Six engaging critical thinking activities with class discussions

Critical thinking is one of the most valuable skills students can develop to help them navigate their personal, academic, and professional worlds. By fostering these skills in the classroom, educators can ensure students don’t simply absorb information passively, but rather learn to question, analyze, and draw informed conclusions.
Kialo Edu is a great (and completely free ) tool for critical thinking activities. In Kialo discussions, students collaborate while exploring a topic, working together to break down complex ideas into more manageable chunks. Let’s take a look at some engaging critical thinking activities to try out with your students on Kialo Edu!

How to encourage critical thinking in the classroom
You can weave critical thinking into many types of activities, but here are some key types of activities that help students move beyond surface-level understanding. Use activities which contain the following attributes:
- Encourage active inquiry
- Promote curiosity
- Challenge assumptions
- Consider multiple perspectives and viewpoints
- Emphasize evidence and reasoning
- Foster collaboration
- Encourage reflection
- Engage in problem solving and decision making
- Use real world contexts and cross-disciplinary knowledge
- Foster metacognition
By incorporating such strategies, teachers can create an environment where students learn to question, evaluate, and synthesize information effectively. An added bonus is an improved classroom climate that encourages dialogue, diverse thinking, and peer learning. Students not only build self-awareness, but also develop the skills needed to think deeply and make informed decisions.
Critical thinking activities for the classroom on Kialo Edu
Kialo Edu discussions are designed to support critical thinking skills , encouraging students to think deeply, collaborate, and explore creative solutions to real world issues.
Try out these critical thinking activities on Kialo Edu with your students to guide them to become 21st-century learners! As Kialo discussions help students visualize their thinking, students are better able to draw connections between ideas, challenge their own reasoning, and evaluate the strength of their arguments.
1. Identify logical fallacies and evaluate information

This activity explicitly addresses the flawed reasoning and misinformation commonly found in many online interactions.
Divide your class into groups, assigning each group a distinct thesis to discuss. Instruct each group to develop their discussion using both substantive pro and con claims, as well as some claims containing logical fallacies .
Students can also use this approach to practice evaluating evidence. Task them to include sources of varying quality in their discussion. You can adapt this to the level of your students; for beginners, this could mean including a mix of reliable and not-so-reliable sources, or simply omitting a needed source. More experienced classes might also cherry-pick or misrepresent information from reputable sources.
As they incorporate these fallacious claims or questionable sources, encourage students to name them and discuss how they weaken their arguments. To extend this activity, have each group peer review another group’s discussion to first identify the fallacies and problematic sources, and then rework the claims to make them stronger.
2. Analyze an influential argument
In this activity, students critically analyze a well-known argument to explore its layout, flow, logic, and approach.
Choose a famous argument, a political speech, or an opinion piece in a newspaper for groups of students to delve into. You can use Small Group Mode to streamline the process. This handy feature divides your class into groups, while you monitor each group working from a copy of a template discussion you create.
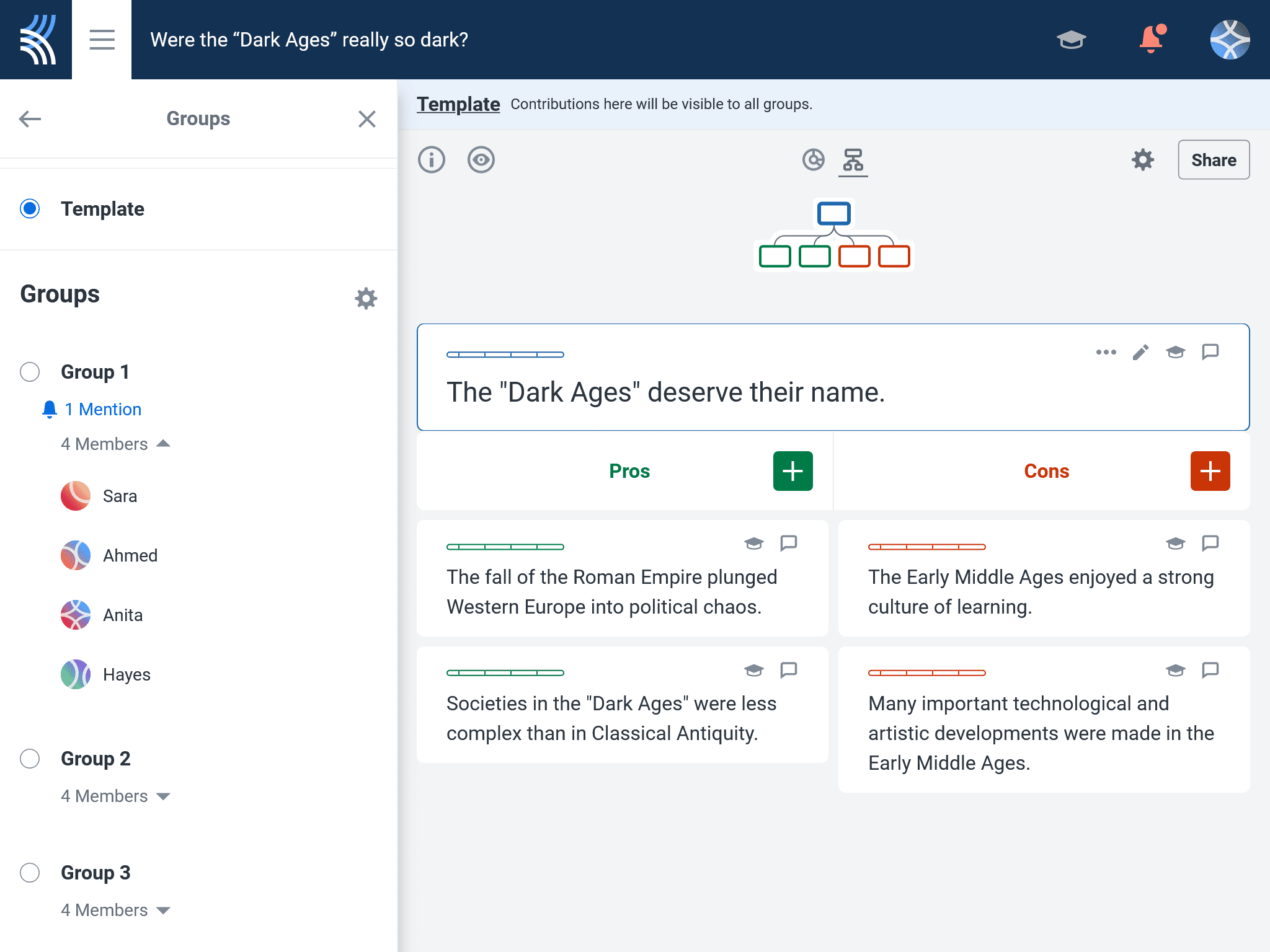
Then, have students map out the argument on Kialo, identifying the reasoning, central arguments, and supporting evidence the writer is citing as they go. Remind them that they can edit , and move and link their claims to different locations to refine the discussion as they work.
Next, have students vote on the claims and discuss their view on the argument. This helps students see how persuasive arguments are structured, while also giving them practice in articulating their own views clearly.
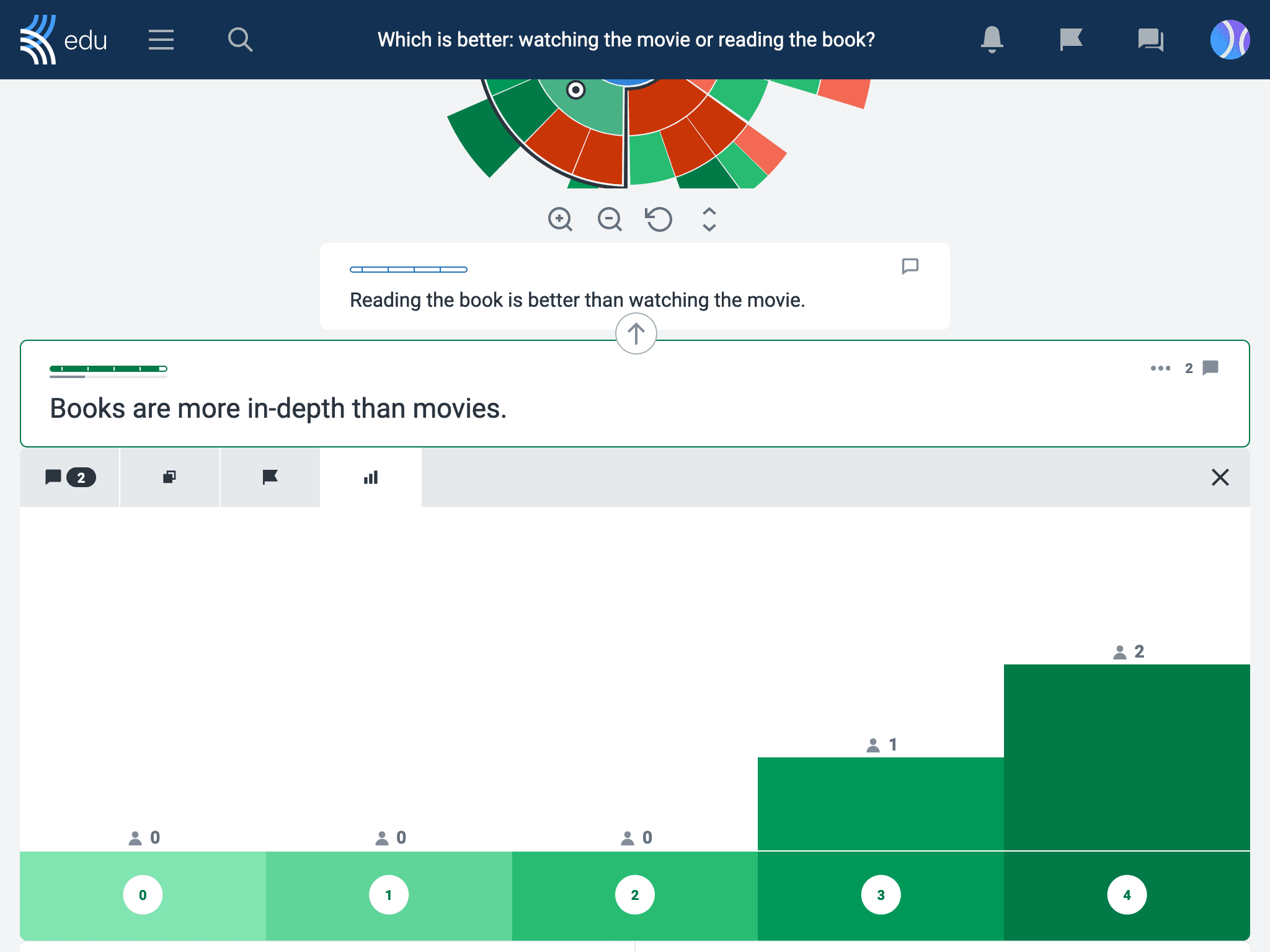
To extend this, have students return to the discussion from an opposing or simply neutral perspective to develop it further. This encourages perspective-taking and engagement with multiple viewpoints, which is crucial for gaining a deeper understanding of complex issues and fostering critical thinking.
3. Map out policy decisions
In this activity, students engage with real-world and meaningful issues that affect society through analyzing policy proposals. They’ll develop critical thinking skills and gain an understanding of political processes, enhancing their political literacy skills.
Should schools provide free meals for all students? — kialo-edu.com
Choose a relevant policy for students to explore, or let them pick one as a group based on their common interests. Some relevant topics could be ones related to minimum wage laws , healthcare reform , or educational funding .
To prepare for the discussion, have students investigate the central intention of the policy, research the reasoning behind it, and find data, studies, and evidence to strengthen the case for its adoption. They then research the counterarguments and the different viewpoints on the policy.
Afterwards, have students input the information into a Kialo discussion to organize and visualize their analysis. This structure helps them better assess the strength of the policy and identify any unresolved claims.
To take it a step further, encourage students to seek out alternative policies or brainstorm different solutions. Then, use a multi-thesis discussion to give students a space to compare the different policy directions, sharpening their ability to weigh alternatives and synthesize information.
4. Roleplay a courtroom case
This activity blends debate and role play to encourage deep analysis of evidence and constructive dialogue.
Students first work in groups to explore a topic in-depth through a Kialo discussion. Let them know they’ll later have to represent and defend one side of the thesis (without revealing which) to ensure they examine both sides equally.
Students then form new groups of six, with two acting as experts and two as lawyers — one of each representing one side of the thesis — while the remaining two serve as jurors.
The experts present their knowledge on the thesis, while the lawyers question, encourage, and challenge their arguments. The jurors listen carefully, weigh the evidence, and identify any misrepresentation or bias before presenting their verdict and reasoning.
With each role, students will engage with the topic in different ways. Experts convey accurate and well-researched information, lawyers construct convincing and persuasive arguments, and jurors evaluate and summarize evidence. By giving all students the opportunity to articulate their understanding of the topic, this activity builds communication skills alongside critical thinking skills.
5. Reflecting on changes in thinking
This activity prompts students to explore how opinions are formed and evolve.
Start by instructing students to vote on a thesis before starting a Kialo discussion. Set the Voting visibility to “Users only see their own votes”’ to reduce peer influence and social pressure, so students feel free to be candid with their own votes.
Students then work in their groups to build their discussion. Alternatively, to further personalize this approach, you might ask students to each identify a strongly-held belief to explore in an individual discussion.
When your students have finished the discussion, ask them to revisit their vote again to see where their vote now lies on the Impact Meter , and whether their ideas have been reinforced or challenged. You can provide critical thinking questions to guide their reflection, such as:
- What was the turning point in the discussion?
- Did your opinion change?
- Were any of your assumptions challenged?
- What new perspective or information have you gained?
- What lessons can you take away from this activity?
By critically examining their own beliefs, students can recognize that changing one’s mind can be a sign of intellectual growth and that opinions can be reinforced and strengthened through evidence and deep analysis.
We’d love to hear about your thoughts and ideas on developing critical thinking skills in the classroom! Please do get in touch at [email protected] or on any of our social media channels.
Want to try Kialo Edu with your class?
Sign up for free and use Kialo Edu to have thoughtful classroom discussions and train students’ argumentation and critical thinking skills.
Table of Contents

How to Support Critical Thinking with Classroom Discussions
- Morgan Love
- October 23, 2024
In today’s world, critical thinking is one of the most important skills we can help students develop. It allows them to navigate information, form well-rounded opinions, and communicate effectively. One of the best ways to foster this skill in the classroom is through discussions that challenge students to analyze real-world issues, consider multiple perspectives, and build logical arguments.
The Juice uses current events, news articles, and nonfiction texts to teach informational literacy to students. It provides foundational content for teachers to support critical thinking in their students with classroom discussions.
By incorporating these articles into lessons, teachers give students the tools they need to
- Think deeply
- Express their opinions clearly
- Engage meaningfully with the world
In this blog, we’ll explore how The Juice’s current events for students promote critical thinking through better classroom discussions. We’ll also provide critical thinking examples for students and strategies you can use to bring these discussions to life.
Why do classroom discussions matter for teaching critical thinking?
Classroom discussions are an essential part of any critical thinking curriculum. They allow students to
- Share ideas
- Challenge each other’s viewpoints
- Develop reasoning skills
- Build a collaborative environment
The benefits are clear:
Students who regularly engage in discussions tend to have stronger problem-solving abilities, better communication skills, and greater confidence in expressing their thoughts.
When you incorporate real-world informational texts like The Juice’s current events articles into discussions, students have the chance to apply critical thinking characteristics to topics that matter. Students learn to
- Analyze events
- Question assumptions
- Connect what they learn to larger societal systems
What are the benefits of classroom discussions?
- Promotes Engagement : Students are more engaged when they can voice their opinions on current events for students and real-world topics.
- Encourages Multiple Perspectives : Discussing current events helps students consider different viewpoints and cultural contexts.
- Develops Reasoning Skills : Students learn to back up their opinions with evidence, improving their ability to reason and argue logically.
How does The Juice support critical thinking and classroom discussions?
Juice articles are specifically designed to make classroom discussions more effective by providing students with sources and discussion prompts that are based on real-world events and can be used to support any critical thinking activity.
Here’s how The Juice helps teachers teach informational literacy, support critical thinking education, and manage classroom discussions at the same time.
Current events offer diverse viewpoints
The Juice’s news articles for students cover a wide range of perspectives on important issues, allowing students to see multiple sides of a debate. This is essential for promoting critical thinking because it encourages students to look beyond their own biases and consider how others might see the world.
- Critical Thinking Benefits : By exposing students to different viewpoints, they learn to analyze arguments and assess the validity of various perspectives — key components of critical thinking exercises.
- Example : A classroom discussion on climate change might start with an article from The Juice that presents both the scientific consensus and the economic concerns of industries affected by environmental regulations.
Foster social-emotional skills with The Juice.
Background information gives context to build informed opinions
Effective critical thinking depends on a deep understanding of the topics being discussed. The Juice provides students with the essential background information they need to participate in discussions with confidence.
The Juice’s current events articles include “Extra Juices,” which offer background information that provides context for the news.
- Critical Thinking Examples for Students : When discussing current events, students can use the detailed background provided in the Extra Juices to form well-informed opinions rather than relying on limited information, assumptions, or emotions.
- Critical Thinking Framework : This approach teaches students to seek out and use accurate information when building their arguments — a core aspect of critical thinking practice.
Current events for students promote information literacy
The Juice’s information literacy platform teaches students how to analyze and evaluate the credibility of sources. This skill is crucial for any critical thinking curriculum as it ensures that students can distinguish between reliable and unreliable information in a media-saturated world.
- Informational Literacy : By reading articles from trusted sources, students develop the ability to assess the quality of information, a key characteristic of critical thinking.
Vocabulary development helps students express their opinions
Strong critical thinking requires students to articulate their ideas clearly, and The Juice helps by enhancing their vocabulary. The Juice’s current events articles introduce students to new vocabulary words with built-in scaffolds, giving them the language they need to engage in meaningful discussions.
- Vocabulary Development : As students encounter new words in nonfiction texts with our built-in vocabulary supports, they improve their ability to express complex ideas — a critical aspect of critical thinking exercises.

Accessible nonfiction texts for shared classroom reading
One of the most powerful features of The Juice is its ability to deliver the same article at multiple reading levels, allowing all students to participate in discussions, regardless of their reading ability. This promotes equity in the classroom, ensuring every student has the same information to build their opinions on for a classroom discussion.
- Critical Thinking Framework : By reading the same content, students engage in discussions with a shared understanding, which encourages more focused and productive conversations.
- Critical Thinking Practice : This approach allows students of all abilities to practice critical thinking through shared experiences.
How to use The Juice for classroom discussions
Here are some practical ways you can use The Juice to enhance classroom discussions and foster critical thinking:
Start with a question
Begin by asking an open-ended question based on a current events article. This could be something like, “How do you think this event will impact our community?” or “What are the potential consequences of this policy?”
Use think-pair-share
After reading the nonfiction article, have students think about their responses individually, discuss them with a partner, and then share their thoughts with the class. This gives them time to develop their ideas before sharing.
Encourage evidence-based arguments
Remind students to back up their opinions with evidence from the news article. This reinforces the importance of using accurate information when forming opinions — one of the key critical thinking characteristics.
Take on another point of view
Assign students different perspectives from the article and have them argue their case. This is a great way to promote empathy and understanding while encouraging critical thinking.
Strengthening student’s critical thinking with The Juice
By using The Juice’s current events for students, teachers can support the development of critical thinking characteristics through engaging discussions based on real-world news. The Juice empowers students to think deeply, analyze multiple perspectives, and express their ideas clearly.
With features like differentiated reading levels, detailed background information, and diverse viewpoints, The Juice makes it easier than ever to incorporate critical thinking practice into your classroom.
Ready to start fostering better discussions and developing critical thinkers in your classroom? Incorporate The Juice today and see the difference it makes!
With these strategies and resources, your students will develop the skills they need to think critically about the world, express themselves clearly, and participate meaningfully in conversations that matter

Classroom Q&A
With larry ferlazzo.
In this EdWeek blog, an experiment in knowledge-gathering, Ferlazzo will address readers’ questions on classroom management, ELL instruction, lesson planning, and other issues facing teachers. Send your questions to [email protected]. Read more from this blog.
Eight Instructional Strategies for Promoting Critical Thinking

- Share article
(This is the first post in a three-part series.)
The new question-of-the-week is:
What is critical thinking and how can we integrate it into the classroom?
This three-part series will explore what critical thinking is, if it can be specifically taught and, if so, how can teachers do so in their classrooms.
Today’s guests are Dara Laws Savage, Patrick Brown, Meg Riordan, Ph.D., and Dr. PJ Caposey. Dara, Patrick, and Meg were also guests on my 10-minute BAM! Radio Show . You can also find a list of, and links to, previous shows here.
You might also be interested in The Best Resources On Teaching & Learning Critical Thinking In The Classroom .
Current Events
Dara Laws Savage is an English teacher at the Early College High School at Delaware State University, where she serves as a teacher and instructional coach and lead mentor. Dara has been teaching for 25 years (career preparation, English, photography, yearbook, newspaper, and graphic design) and has presented nationally on project-based learning and technology integration:
There is so much going on right now and there is an overload of information for us to process. Did you ever stop to think how our students are processing current events? They see news feeds, hear news reports, and scan photos and posts, but are they truly thinking about what they are hearing and seeing?
I tell my students that my job is not to give them answers but to teach them how to think about what they read and hear. So what is critical thinking and how can we integrate it into the classroom? There are just as many definitions of critical thinking as there are people trying to define it. However, the Critical Think Consortium focuses on the tools to create a thinking-based classroom rather than a definition: “Shape the climate to support thinking, create opportunities for thinking, build capacity to think, provide guidance to inform thinking.” Using these four criteria and pairing them with current events, teachers easily create learning spaces that thrive on thinking and keep students engaged.
One successful technique I use is the FIRE Write. Students are given a quote, a paragraph, an excerpt, or a photo from the headlines. Students are asked to F ocus and respond to the selection for three minutes. Next, students are asked to I dentify a phrase or section of the photo and write for two minutes. Third, students are asked to R eframe their response around a specific word, phrase, or section within their previous selection. Finally, students E xchange their thoughts with a classmate. Within the exchange, students also talk about how the selection connects to what we are covering in class.
There was a controversial Pepsi ad in 2017 involving Kylie Jenner and a protest with a police presence. The imagery in the photo was strikingly similar to a photo that went viral with a young lady standing opposite a police line. Using that image from a current event engaged my students and gave them the opportunity to critically think about events of the time.
Here are the two photos and a student response:
F - Focus on both photos and respond for three minutes
In the first picture, you see a strong and courageous black female, bravely standing in front of two officers in protest. She is risking her life to do so. Iesha Evans is simply proving to the world she does NOT mean less because she is black … and yet officers are there to stop her. She did not step down. In the picture below, you see Kendall Jenner handing a police officer a Pepsi. Maybe this wouldn’t be a big deal, except this was Pepsi’s weak, pathetic, and outrageous excuse of a commercial that belittles the whole movement of people fighting for their lives.
I - Identify a word or phrase, underline it, then write about it for two minutes
A white, privileged female in place of a fighting black woman was asking for trouble. A struggle we are continuously fighting every day, and they make a mockery of it. “I know what will work! Here Mr. Police Officer! Drink some Pepsi!” As if. Pepsi made a fool of themselves, and now their already dwindling fan base continues to ever shrink smaller.
R - Reframe your thoughts by choosing a different word, then write about that for one minute
You don’t know privilege until it’s gone. You don’t know privilege while it’s there—but you can and will be made accountable and aware. Don’t use it for evil. You are not stupid. Use it to do something. Kendall could’ve NOT done the commercial. Kendall could’ve released another commercial standing behind a black woman. Anything!
Exchange - Remember to discuss how this connects to our school song project and our previous discussions?
This connects two ways - 1) We want to convey a strong message. Be powerful. Show who we are. And Pepsi definitely tried. … Which leads to the second connection. 2) Not mess up and offend anyone, as had the one alma mater had been linked to black minstrels. We want to be amazing, but we have to be smart and careful and make sure we include everyone who goes to our school and everyone who may go to our school.
As a final step, students read and annotate the full article and compare it to their initial response.
Using current events and critical-thinking strategies like FIRE writing helps create a learning space where thinking is the goal rather than a score on a multiple-choice assessment. Critical-thinking skills can cross over to any of students’ other courses and into life outside the classroom. After all, we as teachers want to help the whole student be successful, and critical thinking is an important part of navigating life after they leave our classrooms.

‘Before-Explore-Explain’
Patrick Brown is the executive director of STEM and CTE for the Fort Zumwalt school district in Missouri and an experienced educator and author :
Planning for critical thinking focuses on teaching the most crucial science concepts, practices, and logical-thinking skills as well as the best use of instructional time. One way to ensure that lessons maintain a focus on critical thinking is to focus on the instructional sequence used to teach.
Explore-before-explain teaching is all about promoting critical thinking for learners to better prepare students for the reality of their world. What having an explore-before-explain mindset means is that in our planning, we prioritize giving students firsthand experiences with data, allow students to construct evidence-based claims that focus on conceptual understanding, and challenge students to discuss and think about the why behind phenomena.
Just think of the critical thinking that has to occur for students to construct a scientific claim. 1) They need the opportunity to collect data, analyze it, and determine how to make sense of what the data may mean. 2) With data in hand, students can begin thinking about the validity and reliability of their experience and information collected. 3) They can consider what differences, if any, they might have if they completed the investigation again. 4) They can scrutinize outlying data points for they may be an artifact of a true difference that merits further exploration of a misstep in the procedure, measuring device, or measurement. All of these intellectual activities help them form more robust understanding and are evidence of their critical thinking.
In explore-before-explain teaching, all of these hard critical-thinking tasks come before teacher explanations of content. Whether we use discovery experiences, problem-based learning, and or inquiry-based activities, strategies that are geared toward helping students construct understanding promote critical thinking because students learn content by doing the practices valued in the field to generate knowledge.

An Issue of Equity
Meg Riordan, Ph.D., is the chief learning officer at The Possible Project, an out-of-school program that collaborates with youth to build entrepreneurial skills and mindsets and provides pathways to careers and long-term economic prosperity. She has been in the field of education for over 25 years as a middle and high school teacher, school coach, college professor, regional director of N.Y.C. Outward Bound Schools, and director of external research with EL Education:
Although critical thinking often defies straightforward definition, most in the education field agree it consists of several components: reasoning, problem-solving, and decisionmaking, plus analysis and evaluation of information, such that multiple sides of an issue can be explored. It also includes dispositions and “the willingness to apply critical-thinking principles, rather than fall back on existing unexamined beliefs, or simply believe what you’re told by authority figures.”
Despite variation in definitions, critical thinking is nonetheless promoted as an essential outcome of students’ learning—we want to see students and adults demonstrate it across all fields, professions, and in their personal lives. Yet there is simultaneously a rationing of opportunities in schools for students of color, students from under-resourced communities, and other historically marginalized groups to deeply learn and practice critical thinking.
For example, many of our most underserved students often spend class time filling out worksheets, promoting high compliance but low engagement, inquiry, critical thinking, or creation of new ideas. At a time in our world when college and careers are critical for participation in society and the global, knowledge-based economy, far too many students struggle within classrooms and schools that reinforce low-expectations and inequity.
If educators aim to prepare all students for an ever-evolving marketplace and develop skills that will be valued no matter what tomorrow’s jobs are, then we must move critical thinking to the forefront of classroom experiences. And educators must design learning to cultivate it.
So, what does that really look like?
Unpack and define critical thinking
To understand critical thinking, educators need to first unpack and define its components. What exactly are we looking for when we speak about reasoning or exploring multiple perspectives on an issue? How does problem-solving show up in English, math, science, art, or other disciplines—and how is it assessed? At Two Rivers, an EL Education school, the faculty identified five constructs of critical thinking, defined each, and created rubrics to generate a shared picture of quality for teachers and students. The rubrics were then adapted across grade levels to indicate students’ learning progressions.
At Avenues World School, critical thinking is one of the Avenues World Elements and is an enduring outcome embedded in students’ early experiences through 12th grade. For instance, a kindergarten student may be expected to “identify cause and effect in familiar contexts,” while an 8th grader should demonstrate the ability to “seek out sufficient evidence before accepting a claim as true,” “identify bias in claims and evidence,” and “reconsider strongly held points of view in light of new evidence.”
When faculty and students embrace a common vision of what critical thinking looks and sounds like and how it is assessed, educators can then explicitly design learning experiences that call for students to employ critical-thinking skills. This kind of work must occur across all schools and programs, especially those serving large numbers of students of color. As Linda Darling-Hammond asserts , “Schools that serve large numbers of students of color are least likely to offer the kind of curriculum needed to ... help students attain the [critical-thinking] skills needed in a knowledge work economy. ”
So, what can it look like to create those kinds of learning experiences?
Designing experiences for critical thinking
After defining a shared understanding of “what” critical thinking is and “how” it shows up across multiple disciplines and grade levels, it is essential to create learning experiences that impel students to cultivate, practice, and apply these skills. There are several levers that offer pathways for teachers to promote critical thinking in lessons:
1.Choose Compelling Topics: Keep it relevant
A key Common Core State Standard asks for students to “write arguments to support claims in an analysis of substantive topics or texts using valid reasoning and relevant and sufficient evidence.” That might not sound exciting or culturally relevant. But a learning experience designed for a 12th grade humanities class engaged learners in a compelling topic— policing in America —to analyze and evaluate multiple texts (including primary sources) and share the reasoning for their perspectives through discussion and writing. Students grappled with ideas and their beliefs and employed deep critical-thinking skills to develop arguments for their claims. Embedding critical-thinking skills in curriculum that students care about and connect with can ignite powerful learning experiences.
2. Make Local Connections: Keep it real
At The Possible Project , an out-of-school-time program designed to promote entrepreneurial skills and mindsets, students in a recent summer online program (modified from in-person due to COVID-19) explored the impact of COVID-19 on their communities and local BIPOC-owned businesses. They learned interviewing skills through a partnership with Everyday Boston , conducted virtual interviews with entrepreneurs, evaluated information from their interviews and local data, and examined their previously held beliefs. They created blog posts and videos to reflect on their learning and consider how their mindsets had changed as a result of the experience. In this way, we can design powerful community-based learning and invite students into productive struggle with multiple perspectives.
3. Create Authentic Projects: Keep it rigorous
At Big Picture Learning schools, students engage in internship-based learning experiences as a central part of their schooling. Their school-based adviser and internship-based mentor support them in developing real-world projects that promote deeper learning and critical-thinking skills. Such authentic experiences teach “young people to be thinkers, to be curious, to get from curiosity to creation … and it helps students design a learning experience that answers their questions, [providing an] opportunity to communicate it to a larger audience—a major indicator of postsecondary success.” Even in a remote environment, we can design projects that ask more of students than rote memorization and that spark critical thinking.
Our call to action is this: As educators, we need to make opportunities for critical thinking available not only to the affluent or those fortunate enough to be placed in advanced courses. The tools are available, let’s use them. Let’s interrogate our current curriculum and design learning experiences that engage all students in real, relevant, and rigorous experiences that require critical thinking and prepare them for promising postsecondary pathways.

Critical Thinking & Student Engagement
Dr. PJ Caposey is an award-winning educator, keynote speaker, consultant, and author of seven books who currently serves as the superintendent of schools for the award-winning Meridian CUSD 223 in northwest Illinois. You can find PJ on most social-media platforms as MCUSDSupe:
When I start my keynote on student engagement, I invite two people up on stage and give them each five paper balls to shoot at a garbage can also conveniently placed on stage. Contestant One shoots their shot, and the audience gives approval. Four out of 5 is a heckuva score. Then just before Contestant Two shoots, I blindfold them and start moving the garbage can back and forth. I usually try to ensure that they can at least make one of their shots. Nobody is successful in this unfair environment.
I thank them and send them back to their seats and then explain that this little activity was akin to student engagement. While we all know we want student engagement, we are shooting at different targets. More importantly, for teachers, it is near impossible for them to hit a target that is moving and that they cannot see.
Within the world of education and particularly as educational leaders, we have failed to simplify what student engagement looks like, and it is impossible to define or articulate what student engagement looks like if we cannot clearly articulate what critical thinking is and looks like in a classroom. Because, simply, without critical thought, there is no engagement.
The good news here is that critical thought has been defined and placed into taxonomies for decades already. This is not something new and not something that needs to be redefined. I am a Bloom’s person, but there is nothing wrong with DOK or some of the other taxonomies, either. To be precise, I am a huge fan of Daggett’s Rigor and Relevance Framework. I have used that as a core element of my practice for years, and it has shaped who I am as an instructional leader.
So, in order to explain critical thought, a teacher or a leader must familiarize themselves with these tried and true taxonomies. Easy, right? Yes, sort of. The issue is not understanding what critical thought is; it is the ability to integrate it into the classrooms. In order to do so, there are a four key steps every educator must take.
- Integrating critical thought/rigor into a lesson does not happen by chance, it happens by design. Planning for critical thought and engagement is much different from planning for a traditional lesson. In order to plan for kids to think critically, you have to provide a base of knowledge and excellent prompts to allow them to explore their own thinking in order to analyze, evaluate, or synthesize information.
- SIDE NOTE – Bloom’s verbs are a great way to start when writing objectives, but true planning will take you deeper than this.
QUESTIONING
- If the questions and prompts given in a classroom have correct answers or if the teacher ends up answering their own questions, the lesson will lack critical thought and rigor.
- Script five questions forcing higher-order thought prior to every lesson. Experienced teachers may not feel they need this, but it helps to create an effective habit.
- If lessons are rigorous and assessments are not, students will do well on their assessments, and that may not be an accurate representation of the knowledge and skills they have mastered. If lessons are easy and assessments are rigorous, the exact opposite will happen. When deciding to increase critical thought, it must happen in all three phases of the game: planning, instruction, and assessment.
TALK TIME / CONTROL
- To increase rigor, the teacher must DO LESS. This feels counterintuitive but is accurate. Rigorous lessons involving tons of critical thought must allow for students to work on their own, collaborate with peers, and connect their ideas. This cannot happen in a silent room except for the teacher talking. In order to increase rigor, decrease talk time and become comfortable with less control. Asking questions and giving prompts that lead to no true correct answer also means less control. This is a tough ask for some teachers. Explained differently, if you assign one assignment and get 30 very similar products, you have most likely assigned a low-rigor recipe. If you assign one assignment and get multiple varied products, then the students have had a chance to think deeply, and you have successfully integrated critical thought into your classroom.

Thanks to Dara, Patrick, Meg, and PJ for their contributions!
Please feel free to leave a comment with your reactions to the topic or directly to anything that has been said in this post.
Consider contributing a question to be answered in a future post. You can send one to me at [email protected] . When you send it in, let me know if I can use your real name if it’s selected or if you’d prefer remaining anonymous and have a pseudonym in mind.
You can also contact me on Twitter at @Larryferlazzo .
Education Week has published a collection of posts from this blog, along with new material, in an e-book form. It’s titled Classroom Management Q&As: Expert Strategies for Teaching .
Just a reminder; you can subscribe and receive updates from this blog via email (The RSS feed for this blog, and for all Ed Week articles, has been changed by the new redesign—new ones won’t be available until February). And if you missed any of the highlights from the first nine years of this blog, you can see a categorized list below.
- This Year’s Most Popular Q&A Posts
- Race & Racism in Schools
- School Closures & the Coronavirus Crisis
- Classroom-Management Advice
- Best Ways to Begin the School Year
- Best Ways to End the School Year
- Student Motivation & Social-Emotional Learning
- Implementing the Common Core
- Facing Gender Challenges in Education
- Teaching Social Studies
- Cooperative & Collaborative Learning
- Using Tech in the Classroom
- Student Voices
- Parent Engagement in Schools
- Teaching English-Language Learners
- Reading Instruction
- Writing Instruction
- Education Policy Issues
- Differentiating Instruction
- Math Instruction
- Science Instruction
- Advice for New Teachers
- Author Interviews
- Entering the Teaching Profession
- The Inclusive Classroom
- Learning & the Brain
- Administrator Leadership
- Teacher Leadership
- Relationships in Schools
- Professional Development
- Instructional Strategies
- Best of Classroom Q&A
- Professional Collaboration
- Classroom Organization
- Mistakes in Education
- Project-Based Learning
I am also creating a Twitter list including all contributors to this column .
The opinions expressed in Classroom Q&A With Larry Ferlazzo are strictly those of the author(s) and do not reflect the opinions or endorsement of Editorial Projects in Education, or any of its publications.
Sign Up for EdWeek Update
Edweek top school jobs.

Sign Up & Sign In

The Harriet W. Sheridan Center for Teaching and Learning
Questions to provoke critical thinking.
- Teaching Resources
- Classroom Practices
- Discussions and Seminars
Varying question stems can sustain engagement and promote critical thinking. The timing, sequence and clarity of questions you ask students can be as important as the type of question you ask. The table below is organized to help formulate questions provoking gradually higher levels of thinking.
Lower Levels
Higher levels.
1 From Alison King, “Inquiring Minds Really Do Want to Know: Using Questioning to Teach Critical Thinking,” Teaching of Psychology 22 (1995): 14.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
3. Map out policy decisions. In this activity, students engage with real-world and meaningful issues that affect society through analyzing policy proposals. They’ll develop critical thinking skills and gain an understanding of political processes, enhancing their political …
This guide dispels many common perceptions about potential disadvantages associated with discussion-based pedagogy, and provides user templates for three specific discussion-based strategies: (1) deliberative discussion, (2) …
In this blog, we’ll explore how The Juice’s current events for students promote critical thinking through better classroom discussions. We’ll also provide critical thinking …
Critical thinking is the intellectually disciplined process of actively and skillfully conceptualizing, applying, analyzing, synthesizing, and/or evaluating information gathered from, or generated …
Planning for critical thinking focuses on teaching the most crucial science concepts, practices, and logical-thinking skills as well as the best use of instructional time.
Critical thinking has seven critical features: being inquisitive and curious, being open-minded to different sides, being able to think systematically, being analytical, being persistent to truth, …
Varying question stems can sustain engagement and promote critical thinking. The timing, sequence and clarity of questions you ask students can be as important as the type of question …