Educationise

11 Activities That Promote Critical Thinking In The Class
Ignite your child’s curiosity with our exclusive “Learning Adventures Activity Workbook for Kids” a perfect blend of education and adventure!
Critical thinking activities encourage individuals to analyze, evaluate, and synthesize information to develop informed opinions and make reasoned decisions. Engaging in such exercises cultivates intellectual agility, fostering a deeper understanding of complex issues and honing problem-solving skills for navigating an increasingly intricate world.
Through critical thinking, individuals empower themselves to challenge assumptions, uncover biases, and constructively contribute to discourse, thereby enriching both personal growth and societal progress.
Critical thinking serves as the cornerstone of effective problem-solving, enabling individuals to dissect challenges, explore diverse perspectives, and devise innovative solutions grounded in logic and evidence. For engaging problem solving activities, read our article problem solving activities that enhance student’s interest.
52 Critical Thinking Flashcards for Problem Solving
What is Critical Thinking?
Critical thinking is a 21st-century skill that enables a person to think rationally and logically in order to reach a plausible conclusion. A critical thinker assesses facts and figures and data objectively and determines what to believe and what not to believe. Critical thinking skills empower a person to decipher complex problems and make impartial and better decisions based on effective information.
More Articles from Educationise
- 10 Innovative Strategies for Promoting Critical Thinking in the Classroom
- 9 Must-Have AI Tools for Teachers to Create Interactive Learning Materials
- The Future of Education: 8 Predictions for the Next Decade
- The Latest in EdTech: 5 Innovative Tools and Technologies for the Classroom
- 8 Free Math Problem Solving Websites and Applications
Importance of Acquiring Critical Thinking Skills
Critical thinking skills cultivate habits of mind such as strategic thinking, skepticism, discerning fallacy from the facts, asking good questions and probing deep into the issues to find the truth. Acquiring critical thinking skills was never as valuable as it is today because of the prevalence of the modern knowledge economy.
Today, information and technology are the driving forces behind the global economy. To keep pace with ever-changing technology and new inventions, one has to be flexible enough to embrace changes swiftly.
Today critical thinking skills are one of the most sought-after skills by the companies. In fact, critical thinking skills are paramount not only for active learning and academic achievement but also for the professional career of the students.
The lack of critical thinking skills catalyzes memorization of the topics without a deeper insight, egocentrism, closed-mindedness, reduced student interest in the classroom and not being able to make timely and better decisions.
Incorporating critical thinking lessons into the curriculum equips students with the tools they need to navigate the complexities of the modern world, fostering a mindset that is adaptable, inquisitive, and capable of discerning truth from misinformation.
Benefits of Critical Thinking for Students
Certain strategies are more eloquent than others in teaching students how to think critically. Encouraging critical thinking in the classroom is indispensable for the learning and growth of the students. In this way, we can raise a generation of innovators and thinkers rather than followers. Some of the benefits offered by thinking critically in the classroom are given below:
- It allows a student to decipher problems and think through the situations in a disciplined and systematic manner
- Through a critical thinking ability, a student can comprehend the logical correlation between distinct ideas
- The student is able to rethink and re-justify his beliefs and ideas based on facts and figures
- Critical thinking skills make the students curious about things around them
- A student who is a critical thinker is creative and always strives to come up with out of the box solutions to intricate problems
- Critical thinking skills assist in the enhanced student learning experience in the classroom and prepares the students for lifelong learning and success
- The critical thinking process is the foundation of new discoveries and inventions in the world of science and technology
- The ability to think critically allows the students to think intellectually and enhances their presentation skills, hence they can convey their ideas and thoughts in a logical and convincing manner
- Critical thinking skills make students a terrific communicator because they have logical reasons behind their ideas
Critical Thinking Lessons and Activities
11 Activities that Promote Critical Thinking in the Class
We have compiled a list of 11 critical thinking activities for students that will facilitate you to promote critical thinking abilities in the students. By incorporating these activities, educators can introduce real-world examples of critical thinking in the classroom, empowering students to apply these skills in everyday situations.
We have also covered problem solving activities that enhance student’s interest in our another article. Click here to read it.
1. Worst Case Scenario
Divide students into teams and introduce each team with a hypothetical challenging scenario. Allocate minimum resources and time to each team and ask them to reach a viable conclusion using those resources.
The scenarios can include situations like stranded on an island or stuck in a forest. Students will come up with creative solutions to come out from the imaginary problematic situation they are encountering. Besides encouraging students to think critically, this activity will enhance teamwork, communication and problem-solving skills of the students.
This critical thinking activity not only pushes students to devise innovative solutions in challenging scenarios but also strengthens their teamwork, communication, and problem-solving abilities, making it an engaging and educational experience.
Read our article: 10 Innovative Strategies for Promoting Critical Thinking in the Classroom
2. If You Build It
It is a very flexible game that allows students to think creatively. To start this activity, divide students into groups. Give each group a limited amount of resources such as pipe cleaners, blocks, and marshmallows etc.
Every group is supposed to use these resources and construct a certain item such as building, tower or a bridge in a limited time. You can use a variety of materials in the classroom to challenge the students. This activity is helpful in promoting teamwork and creative skills among the students.
Incorporating critical thinking games like this into your classroom not only promotes teamwork and creativity but also challenges students to think outside the box as they work together to build their structures.
It is also one of the classics which can be used in the classroom to encourage critical thinking. Print pictures of objects, animals or concepts and start by telling a unique story about the printed picture. The next student is supposed to continue the story and pass the picture to the other student and so on.
This engaging exercise is one of the most effective critical thinking activities for kids, as it encourages them to use their creativity and problem-solving skills while working together to construct innovative structures with limited resources.
4. Keeping it Real
In this activity, you can ask students to identify a real-world problem in their schools, community or city. After the problem is recognized, students should work in teams to come up with the best possible outcome of that problem.
5. Save the Egg
Make groups of three or four in the class. Ask them to drop an egg from a certain height and think of creative ideas to save the egg from breaking. Students can come up with diverse ideas to conserve the egg like a soft-landing material or any other device. Remember that this activity can get chaotic, so select the area in the school that can be cleaned easily afterward and where there are no chances of damaging the school property.
6. Start a Debate
In this activity, the teacher can act as a facilitator and spark an interesting conversation in the class on any given topic. Give a small introductory speech on an open-ended topic. The topic can be related to current affairs, technological development or a new discovery in the field of science. Encourage students to participate in the debate by expressing their views and ideas on the topic. Conclude the debate with a viable solution or fresh ideas generated during the activity through brainstorming.
7. Create and Invent
This project-based learning activity is best for teaching in the engineering class. Divide students into groups. Present a problem to the students and ask them to build a model or simulate a product using computer animations or graphics that will solve the problem. After students are done with building models, each group is supposed to explain their proposed product to the rest of the class. The primary objective of this activity is to promote creative thinking and problem-solving skills among the students.
8. Select from Alternatives
This activity can be used in computer science, engineering or any of the STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, Mathematics) classes. Introduce a variety of alternatives such as different formulas for solving the same problem, different computer codes, product designs or distinct explanations of the same topic.
Form groups in the class and ask them to select the best alternative. Each group will then explain its chosen alternative to the rest of the class with reasonable justification of its preference. During the process, the rest of the class can participate by asking questions from the group. This activity is very helpful in nurturing logical thinking and analytical skills among the students.
9. Reading and Critiquing
Present an article from a journal related to any topic that you are teaching. Ask the students to read the article critically and evaluate strengths and weaknesses in the article. Students can write about what they think about the article, any misleading statement or biases of the author and critique it by using their own judgments.
In this way, students can challenge the fallacies and rationality of judgments in the article. Hence, they can use their own thinking to come up with novel ideas pertaining to the topic.
10. Think Pair Share
In this activity, students will come up with their own questions. Make pairs or groups in the class and ask the students to discuss the questions together. The activity will be useful if the teacher gives students a topic on which the question should be based.
For example, if the teacher is teaching biology, the questions of the students can be based on reverse osmosis, human heart, respiratory system and so on. This activity drives student engagement and supports higher-order thinking skills among students.
11. Big Paper – Silent Conversation
Silence is a great way to slow down thinking and promote deep reflection on any subject. Present a driving question to the students and divide them into groups. The students will discuss the question with their teammates and brainstorm their ideas on a big paper.
After reflection and discussion, students can write their findings in silence. This is a great learning activity for students who are introverts and love to ruminate silently rather than thinking aloud.
Incorporating critical thinking activities for high school students, like silent reflection and group brainstorming, encourages deep thought and collaboration, making it an effective strategy for engaging both introverted and extroverted learners.
Finally, for students with critical thinking, you can go to GS-JJ.co m to customize exclusive rewards, which not only enlivens the classroom, but also promotes the development and training of students for critical thinking.
Share this:
Discover more from educationise.
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
Type your email…
4 thoughts on “ 11 Activities That Promote Critical Thinking In The Class ”
- Pingback: What is Growth Mindset? 50+ Motivational Quotes on Growth Mindset - Educationise
- Pingback: 6 Steps To Implement Project-Based Learning In The Classroom - Educationise
- Pingback: Engaging Problem-Solving Activities That Spark Student Interest - Educationise
Thanks for the great article! Especially with the post-pandemic learning gap, these critical thinking skills are essential! It’s also important to teach them a growth mindset. If you are interested in that, please check out The Teachers’ Blog!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Continue reading

- Productivity
- Thoughtful learning

Become a better critical thinker with these 7 critical thinking exercises

Critical thinking is a skill you can use in any situation. Whether you're a student, entrepreneur, or business executive, critical thinking can help you make better decisions and solve problems.
But learning critical thinking skills isn't always an easy task. Many tools, techniques, and strategies are available, and choosing the right one can be challenging. Vague suggestions on the internet like "read more" aren't very helpful, and elaborate business examples don’t apply to many of us.
As average problem-solvers, we need actionable thinking exercises to improve our critical thinking skills and enhance our thinking processes. Regularly performing exercises that specifically stretch our decision-making and reasoning skills is the most effective method of improving our thinking abilities.
This article will explore several exercises that will help you develop critical thinking skills. Whether you are preparing for an exam, making an influential decision for your business, or going about your daily life, these fun activities can build your reasoning skills and creative problem-solving abilities.
Boost your logical thinking skills and start practicing a critical mindset with these 10 critical thinking exercises.
A Quick Look at Critical Thinking
As a thoughtful learner, you likely already understand the basics of critical thinking, but here's a quick refresher.
Critical thinking involves analyzing problems or issues objectively and rationally. Critical thinkers are able to understand their own biases and assumptions, as well as those of others. They’re also able to see the world from a different point of view and understand how their experiences impact their thinking.
Developing critical thinking skills is essential because it allows us to see things from multiple perspectives, identify biases and errors in reasoning, and be open to possible solutions. Making informed decisions is easier when we have a better understanding of the world around us.
Why We Need to Practice Critical Thinking

We aren't born with critical thinking skills, and they don’t naturally develop beyond survival-level thinking. To master critical thinking, we must practice it and develop it over time.
However, learning to think critically isn't as easy as learning to ride a bicycle. There aren't any step-by-step procedures to follow or supportive guides to fall back on, and it is not taught in public schools consistently or reliably. To ensure students' success, teachers must know higher-order thinking skills (HOTS) and how to teach them, research says.
Unfortunately, although teachers understand the importance of HOTS and attempt to teach it, studies show that their capacity to measure students' HOTS is low. Educator and author Dr. Kulvarn Atwal says, "It seems that we are becoming successful at producing students who are able to jump through hoops and pass tests."
As critical thinking skills become more important in higher grades, some students find it challenging to understand the concept of critical thinking. To develop necessary thinking skills, we must set aside our assumptions and beliefs. This allows us to explore and question topics from a "blank page" point of view and distinguish fact from opinion.
Be the first to try it out!
We're developing ABLE, a powerful tool for building your personal knowledge, capturing information from the web, conducting research, taking notes, and writing content.
7 Critical Thinking Exercises To Improve Your Critical Thinking Skills

The good news is that by assessing, analyzing, and evaluating our thought processes, we can improve our skills. Critical thinking exercises are key to this improvement. Our critical thinking builds and improves with regular practice, just like a muscle that gets stronger with use.
If you want to become a better critical thinker , here are some critical thinking exercises to try:
Exercise #1: The Ladder of Inference
You can exercise your critical thinking skills by using the Ladder of Inference model . This thinking model was developed by renowned organizational psychologist Chris Argyris. Each rung on the ladder of inference represents a step you take to arrive at your conclusions.
The decision-making process starts when we are faced with a problem or situation. As soon as we observe something problematic or important, we presume what is causing it, and then we use that assumption to draw conclusions. Based on those conclusions, we take action.
For example, say you're at a party and see a friend across the room. You catch their eye and wave, but they turn and walk away. Using the ladder, you might climb the rungs as follows:
- Observe that your friend walked away.
- Select a few details of the situation, including your wave and your assumption that they saw you.
- Meaning is attached based on the environment, making you think your friend must have other people to talk to at the party.
- Assumptions are made based on that meaning, assuming that means your friend doesn’t like you as much as them.
- Conclusions are drawn from the assumption, and you determine that your friend must be mad at you or doesn't want you to be at the party.
- Beliefs are formed, making you think you're not welcome.
- Action is taken, and you leave the party.
In this example, you started with a situation (someone walking away at a crowded party) and made a series of inferences to arrive at a conclusion (that the person is mad at you and doesn't want you there).
The Ladder of Inference can be a helpful tool to frame your thinking because it encourages you to examine each step of your thought process and avoid jumping to conclusions. It's easy to make assumptions without realizing it, as in this scene. Perhaps your friend never even saw you wave from across the crowded room.
Exercise #2: The Five Whys
The "Five Whys" technique is an analytical skill that can help you uncover the source of a problem. The activity was created by Sakichi Toyoda, the founder of Toyota, and consists of repeatedly asking “why?” when a problem is encountered to determine its root cause.
This exercise can be difficult because knowing if you've discovered the source of your problem is challenging. The "five" in "Five Whys" is just a guideline — you may need to ask more. When you can't ask anything else, and your response is related to the original issue, you've probably arrived at the end.
Even if you need several rounds of questioning, just keep going. The important part that helps you practice critical thinking is the process of asking "why?" and uncovering the deeper issues affecting the situation.
For instance, say you're trying to figure out why your computer keeps crashing.
- You ask " why ," and the answer is that there's a software problem.
- Why? Because the computer keeps running out of memory.
- Why? Because too many programs are running at the same time.
- Why? Because too many browser tabs are open .
- Why? Because multitasking is fragmenting your focus, you're doing too many things at once.
In this example, working through the "why's" revealed the underlying cause. As a result, you can find the best solution, which is concentrating on just one thing at a time.
Exercise #3: Inversion

Inversion is another critical thinking exercise that you can use in any situation. Inversion is sort of like taking on the role of the devil's advocate. In this exercise, adopt the opposite view of whatever issue you're exploring and consider the potential arguments for that side. This will help broaden your critical thinking skills and enable you to see other perspectives on a situation or topic more clearly.
For example, let's say you're thinking about starting your own business. Using inversion, you would explore all of the potential arguments for why starting your own business is bad. This might include concerns like:
- You could end up in debt.
- The business might fail.
- It's a lot of work.
- You might not have time for anything else.
By exploring these potentially adverse outcomes, you can identify the potential risks involved in starting your own business and make a more sound decision. You might realize that now is not the right time for you to become an entrepreneur. And if you do start the company, you'll be better prepared to deal with the issues you identified when they occur.
Exercise #4: Argument Mapping
Argument mapping can be a beneficial exercise for enhancing critical thinking skills. Like mind mapping, argument mapping is a method of visually representing an argument's structure. It helps analyze and evaluate ideas as well as develop new ones.
In critical thinking textbooks, argument diagramming is often presented to introduce students to argument constructions. It can be an effective way to build mental templates or schema for argument structures, which researchers think may make critical evaluation easier .
Argument maps typically include the following:
- Conclusion: What is being argued for or against
- Premises: The reasons given to support the conclusion
- Inferences: The connections made between the premises and conclusion
The argument map should be as clear and concise as possible, with a single word or phrase representing each element. This will help you make connections more easily. After the map is completed, you can use it to identify any weak points in the argument. If any areas aren't well-supported, additional premises can be added.
Argument mapping can be applied to any situation that requires critical thinking skills. The more time you take to map out an argument, the better you'll understand how the pieces fit together. Ultimately, this will help you think more creatively and critically, and make more informed decisions.
Exercise #5: Opinion vs. Fact
Critical thinking activities that focus on opinions and facts are particularly valuable and relevant new learning opportunities. Our constantly-connected world makes it easy to confuse opinions and facts , especially with sensationalist news articles and click-bait headlines.
How can you tell a fact from an opinion? Facts are generally objective and established, whereas opinions are subjective and unproven. For example, "the cloud is in the air" is a fact. "That dress looks good on you" is an opinion.
Practice your critical thinking skills by reading or listening to the news. See if you can identify when someone is stating an opinion rather than a fact. Ask yourself the following questions:
- Who is saying what? What reasons might be behind their statements?
- Does the claim make sense? Who would disagree with it and why?
- How can you tell if the data is reliable? Can it be fact-checked? Has it been shared by other credible publishers?
- How do you know whether or not the presenter is biased? What kind of language is being used?
This powerful exercise can train your mind to start asking questions whenever presented with a new claim. This will help you think critically about the information you're taking in and question what you're hearing before accepting it as truth.
Exercise #6: Autonomy of an Object
In her book " The Critical Thinking Tool Kit ," Dr. Marlene Caroselli describes a critical thinking exercise called "Living Problems, Lively Solutions." This exercise uses the autonomy of an object as a problem-solving tool to find a possible solution.
To do this, you'll personify your problem and place it in another context — a different time or place. This allows you to uncover unique solutions to the problem that might be tied to your mental associations with that setting.
For example, if your problem is poor time management , you might personify the issue as a thief of your time. The idea of a thief could make you think of jail, which might prompt thoughts of locking up specific distractions in your life. The idea of jail could also make you think of guards and lead you to the possible solution of checking in with an accountability buddy who can make sure you're sticking to your schedule.
The autonomy-of-object technique works because it stimulates thoughts you wouldn’t have considered without the particular context in which you place the problem.
Exercise #7: The Six Thinking Hats
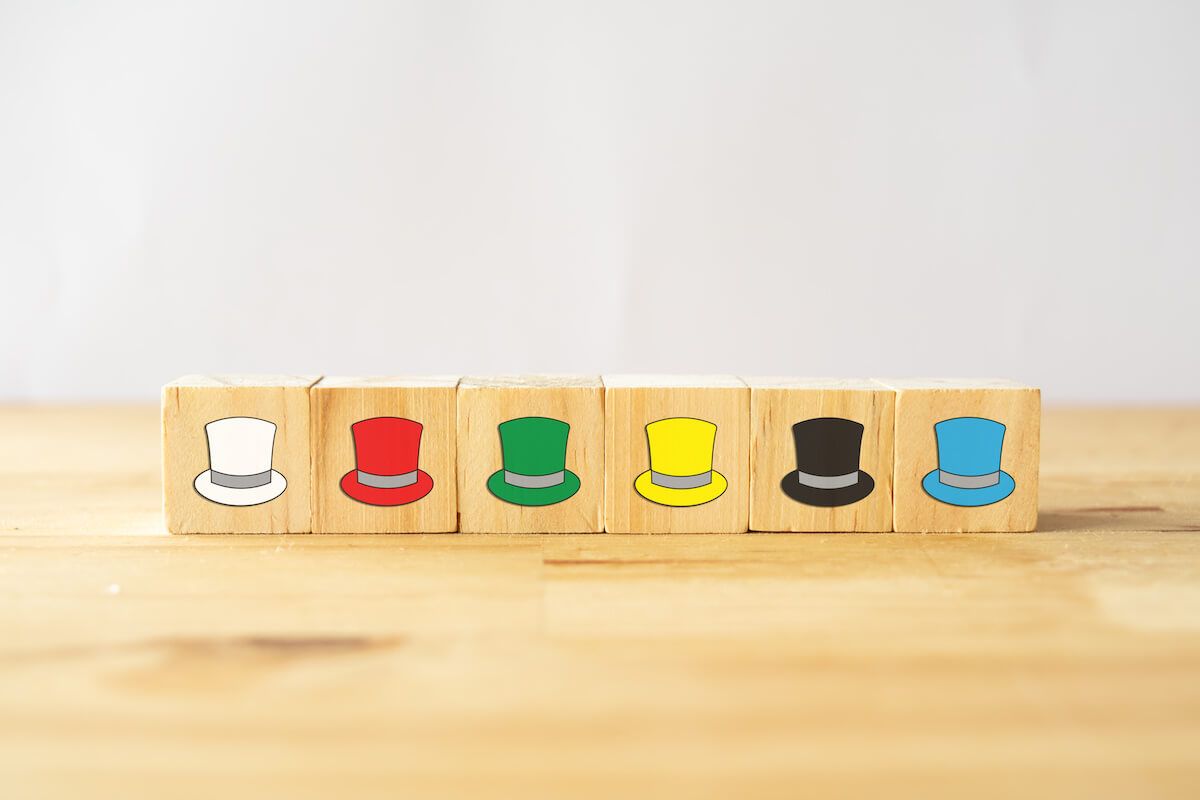

Designed by Edward de Bono, the Six Thinking Hats is a critical thinking exercise that was created as a tool for groups to use when exploring different perspectives on an issue. When people use other thinking processes, meetings can become challenging rather than beneficial.
To help teams work more productively and mindfully, de Bono suggests dividing up different styles of thinking into six categories, represented as hats:
- The white hat is objective and focuses on facts and logic
- The red hat is intuitive, focusing on emotion and instinct
- The black hat is cautious and predicts negative outcomes
- The yellow hat is optimistic and encourages positive outcomes
- The green hat is creative, with numerous ideas and little criticism
- The blue hat is the control hat used for management and organization
With each team member wearing a different hat, a group can examine an issue or problem from many different angles, preventing one viewpoint (or individual) from dominating the meeting or discussion. This means that decisions and solutions reached using the Six Thinking Hats approach will likely be more robust and effective, and everyone’s creative thinking skills will benefit.
Train Your Brain With Critical Thinking Exercises
Using critical thinking regularly in various situations can improve our ability to evaluate and analyze information. These seven critical thinking exercises train your brain for better critical thinking skills . With daily practice, they can become habits that will help you think more critically each day.
Improve your critical thinking with ABLE
Ask better questions and get better answers with ABLEs integrated web search, annotation and note-taking features. Check how ABLE helps you to improve your critical thinking.
I hope you have enjoyed reading this article. Feel free to share, recommend and connect 🙏
Connect with me on Twitter 👉 https://twitter.com/iamborisv
And follow Able's journey on Twitter: https://twitter.com/meet_able
And subscribe to our newsletter to read more valuable articles before it gets published on our blog.
Now we're building a Discord community of like-minded people, and we would be honoured and delighted to see you there.

Straight from the ABLE team: how we work and what we build. Thoughts, learnings, notes, experiences and what really matters.
Read more posts by this author
follow me :
Mental models: 13 thinking tools to boost your problem-solving skills
7 note-taking strategies to improve your study skills.

What is abstract thinking? 10 activities to improve your abstract thinking skills

5 examples of cognitive learning theory (and how you can use them)
0 results found.
- Aegis Alpha SA
- We build in public
Building with passion in
