
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.

22 Develop an Assignment Plan
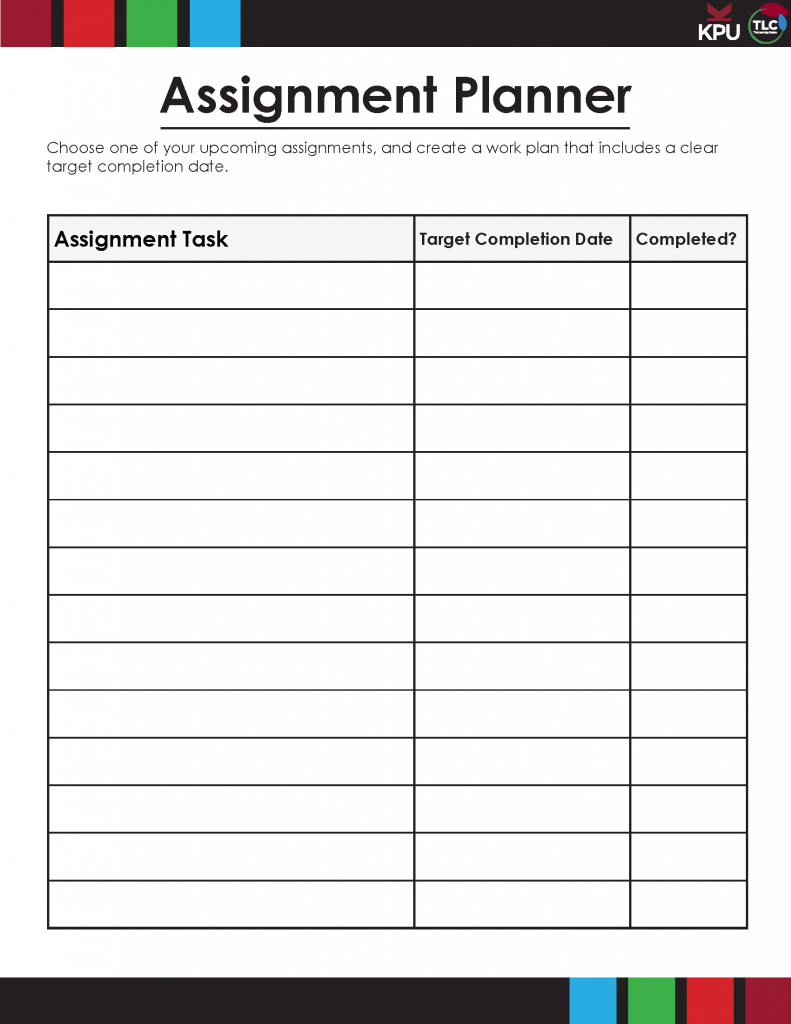
Now that you have a clear idea of what you need to do, the next step is to break down the assignment into manageable “chunks”. The idea of completing a major research paper may seem overwhelming, but if you can divide the task into achievable steps you will be on your way to success.
Use the chart below to break your assignment into smaller steps. You will want to create steps that can be done easily in one day, and preferably in a single work period. Consider the following example breakdown for a research paper.
In the above example, the assignment is divided into smaller pieces, with a manageable amount to complete each day. It is also clear when each task has been completed. A daily work goal like “work on research paper” is not well-defined, and can seem overwhelming. This can make it easy to procrastinate. By choosing specific and achievable goals, you may become more motivated to get started, and you will be able to measure your progress each day. Remember to reward yourself for meeting your goals along the way.
Choose one of your upcoming assignments, and create a work plan modelled on the example above.
Download the assignment planner worksheet .
University 101: Study, Strategize and Succeed Copyright © 2018 by Kwantlen Polytechnic University is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
- Guide Framework
- Guide Navigation
- Learning & Reflection
- Time Management
- Assignment Planning
- Reading & Note-Taking
- Exam Writing & Preparation
- Group Work & Collaboration
- Motivation & Goal Setting
- Additional Resources
Study Skills & Learning Strategies: Assignment Planning
Assignment planning steps.

Need more help?
Attend a workshop
USask Assignment Planner
Assignment Planning Templates
- Understanding Your Assignment Checklist (pdf)
- Assignment Planner (pdf)
- << Previous: Time Management
- Next: Reading & Note-Taking >>
- Library A to Z
- Follow on Facebook
- Follow on Twitter
- Follow on YouTube
- Follow on Instagram
The University of Saskatchewan's main campus is situated on Treaty 6 Territory and the Homeland of the Métis.
© University of Saskatchewan Disclaimer | Privacy
- Last Updated: Apr 23, 2024 1:40 PM
- URL: https://libguides.usask.ca/StudySkillsAndLearningStrategies
Planning and Structuring Assignments
- Book a session
Steps to planning your writing
Understanding the assignment, planning your content, structuring your answer, writing your answer, signposting language.
- Quick resources (5-10 mins)
- e-learning and books (30 mins+)
- SkillsCheck This link opens in a new window
- ⬅ Back to Skills Centre This link opens in a new window

Looking for sessions and tutorials on this topic? Find out more about our session types and how to register to book for sessions. You can view our full and up-to-date availability in UniHub Appointments and Events .
Not sure where to start developing your academic skills? Take the SkillsCheck for personalised recommendations on how to build your academic writing and study skills alongside your course.
Planning is an essential part of writing a successful assignment and ensuring you reach your full potential. Key benefits to a clear plan are that it:
- Helps you to manage and make efficient use of your time
- Ensures that you understand and appropriately fulfil the assignment criteria
- Makes the writing process easier and helps you to produce a coherent and well-structured assignment.
At the start of writing your assignments, it is helpful to create a schedule to help organise your time and break the assignment process up into manageable chunks. Your schedule should include:
- Analysing the question
- Research, reading and note taking
- Planning your answer
- Writing the first draft
- Time to meet with your tutor or module lead (if needed)
- 1 st edit, further research, amendments
- Proofing and formatting
What type of assignment is it?
It’s crucial to understand what type of assignment you are being asked to produce – is it an essay, a literature review, a report, annotated bibliography, or a piece of reflective writing? Each type of assignment has different conventions and will have different requirements to be successful.
Understanding the title
Break down your question to make sure you understand what is being asked of you and what your focus should be.
Questions can usually be split into three sections:
- Instruction words – these will guide/instruct you in how you should approach addressing the question . A list of definitions for commonly used instruction verbs can be downloaded at the bottom of this box.
- Topic words – these will tell you the primary subject of the assignment and may draw your attention to an aspect of the subject that should be given consideration in your response.
- Limiting words – these function as restrictions that help narrow the scope of the question and focus your response.
Let’s look at an example:
The green topic words give us our focus – these can be used as key search terms in Library Search as a way of kickstarting your research on the topic. The red term acts as a restriction – if we started to write about how Batman’s actions had impacted crimes in neighbouring cities, or on a national scale, this would fall outside of the boundaries of the question, and therefore would not gain any marks in this particular assignment.
Question the question
Once you understand the assignment type and have analysed the question, there are a few more questions you should ask:
- Are there key concepts/theories that you will need to define?
- Are there particular aspects of the topic that you want to emphasise?
- If you are required to make a judgement, or give a verdict on something, how will you make this decision?
- Are you going to impose any of your own limiting factors? (This can be a helpful way of focusing a very broad question topic. You can impose your own limiting factors by including them in the introduction of your essay)
Practical considerations
Finally, there are a few practical considerations before you start your essay plan:
- What’s the word count?
- What’s the referencing style? For help with APA referencing look here [insert hyperlink]
- How am I being asked to present my work? Can I include subheadings? What are the requirements for font and size?
It’s useful to know these from the start to save time making changes later in the process.
- Essay terms explained Download our list of instruction words and their definitions to help identify the tasks from your assignment briefs and assessment criteria.
- Essay planning template An A3 guide to essay structure and what each section should include.
Prior knowledge and resources
As you start to plan your answer, the first step should be to consider what you already know about the topic. Think about what has been covered in your lectures/seminar/labs/reading – you may already have quite a lot of relevant information to help you. Likewise, check to see if there are any online reading lists available as these are a very useful starting point.
From here you should have a good idea of what aspects of the question you will need to research in greater detail and where to focus your reading.
When you are reading, your note taking should be an active process. This means engaging with the text rather than just being a passive reader mindlessly highlighting large chunks of text. Here are some key tips to make sure you are an active reader/note-taker:
- Keep your notes selective and concise
- Write notes in your own words as this will help your understanding of the topic
- If you do want to use any direct quotations, keep them short and purposeful. Also, remember to note down the page number straight away so you don’t struggle to find it later!
- Look out for links between what you are reading and what you’ve previously read - do authors agree/disagree? Are theories/models well supported/poorly supported? Are there key challenges?
- Use sub-headings to organise your notes as this well help when you come to write your essay plan.
- Don’t be afraid of making your notes memorable – use colours, underlining and highlighting to draw attention to important information.
For more information, visit our online study guides to critical writing and effective reading .
Throughout this process you should try to reflect on your position in relation to the question and start thinking about what your conclusion might be. This is especially important for questions that are looking for you to give your verdict or opinion on a topic/debate. To help support this it can be useful to try and sum up your argument in one or two short sentences; this helps to ensure that your argument is clear and will help keep your response well-structured and coherent once you start writing.
Now that you’ve completed your reading, it’s time to structure your writing:
- Establish links between different parts of your reading through mind-mapping or identifying common themes.
- Create headings to organise your links – these will become the basis for your paragraphs.
- Start to structure these headings into a logical order and consider how you will order and use these examples to construct and support your response to the assignment.
- There are several different ways you can structure your response, and this might be dependant on what your assignment is asking you to do. For example, if your assignment is organised around themes it might be structured something like this:
Alternatively, if you were contrasting two theories it might look like this:
Of course, these aren’t the only ways to structure your writing and it’s likely that you will need to adapt your plan for each assignment depending on what is required. However, remember that a plan should always help to organise your content so that your response is clear, coherent and well-structured.
In the same way that essays have a clear structure (introduction, main body, conclusion), the paragraphs within your essay should also follow a pattern. Considering how you structure your paragraphs is important as it helps to improve the clarity of your writing by presenting your chosen evidence and subsequent critical response in a clear and effective way.
Paragraphs should be TIED together:
- Topic sentence – The first sentence of your paragraph should introduce the main topic, theme or next step of your argument. It should summarise what the reader can expect from your paragraph. If the paragraph links directly to the question or assessment criteria you’ve been set, think about what key words make this clear to the reader.
- Introduce evidence - Before discussing your evidence, it is helpful to signpost to the reader what aspect of the literature you will talk about in more detail. This can be achieved by drawing their attention to something interesting or contextually important that will be relevant in the following section of the paragraph.
- Evidence – This is where you introduce references and highlight how these support your argument. You could also include counterpoints to your position within this section (and why these challenges are not upheld) or you could have this as a separate paragraph – the choice is up to you!
- Discussion – Your paragraph should end with your interpretation of the evidence and how this links back to the assignment topic. Within these sentences you may explore ideas such as relevance, significance, impact and future directions – for more help with this, check out our guide to critical writing [insert hyperlink]
Let’s look at this in an example:
"As noted by Alexander (2017), talk has always been an essential component of teaching, and, consequently, learning. Evidence has demonstrated that talking about prose can enhance written responses to texts through increasing student confidence about qualities such as character, theme, and motifs ( Coultas , 2006). Despite this however, the most recent version of the National Curriculum has hugely decreased the role of speaking and listening; this includes even going so far as to remove speaking and listening from formal assessment in GCSE specifications. Furthermore, as noted by Yandell (2013), this has included moving the focus of talk as a collaborative experience to only being on the speaker, thus relegating listening as a key skill. Parallel to this, the types of talk discussed within the classroom has considerably narrowed, to the extent that what students now understand as spoken English, is little more than public speaking. Consequently, teachers are now faced with the responsibility of instilling the foundational skills of speaking and listening in students at an earlier age, to ensure that they have the necessary skills to navigate the complex social world.
Linking your ideas
Signposting language is also a key part of academic writing. Signposts are words or phrases that show a link between two ideas and can also be used to signal transition in your writing. This helps to make your writing more coherent and avoids any jarring changes of topic that leave your reader struggling to understand the connection between two paragraphs. Likewise, you can use signposting to develop your argument by identifying ideas that support or contrast one another, or ideas/findings that have built upon the outcomes of prior work. Ultimately, signposting helps to show the reader the structure of your argument and the direction of your response.
In terms of your planning and structuring, you should think carefully about to use signposting language to link the ideas between your paragraphs, signal key transitions develop your argument. Some examples are included below:
To reference other parts of your essay
- As noted above
- As previously stated,
- Given the evidence outlined earlier in the essay
To introduce a supporting point
- In the same way,
To introduce a contrasting point
- Against this,
- A clear challenge for
- By contrast
To introduce reason/outcomes
- Consequently,
- Taken together the evidence seems to suggest
- Accordingly,
To introduce a conclusion
- As this essay has demonstrated
- From the evidence detailed here, it seems that
- In summary,
- In conclusion,
- << Previous: Book a session
- Next: Quick resources (5-10 mins) >>
- Last Updated: Apr 17, 2024 1:52 PM
- URL: https://libguides.shu.ac.uk/essayplanning


IOE Writing Centre
Plan Your Assignment

Follow the basic steps below to plan your assignment. Use the menu on the left for more detail about any of the sections.
1. Check the assessment criteria 2. Address the question 3. Plan the structure 4. Combine your own ideas with the work of others
1. Check the assessment criteria
Check the current student handbook (you will need to download the pdf file from the Moodle page for your course).
Search for the criteria in the handbook using the 'Search' function. Please look at these criteria before you start writing your assignment.
^Back to top
2. Address the question/assignment/instructions
It is important to address the question(s) or instructions as directly as possible. Follow these three steps:
Step 1. Analyse the question/title. Step 2. Gather information Step 3. Generate ideas
1) Analyse the question/title
What type of question, title, or instruction is it?
Is it a yes/no question? Is it a why question? Is it an open question? Is it asking you to critically discuss an issue? Are there two sides? (Are there more than two sides?) Is it asking for a comparison? Is it asking for an evaluation of evidence? Is it asking for a discussion of a causal relationship (a relationship of cause and effect/contributing factors)? Is it asking for a critical discussion of an article or book chapter?
Try to look past the details and identify what the simplest form of the question/ instruction is. In simple terms, what might the answer to this question be? What evidence would be needed to support this type of answer? ("Yes, because...")
Generally, assignment instructions are not invitations to discuss an issue in a roundabout way. They are asking for a direct response. Try to identify what type of response is required. You also need to pay attention to what type of information will be required when answering the question. Are there any particular theories which you will need to refer to?
Are there any terms in the title which need to be defined, for the purposes of your discussion? This might include terms which can have different meanings in different circumstances. You can probably find definitions of terms in one of the recommended books, by looking in the introduction or first chapter.
Further reading: Titles and Instructions
2) Gather information
Before you can write your answer to the question, you need to gather information . In an academic context, this means information from relevant textbooks, journal articles, or published research reports or government policies.
If you have a reading list from the course tutor, look at the recommended books on the reading list, and identify which will be relevant to your question. If you are not provided with a reading list, you should try to identify a textbook which provides an overview of the field, such as an introductory textbook.
Next, search in the content pages and index of the book to identify relevant sections. Read these sections, making notes about anything that might be connected to your question. Don't forget to record page numbers so that you can easily find the information again, and so that you can refer to it correctly in your essay.
If you are being asked to review an article or book chapter, you will need to read this thoroughly several times. Unfortunately, there are no shortcuts to reading the text thoroughly. The more times you read it, the more you will be able to say about it.
Further reading: Read Confidently
3) Generate ideas
Look at the information you have gathered, and work out how this could fit into a direct response to the essay title or an answer to the question. Make sure that you have evidence to support your claims . The evidence needs to be taken from the reading you have done (and don't forget you will report it with references, as described below).
Further reading: Critical Reading Questions ; Beginner's Guide to Avoiding Plagiarism
3. Plan the structure
A) plan your organisation/structure.
The overall structure will be as follows: title, introduction, main body, conclusion. You will need an introduction and conclusion, but these do not add much to the content of your essay. Most of your planning needs to be how to organise the ideas in the main body. For the main body, make sure you plan how many sections you need to answer the question or address the title in the way you planned in step three above. You can experiment with planning different ways of organising the information. Choose an organisation that seems logical and that will be easy to read and follow.
b) What goes in the introduction?
- A brief explanation of why the topic is important, and the perspective you will take
- If necessary, a definition of any terms from the title for the purposes of this essay.
- An outline of the organisation/structure your essay will follow
- A brief statement or summary of your response/ your answer to the question (sometimes called your "conclusion" or "thesis statement".)
c) A logical structure for the main body
In the main body, how can I persuade the reader that my structure is logical?
Many different structures can work, but if you add linking sections at the beginning or end of your paragraphs, it will help the reader feel like there is a logical flow through the essay. Linking sections can include phrases such as "having discussed these two theories, the following section will provide an evaluation".
You can see other examples of linking sections in many pieces of academic writing, and probably in the reports, articles or books you use to inform your own writing.
d) What goes in the conclusion?
- Re-state your answer to the question (sometimes called your "conclusion" or "thesis statement".)
- A summary of your discussion
- Any implications, consequences, or suggestions for further research.
e) Editing (important)
When I edit my essay, how can I check that I have persuaded the reader that I have answered the question directly?
Read your essay again, and check that each paragraph is either connected to the next through a linking phrase, or that there is some link to the question. As mentioned above, you can see examples of this when you read other academic work or textbooks.
Further reading: Introduction ; Conclusion ; Organise and Structure your Writing ; Linking and Transitions ; Editing Tips
4. Combine your own ideas with the work of others
This is an important aspect of the essay, but many people find it challenging. The most important aspects are understanding how to include your own judgement in an acceptable way in an academic context , and how to make sure you are referring to information in an acceptable format .
The section on avoiding plagiarism shows you some examples of this.
Further reading: Beginner's Guide to Avoiding Plagiarism
Can I give my own opinion?
In every case, you need to make sure that any claim you make is supported with suitable evidence . Usually, in a straightforward essay, the best evidence comes from published work. This means that when you give your own opinion, it will be based on what another author has said. In an academic context, your opinion usually seems more valid if it is based on published evidence , for example explaining how or why you are convinced (or not convinced) by what someone else has written.
Sometimes people think the advice given above sounds strange, as they want to give their own view, but you need to remember the context in which you are writing. In an academic context, your opinion is much more "interesting" if it is an opinion about another piece of academic work or evidence from research, rather than something completely unsupported. Unfortunately, rather than seeing this as creative thinking, the academic community will be more likely to see it as lacking suitable evidence, examples or support.
The safest way to give your own judgement in an academic situation, therefore, is to base your judgement on what someone else has written in a book or journal article, and reference that author .
How do I reference correctly?
Look at the section on referencing now, and make sure you are referencing correctly.
Further reading: Referencing
IOE Writing Centre Online
Self-access resources from the Academic Writing Centre at the UCL Institute of Education.
Anonymous Suggestions Box
Information for Staff
Academic Writing Centre
Academic Writing Centre, UCL Institute of Education [email protected] Twitter: @AWC_IOE Skype: awc.ioe
How to Write a Plan for Your Assignment
“Give me six hours to chop down a tree and I will spend the first four sharpening the axe.” ― Abraham Lincoln
Lincoln’s wise words ring true for all walks of life and none more so than university assignments. Assignments are a key part of the university. Students who learn how to plan an assignment early on in their university career will find their assignments less daunting, easier to write and crucially, more highly graded. Below are some key tips on how you can successfully plan a great assignment.
Read the Question!
This might seem obvious, but not fully understanding the question is a surprisingly common (and totally avoidable) stumbling block for students. Make sure you understand exactly what is being asked of you and if you aren’t 100% sure, seek clarification from your peers or your tutor. Try breaking the question down to ensure you cover everything asked.
Reading widely is absolutely key for a successful assignment. It will be obvious to any marker if the student has not read key texts. By limiting your reading, you immediately limit your essay. You don’t have to read every article or textbook before writing your assignment plan, you may well discover some along the way. The footnotes and bibliographies of the earlier articles and textbooks you do read are a great source of further reading.
When you do your reading, it is essential that you make notes.
Top tip: when making notes on an article or book always include the full reference with your notes – this will save you time and stress when you come to your footnotes and bibliography.
Create a Skeleton Plan
A good early technique when creating an assignment plan is to begin with a skeleton of what your final essay may contain. This needn’t be greatly detailed and you may add or drop things from it as you progress with your research and the essay itself, but starting with a basic outline helps to give you early direction and focuses your reading.
Draft, then Redraft
An assignment draft is essential, it gives you the opportunity to see your thoughts and ideas on the page and see if they link together in the way you envisage. Once you have written your first assignment draft, take a break, and then come back with a fresh pair of eyes. This is key for spotting any errors and inconsistencies in the essay. Your second assignment draft should iron out these inconsistencies, make the assignment a coherent whole and leave you with minor refinements before deadline day.
Find what Works for You
While all of the above are solid techniques for assignment planning, every student is different. Some people like doing mind maps, some bullet points; others just jump straight into the writing. It may take some time to discover what works best for you when writing assignments, so don’t be afraid to experiment!
A good assignment plan equals a good assignment. Remember Uncle Abe’s advice; don’t just start hacking at that assignment, give yourself the tools to do the job properly and efficiently.
You may also like

NCI LIBRARY
Academic writing skills guide: structuring your assignment.
- Key Features of Academic Writing
- The Writing Process
- Understanding Assignments
- Brainstorming Techniques
- Planning Your Assignments
- Thesis Statements
- Writing Drafts
- Structuring Your Assignment
- How to Deal With Writer's Block
- Using Paragraphs
- Conclusions
- Introductions
- Revising & Editing
- Proofreading
- Grammar & Punctuation
- Reporting Verbs
- Signposting, Transitions & Linking Words/Phrases
- Using Lecturers' Feedback
Keep referring back to the question and assignment brief and make sure that your structure matches what you have been asked to do and check to see if you have appropriate and sufficient evidence to support all of your points. Plans can be structured/restructured at any time during the writing process.
Once you have decided on your key point(s), draw a line through any points that no longer seem to fit. This will mean you are eliminating some ideas and potentially letting go of one or two points that you wanted to make. However, this process is all about improving the relevance and coherence of your writing. Writing involves making choices, including the tough choice to sideline ideas that, however promising, do not fit into your main discussion.
Eventually, you will have a structure that is detailed enough for you to start writing. You will know which ideas go into each section and, ideally, each paragraph and in what order. You will also know which evidence for those ideas from your notes you will be using for each section and paragraph.
Once you have a map/framework of the proposed structure, this forms the skeleton of your assignment and if you have invested enough time and effort into researching and brainstorming your ideas beforehand, it should make it easier to flesh it out. Ultimately, you are aiming for a final draft where you can sum up each paragraph in a couple of words as each paragraph focuses on one main point or idea.

Communications from the Library: Please note all communications from the library, concerning renewal of books, overdue books and reservations will be sent to your NCI student email account.
- << Previous: Writing Drafts
- Next: How to Deal With Writer's Block >>
- Last Updated: Apr 23, 2024 1:31 PM
- URL: https://libguides.ncirl.ie/academic_writing_skills

Assignment Writing: Planning
- Following the Brief
- Researching
- Reading Tips
- Writing Tips
- Writing a First Draft
- Proofreading and Editing
- Formatting Assignments
- Assignment Submission
- Using Feedback

Planning is the key to writing a good assignment. Taking the time to plan your assignment will make it easier to understand what you are doing , ensure you are doing everything you are being asked to do, and help you achieve the task quicker . This guide introduces you to a range of planning examples.
What should I do when planning?
There are two main things to think about when planning .
Create a structure for your assignment. Your assignment sheet can help you do this.
We recommend using a writing frame (there is an example on this page) or a graphic organiser
When you know what you need to do, create a time plan. We recommend using a time planner
These plans might change as you move through the process and learn more. That's ok. If that happens, simply adjust your plan as needed.
For tips on planning your time, visit our Time Management guide
Planning your time

It's important to think about all tasks involved in the assignment writing process, and how long those tasks might take you.
Ask yourself, how much time do I need to complete all of the tasks? This will be different for everyone. You might need more time for researching, while someone else might need more time for writing.
When you know what you need to do, create a time plan. We recommend using a time planner.
Check out this video to learn how to plan your time around the tasks you need to complete. Then download the planning template below to help you plan your time from start to finish.
- Assignment planning template Try this template from Melbourne University to set deadlines for completing tasks within your assignment. Adapt the template to include the different tasks you have to do for your specific assignment.
- Stages of assignment writing from start to finish
Essay planning and writing templates
State Library Victoria includes several different templates to help you with different parts of your assignment planning and writing.
- Understanding the question
- Essay plan template
- Organising essay ideas
- Note-taking ideas
- Bibliography (Referencing) template
How to write an essay plan (7 simple steps) by Helpful Professor
Structure your assignment with a writing frame
A writing frame allows you to organise your tasks or ideas into sections and put your ideas into a logical order.
Do you remember the assignment brief from the previous page? Below we show you how you can organise the tasks into sections.
Written Assignment (Summative) - Te Tiriti o Waitangi in Aotearoa New Zealand
Due date: 12 October
Word count: 1200 (+/-10%)
Some students like to add an extra column to their writing frame so they can write what they learn straight into their plan.
- Click here to download a writing frame template
Take a moment

Take a moment - It's your turn to plan your assignment.
- What is the purpose of the assignment?
- What do I have to do?
- How am I being marked?
- What information do I want to include?
- When is my assignment due?
- When do I need to start working on my assignment?
- How long do I need for the different stages?
- How long should I give myself to complete it?

Image citation: Possessed Photography. (2019, September 8). Rerouting [Photograph]. Unsplash. https://unsplash.com/photos/0La7MwJhSyo
- << Previous: Following the Brief
- Next: Researching >>
- Last Updated: Mar 11, 2024 2:50 PM
- URL: https://whitireia.libguides.com/Assignment_Writing
- Student Support Services
- Subject Guides
Essential Study Skills
- Introduction to Time Management
- Getting Things Done
- Creating a Weekly Schedule
- Creating a Semester Plan
- Planning an Assignment
- Creating a Task List
- Putting it all together
- Additional Resources
- Coping With Stress
- Changing Your Perception of Stress
- Problem Solving To Manage Stress
- Reading with Purpose
- Taking Notes in Class
- Deciding What To Study
- Knowing How to Study
- Memorizing and Understanding Concepts
- Taking Tests & Exams
- Creating and Preparing For a Presentation
- Presentation Anxiety
- Delivering Presentations
- Exploring Career Options
- Identifying Areas of Interest
- Knowing Yourself
- Exploring the Labour Market
- Researching College Programs
- Setting Goals
- Tackling Problems
- Bouncing Back
- Sleep Matters
- Sleep Habits
- Sleep Strategies
- Meeting with Your Group
- Agreeing on Expectations
- Dealing With Problems
- Study in Groups
How do you plan an assignment ?
If a task seems too difficult or you don’t know where to start, breaking it into smaller tasks can help make it easier to do. An assignment tracker is a document that you can use to break big assignments into smaller, more manageable steps. This module will show you how to plan out the time you need to complete your assignments.
Strategies for Using the Assignment Tracker
Breaking Down Assignments
- How to Use the Assignment Tracker
Step 1: Gather Information
- If possible, print off a hard copy of the assignment.
- Read the entire assignment out loud.
- Brainstorm ideas.
Step 2: Calculate the Assignment Time
Use the chart below to calculate how long you should spend on an assignment. For every 5% the assignment is worth, you should plan to work 2 hours.
Step 3: Use the Assignment tracker
Fill out your assignment tracker:
- Assignment Tracker Template (PDF)
- Assignment Tracker Template (Word)
Watch the video and use the steps below to learn how to fill out the template. Make sure to start work at least two weeks before your assignment is due. You can also download the How to Use Assignment Tracker video transcript
Instructions for filling out the assignment tracker template
- Fill out the beginning of the form with the name of the course, the assignment title and value, the hours of work required, today’s date and the due date.
- In the ‘Stages’ column, create a list of all of the things that you need to do to complete this assignment, e.g. brainstorming ideas, creating an outline, writing a rough draft. Use one line for each stage.
- Give yourself a completion deadline for each task.
- Check off each task as you finish them.
- << Previous: Creating a Semester Plan
- Next: Creating a Task List >>
- Last Updated: Apr 25, 2024 2:07 PM
- URL: https://algonquincollege.libguides.com/studyskills

Understanding Assignments
What this handout is about.
The first step in any successful college writing venture is reading the assignment. While this sounds like a simple task, it can be a tough one. This handout will help you unravel your assignment and begin to craft an effective response. Much of the following advice will involve translating typical assignment terms and practices into meaningful clues to the type of writing your instructor expects. See our short video for more tips.
Basic beginnings
Regardless of the assignment, department, or instructor, adopting these two habits will serve you well :
- Read the assignment carefully as soon as you receive it. Do not put this task off—reading the assignment at the beginning will save you time, stress, and problems later. An assignment can look pretty straightforward at first, particularly if the instructor has provided lots of information. That does not mean it will not take time and effort to complete; you may even have to learn a new skill to complete the assignment.
- Ask the instructor about anything you do not understand. Do not hesitate to approach your instructor. Instructors would prefer to set you straight before you hand the paper in. That’s also when you will find their feedback most useful.
Assignment formats
Many assignments follow a basic format. Assignments often begin with an overview of the topic, include a central verb or verbs that describe the task, and offer some additional suggestions, questions, or prompts to get you started.
An Overview of Some Kind
The instructor might set the stage with some general discussion of the subject of the assignment, introduce the topic, or remind you of something pertinent that you have discussed in class. For example:
“Throughout history, gerbils have played a key role in politics,” or “In the last few weeks of class, we have focused on the evening wear of the housefly …”
The Task of the Assignment
Pay attention; this part tells you what to do when you write the paper. Look for the key verb or verbs in the sentence. Words like analyze, summarize, or compare direct you to think about your topic in a certain way. Also pay attention to words such as how, what, when, where, and why; these words guide your attention toward specific information. (See the section in this handout titled “Key Terms” for more information.)
“Analyze the effect that gerbils had on the Russian Revolution”, or “Suggest an interpretation of housefly undergarments that differs from Darwin’s.”
Additional Material to Think about
Here you will find some questions to use as springboards as you begin to think about the topic. Instructors usually include these questions as suggestions rather than requirements. Do not feel compelled to answer every question unless the instructor asks you to do so. Pay attention to the order of the questions. Sometimes they suggest the thinking process your instructor imagines you will need to follow to begin thinking about the topic.
“You may wish to consider the differing views held by Communist gerbils vs. Monarchist gerbils, or Can there be such a thing as ‘the housefly garment industry’ or is it just a home-based craft?”
These are the instructor’s comments about writing expectations:
“Be concise”, “Write effectively”, or “Argue furiously.”
Technical Details
These instructions usually indicate format rules or guidelines.
“Your paper must be typed in Palatino font on gray paper and must not exceed 600 pages. It is due on the anniversary of Mao Tse-tung’s death.”
The assignment’s parts may not appear in exactly this order, and each part may be very long or really short. Nonetheless, being aware of this standard pattern can help you understand what your instructor wants you to do.
Interpreting the assignment
Ask yourself a few basic questions as you read and jot down the answers on the assignment sheet:
Why did your instructor ask you to do this particular task?
Who is your audience.
- What kind of evidence do you need to support your ideas?
What kind of writing style is acceptable?
- What are the absolute rules of the paper?
Try to look at the question from the point of view of the instructor. Recognize that your instructor has a reason for giving you this assignment and for giving it to you at a particular point in the semester. In every assignment, the instructor has a challenge for you. This challenge could be anything from demonstrating an ability to think clearly to demonstrating an ability to use the library. See the assignment not as a vague suggestion of what to do but as an opportunity to show that you can handle the course material as directed. Paper assignments give you more than a topic to discuss—they ask you to do something with the topic. Keep reminding yourself of that. Be careful to avoid the other extreme as well: do not read more into the assignment than what is there.
Of course, your instructor has given you an assignment so that he or she will be able to assess your understanding of the course material and give you an appropriate grade. But there is more to it than that. Your instructor has tried to design a learning experience of some kind. Your instructor wants you to think about something in a particular way for a particular reason. If you read the course description at the beginning of your syllabus, review the assigned readings, and consider the assignment itself, you may begin to see the plan, purpose, or approach to the subject matter that your instructor has created for you. If you still aren’t sure of the assignment’s goals, try asking the instructor. For help with this, see our handout on getting feedback .
Given your instructor’s efforts, it helps to answer the question: What is my purpose in completing this assignment? Is it to gather research from a variety of outside sources and present a coherent picture? Is it to take material I have been learning in class and apply it to a new situation? Is it to prove a point one way or another? Key words from the assignment can help you figure this out. Look for key terms in the form of active verbs that tell you what to do.
Key Terms: Finding Those Active Verbs
Here are some common key words and definitions to help you think about assignment terms:
Information words Ask you to demonstrate what you know about the subject, such as who, what, when, where, how, and why.
- define —give the subject’s meaning (according to someone or something). Sometimes you have to give more than one view on the subject’s meaning
- describe —provide details about the subject by answering question words (such as who, what, when, where, how, and why); you might also give details related to the five senses (what you see, hear, feel, taste, and smell)
- explain —give reasons why or examples of how something happened
- illustrate —give descriptive examples of the subject and show how each is connected with the subject
- summarize —briefly list the important ideas you learned about the subject
- trace —outline how something has changed or developed from an earlier time to its current form
- research —gather material from outside sources about the subject, often with the implication or requirement that you will analyze what you have found
Relation words Ask you to demonstrate how things are connected.
- compare —show how two or more things are similar (and, sometimes, different)
- contrast —show how two or more things are dissimilar
- apply—use details that you’ve been given to demonstrate how an idea, theory, or concept works in a particular situation
- cause —show how one event or series of events made something else happen
- relate —show or describe the connections between things
Interpretation words Ask you to defend ideas of your own about the subject. Do not see these words as requesting opinion alone (unless the assignment specifically says so), but as requiring opinion that is supported by concrete evidence. Remember examples, principles, definitions, or concepts from class or research and use them in your interpretation.
- assess —summarize your opinion of the subject and measure it against something
- prove, justify —give reasons or examples to demonstrate how or why something is the truth
- evaluate, respond —state your opinion of the subject as good, bad, or some combination of the two, with examples and reasons
- support —give reasons or evidence for something you believe (be sure to state clearly what it is that you believe)
- synthesize —put two or more things together that have not been put together in class or in your readings before; do not just summarize one and then the other and say that they are similar or different—you must provide a reason for putting them together that runs all the way through the paper
- analyze —determine how individual parts create or relate to the whole, figure out how something works, what it might mean, or why it is important
- argue —take a side and defend it with evidence against the other side
More Clues to Your Purpose As you read the assignment, think about what the teacher does in class:
- What kinds of textbooks or coursepack did your instructor choose for the course—ones that provide background information, explain theories or perspectives, or argue a point of view?
- In lecture, does your instructor ask your opinion, try to prove her point of view, or use keywords that show up again in the assignment?
- What kinds of assignments are typical in this discipline? Social science classes often expect more research. Humanities classes thrive on interpretation and analysis.
- How do the assignments, readings, and lectures work together in the course? Instructors spend time designing courses, sometimes even arguing with their peers about the most effective course materials. Figuring out the overall design to the course will help you understand what each assignment is meant to achieve.
Now, what about your reader? Most undergraduates think of their audience as the instructor. True, your instructor is a good person to keep in mind as you write. But for the purposes of a good paper, think of your audience as someone like your roommate: smart enough to understand a clear, logical argument, but not someone who already knows exactly what is going on in your particular paper. Remember, even if the instructor knows everything there is to know about your paper topic, he or she still has to read your paper and assess your understanding. In other words, teach the material to your reader.
Aiming a paper at your audience happens in two ways: you make decisions about the tone and the level of information you want to convey.
- Tone means the “voice” of your paper. Should you be chatty, formal, or objective? Usually you will find some happy medium—you do not want to alienate your reader by sounding condescending or superior, but you do not want to, um, like, totally wig on the man, you know? Eschew ostentatious erudition: some students think the way to sound academic is to use big words. Be careful—you can sound ridiculous, especially if you use the wrong big words.
- The level of information you use depends on who you think your audience is. If you imagine your audience as your instructor and she already knows everything you have to say, you may find yourself leaving out key information that can cause your argument to be unconvincing and illogical. But you do not have to explain every single word or issue. If you are telling your roommate what happened on your favorite science fiction TV show last night, you do not say, “First a dark-haired white man of average height, wearing a suit and carrying a flashlight, walked into the room. Then a purple alien with fifteen arms and at least three eyes turned around. Then the man smiled slightly. In the background, you could hear a clock ticking. The room was fairly dark and had at least two windows that I saw.” You also do not say, “This guy found some aliens. The end.” Find some balance of useful details that support your main point.
You’ll find a much more detailed discussion of these concepts in our handout on audience .
The Grim Truth
With a few exceptions (including some lab and ethnography reports), you are probably being asked to make an argument. You must convince your audience. It is easy to forget this aim when you are researching and writing; as you become involved in your subject matter, you may become enmeshed in the details and focus on learning or simply telling the information you have found. You need to do more than just repeat what you have read. Your writing should have a point, and you should be able to say it in a sentence. Sometimes instructors call this sentence a “thesis” or a “claim.”
So, if your instructor tells you to write about some aspect of oral hygiene, you do not want to just list: “First, you brush your teeth with a soft brush and some peanut butter. Then, you floss with unwaxed, bologna-flavored string. Finally, gargle with bourbon.” Instead, you could say, “Of all the oral cleaning methods, sandblasting removes the most plaque. Therefore it should be recommended by the American Dental Association.” Or, “From an aesthetic perspective, moldy teeth can be quite charming. However, their joys are short-lived.”
Convincing the reader of your argument is the goal of academic writing. It doesn’t have to say “argument” anywhere in the assignment for you to need one. Look at the assignment and think about what kind of argument you could make about it instead of just seeing it as a checklist of information you have to present. For help with understanding the role of argument in academic writing, see our handout on argument .
What kind of evidence do you need?
There are many kinds of evidence, and what type of evidence will work for your assignment can depend on several factors–the discipline, the parameters of the assignment, and your instructor’s preference. Should you use statistics? Historical examples? Do you need to conduct your own experiment? Can you rely on personal experience? See our handout on evidence for suggestions on how to use evidence appropriately.
Make sure you are clear about this part of the assignment, because your use of evidence will be crucial in writing a successful paper. You are not just learning how to argue; you are learning how to argue with specific types of materials and ideas. Ask your instructor what counts as acceptable evidence. You can also ask a librarian for help. No matter what kind of evidence you use, be sure to cite it correctly—see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial .
You cannot always tell from the assignment just what sort of writing style your instructor expects. The instructor may be really laid back in class but still expect you to sound formal in writing. Or the instructor may be fairly formal in class and ask you to write a reflection paper where you need to use “I” and speak from your own experience.
Try to avoid false associations of a particular field with a style (“art historians like wacky creativity,” or “political scientists are boring and just give facts”) and look instead to the types of readings you have been given in class. No one expects you to write like Plato—just use the readings as a guide for what is standard or preferable to your instructor. When in doubt, ask your instructor about the level of formality she or he expects.
No matter what field you are writing for or what facts you are including, if you do not write so that your reader can understand your main idea, you have wasted your time. So make clarity your main goal. For specific help with style, see our handout on style .
Technical details about the assignment
The technical information you are given in an assignment always seems like the easy part. This section can actually give you lots of little hints about approaching the task. Find out if elements such as page length and citation format (see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial ) are negotiable. Some professors do not have strong preferences as long as you are consistent and fully answer the assignment. Some professors are very specific and will deduct big points for deviations.
Usually, the page length tells you something important: The instructor thinks the size of the paper is appropriate to the assignment’s parameters. In plain English, your instructor is telling you how many pages it should take for you to answer the question as fully as you are expected to. So if an assignment is two pages long, you cannot pad your paper with examples or reword your main idea several times. Hit your one point early, defend it with the clearest example, and finish quickly. If an assignment is ten pages long, you can be more complex in your main points and examples—and if you can only produce five pages for that assignment, you need to see someone for help—as soon as possible.
Tricks that don’t work
Your instructors are not fooled when you:
- spend more time on the cover page than the essay —graphics, cool binders, and cute titles are no replacement for a well-written paper.
- use huge fonts, wide margins, or extra spacing to pad the page length —these tricks are immediately obvious to the eye. Most instructors use the same word processor you do. They know what’s possible. Such tactics are especially damning when the instructor has a stack of 60 papers to grade and yours is the only one that low-flying airplane pilots could read.
- use a paper from another class that covered “sort of similar” material . Again, the instructor has a particular task for you to fulfill in the assignment that usually relates to course material and lectures. Your other paper may not cover this material, and turning in the same paper for more than one course may constitute an Honor Code violation . Ask the instructor—it can’t hurt.
- get all wacky and “creative” before you answer the question . Showing that you are able to think beyond the boundaries of a simple assignment can be good, but you must do what the assignment calls for first. Again, check with your instructor. A humorous tone can be refreshing for someone grading a stack of papers, but it will not get you a good grade if you have not fulfilled the task.
Critical reading of assignments leads to skills in other types of reading and writing. If you get good at figuring out what the real goals of assignments are, you are going to be better at understanding the goals of all of your classes and fields of study.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
24 Create an Assignment Plan
Now that you have a clear idea of what you need to do, the next step is to break down the assignment into manageable “chunks”. The idea of completing a major research paper may seem overwhelming, but if you can divide the task into achievable steps you will be on your way to success.
Use the chart below to break your assignment into smaller steps. You will want to create steps that can be done easily in one day, and preferably in a single work period. Consider the following example breakdown for a research paper.
In the above example, the assignment is divided into smaller pieces, with a manageable amount to complete each day. It is also clear when each task has been completed. A daily work goal like “work on research paper” is not well-defined, and can seem overwhelming. This can make it easy to procrastinate. By choosing specific and achievable goals, you may become more motivated to get started, and you will be able to measure your progress each day. Remember to reward yourself for meeting your goals along the way.
Choose one of your upcoming assignments, and create a work plan modeled on the example above.
Download the assignment planner worksheet .
Learning to Learn Online Copyright © 2018 by Marti Alger, Christina Page, and Adam Vincent is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

- Study and research support
- Academic skills
Plan your writing
Interpret your assignment.
Planning how you approach your writing will make sure that you understand the task, can manage your time, and present a researched, structured and focused assignment.
Before you start writing, you need to understand what type of writing you are required to produce. For example, you might be asked to produce a report, an essay, an annotated bibliography or a literature review. This will shape how you will prepare, research and write your assignment. Take time to understand the conventions of each type of assignment and what is expected of you.
Understand instructional words
Instructional verbs in the assignment task will indicate how to plan your approach. Choose the instructional words that you have been given below to reveal what they mean.
Instructional verbs
Examine an issue in close detail and break it into its constituent parts. Look in depth at each part, consider the evidence, and show you understand the relationship between them.
Decide on the importance or usefulness of something and give reasons and evidence for your decision.
Identify similarities and differences between two or more things, problems or arguments. Draw a conclusion about which (if either) you think is preferable or more convincing.
Outline the meaning of a word, concept or theory as it is used in your discipline. In some cases it may be necessary or desirable to examine different possible, or often used, definitions.
Present factual information about something, using appropriate evidence to support your description.
Examine the arguments and the evidence to support them. Consider different sides of the issue and weigh up the implications of each argument.
Make an appraisal of the worth of something, an argument or a set of beliefs, in the light of its validity or value. This does involve making your own judgements, but they must be supported by an evidenced argument and justification.
Explain or clarify something using evidence, diagrams, figures, or case studies.
Provide adequate reasons for a decision or a conclusion by supporting it with sufficient evidence and argument; answer the main objections that are likely to be made to it.
Summarise the main features or the general principles of a subject, topic or theory.
Provide a thorough examination of a topic. You may be asked to draw your own conclusions.
To what extent
Explore and present the argument(s) for a particular topic and state the degree to which you agree with them.
Accordion 1
Sample accordion 1
Adapted from: Greetham, B. 2018. How to write better essays . 4th ed. London: Palgrave Macmillan.
Scope and focus
Look at the assignment task to identify whether there is a specific aspect of the topic that you are being asked to focus on. For example:
- Is the topic or question limited to a certain time period, region, or group of people?
- Are you being asked to consider a particular angle (for example, political, social, economic aspects of the topic)?
If the assignment task does not include information about the scope or limitations of the topic, you should choose these yourself. Think about what key issues have been covered in your module and whether you could use any of these to produce a focused answer to the question.
If something in the assignment brief is unclear, check with your module leader as soon as possible before starting to plan your answer.
Watch this short video on how to plan and get started with your assignment.
Define your purpose and reader
The next step before writing is to clearly define the purpose of the writing and the audience.
Most formal academic writing at university is set by, and written for, an academic tutor or assessor. There should be clear criteria against which they will mark your work. Your tutor may ask you to write for different audiences such as a lay audience or your peers, so make sure you know who your intended audience is before you start writing.
Once you have a clear idea of what is required for your assignment, you can start to plan what you are going to write.


Study Support: Assignment Planning
- Using the Library
- Online Resources
- Study Preparation
- Skills Assessment
- Learning Approaches
- Digital Literacy
Assignment Planning
- Academic Writing
- Critical Thinking
- Presentation Skills
- Referencing & Citing
- Academic Research
- Academic Reading
- Evaluating Resources
- Taking Notes
- Managing Your Time
- Exam Preparation
- Mental Health
- Stress Management
- Reading 4 Pleasure
Introduction to Planning your Assignment

During your studies you will be required to submit assignments which may include essays, reports and reflective writing. It is important that you spend time planning your assignment before you begin to write your first draft which will help to ensure that you answer the question and meet the assessment criteria. This section will provide you with information regarding understanding the assignment question, managing your time, searching for relevant academic research and writing an assignment plan.
Your programme will require your assignments to be structured and formatted in a particular way. You should always follow any instructions or guidance that you have been issued with, if you are unsure, please contact your Personal Tutor or Student Support Officer for advice.
Recommended Websites

Recommended Apps

- Assignment Question
- Time Management

It is important that you read the assignment question several times to ensure that you fully understand what you are being asked to do and avoid losing valuable marks.
Some students find it helpful to highlight the keywords in the assignment task including any verbs such as Assess and Evaluate.
The Impact that the use of Electri c C ars has on the Environment
Also carefully read the assessment criteria, find out what the word count is, the referencing style that you need to use and how the assignment needs to be presented.
If you are unsure about what you are being asked to do you need to speak to your lecturer or tutor.
It is important that you plan when you will be able to work on an assignment to ensure that you make the most of the time available and hand your work in on time. You could use an online calendar to help you manage your time and the assignment writing process can be divided into the following steps:
- Understand the assignment question
- Search for information
- Plan the assignment
- Write the first draft of the assignment
- Edit assignment
- Proofread assignment
- Submit assignment
Further information is also available from the Managing your Time page.

This stage involves searching for print and online sources that will provide you with the information that you need. You could start by thinking about what you already know about the subject. A useful starting point could be your lecture notes and the module reading list.
The Online Library website provides you with access to different resources that you can search to find both print and online resources.
Further information is available from the Academic Research section.
Assignment Plan

After you have read and made notes on the different sources the next stage is to create an assignment plan. It is important that you check the assessment criteria and the word count which will help you you to identify topics that you may need to research further.
Most assignments follow the structure displayed in the table below:
- Assignment Plan Template
Generative AI Online Videos
The following online videos will provide you with information regarding using Generative AI tools in your assignments:
Recommended Books
- << Previous: Writing Skills
- Next: Academic Writing >>
- Last Updated: Apr 25, 2024 3:07 PM
- URL: https://bpp.libguides.com/studySupport
Writing your assignment
The Writing your assignment resource is designed and monitored by Learning Advisers and Academic Librarians at UniSA.
Part of writing an assignment is creating a plan, and in some courses, you may be tasked with creating a plan as part of your assignment. A plan should build on your original brainstorming session and be informed by your research. A good place to start is the marking criteria. Use the marking criteria, in conjunction with the assessment instructions, to help you with establishing your plan.
As you are searching, develop the argument you are going to present as early as you can. In this way, you will be more targeted in trying to find information that will assist you with presenting this argument. Check that your argument, and your topic paragraphs, fit with the assessment details and the marking criteria before moving forward. Keep in mind, the plan is a fluid document that may change as you explore your topic further.
What should an essay plan include?
- This is the argument your essay is going to make in response to the assignment question.
- The main points are going to provide the supporting evidence in answer to the assignment question. Each main point will form one of the body paragraphs.
- For example, an introduction, body and conclusion
- Put in your own words the evidence you have sourced and place this under the relevant main point. Ensure you provide an in-text citation with your notes
Note: Although this video focuses on essay planning, a similar process can be applied to other assignment types. Watch the Report writing and/or Reflective writing videos to help you consider the structure and content of these types of writing when planning for your assignment.

Here we provide you with a number of example essay plans. Choose the style that suits you best when creating your own. If you are set an assignment task that asks for an essay plan, be sure to check the assignment requirements before creating one.
- Sample Essay Plan - Simple (pdf)
- Sample Essay Plan - Linear, structured (pdf)
- Sample Essay Plan - Mind Map (pdf)
As you review this sample essay plan, hover over the underlined text for more information.
Note: In some browsers you may need to click on the highlighted text to read the extra information.
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Understanding Writing Assignments

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
How to Decipher the Paper Assignment
Many instructors write their assignment prompts differently. By following a few steps, you can better understand the requirements for the assignment. The best way, as always, is to ask the instructor about anything confusing.
- Read the prompt the entire way through once. This gives you an overall view of what is going on.
- Underline or circle the portions that you absolutely must know. This information may include due date, research (source) requirements, page length, and format (MLA, APA, CMS).
- Underline or circle important phrases. You should know your instructor at least a little by now - what phrases do they use in class? Does he repeatedly say a specific word? If these are in the prompt, you know the instructor wants you to use them in the assignment.
- Think about how you will address the prompt. The prompt contains clues on how to write the assignment. Your instructor will often describe the ideas they want discussed either in questions, in bullet points, or in the text of the prompt. Think about each of these sentences and number them so that you can write a paragraph or section of your essay on that portion if necessary.
- Rank ideas in descending order, from most important to least important. Instructors may include more questions or talking points than you can cover in your assignment, so rank them in the order you think is more important. One area of the prompt may be more interesting to you than another.
- Ask your instructor questions if you have any.
After you are finished with these steps, ask yourself the following:
- What is the purpose of this assignment? Is my purpose to provide information without forming an argument, to construct an argument based on research, or analyze a poem and discuss its imagery?
- Who is my audience? Is my instructor my only audience? Who else might read this? Will it be posted online? What are my readers' needs and expectations?
- What resources do I need to begin work? Do I need to conduct literature (hermeneutic or historical) research, or do I need to review important literature on the topic and then conduct empirical research, such as a survey or an observation? How many sources are required?
- Who - beyond my instructor - can I contact to help me if I have questions? Do you have a writing lab or student service center that offers tutorials in writing?
(Notes on prompts made in blue )
Poster or Song Analysis: Poster or Song? Poster!
Goals : To systematically consider the rhetorical choices made in either a poster or a song. She says that all the time.
Things to Consider: ah- talking points
- how the poster addresses its audience and is affected by context I'll do this first - 1.
- general layout, use of color, contours of light and shade, etc.
- use of contrast, alignment, repetition, and proximity C.A.R.P. They say that, too. I'll do this third - 3.
- the point of view the viewer is invited to take, poses of figures in the poster, etc. any text that may be present
- possible cultural ramifications or social issues that have bearing I'll cover this second - 2.
- ethical implications
- how the poster affects us emotionally, or what mood it evokes
- the poster's implicit argument and its effectiveness said that was important in class, so I'll discuss this last - 4.
- how the song addresses its audience
- lyrics: how they rhyme, repeat, what they say
- use of music, tempo, different instruments
- possible cultural ramifications or social issues that have bearing
- emotional effects
- the implicit argument and its effectiveness
These thinking points are not a step-by-step guideline on how to write your paper; instead, they are various means through which you can approach the subject. I do expect to see at least a few of them addressed, and there are other aspects that may be pertinent to your choice that have not been included in these lists. You will want to find a central idea and base your argument around that. Additionally, you must include a copy of the poster or song that you are working with. Really important!
I will be your audience. This is a formal paper, and you should use academic conventions throughout.
Length: 4 pages Format: Typed, double-spaced, 10-12 point Times New Roman, 1 inch margins I need to remember the format stuff. I messed this up last time =(
Academic Argument Essay
5-7 pages, Times New Roman 12 pt. font, 1 inch margins.
Minimum of five cited sources: 3 must be from academic journals or books
- Design Plan due: Thurs. 10/19
- Rough Draft due: Monday 10/30
- Final Draft due: Thurs. 11/9
Remember this! I missed the deadline last time
The design plan is simply a statement of purpose, as described on pages 40-41 of the book, and an outline. The outline may be formal, as we discussed in class, or a printout of an Open Mind project. It must be a minimum of 1 page typed information, plus 1 page outline.
This project is an expansion of your opinion editorial. While you should avoid repeating any of your exact phrases from Project 2, you may reuse some of the same ideas. Your topic should be similar. You must use research to support your position, and you must also demonstrate a fairly thorough knowledge of any opposing position(s). 2 things to do - my position and the opposite.
Your essay should begin with an introduction that encapsulates your topic and indicates 1 the general trajectory of your argument. You need to have a discernable thesis that appears early in your paper. Your conclusion should restate the thesis in different words, 2 and then draw some additional meaningful analysis out of the developments of your argument. Think of this as a "so what" factor. What are some implications for the future, relating to your topic? What does all this (what you have argued) mean for society, or for the section of it to which your argument pertains? A good conclusion moves outside the topic in the paper and deals with a larger issue.
You should spend at least one paragraph acknowledging and describing the opposing position in a manner that is respectful and honestly representative of the opposition’s 3 views. The counterargument does not need to occur in a certain area, but generally begins or ends your argument. Asserting and attempting to prove each aspect of your argument’s structure should comprise the majority of your paper. Ask yourself what your argument assumes and what must be proven in order to validate your claims. Then go step-by-step, paragraph-by-paragraph, addressing each facet of your position. Most important part!
Finally, pay attention to readability . Just because this is a research paper does not mean that it has to be boring. Use examples and allow your opinion to show through word choice and tone. Proofread before you turn in the paper. Your audience is generally the academic community and specifically me, as a representative of that community. Ok, They want this to be easy to read, to contain examples I find, and they want it to be grammatically correct. I can visit the tutoring center if I get stuck, or I can email the OWL Email Tutors short questions if I have any more problems.

How to write an assignment plan
An important component of many international tests is to write an assignment. The problem of this task is usually connected with one’s knowledge and time-management skills. Listen to our tips on writing a plan for an assignment ! Plan assignment writing is a very difficult task, which requires a perfect knowledge of the language. Taking advantage of our advice, you can easily cope with this requirement. Here you will learn about the most useful tips regarding how to write a assignment plan.
Action plan for an assignment
Start to think about the subject as early as possible. Action plan for an assignment will help you. The time reserve will give you the opportunity to collect the maximum amount of information you need. If you focus entirely on thinking about a topic, you will soon notice that the necessary data appear as if out of nowhere.
Don’t waste your time! Order your assignment!
A similar effect occurs when learning a new word when it suddenly begins to encounter in the text more often than before. Since you are configuring information of a certain type and the first of all pay attention to it.
What is more important, it is also good to know how to plan an assignment for students. First, try to sketch an exemplary essay plan. Organize all the information you have on this subject. This will help you determine the direction of your work. Make an approximate plan of the work, write down the main questions that you will need to answer. In the process of studying the material, this list will be replenished with new, more specific questions.
Do not be afraid to start
It is said that even professional writers occasionally experience a sense of insecurity and fear before they embark on new work. This is can be difficult for you as well, so sit down and start to work. You can begin with anything; do not think about style and spelling. The main thing is to move from the dead point. Having sketched the main theses, begin to elaborate on the structure of his assignment in detail. But always remember that you can always buy an assignment online .
By typing assignment on a computer, you can rearrange pieces of text as you need it. If you are writing on paper, leave a few blank lines after each basic idea to supplement it. Try to follow a classical type of structure, there should be: introduction, the main part, and the last one is the conclusion.
How to write a plan for assignment
In order to be completely ready for writing an assignment, you need to imagine a plan for future work clearly. How to make a plan for assignment? What do you need to do to prevent mistakes? A good plan, what is it? How to plan an assignment for students?
Remember that the plan for writing is the ultimate brevity and the capacity of concepts and phrases. It is impossible to write a good and complete work without a plan. To develop the ability to consistently and logically think, you need to learn how to make a plan
Introduction
You can start your assignment with a quote that is appropriate to the topic: it can be taken from the text provided or from different literature and newspapers. Instead of quoting, it is good to use a rhetorical question, and it shows the main idea of the discussed problem.
The correct form of the plan is known to everyone.
It is erroneous to write in the plain words: introduction, the main part, conclusion, because Roman numerals replace these names.
This scheme is a strict logical construction, somewhat reminiscent of the construction of a geometric theorem. In I — “what is given,” in the wording of the second paragraph — “what is required to prove,” and paragraphs 1,2,3 and the proof itself, and point III — “what was required to prove.”
It is best evaluated and perceived what is and how it is said at the very beginning and end. How can we find and formulate a clause of the plan? In the introduction, we usually attract some idea, which gives the originality of the introductory. It can be information about the era, facts from the biography of the writer or some general reasoning about the topic.
In accordance with this, the following entries are distinguished:
- historical (epoch);
- analytical (analyzing any concept, included in the wording of the topic);
- biographical (facts from the biography of the writer);
- comparative (on literary traditions);
- picturesque (with a description of the picture);
- lyrical (personal perception of the topic);
- academic (or school), etc.
Recommendations for the formulation of the main body
- Subparagraphs should be 4, more than 5 points threatens to overwork the essay.
- To find evidence of ideas, go from examples to thoughts.
- Thought should confirm the validity of the idea of writing.
- Choose arguments for your thoughts.
Conclusion Part
The final part of the essay should have a logical connection with the main section and contain a generalized conclusion. You can draw up the conclusion with the help of summing up the main ideas of the author. Rhetorical question embodies the essence of your conclusion. An appeal to the reader, aimed at inducing action or reassessment of the attitude to the topic. Quotations from the text clearly reflect the author’s point of view and sum up the whole article.
The conclusion must be original in form, clear and expressive in thought.
- It is desirable that in conclusion a new thesis extending the main part be put forward.
- It can be an ending — a conclusion, a reflection, a study, a rhetorical question, an ending — citations and others.
- The original conclusion is remarkable for its suddenness, novelty.
- A good ending may be an aphorism or a biblical saying.
Your point of view and its argumentation.
In this part, it is not enough to express your support for the author or disagreement with his opinion. Here you must provide evidence in favor of the writer’s idea or against his theses. If you agree with the position of the narrator, then you need to give two arguments in defense of his position: here, as evidence, you need not use quotes from the text, but arguments from your own experience and literature. Do not repeat the author’s thoughts reflected in the text: you need to formulate your personal opinion. If you are against the writer’s position, you need to strengthen your reasoning with appropriate arguments and try to change the reader’s point of view about the issue raised.
How to do a plan for assignment?
Study the theme of the essay and try to understand what it will be said about clearly. Focus on the title if available: the name should show the reader the main problem, or idea of the text. It is also important to give your comment to the title, but if it is missing, it is not obvious to create a new idea. Analyze the article and identify its main problem. Answer the questions: what was his intention to tell the reader? It is important here to determine its position on the given problems and to disclose its conclusions.
Tell us about your thoughts on the issue raised. It’s not enough to briefly tell us your thoughts about the topic, noting only your consent or reasons why you do not agree with the author’s point of view. It is important to bring your own arguments, which can be your personal experience, as well as examples from literature and other sources. It is acceptable not to share the position of the writer. It would be better to formulate your objections in a soft form. Do not be afraid of your opinion, because the score for writing (essay) is set out entirely by other criteria. Here it is important to disclose the basis of your reasoning and reinforce them with the weak and insufficiently substantiated theses of the author: perhaps you will find in the article any inaccuracies, inconsistency of the writer’s words, unnecessarily emotional statements, etc. Do not be afraid of plan writing for an assignment, it is an easy task if you know how to do an assignment plan .
Related assignments:
- How to Write an Assignment
- How to Write Guide Assignment
- How to write an assignment in the first person guidelines
- How to write an attractive assignment quickly and qualitatively
Haven't Found The Paper You Want?
For Only $13.90/page
Ohio State nav bar
The Ohio State University
- BuckeyeLink
- Find People
- Search Ohio State
2024 Lesson Plan Assignment
Lesson Plan Deadline: August 15, 2024
- GTS 2023 Lesson Plan Template (google slide)
- GTS-2023-Lesson-Plan-Template (Word Doc)
Instructional Strategies and Other Lesson Planning Resources
- Instructional Strategies, Asking Better Questions, and Inquiry Based Learning
- Strategies and Materials for Complex Topics
- Formative Assessments, Tech Resources, and tools for Building Community
- Ideas of Race and Racism in History
Notes from Daniel Redman about Lesson Plans:
- Try to pick one specific thread or idea from the things you’ve learned about in our sessions to focus on in your lesson – you don’t want to go to broad or ambitious for it to be useful.
- What about that standard can the content you’ve learned in our sessions help you explore? How can these things you’re learning help to teach that standard?
- Thinking about the standard(s) you’ve chosen, write 1-2 Essential Questions that will drive the lesson. What is the big idea or big question you want your students to be able to answer after this lesson? Make it focused enough to be achievable in this lesson, since you’re not planning a full sequence or unit.
- My advice is to make two LOs, but I wouldn’t do more than three at maximum.
- It can help to start LOs with your classic “SWBAT” – “Students will be able to…” and then follow up with a Bloom’s Taxonomy verb.
- Blooms Verbs: Bloom’s Taxonomy | Center for Teaching | Vanderbilt University
- LO1: Students will be able to identify key aspects of the medical system in Estonia
- LO2: Students will be able to develop a model for how other nations could implement some Estonian innovations in medicine
- Identify your plans for a pre-assessment and think of it as an opener for the lesson
- The rest is self-explanatory: your 5-7 basic instructional steps outlining the strategies you have in mind for how the students will achieve your Learning Objectives, a closing activity that brings it all together and addresses your Learning Objectives so you can assess how well students learned, and what post-assessment tool you’re going to use to collect that data (e.g., an Exit Ticket, Mini-Quiz, etc.)
- There is value in the reflection section, but our focus is on the Lesson Plans, so pay more attention to the resources and extensions as you wrap things up.
- Get started
- Project management
- CRM and Sales
- Work management
- Product development life cycle
- Comparisons
- Construction management
- monday.com updates
What is a project plan and how to write a project plan in 6 steps
A project plan is an essential document for keeping your project on track. It states the purpose of your project and identifies the scope, structure, resources, goals, deliverables, and timelines.
Without a solid plan, projects typically get delayed and run over budget.
In this high-level guide, we’ll show you how to write a project plan in six steps and share five monday.com templates to get you up and running quickly. But first, let’s define a project plan and its various components.
What is a project plan?

A project plan is a formal document that outlines an entire project’s goals and objectives, specific tasks, and what success looks like.
In addition to setting the purpose of your project, it should include other materials and deliverables relevant to the project, such as:
- Timelines and Gantt charts for key milestones — like start and end dates, getting your 200th customer, or launching an event or app.
- Communication plans — to keep everyone informed of progress, achievements, and potential roadblocks.
- Work breakdown structure — especially if you have multiple team members working on different or simultaneous tasks, in which case, you may also need a Project Planner .
- Resources needed to complete the project — like project management tools , cash, freelancers, and more.
In short, your project plan serves as a central hub to define, organize, prioritize, and assign activities and resources throughout your project’s life cycle.
What is project planning?
Project planning is the second phase in the project management lifecycle :
- PHASE 1: Project Initiation — where you identify a business need or problem and a potential solution.
- PHASE 2: Project Planning — where you define specific tasks, assign responsibilities, and create the project schedule.
- PHASE 3: Project Execution — where you touch base with resources, monitor the timeline and budget, and report back to stakeholders.
- PHASE 4: Project Close-out — where you review the success of the project.
During the project planning phase, you extend the project charter document from the initiation phase to create your detailed project plan. Typical tasks within the project planning phase include:
- Setting a budget.
- Defining a project schedule or timeline.
- Creating work breakdown structures.
- Identifying resources and ensuring availability.
- Assessing any potential roadblocks and planning for those scenarios .
- Defining project objectives , roles, deadlines, responsibilities, and project milestones .
Project plan elements
Here’s how a project plan differs from other project planning elements.
Project plan vs. work plan
Although similar, work plans are not as comprehensive as project plans. A work plan focuses on helping project teams achieve smaller objectives, whereas a project plan provides a high-level overview of an entire project’s goals and objectives.
Project plan vs. project charter
A project charter provides an overview of a project. It’s a formal short document that states a project’s existence and authorizes project managers to commence work. The charter describes a project’s goals, objectives, and resource requirements. You create it in the project initiation phase before your project plan and present it to key stakeholders to get the project signed off.
Project plan vs. project scope
Part of your project plan includes the project scope , which clearly defines the size and boundaries of your project. You document the project scope in three places: a scope statement, work breakdown structure (WBS), and WBS dictionary. It serves as a reference point to monitor project progress, compare actual versus planned results, and avoid scope creep.
Project plan vs. work breakdown structure
A work breakdown structure (WBS) is a hierarchical outline of the tasks required to complete your project. It breaks down large or complicated goals into more manageable tasks so you can execute the project plan. The WBS breaks down the project scope into phases, subprojects, deliverables, and work packages that lead to your final deliverable.
Project plan vs. agile project
An agile project is the opposite of a traditional project plan. Agile projects use an incremental, iterative approach to deliver a project, whereas traditional projects — also known as a waterfall approach — use a cascading, step-by-step planning process. Agile projects are synonymous with software development teams, but you can use them in any field.
Why are project plans important?
Over a third of all projects experience something called scope creep . This is where the team ends up doing more work than originally planned. Much of this can be avoided by accounting for unexpected hold-ups or changes in circumstances within your project plan. A project plan also makes it easy to pinpoint when problems arose, so you can be better prepared for future projects.
If you look at the numbers related to project management, it’s easy to understand where a project management plan could have a positive impact— 45% of projects aren’t completed on time, and 38% of projects are over budget.

A project plan can help to curtail wily overspending and late turnaround by identifying these issues early. This leaves no room for confusion and delays in the workflow and progress of your projects.
How to create a project plan in 6 steps
There are no hard-and-fast rules for a project plan. However, we recommend you use the following six steps as a springboard for creating one.
1. Start with an executive summary
The executive summary goes at the beginning of your project plan and should summarize the key points of the project plan . It should restate the purpose of the project plan, highlight the major points of the plan, and describe any results, conclusions, or recommendations from the project.
Even though it is at the beginning of your project plan , it’s something you will write last , as you’ll be pulling out the main points from the rest of your plan.
It should be no longer than a page, offering a brief overview of:
- The project objectives and goals
- Your chosen project methodology/framework
- The final deliverables and acceptance criteria
- Key scope risks and countermeasures
- Summary of milestones
- An overview of the project timeline and schedule-based risks
- Resource and spending estimates
This snapshot of your project makes it easy for key stakeholders who aren’t actively involved in the mechanics of the project to understand it. For project managers, the executive summary serves as a quick reminder of the key project goal, scope, expectations, and limitations. Since almost a third of projects don’t meet their original goals, it’s important that project managers review the project plan regularly to stay on track.
2. Define the project scope
There are few things worse than starting on a project only for it to balloon. By defining a project’s scope , you set the boundaries for a project’s start and end dates as well as expectations about deliverables and who approves requests—and what merits approval— throughout a project.
It also involves outlining the potential risks associated with meeting these expectations and providing countermeasures to mitigate these risks. Identifying exactly who’s accountable for tracking these risks is essential.
This step will help you prevent scope creep, or how a project’s requirements tend to increase over a project lifecycle. Organizations complain that 34% of all their projects experience scope creep, yet only 52% of organizations go to the effort of mostly or always creating a scoping document every time.
3. Structure your project
There are several frameworks you could use to guide your project and this will affect your workflow’s organizations and how deliverables are produced and assigned.
For example, if you’re using the waterfall framework , you’ll be planning everything in advance, working through each stage of development sequentially, and specialized task owners executing their work at a defined time.
Remember that creating too many dependencies within your project structure can negatively impact success, so try to work out ways that teams can work autonomously to achieve deliverables in a timely manner. It’s also good to consider how many approvers are needed to maintain order but also to prevent bottlenecks.
Above all else, it’s important to incorporate set times for team knowledge-sharing, so your projects can be more successful. Make a note of the communication structures you’ll use to encourage collaboration .
4. Check what project resources you have available
Define the resources you have available for this project:
- Physical resources
You need to be precise when you’re assessing what you’ll need, otherwise you’re baking a cake with all the wrong ingredients. A resource manager or project manager can lead this.
As an example, when teams have the right highly skilled people, projects are 30% more likely to succeed. Yet, a third of people don’t believe their teams have all the right skills for the project—a recipe for failure.
The quantity of team members is also important—if the ratio of work to available people is off, efficiency and quality will suffer. If you want to effectively allocate your resources to meet expectations, you’ll need to be realistic about resource limitations.
This may, for example, mean adjusting timescales if you’re short on staff or increasing your budget if you need more specialist equipment.
5. Map out your project timeline
Organizations that implement time frames into project plans are more likely to succeed. Despite this, 52% of projects don’t always set baseline schedules. That’s probably why 45% of organizations say they rarely or never complete successful projects on time.
In this sense, it’s wise to add a project schedule section to your project plan. This part of your plan should set expectations on when you’ll deliver and how you’ll stick to your project timeline.

Your project schedule will look a little different depending on which framework you choose.
The tasks that you have a ‘Work in Progress’ (WIP) will depend on your team’s capacity. In this section, you should set your maximum number of WIPs you can have in each column at each time.
6. Manage your project changes
Organizations put change control in their top three project challenges. If you don’t solidify a change management plan , your team will be clueless about what to do when unplanned change hits. A dynamic change management plan will outline the steps to follow and the person to turn to when unforeseen changes occur.
A key part of this is having a change management tool in place. And monday work management is flexible enough to help you manage all parts of the project life cycle — from planning and monitoring to reporting and resource management. Let’s take a look at a few of our templates that can help you get started.
5 project planning templates to help you write a good project plan
monday.com templates can be lifesavers when it comes to visualizing each section of your project plan, and they make it easy to get started. Try these 5 project plan templates to kickstart your project planning process.
1. Project Plan Template
Looking for a general project plan template? Try one of our project plan templates .

Using this highly visual template by monday.com, you can structure your subprojects by set time periods and allocate accountable personnel to each phase.
Prioritize each project and add a timeline to show when deliverables are expected.
2. Resource Utilization Template
Resource management allows teams to focus on executing tasks, projects, and processes efficiently and achieve shared goals at scale.

You can allocate resources to individuals and tack on timescales so your staff knows what resources they’re responsible for in which phase. Adding a location makes it easy for teams to know where to hand over resources as they transition from one phase to the next—and they can check this on our mobile app.
Use the Workload view to manage your team’s time proactively and get an overview of the workload and capacity of each person on the team.

3. Project Cost Management Template
It’s far easier to plan a budget when you can see all your costs in one place.
That’s why this Project Cost Management Template from monday.com is so incredibly handy.

Add each subproject and plan out projected costs, allocating totals to each department. You can use the document to estimate the budget you’ll need and to record your approved project budget. You can then use our dashboards or reports to see the information in a different, more colorful way.
4. Project Timeline Template
Plan out your schedules with this Project Timeline Template .

While this dashboard isn’t really suitable if you’re working with the Kanban framework, it’s ideal for those operating under Waterfall or Scrum frameworks.
For Waterfall projects, add in your milestones, attach a timeline, and allocate a set number of workdays to complete the tasks for each milestone.
Tag the team leader for each phase so project managers know which milestones they’re responsible for.
During project execution, teams can use the status bar to track progress. They can also add updates to each milestone by clicking on each item, which encourages inter-team collaboration.
For Scrum projects, you can organize the dashboard by Sprints, adding in the specific tasks as they’re decided.
5. Program Risk Register Template
Visualize all your project scope and schedule risks in this Program Risk Register Template .

Use color-coded status bars to illustrate risk status, risk probability, and risk impact for your project scope and schedule.
You can even categorize risks, add a risk owner, and suggest mitigation strategies. That way other project team members know what to do if these risks start to blossom into real glitches.
Optimize your project management plan with the right tool
Project plans are an essential part of your team’s success.
While they are detail-oriented and complex, creating one and managing it shouldn’t be a struggle. Use monday.com’s pre-built planning templates to help you break down each section of the plan as you go and monitor everything in real-time.
Try monday work management, and see for yourself how much smoother your next project will run when you can consolidate all your project planning materials in one place.

Aubrey O'Day Claims Diddy Wanted to Buy Silence in Return for Publishing Rights

Bikini Babes In Cowboy Hats ... Well Hay There Hollywood Hotties!
Caitlyn Jenner Confronts Pro-Palestinian Protesters at Correspondents' Dinner

Miranda Lambert Good Genes or Good Docs?!

President Joe Biden Pokes Fun at Donald Trump At WH Correspondents' Dinner
Kamala harris' secret service agent attacked supervisor, off assignment, kamala harris secret service agent off assignment ... attacked supervisor.
Kamala Harris ' Secret Service team faced a violent threat this week, having to defend one of their agents ... from one of their own!!!
Secret Service representative Anthony Guglielmi tells TMZ ... at around 9 AM Monday, a U.S. Secret Service special agent supporting the Vice President’s departure from Joint Base Andrews started to display signs his colleagues found distressing.
We're told they removed the agent from the assignment and summoned medical personnel. The Veep wasn't around when the incident occurred, and it did not affect her takeoff.
A federal source with direct knowledge tells us at least one of the distressing signs displayed by the agent was obvious ... as the agent attacked the detail's supervising agent.
Other outlets are reporting the agent who attacked the supervisor was reportedly handcuffed after the incident.
Harris was reportedly on her way from Joint Base Andrews in Maryland to New York City ... where she was scheduled to appear on "The Drew Barrymore Show."
The Vice President was reportedly notified about the fight, though she hasn't made any public statement about the incident.
- Share on Facebook
related articles

White House Hosts Rich, Powerful and Sexy for Lavish State Dinner

Joe Biden Again Reads Teleprompter Instruction During Speech, 'Pause'
Old news is old news be first.
Returning Student Assignment Consolidation
UND is experiencing increasing student enrollment and a higher demand for on-campus housing.
To meet the needs of all new students required to live on campus, and current students who have requested assignments for 2024-25, we must use all available housing spaces.
It is my hope that you participated in the Virtual Town Hall for returning students assigned to on-campus housing on April 23. We appreciated the conversation and the questions that were raised. If you were unable to attend you may view the recording . If you are unsure about what was communicated or still have questions, we will meet with you individually. Visit our booking page to choose a meeting time that works best for you.
Also discussed last evening, returning students in Brannon, McVey, Noren, Selke, and West assigned to double occupancy rooms will be reassigned to double occupancy units in University Place and Swanson Hall. Residents currently living in a room designed for single occupancy will not be reassigned.
We fully acknowledge the inconvenience of these reassignments and are offering the incentives listed below should you choose to be reassigned to University Place or Swanson Hall in a double occupancy room.
- The single occupancy rate for University Place was $6870. The double occupancy rate will be $3870.
- The single occupancy rate for Swanson Hall was $6860. The double occupancy rate will be $3860.
- Dining Dollars in the amount of $200 ($100 per semester).
- Early access to purchase your parking permit for priority access to desired lots.
- Swanson Hall residents may purchase a ramp permit for $240. The normal price is $400.
- $50 waiver of Outpost Center Rental at the Student Wellness Center.
We know that all students may not choose to be reassigned. If you choose to opt out of the reassignment process, you will be released from your license agreement without financial penalty as outlined further below. For a better understanding of your license agreement, please visit your Apartment Style Housing License Agreement (Sections C and G) or Residence Hall Room and Meal Plan Agreement . These agreements provide information about UND's ability to make this decision when extenuating circumstances occur.
Please indicate your preference to stay on campus for 2024-25 in Swanson Hall or University Place in a double occupancy unit at a greatly reduced rate, or request to be released from your license agreement by visiting the Housing Self Service portal and complete Consolidation Process (Fall 2024) under Applications and Forms.
Please notify us of your preference by Monday, May 20, 2024. If you do not indicate a preference by Monday, May 20, 2024, you will be included in the reassignment process.
- April 25–May 20: Indicate your decision to accept a double occupancy assignment in University Place or Swanson Hall. You will be asked for roommate preference and room locations to better assist us with your assignment.
- April 29: University Place and Swanson Hall reassignment process begins. Current University Place and Swanson Hall residents will receive first consideration for reassignment into their respective buildings. Assignments and roommate requests will be made according to date of their original housing application. Reassignment to University Place will begin on floors one and two and will expand as space is needed.
- May 3: Brannon, Johnstone, McVey, Noren, Selke, Smith, and West returning students consolidation process begins. Assignments and roommate requests will be made according to updated space availability in Swanson and University place and the date of their original housing application.
- May 20: Any returning students who did not respond in Housing Self Service will be assigned to a space with a roommate. Students requesting release from their agreement after this date may be subject to our cancellation policy as indicated in their agreement.
- May 21: All returning students will receive verification of their assignment with the name of their roommate via UND email.
We appreciate your patience and understanding as we continue to work to provide housing for all UND students. We will work with each individual student to meet your individual housing needs by sharing information with you regarding available space in our on-campus apartments and other off-campus housing options near UND.
If you have questions, please schedule a meeting, email [email protected] or call the Housing & Residence Life office at 701.777.4251 we get back to you within 24 hours Monday-Friday during normal business hours.
What is the first thing I need to do? ( Open this section)
Complete the "Consolidation Process Form" and select one of three options.
- You will be asked follow-up questions about where you want to live and who you would like to live with.
- Select that you are in a designed single and want to stay where you are currently located.
- You will be asked what hall you are assigned to – Uplace or Swanson.
- If Swanson, you will be asked to verify by typing in your full name.
- I have summer and fall assignment and only want to cancel fall.
- I have summer only and want to cancel.
- I have fall only and want to cancel.
Where can I find the Consolidation Process Form? ( Open this section)
This form can be found under "Applications and Forms" on your Housing Self Service .
I signed up for University Place to stay 12 months beginning in May/June through May next year. What are my options? ( Open this section)
- If you want to stay for summer and be released for fall that is approved.
- You can be released immediately for summer and fall.
I am not planning to consolidate and would like an extension past May 20 to finalize my decision. ( Open this section)
This is a possibility, but you need to reach out to Troy Noeldner, [email protected] or Rohini Gawande, [email protected] for approval of a date.
I need/want to consolidate but I don’t know of anyone. ( Open this section)
- If you do not request someone, you will be assigned someone.
- We will be looking at ages to match as closely as we are able.
When will I know my assignment? ( Open this section)
- We will begin the process of assigning spaces as they become available on Monday, April 29. It will be an ongoing assignment process as students continue to make decisions.
- Final assignments will be emailed out on May 21.
Is there any way I can keep my private room? ( Open this section)
- All spaces that have capacity to be double will be assigned as double.
- If designed singles become available, we will reach out to people on the Consolidated Student Single Room Waitlist. We will prioritize these requests before any other single room waitlists. They must request to be on this list by email and we will add them individually. Priority will be based on length of stay in housing.
I am in a studio apartment in University Place. Can I stay? ( Open this section)
- No, any students assigned in these seven spaces for fall are being asked to move out . Please work with Rohini Gawande, [email protected] or Troy Noeldner, [email protected] individually .
- We are planning to give you extra priority for possible apartment housing applications . You are also able to stay in University Place or Swanson but will need to have a roommate.
I would like to look at on campus apartments. ( Open this section)
- If they know of a space in apartment and want to be added to the lease.
- Email Rohini Gawande, [email protected] and she will go through the process with you.
- If you are interested in applying for a new apartment we will place you on the Consolidated Student Apartment Wait List.
- There will not be a fee to be placed on this waitlist for this group of students only.
- You should indicate in the email three apartment options the would consider.
- If an apartment becomes available in the future we will contact you. If you accept the unit we have available you will be required to apply for the apartment and pay the $60 application fee at that time .
By clicking any link on this page you are giving your consent for us to set cookies, Privacy Information .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
This template is designed to assist you with the collection and organisation of information into your notes and to plan the structure of your work before you start writing your first draft. The Assignment Planning - Guidelines has four stages: Stage #1 - Collecting Information. Use the collecting information sheets to insert paraphrases from ...
WHY SHOULD I CREATE AN ASSIGNMENT PLAN? Planning your assignment can help in several ways. Firstly it focuses you on what the assignment is really asking for. It then helps you create a structure for your assignment, and then guides you through populating that structure. It gives you a timescale to work to which, if followed, will help avoid ...
22 Develop an Assignment Plan. 22. Develop an Assignment Plan. Now that you have a clear idea of what you need to do, the next step is to break down the assignment into manageable "chunks". The idea of completing a major research paper may seem overwhelming, but if you can divide the task into achievable steps you will be on your way to ...
Using an Assignment Planner describes how to plan backwards from the assignment deadline. Make a habit of using *USask's Assignment Planner for help with developing completion timelines and finding resources for stages of the writing process. TrentU's 10 Steps to Complete Your Assignments describes the steps in the planning process.
Planning is an essential part of writing a successful assignment and ensuring you reach your full potential. Key benefits to a clear plan are that it: Helps you to manage and make efficient use of your time. Ensures that you understand and appropriately fulfil the assignment criteria. Makes the writing process easier and helps you to produce a ...
Follow the basic steps below to plan your assignment. Use the menu on the left for more detail about any of the sections. Contents. 1. Check the assessment criteria 2. Address the question 3. Plan the structure 4. Combine your own ideas with the work of others. 1. Check the assessment criteria
Create a Skeleton Plan. A good early technique when creating an assignment plan is to begin with a skeleton of what your final essay may contain. This needn't be greatly detailed and you may add or drop things from it as you progress with your research and the essay itself, but starting with a basic outline helps to give you early direction ...
The outline plan is a more structured and detailed plan than the initial plan you created at the brainstorming stage. It should give you a step-by-step overview of the assignment. Convert your initial plan into an outline plan listing:
Assignment Writing: Planning. This guide will help you plan, research and write your written assignments. Planning is the key to writing a good assignment. Taking the time to plan your assignment will make it easier to understand what you are doing, ensure you are doing everything you are being asked to do, and help you achieve the task quicker.
Plan enough time. Be prepared to invest an average of 2 solid hours for every 5% an assignment is worth. Start planning your time early in the semester. The earlier you start managing your time, the easier it is. Get into good habits early so you don't fall behind. Start assignments early. Start at least two weeks before the due date.
Plan enough time. Be prepared to invest an average of 2 solid hours for every 5% an assignment is worth. Start planning your time early in the semester. The earlier you start managing your time, the easier it is. Get into good habits early so you don't fall behind. Start assignments early. Start at least two weeks before the due date.
What this handout is about. The first step in any successful college writing venture is reading the assignment. While this sounds like a simple task, it can be a tough one. This handout will help you unravel your assignment and begin to craft an effective response. Much of the following advice will involve translating typical assignment terms ...
Introduction to 'Planning and preparing to write assignments'. This handbook on preparing to write assignments is designed to help you develop your strategies for planning. Hopefully, it will help you to get the most out of your experience of writing at University and provide encouragement for managing this type of assessment.
24. Create an Assignment Plan. Now that you have a clear idea of what you need to do, the next step is to break down the assignment into manageable "chunks". The idea of completing a major research paper may seem overwhelming, but if you can divide the task into achievable steps you will be on your way to success.
An essay plan is a way to identify, select, and order the points you want to make in your essay. It helps you to work out your argument and your structure before writing, which should make the writing process more efficient and focussed. Sometimes essay plans are set as formative assignments so tutors can provide feedback before you write your ...
The Research Assignment Plan Template. As a rule, your assignment plan will always differ, depending on your subject and assignment type, yet the most common assignment plan example will include the following seven paragraphs: Project's Name: start date, end date, completed. Research Objectives: up to 150-300 words. It should speak about the ...
Interpret your assignment. Create a plan. Planning how you approach your writing will make sure that you understand the task, can manage your time, and present a researched, structured and focused assignment. Before you start writing, you need to understand what type of writing you are required to produce. For example, you might be asked to ...
Introduction to Planning your Assignment. During your studies you will be required to submit assignments which may include essays, reports and reflective writing. It is important that you spend time planning your assignment before you begin to write your first draft which will help to ensure that you answer the question and meet the assessment ...
Part of writing an assignment is creating a plan, and in some courses, you may be tasked with creating a plan as part of your assignment. A plan should build on your original brainstorming session and be informed by your research. A good place to start is the marking criteria. Use the marking criteria, in conjunction with the assessment ...
Many instructors write their assignment prompts differently. By following a few steps, you can better understand the requirements for the assignment. The best way, as always, is to ask the instructor about anything confusing. Read the prompt the entire way through once. This gives you an overall view of what is going on.
First, try to sketch an exemplary essay plan. Organize all the information you have on this subject. This will help you determine the direction of your work. Make an approximate plan of the work, write down the main questions that you will need to answer. In the process of studying the material, this list will be replenished with new, more ...
2024 Lesson Plan Assignment. Lesson Plan Deadline: August 15, 2024. GTS 2023 Lesson Plan Template (google slide) GTS-2023-Lesson-Plan-Template (Word Doc) Instructional Strategies and Other Lesson Planning Resources. Padlets: Instructional Strategies, Asking Better Questions, and Inquiry Based Learning. Strategies and Materials for Complex Topics.
What is a project plan and how to write a project plan in 6 steps. A project plan is an essential document for keeping your project on track. It states the purpose of your project and identifies the scope, structure, resources, goals, deliverables, and timelines. Without a solid plan, projects typically get delayed and run over budget.
Assignment meaning is the tasks given to students by their teachers and tutors to complete in a defined time. They can also be referred to as the work given to someone as a part of learning. Assignments can be in the form of written, practical, art or fieldwork, or even online. Their purpose is to ensure that students understand the subject ...
Assignability clauses. Assignability clauses are often encountered in real estate contracts, where they allow the transfer of property or leases. Assignment of contract can also be applied to some options and futures contracts. Not all contracts have an assignment provision. If one does, it can be found in the contract's terms.
A contingent beneficiary could be: An individual, including minors in many cases. However, naming a minor as a contingent beneficiary generally means you need to designate a legal guardian or ...
Kamala Harris' Secret Service team faced a violent threat this week, having to defend one of their agents ... from one of their own!!!
May 3: Brannon, Johnstone, McVey, Noren, Selke, Smith, and West returning students consolidation process begins. Assignments and roommate requests will be made according to updated space availability in Swanson and University place and the date of their original housing application. May 20: Any returning students who did not respond in Housing ...