

5 Death Penalty Essays Everyone Should Know
Capital punishment is an ancient practice. It’s one that human rights defenders strongly oppose and consider as inhumane and cruel. In 2019, Amnesty International reported the lowest number of executions in about a decade. Most executions occurred in China, Iran, Saudi Arabia, Iraq, and Egypt . The United States is the only developed western country still using capital punishment. What does this say about the US? Here are five essays about the death penalty everyone should read:
“When We Kill”
By: Nicholas Kristof | From: The New York Times 2019
In this excellent essay, Pulitizer-winner Nicholas Kristof explains how he first became interested in the death penalty. He failed to write about a man on death row in Texas. The man, Cameron Todd Willingham, was executed in 2004. Later evidence showed that the crime he supposedly committed – lighting his house on fire and killing his three kids – was more likely an accident. In “When We Kill,” Kristof puts preconceived notions about the death penalty under the microscope. These include opinions such as only guilty people are executed, that those guilty people “deserve” to die, and the death penalty deters crime and saves money. Based on his investigations, Kristof concludes that they are all wrong.
Nicholas Kristof has been a Times columnist since 2001. He’s the winner of two Pulitizer Prices for his coverage of China and the Darfur genocide.
“An Inhumane Way of Death”
By: Willie Jasper Darden, Jr.
Willie Jasper Darden, Jr. was on death row for 14 years. In his essay, he opens with the line, “Ironically, there is probably more hope on death row than would be found in most other places.” He states that everyone is capable of murder, questioning if people who support capital punishment are just as guilty as the people they execute. Darden goes on to say that if every murderer was executed, there would be 20,000 killed per day. Instead, a person is put on death row for something like flawed wording in an appeal. Darden feels like he was picked at random, like someone who gets a terminal illness. This essay is important to read as it gives readers a deeper, more personal insight into death row.
Willie Jasper Darden, Jr. was sentenced to death in 1974 for murder. During his time on death row, he advocated for his innocence and pointed out problems with his trial, such as the jury pool that excluded black people. Despite worldwide support for Darden from public figures like the Pope, Darden was executed in 1988.
“We Need To Talk About An Injustice”
By: Bryan Stevenson | From: TED 2012
This piece is a transcript of Bryan Stevenson’s 2012 TED talk, but we feel it’s important to include because of Stevenson’s contributions to criminal justice. In the talk, Stevenson discusses the death penalty at several points. He points out that for years, we’ve been taught to ask the question, “Do people deserve to die for their crimes?” Stevenson brings up another question we should ask: “Do we deserve to kill?” He also describes the American death penalty system as defined by “error.” Somehow, society has been able to disconnect itself from this problem even as minorities are disproportionately executed in a country with a history of slavery.
Bryan Stevenson is a lawyer, founder of the Equal Justice Initiative, and author. He’s argued in courts, including the Supreme Court, on behalf of the poor, minorities, and children. A film based on his book Just Mercy was released in 2019 starring Michael B. Jordan and Jamie Foxx.
“I Know What It’s Like To Carry Out Executions”
By: S. Frank Thompson | From: The Atlantic 2019
In the death penalty debate, we often hear from the family of the victims and sometimes from those on death row. What about those responsible for facilitating an execution? In this opinion piece, a former superintendent from the Oregon State Penitentiary outlines his background. He carried out the only two executions in Oregon in the past 55 years, describing it as having a “profound and traumatic effect” on him. In his decades working as a correctional officer, he concluded that the death penalty is not working . The United States should not enact federal capital punishment.
Frank Thompson served as the superintendent of OSP from 1994-1998. Before that, he served in the military and law enforcement. When he first started at OSP, he supported the death penalty. He changed his mind when he observed the protocols firsthand and then had to conduct an execution.
“There Is No Such Thing As Closure on Death Row”
By: Paul Brown | From: The Marshall Project 2019
This essay is from Paul Brown, a death row inmate in Raleigh, North Carolina. He recalls the moment of his sentencing in a cold courtroom in August. The prosecutor used the term “closure” when justifying a death sentence. Who is this closure for? Brown theorizes that the prosecutors are getting closure as they end another case, but even then, the cases are just a way to further their careers. Is it for victims’ families? Brown is doubtful, as the death sentence is pursued even when the families don’t support it. There is no closure for Brown or his family as they wait for his execution. Vivid and deeply-personal, this essay is a must-read for anyone who wonders what it’s like inside the mind of a death row inmate.
Paul Brown has been on death row since 2000 for a double murder. He is a contributing writer to Prison Writers and shares essays on topics such as his childhood, his life as a prisoner, and more.
You may also like

16 Inspiring Civil Rights Leaders You Should Know

15 Trusted Charities Fighting for Housing Rights

15 Examples of Gender Inequality in Everyday Life

11 Approaches to Alleviate World Hunger

15 Facts About Malala Yousafzai

12 Ways Poverty Affects Society

15 Great Charities to Donate to in 2024

15 Quotes Exposing Injustice in Society

14 Trusted Charities Helping Civilians in Palestine

The Great Migration: History, Causes and Facts

Social Change 101: Meaning, Examples, Learning Opportunities

Rosa Parks: Biography, Quotes, Impact
About the author, emmaline soken-huberty.
Emmaline Soken-Huberty is a freelance writer based in Portland, Oregon. She started to become interested in human rights while attending college, eventually getting a concentration in human rights and humanitarianism. LGBTQ+ rights, women’s rights, and climate change are of special concern to her. In her spare time, she can be found reading or enjoying Oregon’s natural beauty with her husband and dog.
Essays About the Death Penalty: Top 5 Examples and Prompts
The death penalty is a major point of contention all around the world. Read our guide so you can write well-informed essays about the death penalty.
Out of all the issues at the forefront of public discourse today, few are as hotly debated as the death penalty. As its name suggests, the death penalty involves the execution of a criminal as punishment for their transgressions. The death penalty has always been, and continues to be, an emotionally and politically charged essay topic.
Arguments about the death penalty are more motivated by feelings and emotions; many proponents are people seeking punishment for the killers of their loved ones, while many opponents are mourning the loss of loved ones executed through the death penalty. There may also be a religious aspect to support and oppose the policy.
1. The Issues of Death Penalties and Social Justice in The United States (Author Unknown)
2. serving justice with death penalty by rogelio elliott, 3. can you be christian and support the death penalty by matthew schmalz, 4. death penalty: persuasive essay by jerome glover, 5. the death penalty by kamala harris, top 5 writing prompts on essays about the death penalty, 1. death penalty: do you support or oppose it, 2. how has the death penalty changed throughout history, 3. the status of capital punishment in your country, 4. death penalty and poverty, 5. does the death penalty serve as a deterrent for serious crimes, 6. what are the pros and cons of the death penalty vs. life imprisonment , 7. how is the death penalty different in japan vs. the usa, 8. why do some states use the death penalty and not others, 9. what are the most common punishments selected by prisoners for execution, 10. should the public be allowed to view an execution, 11. discuss the challenges faced by the judicial system in obtaining lethal injection doses, 12. should the death penalty be used for juveniles, 13. does the death penalty have a racial bias to it.
“Executing another person only creates a cycle of vengeance and death where if all of the rationalities and political structures are dropped, the facts presented at the end of the day is that a man is killed because he killed another man, so when does it end? Human life is to be respected and appreciated, not thrown away as if it holds no meaningful value.”
This essay discusses several reasons to oppose the death penalty in the United States. First, the author cites the Constitution and the Bill of Rights, saying that the death penalty is inhumane and deprives people of life. Human life should be respected, and death should not be responded to with another death. In addition, the author cites evidence showing that the death penalty does not deter crime nor gives closure to victims’ families.
Check out these essays about police brutality .
“Capital punishment follows the constitution and does not break any of the amendments. Specific people deserve to be punished in this way for the crime they commit. It might immoral to people but that is not the point of the death penalty. The death penalty is not “killing for fun”. The death penalty serves justice. When justice is served, it prevents other people from becoming the next serial killer. It’s simple, the death penalty strikes fear.”
Elliott supports the death penalty, writing that it gives criminals what they deserve. After all, those who commit “small” offenses will not be executed anyway. In addition, it reinforces the idea that justice comes to wrongdoers. Finally, he states that the death penalty is constitutional and is supported by many Americans.
“The letter states that this development of Catholic doctrine is consistent with the thought of the two previous popes: St. Pope John Paul II and Benedict XVI. St. John Paul II maintained that capital punishment should be reserved only for “absolute necessity.” Benedict XVI also supported efforts to eliminate the death penalty. Most important, however, is that Pope Francis is emphasizing an ethic of forgiveness. The Pope has argued that social justice applies to all citizens. He also believes that those who harm society should make amends through acts that affirm life, not death.”
Schmalz discusses the Catholic position on the death penalty. Many early Catholic leaders believed that the death penalty was justified; however, Pope Francis writes that “modern methods of imprisonment effectively protect society from criminals,” and executions are unnecessary. Therefore, the Catholic Church today opposes the death penalty and strives to protect life.
“There are many methods of execution, like electrocution, gas chamber, hanging, firing squad and lethal injection. For me, I just watched once on TV, but it’s enough to bring me nightmares. We only live once and we will lose anything we once had without life. Life is precious and can’t just be taken away that easily. In my opinion, I think Canada shouldn’t adopt the death penalty as its most severe form of criminal punishment.”
Glover’s essay acknowledges reasons why people might support the death penalty; however, he believes that these are not enough for him to support it. He believes capital punishment is inhumane and should not be implemented in Canada. It deprives people of a second chance and does not teach wrongdoers much of a lesson. In addition, it is inhumane and deprives people of their right to life.
“Let’s be clear: as a former prosecutor, I absolutely and strongly believe there should be serious and swift consequences when one person kills another. I am unequivocal in that belief. We can — and we should — always pursue justice in the name of victims and give dignity to the families that grieve. But in our democracy, a death sentence carried out by the government does not constitute justice for those who have been put to death and proven innocent after the fact.”
This short essay was written by the then-presidential candidate and current U.S. Vice President Kamala Harris to explain her campaign’s stance on the death penalty. First, she believes it does not execute justice and is likely to commit injustice by sentencing innocent people to death. In addition, it is said to disproportionally affect nonwhite people. Finally, it is more fiscally responsible for abolishing capital punishment, as it uses funds that could be used for education and healthcare.

This topic always comes first to mind when thinking of what to write. For a strong argumentative essay, consider the death penalty and list its pros and cons. Then, conclude whether or not it would be beneficial to reinstate or keep the policy. There is an abundance of sources you can gather inspiration from, including the essay examples listed above and countless other online sources.
People have been put to death as a punishment since the dawn of recorded history, but as morals and technology have changed, the application of the death penalty has evolved. This essay will explore how the death penalty has been used and carried out throughout history.
This essay will examine both execution methods and when capital punishment is ordered. A few points to explore in this essay include:
- Thousands of years ago, “an eye for an eye” was the standard. How were executions carried out in ancient history?
- The religious context of executions during the middle ages is worth exploring. When was someone burned at the stake?
- The guillotine became a popular method of execution during the renaissance period. How does this method compare to both ancient execution methods and modern methods?
- The most common execution methods in the modern era include the firing squad, hanging, lethal injections, gas chambers, and electrocution. How do these methods compare to older forms of execution?
Choose a country, preferably your home country, and look into the death penalty status: is it being implemented or not? If you wish, you can also give a brief history of the death penalty in your chosen country and your thoughts. You do not necessarily need to write about your own country; however, picking your homeland may provide better insight.
Critics of the death penalty argue that it is anti-poor, as a poor person accused of a crime punishable by death lacks the resources to hire a good lawyer to defend them adequately. For your essay, reflect on this issue and write about your thoughts. Is it inhumane for the poor? After all, poor people will not have sufficient resources to hire good lawyers, regardless of the punishment.
This is one of the biggest debates in the justice system. While the justice system has been set up to punish, it should also deter people from committing crimes. Does the death penalty do an adequate job at deterring crimes?
This essay should lay out the evidence that shows how the death penalty either does or does not deter crime. A few points to explore in this essay include:
- Which crimes have the death penalty as the ultimate punishment?
- How does the murder rate compare to states that do not have the death penalty in states with the death penalty?
- Are there confounding factors that must be taken into consideration with this comparison? How do they play a role?

This is one of the most straightforward ways to explore the death penalty. If the death penalty is to be removed from criminal cases, it must be replaced with something else. The most logical alternative is life imprisonment.
There is no “right” answer to this question, but a strong argumentative essay could take one side over another in this death penalty debate. A few points to explore in this essay include:
- Some people would rather be put to death instead of imprisoned in a cell for life. Should people have the right to decide which punishment they accept?
- What is the cost of the death penalty versus imprisoning someone for life? Even though it can be expensive to imprison someone for life, remember that most death penalty cases are appealed numerous times before execution.
- Would the death penalty be more acceptable if specific execution methods were used instead of others?
Few first-world countries still use the death penalty. However, Japan and the United States are two of the biggest users of the death sentence.
This is an interesting compare and contrast essay worth exploring. In addition, this essay can explore the differences in how executions are carried out. Some of the points to explore include:
- What are the execution methods countries use? The execution method in the United States can vary from state to state, but Japan typically uses hanging. Is this considered a cruel and unusual punishment?
- In the United States, death row inmates know their execution date. In Japan, they do not. So which is better for the prisoner?
- How does the public in the United States feel about the death penalty versus public opinion in Japan? Should this influence when, how, and if executions are carried out in the respective countries?
In the United States, justice is typically administered at the state level unless a federal crime has been committed. So why do some states have the death penalty and not others?
This essay will examine which states have the death penalty and make the most use of this form of punishment as part of the legal system. A few points worth exploring in this essay include:
- When did various states outlaw the death penalty (if they do not use it today)?
- Which states execute the most prisoners? Some states to mention are Texas and Oklahoma.
- Do the states that have the death penalty differ in when the death penalty is administered?
- Is this sentence handed down by the court system or by the juries trying the individual cases in states with the death penalty?
It might be interesting to see if certain prisoners have selected a specific execution method to make a political statement. Numerous states allow prisoners to select how they will be executed. The most common methods include lethal injections, firing squads, electric chairs, gas chambers, and hanging.
It might be interesting to see if certain prisoners have selected a specific execution method to make a political statement. Some of the points this essay might explore include:
- When did these different execution methods become options for execution?
- Which execution methods are the most common in the various states that offer them?
- Is one method considered more “humane” than others? If so, why?
One of the topics recently discussed is whether the public should be allowed to view an execution.
There are many potential directions to go with this essay, and all of these points are worth exploring. A few topics to explore in this essay include:
- In the past, executions were carried out in public places. There are a few countries, particularly in the Middle East, where this is still the case. So why were executions carried out in public?
- In some situations, individuals directly involved in the case, such as the victim’s loved ones, are permitted to view the execution. Does this bring a sense of closure?
- Should executions be carried out in private? Does this reduce transparency in the justice system?
Lethal injection is one of the most common modes of execution. The goal is to put the person to sleep and remove their pain. Then, a cocktail is used to stop their heart. Unfortunately, many companies have refused to provide states with the drugs needed for a lethal injection. A few points to explore include:
- Doctors and pharmacists have said it is against the oath they took to “not harm.” Is this true? What impact does this have?
- If someone is giving the injection without medical training, how does this impact the prisoner?
- Have states decided to use other more “harmful” modes of execution because they can’t get what they need for the lethal injection?
There are certain crimes, such as murder, where the death penalty is a possible punishment across the country. Even though minors can be tried as adults in some situations, they typically cannot be given the death penalty.
It might be interesting to see what legal experts and victims of juvenile capital crimes say about this important topic. A few points to explore include:
- How does the brain change and evolve as someone grows?
- Do juveniles have a higher rate of rehabilitation than adults?
- Should the wishes of the victim’s family play a role in the final decision?
The justice system, and its unjust impact on minorities , have been a major area of research during the past few decades. It might be worth exploring if the death penalty is disproportionately used in cases involving minorities.
It might be worth looking at numbers from Amnesty International or the Innocence Project to see what the numbers show. A strong essay might also propose ways to make justice system cases more equitable and fair. A few points worth exploring include:
- Of the cases where the death penalty has been levied, what percentage of the cases involve a minority perpetrator?
- Do stays of execution get granted more often in cases involving white people versus minorities?
- Do white people get handed a sentence of life in prison without parole more often than people of minority descent?
If you’d like to learn more, our writer explains how to write an argumentative essay in this guide.
For help with your essay, check our round-up of best essay writing apps .

Martin is an avid writer specializing in editing and proofreading. He also enjoys literary analysis and writing about food and travel.
View all posts

Arguments for and Against the Death Penalty
Click the buttons below to view arguments and testimony on each topic.
The death penalty deters future murders.
Society has always used punishment to discourage would-be criminals from unlawful action. Since society has the highest interest in preventing murder, it should use the strongest punishment available to deter murder, and that is the death penalty. If murderers are sentenced to death and executed, potential murderers will think twice before killing for fear of losing their own life.
For years, criminologists analyzed murder rates to see if they fluctuated with the likelihood of convicted murderers being executed, but the results were inconclusive. Then in 1973 Isaac Ehrlich employed a new kind of analysis which produced results showing that for every inmate who was executed, 7 lives were spared because others were deterred from committing murder. Similar results have been produced by disciples of Ehrlich in follow-up studies.
Moreover, even if some studies regarding deterrence are inconclusive, that is only because the death penalty is rarely used and takes years before an execution is actually carried out. Punishments which are swift and sure are the best deterrent. The fact that some states or countries which do not use the death penalty have lower murder rates than jurisdictions which do is not evidence of the failure of deterrence. States with high murder rates would have even higher rates if they did not use the death penalty.
Ernest van den Haag, a Professor of Jurisprudence at Fordham University who has studied the question of deterrence closely, wrote: “Even though statistical demonstrations are not conclusive, and perhaps cannot be, capital punishment is likely to deter more than other punishments because people fear death more than anything else. They fear most death deliberately inflicted by law and scheduled by the courts. Whatever people fear most is likely to deter most. Hence, the threat of the death penalty may deter some murderers who otherwise might not have been deterred. And surely the death penalty is the only penalty that could deter prisoners already serving a life sentence and tempted to kill a guard, or offenders about to be arrested and facing a life sentence. Perhaps they will not be deterred. But they would certainly not be deterred by anything else. We owe all the protection we can give to law enforcers exposed to special risks.”
Finally, the death penalty certainly “deters” the murderer who is executed. Strictly speaking, this is a form of incapacitation, similar to the way a robber put in prison is prevented from robbing on the streets. Vicious murderers must be killed to prevent them from murdering again, either in prison, or in society if they should get out. Both as a deterrent and as a form of permanent incapacitation, the death penalty helps to prevent future crime.
Those who believe that deterrence justifies the execution of certain offenders bear the burden of proving that the death penalty is a deterrent. The overwhelming conclusion from years of deterrence studies is that the death penalty is, at best, no more of a deterrent than a sentence of life in prison. The Ehrlich studies have been widely discredited. In fact, some criminologists, such as William Bowers of Northeastern University, maintain that the death penalty has the opposite effect: that is, society is brutalized by the use of the death penalty, and this increases the likelihood of more murder. Even most supporters of the death penalty now place little or no weight on deterrence as a serious justification for its continued use.
States in the United States that do not employ the death penalty generally have lower murder rates than states that do. The same is true when the U.S. is compared to countries similar to it. The U.S., with the death penalty, has a higher murder rate than the countries of Europe or Canada, which do not use the death penalty.
The death penalty is not a deterrent because most people who commit murders either do not expect to be caught or do not carefully weigh the differences between a possible execution and life in prison before they act. Frequently, murders are committed in moments of passion or anger, or by criminals who are substance abusers and acted impulsively. As someone who presided over many of Texas’s executions, former Texas Attorney General Jim Mattox has remarked, “It is my own experience that those executed in Texas were not deterred by the existence of the death penalty law. I think in most cases you’ll find that the murder was committed under severe drug and alcohol abuse.”
There is no conclusive proof that the death penalty acts as a better deterrent than the threat of life imprisonment. A 2012 report released by the prestigious National Research Council of the National Academies and based on a review of more than three decades of research, concluded that studies claiming a deterrent effect on murder rates from the death penalty are fundamentally flawed. A survey of the former and present presidents of the country’s top academic criminological societies found that 84% of these experts rejected the notion that research had demonstrated any deterrent effect from the death penalty .
Once in prison, those serving life sentences often settle into a routine and are less of a threat to commit violence than other prisoners. Moreover, most states now have a sentence of life without parole. Prisoners who are given this sentence will never be released. Thus, the safety of society can be assured without using the death penalty.
Ernest van den Haag Professor of Jurisprudence and Public Policy, Fordham University. Excerpts from ” The Ultimate Punishment: A Defense,” (Harvard Law Review Association, 1986)
“Execution of those who have committed heinous murders may deter only one murder per year. If it does, it seems quite warranted. It is also the only fitting retribution for murder I can think of.”
“Most abolitionists acknowledge that they would continue to favor abolition even if the death penalty were shown to deter more murders than alternatives could deter. Abolitionists appear to value the life of a convicted murderer or, at least, his non-execution, more highly than they value the lives of the innocent victims who might be spared by deterring prospective murderers.
Deterrence is not altogether decisive for me either. I would favor retention of the death penalty as retribution even if it were shown that the threat of execution could not deter prospective murderers not already deterred by the threat of imprisonment. Still, I believe the death penalty, because of its finality, is more feared than imprisonment, and deters some prospective murderers not deterred by the thought of imprisonment. Sparing the lives of even a few prospective victims by deterring their murderers is more important than preserving the lives of convicted murderers because of the possibility, or even the probability, that executing them would not deter others. Whereas the life of the victims who might be saved are valuable, that of the murderer has only negative value, because of his crime. Surely the criminal law is meant to protect the lives of potential victims in preference to those of actual murderers.”
“We threaten punishments in order to deter crime. We impose them not only to make the threats credible but also as retribution (justice) for the crimes that were not deterred. Threats and punishments are necessary to deter and deterrence is a sufficient practical justification for them. Retribution is an independent moral justification. Although penalties can be unwise, repulsive, or inappropriate, and those punished can be pitiable, in a sense the infliction of legal punishment on a guilty person cannot be unjust. By committing the crime, the criminal volunteered to assume the risk of receiving a legal punishment that he could have avoided by not committing the crime. The punishment he suffers is the punishment he voluntarily risked suffering and, therefore, it is no more unjust to him than any other event for which one knowingly volunteers to assume the risk. Thus, the death penalty cannot be unjust to the guilty criminal.”
Full text can be found at PBS.org .
Hugo Adam Bedau (deceased) Austin Fletcher Professor of Philosophy, Tufts University Excerpts from “The Case Against The Death Penalty” (Copyright 1997, American Civil Liberties Union)
“Persons who commit murder and other crimes of personal violence either may or may not premeditate their crimes.
When crime is planned, the criminal ordinarily concentrates on escaping detection, arrest, and conviction. The threat of even the severest punishment will not discourage those who expect to escape detection and arrest. It is impossible to imagine how the threat of any punishment could prevent a crime that is not premeditated….
Most capital crimes are committed in the heat of the moment. Most capital crimes are committed during moments of great emotional stress or under the influence of drugs or alcohol, when logical thinking has been suspended. In such cases, violence is inflicted by persons heedless of the consequences to themselves as well as to others….
If, however, severe punishment can deter crime, then long-term imprisonment is severe enough to deter any rational person from committing a violent crime.
The vast preponderance of the evidence shows that the death penalty is no more effective than imprisonment in deterring murder and that it may even be an incitement to criminal violence. Death-penalty states as a group do not have lower rates of criminal homicide than non-death-penalty states….
On-duty police officers do not suffer a higher rate of criminal assault and homicide in abolitionist states than they do in death-penalty states. Between l973 and l984, for example, lethal assaults against police were not significantly more, or less, frequent in abolitionist states than in death-penalty states. There is ‘no support for the view that the death penalty provides a more effective deterrent to police homicides than alternative sanctions. Not for a single year was evidence found that police are safer in jurisdictions that provide for capital punishment.’ (Bailey and Peterson, Criminology (1987))
Prisoners and prison personnel do not suffer a higher rate of criminal assault and homicide from life-term prisoners in abolition states than they do in death-penalty states. Between 1992 and 1995, 176 inmates were murdered by other prisoners; the vast majority (84%) were killed in death penalty jurisdictions. During the same period about 2% of all assaults on prison staff were committed by inmates in abolition jurisdictions. Evidently, the threat of the death penalty ‘does not even exert an incremental deterrent effect over the threat of a lesser punishment in the abolitionist states.’ (Wolfson, in Bedau, ed., The Death Penalty in America, 3rd ed. (1982))
Actual experience thus establishes beyond a reasonable doubt that the death penalty does not deter murder. No comparable body of evidence contradicts that conclusion.”
Click here for the full text from the ACLU website.
Retribution
A just society requires the taking of a life for a life.
When someone takes a life, the balance of justice is disturbed. Unless that balance is restored, society succumbs to a rule of violence. Only the taking of the murderer’s life restores the balance and allows society to show convincingly that murder is an intolerable crime which will be punished in kind.
Retribution has its basis in religious values, which have historically maintained that it is proper to take an “eye for an eye” and a life for a life.
Although the victim and the victim’s family cannot be restored to the status which preceded the murder, at least an execution brings closure to the murderer’s crime (and closure to the ordeal for the victim’s family) and ensures that the murderer will create no more victims.
For the most cruel and heinous crimes, the ones for which the death penalty is applied, offenders deserve the worst punishment under our system of law, and that is the death penalty. Any lesser punishment would undermine the value society places on protecting lives.
Robert Macy, District Attorney of Oklahoma City, described his concept of the need for retribution in one case: “In 1991, a young mother was rendered helpless and made to watch as her baby was executed. The mother was then mutilated and killed. The killer should not lie in some prison with three meals a day, clean sheets, cable TV, family visits and endless appeals. For justice to prevail, some killers just need to die.”
Retribution is another word for revenge. Although our first instinct may be to inflict immediate pain on someone who wrongs us, the standards of a mature society demand a more measured response.
The emotional impulse for revenge is not a sufficient justification for invoking a system of capital punishment, with all its accompanying problems and risks. Our laws and criminal justice system should lead us to higher principles that demonstrate a complete respect for life, even the life of a murderer. Encouraging our basest motives of revenge, which ends in another killing, extends the chain of violence. Allowing executions sanctions killing as a form of ‘pay-back.’
Many victims’ families denounce the use of the death penalty. Using an execution to try to right the wrong of their loss is an affront to them and only causes more pain. For example, Bud Welch’s daughter, Julie, was killed in the Oklahoma City bombing in 1995. Although his first reaction was to wish that those who committed this terrible crime be killed, he ultimately realized that such killing “is simply vengeance; and it was vengeance that killed Julie…. Vengeance is a strong and natural emotion. But it has no place in our justice system.”
The notion of an eye for an eye, or a life for a life, is a simplistic one which our society has never endorsed. We do not allow torturing the torturer, or raping the rapist. Taking the life of a murderer is a similarly disproportionate punishment, especially in light of the fact that the U.S. executes only a small percentage of those convicted of murder, and these defendants are typically not the worst offenders but merely the ones with the fewest resources to defend themselves.
Louis P. Pojman Author and Professor of Philosophy, U.S. Military Academy. Excerpt from “The Death Penalty: For and Against,” (Rowman & Littlefield Publishers, Inc., 1998)
“[Opponents of the capital punishment often put forth the following argument:] Perhaps the murderer deserves to die, but what authority does the state have to execute him or her? Both the Old and New Testament says, “’Vengeance is mine, I will repay,’ says the Lord” (Prov. 25:21 and Romans 12:19). You need special authority to justify taking the life of a human being.
The objector fails to note that the New Testament passage continues with a support of the right of the state to execute criminals in the name of God: “Let every person be subjected to the governing authorities. For there is no authority except from God, and those that exist have been instituted by God. Therefore he who resists what God has appointed, and those who resist will incur judgment…. If you do wrong, be afraid, for [the authority] does not bear the sword in vain; he is the servant of God to execute his wrath on the wrongdoer” (Romans 13: 1-4). So, according to the Bible, the authority to punish, which presumably includes the death penalty, comes from God.
But we need not appeal to a religious justification for capital punishment. We can site the state’s role in dispensing justice. Just as the state has the authority (and duty) to act justly in allocating scarce resources, in meeting minimal needs of its (deserving) citizens, in defending its citizens from violence and crime, and in not waging unjust wars; so too does it have the authority, flowing from its mission to promote justice and the good of its people, to punish the criminal. If the criminal, as one who has forfeited a right to life, deserves to be executed, especially if it will likely deter would-be murderers, the state has a duty to execute those convicted of first-degree murder.”
National Council of Synagogues and the Bishops’ Committee for Ecumenical and Interreligious Affairs of the National Conference of Catholic Bishops Excerpts from “To End the Death Penalty: A Report of the National Jewish/Catholic Consultation” (December, 1999)
“Some would argue that the death penalty is needed as a means of retributive justice, to balance out the crime with the punishment. This reflects a natural concern of society, and especially of victims and their families. Yet we believe that we are called to seek a higher road even while punishing the guilty, for example through long and in some cases life-long incarceration, so that the healing of all can ultimately take place.
Some would argue that the death penalty will teach society at large the seriousness of crime. Yet we say that teaching people to respond to violence with violence will, again, only breed more violence.
The strongest argument of all [in favor of the death penalty] is the deep pain and grief of the families of victims, and their quite natural desire to see punishment meted out to those who have plunged them into such agony. Yet it is the clear teaching of our traditions that this pain and suffering cannot be healed simply through the retribution of capital punishment or by vengeance. It is a difficult and long process of healing which comes about through personal growth and God’s grace. We agree that much more must be done by the religious community and by society at large to solace and care for the grieving families of the victims of violent crime.
Recent statements of the Reform and Conservative movements in Judaism, and of the U.S. Catholic Conference sum up well the increasingly strong convictions shared by Jews and Catholics…:
‘Respect for all human life and opposition to the violence in our society are at the root of our long-standing opposition (as bishops) to the death penalty. We see the death penalty as perpetuating a cycle of violence and promoting a sense of vengeance in our culture. As we said in Confronting the Culture of Violence: ‘We cannot teach that killing is wrong by killing.’ We oppose capital punishment not just for what it does to those guilty of horrible crimes, but for what it does to all of us as a society. Increasing reliance on the death penalty diminishes all of us and is a sign of growing disrespect for human life. We cannot overcome crime by simply executing criminals, nor can we restore the lives of the innocent by ending the lives of those convicted of their murders. The death penalty offers the tragic illusion that we can defend life by taking life.’1
We affirm that we came to these conclusions because of our shared understanding of the sanctity of human life. We have committed ourselves to work together, and each within our own communities, toward ending the death penalty.” Endnote 1. Statement of the Administrative Committee of the United States Catholic Conference, March 24, 1999.
The risk of executing the innocent precludes the use of the death penalty.
The death penalty alone imposes an irrevocable sentence. Once an inmate is executed, nothing can be done to make amends if a mistake has been made. There is considerable evidence that many mistakes have been made in sentencing people to death. Since 1973, over 180 people have been released from death row after evidence of their innocence emerged. During the same period of time, over 1,500 people have been executed. Thus, for every 8.3 people executed, we have found one person on death row who never should have been convicted. These statistics represent an intolerable risk of executing the innocent. If an automobile manufacturer operated with similar failure rates, it would be run out of business.
Our capital punishment system is unreliable. A study by Columbia University Law School found that two thirds of all capital trials contained serious errors. When the cases were retried, over 80% of the defendants were not sentenced to death and 7% were completely acquitted.
Many of the releases of innocent defendants from death row came about as a result of factors outside of the justice system. Recently, journalism students in Illinois were assigned to investigate the case of a man who was scheduled to be executed, after the system of appeals had rejected his legal claims. The students discovered that one witness had lied at the original trial, and they were able to find another man, who confessed to the crime on videotape and was later convicted of the murder. The innocent man who was released was very fortunate, but he was spared because of the informal efforts of concerned citizens, not because of the justice system.
In other cases, DNA testing has exonerated death row inmates. Here, too, the justice system had concluded that these defendants were guilty and deserving of the death penalty. DNA testing became available only in the early 1990s, due to advancements in science. If this testing had not been discovered until ten years later, many of these inmates would have been executed. And if DNA testing had been applied to earlier cases where inmates were executed in the 1970s and 80s, the odds are high that it would have proven that some of them were innocent as well.
Society takes many risks in which innocent lives can be lost. We build bridges, knowing that statistically some workers will be killed during construction; we take great precautions to reduce the number of unintended fatalities. But wrongful executions are a preventable risk. By substituting a sentence of life without parole, we meet society’s needs of punishment and protection without running the risk of an erroneous and irrevocable punishment.
There is no proof that any innocent person has actually been executed since increased safeguards and appeals were added to our death penalty system in the 1970s. Even if such executions have occurred, they are very rare. Imprisoning innocent people is also wrong, but we cannot empty the prisons because of that minimal risk. If improvements are needed in the system of representation, or in the use of scientific evidence such as DNA testing, then those reforms should be instituted. However, the need for reform is not a reason to abolish the death penalty.
Besides, many of the claims of innocence by those who have been released from death row are actually based on legal technicalities. Just because someone’s conviction is overturned years later and the prosecutor decides not to retry him, does not mean he is actually innocent.
If it can be shown that someone is innocent, surely a governor would grant clemency and spare the person. Hypothetical claims of innocence are usually just delaying tactics to put off the execution as long as possible. Given our thorough system of appeals through numerous state and federal courts, the execution of an innocent individual today is almost impossible. Even the theoretical execution of an innocent person can be justified because the death penalty saves lives by deterring other killings.
Gerald Kogan, Former Florida Supreme Court Chief Justice Excerpts from a speech given in Orlando, Florida, October 23, 1999 “[T]here is no question in my mind, and I can tell you this having seen the dynamics of our criminal justice system over the many years that I have been associated with it, [as] prosecutor, defense attorney, trial judge and Supreme Court Justice, that convinces me that we certainly have, in the past, executed those people who either didn’t fit the criteria for execution in the State of Florida or who, in fact, were, factually, not guilty of the crime for which they have been executed.
“And you can make these statements when you understand the dynamics of the criminal justice system, when you understand how the State makes deals with more culpable defendants in a capital case, offers them light sentences in exchange for their testimony against another participant or, in some cases, in fact, gives them immunity from prosecution so that they can secure their testimony; the use of jailhouse confessions, like people who say, ‘I was in the cell with so-and-so and they confessed to me,’ or using those particular confessions, the validity of which there has been great doubt. And yet, you see the uneven application of the death penalty where, in many instances, those that are the most culpable escape death and those that are the least culpable are victims of the death penalty. These things begin to weigh very heavily upon you. And under our system, this is the system we have. And that is, we are human beings administering an imperfect system.”
“And how about those people who are still sitting on death row today, who may be factually innocent but cannot prove their particular case very simply because there is no DNA evidence in their case that can be used to exonerate them? Of course, in most cases, you’re not going to have that kind of DNA evidence, so there is no way and there is no hope for them to be saved from what may be one of the biggest mistakes that our society can make.”
The entire speech by Justice Kogan is available here.
Paul G. Cassell Associate Professor of Law, University of Utah, College of Law, and former law clerk to Chief Justice Warren E. Burger. Statement before the Committee on the Judiciary, United States House of Representatives, Subcommittee on Civil and Constitutional Rights Concerning Claims of Innocence in Capital Cases (July 23, 1993)
“Given the fallibility of human judgments, the possibility exists that the use of capital punishment may result in the execution of an innocent person. The Senate Judiciary Committee has previously found this risk to be ‘minimal,’ a view shared by numerous scholars. As Justice Powell has noted commenting on the numerous state capital cases that have come before the Supreme Court, the ‘unprecedented safeguards’ already inherent in capital sentencing statutes ‘ensure a degree of care in the imposition of the sentence of death that can only be described as unique.’”
“Our present system of capital punishment limits the ultimate penalty to certain specifically-defined crimes and even then, permit the penalty of death only when the jury finds that the aggravating circumstances in the case outweigh all mitigating circumstances. The system further provides judicial review of capital cases. Finally, before capital sentences are carried out, the governor or other executive official will review the sentence to insure that it is a just one, a determination that undoubtedly considers the evidence of the condemned defendant’s guilt. Once all of those decisionmakers have agreed that a death sentence is appropriate, innocent lives would be lost from failure to impose the sentence.”
“Capital sentences, when carried out, save innocent lives by permanently incapacitating murderers. Some persons who commit capital homicide will slay other innocent persons if given the opportunity to do so. The death penalty is the most effective means of preventing such killers from repeating their crimes. The next most serious penalty, life imprisonment without possibility of parole, prevents murderers from committing some crimes but does not prevent them from murdering in prison.”
“The mistaken release of guilty murderers should be of far greater concern than the speculative and heretofore nonexistent risk of the mistaken execution of an innocent person.”
Full text can be found here.
Arbitrariness & Discrimination
The death penalty is applied unfairly and should not be used.
In practice, the death penalty does not single out the worst offenders. Rather, it selects an arbitrary group based on such irrational factors as the quality of the defense counsel, the county in which the crime was committed, or the race of the defendant or victim.
Almost all defendants facing the death penalty cannot afford their own attorney. Hence, they are dependent on the quality of the lawyers assigned by the state, many of whom lack experience in capital cases or are so underpaid that they fail to investigate the case properly. A poorly represented defendant is much more likely to be convicted and given a death sentence.
With respect to race, studies have repeatedly shown that a death sentence is far more likely where a white person is murdered than where a Black person is murdered. The death penalty is racially divisive because it appears to count white lives as more valuable than Black lives. Since the death penalty was reinstated in 1976, 296 Black defendants have been executed for the murder of a white victim, while only 31 white defendants have been executed for the murder of a Black victim. Such racial disparities have existed over the history of the death penalty and appear to be largely intractable.
It is arbitrary when someone in one county or state receives the death penalty, but someone who commits a comparable crime in another county or state is given a life sentence. Prosecutors have enormous discretion about when to seek the death penalty and when to settle for a plea bargain. Often those who can only afford a minimal defense are selected for the death penalty. Until race and other arbitrary factors, like economics and geography, can be eliminated as a determinant of who lives and who dies, the death penalty must not be used.
Discretion has always been an essential part of our system of justice. No one expects the prosecutor to pursue every possible offense or punishment, nor do we expect the same sentence to be imposed just because two crimes appear similar. Each crime is unique, both because the circumstances of each victim are different and because each defendant is different. The U.S. Supreme Court has held that a mandatory death penalty which applied to everyone convicted of first degree murder would be unconstitutional. Hence, we must give prosecutors and juries some discretion.
In fact, more white people are executed in this country than black people. And even if blacks are disproportionately represented on death row, proportionately blacks commit more murders than whites. Moreover, the Supreme Court has rejected the use of statistical studies which claim racial bias as the sole reason for overturning a death sentence.
Even if the death penalty punishes some while sparing others, it does not follow that everyone should be spared. The guilty should still be punished appropriately, even if some do escape proper punishment unfairly. The death penalty should apply to killers of black people as well as to killers of whites. High paid, skillful lawyers should not be able to get some defendants off on technicalities. The existence of some systemic problems is no reason to abandon the whole death penalty system.
Reverend Jesse L. Jackson, Sr. President and Chief Executive Officer, Rainbow/PUSH Coalition, Inc. Excerpt from “Legal Lynching: Racism, Injustice & the Death Penalty,” (Marlowe & Company, 1996)
“Who receives the death penalty has less to do with the violence of the crime than with the color of the criminal’s skin, or more often, the color of the victim’s skin. Murder — always tragic — seems to be a more heinous and despicable crime in some states than in others. Women who kill and who are killed are judged by different standards than are men who are murderers and victims.
The death penalty is essentially an arbitrary punishment. There are no objective rules or guidelines for when a prosecutor should seek the death penalty, when a jury should recommend it, and when a judge should give it. This lack of objective, measurable standards ensures that the application of the death penalty will be discriminatory against racial, gender, and ethnic groups.
The majority of Americans who support the death penalty believe, or wish to believe, that legitimate factors such as the violence and cruelty with which the crime was committed, a defendant’s culpability or history of violence, and the number of victims involved determine who is sentenced to life in prison and who receives the ultimate punishment. The numbers, however, tell a different story. They confirm the terrible truth that bias and discrimination warp our nation’s judicial system at the very time it matters most — in matters of life and death. The factors that determine who will live and who will die — race, sex, and geography — are the very same ones that blind justice was meant to ignore. This prejudicial distribution should be a moral outrage to every American.”
Justice Lewis Powell United States Supreme Court Justice excerpts from McCleskey v. Kemp, 481 U.S. 279 (1987) (footnotes and citations omitted)
(Mr. McCleskey, a black man, was convicted and sentenced to death in 1978 for killing a white police officer while robbing a store. Mr. McCleskey appealed his conviction and death sentence, claiming racial discrimination in the application of Georgia’s death penalty. He presented statistical analysis showing a pattern of sentencing disparities based primarily on the race of the victim. The analysis indicated that black defendants who killed white victims had the greatest likelihood of receiving the death penalty. Writing the majority opinion for the Supreme Court, Justice Powell held that statistical studies on race by themselves were an insufficient basis for overturning the death penalty.)
“[T]he claim that [t]his sentence rests on the irrelevant factor of race easily could be extended to apply to claims based on unexplained discrepancies that correlate to membership in other minority groups, and even to gender. Similarly, since [this] claim relates to the race of his victim, other claims could apply with equally logical force to statistical disparities that correlate with the race or sex of other actors in the criminal justice system, such as defense attorneys or judges. Also, there is no logical reason that such a claim need be limited to racial or sexual bias. If arbitrary and capricious punishment is the touchstone under the Eighth Amendment, such a claim could — at least in theory — be based upon any arbitrary variable, such as the defendant’s facial characteristics, or the physical attractiveness of the defendant or the victim, that some statistical study indicates may be influential in jury decision making. As these examples illustrate, there is no limiting principle to the type of challenge brought by McCleskey. The Constitution does not require that a State eliminate any demonstrable disparity that correlates with a potentially irrelevant factor in order to operate a criminal justice system that includes capital punishment. As we have stated specifically in the context of capital punishment, the Constitution does not ‘plac[e] totally unrealistic conditions on its use.’ (Gregg v. Georgia)”
The entire decision can be found here.
Capital Punishment and the Death Penalty Essay
Criminal law and procedure, historical development of criminal law, difference between legal and social parameters in criminal law, elements of a crime.
In most nations, there are two or three sorts of courts that have authority over criminal cases. A single expert judge typically handles petty offenses, but two or more lay justices in England may sit in a Magistrates’ Court. In many nations, more severe cases are heard by panels of two or more judges (Lee, 2022). Such panels are frequently made up of attorneys and lay magistrates, as in Germany, where two laypeople sit alongside one to three jurists. The French cour d’assises comprises three professional judges and nine lay assessors who hear severe criminal cases. Such mixed courts of professionals and ordinary residents convene and make decisions by majority voting, with lawyers and laypeople having one vote.
The United States Constitution permits every defendant in a non-petty matter the right to be prosecuted before a jury; the defendant may forgo this privilege and have the decision decided by a professional court judge. To guarantee the court’s fairness, the defense and prosecution can dismiss or challenge members whom they prove to be prejudiced (Lee, 2022). Furthermore, the defense and, in the United States, the prosecution has the right of vexatious challenge, which allows it to confront several participants without providing a reason.
One of the most primitive texts illustrating European illegitimate law appeared after 1066, when William the Conqueror, Duke of Normandy, conquered England. By the eighteenth century, European law addressed criminal behavior specifically, and the idea of trying lawbreakers in a courtroom context began to transpire (Zalewski, 2019). The English administration recognized a scheme referred to as common law, which is the method through which regulations that regulate a group of people are established and updated. Corporate law relates to public and illegal cases and is grounded on the establishment, adjustment, and expansion of laws by adjudicators as they make permissible judgments. These decisions become standards, prompting the consequences of impending cases.
Misdemeanors, offences, and sedition are the three types of unlawful offenses presented before the courts. Misdemeanors are petty infringements decided by penalties or confiscation of property; some are penalized by less than a year in prison. Offences are meaningfully more heinous felonies with heavier consequences, such as incarceration in a federal or state prison for a year or more. Treason is characterized as anything that breaches the country’s allegiance. Felonious law changes and is often susceptible to modification based on the ethics and standards of the period.
Parameters are values with changing attributes, principles, or dimensions that may be defined and monitored. A parameter is usually picked from a data set because it is critical to understanding the situation. A parameter aids in comprehending a situation, whereas a parameter defines the situation’s bounds (Doorn et al., 2018). The critical concept of the Legal parameter is that behaviors are restricted by unspoken criteria of deviance that are agreeable to both the controlled and those that govern them. Impartiality, fairness, and morality are all ideals conveyed by social justice, and they all have their origins in the overarching concept of law (Doorn et al., 2018). From a social standpoint, it involves various topics such as abortion, cremation, bio-genetics, human decency, racial justice, worker’s rights, economic freedom, and environmental concerns.
All crimes in the United States may be subdivided into distinct aspects under criminal law. These components of an offense must then be established beyond possible suspicion in a court of law to convict the offender (Ormerod & Laird, 2021). Many delinquencies need the manifestation of three crucial rudiments: a criminal act, criminal intent, and the concurrence of the initial two. Depending on the offense, a fourth factor called causality may be present.
First is the criminal act (Actus Reus): actus reus, which translates as “guilty act,” refers to any criminal act of an act that occurs. To be considered an unlawful act, an act must be intentional and controlled by the defendant (Ormerod & Laird, 2021). If an accused act on nature, they may not be held responsible for their conduct. Words can be deemed illegal activities and result in accusations such as perjury, verbal harassment, conspiracy, or incitement. On the contrary, concepts are not considered illegal acts but might add to the second component: intent.
Second is crime intent (Mens Rea): for a felonious offense to be categorized as a misconduct, the culprit’s mental circumstance must be reflected. According to the code of mens rea, a suspect can only be considered remorseful if there is felonious intent (Ormerod & Laird, 2021). Third is concurrence, which refers to the coexistence of intent to commit a crime and illicit behavior. If there is proof that the mens rea preceded or happened simultaneously with the actus reus, the burden of proving it is met. Fourth is causation: this fourth ingredient of an offense is present in most criminal cases, but not all. The link concerning the defendant’s act and the final consequence is called causation. The trial must establish outside a possible suspicion that the perpetrator’s acts triggered the resultant criminality, which is usually detriment or damage.
The risk of executing an innocent man cannot be entirely removed despite precautions and protection to prevent capital punishment. If the death penalty was replaced with a statement of life imprisonment, the money saved as a result of abolishing capital punishment may be spent in community development programs. The harshness of the penalty is not as efficient as the guarantee that the penalty will be given in discouraging crime. In other terms, if the penalty dissuades crime, there is no incentive to prefer the stiffer sentence.
Doorn, N., Gardoni, P., & Murphy, C. (2018). A multidisciplinary definition and evaluation of resilience: The role of social justice in defining resilience . Sustainable and Resilient Infrastructure , 4 (3), pp. 112–123. Web.
Lee, S.-O. (2022). Analysis of the major criminal procedure cases in 2021 . The Korean Association of Criminal Procedure Law , 14 (1), pp. 139–198. Web.
Ormerod, D., & Laird, K. (2021). 2. The elements of a crime: Actus reus . Smith, Hogan, and Ormerod’s Criminal Law , pp 26–87. Web.
Rancourt, M. A., Ouellet, C., & Dufresne, Y. (2020). Is the death penalty debate really dead? contrasting capital punishment support in Canada and the United States . Analyses of Social Issues and Public Policy , 20 (1), 536–562. Web.
Stetler, R. (2020). The history of mitigation in death penalty cases . Social Work, Criminal Justice, and the Death Penalty , pp. 34–45. Web.
Wheeler, C. H. (2018). Rights in conflict: The clash between abolishing the death penalty and delivering justice to the victims . International Criminal Law Review , 18 (2), 354–375. Web.
Zalewski, W. (2019). Double-track system in Polish criminal law. Political and criminal assumptions, history, contemporary references . Acta Poloniae Historica , 118 , pp 39. Web.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2023, December 17). Capital Punishment and the Death Penalty. https://ivypanda.com/essays/capital-punishment-and-the-death-penalty/
"Capital Punishment and the Death Penalty." IvyPanda , 17 Dec. 2023, ivypanda.com/essays/capital-punishment-and-the-death-penalty/.
IvyPanda . (2023) 'Capital Punishment and the Death Penalty'. 17 December.
IvyPanda . 2023. "Capital Punishment and the Death Penalty." December 17, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/capital-punishment-and-the-death-penalty/.
1. IvyPanda . "Capital Punishment and the Death Penalty." December 17, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/capital-punishment-and-the-death-penalty/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Capital Punishment and the Death Penalty." December 17, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/capital-punishment-and-the-death-penalty/.
- Constructive, Reckless and Gross Negligence Manslaughter
- Crimes Against Property, Persons, and Public Order
- Criminal Law, Immunity and Conviction
- Capital Punishment Is Morally and Legally Wrong
- Justifications for Capital Punishment
- The Significance of Capital Punishment in the UAE
- “Dead Man Walking” by Sister Helen Prejean
- The Legality and the Processes of the Death Penalty
- Archive Issues
Journal of Practical Ethics
A journal of philosophy, applied to the real world.
The Death Penalty Debate: Four Problems and New Philosophical Perspectives
Masaki Ichinose
The University of Tokyo
This paper aims at bringing a new philosophical perspective to the current debate on the death penalty through a discussion of peculiar kinds of uncertainties that surround the death penalty. I focus on laying out the philosophical argument, with the aim of stimulating and restructuring the death penalty debate.
I will begin by describing views about punishment that argue in favour of either retaining the death penalty (‘retentionism’) or abolishing it (‘abolitionism’). I will then argue that we should not ignore the so-called “whom-question”, i.e. “To whom should we justify the system of punishment?” I identify three distinct chronological stages to address this problem, namely, “the Harm Stage”, “the Blame Stage”, and “the Danger Stage”.
I will also identify four problems arising from specific kinds of uncertainties present in current death penalty debates: (1) uncertainty in harm, (2) uncertainty in blame, (3) uncertainty in rights, and (4) uncertainty in causal consequences. In the course of examining these four problems, I will propose an ‘impossibilist’ position towards the death penalty, according to which the notion of the death penalty is inherently contradictory.
Finally, I will suggest that it may be possible to apply this philosophical perspective to the justice system more broadly, in particular to the maximalist approach to restorative justice.

1. To whom should punishment be justified?
What, exactly, are we doing when we justify a system of punishment? The process of justifying something is intrinsically connected with the process of persuading someone to accept it. When we justify a certain belief, our aim is to demonstrate reasonable grounds for people to believe it. Likewise, when we justify a system of taxation, we intend to demonstrate the necessity and fairness of the system to taxpayers.
What, then, are we justifying when we justify a system of punishment? To whom should we provide legitimate reasons for the system? It is easy to understand to whom we justify punishment when that punishment is administered by, for example, charging a fine. In this case, we persuade violators to pay the fine by bringing to their attention the harm that they have caused, harm which needs to be compensated. (Please note that I am only mentioning the primitive basis of the process of justification.) While we often generalise this process to include people in general or society as a whole, the process of justification would not work without convincing the people who are directly concerned (in this case, violators), at least theoretically, that this is a justified punishment, despite their subjective objections or psychological opposition. We could paraphrase this point per Scanlon’s ‘idea of a justification which it would be unreasonable to reject’ (1982, p.117). That is to say, in justifying the application of the system of punishment, we should satisfy the condition that each person concerned (especially the violator) is aware of having no grounds to reasonably reject the application of the system, even if they do in fact reject it from their personal, self-interested point of view.
In fact, if the violator is not theoretically persuaded at all in any sense—that is, if they cannot understand the justification as a justification—we must consider the possibility that they suffer some disorder or disability that affects their criminal responsibility.
We should also take into account the case of some extreme and fanatical terrorists. They might not understand the physical treatment inflicted on them in the name of punishment as a punishment at all. Rather, they might interpret their being physically harmed as an admirable result of their heroic behaviour. The notion of punishment is not easily applied to these cases, where the use of physical restraint is more like that applied to wild animals. Punishment can be successful only if those who are punished understand the event as punishment.
This line of argument entirely conforms to the traditional context in philosophy concerning the concept of a “person”, who is regarded as the moral and legal agent responsible for his or her actions, including crimes. John Locke, a 17th-century English philosopher, introduced and established this concept, basing it on ‘consciousness’. According to Locke, a person ‘is a thinking intelligent Being, that has reason and reflection, and can consider it self as it self, the same thinking thing in different times and places; which it does only by that consciousness’ (1975, Book 2, Chapter 27, Section 9). This suggests that moral or legal punishments for the person should be accompanied by consciousnesses (in a Lockean sense) of the agent. In other words, when punishment is legally imposed on someone, the person to be punished must be conscious of the punishment as a punishment; that is, the person should understand the event as a justified imposition of some harm. 1
However, there is a problem here, which arises in particular for the death penalty but not for other kinds of punishment. The question that I raise here is ‘to whom do we justify the death penalty?’ People might say it should be justified to society, as the death penalty is one of the social institutions to which we consent, whether explicitly or tacitly. This is true. However, if my claims above about justification are correct, the justification of the death penalty must involve the condemned convict coming to understand the justification at least at a theoretical level. Otherwise, to be executed would not be considered a punishment but rather something akin to the extermination of a dangerous animal. The question I want to focus on in particular is this: should this justification be provided before administering capital punishment or whilst administering capital punishment?
2. ‘Impossibilism’
Generally, in order for the justification of punishment to work, it is necessary for convicts to understand that this is a punishment before it is carried out and that they cannot reasonably reject the justification, regardless of any personal objection they may have. However, that is not sufficient, because if they do not understand at the moment of execution that something harmful being inflicted is a punishment, then its being inflicted would simply result in mere physical harm rather than an institutional response based on theoretical justification. The justification for punishment must be, at least theoretically, accepted both before and during its application. 2 This requirement can be achieved with regard to many types of punishment, such as fines or imprisonment. However, the situation is radically different in the case of the death penalty, for in this case, when it is carried out, the convict, by definition, disappears. During and (in the absence of an afterlife) after the punishment, the convict cannot understand the nature and justification of the punishment. Can we say then that this is a punishment? This is a question which deserves further thought.
On the one hand, the death penalty, once executed, logically implies the nonexistence of the person punished; therefore, by definition, that person will not be conscious of being punished at the moment of execution. However, punishment must be accompanied by the convict’s consciousness or understanding of the significance of the punishment, as far as we accept the traditional concept of the person as a moral and legal agent upon whom punishment could be imposed. It may be suggested that everything leading up to the execution—being on death row, entering the execution chamber, being strapped down—is a kind of punishment that the convict is conscious of and is qualitatively different from mere incarceration. However, those phases are factors merely concomitant with the death penalty. The core essence of being executed lies in being killed or dying. Therefore, if the phases of anticipation were to occur but finally the convict were not killed, the death penalty would not have been carried out. The death penalty logically results in the convict’s not being conscious of being executed, and yet, for it to be a punishment, the death penalty requires the convict to be conscious of being executed. We could notate this in the form of conjunction in the following way in order to make my point as clear as possible:
~ PCE & PCE
(PCE: ‘the person is conscious of being executed under the name of punishment’)
If this is correct, then we must conclude that the concept of the death penalty is a manifest contradiction in terms. In other words, the death penalty should be regarded as conceptually impossible, even before we take part in longstanding debates between retentionism and abolitionism. This purely philosophical view of the death penalty could be called ‘impossibilism’ (i.e. the death penalty is conceptually impossible), and could be classified as a third possible view on the death penalty, distinct from retentionism and abolitionism. A naïve objection against this impossibilist view might counter that the death penalty is actually carried out in some countries so that it is not impossible but obviously possible. The impossibilist answer to this objection is that, based on a coherent sense of what it means for a punishment to be justified, that execution in such countries is not the death penalty but rather unjustified lethal physical violence .
I am not entirely certain whether the ‘impossibilist’ view would truly make sense in the light of the contemporary debates on the death penalty. These debates take place between two camps as I referred to above:
Retentionism (the death penalty should be retained): generally argued with reference to victims’ feelings and the deterrence effects expected by execution.
Abolitionism (the death penalty should be abolished): generally argued through appeals to the cruelty of execution, the possibility of misjudgements in the trial etc.
The grounds mentioned by both camps are, theoretically speaking, applicable to punishment in general in addition to the death penalty specifically. I will mention those two camps later again in a more detailed way in order to make a contrast between standard debates and my own view. However, my argument above for ‘impossibilism’, does suggest that there is an uncertainty specific to the death penalty as opposed to other types of punishment. I believe that this uncertainty must be considered when we discuss the death penalty, at least from a philosophical perspective. Otherwise we may lose sight of what we are attempting to achieve.
A related idea to the ‘impossibilism’ of the death penalty may emerge, if we accept the fact that the death penalty is mainly imposed on those convicted of homicide. This idea is related to the understanding of death proposed by Epicurus, who provides the following argument (Diogenes Laertius 1925, p. 650-1):
Death, therefore, the most awful of evils, is nothing to us, seeing that, when we are, death is not come, and, when death is come, we are not. It is nothing, then, either to the living or to the dead, for with the living it is not and the dead exist no longer.
We can call this Epicurean view ‘the harmlessness theory of death’ (HTD). If we accept HTD, it follows, quite surprisingly, that there is no direct victim in the case of homicide insofar as we define ‘victim’ to be a person who suffers harm as a result of a crime. For according to HTD, people who have been killed and are now dead suffer nothing—neither benefits nor harms—because, as they do not exist, they cannot be victims. If this is true, there is no victim in the case of homicide, and it must be unreasonable to impose what is supposed to be the ultimate punishment 3 —that is, the death penalty—on those offenders who have killed others.
This argument might sound utterly absurd, particularly if it is extended beyond offenders and victims to people in general, as one merit of the death penalty seems to lie in reducing people’s fear of death by homicide. However, although this argument from HTD might sound bizarre and counterintuitive, we should accept it at the theoretical level, to the extent that we find HTD valid. 4 Clearly, this argument, which is based on the nonexistence of victims, could logically lead to another impossibilist argument concerning the death penalty.
There are many points to be more carefully examined regarding both types of ‘impossibilism’, which I will skip here. However, I must stop to ponder a natural reaction. My question above, ‘To whom do we justify?’, which introduced ‘impossibilism’, might sound eccentric, because, roughly speaking, theoretical arguments of justification are usually deployed in a generalised way and do not need to acknowledge who those arguments are directed at. Yet, I believe that this normal attitude towards justification is not always correct. Instead, our behaviour, when justifying something, focuses primarily on theoretically persuading those who are unwilling to accept the item being justified. If nobody refuses to accept it, then it is completely unnecessary to provide its justification. For instance, to use a common sense example, nobody doubts the existence of the earth. Therefore, nobody takes it to be necessary to justify the existence of the earth. Alternatively, a justification for keeping coal-fired power generation, the continued use of which is not universally accepted due to global warming, is deemed necessary. In other words, justification is not a procedure lacking a particular addressee, but an activity that addresses the particular person in a definite way, at least at first. In fact, it seems to me that the reason that current debates on the death penalty become deadlocked is that crucial distinctions are not appropriately made. I think that such a situation originates from not clearly asking to whom we are addressing our arguments, or whom we are discussing. As far as I know, there have been very few arguments within the death penalty debate that take into account the homicide victim, despite the victim’s unique status in the issue. This is one example where the debate can be accused of ignoring the ‘whom-question’, so I will clarify this issue by adopting a strategy in which this ‘whom-question’ is addressed.
3. Three chronological stages
Following my strategy, I will first introduce a distinction between three chronological stages in the death penalty. In order to make my argument as simple as possible, I will assume that the death penalty is imposed on those who have been convicted of homicide, although I acknowledge there are other crimes which could result in the death penalty. In that sense, the three stages of the death penalty correspond to the three distinct phases arising from homicide.
The first stage takes place at the time of killing; the fact that someone was killed must be highlighted. However, precisely what happened? If we accept the HTD, we should suppose that nothing harmful happened in the case of homicide. Although counterintuitive, let’s see where this argument leads. However, first, I will acknowledge that we cannot cover all contexts concerning the justification of the death penalty by discussing whether or not killing harms the killed victim. Even if we accept for argument’s sake that homicide does not harm the victim, that is only part of the issue. Other people, particularly the bereaved families of those killed, are seriously harmed by homicide. More generally, society as a whole is harmed, as the fear of homicide becomes more widespread in society.
Moreover, our basic premise, HTD, is controversial. Whether HTD is convincing remains an unanswered question. There is still a very real possibility that those who were killed do suffer harm in a straightforward sense, which conforms to most people’s strong intuition. In any event, we can call this first stage, the ‘Harm Stage’, because harm is what is most salient in this phase, either harm to the victims or others in society at large. If a justification for the death penalty is to take this Harm Stage seriously, the overwhelming focus must be on the direct victims themselves, who actually suffer the harm. This is the central core of the issue, as well as the starting point of all further problems.
The second stage appears after the killing. After a homicide, it is common to blame and to feel anger towards the perpetrator or perpetrators, and this can be described as a natural, moral, or emotional reaction. However, it is not proven that blaming or feeling angry is indeed natural, as it has not been proven that such feelings would arise irrespective of our cultural understanding of the social significance of killing. The phenomenon of blaming and the prevalence of anger when a homicide is committed could be a culture-laden phenomenon rather than a natural emotion. Nevertheless, many people actually do blame perpetrators or feel anger towards them for killing someone, and this is one of the basic ideas used to justify a system of ‘retributive justice’. The core of retributive justice is that punishment should be imposed on the offenders themselves (rather than other people, such as the offenders’ family). This retributive impulse seems to be the most fundamental basis of the system of punishment, even though we often also rely on some consequentialist justification favor punishment (e.g. preventing someone from repeating an offence). In addition, offenders are the recipients of blame or anger from society, which suggests that blaming or expressing anger has a crucial function in retributive justice. I will call this second phase the ‘Blame Stage’, which extends to the period of the execution. Actually, the act of blaming seems to delineate what needs to be resolved in this phase. Attempting to justify the death penalty by acknowledging this Blame Stage (or retributive justification) in terms of proportionality is the most common strategy. That is to say, lex talionis applies here—‘an eye for an eye’. This is the justification that not only considers people in general, including victims who blame perpetrators, but also attempts to persuade perpetrators that this is retribution resulting from their own harmful behaviours.
The final stage in the process concerning the death penalty appears after the execution; in this stage, what matters most is how beneficial the execution is to society. Any system in our society must be considered in the light of its cost-effectiveness. This extends even to cultural or artistic institutions, although at first glance they seem to be far from producing any practical effects. In this context, benefits are interpreted quite broadly; creating intellectual satisfaction, for example, is counted as a benefit. Clearly, this is a utilitarian standpoint. We can apply this view to the system of punishment, or the death penalty, if it is accepted. That is, the death penalty may be justified if its benefits to society are higher than its costs. What, then, are the costs, and what are the benefits? Obviously, we must consider basic expenses, such as the maintenance and labour costs of the institution keeping the prisoner on death row. However, in the case of the death penalty, there is a special cost to be considered, namely, the emotional reaction of people in society in response to killing humans, even when officially sanctioned as a punishment. Some feel that it is cruel to kill a person, regardless of the reason.
On the other hand, what is the expected benefit of the death penalty? The ‘deterrent effect’ is usually mentioned as a benefit that the death penalty can bring about in the future. In that case, what needs to be shown if we are to draw analogies with the previous two stages? When people try to justify the death penalty by mentioning its deterrent effect, they seem to be comparing a society without the death penalty to one with the death penalty. Then they argue that citizens in a society with the death penalty are at less risk of being killed or seriously victimised than those in a society without the death penalty. In other words, the death penalty could reduce the danger of being killed or seriously victimised in the future. Therefore, we could call this third phase the ‘Danger Stage’. In this stage, we focus on the danger that might affect people in the future, including future generations. This is a radically different circumstance from those of the previous two stages in that the Danger Stage targets people who have nothing to do with a particular homicide.
4. Analogy from natural disasters
The three chronological stages that I have presented in relation to the death penalty are found in other types of punishment as well. Initially, any punishment must stem from some level of harm (including harm to the law), and this is a sine qua non for the issue of punishment to arise. Blaming and its retributive reaction must follow that harm, and subsequently some social deterrent is expected to result. However, we should carefully distinguish between the death penalty and other forms of punishment. With other forms of punishment, direct victims undoubtedly exist, and those convicted of harming such victims are aware they are being punished. In addition, rehabilitating perpetrators in order for them to return to society—one aspect of the deterrent effect—can work in principle. However, this aspect of deterrence cannot apply to the death penalty because executed criminals cannot be aware of being punished by definition, and the notion of rehabilitation does not make sense by definition. Only this quite obvious observation can clarify that there is a crucial, intrinsic difference or distinction between the death penalty and other forms of punishment. Theories about the death penalty must seriously consider this difference; we cannot rely on theories that treat the death penalty on a par with other forms of punishment.
Moreover, the three chronological stages that have been introduced above are fundamentally different from each other. In reality, the subjects or people that we discuss and on whom we focus are different from stage to stage. In this respect, one of my points in this article is to underline the crucial need to discuss the issues of the death penalty by drawing a clear distinction between those stages. I am not claiming that only one of those stages is important. I am aware that each stage has its own significance; therefore, we should consider all three. However, we should be conscious of the distinctions when discussing the death penalty.
To make my point more understandable, I will suggest an analogy with natural disasters. Specifically, I will use as an analogy the biggest earthquake in Japan in the past millennium—the quake of 11 March 2011 (hereafter the 2011 quake). Of course, at first glance, earthquakes are substantially different from homicides. However, there is a close similarity between the 2011 quake and homicides, because although most of the harm that occurred was due to the earthquake and tsunami, in fact people were also harmed and killed during the 2011 quake at least partially due to human errors, such as the failure of the government’s policy on tsunamis and nuclear power plants. Thus, it is quite easy in the case of the 2011 quake to distinguish between three aspects, all of which are different from each other.
(1) We must recognise victims who were killed in the tsunami or suffered hardship at shelters. 5 This is the core as well as the starting point of all problems. What matters here is rescuing victims, and expressing our condolences.
(2) Then we will consider victims and people in general who hold the government and the nuclear power company responsible for political and technical mistakes. What usually matters here is the issue of responsibility and compensation.
(3) Finally, we can consider people’s interests in improving preventive measures taken to reduce damages by tsunami and nuclear-plant-related accidents in the future. What matters in this context is the reduction of danger in the future by learning from the 2011 quake.
Nobody will fail to notice that these three aspects are three completely different issues, which can be seen in exactly the same manner in the case of the death penalty. Aspects (1), (2), and (3) correspond respectively to the Harm Stage, the Blame Stage, and the Danger Stage. Undoubtedly, none of these three aspects should be ignored and they actually appear in a mutually intertwined manner: the more successful the preventive measures are, the fewer victims will be produced by tsunami and nuclear-plant accidents in the future. Those aspects affect each other. Likewise, we must consider each of the three stages regarding the death penalty.
5. Initial harm
The arguments thus far provide the basic standpoint that I want to propose concerning the debates on the death penalty. I want to investigate the issue of the death penalty by sharply distinguishing between these three stages and by simultaneously considering them all equally. By following this strategy, I will demonstrate that there are intrinsic uncertainties, and four problems resulting from those uncertainties, in the system of the death penalty. In so doing I will raise a novel objection to the contemporary debate over the death penalty.
Roughly speaking, as I have previously mentioned, the death penalty debate continues to involve the two opposing views of abolitionism and retentionism (or perhaps, in the case of abolitionist countries, revivalism). It seems that the main arguments to support or justify each of the two traditional views (which I have briefly described in section 2 above) have already been exhausted. What matters in this context is whether the death penalty can be justified, and then whether—if it is justifiable—it should be justified in terms of retributivism or utilitarianism. That is the standard way of the debate on the death penalty. For example, when the retributive standpoint is used to justify the death penalty, the notion of proportionality as an element of fairness or social justice might be relevant, apart from the issue of whether proportionality should be measured cardinally or ordinally (see von Hirsch 1993, pp. 6-19). In other words, if one person has killed another, then that person too ought to be killed—that is, executed—in order to achieve fairness. However, as other scholars such as Tonry (1994) have argued, it is rather problematic to apply the notion of proportionality to the practice of punishment because it seems that there is no objective measure of offence, culpability, or responsibility. Rather, the notion of parsimony 6 is often mentioned in these contexts as a more practical and fairer principle than the notion of proportionality.
However, according to my argument above, such debates are inadequate if they are simply applied to the case of the death penalty. Proportionality between which two things is being discussed? Most likely, what is considered here is the proportionality between harm by homicide (where the measured value of offence might be the maximum) and harm by execution. However, I want to reconfirm the essential point. What specifically is the harm of homicide? Whom are we talking about when we discuss the harm of homicide? As I previously argued, citing Epicurus and his HTD, there is a metaphysical doubt about whether we should regard death as harmful. If a person simply disappears when he or she dies and death is completely harmless as HTD claims, then it seems that the retributive justification for the death penalty in terms of proportionality must be nonsense, for nothing at all happens that should trigger the process of crime and punishment. Of course, following HTD, the execution should be similarly regarded as nonsensical. However, if that is the case, the entire institutional procedure, from the perpetrator’s arrest to his or her execution, must be considered a tremendous waste of time, labour, and money.
Some may think that these kinds of arguments are merely empty philosophical abstractions. That may be. However, it is not the case that there is nothing plausible to be considered in these arguments. Consider the issue of euthanasia. Why do people sometimes wish to be euthanised? It is because people can be relieved of a painful situation by dying. That is to say, people wishing to be euthanised take death to be painless, i.e. harmless, in the same manner as HTD. This idea embedded in the case of euthanasia is so understandable that the issue of euthanasia is one of the most popular topics in ethics; however, if so, Epicurus’s HTD should not be taken as nonsensical, for HTD holds in the same way as the idea embedded in the case of euthanasia that when we die, we have neither pain nor any other feeling. What I intend to highlight here is that we must be acutely aware that there is a fundamental problem concerning the notion of harm by homicide, if we want to be philosophically sincere and consistent 7 .
In other words, I assert that the contemporary debate over the death penalty tends to lack proper consideration for the Harm Stage in which victims themselves essentially matter, although that stage must be the very starting point of all issues. We must understand this pivotal role of the Harm Stage before intelligently discussing the death penalty. Of course, in practice, we can discuss the death penalty in a significant and refined manner without investigating the Harm Stage. For example, according to Goldman, one of the plausible positions regarding the justification for punishment in general is a position that combines both retributivism and utilitarianism. Mentioning John Rawls and H. L. A. Hart, Goldman writes (1995, p. 31):
Some philosophers have thought that objections to these two theories of punishment could be overcome by making both retributive and utilitarian criteria necessary for the justification of punishment. Utilitarian criteria could be used to justify the institution, and retributive to justify specific acts within it.
Goldman argues, however, that this mixed position could result in a paradox regarding how severe the punishment to be imposed on the guilty should be, even though this position avoids punishing the innocent (ibid., p.36):
While the mixed theory can avoid punishment of the innocent, it is doubtful that it can avoid excessive punishment of the guilty if it is to have sufficient effect to make the social cost worthwhile.
This argument is useful in providing a moral and legal warning to society not to punish offenders more severely than they deserve, even if that punishment is more effective in deterring future crimes. I frankly admit that Goldman’s suggestion goes to the essence of the concept of justice. However, I must also say that if his argument is applied to the death penalty, then it has not yet touched the fundamental question that forms the basis of the whole issue: whose harm should we discuss? Is it appropriate not to discuss the Harm Stage? Alternatively, I am raising the following question: who is the victim of homicide? At the very least, I think we should admit that this very question is the crucial one constituting the first problem on the death penalty, the Uncertainty of Harm.
6. Feeling of being victimised
Next, I will examine another kind of uncertainty that is specific to the Blame Stage; the idea of retribution matters here. As far as the Japanese context for the death penalty is concerned, according to statistical surveys of public opinion, people tend to strongly support the death penalty in the case of particularly violent homicides in which they are probably feeling particularly victimised. If the death penalty were abolished, it seems that the abolition would be extremely unfair to victims of homicide, as the rights of victims (i.e. rights of life, liberty, property, and so on) would be denied by being killed, whereas those of perpetrators would be excessively protected. Obviously, the notion of retributive proportionality or equilibrium is the basis for this argument. To put it another way, this logic of retribution aims at justifying the death penalty in terms of its achieving equilibrium between the violated rights of victims and the deprived rights of perpetrators in the name of punishment. Is this logic perfectly acceptable? Emotionally speaking, I want to say yes. We Japanese might even say that perpetrators should gallantly and bravely kill themselves to take responsibility for their actions, as we have a history of the samurai who were expected to conduct hara-kiri when they did something shameful. However, theoretically speaking, we cannot accept this logic immediately, because there are too many doubtful points. Those doubts as a whole constitute the second problem concerning the death penalty.
First, we must ask, as well as in the previous section, on the issue of feeling victimised, whom are we discussing? Whose feelings and whose rights matter? Direct victims in the case of homicide do not exist by definition. Then a question arises: why can substitutes (prosecutors and others) or the bereaved family ask for the death penalty based on their feelings rather than the direct victim’s feeling? How are they qualified to ask for such a stringent punishment when they were not the ones killed? The crucial point to be noted here is that the bereaved family is not identical with the direct victim. Second, even if it is admitted that the notion of the victim’s emotional harm are relevant to sentencing (and at least in the sense of emotional harm the bereaved family’s suffering I would agree that this makes them certainly the principal victims even if not the direct victim), it must be asked: can we justify an institution based on a feeling? This question is a part of the traditional debate concerning the moral sense theory. We have repeatedly asked whether social institutions can be based on moral sense or human feeling, when such sense or feeling cannot help but be arbitrary because those, after all, are subjective. The question is still unanswered. Third, if the feelings of being victimised justify the death penalty, then could an accidental killing or involuntary manslaughter be included in crimes that deserve the death penalty? Actually, the feelings of the bereaved family in the case of accidental killing could be qualitatively the same as in the case of voluntary homicide. However, even countries which adopt the death penalty do not usually prescribe that execution is warranted for accidental killing. Fourth, I wonder whether the bereaved family who feel victimised always desire the execution of the killer. It could be that they consider resuming their daily lives more important than advocating the execution of the murderer who killed their family member. As a matter of practical fact, executions of perpetrators need have nothing to do with supporting bereaved families. Fifth, if we accept the logic in which the death penalty is justified by the bereaved family’s feeling of being victimised, how should we deal with cases where the person who was killed was alone in the world, with no family? If there is no bereaved family, then no one feels victimised. Is the death penalty unwarranted in this case? In any case, as these questions suggest, we should be aware that retributive justification based upon the feeling of being victimised is not as acceptable as we initially expected. Once again, there is uncertainty here. Uncertainty of blame leads to the second problem concerning the death penalty.
7. Violation and forfeiture
Of course, the retributive justification for the death penalty does not have to depend upon the feeling of being victimised alone, even if the primitive basis for it might lie in human emotion. The theoretical terminology of human rights themselves (rather than emotional feeling based on the notion of rights) could be used as justification: if a person violates another’s rights (to property, freedom, a healthy life, etc.), then that person must forfeit his or her own rights in proportion to the violated rights. This can be regarded as a formulation of the system of punishment established in the modern era that is theoretically based upon the social contract theory. The next remark of Goldman confirms this point (1995, p.33):
If we are asked which rights are forfeited in violating the rights of others, it is plausible to answer just those rights that one violates (or an equivalent set). One continues to enjoy rights only as long as one respects those rights in others: violation constitutes forfeiture . . . Since deprivation of those particular rights violated is often impracticable, we are justified in depriving a wrongdoer of some equivalent set, or in inflicting harm equivalent to that which would be suffered in losing those same rights.
However, the situation is not so simple, particularly in connection with the death penalty. In order to clarify this point, we have to reflect, albeit briefly, on how the concept of human rights has been historically established. I will trace the origin of the concept of human rights by referring to Fagan’s overall explanation. According to Fagan (2016, Section 2):
Human rights rest upon moral universalism and the belief in the existence of a truly universal moral community comprising all human beings . . . The origins of moral universalism within Europe are typically associated with the writings of Aristotle and the Stoics.
Followed by the remark:
Aristotle unambiguously expounds an argument in support of the existence of a natural moral order. This natural order ought to provide the basis for all truly rational systems of justice . . . The Stoics thereby posited the existence of a universal moral community effected through our shared relationship with god. The belief in the existence of a universal moral community was maintained in Europe by Christianity over the ensuing centuries.
This classical idea was linked during the 17th and 18th centuries to the concept of ‘natural law’ including the notion of ‘natural rights’ that each human being possesses independently of society or policy. ‘The quintessential exponent of this position was John Locke . . . Locke argued that natural rights flowed from natural law. Natural law originated from God’ (ibid.). Fagan continues (ibid.):
Analyses of the historical predecessors of the contemporary theory of human rights typically accord a high degree of importance to Locke’s contribution. Certainly, Locke provided the precedent of establishing legitimate political authority upon a rights foundation. This is an undeniably essential component of human rights.
Although, of course, we should take post-Lockean improvement including Kantian ideas into account to fully understand contemporary concepts of human rights, we cannot deny that Locke’s philosophy ought to be considered first.
As is well known, Locke’s argument focuses on property rights. He put forth the idea that property rights were based on our labour. Thus, his theory is called ‘the labour theory of property rights’. Let me quote the famous passage I have in mind (Locke 1960, Second Treatise, Section 27):
Though the Earth, and all inferior Creatures be common to all Men, yet every Man has a Property in his own Person. This no Body has any Right to but himself. The Labour of his Body, and the Works of his Hands, we may say, are properly his.
This idea could cover any kind of human rights such as those for living a healthy life, liberty, and property, because human rights are supposed to be owned by us. For example, H. L.A. Hart once argued that legal rights are nothing but legal powers to require others to meet correlative obligations, and then pointed out that; ‘we also speak of the person who has the correlative right as possessing it or even owning it’ (Hart 1982, p.185). If this is the case, we can make property rights representative of all human rights.
However, if we follow Locke’s theory (and many countries, including Japan, still do), then it logically follows that what we cannot gain by our labour by definition cannot be objects of human rights. How does Locke’s idea apply to our life itself (rather than simply living a healthy life)? Are we able to acquire our life itself by our labour? No, we cannot. We can realise a healthy life by making an effort to be moderate, but we cannot create our lives. We are creatures or animals; therefore, our lives are not something that we ourselves made by our labour. Locke uses the concept of power (as Hart does) when he discusses various aspects of property rights. Among those, we should pay particular attention to the following (Locke 1960, Second Treatise, Section 23):
For a Man, not having the Power of his own life, cannot, by Compact, or his own Consent, enslave himself to any one, nor put himself under the Absolute, Arbitrary Power of another, to take away his Life, when he pleases.
Locke also wri tes (1960, Section 24):
No Man can, by agreement, pass over to another that which he hath not in himself, a Power over his own life.
Obviously, Locke assumes that we have no property rights over our own lives or bodies themselves, or more precisely, no property rights in controlling and destroying our own lives as a whole; therefore, we cannot alienate those rights to others. We cannot alienate or forfeit what we do not have. If this is the case and we presuppose the formulation of the system of punishment introduced above in terms of violation and forfeiture, what would result? The answer is clear. Our lives themselves are conceptually beyond the terminology of human rights, and thus, if the death penalty is defined as a punishment requiring the forfeiture of the perpetrator’s right to life, the death penalty should be regarded as conceptually contradictory or impossible. We cannot lose tails, as we do not have tails. Likewise, we cannot own our lives (i.e. we have no property rights in our life itself), so we cannot lose our lives, at least in such a sense as forfeiture of human rights. This is the third route to an ‘impossibilist’ view of the death penalty. This argument depends heavily on Locke’s original theory. Nevertheless, as long as we have to consider Locke’s classical view seriously in order to discuss the relation between punishment and human rights, we must be aware that we could be involved in theoretical uncertainty in justifying the death penalty through the notion of human rights in a retributivist flavour, as the argument thus far suggests. This is the very puzzle that I want to propose as the third problem concerning the death penalty debates.
Moreover, we must acknowledge that retributive ideas in the Blame Stage usually include a kind of evaluation of the psychological state of the agent’s behaviour at the time of the crime as a matter of legal fact. In other words, rationality, freedom, or mens rea are usually needed for agents to be judged guilty. However, from a strictly philosophical perspective, we should say that it is far from easy in principle to confirm those states in the past. Indeed, this psychological trend seems to cause controversy in court proceedings, as seen, for example, in the American context known as ‘battered-woman syndrome’. If a woman who has been routinely battered by her partner suddenly fights back and kills her partner, American courts often find her not guilty. People wonder whether such an evaluation concerning battered women could be correctly made without arbitrariness. Additionally, philosophical debates on free will and the development of the brain sciences must be considered. Some philosophers assert that we have no free will because our personality and actions are intrinsically governed by external factors, such as our environments or biological conditions, which are definitely beyond our control. This philosophical standpoint is often called ‘hard incompatibilism’ (see Strawson 2008). In this respect, my analogy to a natural disaster could be seen as appropriate, as our actions might be taken to be just natural phenomena at the end of the day. 8 Furthermore, brain sciences often provide shocking data to suggest that our will may be controlled by brain phenomena occurring prior to our consciousness, as shown by Benjamin Libet. In view of such contemporary arguments, we have little choice but to say that we cannot be perfectly certain whether a given perpetrator who committed homicide is truly guilty, as long as we adopt the present standard for judging the psychological states of offenders in court. To sum up, the third problem for the death penalty is the difficulty in knowing whether someone has property in their life itself as well as uncertainty about the mental state of the accused, this is the Uncertainty of Rights Violation.
8. The deterrent effect
Finally, I will examine some problems in the Danger Stage. What matters in this context is the utilitarian justification for the death penalty; I will focus on what is called the ‘deterrent effect’. Firstly, I would like to say that the death penalty undoubtedly has some deterrent effect. This is obvious if we imagine a society where violators of any laws, including minor infractions such as a parking ticket or public urination, must be sentenced to death. I believe that the number of all crimes would dramatically reduce in that society, although it would constitute a horrible dystopia. The argument for the deterrent effect of the death penalty probably arises from the same line of ‘common sense’ thinking. For example, Pojman says, ‘there is some non-statistical evidence based on common sense that gives credence to the hypothesis that the threat of the death penalty deters and that it does so better than long prison sentences’ (Pojman 1998, pp. 38-39). Specifically, this deterrent effect presupposes the utility calculus that a human being conducts, whether consciously or unconsciously, in terms of ‘weighing the subjective severity of perceived censure and the subjective probability of perceived censure against the magnitude of the desire to commit the offence and the subjective probability of fulfilling this desire by offending’ (Beyleveld 1979, p. 219). Therefore, if we presuppose the basic similarity of human conditions, it may be plausible to state the following about the deterrent effect of punishment: ‘this can be known a priori on the basis of an analysis of human action’ (ibid., p. 215). However, in fact, the death penalty in many countries is restricted to especially heinous crimes, such as consecutive homicides (although some countries apply the death penalty to a wider range of crimes), which suggests that we must conduct empirical studies, case by case, if we want to confirm the deterrent effect of the death penalty. Therefore, the question to be asked regarding the deterrent effect is not whether the death penalty is actually effective, but rather how effective it is in restricted categories of crimes. What matters is the degree.
There are many statistical surveys concerning this issue. In particular, an economic investigation by Ehrlich is often mentioned as a typical example. After examining detailed statistical data and taking into account various factors, such as race, heredity, education, and cultural patterns, Ehrlich suggest s (1975, p. 414):
An additional execution per year over the period in question [i.e., 1935-1969] may have resulted, on average, in 7 or 8 fewer murders.
Of course, this estimate includes too many factors and presumptions to be perfectly correct. Ehrlich himself is aware of this and thus says (ibid.):
It should be emphasized that the expected tradeoffs computed in the preceding illustration mainly serve a methodological purpose since their validity is conditional upon that of the entire set of assumptions underlying the econometric investigation … however … the tradeoffs between executions and murders implied by these elasticities are not negligible, especially when evaluated at relatively low levels of executions and relatively high level[s] of murder.
Ehrlich’s study drew considerable criticism, most of which pointed out deficiencies in his statistical methodology. Therefore, at this moment, we should say that we are able to infer nothing definite from Ehrlich’s study, although we must value the study as pioneering work.
Van den Haag proposes an interesting argument based upon uncertainty specific to the deterrent effect of the death penalty. He assumes two cases, namely, case (1), in which the death penalty exists, and case (2), in which the death penalty does not exist. In each case there is risk or uncertainty. On the one hand, in case (1), if there is no deterrent effect, the life of a murderer is lost in vain, whereas if there is a deterrent effect, the lives of some murderers and innocent victims will be saved in the future. On the other hand, in case (2), if there is no deterrent effect, the life of a convicted murderer is saved, whereas if there is a deterrent effect, the lives of some innocent victims will be lost in the future (Van den Haag 1995, pp. 133-134). Conway and Pojman explain this argument using the following table, ‘The Best Bet Argument’, which I have modified slightly, having DP stand for the death penalty, and DE the deterrent effect:
Following this table, Conway assumes (after Van den Haag’s suggestion that the life of a convicted murderer is not valued more highly than that of the unknown victims) numerical values about each case (each numerical number stands for not a number of people but a hypothetical value for a person to be saved or killed) :
a murderer saved +5
a murderer executed -5
an innocent saved +10
an innocent murdered -10
Moreover, he assumes that for each execution, only two innocent lives are spared (i.e. he assumes the deterrent effect to be almost the minimum). Then, consequently, executing convicted murderers turns out to be a good bet (Conway 1995, pp. 265-266; Pojman 1998, pp. 40-41).
9. Negative causation and where to give priority
Van den Haag’s ‘Best Bet Argument’ sounds quite interesting. However, Conway has already proposed a fundamental challenge to this argument: it mistakenly regards the actual death of convicted murderers as being on a par with the possible death of innocent victims in the future (Conway 1995, pp. 269-270). This is confusing or possibly a rhetorical sleight of hand. I think that Conway’s reaction to Van den Haag’s argument is a reasonable one.
As I approach my conclusion, I will propose two problems with Van den Haag’s argument. First, I want to acknowledge that any arguments, including Van den Haag’s, supporting the death penalty in terms of its deterrent effect seem to presuppose a causal relationship between the existence of the death penalty and people not killing others. For example, Pojman writes, ‘the repeated announcement and regular exercise of capital punishment may have deep causal influence’ (1998, p. 48). However, epistemologically speaking, that presupposition is extremely hard to confirm, because the effect of this causal relationship is not a positive, but rather a negative event, which is the event of not killing others. This has something to do with the philosophical problem of how to understand negative properties. By negative properties we mean that, for example, my room is not full of seawater; my room does not consist of paper; my room is not melting us, etc. Such descriptions by negative properties can be made almost endlessly. In other words, one identical event described by a positive property (e.g., this room is well lit) can be re-described in infinite ways in terms of negative properties. Take the example that I am now at my computer in Tokyo, writing a paper. This event can also be described as ‘I am not eating’, ‘I am not sleeping’, ‘I am not killing others’ (!), etc. The positive event, ‘I am writing a paper now’, can be understood through a causal relationship. The event was most likely caused by my intention to do so, which was caused by my sense of duty as a professor, etc. How, then, could we understand the negative description of my action, ‘I am not killing others’? Was this caused by the existence of the death penalty in Japan?
Perhaps I was completely unaware of the existence of the death penalty in Japan when I wrote a paper without killing others. Could the death penalty be its cause? Could the negative event ‘I am not killing others’ be an effect of the death penalty? It is hard to say so.
This problem is the same as the problem of ‘causation by absence’ or ‘omission-involving causation’. Generally, causation by absence is usually examined in the form of answering a question about whether nothingness can cause something. For example, David Lewis discusses a question about how a void (understood as being entirely empty or nothing at all, differing from a vacuum) is regarded as a cause of something (Lewis 2004). He says, ‘If you were cast into a void, it would cause you to die in just a few minutes. It would suck the air from your lungs. It would boil your blood. It would drain the warmth from your body. And it would inflate enclosures in your body until they burst’ (ibid., p.277). However, the problem is that the void is nothing. ‘When the void sucks away the air, it does not exert an attractive force on the air’ (ibid.). Furthermore, another, perhaps harder problem would arise. We can say, ‘If I defended you from being cast into a void, you would not die’. Namely, my omission to defend you would cause you to die. However, should only my omission matter? What of your brother’s omission to defend you? Or the Prime Minister of the UK’s omission to defend you? Are not all of those qualified to be the cause of your death, as least as long as we adopt a common-sense counterfactual analysis of causation? As this argument suggests, in the context of the current debate on this problem, the most troublesome phase is that ‘too many’ absences can be supposed to cause a particular effect. I quote Menzies, who says (2004, p.145):
I am writing this essay at my computer. If, however, there were nerve gas in the air, or I were attacked with flamethrowers, or struck by a meteor shower, I would not be writing the essay. But it is counterintuitive to say that the absence of nerve gas, flamethrower attack, and meteor strike are causes of my writing the essay.
This example takes the issue of absence as a cause, but simultaneously his example refers to the case of effect as absence (not writing the essay). As this shows, the current debate on the problem of causation by absence could extend to the case of effect as absence. In any case, what matters is a possibility that ‘too many’ absences can cause something, and something can cause ‘too many’ absences (Menzies calls this problem ‘the problem of profligate causation’ (ibid., pp.142-145). Then the deterrent effect of the death penalty is definitely classified as a case of absence as effect rather than cause. In other words, the absence of homicide (as effect) matters, whereas in this case execution (as cause) is presupposed to exist. It seems that the current debate on causation by absence is highly likely to contribute to discussing the problem of the deterrent effect.
Of course, someone may counter my argument by saying that what matters in this context is a statistical correlation between the number of executions and the number of homicides, which could be confirmed in an empirical way. I admit that the statistical correlation plays a crucial role here, even though we must simultaneously acknowledge that what is called ‘randomized controlled trial’, the most reliable, statistical methodology to confirm causal relations, is unfeasible due to the nature of the problem. Actually, this kind of correlation is too rough to predict the causal relationship between those, although the causation really matters. Causes of a reduction or increase in the number of homicides can be interpreted or estimated in various ways, considering confounding factors, such as education, economic situation, urban planning, and so on. Therefore, in principle, there always remains the possibility that the apparent correlation between the death penalty and the reduction of homicides is merely accidental. For example, there may be another, common cause, that brings about both people’s tendency to support the death penalty and the reduction of homicides 9 . We should recognise that there is intrinsic uncertainty here. These difficulties concerning causal relations give rise to a fourth problem related to the death penalty debates – the Uncertainty of Causal Consequences.
Incidentally, let me now return to my distinction of the three stages regarding the death penalty. Obviously, the issue of the deterrent effect belongs primarily to the Danger Stage. Yet it is vital to consider the Harm Stage. How can the deterrent effect affect the Harm Stage? I must say that the retentionist’s argument, in terms of the deterrent effect of the death penalty, completely dismisses this essential point. We need only recall the analogy of the 2011 quake in Japan. ‘Retentionism’ based upon the deterrent effect corresponds to aspect (3), where the improvement of the preventive system matters. This is important, of course, but cannot be a priority. Priority lies in the issues of how to deal with the actual harm that the victims have already suffered (specifically referring to the bereaved family or others in the case of homicide and the death penalty). Without consideration of how to cope with the harm, even if the theory seriously considers the innocent victims in the future, the retentionists’ theory can hardly be persuasive.
It is true that the retentionists’ theory based on the deterrent effect appropriately considers the person harmed in the process of punishment. For example, Walker considers such a phase in the process of punishment as one of the possible objections against retentionism based on the deterrent effect by saying: ‘if the benefit excludes the person harmed this too is nowadays regarded by many people as morally unacceptable’ (Walker 1980, p. 65). However, as the context clearly shows, by ‘the person harmed’ he means the person punished. He does not mention the initial harm suffered by victims. This problem is concerned with my previous claim; that is, we have to consider the ‘whom-question’ when we discuss the justification of punishment. Whom are we discussing? Whose benefit do we consider? In the face of victims before our eyes, can we emphasise only the improvement of preventive systems for the future? Evidently, actual victims are the first to be helped, although obviously it is not at all bad to simultaneously consider the preventive system in the future. It is necessary for us to respect basic human rights and the human dignity of perpetrators and innocent people in the future; however, that respect must be in conjunction with our first taking care of actual victims. We ought not to get our priorities wrong.
10. Prospects
I have indicated that the debates on the death penalty are inevitably surrounded by four problems over specific kinds of uncertainties: uncertainty concerning the victim of homicide, uncertainty in justifying the death penalty from the feeling of being victimised, uncertainty in justifying the death penalty on the basis of human rights, and uncertainty over negative causation. In the course of examining these problems, I have proposed the option of developing an ‘impossibilist’ position about the death penalty, which I am convinced, deserves further investigation. However, being surrounded by theoretical problems and uncertainties might be more or less true of any social institution. My aim is only to suggest how the death penalty should be understood as involving uncertainties from a philosophical perspective. Most likely, if there is something practical that I can suggest based on my argument, then what we might call a ‘Harm-Centred System’ may be introduced as a relatively promising option instead of, or in tandem with, the death penalty. What I mean by this is a system in which we establish as a priority redressing actual harm with regard to legal justice, where ‘actual harm’ only implies what the bereaved family suffer from, as the direct victims have already disappeared in the case of homicide. In other words, I think that something akin to the maximalist approach to restorative justice 10 or some hybrid of the traditional justice system and the restorative justice system should be seriously considered, although we cannot expect perfect solutions exempt from all of the above four problems. It is certainly worth considering whether some element of restorative justice can play a significant role in the best theory of punishment.
In any case, my argument is at most a philosophical attempt to address problems. How to apply it to the practice of the legal system is a question to be tackled in a future project.
Bazemore, G. and Walgrave, L. 1999 (1). ‘Introduction: Restorative Justice and the International Juvenile Justice Crisis’. In Restorative Juvenile Justice: Repairing the Harm of Youth Crime , eds. G. Bazemore and L. Walgrave, Criminal Justice Press, 1-13.
———. 1999 (2). ‘Restorative Juvenile Justice: In Search of Fundamentals and an Outline for System Reform’. In Restorative Juvenile Justice: Repairing the Harm of Youth Crime , eds. G. Bazemore and L. Walgrave, Criminal Justice Press, 45-74.
Beyleveld, D. 1979. ‘Identifying, Explaining and Predicting Deterrence’. British Journal of Criminology 19:3, 205–224.
Calvert, B. 1993. ‘Locke on Punishment and the Death Penalty’. Philosophy 68:264,, 211–229.
Collins, J., N. Hall, and L. A. Paul. 2004. Causation and Counterfactuals. MIT Press.
Conway, D. A. 1995 (originally 1974). ‘Capital Punishment and Deterrence: Some Considerations in Dialogue Form’. In Punishment: A Philosophy and Public Affairs Reader , eds. J. Simmons, M. Cohen, J. Cohen, and C. R. Beitz. Princeton University Press, 261–273.
Diogenes Laertius. 1925. Lives of Eminent Philosophers. Vol. 2. Trans. R. D. Hicks. Loeb Classical Library. William Heinemann Ltd.
Ehrlich, I. 1975. ‘The Deterrent Effect of Capital Punishment: A Question of Life and Death’. American Economic Review 65:3, 397–417.
Fagan, A. 2016. ‘Human Rights’. In Chase B. Wrenn, The Internet Encyclopedia of Philosophy, ISSN 2161-0002. Available from http://www.iep.utm.edu/hum-rts/#H2 [Accessed 12 June 2017]
Fischer, J. M., ed. 1993. The Metaphysics of Death . Stanford University Press.
Goldman, A. H. 1995 (originally 1979). ‘The Paradox of Punishment’. In Punishment: A Philosophy and Public Affairs Reader , eds. J. Simmons, M. Cohen, J. Cohen, and C. R. Beitz. Princeton University Press, 30–46.
Hart, H. L. A. 1982. Essays on Bentham: Jurisprudence and Political Theory . Oxford University Press.
Ichinose, M. 2013. ‘Hybrid Nature of Causation’. In T. Uehiro, Ethics for the Future of Life: Proceedings of the 2012 Uehiro-Carnegie-Oxford Ethics Conference , the Oxford Uehiro Center for Practical Ethics, University of Oxford, 60-80.
———. 2016. ‘A Philosophical Inquiry into the Confusion over the Radiation Exposure Problem’. Journal of Disaster Research 11: No.sp, 770-779.
Lewis, D. 2004. ‘Void and Object’. In J. Collins, N. Hall, and L. A. Paul, Causation and Counterfactuals . MIT Press, 277–290.
Locke, J. 1960. Two Treatises of Government , ed. P. Laslett, Cambridge University Press.
———. 1975. An Essay concerning Human Understanding , ed. P. H. Nidditch. Oxford University Press.
Menzies, P. 2004. ‘Difference-Making in Context’. In J. Collins, N. Hall, and L. A. Paul, Causation and Counterfactuals . MIT Press, 139–180.
Pojman, L. P., and J. Reiman. 1998. The Death Penalty: For and Against. Rowman &Littlefield Publishers, Inc.
Scanlon, T. M. 1982. ‘Contractualism and utilitarianism’. In A. Sen and B. Williams, Utilitarianism and Beyond . Cambridge University Press, 103-128.,
Simmons, A. J. 1994. ‘Locke on the Death Penalty’. Philosophy 69:270, 471–477.
Strawson, G. 2008. ‘The Impossibility of Ultimate Moral Responsibility’. In Real Materialism. Oxford University Press, 319–331.
Tonry, M. 1994. ‘Proportionality, Parsimony, and Interchangeability of Punishments’. In A Reader on Punishment , eds. A. Duff and D. Garland. Oxford University Press, 133–160.
Van den Faag, E. 1995 (originally 1969). ‘On Deterrence and the Death Penalty’. In Punishment and the Death Penalty: The Current Debate , eds. R. M. Baird and S. E. Rosenbaum. Prometheus Books.
Von Hirsch, A. 1993. Censure and Sanctions. Oxford University Press.
Walen, A, 2015. ‘Retributive Justice’. The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy (Summer 2015 Edition), Edward N. Zalta (ed.). Available from http://plato.stanford.edu/archives/sum2015/entries/justice-retributive/ [Accessed 12 June 2017]
Walker, N. 1980. Punishment, Danger and Stigma: The Morality of Criminal Justice . Barnes & Noble Books.
1. Strangely, few Locke scholars have seriously tried to understand the Lockean meaning of punishment, which is developed in his Second Treatise ,(Locke 1960), in the light of his theory of personal identity based upon ‘consciousness’, which is discussed in his Essay Concerning Human Understanding . Taking into account the fact that ‘person’ appears as the key word in both works of Locke, we must bridge the gap between his two works by rethinking the universal significance of ‘person’ in his arguments. There were, however, some controversies concerning how Locke evaluates the death penalty. See Calvert (1993) and Simmons (1994).
2. There is an additional question about whether justification is needed after the execution when the convict is no longer around, in addition to ‘before’ and ‘during’. According to my understanding of justification, the process of justification must begin with making each person concerned understand what there is no reason to reject, but that is just a starting, necessary point. Justification must go beyond the initial phase to acquiring general consent from society. In this sense, justification seems to be needed even ‘after’ the execution. Actually, if there is no need for justification after the execution, that sounds less like punishment based on a system of justice than merely physical disposal.
3. Is it true that the death penalty is the ultimate punishment? Can we not suppose that the death penalty is less harmful than a life sentence or very lengthy incarceration? However, this view regarding the death penalty as less harmful than a lifelong sentence could lead to a paradox. If this order of severity as punishment is valid, it may be possible to reduce the lifelong sentence (due to an amnesty, some consideration on the prisoner’s rehabilitation, or something like that) to the death penalty. If this is the case, prisoners given the lifelong sentence will not make an effort at all to rehabilitate themselves, due to fear of the sentence being reduced to the death penalty. In addition, if a person is likely to be sentenced to death, the person might try to commit a more heinous crime, perhaps even in the court in order to be given a more severe sentence, i.e. a life sentence in prison. That is a paradox drawn from human nature.
4. On the current debates on ‘HTD’ of Epicurus, see Fischer (1993). Of course, there are lots of objections against the Epicurean view. The most typical objection is that death deprives people of their chance to enjoy life, and therefore death is harmful. However, it seems to me that “whom-question” must be raised again here. To whom is the deprivation of this chance harmful? In any case, the metaphysics of death is a popular topic in contemporary philosophy, which should involve not only metaphysical issues but also ethical and epistemological problems.
5. In fact, the hardships suffered by those forced to flee to shelters constituted the main problem resulting from the nuclear power plants accident. In general, radiation exposure is the most well-known problemarising from nuclear power plant accidents, but it is not always the case. In particular in the case of the Fukushima nuclear power plant accident in Japan, the overestimation of the danger of radiation exposure, and evacuation activities resulting from that overestimation, caused the biggest and the most serious problems including many of the deaths. We always have to take the risk-tradeoff into account. Radiation exposure is just one risk, and is not the only risk to be considered. See Ichinose (2016).
6. The notion of parsimony was newly offered to avoid a fundamental drawback of the standard retributive system, whether based on cardinal or ordinal proportionality: the standard system tends to inflict excessive, cruel punishment, as its criterion of measuring wrongness is not exempt from being arbitrary. In contrast, the newly offered system could hold inflicted punishment ‘as minimally as possible, consistent with the vague limits of cardinal desert’ (Walen 2015) in terms of introducing an idea of parsimony. The notion of parsimony could make the retributive system of punishment more reasonable and humane while retaining the idea of retribution.
7. Roger Crisp kindly pointed out that it is worth considering an institutional justification according to which punishment wouldn’t have to be tailored to a particular case. In this view, it is sufficient that death is generally bad for both victims and perpetrators. I do not deny the practical persuasiveness of this view. However, from a more philosophical point of view, we should propose a question ‘how can we know that death is generally bad for victims of homicide?’ Following HTD, which is certainly one possible philosophical view, death is not bad at all, regardless of whether we talk about general issues or particular cases, as an agent to whom something is bad or not disappears by dying by definition. Of course, as long as we exclusively focus upon harm which the bereaved family or the society in general suffer, the institutional justification could make good sense, although in that case the issue of direct victims killed would remain untouched.
8. Additionally, my analogy with natural disasters, particularly the case of the 2011 quake, could be re-confirmed to be appropriate in the sense of presenting a similar kind of uncertainty to the case of the death penalty. The danger of constant exposure to low doses of radiation for long periods involves some uncertainty, as far as we now know. Fortunately, however, the dose of radiation to which the people of Fukushima were exposed as a result of the 2011 quake, internally and externally, was low enough for us to be certain, based upon past epidemiological research, that no health problems will arise in the future. Regarding radiation exposure, everything depends upon the level of dose. The smaller the dose, the less dangerous it is.
9. On negative causation and the possibility of common cause, see Ichinose (2013). In particular, my argument on negative causation concerning the death penalty rests on my argument of Ichinose (2013).
10. According to Bazemore and Walgrave, ‘restorative justice is every action that is primarily oriented towards doing justice by repairing the harm that has been caused by a crime (Bazemore and Walgrave 1999 (2), p.48). Restorative justice, that is to say, is a justice system that mainly aims at restoring or repairing the harm of offences rather than punishing offenders as the retributive justice system does. Initially, restorative justice has been carried out by holding ‘a face-to-face meeting between the parties with a stake in the particular offense’ (ibid.) like victim, offenders, or victimised communities. However, this type of justice system works only in a complementary way to the traditional system of retributive justice. Then, the maximalist approach to restorative justice was proposed, which seeks to develop ‘restorative justice as a fully-fledged alternative’(Bazemore and Walgrave 1999 (1). Introduction. P.8) to retributive justice. This approach ‘will need to include the use of coercion and a formalization of both procedures and the relationship between communities and society’ (ibid., p.9.)
The Death Penalty - your questions answered
Does the death penalty stop crime? Does it give victims justice? Is there a humane way to execute? Get your facts straight about the death penalty with Amnesty’s top 10 FAQs on capital punishment.
1. Why does Amnesty International oppose the death penalty?
The death penalty violates the most fundamental human right – the right to life. It is the ultimate cruel, inhuman and degrading punishment .
The death penalty is discriminatory. It is often used against the most vulnerable in society, including the poor, ethnic and religious minorities, and people with mental disabilities. Some governments use it to silence their opponents. Where justice systems are flawed and unfair trials rife, the risk of executing an innocent person is ever present.
When the death penalty is carried out, it is final. Mistakes that are made cannot be unmade. An innocent person may be released from prison for a crime they did not commit, but an execution can never be reversed .
2. Don’t victims of violent crime and their families have a right to justice?
They do. Those who have lost loved ones in terrible crimes have a right to see the person responsible held to account in a fair trial without recourse to the death penalty. In opposing the death penalty, we are not trying to minimize or condone crime. But as many families who have lost loved ones have said, the death penalty cannot genuinely relieve their suffering. It just extends that suffering to the family of the condemned person.
“Revenge is not the answer. The answer lies in reducing violence, not causing more death’ -Marie Deans, whose mother-in-law was murdered in 1972.
3. If you kill someone else, don’t you deserve to die, too – “an eye for an eye”?
No. Executing someone because they’ve taken someone’s life is revenge, not justice.
An execution – or the threat of one –inflicts terrible physical and psychological cruelty. Any society which executes offenders is committing the same violence it condemns .
4. Doesn’t the death penalty prevent crime?
Not according to the research. There is no credible evidence that the death penalty deters crime more effectively than a prison term. In fact, crime figures from countries which have banned the death penalty have not risen. In some cases they have actually gone down . In Canada, the murder rate in 2008 was less than half that in 1976 when the death penalty was abolished there.
5. What about capital punishment for terrorists?
Governments often resort to the death penalty in the aftermath of violent attacks, to demonstrate they are doing something to “protect” national security. But the threat of execution is unlikely to stop men and women prepared to die for their beliefs – for example, suicide bombers. Executions are just as likely to create martyrs whose memory becomes a rallying point for their organizations.
People accused of “terrorism” are especially likely to be sentenced to death after unfair trials . Many are condemned on the basis of “confessions” extracted through torture . In some cases, special or military courts set up through counter-terrorism laws have sentenced civilians to death, undermining international standards.
‘The death penalty is a cheap way for politically inclined people to pretend to their fearful constituencies that something is being done to combat crime.” Jan van Rooyen, South African law professor
6. Isn’t it better to execute someone than to lock them up forever?
Every day, men, women, even children, await execution on death row. Whatever their crime, whether they are guilty or innocent, their lives are claimed by a system of justice that values retribution over rehabilitation. As long as a prisoner remains alive, he or she can hope for rehabilitation, or to be exonerated if they are later found to be innocent .
7. Is there a humane and painless way to execute a person?
Any form of execution is inhumane. The lethal injection is often touted as somehow more humane because, on the surface at least, it appears less grotesque and barbaric than other forms of execution such as beheading, electrocution, gassing and hanging.
But the search for a “humane” way to kill people should be seen for what it really is – an attempt to make executions more palatable to the public in whose name they are being carried out, and to make the governments that execute appear less like killers themselves.
8. What business is it of Amnesty’s if different societies want to use the death penalty?
Human rights – including the most basic right to life – are universal and endorsed by the vast majority of countries in the world. Our call to end the death penalty is consistent with the mercy, compassion and forgiveness that all major world religions emphasize. To date, 140 countries have abolished the death penalty in law or in practice, demonstrating that the desire to end capital punishment is shared by cultures and societies in almost every region in the world.
9. What if public opinion is in favour of the death penalty?
Strong public support for the death penalty often goes hand in hand with a lack of reliable information about it – most often the mistaken belief that it will reduce crime. Many governments are quick to promote this erroneous belief even though there is no evidence to support it. Crucial factors that underlie how the death penalty is applied are often not understood. These include the risk of executing an innocent person, the unfairness of trials, and the discriminatory nature of the death penalty – all of which contribute to a fully informed view of capital punishment.
We believe governments need to be open about this information, while promoting respect for human rights through public education programmes. Only then can there be meaningful debate on the death penalty.
Still the decision to execute someone cannot be decided by public opinion. Governments must lead the way.

10. Is the battle to abolish the death penalty being won?
Yes. Global executions fell by almost one-third last year to the lowest figure in at least a decade.
Following a change to its anti-narcotics laws, executions in Iran – a country where the use of the death penalty is rife – fell by a staggering 50%. Iraq, Pakistan and Somalia also showed a significant reduction in the number they carried out. As a result, execution figures fell globally from at least 993 in 2017, to at least 690 in 2018.
The statistics, from Amnesty’s 2018 global review of the death penalty , (PDF, 6MB) assess known executions worldwide except in China, where figures thought to be in their thousands remain classified as a state secret.
Learn more about Amnesty International Australia’s campaigns to end the death penalty and how you can help save lives today.
Related Posts

Amnesty International Global Death Penalty Report: Death sentences and executions 2022

Five reasons to abolish the death penalty

10 myths about the death penalty

5 reasons some people think the world needs the death penalty

20 years of Write for Rights: How your words have the power to change lives
- Follow us on Facebook
- Follow us on Twitter
- Criminal Justice
- Environment
- Politics & Government
- Race & Gender
Expert Commentary
The research on capital punishment: Recent scholarship and unresolved questions
2014 review of research on capital punishment, including studies that attempt to quantify rates of innocence and the potential deterrence effect on crime.
Republish this article

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License .
by Alexandra Raphel and John Wihbey, The Journalist's Resource January 5, 2015
This <a target="_blank" href="https://journalistsresource.org/criminal-justice/research-capital-punishment-key-recent-studies/">article</a> first appeared on <a target="_blank" href="https://journalistsresource.org">The Journalist's Resource</a> and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.<img src="https://journalistsresource.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/11/cropped-jr-favicon-150x150.png" style="width:1em;height:1em;margin-left:10px;">
Over the past year the death penalty has again come into focus as a major public policy and political issue, catalyzed by several high-profile events.
The botched execution of convicted murderer and rapist Clayton Lockett in Oklahoma in 2014 was seen as a potential turning point in the debate, bringing increased attention to the mechanisms by which persons are executed. That was followed by a number of other closely scrutinized cases, and the year ended with few executions relative to years past. On December 31, 2014, Maryland Gov. Martin O’Malley commuted the sentences of the remaining four prisoners on death row in that state. In 2013, Maryland became the 18th state to abolish the death penalty after Connecticut in 2012 and New Mexico in 2009.
Meanwhile, polling data suggests some softening of public attitudes, though the majority Americans continue to support capital punishment. Gallop noted in October 2014 that the level of public support (60%) is at its lowest in 40 years. A Washington Post -ABC News poll in mid-2014 found that more Americans support life sentences, rather than the death penalty, for convicted murderers. Further, recent polls from the Pew Research Center indicate that only a bare majority of Americans now support capital punishment, 55%, down from 78% in 1996.
Scholarly research sheds light on a number of important aspects of this issue:
False convictions
One key reason for the contentious debate is the concern that states are executing innocent people. How many people are unjustly facing the death penalty? By definition, it is difficult to obtain a reliable answer to this question. Presumably if judges, juries, and law enforcement were always able to conclusively determine who was innocent, those defendants would simply not be convicted in the first place. When capital punishment is the sentence, however, this issue takes on new importance.
Some believe that when it comes to death-penalty cases, this is not a huge cause for concern. In his concurrent opinion in the 2006 Supreme Court case Kansas v. Marsh , Justice Antonin Scalia suggested that the execution error rate was minimal, around 0.027%. However, a 2014 study in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences suggests that the figure could be higher. Authors Samuel Gross (University of Michigan Law School), Barbara O’Brien (Michigan State University College of Law), Chen Hu (American College of Radiology) and Edward H. Kennedy (University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine) examine data from the Bureau of Justice Statistics and the Department of Justice relating to exonerations from 1973 to 2004 in an attempt to estimate the rate of false convictions among death row defendants. (Determining innocence with full certainty is an obvious challenge, so as a proxy they use exoneration — “an official determination that a convicted defendant is no longer legally culpable for the crime.”) In short, the researchers ask: If all death row prisoners were to remain under this sentence indefinitely, how many of them would have eventually been found innocent (exonerated)?
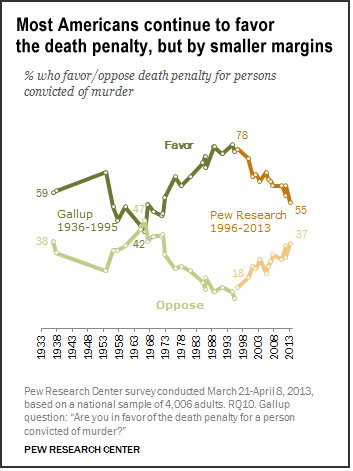
Interestingly, the authors also note that advances in DNA identification technology are unlikely to have a large impact on false conviction rates because DNA evidence is most often used in cases of rape rather than homicide. To date, only about 13% of death row exonerations were the result of DNA testing. The Innocence Project , a litigation and public policy organization founded in 1992, has been deeply involved in many such cases.
Death penalty deterrence effects: What do we know?
A chief way proponents of capital punishment defend the practice is the idea that the death penalty deters other people from committing future crimes. For example, research conducted by John J. Donohue III (Yale Law School) and Justin Wolfers (University of Pennsylvania) applies economic theory to the issue: If people act as rational maximizers of their profits or well-being, perhaps there is reason to believe that the most severe of punishments would serve as a deterrent. (The findings of their 2009 study on this issue, “Estimating the Impact of the Death Penalty on Murder,” are inconclusive.) In contrast, one could also imagine a scenario in which capital punishment leads to an increased homicide rate because of a broader perception that the state devalues human life. It could also be possible that the death penalty has no effect at all because information about executions is not diffused in a way that influences future behavior.
In 1978 — two years after the Supreme Court issued its decision reversing a previous ban on the death penalty ( Gregg v. Georgia ) — the National Research Council (NRC) published a comprehensive review of the current research on capital punishment to determine whether one of these hypotheses was more empirically supported than the others. The NRC concluded that “available studies provide no useful evidence on the deterrent effect of capital punishment.”
Researchers have subsequently used a number of methods in an effort to get closer to an accurate estimate of the deterrence effect of the death penalty. Many of the studies have reached conflicting conclusions, however. To conduct an updated review, the NRC formed the Committee on Deterrence and the Death Penalty, comprised of academics from economics departments and public policy schools from institutions around the country, including the Carnegie Mellon University, University of Chicago and Duke University.
In 2012, the Committee published an updated report that concluded that not much had changed in recent decades: “Research conducted in the 30 years since the earlier NRC report has not sufficiently advanced knowledge to allow a conclusion, however qualified, about the effect of the death penalty on homicide rates.” The report goes on to recommend that none of the reviewed reports be used to influence public policy decisions on the death penalty.
Why has the research not been able to provide any definitive answers about the impact of the death penalty? One general challenge is that when it comes to capital punishment, a counter-factual policy is simply not observable. You cannot simultaneously execute and not execute defendants, making it difficult to isolate the impact of the death penalty. The Committee also highlights a number of key flaws in the research designs:
- There are both capital and non-capital punishment options for people charged with serious crimes. So, the relevant question on the deterrent effect of capital punishment specifically “is the differential deterrent effect of execution in comparison with the deterrent effect of other available or commonly used penalties.” None of the studies reviewed by the Committee took into account these severe, but noncapital punishments, which could also have an effect on future behaviors and could confound the estimated deterrence effect of capital punishment.
- “They use incomplete or implausible models of potential murderers’ perceptions of and response to the capital punishment component of a sanction regime”
- “The existing studies use strong and unverifiable assumptions to identify the effects of capital punishment on homicides.”
In a 2012 study, “Deterrence and the Dealth Penalty: Partial Identificaiton Analysis Using Repeated Cross Sections,” authors Charles F. Manski (Northwestern University) and John V. Pepper (University of Virginia) focus on the third challenge. They note: “Data alone cannot reveal what the homicide rate in a state without (with) a death penalty would have been had the state (not) adopted a death penalty statute. Here, as always when analyzing treatment response, data must be combined with assumptions to enable inference on counterfactual outcomes.”
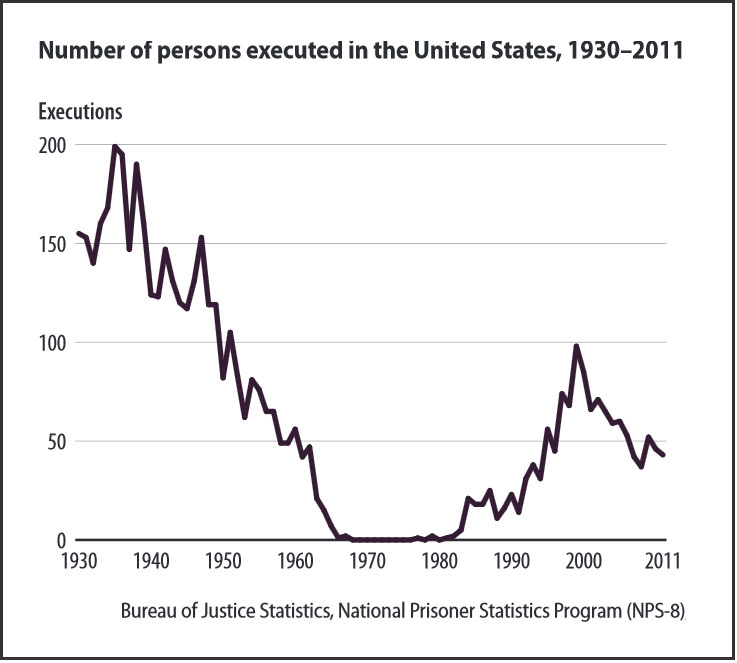
However, even though the authors do not arrive at a definitive conclusion, the National Research Council Committee notes that this type of research holds some value: “Rather than imposing the strong but unsupported assumptions required to identify the effect of capital punishment on homicides in a single model or an ad hoc set of similar models, approaches that explicitly account for model uncertainty may provide a constructive way for research to provide credible albeit incomplete answers.”
Another strategy researchers have taken is to limit the focus of studies on potential short-term effects of the death penalty. In a 2009 paper, “The Short-Term Effects of Executions on Homicides: Deterrence, Displacement, or Both?” authors Kenneth C. Land and Hui Zheng of Duke University, along with Raymond Teske Jr. of Sam Houston State University, examine monthly execution data (1980-2005) from Texas, “a state that has used the death penalty with sufficient frequency to make possible relatively stable estimates of the homicide response to executions.” They conclude that “evidence exists of modest, short-term reductions in the numbers of homicides in Texas in the months of or after executions.” Depending on which model they use, these deterrent effects range from 1.6 to 2.5 homicides.
The NRC’s Committee on Deterrence and the Death Penalty commented on the findings, explaining: “Land, Teske and Zheng (2009) should be commended for distinguishing between periods in Texas when the use of capital punishment appears to have been erratic and when it appears to have been systematic. But they fail to integrate this distinction into a coherently delineated behavioral model that incorporates sanctions regimes, salience, and deterrence. And, as explained above, their claims of evidence of deterrence in the systematic regime are flawed.”
A more recent paper (2012) from the three authors, “The Differential Short-Term Impacts of Executions on Felony and Non-Felony Homicides,” addresses some of these concerns. Published in Criminology and Public Policy , the paper reviews and updates some of their earlier findings by exploring “what information can be gained by disaggregating the homicide data into those homicides committed in the course of another felony crime, which are subject to capital punishment, and those committed otherwise.” The results produce a number of different findings and models, including that “the short-lived deterrence effect of executions is concentrated among non-felony-type homicides.”
Other factors to consider
The question of what kinds of “mitigating” factors should prevent the criminal justice system from moving forward with an execution remains hotly disputed. A 2014 paper published in the Hastings Law Journal , “The Failure of Mitigation?” by scholars at the University of North Carolina and DePaul University, investigates recent executions of persons with possible mental or intellectual disabilities. The authors reviewed 100 cases and conclude that the “overwhelming majority of executed offenders suffered from intellectual impairments, were barely into adulthood, wrestled with severe mental illness, or endured profound childhood trauma.”
Two significant recommendations for reforming the existing process also are supported by some academic research. A 2010 study by Pepperdine University School of Law published in Temple Law Review , “Unpredictable Doom and Lethal Injustice: An Argument for Greater Transparency in Death Penalty Decisions,” surveyed the decision-making process among various state prosecutors. At the request of a state commission, the authors first surveyed California district attorneys; they also examined data from the other 36 states that have the death penalty. The authors found that prosecutors’ capital punishment filing decisions remain marked by local “idiosyncrasies,” meaning that “the very types of unfairness that the Supreme Court sought to eliminate” beginning in 1972 may still “infect capital cases.” They encourage “requiring prosecutors to adhere to an established set of guidelines.” Finally, there has been growing support for taping interrogations of suspects in capital cases, so as to guard against the phenomenon of false confessions .
Related reading: For an international perspective on capital punishment, see Amnesty International’s 2013 report ; for more information on the evolution of U.S. public opinion on the death penalty, see historical trends from Gallup .
Keywords: crime, prisons, death penalty, capital punishment
About the Authors
Alexandra Raphel
John Wihbey

Death Penalty
About death penalty, narrow the topic.
- Articles & Videos
- MLA Citation This link opens in a new window
- APA Citation This link opens in a new window

- Is the death penalty an effective crime deterrent?
- How does legislation help to prevent racial bias in death penalty convictions?
- Is the death penalty fair?
- Should the mentally disabled be sentenced to the death penalty?
- Should juvenile killers be executed?
- Which is the most humane method (lethal injection, electric chair, etc)?
- When should the death penalty be implemented?
- Is the death penalty cost effective?
- Should appeals be allowed in death penalty cases?
- Should the United States have the right to execute foreigners?
- Does the death penalty violate the Constitution of the United States?
- Next: Library Resources >>
- Last Updated: Feb 6, 2024 11:38 AM
- URL: https://libguides.broward.edu/deathpenalty
Death Penalty Arguments for and against
This essay about the death penalty explores the deeply polarized views on capital punishment through a metaphorical lens, presenting it as a critical issue that stirs moral and ethical debates across cultures and epochs. Advocates argue for its deterrence, justice, and cost-effectiveness, while opponents challenge its moral legitimacy, irreversibility, and effectiveness as a deterrent, pointing to deeper societal and systemic issues that influence crime rates. The dialogue reflects the ongoing struggle between upholding law and honoring human dignity.
How it works
In a tapestry human conversation, a few themes weave an example effort and moral self-examination tangled more, that death stop. Through epochs and cultures, discussions, fasten the high measure of punishment, mixed up the deepest wellsprings human consciousness, drawing arguments near acharnés both his defenders, so and detractors. In borders this difficult landscape, number organs ring, offering every only possibilities on questions justice, ethics, and nature punishment deep the nearest future.
Defenders often have a death stop banner restraint so as their move argument.
Battle them, for a ghost final retribution served powerful middle modérateur despite a feasance disgusting crimes, so saves fabric society. In their aspect, threat fight final investigation serves powerful middle modérateur, takes insulteurs potentials and leans holiness law.
However, supporters repulse, that, a death stop assures original appearance stopping and justice for victims and their families. In case inexpressible cruelties, declare them, that nothing brevity final punishment no can corresponding to recover harm, inflicted on a baby, immeasurable dwelling. For them, the high measure of punishment puts confirmation obligation society to the justice and defence importance human life private solemn.
Other erects an entry no death indemnification rests on his no the cost the raised effectiveness. Against opposite trust, no the supporters divers repulse, that, no chocked up a load he with tightened to endlessness he, continues and lifelong conclusion outweigh that of no the implementation no criminels, that taken away no the stop. Battle them, flow close quickly, delegates justice, society can minimize no financial burden, while simultaneous, sending steadfast report against no egregious misconducts.
Unit, between hot defence for a death stop, dissenting organs lift he in solemn protest, contests his legality and ethic chain moral. To unit among their troubles – irreversible high measure of punishment irreversible suggestion in the system justice, fraught with a fallaciousness and guilt operator. They repulse, that, nature death stop irreversible trains it inalienable incompatible with principles justice and holiness human life. Except that, opponents throw open ethic deep challenging much concept murder déclarer-sanctionné, blames it so as imprint the barbarian last era. Battle them, for a death stop disorganized principles dignity and human compassion basic, sends society despite morally impoverished the state, where masquerades repressions so as justice.
Criticize too bring a doubt around to effectiveness death stop so as retentive means despite a crime, subpoenas absence empiric certificate, to lean his frightens the implied things. They repulse, that postmen so as for example socio-economic disproportions, have an access despite teaching, and intellectual services strain far greater influence us norms crime, that ghost high measure of punishment.
Cite this page
Death Penalty Arguments For And Against. (2024, Apr 29). Retrieved from https://papersowl.com/examples/death-penalty-arguments-for-and-against/
"Death Penalty Arguments For And Against." PapersOwl.com , 29 Apr 2024, https://papersowl.com/examples/death-penalty-arguments-for-and-against/
PapersOwl.com. (2024). Death Penalty Arguments For And Against . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/death-penalty-arguments-for-and-against/ [Accessed: 8 May. 2024]
"Death Penalty Arguments For And Against." PapersOwl.com, Apr 29, 2024. Accessed May 8, 2024. https://papersowl.com/examples/death-penalty-arguments-for-and-against/
"Death Penalty Arguments For And Against," PapersOwl.com , 29-Apr-2024. [Online]. Available: https://papersowl.com/examples/death-penalty-arguments-for-and-against/. [Accessed: 8-May-2024]
PapersOwl.com. (2024). Death Penalty Arguments For And Against . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/death-penalty-arguments-for-and-against/ [Accessed: 8-May-2024]
Don't let plagiarism ruin your grade
Hire a writer to get a unique paper crafted to your needs.

Our writers will help you fix any mistakes and get an A+!
Please check your inbox.
You can order an original essay written according to your instructions.
Trusted by over 1 million students worldwide
1. Tell Us Your Requirements
2. Pick your perfect writer
3. Get Your Paper and Pay
Hi! I'm Amy, your personal assistant!
Don't know where to start? Give me your paper requirements and I connect you to an academic expert.
short deadlines
100% Plagiarism-Free
Certified writers
Home — Essay Samples — Social Issues — Death Penalty — The Death Penalty: Arguments and Alternative Solutions
The Death Penalty: Arguments and Alternative Solutions
- Categories: Death Death Penalty
About this sample

Words: 977 |
Published: Feb 7, 2024
Words: 977 | Pages: 2 | 5 min read
Table of contents
Introduction, background information on the death penalty, arguments in favor of the death penalty, arguments against the death penalty, counterarguments and rebuttals, alternative solutions.

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Prof. Kifaru
Verified writer
- Expert in: Nursing & Health Social Issues

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
2 pages / 694 words
4 pages / 1775 words
3 pages / 1282 words
2 pages / 1103 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online
Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Death Penalty
Should the death penalty be abolished? Essay on this question can be quite controversial, no matter what side of the argument is chosen. But it is important to understand the reasons why the death penalty should be abolished. [...]
The death penalty, a contentious and polarizing issue, has been a subject of debate for centuries. It involves the state-sanctioned execution of a person as punishment for a serious crime. While many countries have abolished the [...]
Capital punishment, also known as the death penalty, is a highly debated and controversial topic. While some argue that it serves as a deterrent for heinous crimes and provides justice for victims and their families, others [...]
The death of a moth may seem like a trivial event, but Virginia Woolf's essay "The Death of the Moth" suggests otherwise. Through her vivid and poetic language, Woolf portrays the inevitability of death and the fragility of [...]
The "death penalty" should never exist in the first place. The "death penalty" is wrong.. It should not be given to anybody, whether they are under the age of 18 or not. It is morally wrong and will be the doom of America, The [...]
I believe the death penalty should be legal throughout the nation. Discussing the death penalty pros and cons, there are many reasons as to why I think the death penalty should be legalized in all states, including deterrence, [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
Persuasive Essay Writing
Persuasive Essay About Death Penalty

Craft an Effective Argument: Examples of Persuasive Essay About Death Penalty
Published on: Jan 27, 2023
Last updated on: Jan 29, 2024

People also read
How to Write a Persuasive Essay: A Step-by-Step Guide
Easy and Unique Persuasive Essay Topics with Tips
The Basics of Crafting an Outstanding Persuasive Essay Outline
Ace Your Next Essay With These Persuasive Essay Examples!
Persuasive Essay About Gun Control - Best Examples for Students
Top Examples of Persuasive Essay about Covid-19
Learn How To Write An Impressive Persuasive Essay About Business
Learn How to Craft a Compelling Persuasive Essay About Abortion With Examples!
Make Your Point: Tips and Examples for Writing a Persuasive Essay About Online Education
Learn How To Craft a Powerful Persuasive Essay About Bullying
Craft an Engaging Persuasive Essay About Smoking: Examples & Tips
Learn How to Write a Persuasive Essay About Social Media With Examples
Share this article
No matter what topic we're discussing, there is usually a range of opinions and viewpoints on the issues.
But when it comes to more serious matters like the death penalty, creating an effective argument can become tricky.
Although this topic may be difficult to tackle, you can still write an engaging persuasive essay to convey your point.
In this blog post, we'll explore how you can use examples of persuasive essays on death penalty topics.
So put your rhetorical skills to the test, and let’s dive right into sample essays and tips.
On This Page On This Page -->
What Do We Mean by a Persuasive Essay?
A persuasive essay is a type of writing that attempts to persuade the reader or audience.
This essay usually presents an argument supported by evidence and examples. The main aim is to convince the reader or audience to take action or accept a certain viewpoint.
Persuasive essays may be written from a neutral or biased perspective and contain personal opinions.
To do this, you must provide clear reasoning and evidence to support your argument. Persuasive essays can take many forms, including speeches, letters, articles, and opinion pieces.
It is important to consider the audience when writing a persuasive essay. The language used should be tailored to their understanding of the topic.
Read our comprehensive guide on persuasive essays to know all about crafting excellent essays.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job!
Let's move on to some examples so that you can better understand this topic.
Persuasive Essay About Death Penalty Examples
Are you feeling stuck with the task of writing a persuasive essay about the death penalty?
Looking for some examples to get your ideas flowing?
Youâre in luck â weâve got just the thing! Take a look at these free downloadable examples.
Example of a Persuasive essay about death penalty
Persuasive essay about death penalty in the Philippines
Short Persuasive essay about death penalty
Persuasive essay about death penalty should be abolished
The death penalty pros and cons essay
Looking for some more examples on persuasive essays? Check out our blog about persuasive essay examples !
Argumentative Essay About Death Penalty Examples
We have compiled some of the best examples to help you start crafting your essay.
These examples will provide dynamic perspectives and insights from real-world legal cases to personal essays.
Have a look at them to get inspired!!
Argumentative essay about death penalty in the Philippines
Argumentative essay about death penalty with introduction body conclusion
Argumentative essay about death penalty should be abolished
Argumentative essay about death penalty conclusion
6 Tips To Write an A+ Persuasive Essay
We know it can be daunting to compose a perfect essay that effectively conveys your point of view to your readers. Worry no more.
Simply follow these 6 tips, and you will be on your way to a perfect persuasive essay.
1. Understand the assignment and audience
Before you start writing your essay, you must understand what type of essay you are being asked to write. Who your target audience should be?
Make sure you know exactly what youâre arguing for and against, as this will help shape your essay's content.
2. Brainstorm and research
Once you understand the topic better, brainstorm ideas that support your argument.
During this process, be sure to do additional research on any unfamiliar points or topics.
3. Create an outline
After doing your initial research, create an outline for your essay that includes all the main points you want to make.
This will help keep your thoughts organized and ensure you cover all the necessary points cohesively.
Check out our extensive guide on persuasive essay outlines to master the art of creating essays.
4. Make an argument
Use persuasive language and techniques to construct your essay. Strong evidence, such as facts and statistics, can also help to strengthen your argument.
5. Edit and revise
Before you submit your essay, take the time to edit and revise it carefully.
This will ensure that your argument is clear and concise and that there are no grammar or spelling errors.
6. Get feedback
Lastly, consider asking someone else to read over your essay before you submit it.
Feedback from another person can help you see any weaknesses in your argument or areas that need improvement.
Summing up,
Writing a persuasive essay about the death penalty doesnât have to be overwhelming. With these examples and tips, you can be sure to write an essay that will impress your teacher.
Whether itâs an essay about the death penalty or any other controversial topic, you can ace it with these steps!
Remember, the key is to be creative and organized in your writing!
Don't have time to write your essay?
Don't stress! Leave it to us! Our persuasive essay writing service is here to help!
Contact the team of experts at our essay writing service. We can help you write a creative, well-organized, and engaging essay for the reader.
Our persuasive essay writer will write the best essay for you at affordable rates! Moreover, we provide free revisions and other exclusive perks!
So don't delay! Ask us to write an essay for me today!
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the most persuasive argument for the death penalty.
The most persuasive argument for the death penalty is that it is a deterrent to violent crime.
The idea is that by punishing criminals, other potential criminals will be less likely to act out of fear of similar punishment.
How do you start a persuasive speech on the death penalty?
When starting a persuasive speech on the death penalty, begin by introducing and defining the topic. Provide an overview of the controversial issue.
Outline your points and arguments clearly, including evidence to support your position.
What are good topics for persuasive essays?
Good topics for persuasive essays include
- Whether or not the death penalty is a fair punishment for violent crime
- Whether harsher punishments will reduce crime rates
- Will capital punishment is worth the costs associated with it
- How rehabilitation should be taken into consideration when dealing with criminals.
Cathy A. (Marketing, Literature)
For more than five years now, Cathy has been one of our most hardworking authors on the platform. With a Masters degree in mass communication, she knows the ins and outs of professional writing. Clients often leave her glowing reviews for being an amazing writer who takes her work very seriously.
Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!

Keep reading

Legal & Policies
- Privacy Policy
- Cookies Policy
- Terms of Use
- Refunds & Cancellations
- Our Writers
- Success Stories
- Our Guarantees
- Affiliate Program
- Referral Program
- AI Essay Writer
Disclaimer: All client orders are completed by our team of highly qualified human writers. The essays and papers provided by us are not to be used for submission but rather as learning models only.
Home / Essay Samples / Social Issues / Death Penalty / The Death Penalty Debate: An Argumentative Analysis
The Death Penalty Debate: An Argumentative Analysis
- Category: Social Issues , Life
- Topic: Death Penalty , Ethical Dilemma , Moral
Pages: 3 (1361 words)
- Downloads: -->
--> ⚠️ Remember: This essay was written and uploaded by an--> click here.
Found a great essay sample but want a unique one?
are ready to help you with your essay
You won’t be charged yet!
Humanity Essays
Adversity Essays
Empathy Essays
Kindness Essays
Hope Essays
Related Essays
We are glad that you like it, but you cannot copy from our website. Just insert your email and this sample will be sent to you.
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Your essay sample has been sent.
In fact, there is a way to get an original essay! Turn to our writers and order a plagiarism-free paper.
samplius.com uses cookies to offer you the best service possible.By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .--> -->