challenges for policy development and implementation. Where relevant policies are designed and implemented in isolation, opportunities for co-benefits may be missed and interventions may produce unintended consequences [ 31 ]. Finally, while evaluative evidence is key to informing future policy decisions, the complex systems in which policies are often implemented make evaluation challenging [ 32 ].
Aims and scope
To provide insights around how to use policy to successfully prevent zoonotic spillover events, it is necessary to synthesise the available evaluative evidence. A One Health perspective allows this evidence synthesis to incorporate a wide range of policy instruments and actors and to identify approaches to successfully implementing and evaluating policies in this complex, multi-sectoral context.
Approaches to managing epidemic and pandemic infectious pathogens when they have entered human populations have been systematically catalogued in the medical literature [ 33 , 34 , 35 , 36 , 37 , 38 , 39 ]. These measures include hand washing, face masks, school closures, contact tracing, vaccination and case isolation. Further upstream, systematic reviews of interventions targeting the spillover pathway have predominantly focused on programmes rather than policies, and have been restricted by various characteristics such as geographic region [ 28 ] or pathogen type [ 29 ], or focused on programmes with an explicit endorsement of a One Health approach [ 27 ]. In consequence, a comprehensive understanding of what policies to prevent zoonotic spillover have been evaluated, what actors are involved, and how to successfully implement and evaluate them, is lacking. To address these research gaps, our objective was to synthesise the existing evaluative evidence around policies that target the determinants of zoonotic spillover.
Our approach to identifying and analysing this literature was informed by a One Health perspective, acknowledging the inter-connectedness of human, animal and environmental health.
We conducted a systematic scoping review of evaluations of policies aimed at preventing zoonotic spillover events, based on a previously published protocol [ 40 ]. Results are reported in accordance with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses Extension for Scoping Reviews [ 41 ]. The scoping review was conducted in line with guidelines published by Arksey and O’Malley and refined by Levac and colleagues [ 42 , 43 , 44 ], which emphasise an iterative approach suited to an exploratory research question.
The One Health perspective guided the development of the review methodology. This included the search strategy and inclusion criteria, which allow for the inclusion of policies focused on human, animal or environmental health (or any combination of these areas) and with leadership from one or more of these sectors, and the research questions, which seek to outline the policies and the range of sectors involved in implementation. While our focus on the spillover pathway meant we only included policies that had been evaluated in terms of their impacts on animal and human population distributions, health and interactions, we explicitly searched for environment-focused policies (e.g., protection of wetlands and other wildlife habitats) that might have been evaluated from this perspective. We also aimed to interrogate the One Health approach to governance, by assessing to what extent cross-sectoral collaboration – a key tenet of One Health practice [ 25 ] – emerged as a reason for policy success.
Stage 1: identifying the research question
Informed by our research objective, our research questions were:
What policies aimed at preventing zoonotic spillover (i.e., policies that target the determinants of zoonotic spillover included in the spillover pathway [ 12 ]: population distribution, health and interactions) have been evaluated?
What are the types of policies?
Which policy actors (single department, multi-sectoral, whole of government) are involved?
What are the reasons for policy success and failure, and the unintended consequences of implementing these policies?
How has evaluation of these policies been approached in the literature?
What are the methods or study designs used?
What are the outcomes?
What are the opportunities and challenges for evaluation?
Stage 2: identifying relevant studies
We systematically searched four electronic databases (Medline, Scopus, Web of Science, Global Health) in May 2021. The search strategy was organized by the main concepts in our research question: the spillover pathway; public policy; prevention; and zoonotic pathogens. The search strategy was developed iteratively, informed by existing systematic reviews focused on related concepts [ 28 , 45 , 46 , 47 , 48 , 49 ] and known indicator papers meeting inclusion criteria. We also searched the websites of 18 organisations involved in the prevention of zoonotic spillover to identify relevant grey literature. The choice of organisations was informed by an actor mapping exercise in which we identified key international organisations working on the prevention of emerging zoonoses using network sampling [ 50 ]. We searched the websites of a subset of these organisations, focusing on inter-governmental organisations and organisations whose main focus was zoonotic disease. See Supplementary File 1 for details of academic database and grey literature search strategies.
Stage 3: study selection
Studies were included if they met the following criteria:
Primary empirical study with an English-language abstract from any country or region (reviews were excluded);
Study reporting empirical findings from an evaluation of any sort; and.
Study focused on a policy implemented by government that targets the determinants of zoonotic spillover.
Academic records identified through the searches were collated and double screened using the online platform Covidence [ 51 ]. Two researchers (CCA and KML) initially screened titles and abstracts. Title and abstract screening of an initial set of 100 papers was undertaken by both researchers independently. Results were compared to ensure consistency in decisions around study eligibility, and discrepancies were resolved through consensus. This process was repeated until an acceptable level of agreement (> 90%) was reached. The remaining papers were then screened by one of the two reviewers. Full-text screening was undertaken by two independent researchers and discrepancies were resolved by consensus. Studies with full-texts in any language were eligible for inclusion if they include an English-language abstract. Full-text studies published in French, Spanish or Chinese were single-screened by a member of the research team fluent in that language (CCA or AY). Studies published in other languages were translated as necessary.
Grey literature was screened by one researcher (CCA) to determine whether it met the inclusion criteria. Publications were initially screened by looking at titles, tables of contents and executive summaries. Where these indicated that the publication might be eligible, documents were read in full to determine if inclusion criteria were met.
In line with published guidelines, the approach to study selection was refined iteratively when reviewing articles for inclusion [ 42 , 43 , 44 ].
Stage 4: charting the data
Data charting was conducted using a form designed to identify the information required to answer the research question and sub-research questions (see Supplementary File 2). Data charting focused on characteristics of the study, the policy, and the evaluation. For each policy, this included identifying which determinant of zoonotic spillover situated along the spillover pathway was being targeted. For the purpose of this study, we used a model of the spillover pathway adapted from Plowright et al.’s work [ 12 , 13 ], in which we differentiated between wildlife and domesticated animals (Fig. 1 ). This differentiation is important in the policy context, as the wildlife-domesticated animal interface is an important site for intervention, as well as the human-animal interface.
The data charting form was piloted with ten records to ensure that it was consistent with the research question, and revised iteratively [ 42 , 43 , 44 ]. Data charting was conducted by one researcher (CCA, RM, JC, AD or PS) and checked by a second researcher (CCA or KML). Discrepancies were resolved by consensus.
Stage 5: collating, summarising and reporting the results
Our protocol stated that we would use the Quality Assessment Tool for Quantitative Studies developed by the Effective Public Health Practice Project [ 52 ] to assess study quality [ 40 ]. However, on reviewing the included studies we selected two tools that were more appropriate to their characteristics: (1) ROBINS-I [ 53 ] for quantitative outcome evaluations and (2) a tool developed by the authors of a previous review [ 54 ] – based on Dixon-Woods et al.’s approach to assessing study credibility and contribution [ 55 ] – for all other study types. Two researchers (CCA and KML) assessed study quality independently for an initial set of 10 studies, before comparing assessments and reaching agreement where discrepancies occurred. This process was repeated until an adequate level of agreement was reached (> 90%). The remaining studies were assessed by a single researcher (CCA or KML). Records were not excluded based on quality assessment. Instead, assessments were primarily used to help synthesize the literature on how policies were evaluated. Quality assessment was not performed on grey literature due to the wide variability in the format and comprehensiveness of included publications.
We analysed the charted data, presenting a numerical summary of the included studies in table form, allowing us to describe the range of policy interventions that have been evaluated, aspects of policy implementation and approaches to evaluation. Based on the charted data, we inductively grouped evaluated policies with similar characteristics into policy types and assigned a policy instrument to each policy type: communication/marketing, guidelines, fiscal, regulation, legislation, environmental/social planning or service provision. We mapped policy types onto the spillover pathway shown in Fig. 1 to outline the policies that have been used to target each of these determinants. Thematic analysis was conducted using the approach described by Braun and Clarke where the focus is guided by the researcher’s analytic interests [ 56 ], with five overarching themes chosen as an a priori coding framework: (1) reasons for policy success; (2) reasons for policy failure; (3) unintended consequences of policy implementation; (4) opportunities for policy evaluation; and (5) challenges for policy evaluation. We selected these themes based on our research questions and previous familiarisation with the included articles during the process of article selection, data extraction and quality assessment. Sub-themes were subsequently identified through close reading and coding of the included articles. Thematic analysis was conducted by one researcher (RM) using the qualitative data analysis software Dedoose [ 57 ] and reviewed by the lead author (CCA).
Study characteristics
After removing duplicates, our searches identified a total of 5064 academic records. After screening titles and abstracts, we considered 330 records for full-text review. We also identified 11 relevant publications through our grey literature search. Grey literature reports were published by five organisations: four organisations focused on health and disease, including an intergovernmental organisation (the World Organisation for Animal Health) and three non-governmental organisations (the One Health Commission, the Global Alliance for Rabies Control and EcoHealth Alliance); and one non-governmental organisation focused on wildlife trade (TRAFFIC). In total, we included 95 publications in this review (PRISMA diagram in Fig. 2 ) [ 58 ].
We excluded studies which assessed the unintended consequences of policies to prevent zoonotic spillover without evaluating their effectiveness. This included studies that looked exclusively at the mental health impacts of mandatory livestock culls on farm workers [ 59 ]; studies which focused on potentially relevant factors, such as the wildlife trade, but with no consideration of outcomes situated on the spillover pathway [ 60 ]; and studies which assessed the detection power of surveillance systems without assessing the impact of associated policy interventions [ 61 , 62 , 63 ].
Policy characteristics
The characteristics of the policies evaluated in the included studies are presented in Supplementary File 3 and summarised in Table 1 . Some studies evaluated more than one policy, particularly modelling studies which compared the impacts of several policy options and process evaluations focused on a range of activities undertaken by a single government. Therefore, the number of evaluated policies (n = 111) is greater than the number of included studies (n = 95).
Most policies were evaluated for their impact on human exposure (21%), pathogen prevalence in domesticated animals (18%), barriers within domesticated animals (15%), and pathogen survival and spread in domesticated animals (9%). There were also a number of multi-component policies studies across multiple stages of the spillover pathway (18%). Fewer studies focused on wildlife health and populations, and none of the included studies evaluated policies for their impact on infection intensity and pathogen release in either domesticated animals or wildlife.
Where the government department responsible for implementing a policy was identified in the paper, most policies were implemented by a single department (35%), although there were a number of multi-sectoral efforts (24%). The range of government sectors responsible for implementing policies to prevent zoonotic spillover included human health, animal health, food safety, agriculture, conservation, national parks, forestry, fisheries, environmental protection, border control and foreign affairs. Policies were predominantly intended to be implemented by private sector actors, including individuals and organisations working in trade, retail, hunting and animal agriculture. However, some policies were also implemented by public sector actors working in public health, veterinary public health and environmental conservation.
Most policies were situated in high-income (49%) and upper middle-income (28%) countries, with studies from East Asia and the Pacific (43%) and Europe and Central Asia (19%) dominating. Publications focused on policies targeting various zoonotic diseases, with the most common being avian influenza (50%), rabies (19%), brucellosis (11%) and Hendra virus (4%).
Most policies were evaluated using process (38%) or outcome (31%) evaluation. The most frequently used policy instrument was legislation (59%), particularly for managing pathogen spread in domesticated animals through measures such as mandatory vaccination, culls or disinfection protocols. Meanwhile, communication and marketing or service provision was more typically used to reduce risk in wildlife and human populations, for example by providing guidance around recommended hygiene protocol, by distributing oral vaccination in wildlife habitat or by offering vaccination to human populations.
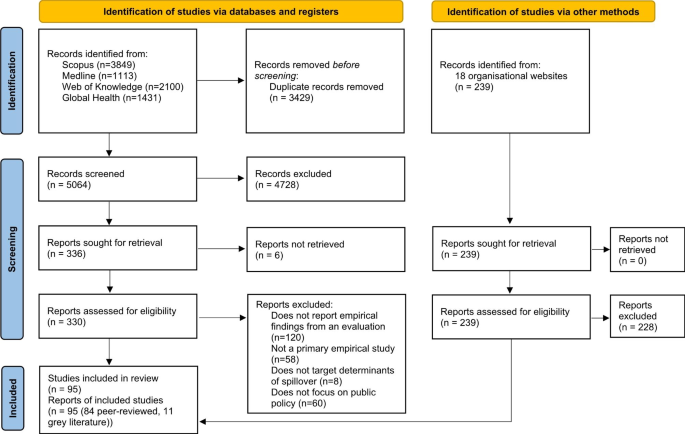
PRISMA 2020 diagram [ 58 ]
What policies aimed at preventing zoonotic spillover have been evaluated?
Policy types targeted different determinants across the pathway to zoonotic spillover and used various approaches with different evidence of success (Table 2 ). We identified policy options including culling – both general and targeted – of wild and domesticated animals; habitat protection (limiting activities such as agriculture and animal husbandry in wildlife habitats); supplemental feeding to control wildlife movements; vaccination of both wildlife, domesticated animals and human populations with occupational exposure to animals; policies to improve biosecurity in sites where animals are kept, slaughtered and sold, including mandates and information campaigns; live animal market closures; and bans on hunting and selling wildlife. Where outcomes or impacts were evaluated, most policies saw some level of success (i.e., outcome measures were found to vary in a direction that indicated policy success), though relative effectiveness was not assessed due to variation in study design and outcome measure. Policies with consistent evidence of effectiveness – where outcome measures varied in a direction that indicated policy success in all studies included in the review – included culling and sterilisation of wildlife populations, habitat protection, vaccination in wildlife and domesticated animal populations and mandated disinfection protocols. Policies with equivocal evidence of success (i.e., outcome measures varied in different directions or studies had different findings, some indicating success and some indicating failure) included supplemental feeding of wildlife, pre-emptive livestock culls, live animal market closures and bans on wildlife hunting, trade and consumption. For many policies, there were no impact or outcome evaluations identified in this review.
What are the reasons for policy success?
The evidence from the identified impact and outcome evaluations suggests that most of the policies succeeded to some extent. A range of factors contributed to policy success. First, studies emphasized the importance of effective collaboration and coordination between various agencies, disciplines, and levels of government in the execution of policy directives [ 114 , 115 ], in line with a One Health approach to policy and governance. Policy success was attributed, in part, to strong working relationships that encouraged effective communication between various government agencies, and facilitated timely and appropriate policy responses [ 115 ]. Synergy between agencies responsible for surveillance and the execution of control strategies was also reported to be beneficial. For example, prompt communication and effective collaboration between laboratories testing samples and agencies implementing culls in the field was seen as important in the control of highly pathogenic avian influenza in Nigeria [ 116 ]. Similarly, authors also identified the importance of private-public relations and private sector contributions to implementing policies to prevent zoonotic spillover [ 112 ]. This included stronger government engagement with private veterinarians as a factor for success in reducing the spillover of Hendra virus in Queensland [ 109 ], and with farmers, poultry companies and national farming and poultry processing associations in Ghana as part of a successful campaign to reduce risk from highly pathogenic avian influenza [ 112 ]. Studies suggest that the inclusion of private sector stakeholders in the policy process has the potential to improve compliance through transparent dialogue around disease ecology, risk and risk mitigation [ 90 , 91 , 103 , 117 ]; and highlight the utility of participatory approaches in prompting behaviour changes [ 91 ].
Second, authors emphasised the significance of economic incentives, suggesting that policy impact is dependent on private actors’ appraisal of costs and benefits. Studies illustrated how incentives, including compensation, subsidies, rebates, and fines, have had varying degrees of success [ 91 , 97 , 112 , 115 ]. Compensation levels [ 104 , 114 ] and enforcement practices [ 92 ] were identified as salient factors for compliance and adherence. For example, fear of sanctions for bushmeat hunting while a ban was in place in some parts of West Africa were identified as a stronger incentive to avoid bushmeat hunting than the fear of contracting Ebola virus [ 97 ]. Culls were seen as particularly challenging in this regard: while the long-term benefits for farmers may outweigh the financial loss [ 104 ], authorities need to be conscientious of the substantial economic impacts when considering policies that mandate culling or safe disposal [ 95 ]. The direct losses related to compliance (time, labour and expenses) and indirect losses due to price fluctuations and decreases in trade volume, as well as losses to associated industries, are substantial [ 88 , 96 , 113 , 118 ].
Third, trust in government and public support for implemented policy were specified as critical factors influencing the effectiveness of disease control strategies, and research suggests that strategic engagement to facilitate compliance is a necessary step in the policy process [ 97 ]. Participatory approaches that attempt to identify and understand factors influencing compliance have been consistently used to overcome resistance to policy, as insights from engagement and consultation can lead to solutions that facilitate behaviour change at the population level [ 91 , 103 ]. For example, a World Health Organization initiative to reduce avian influenza transmission in poultry markets in Indonesia worked alongside market vendors to achieve its aims, carrying out repeated consultations with the vendors and implementing market infrastructure (such as energy and running water in the market) in collaboration with local authorities to support vendor behaviour change [ 91 ].
Fourth, studies also demonstrated the importance of public communication. The quality of information, as well as the volume, complexity and delivery of public health messages, were key factors [ 75 , 114 ]. Authors contend that communication strategies must understand the target audience and how they interpret and engage with messages [ 97 ], for example by building on relationships where there is exiting trust, such as between veterinarians advising animal vaccination and animal owners [ 117 ]. Homogenously delivered communication strategies were ineffectual: they limited opportunities for open discourse; discounted contradictory lived experiences and expressions of uncertainty; and ultimately contributed to scepticism surrounding implemented policies [ 97 , 117 ].
Finally, studies underscored the importance of surveillance infrastructure to inform intervention strategies. Surveillance programs with the ability to collect and operationalize relevant data were essential to the development of appropriate interventions that are responsive to each unique context [ 115 , 119 ]. Implementing effective surveillance programmes requires the appropriate evaluation tools [ 120 ] and trained personnel [ 81 ].
What are the reasons for policy failure?
Studies showed that perceptions of acceptability and appropriateness were crucial to the effectiveness of implemented policies [ 101 , 104 ]. Several factors were identified that negatively affected acceptability and appropriateness, including: additional expenses for private sector actors without sufficient support [ 75 , 100 , 104 , 112 , 114 ], particularly were culls were demanded but reimbursement for farmers was slow and inadequate, as in a brucellosis eradication campaign in Macedonia [ 81 ]; lack of affordable alternatives [ 97 ]; impracticality of implemented strategies [ 75 , 101 ]; lack of cultural understanding in designing policy interventions [ 97 , 100 ], for example the distribution of footwear to pig farmers in a Polynesian context where footwear was not traditionally worn [ 100 ]; lack of understanding of viral ecology [ 100 ]; as well as public scepticism and distrust [ 97 , 114 ].
Additionally, policy ineffectiveness was associated with poor planning and execution of intervention strategies, including lack of clear direction [ 114 ]; incomplete or inconsistent implementation of control measures (17); limited scope of intervention [ 114 ]; and poor enforcement [ 92 ]. A lack of adequate resources to implement strategies also contributed to policy failure [ 81 ]. Adequate financial resources were necessary to hire and train staff to run surveillance and control operations [ 81 ]. Financial resources were also necessary to fund compensation mechanisms that facilitate compliance. Willingness to adopt policy-prescribed disposal practices was found to be associated with compensation levels (incentives) as a proportion of production price, dependency on income from activities driving zoonotic risk, and contact with prevention staff [ 92 ].
What are the unintended consequences of implementing policies to prevent zoonotic spillover?
A small number of the included studies collected data on the unintended consequences of policies to prevent zoonotic spillover (n = 18). In some instances, unintended consequences were due to disease ecology or human behaviour as a result of policy failure. For example, a study assessing the impacts of the closure of a live poultry market found that, following the closure, vendors travelled to neighbouring markets to sell their animals [ 94 ]. As a result, while cases of avian influenza decreased in the area surrounding the closed market, cases increased in these neighbouring markets, leading to the wider geographic spread of the disease. In another study, elk were provided with supplementary feeding grounds to discourage them from coming into contact with the livestock who shared their range [ 65 ]. While this intervention had the intended consequence of reducing the transmission of brucellosis between elk and livestock, the spread of brucellosis between the elk using the supplementary feeding grounds – who were gathering in larger, tighter groups for longer periods, resulting in higher within-herd transmission – and other elk populations in the area increased. This resulted in an increasing prevalence of brucellosis among the elk, potentially increasing the risk of spillover to livestock. These examples illustrate the complexity of the social and ecological systems in which these policies are implemented, further suggesting the need for a One Health approach to policies to prevent zoonotic spillover.
A key unintended consequence can be attributed to the loss of profits and livelihoods sometimes associated with policies to prevent zoonotic spillover, as described above. The losses incurred by complying with regulations made farmers, hunters and other private sector actors reluctant to report potential infections, contributing to increased unauthorized or illegal activity, and unrestrained spread of disease [ 90 , 92 , 94 , 98 , 112 , 114 ]. Studies investigated the creative ways policy enforcement was circumvented, including hiding hunting equipment on the outskirts of towns or developing informal trade markets and networks [ 97 , 98 ]. Unintended consequences identified in the included evaluations emphasize an opportunity for policymakers to improve sector compliance through public education, levying the influence of consumer attitudes on industry standards [ 104 , 113 ].
A range of study designs were used to evaluate policies. Outcome evaluations (n = 33) used time series or repeat cross-sectional data to conduct evaluations of natural experiments, though most studies did not include a control group for comparison. Outcome evaluations also used case-control and modelling approaches to assess policy impact on an outcome of interest. Process evaluations (n = 30) used cross-sectional and qualitative approaches, as well as study designs combining multiple sources of data, to understand aspects of policy implementation such as the extent to which the policy was being implemented as designed, and the responses and attitudes of stakeholders involved in policy implementation. Economic evaluations (n = 11) included cost-benefit analyses, risk-benefit analyses and modelling studies. Formative evaluations (n = 17) used modelling approaches to estimate what the impacts of a proposed policy option would be in a specific context.
Outcome variables interpreted as indicators of policy success were also numerous and represented determinants along the spillover pathway. As expected, many studies assessed impact on disease transmission, including disease prevalence and incidence, disease eradication, case numbers, and basic reproduction number in human and animal populations, as well as evidence of disease in environmental samples, such as in live animal markets or at carcass disposal sites. Studies also assessed impacts on intermediate factors indicative of successful implementation of specific policies, such as the availability of wild species in markets where a trade ban had been implemented, or knowledge and practices of stakeholders in response to an educational or information campaign.
While most studies found a reduced risk of zoonotic spillover following policy implementation, comparing the magnitude of these impacts was challenging due to the variety of study designs and outcome measures used in the included studies. However, we identified several studies which used modelling to directly compare the impacts of policy options. These studies evaluated various policy scenarios: different combinations within multi-component policy interventions [ 121 ]; culling versus vaccinating wildlife [ 122 ] and livestock [ 84 , 85 ] populations; targeting strategies to humans exclusively versus targeting humans and livestock [ 108 ]; and altering the parameters for culling and vaccination strategies, for example by modelling different ranges for culling and vaccination near infected farms [ 85 ]. These studies often highlighted trade-offs between the effectiveness of policy measures and their cost. For example, estimates of the number of infected flocks were lower when incorporating a ring cull (cull of animals on farms surrounding an outbreak) into a multi-component control strategy for highly pathogenic avian influenza [ 121 ]. However, livestock vaccination was estimated to be a highly effective strategy, with one study findings livestock vaccination to be as or more effective than a pre-emptive cull for outbreak control purposes (depending on the extent of vaccination coverage), while minimising the number of animals culled [ 85 ]. One study jointly modelled costs and benefits of strategies, and found that livestock vaccination had a higher cost-benefit ratio than a wildlife cull [ 122 ]. A final study highlighted the potential of holistic approaches, with drug administration in humans and livestock having a lower cost per disability-adjusted life year averted than intervention in humans alone [ 108 ].
Study authors noted a number of challenges encountered while evaluating policies to prevent zoonotic spillover. One study noted the difficulty of determining the impact of policies aiming to reduce spillover events between wildlife, livestock and humans, as the number of spillover events is often relatively small [ 65 ]. This highlights the importance of considering upstream determinants and risk factors as outcome measures in attempting to evaluate these policies, particularly where spillover events may happen infrequently or not at all during the period of observation. Studying changes in risk factors for spillover can provide insight on the effectiveness of different policies in tackling spillover risk.
Lack of suitable data was a frequently cited barrier to policy evaluation. As policies to prevent zoonotic spillover are often reactive, being implemented in response to an outbreak in animal populations, accessing data from before a policy was implemented was challenging. Studies highlighted the value of routinely collected data, which was often the only data available and was frequently used for policy evaluation [ 65 , 66 , 94 , 115 , 119 , 123 ]. However, in many contexts routine data on animal health is not collected [ 80 ]. Routine testing data from livestock can sometimes be used for evaluation where it exists, but it does not always provide sufficient detail for examining the potential for a policy to prevent zoonotic spillover. For example, some tests do not differentiate between current and past infection, making it difficult to identify where and when spillover occurred [ 65 ], and animal health data may not be granular enough for policy evaluation, particularly in terms of evaluating local policies [ 94 ]. Studies also highlighted instances where the private sector may own data sets reporting disease prevalence and transmission, but may be reluctant to share the data for evaluation purposes [ 121 ]. In such instances, open communication and good relationships with the private sector may be facilitators to evaluation.
Beyond the lack of baseline data, studies highlighted the difficulty in collecting information about policy compliance. As failing to comply often puts farmers and hunters at risk of fines or imprisonment, they were reluctant to disclose information about non-compliance or participation in illegal trade and sale of animals [ 86 , 92 , 97 , 112 ]. This made it difficult to determine policy effectiveness.
Quality assessment
Of the 44 quantitative evaluations, 37 were evaluated as being at moderate or higher risk of bias (see Supplementary File 4), given the possibility of bias in the assessment of intervention impact due to the presence of confounding effects. A small number of studies were determined to be at serious (n = 6) or critical (n = 1) risk of bias, for two main reasons: only having data from after the intervention was implemented; or using a case-control study model without measuring and adjusting for important potential confounders, such as the prevalence of a targeted disease prior to policy implementation. These limitations may reflect the nature of zoonotic spillover events and policy responses, which can happen quickly and leave little time for baseline data collection. Many of the included studies relied on surveillance data, but where such data sets are not available, post-test and case-control study designs may be the only options.
The quality of studies assessed with the tool developed based on Dixon-Woods’ approach [ 55 ] was high overall (n = 41, see Supplementary file 5). Most studies were rated as high in terms of clearly and comprehensively presenting their results (n = 37), analysis (n = 34), research design (n = 33), aims (n = 32) and research process (n = 28). Most studies also had a high relevance to the research question (n = 31), indicating that the research was embedded in policy, being commissioned, co-designed or conducted in partnership with government stakeholders.
We identified a range of policies targeting different parts of the spillover pathway implemented by various policy and governance sectors, including some multi-sectoral initiatives. Policies tended to rely heavily on private sector actors (including actors ranging from small-scale farmers and hunters to larger commercial operations) for implementation, suggesting that open communication and collaboration with these actors was essential for successful policy implementation. Policy success was undermined by lack of collaboration between government agencies; lack of communication between surveillance and control operations; poor understanding of the context in which policies were implemented; and inadequate financial compensation for private sector actors who lost profits and incurred additional costs by complying with policies. Where policies were ineffective, this tended to be due to unintended consequences relating to complex dynamics within the social and ecological systems where policies were implemented. Lack of appropriate data was a key obstacle to policy evaluation, and studies emphasised the importance of robust surveillance infrastructure in evaluating policies that tended to be implemented reactively, in response to an outbreak of zoonotic disease in animal or human populations.
Implications for policy and practice
The key role that the private sector and industry actors play in implementing policies to prevent zoonotic spillover is an important consideration for policymakers. Our findings suggest that many of these policies must be complied with by farmers – from subsistence and smallholder farmers to large corporations – as well as by other actors, such as hunters. Lack of awareness as well as financial costs of compliance among these groups present key barriers to policy success in this area. This set of stakeholders is complex as some may make very marginal profits, if any, and may struggle to afford the additional costs of implementing preventive policies. However, powerful actors and profitable industries are also involved, including large-scale farms and primary resource extraction enterprises [ 22 ]. Acknowledging the differences across these stakeholder groups, and in particular assessing their capacity to bear some of the costs related to prevention, emerges as crucial in successful policy implementation.
Finally, our findings highlight the importance of disease surveillance in efforts to reduce the risk of spillover events. As well as acting as an early warning system, surveillance provides a source of data to evaluate the impact of preventive policies. We found the availability of surveillance data to be a key enabling factor in evaluating policies. In addition, close collaboration between agencies responsible for disease surveillance and control efforts was key to policy success. National surveillance efforts, as well as cross-country collaboration to support global efforts, such as the United States Agency for International Development’s PREDICT program supporting surveillance in areas at high risk for zoonotic disease outbreaks [ 124 ], must be sustained and expanded. In complex areas such as the prevention of zoonotic spillover, approaches to surveillance which encompass risk factors and transmission pathways [ 125 ], as well as One Health surveillance systems which harmonise and integrate data collection and analysis from across human, animal and environmental sectors [ 126 ], are promising approaches to developing surveillance systems that support risk. This context also involves a need to strengthen surveillance capacity in remote and rural locations, as communities living in these contexts may have exposure to numerous pathogens of wildlife origin. This will require strengthening clinical and diagnostic capacity in these settings, as well as engaging with stakeholders such as community human and animal health workers and wildlife or national park rangers [ 127 ].
Comparison with existing literature
This review sought to map the range of policies implemented to reduce the risk of zoonotic spillover, and the various approaches taken to evaluation, and identify factors behind the success and failure of policy implementation and evaluation. Due to this broad scope, comparing relative effectiveness of policy interventions was challenging. Existing systematic reviews with a more specific focus could apply meta-analysis to determine which interventions were most effective. For example, a review of market-level biosecurity measures aiming to reduce the transmission of avian influenza found that reducing market size, separating poultry species, cleaning and disinfecting premises, closing markets and banning overnight storage were highly effective interventions [ 45 ]. However, our findings suggest that studies focused on the control of avian influenza dominate the literature in this space (55 out of 111 evaluated policies), and many of these are focused on market-level measures. Systematic reviews focused on other approaches to reduce spillover risk, such as on-farm biosecurity [ 47 ]; biosecurity for backyard poultry rearing [ 46 ]; and community-based interventions [ 28 ] comment on the paucity of high-quality evidence around the impacts of such approaches. By taking a broad perspective, we hope our findings will provide policy options for consideration in a number of contexts, and guide researchers in focusing their efforts on areas where evidence is lacking.
Strengths and weaknesses of the study
To our knowledge, this is the first attempt to systematically identify and document evaluations of policies aiming to prevent the spillover of zoonotic pathogens into human populations. However, because of the complex drivers of spillover events, some potentially relevant policy evaluations may be excluded where their outcome measures are too far removed from zoonotic spillover. While relevant, such evaluations will be difficult to systematically identify as they make no reference to zoonotic disease.
In addition, this review focused on policy evaluations that have been reported in the peer-reviewed literature and the grey literature published by international agencies and organisations working on these topics. Policies that have been implemented but not evaluated, or evaluated but not published in these literatures, will therefore be excluded from this review. As a result, potentially effective and important policies in the prevention of zoonotic spillover events may not have been identified. However, we hope that the findings from this review will highlight these gaps in the evaluative evidence. We also hope that this review, by extracting practical dimensions, such as study design, outcome measures and the challenges encountered in the evaluation process, will support policymakers and researchers in carrying out further policy evaluations in this space.
Unanswered questions and future research
Our findings highlight several important gaps in the evidence. First, while observational evidence emphasises the importance of upstream determinants such as environmental and ecosystem health in the increasing rate of zoonotic spillover [ 1 , 15 ], we only identified a single evaluation of a policy attempting to target one of these upstream determinants: an evaluation carried out in China to assess the impact of the Ramstar wetland protection program on avian influenza in migratory waterfowl [ 66 ]. This study found that proximity to protected wetlands reduced outbreak risk. Authors hypothesised that this effect was due to the separation of wild waterfowl and poultry populations and the diversion of wild waterfowl away from human-dominated landscapes and toward protected natural habitats. Our findings support existing calls for more quantitative and mechanistic studies of the impact of interventions supporting environmental and ecosystem health on zoonotic spillover risk [ 128 ], as well as calls for greater integration of the environment into One Health research, policy and practice [ 31 ]. Further evaluations of environment and habitat protection policies would strengthen our understanding of this area. In addition, the impact of policies to reduce deforestation or expand forest coverage, such as China’s Grain-to-Green program [ 129 ], on the spillover pathway could be evaluated. Such evaluations might consider potential unintended consequences, as these policies could promote healthier wildlife populations with better disease resistance, but may also facilitate wildlife population growth and higher rates of wildlife-human encounters [ 130 ].
There is also a lack of evaluation of policies targeting infection intensity and pathogen release in either wildlife or domesticated animals. These could include approaches such as improving animal health and welfare to make these populations more resistant to disease [ 13 ]. While arguments have been made for strengthening legal structures supporting animal welfare in order to reduce the risk of zoonotic pathogen transmission [ 131 ], there is a need to evaluate policies that take this approach.
Our review found publications evaluating a wide range of policy interventions spanning the spillover pathway, including habitat protection; trade regulations; border control and quarantine procedures; farm and market biosecurity measures; public information campaigns; and vaccination programmes for wildlife and domesticated animals, as well as human populations with occupational exposure to animals. A wide range of governance sectors implemented these policies, highlighting the prevention of zoonotic spillover as a cross-sectoral issue, though most policies were implemented by a single sector. Our findings highlight the importance of industry and private actors in implementing policies to prevent zoonotic spillover, and the need for thoughtful and effective engagement with this wide range of actors, from subsistence hunters and farmers through to industrial animal agriculture operations to address their concerns through a range of incentives. We also identified the centrality of surveillance data in evaluating policies that are often implemented reactively, and effective collaboration between surveillance and control operations as a central factor in successful policy implementation.
Data Availability
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article and its supplementary information files. Analysis code for descriptive characteristics of included policies is available on GitHub.
Abbreviations
Emerging infectious disease
Morse SS, Mazet JA, Woolhouse M, Parrish CR, Carroll D, Karesh WB, Zambrana-Torrelio C, Lipkin WI, Daszak P. Prediction and prevention of the next pandemic zoonosis. The Lancet. 2012;380:1956–65.
Article Google Scholar
Pulliam JRC, Epstein JH, Dushoff J, Rahman SA, Bunning M, Jamaluddin AA, Hyatt AD, Field HE, Dobson AP, Daszak P. Agricultural intensification, priming for persistence and the emergence of Nipah virus: a lethal bat-borne zoonosis. J Royal Soc Interface. 2012;9:89–101.
IPCC. In: Pörtner H-O, Roberts DC, Tignor M, Poloczanska ES, Mintenbeck K, Alegría A, Craig M, Langsdorf S, Löschke S, Möller V, Okem A, Rama B, editors. Climate Change 2022: impacts, adaptation and vulnerability, contribution of Working Group II to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. In press ed. Cambridge University Press; 2022.
Brenner N, Ghosh S. Between the colossal and the catastrophic: planetary urbanization and the political ecologies of emergent Infectious Disease. Environ Plan A. 2022;54:867–910.
Gallo-Cajiao E, Lieberman S, Dolšak N, et al. Global governance for pandemic prevention and the wildlife trade. Lancet Planet Health. 2023;7:e336–45.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Marco MD, Baker ML, Daszak P, et al. Opinion: sustainable development must account for pandemic risk. PNAS. 2020;117:3888–92.
Heymann DL, Dixon M. Infections at the Animal/Human interface: shifting the paradigm from emergency response to Prevention at source. In: Mackenzie JS, Jeggo M, Daszak P, Richt JA, editors. One health: the human-animal-environment interfaces in Emerging Infectious Diseases: Food Safety and Security, and International and National plans for implementation of one health activities. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer; 2013. pp. 207–15.
Google Scholar
United Nations Environment Programme, International Livestock Research Institute. (2020) Preventing the next pandemic: Zoonotic diseases and how to break the chain of transmission. 82.
Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform On Biodiversity And Ecosystem Services (IPBES). (2020) Workshop Report on Biodiversity and Pandemics of the Intergovernmental Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services (IPBES). https://doi.org/10.5281/ZENODO.4147317 .
One Health theory of change. https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/one-health-theory-of-change . Accessed 30 Jan 2023.
Vinuales J, Moon S, Moli GL, Burci G-L. A global pandemic treaty should aim for deep prevention. The Lancet. 2021;397:1791–2.
Article CAS Google Scholar
Plowright RK, Parrish CR, McCallum H, Hudson PJ, Ko AI, Graham AL, Lloyd-Smith JO. Pathways to zoonotic spillover. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2017;15:502–10.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Sokolow SH, Nova N, Pepin KM, et al. Ecological interventions to prevent and manage zoonotic pathogen spillover. Philosophical Trans Royal Soc B: Biol Sci. 2019;374:20180342.
Johnson CK, Hitchens PL, Pandit PS, Rushmore J, Evans TS, Young CCW, Doyle MM. Global shifts in mammalian population trends reveal key predictors of virus spillover risk. Proc Royal Soc B: Biol Sci. 2020;287:20192736.
Allen T, Murray KA, Zambrana-Torrelio C, Morse SS, Rondinini C, Di Marco M, Breit N, Olival KJ, Daszak P. Global hotspots and correlates of emerging zoonotic Diseases. Nat Commun. 2017;8:1124.
Gandy M. THE ZOONOTIC CITY: Urban Political Ecology and the pandemic imaginary. Int J Urban Reg Res. 2022;46:202–19.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Hardi R, Babocsay G, Tappe D, Sulyok M, Bodó I, Rózsa L. Armillifer-infected snakes sold at Congolese Bushmeat Markets Represent an emerging zoonotic threat. EcoHealth. 2017;14:743–9.
Steve A-M, Ahidjo A, Placide M-K, et al. High prevalences and a wide genetic diversity of Simian Retroviruses in non-human Primate Bushmeat in Rural areas of the Democratic Republic of Congo. EcoHealth. 2017;14:100–14.
Weiss S, Nowak K, Fahr J, Wibbelt G, Mombouli J-V, Parra H-J, Wolfe ND, Schneider BS, Leendertz FH. Henipavirus-related sequences in Fruit Bat Bushmeat, Republic of Congo. Emerg Infect Dis. 2012;18:1536–7.
Aguirre AA, Catherina R, Frye H, Shelley L. Illicit Wildlife Trade, Wet Markets, and COVID-19: preventing future pandemics. World Med Health Policy. 2020;12:256–65.
Nadimpalli ML, Pickering AJ. A call for global monitoring of WASH in wet markets. Lancet Planet Health. 2020;4:e439–40.
Viliani F, Edelstein M, Buckley E, Llamas A, Dar O. Mining and emerging infectious Diseases: results of the Infectious Disease Risk Assessment and Management (IDRAM) initiative pilot. The Extractive Industries and Society. 2017;4:251–9.
Wegner GI, Murray KA, Springmann M, Muller A, Sokolow SH, Saylors K, Morens DM. Averting wildlife-borne Infectious Disease epidemics requires a focus on socio-ecological drivers and a redesign of the global food system. eClinicalMedicine. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eclinm.2022.101386 .
Daszak P. Anatomy of a pandemic. The Lancet. 2012;380:1883–4.
Joint Tripartite (FAO, OIE, WHO) and UNEP Statement. Tripartite and UNEP support OHHLEP’s definition of one health. ” OIE - World Organisation for Animal Health; 2021.
(2022) One Health Joint Plan of Action, 2022–2026. https://doi.org/10.4060/cc2289en .
Baum SE, Machalaba C, Daszak P, Salerno RH, Karesh WB. Evaluating one health: are we demonstrating effectiveness? One Health. 2017;3:5–10.
Halton K, Sarna M, Barnett A, Leonardo L, Graves N. A systematic review of community-based interventions for emerging zoonotic infectious Diseases in Southeast Asia. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2013;11:1–235.
Article PubMed Central Google Scholar
Meyer A, Holt HR, Selby R, Guitian J. Past and Ongoing Tsetse and Animal Trypanosomiasis Control Operations in five African countries: a systematic review. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2016;10:e0005247.
Howlett M, Cashore B. Conceptualizing Public Policy. In: Engeli I, Allison CR, editors. Comparative Policy studies: conceptual and methodological challenges. London: Palgrave Macmillan UK; 2014. pp. 17–33.
Chapter Google Scholar
Barrett MA, Bouley TA. Need for enhanced environmental representation in the implementation of one health. EcoHealth. 2015;12:212–9.
Barbrook-Johnson P, Proctor A, Giorgi S, Phillipson J. How do policy evaluators understand complexity? Evaluation. 2020;26:315–32.
Saunders-Hastings P, Crispo JAG, Sikora L, Krewski D. Effectiveness of personal protective measures in reducing pandemic Influenza transmission: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Epidemics. 2017;20:1–20.
Bin Nafisah S, Alamery AH, Al Nafesa A, Aleid B, Brazanji NA. School closure during novel Influenza: a systematic review. J Infect Public Health. 2018;11:657–61.
Viner RM, Russell SJ, Croker H, Packer J, Ward J, Stansfield C, Mytton O, Bonell C, Booy R. School closure and management practices during coronavirus outbreaks including COVID-19: a rapid systematic review. The Lancet Child & Adolescent Health. 2020;4:397–404.
Juneau C-E, Pueyo T, Bell M, Gee G, Collazzo P, Potvin L. (2020) Evidence-Based, cost-effective interventions to suppress the COVID-19 pandemic: a systematic review. medRxiv 2020.04.20.20054726.
MacIntyre CR, Chughtai AA. Facemasks for the prevention of Infection in healthcare and community settings. BMJ. 2015;350:h694.
Smith SMS, Sonego S, Wallen GR, Waterer G, Cheng AC, Thompson P. Use of non-pharmaceutical interventions to reduce the transmission of Influenza in adults: a systematic review. Respirology. 2015;20:896–903.
Jefferson T, Del Mar CB, Dooley L et al. (2011) Physical interventions to interrupt or reduce the spread of respiratory viruses. Cochrane Database Syst Rev CD006207.
Astbury CC, Lee KM, Aguiar R, et al. Policies to prevent zoonotic spillover: protocol for a systematic scoping review of evaluative evidence. BMJ Open. 2022;12:e058437.
Tricco AC, Lillie E, Zarin W, et al. PRISMA Extension for scoping reviews (PRISMA-ScR): Checklist and Explanation. Ann Intern Med. 2018;169:467–73.
Arksey H, O’Malley L. Scoping studies: towards a methodological framework. Int J Soc Res Methodol. 2005;8:19–32.
Levac D, Colquhoun H, O’Brien KK. Scoping studies: advancing the methodology. Implement Sci. 2010;5:69.
Colquhoun HL, Levac D, O’Brien KK, Straus S, Tricco AC, Perrier L, Kastner M, Moher D. Scoping reviews: time for clarity in definition, methods, and reporting. J Clin Epidemiol. 2014;67:1291–4.
Zhou X, Wang Y, Liu H, Guo F, Doi SA, Smith C, Clements ACA, Edwards J, Huang B, Soares Magalhães RJ. Effectiveness of Market-Level Biosecurity at reducing exposure of Poultry and humans to Avian Influenza: a systematic review and Meta-analysis. J Infect Dis. 2018;218:1861–75.
Conan A, Goutard FL, Sorn S, Vong S. Biosecurity measures for backyard poultry in developing countries: a systematic review. BMC Vet Res. 2012;8:240.
Youssef DM, Wieland B, Knight GM, Lines J, Naylor NR. The effectiveness of biosecurity interventions in reducing the transmission of bacteria from livestock to humans at the farm level: a systematic literature review. Zoonoses Public Health. 2021;68:549–62.
Shi N, Huang J, Zhang X, Bao C, Yue N, Wang Q, Cui T, Zheng M, Huo X, Jin H. Interventions in live poultry markets for the Control of Avian Influenza: a systematic review and Meta-analysis. J Infect Dis. 2020;221:553–60.
Cupertino MC, Resende MB, Mayer NA, Carvalho LM, Siqueira-Batista R. Emerging and re-emerging human infectious Diseases: a systematic review of the role of wild animals with a focus on public health impact. Asian Pac J Trop Med. 2020;13:99.
Clifford Astbury C, Demeshko A, McLeod R, Wiktorowicz M, Gallo Caijao E, Cullerton K, Lee KM, Viens AM, Penney TL. (2023) Governance of the wildlife trade and prevention of emerging zoonoses: a mixed methods network analysis of global organisations. [In preparation].
Covidence - Better. systematic review management. https://www.covidence.org/home . Accessed 17 Jul 2020.
Effective Public Health Practice Project. (2009) Quality Assessment Tool for Quantitative Studies. 4.
Sterne JA, Hernán MA, Reeves BC, et al. ROBINS-I: a tool for assessing risk of bias in non-randomised studies of interventions. BMJ. 2016;355:i4919.
Clifford Astbury C, McGill E, Egan M, Penney TL. Systems thinking and complexity science methods and the policy process in non-communicable Disease prevention: a systematic scoping review protocol. BMJ Open. 2021;11:e049878.
Dixon-Woods M, Cavers D, Agarwal S, et al. Conducting a critical interpretive synthesis of the literature on access to healthcare by vulnerable groups. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2006;6:35.
Braun V, Clarke V. Using thematic analysis in psychology. Qualitative Res Psychol. 2006;3:77–101.
(2021) Dedoose Version 8.3.47, web application for managing, analyzing, and presenting qualitative and mixed method research data.
Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. 2021;372:n71.
Park H, Chun MS, Joo Y. Traumatic stress of frontline workers in culling livestock animals in South Korea. Animals. 2020;10:1–11.
Programme UNE. Effectiveness of policy interventions relating to the illegal and unsustainable. Wildlife Trade - Policy Brief; 2019.
Cito F, Narcisi V, Danzetta ML, Iannetti S, Sabatino DD, Bruno R, Carvelli A, Atzeni M, Sauro F, Calistri P. Analysis of Surveillance systems in Place in European Mediterranean Countries for West Nile Virus (WNV) and Rift Valley Fever (RVF). Transbound Emerg Dis. 2013;60:40–4.
Schwind JS, Goldstein T, Thomas K, Mazet JA, Smith WA, PREDICT Consortium. Capacity building efforts and perceptions for wildlife surveillance to detect zoonotic pathogens: comparing stakeholder perspectives. BMC Public Health. 2014;14:684.
Reisen WK, Kramer VL, Barker CM. CALIFORNIA STATE MOSQUITO-BORNE VIRUS SURVEILLANCE AND RESPONSE PLAN: A RETROSPECTIVE EVALUATION USING CONDITIONAL SIMULATIONS *. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2003;68:508–18.
Smith GC, Cheeseman CL. A mathematical model for the control of Diseases in wildlife populations: culling, vaccination and fertility control. Ecol Model. 2002;150:45–53.
Brennan A, Cross PC, Portacci K, Scurlock BM, Edwards WH. Shifting brucellosis risk in livestock coincides with spreading seroprevalence in elk. PLoS ONE. 2017;12:e0178780.
Wu T, Perrings C, Shang C, Collins JP, Daszak P, Kinzig A, Minteer BA. Protection of wetlands as a strategy for reducing the spread of avian Influenza from migratory waterfowl. Ambio. 2020;49:939–49.
Basinski AJ, Nuismer SL, Remien CH. A little goes a long way: weak vaccine transmission facilitates oral vaccination campaigns against zoonotic pathogens. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2019;13:e0007251.
Selhorst T. (1999) An evaluation of the efficiency of rabies control strategies in fox (Vulpes 6ulpes) populations using a computer simulation program. Ecol Model 12.
Shwiff SA, Sterner RT, Hale R, Jay MT, Sun B, Slate D. Benefit cost scenarios of potential oral rabies vaccination for Skunks in California. J Wildl Dis. 2009;45:227–33.
García-Díaz P, Ross JV, Woolnough AP, Cassey P. Managing the risk of wildlife Disease introduction: pathway‐level biosecurity for preventing the introduction of alien ranaviruses. J Appl Ecol. 2017;54:234–41.
Hassim A, Dekker EH, Byaruhanga C, Reardon T, van Heerden H. A retrospective study of anthrax on the Ghaap Plateau, Northern Cape province of South Africa, with special reference to the 2007–2008 outbreaks. Onderstepoort J Vet Res. 2017;84:a1414.
Knight-Jones TJD, Gibbens J, Wooldridge M, Staerk KDC. Assessment of Farm-Level Biosecurity Measures after an outbreak of Avian Influenza in the United Kingdom. Transbound Emerg Dis. 2011;58:69–75.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Karabozhilova I, Wieland B, Alonso S, Salonen L, Häsler B. Backyard chicken keeping in the Greater London Urban Area: welfare status, biosecurity and Disease control issues. Br Poult Sci. 2012;53:421–30.
Manyweathers J, Field H, Jordan D, Longnecker N, Agho K, Smith C, Taylor M. Risk mitigation of emerging zoonoses: Hendra Virus and Non-vaccinating Horse Owners. Transbound Emerg Dis. 2017;64:1898–911.
Kung N, McLaughlin A, Taylor M, Moloney B, Wright T, Field H. Hendra virus and horse owners - risk perception and management. PLoS ONE. 2013. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0080897 .
Rasouli J, Holakoui K, Forouzanfar MH, Salari S, Bahoner, Rashidian A. Cost effectiveness of livestock vaccination for brucellosis in West-Azerbayjan province. Urmia Med J. 2009;20:Pe13–En77.
El Masry I, Rijks J, Peyre M, Taylor N, Lubroth J, Jobre Y. Modelling Influenza A H5N1 vaccination strategy scenarios in the household poultry sector in Egypt. Trop Anim Health Prod. 2014;46:57–63.
Mroz C, Gwida M, El-Ashker M, Ziegler U, Homeier-Bachmann T, Eiden M, Groschup MH. Rift valley Fever virus Infections in Egyptian cattle and their prevention. Transbound Emerg Dis. 2017;64:2049–58.
Pinsent A, Pepin KM, Zhu H, Guan Y, White MT, Riley S. (2017) The persistence of multiple strains of avian influenza in live bird markets. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences 284:20170715.
Abbas B, Yousif MA, Nur HM. Animal health constraints to livestock exports from the Horn of Africa: -EN- -FR- restrictions sanitaires imposées aux exportations de bétail à partir de la corne de l’Afrique -ES- limitaciones zoosanitarias a las exportaciones de ganado desde El Cuerno De África. Rev Sci Tech OIE. 2014;33:711–21.
Naletoski I, Kirandziski T, Mitrov D, Krstevski K, Dzadzovski I, Acevski S. Gaps in brucellosis eradication campaign in Sheep and goats in Republic of Macedonia: lessons learned. Croat Med J. 2010;51:351–6.
Weaver JT, Malladi S, Bonney PJ, Patyk KA, Bergeron JG, Middleton JL, Alexander CY, Goldsmith TJ, Halvorson DA. A Simulation-based evaluation of Premovement active surveillance Protocol options for the Managed Movement of Turkeys to Slaughter during an outbreak of highly pathogenic avian Influenza in the United States. Avian Dis. 2016;60:132–45.
Andronico A, Courcoul A, Bronner A, Scoizec A, Lebouquin-Leneveu S, Guinat C, Paul MC, Durand B, Cauchemez S. Highly pathogenic avian Influenza H5N8 in south-west France 2016–2017: a modeling study of control strategies. Epidemics. 2019;28:100340.
Backer JA, van Roermund HJW, Fischer EAJ, van Asseldonk MAPM, Bergevoet RHM. Controlling highly pathogenic avian Influenza outbreaks: an epidemiological and economic model analysis. Prev Vet Med. 2015;121:142–50.
Backer JA, Hagenaars TJ, van Roermund HJW, de Jong MCM. Modelling the effectiveness and risks of vaccination strategies to control classical swine Fever epidemics. J R Soc Interface. 2009;6:849–61.
Fournie G, Guitian FJ, Mangtani P, Ghani AC. Impact of the implementation of rest days in live bird markets on the dynamics of H5N1 highly pathogenic avian Influenza. J R Soc Interface. 2011;8:1079–89.
Kung NY, Guan Y, Perkins NR, Bissett L, Ellis T, Sims L, Morris RS, Shortridge KF, Peiris JSM. The impact of a monthly Rest Day on Avian Influenza Virus isolation rates in Retail Live Poultry markets in Hong Kong. Avian Dis. 2003;47:1037–41.
Horigan V, Gale P, Adkin A, Brown I, Clark J, Kelly L. A qualitative risk assessment of cleansing and disinfection requirements after an avian Influenza outbreak in commercial poultry. Br Poult Sci. 2019;60:691–9.
Yuan J, Lau EHY, Li K, et al. Effect of live Poultry Market Closure on Avian Influenza A(H7N9) virus activity in Guangzhou, China, 2014. Emerg Infect Dis. 2015;21:1784–93.
Fournie G, Guitian J, Desvaux S, Cuong VC, Dung DH, Pfeiffer DU, Mangtani P, Ghani AC. Interventions for avian Influenza A (H5N1) risk management in live bird market networks. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2013;110:9177–82.
Samaan G, Hendrawati F, Taylor T, Pitona T, Marmansari D, Rahman R, Lokuge K, Kelly PM. Application of a healthy food markets guide to two Indonesian markets to reduce transmission of avian Flu. Bull World Health Organ. 2012;90:295–300.
Huang Z, Wang J, Zuo A. Chinese farmers’ willingness to accept compensation to practice safe disposal of HPAI infected chicken. Prev Vet Med. 2017;139:67–75.
Graiver DA, Topliff CL, Kelling CL, Bartelt-Hunt SL. Survival of the avian Influenza virus (H6N2) after land disposal. Environ Sci Technol. 2009;43:4063–7.
Li Y, Wang Y, Shen C, Huang J, Kang J, Huang B, Guo F, Edwards J. Closure of live bird markets leads to the spread of H7N9 Influenza in China. PLoS ONE. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0208884 .
Ma J, Yang N, Gu H, Bai L, Sun J, Gu S, Gu J. Effect of closure of live poultry markets in China on prevention and control of human Infection with H7N9 avian Influenza: a case study of four cities in Jiangsu Province. J Public Health Policy. 2019;40:436–47.
Chen Y, Cheng J, Xu Z, Hu W, Lu J. Live poultry market closure and avian Influenza A (H7N9) Infection in cities of China, 2013–2017: an ecological study. BMC Infect Dis. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12879-020-05091-7 .
Bonwitt J, Dawson M, Kandeh M, Ansumana R, Sahr F, Brown H, Kelly AH. Unintended consequences of the `bushmeat ban’ in West Africa during the 2013–2016 Ebola virus Disease epidemic. Soc Sci Med. 2018;200:166–73.
Brooks-Moizer F, Roberton SI, Edmunds K, Bell D. Avian Influenza H5N1 and the wild Bird Trade in Hanoi, Vietnam. Ecol Soc. 2009;14:28.
Cardador L, Tella JL, Anadon JD, Abellan P, Carrete M. The European trade ban on wild birds reduced invasion risks. Conserv Lett. 2019;12:e12631.
Guerrier G, Foster H, Metge O, Chouvin C, Tui M. Cultural contexts of swine-related Infections in Polynesia. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2013;19:595–9.
Massey PD, Polkinghorne BG, Durrheim DN, Lower T, Speare R. Blood, guts and knife cuts: reducing the risk of swine brucellosis in feral pig hunters in north-west New South Wales, Australia. Rural Remote Health. 2011;11:1793.
CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Lauterbach SE, Nelson SW, Martin AM, Spurck MM, Mathys DA, Mollenkopf DF, Nolting JM, Wittum TE, Bowman AS. (2020) Adoption of recommended hand hygiene practices to limit zoonotic Disease transmission at agricultural fairs. Preventive Veterinary Medicine. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prevetmed.2020.105116 .
Stewart RJ, Rossow J, Conover JT, et al. Do animal exhibitors support and follow recommendations to prevent transmission of variant Influenza at agricultural fairs? A survey of animal exhibitor households after a variant Influenza virus outbreak in Michigan. Zoonoses Public Health. 2018;65:195–201.
Lin X, Zhang D, Wang X, Huang Y, Du Z, Zou Y, Lu J, Hao Y. Attitudes of consumers and live-poultry workers to central slaughtering in controlling H7N9: a cross-sectional study. BMC Public Health. 2017;17:517.
Huot C, De Serres G, Duval B, Maranda-Aubut R, Ouakki M, Skowronski DM. The cost of preventing rabies at any cost: post-exposure prophylaxis for occult bat contact. Vaccine. 2008;26:4446–50.
De Serres G, Skowronski DM, Mimault P, Ouakki M, Maranda-Aubut R, Duval B. Bats in the bedroom, bats in the Belfry: reanalysis of the rationale for rabies postexposure Prophylaxis. Clin Infect Dis. 2009;48:1493–9.
Vivancos R, Showell D, Keeble B, Goh S, Kroese M, Lipp A, Battersby J. Vaccination of Poultry workers: delivery and uptake of Seasonal Influenza immunization. Zoonoses Public Health. 2011;58:126–30.
Okello AL, Thomas LF. Human taeniasis: current insights into prevention and management strategies in endemic countries. RISK MANAG HEALTHC POLICY. 2017;10:107–16.
Mendez D, Buttner P, Speare R. Hendra virus in Queensland, Australia, during the winter of 2011: veterinarians on the path to better management strategies. Prev Vet Med. 2014;117:40–51.
Häsler B, Howe KS, Hauser R, Stärk KDC. A qualitative approach to measure the effectiveness of active avian Influenza virus surveillance with respect to its cost: a case study from Switzerland. Prev Vet Med. 2012;105:209–22.
Brinkley C, Kingsley JS, Mench J. A Method for Guarding Animal Welfare and Public Health: tracking the rise of Backyard Poultry ordinances. J Community Health. 2018;43:639–46.
Turkson PK, Okike I. Assessment of practices, capacities and incentives of poultry chain actors in implementation of highly pathogenic avian Influenza mitigation measures in Ghana. Vet Med Sci. 2016;2:23–35.
Akunzule AN, Koney EBM, Tiongco M. Economic impact assessment of highly pathogenic avian Influenza on the poultry industry in Ghana. Worlds Poult Sci J. 2009;65:517–27.
Hunter C, Birden HH, Toribio J-A, Booy R, Abdurrahman M, Ambarawati AIGAA, Adiputra N. (2014) Community preparedness for highly pathogenic avian Influenza on Bali and Lombok, Indonesia. Rural Remote Health 14.
Tustin J, Laberge K, Michel P, et al. A National Epidemic of Campylobacteriosis in Iceland, lessons learned. Zoonoses Public Health. 2011;58:440–7.
Oladokun AT, Meseko CA, Ighodalo E, John B. Ekong PS Effect of intervention on the control of highly pathogenic avian Influenza in Nigeria. 8.
Manyweathers J, Field H, Longnecker N, Agho K, Smith C, Taylor M. Why won’t they just vaccinate? Horse owner risk perception and uptake of the Hendra virus vaccine. BMC Vet Res. 2017;13:103.
Zhu G, Kang M, Wei X, Tang T, Liu T, Xiao J, Song T, Ma W. Different intervention strategies toward live poultry markets against avian Influenza A (H7N9) virus: model-based assessment. Environ Res. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2020.110465 .
Chowell G, Simonsen L, Towers S, Miller MA, Viboud C. Transmission potential of Influenza A/H7N9, February to May 2013, China. BMC Med. 2013;11:214.
Bodenham RF, Mtui-Malamsha N, Gatei W, et al. Multisectoral cost analysis of a human and livestock anthrax outbreak in Songwe Region, Tanzania (December 2018–January 2019), using a novel Outbreak Costing Tool. One Health. 2021;13:100259.
Lewis N, Dorjee S, Dube C, VanLeeuwen J, Sanchez J. Assessment of Effectiveness of Control Strategies against Simulated Outbreaks of Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza in Ontario, Canada. Transbound Emerg Dis. 2017;64:938–50.
Anderson A, Shwiff S, Gebhardt K, Ramírez AJ, Shwiff S, Kohler D, Lecuona L. Economic evaluation of Vampire Bat ( Desmodus rotundus) rabies Prevention in Mexico. Transbound Emerg Dis. 2014;61:140–6.
Walker PGT, Cauchemez S, Metras R, Dung DH, Pfeiffer D, Ghani AC. A bayesian Approach to quantifying the effects of Mass Poultry Vaccination upon the spatial and temporal dynamics of H5N1 in Northern Vietnam. PLoS Comput Biol. 2010;6:e1000683.
PREDICT Project. In: PREDICT Project. https://p2.predict.global. Accessed 9 Sep 2022.
Loh EH, Zambrana-Torrelio C, Olival KJ, Bogich TL, Johnson CK, Mazet JAK, Karesh W, Daszak P. Targeting transmission pathways for emerging zoonotic Disease Surveillance and Control. Vector-Borne and Zoonotic Diseases. 2015;15:432–7.
Bordier M, Uea-Anuwong T, Binot A, Hendrikx P, Goutard FL. Characteristics of one health surveillance systems: a systematic literature review. Prev Vet Med. 2020;181:104560.
Worsley-Tonks KEL, Bender JB, Deem SL, et al. Strengthening global health security by improving Disease surveillance in remote rural areas of low-income and middle-income countries. The Lancet Global Health. 2022;10:e579–84.
Reaser JK, Witt A, Tabor GM, Hudson PJ, Plowright RK. Ecological countermeasures for preventing zoonotic Disease outbreaks: when ecological restoration is a human health imperative. Restor Ecol. 2021;29:e13357.
Chen HL, Lewison RL, An L, Tsai YH, Stow D, Shi L, Yang S. Assessing the effects of payments for ecosystem services programs on forest structure and species biodiversity. Biodivers Conserv. 2020;29:2123–40.
Chen Y, Marino J, Tao Q, Sullivan CD, Shi K, Macdonald DW. Predicting hotspots of human-elephant conflict to inform mitigation strategies in Xishuangbanna, Southwest China. PLoS ONE. 2016. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0162035 .
Whitfort A. COVID-19 and Wildlife Farming in China: legislating to Protect Wild Animal Health and Welfare in the wake of a global pandemic. J Environ Law. 2021;33:57–84.
Download references
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
CCA, JC and TLP acknowledge internal research support from York University. MW and CCA acknowledge internal research support from the Dahdaleh Institute for Global Health Research. KML acknowledges funding from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research through a Health System Impact Fellowship. AY is funded by the BBSRC through the Mandala project (grant number BB/V004832/1). AMV acknowledges support from York University through a York Research Chair in Population Health Ethics & Law. This review was undertaken as part of a project funded by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research, Grant Reference Number VR5-172686. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Global Health, York University, Toronto, ON, Canada
Chloe Clifford Astbury, Kirsten M. Lee, Ryan Mcleod, Asma Atique, Janielle Clarke, Anastassia Demeshko, A. M. Viens, Mary Wiktorowicz & Tarra L. Penney
Dahdaleh Institute for Global Health Research, York University, Toronto, ON, Canada
Chloe Clifford Astbury, Kirsten M. Lee, Raphael Aguiar, Mary Wiktorowicz & Tarra L. Penney
Global Strategy Lab, York University, Toronto, ON, Canada
Chloe Clifford Astbury, A. M. Viens & Tarra L. Penney
Applied Microbiology for Health and Environment Research Group, College of Arts and Sciences, University of the Philippines Manila, Manila, Philippines
Marilen Balolong & Kathleen Chelsea Togño
School of Epidemiology and Public Health, University of Ottawa, Ottawa, ON, Canada
Ronald Labonté & Arne Ruckert
School of Health Policy and Management, York University, Toronto, ON, Canada
Priyanka Sibal
School of Public Health, University of Kinshasa, Kinshasa, Democratic Republic of Congo
Marc K. Yambayamba
Department of Public Health, Environments and Society, London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine, London, UK
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Conception and design: CCA, KLM and TLP. Acquisition of data: CCA, KLM and AY. Analysis and interpretation of data: CCA, KML, RM, JC, AD and PS. Drafting of the manuscript: CCA and RM. Critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content: KML, RA, AA, MB, JC, AD, RL, AR, PS, KCT, AMV, MW, MKY, AY and TLP. Obtaining funding: TLP and MW.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Tarra L. Penney .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate, consent for publication, competing interests.
The authors declare that they have no competing interests. RL is a co-editor-in-chief of Globalization and Health.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Material 1
Supplementary material 2, supplementary material 3, supplementary material 4, supplementary material 5, rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Clifford Astbury, C., Lee, K.M., Mcleod, R. et al. Policies to prevent zoonotic spillover: a systematic scoping review of evaluative evidence. Global Health 19 , 82 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12992-023-00986-x
Download citation
Received : 05 May 2023
Accepted : 01 November 2023
Published : 08 November 2023
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12992-023-00986-x
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Zoonotic spillover
- Public policy
- Emerging zoonoses
- Deep prevention
Globalization and Health
ISSN: 1744-8603
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
- General enquiries: [email protected]

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Step 1: Restate the problem. The first task of your conclusion is to remind the reader of your research problem. You will have discussed this problem in depth throughout the body, but now the point is to zoom back out from the details to the bigger picture. While you are restating a problem you've already introduced, you should avoid phrasing ...
1. Market Research Report: Brand Analysis. Our first example shares the results of a brand study. To do so, a survey has been performed on a sample of 1333 people, information that we can see in detail on the left side of the board, summarizing the gender, age groups, and geolocation. **click to enlarge**.
The conclusion in a research paper is the final section, where you need to summarize your research, presenting the key findings and insights derived from your study. Check out this article on how to write a conclusion for a research paper, with examples.
Here are some steps you can follow to write an effective research paper conclusion: Restate the research problem or question: Begin by restating the research problem or question that you aimed to answer in your research. This will remind the reader of the purpose of your study. Summarize the main points: Summarize the key findings and results ...
With a nudge in the right direction, you'll write a conclusion that will bring your paper to an effective close. Summarize the main argument of your paper without repeating too much. Point out why the argument is significant to the research and issue at hand to bring them to a concluding point. Explain the strengths and limitations of your ...
Download HubSpot's free, editable market research report template here. 1. Five Forces Analysis Template. Use Porter's Five Forces Model to understand an industry by analyzing five different criteria and how high the power, threat, or rivalry in each area is — here are the five criteria: Competitive rivalry.
Begin your conclusion by restating your thesis statement in a way that is slightly different from the wording used in the introduction. Avoid presenting new information or evidence in your conclusion. Just summarize the main points and arguments of your essay and keep this part as concise as possible. Remember that you've already covered the ...
Step 1: Restate the problem. Always begin by restating the research problem in the conclusion of a research paper. This serves to remind the reader of your hypothesis and refresh them on the main point of the paper. When restating the problem, take care to avoid using exactly the same words you employed earlier in the paper.
1. Remember about the main topic. The statement must be written clearly and concisely to be effective, just one sentence. Remember that your conclusion should be concise and precise, expressing only the most important elements. 2. Reaffirm your thesis. Restate the research paper's thesis after that.
There are different ways to approach market research, including primary and secondary research and qualitative and quantitative research. The strongest approaches will include a combination of all four. "Virtually every business can benefit from conducting some market research," says Niles Koenigsberg of Real FiG Advertising + Marketing.
Example of a research paper conclusion Here is an example of an effective research paper conclusion: Digital marketing remains the best and most cost-effective means for companies to build their brands and retain customers. Over a decade worth of research supports this fact, with major corporations like Kent industries, Pear Inc., and Hardwood Limited Industries experiencing significant growth ...
June 3, 2021 28 min read. Market research is a process of gathering, analyzing, and interpreting information about a given market. It takes into account geographic, demographic, and psychographic data about past, current, and potential customers, as well as competitive analysis to evaluate the viability of a product offer.
The conclusion is intended to help the reader understand why your research should matter to them after they have finished reading the paper. A conclusion is not merely a summary of the main topics covered or a re-statement of your research problem, but a synthesis of key points derived from the findings of your study and, if applicable, where you recommend new areas for future research.
Market Research Conclusion Prioritization Tool. Use this tool to evaluate a series of research conclusions and find which conclusions will be helpful in gaining a better market position. Estimated time required: 2 hours. Skills required: Microsoft Excel (advanced)
Along with Meredith Harris. Hannah, a writer and editor since 2017, specializes in clear and concise academic and business writing. She has mentored countless scholars and companies in writing authoritative and engaging content. To write an exemplary research paper conclusion, review what you've found and what it means. Summarize like a star ...
Step 2: Design the Research. The next step in the marketing research process is to do a research design. The research design is your "plan of attack.". It outlines what data you are going to gather and from whom, how and when you will collect the data, and how you will analyze it once it's been obtained.
Market research is defined as the systematic collection, analysis, and interpretation of data about a specific market, industry, or consumer segment. It involves studying customers, competitors, and market dynamics to identify opportunities, mitigate risks, and make informed business decisions. Market research provides valuable insights into ...
A conclusion is the final paragraph of a research paper and serves to help the reader understand why your research should matter to them. The conclusion of a conclusion should: Restate your topic and why it is important. Restate your thesis/claim. Address opposing viewpoints and explain why readers should align with your position.
Integrate with 100+ apps and plug-ins to get more done. SurveyMonkey Forms. Build and customize online forms to collect info and payments. SurveyMonkey Genius. Create better surveys and spot insights quickly with built-in AI. Market Research Solutions. Purpose-built solutions for all of your market research needs. INDUSTRIES.
Summary and Conclusion. MARKETING IS the most exciting of all business sports. It is the heartbeat of every successful business. It is continually changing in response to the explosion of information, the expansion of technology, and the aggressiveness of competition, at all levels and everywhere. All business strategy is marketing strategy.
Conclusion. In the conclusion, repeat the highlights. Summarize the target market, the offer, and the communication plan. Your conclusion should remind the reader of all the reasons why your plan is the best choice. Of course, the written plan is itself a marketing tool. You want it to convince someone to invest in your ideas, so you want to ...
THE IMPORTANCE OF MARKET RESEARCH 5 Conclusion Marketing research is usually the first step in the marketing process, after ideas for products are conceived. Businesses conduct marketing research to obtain information from the marketplace. They use it to solve problems, obtain information on competitors and determine the needs and wants of non-paying consumers and customers.
Conclusion. To summarize, the best proxies for market research can make a massive difference. You get the anonymity and security to bypass website blocks while collecting all the business data you need. You're then left with a valuable resource that helps you understand your target market and competitors. From there, your business is sure to ...
Conclusion. The shift toward higher-for-longer monetary policy has contributed to recent selling pressure in an overbought equity market. Treasury yields have rerated higher, but the increase can be attributed more to growth expectations outpacing inflation expectations. ... LPL Research brings the market directly to you with a publication ...
Conclusion . Each company highlighted in this article has gained a competitive advantage early. Not only are they well-suited for the upcoming digital product passport mandates set by the EU, but their supply chain digitalization journeys are accelerating faster than those of other brands in their industry. ... 4 Market Research Case Studies ...
5. Conclusion and recommendation. The findings from this study shed light on several influential factors, including repeat tourists' demographic characteristics which shape tourists' decisions. Notably, family size, income level, Employment status, and Regions of origin exhibit a predilection for wildlife attraction.
The Drum draws on major research carried out by EY - which was recently unveiled at Possible Miami - to gain insights into subscription struggles at Pret a Manger and Krispy Kreme.
(Getty Images) The COVID-19 pandemic set off nearly unprecedented churn in the U.S. labor market. Widespread job losses in the early months of the pandemic gave way to tight labor markets in 2021, driven in part by what's come to be known as the Great Resignation.The nation's "quit rate" reached a 20-year high last November. A new Pew Research Center survey finds that low pay, a lack ...
Conclusion. Securing the best office rental deals in Hong Kong requires a combination of research, flexibility, negotiation skills, and market savvy. By understanding the dynamics of the market, being proactive in your approach, and leveraging the expertise of professionals, you can find an office space that meets your needs at a competitive rate.
For example, a review of market-level biosecurity measures aiming to reduce the transmission of avian influenza found that reducing market size, separating poultry species, cleaning and disinfecting premises, closing markets and banning overnight storage were highly effective interventions . However, our findings suggest that studies focused on ...