Find the Best Online Master's in Education Programs
Some school districts require their teachers to earn an education master's degree within five years of entering the profession. Completing an education degree online can lead to career growth for current and future educators.


Best Online Education Programs
U.S. News evaluated several factors to rank the best online education degree programs, including faculty credentials, graduation rates and reputation.
Clemson, SC
Gainesville, FL
Charlottesville, VA

Online Education Program Specialty Rankings
Explore the best online education master’s programs offering the specialties below and get a feel for the curriculum and topics each area covers.
- Curriculum and Instruction
- Educational Administration
- Instructional Media
- Special Education
Online Education Program Concentration Rankings
See how online education master’s programs rank in concentrations offered, and discover more about where each focus area can take your career.
- Educational Administration and Supervision
- Educational Assessment, Evaluation, and Research
- Educational/Instructional Media Design
- Educational Psychology
- Education, General
- International and Comparative Education
- Bilingual, Multilingual and Multicultural Education
- Social and Philosophical Foundations of Education
- Special Education and Teaching
- Student Counseling and Personnel Services
- Teacher Education and Professional Development, Specific Levels and Methods
- Teacher Education and Professional Development, Specific Subject Areas
- Teaching Assistants/Aides
- Teaching English or French as a Second or Foreign Language
Online Graduate Education Degree Overviews
The degree types below can help you tailor your online education degree. Learn how an online early childhood education master's degree is different from an online education specialist degree, for example, to discover which is right for you.
- Adult Education
- Child Development
- Curriculum and Instruction (doctorate)
- Doctor of Education
- Early Childhood Education
- Education Administration
- Education Administration (doctorate)
- Education Leadership and Administration
- Education Specialist
- Educational Leadership (Doctorate)
- Educational Technology (Doctorate)
- Elementary Education
- Gifted and Talented Education
- Higher Education (doctorate)
- Higher Education Administration
- Instructional Technology
- Master of Arts in Teaching
- Master of Education
- Math Education
- Online Doctorate in Educational Psychology
- Online Teaching
- Reading and Literacy
- School Counseling
- Science Education
- Secondary Education
- Social Studies Education
- Special Education (doctorate)
Online Undergraduate Education Degree Overviews
Explore more in depth what it takes to earn an online education degree using the following guides.
- Early Childhood Education (Associate)
- Education (Associate)
- English Language Learning
FAQs about Online Education Master’s Programs
Online education degrees are respected when earned from an accredited program with a good reputation. Institutions must be accredited by an organization that has been recognized by either the U.S. Department of Education or the nonprofit Council for Higher Education Accreditation. Many institutions award the same graduate education degrees to students enrolled in online and on-campus programs. However, some schools do have different in-person and online degree offerings, so students should check that the specialization they’re interested in is offered online.
Employers want to know that you earned your online education degree from an accredited program and that you’re certified to teach in the state in which the job is located. If you enroll in a graduate program that offers state certification as part of the degree requirements, where you obtain your education master’s degree matters. In any case, hiring managers may be more interested in why you earned your degree and how it fits with your career goals than whether you earned it online or in person.
Enrolling in an online graduate education program is not an inherently easier option than enrolling in a traditional in-person program. Any format of an accredited graduate-level education program is rigorous. While the flexibility of online school helps students who are balancing work and family stay on track, many online programs have the same study materials and time commitments as on-campus programs.
Not everyone who enters an online education master’s program will attain a degree, either. According to U.S. News survey data, 73% of online master's in education students who entered in the 2018-2019 academic year graduated by June 2022. Online courses may require students to have more self-discipline to complete assignments. And some online programs still require in-person activities, like student teaching, for credit.
The time and effort to attain your education master’s degree may be worth it to earn a higher salary. Prospective students should weigh the cost of graduate student loans against the likely long-term payoff from a graduate degree. Opportunities for advancement in leadership positions are more likely for those who earn an education master’s degree than for those who have a bachelor’s degree alone. Education professionals with master’s degrees can become school principals or administrators, roles that earn a higher salary than most teaching positions. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics , the median annual salary for elementary, middle and high school principals was $98,420 in 2021. High school teachers , who need at least a bachelor’s degree, earned a median salary of $61,820 in 2021.
A graduate education degree helps you advance your career to administrative and leadership roles and keeps you competitive for new opportunities. You can use your degree in settings including pre-K-12 schools, colleges and universities, nonprofits, government agencies, and policy organizations.
In addition to being prepared for higher paying principal positions, graduates of education-related master’s degrees can become postsecondary education administrators – a job which can take many forms, from helping students sign up for classes to coordinating the activities of a college while serving as dean. According to the BLS, these positions earned a median salary of $96,910 in 2021. In addition, training and development managers , who identify the training needs of an organization and create or select course content for training programs, earned a median salary of $120,130 in 2021. Some higher education institutions hire postsecondary teachers who have a master’s degree, while others require teachers to have earned a doctorate as well. In 2021, postsecondary teachers earned a median salary of $79,640.

Education Degrees
Ultimate guide to education degrees.
The COVID-19 pandemic brought a sense of urgency to what we view as an essential occupation. As kitchen tables became desks and the weight of the classroom shifted from the schoolhouse to the home, the value of teachers in educational and civic life was more evident than ever.
Teachers don’t get into the education business for the money. However, this career path does provide stability and a consistent level of growth that allows for:
- Career advancement
- Increased pay
- Incentivized educational opportunities
- Access to leadership roles
According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, education careers from kindergarten teachers to high school principals show a projected 7% growth over the next decade. As exiting teachers and educators retire, more positions will become available, too.
The following guide explores the various levels of education degrees, what you can expect from these programs, and what these degrees can do for your career. We also highlight academic concentrations, detail standout academic programs, and review a list of scholarship opportunities. Continue reading to learn more about education degrees and how you can begin your academic journey toward a career in this essential field.
Types Of Education Degrees
From associate degrees to doctoral programs, education degrees exist for students with varying levels of academic and professional experience. The following section examines the different educational options, what each degree involves, and what you can expect as a student. Additionally, we spotlight several standout academic programs.
Education Certificate Program
Education certificate programs offer bachelor’s-holding teachers a pathway to academic specializations and career advancement without having to earn a graduate-level degree. An especially appealing option for individuals without the time or money to attend graduate school, education certificate programs can introduce new teaching content areas or prepare teachers to work with different grade levels.
Keep in mind, education certificate programs are designed for licensed teachers or recent education grads who plan on earning their teaching license. Education certificate programs are not a pathway to teacher licensure. Various teaching certificates exist, including the following:
- Adult Education
- Administration and Leadership
- Early Childhood Education
- Educational Technology
- English as a Second Language
- Gifted and Talented Education
- Special Education
Teachers interested in pursuing a career-advancing educational certificate must have a bachelor’s degree, and many programs require a minimum cumulative GPA of around 3.0. Additionally, some programs may require you to submit proof of teacher licensure.
Education Certificate Program Spotlight
The University of Florida offers several online certificates through its educational technology program. These include K-12 teaching with technology, instructional design, managing distance education environments, and online teaching and learning. Each certificate encompasses 12 credits of coursework, and students complete requirements entirely online.
Online certificate students can choose from various tech-based education classes, including foundations of educational technology, designing technology-rich curriculum, using the internet in education, and issues and trends in educational technology research.
Associate Degree in Education
An online associate degree—and associate degrees, generally—offer students a unique opportunity to knock out general education requirements and seamlessly transition into four-year programs. Additionally, many associate degrees in education provide paraeducator career training and a pathway to pre-K licensure.
Associate degrees are often part of a 2+2 program where students complete their first two years at a community college and then transfer to a four-year institution to finish their bachelor’s degree. Throughout their associate degree, students tackle general education requirements like English composition and U.S. history while engaging with concentration areas like special education, early childhood education, and secondary education.
AA vs AS in Education: Which Degree Should You Get?
Associate degrees traditionally come in two forms: an associate of arts (AA) or an associate of science (AS). AA degrees typically focus more on the humanities, with students taking more electives in areas like history, English, and foreign language studies. AS degrees tend towards math and science. For students interested in teaching in STEM areas, earning an AS degree is a practical academic option.
Education Associate Program Spotlight
Offered through the Ohio State University’s roster of online learning opportunities, this online associate of arts degree focuses on early childhood development and education. Encompassing 60 credits, this academic path provides students a clear path towards their bachelor’s degree and career in education. Additionally, this program allows graduates to teach preschool and work in childcare environments. Graduates are also eligible for pre-kindergarten teacher licensure and prepare them to take their licensure exams.
Students can complete this associate degree entirely online and tackle classes including family development, childhood development, and managing and supporting behavior in social contexts. AA students also complete various general education requirements, preparing them to transfer to a four-year institution.
OSU reviews applications holistically on a case-by-case basis. Admissions officials consider various criteria, including high school GPA, standardized test scores, work and volunteer experience, and the applicant’s unique life experiences.
Bachelor’s Degree in Education
Earning a bachelor’s degree in education is often the first step toward beginning your teaching career. A typical major offered by colleges and universities across the country, a bachelor’s in education traditionally requires students to complete 120 credits of coursework and takes most students at least four years to complete.
In addition to general education and core education requirements, many education programs allow students to focus on a chosen subject, age, or student population. Common areas of academic concentration include:
- Elementary education
- Secondary education
- Special education
- Early childhood education
Students earning an online bachelor’s in education can complete the vast majority of coursework online and at their own pace. That said, education programs do require extensive hands-on learning through various student teaching and internship experiences.
BA vs BS in Education: Which Degree Should You Get?
Each college or university largely determines whether a bachelor’s in education is identified as a bachelor of arts (BA) or a bachelor of science (BS). These designations do not reflect a program’s rigor and are often influenced by how a particular school catalogs its classes.
That said, a BA degree usually requires a foreign language component, while a BS may involve more math and science coursework. Be sure a program has the appropriate accreditation and leads to teacher licensure .
Bachelor's in Education Program Spotlights
UNCW offers students a bachelor’s in elementary education that they can complete almost entirely online. Designed as a degree completion program in partnership with state community colleges, this program marries online classes with hands-on learning experiences through extensive fieldwork, classroom visits, and tutoring.
Students complete core education requirements that include classes like elementary school literature, psychological foundations of teaching, and teaching diverse learners. Additionally, degree-seekers complete three 40-hour apprenticeships in an elementary classroom. Before graduation, complete a 14-credit internship that acts as a degree-culminating experience.
Prospective transfer students must have earned their GED or high school diploma and have at least 24-credits of transferable, college-level coursework. Additionally, students must have a minimum cumulative GPA of 2.5.
The University of Louisiana-Monroe plays home to an online bachelor’s in elementary education that holds programmatic accreditation from the National Council for the Accreditation of Teacher Education (NCATE). Designed to build teaching skills while enhancing the student experience, ULM’s online degree includes general education studies, pedagogical studies, and various field experiences.
Students complete 120 credits before graduation throughout their degree—of the 120 credits, 57 are dedicated to major requirements. Some of the core requirements include mathematics methods for the classroom, survey of the education of children with special needs, and educational foundations for diverse learning environments.
Even though they’re online learners, students at ULM get access to various online resources to ensure that they receive the best academic experience possible. In addition to 24/7 tech help, students have access to free online tutoring, mental health services, and career services.
Master’s Degree in Education
The desire to earn a master’s degree in education often stems from two practical reasons:
- A working teacher wants to enhance their skills and expand career options, or
- An individual has a bachelor’s degree and wants to begin their career in teaching
Either way, these degrees explore the most cutting-edge research in the education field and prep graduates for various administrative and leadership roles.
Like many master’s programs, this advanced education degree typically requires students to complete 30+ credits of coursework. Full-time master’s students can complete these programs in 1-2 years. Standard master’s-level classes include research in education, planning for school improvement, teacher leadership, and instructional strategies and models. Before graduation, these programs require a degree-culminating experience in the form of a thesis, research project, or professional portfolio.
While admission requirements vary between programs, students are expected to hold a bachelor’s degree from a regionally accredited college or university. Other standard requirements include a minimum 3.0 GPA, letters of recommendation, and a valid teaching license.
MEd vs MAT: Which Degree Should You Get?
Once you’ve decided to earn a Master’s in Education , there are two distinct academic tracks : master of arts in teaching (MAT) or master of education (MEd). An MAT degree primarily focuses on teaching and highlights topics like pedagogical theory, instructional strategies, and student teaching. An MAT is the degree of choice for career-changers who want to begin their teaching career—many programs offer a pathway to teacher licensure.
Alternately, an MEd degree is primarily for experienced educators and focuses on educational administration , student counseling, and curricular design. To gain admission, the programs typically require at least two years of teaching experience.
Master's in Education Program Spotlights
CSUB’s online master’s in education focuses on curriculum and instruction, prioritizing the skills working teachers need to create a robust learning environment that utilizes educational technology to expand equity in schools. Full-time master’s students can complete this 30-credit program in just one year through a flexible, asynchronous online delivery.
This online program’s curriculum comprises 12 credits of core requirements, 18 credits of electives, and one three-hour degree culminating experience. Core courses include research methods for educational leaders, teaching for diversity and social justice, educational leadership, and curriculum development and transformation. Additionally, while completing this online M.A. degree, students can also complete a Leadership in Educational Technology Certificate.
Prospective master’s students must hold a bachelor’s degree from a regionally accredited college or university. Applicants should submit transcripts showing a minimum 3.0 GPA from their last 60 credits of undergraduate coursework and must hold a valid teaching license.
Based in Sioux Falls, South Dakota, this private institution was founded in 1860 and offers an online master’s in education that students can complete in as few as 13 months. Designed for working educators, this academic track explores historical and current educational trends, utilizes technology to enhance the classroom experience, and helps students build the skills needed for future leadership roles.
This 30 credit master’s program includes 21 credits of core requirements and nine credits dedicated to the student’s chosen academic concentration. Core classes include issues in education, history, and philosophy of education, and foundations and principles of curriculum. Additionally, students select from five academic concentrations: instructional strategies, reading, special populations, STEM, or technology.
Applicants for this online master’s in education must hold a bachelor’s degree with a cumulative GPA of at least 3.0. Prospective learners must also submit proof of licensure, two letters of recommendation, and a short essay outlining academic and career goals.
Doctoral Degree (EdD) or PhD
A doctorate in education is the premier degree for education professionals. In addition to opening up post-secondary teaching opportunities, this high-level degree often qualifies graduates for administration roles like a school principal or superintendent.
Whether online or on-campus, these doctoral degrees usually require that students complete 45-60 credits before graduation. Degree-seekers with a master’s degree can often complete their doctorate in approximately three years. In addition to core requirements, doctoral candidates choose from common academic specializations such as:
- Instructional design
- Diversity and equity in education
Prospective students are traditionally expected to have experience in the classroom or with educational administration. Applicants should expect to submit a professional resume, academic transcripts, letters of recommendation, and a statement of purpose outlining academic and career goals.
EdD vs PhD: Which Degree Should You Get?
While earning a Doctorate in Education can expand career options and earning potential, these degrees lead to distinct roles. A PhD in Education is research-heavy and leads to careers in academia and various research settings. On the other hand, an EdD degree is a common choice for individuals seeking leadership roles in education, focusing on the practical application of educational theory and research.
Doctorate in Education Program Spotlights
Lynchburg, Virginia’s Liberty University offers an extensive roster of online degrees, including a doctorate in education that many students complete in just three years. This program holds programmatic accreditation through the National Council for Accreditation of Teacher Education (NCATE) and covers essential topics like education administration, curriculum development, and learning theory.
Within this EdD program, students can choose from academic concentrations, including administration and supervision, curriculum and instruction, educational leadership, and higher education administration. Throughout this approximately three-year program, students tackle 54 credits of coursework and complete a degree-culminating project before graduation.
Prospective EdD students must submit an online application and hold a master’s degree with a minimum 3.0 GPA. Applicants must submit official transcripts and provide Liberty University with proof of English language proficiency.
Recognized worldwide as a leading research institution, Northeastern University is a private school that plays home to an online doctorate in education . In addition to its flexible online format, Northeastern supplies doctorate students with the ability to select their academic concentration and tailor their degree to academic and career goals. Academic concentrations offered include higher education administration, innovative teaching and learning, transformative school leadership, workplace learning, and integrative studies.
EdD students can enroll as full-time or part-time learners, and full-time students often complete this academic track in as few as three years. Required foundational courses include collaborative leadership, leadership for social justice, and introduction to action research and social change. While this degree is completed almost entirely online, students must attend two residency events.
Unlike other EdD programs, degree-seekers begin their dissertation when the program starts. During the first semester, students are assigned a faculty advisor who guides them through their research and dissertation.
Education Program Areas and Specializations
Education degrees cover a vast array of topics, grade levels, and career outcomes. Because of this, most programs include specializations to help students focus their knowledge and training in a specific area that leads to their intended career.
In the following section, we look at a few of these specializations. This does not constitute an exhaustive list, so make sure you research several schools to find one with a specialization that aligns with your interests.
Also known as the Early Years Foundation Stage (EYFS), early childhood education covers educational programming for children from birth through eight years old. Because these first eight years cover significant developmental milestones, completing this currently provides the training needed to work with students ranging from nursery through early elementary education.
Rather than covering a specific academic topic (e.g., mathematics, science, etc.), early childhood education students focus on topics such as general knowledge, language and literacy, social-emotional development, and physical development. Students typically choose between a bachelor’s or master’s degree .
Elementary education specializations typically prepare graduates to teach learners in kindergarten through sixth grade. While this specialization does overlap with early childhood education, it is designed for degree-seekers who likely want to work with children once they reach elementary school rather than nursery or pre-K.
Elementary education students can choose from online programs offered at the bachelor’s and master’s levels. They should plan to participate in a student teaching placement to gain real-world skills in K-6 classrooms before graduating.
The definition of secondary education varies based on the state where you plan to live and teach: some states use the term to mean exclusively high school , while others include middle school in the definition. Check with your state board of education to learn which term represents your ideal teaching area before selecting a specialization.
Aside from focusing on older students, many secondary education degree seekers also choose a specific academic concentration. These can include:
- Mathematics
- English language learning
- Earth science
Always make sure your chosen school offers the specific content area you want to study.
After working in the K-12 system as classroom teachers, some of these professionals decide to go back to school to earn the qualifications needed to educate the next generation of teachers. Teacher education programs train students in pedagogy, instructional and curriculum design, education theory, and specific academic topics to ensure they possess a well-rounded set of knowledge.
Educational requirements vary based on your previous, relevant experience and individual college and university requirements. Most teacher educators hold an MEd or an EdD. These programs may also offer additional concentrations based on your chosen teaching area, including early childhood teacher education, elementary and middle school teacher education, secondary school teacher education, vocational teacher training, and higher education teacher training.
Special education specializations provide the qualifications and training needed to educate students with physical, mental, social, or learning disabilities who require additional support. Working in this area can be both challenging and rewarding, but many students find the experience worth it .
Rather than focusing on a specific grade area, special education concentrations look at the various disabilities common in K-12 students and the pedagogical and instructional tools available to those who teach them.
Some colleges and universities now provide more specific concentrations in special education , with standard offerings including autism spectrum disorders, gifted and talented student education, applied behavior analysis, visual impairment, and special education for early childhood education.
Pursuing a curriculum and instruction specialization enables graduates to work with textbook publishers and designers to create innovative, cutting-edge curricula based on best practices in pedagogy and learning outcomes.
Typically offered as part of a master’s in education curriculum, these specializations support teachers who already possess some classroom experience but want to transition to a new discipline area. Aside from working with publishers, graduates may also work in school districts or departments of education to set curricular guidelines and requirements.
With a focus on topics such as educational policy, assessment strategies, management practices, and financial management, educational leadership specializations prepare graduates to take on roles as school principals , preschool directors, university deans, and district supervisors.
Most programs exist at the master’s level and offer training in areas required for high-level managerial positions. Some students may decide to focus on Birth-12 settings while others want to work in higher education administration.
What Can I Do With An Education Degree?
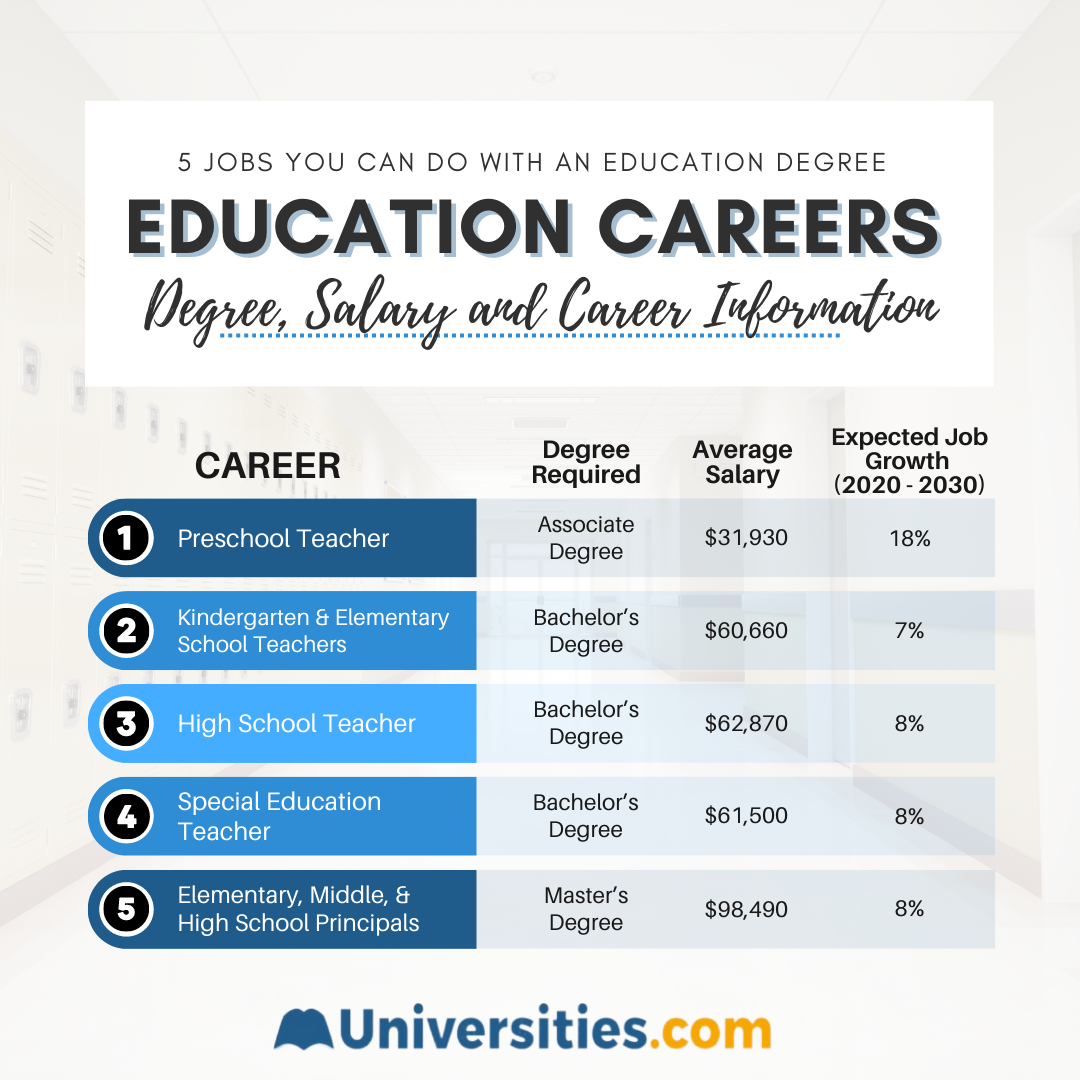
While various factors determine the annual salary for teachers, one statistic remains constant for teachers nationwide: from kindergarten teachers to high school principals, the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) projects that the job market for educators should expand between 2020-2030. Salaries can fluctuate significantly depending on an area’s cost of living, and as a general rule, educators with a master’s degree tend to make more.
We’ve highlighted various teaching careers below and included their average salary, projected job growth, and the level of education required.
Education Career Salaries, Career Outlook, and Job Requirements
How to become a teacher: education and teaching licensure, 1. earn your bachelor’s degree.
Whether or not you earn a bachelor’s in education, you’ll need a bachelor’s degree to teach in almost any primary or secondary educational setting. Students earning a bachelor’s in education have a clear path towards teaching licensure .
Students with an undergraduate degree in an unrelated field can supplement their bachelor’s with a master’s degree in teaching . Many of these programs offer a pathway towards a teaching license. Teacher preparation tracks do exist, but if you’re already taking the time to complete college-level coursework, earning a master’s degree can also lead to a higher salary and expanded career options.
2. Teaching Licensure
Once you’ve completed your requisite college-level coursework, the next vital step is securing your teaching license . While private schools are traditionally free to set their own hiring guidelines, public teachers jobs require applicants to have an active teachers license.
Education students at a state-approved program often complete many licensure requirements as part of their degree. Students either complete the national Praxis exam or complete a state-specific examination.
For state-specific licensure requirements, the U.S. Department of Education offers a handy resource where you can access contact information for each state.
Teaching Degree Accreditation
While students have access to thousands of colleges and universities throughout the United States, not all schools and academic programs are created equally. When searching for the right education degree program, enrolling in a regionally accredited institution is essential. Regionally accredited schools have met rigorous standards to ensure that you get your money’s worth. Accreditation can also influence your ability to receive Federal financial aid and whether or not the credits you earn can be transferred to other institutions.
It’s also vital that your education program holds programmatic accreditation. This is especially important if you are working towards teacher licensure. The National Council for Accreditation of Teacher Education (NCATE) is a common accrediting agency for education programs.
The U.S. Department of Education’s Office of Postsecondary Education offers a valuable database of accredited institutions and programs.
Scholarships For Education Students
A vast number of scholarships are available for education students. And whether you’re tackling your bachelor’s degree or MEd, funding exists. Additionally, many states offer tuition reimbursements for students dedicated to working in a particular state. We’ve highlighted five generous scholarships below. For a more extensive and personalized list of scholarships, visit our scholarship search tool .
Indiana Retired Teachers Foundation Scholarship : Awarded to full-time college sophomores and juniors at Indiana colleges or universities, the Indiana Retired Teachers Association provides scholarships exceeding $2,000. Applicants must submit academic transcripts, letters of recommendation, and documentation of financial need.
Minority Teacher Education Scholarship Program : Sponsored by the Florida Fund for Minority Teachers, this scholarship initiative offers a merit-based program providing funding exceeding $4,000. Applicants submit an electronic application and a short essay.
Next Generation Hoosier Educators Scholarship : For students planning to teach in Indiana schools after graduation, this scholarship awards over $7,500 in funding. Applicants must graduate in the top 20% of their high school class or have a top 20% SAT/ACT score.
PNC Foundation Scholarship : In partnership with the United Negro College Fund (UNCF), this scholarship program was founded to expand educational access to minority students in New Jersey. Students must enroll in an education program and submit a completed application, academic transcripts, and a personal essay.
Winifred R. Reynolds Educational Scholarship : Offering winners up to $7,000, this scholarship is open to students pursuing graduate degrees focusing on early childhood education, childhood development, or an equivalent field.
Frequently Asked Education Degree Questions
- The best major in education is the one that fits your academic and career goals. For some, an associate degree is an excellent entry into the field, while working educators may want to expand their career options through a master’s or doctorate program. College admission workers and academic departments are always happy to answer any questions you may have.
- Education degrees span from associate degrees at community colleges to PhD and EdD programs. Students pursuing a career in teaching will inevitably tackle a Bachelor’s Degree in Education. A Master’s in Education is a practical way for working teachers to enhance career options and boost their earning potential.
- An Associate Degree in Education takes about two years for full-time students, and a bachelor’s degree requires about four years of coursework. Working educators can often complete a master’s degree in 1-2 years. For educators with a master’s degree, a doctorate usually takes about 3-4 years to complete. A student’s status as a full-time or part-time student can significantly impact the time it takes to graduate.
- Salaries can vary significantly based on experience, level of education, and location. That said, according to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, the median annual salary for high school teachers is about $62,000.
- Traditional primary and secondary education roles require a bachelor’s degree, and most undergraduate degrees are designed to be completed in about four years. Students can reduce the time and cost of their degree by completing a significant portion of general education requirements at a community college.
Check out our newsletter to stay updated on college updates, news, advice, and more.
- Request Info
- Give to SFCC
We're Here for You!
- New Students
- Returning Student Registration
- High School Equivalency/GED
- High School Students
- International Students
- Transfer Students
- Meet with an Advisor
- Student Wellness Center
- Technology Help Desk
- Career Coach
- Online Learning Resources
- Transcripts
- Apply and Register
- Financial Aid
- Student Orientation
- Online Advising
- Welcome and Advising Center (WAC)

- Educational Pathways
- All Programs
- Degrees & Certificates
- Look for a Credit Class
- Adult Education
- Continuing Education
- Look up Credit Classes
- College Catalog
- Continuing Education Classes
- Academic Calendar
Programs & Departments
- Adult Education (GRE/HSE)
- Student Affairs
- William C. Witter Fitness Education Center
Internship Opportunities
- APRENDE Early Childhood Apprenticeship
- PILAS Paid Internships
- Engineering Machining Technology (LANL Cohort)
Helping You Succeed
- Office of Student Engagement
- Counseling Services
- Parenting Student Resources
- Veterans Resource Center
Paying for School
- Apply for Financial Aid
- Disbursements & Refunds
- Scholarships, Grants & Loans
- Registration and Payment Deadlines
- Tuition and Fees for Credit Classes
- How to Pay Your Bill
Support Services
- Accessibility Services
- Testing Center
- Tutoring Center
- Student Resource Center (Community Resources)
- Career & Transfer Services

- Jobs at SFCC
- Weather Alerts and Holiday Closures
- How to Get Your Grades
- Educational Resources
- Student Handbook
- Student Policies
- Title IX and Santa Fe Community College

Teacher Education
Santa Fe Community College’s teacher education associate degree program is designed to prepare you to transfer and earn a bachelor’s degree in elementary, bilingual and special education, language arts, social studies and foreign language, or math, science and physical education.
The program offers a wide range of courses that include field-based teaching observations, orientation to the teaching profession, and theories of teaching and learning. Your teacher training can include studying child growth, development and learning, as well as family and community collaboration and integrating technology in the classroom.
The courses are patterned after the lower-division courses at four-year colleges so you’ll get the required general education courses, plus core requirements relating to all three areas of specialization.
NOTE: People who already have a college degree can earn a license in teaching through SFCC’s state-accredited alternative teacher licensure program.
Teachers are in currently in high demand, especially in the areas of bilingual and special education, high school math and science, and English as a second language. The field offers many career opportunities, including school teachers, who earn a median annual salary of $61,400.
SFCC Pathways
- Explore Other Pathways
- Teacher Education Pathway
Related Programs
- Alternative Teacher Licensure Program
- Early Childhood Education
- APRENDE Early Childhood Apprenticeship Program
Program Resources
- Summer 24 Education Foundation Classes
- Fall 24 Education Foundation Classes
- Dept. of Teacher Education
- Contact an Academic Advisor
- Take Our Pathway Quiz
- Teacher Education, A.A.
- Teacher Education, A.A. – 2-Year Program Map
Faculty and Staff

Jonathan D. Harrell, MA
Academic Advisor, Undecided & Exploratory Advising, School of Education
Information
A Guide to Master’s Degrees in Education and Teaching
BestColleges.com is committed to delivering content that is objective and actionable. To that end, we have built a network of industry professionals across higher education to review our content and ensure we are providing the most helpful information to our readers.
Drawing on their firsthand industry expertise, our Integrity Network members serve as an additional step in our editing process, helping us confirm our content is accurate and up to date. These contributors:
- Suggest changes to inaccurate or misleading information.
- Provide specific, corrective feedback.
- Identify critical information that writers may have missed.
Integrity Network members typically work full time in their industry profession and review content for BestColleges.com as a side project. All Integrity Network members are paid members of the Red Ventures Education Integrity Network.
Explore our full list of Integrity Network members.
There are several types of master’s degrees in education , the predominant two being the master of education (M.Ed.) and the master of arts in teaching (MAT). But what’s an M.Ed. vs. MAT ? MAT programs prepare students for classroom teaching careers whereas M.Ed. programs can prepare students for a wider selection of educational roles, including teaching, administrative, and corporate positions.
The curriculum of a master’s in education or teaching program varies broadly depending on degree type and concentration, but most programs include foundational courses in curriculum development and instructional strategies. Programs that lead to licensure or certification typically include student teaching or other field experiences.
Featured Online Master’s in Education Programs
Learn about start dates, transferring credits, availability of financial aid, and more by contacting the universities below.
Popular Master’s in Education Online Programs
We chose to highlight the following schools based on several factors, including top position in organic or paid search results (as of August 2023), relevancy of program offerings, and categorization as a nonprofit. These programs are listed alphabetically by school and not weighed against each other in our methodology.

Arizona State University (ASU)
- Public institution in Arizona
- 18 online program options
- 30-47 credits | $692 per credit
Arizona State University’s online master’s in education programs provide analytical and research skills for current and future educators. ASU’s degrees emphasize foundations in instructional strategies and learning methods.
Eastern Washington University (EWU)
- Public institution in Washington
- 15 online program options
- 49-50 credits | $300 per credit
Eastern Washington University online master’s in education does not require recommendation letters or writing samples for admissions, unlike most programs. EWU offers 15 graduate education programs, including early childhood education, library media, and literacy.
Tulane University
- Private, nonprofit institution in Louisiana
- 4 online program options
- 30-33 credits | $1,210 per credit
Tulane University’s online master’s in education program has four specialization options. Students design their curriculum around these specializations, including learning experience design and special education, to prepare them for their chosen career path.
University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign (UIUC)
- Public institution in Illinois
- 8 online program options
- 32 credits | $510 per credit
The University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign’s online master’s in education programs prepare students to navigate challenging education issues. Other focuses include teaching strategies for diverse settings, leadership, and technological applications for education.
Western Governors University (WGU)
- Private, nonprofit institution in Utah
- Competency-based | $3,975 per term
Western Governors University has a competency-based model for its online master’s in education programs. WGU students progress through courses once they’re ready, speeding up if they’re familiar or slowing down when they need extra time.
Overview of an Online Master’s in Education
A master’s in education can take the form of M.Ed., MAT, or even of master of arts or science in education. And while there is slight variation between each of these degrees, the time takes to complete each degree, as well as the cost, is typically the same (or very similar).
Average Length of M.Ed.
Number of Years 1-2 (Full Time) 3-4 (Part Time)
Credits Required 30-50
Average Annual Cost of M.Ed.
Online Program $7,991
On-Campus Program $12,600
“[One] key consideration in choosing a master’s in education is truly determining if it is aligned with a student’s career aspirations. Is the degree required for career goals? Will the degree be worth the investment in time and money? Many adult learners must weigh the benefit of the investment personally and professionally.”

— Dr. Stacey Ludwig Johnson , Senior VP and Executive Dean of the School of Education, Western Governors University
Online Master’s in Education Admission Requirements
Most master’s in education programs require you to have the following when you apply:
- Bachelor’s degree with a GPA of at least 3.0
- Letters of recommendation
- Personal statement
- Proof of English proficiency
Additionally, some programs may require you to submit GRE test scores . Others, such as educational administration programs, may require that you have prior teaching experience or hold a valid teaching license.
Online Master’s in Education Concentrations
Early childhood education.
Master’s in early childhood education programs focus on how to educate young children from infancy to age eight. Attendees will learn how to teach multiple subjects to children through courses including research literature, the critical role of early educators, and best teaching practices. Graduates can pursue many roles, including as preschool directors, early education curriculum developers, and classroom teachers.
Elementary Education
A master’s in education with a concentration in elementary education prepares enrollees to work with students at the K-8 level. Learners study classroom management, learning design, and inclusive teaching methods to create optimized learning environments. Degree holders can pursue roles as educators, teaching assistants, and tutors.
Secondary Education
Master’s in secondary education programs focus on the skills and knowledge necessary to promote education from grades 6-12. Programs may allow attendees to choose a preferred content subject including math, science, or social studies. Graduates typically pursue teaching roles, including middle school teacher, high school teacher, and teaching assistant.
Higher Education
Higher education graduate programs teach foundational knowledge regarding the current higher education landscape, costs, and structure. Students may study various topics, including higher education finance, college student health, and public policy in higher education. Enrollees can specialize in a subject by choosing a concentration such as diversity, public policy, or research. Prospective careers for graduates include community college president, resident director, or policy analyst.
Adult Education
Adult education master’s programs help students understand how adults learn and how to design adult curriculums. Program curriculums may include teaching in an online environment, instructional strategies, and research courses. Adult education graduates can pursue roles as adult educators, administrators, or human resources managers.
Special Education
Special education graduate programs cover the laws and policies governing special education services. Coursework includes instruction on behavior management, goal and objective writing, and data collection and interpretation. Graduates can work as special education teachers, resource room teachers, adjunct faculty, and individualized education program case managers.
Gifted and Talented Education
Master’s programs in gifted and talented education teach students how to educate, motivate, and empower academically talented learners. Graduates can support gifted students’ development as gifted educators, elementary educators, or tutors.
English Language Learning (ELL)
Master’s in ELL or TESOL (teaching English to speakers of other languages) students learn teaching techniques and strategies to help English language learners succeed. Graduates often become ELL teachers in K-12 or adult education settings.
Educational Administration
Educational administration graduate programs provide an understanding of methods and ideas that keep schools running efficiently. Attendees study standards-based systems theory, data analysis for decision-making, and how to manage resources. Educational administration degree holders can utilize their skills in school principal, dean, or athletic director roles.
Educational Leadership
Enrollees in master’s in educational leadership programs prepare to be effective educational leaders by studying education theories, leadership, and finance. Attendees learn how to ensure student safety, manage budgets, and lead other educators. Educational leaders can pursue roles as principals, curriculum developers, and educational consultants.
Curriculum and Instruction
Master’s students studying curriculum and instruction often specialize in a specific area like secondary language arts or elementary education. They learn how to evaluate different learning materials, create meaningful assessments, and interpret data.
Reading and Literacy
Reading and literacy master’s programs help prospective educators gain a deeper understanding of reading and writing curriculums and theories. The program’s curriculum generally focuses on K-12 students. Graduates can pursue roles as primary, secondary, or special education teachers.
Social Studies
Master’s students in social studies programs learn about history and how to pass on their knowledge to secondary school students. Enrollees can learn about multiple history topics, including U..S history, traditional Chinese history, and modern European history. Graduates can earn a teaching degree to teach social studies in secondary schools.
Music Education
Music education master’s programs provide instruction on both musical theory and music teaching strategies. Attendees learn about musical analytic techniques, how to develop musical educational materials, and how to utilize music technology in classrooms. Specialists in music education can become educators, program directors, or musicians.
Math Education
Math education graduate programs provide high-level mathematics knowledge and teaching methods to help elementary or secondary students excel in the subject. Degree holders may pursue teaching careers in subjects like algebra, calculus, and Java.
Science Education
Attendees in science education master’s programs can choose to learn specialized knowledge in a science discipline, including biology, physics, or environmental studies. Science educators can pursue teaching roles in a public school setting or private setting, including at zoos and museums.
Educational Technology (EdTech)
A master’s in EdTech covers the latest technological developments in the classroom. Graduates can become technology coordinators at schools, lead STEM teams, and help determine assistive technology for students.
Educational Assessment
Educational assessment graduate programs teach enrollees how to gather, analyze, and interpret data. Assessment and measurement professionals can be used at schools to determine students’ performance or at private institutions to make data-driven decisions.
School Counseling
A school counseling master’s program can prepare students to become K-12 counselors. Graduates may consider pursuing further education in school psychology or counselor education. Coursework for this specialization may cover group counseling, crisis counseling, and ethical practices.
Master’s in coaching programs educate attendees on the importance of proper coaching practices, sports tactics, and team development. Aspiring coaches can pursue roles at educational institutions, at community centers, and with professional sports teams.
Child Development
Child development master’s programs cover the major theories regarding the cognitive, social, and physical development of children. Individuals that understand the development process of children from infancy to adolescence can pursue roles as childcare administrators, children’s advocates, and community outreach specialists.
Why Should You Get Your Master’s in Education Online?
One of the big advantages of getting a master’s in education online is that you don’t have to leave the workforce. Many M.Ed. programs allow students to earn their degree part time, so they can balance their studies , work, and personal obligations.
That’s one positive. Other benefits of online education include:
- Freedom to learn from anywhere
- More flexible class schedules
- Ability to change careers at your convenience
- Self-paced and self-directed learning
- More neurodivergent-friendly learning methods
“Online is the best option if you do not have the time to spend in a classroom because of personal obligations. To be successful, you must have excellent time management skills, be an effective communicator, and know how to collaborate with classmates virtually.”

— Charesha Barrett , M.Ed., Cleveland State University
What Can You Do With a Master’s in Education?
A master’s in education or teaching can lead to many in-demand education careers , including K-12 teacher, school principal, administrator, curriculum consultant, and other leadership positions.
And here’s more good news: Your degree opens the door to jobs outside the education setting , too.
“Of course a master’s degree in education can lead to opportunities in an educational setting. However, students tend to underestimate how the degree can support a career in other industries and career paths, like EdTech, learning and development, human resources, [and] project management.”

— Dr. Emmanuela Stanislaus , Instructor, Florida International University’s MS in Higher Education Administration Program
Here are popular teaching and non-teaching jobs for master’s in education graduates, including how much they pay and how much they’re expected to grow over the next decade:
Do Online Master’s in Education Programs Lead to Licensure?
A teaching license or certification provides people the authority to teach legally. Teachers and principals need licenses to work in P-12 public schools. State governments issue licenses if you meet predetermined criteria, such as having a degree, completing field experiences, and passing a state exam. Specific requirements vary by state and by the type of license, certification, or endorsement.
An online master’s in education can be a pathway to licensure if the program is approved by the state. Online programs that lead to an initial teaching license typically include an in-person student-teaching component. If you already have a teaching license, you can apply to master’s programs that lead to add-on endorsements or other certifications, such as an administrator license.
Non-licensure M.Ed. programs are typically designed for students who already hold a teaching credential or who plan to work in settings that do not require a license, such as private schools. These online programs often don’t have any field requirements.
Learn How to Become a Teacher in Your State
- Connecticut
- Massachusetts
- Mississippi
- New Hampshire
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- West Virginia
Does Accreditation Matter for Master’s in Education Programs?
Before enrolling in an online master’s in education program, check the school’s accreditation status . Institutional accreditation recognizes overall academic quality and legitimizes your degree. You must attend an accredited school to receive federal financial aid.
Programmatic accreditation recognizes programs or departments that adequately prepare students for their careers. Not all education programs have programmatic accreditation. Those that do have an additional marker of a high-quality education.
There are two main programmatic accreditors for educator preparation programs:
- Council for the Accreditation of Educator Preparation ( CAEP )
- Association for Advancing Quality in Educator Preparation ( AAQEP )
For more specific subfields of education, you may also come across these accrediting bodies:
- National Association for the Education of Young Children ( NAEYC ) for early childhood education and child development programs
- National Association of Schools of Music ( NASM ) for music education programs
- Council for Accreditation of Counseling and Related Educational Programs ( CACREP ) for school counseling, career counseling, and counselor education programs
Is an Education Master’s Degree Worth It? Grads and Instructors Weigh In
The graduates and instructors we spoke to agreed that a master’s in education leads to better opportunities, better pay, and greater impact — though you need to be mindful of the reasons why you want it.
They also say the degree helped them reach specific career goals, which varied depending on their values.
What Grads Are Saying
“A master’s in education gives a teacher a far wider perspective on how the system works and how students learn. A graduate with a master’s in education becomes a problem-solver who can zoom in and out of a problem, seeing it at both micro and macro levels.”

— Mindy Kay Smith , M.Ed., Ohio University
“[A master’s in education] has served me well. … I’m a more creative problem-solver, a more empathetic product builder, and a stronger collaborator because I have spent time deeply understanding the problems and people in my industry.”

— Lisa Jiang , MA in Education, Stanford University
“My master’s degrees helped me get more leadership positions in education and helped me attain committee roles with the Ohio Department of Education and the U.S. Department of Education. In addition, I am able to provide professional development at the collegiate level because of my two graduate degrees.”
What Instructors and Administrators Are Saying
“I think that it is worth it to pursue a master’s in education. Having said that, I think that it is important for students to be strategic if and when they decide to pursue it. Go through the exercise of asking yourself why you want to pursue the degree. What opportunities will a master’s degree open up for you, and will it be enough to support your lifestyle?”
“I consider a bachelor’s degree to be like an appetizer when it comes to education. You just get a little taste and you don’t have the full understanding of what it means to be an educator. After being in the classroom, having exposure to systems and structures, individuals pursuing a master’s degree begin to ask better questions, challenge inequitable practices, and gain confidence in using their voice to advocate for research-based approaches to supporting students and programs.”

— Dr. Kasey Johnson , Lead Faculty, Ottawa University School of Education
“Earning a master’s degree in education will help graduates be a part of a group of professionals who have the credentials, licensures, and industry-relevant skills and knowledge that current employers seek.”
Frequently Asked Questions About Master’s Degrees in Education
Do most teachers have a master’s degree.
Yes. According to the National Center for Education Statistics , 51% of public school teachers held master’s degrees in 2021. And 53% of secondary teachers had a master’s degree. Teaching requirements vary by state, with some states requiring a master’s degree to become a certified teacher. Private schools can enact their own rules and may not require teachers to hold master’s degrees.
Which master’s degree in education pays the most?
Individuals with a master’s degree in education earn a wide range of salaries based on their career paths, not their degree choice. According to the BLS, school principals earn some of the highest salaries among educators, with a median annual wage of $100,000 in 2023.
Is there a difference between a master’s in teaching and a master’s in education?
Yes. Master’s in teaching degree programs focus on preparing enrollees for teaching roles while education degree curriculums can prepare students for a wider variety of positions. Online master’s in education graduates can utilize their skills as teachers, administrators, social workers, human resource representatives, and more.
Can you be a professor with a master’s in education?
Some higher education institutions, particularly community colleges, may allow professors to teach with a master’s in education, but other schools may require a doctorate in education . Individuals with a master’s in higher education may have additional opportunities to pursue careers at the postsecondary level.
Note: The insights on this page — excluding school descriptions — were reviewed by an independent third party compensated for their time by BestColleges. Page last reviewed February 2, 2024.
Explore More College Resources

Considering a Master’s in Education? Follow These 5 Steps Before Choosing a Program
Considering a master’s in education? Follow these five steps to choose the right program for your career goals, whether online or in person.

by Margaret Weinhold
Updated April 10, 2024

Scholarships for Education Majors
For those looking to become teachers, financing your degree can be a challenge. Learn what scholarships are available for education majors.

by Ellery Weil, Ph.D.
Updated April 19, 2024

The Student’s Guide to Financial Aid and the FAFSA
What is financial aid? What is the FAFSA? Learn about the different types of aid you can get for college and how to fill out the FAFSA.

by Matthew Arrojas
Updated August 26, 2024
