
Retail Business Plan Template
Written by Dave Lavinsky
Retail Business Plan
You’ve come to the right place to create your retail business plan.
We have helped over 10,000 entrepreneurs and business owners create business plans and many have used them to start or grow their retail companies.
Retail Business Plan Template & Sample
Below is a retail business plan template to help you create each section of your retail store business plan.
Executive Summary
Business overview.
Artisan Home & Decor is a startup retail shop located in Pasadena, California. The company is founded by Joyce Hernandez, a retailer who has worked as a store manager of a local home decor store for nearly a decade. Joyce has recently graduated from California University with a Bachelor’s degree in Business Management. Now that she has gained real-world experience managing a store and the education on how to run a retail business, she is inspired to start her own company, Artisan Home & Decor. Joyce is confident that her ability to effectively manage employees, customer relationships, and retail operations will help her establish a profitable retail store. Joyce plans on recruiting a team of highly qualified sales associates, accountants, and buyers to help manage the day to day complexities of retail – marketing, sales, budgeting, sourcing, and purchasing.
Artisan Home & Decor will provide uniquely curated home decor products created by local artisans. The home decor shop will be the ultimate choice for customers in Pasadena who value one-of-a-kind pieces for their homes. Artisan Home & Decor will provide its customers with a refreshingly personalized shopping experience they can’t get anywhere else. The shop’s sales associates will be able to help customers find the perfect pieces to suit their individual preferences and styles.
Product Offering
The following are the products that Artisan Home & Decor will provide:
- Lamps & Lighting
- Throw Blankets
- Photo Frames
- Cookware Sets
- Kitchen Gadgets
- Kitchen and Bathroom Fixtures
- Waste Baskets
- Soap Dispensers
Customer Focus
Artisan Home & Decor will target home decor shoppers looking for a personalized experience and unique pieces in Pasadena. The company will target boomer, millennial, and gen z consumers looking for unique decor for their homes, apartments, or condos. They will also target businesses looking for special pieces to furnish their corporate offices, waiting rooms, and lobbies. No matter the client, Artisan Home & Decor will deliver the best communication, service, and high quality products.
Management Team
Artisan Home & Decor will be owned and operated by Joyce Hernandez, a retailer who has worked as a store manager of a local home decor store for nearly a decade. Joyce has recently graduated from California University with a Bachelor’s degree in Business Management. Now that she has gained real-world experience managing retail stores and the education on how to run a retail business, she is inspired to start her own company, Artisan Home & Decor.
Joyce Hernandez has recruited her former assistant manager, Melissa Jacobs to come on board to help her manage Artisan Home & Decor. While Joyce will oversee the employees, day-to-day operations, and client relationships, Melissa will be the Inventory Manager. She will be in charge of sourcing, purchasing, and pricing all inventory. Melissa will work directly with suppliers to stock the retail shop with unique artisan pieces.
Melissa is a graduate of the University of California with a Bachelor’s degree in Interior Design. She has been working at a local retail home decor company for over a decade as an assistant manager. Melissa has an eye for design and keen organizational skills that will allow her to effectively manage Artisan Home & Decor’s one-of-a-kind inventory. Her communication skills will enable her to establish and maintain working relationships with artisans and suppliers.
Success Factors
Artisan Home & Decor will be able to achieve success by offering the following competitive advantages:
- Friendly, knowledgeable, and highly qualified team of sales associates and interior design experts that are able to provide a personalized customer experience and help each client find the right home decor pieces to suit their preferences.
- Artisan Home & Decor will bring fresh inventory into their retail store on a regular basis so there will always be something new for customers to check out. In addition to in-store sales, the company will sell pieces online through its website.
- Artisan Home & Decor offers one-of-kind pieces created by local artisans to suit a wide variety of home decor styles and tastes. By purchasing from the shop, customers are supporting these local artisans and getting fresh decor that no one else will have.
Financial Highlights
Artisan Home & Decor is seeking $210,000 in debt financing to launch its retail business. The funding will be dedicated towards securing and building out the retail space and purchasing the initial inventory. Funds will also be dedicated towards three months of overhead costs to include payroll of the staff, rent, and marketing costs for print ads, website and SEO marketing initiatives, and association memberships. The breakout of the funding is below:
- Retail space build-out: $25,000
- Retail store shelving, displays, equipment, supplies, and materials: $40,000
- Three months of overhead expenses (payroll, rent, utilities): $120,000
- Marketing costs: $15,000
- Working capital: $10,000
The following graph below outlines the pro forma financial projections for Artisan Home & Decor.
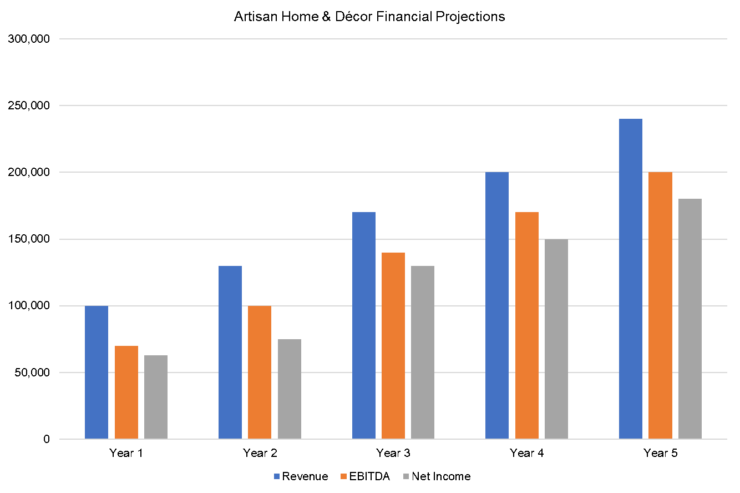
Company Overview
Who is artisan home & decor.
Artisan Home & Decor is a newly established retail company in Pasadena, California. The new home decor shop will be the ultimate choice for people looking for uniquely curated one-of-a-kind furniture and other home products crafted by local artisans. Artisan Home & Decor will provide its customers with a refreshingly personalized shopping experience they can’t get anywhere else. The shop’s sales associates and experienced interior designers will be able to help customers find the right pieces to suit their preferences and styles.
Artisan Home & Decor will be able to provide a personalized shopping experience for serving customers in-store and online. The team of professionals and sales associates are highly qualified and experienced in interior design, home decor, and the customer experience. Artisan Home & Decor removes all headaches and issues of the home decor shopper and ensures all issues are taken care off expeditiously while delivering the best customer service.
Artisan Home & Decor History
Artisan Home & Decor is owned and operated by Joyce Hernandez, a retailer who has worked as a store manager of a local home decor store for nearly a decade. Joyce has recently graduated from California University with a Bachelor’s degree in Business Management. Now that she has gained real-world experience managing retail stores and the education on how to run a retail business, she is ready to start her own company. Joyce is confident that her ability to effectively manage employees, customer relationships, and retail operations will help her establish a profitable retail store. Joyce has begun recruiting a team of highly qualified sales associates, accountants, and buyers to help manage the day to day complexities of retail – marketing, sales, budgeting, sourcing, and purchasing.
Since incorporation, Artisan Home & Decor has achieved the following milestones:
- Registered Artisan Home & Decor, LLC to transact business in the state of California.
- Has a contract in place to lease the retail space.
- Reached out to numerous local artisans to advise them on the upcoming retail shop in order to start getting supplier contracts.
- Began recruiting a staff of sales associates, interior designers, an accountant/bookkeeper, marketing director, and assistant manager to work at Artisan Home & Decor.
Artisan Home & Decor Services
Industry analysis.
The retail industry in the United States is valued at over $4T currently and is forecasted to reach $4.9T by the end of 2022. This is up from $3.8T in 2019. After a decade of retail decline between 2010 and 2020, the market is rebounding at a surprising rate. There were twice as many store openings as closings in 2021 alone. The number of brick-and-mortar retail establishments is increasing even as ecommerce shopping has grown by 70% in the last three years.
The role of retail stores is evolving and industry operators are discovering in-store experiences are still vital from the customer perspective. Successful brick-and-mortar industry operators are incorporating ecommerce into their business models. Trends include providing ship-from-store and buy online, pickup in store options to give customers more flexibility in the way they can shop. Key success factors include the level of customer satisfaction, product selection, prices, and convenience.
Customer Analysis
Demographic profile of target market.
The precise demographics for Pasadena, California are:
Customer Segmentation
Artisan Home & Decor will primarily target the following customer profiles:
- Millennial customers looking for one-of-a-kind home decor
- Boomer customers looking for one-of-a-kind home decor
- Gen z customers looking for one-of-a-kind home decor
- Businesses looking for unique decor for their offices, waiting rooms, or lobbies
Competitive Analysis
Direct and indirect competitors.
Artisan Home & Decor will face competition from other retailers with similar business profiles. A description of each competitor company is below.
Pasadena Home Decor
Pasadena Home Decor provides high-end home decor for the conscientious consumer. Located in Pasadena, California, the home decor retailer is able to provide a tailored shopping experience for its customers. The store’s list of products includes tables, chairs, wall hangings, rugs, vases, photo frames, candles, office decor, and paintings by local artists. Pasadena Home Decor sells online and in-store to give customers flexibility.
Pasadena Home Decor’s promise is to deliver high quality pieces that will stand out. Customers who purchase furniture and home decor from Pasadena Home Decor will be delighted with the customer service, cleanliness of the store, and personalized design services the company offers.
Home Shoppe
Home Shoppe is a California-based home decor retail store that provides outstanding pieces for discerning clientele. Home Shoppe stocks unique furniture and other decor items that are 100% hand-crafted. The owners of Home Shoppe are experienced craftsmen themselves, so they know how quality furniture and home decor pieces should be made. Clients can depend on their selection of products for durability, style, and eco-friendly materials. Choose Home Shoppe for your next home decor project and let the sales team take the stress out of the redecorating process by helping you select the best products for your home.
Redecorating For You
Redecorating For You is a trusted Pasadena retail company that provides superior home decor products for shoppers in Pasadena and the surrounding areas. The shop offers an extensive inventory of home decor items in a variety of styles so there is something for every taste. Redecorating For You is able to provide premium pieces that fill every space with elegance and style. The shop also eases the stress of redecorating by providing in-store pickup and delivery options for busy customers.
Competitive Advantage
Artisan Home & Decor will be able to offer the following advantages over their competition:
- Artisan Home & Decor will bring fresh inventory into the store on a regular basis so there will always be something new for customers to check out. In addition to in-store sales, the company will sell pieces online through its website.
- Artisan Home & Decor offers one-of-kind pieces created by local artisans to suit a wide variety of home decor styles and tastes.
Marketing Plan
Brand & value proposition.
Artisan Home & Decor will offer the unique value proposition to its clientele:
- Artisan Home & Decor will make redecorating easy for customers by providing in-store shopping, pickup, delivery, online shopping, ship-from-store, and buy online-pickup in store options.
- By purchasing from the shop, customers are supporting local artisans and getting fresh decor that no one else will have.
Promotions Strategy
The promotions strategy for Artisan Home & Decor is as follows:
Social Media Marketing
The company will use various social media platforms such as TikTok, Instagram, Facebook, LinkedIn, YouTube, and Snapchat to promote the shop, feature artisans, and show off new pieces. The marketing director will oversee the social media marketing activities to grow the customer base.
Professional Associations and Networking
Artisan Home & Decor will become a member of professional associations such as the National Retail Federation, California Retailers Association, and the Home Furnishings Association. The company will focus its networking efforts on expanding its network of clients, designers, and artisans.
Print Advertising
Artisan Home & Decor will invest in professionally designed print ads to display in programs or flyers at industry networking events, in home decor publications, and direct mailers.
Website/SEO Marketing
Artisan Home & Decor’s marketing director will be responsible for creating and maintaining the company website. The website will be well organized, informative, and list all of the products currently available for purchase online.
The marketing director will also manage Artisan Home & Decor’s website presence with SEO marketing tactics so that any time someone types in the Google or Bing search engine “Pasadena home decor retailer” or “home decor store near me”, Artisan Home & Decor will be listed at the top of the search results.
The pricing of Artisan Home & Decor will be premium and on par with competitors so customers feel they receive value when purchasing the one-of-a-kind products.
Operations Plan
The following will be the operations plan for Artisan Home & Decor.
Operation Functions:
- Joyce Hernandez will be the Owner and Manager of the store. She will oversee all staff and manage day-to-day operations. Joyce has spent the past year recruiting the following staff:
- Melissa Jacobs – Inventory Manager who will be responsible for sourcing, purchasing, pricing, and maintaining the inventory.
- Robert Brown – Staff Accountant/bookkeeper who will provide all store accounting, tax payments, and monthly financial reporting.
- Bill Johnson – Marketing Director who will provide all marketing and sales activities for Artisan Home & Decor including maintaining the website, social media, print advertising, and promotions.
- Julia Smith – Lead Sales Associate & Designer who will manage all sales associates and provide design services for customers.
Milestones:
Artisan Home & Decor will have the following milestones complete in the next six months.
9/1/2022 – Finalize contract to lease the retail space.
9/15/2022 – Finalize personnel and staff employment contracts for the management team.
10/1/2022 – Finalize contracts for suppliers.
10/15/2022 – Begin networking at industry events and implement the marketing plan.
10/22/2022 – Begin moving into the Artisan Home & Decor shop.
11/1/2022 – Artisan Home & Decor opens for business.
Artisan Home & Decor will be owned and operated by Joyce Hernandez, a retailer who has worked as a store manager of a local home decor store for nearly a decade. Joyce has recently graduated from California University with a Bachelor’s degree in Business Management. Now that she has gained real-world experience managing a store and the education on how to run a retail business, she is inspired to start her own company, Artisan Home & Decor.
Melissa is a graduate of the University of California with a Bachelor’s degree in Interior Design. She has been working at a local retail home decor company for over a decade as an assistant manager. Melissa has an eye for design and keen organizational skills that will allow her to effectively manage Artisan Home & Decor’s one-of-a-kind inventory. Her communication skills will enable her to establish and maintain working relationships with suppliers.
Financial Plan
Key revenue & costs.
The revenue drivers for Artisan Home & Decor are the retail fees they will charge to the customers in exchange for their products. The shop will charge a healthy margin to make sure artisans are paid well for their products while ensuring a solid profit for the business.
The cost drivers will be the overhead costs required in order to staff a retail store. The expenses will be the payroll cost, rent, utilities, store supplies, and marketing materials.
Funding Requirements and Use of Funds
- Store shelving, displays, equipment, supplies, and materials: $40,000
Key Assumptions
The following outlines the key assumptions required in order to achieve the revenue and cost numbers in the financials and in order to pay off the startup business loan.
- Average number of items sold per month: 300
- Average sales per month: $90,000
- Retail space lease per year: $100,000
Financial Projections
Income statement, balance sheet, cash flow statement, retail business plan template faqs, what is a retail business plan.
A retail business plan is a plan to start and/or grow your retail business. Among other things, it outlines your business concept, identifies your target market, presents your marketing plan and details your financial projections.
You can easily complete your retail business plan using our Retail Business Plan Template here .
What are the Main Types of Retail Businesses?
There are a number of different kinds of retail businesses, some examples include: Specialty Store, Off-Priced/Used Goods Store, Department Store, Convenience Store, Drug Store/Pharmacy, Discount Store, Hypermarket, and E-commerce.
How Do You Get Funding for Your Retail Business Plan?
Retail businesses are often funded through small business loans. Personal savings, credit card financing and angel investors are also popular forms of funding.
A solid retail business plan with comprehensive financial statements will help show investors your are well-prepared to start your own business. A retail business plan template will help you quickly and easily get started.
What are the Steps To Start a Retail Business?
Starting a retail business can be an exciting endeavor. Having a clear roadmap of the steps to start a business will help you stay focused on your goals and get started faster.
1. Develop A Retail Business Plan - The first step in starting a business is to create a detailed retail store business plan that outlines all aspects of the venture. This should include supporting market research, your potential market size and target customers, the services or products you will offer, marketing strategy, your competitive advantages and detailed financial projections.
2. Choose Your Legal Structure - It's important to select an appropriate legal entity for your retail business. This could be a limited liability company (LLC), corporation, partnership, or sole proprietorship. Each type has its own benefits and drawbacks so it’s important to do research and choose wisely so that your retail business is in compliance with local laws.
3. Register Your Retail Business - Once you have chosen a legal structure, the next step is to register your retail business with the government or state where you’re operating from. This includes obtaining licenses and permits as required by federal, state, and local laws.
4. Identify Financing Options - It’s likely that you’ll need some capital to start your retail business, so take some time to identify what financing options are available such as bank loans, investor funding, grants, or crowdfunding platforms.
5. Choose a Location - Whether you plan on operating out of a physical location or not, you should always have an idea of where you’ll be based should it become necessary in the future as well as what kind of space would be suitable for your operations.
6. Hire Employees - There are several ways to find qualified employees including job boards like LinkedIn or Indeed as well as hiring agencies if needed – depending on what type of employees you need it might also be more effective to reach out directly through networking events.
7. Acquire Necessary Retail Equipment & Supplies - In order to start your retail business, you'll need to purchase all of the necessary equipment and supplies to run a successful operation.
8. Market & Promote Your Business - Once you have all the necessary pieces in place, it’s time to start promoting and marketing your retail business. This includes creating a website, utilizing social media platforms like Facebook or Twitter, and having an effective Search Engine Optimization (SEO) strategy. You should also consider traditional marketing techniques such as radio or print advertising.
Where Can I Get a Retail Business Plan PDF?
You can download our free retail business plan template PDF here . This is a sample retail business plan template you can use in PDF format.
Other Helpful Business Plan Templates
Ecommerce Business Plan Template Clothing Store Business Plan Template Beauty Supply Store Business Plan Template T-Shirt Business Plan Template

How to Write the Market Analysis Section of a Business Plan
Written by Dave Lavinsky

What is the Market Analysis in a Business Plan?
The market analysis section of your business plan is where you discuss the size of the market in which you’re competing and market trends that might affect your future potential such as economic, political, social and/or technological shifts.
This helps you and readers understand if your market is big enough to support your business’ growth, and whether future conditions will help or hurt your business. For example, stating that your market size is $56 billion, has been growing by 10% for the last 10 years, and that trends are expected to further increase the market size bodes well for your company’s success.
Download our Ultimate Business Plan Template here
What Should a Market Analysis Include?
You’ll want to address these issues in your market analysis:
- Size of Industry – How big is the overall industry?
- Projected Growth Rate of Industry – Is the industry growing or shrinking? How fast?
- Target Market – Who are you targeting with this product or service?
- Competition – How many businesses are currently in the same industry?
Learn how to write the full market analysis below.
How to Write a Market Analysis
Here’s how to write the market analysis section of a business plan.
- Describe each industry that you are competing in or will be targeting.
- Identify direct competition, but don’t forget about indirect competition – this may include companies selling different products to the same potential customer segments.
- Highlight strengths and weaknesses for both direct and indirect competitors, along with how your company stacks up against them based on what makes your company uniquely positioned to succeed.
- Include specific data, statistics, graphs, or charts if possible to make the market analysis more convincing to investors or lenders.
Finish Your Business Plan Today!
Industry overview.
In your industry overview, you will define the market in which you are competing (e.g., restaurant, medical devices, etc.).
You will then detail the sub-segment or niche of that market if applicable (e.g., within restaurants there are fast food restaurants, fine dining, etc.).
Next, you will describe the key characteristics of your industry. For example, discuss how big the market is in terms of units and revenues. Let the reader know if the market is growing or declining (and at what rate), and what key industry trends are facing your market.
Use third-party market research as much as possible to validate the discussion of your industry.
Here is a list of additional items you may analyze for a complete industry overview:
- An overview of the current state of the industry . How big is it, how much does it produce or sell? What are its key differentiators from competitors? What is its target customer base like – demographic information and psychographics? How has the industry performed over time (global, domestic)?
- Analyze the macro-economic factors impacting your industry . This includes items such as economic growth opportunities, inflation, exchange rates, interest rates, labor market trends, and technological improvements. You want to make sure that all of these are trending in a positive direction for you while also being realistic about them. For example, if the economy is in shambles you might want to wait before entering the particular market.
- Analyze the political factors impacting your industry . This is an often-overlooked section of any business plan, but it can be important depending on what type of company you are starting. If you’re in a highly regulated industry (such as medical devices), this is something that you’ll want to include.
- Analyze the social factors impacting your industry . This includes analyzing society’s interest in your product or service, historical trends in buying patterns in your industry, and any effects on the industry due to changes in culture. For example, if there is a growing counter-culture trend against big oil companies you might want to position yourself differently than a company in this industry.
- Analyze the technological factors impacting your industry . This includes analyzing new technologies being developed in software, hardware, or applications that can be used to improve your product or service. It also includes emerging consumer trends and will be highly dependent on your business type. In a technology-related venture, you would analyze how these changes are impacting consumers. For an educational-related venture, you would analyze how these changes are impacting students, teachers, and/or administrators.
For each of these items, you want to provide some detail about them including their current state as well as what external factors have played a role in the recent past. You can also include many other important factors if they apply to your business including demographic trends, legal issues, environmental concerns, and sustainability issues.
When you are done analyzing all of these factors, wrap it up by summing them up in a statement that includes your view on the future of the industry. This should be positive to attract investors, potential customers, and partners.
If you’re having trouble thinking about all of these factors then it might be helpful to first develop a SWOT analysis for your business.
Once you have an understanding of the market, you’ll need to think about how you will position yourself within that potential market.
Picking Your Niche
You want to think about how large your market is for this venture. You also want to consider whether you’d like to pick a niche within the overall industry or launch yourself into the mainstream.
If you have an innovative product it can be easier to enter the mainstream market – but at the same time, you might face some additional competition if there are similar products available.
You can choose to specialize in a niche market where you’ll face less competition – but might be able to sell your services at a higher price point (this could make it easier for you to get potential customers).
Of course, if your product or service is unique then there should be no competition. But, what happens if it isn’t unique? Will you be able to differentiate yourself enough to create a competitive advantage or edge?
If you are planning on entering the mainstream market, think about whether there are different sub-niches within your specific market. For example, within the technology industry, you can choose to specialize in laptops or smartphones or tablets, or other categories. While it will be more difficult to be unique in a mainstream market, you will still be able to focus on one type or category of products.
How Will You Stand Out?
Many companies are able to stand out – whether by offering a product that is unique or by marketing their products in a way that consumers notice. For example, Steve Jobs was able to take a business idea like the iPhone and make it into something that people talked about (while competitors struggled to play catch up).
You want your venture to stand out – whether with an innovative product or service or through marketing strategies. This might include a unique brand, name, or logo. It might also include packaging that stands out from competitors.
Write down how you will achieve this goal of standing out in the marketplace. If it’s a product, then what features do you have that other products don’t? If it’s a service, then what is it about this service that will make people want to use your company rather than your competition?
You also need to think about marketing. How are you going to promote yourself or sell your product or service? You’ll need a marketing plan for this – which might include writing copy, creating an advertisement, setting up a website, and several other activities. This should include a description of each of these strategies.
If you’re struggling with the details of any of these sections, it might be helpful to research what other companies in your market are doing and how they’ve been successful. You can use this business information to inform your own strategies and plans.
Relevant Market Size & Competition
In the second stage of your analysis, you must determine the size and competition in your specific market.
Target Market Section
Your company’s relevant market size is the amount of money it could make each year if it owned a complete market share.
It’s simple.
To begin, estimate how many consumers you expect to be interested in purchasing your products or services each year.
To generate a more precise estimate, enter the monetary amount these potential customers may be ready to spend on your goods or services each year.
The size of your market is the product of these two figures. Calculate this market value here so that your readers can see how big your market opportunity is (particularly if you are seeking debt or equity funding).
You’ll also want to include an analysis of your market conditions. Is this a growing or declining market? How fast is it growing (or declining)? What are the general trends in the market? How has your market shifted over time?
Include all of this information in your own business plan to give your readers a clear understanding of the market landscape you’re competing in.
The Competition
Next, you’ll need to create a comprehensive list of the competitors in your market. This competitive analysis includes:
- Direct Competitors – Companies that offer a similar product or service
- Indirect Competitors – Companies that sell products or services that are complementary to yours but not directly related
To show how large each competitor is, you can use metrics such as revenue, employees, number of locations, etc. If you have limited information about the company on hand then you may want to do some additional research or contact them directly for more information. You should also include their website so readers can learn more if they desire (along with social media profiles).
Once you complete this list, take a step back and try to determine how much market share each competitor has. You can use different methods to do this such as market research, surveys, or conduct focus groups or interviews with target customers.
You should also take into account the barriers to entry that exist in your market. What would it take for a new company to enter the market and start competing with you? This could be anything from capital requirements to licensing and permits.
When you have all of this information, you’ll want to create a table like the one below:
Once you have this data, you can start developing strategies to compete with the other companies which will be used again later to help you develop your marketing strategy and plan.
Writing a Market Analysis Tips
- Include an explanation of how you determined the size of the market and how much share competitors have.
- Include tables like the one above that show competitor size, barriers to entry, etc.
- Decide where you’re going to place this section in your business plan – before or after your SWOT analysis. You can use other sections as well such as your company summary or product/service description. Make sure you consider which information should come first for the reader to make the most sense.
- Brainstorm how you’re going to stand out in this competitive market.
Formatting the Market Analysis Section of Your Business Plan
Now that you understand the different components of the market analysis, let’s take a look at how you should structure this section in your business plan.
Your market analysis should be divided into two sections: the industry overview and market size & competition.
Each section should include detailed information about the topic and supporting evidence to back up your claims.
You’ll also want to make sure that all of your data is up-to-date. Be sure to include the date of the analysis in your business plan so readers know when it was conducted and if there have been any major changes since then.
In addition, you should also provide a short summary of what this section covers at the beginning of each paragraph or page. You can do this by using a title such as “Industry Overview” or another descriptive phrase that is easy to follow.
As with all sections in a business plan, make sure your market analysis is concise and includes only the most relevant information to keep your audience engaged until they reach your conclusion.
A strong market analysis can give your company a competitive edge over other businesses in its industry, which is why it’s essential to include this section in your business plan. By providing detailed information about the market you’re competing in, you can show your readers that you understand the industry and know how to capitalize on current and future trends.
Business Plan Market Analysis Examples
The following are examples of how to write the market analysis section of a business plan:
Business Plan Market Analysis Example #1 – Hosmer Sunglasses, a sunglasses manufacturer based in California
According to the Sunglass Association of America, the retail sales volume of Plano (non-prescription) sunglasses, clip-on sunglasses, and children’s sunglasses (hereinafter collectively referred to as “Sunwear”) totaled $2.9 billion last year. Premium-priced sunglasses are driving the Plano Sunwear market. Plano sunglasses priced at $100 or more accounted for more than 49% of all Sunwear sales among independent retail locations last year.
The Sunglass Association of America has projected that the dollar volume for retail sales of Plano Sunwear will grow 1.7% next year. Plano sunglass vendors are also bullish about sales in this year and beyond as a result of the growth of technology, particularly the growth of laser surgery and e-commerce.
Business Plan Market Analysis Example #2 – Nailed It!, a family-owned restaurant in Omaha, NE
According to the Nebraska Restaurant Association, last year total restaurant sales in Nebraska grew by 4.3%, reaching a record high of $2.8 billion. Sales at full-service restaurants were particularly strong, growing 7% over 2012 figures. This steady increase is being driven by population growth throughout the state. The Average Annual Growth Rate (AGR) since 2009 is 2.89%.
This fast growth has also encouraged the opening of new restaurants, with 3,035 operating statewide as of this year. The restaurant industry employs more than 41,000 workers in Nebraska and contributes nearly $3 billion to the state economy every year.
Nebraska’s population continues to increase – reaching 1.9 million in 2012, a 1.5% growth rate. In addition to population, the state has experienced record low unemployment every year since 2009 – with an average of 4.7% in 2013 and 2014.
Business Plan Market Analysis Example #3 – American Insurance Company (AIC), a chain of insurance agencies in Maine
American Insurance Company (AIC) offers high-quality insurance at low prices through its chain of retail outlets in the state of Maine. Since its inception, AIC has created an extensive network of agents and brokers across the country with expanding online, call center and retail business operations.
AIC is entering a market that will more than double in size over the next 50 years according to some industry forecasts. The insurance industry is enjoying low inflation rates, steady income growth, and improving standards of living for most Americans during what has been a difficult period for much of American business. This makes this a good time to enter the insurance industry as it enjoys higher margins because customers are purchasing more coverage due to increased costs from medical care and higher liability claims.
American Insurance Company provides affordable homeowners, auto, and business insurance through high-quality fulfillment centers across America that have earned a reputation for top-notch customer service.
AIC will face significant competition from both direct and indirect competitors. The indirect competition will come from a variety of businesses, including banks, other insurance companies, and online retailers. The direct competition will come from other well-funded start-ups as well as incumbents in the industry. AIC’s competitive advantages include its low prices, high quality, and excellent customer service.
AIC plans to grow at a rate that is above average for the industry as a whole. The company has identified a market that is expected to grow by more than 100% in the next decade. This growth is due to several factors: the increase in the number of two-income households, the aging population, and the impending retirement of many baby boomers will lead to an increase in the number of people who are purchasing insurance.
AIC projects revenues of $20M in year one, which is equivalent to 100% growth over the previous year. AIC forecasts revenue growth of 40%-60% each year on average for 10 years. After that, revenue growth is expected to slow down significantly due to market saturation.
The following table illustrates these projections:
Competitive Landscape
Direct Competition: P&C Insurance Market Leaders
Indirect Competition: Banks, Other Insurance Companies, Retailers
Market Analysis Conclusion
When writing the market analysis section, it is important to provide specific data and forecasts about the industry that your company operates in. This information can help make your business plan more convincing to potential investors.
If it’s helpful, you should also discuss how your company stacks up against its competitors based on what makes it unique. In addition, you can identify any strengths or weaknesses that your company has compared to its competitors.
Based on this data, provide projections for how much revenue your company expects to generate over the next few years. Providing this information early on in the business plan will help convince investors that you know what you are talking about and your company is well-positioned to succeed.
How to Finish Your Business Plan in 1 Day!
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your business plan?
With Growthink’s Ultimate Business Plan Template you can finish your plan in just 8 hours or less!
Other Resources for Writing Your Business Plan
How to Write a Great Business Plan Executive Summary How to Expertly Write the Company Description in Your Business Plan The Customer Analysis Section of Your Business Plan Completing the Competitive Analysis Section of Your Business Plan The Management Team Section of Your Business Plan Financial Assumptions and Your Business Plan How to Create Financial Projections for Your Business Plan Everything You Need to Know about the Business Plan Appendix Best Business Plan Software Business Plan Conclusion: Summary & Recap
Other Helpful Business Planning Articles & Templates

- Success Stories
Here is the first retail business plan example. Fuel & Fire is a typical convenience store and gas station business.
Introduction
In today’s fast-paced world, the convenience store and gas station industry plays a pivotal role for daily commuters, weekend travelers, and community residents. “Fuel & Flee” is poised to redefine this sector by delivering top-notch vehicle fuels and a diverse array of essential items for on-the-go consumers. By harnessing Solink’s potent tools, we anticipate an enhanced security atmosphere and precise, actionable business insights.
- Name and nature: “Fuel & Flee” is designed to be a dual-function entity, melding a state-of-the-art gas station with a fully-stocked convenience store.
- Prime location: The business will reside at the intersection of Main Street and Highway 101, capturing both the local and highway traffic.
- Vision statement: Our aim is to emerge as the number one pit-stop choice for every traveler and local resident within a 10-mile radius.
- Holistic offerings: Apart from standard fuel services, a variety of convenience products such as fresh food, beverages, and daily essentials will be available.
- Legal backbone: Registered as a Limited Liability Company (LLC), ensuring protection and flexibility.
- Location details: A spacious location with 4 fuel pumps, 12 parking spots, and a 2,500 sqft store, all primed for quick and easy access.
- Industry insight: A 5% annual growth has been noted in the convenience store and gas station sector, especially in highway-adjacent areas.
- Target audience: Segment 1: Daily commuters (40%); Segment 2: Long-distance travelers (35%); Segment 3: Local families (25%).
- Competition analysis: Within a 15-mile radius, there are three major competitors—two national chains and one local establishment.
- Fuel varieties: Regular, mid-grade, premium, and diesel options for diverse vehicle needs.
- Store inventory: Over 1,000 unique items including snacks, drinks, automotive products, and a dedicated section for organic and local produce.
- Added amenities: A 24-hour ATM, a self-service air pump, and a mini cafe offering fresh coffee and pastries.
- Technological boost: The Solink system will provide unparalleled management insights, monitoring transaction data to understand optimal restocking times.
- Visual branding: Vibrant signboards and in-store displays to attract and retain customer attention.
- Promotional moves: Monthly deals such as “Fill & Feast” offering discounts on combined fuel and store purchases, aiming to increase average ticket size by 15%.
- Financial forecast: Anticipated revenue growth of 20% in the first year, scaling to 30% by the third year due to strategic promotions and customer loyalty initiatives.
- Supplier ties: Established contracts with top-tier fuel suppliers and local product distributors, ensuring consistent quality and timely deliveries.
- Inventory tactics: Bi-weekly stock checks and data-driven restocking decisions supported by Solink’s analytical prowess.
- Safety and surveillance: Continuous monitoring with Solink’s cloud-based video surveillance , ensuring a secure shopping environment and deterring potential thefts.
- Key staff: A seasoned store manager with 10 years in the retail and fuel sectors, supported by four cashiers, six fuel attendants, and three part-time staff members for restocking and cleaning.
- Employee growth: A commitment to staff development through quarterly training sessions focusing on safety protocols, customer service enhancements, and product knowledge.
- Startup costs: An initial outlay of $500,000 covering land lease, construction, and the first stock of inventory.
- Recurring expenditures: Estimated monthly expenses of $50,000 including salaries, utilities, and replenishing stock.
- Revenue breakdown: Anticipated monthly earnings from fuel sales ($120,000), convenience store sales ($80,000), and additional services ($10,000) totaling $210,000.
- Profit milestone: Predicted to hit the break-even point by the eighth month, with steady profit growth thereafter.
With its strategic offerings and location, “Fuel & Flee” stands on the precipice of becoming a dominant force in the convenience store and gas station domain. Tools like Solink can drastically amplify its operational capabilities and security levels, ensuring the venture is both profitable and remains a top pick for its diverse clientele.
Business plan example 2: "Buy Right", a grocery store
Here is the second business plan example. In this case, we are looking at opening a franchised grocery store. The overall size of the property is much higher, as are the startup costs.
In an era where consumer preferences lean towards vast selections and one-stop shopping experiences, grocery stores have an immense role. “Buy Right” seeks to harness this demand by inaugurating a large franchised grocery outlet, ensuring customers have access to a diverse range of products under one roof.
Partnering with Solink, the store aims to guarantee safety, loss prevention, and deep business insights for continual improvement.
- Business essence: “Buy Right” will function as a large-scale franchised grocery store, offering everything from daily essentials to gourmet items.
- Strategic location: Situated in the bustling commercial hub of Maple Street, ensuring easy access for a large population.
- Mission: Delivering quality products at competitive prices while ensuring an unmatched shopping experience.
- Store blueprint: A sprawling 20,000 sqft store with dedicated sections for fresh produce, dairy, bakery, meats, international goods, and more.
- Legal design: Operating as a franchise under a well-renowned grocery chain ensures brand recognition and trust.
- Facility features: Equipped with 15 checkout counters (including 6 self-checkouts ), a deli, a bakery, and ample parking for over 100 vehicles.
- Industry dynamics: A consistent 4% annual growth in the large grocery store sector, particularly in urban areas.
- Target demographic: Segment 1: Families (50%); Segment 2: Young working professionals (30%); Segment 3: Seniors (20%).
- Competitive landscape: Three direct competitors within a 10-mile radius, including another franchised store and two local grocery chains.
- Comprehensive offerings: Over 15,000 unique SKUs from local, national, and international brands.
- Value-added services: A bakery producing fresh items daily, a deli offering cold cuts, and a pharmacy section.
- Tech enhancement: Implementation of Solink to monitor customer shopping patterns, ensuring inventory is aligned with demand and improving store layout based on customer heatmaps .
- Promotion: Weekly flyers highlighting discounts, in-store product sampling, and seasonal sales to boost footfall.
- Loyalty programs: “Buy More, Save More” program, aiming to increase average customer spending by 10% within the first year.
- Sales projections: Expected to serve over 500 customers daily, with an average spending of $50 per customer.
- Supply chain dynamics: Tie-ups with established distributors, ensuring regular stock replenishment and fresh produce every alternate day.
- Inventory management: Use of Solink to prevent POS employee theft , audit shelves for stock levels, and detect any irregular activities in real time.
- Security measures: Enhanced surveillance with Solink Video Alarms Monitoring Service .
- Management team: A store manager backed by a decade of retail experience, along with two assistant managers.
- Staff structure: A team of 40 which includes cashiers, stockers, bakery and deli staff, and customer service representatives.
- Training paradigm: Monthly training on product knowledge, customer service etiquette, and safety measures.
- Initial investment: Estimated at $1.5 million, covering franchising fees, store setup, and initial inventory.
- Ongoing expenses: Monthly costs projected at $200,000, which includes salaries, utilities, rent, and inventory purchases.
- Revenue estimates: Anticipated monthly revenue of $750,000, with the goal of achieving a break-even point by the seventh month.
“Buy Right” holds the potential to redefine grocery shopping in the Maple Street area by offering a comprehensive selection in a customer-friendly environment. The added advantage of Solink ensures security, streamlined operations , and valuable insights. With this robust plan, “Buy Right” is geared to flourish in the competitive grocery market.
Business plan example 3: "Green Groves", an eco-friendly store
This is the third retail business plan example. It is a unique concept store focusing on the green market. The business operates as an eco-friendly, zero waste store catering to environmentally conscious consumers.
In a world grappling with environmental issues, sustainable solutions are at the forefront of consumer choices. “Green Groves” aspires to be a game-changer in retail by offering an eco-friendly zero waste shopping experience. With the integration of Solink’s capabilities, security and insightful business analysis will be assured.
- Business ethos: “Green Groves” will pioneer a zero waste, packaging-free retail environment.
- Strategic spot: Positioned in the heart of EcoVille, a community known for its green initiatives.
- Objective: To nurture a sustainable shopping culture and diminish the carbon footprint of retail.
- Store design: A 5,000 sqft open-plan store, equipped with bulk bins, refill stations, and reusable container displays.
- Business form: Operates as a sole proprietorship, with strong ties to local organic farmers and ethical suppliers.
- Store features: Apart from bulk goods, there’s a section for sustainable living products like bamboo toothbrushes, metal straws, and cloth bags.
- Eco trend: A 7% yearly increase in consumers seeking sustainable shopping options.
- Target demographic: Segment 1: Eco-conscious families (45%); Segment 2: Millennials and Gen-Z (40%); Segment 3: Sustainable lifestyle adopters (15%).
- Rivals: Two health stores in the vicinity, but none offer a complete zero waste experience.
- Goods galore: A range of organic foods, personal care items, household cleaning products, all sold without packaging.
- Eco tools: Reusable containers for sale and rent, ensuring customers can shop even if they forget theirs.
- Tech integration: Solink will monitor the POS , preventing operational shrink, and will provide insights on consumer purchase patterns.
- Eco-campaigns: Monthly workshops on sustainable living, zero waste challenges, and rewards for consistent zero waste shoppers.
- Loyalty perks: “Sustain & Save” program, targeting a 12% hike in repeat customers within the initial year.
- Revenue forecast: Expecting an average daily footfall of 200 customers, with an average spend of $30.
- Supply chain: Direct collaborations with organic farmers and ethical product makers, ensuring fresh stock and product authenticity.
- Stock management: Remote video monitoring of the store and stockroom will help keep the right amount of inventory available for purchase.
- Safety and security: Enhanced by Solink’s surveillance capabilities, ensuring a safe and theft-free shopping environment.
- Lead team: Store manager with a passion for sustainable living, backed by a degree in environmental studies.
- Crew composition: A mix of 10 full-time and part-time staff members, including stockers, cashiers, and a dedicated person for customer education on zero waste.
- Kick-off capital: An estimated $250,000, which includes store setup, initial inventory, and marketing efforts.
- Recurring costs: Monthly operational expenses estimated at $30,000, covering salaries, rent, utilities, and stock replenishments.
“Green Groves” stands out as a beacon for sustainable shopping in EcoVille. With Solink in its arsenal, the store is not only set to offer a secure and streamlined shopping experience but also a data-driven approach to meet consumer demands effectively. This venture promises not just profitability but also a positive impact on the planet.
Add Solink to your retail business plan
In the evolving retail landscape, having a robust business plan is only the beginning. The real differentiator lies in harnessing cutting-edge tools that optimize operations, enhance security, and provide actionable insights. Solink stands out as a transformative solution in this realm.
By integrating Solink into your retail strategy, businesses are not merely investing in surveillance but in a comprehensive tool that brings loss prevention, advanced security, and invaluable business insights to the fore.
As demonstrated with “Green Groves”, a store with a vision, the marriage of sustainability and technology can create a retail environment that’s both profitable and in tune with modern needs. For any retailer crafting or refining their business plan, Solink isn’t just an option; it’s a forward-thinking imperative.
To see why Solink should be part of every retail business plan, sign up for a demo today.
110-390 March Rd. Ottawa, Ontario K2K 0G7 Canada 1-844-635-7305
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience, serve personalized Ads or content, and analyze our traffic. By clicking "Accept", you consent to our use of cookies. Cookie Policy
Request co-branded marketing documents
[gravityform id=”5″ title=”false”]
JD enjoys teaching people how to use ZoomShift to save time spent on scheduling. He’s curious, likes learning new things everyday and playing the guitar (although it’s a work in progress).
- Feb 11, 2024
How to Create a Winning Retail Business Plan

You’re about to learn how to create a winning retail business plan. You can use this plan to either start or grow your retail business . Importantly, rather than simply learning the key sections to include in your plan, you’ll see below the strategic questions that, upon answering, can help your business soar.
Your retail business plan must include 10 sections.
1. Executive Summary 2. Company Overview 3. Industry Analysis 4. Customer Analysis 5. Competitive Analysis 6. Marketing Plan 7. Operations Plan 8. Management Team 9. Financial Plan 10. Appendix
Each section is discussed below in showing you how to create a business plan for your retail business.
Elements of a Retail Business Plan
1. executive summary.
Your Executive Summary gives a recap of your entire business plan. In addition to providing an overview of your retail business, you’ll briefly describe your customers, competitors, marketing plan, operations plan, management team and financial projections.
Importantly, winning retail business plans answer two key questions both in their executive summaries and in the other sections of the plan. These 2 questions are as follows:
Why is my retail business uniquely qualified to succeed?
There are many reasons why you could be uniquely qualified to succeed; perhaps you have the perfect location, or the best product mix, or special relationship with vendors or suppliers. Maybe you have an extremely loyal customer base. Or a management team or employees who are highly skilled and motivated.
What do I hope my retail business will look like in 5 years?
If you don’t know where you’re going, unfortunately you’ll never get there. As such, a critical strategic exercise to complete in your business plan is to set goals for your retail business in 5-years’ time.
The first question you should answer is this: what would you like your revenues to be in five years? Then, think about how your business would look if you reached that goal. For example, how many employees would you have? Would your management team be the same, or would you have added or replaced current members? How many customers would you be serving each day? Would you be operating new locations? What marketing strategies would have helped you reach your revenue goals?
2. Company Overview
Your company overview section gives background information on your company. But it can and should have strategic value to your company. Here’s how. Include your key accomplishments to-date in this section of your business plan. For example, list dates and accomplishments you’ve achieved so far such as the dates when you reached a certain level of sales, or hired your Xth employee.
Not only will documenting these accomplishments motivate you and others that read the plan, but think through the strategies you employed that allowed you to accomplish these goals. And make sure you continue to use these strategies that have worked well for you in the past. Conversely, too many companies keep trying new strategies while those they’ve already used successfully go by the wayside.

3. Industry Analysis
In the Industry Analysis section of your plan, document the size of your current market and trends that are affecting it. Ideally you can access third party research on your industry that includes this data. Typically trade associations conduct and publish such research.
Importantly, make sure your growth strategies are in line with these trends. For example, if there’s a trend towards ordering online and picking up in-store, make sure you offer this option to customers.
While you want to enjoy near-term success, you also want to realize long-term growth and success. So look at your industry’s trends and forecasts to ensure both your industry and your company are moving in the same direction.
4. Customer Analysis
Your customer analysis identifies your target customers and their wants and needs. By better understanding your customers you can a) better target them with promotions, and b) make sure you offer them the right mix of products and services.
So make sure your proposed strategies are in line with your target customers, or think through ways to reach new customer segments.
5. Competitive Analysis
The competitive analysis section of your retail business plan identifies your key competitors and their strengths and weaknesses.
Think through your competitors’ strengths and see how you can combat them. LIkewise, assess their weaknesses and see how you can exploit them. The goal of this section is to figure out if you have and/or how you can build lasting competitive advantage.
6. Marketing Plan
The marketing plan includes the “4 P’s” as follows: Product, Price, Place, Promotions.
- Product : here’s where you describe your current product/service mix and what products/services you need to add to reach your desired long-term goals.
- Price : here you’ll document your pricing strategy.
- Place : Place refers to the location of your retail business. Any store expansion plans would be discussed here.
- Promotions : Your promotions section details how you will reach new customers. There are numerous ways to do this, from pay-per-click ads to print advertising to social media marketing and customer referral programs. Document the strategies that you’re currently using, those that have worked well in the past, and those you’ll employ in the future to allow you to realize your growth goals.
7. Operations Plan
In your operations plan, you must document and detail your long-term and short-term milestones.
Start by identifying and documenting your 5-year goals in terms of sales, number of employees, customers served, store openings and/or other relevant metrics.
Then you need to work backwards. Identify the key goals you need to reach in each of the next 5 years to reach your ultimate goal. Finally, you need to get even more granular for the first year. That is, document your goals for each quarter of the coming year.
For example, if you currently have a headcount of 50 and your goal is to get to 500 employees, your goals might be to add 10 employees in the first quarter, 15 employees in the second quarter, 20 employees in the third quarter, 25 employees in the fourth quarter, 80 employees in the second year, 90 employees in the third year, 100 employees in the fourth year, and 110 employees in the fifth year.
Likewise, document your plan for employee retention , as losing key employees will hinder your ability to achieve your growth objectives.
By using this process, you can truly identify and then attain your goals.

8. Management Team
In this section of your plan you’ll document your management team.
Importantly, you need to think through whether your current management team is capable of growing your business to the desired level. Think about which management team members can grow with you. Think through whether you should invest in them to improve their skill sets. Also, figure out if you need to add or replace current members. If so, write a job description of the team members you’ll need to add and the dates you’d like to bring them on.
9. Financial Plan
The financial plan section of your business plan includes an Income Statement, Balance Sheet and Cash Flow Statement. It also lists the key assumptions you’ve used in deriving these 5-year projections.
Among other things, your financial plan will identify how much money is needed to execute on your plan. Likewise it will alert you to potential cash crunches. For example, purchasing new equipment or software might help your business grow, but it may require an investment that your bank account doesn’t currently support.
If you’re looking for outside funding to grow your business, banks and equity lenders will review your financial plan to ensure they will be repaid or get an adequate return on their investment. But even if outside funding is not required, developing your financial plan is critical.
One key benefit of your financial plan and forecasts is that they allow you to assess new opportunities. For example, you should be able to tell the cash requirements and potential returns for different strategies you might pursue. Use your forecasts to select only the best ones.
Finally, your financial projections will give you goals. They serve as a financial scorecard against which you should judge actual performance. Each month and quarter, judge your actual financial performance against your forecasts. See where you’ve succeeded and where you’ve fallen short. And if you’ve fallen short, strategize regarding what you can do differently to improve your success going forward.
10. Appendix
The appendix of your plan includes any supporting information. For example management team resumes or vendor agreements could be included if they bolster arguments stated in your plan.
Creating a business plan for your retail business puts you on the path to creating competitive advantage and enjoying long-term success. It starts with simply dreaming about what you’d like the future to look like. Then, you strategize to put plans in place to ensure that vision becomes a reality.
Jump to section
Related articles.


Retail business plan: how to write guide .
Sep 30, 2023 | Business Consulting , Business Plan , Financial Plan , Market Analysis , Strategy

How to write a retail business plan
If you’re thinking of how to write a retail business plan for your store, it’s essential to have a well-planned business strategy in place. A detailed retail business plan can help you secure funding from investors and banks and provide a roadmap for achieving your short-term and long-term goals. Your plan should cover operations, growth, finances, funding, and objectives for 6-12 months. Creating a comprehensive retail business plan can increase your chances of success and stay on track toward reaching your business objectives.
What is a retail business plan?
A retail business plan is a comprehensive document that lays out the objectives and goals of a new business owner. It typically covers the business idea, background, financial information, and the guidelines and rules that the business will follow.
Why should you create a retail business plan?
If a company seeks a business loan or investors, presenting a comprehensive retail business plan is beneficial. This demonstrates to potential investors and loan officers that your business concept and structure have been carefully considered. A well-crafted retail business plan can also mitigate the risks associated with starting a business by accounting for all aspects of operations from the beginning.
Here are some critical elements of writing your retail business plan
We have compiled essential tips for how to write a retail business plan to help establish a successful organization.

Starting and running a successful store begins with writing a retail business plan.
Give an overview of your company.
The company overview section of your retail business plan is of utmost importance. It should highlight how you want your business to be perceived by the public, including your brand guidelines, logo design, vision/mission statement, proprietorship and business legal structure, design, and layout. In this section, it’s crucial to list the leaders of your team as well as any company ownership and percentage shares. If you’re having difficulty creating a value proposition, consider a unique retail shop you admire. Take note of the elements you enjoyed and the market position you want to incorporate into your retail business plan.
Create an organizational structure.
Suppose you are going to operate a thriving retail business. In that case, the bank and funding partners will want to know your entity status, company type, entity ownership, formation date, and legal structure. Will you operate as a nonprofit, self-employed, sole trader, partnership, private limited, or limited liability company? Choosing a business entity determines leadership responsibilities, business model profitability, and tax declaration requirements.
Additionally, you must include your hiring plans and how many team members your retail shop employs, whether on a full-time, part-time, or contract basis. Who will serve on the management team? Who will collaborate with the leadership? How will the unit operate daily (i.e., with daily team huddles, weekly cash flow reviews, and monthly development plans)? What ongoing governance oversight is needed to support the company’s operational structure?
Describe your business model, products, and services.
Your business model is how you create income. Most of your readers, especially banks and investor partners, want to know what type of retail business you operate, what customers will buy, and what additional services you will offer at your retail store. Within your retail business plan, you should provide comprehensive details on the items you will be retailing and how you expect customers to purchase the products (i.e., debit card, gift cards, buy now pay later Klarna).
For example, if it is a pet store, include whether there will be food, beds, toys, accessories, and other onsite retail services (i.e., grooming suite, vets, doggy daycare, product delivery to home service). Will customers be able to buy medicines and larger bulk pet supplies at your store? What range of products will you have in stock (i.e., Mars Pedigree, bird food)? What about farming animals’ feed supply and hay? You aim to show that you have a good grasp of your retail business product offering and can comfortably describe your store layout and product catalog so the reader gets an idea of your retail business.
To ensure successful retail business shelf fulfillment, it is essential to provide the reader with specific details on strategic partners, local suppliers, wholesale companies, and initial contract conditions. You should consider whether your items will be sourced locally or shipped from abroad and if there are any holding periods before you can sell the goods. It would be best to have a plan for controlling stock, waste, and damage and for any short-shelf-life products or slow sellers.
Additionally, be sure to have a clear pricing strategy that considers the costs of purchasing the goods and the desired retail price so that you can accurately describe your margins. You may also consider offering promotional discounts, seasonal sales, retail store memberships, loyalty schemes, and at-home delivery or online ordering for store pickup services to attract customers.
You must show your expected sales forecast within your financial plan to detail your daily/ monthly/ annual revenues.
Include market research for the target market, competition, and industry analysis.
As you write a retail business plan for your store, conducting a thorough market analysis is crucial. This involves delving into your primary industry, target audience, competition, and location. By understanding these factors, you can showcase the potential demand for your retail business and give confidence to potential funders that your proposal aligns with the local economy and presents an appealing opportunity.
Knowing your target market and ideal customers:
Based on feedback from our clients, we understand that many retail business owners tend to have a broad target audience, such as all locals or pet owners, as demonstrated in this retail business plan example. However, narrowing your focus to a specific group of customers is often effective. This helps you better understand your audience and tailor your marketing efforts to their needs.
To do this, it is essential to identify your target market’s attributes and buying habits. Collecting data on customer demographics, such as age, gender, marital status, education, and job level, as well as their purchasing habits, including frequency of shopping, browsing preferences, and buying tendencies, can provide valuable insights. By doing so, you can refine your business proposition to meet the needs of your ideal customers better and increase your chances of success in the market.
Industry analysis and sub-segment:
Industry analysis involves qualitative and quantitative evaluations of your retail market. This includes examining the industry’s size, upcoming retail trends, sales patterns, and growth opportunities. It’s essential to differentiate your business model by considering factors such as offering cheap, bulk bargains or luxury goods. Once you understand the industry well, you can focus on specific product categories and how they can benefit your business.
Consider customer analysis to determine how to develop a product mix that aligns with industry trends, such as offering organic or plant-based foods. You can also leverage different selling channels, like social media and websites, and in-store point-of-sale systems for wholesale orders. You can secure the resources needed to grow your business by demonstrating profitability and success metrics to funding partners.
Competitor analysis:
An excellent retail business plan will include a competitor analysis. At a minimum, you would want to review two competitors to see how your business fits the market demand. These could be direct (other pet stores) or non-direct (supermarkets selling similar products).
When analyzing your target retail market and location, research which of your competitors has the most significant market share, how close competitor retailers are to your retail location, and what competitive advantages your company brand has over these competitors.
SWOT analysis:
Another good idea is to include a SWOT analysis. This strategy tool helps you review your internal capabilities, strengths and weaknesses, and any external opportunities and threats your company can address. As you include the SWOT analysis in your retail business plan, it will help you to reflect on your focus points, prioritize your strengths, and mitigate against weaknesses and external threats (i.e., cost of goods, competition) while demonstrating the growth potential with the opportunities (partnership with specific brands, new locations)
Evaluate marketing, pricing, and sales.
This guide will provide strategies to market your retail business and attract customers. Your retail business plan should include a situational analysis of your current state, marketing objectives, process, and tactics. To develop a positioning statement, consider how your retail shop differs from competitors, what sets your products and services apart, and why your business is the best choice for your target customers.
Planning your marketing activities over a specific period, such as a month or a year, is essential. Consider creating an annual plan with monthly promotional activities that align with your advertising, direct mail campaigns, and in-store promotions. For instance, if you sell summer products, you might want to promote items like tick medication and cooling mats before the season begins.
When customers purchase a product, the retail price is the amount they pay for the final item. Unlike distributors or manufacturers, these customers buy the product for personal use, not resale. It’s important to note that there are distinct differences between the retail price, manufacturer price, and distributor price.
When planning your sales activities, consider the different methods you will use to operate your retail business, such as traditional checkout, in-store POS, or online ordering. It would be best to consider the channels you will use to promote your business, including your store website. These social media platforms, like Facebook and Instagram, offer direct mail vouchers, loyalty programs, exclusive promotional events, reward points, free products, and delivery services.
Define operating structure
As you start your retail business, how the business operations will run is essential, as it helps fuel your growth plans and should be included when you write your business plan. Therefore, assessing several local retailers is worthwhile to help determine a custom strategy for your retail business and how customers complete their journey around your store. After all, changing the store planogram becomes much more complex once the shelves and stock are in place.
Supply chain management:
Within this aspect, you will forecast, procure, store, and manage your inventory management. Ensuring your supply chain runs smoothly is the best way to ensure profits. Incorporate how you will control, order, deliver, and address inventory needs, store that inventory in-store or offsite at a warehouse, and manage the product portfolio to ensure you have no empty shelves or redundant products for sale, which helps to ensure you never run out of products or overpay for them.
- Will you manage the product development lifecycle or outsource?
- Do you plan to introduce your portfolio to new stock-keeping units (SKUs)? How will you keep the store secure?
Technology:
This is an essential part of a retail business. You can do everything manually or leverage technology solutions to streamline your day-to-day operations, from customer relationship (CRM), stock ordering, accounting software (i.e., QuickBooks, Xero, Sage), and customer payments to inventory management.
Data Security:
As a retail business, a plethora of data will be exchanged between your store, suppliers, and customers. Therefore, ensuring you have sufficient data stored securely and compliant with your market legislation (i.e., GDPR) is crucial.
Provide a financial plan within your retail business plan.
Your financial plan helps banks and investors appreciate how your company will make money to realize its growth plans and future goals. For your retail shop, you must complete a thorough financial analysis by analyzing your startup budget needs, ongoing operational expenses, projected sales forecast, salary costs, funding options, break-even point, cash flow needs, and projected profit and loss. A good grasp of your cash flow helps you balance your inventory and staffing needs with available funds.
Operating Costs:
As you analyze your operational costs, you should consider all aspects of operating your retail store successfully. That includes all resources, inventory, marketing materials, staff uniforms, security, website, supporting technology (i.e., CRM, POS, Email, stock control), and ongoing store maintenance costs. Banks and funding partners would like to know how much your retail store will cost upfront and when you will reach a point demonstrating a return on investment (ROI) and are comfortable with any debt repayment plans (i.e., loans).
Financial Plan Creation:
Your financial plan is typically created in Microsoft Excel, or you can use business planning software like Liveplan . As a minimum 24-month cash flow forecast, some banks and investors may require up to five years of forecast projections. So, checking with your funding partners or the bank’s website first is always worthwhile to develop a robust forecast.
Speak with a Noirwolf consultant to review your retail business plan or explore how the appropriate business planning software, like Liveplan , can demonstrate to investors and partners that your business plan is serious.
Get in Touch
Are you looking to grow your business but unsure where to start? Our small business consulting and leadership coaching services are here to help! We’ll work with you to scale your operations and achieve your goals. Plus, we offer a free 30-minute consultation to ensure we fit your needs correctly. Let’s get started!
Contact Noirwolf Consulting today using the website contact form or by emailing [email protected] or call us at +44 113 328 0868.
Recent posts .

What is Program Management?
Apr 2, 2024
Program management is a vital component of organizational success, as it enables the coordinated execution of interdependent projects that yield benefits beyond the scope of individual project management. It involves the judicious application of knowledge, skills, tools, and techniques to meet specific program requirements. Our experience has demonstrated that organizations with well-developed program management and program management offices (PMOs) consistently outperform those that lack such structures. Therefore, it is imperative that organizations prioritize the establishment of robust program management frameworks to achieve their strategic objectives.

Business Transformation Strategy: A 10-Step Strategy Guide
Mar 4, 2024
Business transformation strategy is a complex and dynamic process that fundamentally restructures an organization’s strategy, processes, and systems. Though each business transformation is unique, several critical steps remain foundational to a successful change management plan. A comprehensive business transformation framework ensures a smooth and practical transformation. This framework should encompass various elements, such as defining the vision and aims of the transformation, assessing the current state of the business, identifying gaps and areas of improvement, developing a roadmap and action plan, implementing the changes, monitoring and measuring progress, and continuously refining the transformation approach as needed.

What is the Change Management Process?
Feb 2, 2024
Change is the only constant in today’s fast-paced world, and organizations must adapt to stay ahead. Fortunately, change management provides a structured and coordinated approach that enables businesses to move from their current state to a future desirable state. To deliver business value, organizations introduce change through projects, programs, and portfolios. However, introducing change is just the beginning! The real challenge is to embed the change and make it a new normal state for the organization. This calls for implementing the main principles of change management, which we will discuss in this article. Get ready to transform your organization and achieve your desired outcomes by mastering the art of change management!
Happy clients .
Trevor mcomber, us.
I recently worked with Zoe@Noirwolf, who provided me with an outstanding 5-year business plan. The expertise in financial planning, market research, SWOT analysis, and consulting was exceptional. Zoe provided me with a comprehensive and well-researched plan tailored to my business. The entire process was professional, timely, and communicative.
Bill Walton, Leeds
Zoe provided first-rate work and is an excellent business consultant. I was trying to figure out my cash flow forecast for my startup. Zoe gave me an interactive consultation session over MS teams, which was valuable and saved me a lot of time. She is super quick in excel and knowledgeable about what to include in your estimates. She was able to offer me ideas & choices that I hadn't considered. Highly recommended.
Jeendanie Lorthe, US
Warren kim, us, oscar sinclair, london, get in touch ..
Looking to grow your business but feeling unsure about where to start? Our small business consulting and leadership coaching services are here to help! We'll work with you to scale your operations and achieve your goals. Plus, we offer a free one-hour consultation to ensure we fit your needs correctly. Let's get started!
- Get Started
Home >> #realtalk Blog >> Manage a business >> How to create a reta…
How to create a retail store business plan
By Andrea Nazarian

A successful retail business starts with a well-thought-out retail business plan. While you may think you have your business ideas all figured out in your head, putting them down on paper in the form of a business plan is crucial for several reasons.
In this post, we’ll explore what a retail business plan is, why it’s different from other business plans, what to include in it, common mistakes to avoid, and how to make your plan stand out.
What Is a Retail store business plan and why do you need one?
A retail store business plan is a comprehensive document that outlines your business model, identifies your target customers, and lays out a roadmap for turning your retail store or online shop into a profitable business.
It’s a planning and forecasting tool that provides clarity and direction for your business. With a good business plan, you’re more likely to achieve success.
Here’s why having a retail store business plan is essential:
Planning and forecasting
A retail store business plan helps you plan and set clear goals for your business’s short-term and long-term success.
Planning helps you set goals, allocate resources wisely, and stay on track. It ensures that day-to-day operations run smoothly. Forecasting, on the other hand, helps businesses anticipate future trends and challenges, allowing them to make informed decisions and adapt to changing circumstances.
Together, planning and forecasting help you avoid costly mistakes, reduce labor costs , seize opportunities, and achieve both short-term and long-term objectives. In essence, they’re like a GPS for your retail business, guiding it towards profitability and sustainability.
Securing investment
A retail store business plan helps secure investment by demonstrating a clear and well-thought-out strategy. It shows potential investors that you’ve done your homework, understand your market, and have a solid plan for success.
The plan outlines your business goals, target market, competitive analysis, and financial projections, instilling confidence in investors that their money will be used wisely. It also highlights your commitment and professionalism, making you a more attractive investment opportunity.
Essentially, a strong retail business plan reassures investors that your venture is a sound investment with a higher likelihood of delivering returns on their capital.
Guiding business operations
A retail store business plan serves as a roadmap for guiding business operations. It outlines your business’s goals, strategies, and tactics, providing a clear direction for daily activities.
It helps you make informed decisions about product offerings, retail staff scheduling , pricing, local business marketing , online marketing and staffing. The plan also includes financial projections and budgeting, ensuring you manage resources effectively.
Regularly reviewing the plan allows you to track progress, identify areas needing improvement, and adjust strategies accordingly. Overall, it keeps the business focused, organized, and aligned with its objectives, making day-to-day operations more efficient and effective in achieving long-term success.
Get your team in sync with our easy-to-use, all-in-one employee app.
How is a retail business plan different from other business plans?
Retail businesses are unique in many ways, and your business plan should reflect that. Unlike other businesses, retail operations involve factors such as inventory management , supply chains, order fulfillment, deliveries, and customer returns.
Here’s how a retail store business plan differs:
Inventory management
Unlike other business plans, retail plans must handle challenges like seasonal sales variations and predicting what customers will buy. Inventory management in retail business plans is about keeping the right amount of products in stock to meet customer demand while avoiding excess or shortages.
They also need to explain how they get products, where they store them, and how they restock when items run low. In contrast, many other businesses don’t deal with these inventory issues.
Retail store business plans focus more on handling and controlling inventory to make sure they always have what customers want and don’t waste money on too much stock.
Marketing strategy
Marketing strategy in retail store business plans, compared to other business plans, often emphasizes attracting customers to physical or online stores, creating appealing displays, and running promotions like sales or loyalty programs.
Retail plans typically prioritize reaching a broad consumer base and enticing them with visually appealing products. In contrast, other business plans might focus on more specialized marketing, like B2B partnerships or online advertising.
Retailers also consider factors like store location and layout, which are less significant for many other businesses. So, simply put, retail business plans concentrate on tactics to draw in shoppers and make their shopping experience enjoyable and memorable.
Growth strategy
Growth strategy in retail store business plans, unlike other business plans, often centers on expanding to new locations, introducing new product lines, or attracting more customers. Retailers aim to increase sales by opening additional stores, going online, or diversifying their offerings.
In contrast, some businesses may focus on improving internal processes or targeting specific niche markets.
Retailers typically rely on broadening their reach to fuel growth, making strategies like franchising, adding new store branches, or exploring e-commerce crucial components of their plans. So, in simpler terms, retail business plans tend to emphasize expanding the business footprint and customer base as a primary path to success.
What to do before you start writing your retail store business plan
Research your market.
T horough market research is essential. Investors look for evidence of a healthy market and an unmet need that your business can address.
You’ll want to gather data on who your customers are, what they want, and where they’re located. Analyze your competition to see what makes your business unique. This research helps investors see that there’s a demand for your products or services and that your business can thrive in the market.
It’s about proving that your idea is well-informed and has the potential to succeed. So, in simple terms, thorough market research shows investors that your business plan is based on a strong foundation of knowledge and understanding.
Understand your competitors
Know your competition inside out. Understanding what sets you apart is crucial.
You need to know who you’re up against and what makes them tick. Research your competitors thoroughly: their strengths, weaknesses, and strategies. Identify what sets your business apart – your unique selling points.
Investors want to see that you’ve done your homework and can explain how your retail store will outshine the competition. Maybe it’s better prices, superior quality, or outstanding customer service.
This knowledge not only helps you stand out but also shows investors that you’re ready to face the competition head-on, which can boost their confidence in your business’s potential success.
Have a growth strategy
Define a clear growth strategy to demonstrate how your business will expand once it’s up and running. It shows investors that you’re not just focused on starting your business but also on making it grow in the long run.
You can outline different growth strategies like market penetration (selling more to existing customers), product development (creating new products for existing customers), market development (selling existing products to new markets), or diversification (introducing new products to new markets).
This helps investors understand your vision and how you plan to increase your business’s value over time, making your retail venture a more attractive investment opportunity.
What to Include in your retail store business plan
Business overview.
Provide a high-level description of your retail business, including your company’s structure, location, and the products or services you’ll offer.
Business goals
Explain your business goals, whether they’re related to market share, product ranges, or online expansion.
It should give a clear, simple picture of your retail business. Explain whether your business will operate in a physical store, online, or both.
Mention the legal name of your company, where it’s located, and briefly describe the products or services you plan to sell. Keep it straightforward and easy to understand, so anyone reading your plan can quickly grasp what your retail business is all about.
This section sets the stage for the rest of your plan, helping readers get a sense of your business from the get-go.
Your industry experience
In the “Your industry experience” section of your retail store business plan, it’s your time to shine. Tell the readers about your background and expertise, especially if you’ve held important positions in recognized retail businesses.
If you’ve previously led successful growth initiatives or managed to open new stores that flourished, this is the place to mention it. Basically, this section is all about showcasing your qualifications and experience in the retail world.
It helps build trust and confidence that you’re the right person to turn your retail business idea into a thriving reality. Keep it concise but impressive.
The “ Marketing strategy ” section of your retail store business plan is where you paint a picture of how you’ll present your store to the world. Explain your store’s image, the strategy for your brand, and how you plan to market your products or services.
Don’t forget to dive into the 4Ps of retail marketing:
- Product : Describe what you’re selling and what makes it special.
- Pricing : Explain how you’ll price your products and why.
- Place : Tell where you’ll sell your products, be it online, in-store, or both.
- Promotion : Detail your strategies for promoting your store and products.
This section gives a clear roadmap for how you’ll attract customers and make your business a success. Keep it straightforward and compelling.
Financial strategy and forecast
The “Financial strategy and forecast” section of your retail store business plan is where you show the money side of your business. Investors want to see the numbers, so include things like:
- Estimated capital requirements : How much money do you need to get started and keep going?
- Profit and revenue models : Explain how you plan to make money and what your sales goals are.
- Sales volume projections : Predict how many products you expect to sell.
- Financial statements : Include balance sheets, cash flow projections, and any other financial documents.
These details help investors understand your business’s financial health and potential. Make sure your numbers are realistic and based on careful research and planning.
Management structure
In the “Management structure” section of your retail store business plan, you’ll provide details on how you intend to organize your team and manage your business effectively. This section involves explaining several key aspects:
Firstly, you’ll specify the number of team members you plan to hire. This is essential to understand the size and scope of your workforce.
Secondly, you’ll describe the roles and responsibilities of each team member. This clarification ensures that everyone knows their specific duties and contributes to the smooth operation of the business.
Lastly, you’ll illustrate how each team member fits into your overall business plan. This section helps investors and stakeholders comprehend how your team will collaborate and work together to achieve the business’s goals and objectives.
A well-defined retail management structure assures potential investors that you have a competent team ready to execute your business plan effectively.
Homebase offers user-friendly employee management tools to streamline team communication , time tracking, and scheduling , helping you refine your management structure.
Common mistakes to avoid when making your retail store business plan
A successful business plan is as much about what you leave out as what you put in. Here are some common mistakes to avoid:
Too much detail
Avoid long, rambling text. Use visuals and graphics when possible and attach heavy content as appendices.
Poor financial planning
Account for growing expenses, taxes, and market influences in your financial projections.
Poor spelling and grammar
Basic errors can undermine how partners and investors view your plan.
Strengthening your business plan
To strengthen your business plan, consider your audience, which may include potential investors, business partners, and financial institutions. Be transparent, avoid exaggerations, and demonstrate the value of your idea.
Conclusion: Finishing your retail store business plan
A well-crafted retail store business plan is more than just a guide; it’s a tool to attract investors, secure funding, and set the foundation for a successful retail business. Leveraging tools like Homebase can help you stay competitive and efficient in the retail industry.
Don’t delay writing your plan—it could be the first step towards realizing your retail business dreams.
FAQs about writing a retail store business plan
What is a retail store business plan, and why is it important.
A retail store business plan is a comprehensive document outlining your retail store business’s model, goals, and strategies. It’s crucial as it provides clarity, attracts investors, and guides daily operations for success.
How does a retail store business plan differ from other business plans?
Retail store business plans are unique due to their focus on inventory management, marketing tactics to attract shoppers, and growth strategies centered on expanding customer reach.
What should I include in my retail store business plan’s business overview section?
In the business overview, provide a concise description of your retail business, including its structure, location, and the products or services you intend to offer.
How can a retail store business plan help secure investment?
A retail store business plan demonstrates a well-thought-out strategy, outlining business goals, target market, competitive analysis, and financial projections. It reassures investors, making your venture a more appealing investment opportunity.
What common mistakes should I avoid when creating a retail store business plan?
Common mistakes include excessive detail, poor financial planning, and grammar/spelling errors. To avoid these, focus on clarity, accurate financial projections, and proofreading.
Remember: This is not legal advice. If you have questions about your particular situation, please consult a lawyer, CPA, or other appropriate professional advisor or agency.
Related posts
April 19, 2024
The Art of Hiring, Training, and Managing Small Business Teams
No doubt you’ve heard that the most valuable asset a company has is its employees. As cliché as that is,…
April 18, 2024
Protected: The 2024 Homebase Small Business Team Fulfillment Index
There is no excerpt because this is a protected post.
April 16, 2024

Financing Strategies for Small Business Ownership
You’ve been dreaming about it, likely for years, and you’re ready to make it happen. It’s right there in front…
How to Set and Achieve Small Business Goals
Want to stay on track, hit milestones, and take your business to new heights? Setting goals is the way to…
Watch Out for these Common Small Business Missteps
Starting a new business is both exciting and challenging. It’s exciting because your new business is full of promise. It’s…
Workers’ Compensation 101 for Small Business Owners
As a small business owner, your employee’s safety is likely a top concern. Whether your employees work behind a counter,…
Subscribe to our newsletter
Looking for ways to stay up to date on employment laws and small business news?
Homebase makes managing hourly work easier for over 100,000 local businesses. With free employee scheduling , time tracking , and team communication , managers and employees can spend less time on paperwork and more time on growing their business.
- Hiring & onboarding
- Team communication
- Employee happiness
- HR & compliance
- Integrations
- Food & beverage
- Beauty & wellness
- Medical & veterinary
- Home & repair
- Hospitality & leisure
- Education & caregiving
- Contact sales
- Become a Partner
- Careers – We’re hiring!
- #realtalk Blog
The path forward for the US retail industry
Today, months after COVID-19 first hit US shores, it’s increasingly clear that most retailers won’t be able to rely on their old strategies and business models to compete effectively in the next normal. In this episode of the McKinsey on Consumer and Retail podcast, McKinsey’s Steven Begley, Becca Coggins, and Steve Noble consider how the US retail landscape has changed and what companies must do to thrive in the postpandemic world. An edited version of their conversation with McKinsey Global Publishing’s Monica Toriello follows. Subscribe to the podcast .
Monica Toriello: Hello, and thanks for joining us today. We’re now three-quarters of the way through the year 2020, and it’s been a year like no other for people and businesses all over the world. In this episode, we’ll talk about one of the industries most greatly affected by the pandemic: the retail industry. We’ll focus today’s discussion on the US retail sector, but many of the lessons and imperatives we’ll discuss apply to retailers all around the world.
Joining us to share their perspectives are three McKinsey partners who have worked extensively with retailers from every subsector, including grocery, restaurant, and fashion. They’ve each written several articles on the retail sector, which you can find on McKinsey.com. Recently, the three of them coauthored an article titled, “ The next normal in retail: Charting a path forward .” Let’s meet our guests. First, we have Steven Begley, a partner in McKinsey’s New Jersey office. Also joining us is Becca Coggins, a senior partner based in the Chicago office and a longtime leader of McKinsey’s global Retail Practice. And finally, Steve Noble is a senior partner in Minneapolis who coleads McKinsey’s global work in retail transformation.
To start, I’d like to ask each of you for a short answer to my first question. One of the things that McKinsey has been tracking and that you’ve all been writing about is the shifts in consumer behavior , which have become evident over the past few months. What’s one way that your own shopping behavior has changed during this pandemic?
Becca Coggins: Monica, I might sound like a cliché. My shopping was already very heavily online. It has accelerated that way, but, like many Americans , what I buy has shifted a fair bit. I’m a bit of an apparel junkie, but that’s taken a backseat to new hobbies, new things for the home, and things to keep the kids engaged around the house.
Steven Begley: My grocery experience has gone completely digital. And my grocery experience has actually accelerated. I live in Manhattan, and I didn’t frequent grocery stores prior to the pandemic, but now I’m constantly purchasing groceries, and I only do it online. So it’s a different experience for me.
Steve Noble: I’ll break the rule of one thing, but I’ll be brief. One, my front porch looks like a warehouse full of boxes each day, so lots of online shopping. I no longer buy pants; I buy a lot more wine instead.
The migration to e-commerce
Monica Toriello: You’ve all brought up the migration to e-commerce, which has been one of the biggest and most obvious shifts during this period. What has worked there, and what hasn’t worked? In other words, as consumers have shifted more of their spending online, what are retailers getting right? And what are they still getting wrong?
Steve Noble: I’ve been impressed with how quickly retailers have adapted to this new way consumers are shopping—ramping up online and curbside delivery. I live in Minneapolis; Hy-Vee is one of the local grocers, and they’ve always had a curbside drive-through pickup. But that capability, as you might imagine, was quickly overwhelmed. While it wasn’t pretty, I was impressed with how quickly they mobilized to create more scale. They basically cordoned off a section of the parking lot and set it up with refrigerated shipping containers. You place the order online, and you give them an indication of when you’ll be coming. They don’t give you a slot; rather, you give them a slot. You pull up, they load the groceries in the back of your vehicle, and you drive off.
It was a great experience, and I appreciated how quickly they adapted. I imagine that over time they will reimagine the look and feel of that experience. Because things, in many cases, were stood up so quickly, they weren’t done initially with, “How do you create a great customer experience ?” They were done with just, “How do you get the bare minimum in place?” Now there’s an opportunity to continue to think about how to make some of those delivery or fulfillment models better, more sustainable, and more enduring customer experiences.
Becca Coggins: It almost makes me think we’re in the foothills of what omnichannel-driven convenience will look like—and that there’ll be some big innovations that scale now that consumer expectations have been reset. That’s where we’ll start to see some more innovative models and some more interesting partnerships—as players try to think about new ways to meet those needs.
If you look at how many more consumers are using e-commerce—such as using curbside pickup and buying online and picking up in store—most of them like it and plan to stick with it after the pandemic. So you have the consumer need. And retailers have done a good job of standing up things, as Steve said, to be able to meet that need. The next challenge is figuring out how to do it as a more seamless experience—in a way that’s not temporary but that meets these emerging needs around convenience and speed, especially.
Subscribe to the McKinsey on Consumer and Retail podcast
A ‘shock to loyalty’.
Monica Toriello: Becca, you mentioned that consumers plan to stick with behaviors they tried for the first time during the pandemic and that they liked. Another shift you describe in your article is the “shock to loyalty”—a greater willingness among consumers to switch brands and retailers. As you say in your article, “The beneficiaries of this shift include big brands, which are seeing 50 percent growth during the crisis,” and private labels. “Some 80 percent of consumers who started buying private-label products during the pandemic indicate that they intend to continue doing so even after the COVID-19 crisis subsides.” A couple of questions about that. First, should we believe consumers? Will they indeed stick with big brands and private labels postpandemic? And what are the implications for retailers?
Becca Coggins: What’s interesting to us about this phenomenon is that it’s not just brand switches, it’s not just retail switches, it’s not just channel switches. It’s all of the above—to the point where three out of four Americans will change something meaningful about the way they shop, including relationships that were previously sticky and stable, like with your neighborhood grocery store, for example. Some of the examples you cited, Monica, are some of the ones that stick out. We expect these could still be dynamic—but on private label, for example, it’s a bit unsurprising, given that consumers are focused on value, and they’re buying more categories that are in essential consumption categories.
While some of these shocks to loyalty, whether it’s the shift to larger brands or the one to private labels, started out of sheer availability—“I went to the store and didn’t see the brand I typically buy, so I bought the alternative”—the reasons for the shift have started to evolve to reflect much more the shift around value and, on the retail side, where to actually get that omnichannel convenience you’re looking for. So now it’s all three of those things: availability, value, and convenience. We do tend to believe consumers. The private-label switch, for example, we’ve seen in prior recessionary periods pick up at about the same clip. Overall, the level of switching is something we haven’t seen in this era, so probably it could moderate some. But consumers are satisfied , and they’re continuing to shift some of those things.
The implications for retail are along the same lines of why consumers are switching. Are you providing available products, particularly in essential categories that are at the top of consumers’ shopping lists? Are you providing everyday value? And are you providing the type of convenience that balances consumers’ ability to get it when they need it but also in the mode that they want it—without having to navigate big crowded stores, et cetera? I think the implications are, very simply, how fast retailers can adapt to the new consumer reality, which is more focused on value and convenience than even before the COVID-19 crisis.
Monica Toriello: The migration to e-commerce is happening at the same time as another one of the shifts that you’ve just pointed out, which is a focus on essentials and value. Talk about what that means for omnichannel pricing. Steven, in an article you wrote in February, before the pandemic, you observed that, at least in grocery, some retailers had online price-matching policies , whereas others didn’t: they had different prices online and in store. At the time, you said that the jury was out on which is the right approach. What’s your latest thinking on pricing?
Steven Begley: What we’re seeing is that retailers have had an opportunity to pull back on promotions as a result of the last couple of months because of the increased demand; consumers’ willingness to pay has been a lot higher. Fundamentally what we’re seeing, though, is at the end of the day, pricing is one of the top value drivers for why a consumer selects one retailer over another. Pricing will continue to be a core differentiator, a core pillar, in retailers’ strategies going forward. We’ll continue to see retailers experiment with the interplay between online versus offline pricing. But one thing we’re pretty confident about is that price matching will continue to be something that most or all retailers do.
Going beyond incremental thinking
Monica Toriello: Let’s talk about things that all retailers should do. In the article that the three of you coauthored, you name five critical areas for the next normal: revenue management, operating model, digital capabilities, capital investments, and M&A and partnerships. Those cover a lot of ground. Instead of elaborating on all five, I’d like each of you to pick one that you think retailers aren’t paying enough attention to or somehow not adequately addressing. Out of those five, which one are retailers neglecting or overlooking?
Steve Noble: I’ll start with revenue management. And I’d start with a perspective rooted in the financial crisis of 2008 and 2009. When we studied that crisis, we looked at what allowed some retailers to be resilient and come through relatively strongly. One of the big drivers of resiliency and success through that period of disruption and crisis was, “Did you focus sufficiently on driving the top line and on the consumer in your business?”
Many retailers had the reaction, “We need to look first, second, and third at cost and take out every bit of cost we can, given the pressure on our business.” The retailers that were most successful certainly thought about cost—but they thought much more about, “How do we make sure we’re delivering a great customer experience? How do we make sure we’re driving the top line? How do we think through our pricing, our assortment, and our frontline sales model to deliver a great customer experience in the spirit of taking share?” If you then fast-forward to where we are today, much of the same will apply.
We’re not saying, don’t think about or take out costs where it’s prudent. But our belief is that retailers that will come through this the most successfully are those that are thinking about all the potential revenue levers to drive their business and outcompete those they are positioned against. We of course know that some parts of retail are experiencing record growth and others are experiencing record decline, so this is not to say that everyone should be growing robustly. But it is a real time to outplay and go on the offensive relative to your competitive set—an approach that we believe will allow you to come out of this in a much better place in the long term.
Steven Begley: Monica, I’d say the five areas that we wrote about do cover, as you pointed out, a broad swath of capabilities across any retailer’s business. Now is a great time to put everything on the table and rethink it from the perspective of transformation—whether it’s finally pivoting your merchandising organization to be omnichannel and tech enabled or personalizing your customer experience to a level you’ve never seen before. Now is a good time to release those old constraints and prepare for the next normal.
That said, on the M&A point in particular, we tend to see a lot of M&A and partnership activity anytime an industry is disrupted, and we’re certainly in one of those times right now. We expect to see a lot of the traditional consolidation plays that you typically see: optimizing for COGS [cost of goods sold] and SG&A [selling, general, and administrative] opportunities. But there’s also a real uptick in channel expansion and making M&A or partnership plays that allow retailers to buy into new capabilities.
A good example of this would be in the fulfillment value chain. It’ll be much easier and much more practical for folks to buy into some of these technologies—like microfulfillment, for example—versus trying to build them themselves. The same argument could be made for commercial analytics. For a lot of these advanced analytics algorithms that drive pricing and promotional decisions, it’s going to be much easier and much more efficient from a capital standpoint to buy these capabilities and embed them in the organization versus trying to build them from scratch. I do think we’ll see quite a bit of M&A and partnership activity, particularly on the capability-building front.
Becca Coggins: There is some good news, actually, on operating model, and I would start there. Many executives we talked to are, frankly, pleasantly surprised at how quickly and effectively their companies were able to pivot in the face of the biggest exogenous shock most of us will have seen in our careers. One of the examples I find inspiring is Best Buy. They stood up curbside pickup, when all of their stores were closed, in 48 hours nationwide. That process, for a retailer of that size and scale, would typically take several months of piloting to stand up and get the kinks out. But they had a high-quality, effective, customer-friendly solution available in a weekend.
The challenge side of that, and a place we think retailers need to be focused and introspective, is how to redesign the operating model to sustainably deliver these types of outcomes. That’s true for speed, it’s true for efficiency, and it’s likely true for ensuring that the operating model is delivering on what we’ve already described as new or accelerated consumer preferences and behaviors. Have you sustainably redesigned for speed and for omnichannel and for efficiency so you can deliver the best value to your customers?
Steve Noble: I might just add a broader point that sits a level above the five specific topics we’re talking about. In retail, prior to six months ago, the mindset of most retail executives would be, “if I have a business that’s growing at a 2 percent same-store comp rate, and I can get that to 3 percent, I’m feeling pretty good. If my margin is 4.5 percent, and I can get that to 5 percent, I’m feeling pretty good.” The notion of the industry is that it’s a low-growth, low-margin business in general. That tends to foster incremental-type thinking: “I don’t need to get a big bump to actually feel pretty good about my performance.”
If you look at where things are now, what may have been a 2 percent or 3 percent comp-growth business is now up 20 percent or maybe down 20 percent. Likewise, margins are up and down dramatically. It is a good forcing function to break the mold of incremental thinking and rethink more fundamentally how you want to reach your customer. From stores versus online versus combined channels, how do you want to think about technology as a way to reimagine the customer experience and the labor and service model that you might be delivering? The amount of disruption happening right now does create some space to think pretty big and bold in a way that just wasn’t quite as typical of retail historically.
The battle for talent
Monica Toriello: These areas that you’ve described all sound like they require new capabilities, especially in tech and digital and analytics—which leads me to a question about talent. Steven, again, in your February article, you say, “Digital talent may be the single-most-important determinant of a company’s likelihood to succeed in the grocery market in the next few years.” And that’s probably even truer now, right? You had offered up some steps for retailers to take, such as hiring a chief digital officer, rethinking location strategies, and looking beyond brand-name universities. But can you talk about the battle for talent today and what retailers can do to become attractive employers for the kinds of talent they need?
Steven Begley: The battle for talent is real. And retail is not necessarily a sector that folks coming from data-science backgrounds and technology backgrounds would gravitate toward first. That said, we’re seeing the disruption play out in a space where we’re at just the beginning of the acceleration of many of the trends that we’ve talked about, so in terms of a sector that is primed for impact, retail is potentially the biggest one out there. What that means for retailers is, they need to be out in front of these populations of technologists and data scientists and statisticians and others, making the case for why retail is such an exciting place to be right now. I think all of us on this podcast would agree that it is.
We’ve seen a number of retailers shifting their digital businesses to more urban environments, trying to change their formats, and even changing the physical look and feel of their office structures to attract this type of talent. I think we’ll see more of that and a continued pitch to the industry, so to speak, on why retail is such a great place to be.
Becca Coggins: Now is the time for retailers to get aggressive about winning the war for this talent. We’re seeing, and will continue to see, a displacement of digital talent and analytics talent, certainly within the industry, where there’s been momentum versus decline, but also within adjacent industries. You can imagine a pretty big influx of talent—analytical talent, especially—from sectors like travel and hospitality into retail, as well as across different subsectors of retail.
Steve Noble: I agree. The war for talent is real, and now is an important time to play it aggressively. It begs the question, what allows one retailer to differentiate itself from the next in terms of winning that war? Certainly, part of it is whether they are investing in things that are exciting, et cetera. But maybe more than ever, there’s also a chance to see what a company’s “DNA” is and what its values are.
The nature of the crisis we’re in allows you to understand what different retailers think about caring for their people from a health-and-safety point of view. What do they think about creating flexibility for a workforce that may have kids schooling from home or family members who need to be cared for at home? What do they think about diversity and inclusion ? There are a lot of different markers that we’re seeing more acutely now that allow you to stare into the soul of the company a little bit. That will be probably as big a marker of which businesses win the war for talent as job descriptions and capabilities being built. Not to say those aren’t important, but I do think the balance between those is probably different than it was six months ago as well.
Becca Coggins: Interestingly, customers are starting to pay a lot more attention to those same attributes: how a company treats its employees, what kind of diversity and inclusion policies they have, and how that shows up to the market. We’ll start to see the whole ecosystem focus more on those things.
Steven Begley: One industry-wide example is that Eightfold AI and FMI, an industry association, came together to create something called the “Talent Exchange,” which we supported. It essentially matched retailers that had employees who needed jobs with those that had opportunities for them. And when the COVID-19 crisis first hit in March and early April, it was impressive to see the speed at which those organizations came together to create the Talent Exchange and the speed at which retailers signed up to become a part of it. Companies like Macy’s, Walmart, and United Airlines quickly came to the table to put opportunities into the exchange and also to create opportunities on the exchange. I thought that was a great example of the industry coming together quickly to do something good for the community.
Monica Toriello: It’s been a tough year for many retailers, and it could be a long road to recovery. Last question: If a retail CEO says to you, “I want my company to thrive in the next normal. Give me your single-most-important piece of advice,” what would you say?
Steven Begley: Chart out what your customers’ demands are going to be three years from now, five years from now. Create that vision, get your organization aligned on it, and work back from there to figure out the costs, the implications, and the investments you need to make. Focus on who that customer is going to be, and plan from there.
Becca Coggins: I think the same thing. Follow the customer. Understand what you can do distinctively for them, and orient your business to be able to do that.
Steve Noble: Given the uncertainty and volatility in retail, you need to plan in short cycles: what’s going to happen next week, next month, next quarter. But don’t forget to also plan for two or three years out. How does your business look fundamentally different on the backside of this than it did prior to the pandemic, or even now? So it’s that balance of being agile in the short term but also putting real thought into what comes out on the back end so you don’t end up with an answer two years from now that’s the amalgamation of a set of small choices. Instead, it’s an intentional view of creating a much better and different business.
Monica Toriello: Great advice. Thanks for spending time with us today, and thanks to all our listeners. Join us again in a few weeks for the next episode of the McKinsey on Consumer and Retail podcast .
Steven Begley is a partner in McKinsey’s New Jersey office, Becca Coggins is a senior partner in the Chicago office, and Steve Noble is a senior partner in the Minneapolis office. Monica Toriello , a member of McKinsey Global Publishing, is based in the New York office.
Explore a career with us
Related articles.

The next normal in retail: Charting a path forward

The next normal: Retail M&A and partnerships after COVID-19

What matters now in the consumer sector

Item added to your cart
Here is a free business plan sample for a retail store.

Are you eager to launch your own retail store but unsure where to start your journey?
In the content that follows, we will present to you a comprehensive sample business plan tailored for the retail industry.
As an aspiring entrepreneur, you're likely aware that a strategic business plan is a cornerstone of any successful venture, providing a clear outline of your business concept, objectives, and the tactics you'll employ to achieve them.
To streamline the creation of an effective plan, you're invited to utilize our retail business plan template. Additionally, our specialists are on hand to offer a complimentary review and refinement of your plan.

How to draft a great business plan for your retail store?
A good business plan for a retail store must be tailored to the nuances of the retail industry.
Initially, it's imperative to provide a comprehensive overview of the retail market you're entering. This includes up-to-date statistics and an analysis of emerging trends, similar to what we've outlined in our retail business plan template .
Your business plan should articulate your vision clearly. Define your target demographic (such as families, young professionals, or students), and establish your store's unique selling proposition (USP), whether it's competitive pricing, product variety, exclusive items, or customer service excellence.
Market analysis is a critical component. You need to thoroughly understand your competitors, the local market dynamics, and consumer behavior patterns.
For a retail store, it's vital to detail the range of products you will carry. Describe the categories - clothing, electronics, home goods, etc. - and explain how these selections cater to the preferences and needs of your intended customer base.
The operational plan is key. It should outline the location of your store, the layout of the shopping and inventory space, supplier relationships, and inventory management systems.
In retail, it's crucial to highlight your procurement strategies, inventory turnover rates, and loss prevention measures.
Then, delve into your marketing and sales strategies. How do you plan to attract shoppers and foster loyalty? Discuss promotional tactics, customer service policies, and potential ancillary services (like personal shopping or in-store events).
Embracing digital strategies, such as an e-commerce platform or a robust social media presence, is increasingly important in the retail sector.
The financial aspect is another cornerstone. This section should cover the initial investment, projected sales, operating expenses, and the point at which you expect to break even.
In retail, product margins can vary widely, so precise financial planning and a solid understanding of your cost structure are essential. For assistance, consider using our financial forecast for a retail store .
Compared to other business plans, a retail store's plan must pay closer attention to inventory management, customer traffic patterns, and peak shopping seasons.
A well-crafted business plan is not just a roadmap for the store owner; it's also a tool to attract investors or secure loans.
Lenders and investors are looking for a thorough market analysis, realistic financial projections, and a clear plan for day-to-day operations.
By presenting a comprehensive and substantiated business plan, you showcase your dedication and readiness to make your retail store a success.
To streamline the process and ensure you cover all necessary points, feel free to utilize our retail business plan template .

A free example of business plan for a retail store
Here, we will provide a concise and illustrative example of a business plan for a specific project.
This example aims to provide an overview of the essential components of a business plan. It is important to note that this version is only a summary. As it stands, this business plan is not sufficiently developed to support a profitability strategy or convince a bank to provide financing.
To be effective, the business plan should be significantly more detailed, including up-to-date market data, more persuasive arguments, a thorough market study, a three-year action plan, as well as detailed financial tables such as a projected income statement, projected balance sheet, cash flow budget, and break-even analysis.
All these elements have been thoroughly included by our experts in the business plan template they have designed for a retail .
Here, we will follow the same structure as in our business plan template.

Market Opportunity
Market data and figures.
The retail industry is a cornerstone of the global economy with significant impact and reach.
As of recent estimates, the global retail market value stands at approximately 25 trillion dollars, with projections indicating continued growth driven by e-commerce and evolving consumer behaviors.
In the United States alone, there are over 1 million retail establishments, contributing to an annual turnover of nearly 5 trillion dollars. This underscores the retail sector's vital role in the American economy and its influence on consumer lifestyles.
These figures highlight the retail industry's expansive nature and its capacity to adapt to changing market dynamics.
The retail landscape is witnessing a transformation, influenced by technological advancements and shifting consumer expectations.
E-commerce is on the rise, with more consumers opting for the convenience of online shopping. This trend has been accelerated by the global pandemic, leading to a surge in online retail sales.
Sustainability is becoming a priority, with an increasing number of consumers preferring products that are eco-friendly and ethically sourced. Retailers are responding by incorporating sustainable practices into their operations and product selections.
Personalization is another key trend, as retailers leverage data analytics to offer tailored shopping experiences and curated product recommendations to their customers.
Omnichannel strategies are being adopted to provide a seamless shopping experience across various platforms, from brick-and-mortar stores to mobile apps and online marketplaces.
Lastly, the demand for contactless transactions and digital payment options has grown, offering convenience and safety for both consumers and retailers.
These trends are shaping the future of retail, with businesses adapting to meet the evolving needs and preferences of modern consumers.
Success Factors
Several factors contribute to the success of a retail business.
Product assortment is critical; retailers must offer a diverse range of high-quality products that cater to the needs and desires of their target market.
Customer experience is paramount, with successful retailers providing exceptional service, convenient shopping solutions, and a pleasant store atmosphere.
Location remains a key factor, as a strategically placed retail store can attract significant foot traffic and visibility.
Adaptability is also essential, as retailers must be agile in responding to market trends, economic shifts, and consumer behavior changes.
Effective supply chain management ensures that products are available when and where they are needed, minimizing stockouts and overstock situations.
Lastly, embracing digital transformation and innovative technologies can help retailers stay competitive and relevant in an increasingly digital world.
By focusing on these success factors, retailers can position themselves for growth and longevity in the dynamic retail landscape.
The Project
Project presentation.
Our retail store project is designed to cater to the increasing consumer interest in eco-friendly and sustainable products. Situated in a high-traffic shopping district or near eco-conscious communities, this retail store will offer a diverse selection of environmentally responsible goods, ranging from organic clothing and reusable household items to biodegradable personal care products and zero-waste accessories, all sourced from ethical suppliers and crafted with sustainability in mind.
The emphasis will be on the quality, durability, and environmental impact of the products to provide a responsible shopping experience.
This eco-conscious retail store aims to become a go-to destination for sustainable goods, thereby contributing to the promotion of environmentally friendly lifestyles and practices.
Value Proposition
The value proposition of our eco-friendly retail store project is centered on providing a curated selection of sustainable and ethically produced goods that cater to the needs of environmentally conscious consumers.
Our dedication to offering products that minimize ecological footprints offers a meaningful shopping experience, while contributing to the preservation of our planet.
We are committed to fostering a community where individuals can find eco-friendly alternatives to conventional products and aim to educate our customers about the importance of sustainability and conscious consumerism.
Our retail store aspires to be a cornerstone of the community, offering a tangible solution to the environmental challenges we face and improving the quality of life of our customers through responsible consumption.
Project Owner
The project owner is an entrepreneur with a strong passion for environmental conservation and sustainable living.
With a background in retail management and a deep commitment to eco-friendly practices, they are determined to create a retail store that stands out for its dedication to sustainability, ethical sourcing, and community engagement.
With a vision of inspiring change and promoting green alternatives, they are resolved to provide products that support a sustainable lifestyle while contributing to the well-being of the planet.
Their commitment to environmental stewardship and their zeal for innovative retail solutions make them the driving force behind this project, aiming to empower consumers to make choices that benefit both themselves and the environment.
The Market Study
Market segments.
The market segments for this specialized gluten-free retail store are diverse and multifaceted.
Firstly, there are individuals with gluten intolerance or celiac disease who require gluten-free products as a necessity for their health and well-being.
Additionally, there is a growing demographic of health-conscious consumers who opt for gluten-free products to support their lifestyle choices.
The market also caters to those who are exploring gluten-free options out of curiosity or for the perceived health benefits, even without a medical need.
Healthcare professionals, including dietitians and general practitioners, represent another segment as they often recommend gluten-free products to patients with sensitivities or dietary restrictions.
SWOT Analysis
A SWOT analysis of the gluten-free retail store project highlights several key factors.
Strengths include a specialized focus on gluten-free products, a knowledgeable staff trained to assist customers with dietary needs, and a robust supply chain for sourcing high-quality gluten-free goods.
Weaknesses may involve the niche market limiting the customer base and the potential for higher pricing due to the specialty nature of the products.
Opportunities can be found in the increasing awareness and popularity of gluten-free diets, the potential to expand product lines, and the ability to create a community around health and wellness.
Threats include the entry of larger retailers into the gluten-free space, price competition, and the volatility of prices for gluten-free ingredients.
Competitor Analysis
Competitor analysis in the gluten-free retail sector indicates a competitive landscape.
Direct competitors include other specialty health food stores, supermarkets with dedicated gluten-free sections, and online retailers specializing in gluten-free products.
These competitors vie for the attention of a discerning customer base that values product variety, ingredient transparency, and convenience.
Potential competitive advantages for our store include a highly curated product selection, personalized customer service, community engagement, and loyalty programs.
Understanding the competitive landscape is crucial for carving out a unique position in the market and for customer acquisition and retention.
Competitive Advantages
Our gluten-free retail store's competitive edge lies in our unwavering dedication to providing a wide array of gluten-free products that meet the needs of our customers.
We offer an extensive selection of gluten-free groceries, from staples to gourmet items, ensuring that our customers do not have to compromise on choice or quality.
Our knowledgeable staff are trained to offer guidance and support to customers, whether they are new to a gluten-free diet or seasoned gluten-free shoppers.
We are committed to transparency and education, helping our customers make informed choices and fostering a sense of community among those who shop with us.
You can also read our articles about: - how to open a retail store: a complete guide - the customer segments of a retail store - the competition study for a retail store
The Strategy
Development plan.
Our three-year development plan for the specialized gluten-free retail store is designed to be progressive and responsive to market demands.
In the first year, our goal is to establish a strong foothold in the local market by offering a diverse range of high-quality gluten-free products and exceptional customer service.
During the second year, we plan to expand our reach by opening additional locations in key shopping districts and residential areas to increase accessibility for our customers.
The third year will focus on enhancing our product line with exclusive gluten-free items and collaborating with suppliers to offer unique products. We will also explore online sales channels to broaden our market reach.
Throughout this period, we will prioritize customer satisfaction, product excellence, and innovative retail experiences to solidify our brand as a leader in the gluten-free retail sector.
Business Model Canvas
The Business Model Canvas for our gluten-free retail store is centered around serving individuals with gluten sensitivities and those who prefer gluten-free products for lifestyle reasons.
Our value proposition lies in providing a wide selection of gluten-free goods, convenience, and a knowledgeable staff to assist customers in making informed choices.
We will operate through our physical retail locations and an e-commerce platform, utilizing our key resources such as our relationships with gluten-free product suppliers and our retail expertise.
Key activities include inventory management, customer service, and community engagement.
Our revenue streams will be generated from the sales of gluten-free products, while our costs will be mainly associated with inventory procurement, store operations, and marketing initiatives.
Access a comprehensive and editable real Business Model Canvas in our business plan template .
Marketing Strategy
Our marketing strategy is centered on differentiation and customer engagement.
We aim to distinguish ourselves by offering an extensive range of gluten-free products and by providing a shopping environment that educates customers about the benefits of gluten-free living. Our marketing efforts will include in-store promotions, loyalty programs, and educational workshops.
We will also establish partnerships with nutritionists and health influencers to endorse our products and store.
Additionally, we will leverage social media platforms and online marketing to increase our visibility and attract a wider customer base, while emphasizing the quality and variety of our gluten-free offerings.
Risk Policy
The risk policy for our gluten-free retail store is focused on mitigating risks associated with product sourcing, inventory management, and customer satisfaction.
We will implement strict quality control measures to ensure all products meet gluten-free standards and maintain strong relationships with reputable suppliers to guarantee product availability and quality.
Regular training for staff on gluten-free products and customer service will help maintain high standards. We will also adopt a conservative financial approach to manage costs effectively.
Comprehensive insurance coverage will be in place to protect against potential liabilities. Our commitment is to provide safe, high-quality gluten-free products while ensuring a positive shopping experience for our customers.
Why Our Project is Viable
We are committed to establishing a retail store that specializes in gluten-free products, addressing the increasing demand from health-conscious consumers and those with dietary restrictions.
With our dedication to offering a wide range of products, exceptional customer service, and a focus on education and community, we believe our business is well-positioned for success in the growing gluten-free market.
We are enthusiastic about the opportunity to enhance the lives of our customers through our offerings and are prepared to adapt to market changes to achieve our objectives. We are optimistic about the future prospects of our gluten-free retail store.
You can also read our articles about: - the Business Model Canvas of a retail store - the marketing strategy for a retail store
The Financial Plan
Of course, the text presented below is far from sufficient to serve as a solid and credible financial analysis for a bank or potential investor. They expect specific numbers, financial statements, and charts demonstrating the profitability of your project.
All these elements are available in our business plan template for a retail and our financial plan for a retail .
Initial expenses for our gluten-free retail store include costs associated with leasing a retail space in a strategic location, outfitting the store with appropriate shelving and display units for gluten-free products, purchasing initial inventory from certified gluten-free suppliers, training staff on the importance of cross-contamination prevention, as well as expenses for branding and targeted marketing campaigns to attract customers with gluten sensitivities or preferences.
Our revenue assumptions are based on a thorough market analysis of the demand for gluten-free goods, taking into account the increasing number of people adopting gluten-free lifestyles for health and dietary reasons.
We expect a steady growth in sales, beginning with conservative estimates and expanding as the reputation of our gluten-free retail store strengthens in the community.
The projected income statement outlines expected revenues from the sales of gluten-free products, cost of goods sold (including inventory procurement and handling), and operating expenses (lease, marketing, staff wages, etc.).
This leads to a forecasted net profit that is essential for assessing the long-term viability of our retail business.
The projected balance sheet will display assets unique to our retail operation, such as store fixtures, initial product inventory, and liabilities like loans and projected operational costs.
It will provide a snapshot of the financial condition of our gluten-free retail store at the end of each fiscal period.
Our projected cash flow statement will detail the cash inflows from sales and outflows for expenses, helping us to predict our financial needs. This is crucial for maintaining adequate cash reserves to handle day-to-day business transactions.
The projected financing plan will enumerate the various sources of funding we intend to tap into to cover our initial costs, including potential loans or investor capital.
The working capital requirement for our gluten-free retail store will be diligently tracked to ensure we have sufficient funds to support everyday business activities, such as restocking inventory, managing accounts receivable and payable, and meeting payroll obligations.
The break-even analysis will pinpoint the sales volume required to cover all our costs, including the initial setup expenses, and begin generating profits.
It will signal the point at which our retail operation becomes financially sustainable.
Key performance indicators we will monitor include the gross margin on our gluten-free products, the current ratio to evaluate our ability to meet short-term liabilities, and the return on investment to gauge the efficiency of the capital we have invested in our retail venture.
These metrics will assist us in gauging the financial performance and overall success of our gluten-free retail store.
If you want to know more about the financial analysis of this type of activity, please read our article about the financial plan for a retail store .
- Choosing a selection results in a full page refresh.
- Opens in a new window.
What is a retail business plan and how do you write one for a retail store?
- March 18, 2024 March 19, 2024
- by Aishwarya
Small Business Trends
How to create a business plan: examples & free template.
This is the ultimate guide to creating a comprehensive and effective plan to start a business . In today’s dynamic business landscape, having a well-crafted business plan is an important first step to securing funding, attracting partners, and navigating the challenges of entrepreneurship.
This guide has been designed to help you create a winning plan that stands out in the ever-evolving marketplace. U sing real-world examples and a free downloadable template, it will walk you through each step of the process.
Whether you’re a seasoned entrepreneur or launching your very first startup, the guide will give you the insights, tools, and confidence you need to create a solid foundation for your business.
Table of Contents
How to Write a Business Plan
Embarking on the journey of creating a successful business requires a solid foundation, and a well-crafted business plan is the cornerstone. Here is the process of writing a comprehensive business plan and the main parts of a winning business plan . From setting objectives to conducting market research, this guide will have everything you need.
Executive Summary

The Executive Summary serves as the gateway to your business plan, offering a snapshot of your venture’s core aspects. This section should captivate and inform, succinctly summarizing the essence of your plan.
It’s crucial to include a clear mission statement, a brief description of your primary products or services, an overview of your target market, and key financial projections or achievements.
Think of it as an elevator pitch in written form: it should be compelling enough to engage potential investors or stakeholders and provide them with a clear understanding of what your business is about, its goals, and why it’s a promising investment.
Example: EcoTech is a technology company specializing in eco-friendly and sustainable products designed to reduce energy consumption and minimize waste. Our mission is to create innovative solutions that contribute to a cleaner, greener environment.
Our target market includes environmentally conscious consumers and businesses seeking to reduce their carbon footprint. We project a 200% increase in revenue within the first three years of operation.
Overview and Business Objectives

In the Overview and Business Objectives section, outline your business’s core goals and the strategic approaches you plan to use to achieve them. This section should set forth clear, specific objectives that are attainable and time-bound, providing a roadmap for your business’s growth and success.
It’s important to detail how these objectives align with your company’s overall mission and vision. Discuss the milestones you aim to achieve and the timeframe you’ve set for these accomplishments.
This part of the plan demonstrates to investors and stakeholders your vision for growth and the practical steps you’ll take to get there.
Example: EcoTech’s primary objective is to become a market leader in sustainable technology products within the next five years. Our key objectives include:
- Introducing three new products within the first two years of operation.
- Achieving annual revenue growth of 30%.
- Expanding our customer base to over 10,000 clients by the end of the third year.
Company Description

The Company Description section is your opportunity to delve into the details of your business. Provide a comprehensive overview that includes your company’s history, its mission statement, and its vision for the future.
Highlight your unique selling proposition (USP) – what makes your business stand out in the market. Explain the problems your company solves and how it benefits your customers.
Include information about the company’s founders, their expertise, and why they are suited to lead the business to success. This section should paint a vivid picture of your business, its values, and its place in the industry.
Example: EcoTech is committed to developing cutting-edge sustainable technology products that benefit both the environment and our customers. Our unique combination of innovative solutions and eco-friendly design sets us apart from the competition. We envision a future where technology and sustainability go hand in hand, leading to a greener planet.
Define Your Target Market

Defining Your Target Market is critical for tailoring your business strategy effectively. This section should describe your ideal customer base in detail, including demographic information (such as age, gender, income level, and location) and psychographic data (like interests, values, and lifestyle).
Elucidate on the specific needs or pain points of your target audience and how your product or service addresses these. This information will help you know your target market and develop targeted marketing strategies.
Example: Our target market comprises environmentally conscious consumers and businesses looking for innovative solutions to reduce their carbon footprint. Our ideal customers are those who prioritize sustainability and are willing to invest in eco-friendly products.
Market Analysis

The Market Analysis section requires thorough research and a keen understanding of the industry. It involves examining the current trends within your industry, understanding the needs and preferences of your customers, and analyzing the strengths and weaknesses of your competitors.
This analysis will enable you to spot market opportunities and anticipate potential challenges. Include data and statistics to back up your claims, and use graphs or charts to illustrate market trends.
This section should demonstrate that you have a deep understanding of the market in which you operate and that your business is well-positioned to capitalize on its opportunities.
Example: The market for eco-friendly technology products has experienced significant growth in recent years, with an estimated annual growth rate of 10%. As consumers become increasingly aware of environmental issues, the demand for sustainable solutions continues to rise.
Our research indicates a gap in the market for high-quality, innovative eco-friendly technology products that cater to both individual and business clients.
SWOT Analysis

A SWOT analysis in your business plan offers a comprehensive examination of your company’s internal and external factors. By assessing Strengths, you showcase what your business does best and where your capabilities lie.
Weaknesses involve an honest introspection of areas where your business may be lacking or could improve. Opportunities can be external factors that your business could capitalize on, such as market gaps or emerging trends.
Threats include external challenges your business may face, like competition or market changes. This analysis is crucial for strategic planning, as it helps in recognizing and leveraging your strengths, addressing weaknesses, seizing opportunities, and preparing for potential threats.
Including a SWOT analysis demonstrates to stakeholders that you have a balanced and realistic understanding of your business in its operational context.
- Innovative and eco-friendly product offerings.
- Strong commitment to sustainability and environmental responsibility.
- Skilled and experienced team with expertise in technology and sustainability.
Weaknesses:
- Limited brand recognition compared to established competitors.
- Reliance on third-party manufacturers for product development.
Opportunities:
- Growing consumer interest in sustainable products.
- Partnerships with environmentally-focused organizations and influencers.
- Expansion into international markets.
- Intense competition from established technology companies.
- Regulatory changes could impact the sustainable technology market.
Competitive Analysis

In this section, you’ll analyze your competitors in-depth, examining their products, services, market positioning, and pricing strategies. Understanding your competition allows you to identify gaps in the market and tailor your offerings to outperform them.
By conducting a thorough competitive analysis, you can gain insights into your competitors’ strengths and weaknesses, enabling you to develop strategies to differentiate your business and gain a competitive advantage in the marketplace.
Example: Key competitors include:
GreenTech: A well-known brand offering eco-friendly technology products, but with a narrower focus on energy-saving devices.
EarthSolutions: A direct competitor specializing in sustainable technology, but with a limited product range and higher prices.
By offering a diverse product portfolio, competitive pricing, and continuous innovation, we believe we can capture a significant share of the growing sustainable technology market.
Organization and Management Team

Provide an overview of your company’s organizational structure, including key roles and responsibilities. Introduce your management team, highlighting their expertise and experience to demonstrate that your team is capable of executing the business plan successfully.
Showcasing your team’s background, skills, and accomplishments instills confidence in investors and other stakeholders, proving that your business has the leadership and talent necessary to achieve its objectives and manage growth effectively.
Example: EcoTech’s organizational structure comprises the following key roles: CEO, CTO, CFO, Sales Director, Marketing Director, and R&D Manager. Our management team has extensive experience in technology, sustainability, and business development, ensuring that we are well-equipped to execute our business plan successfully.
Products and Services Offered

Describe the products or services your business offers, focusing on their unique features and benefits. Explain how your offerings solve customer pain points and why they will choose your products or services over the competition.
This section should emphasize the value you provide to customers, demonstrating that your business has a deep understanding of customer needs and is well-positioned to deliver innovative solutions that address those needs and set your company apart from competitors.
Example: EcoTech offers a range of eco-friendly technology products, including energy-efficient lighting solutions, solar chargers, and smart home devices that optimize energy usage. Our products are designed to help customers reduce energy consumption, minimize waste, and contribute to a cleaner environment.
Marketing and Sales Strategy

In this section, articulate your comprehensive strategy for reaching your target market and driving sales. Detail the specific marketing channels you plan to use, such as social media, email marketing, SEO, or traditional advertising.
Describe the nature of your advertising campaigns and promotional activities, explaining how they will capture the attention of your target audience and convey the value of your products or services. Outline your sales strategy, including your sales process, team structure, and sales targets.
Discuss how these marketing and sales efforts will work together to attract and retain customers, generate leads, and ultimately contribute to achieving your business’s revenue goals.
This section is critical to convey to investors and stakeholders that you have a well-thought-out approach to market your business effectively and drive sales growth.
Example: Our marketing strategy includes digital advertising, content marketing, social media promotion, and influencer partnerships. We will also attend trade shows and conferences to showcase our products and connect with potential clients. Our sales strategy involves both direct sales and partnerships with retail stores, as well as online sales through our website and e-commerce platforms.
Logistics and Operations Plan

The Logistics and Operations Plan is a critical component that outlines the inner workings of your business. It encompasses the management of your supply chain, detailing how you acquire raw materials and manage vendor relationships.
Inventory control is another crucial aspect, where you explain strategies for inventory management to ensure efficiency and reduce wastage. The section should also describe your production processes, emphasizing scalability and adaptability to meet changing market demands.
Quality control measures are essential to maintain product standards and customer satisfaction. This plan assures investors and stakeholders of your operational competency and readiness to meet business demands.
Highlighting your commitment to operational efficiency and customer satisfaction underlines your business’s capability to maintain smooth, effective operations even as it scales.
Example: EcoTech partners with reliable third-party manufacturers to produce our eco-friendly technology products. Our operations involve maintaining strong relationships with suppliers, ensuring quality control, and managing inventory.
We also prioritize efficient distribution through various channels, including online platforms and retail partners, to deliver products to our customers in a timely manner.
Financial Projections Plan

In the Financial Projections Plan, lay out a clear and realistic financial future for your business. This should include detailed projections for revenue, costs, and profitability over the next three to five years.
Ground these projections in solid assumptions based on your market analysis, industry benchmarks, and realistic growth scenarios. Break down revenue streams and include an analysis of the cost of goods sold, operating expenses, and potential investments.
This section should also discuss your break-even analysis, cash flow projections, and any assumptions about external funding requirements.
By presenting a thorough and data-backed financial forecast, you instill confidence in potential investors and lenders, showcasing your business’s potential for profitability and financial stability.
This forward-looking financial plan is crucial for demonstrating that you have a firm grasp of the financial nuances of your business and are prepared to manage its financial health effectively.
Example: Over the next three years, we expect to see significant growth in revenue, driven by new product launches and market expansion. Our financial projections include:
- Year 1: $1.5 million in revenue, with a net profit of $200,000.
- Year 2: $3 million in revenue, with a net profit of $500,000.
- Year 3: $4.5 million in revenue, with a net profit of $1 million.
These projections are based on realistic market analysis, growth rates, and product pricing.
Income Statement

The income statement , also known as the profit and loss statement, provides a summary of your company’s revenues and expenses over a specified period. It helps you track your business’s financial performance and identify trends, ensuring you stay on track to achieve your financial goals.
Regularly reviewing and analyzing your income statement allows you to monitor the health of your business, evaluate the effectiveness of your strategies, and make data-driven decisions to optimize profitability and growth.
Example: The income statement for EcoTech’s first year of operation is as follows:
- Revenue: $1,500,000
- Cost of Goods Sold: $800,000
- Gross Profit: $700,000
- Operating Expenses: $450,000
- Net Income: $250,000
This statement highlights our company’s profitability and overall financial health during the first year of operation.
Cash Flow Statement

A cash flow statement is a crucial part of a financial business plan that shows the inflows and outflows of cash within your business. It helps you monitor your company’s liquidity, ensuring you have enough cash on hand to cover operating expenses, pay debts, and invest in growth opportunities.
By including a cash flow statement in your business plan, you demonstrate your ability to manage your company’s finances effectively.
Example: The cash flow statement for EcoTech’s first year of operation is as follows:
Operating Activities:
- Depreciation: $10,000
- Changes in Working Capital: -$50,000
- Net Cash from Operating Activities: $210,000
Investing Activities:
- Capital Expenditures: -$100,000
- Net Cash from Investing Activities: -$100,000
Financing Activities:
- Proceeds from Loans: $150,000
- Loan Repayments: -$50,000
- Net Cash from Financing Activities: $100,000
- Net Increase in Cash: $210,000
This statement demonstrates EcoTech’s ability to generate positive cash flow from operations, maintain sufficient liquidity, and invest in growth opportunities.
Tips on Writing a Business Plan

1. Be clear and concise: Keep your language simple and straightforward. Avoid jargon and overly technical terms. A clear and concise business plan is easier for investors and stakeholders to understand and demonstrates your ability to communicate effectively.
2. Conduct thorough research: Before writing your business plan, gather as much information as possible about your industry, competitors, and target market. Use reliable sources and industry reports to inform your analysis and make data-driven decisions.
3. Set realistic goals: Your business plan should outline achievable objectives that are specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). Setting realistic goals demonstrates your understanding of the market and increases the likelihood of success.
4. Focus on your unique selling proposition (USP): Clearly articulate what sets your business apart from the competition. Emphasize your USP throughout your business plan to showcase your company’s value and potential for success.
5. Be flexible and adaptable: A business plan is a living document that should evolve as your business grows and changes. Be prepared to update and revise your plan as you gather new information and learn from your experiences.
6. Use visuals to enhance understanding: Include charts, graphs, and other visuals to help convey complex data and ideas. Visuals can make your business plan more engaging and easier to digest, especially for those who prefer visual learning.
7. Seek feedback from trusted sources: Share your business plan with mentors, industry experts, or colleagues and ask for their feedback. Their insights can help you identify areas for improvement and strengthen your plan before presenting it to potential investors or partners.
FREE Business Plan Template
To help you get started on your business plan, we have created a template that includes all the essential components discussed in the “How to Write a Business Plan” section. This easy-to-use template will guide you through each step of the process, ensuring you don’t miss any critical details.
The template is divided into the following sections:
- Mission statement
- Business Overview
- Key products or services
- Target market
- Financial highlights
- Company goals
- Strategies to achieve goals
- Measurable, time-bound objectives
- Company History
- Mission and vision
- Unique selling proposition
- Demographics
- Psychographics
- Pain points
- Industry trends
- Customer needs
- Competitor strengths and weaknesses
- Opportunities
- Competitor products and services
- Market positioning
- Pricing strategies
- Organizational structure
- Key roles and responsibilities
- Management team backgrounds
- Product or service features
- Competitive advantages
- Marketing channels
- Advertising campaigns
- Promotional activities
- Sales strategies
- Supply chain management
- Inventory control
- Production processes
- Quality control measures
- Projected revenue
- Assumptions
- Cash inflows
- Cash outflows
- Net cash flow
What is a Business Plan?
A business plan is a strategic document that outlines an organization’s goals, objectives, and the steps required to achieve them. It serves as a roadmap as you start a business , guiding the company’s direction and growth while identifying potential obstacles and opportunities.
Typically, a business plan covers areas such as market analysis, financial projections, marketing strategies, and organizational structure. It not only helps in securing funding from investors and lenders but also provides clarity and focus to the management team.
A well-crafted business plan is a very important part of your business startup checklist because it fosters informed decision-making and long-term success.

Why You Should Write a Business Plan
Understanding the importance of a business plan in today’s competitive environment is crucial for entrepreneurs and business owners. Here are five compelling reasons to write a business plan:
- Attract Investors and Secure Funding : A well-written business plan demonstrates your venture’s potential and profitability, making it easier to attract investors and secure the necessary funding for growth and development. It provides a detailed overview of your business model, target market, financial projections, and growth strategies, instilling confidence in potential investors and lenders that your company is a worthy investment.
- Clarify Business Objectives and Strategies : Crafting a business plan forces you to think critically about your goals and the strategies you’ll employ to achieve them, providing a clear roadmap for success. This process helps you refine your vision and prioritize the most critical objectives, ensuring that your efforts are focused on achieving the desired results.
- Identify Potential Risks and Opportunities : Analyzing the market, competition, and industry trends within your business plan helps identify potential risks and uncover untapped opportunities for growth and expansion. This insight enables you to develop proactive strategies to mitigate risks and capitalize on opportunities, positioning your business for long-term success.
- Improve Decision-Making : A business plan serves as a reference point so you can make informed decisions that align with your company’s overall objectives and long-term vision. By consistently referring to your plan and adjusting it as needed, you can ensure that your business remains on track and adapts to changes in the market, industry, or internal operations.
- Foster Team Alignment and Communication : A shared business plan helps ensure that all team members are on the same page, promoting clear communication, collaboration, and a unified approach to achieving the company’s goals. By involving your team in the planning process and regularly reviewing the plan together, you can foster a sense of ownership, commitment, and accountability that drives success.
What are the Different Types of Business Plans?
In today’s fast-paced business world, having a well-structured roadmap is more important than ever. A traditional business plan provides a comprehensive overview of your company’s goals and strategies, helping you make informed decisions and achieve long-term success. There are various types of business plans, each designed to suit different needs and purposes. Let’s explore the main types:
- Startup Business Plan: Tailored for new ventures, a startup business plan outlines the company’s mission, objectives, target market, competition, marketing strategies, and financial projections. It helps entrepreneurs clarify their vision, secure funding from investors, and create a roadmap for their business’s future. Additionally, this plan identifies potential challenges and opportunities, which are crucial for making informed decisions and adapting to changing market conditions.
- Internal Business Plan: This type of plan is intended for internal use, focusing on strategies, milestones, deadlines, and resource allocation. It serves as a management tool for guiding the company’s growth, evaluating its progress, and ensuring that all departments are aligned with the overall vision. The internal business plan also helps identify areas of improvement, fosters collaboration among team members, and provides a reference point for measuring performance.
- Strategic Business Plan: A strategic business plan outlines long-term goals and the steps to achieve them, providing a clear roadmap for the company’s direction. It typically includes a SWOT analysis, market research, and competitive analysis. This plan allows businesses to align their resources with their objectives, anticipate changes in the market, and develop contingency plans. By focusing on the big picture, a strategic business plan fosters long-term success and stability.
- Feasibility Business Plan: This plan is designed to assess the viability of a business idea, examining factors such as market demand, competition, and financial projections. It is often used to decide whether or not to pursue a particular venture. By conducting a thorough feasibility analysis, entrepreneurs can avoid investing time and resources into an unviable business concept. This plan also helps refine the business idea, identify potential obstacles, and determine the necessary resources for success.
- Growth Business Plan: Also known as an expansion plan, a growth business plan focuses on strategies for scaling up an existing business. It includes market analysis, new product or service offerings, and financial projections to support expansion plans. This type of plan is essential for businesses looking to enter new markets, increase their customer base, or launch new products or services. By outlining clear growth strategies, the plan helps ensure that expansion efforts are well-coordinated and sustainable.
- Operational Business Plan: This type of plan outlines the company’s day-to-day operations, detailing the processes, procedures, and organizational structure. It is an essential tool for managing resources, streamlining workflows, and ensuring smooth operations. The operational business plan also helps identify inefficiencies, implement best practices, and establish a strong foundation for future growth. By providing a clear understanding of daily operations, this plan enables businesses to optimize their resources and enhance productivity.
- Lean Business Plan: A lean business plan is a simplified, agile version of a traditional plan, focusing on key elements such as value proposition, customer segments, revenue streams, and cost structure. It is perfect for startups looking for a flexible, adaptable planning approach. The lean business plan allows for rapid iteration and continuous improvement, enabling businesses to pivot and adapt to changing market conditions. This streamlined approach is particularly beneficial for businesses in fast-paced or uncertain industries.
- One-Page Business Plan: As the name suggests, a one-page business plan is a concise summary of your company’s key objectives, strategies, and milestones. It serves as a quick reference guide and is ideal for pitching to potential investors or partners. This plan helps keep teams focused on essential goals and priorities, fosters clear communication, and provides a snapshot of the company’s progress. While not as comprehensive as other plans, a one-page business plan is an effective tool for maintaining clarity and direction.
- Nonprofit Business Plan: Specifically designed for nonprofit organizations, this plan outlines the mission, goals, target audience, fundraising strategies, and budget allocation. It helps secure grants and donations while ensuring the organization stays on track with its objectives. The nonprofit business plan also helps attract volunteers, board members, and community support. By demonstrating the organization’s impact and plans for the future, this plan is essential for maintaining transparency, accountability, and long-term sustainability within the nonprofit sector.
- Franchise Business Plan: For entrepreneurs seeking to open a franchise, this type of plan focuses on the franchisor’s requirements, as well as the franchisee’s goals, strategies, and financial projections. It is crucial for securing a franchise agreement and ensuring the business’s success within the franchise system. This plan outlines the franchisee’s commitment to brand standards, marketing efforts, and operational procedures, while also addressing local market conditions and opportunities. By creating a solid franchise business plan, entrepreneurs can demonstrate their ability to effectively manage and grow their franchise, increasing the likelihood of a successful partnership with the franchisor.
Using Business Plan Software

Creating a comprehensive business plan can be intimidating, but business plan software can streamline the process and help you produce a professional document. These tools offer a number of benefits, including guided step-by-step instructions, financial projections, and industry-specific templates. Here are the top 5 business plan software options available to help you craft a great business plan.
1. LivePlan
LivePlan is a popular choice for its user-friendly interface and comprehensive features. It offers over 500 sample plans, financial forecasting tools, and the ability to track your progress against key performance indicators. With LivePlan, you can create visually appealing, professional business plans that will impress investors and stakeholders.
2. Upmetrics
Upmetrics provides a simple and intuitive platform for creating a well-structured business plan. It features customizable templates, financial forecasting tools, and collaboration capabilities, allowing you to work with team members and advisors. Upmetrics also offers a library of resources to guide you through the business planning process.
Bizplan is designed to simplify the business planning process with a drag-and-drop builder and modular sections. It offers financial forecasting tools, progress tracking, and a visually appealing interface. With Bizplan, you can create a business plan that is both easy to understand and visually engaging.
Enloop is a robust business plan software that automatically generates a tailored plan based on your inputs. It provides industry-specific templates, financial forecasting, and a unique performance score that updates as you make changes to your plan. Enloop also offers a free version, making it accessible for businesses on a budget.
5. Tarkenton GoSmallBiz
Developed by NFL Hall of Famer Fran Tarkenton, GoSmallBiz is tailored for small businesses and startups. It features a guided business plan builder, customizable templates, and financial projection tools. GoSmallBiz also offers additional resources, such as CRM tools and legal document templates, to support your business beyond the planning stage.
Business Plan FAQs
What is a good business plan.
A good business plan is a well-researched, clear, and concise document that outlines a company’s goals, strategies, target market, competitive advantages, and financial projections. It should be adaptable to change and provide a roadmap for achieving success.
What are the 3 main purposes of a business plan?
The three main purposes of a business plan are to guide the company’s strategy, attract investment, and evaluate performance against objectives. Here’s a closer look at each of these:
- It outlines the company’s purpose and core values to ensure that all activities align with its mission and vision.
- It provides an in-depth analysis of the market, including trends, customer needs, and competition, helping the company tailor its products and services to meet market demands.
- It defines the company’s marketing and sales strategies, guiding how the company will attract and retain customers.
- It describes the company’s organizational structure and management team, outlining roles and responsibilities to ensure effective operation and leadership.
- It sets measurable, time-bound objectives, allowing the company to plan its activities effectively and make strategic decisions to achieve these goals.
- It provides a comprehensive overview of the company and its business model, demonstrating its uniqueness and potential for success.
- It presents the company’s financial projections, showing its potential for profitability and return on investment.
- It demonstrates the company’s understanding of the market, including its target customers and competition, convincing investors that the company is capable of gaining a significant market share.
- It showcases the management team’s expertise and experience, instilling confidence in investors that the team is capable of executing the business plan successfully.
- It establishes clear, measurable objectives that serve as performance benchmarks.
- It provides a basis for regular performance reviews, allowing the company to monitor its progress and identify areas for improvement.
- It enables the company to assess the effectiveness of its strategies and make adjustments as needed to achieve its objectives.
- It helps the company identify potential risks and challenges, enabling it to develop contingency plans and manage risks effectively.
- It provides a mechanism for evaluating the company’s financial performance, including revenue, expenses, profitability, and cash flow.
Can I write a business plan by myself?
Yes, you can write a business plan by yourself, but it can be helpful to consult with mentors, colleagues, or industry experts to gather feedback and insights. There are also many creative business plan templates and business plan examples available online, including those above.
We also have examples for specific industries, including a using food truck business plan , salon business plan , farm business plan , daycare business plan , and restaurant business plan .
Is it possible to create a one-page business plan?
Yes, a one-page business plan is a condensed version that highlights the most essential elements, including the company’s mission, target market, unique selling proposition, and financial goals.
How long should a business plan be?
A typical business plan ranges from 20 to 50 pages, but the length may vary depending on the complexity and needs of the business.
What is a business plan outline?
A business plan outline is a structured framework that organizes the content of a business plan into sections, such as the executive summary, company description, market analysis, and financial projections.
What are the 5 most common business plan mistakes?
The five most common business plan mistakes include inadequate research, unrealistic financial projections, lack of focus on the unique selling proposition, poor organization and structure, and failure to update the plan as circumstances change.
What questions should be asked in a business plan?
A business plan should address questions such as: What problem does the business solve? Who is the specific target market ? What is the unique selling proposition? What are the company’s objectives? How will it achieve those objectives?
What’s the difference between a business plan and a strategic plan?
A business plan focuses on the overall vision, goals, and tactics of a company, while a strategic plan outlines the specific strategies, action steps, and performance measures necessary to achieve the company’s objectives.
How is business planning for a nonprofit different?
Nonprofit business planning focuses on the organization’s mission, social impact, and resource management, rather than profit generation. The financial section typically includes funding sources, expenses, and projected budgets for programs and operations.
Image: Envato Elements

Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
© Copyright 2003 - 2024, Small Business Trends LLC. All rights reserved. "Small Business Trends" is a registered trademark.
Don't bother with copy and paste.
Get this complete sample business plan as a free text document.
Sporting Goods Retail Store Business Plan
Start your own sporting goods retail store business plan
Sportsuchtig
Executive summary executive summary is a brief introduction to your business plan. it describes your business, the problem that it solves, your target market, and financial highlights.">.
The purpose of this business plan is to secure a seven-hundred thousand dollar ($700,000 to $800,000) conventional business loan from a financial institution in order to purchase the assets of the business known as Sportsuchtig. It will be purchased by Johnson Sporting Goods, LLC, a limited liability company formed for this purpose by John and Lisa Johnson. The business will continue to be known and operated as Sportsuchtig.
Sportsuchtig sells quality sporting goods equipment for the entire family, primarily focused on and specializing in baseball and softball equipment, apparel and accessories from major manufacturers such as Easton, Louisville Slugger, Wilson, Worth, Mizuno, Miken, and Under Armour. The company was established as a retail store in 1986 and created an Internet sports store in 1996. The company currently operates with 10 employees out of a 7,400 square foot facility which houses the combined retail store, call center, office, and product warehouse. Over the last 3 years the company has averaged $2.5 million in sales and a gross margin of 25%, with 52% of the sales generated by the website and 48% coming from the retail store.
In the last 3 years, Sportsuchtig has generated verifiable pre-tax income averaging $194,000 and total owner’s benefit averaging over $323,000. This is a strong business that is positioned well for accelerated growth. We believe the business can reach revenue levels of over $5 million in 5 years by implementing this business plan. Sales are projected to be flat in year one and then grow at 20% in years 2-5. This growth forecast is based on the assumption that the company acts on these key opportunities:
- Redesign, upgrade and marketing of the Internet store.
- Relocating the existing retail store.
- Adding additional product lines for sports played in other seasons than baseball/softball.
- Creation of an outside sales team to gain a significant share of the team sales market.
- Optimization of inventory purchasing, management and tracking.
We will plan to relocate the business near the end of year 1 which should help position us for increased retail sales beginning in year 2. The website will be redesigned in the first 6 months and the Web marketing strategy will be timed to coincide with the implementation of the new site. Expansion into at least one new product participant segment will be planned for each year, beginning in year 1. An outside sales team manager will be hired in year 1, but ramp-up of the sales team is not planned until early in year 2.
The business will be managed by owner John Johnson who will act as President and CEO. Mr. Johnson’s high technology and sports business backgrounds, coupled with his entrepreneurial experience, makes him the ideal leader to drive this sporting goods retail/internet endeavor. He spent almost 20 years leading research and development efforts for high technology stalwarts such as Lucent Technologies and ;Motorola Systems, and was a founding employee and Vice President of a high-tech startup. Mr. Johnson also founded and currently owns two other businesses, Johnson Enterprises, LLC and Johnson Investments, LLC. Johnson Enterprises, LLC sells, designs, and constructs custom game courts (basketball, tennis, etc.), synthetic putting greens, and sporting goods products. Mr. Johnson received a Bachelor of Science in Computer Science from Stone College in Boulder, Colorado and a Masters in Business Administration from the University of Illinois.
1.1 Objectives
- Maintain or exceed in year 1 the recent two-year levels of sales ($2.5 million), gross margin (25%), and net margin (12%).
- Realize an annual sales growth rate of 20% in years 2-5, reaching over $5 million in sales by the end of year 5.
- Improve gross margins from 25% to 35% by the end of year 5.
- Improve net margins by the end of year 5.
- Redesign and upgrade the Internet e-commerce store by the end of the first year.
- Increase website site traffic 50% and sales 20% in years 1-5 by investing in aggressive Web search optimization and marketing.
- Enhance the retail store location in the second half of year 1 by relocating the current store from its current location to a more prime location in the metropolitan area.
- Establish relationships with local nonprofit organizations, to help underprivileged children build confidence and self esteem through youth sports programs.
- Run the business as a family-run and -oriented business with emphasis on truth, integrity, quality relationships, fun, and giving back to the community.
1.2 Mission
To become the sports equipment supplier of choice, based on product expertise, price, quality, and level of service, by developing a long term relationship with our customers. Become the “family expert” for sporting goods equipment by treating customers like friends and family and by maintaining an experienced, knowledgeable, and caring staff that can help the customer make the right purchase for them, whether they are individuals outfitting their family, or coaches, athletic directors and league representatives supplying their teams.
1.3 Keys to Success
- Upgrade the website so that it is more professional and user friendly, offers incentives, features, and promotions to draw customers back to the site repeatedly, and is optimized for maximum search results.
- Relocate the existing retail store to a more densely populated, growing location.
- Negotiate optimal agreements with the major suppliers that allow us to improve margins, hold down costs, and maximize the control and turnover of our inventory.
- Implement a state-of-the-art, computerized inventory management system to improve inventory turnover and tracking.
- Expand the product line by offering equipment for additional sports that are typically in demand during current Sportsuchtig slow seasons.
- Create an outside sales team that calls on schools, leagues, and associations and is known for product expertise and top service.
- Train employees on product features and on how to provide family-oriented sales and customer support.
- Train an existing employee, or hire from outside, a store manager to cover for and be the backup for the Owner/President.
- Advertise and market in areas where our target customer base can learn about our retail and internet stores.
- Build a reliable operations infrastructure that is ready to serve customers, prepare accurate billing and accounting, follow up on orders and shipping, manage the Web site, and maintain a close watch on expenses and collection of accounts receivable.
- Be an active member of the community by participating in nonprofit activities and by sponsoring local sports teams, leagues, and tournaments.
- Ensure through daily management practices that the values of The Sportsuchtig mission are followed, so that a successful and growth-oriented business is developed and maintained.
Company Summary company overview ) is an overview of the most important points about your company—your history, management team, location, mission statement and legal structure.">
Sportsuchtig sells quality sporting goods equipment for the entire family, primarily focused on and specializing in baseball and softball equipment, apparel and accessories (although we do sell a small amount of volleyball, basketball and football equipment). The company was established as a retail store in 1986 and created an Internet sports store in 1998. The company currently operates out of a 7,400 square foot facility which houses the combined retail store, call center, office, and product warehouse. Over the last 3 years, the company has averaged $2.5 million in sales and a gross margin of 25%, with 52% of the sales generated by the website and 48% coming from the retail store.
The retail store is open Monday through Saturday from 9:00 am to 7:00 pm and is closed on Sunday. Orders are retrieved four to six times daily except on Sunday and the 800 call center number is staffed during retail store hours.
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
2.1 Start-up Summary
The startup expenses include Legal Fees for services in regards to the purchase of the business such as the Letter of Intent, the Asset Purchase Agreement, due diligence activities, and the business organization. The Accounting fees are for services regarding the business evaluation and due diligence activities. Rent and insurance for the retail facility must be prepaid before the business takeover. Also listed are expenses related to the creation and production of this business plan.
The startup assets listed are the assets that are being purchased. The purchase price of $1 million for the business is based almost entirely on the value of the assets. The large majority of the company assets, almost $900,000 worth, will reside in inventory. The $25,000 of current assets include furniture, fixtures, display cases, and accounts receivable. The $25,000 of long term assets include 7 computers and a server, printers, and associated software.
The starting cash of $50,000 is working capital to cover 2 months of expenses ($45,000), to provide for initial marketing efforts and as a contingency fund to cover unforEseen expenses related to the takeover of the business.
The purpose of this business plan is to secure a $700,000 conventional or SBA loan for the purchase of the business. The remainder of the purchase and startup costs ($300,000) will be financed through owner investment.

2.2 Company Ownership
The assets of Sportsuchtig are being purchased by John and Lisa Johnson. The company will be organized initially as a Limited Liability Corporation named Johnson Sporting Goods, LLC, doing business as Sportsuchtig.
Sportsuchtig will sell the latest and most popular name-brand sporting goods, apparel, and accessories. Consumers will be educated as to the proper size, style, fit, and design needed for their particular use. Initially these sporting goods will be for the sports of baseball, softball, volleyball, basketball, and football, with the focus primarily on softball and baseball.
The products are purchased from the top manufacturers in the world, such as Easton, Louisville Slugger, Wilson, Worth, Mizuno, Miken, Under Armour, Jugs, Adams, ATEC, Playmaker, TrueSports, Bike. Inventory is tracked through our POS cash register and computerized tracking system. Each day we will be aware of the style, size, and quantity of every item sold in the retail and internet stores.
The general list of products initially to be offered includes the following:
Baseball/Softball Equipment
Baseball Bats, Baseball Gloves, Batting Helmets, Batting Tees, Bases, Catcher’s Equipment, Bat Hangouts, Batting Gloves, Easy Toss Machine, Instant Screens/Nets, Hit-N-Stik, Equipment Bags, Hats, Training Aides, Sunglasses, Baseballs, Softballs, Shoes/Cleats, Umpire Equipment, Ball Buckets, Eye Black, Scorebooks, Pitching Machines, Backstop/Batting Cages, Ball Feeders, Protective Screens, Field Maintenance Equipment, Ankle/Knee Braces, Athletic Supporters, Sliding Shorts, Coaches’ Shorts, Coaching/Training Aids & Videos, Wraps, Ice Packs, First Aid, Mouth/Lip Guards, and Protective Aids.
Baseball/ Softball Uniforms & Apparel
Uniforms for Men, Women and Youth. Uniform Jerseys, Uniform Pants, Uniform Hats, Socks, and Belts. Custom screen printing of uniform names and numbers. Under Armour Gear – Heat, Cold, All Season, Turf, Loose, Performance, and Street. Manufacturer T-shirts and caps.
Volleyballs, Volleyball Bags, Portable Scoreboard, Knee Pads, ClipBoard, Volleyball Carts.
Basketballs, Basketball Systems/Hoops, Basketball Courts, Basketball Fencing, Lighting Systems.
Footballs, Shoulder Pads, Knee Pads, Thigh Pads, Helmets, Gloves, and WristCoach.
Synthetic putting greens.
Future Products
After the assumption of the business, we will look to increase our product line laterally by offering additional product categories. Initially, this will be done to increase revenue in months that are historically slower for Sportsuchtig. We will also significantly grow the existing Volleyball, Basketball, and Football lines in year 1.
We will evaluate introducing products for the sports of Soccer, Field Hockey, Lacrosse, Hockey, Golf, Swimming, Tennis, Wrestling, Running and Cheerleading. We will also evaluate the introduction of Major League and College sports team logo apparel such as NFL, NBA, MLB, NHL, NCAA and NHL.
In addition, in order to serve the older and more affluent sports participant, we will evaluate less vigorous and more relaxing sports lines such as camping, fishing, and golf.
Market Analysis Summary how to do a market analysis for your business plan.">
The sporting goods market as a whole is a multi-billion dollar industry, with retail sales of sporting goods reaching $45.8 billion in 2003. Sales are expected to grow 2% in 2004 to $46.7 billion. The personal consumption of sporting goods is forecast to grow at an annual compounded rate of 4.8% between 2004 and 2007. Retail sales at sporting goods stores are very sensitive to the health of the economy, because most sports are a leisure activity. Spending on sporting goods correlates strongly with consumer confidence and level of personal disposable income.
The sporting goods market has a myriad of segments that can be categorized by product, sport, geography, behavior, participation, organization and standard demographics. Demographics play a big part in sporting goods sales, since population growth and age groups distinctly impact sport participation.
Our main sales categories break down customer groups by Sports Participation – ie., for which sport(s) the person is buying equipment. These customers have needs based on the specific sport(s) in which they participate. For example, Baseball participants are looking specifically for baseball equipment, uniforms, training aids, etc. We will initially focus on players of Baseball, Softball, Volleyball, Basketball, and Football.
However, in terms of marketing, we will take different approaches to attracting the attention of potential customers based on their relation to the sport or sports player (customer type), and on their buying method/location (retail/online).
- Customer Type – These customers have needs based upon the type of role they play in regards to the sports participants. For example, many times those making sporting goods purchases are not those actually participating in the sport, but instead are parents, athletic directors, and coaches. These segments include: Individual Participants, Parents, League Representatives, Independent Team Coaches, School Athletic Coaches and Directors, Sports Performance Businesses.
- Retail/Online – For retail stores, geographic and demographic divisions are critical, especially in understanding the different needs of our local and online customers. Appeals to soccer moms work one way in the local paper, where the convenience factor is a nearby location with great customer service, and a different way online, where convenience may come in the form of free shipping for larger orders, or free telephone assistance in choosing a size.
4.1 Market Segmentation
Sportsuchtig’ market is both nationwide (even some international) via the internet store, and local, via the retail store, in the local metropolitan region. Market segmentation for Sportsuchtig has several layers and can be analyzed and targeted from many different angles.
The targeted customer market will be segmented in multiple layers as follows:
Sports Participation – These customers have needs based on the specific sport(s) in which they participate. For example Baseball participants are looking specifically for baseball equipment, uniforms, training aids, etc. The National Sporting Goods Association (NSGA) reports in a 2003 report on sports participation in the U.S. for those 7 years of age and older, that there were over 256 million sports participants in 2003 (some participated in multiple sports). The major sports participation segments initially for Sportsuchtig:
Baseball – According to the NSGA 2003 report, for those 7 years of age and older, over 14.6 million people participated in Baseball. Of these 14.6 million, 4.5 million were aged 7-11 and 4.1 million were aged 12-17. Softball – According to the NSGA 2003 report, for those 7 years of age and older, over 11.8 million people participated in Softball. Of these 11.8 million, 1.9 million were aged 7-11 and 2.9 million were aged 12-17. Volleyball – According to the NSGA 2003 report, for those 7 years of age and older, over 10.4 million people participated in Volleyball. Of these 10.4 million, 1.3 million were aged 7-11 and 3.4 million were aged 12-17. Basketball – According to the NSGA 2003 report, for those 7 years of age and older, over 27.9 million people participated in Basketball. Of these 27.9 million, 6.3 million were aged 7-11 and 7.9 million were aged 12-17. Football – According to the NSGA 2003 report, for those 7 years of age and older, over 8.7 million people participated in tackle Football and 9.3 million in touch Football. Other Sports (Future for Sportsuchtig) – According to the NSGA 2003 report, for those 7 years of age and older, over 173.4 million people reported participating in other sports than those that Sportsuchtig currently targets. This represents a huge growth opportunity for Sportsuchtig as it moves to target these sports segments.
These millions of participants are all potential customers for the internet store. The local area has a large number of youth recreation, adult recreation, and school leagues for these sports.
Customer Type – These customers have needs based upon the type of role they play in regards to the sports participants. For example, many times those making sporting goods purchases are not those actually participating in the sport, but instead are parents, athletic directors, and coaches.
Individual Participants – These are the actual sports participants. Typically, these would be adult participants or older youths who have the technical knowledge and disposable income to purchase sporting goods equipment and apparel on their own. Parents – Parents buy on their own, or are present during the purchase of over 90% of sporting goods purchases for youths ages 5-18. This segment can be heavily influenced by their children in regards to the “hot” or best products. They are also the segment in most need of technical assistance from sporting goods store staff. League Representatives – Members of adult and youth athletic associations are responsible for league equipment and uniform purchases to outfit league teams. Long-term relationships and sponsorship participation are important to this segment. They usually have technical proficiency and want to deal with someone that is on or above their technical level of expertise. This segment is usually well informed about recent product offerings and can be a solid channel for introducing new products. They are also a marketing channel to all the participants and parents involved with their league. Independent Team Coaches – Typically those organizing and coaching adult sports teams, or individual advanced youth teams (such as AAU teams), they are responsible for the design and purchase of their individual team uniforms. School Athletic Coaches and Directors – Public and private middle and high school athletic directors must outfit their teams with high quality sporting goods equipment and uniforms. Establishing ;relationships with this segment is difficult, but can be lucrative if all of the school’s sporting goods needs can be met. Sports Performance Businesses – These are organizations that sell services to enhance the participant’s performance in his or her sport. Many times, they operate recreational/training facilities and offer individual or team training programs. Selling equipment to these facilities provides a channel, not only to the facilities’ customers, but also to the many area school and league coaches, who are typically part-time employees of these companies.
Retail/Online – It is critical for us, as a retail store, to understand the demographics of our different sales bases.
National – The demographic for the internet store is truly nationwide. The potential customer segment is all of the 256 million sports participants that have access to the internet. Products have been sold and shipped from this site to most of the 50 states in the U.S. In fact, products have also been sold internationally in Japan, Singapore, etc. Metropolitan Area – The metropolitan area has a population of just over 1 million. This area is made up of 13 counties and cities and grew 15% from 1990 to 2000. Jansen county is the county where most of Sportsuchtig current retail customers live. Jansen county has a population of 278 million and a recent growth rate of 2%. Jansen county alone has 52,000 students, 36 elementary schools, 12 middle schools, and 10 high schools. The other largest counties – Jefferson and Lucas – are growing at 1.5% and 2.3% respectively. We believe that relocating the retail store north will provide significantly better accessibility for the sports participants in these counties, especially with the opening of the new highway around the western edge of the metropolitan area.

4.2 Target Market Segment Strategy
The focus will initially be on the Baseball and Softball participant segment, because this is Sportsuchtig’ current core competency and because the number of participants, both nationally and locally, is quite large. We will look to leverage current Sportsuchtig relationships in this segment and move aggressively to increase sales and margins through a targeted marketing campaign.
We will then strategically target other participation segments to try and increase sales during the non-peak baseball/softball sales months. This is a huge opportunity for growth for the company, as evidenced by the large number of participants present in the other participant segments. Changing tastes in sports and strong sales of sporting goods in recent years partly reflect the changing composition of the U.S. population. In particular, the number of older (and more affluent) people has increased rapidly in the past decade. As the Baby Boomers age, they participate less in vigorous sports like baseball, basketball, and tennis, and more in relaxed sports like camping, fishing, and golf. We believe quickly moving into at least one sport that serves this aging market to be critical to meeting sales goals.
Due to the fact that the company has both an internet store and a retail store it is important to understand the market segmentation and demographics on both a national and local level. The internet store has made substantial sales (almost 1.3 million in 2003) with a weak user presentation experience and basically no Web marketing strategy. The analysis of the number of sports participants nationwide, not to mention internationally, illuminates the fact that attacking this nationwide segment through a focused Web strategy could bring significant returns.
4.3 Industry Analysis
In the U.S., about 20,000 companies operate retail sporting goods stores, with combined annual revenue of $25 billion. Most operate a single retail location. Large chain operators include Sports Authority ($1.4 billion revenue), Gart Sports ($936 million), Dick’s Sporting Goods ($2 billion – including the recent acquisition of Galyan’s), and Hibbett Sporting Goods ($241 million). The industry is highly fragmented. There are 150 companies with more than 5 stores, but the 20 largest chains hold only about 35 percent of the national market.
Sporting goods stores vary according to format and merchandise. Large format stores (Dick’s, Sports Authority), also known as “Big Box” stores, are from 20,000 to 100,000 square feet, stock a large number of items, and are typically found as anchor stores in strip malls or in stand-alone locations. Traditional sporting goods’ retail stores (Happy Sports, Don’s Sporting Goods in the metro area) are from 5,000 to 20,000 square feet, carry a more limited number of items, and are typically found in strip or enclosed malls. Sportsuchtig falls into this traditional format with 7,400 square feet, 2.5 million in sales, and 10-12 employees. Large format stores typically have more than $5 million in annual revenue and more than 50 employees. raditional retail stores typically have $1-$5 million in sales and 10-50 employees. In the U.S., there are about 8,000 large-format and traditional sporting goods stores, with 50% of industry revenue.
Sporting goods are also sold by mass merchandisers like Wal-Mart, Kmart, and Target, and by catalog and Internet retailers like Cabela’s and L.L. Bean. Although large chains sell a broad range of merchandise at lower prices, small local stores can successfully compete by offering better service or specializing in a particular sport(s). Because the equipment of many sports is very technical, knowledgeable salespeople are a strong competitive factor. Employees must be trained to understand and explain differences. Companies typically try to recruit employees who are avid sports’ participants.
Marketing is typically through a combination of advertising and sports events. Advertising is most often through newspaper ads, inserts, direct mailings, and sometimes radio. Word-of-mouth advertising is especially important to traditional sporting goods stores that provide superior service and expertise. Many companies sponsor local sports events or competitions and host appearances by sports celebrities. Some stores provide technical services and “participation areas” like basketball hoops, putting greens, and climbing walls. In addition to selling individual items, many stores (Happy, Don’s) specialize in selling team uniforms and equipment to local schools and clubs.
Inventory management is a major concern for all sporting goods retailers because of the large numbers of items they sell and the short selling season for many sports. Insufficient inventory produces missed sales, but excess inventory can’t easily be sold once a sports season is over. Many companies use highly sophisticated computerized inventory management systems.
4.3.1 Competition and Buying Patterns
The competition for Sportsuchtig’ retail store in the metropolitan area includes one large format sporting goods chain with 4 locations, 2 well known traditional format sporting goods stores with 1 location each, and around 18 specialty, or niche, sporting goods stores.
The large format store is Dick’s Sporting Goods, which is based in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. With its recent purchase of Galyan’s Trading Company, Dick’s now has annual sales of over $2 billion and operates 221 stores in 32 states. Dick’s has 4 big box stores in the metropolitan area. Dick’s offers a very wide variety of sports equipment and products, but the selection within each sport is usually limited and narrow. Their stores are big and impressive and found in upscale areas. The stores appear to be under-staffed, as it is usually hard to find ready assistance. Once found, the employees are not very knowledgeable in regards to product offerings and/or location of the products in the store. Most of the time the employees are teenagers. Products are generally priced higher than the competition, although they do have frequent sales and discounts. They utilize a “Score Card” discount club program that allows frequent customers to benefit from specials and discounts once they reach a certain level of points based on past purchases. They actually give the customer a credit-card-sized card to present when making purchases. They utilize the information gathered during registration for this program to send direct mail and email offers to the members. Customers generally purchase from Dick’s when they don’t need technical assistance, a generic product with small selection is sufficient, and price is not a driver. Dick’s is the most dominant and visible player in the market, because of their advertising and high profile stores. Dick’s also has a Web store from which they sell products and provide store location services.
The two traditional sporting goods stores in the metropolitan area are Don’s Sporting Goods and Happy Sports. Both of these stores are very well known and have been in the local market for over 30 years. These 2 stores are in the same class and format as Sportsuchtig.
Don’s Sporting Goods had been a family owned business sice 1952, until it was sold in June of 2004 to a publicly traded company. Don’s had annual sales in 2003 of around $18 million and operates eight warehouses and showrooms in this region. It operates one showroom in the local area at its headquarters in the near west end. Don’s showrooms are usually around 3,000-3,500 square feet and contain many sports but very sparse selection. The store layout is changed frequently, following the seasonality of the sports. Typically their store staff members have technical knowledge and can help customers determine the right product for them. Don’s strength is in its 35-40 strong nationwide sales force that specializes in the distribution of team uniforms and school equipment. Don’s also has a nice Web site and e-commerce store from which they sell individual and team products.
Happy Sports is family-owned and opened in 1970. They operate one retail store in a west-end shopping center. The store is around 4,500 square feet and offers many different sports products. The store has been upgraded in recent years and the variety and selection are broader now than in previous years. They claim to have a knowledgeable staff but personal visits to this store have proven this not to be true. Happy also has a fairly strong Team Division which sells to schools and recreation leagues. Happy also utilizes a credit card size “Discount Card” that allows frequent customers to benefit from specials and discounts once they reach a certain level of points based on past purchases. They recently did an advertising campaign through local radio stations. They have a Web site that lists some of their products but it is not e-commerce, as you can not purchase products directly from the site.
Play It Again Sports is part of a 450-store national franchise chain that has been operating since 1988. They have 4 franchises in the local area. Play It Again’s niche is that they buy, sell, and trade used and new sports equipment. They claim that because their customers can sell or trade-in their used gear for cash or store credit that they are able to get deeper discounts and better prices on really great used and new equipment. Generally these stores appear to be poorly staffed, both from a numbers and a technical knowledge standpoint. We found their prices not much more competitive than those at Dick’s.
The 18 or so specialty stores found around the local metropolitan area specialize in golf, tennis, soccer, biking, swimming, running, etc. Most operate very small, 1,000-1,500 square foot, stores. As Sportsuchtig moves into other sports, some of these will become direct competitors. For example, All About Soccer operates 2 stores – one in the west end, and another on the south side. They focus purely on Soccer products – balls, shin guards, and cleats.
The competition for our Internet store is significant. There are many Internet sports stores vying for the online customer’s dollars – over 50. The most significant of these include big box stores like Dick’s and The Sports Authority, but also smaller more traditional ;companies such as Fog Dog, Blackwater, Annaconda, Direct Sports, Bassco, Big 5 Sporting Goods, Planet Sports, Baseball Corner, and Baseball Express. Most of these internet stores offer a full range of sports products and their Web sites are professionally done and usually feature tools designed to draw the customer back to the site repeatedly.
We believe the internet store has done extremely well to date against this competition and that with an improved Web site design and a Web marketing strategy we can significantly increase our sales through this channel. On the retail side, we believe our large selection and inventory, our staff’s technical knowledge, and our unique customer service will help us compete against our competitors in the local market.
Strategy and Implementation Summary
Sportsuchtig will leverage its expertise, product offerings, and marketing strategy to increase its customer base while driving sales and profit. The following sections review the various strategies that will support this effort.
5.1 Sales Strategy
Sportsuchtig will approach retail sales from a salesperson-customer relationship basis. All sales associates will be trained and encouraged to assist customers in a personal manner, utilizing first names and asking the questions needed to provide the customers with the services they desire. The current Point-Of-Sale system is already set up to collect the customer’s name, address, and purchases. Gathering key customer information and seeking performance feedback on the products and services offered will assist us in the following ways:
- Targeting our marketing efforts more effectively.
- Offering products and merchandising formats that will increase sales.
- Developing services that enhance the shopping experience.
- Training and developing sales associates in order to effectively service the customer.
- Increase awareness of Sportsuchtig within the retail consumer marketplace.
- Develop future sales opportunities that allow for continued growth of the business.
We want our customers to come back and specifically ask for a salesperson by name, because they were so satisfied with the service previously provided.
Currently the format of the retail store separates the customer from the merchandise. The customer must be assisted by a salesperson or they cannot touch or browse the merchandise. We believe this leads to walk-outs when all the available salespeople are tied up assisting other customers. Usually, these customers will leave and never return. We plan to reformat the store so that the products will be showcased via lifestyle merchandising that inspires and promotes multiple purchases. We look to create a strong visual impact, creating an invitation to touch and purchase.
In order to provide the customer with the most up-to-date products on the market and a wide selection, we will attend sporting goods trade shows which showcase all of the products manufactured within the sporting goods industry. Attending shows and seminars will not only allow us to ensure our product mix is current and up-to-date, but will also provide us with fresh, new store merchandising and display ideas. To stay abreast of market and product trends, we will utilize trade publications, trade associations, and their associated Web sites.
It is the goal of Sportsuchtig to offer selection and quality at a value to the consumer. Our pricing structure will support a 25-35% gross margin and position us competitively within the marketplace. Seasonal promotional offers, discounts for end of season, and sale “events” will encourage additional sales and multiple unit purchases.
Employees of Sportsuchtig are an integral part of the shopping experience for the customer. All employees will be developed for growth and advancement, and compensated fairly with effective training that will enable them to confidently service and sell the customer.
Currently there is no sales force to actively pursue sales to the League, School, and Team market segments. Key to the new sales strategy is direct sales calls on these market segments. Currently these sales calls are made by the current owner, by virtue of his background and knowledge of the products and competitors. Experience has proven that the more time he devotes to sales, the more sales result. Initially, this sales task will be transferred to the new managing owner, John Johnson. However, it is strategically necessary to hire and develop a sales team to attack these markets. The competition well-established with many of our potential customers, so a full-time team sales manager will be found and added as soon as possible. His/her task will be to grow the sales in these segments and to build the sales team. Without this person, too much of John Johnson’s time will be deflected away from his major role of strategically operating and growing the business.
There are currently 2 part-time commissioned external sales people. One of them is a well-known Softball pitching coach who has a small training facility/store in the area. She sells Sportsuchtig’ products to her students and others that come to her store. Her commission is 50% of the margin gained from these sales. There is another saleswoman who pulls a trailer of Sportsuchtig products with her when she goes to softball tournaments around the region. Her commission is also 50% of the gross margin on the sales. These relationships and channels for sales will be investigated and formalized into a sales program if deemed beneficial.
Web sales are handled electronically via the internet store Shopping Cart or via phone sales representatives taking calls on the 800 telephone number. There are currently 4 computer/phone stations for these sales reps. These sales representatives need to be thoroughly trained in product offerings and have good phone communication skills. They need to be trained to follow a general sales script when dealing with customers. Having good images of products and detailed product benefits and features on the Web site is critical to getting the customers to commit to an online purchase without talking with a sales representative. A functioning site search engine that helps customers locate product also needs to be added to the internet site.
5.1.1 Sales Forecast
The following table and chart give a run down on forecasted sales. We expect sales in year 1 to be flat as the new owner comes into operating the business. Businesses generally see a sales decline in the first year of new ownership. We believe, however, that this business is strong and that we can at least maintain the current level of sales ($2.5 million) in year 1.
We have projected 20% sales growth in years 2-5, reaching over $5 million in sales by the end of year 5. This growth forecast is based on the assumption that the company acts on the keys to success outlined earlier in this plan: upgrade the website, relocate the existing retail store, negotiate optimal agreements with the major suppliers, expand the product line by offering equipment for additional sports, create an outside sales team that calls on schools, leagues, and associations, train employees, train or hire a store manager, advertisement and promotion, build a reliable operations infrastructure, be an active member of the community, and ensure through daily management practices that the values of The Sportsuchtig mission are followed.
We will look to relocate the store near the end of year 1, which should help position us for increased retail sales beginning in year 2. The website and internet store will be redesigned after the first 6 months and the Web marketing strategy will be timed to coincide with the implementation of the new site. Expansion into at least one new product participant segment will be planned for each year, beginning in year 1. An outside sales team manager will be hired in year 1 but ramp up of the sales team is not planned until early in year 2.
The other assumption built into the forecast is that gross margins will be flat in year 1 but able to be continually improved through years 2-5. This assumption is based on improved purchase agreements with major suppliers and better inventory management, so that fewer products have to be discounted at product season end.
The sales forecast could turn downward if the outside sales team has difficulty gaining traction. The competition is comfortably entrenched in the segments to be targeted, so success is not guaranteed.

5.2 Milestones
The accompanying milestone table highlights our plan with specific dates. This schedule reflects our strong committment to organization and detail. Milestone responsibility is assigned to the functional departments in the company – Sales, Marketing, HR, Operations, and President’s Office.
The Milestone table reflects critical dates for the acquisition and takeover schedule, systems reviews and upgrades, the website re-design and deployment, the retail store relocation, and new product identification and rollout. We also define our target dates for policy definition and implementation as well as documented employee training and evaluation processes.
5.3 Marketing Strategy
The marketing strategy of Sportsuchtig centers on defining our market niche in terms that benefit our customer. Retail and internet store marketing will be integrated and synchronized. We plan to establish a consistent and coherent marketing plan and calendar that take into account and utilize all effective forms of publicity, advertising, and other marketing tools. Specific strategies that will potentially be used are as follows:
- Newspaper/Print Ads – It will be necessary to keep the Sportsuchtig name in front of the customer while getting established will be necessary. We plan on running limited-space ads in the local newspapers to keep our name and phone number in front of the consumer. We may offer clip out coupons as an incentive to visit the store and also as a way to track revenue from the ads. Use of magazine print ads is deemed to have little potential return.
- Press Releases – The local paper has regular sections that highlight business purchases and new business openings. We will make sure they give coverage to the grand opening when the store relocates and any time we sponsor or are involved with local nonprofit organizations.
- Team/Tournament Sponsorship – We will selectively sponsor local teams and leagues, preferably by providing equipment or uniforms versus cash. We will encourage links to/from our Web site with these entities. We will look to sponsor a “Sportsuchtig” softball and/or baseball tournament once a year.
- Event Sponsorship – We will investigate opportunities for being sponsors of large area events, especially those managed by the local sports facilitation group, such as a marathon, and biking or ironman events.
- Decals – We will have decals/stickers manufactured with the Sportsuchtig logo. We will include these with all of the orders that we ship. Children in particular enjoy displaying decals/stickers on just about everything.
- Apparel – We will outfit our retail staff with Sportsuchtig branded shirts and have shirts, hats, and other apparel available for event and sales giveaways.
- Grand Opening – A Grand Opening is the most successful of any in-store promotions. With manufacturer support, a large number of door prizes can be given away while instantly building a mailing list. Loss leader pricing on a few high volume consumable products will attract in-store traffic. Vendors will subsidize loss leader pricing with a rebate. Appearances by local celebrities would also expose potential customers to Sportsuchtig. A planned series of events, such as demonstrations, free clinics, celebrity appearances, registration for free prize giveaways, and competitions can all be utilized to extend the grand opening and continually draw customers back so they become familiar and comfortable with the store.
- Trade Shows – We will attend industry trade shows in order to keep abreast of new products and trends. This will also allow us to make and maintain industry contacts.
- Word of Mouth – By giving first-time customers great service and a fair price, the word is sure to spread. Also, the many sports contacts that we already have in the area will prove to be most beneficial in spreading the word.
- Yellow Pages – We will advertise in the local yellow pages.
- Flyers – Flyers will be distributed to all local leagues at season start. These flyers will offer discounts for purchasing from the retail and internet stores. These discounts could be structured so that a certain percentage of the discount goes directly to the customer and other percentages go to the customer’s league or a nonprofit entity being sponsored by Sportsuchtig.
- MailBox Flyers – We will also evaluate placing flyers in local area neighborhood mailboxes.
- Customer Discount Card – The implementation of a customer discount program and card will be investigated to entice customers to shop repeatedly with Sportsuchtig. Information gathered through this program can be utilized to feed direct mail and email campaigns for special program discounts or information.
- Business Networking – Business networking organizations, such as Business Network International, will be visited and potentially joined as a way to increase awareness and create a virtual sales force.
- Direct Mail – A direct mail program utilizing low-cost postcards or other mechanism will be evaluated.
- Radio – A radio campaign will be investigated. Happy Sports recently ran a campaign with some success.
- Catalog – The creation and distribution of a product catalog will be evaluated.
- Web Marketing – A variety of Web marketing channels and vehicles will be researched and tested.
- Press releases, articles, and/or advertising on local internet sites.
- Search engine marketing
- URL Links to/from organizations, teams, leagues, co-marketers
- Email marketing
- Trivia questions with weekly winners
- Sports Tickers
- Retail store event publicity and schedule
- Participation Areas and Contests – When the store is relocated we will, if possible and feasible, leverage the TrueSports product line from the owner’s other business and build a basketball court and putting green into the layout and flooring of the new store. This will allow us to have areas where promotional competitions, demonstrations, clinics, and customer product tryout can be conducted. This will draw customers to the store and also allow a showcase for the TrueCourt and TrueTurf product lines.
- Non-Profit Relationship(s) – Sportsuchtig will build a relationship with, and be an on-going sponsor for, at least one nonprofit organization. Events will be held or sponsored in order to raise money for the nonprofit, or a percentage of profits for certain Sportsuchtig promotions will be credited to the nonprofit for its use in exchanging that credit for Sportsuchtig products. In addition to giving back to the community, we anticipate significant free publicity because of this community support program. Because we are giving help to these organizations, they will get the word out to their benefactors/customers/employees/partners about Sportsuchtig. Word of mouth has always proven to be the greatest advertising program a company can instill. In addition, the media will be more than willing to promote the charitable aspects of Sportsuchtig and provide the opportunity for more exposure every time we provide assistance to another organization.
All marketing decisions with regard to specific media choices, frequency, size, and expenditures will be conducted on an on-going basis with careful considerations of returns generated. All marketing vehicles and channels will be tracked for results.
5.4 Competitive Edge
Sportsuchtig looks to establish itself competitively as a unique sporting goods provider in the local metropolitan area and internet sports market through its product offerings, the scope and level of services it provides, and the expertise of its employees.
Products: Sourced through established and internationally-known manufacturers, the products offered provide a high level of quality and value to the consumer. The depth and range of products will be extensive, separating us from others in the marketplace.
Services: Connecting with the customer is a key focus for Sportsuchtig. It is our desire that customers look to us as their valued resource to obtain the equipment, apparel and accessories that meet their needs. Our internet store will provide prompt courteous service, and deliver products at reasonable shipping rates within expected time frames.
Employees: Employees of Sportsuchtig will enjoy a friendly, fair and creative work environment, which respects diversity, new ideas and hard work. Development through experience and training will be a primary focus. It is our desire that employees are long-term, ensuring an expertise that will support the customer experience. Our employees will be a competitive advantage because their technical product knowledge will be superior to that of the competition. We want customers to form a relationship with a salesperson and ask for them by name when they return for a subsequent purchase.
Web Plan Summary
Sportsuchtig has an existing Website that has been generating $1.3 million in sales the last 2 years. However, we believe that a user interface redesign would generate significantly more revenue. According to market research from the Gartner Group, more than 50% of Web sales are lost because visitors can’t find the content they’re looking for. Another study by usability consultants Creative Good estimated that improving the customer experience increases the number of buyers by 40% and increases overall order size by 10%. We plan to redesign and implement a new website in year 1.
The new site will be designed and coded with internet marketing optimization at the forefront of requirements. The basis for our Website marketing strategy is to utilize search engine optimization, keyword density, direct navigation, targeted link popularity and systematic submissions. It is critical to sales growth that the website gains and maintains a high search engine placement. A full website marketing plan will be developed and implemented.
The website is a primary sales channel for us and is critical to the sales goals of the company. We will implement the new site to showcase the product offerings and provide technical information and assistance to help the customer in their product selection. To further show off its expertise, the website will provide a resources area, offering articles, research, product information and website links of interest to its customers.
The website will mirror the image and branding elements showcased in the retail store and at the same time, keep up with the latest trends in user interface design. The key to the website strategy will be combining a well designed front-end, an excellent and fast shopping cart experience, and a back-end capable of capturing “hits” and customer data for use in future marketing endeavors.
6.1 Website Marketing Strategy
The basis for our website marketing strategy is to utilize search engine optimization, keyword density, direct navigation, targeted link popularity and systematic submissions. Our Website marketing strategy will adhere to each search engine’s no-Spam policies, while generating highly-qualified web traffic. We believe a successful marketing system is much more than simply optimizing our website to be search-engine friendly. The system should also provide support for other strategies, such as link popularity, site design and content, the “stickiness” of our site, consistent search engine submissions, and ethical marketing practices.
It is extremely important to gain and maintain a high search engine placement. A December 2002 study by DoubleClick revealed that people prefer to use search engines almost 2 to 1 over any other source to find products and services on the Internet. 85% of all searches on the internet start on search engines.
In addition, we will implement the following mechanisms to make our website URL and domain name visible and effective:
- We will place our Web address on every form of literature that goes out of our business, such as letterhead, business cards, envelopes, invoices, payments, etc.
- We will place our Web address in all print advertising, such as newspaper ads, magazine ads, professional trade magazines, etc.
- Our internet Web address will be part of our on-hold or answering systems for both the internet 800 numbers and the retail store phone.
- Electronic advertisements such as radio ads will feature our Web address.
- We will develop our new website from inception, and modify the existing one as practical, with Web marketing as a key objective. There are huge advantages to developing the site with marketing in mind. Position of keyword phrases in the text, the alt tag description, the titles of the pages, the page URL, and Meta Tags in the heading area all have a role to play.
- We will avoid using frames on our website because many browsers do not support frames and many search engines do not rank sites with frames very high.
- Although we need pictures to display our many products, we will try to avoid putting too many graphics on a page, so we don’t reduce the page load time to a crawl. If a site does not start to download within 8 seconds a prospective customer will go to another site, and customers with dial-up links find sites with too many images make it painfully slow to load pages.
6.2 Development Requirements
A full development plan will be generated as documented in the milestones. Costs that Sportsuchtig will expect to incur with development of its new website include:
Development Costs
- User interface design – $3,000.
- Site development and testing – $6,000.
- Site Implementation – $1,000.
This development will be outsourced.
Ongoing Costs
- Website name registration – $70 per year.
- Site Hosting – $30 or less per month.
- Site design changes, updates and maintenance are considered part of Marketing.
Management Summary management summary will include information about who's on your team and why they're the right people for the job, as well as your future hiring plans.">
Owner John Johnson will act as President and CEO and will be responsible for all aspects of managing and operating the company. Mr. Johnson spent almost 20 years leading research and development efforts for high technology stalwarts such as Lucent Technologies and Motorola Systems, and was a founding employee of a high-tech start-up. As the Vice President of Development for the start-up, he built the research and development team from the ground up and developed it into an 80 person team which produced leading-edge software technology that enticed Motorola Systems to purchase the company. In late 2002, Mr. Johnson made the decision to apply his entrepreneurial experience and drive to a business of his own and founded Johnson Enterprises, LLC. Johnson Enterprises is a leader in the design and construction of custom indoor and outdoor sports recreation facilities, and specializes in game courts (basketball, tennis, etc.), synthetic putting greens, and sporting goods products. Mr. Johnson also started Johnson Investments, LLC in 2004, a company that specializes in residential and commercial real estate investment.
Mr. Johnson received a Bachelor of Science in Computer Science degree from Stone College in Boulder, Colorado and a Masters in Business Administration degree from the University of Illinois in Champaign, Illinois. He is married with two sons, 10 and 14.
Mr. Johnson’s high technology and sports business backgrounds, coupled with his entrepreneurial experience, makes him the ideal leader to drive this sporting goods retail/internet endeavor.
Overhead for management will be kept to a minimum and all managers will be “hands-on” workers. There is no intention of having a top-heavy organization that drains profits and complicates decisions. At the zenith of this five-year plan, there will be managers for Warehouse/Shipping and Receiving, Team Sales, and two Retail Store managers. John Johnson will be responsible for overall Retail and Internet Sales management, although the Store Managers will also be responsible for sales performance and will have sales-based incentives. Accounting functions could potentially be outsourced. The website management and computer systems management and maintenance will be initially be managed by Mr. Johnson, but will be outsourced in the future. Mr. Johnson will be directly responsible for purchasing, inventory management and control, and marketing (although some marketing will be outsourced).
Currently the company has 10 employees: two warehouse/shipping and receiving clerks, one accounting person that also does internet phone sales, two internet phone salespeople, 4 part-time retail salespeople, and a clerk that does retail sales and is also responsible for answering the retail store phone. The number of employees will grow progressively over time to 25 by the end of year 5.
7.1 Personnel Plan
The Sportsuchtig retail store and phone sales hours are currently Monday through Saturday, 9:00 a.m. to 7:00 p.m. and closed on Sunday. These hours will be evaluated, with the hours most likely being changed to 10:00 a.m. to 7:00 p.m. Monday through Saturday and open on Sunday from 12 p.m. to 5:00 p.m. The Personnel Plan, as detailed in the table following, has been developed to support these store hours and expected volumes, as per the Sales Forecast section.
Assumptions regarding personnel have been made for year 1 through year 5 as follows:
- Year 1 Ending October 2005 – The number of employees inherited from the previous owners are sufficient to operate the business in order to reach the Year 1 sales goals – which is equal to the previous year. John Johnson will be acting President and CEO and will take $60,000 salary in the first year. The support of a trusted and experienced employee will be needed to enable John to be away from the store when necessary and to manage coordination of the planned store relocation, the website redesign/implementation, and to sell products. In January of 2005, a Store Manager will be hired or promoted to fill this need.
- Year 2 Ending October, 2006 – Based on sales volume, it will be necessary to add another Retail Sales person. Salary for John Johnson will increase to $75,000 beginning in November 2006. Current full-time and part-time employees will be provided salary reviews and given appropriate salary increases – 5% has been factored in. In November 2005, a Team Sales Manager will be hired to take over Team Sales from Mr. Johnson and to start aggressively targeting the team segments.
- Year 3 Ending October, 2007 – Salary for John Johnson will increase to $100,000 beginning in November 2007. Current full-time and part-time employees will be provided salary reviews and given appropriate salary increases – 5% has been factored in. Increased sales volume will drive the hiring of 6 new employees. Another Retail Salesperson and an assistant accounting/retail phone clerk will be hired. Increased sales from the website will drive the hiring of an additional Warehouse/Shipping & Receiving clerk and also an additional Internet Phone Salesperson. An additional Store Manager will be hired to relieve Mr. Johnson from day to day store management tasks. We will also hire an additional Salesperson for the Team Sales team.
- Year 4 Ending October, 2008 – Salary for John Johnson will increase to $125,000 beginning in November 2008. Current full-time and part-time employees will be provided salary reviews and given appropriate salary increases – 5% has been factored in. Increased sales volume will drive the hiring of 2 new employees, another Retail Salesperson and an Internet Phone Salesperson.
- Year 5 Ending October, 2009 – Salary for John Johnson will increase to $150,000 beginning in November 2009. Current full-time and part-time employees will be provided salary reviews and given appropriate salary increases – 5% has been factored in. Increased sales volume will drive the hiring of 4 new employees. Increased sales from the website will drive the hiring of an additional Warehouse/Shipping & Receiving clerk and also an additional Internet Phone Salesperson. An additional Retail Salesperson and an additional Salesperson for the Team Sales team will be added.
Financial Plan investor-ready personnel plan .">
The Sportsuchtig financial picture is quite promising. Since Sportsuchtig is a currently operating business, there will be sales and cash coming into the business on day 1 when the operation is taken over by the Johnson’s. An initial working capital investment of $50,000 dollars will be necessary to assure that expenses are covered in the first 2 months, but after that it is assumed that cash from operations will be sufficient to fund and reach the milestones in this plan.
The owners have a personal equity line sufficient to finance any monthly cash-flow shortage; however, a business line of credit will be established as soon as possible. We anticipate very few accounts receivables initially, with 95% of sales cash and carry (cash, checks, credit cards). Marketing and advertising will remain at or below 5% of sales. We will continue to reinvest residual profits into company expansion, and personnel.
8.1 Start-up Funding
An approximately $700,000 loan will be obtained from a conventional or SBA lender. At least $340,000 capital will be provided by the purchasers/owners – the Johnsons. It is possible that some financing may be provided by an active investor or partner in exchange for some level of ownership in the business. If an agreement with an investor or partner cannot be reached, then the owners will contribute all of the funding outside of the loan funding.
8.2 Important Assumptions
The financial plan depends on important assumptions, most of which are shown in the following table. The key underlying assumptions are:
- We assume access to financing sufficient to maintain our financial plan as shown in the tables.
- We assume inventory can be turned in 6-8 months.
- Accounts receivable are small except for periodic sales to teams. Everything else is cash/credit and carry. We accept cash and checks, Visa, MasterCard, Discover and American Express. All sales paid via credit cards will be deposited in our business checking account within 48 hours.
- We anticipate that we will be able to complete required financing, lease documents, and due diligence to allow for a November or December 2004 closing and business take over.
- We assume a slow-growth economy, without major recession.
8.3 Break-even Analysis
For our break-even analysis, we assume running costs which include payroll, rent, utilities, interest expense on the funding loan, and an estimation of other running costs. These estimations are based on real financial history data provided by the sellers of the business. Our sales forecast indicates that monthly sales are expected to be much greater than the break-even point.

8.4 Projected Profit and Loss
The projected Profit and Loss for five years is detailed in the table and charts following. Monthly projected Profit and Loss for year 1 is available in the Appendix. Some assumptions and inclusions to be noted are:
- First year expense and revenue projections are based on the previous 2 years of actual financial data provided by the business seller. Since this is an existing business being purchased, we have lots of real historical financial information to analyze for trends.
- Insurance includes: Business property and inventory, liability and interruption, and key person life insurance.
- We have made assumptions, based on past results, that certain expenses will rise in direct proportion to sales. For example, Bank Card Debit & Service Fees will rise in direct proportion to sales because more sales results in more credit cards being used for purchase transactions. Also, Freight In will rise in proportion because more inventory will need to be shipped in as sales rise. Other expenses that have been projected proportionally to sales increases include Insurance (for inventory), Office Supplies, and Telephone.
- Freight In historically has been .5% of gross sales.
- Bank Card and Debit Service Fees incurred because of credit card sales are calculated at 2.0%.
- Rent increases significantly in years 2-5 because of the retail store and warehouse relocation.
- Marketing/Promotion expenditures will be increased significantly from the past in years 1 and 2 and then be increased as the business grows and expands.
- Payroll expenses will increase as the business grows and we need to hire additional staff.
We expect to be profitable in the first year, with net profits increasing steadily as the reputation of our business, its employees, and services become apparent to the local market and we reap the expected revenue gains from relocating the retail store, enhancing the Website, and expanding into additional products.

8.5 Projected Cash Flow
Cash flow will have to be carefully monitored, as in any business, but Sportsuchtig has the advantage of operating a primarily cash and carry business. After the initial investment and start-up costs are covered, the business will become relatively self-sustaining. The principle payments to service the $700,000 funding loan are reflected in the Cash Flow table.
The key to managing cash flow is to understand the current monthly sales data and to successfully manage the timing of inventory purchases. Sales for Sportsuchtig typically spike in the spring months of February, March, April, May and June. Inventory for this spring season is purchased in bulk from the four major suppliers in the fall months and can cost between $500,000 to $800,000, depending upon the extent of the orders. The suppliers provide significant price breaks on the bulk orders and do not require payment until April 1. Some of the payables associated with this inventory are paid over the 5-6 months before April 1, but the majority is kept in the cash account until full payment on April 1. Additional orders besides the fall bulk orders are also placed as needed throughout the rest of the year. Terms on these inventory orders are typically Net 30 and they are paid in in 30 days. Inventory levels are usually maintained at high levels, due to the need to have product in stock and available when customers need it and it is turned every 6-8 months. We will focus on reducing inventory levels in order to improve cash flow.
The significant cash flow negative in April is expected and is a result of paying the inventory accounts payable that have accrued over the 5-6 months between purchase and the April 1 payment.
Any amounts above $50,000 will be invested into semi-liquid stock portfolios to decrease the opportunity cost of cash held. The interest will show up as Interest Income in the Profit and Loss table and will be updated quarterly.
Cash flow projections are critical to our success. The following table shows cash flow for the first five years, and the chart illustrates monthly cash flow in the first year. Monthly cash flow projections are included in the appendix.

8.6 Projected Balance Sheet
Sportsuchtig’ projected balance sheet shows an increase in net worth by 2009, at which point it expects to be making significant after-tax profit on sales of $5 million. With the present financial projections, Sportsuchtig expects to build a company with strong profit potential, and a solid balance sheet that will be asset heavy and flush with cash at the end of five years. We plan on using the excess cash for continued growth.
The projected Balance Sheet for five years is detailed in the table following. Monthly projections for the first year Balance Sheet are available for review in the Appendix.
8.7 Business Ratios
Business ratios for the years of this plan are shown below. Industry profile ratios based on the Standard Industrial Classification (SIC) code 5941, Sporting Goods and Bicycle Shops, are shown for comparison.

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
The Business of Fashion
Agenda-setting intelligence, analysis and advice for the global fashion community.
News & Analysis
- Professional Exclusives
- The News in Brief
- Sustainability
- Direct-to-Consumer
- Global Markets
- Fashion Week
- Workplace & Talent
- Entrepreneurship
- Financial Markets
- Newsletters
- Case Studies
- Masterclasses
- Special Editions
- The State of Fashion
- Read Careers Advice
- BoF Professional
- BoF Careers
- BoF Insights
- Our Journalism
- Work With Us
- Read daily fashion news
- Download special reports
- Sign up for essential email briefings
- Follow topics of interest
- Receive event invitations
- Create job alerts
Nike Says Job Cuts at Oregon Headquarters to Total More Than 700

Nike Inc. will have eliminated about 740 jobs at its headquarters by late June as part of its multiyear cost-cutting plan.
In a filing with the state of Oregon on Friday, Nike’s vice president of people solutions, Michele Adams, said that this represents a “second phase of impacts” as the world’s largest sportswear company trims its workforce.
Chief Executive Officer John Donahoe said in December that Beaverton, Oregon-based Nike would slash its global headcount by 2% as management seeks as much as $2 billion in cost savings over the next three years.
Initial layoffs at Nike began in February and the company expected to conclude the process by the end of its fiscal year, according to an internal memo reviewed by Bloomberg News.
ADVERTISEMENT
“To compete, we must edit, shift and divest less critical work to create greater focus and capacity for what matters most,” Donahoe said in the memo.
By Kim Bhasin and Leslie Patton; With assistance from Bill Haubert
Learn more:
How Nike Ran Off Course
The American sportswear giant is experiencing its worst slump in a decade. New competition is part of the problem but according to industry insiders and athletes, many of Nike’s wounds are self-inflicted: the results of disruptive restructurings, stalled innovation and uninspiring marketing.
- John Donahoe
© 2024 The Business of Fashion. All rights reserved. For more information read our Terms & Conditions

How Rent the Runway Came Back From the Brink
The rental platform saw its stock soar last week after predicting it would hit a key profitability metric this year. A new marketing push and more robust inventory are the key to unlocking elusive growth, CEO Jenn Hyman tells BoF.
For Struggling Public Companies, Going Private Is No Panacea
Nordstrom, Tod’s and L’Occitane are all pushing for privatisation. Ultimately, their fate will not be determined by whether they are under the scrutiny of public investors.

Why Esprit’s Ambitious Rebrand Fell Short
The company is in talks with potential investors after filing for insolvency in Europe and closing its US stores. Insiders say efforts to restore the brand to its 1980s heyday clashed with its owners’ desire to quickly juice sales in order to attract a buyer.

How Adidas Sambas Took Over the World
The humble trainer, once the reserve of football fans, Britpop kids and the odd skateboarder, has become as ubiquitous as battered Converse All Stars in the 00s indie sleaze years.
Subscribe to the BoF Daily Digest
The essential daily round-up of fashion news, analysis, and breaking news alerts.
Our newsletters may include 3rd-party advertising, by subscribing you agree to the Terms and Conditions & Privacy Policy .
Our Products
- BoF Insights Opens in new window

- Login / Register
- You are here: Skills
New skills partnerships unveiled in CITB business plan
22 Apr 2024 By Colin Marrs
The Construction Industry Training Board is to launch four more sector-specific skills partnerships, including one for repairs & maintenance, it announced today in its 2024-25 business plan.
The new sector plans, designed to support employers’ training needs, will cover repairs & maintenance and the commercial, public and industrial sectors, and join existing plans for homebuilding and infrastructure.
Overall, the business plan covers £267m of investment over the coming year, focusing on three key areas — getting more trained people into industry, training provision, and skills development of the existing workforce.
Tim Balcon, CITB chief executive, said: “We will work in partnership with employers, from the smallest to the largest, so that the training demands of the construction industry can be met with high-quality training provision.
“Changing the skills landscape is not an easy task and not one that can be achieved overnight, but this year’s Plan is a significant step forward.”
Among other new measures, the CITB will design, develop, and test a new Training Needs Analysis (TNA) service for small businesses.
The New Entrant Support Team (NEST) launched in 2023-24 will be further expanded, along with the board’s, Industry Impact Fund which funds employers to design and test new solutions for talent recruitment and retention challenges.
CITB’s Go Construct platform will continue to provide free to access, self-service digital careers information; inspiring new entrants to consider a career in construction and the built environment.
By 2025, CITB aims to increase the number of employers it supports to train and upskill their workforce by 14% and boost the number of individuals supported by 13%.
The business plan also sets out how CITB will invest £30m on buildings, infrastructure, and plan at the National Construction College’s three sites.
More analysis to come…
- Add to Bookmarks
Related articles
Have your say.
Sign in or Register a new account to join the discussion.
- International edition
- Australia edition
- Europe edition

‘No dividing line’: consultants advising private water companies also work for their regulator, Ofwat
Campaigners call for the whole regulatory system to be replaced after Observer analysis finds watchdog spent more than £25m with consultancies
The water industry regulator has spent £26.7m on business consultants in the past five years, including several companies that have simultaneously worked for private water firms, the Observer can reveal.
The findings prompted environmental campaigner Feargal Sharkey to call for Ofwat to be abolished as fellow campaigners said there appeared to be no dividing line between “those who are meant to enforce the law and those who routinely break it”.
The Observer analysed invoices paid to Ofwat’s private sector suppliers from 2019 to the first three months of 2024, collated by procurement specialists Tussell.
The firm that received by far the most income from Ofwat over that period was PwC – which netted more than £11.5m, almost half the total.
PwC audits the accounts of Thames Water , which submitted plans last week to raise bills by 56% over the next five years, as well as providing services to the wider sector.
In a document sent to potential industry clients in 2013, the firm said its “leading role in professional and standard-setting organisations puts us in an ideal position to advise on regulatory, operating effectiveness and other developments”.
Several of the other consultancy companies used by Ofwat advertise their services working for the water industry on their websites.
In March it was revealed that raw sewage was discharged into waterways for 3.6m hours in 2023 by England’s privatised water firms, more than double the figure in 2022.
At the core of the issue has been claims that water companies have invested too little in infrastructure while paying huge dividends to shareholders.
The water industry has paid shareholders £78bn in dividends in the just over three decades since it was privatised, while amassing £64bn of debt, despite being debt-free when sold to the private sector.
“What we’re looking at right now is nothing more than the physical manifestation of three decades of political neglect, regulatory failure and corporate greed,” said Sharkey. “Ofwat needs to be abolished, and it needs to happen today,” he added. “The whole of the regulatory system of the water industry needs dismantling and utter reform, as do those companies that have milked us for nearly £80bn worth of cash, leaving over £60bn of debt behind them.
“The truth is we need to point the finger at the regulator, who simply wasn’t up to it, wasn’t capable and has to go.”
Surfers Against Sewage chief executive, Giles Bristow said: “The regulators have already been exposed for schmoozing water industry fat cats at exclusive members clubs and now this - is there anything that divides those who are meant to enforce the law and those who routinely break it?
“For people across the country, who are rightly furious about the sewage being dumped into our rivers and seas, this is a bad look at a bad time for a supposedly expert independent body.
“It’s time for Ofwat to get their house in order and put clear water between themselves and our scandal-ravaged water industry, because, right now, the picture looks very murky indeed.”
An Ofwat spokesperson said PwC was its “main delivery partner” during its price review process – where Ofwat outlines the maximum water companies can charge to users and service standards for the industry. The spokesperson said the firm delivered “additional technical expertise in areas such as financial modelling, economics and engineering”.
They added that a “rigorous conflict procedure” ensured that “any potential conflicts of interest were identified and managed appropriately”.
A spokesperson for PwC said the firm adheres “strictly to all regulatory, professional, ethical and independence standards”, and has no “decision-making responsibility” in its services to Ofwat.
- Water industry
- The Observer

Thames Water could raise bills to £627 a year to help fix leaks

Thames Water-linked firm paid £14m in dividends despite concerns over group

‘Dirty secret’: insiders say UK water firms knowingly break sewage laws

Thames Water nationalisation plan could move bulk of £15bn debt to state

Thames Water to add to debt mountain in bid for survival

Thames Water break-up is a promising idea

Thames Water has six weeks to agree survival plan with Ofwat

Australia’s Macquarie among lenders to Thames Water’s parent company

Thames Water parent tells creditors it has defaulted on debt
Most viewed.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Traditionally, a marketing plan includes the four P's: Product, Price, Place, and Promotion. For a retail business plan, your marketing plan should include the following: Product: in the product section you should reiterate the type of retail business that you documented in your Company Analysis.
Industry Analysis. The retail industry in the United States is valued at over $4T currently and is forecasted to reach $4.9T by the end of 2022. This is up from $3.8T in 2019. After a decade of retail decline between 2010 and 2020, the market is rebounding at a surprising rate.
Here's how to write the market analysis section of a business plan. Describe each industry that you are competing in or will be targeting. Identify direct competition, but don't forget about indirect competition - this may include companies selling different products to the same potential customer segments.
An example of a Use of funds slide for a retail store ( source) 2. Business Overview. The business overview is essentially the company description. The second section of your business plan, it should cover the following for a retail store: The products you will sell in your store. The price range of the products.
Outline your plan for technology and retail operations. In this part of your business plan, detail how you'll harness retail technology to streamline operations, enhance customer experience and expand your market reach. List your options for POS systems, why you're considering them, their opportunities for growth and their annual cost.
A business plan for the retail industry serves as a structured document that outlines the objectives, strategies, and operations of a retail venture. ... Competition analysis: Within a 15-mile radius, there are three major competitors—two national chains and one local establishment. 4. Product and services .
Include information from target market and industry analysis. A retail market analysis is a deep look at your industry, competition, and geography. All of these things need to be defined in your retail business plan in order for investors to have a full picture of what your particular brand is and how it fits into the overall retail puzzle.
3. Industry Analysis 4. Customer Analysis 5. Competitive Analysis 6. Marketing Plan 7. Operations Plan 8. Management Team 9. Financial Plan 10. Appendix. Each section is discussed below in showing you how to create a business plan for your retail business. Elements of a Retail Business Plan 1. Executive Summary
This guide will provide strategies to market your retail business and attract customers. Your retail business plan should include a situational analysis of your current state, marketing objectives, process, and tactics. To develop a positioning statement, consider how your retail shop differs from competitors, what sets your products and ...
A retail store business plan helps secure investment by demonstrating a clear and well-thought-out strategy. It shows potential investors that you've done your homework, understand your market, and have a solid plan for success. The plan outlines your business goals, target market, competitive analysis, and financial projections, instilling ...
In retail, prior to six months ago, the mindset of most retail executives would be, "if I have a business that's growing at a 2 percent same-store comp rate, and I can get that to 3 percent, I'm feeling pretty good. If my margin is 4.5 percent, and I can get that to 5 percent, I'm feeling pretty good."
A good business plan for a retail store must be tailored to the nuances of the retail industry. Initially, it's imperative to provide a comprehensive overview of the retail market you're entering. This includes up-to-date statistics and an analysis of emerging trends, similar to what we've outlined in our retail business plan template. Your ...
A well-crafted business plan for a retail business should emphasize the optimization of pricing and promotions for each item. Understanding market segments and tailoring item planning accordingly ensures a dynamic and responsive approach. Demand forecasting. Anticipating customer demand is a crucial element of any retail business plan.
Tips on Writing a Business Plan. 1. Be clear and concise: Keep your language simple and straightforward. Avoid jargon and overly technical terms. A clear and concise business plan is easier for investors and stakeholders to understand and demonstrates your ability to communicate effectively. 2.
6. Real-time and Collaborative. Invite your team members to initiate conversations, discuss ideas and strategies in real-time, share respective feedback, and write your business plan. Join over 100k+ entrepreneurs who have used Upmetrics to create their business plans. Start writing your business plan today.
How to Conduct Industry Analysis for a Business Plan. 1. Analyze the competition. Of the three factors listed above, the competition may prove the most difficult to analyze, especially if you are new to the industry. But there are ways to simplify the task. You can start by looking at your direct competitors.
Three key economic trends will likely influence retail sales: 5. A slowing economy will keep retail sales growth in check. 6 In our baseline scenario (55% probability), we forecast GDP growth to slow to 0.9% in 2023 from an estimated 2% in 2022 and 5.9% in 2021. 7 A relatively healthy labor market will, however, continue to boost sales.
Industry analysis in a business plan is a tool that enables a company to understand its position relative to other companies that produce similar products or services like it. While considering the strategic planning process, a company must understand the overall industry's forces. ... India has allowed 51 % FDI in multi-brand retail;
The sporting goods market as a whole is a multi-billion dollar industry, with retail sales of sporting goods reaching $45.8 billion in 2003. Sales are expected to grow 2% in 2004 to $46.7 billion. The personal consumption of sporting goods is forecast to grow at an annual compounded rate of 4.8% between 2004 and 2007.
A retail discount store business plan is essential in today's competitive market. A well-crafted plan helps determine if your store is viable, identifies your products' market, and evaluates potential profitability. It also helps create an effective marketing strategy, forecast sales, and determine the best pricing approach.
4. Price optimization: Retailers have to constantly adapt their pricing strategies to succeed. AI systems analyze broad market trends, buyer behavior, competitor pricing, demand flows, and ...
Connect retail operations with reliable, nationwide business internet. Break free from the constraints of other providers with fast, flexible 5G internet for just $50/month. Set it up in 15 minutes and enjoy a network that can power your store, POS system, security system, and more. 5G: Capable device req'd; coverage not available in some areas.
Retail sales volumes (quantity bought) were estimated to be flat (0.0%) in March 2024, following an increase of 0.1% in February 2024 (revised from 0.0%). Within retail, sales were mixed, with automotive fuel and non-food stores sales volumes rising by 3.2% and 0.5%, respectively. This was offset by falls in food stores and non-store retailers ...
Nike Inc. will have eliminated about 740 jobs at its headquarters by late June as part of its multiyear cost-cutting plan. In a filing with the state of Oregon on Friday, Nike's vice president of people solutions, Michele Adams, said that this represents a "second phase of impacts" as the world's largest sportswear company trims its workforce.
The business plan also sets out how CITB will invest £30m on buildings, infrastructure, and plan at the National Construction College's three sites. More analysis to come… 2024-04-22
The water industry regulator has spent £26.7m on business consultants in the past five years, including several companies that have simultaneously worked for private water firms, the Observer can ...