- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences

What It Takes to Give a Great Presentation
- Carmine Gallo

Five tips to set yourself apart.
Never underestimate the power of great communication. It can help you land the job of your dreams, attract investors to back your idea, or elevate your stature within your organization. But while there are plenty of good speakers in the world, you can set yourself apart out by being the person who can deliver something great over and over. Here are a few tips for business professionals who want to move from being good speakers to great ones: be concise (the fewer words, the better); never use bullet points (photos and images paired together are more memorable); don’t underestimate the power of your voice (raise and lower it for emphasis); give your audience something extra (unexpected moments will grab their attention); rehearse (the best speakers are the best because they practice — a lot).
I was sitting across the table from a Silicon Valley CEO who had pioneered a technology that touches many of our lives — the flash memory that stores data on smartphones, digital cameras, and computers. He was a frequent guest on CNBC and had been delivering business presentations for at least 20 years before we met. And yet, the CEO wanted to sharpen his public speaking skills.
- Carmine Gallo is a Harvard University instructor, keynote speaker, and author of 10 books translated into 40 languages. Gallo is the author of The Bezos Blueprint: Communication Secrets of the World’s Greatest Salesman (St. Martin’s Press).
Partner Center

How it works
Transform your enterprise with the scalable mindsets, skills, & behavior change that drive performance.
Explore how BetterUp connects to your core business systems.
We pair AI with the latest in human-centered coaching to drive powerful, lasting learning and behavior change.
Build leaders that accelerate team performance and engagement.
Unlock performance potential at scale with AI-powered curated growth journeys.
Build resilience, well-being and agility to drive performance across your entire enterprise.
Transform your business, starting with your sales leaders.
Unlock business impact from the top with executive coaching.
Foster a culture of inclusion and belonging.
Accelerate the performance and potential of your agencies and employees.
See how innovative organizations use BetterUp to build a thriving workforce.
Discover how BetterUp measurably impacts key business outcomes for organizations like yours.
A demo is the first step to transforming your business. Meet with us to develop a plan for attaining your goals.

- What is coaching?
Learn how 1:1 coaching works, who its for, and if it's right for you.
Accelerate your personal and professional growth with the expert guidance of a BetterUp Coach.
Types of Coaching
Navigate career transitions, accelerate your professional growth, and achieve your career goals with expert coaching.
Enhance your communication skills for better personal and professional relationships, with tailored coaching that focuses on your needs.
Find balance, resilience, and well-being in all areas of your life with holistic coaching designed to empower you.
Discover your perfect match : Take our 5-minute assessment and let us pair you with one of our top Coaches tailored just for you.

Research, expert insights, and resources to develop courageous leaders within your organization.
Best practices, research, and tools to fuel individual and business growth.
View on-demand BetterUp events and learn about upcoming live discussions.
The latest insights and ideas for building a high-performing workplace.
- BetterUp Briefing
The online magazine that helps you understand tomorrow's workforce trends, today.
Innovative research featured in peer-reviewed journals, press, and more.
Founded in 2022 to deepen the understanding of the intersection of well-being, purpose, and performance
We're on a mission to help everyone live with clarity, purpose, and passion.
Join us and create impactful change.
Read the buzz about BetterUp.
Meet the leadership that's passionate about empowering your workforce.

For Business
For Individuals
6 presentation skills and how to improve them

Jump to section
What are presentation skills?
The importance of presentation skills, 6 presentation skills examples, how to improve presentation skills.
Tips for dealing with presentation anxiety
Learn how to captivate an audience with ease
Capturing an audience’s attention takes practice.
Over time, great presenters learn how to organize their speeches and captivate an audience from start to finish. They spark curiosity, know how to read a room , and understand what their audience needs to walk away feeling like they learned something valuable.
Regardless of your profession, you most likely use presentation skills on a monthly or even weekly basis. Maybe you lead brainstorming sessions or host client calls.
Developing effective presentation skills makes it easier to contribute ideas with confidence and show others you’re someone to trust. Although speaking in front of a crowd sometimes brings nerves and anxiety , it also sparks new opportunities.
Presentation skills are the qualities and abilities you need to communicate ideas effectively and deliver a compelling speech. They influence how you structure a presentation and how an audience receives it. Understanding body language , creating impactful visual aids, and projecting your voice all fall under this umbrella.
A great presentation depends on more than what you say. It’s about how you say it. Storytelling , stage presence, and voice projection all shape how well you express your ideas and connect with the audience. These skills do take practice, but they’re worth developing — especially if public speaking makes you nervous.
Engaging a crowd isn’t easy. You may feel anxious to step in front of an audience and have all eyes and ears on you.
But feeling that anxiety doesn’t mean your ideas aren’t worth sharing. Whether you’re giving an inspiring speech or delivering a monthly recap at work, your audience is there to listen to you. Harness that nervous energy and turn it into progress.
Strong presentation skills make it easier to convey your thoughts to audiences of all sizes. They can help you tell a compelling story, convince people of a pitch , or teach a group something entirely new to them. And when it comes to the workplace, the strength of your presentation skills could play a part in getting a promotion or contributing to a new initiative.
To fully understand the impact these skills have on creating a successful presentation, it’s helpful to look at each one individually. Here are six valuable skills you can develop:
1. Active listening
Active listening is an excellent communication skill for any professional to hone. When you have strong active listening skills, you can listen to others effectively and observe their nonverbal cues . This helps you assess whether or not your audience members are engaged in and understand what you’re sharing.
Great public speakers use active listening to assess the audience’s reactions and adjust their speech if they find it lacks impact. Signs like slouching, negative facial expressions, and roaming eye contact are all signs to watch out for when giving a presentation.
2. Body language
If you’re researching presentation skills, chances are you’ve already watched a few notable speeches like TED Talks or industry seminars. And one thing you probably noticed is that speakers can capture attention with their body language.
A mixture of eye contact, hand gestures , and purposeful pacing makes a presentation more interesting and engaging. If you stand in one spot and don’t move your body, the audience might zone out.

3. Stage presence
A great stage presence looks different for everyone. A comedian might aim for more movement and excitement, and a conference speaker might focus their energy on the content of their speech. Although neither is better than the other, both understand their strengths and their audience’s needs.
Developing a stage presence involves finding your own unique communication style . Lean into your strengths, whether that’s adding an injection of humor or asking questions to make it interactive . To give a great presentation, you might even incorporate relevant props or presentation slides.
4. Storytelling
According to Forbes, audiences typically pay attention for about 10 minutes before tuning out . But you can lengthen their attention span by offering a presentation that interests them for longer. Include a narrative they’ll want to listen to, and tell a story as you go along.
Shaping your content to follow a clear narrative can spark your audience’s curiosity and entice them to pay careful attention. You can use anecdotes from your personal or professional life that take your audience along through relevant moments. If you’re pitching a product, you can start with a problem and lead your audience through the stages of how your product provides a solution.
5. Voice projection
Although this skill may be obvious, you need your audience to hear what you’re saying. This can be challenging if you’re naturally soft-spoken and struggle to project your voice.
Remember to straighten your posture and take deep breaths before speaking, which will help you speak louder and fill the room. If you’re talking into a microphone or participating in a virtual meeting, you can use your regular conversational voice, but you still want to sound confident and self-assured with a strong tone.
If you’re unsure whether everyone can hear you, you can always ask the audience at the beginning of your speech and wait for confirmation. That way, they won’t have to potentially interrupt you later.
Ensuring everyone can hear you also includes your speed and annunciation. It’s easy to speak quickly when nervous, but try to slow down and pronounce every word. Mumbling can make your presentation difficult to understand and pay attention to.

6. Verbal communication
Although verbal communication involves your projection and tone, it also covers the language and pacing you use to get your point across. This includes where you choose to place pauses in your speech or the tone you use to emphasize important ideas.
If you’re giving a presentation on collaboration in the workplace , you might start your speech by saying, “There’s something every workplace needs to succeed: teamwork.” By placing emphasis on the word “ teamwork ,” you give your audience a hint on what ideas will follow.
To further connect with your audience through diction, pay careful attention to who you’re speaking to. The way you talk to your colleagues might be different from how you speak to a group of superiors, even if you’re discussing the same subject. You might use more humor and a conversational tone for the former and more serious, formal diction for the latter.
Everyone has strengths and weaknesses when it comes to presenting. Maybe you’re confident in your use of body language, but your voice projection needs work. Maybe you’re a great storyteller in small group settings, but need to work on your stage presence in front of larger crowds.
The first step to improving presentation skills is pinpointing your gaps and determining which qualities to build upon first. Here are four tips for enhancing your presentation skills:
1. Build self-confidence
Confident people know how to speak with authority and share their ideas. Although feeling good about your presentation skills is easier said than done, building confidence is key to helping your audience believe in what you’re saying. Try practicing positive self-talk and continuously researching your topic's ins and outs.
If you don’t feel confident on the inside, fake it until you make it. Stand up straight, project your voice, and try your best to appear engaged and excited. Chances are, the audience doesn’t know you’re unsure of your skills — and they don’t need to.
Another tip is to lean into your slideshow, if you’re using one. Create something colorful and interesting so the audience’s eyes fall there instead of on you. And when you feel proud of your slideshow, you’ll be more eager to share it with others, bringing more energy to your presentation.
2. Watch other presentations
Developing the soft skills necessary for a good presentation can be challenging without seeing them in action. Watch as many as possible to become more familiar with public speaking skills and what makes a great presentation. You could attend events with keynote speakers or view past speeches on similar topics online.
Take a close look at how those presenters use verbal communication and body language to engage their audiences. Grab a notebook and jot down what you enjoyed and your main takeaways. Try to recall the techniques they used to emphasize their main points, whether they used pauses effectively, had interesting visual aids, or told a fascinating story.

3. Get in front of a crowd
You don’t need a large auditorium to practice public speaking. There are dozens of other ways to feel confident and develop good presentation skills.
If you’re a natural comedian, consider joining a small stand-up comedy club. If you’re an avid writer, participate in a public poetry reading. Even music and acting can help you feel more comfortable in front of a crowd.
If you’d rather keep it professional, you can still work on your presentation skills in the office. Challenge yourself to participate at least once in every team meeting, or plan and present a project to become more comfortable vocalizing your ideas. You could also speak to your manager about opportunities that flex your public speaking abilities.
4. Overcome fear
Many people experience feelings of fear before presenting in front of an audience, whether those feelings appear as a few butterflies or more severe anxiety. Try grounding yourself to shift your focus to the present moment. If you’re stuck dwelling on previous experiences that didn’t go well, use those mistakes as learning experiences and focus on what you can improve to do better in the future.
Tips for dealing with presentation anxiety
It’s normal to feel nervous when sharing your ideas. In fact, according to a report from the Journal of Graduate Medical Education, public speaking anxiety is prevalent in 15–30% of the general population .
Even though having a fear of public speaking is common, it doesn’t make it easier. You might feel overwhelmed, become stiff, and forget what you were going to say. But although the moment might scare you, there are ways to overcome the fear and put mind over matter.
Use these tactics to reduce your stress when you have to make a presentation:
1. Practice breathing techniques
If you experience anxiety often, you’re probably familiar with breathing techniques for stress relief . Incorporating these exercises into your daily routine can help you stop worrying and regulate anxious feelings.
Before a big presentation, take a moment alone to practice breathing techniques, ground yourself, and reduce tension. It’s also a good idea to take breaths throughout the presentation to speak slower and calm yourself down .
2. Get organized
The more organized you are, the more prepared you’ll feel. Carefully outline all of the critical information you want to use in your presentation, including your main talking points and visual aids, so you don’t forget anything. Use bullet points and visuals on each slide to remind you of what you want to talk about, and create handheld notes to help you stay on track.
3. Embrace moments of silence
It’s okay to lose your train of thought. It happens to even the most experienced public speakers once in a while. If your mind goes blank, don’t panic. Take a moment to breathe, gather your thoughts, and refer to your notes to see where you left off. You can drink some water or make a quick joke to ease the silence or regain your footing. And it’s okay to say, “Give me a moment while I find my notes.” Chances are, people understand the position you’re in.

4. Practice makes progress
Before presenting, rehearse in front of friends and family members you trust. This gives you the chance to work out any weak spots in your speech and become comfortable communicating out loud. If you want to go the extra mile, ask your makeshift audience to ask a surprise question. This tests your on-the-spot thinking and will prove that you can keep cool when things come up.
Whether you’re new to public speaking or are a seasoned presenter, you’re bound to make a few slip-ups. It happens to everyone. The most important thing is that you try your best, brush things off, and work on improving your skills to do better in your next presentation.
Although your job may require a different level of public speaking than your favorite TED Talk , developing presentation skills is handy in any profession. You can use presentation skills in a wide range of tasks in the workplace, whether you’re sharing your ideas with colleagues, expressing concerns to higher-ups, or pitching strategies to potential clients.
Remember to use active listening to read the room and engage your audience with an interesting narrative. Don’t forget to step outside your comfort zone once in a while and put your skills to practice in front of a crowd. After facing your fears, you’ll feel confident enough to put presentation skills on your resume.
If you’re trying to build your skills and become a better employee overall, try a communications coach with BetterUp.
Elevate your communication skills
Unlock the power of clear and persuasive communication. Our coaches can guide you to build strong relationships and succeed in both personal and professional life.
Elizabeth Perry, ACC
Elizabeth Perry is a Coach Community Manager at BetterUp. She uses strategic engagement strategies to cultivate a learning community across a global network of Coaches through in-person and virtual experiences, technology-enabled platforms, and strategic coaching industry partnerships. With over 3 years of coaching experience and a certification in transformative leadership and life coaching from Sofia University, Elizabeth leverages transpersonal psychology expertise to help coaches and clients gain awareness of their behavioral and thought patterns, discover their purpose and passions, and elevate their potential. She is a lifelong student of psychology, personal growth, and human potential as well as an ICF-certified ACC transpersonal life and leadership Coach.
The 11 tips that will improve your public speaking skills
The importance of good speech: 5 tips to be more articulate, show gratitude with “thank you for your leadership and vision” message examples, learn types of gestures and their meanings to improve your communication, why it's good to have a bff at work and how to find one, why we need to reframe potential into readiness, love them or hate them, meetings promote social learning and growth, what is a career path definition, examples, and steps for paving yours, goal-setting theory: why it’s important, and how to use it at work, similar articles, how to write a speech that your audience remembers, 8 tip to improve your public speaking skills, impression management: developing your self-presentation skills, 30 presentation feedback examples, your guide to what storytelling is and how to be a good storyteller, how to give a good presentation that captivates any audience, 8 clever hooks for presentations (with tips), how to make a presentation interactive and exciting, stay connected with betterup, get our newsletter, event invites, plus product insights and research..
3100 E 5th Street, Suite 350 Austin, TX 78702
- Platform Overview
- Integrations
- Powered by AI
- BetterUp Lead
- BetterUp Manage™
- BetterUp Care™
- Sales Performance
- Diversity & Inclusion
- Case Studies
- Why BetterUp?
- About Coaching
- Find your Coach
- Career Coaching
- Communication Coaching
- Life Coaching
- News and Press
- Leadership Team
- Become a BetterUp Coach
- BetterUp Labs
- Center for Purpose & Performance
- Leadership Training
- Business Coaching
- Contact Support
- Contact Sales
- Privacy Policy
- Acceptable Use Policy
- Trust & Security
- Cookie Preferences
21 Ways To Improve Your Presentation Skills
Published: April 07, 2023
You know the feeling of sitting through a boring presentation. A text distracts you. A noise outside pulls your gaze. Your dog begs for attention. By the time the presentation ends, you question why you needed to sit and listen in the first place.
Effective presentation skills can stop you from boring an audience to oblivion. Delivering strong presentations can help you stand out as a leader, showcase your expertise, and build confidence.
Table of contents:
- Presentation skills definition
- Importance of presentation skills
- How to improve presentation skills
- Effective presentation skills
- Presentation skills for executives
![development plan for presentation skills → Free Download: 10 PowerPoint Presentation Templates [Access Now]](https://no-cache.hubspot.com/cta/default/53/2d0b5298-2daa-4812-b2d4-fa65cd354a8e.png)
Presentation Skills Definition
Presentation skills include anything you need to create and deliver clear, effective presentations to an audience. This includes creating a compelling set of slides , ensuring the information flows, and keeping your audience engaged.
Speakers with strong presentation skills can perform the following tasks:
- Bring together different sources of information to form a compelling narrative
- Hook audiences with a strong beginning and end
- Ensure audiences engage with their content through questions or surveys
- Understand what their audience wants and needs from their presentation
Importance of Presentation Skills
At some point in your career, you will present something. You might pitch a startup to a group of investors or show your research findings to your manager at work. Those in leading or executive roles often deliver presentations on a weekly or monthly basis.
Improving your presentation skills betters different aspects of your working life, including the following:
Communication: Improving your presentation skills can make you a better communicator with your co-workers and friends.
Confidence: 75% of people fear public speaking. By working on your presentation skills, you can gain confidence when speaking in front of a crowd.
Creativity: You learn to understand how to use imagery and examples to engage an audience.
Management: Presentations involve pulling together information to form a succinct summary, helping you build project and time management skills.
How To Improve Presentation Skills
1. create an outline.
Before designing slides and writing a script, outline your presentation. Start with your introduction, segue into key points you want to make, and finish with a conclusion.
2. Practice, Practice, Practice
Almost 8 in 10 professionals practice their presentations for at least an hour. So, practice your presentation in the mirror or to a close friend.
3. Start With a Hook
When presenting, grab your audience with a hook. Consider starting with a surprising statistic or a thoughtful question before diving into the core information.
4. Stay Focused on Your Topic
You might want to cover everything under the sun, but information overload can overwhelm your audience. Instead, stay focused on what you want to cover. Aim for key points and avoid including unnecessary details.
5. Remember To Introduce Yourself
At the beginning of the presentation, introduce yourself. Kill any tension in the room by mentioning your name, your role, and any other helpful details. You could even mention a fun fact about yourself, putting the audience at ease.
6. Work on Your Body Language
55% of people look to nonverbal communication when judging a presentation. Straighten your back, minimize unnecessary gestures, and keep your voice confident and calm. Remember to work on these aspects when practicing.
7. Memorize Structure, Not Words
You might feel better knowing exactly what you want to say. But skip the script and stick to memorizing the key points of your presentation. For example, consider picking three to four phrases or insights you want to mention for each part of your presentation rather than line-by-line memorization.
8. Learn Your Audience
Before crafting a killer outline and slide deck, research your audience. Find out what they likely already know, such as industry jargon, and where they might need additional information. Remember: You're presenting for them, not you.
9. Reframe Your Anxiety as Excitement
A study conducted by Harvard Business School demonstrates that reframing your anxiety as excitement can improve performance. For example, by saying simple phrases out loud, such as “I’m excited,” you then adopt an opportunity-oriented mentality.
10. Get Comfortable With the Setting
If you plan to present in person, explore the room. Find where you’re going to stand and deliver your presentation. Practice looking into the seats. By decreasing the number of unknowns, you can clear your head and focus on the job.
11. Get Familiar With Technology
Presenting online has unique challenges, such as microphone problems and background noise. Before a Zoom presentation, ensure your microphone works, clean up your background, test your slides, and consider any background noise.
12. Think Positively
Optimistic workers enjoy faster promotions and happier lives. By reminding yourself of the positives — for example, your manager found your last presentation impressive — you can shake off nerves and find joy in the process.
13. Tell a Story
To engage your audience, weave storytelling into your presentation — more than 5 in 10 people believe stories hold their focus during a presentation. Consider ways to connect different parts of your slides into a compelling narrative.
14. Prepare for Questions
At the end of your presentation, your audience will likely have questions. Brainstorm different questions and potential answers so you’re prepared.
15. Maintain Eye Contact
Eye contact signals honesty. When possible, maintain eye contact with your audience. For in-person presentations, pay attention to each audience member. For online ones, stare at your camera lens as you deliver.
16. Condense Your Presentation
After you finish the first draft of your outline, think about ways to condense it. Short and sweet often keeps people interested instead of checking their phones.
17. Use Videos
Keep your audience’s attention by incorporating video clips when relevant. For example, videos can help demonstrate examples or explain difficult concepts.
18. Engage With Your Audience
Almost 8 in 10 professionals view presentations as boring. Turn the tide by engaging with your audience. Encourage audience participation by asking questions or conducting a live survey.
19. Present Slowly and Pause Frequently
When you get nervous, you talk faster. To combat this, remember to slow yourself down when practicing. Place deep pauses throughout your presentation, especially when transitioning between slides, as it gives you time to breathe and your audience time to absorb.
20. Start and End With a Summary
A summary at the start of a presentation can pique your audience’s interest. One at the end brings everything together, highlighting key points your audience should take with them.
21. Ask for Feedback
You will never deliver the perfect presentation, so ask for feedback. Talk to your managers about where you could improve. Consider surveying your audience for an unbiased look into your presentation skills.
Effective Presentation Skills
Effective presentation skills include communicating clearly, presenting with structure, and engaging with the audience.
As an example, say a content manager is presenting a quarterly review to their team. They start off with a summary. Their introduction mentions an unprecedented 233% growth in organic traffic — numbers their team has not seen in years. Immediately, the presenter grabs their team’s attention. Now, everyone wants to know how they achieved that in one quarter.
Alternatively, think of an entrepreneur delivering their pitch to a group of investors. They start with a question: How many of you struggle to stay awake at work? They then segue into an exciting product designed to improve the sleep quality of working professionals. Their presentation includes videos demonstrating the science behind sleep and surprising statistics about the demand for their product.
Both examples demonstrate effective presentation skills. They incorporate strong attention grabbers, summaries, and attempts to engage the audience.
Think back to strong presentations you viewed as an audience member. Ask yourself: What made them so memorable, and how can I incorporate those elements into my presentations?
Presentation Skills for Executives
Presentations take up a significant portion of an executive’s workload. Executives regularly showcase key company initiatives, team changes, quarterly and annual reviews, and more. Improving your presentation skills as a leader can help with different parts of your job, such as:
Trust: Delivering great, effective presentations can build trust between you and your team.
Confidence: Most people dread presentations — so a strong presenter projects the confidence needed by a leader.
Emotional intelligence: A great presentation taps into the audience’s perspectives, helping executives improve their emotional intelligence .
Expertise: Presentations help executives display their subject-matter expertise, making employees safe in their hands.
Delegation: At times, executives might need to pull information from different sources for a presentation — improving their ability to delegate as managers.
What did you think of this article?
Give Feedback

Don't forget to share this post!
Outline your company's sales strategy in one simple, coherent plan.
Powerful and easy-to-use sales software that drives productivity, enables customer connection, and supports growing sales orgs
Ideas and insights from Harvard Business Publishing Corporate Learning

Powerful and Effective Presentation Skills: More in Demand Now Than Ever

When we talk with our L&D colleagues from around the globe, we often hear that presentation skills training is one of the top opportunities they’re looking to provide their learners. And this holds true whether their learners are individual contributors, people managers, or senior leaders. This is not surprising.
Effective communications skills are a powerful career activator, and most of us are called upon to communicate in some type of formal presentation mode at some point along the way.
For instance, you might be asked to brief management on market research results, walk your team through a new process, lay out the new budget, or explain a new product to a client or prospect. Or you may want to build support for a new idea, bring a new employee into the fold, or even just present your achievements to your manager during your performance review.
And now, with so many employees working from home or in hybrid mode, and business travel in decline, there’s a growing need to find new ways to make effective presentations when the audience may be fully virtual or a combination of in person and remote attendees.
Whether you’re making a standup presentation to a large live audience, or a sit-down one-on-one, whether you’re delivering your presentation face to face or virtually, solid presentation skills matter.
Even the most seasoned and accomplished presenters may need to fine-tune or update their skills. Expectations have changed over the last decade or so. Yesterday’s PowerPoint which primarily relied on bulleted points, broken up by the occasional clip-art image, won’t cut it with today’s audience.
The digital revolution has revolutionized the way people want to receive information. People expect presentations that are more visually interesting. They expect to see data, metrics that support assertions. And now, with so many previously in-person meetings occurring virtually, there’s an entirely new level of technical preparedness required.
The leadership development tools and the individual learning opportunities you’re providing should include presentation skills training that covers both the evergreen fundamentals and the up-to-date capabilities that can make or break a presentation.
So, just what should be included in solid presentation skills training? Here’s what I think.
The fundamentals will always apply When it comes to making a powerful and effective presentation, the fundamentals will always apply. You need to understand your objective. Is it strictly to convey information, so that your audience’s knowledge is increased? Is it to persuade your audience to take some action? Is it to convince people to support your idea? Once you understand what your objective is, you need to define your central message. There may be a lot of things you want to share with your audience during your presentation, but find – and stick with – the core, the most important point you want them to walk away with. And make sure that your message is clear and compelling.
You also need to tailor your presentation to your audience. Who are they and what might they be expecting? Say you’re giving a product pitch to a client. A technical team may be interested in a lot of nitty-gritty product detail. The business side will no doubt be more interested in what returns they can expect on their investment.
Another consideration is the setting: is this a formal presentation to a large audience with questions reserved for the end, or a presentation in a smaller setting where there’s the possibility for conversation throughout? Is your presentation virtual or in-person? To be delivered individually or as a group? What time of the day will you be speaking? Will there be others speaking before you and might that impact how your message will be received?
Once these fundamentals are established, you’re in building mode. What are the specific points you want to share that will help you best meet your objective and get across your core message? Now figure out how to convey those points in the clearest, most straightforward, and succinct way. This doesn’t mean that your presentation has to be a series of clipped bullet points. No one wants to sit through a presentation in which the presenter reads through what’s on the slide. You can get your points across using stories, fact, diagrams, videos, props, and other types of media.
Visual design matters While you don’t want to clutter up your presentation with too many visual elements that don’t serve your objective and can be distracting, using a variety of visual formats to convey your core message will make your presentation more memorable than slides filled with text. A couple of tips: avoid images that are cliched and overdone. Be careful not to mix up too many different types of images. If you’re using photos, stick with photos. If you’re using drawn images, keep the style consistent. When data are presented, stay consistent with colors and fonts from one type of chart to the next. Keep things clear and simple, using data to support key points without overwhelming your audience with too much information. And don’t assume that your audience is composed of statisticians (unless, of course, it is).
When presenting qualitative data, brief videos provide a way to engage your audience and create emotional connection and impact. Word clouds are another way to get qualitative data across.
Practice makes perfect You’ve pulled together a perfect presentation. But it likely won’t be perfect unless it’s well delivered. So don’t forget to practice your presentation ahead of time. Pro tip: record yourself as you practice out loud. This will force you to think through what you’re going to say for each element of your presentation. And watching your recording will help you identify your mistakes—such as fidgeting, using too many fillers (such as “umm,” or “like”), or speaking too fast.
A key element of your preparation should involve anticipating any technical difficulties. If you’ve embedded videos, make sure they work. If you’re presenting virtually, make sure that the lighting is good, and that your speaker and camera are working. Whether presenting in person or virtually, get there early enough to work out any technical glitches before your presentation is scheduled to begin. Few things are a bigger audience turn-off than sitting there watching the presenter struggle with the delivery mechanisms!
Finally, be kind to yourself. Despite thorough preparation and practice, sometimes, things go wrong, and you need to recover in the moment, adapt, and carry on. It’s unlikely that you’ll have caused any lasting damage and the important thing is to learn from your experience, so your next presentation is stronger.
How are you providing presentation skills training for your learners?
Manika Gandhi is Senior Learning Design Manager at Harvard Business Publishing Corporate Learning. Email her at [email protected] .
Let’s talk
Change isn’t easy, but we can help. Together we’ll create informed and inspired leaders ready to shape the future of your business.
© 2024 Harvard Business School Publishing. All rights reserved. Harvard Business Publishing is an affiliate of Harvard Business School.
- Privacy Policy
- Copyright Information
- Terms of Use
- About Harvard Business Publishing
- Higher Education
- Harvard Business Review
- Harvard Business School
We use cookies to understand how you use our site and to improve your experience. By continuing to use our site, you accept our use of cookies and revised Privacy Policy .
Cookie and Privacy Settings
We may request cookies to be set on your device. We use cookies to let us know when you visit our websites, how you interact with us, to enrich your user experience, and to customize your relationship with our website.
Click on the different category headings to find out more. You can also change some of your preferences. Note that blocking some types of cookies may impact your experience on our websites and the services we are able to offer.
These cookies are strictly necessary to provide you with services available through our website and to use some of its features.
Because these cookies are strictly necessary to deliver the website, refusing them will have impact how our site functions. You always can block or delete cookies by changing your browser settings and force blocking all cookies on this website. But this will always prompt you to accept/refuse cookies when revisiting our site.
We fully respect if you want to refuse cookies but to avoid asking you again and again kindly allow us to store a cookie for that. You are free to opt out any time or opt in for other cookies to get a better experience. If you refuse cookies we will remove all set cookies in our domain.
We provide you with a list of stored cookies on your computer in our domain so you can check what we stored. Due to security reasons we are not able to show or modify cookies from other domains. You can check these in your browser security settings.
We also use different external services like Google Webfonts, Google Maps, and external Video providers. Since these providers may collect personal data like your IP address we allow you to block them here. Please be aware that this might heavily reduce the functionality and appearance of our site. Changes will take effect once you reload the page.
Google Webfont Settings:
Google Map Settings:
Google reCaptcha Settings:
Vimeo and Youtube video embeds:
You can read about our cookies and privacy settings in detail on our Privacy Policy Page.
How to make a great presentation
Stressed about an upcoming presentation? These talks are full of helpful tips on how to get up in front of an audience and make a lasting impression.

The secret structure of great talks

The beauty of data visualization

TED's secret to great public speaking

How to speak so that people want to listen

How great leaders inspire action

11 SMART Goals Examples for Your Public Speaking Skills
There might be affiliate links on this page, which means we get a small commission of anything you buy. As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases. Please do your own research before making any online purchase.
Public speaking is one of the most common fears. It is not easy to get on stage with people looking straight at you, and give a speech.
But by working on your public speaking skills, you can get better at it, and start to appear more comfortable when on stage.
One strategy that can help is to set SMART goals that provide milestones you can use to overcome the specific challenges you have related to public speaking.
So, in this article, we will briefly discuss what smart goals are, why they are important for public speaking, and finally we’ll look at 11 SMART goals that you can apply to improve your public speaking .
Let’s get to it.
Table of Contents
What Are SMART Goals?
If we don’t have a compass or a compass that is constantly spinning around, we will probably end up getting nowhere. SMART goals help us set a target and draw a roadmap to get there. The clearer our vision of the target, the easier it is for us to achieve them.
We hear about SMART Goals nearly every day; everyone talks about them. Setting goals is one of the most crucial steps to achieving what is important for you in life; they help us acknowledge and define our objectives, give us a sense of direction, and help us align our compass.
Not All Goals Are as SMART as They Seem
Have you ever made a list of vague goals that ended up in your drawer, never to see the light of day again? How about a list of goals about getting organized that you found in your huge pile of papers lying on the floor beside your desk?
According to Jack Canfield , an American author, “Vague goals lead to vague results.”
Take one common goal that many people set, chase them for a few days, and eventually give up on; “I want to be a better public speaker.” Before we get on stage and speak our hearts out, we need to have a specific objective. Being a better public speaker is a term that is too vague to be a SMART goal.
Without a precise and clearly defined objective, all our plans are likely to fail. SMART goals help us define our objective and allow us to focus on it. The acronym SMART expands into:
- S pecific: Must be narrowed down, focused, and clearly defined
- M easurable: Must have some quantitative factors that help track progress
- A ttainable: Must be achievable
- R elevant: Must be important and have a significant value in our life
- T ime-Bound: Must have a timeline and a deadline
If you are looking for a more detailed overview of SMART goals and how to set them with a few easy steps, then be sure to check out our step-by-step build for setting and achieving SMART goals.
Why SMART Goals Are Important for Public Speaking
Public speaking is a vast field. Setting a goal like “ I want to be a better public speaker ” is too vague to address and work on.
Every public speaker has some room for improvement. So if you want to get better at speaking in front of crowds, then you could set SMART goals that help you focus on:
- Confidently delivering the message
- Maintaining eye contact
- Stop using filler words such as um, ah, like, actually, etc.
- Improving body language
- Improving vocality
- Making your presentations more engaging
Each one of these goals will make you a better public speaker. Working on these more specific tasks will be much easier than working on a vague goal of becoming a better public speaker.

Public speaking is a skill that will take time and practice to improve. If your goals aren’t in the right order, you will not make much progress, exhaust yourself, and eventually give up. It is important to be specific with what you want to achieve.
So let’s dive into 11 examples of SMART goals you could set.
11 SMART Goals Examples for Public Speaking
1. improve stage confidence.
I want to improve my stage confidence and learn how to deliver my message more confidently. I will record my speeches and make it a habit to go over my presentations the next day and list all confidence flaws I find. I will try to eliminate them in my next presentation and aim to have less than five flaws in all my speeches by six months.
Specific: Improve stage confidence, and reduce confidence flaws to less than five
Measurable: The progress can be measured by counting the confidence flaws, and when the flaws drop below five, I will know that I have achieved the goal
Attainable: Using the recordings from the speeches, I can determine if the goal is attainable or not. Also, there is good room for error, and adequate time has been provided to practice and improve.
Relevant: I want to deliver the message more confidently because it will persuade more people. I will also feel better after presenting confidently.
Time-Bound: Since I have set a deadline for this goal, I know that I have to reduce the flaws to less than five in six months.
2. Overcome Stage Fright
I have a big presentation coming up in three months. I want to learn how to manage my nerves. I will practice speaking to small family audiences to overcome my nerves and increase my speech time from 3 minutes to 15 minutes by the end of two months.
Specific: Overcome stage fright and increase speech time to 15 minutes
Measurable: The progress can be measured by measuring the time I stayed on the stage
Attainable: With the help of the family audience, I will be able to speak more easily, and
Relevant: I have a big presentation coming up and want to do well in it
Time-Bound: I have set a timeline that I want to get comfortable by the end of two months and also increase my speech duration to 15 minutes by then.
3. Control Filler Words
I want to eliminate the use of filler words like uhh, umm, so, etc. I want to sound more confident on stage. I hope to minimize the usage of filler words by rehearsing my speech at least five times before delivering it. I plan to have a maximum of two filler words for every ten minutes of presentation by the end of four months .
Specific: Sound more confident by eliminating filler words
Measurable: The progress can be measured by counting the filler words in the speeches. When they are down to two for every ten minutes of speaking, the goal will be achieved
Attainable: With ample time, and room for error, the goal is made attainable
Relevant: I want to sound confident and not waste my efforts in preparing and delivering the speech
Time-Bound: The timeline is clearly defined at four months
4. Build Rapport with Audience
I want to refer less to my notes during my presentation because I would like to build a rapport with the audience. I will rehearse my speech six times before it is due in two weeks.
Specific: Build rapport with the audience, minimize the usage of notes, and rehearse the speech at least six times.
Measurable: The progress can be measured by counting the times I referred to the notes.
Attainable: With proper rehearsals and practice, it is attainable
Relevant: I would like to build a rapport with the audience and make a good impression.
Time-Bound: The timeline is clearly defined at two weeks.
5. Improve Posture
I want to improve my posture and look more confident when on stage. I have to stop myself from slouching when standing up during my presentation. I will consciously correct my posture every time I slouch over the next 30 days .
Specific: Stop slouching and maintain a good posture.
Measurable: The progress can be measured by checking the number of times I slouched during the speech. And also, by the number of times I had to correct my posture consciously.
Attainable: Since the slouching habit can be eliminated within a few days, this goal is attainable
Relevant: I want to look confident and leave a positive impression on the audience
Time-Bound: The timeline is defined as 30 days
6. Control Purposeless Movement
I want to control purposeless movement on stage as it distracts the audience. I will work with my friend and ask them to count the times they think I unintentionally fidgeted on stage. I want to control and eliminate purposeless movement with practice over the next ten presentations .
Specific: Control purposeless movement.
Measurable: The progress can be measured by checking the number of times I fidgeted or moved unintentionally on stage.
Attainable: With practice, purposeless movement can be eliminated, as many novice public speakers have done.
Relevant: I want to look confident and not speak to a distracted audience
Time-Bound: The timeline is ten presentations. This means that I hope to have significantly minimized purposeless movement by the time I start my eleventh.
7. Improve Audience Engagement
I want to improve the audience engagement by adding humor to my speech. After every ten minutes of my forty-minute presentation, I will add a joke to keep the audience alert and engaged.
Specific: Improve audience engagement
Measurable: The progress can be measured by checking the reaction of the audience and the number of times a joke was told during the presentation.
Attainable: Several speakers add humor to their presentations to keep the audience engaged
Relevant: I want to keep the audience engaged and not feel like a television or a radio.
Time-Bound: The timeline is defined as a joke every ten minutes during a forty-minute presentation
8. Improve Eye Contact
I want to improve my eye contact with the audience and improve my credibility. I will practice making eye contact with every audience member for five seconds. I will start by practicing with small audiences of 8-10 people and hope to be comfortable with larger audiences by six months.
Specific: Improve eye contact
Measurable: The progress can be measured by checking the number of times I stared blankly at the floor, ceiling, or wall. It can also be measured by the audience size that I am comfortable with
Attainable: Several speakers can make eye contact with their audience members. If they can, so can I.
Relevant: I want to improve my credibility with the audience
Time-Bound: The timeline is defined as six months’ worth of practice
9. Design Eye-catching Slides
I want to be able to design eye-catching and intriguing presentation slides. I plan to attend an online course on presentation design for two weeks and hope to make professional-looking slides by the end of the course.
Specific: Learn how to design eye-catching slides
Measurable: The progress can be measured by the number of days the course has been attended and also by comparing previous slides to ones after the course
Attainable: The goal is easy to attain
Relevant: I want to impress the audience and keep them intrigued with my presentations
Time-Bound: The timeline is defined with the course of two weeks
10. Improve Voice Modulation
I want to work on adding voice modulation to my speeches. My monotonous voice often causes the audience members to doze off. I will work with a public speaking coach for two months to learn and apply modulation. I will also keep an eye on the members dozing off to know how effective the coaching is.
Specific: Improve voice modulation and keep the audience alert.
Measurable: The progress can be measured by checking the number of audience members who doze off during the presentation and comparing it with previous presentations.
Attainable: The goal is easy to attain with a public speaking coach
Relevant: I want the audience to listen to what I am saying
Time-Bound: The timeline is two months to minimize the number of dozed-off audience members.
11. Improve Hand Gestures
I want to add emphasis to my speeches by adding proper hand gestures. I will take an online public speaking course to learn the skill. I will then record myself during rehearsals and on stage to determine how much I am improving during the course. I hope to be fluent with the gestures within four months .
Specific: Improve hand gestures
Measurable: The progress can be measured by checking the number of times hand gestures were used
Attainable: The goal is easy to attain with practice
Relevant: I want the audience to understand the importance of what I am saying
Time-Bound: The timeline is defined as four months.
Final Thoughts on SMART Goals for Public Speaking
Public speaking is a broad topic. So it’s essential to narrow down the areas you want to improve related to the current challenges you’re facing. Hopefully these 11 examples will provide that spark of inspiration for setting goals that will help you become a more effective public speaker.
Just remember that the key to accomplishing SMART goals is to have them written down and revisit them every day. To get started, you can use one of the SMART goal worksheets and templates that are provided on this page .
And if you want more SMART goal ideas and examples, be sure to check out these blog posts:
- 5 SMART Goal Examples for Your Musician Career
- 6 SMART Goals Examples for Event Coordinators
- 7 SMART Goals Examples for Churches or a Ministry
Finally, if you want to take your goal-setting efforts to the next level, check out this FREE printable worksheet and a step-by-step process that will help you set effective SMART goals .


- PRESENTATION SKILLS
Preparing for a Presentation
Search SkillsYouNeed:
Presentation Skills:
- A - Z List of Presentation Skills
- Top Tips for Effective Presentations
- General Presentation Skills
- What is a Presentation?
- Organising the Material
- Writing Your Presentation
- Deciding the Presentation Method
- Managing your Presentation Notes
- Working with Visual Aids
- Presenting Data
- Managing the Event
- Coping with Presentation Nerves
- Dealing with Questions
- How to Build Presentations Like a Consultant
- 7 Qualities of Good Speakers That Can Help You Be More Successful
- Self-Presentation in Presentations
- Specific Presentation Events
- Remote Meetings and Presentations
- Giving a Speech
- Presentations in Interviews
- Presenting to Large Groups and Conferences
- Giving Lectures and Seminars
- Managing a Press Conference
- Attending Public Consultation Meetings
- Managing a Public Consultation Meeting
- Crisis Communications
- Elsewhere on Skills You Need:
- Communication Skills
- Facilitation Skills
- Teams, Groups and Meetings
- Effective Speaking
- Question Types
Subscribe to our FREE newsletter and start improving your life in just 5 minutes a day.
You'll get our 5 free 'One Minute Life Skills' and our weekly newsletter.
We'll never share your email address and you can unsubscribe at any time.
Preparation is the single most important part of making a successful presentation. It is an absolutely crucial foundation, and you should dedicate as much time to it as possible, avoiding short-cuts. Good preparation will ensure that you have thought carefully about the messages that you want (or need) to communicate in your presentation and it will also help boost your confidence.
There are a number of aspects that you need to consider when preparing a presentation. They include the aim of the presentation, the subject matter, the audience, the venue or place, the time of day, and the length of the talk. All these will affect what you say and how you say it, as well as the visual aids that you use to get your point across.
The Objective
Whenever you are asked to give a presentation or speak to a group of people, you need to start by asking the purpose of the presentation.
In other words, what is the presentation expected to achieve, and what outcome(s) do the organisers and the audience expect?
These outcomes will shape your presentation, because it must be designed to achieve the objective and deliver the desired outcomes.
For example, you might be asked to give a talk to a gardening club. You might be told that the purpose of the talk is to fill a regular meeting slot, and that the members of the club have expressed a desire to learn more about pruning. You therefore know that your talk needs to be entertaining, fairly light, but knowledgeable, and that your audience wants to learn something new.
As you prepare your presentation, make sure you keep asking yourself:
“How is saying this going to help to achieve the objective and outcomes?”
The Subject
The subject of your presentation or talk about comes from the objective. They are linked, but they are not necessarily exactly the same thing.
For example:
The subject may be given to you by the organisation that has invited you (such as talking about pruning to the gardening club).
You may be knowledgeable in a particular field (perhaps you have an interest in local history).
The subject may be entirely your choice within certain limitations (you might, for example, be asked to give a presentation at an interview on a project which you feel has particularly developed your skills).
The Audience
Before preparing material for a presentation, it is worth considering your prospective audience.
Tailoring your talk to the audience is important and the following points should be considered:
The size of the group or audience expected.
The age range - a talk aimed at retired people will be quite different from one aimed at teenagers.
Gender - will the audience be predominantly male or female?
Is it a captive audience or will they be there out of interest?
Will you be speaking in their work or leisure time?
Do they know something about your subject already or will it be totally new to them? Is the subject part of their work?
Are you there to inform, teach, stimulate, or provoke?
Can you use humour and, if so, what would be considered appropriate? If you are in any doubt about this, it is probably best to avoid anything even remotely risqué.
It is important to have as much advance information as possible about the place where you are going to speak.
It can be helpful to arrange to see the venue before the event. It does much to quell fear if you can visualise the place while you are preparing your talk. However, even if you cannot visit, you will probably find it helpful to know:
The size of the room;
The seating arrangements (for example, theatre-style, with rows of seats; or round-table);
The availability of equipment, e.g., microphone, laptop and projector, flip chart;
The availability of power points and if an extension lead is required for any equipment you intend to use;
If the room has curtains or blinds. This is relevant if you intend to use visual aids, and so that you can ensure the correct ambiance for your presentation;
The position of the light switches. Check if you need someone to help if you are using audio/visual equipment and need to turn off the lights;
The likelihood of outside distractions, e.g., noise from another room; and
The availability of parking facilities so you do not have a long walk carrying any equipment you might need to take.
If this information is not available ahead of time, it will help to get there a bit early, to give you time to set up.
There will often be no flexibility in the time of day that a presentation is made. However, it does affect what you can do, and how you might organise your presentation, because of the likely state of your audience (see box).
How time of day can affect your audience
The morning is the best time to speak because people are generally at their most alert. However, as it gets towards lunch time, people begin to feel hungry and lose concentration. This is particularly true if the event has not included a coffee break.
After lunch, people often feel sleepy and lethargic. If you are given a slot immediately after lunch, it is a good idea to get your audience involved. A discussion or getting your audience moving about will work a lot better than simply presenting a lot of slides. A flip chart may also be a more useful tool than a laptop and projector, especially if it means you can open blinds and use natural light.
Towards the end of the afternoon, people again tend to lose concentration as they start to worry about getting home, the traffic or collecting children from school.
Evening or Weekend:
Outside regular office hours, people are more likely to be present because they want to be rather than because they have to be there. There is a better chance of audience attention in the evening. However, if the presentation goes on for too long, people may have to leave before you have finished. People will also be less tolerant of a poor presentation because you are in their time, not their employer’s.
Length of Talk
Always find out how long you have to talk and check if this includes or excludes time for questions.
Find out if there are other speakers and, if so, where you are placed in the running order. Never elect to go last. Beware of over-running, as this could be disastrous if there are other speakers following you.
It is important to remember that people find it difficult to maintain concentration for long periods of time. This is a good reason for making a presentation succinct, well-structured and interesting. Aim for 45 minutes as a maximum single-session presentation, and preferably leave at least 10 or 15 minutes for questions. Nobody minds finishing a session early.
Providing Information in Advance
Always check what information you will need to provide in advance.
Organisers of big events and conferences often like to have all the PowerPoint presentations several days ahead of the event. This gives them time to load all the presentations, and make sure that they are properly branded for the event.
Some events also need speakers’ biographies ahead of time, to put in conference literature. When you are asked to give the presentation, make sure you ask what is needed by when—and then supply it.
You will not be popular if you turn up on the day and announce that you have completely rewritten your presentation on the train. It is entirely possible that the organisers may even not be able to accommodate that, for example if the audio-visual is being supplied by a separate company or by the venue.
And finally…
Being asked to give a presentation is an honour, not a chore.
You are representing your organisation or yourself, if you are self-employed. You are also not there by right, but by invitation. It is therefore important that you put in the time and effort to ensure that you deliver what your audience wants. That way, you may just be invited back another time.
Continue to: Organising the Presentation Material
See also: Can Presentation Science Improve Your Presentation? Preparing for Oral Presentations Managing the Presentation Event Coping with Presentation Nerves

- Essential Business Writing
- Report Writing Courses
- Business Case Writing Courses
- Proposal Writing
- Presentation Skills
- Proposal / Bid Writer
- Business Plan Writer
- Business Case Writer
- Testimonials
- How to Write Highly Effective Business Cases
How To Develop Effective Presentation Skills

Presentations are an essential component of business communication . They are the means of pitching a service or product, revealing findings, or presenting an idea. Taking time to learn and apply the secrets of effective presentation skills gives you the best chance of raising the quality of your presentations to the exceptional. Learn how to become highly effective at writing professional business cases with our business writing courses as well.
This guide outlines the components of presentation skills and how you can learn to deliver messages superbly. From essential planning to developing content, to ending a presentation, here are a set of rules to ensure that you get significant advantage from your presentation skills set.
Number one tip
Confidence and control, effective presentation skills, logistics – how to prepare for a presentation, infographic - do’s & don’ts of presenting, number one tip.
Without doubt, the number one ingredient for a great presentation, is content. Without great content, you cannot produce a great presentation. Quite simply, content is king.
Content also gives you confidence to cope with presentation nerves. Consequently, content is where you need to start. Clarify your objectives and work out the material you need to achieve them.
So, here is what you need to do to deliver the best presentation possible.

Clarify your objectives
You need to be clear about what you want to achieve. Do you want audience opinion on whether to proceed with something? Are you seeking approval to spend money? Are you seeking audience views? Whatever your objectives, they need to be crystal clear, and your presentation needs to be designed – step by step – to achieve them.
Produce content
Divide your presentation into a beginning, a middle, and an end. The audience needs to be clear why they should listen to you from your very first sentence. Ensure that you make a strong start, and make it benefit related. People buy benefits whether of a service, product or an idea.
Slides should be used as signposts
Cluttered slides distract and get in the way of the message. Slides should be signposts and nothing more. They are not for information – that is your job as the presenter.
Work out your key messages
Each part of your presentation must have a theme to support your objectives. Ensure that your messages are simple to understand and to remember.
Produce an audience-inspiring first sentence
The purpose of your first sentence is to sell your second sentence and so on. Ensure that your first sentence is the most interesting, dramatic and inspiring thing you can say about your topic at that time. Then detail the benefits your audience will receive by listening to you and hearing your proposition.
Summarise with an audience-inspiring last sentence
The end of your presentation should refer to your objectives at the beginning. Summarise your proposition – back it up with credibility statements – reaffirm the benefits and conclude with whatever is appropriate to meet those objectives.
Know your set up – where you will be standing and where your audience will be sitting
Familiarisation with the venue is an obvious help – it is not always possible, but when it is, take advantage.
Engage with your audience
Check their reaction to what you are saying so that you know whether to elaborate, slow down or move on.
Focus on your key messages
Make sure that you get your messages across. Simplicity leads to clarity.
Don’t turn your back to the audience to refer to your slides
Amateur presenters often turn their backs to look at slides. Refer to slides by all means but always face forward and always look at the audience.
Given your content excellence, you have nothing to fear. Be confident and fearless – smile, engage with your audience and deliver.
Back To Contents
Confidence and control comes from presentation content, preparation and practice. Like learning a language or a sport, or driving a car, the better your theory and the more practice you take, the better your ability – and in this case the better your capability of how to give a good presentation.
Work out probable audience questions, and prepare complete answers. If you need to know facts and figures, have them to hand. Ask yourself questions throughout each stage of your presentation that the audience might ask. Try Why, Who, When, Where and Why. A narrative which delivers complete information instead of begging questions will give your presentation an air of justifiable professionalism.

Getting attention
A successful presentation or presenter engages with their audience through interesting content applicable to audience needs.
To connect with your audience, you need to start a presentation with an impactful set of words. Your beginning needs to grab attention, attract, and motivate your audience to pay attention to what comes next.
You could start a presentation by showing an image, giving a statistic, asking a question, or by delivering a notable quote. Whatever you show, say, or deliver, ensure it connects to your theme and to your objectives.
Communicating your message
The aim of a presentation is to get your message to resonate with the audience. Great presentation skills and delivering your message effectively is based on content. There is no substitute for great content however good your presentation style.
Concentrate on your core message and keep it simple. Depending on presentation styles, you can learn how to give a great presentation by using a combination of words, voice and body language. All play a vital role in communicating messages.

The Do's of Effective Presentations

Giving a presentation is about presenting content, and the success of a presentation is about how well you sell your content to your audience. If you’re new at delivering presentations, then there are a couple of key do’s you should apply to achieve the most effective presentation techniques.
Practice makes perfect
As well as increasing confidence and helping to calm initial nerves, undertake your own presentation training by practicing beforehand.
Learn how to give a good presentation by running through your slides or notes numerous times and checking your timing.
Introduce yourself
Let your audience know who you are, why you qualified to talk about the subject, and what they will learn by listening to you.
Eye contact
Get your audience engaged – smile and make eye contact.
Use handouts and slides. If you want people to view a chart – it’s easier to read as a handout rather than from a screen. It also helps keep your audience more engaged with your presentation if they have something to do.
Ask questions
Invite your audience to ask questions to help them get involved and to give you feedback. Of course, you may wish to leave that invitation until the end of your presentation.
The Don'ts of Effective Presentations

To ensure that you give a good presentation in terms of delivery, avoid:
Speaking too fast
Slow down your speed of delivery – speaking too fast means people won’t be able to catch everything you are saying.
Reading out loud
People can read a sentence about 4 times more quickly than someone can read the same sentence aloud. Do not read from your slides. In any case, remember slides should be signposts for your audience and nothing more.
Saying 'um'
Practice your answers so that you won’t be caught out. If you want time to think, compliment the questioner on the quality of their good question.
Focus instead.
Logistics - How To Prepare For A Presentation
Whether it’s learning how to prepare a PowerPoint presentation for a job interview or how to make a business presentation:

- Have your slides on a backup USB stick and email yourself a copy.
- Check the room you will be presenting in.
- Find out as much as you can about your audience.
- Dress appropriately for your audience - if in doubt always dress up.
- Print handouts and have them with you.
Infographic - Do's & Don'ts of Presenting
Take a look at some of the Do’s and Don’ts of presenting with the below infographic, created by Walkerstone.com , and channel your nerves to positive effect. The infographic outlines in a clear step-by-step design the do’s of presenting and the don’ts of presenting, some statistics around communicating your message, keeping the attention of your audience, as well as some useful considerations to remember for your presentation.
Use this infographic as a preparation checklist for your presentation and you’ll feel more confident and prepared, come across as a professional speaker which hopefully will result in a successful outcome. If you like what you see, feel free to share the infographic on your own site (crediting Walkerstone.com) and help spread these useful tips for presenting…

Share this Image On Your Site

- Explore courses
- Hire a business writer
- HTML Sitemap
01252 792 270

Walkerstone Limited, Registered office: Sheaves House, Birch Close, Boundstone, Farnham GU10 4TJ. Company number: 06514619. VAT number: 944 1865 05 By using this site, you agree we can set and use cookies. For details of these cookies and how to disable them, click to read our cookie policy | Terms Visit the Walkerstone blog for latest tips and guidance on business writing courses.
- 800-232-LOWE (5693)
- [email protected]
- 58220 Decatur Road, Cassopolis, MI 49031
How to Develop Powerful Presentation Skills
Digital library > building and inspiring an organization > presentations and presentation skills, “how to develop powerful presentation skills”.
Giving a presentation can be a terrifying experience, whether you will be in front of a few people or a packed house. Learn techniques to deal with an audience, control nervousness, and handle yourself with poise and confidencet
Giving a presentation can be a terrifying experience whether you will be in front of a few people or a packed house. This Business Builder will take you step-by-step through the process of developing an effective presentation from choice of a topic and organization of materials through the final question and answer period. You will learn how to deal with an audience, control nervousness and handle yourself with poise and confidence.
WHAT YOU SHOULD KNOW BEFORE GETTING STARTED [ top ]
Why Do You Need Powerful Presentation Skills?
To be able to give presentations with confidence, competence and clarity
To develop and use factual, logical and interesting supporting material
To use non-verbals to add power to your presentation
To control nervousness
To answer questions effectively
How Will You Recognize Your Success?
You will gain a greater sense of personal confidence and security in your ability to present
You will improve your ability to speak to a wide range of groups in different settings
You will enhance your opportunities for career advancement or promotion by achieving higher visibility in your company or community
Watch Out For…
Letting your fear of public speaking prevent you from giving your best presentation
Boring your audience by giving them information they don’t need or is not geared to their level of knowledge
THE PROCESS OF DEVELOPING POWERFUL PRESENTATION SKILLS [ top ]
Any public speaking situation is made up of four major components:
Each affects the other. If a speech is well written, yet the delivery unpolished, it takes away from you the speaker achieving your purpose. If you can’t communicate your message, it does not matter how brilliant that message is. If you don’t know your audience, you will not be able to tailor your message to meet their expectations. If the occasion is celebratory and your speech is serious, you may find yourself in an uncomfortable situation.
The Audience
Even before beginning preparation of your speech, it is essential to know whom you will be talking to. An analysis of the audience will often dictate the approach that you will take in writing your speech. An audience of senior executives will differ greatly from a group of new hires. In the same way that you design products for the consumer, you will design speeches for the specific audience you want to reach.
What do you need to know about the audience?
What is the size of the audience?
Why are they there — required attendance or voluntary?
What are their demographics — age level, educational differences, sex?
Besides the logistical and demographic data, information about your audience’s feelings toward you, your speech, the occasion, and your purpose can directly affect your chances for success. There are five basic types of audiences that you will encounter:
The uninformed audience — when people are unfamiliar with a topic, they generally try to associate it with something they do know about. They will probably have no preconceived attitude toward the subject. In this situation, your goal is to inform your audience so they will have an understanding of this new information.
The apathetic audience — may be indifferent or not care to become involved. You will need to study your audience carefully to determine the nature of their indifference.
The favorable audience — people who support either you personally or your attitude and beliefs. You can’t take a supportive audience for granted; however, you can assume areas of agreement. In this situation, you must look for ways to reinforce existing attitudes and to mobilize participants.
The hostile audience — sometimes the audience will be hostile either to you, your position on a topic or both. You should begin with a friendly position — look for areas of agreement. Try to establish yourself as an honorable person. Answer the audience’s objections to your proposal with valid reasons and reliable information.
The effective speaker tries to gather as much audience data as possible before, during and after the speech. Before the speech gather your information from program organizers, organizational literature, newspaper stories, casual contacts and office personnel. During your speech your best source of information will be the non-verbal (sometimes verbal) cues given by the audience. After your speech you can sometimes remain a few minutes and ask audience members how they liked it.
The Occasion
The occasion will help you determine your subject matter. If it is to be a presentation to generate new business for your company, then you will most likely be part of a team, and have a very specific subject to speak about. If your audience has been forced to assemble and has no idea that your talk is to be about cutbacks and layoffs, then you need to plan enough time for a question-and-answer period. Know exactly what the occasion is before you begin to prepare your presentation.
You will also need to find out about the facility you will be speaking in — what kind of equipment will be supplied (VCR, slide projector, overhead projector, easel, flip chart) and what you will need to supply yourself. It is up to you as the speaker to make sure all necessary arrangements are made and to arrive early enough to ensure everything is set up to your satisfaction, or to make any needed adjustments.
Creating, writing, and delivering an effective speech involves following ten steps: They are:
STEP 1 — Type of Speech
You first need to determine what type of speech you are going to give. There are three types:
The Informative Speech:
contains new and useful information
instructs the audience
motivates the audience to learn the information
The Persuasive Speech
gets your audience to take action
changes their attitudes or beliefs
The Entertaining Speech
is best left to professional speakers or humorists
As business owners you won’t likely be giving entertaining speeches. Therefore, we will focus the Business Builder on informative and persuasive speeches. Once you have chosen the type of speech you will be giving, the next step is to choose your subject and begin preparation.
STEP 2 — Develop a Central Theme
Instead of trying to cram everything there is to know about your subject into your presentation, be selective. Make a list of the key pints you want to cover, eliminating the superficial.
For example, instead of giving a general presentation on "Government Cutback," your presentation might be on "How Reductions in Government Spending Are Hurting the Small Business Owner."
STEP 3 — Collect the Data
Research your topic so that you know everything you possibly can about the subject. Do not include all this information in your speech but be prepared for the questions that will follow at the end of your presentation.
STEP 4 — Select a Method of Organization
The method should reflect the type of speech you have chosen:
Informative Speech
If you will be providing the audience with new information, choose one of these methods:
Chronological order — time of occurrence or time sequence (could use a visual aid showing a time span from start to finish to help the audience see the big picture).
Spatial order — pertains to the nature of space
For example, if you are speaking about how to set up an in-store display area, explain where in the store the display will go and how it will relate to other displays within the store). Visual aids will help the audience see what you are describing and remember what you have told them.
Geographical order — similar to spatial order but may include the use of maps. If your information is too difficult to see using slides or overheads, consider including a map in a handout to be given to the audience.
Topical order — takes a large topic and breaks it down into sub-topics. For example, if your subject is the automotive industry, you could break it down into specific automobile manufacturers or even further into types of vehicles (i.e., trucks, cars, motorcycles).
Comparison and contrast — compares characteristics, features and qualities that are similar and contrasts their differences. For example, you might compare one type computer with another type of computer discussing both their similarities and differences and why you would recommend one over the other.
Characteristics of an Informative Speech
To be effective, your informative speech should have four characteristics:
Contains new and useful information for the audience — if the information isn’t new to the audience, and has no benefit, it does not perform the function of informing at all. The speech should instruct, not merely help an audience pass the time pleasantly.
Helps the audience understand and retain information. Facts should be organized in a systematic way that helps people take the information in, assimilate it, and retain it. A well-organized speech helps communicate instructions. For example, in describing how to ensure that a meeting is effective, you could inform your audience of the responsibilities of a leader before, during, and after the meeting.
Presents the information in an appealing way. Just because the information of your speech is important to the audience and is well organized, does not mean that your speech will be received favorably. A cookbook can provide a lot of information on how to prepare foods, but a chef such as the Frugal Gourmet can take following a recipe and make it into an exciting experience. He adds the dynamics of his personality to the information to make his audience want to run into their kitchens and cook.
Tips on an Informative Speech
Give small amounts of information, repeat your key points several times during your speech; stress the principles. Generalizations and major concepts are better comprehend and retained than are details or specifics. The better the generalizations are, the better the content will be retained. If you must give a large number of details, make printed copies of the information and distribute them. If you overload your audience with details, they will tune out.
Persuasive Speech
When you want your audience to take action or change their attitudes, choose one of these methods:
Motivated Sequence. This is a well-known sales technique. It makes the audience aware of a need for change or creates that need. This format is best described as that used by television infomercials where a speaker uses testimonials by people who have used the product or displays dramatic "before-and-after" photographs. It grabs the audience’s attention, expresses a need and shows how that need can be satisfied.
For example, in a talk about the value of routine car check-ups, you point out the consequences of not addressing a problem in it’s early stages: "You notice a strange noise when starting your car but don’t take it in to the shop. Several days later your car breaks down on the highway causing you to be late for work and holding up other drivers as well. Had you taken your car in for its 60,000 mile check-up you wouldn’t have been stranded."
For example, in a speech about "How Corner Markets Can Operate With The Big Guys," the owner explained. "Our store has lost 15% of our business to the new supermarket on Main Street. I believe we can gain back some of that share by using a combination of double-coupons and special family shopping discount days to encourage store patronage."
For example, in a speech about including exercise in your daily routine, one fitness expert pointed out that if you exercise three or more times every week, your risk for heart attack will be reduced by 50%. Then, he used the body of his speech to support this proposition.
Method of Persuasion
Before you can persuade your audience to do or think what you want them to, you must understand them and plan your strategy.Are they uninformed, apathetic, hostile or favorable? Turning an audience around if their attitudes and beliefs are set is unlikely. You should settle, instead, for a chance to speak your piece and hope that they will give you a fair hearing. It is unrealistic to expect to change their minds with just one speech no matter how convincing you are.
To persuade your audience, you have three options:
Persuading through the factual presentation of information (statistics, documentation, supporting evidence, hard facts)
Persuading through basic social, biological, physiological needs, wants and desires
In most cases of successful persuasion, all three methods are mixed in varying degrees, depending on the speaker’s analysis of his audiences, or his character, and his style.
Planning Your Persuasive Speech
When preparing your persuasive speech, divide a piece of paper into four columns:
1. In the first column, decide whether you want to motivate, convince, or call to action. By writing down your purpose, you will be able to measure your success at the end of your speech and make adjustments, if necessary.
2. The second column, audience, is a brief summary of everything you have learned about your audience. You will need to understand your audience to plan your strategy and be effective when presenting to them. If you realize that you will be dealing with a hostile audience, you may want to change to an informative speech since your chances of changing opinions in one speech are limited.
3. Your third column should list the sources you will be using to compile you information. The data should be current, accurate, relevant and useful. Be straightforward and credible.
4. The last column is organization. As mentioned earlier, there are four options for organization. Decide which is best for your purpose, then decide on your approach. For example:
Proposition to proof. State your proposition at the beginning of your speech to let the audience know what you want them to think or do. Then prove your proposition with three to five points of evidence and an emotional appeal. Finally, review your evidence and give a memorable closing.
Problem to solution. State the problem and offer the solution from your point of view. Spend time developing your definition of the problem. Follow with your solution and present three to five points and supporting material. Sum up with a memorable statement.
Reflective. Start with a problem and prove that it exists. Establish the selection criteria for the solution. Define the solutions that you are discounting, proving with facts that only your solution is the right one.
Now you are ready to do the formal outline of your speech!
STEP 5 — How to Outline Your Speech
Why should you outline your speech rather than write it out completely? When you write out a speech, the tendency is to read it. That cuts down on audience rapport. It also locks you into what you have written without giving you the freedom to adapt to the audience or other speakers. Speaking from an outline lets you be spontaneous yet well organized. It ensures that your speech has form and direction. It is a tool for planning and will give you a visual representation of ideas and data through which you will inform, persuade or entertain your audience.
General Guidelines for Developing an Outline
Write your specific purpose at the top to serve as a reminder of what you expect to accomplish.
Make your outline long enough and detailed enough to remind you of the ideas, points, and data you want to present.
Don’t make your outline too long — it is not a manuscript. Don’t make your outline too generalized. Generalized subject headings have little value.
Use phrases rather than single words or complete sentences.
Use only the top 2/3 of a page to avoid making you put your head down to read further down the page.
Plan transitions from one topic to another so your speech will flow smoothly. Write them down.
Your speech can be on any subject, but your outline should follow this format (Note: Details on introduction, body, and conclusion are covered in Steps 6, 7, and 9.):
Here is an example of a speech outline:
Audience: Philadelphia School Board Association
Speech Purpose: After my speech the audience will agree that schools should guarantee their instruction.
TRANSITION: We can guarantee learning when we understand how it works.
TRANSITION: There are successful examples of these guaranteed learning agreements in our community.
Now that you know how to outline your speech, you next need to know the proper way to introduce it.
STEP 6 — How to Introduce Your Speech
A strong introduction is vital to the success of your presentation because it can win over your audience immediately. Your introduction should serve four major purposes:
Get the attention of the audience and arouse their interest.
Preview the theme, basic idea, subject or main points of your speech.
Establish your credentials.
Establish a climate of good will and develop audience rapport.
Let the audience know when you will be taking their questions.
The Introduction
Without the attention and interest of your audience, you can’t accomplish your purpose. You have a challenge to make the audience want to listen. Here’s how:
Ask a question. For example: "If you had your life to live over again, what would you change?"
State an unusual fact. "Today more people see popular television programs than have seen all the stage performances of Shakespeare’s plays in the more than 400 years since he was born."
Give an illustration, example or story. "Last night I was walking home from the library when I noticed a woman’s purse lying on the ground. As I leaned over to pick it up,…"
Present a quotation. "The human brain is a wonderful thing. It operates from the moment you’re born until the first time you get up to make a speech." Make sure the quote is relevant.
Refer to a historic event. "On this day, more than half a century ago, the United States…"
The Transition
Now that you have your audience’s attention, you need to design a way to get from your attention-getter to your preview. This transition need only be a phrase or a sentence where you suggest the relationship between your opening and your preview. Here are some examples:
"That true story illustrates the need for the new tax proposal I want to suggest to you tonight."
"Those are the shocking facts of what’s happening in some hospitals. Now what can be done about them? Let me offer some suggestions."
The Preview
This part of your speech should be very clear, specific, and precise. Possible techniques:
State the point of your speech, the central idea, your viewpoint, or subject. This should be very brief and direct.
For example: "So today I want to talk with you about the problem of waste in the welfare program." or
For example: "Travel is good because it is educational, economical, and everlasting." or
When introducing your speech…
Start with the attention-getter. In some instances, you may first give a brief greeting.
Be confident in your attitude. Step up with confidence; speak out loudly and clearly; move with assurance; sound authoritative, be pleasant; and exude positive energy.
Get set before you start to speak. Once you’ve begun your speech, you don’t want to arrange your notes, test or adjust the microphone, or move the lectern.
Be alert to tie in your attention-getter with the remarks of the previous speakers, other parts of the program or the person who introduces you. Although the introduction is, in most cases, the smallest part of your presentation, it is critical. It is your job, as you start your speech, to turn that daydreaming, diverse group of individuals into a concentrating, stimulated, involved, thinking and participating audience.
STEP 7 — The Body of Your Speech
In the body of your speech, you will develop the points that you previewed in your introduction. In developing these ideas, organize your materials in a way that the audience will find easy to follow. People have a need for logic. You can provide this by selecting a method of organization that your audience can understand. If you look at organization as though it were a map, you will understand that there are different approaches you can take to get from the beginning point to the conclusion. Your audience and your subject will determine which route you will take.
For example, if your topic is travel within the United States, you could use the comparison and contrast method. "When traveling in the United States you have a range of options to reach your destination. You could fly, take the train, drive, or even take a boat. Let’s look at these options one-by-one."
STEP 8 — Supporting Materials
Using supporting materials effectively in a speech will not guarantee selling a bad idea, but using data effectively can increase the likelihood of your listeners accepting ideas of merit.
Supporting materials can be used to
Supporting materials can be of many types:
example. Can be used to clarify, add interest or make memorable, but not to validate.
story. A story is an account of an event or incident. People like to hear about the experiences of others, but don’t ramble on.
quotation. A quote is a statement by someone who is usually authoritative or experienced on the subject. Essentially the value of a quotation depends largely on the source — on a reputation as knowledgeable, objective, and honest.
definition. A definition is a statement of the meaning of the word or idea. In a speech, using a definition can help prove a point, but is usually presented to make a point more understandable. The major value of a definition is to establish a common basis for views.
comparison and contrast. A comparison presents characteristics, features, and qualities that are similar; a contrast presents differences. They help clarify the unknown by referring to the known.
statistics. You can increase the effectiveness of statistics by comparing the figure with some other fact known to the audience or easily comprehended by the audience.
audio/visual aids. This can be a recording, slide, overhead, diagram, model, etc. They allow you to present your case through an additional communication channel with your audience.
STEP 9 — The Conclusion
The conclusion to your presentation should be presented in two sections — a review and a memorable statement. In these, your objectives are to:
Emphasize the point of your speech
Climax your speech
Leave the audience remembering your speech
Tips on Conclusions
Summarize your points. In a few words, present a brief, an abstract, or viewpoint of your speech.
Repeat your main points. Repeat or rephrase the two to five main points you presented in the body of your speech.
Combine a summary with repetition of key facts.
Present a memorable statement. You can select from the same techniques you used for getting the audience’s attention in the introduction of your speech.
Return to the theme of your attention-getter. This is particularly effective in closing. Use the same story or quote that you used earlier, but now with a different ending or an additional line, insight or explanation. If your opening attention-getter was "How many of you have experienced symptoms of stage fright when giving a presentation?" then the close could be, "Remember, your goal is to turn those feelings of fear into anticipation and excitement."
Look to the future. Pointing to the future invites your audience to consider, explore and think further about your subject.
Do’s and Don’ts for Effective Conclusions
Work on your conclusion carefully, it is the last thing your audience will remember.
Don’t:
Merely stop at the end of your material. Bring your speech to a smooth polished ending. Your speech should have unity and a conclusion should bring it all together.
Stretch it out. Get to the point, summarize and finish.
Continue to speak as you leave the lectern.
Introduce any new points.
Suggestions for Effective Conclusions
It should take 10% or less of your speech’s total time.
It should be consistent with the rest of your speech.
STEP 10 — Handling the Q & A’s:
After you conclude, it will be time to open the floor to your audience by asking for questions.
If there are no questions, be sure you have prepared some in advance.
Step out from behind the podium or lectern to encourage your audience to participate.
Restate or rephrase each question so the audience can hear/understand it.
When repeating the question, look at the questioner; when answering, look at the entire audience.
Try to extract the substance of the question. Don’t get tied up in the details with a "rambler."
Answer briefly.
Anticipate questions in advance.
If you don’t know an answer, say you will find out and get back to the person.
Never get into a sparring match with a hostile questioner.
When confronted with a "stage hog" who asks question after question, answer the initial questions, then cut him off by asking him to write his questions down and meet you after the presentation in order to give others the opportunity to ask questions.
Always answer even hostile questions politely.
If an expert is in the audience, you may refer a question to him but then take back control by thanking him and moving on to the next question.
THE SPEAKER
As the speaker, you will be the center of attention. For most people, that can be an uncomfortable experience leading to physical as well as emotional symptoms of stress. Successful speakers harness that stress and turn it into a feeling of excitement and anticipation. You, too, can become a more confident and relaxed presenter by using these time-tested techniques:
Before or during your speech, your mouth or throat may become dry because you are nervous or because talking brings in air which dries your mouth. Drinking room-temperature water with lemon will keep you from going dry.
If you are unsure how to present yourself, remember to SOFTEN :
O pen Stance
F orward Lean
T one of voice is warm and professional
E ye contact with different members of the audience
N odding to convey understanding and to keep things positive
As the speaker, you can strengthen your message with visual signal and delivery techniques. Choose your clothing to enhance your presentation. Ask the person who has scheduled you to speak what the audience will most likely be wearing and what would be appropriate for you to wear. For business presentations, a suit conveys more authority than a sports coat or blazer for men. A conservative dress or suit is appropriate for a woman. Wear colors that compliment you and jewelry that is inconspicuous.
Posture is a highly visual element of your speech. Often, unpracticed speakers will sway or rock at the podium. Avoid this by standing with your feet spread four to eight inches apart, parallel to each other and pointed straight ahead. Flex your knees and put your weight on the balls of your feet. The space and symmetry of this position will stop any swaying or rocking motion. Keep your posture open. Crossing your arms may be perceived as being defensive. Keep your arms relaxed and hanging down at you side when you are not using them to gesture.
It is important to move when you speak, but avoid pacing. Take at least two steps and get back into position. Use movement to establish contact with people in different parts of the room. You many even want to walk to the back of the room occasionally, depending on the purpose of your presentation.
Gestures should be spontaneous and should support your delivery. Use them sparingly to emphasize your major points.
Varying your pitch will put interest in your presentation. Research has indicated that the deeper the pitch of you voice the longer people will listen to you. Also, control the volume of your voice — too soft or too loud will not be as effective as a mix. Vary your tempo as well. A normal speaking rate is 120-160 words per minute. Some regions of the U.S. have varying speaking rates; you may want to "mirror" the preference of the region in which you are speaking. Also, slow down for people whose primary language is not English. Avoid speaking in a monotone voice.
Use simple, clear, colorful, descriptive language. Keep your sentences short. Avoid using buzz words and jargon. Avoid tag questions. These are questions at the end of a sentence that give the impression that you are unsure of what you just said or that you are looking for approval.
For example, "I think this proposal will work to make our profits soar, don’t you?" The "don’t you" weakens your position and undermines your statement.
If your aim is to encourage comments, ask an independent question.
Common Fears and How to Deal with Them
Fainting is a relatively rare occurrence, almost never experienced by someone in front of an audience. You may think you are going to faint, but it rarely happens. If you feel light-headed, it may be because you are breathing too quickly or at a shallow level. The best way to stop this feeling is to take controlled deep breaths. Before your presentation take a few minutes to take some deep breaths and try to relax.
Boring the audience. If you approach speaking as an audience-centered sport, you will seldom need to worry about boring your audience. You do have the responsibility to provide your audience with useful information geared to their level of knowledge. If you have chosen material that interests them and have backed it up with the facts and figures needed to give credibility, there is no reason for them to be bored. To strengthen your presentation include stories and anecdotes to illustrate your points and entertain the audience.
Having your mind go blank does sometimes happen. When it does, the best way to deal with it is to simply pause, look at your notes or outline and try to pick up again or move on to your next thought. Don’t be afraid to use your notes to help you get back on track. If you mistake a fact and realize it, correct it while you still can. Use humor if you feel comfortable with it. Once you recognize your mistake, correct it, then continue on with your presentation.
Fear of being judged is usually a result of our own judgments of other speakers. You may have noticed a speaker who is dressed inappropriately, uses the same word repeatedly or waves his hands in the air. This makes us fear that we, too, will be judged critically. Most of us are harder on ourselves than others. If you are well prepared, have practiced your presentation, enjoy your subject and can communicate it well to your audience, minor imperfections will most likely go unnoticed.
Becoming a polished speaker takes time, but it is a skill that can be learned. Anyone can become an exceptional speaker by preparing adequately and by observing others to discover what works and what doesn’t. You can acquire new skills along the way and eliminate your weaknesses. Critique yourself after every speaking opportunity to decide what you can change and what you have to live with. Figure out how to compensate for the things you cannot change. Use every opportunity you can to speak because the more you do it, the better you become.
And finally, Practice, Practice, Practice.
CHECKLIST [ top ]
___ What do you need to know about the audience?
___ The size?
___ Required attendance or voluntary?
___ What are their demographics?
___ List the five basic types of audiences you will encounter.
___ Determine your subject matter.
___ Do you know what the occasion is?
___ What type of speech are you going to give?
___ Have you developed a central theme?
___ Have you selected a method of organization?
___ Have you outlined your speech?
___ Follow the general guidelines for developing an outline.
___ Follow a format when doing your outline.
___ Is your introduction strong?
___ Make sure your speech is clear, specific, and precise.
___ Does the body of your speech develop the points that you previewed in your introduction?
___ Do you have supporting materials?
___ Is your conclusion presented in two sections?
___ After you conclude, be prepared to open the floor to your audience for discussion.
The Speaker
___ Relax and PRACTICE, PRACTICE, PRACTICE
RESOURCES [ top ]
How to Give a Terrific Presentation by Karen Kalish. (AMACOM, 1997).
High-Impact Presentations: A Multimedia Approach by Jo Robbins. (Wiley, 1997).
101 Ways to Captivate a Business Audience by Sue Gaulke. (American Management Association, 1997).
Loud and Clear: How to Prepare and Deliver Effective Business and Technical Presentations , 4th ed. by George L. Morrisey et al. (Addison-Wesley, 1997).
Say It with Presentations: How to Design and Deliver Successful Business Presentations by Gene Zelazny. (McGraw-Hill, 2000).
Writer: Marjorie Brody
All rights reserved. The text of this publication, or any part thereof, may not be reproduced in any manner whatsoever without written permission from the publisher.
How to Create a Personal Development Plan: 3 Examples

For successful change, it is vital that the client remains engaged, recognizing and identifying with the goals captured inside and outside sessions. A personal development plan (PDP) creates a focus for development while offering a guide for life and future success (Starr, 2021).
This article introduces and explores the value of personal development plans, offering tools, worksheets, and approaches to boost self-reflection and self-improvement.
Before you continue, we thought you might like to download our three Goal Achievement Exercises for free . These detailed, science-based exercises will help you or your clients create actionable goals and master techniques to create lasting behavior change.
This Article Contains
What is personal development 7 theories, coaching in personal development and growth, how to create a personal development plan, 3 examples of personal development plans, defining goals and objectives: 10 tips and tools, fostering personal development skills, 3 inspiring books to read on the topic, resources from positivepsychology.com, a take-home message, frequently asked questions.
Personal development is a fundamental concept in psychology and encompasses the lifelong process of self-improvement, self-awareness, and personal growth. Crucial to coaching and counseling, it aims to enhance various aspects of clients’ lives, including their emotional wellbeing, relationships, careers, and overall happiness (Cox, 2018; Starr, 2021).
Several psychological models underpin and support transformation. Together, they help us understand personal development in our clients and the mechanisms and approaches available to make positive life changes (Cox, 2018; Passmore, 2021).
The following psychological theories and frameworks underpin and influence the approach a mental health professional adopts.
1. Maslow’s hierarchy of needs
As a proponent of the humanistic or person-centered approach to helping people, Abraham Maslow (1970) suggested that individuals have a hierarchy of needs. Simply put, they begin with basic physiological and safety needs and progress through psychological and self-fulfillment needs.
Personal development is often found in or recognized by the pursuit of higher-level needs, such as self-esteem and self-actualization (Cox, 2018).
2. Erikson’s psychosocial development
Erik Erikson (1963) mapped out a series of eight psychosocial development stages that individuals go through across their lifespan.
Each one involves challenges and crises that once successfully navigated, contribute to personal growth and identity development.
3. Piaget’s cognitive development
The biologist and epistemologist Jean Piaget (1959) focused on cognitive development in children and how they construct their understanding of the world.
We can draw on insights from Piaget’s stages of cognitive development, including intellectual growth and adaptability, to inform our own and others’ personal development (Illeris, 2018).
4. Bandura’s social cognitive theory
Albert Bandura’s (1977) theory highlights the role of social learning and self-efficacy in personal development. It emphasizes that individuals can learn and grow through observation, imitation, and belief in their ability to effect change.
5. Self-determination theory
Ryan and Deci’s (2018) motivational self-determination theory recognizes the importance of autonomy, competence, and relatedness in personal development.
Their approach suggests that individuals are more likely to experience growth and wellbeing when such basic psychological needs are met.
6. Positive psychology
Positive psychology , developed by Martin Seligman (2011) and others, focuses on strengths, wellbeing, and the pursuit of happiness.
Seligman’s PERMA model offers a framework for personal development that emphasizes identifying and using our strengths while cultivating positive emotions and experiences (Lomas et al., 2014).
7. Cognitive-Behavioral Theory (CBT)
Developed by Aaron Beck (Beck & Haigh, 2014) and Albert Ellis (2000), CBT explores the relationship between thoughts, emotions, and behavior.
As such, the theory provides practical techniques for personal development, helping individuals identify and challenge negative thought patterns and behaviors (Beck, 2011).
Theories like the seven mentioned above offer valuable insights into many of the psychological processes underlying personal development. They provide a sound foundation for coaches and counselors to support their clients and help them better understand themselves, their motivations, and the paths they can take to foster positive change in their lives (Cox, 2018).

The client–coach relationship is significant to successful growth and goal achievement.
Typically, the coach will focus on the following (Cox, 2018):
- Actualizing tendency This supports a “universal human motivation resulting in growth, development and autonomy of the individual” (Cox, 2018, p. 53).
- Building a relationship facilitating change Trust clients to find their own way while displaying empathy, congruence, and unconditional positive regard . The coach’s “outward responses consistently match their inner feelings towards a client,” and they display a warm acceptance that they are being how they need to be (Passmore, 2021, p. 162).
- Adopting a positive psychological stance Recognize that the client has the potential and wish to become fully functioning (Cox, 2018).
Effective coaching for personal growth involves adopting and committing to a series of beliefs that remind the coach that the “coachee is responsible for the results they create” (Starr, 2021, p. 18) and help them recognize when they may be avoiding this idea.
The following principles are, therefore, helpful for coaching personal development and growth (Starr, 2021).
- Stay committed to supporting the client. While initially strong, you may experience factors that reduce your sense of support for the individual’s challenges.
- Coach nonjudgmentally. Our job is not to adopt a stance based on personal beliefs or judgment of others, but to help our clients form connections between behavior and results.
- Maintain integrity, openness, and trust. The client must feel safe in your company and freely able to express themselves.
- Responsibility does not equal blame. Clients who take on blame rather than responsibility will likely feel worse about something without acknowledging their influence on the situation.
- The client can achieve better results. The client is always capable of doing and achieving more, especially in relation to their goals.
- Focus on clients’ thoughts and experiences. Collaborative coaching is about supporting the growth and development of the client, getting them to where they want to go.
- Clients can arrive at perfect solutions. “As a coach, you win when someone else does” (Starr, 2021, p. 34). The solution needs to be the client’s, not yours.
- Coach as an equal partnership. Explore the way forward together collaboratively rather than from a parental or advisory perspective.
Creating a supportive and nonjudgmental environment helps clients explore their thoughts, feelings, and goals, creating an environment for personal development and flourishing (Passmore, 2021).

Download 3 Free Goals Exercises (PDF)
These detailed, science-based exercises will help you or your clients create actionable goals and master techniques for lasting behavior change.
Download 3 Free Goals Pack (PDF)
By filling out your name and email address below.
- Email Address *
- Your Expertise * Your expertise Therapy Coaching Education Counseling Business Healthcare Other
- Comments This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
A personal development plan is a powerful document “to create mutual clarity of the aims and focus of a coaching assignment” (Starr, 2021, p. 291). While it is valuable during coaching, it can also capture a client’s way forward once sessions have ended.
Crucially, it should have the following characteristics (Starr, 2021):
- Short and succinct
- Providing a quick reference or point of discussion
- Current and fresh, regularly revised and updated
Key elements of a personal development plan include the following (Starr, 2021):
- Area of development This is the general skill or competence to be worked on.
- Development objectives or goals What does the client want to do? Examples might include reducing stress levels, improving diet, or managing work–life balance .
- Behaviors to develop These comprise what the client will probably do more of when meeting their objectives, for example, practicing better coping mechanisms, eating more healthily, and better managing their day.
- Actions to create progress What must the client do to action their objectives? For example, arrange a date to meet with their manager, sign up for a fitness class, or meet with a nutritionist.
- Date to complete or review the objective Capture the dates for completing actions, meeting objectives, and checking progress.
Check out Lindsey Cooper’s excellent video for helpful guidance on action planning within personal development.
We can write and complete personal development plans in many ways. Ultimately, they should meet the needs of the client and leave them with a sense of connection to and ownership of their journey ahead (Starr, 2021).
- Personal Development Plan – Areas of Development In this PDP , we draw on guidance from Starr (2021) to capture development opportunities and the behaviors and actions needed to achieve them.
- Personal Development Plan – Opportunities for Development This template combines short- and long-term goal setting with a self-assessment of strengths, weaknesses, and development opportunities.
- Personal Development Plan – Ideal Self In this PDP template , we focus on our vision of how our ideal self looks and setting goals to get there.
“The setting of a goal becomes the catalyst that drives the remainder of the coaching conversation.”
Passmore, 2021, p. 80
Defining goals and objectives is crucial to many coaching conversations and is usually seen as essential for personal development.
Check out this video on how you can design your life with your personal goals in mind.
The following coaching templates are helpful, containing a series of questions to complete Whitmore’s (2009) GROW model :
- G stands for Goal : Where do you want to be?
- R stands for Reality : Where are you right now with this goal?
- O stands for Options : What are some options for reaching your goal?
- W stands for Way forward : What is your first step forward?
Goal setting creates both direction and motivation for clients to work toward achieving something and meeting their objectives (Passmore, 2021).
The SMART goal-setting framework is another popular tool inside coaching and elsewhere.
S = Specific M = Measurable A = Attainable/ or Agreed upon R = Realistic T = Timely – allowing enough time for achievement
The SMART+ Goals Worksheet contains a series of prompts and spaces for answers to define goals and capture the steps toward achieving them.
We can summarize the five principles of goal setting (Passmore, 2021) as follows:
- Goals must be clear and not open to interpretation.
- Goals should be stretching yet achievable.
- Clients must buy in to the goal from the outset.
- Feedback is essential to keep the client on track.
- Goals should be relatively straightforward. We can break down complex ones into manageable subgoals.
The following insightful articles are also helpful for setting and working toward goals.
- What Is Goal Setting and How to Do it Well
- The Science & Psychology of Goal-Setting 101

1. People skills
Improving how we work with others benefits confidence, and with other’s support, we are more likely to achieve our objectives and goals. The following people skills can all be improved upon:
- Developing rapport
- Assertiveness and negotiation
- Giving and receiving constructive criticism
2. Managing tasks and problem-solving
Inevitably, we encounter challenges on our path to development and growth. Managing our activities and time and solving issues as they surface are paramount.
Here are a few guidelines to help you manage:
- Organize time and tasks effectively.
- Learn fundamental problem-solving strategies.
- Select and apply problem-solving strategies to tackle more complex tasks and challenges.
- Develop planning skills, including identifying priorities, setting achievable targets, and finding practical solutions.
- Acquire skills relevant to project management.
- Familiarize yourself with concepts such as performance indicators and benchmarking.
- Conduct self-audits to assess and enhance your personal competitiveness.
3. Cultivate confidence in your creative abilities
Confidence energizes our performance. Knowing we can perform creatively encourages us to develop novel solutions and be motivated to transform.
Consider the following:
- Understand the fundamentals of how the mind works to enhance your thinking skills.
- Explore a variety of activities to sharpen your creative thinking.
- Embrace the belief that creativity is not limited to artists and performers but is crucial for problem-solving and task completion.
- Learn to ignite the spark of creativity that helps generate innovative ideas when needed.
- Apply creative thinking techniques to enhance your problem-solving and task completion abilities.
- Recognize the role of creative thinking in finding the right ideas at the right time.
To aid you in building your confidence, we have a whole category of articles focused on Optimism and Mindset . Be sure to browse it for confidence-building inspiration.
With new techniques and technology, our understanding of the human brain continues to evolve. Identifying the vital elements involved in learning and connecting with others offers deep insights into how we function and develop as social beings. We handpicked a small but unique selection of books we believe you will enjoy.
1. The Coaching Manual: The Definitive Guide to the Process, Principles and Skills of Personal Coaching – Julie Starr

This insightful book explores and explains the coaching journey from start to finish.
Starr’s book offers a range of free resources and gives clear guidance to support new and existing coaches in providing practical help to their clients.
Find the book on Amazon .
2. The Big Leap: Conquer Your Hidden Fear and Take Life to the Next Level – Gay Hendricks

Delving into the “zone of genius” and the “zone of excellence,” Hendricks examines personal growth and our path to personal success.
This valuable book explores how we eliminate the barriers to reaching our goals that arise from false beliefs and fears.
3. The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You’re Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You Are – Brené Brown

Brown, a leading expert on shame, vulnerability, and authenticity, examines how we can engage with the world from a place of worthiness.
Use this book to learn how to build courage and compassion and realize the behaviors, skills, and mindset that lead to personal development.
We have many resources available for fostering personal development and supporting client transformation and growth.
Our free resources include:
- Goal Planning and Achievement Tracker This is a valuable worksheet for capturing and reflecting on weekly goals while tracking emotions that surface.
- Adopt a Growth Mindset Successful change is often accompanied by replacing a fixed mindset with a growth one .
- FIRST Framework Questions Understanding a client’s developmental stage can help offer the most appropriate support for a career change.
More extensive versions of the following tools are available with a subscription to the Positive Psychology Toolkit© , but they are described briefly below:
- Backward Goal Planning
Setting goals can build confidence and the skills for ongoing personal development.
Backward goal planning helps focus on the end goal, prevent procrastination, and decrease stress by ensuring we have enough time to complete each task.
Try out the following four simple steps:
- Step one – Identify and visualize your end goal.
- Step two – Reflect on and capture the steps required to reach the goal.
- Step three – Focus on each step one by one.
- Step four – Take action and record progress.
- Boosting Motivation by Celebrating Micro Successes
Celebrating the small successes on our journey toward our goals is motivating and confidence building.
Practice the following:
- Step one – Reflect momentarily on the goal you are working toward.
- Step two – Consider each action being taken to reach that goal.
- Step three – Record the completion of each action as a success.
- Step four – Choose how to celebrate each success.
If you’re looking for more science-based ways to help others reach their goals, check out this collection of 17 validated motivation & goal achievement tools for practitioners. Use them to help others turn their dreams into reality by applying the latest science-based behavioral change techniques.

17 Tools To Increase Motivation and Goal Achievement
These 17 Motivation & Goal Achievement Exercises [PDF] contain all you need to help others set meaningful goals, increase self-drive, and experience greater accomplishment and life satisfaction.
Created by Experts. 100% Science-based.
Personal development has a rich and long history. It is underpinned by various psychological theories and remains a vital aspect of creating fulfilling lives inside and outside coaching and counseling.
For many of us, self-improvement, self-awareness, and personal growth are vital aspects of who we are. Coaching can provide a vehicle to help clients along their journey, supporting their sense of autonomy and confidence and highlighting their potential (Cox, 2018).
Working with clients, therefore, requires an open, honest, and supportive relationship. The coach or counselor must believe the client can achieve better results and view them nonjudgmentally as equal partners.
Personal development plans become essential to that relationship and the overall coaching process. They capture areas for development, skills and behaviors required, and goals and objectives to work toward.
Use this article to recognize theoretical elements from psychology that underpin the process and use the skills, guidance, and worksheets to support personal development in clients, helping them remove obstacles along the way.
Ultimately, personal development is a lifelong process that boosts wellbeing and flourishing and creates a richer, more engaging environment for the individual and those around them.
We hope you enjoyed reading this article. Don’t forget to download our three Goal Achievement Exercises for free .
Personal development is vital, as it enables individuals to enhance various aspects of their lives, including emotional wellbeing, relationships, careers, and overall happiness.
It promotes self-awareness, self-improvement, and personal growth, helping individuals reach their full potential and lead fulfilling lives (Passmore, 2021; Starr, 2021).
Personal development is the journey we take to improve ourselves through conscious habits and activities and focusing on the goals that are important to us.
Personal development goals are specific objectives individuals set to improve themselves and their lives. Goals can encompass various areas, such as emotional intelligence, skill development, health, and career advancement, providing direction and motivation for personal growth (Cox, 2018; Starr, 2021).
A personal development plan typically comprises defining the area of development, setting development objectives, identifying behaviors to develop, planning actions for progress, and establishing completion dates. These five stages help individuals clarify their goals and track their progress (Starr, 2021).
- Bandura, A. (1977). Social learning theory . Prentice-Hall.
- Beck, A. T., & Haigh, E. P. (2014). Advances in cognitive therapy and therapy: The generic cognitive model. Annual Review of Clinical Psychology , 10 , 1–24.
- Beck, J. S. (2011). Cognitive behavior therapy: Basics and beyond . Guilford Press.
- Cottrell, S. (2015). Skills for success: Personal development and employability . Bloomsbury Academic.
- Cox, E. (2018). The complete handbook of coaching . SAGE.
- Ellis, A. (2000). Can rational emotive behavior therapy (REBT) be effectively used with people who have devout beliefs in God and religion? Professional Psychology-Research and Practice , 31 (1), 29–33.
- Erikson, E. H. (1963). Youth: Change and challenge . Basic Books.
- Illeris, K. (2018). An overview of the history of learning theory. European Journal of Education , 53 (1), 86–101.
- Lomas, T., Hefferon, K., & Ivtzan, I. (2014). Applied positive psychology: Integrated positive practice . SAGE.
- Maslow, A. H. (1970). Motivation and personalit y (2nd ed.). Harper & Row.
- Passmore, J. (Ed.). (2021). The coaches’ handbook: The complete practitioner guide for professional coaches . Routledge.
- Piaget, J. (1959): The Psychology of intelligence . Routledge.
- Rose, C. (2018). The personal development group: The students’ guide . Routledge.
- Ryan, R. M., & Deci, E. L. (2018). Self-determination theory: Basic psychological needs in motivation, development, and wellness . Guilford Press.
- Seligman, M. E. (2011). Authentic happiness using the new positive psychology to realize your potential for lasting fulfillment . Nicholas Brealey.
- Starr, J. (2021). The coaching manual: The definitive guide to the process, principles and skills of personal coaching . Harlow: Pearson Education.
- Whitmore, J. (2009). Coaching for performance . Nicholas Brealey.
Share this article:
Article feedback
Let us know your thoughts cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Related articles

Personal Development Goals: Helping Your Clients Succeed
In the realm of personal development, individuals often seek to enhance various aspects of their lives, striving for growth, fulfillment, and self-improvement. As coaches and [...]

How to Perform Somatic Coaching: 9 Best Exercises
Our bodies are truly amazing and hold a wellspring of wisdom which, when tapped into, can provide tremendous benefits. Somatic coaching acknowledges the intricate connection [...]

Training in Lifestyle Coaching: 8 Best Certifications and Courses
What makes the Wizard of Oz storyline so compelling? Maybe it’s that we relate to Dorothy’s struggle and her feelings of being stuck, lost, and [...]
Read other articles by their category
- Body & Brain (50)
- Coaching & Application (57)
- Compassion (26)
- Counseling (51)
- Emotional Intelligence (24)
- Gratitude (18)
- Grief & Bereavement (21)
- Happiness & SWB (40)
- Meaning & Values (26)
- Meditation (20)
- Mindfulness (45)
- Motivation & Goals (45)
- Optimism & Mindset (34)
- Positive CBT (29)
- Positive Communication (20)
- Positive Education (47)
- Positive Emotions (32)
- Positive Leadership (18)
- Positive Parenting (4)
- Positive Psychology (33)
- Positive Workplace (37)
- Productivity (17)
- Relationships (46)
- Resilience & Coping (37)
- Self Awareness (21)
- Self Esteem (38)
- Strengths & Virtues (32)
- Stress & Burnout Prevention (34)
- Theory & Books (46)
- Therapy Exercises (37)
- Types of Therapy (64)
More From Forbes
20 strategies for introverts to improve their presentation skills.
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
Working in business development requires a high level of personal interaction, which can be challenging for people who are naturally introverted. Along with one-on-one meetings, business development leaders often make presentations, a medium where it can be more difficult to create connections with audience members.
Below, 20 members of Forbes Business Development Council share their advice on how introverts can improve their presentation skills. By making time to prepare, utilizing visual aids and leaning into their natural strengths, introverts can showcase their knowledge and make a lasting impression on their audience.
1. Practice Your Presentation
Introverted biz dev leaders can enhance presentation skills by practicing in low-pressure settings, focusing on their strengths and preparing thoroughly. They can also utilize storytelling and active listening to engage audiences, build rapport and make meaningful connections, ultimately driving better results for their bottom line. - Dr. Saju Skaria , Digitech Services
2. Focus On Building Connections
“Supercommunicators,” as introduced by Charles Duhigg, prioritize connection over mere extroversion or polished presentation skills. They excel at building rapport, demonstrating genuine care and asking insightful questions. To enhance your presentation skills, focus on your audience’s interests and find meaningful ways to connect. - Quyen Pham , Releady
3. Showcase Your Passion
Introverted leaders can significantly improve their presentation skills by harnessing their emotional qualities. They should focus on the passion behind their ideas and connect emotionally with the audience. Visualizing success and truly believing in their perspective can turn nervous energy into the most amazing presentations, making genuine connections with their teams. - Jacob Collins , Collins Ecom
‘Outlander’ Finally Comes To Netflix With An Incredible New Season
300 billion perfect storm bitcoin price crash under 60 000 suddenly accelerates as ethereum xrp and crypto brace for shock fed flip, the top 10 richest people in the world may 2024, 4. be prepared by planning ahead.
Here are some strategies through which introverted biz dev leaders can improve their presentation skills: 1. Prepare and practice; 2. Focus on strengths; 3. Utilize visual aids; 4. Engage the audience; 5. Practice active listening; 6. Build authentic connections; 7. Seek feedback and continuous improvement and 8. Leverage technology. - Nandhakumar Purushothaman , Mphasis Limited
5. Be Genuine To Connect With Your Audience
I am an introvert, and a piece of advice that stayed with me was to remember that I was an expert on the topic that I was speaking on. Take a deep breath and look at the experience and expertise that you bring to the table. You are of value. If the topic is interesting to you, then it's likely it will be for others. Be yourself; people connect with those who are genuine. - Sheila Halvorson , Harvest Revenue Group LLC
Forbes Business Development Council is an invitation-only community for sales and biz dev executives. Do I qualify?
6. Draw On Your Personal Experiences
If you are a business development professional and consider yourself an introvert, consider yourself lucky. Your strengths have already overshadowed your perceived weakness in your journey to becoming a professional. Harness your inner introvert power and use it for good. Create presentations that include personal experiences that will resonate with the people you are looking to connect with. - Jason Holden , Akkerman
7. Use Technology To Practice
Introverts may not want to practice presentations in front of their peers or managers. Instead, they can use technology to practice speaking and presentations in a self-paced, bite-size manner. Several AI-powered enablement platforms allow leaders to practice talking points, record themselves and receive AI-generated feedback on their tone, word choice, message delivery and more. - Hayden Stafford , Seismic
8. Focus On Your Strengths
For introverts, preparation is key to success. They have to prepare, prepare, prepare and leverage their inner strengths. So, if someone is passionate about what they do but is introverted, they should focus their presentation on the areas that make that passion come alive. By leaning into those strengths, introverts become more confident and can more easily articulate their ideas. - Wayne Elsey , The Funds2Orgs Group
9. Discover Your Communication Style
Introverted business development leaders can improve their presentation skills by tapping into insights provided by "Human Design" and aligning with one's natural energy patterns. For example, "Projectors" excel when they wait for invitations to share their insights, while "Reflectors" benefit from allowing themselves time to process information, which helps them make more meaningful connections. - Bryce Welker , The CPA Exam Guy
10. Find Opportunities To Hear Feedback
By appraising the total skills to deduce the biz dev resource requirements, diverse team members can enhance team presentation skills. Daily standup for the progress check would be helpful for the introverted leaders because the diverse characters from the team members will create ideas and take charge of the roles in each step to help the biz dev leaders improve their pitch. - Gyehyon Andrea Jo , MVLASF
11. Reduce Presentation Pressure With Small Groups
Introverted leaders should focus on one-on-one or small group interactions, where they're likely to feel more comfortable and can make deeper connections. These settings can be more conducive to building the trust and relationships essential for business development success. Utilizing visual aids and technology can also help by diverting some attention away from the speaker. - Saurabh Choudhuri , SAP
12. Lean On Your Listening Skills
Play to your strengths—thoughtful insights, grounding energy, focused approach and good listening skills. As an introverted leader, you can listen for what's being said (and more importantly, what is not being said) in client and business meetings to drive growth for clients. Introverted biz dev leaders then collaborate effectively to solve client pain points. This creates a win-win situation. - Archana Rao , Innova Solutions
13. Apply Storytelling Techniques
Leveraging deep industry insights, introverted biz dev leaders can hone their presentation skills by focusing on clarity, storytelling and data visualization. Personalizing interactions, even in large settings, fosters stronger connections. By mastering these techniques, they can significantly enhance their impact, driving tangible improvements in their organization's bottom line. - Rahul Saluja , Cyient
14. Stay Focused On Your Audience
Excellent presentations require the presenter to focus on the needs of the recipient, not just the needs of the presenter. Be prepared and rehearse your presentation extensively. During the presentation, manage your anxiety by breathing deeply and building rapport with the audience. - Julie Thomas , ValueSelling Associates
15. Ask Questions For Audience Engagement
Active listening is key. Even when you're presenting to a room full of people, communication is two-way, so listening intently to your audience by asking them thoughtful questions is a tremendous way to foster engagement. This also makes the presentation more of a discussion and could help the introverted leader feel more comfortable and at ease. - Ben Elder , Simpplr
16. Solicit Feedback To Find Ways To Improve
Introverted biz dev leaders can boost presentation skills by thoroughly preparing, leveraging strengths like listening, practicing in smaller groups, using visual aids for engaging storytelling and seeking constructive feedback for continuous improvement. These steps enhance connection and impact. - Tina Gada , Vanguard Group
17. Integrate Visual Aids For Impact
In my experience, introverted leaders are deep thinkers and can be dynamic, thought-provoking presenters. What makes them successful is preparing thoroughly, practicing, using visual aids, engaging the audience and seeking networking opportunities. These strategies help build confidence, deliver compelling presentations and foster meaningful connections to their audience. - Scotty Elliott , AmeriLife
18. Have Confidence In Your Expertise
Focus on the fact that this is not a personal situation, and your main goal is to share your know-how or experience with others. Remember what your skill set is and the added value you bring. Your presentation should not be focused on you and your ego, but on the knowledge you bring to the business world. If you realize the value you bring to others, your introverted preoccupations will go away. - Anna Jankowska , RTB House
19. Train Your Presentation 'Muscles'
My first corporate job out of college was a sales role and I was terrified. I took an improv class to help me think on my feet. If improv classes aren't an option, practice, practice, practice. Record yourself giving an important presentation and critique it. Your ability to communicate is your superpower, and you need to train it like you would any other muscle. - Ashleigh Stanford , PracticeTek
20. Explore Different Ways To Engage
You don't have to push yourself to do public talks. You can still share your knowledge and build your reputation comfortably by writing articles, books or sharing reviews and comments online. This way, you can get your ideas out there without feeling uncomfortable, and it won't drop your visibility or impact. It might even help you connect better with others, improving your bottom line. - Dima Raketa , Reputation House

- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions
404 Not found
We use essential cookies to make Venngage work. By clicking “Accept All Cookies”, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts.
Manage Cookies
Cookies and similar technologies collect certain information about how you’re using our website. Some of them are essential, and without them you wouldn’t be able to use Venngage. But others are optional, and you get to choose whether we use them or not.
Strictly Necessary Cookies
These cookies are always on, as they’re essential for making Venngage work, and making it safe. Without these cookies, services you’ve asked for can’t be provided.
Show cookie providers
- Google Login
Functionality Cookies
These cookies help us provide enhanced functionality and personalisation, and remember your settings. They may be set by us or by third party providers.
Performance Cookies
These cookies help us analyze how many people are using Venngage, where they come from and how they're using it. If you opt out of these cookies, we can’t get feedback to make Venngage better for you and all our users.
- Google Analytics
Targeting Cookies
These cookies are set by our advertising partners to track your activity and show you relevant Venngage ads on other sites as you browse the internet.
- Google Tag Manager
- Infographics
- Daily Infographics
- Template Lists
- Graphic Design
- Graphs and Charts
- Data Visualization
- Human Resources
- Beginner Guides
Blog 14 Individual Development Plan Examples & Templates
14 Individual Development Plan Examples & Templates
Written by: Michelle Martin Feb 15, 2023
The terms Individual Development Plan and Employee Development Plan are often used interchangeably, but the outcome is the same: a document outlining a person’s professional and career goals with an action plan to get there.
Does every employee in your organization have an IDP? Or if you’re here to make one, has your manager discussed a plan for your professional development?
If your answer is “no” to either, you can’t afford to ignore individual development plans any longer. Companies that invest in employee development earn, on average, 11% higher profits than those that don’t.
Not to fear: Here’s everything you need to know about creating useful individual development plans plus easy to use professional IDP templates to boost your profits and attract and retain top talent.
Click to jump ahead:
What is an individual development plan?
Why do you need an individual development plan, 14 individual development plan examples and tips, how to make an individual development plan, individual development plan faqs.
An individual development plan (IDP) is a collaborative document between a manager and an employee to define career goals and map out how to learn new skills or improve current ones. It matches an employee’s strengths and interests to key business objectives.
Usually, individual development plans are part of the annual performance review and general employee development discussion. But you can make or update one anytime.
You can also create an individual development plan for yourself to pursue career or personal learning goals.
IDPs usually include:
- Short and long-term career goals the employee wants to achieve.
- Current skills the employee wants to improve, or new ones to learn.
- Skills the manager wants the employee to further develop.
- Specific action steps to achieve the goals (e.g. taking a course, attending a workshop, finding a mentor, etc).
Many different formats work well for individual development plans, from plain text documents to elaborate tables and timelines. Mix and match blocks, tables, and more with this flexible IDP template to customize it to your career goals.
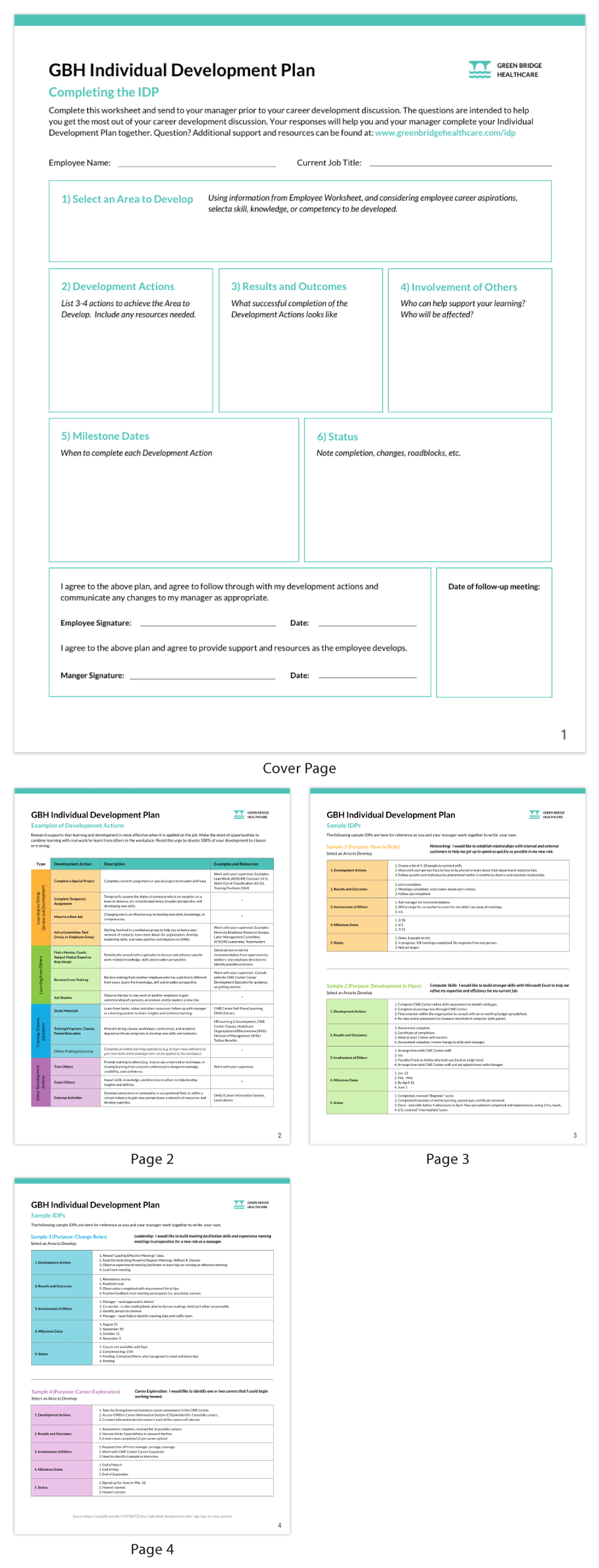
Individual development plans are beneficial to everyone, including the company. IDPs encourage your employees to voice their career goals and co-create a plan to get there. Even if they end up leaving for another company in the future, you benefit from their new skills until then.
Your employee will likely also be grateful for their growth with you and happily refer others to open roles. Since we’re in one of the tightest labor markets ever , referrals and word of mouth can mean the difference between filling your open positions or not.
Individual development plans also address a real business need: 56% of businesses surveyed by Statistics Canada in 2022 said most of their employees weren’t “fully proficient” at their jobs. If your company has over 100 employees, that most certainly applies to you as 93% of large companies responded that way, whereas only 33% of companies with less than four employees did.
IDPs help your employees learn the skills they need to achieve their own goals, but they’re also key to ensuring your business needs are met.
Components of an individual development plan
Remember, an IDP is a flexible tool. As your goals and circumstances change, so should your plan. It’s all about taking ownership of your career development and reaching your full potential!
Here are the key components of an effective IDP:
1. Self-assessment:
- Strengths: What are you good at? What do you enjoy doing?
- Areas for improvement: Be honest – what skills could you use some work on?
- Values: What matters most to you in your career? What kind of impact do you want to make?
2. Goal setting:
- Short-term: Set specific, achievable goals for the next few months that align with your overall career aspirations.
- Long-term: Think bigger! Where do you see yourself in 5-10 years? Set some aspirational goals to keep you motivated.
3. Development activities:
- Identify activities – Think training courses, workshops or taking on new challenges – that will help you reach your goals.
- Create a timeline that’s realistic considering your time and resources.
- Figure out what resources you need – financial support, time off or specific tools.
4. Monitoring and evaluation:
- Have regular check-ins with your manager or advisor to discuss your progress.
- Track your progress and make adjustments to your plan as needed.
- Celebrate your successes and learn from any setbacks.
Individual development plan examples for supervisors
Individual development plans (IDPs) for supervisors serve as roadmaps for team growth, tailoring skill development to specific roles in the team and organizational goals.
These plans aren’t just about meeting company goals; they also help supervisors achieve their career aspirations while supporting the growth of their team members.
Are you (or your employee) a visual person? Just because most individual development plans look like traditional documents doesn’t mean yours has to. Try out this creative and colorful quadrant template to prioritize goals and actions by their importance, due date, or any other criteria that make sense to you.

This template is structured as a corrective action plan but could also work well for an IDP. As a reminder, IDPs aren’t a disciplinary tool or for underperforming employees. Everyone should have an individual development plan focusing on their strengths, while also acknowledging weaknesses that may impact the achievement of career goals.

Give this worksheet-style template to your employee before your IDP meeting to find out their goals and how they view their progress so far. By getting their ideas on paper first, you’ll make better use of meeting time to discuss actions and solutions.

Another great template for visual folks, this serves well as a progress tracker for the action steps in your IDP. The simple, one-page format is quick to update and makes it easy to see progress toward your goals.

Individual development plan examples for leadership
Imagine a leadership-focused IDP as your personal roadmap for tackling the twists and turns of leadership roles. It’s not just about growing your own leadership skills, but also about making a real impact on the success of the whole organization.
A leadership IDP may include targeted training programs to enhance communication, decision-making, and strategic thinking skills.
A stylish table format is effective for communicating career goals and action steps which are both important parts of an IDP. List the goal category on the left, the action step in the middle and a target due date on the right.
For example, a goal category could be “improving public speaking skills.” An action step could be joining a local Toastmasters group or hosting a Lunch and Learn for the office.
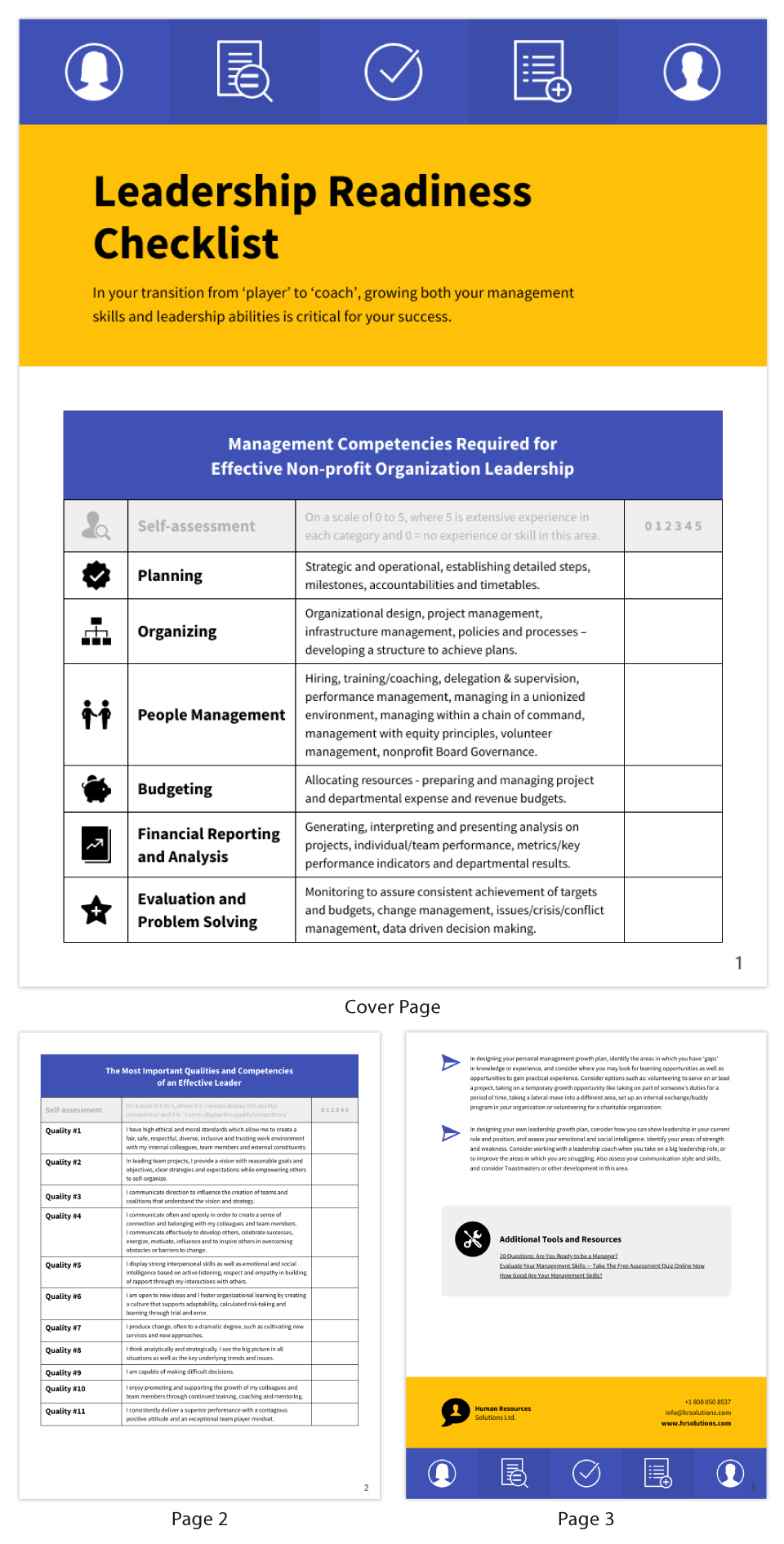
If you’re a manager assessing your team’s leadership skills, this template could be another self-evaluation tool for your employee to fill out prior to your IDP meeting. Or, use it as a progress tracker by listing out the actions and ranking them from “Not Started” to “Complete.”

Individual development plan example for career
Think of your Individual Development Plan (IDP) for your career as your personalized roadmap to success.
For instance, your career-focused IDP might include short-term goals like acquiring new skills through workshops or online courses. Long-term goals may revolve around taking on challenging projects to showcase your capabilities and climbing the professional ladder.
An individual development plan is a lot like a product roadmap, except with your career goals instead of new features. This simple timeline template is a good way to work through the order you’ll need to accomplish action items in and set target deadlines.
It’s also useful for visual thinkers to see a simplistic overview of their trajectory on one page. You can detail each goal or step in subsequent pages.
Using a 30, 60, and 90 day timeline is an effective way to break down large goals into achievable steps per quarter. This can also work as a one-page quarterly plan — just add an extra column — or a multi-year plan.

This template serves as a compact yet detailed action plan that’s perfect for goal tracking in your individual development plan.

Individual development plan examples for managers
Often, an IDP has a big goal in mind, like being the head of a division or something else several steps ahead of you. In order to get there, you need to break it down into smaller goals along the way.
Growing into a C-suite position could mean first managing an important project, then a small team, and then a larger team, and so on. By visually planning the smaller goals along the way, you (or your employee) have realistic expectations of what’s needed to get to the ultimate goal and a focused approach to get there.

This multi-page template is highly flexible so every page of your IDP will look professional and on-brand. Easily add tables, lists, and more to the content pages as needed to create a detailed and aesthetic development plan.

While this is set up as an orientation plan, you could easily customize it as an individual development plan.

If you like a quarterly planning approach, this template is helpful to detail the action steps you need to take for the rest of the year.

Individual development plan example for government employees
Feeling like your career in a government agency could use a refresh? Individual Development Plans (IDPs) can be a helpful tool for that.
IDPs are a great way to take ownership of your career development, gain valuable skills and contribute even more effectively to your government organization’s mission.
For example, as a government healthcare worker, your IDP might involve specific activities like attending relevant workshops, seeking mentorship from experienced colleagues or even shadowing other professionals in your field.
Here’s what it might look like:

Individual development plan examples for IT professionals
Individual Development Plans (IDPs) can be a valuable tool for IT professionals to navigate the ever-changing tech landscape.
When drafting your IT individual development plan, try to find out beforehand if your company offers internal training programs, tuition reimbursement or professional development opportunities.
You could also consider attending industry conferences, workshops and webinars to stay up-to-date on the latest trends and technologies.
Too much to take in? That’s exactly why you need an IDP – It helps you map out goals and the steps to reach them. Check out this quick development plan template to discuss with your manager or colleague.

Any of the templates above can be your starting point for creating your organization’s IDP template, or choose from all our business templates . Some templates are available only to our paid subscribers, but all the options above are free for everyone to use.
Starting with a template saves time and ensures your finished IDP looks polished and professional. It’s easy to customize any of these with our free online editor in just a few clicks.
Step 1: Sign up for a free Venngage account
All you need is an email address to sign up for a free Venngage account .
No free trials, credit card numbers, or any of that. You can edit any of our free templates with your free account… for free , okay?
Step 2: Choose an individual development plan template to customize
Pick one of the templates mentioned above or browse our full database of Human Resources templates , including letters , plans , presentations , and more.

Step 3: Edit the template for your IDP
Once you’ve picked a template, the fun part begins: Making it your own. Click Create on any template to enter the editor where you can change colors, text, graphics, and more.
I’m using this IDP checklist template as an example:

I like to match a new template to my brand first as this saves a lot of time if you want to duplicate the page to add more content later.
Our Business and Premium subscriptions offer My Brand Kit to store your colors, fonts, and logos for easy template customization anywhere for your entire team. But no worries for our free account holders: Editing is just as easy.
Click on any text area or graphic to edit it. Type new text, or use the top menu to change color, font, size, spacing, and more.

You can replace existing graphics with one of our 3 million+ free stock photos , over 40,000 illustrations and icons, or upload your own.
Explore the left side menu to add a background or a new layout, like a graph or table. You can also click and drag objects around the page to your liking. Use the right side menu to duplicate the current page or add a new blank one to your document.

Step 4: Share or save your new IDP
Once you’re happy with your new individual development plan template, click on the Share icon or Download button to save it to your computer (Business or Premium accounts).
So easy, right?

What are good IDP goals?
There aren’t “good” or “bad” goals as each IDP is as unique as the individual it’s for. However, effective IDP goals have a few things in common, like being:
- Related to the employee’s career path.
- Achievable in the specified timeframe. (You can list out big goals but ensure the action steps to start with are reasonable to accomplish, or at least start, within the next year.)
- Collaboratively planned between manager and employee, with both having input.
If your employee wants to lead their department one day but hasn’t managed anyone before, some good IDP goals to set for the upcoming year could be:
- Taking a leadership course or program from a nearby or online business school.
- Leading a big project, including supervising their peers and providing feedback.
- Finding a leadership mentor within the company and regularly checking in with them.
How can I support my employee’s IDP goals?
This depends what your employee’s goals are, but a few general ideas are to:
- Offer time to try new roles and responsibilities to learn new skills.
- Reimburse or partially cover courses, seminars, and other educational tools.
- Encourage your employee to start a side hustle or passion project to learn from.
- Offer professional development days, separate from vacation time.
- Create a mentorship program to connect junior and senior staff.
Unsure what would be most effective? Ask your employees what would help them the most, and check our guide to employee development for more ideas .
What should I put for areas of improvement?
Individual development plans encourage and motivate your employees to achieve their dreams. However, as their manager, you may have some insights they don’t about skills they’re lacking to get them to the next step.
It’s best to bring these up during the planning meeting, so your employee can hear why you think these skills are important and how you’d suggest working on them. Together you can add action items to address them in the IDP.
It’s key to frame these developing areas in a positive and constructive light. You don’t want your employee to feel like they’re doing badly at these things, or their job. After all, no one’s perfect! Be open and honest and chances are, they’ll be grateful for the feedback and eager to improve the skills you’ve identified.
Create a professional IDP today with a customizable Venngage template
Whether you’re preparing for an employee’s annual review or creating an individual development plan for yourself, we’ve got the free templates you need to knock it out of the park.
Get started now and have your new IDP finished by the end of the hour. While you’re at it, why not also create a branded offer letter or onboarding guide ?
For everything in your business, we’ve got a template for that.
Discover popular designs

Brochure maker

White paper online

Newsletter creator

Flyer maker

Timeline maker

Letterhead maker

Mind map maker

Ebook maker
Home Blog Business How to Create and Present a Professional Development Plan
How to Create and Present a Professional Development Plan

Keeping yourself updated with recent trends and new methods used in your line of work is essential to avoid becoming obsolete. Like machines, technology, and processes, people can be outmoded by more efficient individuals in their field of work. Furthermore, a lack of initiative is often why many individuals might find themselves unable to climb the professional ladder. The key to avoiding such pitfalls is to set the right goals and focus on your professional development plan.
Why is Professional Development Important?
Professional development involves learning to enhance or maintain your professional value. Such as by acquiring a degree, undergoing formal or informal training, working with a mentor, etc. Individuals looking to develop their professional credentials actively might set professional development goals, develop a professional development plan, and pursue their desired targets through periodic evaluation.
You might need to reflect your desire for professional development at the workplace to climb the career ladder in various cases. For example, many organizations evaluate the desire for an individual to excel by performing a training needs assessment, setting annual goals for their employees (or allowing them to submit annual goals), and enabling them to take over additional responsibility with their immediate supervisor.
Professional development and the desire to excel can often be reflected in an individual’s attitude. Someone presenting a PowerPoint presentation for a 30-60-90-day plan reflects an individual’s plan for the first 3 months at the job and the desire to excel personally or its lack. Similarly, people actively engaged in seeking and making use of professional development opportunities at the workplace can often improve their chances of career success, such as undergoing optional training courses or voluntarily joining advisory groups.

What is a Professional Development Plan?
When working on your professional development plan, you will find many avenues that can lead you to career growth. There is no magical method to make a plan that can lead to certain success. However, you can start with a few basics and stick to the best course of action by following a few guidelines that can enable you to develop yourself as a robust candidate to stand out from the crowd when looking to move up the professional ladder.
Prioritize Your Professional Development Goals
Knowing what you want is essential to achieve what you need to. It is important to set your professional development goals to understand better the targets you intend to achieve. You can set goals based on some initial evaluation. Such as by researching a bit about your industry, analyzing the achievements of successful individuals, and set SMART goals.
Professional development goals might differ from one individual to another. Once your goals have been achieved, you can also add new goals. Your goals can be short-term, mid-term, and long-term. If you think you lack experience, you can start with short-term goals and refine them later. Someone at the start of their career might look to become an expert at their job. At the same time, someone who is well versed in their line of work might be looking to work in a senior position. You might also need to present a professional development plan when internally applying for a senior position or at least reflect your need to grow in the form of a formal PowerPoint presentation to score some interview marks.
Some job interviews also make it mandatory for candidates to present a plan or course of action to show how they can add value to the organization. It can help you gain a few extra marks during such a presentation if you appear to be looking to continue learning and enhancing your skills while adding value to the work you might do for the organization.
As you grow professionally, your goals will likely become more refined and clear. Showing you better avenues to explore in your professional endeavors.
Enhance Learning and Technical Capacity
Whether you are someone inexperienced at the workplace, at the bottom of the hierarchy, or an individual with several decades of experience, learning is a process that never ends. New processes, technologies, and methods are always on the horizon. Those unable to see the opportunity in them are often left behind. Over the years, many professionals have undergone radical change. Virtually every industry now has better technology, processes, and methods of performing different functions. Those who have been unable to keep up with changing times now find it hard to find work, let alone be successful in their career.
A glance at obsolete professions is sufficient to understand the need to learn and enhance your technical capacity. For example, how many people now use a typewriter? Does any professional photographer use a traditional camera anymore?
Learning and enhancing technical capacity is key to maintain and improve your professional credentials. This not only includes understanding the evolving environment of your industry but also being good at small things that weren’t expected a few years earlier. For example, regardless of their place in the hierarchy, employees are expected to be computer literate and capable of at least performing a few basic functions such as composing software, a printer, or even delivering a PowerPoint presentation when needed.
Identify Barriers and Solutions
Professional development is often not a straight road with a clear view of your destination but a route with several detours and difficult to maneuver pathways. It is quite likely that you would face several barriers when aiming to achieve your professional development goals. These can be anything from a lack of opportunity for growth, a toxic working environment hindering progress due to workplace-related politics to your inability to be as good at your job as others.
Identifying barriers is a good way to find suitable solutions. You can even take notes and write down the possible barriers hindering you from achieving your goals. Doing so can help you reflect on the need for adjusting your professional development plan.
Collaborate and Develop a Professional Network
Sometimes, people lack not skills or experience but rather a network that can help them excel. Several jobs require working in collaboration with others to produce a final output. A freelancer developing websites might also be expected to produce graphics for clients. However, he/she might not be good at the job and may require collaborating with a professional graphic designer to satisfy clients. Similarly, collaborating with people at the workplace or from your network can help you gain different perspectives and ideas to carry your work forward.
Many people remain in touch with former mentors, supervisors, or associates throughout their professional careers. This helps seek them out for help and advice in a professional capacity and act as a reference for a better career opportunity. People also like to work with trusted individuals who have credibility in the industry. If you are someone with a robust professional network, the chances are your reputation might precede you in a job interview, improving your chances of scoring a good job. Developing a professional network is also important to find better job opportunities, understand your profession’s changing nature, and build your professional repute in the industry.
Evaluate and Adjust for Course Correction
Imagine you are someone who trained as an IT support engineer providing hardware repair services for desktop computers a decade ago. At the time, you wanted to climb the professional ladder to become a supervisor but never achieved your goal. However, another individual with similar skills as yours underwent training for repairing handheld devices to excel at the workplace. In such a case, the chances are you missed an opportunity in the wake of evolving market needs and did not update your skills to understand handheld devices’ mechanics. Keeping in view this example, it is necessary to understand the need to constantly evaluate and adjust your professional development plan for course correction.
One of the biggest hurdles to professional development is a lack of initiative, powered by resistance to change. It can be difficult to accept that you might need to undergo cumbersome training and leave your comfort zone to learn something new. However, making a timely decision can enable you to achieve your long-term goals and remain relevant in your line of work.

Continuing Professional Development (CPD)
Continuing Professional Development (CPD) is the continuation of learning to ensure that you have the necessary knowledge and skills to perform your duties at the workplace. CPD is often a requirement in certain professions. People engaged in financial management, risk and safety management, and the healthcare industry.
Continuing Professional Development can include various activities such as work-related learning, formal education, being involved with professional bodies, self-directed learning, or even presenting PowerPoint presentations during conferences. Depending upon your line of work, you can provide evidence for CPD activities to meet the required standards of your industry.
How to Present a Professional Development Plan
Whether you need to present a professional development plan before your supervisor or need to deliver a PowerPoint presentation during a job interview, you can follow the steps mentioned below to create a suitable slide deck.
Know Your Goals
Your presentation must have specific, measurable goals that are achievable, relevant, and time-bound. If it is a presentation meant to gauge your future training needs or set goals by your supervisor, you might want to pick goals that can best suit your career growth. For job interviews, you will have to show a mix of your current skills and the desire to excel while maintaining a balance between the two. This is to ensure that you don’t appear as a novice when applying for a job.
Leverage Your Skills
When presenting a professional development plan, it is best to emphasize your strengths and what you’re good at, as well as the areas you intend to improve. An honest yet professional-looking plan is likely to ensure that you can show your desire to develop without undermining your competence during a presentation professionally. While a supervisor might be aware of your skillset, someone not familiar with your work should see you as a confident and competent individual looking to work hard to succeed.
Mention the Merits of Your Plan
Many organizations spend a hefty amount training employees each year. These organizations also expect the employees to use their professional development to add value to the workplace. It will be redundant for organizations to invest in individuals who move on to other opportunities in different organizations after they have reached their true potential. Similarly, employees that see development opportunities as mere extra work and a ‘waste of time’ are unlikely to benefit from them. Therefore, it is necessary to showcase that you can add value to the final output of the required work if you are given the opportunity for professional development.
Avoid Death by PowerPoint
Presentations can often be dull and boring. When designing your slide deck, you should try to create slides that are easy to grasp, to the point, and carry your presentation based on your knowledge rather than what’s written in text-heavy slides. You can also use a professional development plan template to create your slides with the visual aid of professionally designed layouts.
Final Words
Professional development is not just about clocking hours at training, workshops, or even at the workplace. What makes a professional development plan useful is the qualitative aspects of your efforts. Improving your understanding of evolving needs, applying what you have learned, and ensuring that your professional credentials remain abreast with market needs is essential.
To support your professional development goals, you can look to create a robust network of colleagues, coworkers, and friends who can help you out throughout your career. It is also important to mentor and supports others whenever possible. This will help your network grow and enable you to learn how to lead a team and keep you on your toes to be capable enough to guide the people who look up to you.
1. Creative Resume Slide Template for PowerPoint
Don´t just settle for a traditional lengthy resume, but actually use this PowerPoint Presentation Template to present or send out when seeking work opportunities.
Use This Template

Like this article? Please share
Career Growth, Personal Development, Presentation Tips, Presentations Filed under Business
Related Articles

Filed under Google Slides Tutorials • April 29th, 2024
Best Google Slides Add-Ons
Optimize your Google Slides experience by installing the best Google Slides add-ons available in the market. Full list with photos.

Filed under Design • April 23rd, 2024
How to Create the Perfect Handouts for a Presentation
Learn how to create effective handouts for presentations and the recommended structure for handouts with this guide.

Filed under Google Slides Tutorials • April 19th, 2024
How to Find Trash on Google Slides
Don’t worry if you accidently delete a presentation file. Learn how to find trash on Google Slides with this guide.
Leave a Reply

COMMENTS
Presentation skills are the abilities and qualities necessary for creating and delivering a compelling presentation that effectively communicates information and ideas. They encompass what you say, how you structure it, and the materials you include to support what you say, such as slides, videos, or images. You'll make presentations at various ...
Tip #1: Build a narrative. One memorable way to guarantee presentation success is by writing a story of all the points you desire to cover. This statement is based on the logic behind storytelling and its power to connect with people. Don't waste time memorizing slides or reading your presentation to the audience.
Here are a few tips for business professionals who want to move from being good speakers to great ones: be concise (the fewer words, the better); never use bullet points (photos and images paired ...
To fully understand the impact these skills have on creating a successful presentation, it's helpful to look at each one individually. Here are six valuable skills you can develop: 1. Active listening. Active listening is an excellent communication skill for any professional to hone.
Try to incorporate some of their effective speaking strategies into your own presentation. 3. Learn it without notes. While you can choose to have cue cards available, try to memorize your presentation. Rather than remembering every single line or a script, however, try to give your presentation using a loose outline.
1. Create an Outline. Before designing slides and writing a script, outline your presentation. Start with your introduction, segue into key points you want to make, and finish with a conclusion. 2. Practice, Practice, Practice. Almost 8 in 10 professionals practice their presentations for at least an hour.
This is not surprising. Effective communications skills are a powerful career activator, and most of us are called upon to communicate in some type of formal presentation mode at some point along the way. For instance, you might be asked to brief management on market research results, walk your team through a new process, lay out the new budget ...
The secret structure of great talks. From the "I have a dream" speech to Steve Jobs' iPhone launch, many great talks have a common structure that helps their message resonate with listeners. In this talk, presentation expert Nancy Duarte shares practical lessons on how to make a powerful call-to-action. 18:00.
Tip #3: Keep your slides short and sweet. Tip #4: Focus on your presentation design. Tip #5: Visualize boring numbers and data. Tip #6: Practice in front of a live audience. Tip #7: Meet your audience before presenting. Tip #8: Channel nervous energy into enthusiastic energy.
Presenting or making a speech at a conference or event. Objecting to a planning proposal at a council meeting. Making a speech at a wedding. Proposing a vote of thanks to someone at a club or society. On behalf of a team, saying goodbye and presenting a gift to a colleague who is leaving.
Last updated: May 18, 2022 • 2 min read. Body language, eye contact, and time management are all key to leading an effective presentation. Learn how to improve your presentation skills and confidence speaking in front of an audience.
10. Smile. Smiling increases endorphins, replacing anxiety with calm and making you feel good about your presentation. Smiling also exhibits confidence and enthusiasm to the crowd. And this tip works even if you're doing a webinar and people can't see you. Just don't overdo it - no one enjoys the maniacal clown look.
S pecific: Must be narrowed down, focused, and clearly defined. M easurable: Must have some quantitative factors that help track progress. A ttainable: Must be achievable. R elevant: Must be important and have a significant value in our life. T ime-Bound: Must have a timeline and a deadline.
There are a number of aspects that you need to consider when preparing a presentation. They include the aim of the presentation, the subject matter, the audience, the venue or place, the time of day, and the length of the talk. All these will affect what you say and how you say it, as well as the visual aids that you use to get your point across.
3. Delivery. Once your presentation is ready, the next stage is the actual presentation, which will require strong public speaking skills and excellent verbal and nonverbal communication skills. Project confidence with your body language. As you are speaking, make sure your back is straight and your shoulders are back.
How to create a professional development plan. Follow these five steps to create a simple, thorough professional development plan: 1. Self-assessment. A self-assessment is an evaluation of your professional interests, knowledge and skills. Creating a self-assessment allows you to examine your current position as it relates to your career goals.
Produce content. Divide your presentation into a beginning, a middle, and an end. The audience needs to be clear why they should listen to you from your very first sentence. Ensure that you make a strong start, and make it benefit related. People buy benefits whether of a service, product or an idea.
STEP 3 — Collect the Data. Research your topic so that you know everything you possibly can about the subject. Do not include all this information in your speech but be prepared for the questions that will follow at the end of your presentation. STEP 4 — Select a Method of Organization.
Presentation skills can be defined as a set of abilities that enable an individual to: interact with the audience; transmit the messages with clarity; engage the audience in the presentation; and interpret and understand the mindsets of the listeners. These skills refine the way you put forward your messages and enhance your persuasive powers. The present era places great emphasis on good ...
Bandura's social cognitive theory. Albert Bandura's (1977) theory highlights the role of social learning and self-efficacy in personal development. It emphasizes that individuals can learn and grow through observation, imitation, and belief in their ability to effect change. 5. Self-determination theory.
16. Solicit Feedback To Find Ways To Improve. Introverted biz dev leaders can boost presentation skills by thoroughly preparing, leveraging strengths like listening, practicing in smaller groups ...
Presentation skills are an art. This guide will walk you through the skills needed since public spoken, preparation, delivery, non-verbal communication, also more.
3. Development activities: Identify activities - Think training courses, workshops or taking on new challenges - that will help you reach your goals. Create a timeline that's realistic considering your time and resources. Figure out what resources you need - financial support, time off or specific tools. 4.
Such as by researching a bit about your industry, analyzing the achievements of successful individuals, and set SMART goals. Professional development goals might differ from one individual to another. Once your goals have been achieved, you can also add new goals. Your goals can be short-term, mid-term, and long-term.