
- History & Society
- Science & Tech
- Biographies
- Animals & Nature
- Geography & Travel
- Arts & Culture
- Games & Quizzes
- On This Day
- One Good Fact
- New Articles
- Lifestyles & Social Issues
- Philosophy & Religion
- Politics, Law & Government
- World History
- Health & Medicine
- Browse Biographies
- Birds, Reptiles & Other Vertebrates
- Bugs, Mollusks & Other Invertebrates
- Environment
- Fossils & Geologic Time
- Entertainment & Pop Culture
- Sports & Recreation
- Visual Arts
- Demystified
- Image Galleries
- Infographics
- Top Questions
- Britannica Kids
- Saving Earth
- Space Next 50
- Student Center
- Introduction & Quick Facts
- The highland zone
- The lowland zone
- Plant and animal life
- Ethnic groups
- Rural settlement
- Urban settlement
- Population growth
- Migration patterns
- Agriculture
- Manufacturing
- Labour and taxation
- Transportation and telecommunications
- Constitutional framework
- Regional government
- Local government
- Political process
- The National Health Service
- Cash benefits
- Primary and secondary education
- Private schools
- Higher education
- Daily life and social customs
- Cultural institutions
- Sports and recreation
- Broadcasting
- Neolithic Period
- The conquest
- Army and frontier
- Administration
- Religion and culture
- The decline of Roman rule
- The social system
- The conversion to Christianity
- The golden age of Bede
- The supremacy of Northumbria and the rise of Mercia
- The great age of Mercia
- The church and scholarship in Offa’s time
- The decline of Mercia and the rise of Wessex
- Viking invasions and settlements
- Alfred’s government and his revival of learning
- The reconquest of the Danelaw
- The kingdom of England
- The church and the monastic revival
- The Danish conquest and the reigns of the Danish kings
- The reign of Edward the Confessor and the Norman Conquest
- Resistance and rebellion
- The introduction of feudalism
- Government and justice
- Church–state relations
- William’s accomplishments
- William II Rufus (1087–1100)
- Henry I (1100–35)
- Matilda and Stephen
- England in the Norman period
- Government of England
- Struggle with Thomas Becket
- Rebellion of Henry’s sons and Eleanor of Aquitaine
- Richard I (1189–99)
- Loss of French possessions
- Struggle with the papacy
- Revolt of the barons and Magna Carta
- Economy and society
- Early reign
- The county communities
- Simon de Montfort and the Barons’ War
- Later reign
- Law and government
- The growth of Parliament
- Edward’s wars
- Domestic difficulties
- Social, economic, and cultural change
- Edward II (1307–27)
- The Hundred Years’ War to 1360
- Domestic achievements
- Law and order
- The crises of Edward’s later years
- The Peasants’ Revolt (1381)
- John Wycliffe
- Political struggles and Richard’s deposition
- Economic crisis and cultural change
- The rebellions
- Henry and Parliament
- The French war
- Domestic affairs
- Domestic rivalries and the loss of France
- Cade’s rebellion
- The beginning of the Wars of the Roses
- Edward IV (1461–70 and 1471–83)
- Richard III (1483–85)
- England in the 15th century
- Dynastic threats
- Financial policy
- The administration of justice
- Cardinal Wolsey
- The king’s “Great Matter”
- The Reformation background
- The break with Rome
- The consolidation of the Reformation
- The expansion of the English state
- Henry’s last years
- Edward VI (1547–53)
- Mary I (1553–58)
- The Tudor ideal of government
- Elizabethan society
- Mary, Queen of Scots
- The clash with Spain
- Internal discontent
- Government and society
- Triple monarchy
- Religious policy
- Finance and politics
- Factions and favourites
- The politics of war
- Peace and reform
- Religious reform
- The Long Parliament
- Civil war and revolution
- Commonwealth and Protectorate
- The Restoration
- War and government
- The Popish Plot
- The exclusion crisis and the Tory reaction
- Church and king
- The Revolution of 1688
- The revolution settlement
- A new society
- The sinews of war
- Whigs and Tories
- Tories and Jacobites
- The state of Britain in 1714
- The supremacy of the Whigs
- George II and Walpole
- Foreign policy
- Economic policies
- The electoral system
- Walpole’s loss of power
- The Jacobite rebellion
- The rule of the Pelhams
- Domestic reforms
- Joseph Massie’s categories
- Urban development
- Change and continuity
- The revolution in communications
- Conflict abroad
- Political instability in Britain
- The American Revolution
- Domestic responses to the American Revolution
- William Pitt the Younger
- Economic growth and prosperity
- The Industrial Revolution
- Britain during the French Revolution
- The Napoleonic Wars
- Imperial expansion
- State and society
- The political situation
- Whig reforms
- Chartism and the Anti-Corn Law League
- Peel and the Peelite heritage
- Gladstone and Disraeli
- The development of private life
- Gladstone and Chamberlain
- The Irish question
- Split of the Liberal Party
- Imperialism and British politics
- The return of the Liberals
- The international crisis
- Family and gender
- Mass culture
- The Asquith coalition
- Lloyd George
- The election of 1918
- Harsh peace and hard times
- Ireland and the return of the Conservatives
- The Baldwin era
- Baldwin and the abdication crisis
- Foreign policy and appeasement
- The phases of war
- Political developments
- Labour and the welfare state (1945–51)
- Economic crisis and relief (1947)
- Withdrawal from the empire
- Conservative government (1951–64)
- Labour interlude (1964–70)
- The return of the Conservatives (1970–74)
- Labour back in power (1974–79)
- The Falkland Islands War, the 1983 election, and privatization
- Racial discrimination and the 1981 England riots
- The 2001 England riots
- The “Troubles” in Northern Ireland
- “Thatcherism”
- “Black Wednesday,” epidemic scandals, and Major’s “Citizens Charter”
- “Mad cow disease”
- The struggle for control of Labour
- New Labour, the repeal of Clause IV, and the “third way”
- Navigating the European monetary system and the EU Social Chapter
- The Good Friday Agreement
- London’s local government, House of Lords reform, and devolution for Scotland and Wales
- The royal family’s “annus horribilis,” the death of Princess Diana, and the Millennium Dome
- The battle for the soul of the Conservative Party
- Response to the September 11 attacks
- Weapons of mass destruction and the Iraq War
- The Gordon Brown government (2007–10)
- The U.K. general election of 2010
- First-past-the-post referendum
- Intervention in Libya
- News of the World hacking scandal
- The 2011 riots, the European sovereign debt crisis, and Cameron’s veto of changes to the Lisbon Treaty
- The 2012 London Olympics, Julian Assange’s embassy refuge, and the emergence of UKIP
- The birth of George, rejection of intervention in Syria, and regulation of GCHQ
- Euroskepticism
- Scottish independence referendum
- Economic recovery
- The U.K. general election of 2015
- The “Brexit” referendum
- The resignation of Cameron, the rise of May, and a challenge to Corbyn’s leadership of Labour
- Triggering Article 50
- The Manchester arena bombing and London bridge attacks
- The snap election campaign
- The 2017 U.K. general election
- The Grenfell Tower fire, a novichok attack in Salisbury, and air strikes on Syria
- The wedding of Prince Harry and Meghan Markle, the Chequers plan, and Boris Johnson’s resignation
- EU agreement and Parliamentary opposition to May’s Brexit plan
- Objections to the Irish backstop and a challenge to May’s leadership
- Parliamentary rejection of May’s plan, May’s survival of a confidence vote, and the Independent Group of breakaway MPs
- Parliament rejects May’s plan again
- “Indicative votes,” May’s pledge to resign, a third defeat for her plan, and a new deadline
- Boris Johnson’s ascent, the December 2019 snap election, and Brexit
- The coronavirus pandemic
- “Partygate”
- Further scandal and Johnson’s resignation
- Ascent to office
- The death of Elizabeth II
- Abrupt resignation
- The premiership of Rishi Sunak
- Sovereigns of Britain
- Prime ministers of Great Britain and the United Kingdom

- What is Charles Darwin famous for?
- What is evolution, as Charles Darwin understood it?
- What was Charles Darwin’s educational background?
- What was Charles Darwin’s family life like?
- What were the social impacts of Charles Darwin’s work?


United Kingdom
Our editors will review what you’ve submitted and determine whether to revise the article.
- Historic UK - Historic November
- CRW Flags - Flag of United Kingdom
- Central Intelligence Agency - The World Factbook - United Kingdom
- United Kingdom - Children's Encyclopedia (Ages 8-11)
- United Kingdom - Student Encyclopedia (Ages 11 and up)
- Table Of Contents
Recent News
United Kingdom , island country located off the northwestern coast of mainland Europe . The United Kingdom comprises the whole of the island of Great Britain —which contains England , Wales , and Scotland —as well as the northern portion of the island of Ireland . The name Britain is sometimes used to refer to the United Kingdom as a whole. The capital is London , which is among the world’s leading commercial, financial, and cultural centres. Other major cities include Birmingham , Liverpool , and Manchester in England, Belfast and Londonderry in Northern Ireland , Edinburgh and Glasgow in Scotland, and Swansea and Cardiff in Wales.

The origins of the United Kingdom can be traced to the time of the Anglo-Saxon king Athelstan , who in the early 10th century ce secured the allegiance of neighbouring Celtic kingdoms and became “the first to rule what previously many kings shared between them,” in the words of a contemporary chronicle. Through subsequent conquest over the following centuries, kingdoms lying farther afield came under English dominion . Wales, a congeries of Celtic kingdoms lying in Great Britain’s southwest, was formally united with England by the Acts of Union of 1536 and 1542. Scotland, ruled from London since 1603, formally was joined with England and Wales in 1707 to form the United Kingdom of Great Britain. (The adjective “British” came into use at this time to refer to all the kingdom’s peoples.) Ireland came under English control during the 1600s and was formally united with Great Britain through the Act of Union of 1800. The republic of Ireland gained its independence in 1922, but six of Ulster ’s nine counties remained part of the United Kingdom as Northern Ireland. Relations between these constituent states and England have been marked by controversy and, at times, open rebellion and even warfare. These tensions relaxed somewhat during the late 20th century, when devolved assemblies were introduced in Northern Ireland, Scotland, and Wales. Nonetheless, even with the establishment of a power-sharing assembly after referenda in both Northern Ireland and the Irish republic, relations between Northern Ireland’s unionists (who favour continued British sovereignty over Northern Ireland) and nationalists (who favour unification with the republic of Ireland) remained tense into the 21st century.

The United Kingdom has made significant contributions to the world economy, especially in technology and industry. Since World War II , however, the United Kingdom’s most prominent exports have been cultural, including literature, theatre, film, television, and popular music that draw on all parts of the country. Perhaps Britain’s greatest export has been the English language , now spoken in every corner of the world as one of the leading international mediums of cultural and economic exchange.
The United Kingdom retains links with parts of its former empire through the Commonwealth . It also benefits from historical and cultural links with the United States and is a member of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO). Moreover, the United Kingdom became a member of the European Union in 1973. Many Britons, however, were sometimes reluctant EU members, holding to the sentiments of the great wartime prime minister Winston Churchill , who sonorously remarked, “We see nothing but good and hope in a richer, freer, more contented European commonalty. But we have our own dream and our own task. We are with Europe, but not of it. We are linked, but not comprised . We are interested and associated, but not absorbed.” Indeed, in June 2016, in a referendum on whether the United Kingdom should remain in the EU, 52 percent of British voters chose to leave. After much negotiation, several deadline extensions, prolonged domestic political discord , and two changes of prime minister, an agreement on “Brexit” (British exit from the EU) was reached that satisfied both the EU and the majority of Parliament . Thus, on January 31, 2020, the United Kingdom would become the first country to withdraw from the EU.

The United Kingdom comprises four geographic and historical parts— England , Scotland , Wales , and Northern Ireland . The United Kingdom contains most of the area and population of the British Isles—the geographic term for the group of islands that includes Great Britain, Ireland, and many smaller islands. Together England, Wales, and Scotland constitute Great Britain, the larger of the two principal islands, while Northern Ireland and the republic of Ireland constitute the second largest island, Ireland. England, occupying most of southern Great Britain, includes the Isles of Scilly off the southwest coast and the Isle of Wight off the southern coast. Scotland, occupying northern Great Britain, includes the Orkney and Shetland islands off the northern coast and the Hebrides off the northwestern coast. Wales lies west of England and includes the island of Anglesey to the northwest.
Apart from the land border with the Irish republic, the United Kingdom is surrounded by sea. To the south of England and between the United Kingdom and France is the English Channel . The North Sea lies to the east. To the west of Wales and northern England and to the southeast of Northern Ireland, the Irish Sea separates Great Britain from Ireland, while southwestern England, the northwestern coast of Northern Ireland, and western Scotland face the Atlantic Ocean . At its widest the United Kingdom is 300 miles (500 km) across. From the northern tip of Scotland to the southern coast of England, it is about 600 miles (1,000 km). No part is more than 75 miles (120 km) from the sea. The capital, London, is situated on the tidal River Thames in southeastern England.

The archipelago formed by Great Britain and the numerous smaller islands is as irregular in shape as it is diverse in geology and landscape. This diversity stems largely from the nature and disposition of the underlying rocks, which are westward extensions of European structures, with the shallow waters of the Strait of Dover and the North Sea concealing former land links. Northern Ireland contains a westward extension of the rock structures of Scotland. These common rock structures are breached by the narrow North Channel .
On a global scale, this natural endowment covers a small area—approximating that of the U.S. state of Oregon or the African country of Guinea —and its internal diversity, accompanied by rapid changes of often beautiful scenery, may convey to visitors from larger countries a striking sense of compactness and consolidation. The peoples who, over the centuries, have hewed an existence from this Atlantic extremity of Eurasia have put their own imprint on the environment , and the ancient and distinctive palimpsest of their field patterns and settlements complements the natural diversity.
Great Britain is traditionally divided into a highland and a lowland zone. A line running from the mouth of the River Exe , in the southwest, to that of the Tees, in the northeast, is a crude expression of this division. The course of the 700-foot (213-metre) contour , or of the boundary separating the older rocks of the north and west from the younger southeastern strata, provides a more accurate indication of the extent of the highlands.
United Kingdom
Located off the northwest coast of Europe, the United Kingdom includes England, Scotland, Wales, and Northern Ireland.
The biggest part of the United Kingdom (also called the U.K.) is the island of Great Britain, which is made up of England, Wales, and Scotland. The U.K. also includes Northern Ireland, which is on another island. (South of Northern Ireland is the separate country of Ireland , which gained its independence from the U.K. in 1937.) Northern Ireland is just 12 miles from the island of Great Britain, across the North Channel of the Irish Sea.
Scotland and Wales are the most mountainous parts of the U.K. and are covered in knife-edged mountain ridges separated by deep valleys. This terrain was shaped some 20,000 years ago during the last Ice Age, when thick glaciers covered the land. When the Ice Age glaciers melted in northwest Scotland, they left behind thousands of lakes, called lochs (pronounced LOCKS). Long and narrow, some of the lochs are very deep. (Legends say that a giant monster called Nessie lives in Loch Ness in this region, also called the Scottish Highlands.)
The largest freshwater lake by surface area in the U.K., Lough Neagh (pronounced LOCK NEE), is in Northern Ireland. It stretches 20 miles long and nine miles wide. Rolling hills and plains dot the countryside of both Northern Ireland and England.
PEOPLE AND CULTURE
Government and economy.
The U.K.’s system of government has developed over many centuries. As early as the ninth century, kings and queens ruled with advice from a council of religious leaders and nobles.
Today, the country is a constitutional monarchy, which means the reigning king or queen is the head of state but doesn’t have any real political power.
The old council of advisers eventually expanded into a government body called Parliament. That’s why today, the United Kingdom’s system of governing is called a parliamentary democracy.
Members of Parliament now pass all the country's laws from two chambers: the House of Commons, made up of officials elected by the people, and the House of Lords, in which members are appointed, usually by the reigning king or queen based on recommendations by an independent group called the House of Lords Appointments Commission.
The head of the government is the prime minister, who is usually the leader of the political party in charge of Parliament.
Oil, iron, and steel products are some of the United Kingdom’s main exports, or goods sold to other countries. The country also exports electrical equipment, and parts for automobiles and aircrafts. Its main crops produced include barley, wheat, and potatoes.
Over the centuries, the United Kingdom has accumulated wealth from foreign lands the country colonized, or took control over. Some estimates say the U.K. earned as much as $45 trillion in today’s dollars just from its former colony of India, when trade from goods that India produced went to the U.K’s economy. Other former colonies include Australia , Canada , and South Africa .
Watch "Destination World"
North america, south america, more to explore, u.s. states and territories facts and photos, destination world.
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Your California Privacy Rights
- Children's Online Privacy Policy
- Interest-Based Ads
- About Nielsen Measurement
- Do Not Sell My Info
- National Geographic
- National Geographic Education
- Shop Nat Geo
- Customer Service
- Manage Your Subscription
Copyright © 1996-2015 National Geographic Society Copyright © 2015-2024 National Geographic Partners, LLC. All rights reserved

- My presentations
Auth with social network:
Download presentation
We think you have liked this presentation. If you wish to download it, please recommend it to your friends in any social system. Share buttons are a little bit lower. Thank you!
Presentation is loading. Please wait.
THE UNITED KINGDOM OF GREAT BRITAIN
Published by Reilly Glasscock Modified over 9 years ago
Similar presentations
About project
© 2024 SlidePlayer.com Inc. All rights reserved.
Pete’s PowerPoint Station
- Science Index
- Math/Maths Index
- Language Arts/Literature Index
- Social Studies Index
- Holidays Index
- Art, Music, and Many More, A-Z
- Meteorology
- Four Seasons
- Pre-Algebra
- Trigonometry
- Pre-Calculus & Calculus
- Language Arts
- Punctuation
- Social Studies
- World Religions
- US Government
- Criminal Justice
- Famous People
- American History
- World History
- Ancient History
- The Middle Ages
- Architecture
- All Topics, A–Z
- Privacy & Cookie Policy
- Presentations
United Kingdom
Free presentations in powerpoint format.
"Howe" to See the British Isles
Coming to Britain
Great Britain
Royal Homes of Great Britain
Buckingham Palace
British History 1750-1900
Politics in Britain (list of free presentations)
Welcome to London!
Welcome to London
Tower of London
Famous Landmarks of England
Loch Ness Monster
National Dress in the UK
See Also: Europe
The UK for Kids
For Teachers
Lesson Plans for the United Kingdom
Free Clipart
Free Templates
United Kingdom country profile
- Published 9 July

The United Kingdom is a state made up of the historic countries of England, Wales and Scotland, as well as Northern Ireland. It is known as the home of both modern parliamentary democracy and the Industrial Revolution.
Two world wars and the end of empire diminished its role in the 20th Century, and the 2016 referendum vote to leave the European Union has raised significant questions about the country's global role.
Nonetheless, the United Kingdom remains an economic and military power with great political and cultural influence around the world.
Read more country profiles , external - Profiles by BBC Monitoring , external
UNITED KINGDOM OF GREAT BRITAIN AND NORTHERN IRELAND: FACTS
Capital: London
Area: 242,945 sq km
Population: 67.7 million
Languages: English, also Scots, Ulster Scots, Scottish Gaelic, Irish, Welsh, Cornish
Life expectancy: 79 years (men) 83 years (women)
Head of state: King Charles III
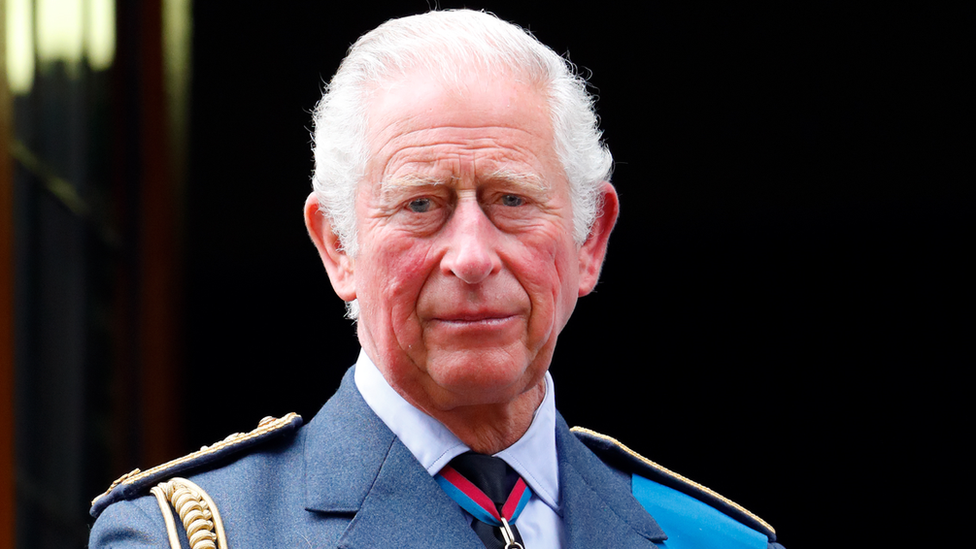

His Majesty King Charles III ascended to the throne in September 2022, on the death of his mother Queen Elizabeth II.
In September 2015, she had become Britain's longest-reigning monarch, surpassing the record of her great-great grandmother Queen Victoria.
At 73, King Charles was the oldest person to have ascended to the British throne. He is also head of state of several independent countries in the Commonwealth.
As a constitutional monarch, his role in the legislative process is largely ceremonial.
Prime Minister: Keir Starmer
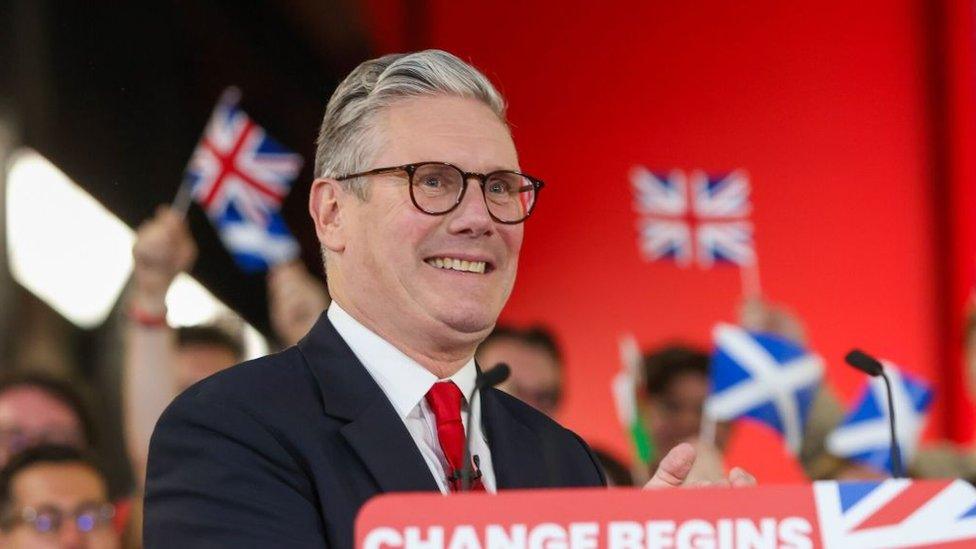

Keir Starmer was elected prime minister in the July 2024 election, which saw a sweeping Labour party victory after 14 years of Conservative or Conservative-led governments, with Labour becoming the largest party in the House of Commons.
Domestically, Starmer has said his administration will focus on economic growth, reforms of the planning system, infrastructure, energy, healthcare, education, childcare, and strengthening workers' rights.
In his first address to parliament following the election, he urged new MPs to deliver "national renewal". He hoped the new parliament would replace the "politics of performance with the politics of service" and that all MPs have a duty to show that politics can be a force for good.
There are numerous challenges facing the Labour government: these include stagnant economic growth and wages, high child poverty and homelessness, crumbling health care and public services, overcrowded prisons and sewage pollution by privatised utility companies.

The UK has a lively media scene
The UK has a strong tradition of public service broadcasting and an international reputation for creative programme-making.
The BBC began daily radio broadcasts in 1922 and quickly came to play a pivotal role in national life. The corporation is funded by a licence fee, which every household with a TV set must pay.
Hundreds of privately-owned radio and TV stations now compete with the BBC for listeners and viewers.
There are many national and local newspapers, but print circulations have been sliding while online readership has surged.
Read full media profile
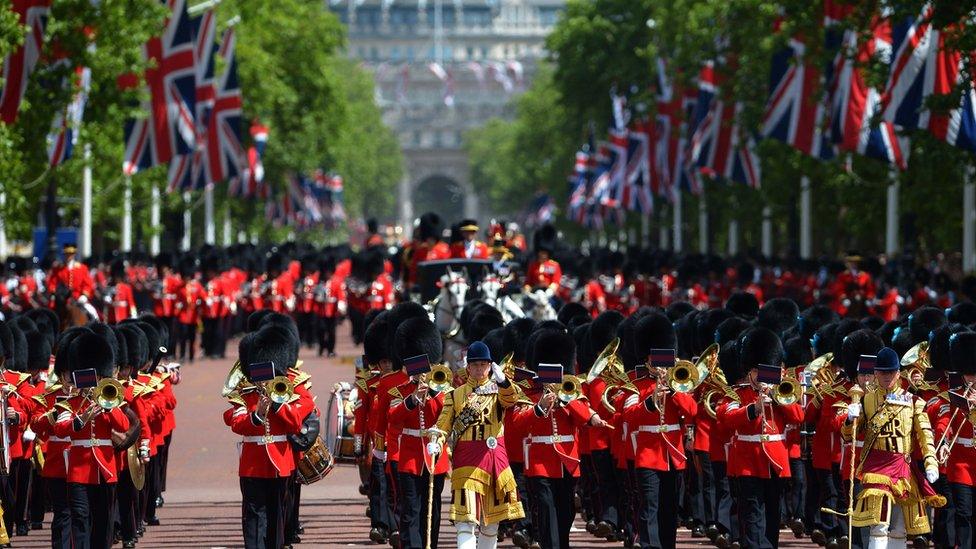

Trooping The Colour, the annual ceremony which commemorates the Monarch's official birthday
Some key dates in modern British history:
1801 - United Kingdom formed by union of the kingdoms of Great Britain and Ireland.
1815 - Role in defeating Napoleon's French Empire leads to Britain becoming pre-eminent imperial power.
1830s - Electoral reform acts begin steady move towards primacy of House of Commons and universal suffrage.
1840s - British industrial power harnessing technological change and boosts free trade and investment worldwide, reaching its peak in the second half of the 19th century.
1880s - Devolved government for Ireland becomes a major political issue, splitting Liberal Party and reviving a violent Irish separatist movement.
1914-18 - World War One.
1916 - Nationalists stage Easter Rising, seizing the General Post Office in Dublin and proclaiming an independent Irish republic. The rising is crushed by the British who execute its leaders.
1919 - Led by Éamon De Valera, the nationalist movement Sinn Féin ('We Ourselves') sets up a Dublin assembly, the Dáil Éireann, which again proclaims Irish independence. A guerrilla campaign by the Irish Republican Army, or IRA, against British forces begins with heavy casualties on both sides.
1921 - Anglo-Irish Treaty establishes the Irish Free State, partitioned from Northern Ireland which remains part of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland.
1924 - First UK government led by the Labour party under Prime Minister Ramsay MacDonald.
1931 - Economic crisis. Millions are unemployed. National Government coalition formed.
1936 - King Edward VIII abdicates over relationship with an American divorcee, Wallis Simpson.
1939 - Germany invades Poland. UK declares war on Germany.
1940 - Winston Churchill becomes prime minister.
1944 - Allied troops invade France from Britain on D-Day (6th June) and begin to fight their way towards Germany.
1945 - Germany surrenders. Labour leader Clement Atlee is elected prime minister. The new Labour government carries out a radical programme of reforms, major industries and public utilities are nationalised, a welfare state is established as well as publicly funded healthcare system, the National Health Service.

Prime Minister Winston Churchill makes his VE Day broadcast in May 1945
1945 - The UK becomes a permanent member of the UN Security Council.
1949 - The UK is one of the founder members of Nato.
1952 - UK becomes world's third country to develop an atomic bomb.
1956 - UK and France, secretly in conjunction with Israel, invade Egypt and occupy the Suez Canal Zone. They are forced to withdraw under US pressure.
1961 - UK application to join European Economic Community vetoed by French President Charles de Gaulle.
1960s - Decolonisation of former British-controlled territories gathers pace.
1969 - British troops are sent to help quell communal unrest in Northern Ireland, which marks the start of The Troubles , triggered by the disputed status of Northern Ireland within the UK and a rising sense of injustice among large sections of the Catholic population. More than 3,000 people are killed between 1969-98.
1973 - The UK joins the European Economic Community, which is endorsed in a referendum two years later.
1979 - Conservative prime minister Margaret Thatcher begins move towards deregulation of economy.
1982 - Argentina invades the Falklands Islands in the South Atlantic. The UK dispatches a task force, which re-takes them.
1984 - The IRA attempts to assassinate Mrs Thatcher in her hotel in Brighton. Several people are killed and injured by a bomb blast, but the prime minister escapes unhurt.
1997 - Referendums in Scotland and Wales back the creation of separate assemblies, which are inaugurated in 1999.
1998 - The Good Friday Agreement on a political settlement for Northern Ireland is approved by voters in the Republic of Ireland and Northern Ireland.
2012 - Britain hosts the Summer Olympics and Paralympics.
2014 - Voters in Scotland reject independence in a referendum, with 55% opting to remain part of the UK and 45% favouring independence.
2016 - UK votes to leave the European Union.
2020 - UK formally leaves the European Union.
2022 - Queen Elizabeth II dies, Charles III becomes king.

London is a major centre for finance and culture
Related topics
- Keir Starmer
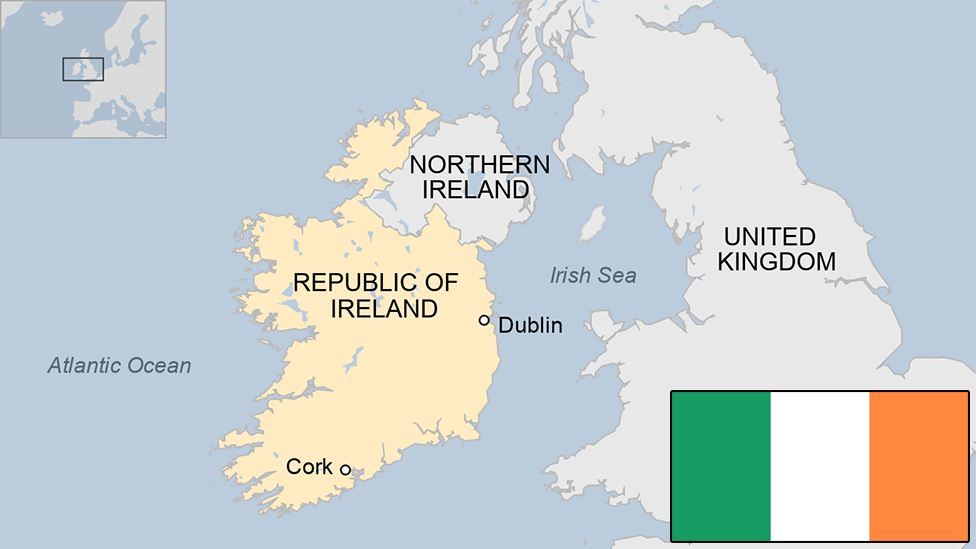
Ireland country profile
- Published 9 April
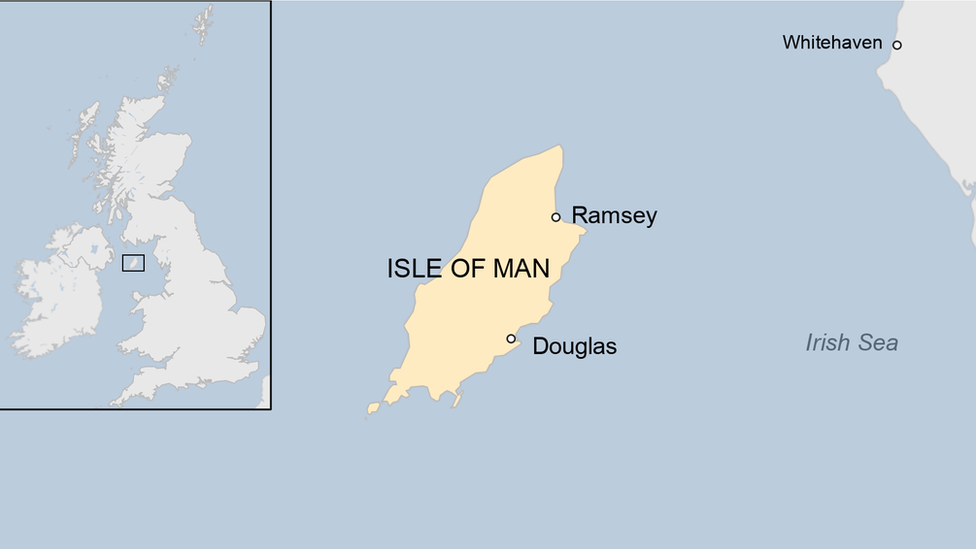
Isle of Man profile
- Published 18 October 2023
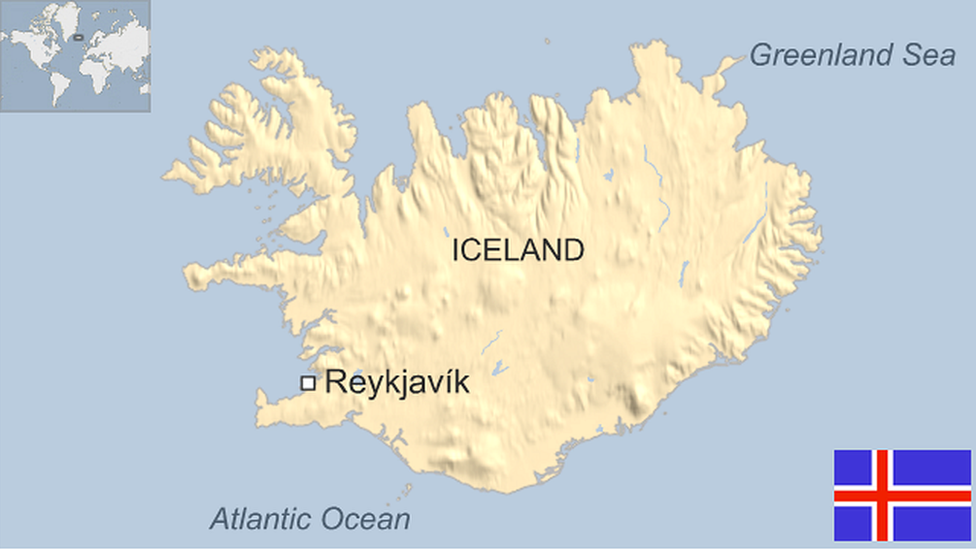
Iceland country profile
- Published 4 June
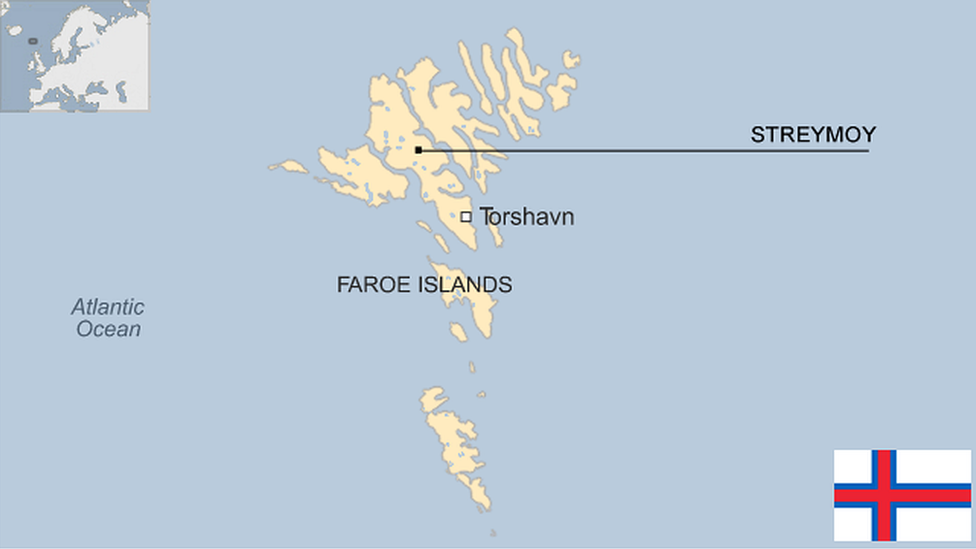
Faroe Islands profile
- Published 15 January
Norway country profile
- Published 28 March 2023
Denmark country profile
Germany country profile
- Published 4 September 2023
Netherlands country profile
- Published 2 July
Belgium country profile
- Published 21 August 2023
Channel Islands profile
France country profile
- Published 9 January
Around the BBC
BBC News - UK Direct
BBC Languages- United Kingdom
Related internet links
Prime minister's office
The British Parliament
The British Monarchy
Visit Britain
English tourist board
Scottish tourist office
Welsh tourist office
Northern Ireland Tourist Board
- English ESL Powerpoints
- Speaking Practice
- Presentation, public speaking
A trip to London presentation
Got any suggestions?
We want to hear from you! Send us a message and help improve Slidesgo
Top searches
Trending searches

fall background
24 templates


fall pumpkin
67 templates

rosh hashanah
38 templates

breast cancer
12 templates

9 templates

cute halloween
16 templates
History of England Class
It seems that you like this template, history of england class presentation, free google slides theme, powerpoint template, and canva presentation template.
How do you make a class on the history of England interesting? With this template, that’s how! With the look of papyrus, it contains charming illustrations of English icons that help you set the scene and give a visual sense of the country through the centuries. You can also add icons to enliven your slides and present your data in a way that keeps your students engaged. So whether you’re jumping through the centuries or focusing on a specific time period, you’ve got everything you need to make it fascinating.
Features of this template
- 100% editable and easy to modify
- 38 different slides to impress your audience
- Contains easy-to-edit graphics such as graphs, maps, tables, timelines and mockups
- Includes 500+ icons and Flaticon’s extension for customizing your slides
- Designed to be used in Google Slides, Canva, and Microsoft PowerPoint
- 16:9 widescreen format suitable for all types of screens
- Includes information about fonts, colors, and credits of the resources used
How can I use the template?
Am I free to use the templates?
How to attribute?
Attribution required If you are a free user, you must attribute Slidesgo by keeping the slide where the credits appear. How to attribute?

Register for free and start downloading now
Related posts on our blog.

How to Add, Duplicate, Move, Delete or Hide Slides in Google Slides

How to Change Layouts in PowerPoint

How to Change the Slide Size in Google Slides
Related presentations.

Premium template
Unlock this template and gain unlimited access

Create your presentation Create personalized presentation content
Writing tone, number of slides.

Register for free and start editing online

Autism Presentation in Females
2 hrs webinar to help understand behaviour and daily challenges of autistic girls
Date and time
Refund policy.
7:00 PM - 7:10 PM
Welcome and Introduction (10 minutes)
7:10 PM - 7:40 PM
Autism in Females – Understanding the Differences
7:40 PM - 8:00 PM
Social Masking and Its Impact on Diagnosis
8:00 PM - 8:10 PM
8:10 PM - 8:30 PM
Early Signs and Red Flags in Girls
8:35 PM - 8:55 PM
Practical Support Strategies for Parents and Professionals
8:55 PM - 9:00 PM
About this event
- Event lasts 2 hours
Autism Presentation in Females: Understanding Unique Experiences and Needs
Autism presents differently in females, often leading to underdiagnosis or misdiagnosis. This webinar is designed to provide both parents and professionals with a comprehensive understanding of the distinct ways autism can manifest in girls and women. We will explore common traits, diagnostic challenges, and strategies to support females on the autism spectrum.
Key Takeaways:
- Differences in how autism presents in females versus males
- Social masking and its impact on diagnosis and support
- Early signs and red flags to look for in girls
- Practical strategies for parents and educators to foster growth and independence
- Understanding sensory sensitivities, communication styles, and emotional needs
- Challenges related to sexuality and puberty
Target Audience: Parents, educators, clinicians, and professionals working with individuals on the autism spectrum
The workshop will be delivered using Teams and all details will be sent to attendees a day before the workshop. There will a be a short break and Q&A at the end.
Please note that we are unable to help with any IT problems. The Link to access the webinar will be sent a day before the webinar- please check your SPAM.
Feedback from previous workshops:
"I can highly recommend attending any of Ola's workshops. As a professional it is great to learn from someone who is 'hands on' experiencing everything she teaches.".
"It was by far the best autism course I have been to, everything related to real experiences rather than a text book. Teachers and Ta’s should go on the course so that our children can actually stand a chance!”
"Ola is lovely lady who made you feel welcome and will try and help you with anything that’s troubling you. This course/session was like a breath of fresh air and would highly recommend it."
I guarantee holistic approach and understanding as I have been through the journey myself.
Thanks for your donations -the funds will be used to support families with autistic children and deliver more online workshops that you will , hopefully, also benefit from.
Frequently asked questions
After you register, you will receive a confirmation email with a link to join the webinar. On the day of the event, simply click the link to join at the scheduled time.
No, the webinar will not be recorded. We encourage all participants to attend the live session to get the most out of the content and interactive Q&A segments.
You’ll need a device with internet access (computer, tablet, or smartphone) and a stable connection. For the best experience, we recommend using a computer with a reliable internet connection, as well as speakers or headphones for clear audio.
Yes, each session will include a dedicated Q&A segment. You can submit your questions using the chat or Q&A feature, and the speaker will address as many as possible within the time limits.
No, each registration is unique to the individual participant. Please encourage others to register so they can receive their own unique access link.
Unfortunately, no live IT support will be available during the webinar. We recommend testing your device and internet connection before the event to ensure a smooth experience. You may also try refreshing your browser or rejoining the session if issues arise.
No special software is needed. The webinar will be hosted on a web-based platform like Zoom, Microsoft Teams, or similar. The link provided will open directly in your web browser.
Any resources shared during the webinar (such as handouts, slides, or links) will be emailed to participants after the event.
Yes, certificates of attendance will be available for professionals who require them for continuing education or professional development.
f you have any questions after the webinar, you can contact the organizer via the provided email. We will do our best to address all queries and provide further support.
- Online Events
- Things To Do Online
- Online Classes
- Online Family & Education Classes
Organized by

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The United Kingdom has made significant contributions to the world economy, especially in technology and industry. Since World War II, however, the United Kingdom's most prominent exports have been cultural, including literature, theatre, film, television, and popular music that draw on all parts of the country. Perhaps Britain's greatest export has been the English language, now spoken in ...
Download the United Kingdom Crown Minitheme presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides and start impressing your audience with a creative and original design. Slidesgo templates like this one here offer the possibility to convey a concept, idea or topic in a clear, concise and visual way, by using different graphic... Multi-purpose.
The biggest part of the United Kingdom (also called the U.K.) is the island of Great Britain, which is made up of England, Wales, and Scotland. The U.K. also includes Northern Ireland, which is on another island. (South of Northern Ireland is the separate country of Ireland, which gained its independence from the U.K. in 1937.)
1 THE UNITED KINGDOM OF GREAT BRITAIN. It is a monarch state situated in the North-West of Europe. UK is composed of four countries: 1-England 2-Scotland 3-Wales 4-Northern Ireland The Uk is surrounded by Atlantic Ocean,the North Sea and the English Channel that separates the UK from the continent. The flag of the UK is the UNION FLAG,also ...
Facts About the United Kingdom. This PowerPoint provides some facts about the UK. There are pictures and flags and other miscellaneous information. It is a very basic presentation for beginners. 978 uses. A selection of English ESL united kingdom ppt slides.
You can use this fantastic PowerPoint to teach your class about the UK. This fantastic and informative PowerPoint about England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland is packed with interesting facts including, currency, national flowers and facts about the UK capital cities. This activity is perfect for the whole class, part of research ...
Free Presentations in PowerPoint format "Howe" to See the British Isles. Coming to Britain. Great Britain. Royal Homes of Great Britain. Buckingham Palace. British History 1750-1900. Politics in Britain (list of free presentations) Welcome to London! Welcome to London. Tower of London. Famous Landmarks of England. Ireland. Celts. Scotland ...
Share this template: The free United Kingdom PowerPoint Template has a blue background image with the Union Jack, the national flag of the United Kingdom that makes it look very beautiful. The template is suitable for various kinds of presentations about UK, its history, geography, culture, cities, people, landmarks, economy, politics, etc.
University of Manchester. Located in the heart of Manchester. Internationally famous for its medical, biology and chemistry programmes. Currently ranked 6th best institution in the UK, 26th Globally. Second largest University in the UK. Birthplace of nuclear physics, where Ernest Rutherford first split the atom.
United Kingdom country profile. The United Kingdom is a state made up of the historic countries of England, Wales and Scotland, as well as Northern Ireland. It is known as the home of both modern ...
London is the capital and most populous city of England and the United Kingdom. Standing on the River Thames in the south east of the island of Great Britain, London has been a major settlement for two millennia. It was founded by the Romans, who named it Londinium. London's ancient core, the City of London, largely retains its 1.12-square-mile medieval boundaries. Since at least the 19th ...
Perfect for whole-class teaching, this United Kingdom Information PowerPoint features some handy information to help support your teaching on this topic along with a few examples and prompts to get the children started. This United Kingdom Information PowerPoint teaches children essential information about the country, including geography, culture, food and more. It also features colourful ...
Features of this template. Contains easy-to-edit graphics such as graphs, maps, tables, timelines and mockups. Includes 500+ icons and Flaticon's extension for customizing your slides. Designed to be used in Google Slides, Canva, and Microsoft PowerPoint. 16:9 widescreen format suitable for all types of screens.
Help. You can use this fantastic PowerPoint to teach your class about the UK. This fantastic and informative PowerPoint about England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland is packed with interesting facts including, currency, national flowers and facts about the UK capital cities. This activity is perfect for whole class, part of a research ...
Autism Presentation in Females: Understanding Unique Experiences and Needs. Autism presents differently in females, often leading to underdiagnosis or misdiagnosis. This webinar is designed to provide both parents and professionals with a comprehensive understanding of the distinct ways autism can manifest in girls and women. We will explore ...