Entrepreneurial Planning


CBSE Class 12 Entrepreneurship Syllabus 2024-25 (PDF Download)
Cbse class 12 entrepreneurship syllabus 2024-25, course structure theory paper.
Time: 3 hours Maximum marks: 70
| -->
|
|
|
|
| Unit 1 | Entrepreneurial Opportunity | 40 | 30 |
| Unit 2 | Entrepreneurial Planning | 40 | |
| Unit 3 | Enterprise Marketing | 40 | 20 |
| Unit 4 | Enterprise Growth Strategies | 20 | |
| Unit 5 | Business Arithmetic | 40 | 20 |
| Unit 6 | Resource Mobilization | 20 | |
|
|
|
| |
|
| 40 | 30 | |
|
|
|
|
COURSE CONTENT
|
| |
|
| |
|
|
|
| · Sensing Entrepreneurial Opportunities · Environment Scanning · Problem Identification · Idea fields · Spotting Trends · Creativity and Innovation · Selecting the Right Opportunity | After going through this unit, the student/ learner would be able to: · Comprehend the concept and elements of business opportunity · Discuss the process of sensing opportunities · Understand the need to scan the environment ·Enlist the various forces affecting business environment · Identify the different idea field |
| · Understand the concept of opportunity and market assessment · Appreciate the ways in which trends can be spotted · Understand the process of creativity and innovation · Transform ideas into business opportunities | |
|
| |
|
| |
|
|
|
| · Forms of business organization- Sole proprietorship, Partnership, Company | After going through this unit, the student/ learner would be able to: · Recall the meaning of the various forms of business organization · Understand the characteristics of the various forms of business organization · Understand the difference between a Public and Private Company · Appreciate the reasons for a private company being more desirable · Appreciate the concept and importance of a Business Plan · Describe the various components of Business plan · Differentiate among the various components of Business plan · Develop a Business Plan |
| · Business Plan: concept, format. | |
| · Components: | |
| Organisational plan; | |
| Operational plan; | |
| Production plan; | |
| Financial plan; | |
| Marketing plan; | |
| Human Resource plan | |
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
| · Marketing and Sales Strategy · Branding, Logo, Tagline ·Promotion Strategy | After going through this unit, the student/ learner would be able to: · Discuss the various marketing strategies used in a business · Explain Marketing Mix. · Understand the concept of Branding, Packaging and Labeling · Describe the various methods of Pricing · Discuss the various factors affecting the channels of distribution · Understand the concept and types of sales strategy · Discuss different tools of promotion · Appreciate the objectives and different modes of Advertising · Understand the concept of personal selling, sales promotion, public relations · Discuss the various techniques of sales promotion |
|
| |
|
| |
|
|
|
| · Franchising: Concept and types · Franchising: Advantages and limitations to franchisor and franchisee. · Mergers and Acquisition: Concept, reasons and types. · Reasons for mergers and acquisitions | After going through this unit, the student/ learner would be able to: · Understand the concept of growth & development of an enterprise · Discuss the concept, types, advantages and limitations of franchising · Appreciate growth of business through mergers and acquisitions · Discuss the different types of mergers and acquisitions · Discuss the reasons for mergers and acquisitions |
|
| |
|
| |
|
|
|
| · Unit of Sale, Unit Cost for multiple products or services · Break even Analysis for multiple products or services · Computation of Working Capital · Inventory Control and EOQ · Return on Investment (ROI) and Return on Equity (ROE) | After going through this unit, the student/ learner would be able to: · Understand the concept of Unit Cost and Unit Price · Calculate Break-even point for Multiple products and services. · Understand the concept of Inventory Control · Compute the working capital of a business. · Calculate Return on Investment; Return on Equity and Economic Order Quantity |
|
| |
|
| |
|
|
|
| · Capital Market: Concept · Primary market: Concept, methods of issue · Angel Investor: Features · Venture Capital: Features, funding. | After going through this unit, the student/ learner would be able to: · Understand the need of finance in Business · Discuss the various sources of funds required for a firm · Understand the ways of raising funds in primary market · Appreciate the Angel Investors and Venture Capitalists as a source of business finance. |
PROJECT WORK
Students have to do TWO projects in the entire academic session.
TOPICS FOR THE PROJECT:
- Business Plan
- Market Survey
- 10 Marks each for 02 Projects
- 5 Marks for Numerical Assessment
- 5 Marks for Viva
Note: Students need to complete both the projects. Guidelines for both projects are given in the CBSE Textbook.
Download PDF
| Download Syllabus PDF | |
| Complete Syllabus |
Market wizard pro
Unleash Potential, Propel Success, Transform Businesses
10 Business Plan Project Ideas For Entrepreneurship Class 12
- Entrepreneurship business
- 1.1 1. E-commerce Startup:
- 1.2 2. Food Truck Venture:
- 1.3 3. Sustainable Fashion Brand:
- 1.4 4. Health and Wellness App:
- 1.5 5. Eco-Tourism Agency:
- 1.6 6. Virtual Reality Arcade:
- 1.7 7. Social Media Marketing Agency:
- 1.8 8. Online Tutoring Platform:
- 1.9 9. Renewable Energy Solutions:
- 1.10 10. Subscription Box Service:
- 2 Conclusion:
Introduction:
Entrepreneurship is an essential skill for students in the modern world. One of the best ways to develop this skill is by working on a business plan project. This project allows students to showcase their creativity, critical thinking, and problem-solving abilities. It also helps them understand the various aspects of starting and running a business. In this article, we will explore 10 exciting business plan project ideas for students in Entrepreneurship Class 12.
1. E-commerce Startup:
Students can create a business plan for an e-commerce startup. They can choose a niche, identify target customers, and outline the marketing strategy. The project can include designing a website, setting up payment gateways, and creating a social media presence.
2. Food Truck Venture:
A food truck venture is a popular choice for young entrepreneurs. Students can develop a business plan for a food truck that offers unique and delicious cuisine. They can research the market, develop a menu, and plan the logistics of operating a food truck.
3. Sustainable Fashion Brand:
In today’s environmentally conscious world, a sustainable fashion brand can be a successful venture. Students can create a business plan for a fashion brand that focuses on ethical sourcing, eco-friendly materials, and fair trade practices.
4. Health and Wellness App:
With the increasing focus on health and wellness, a mobile app can be a lucrative business idea. Students can develop a business plan for a health and wellness app that offers features like workout routines, meal planning, and mental health support.
5. Eco-Tourism Agency:
Eco-tourism is gaining popularity as people become more environmentally conscious. Students can create a business plan for an eco-tourism agency that offers sustainable travel experiences, promotes local culture, and supports conservation efforts.
6. Virtual Reality Arcade:
Virtual reality (VR) is a growing industry with immense potential. Students can develop a business plan for a virtual reality arcade that offers immersive gaming experiences. They can research the latest VR technology, identify target customers, and plan the setup of the arcade.
7. Social Media Marketing Agency:
Social media marketing is crucial for businesses to reach their target audience effectively. Students can create a business plan for a social media marketing agency that offers services like content creation, influencer marketing, and social media management.
8. Online Tutoring Platform:
Online tutoring has become increasingly popular, especially with the rise of remote learning. Students can develop a business plan for an online tutoring platform that connects students with qualified tutors. They can outline the subjects offered, pricing structure, and marketing strategy.
9. Renewable Energy Solutions:
Renewable energy is the future, and students can contribute to this field through a business plan project. They can create a plan for a renewable energy solutions company that offers solar panels, wind turbines, and energy-efficient products for homes and businesses.
10. Subscription Box Service:
Subscription box services have gained significant popularity in recent years. Students can develop a business plan for a subscription box service that caters to a specific niche, such as beauty, fitness, or gourmet food. They can research suppliers, plan the box contents, and develop a marketing strategy.
Conclusion:
These 10 business plan project ideas for Entrepreneurship Class 12 provide students with a platform to showcase their entrepreneurial skills. By working on these projects, students can gain valuable experience in market research, financial planning, and marketing strategy. This hands-on approach to learning will not only help them in their academic journey but also prepare them for real-world business challenges. So, pick a project idea that excites you the most and start working on your business plan today!
Related Stories

7 Steps To Successfully Create A Business In Entrepreneurship
Success stories: how bmcc small business entrepreneurship program is transforming lives.

Business Entrepreneurship And Innovation Jobs
You may have missed, how to improve your winning chances with dpbosss.

- Investment decisions
Celebrating The Woodfibre Lng Final Investment Decision: A Game-Changer For The Energy Industry
- Business strategy
Unlocking Success: The Brilliant Business Strategy Of Bernard Arnault

Crafting Successful Foreign Investment Decisions: A Comprehensive Guide
Please enable javascript in your browser to visit this site.
NCERT Solutions for Class 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 and 12
Entrepreneurial Planning – CBSE Notes for Class 12 Entrepreneurship
January 17, 2024 by Sastry CBSE
1. Entrepreneurial activities are of three major categories: Manufacturing, trading and service providing. 2. Business is ‘A state of being busy or occupied’. 3. Activities undertaken to earn monetary benefits are called economic activities. 4. Activities done out of love and affection and not to earn monetary benefits are called non¬economic activities. 5. There are three main forms of enterprises: Public Sector, Private Sector, Joint Sector, etc. 6. Partnership: Two heads being better than one. 7. The Business Plan is a comprehensively written down document prepared by the entrepreneurship. 8. Business plane is sub-plans from diverse avenues of business, related to: — Marketing — Finance — Operations — Human — Legal 9. Business plan is prepared by an entrepreneur with the assistance of experts & professionals from diversified fields. 10. Four C’s of credit are: Character, Cash Flow, Collateral and Contribution (equity) 11. Depending upon the entrepreneurs experience, knowledge and purpose, following are the basic components/parts of a Business Plan. — Executive summary — Industrial analysis — Description of venture — Production plan — Operation plan — Organisational plan — Financial plan — Marketing plan — Manpower plan 12. Executive summary highlights in a concrete and convincing manner, the key provisions in the Business Plan, yet stimulating the potential investors that the entire plan is worth reading. 13. Objective of production plan is to plan the work in a manner that each step to be taken in the right place, right degree, right time and efficiently. 14. Operations plan is the soul of business plan. 15. Organizational plan is that part of business plan which describes to proposed venture’s form of ownership. 16. Financial plan is a projection of the financial data about the potential investment commitment needed for the new venture and economic feasibility of the enterprise. 17. In order to build up loyal, efficient and dedicated personal, entrepreneurs needs to pay adequate and proper attention to human resource planning. 18. Marketing plan is a guideline regarding the marketing objectives, strategies and activities to be followed by any enterprise. 19. Formalities for starting a business: — Obtain PAN Number from Income Tax Department — Open a Current Account — Register a Limited Liability Partnership (LLP) — Register Your Company (Pvt. Ltd/Public Limited Company) — Register For Service Tax — Register for VAT/Sales Tax — Excise Duty (Check Applicability) — Shop & Establishment Act — Customs Duty — File Entrepreneurship Memorandum at DIC (Optional) — Apply for TAN — Find State Specific Guidelines & Procedures — Permissions Required at the Construction Stage Employee’s Provident Fund — Employees State Insurance (ESI) Scheme
Words That Matter 1. Business: Business is ‘a state of being busy or occupied’. 2. Economic activities: Activities undertaken to earn monetary benefits are called economic activities. 3. Non-economic activities: Activities done out of love and affection and not to earn monetary benefits are called non-economic activities. 4. Organisational Plan: Organizational plan is that part of business plan that describes to proposed venture’s form of ownership. 5. Financial Plan: Financial plan is a projection of the financial data about the potential investment. 6. Marketing plan: Marketing plan is a guideline regarding the marketing objectives, strategies & activities to be followed by any enterprise. 7. Proforma income statement: Proforma income statement is a projected net profit calculated from estimated revenue minus projected costs and expense. 8. Break even analysis: The Break even analysis is a process of determining a point where firm neither makes profit nor a loss. 9. Target market: Target market refers to the specific group of potential customers whose needs the enterprise aims to fulfil. 10. TAN: TAN or Tax Deduction and Collection Account Number is a 10 digit alpha numeric number required to be obtained by all persons who are responsible for deducting or collecting tax. 11. Elevator pitch: Elevator pitch is a three minute summary of the business plan’s executive summary. 12. Production Plan: Production plan is the planning of industrial operations involves four considerations, namely, what work shall be done, how the work shall be done and lastly, when and by whom the work shall be done. 13. PAN: Permanent Account Number (PAN) is a ten-digit alphanumeric number, issued by the Income Tax Department.
CBSE Notes CBSE Notes Entrepreneurship NCERT Solutions Entrepreneurship
Free Resources
NCERT Solutions
Quick Resources
Entrepreneurial Planning: Notes | Entrepreneurship Class 12 - Commerce PDF Download
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? |
What is Entrepreneurial Planning?
Enterprise planning is the process where a detailed study is conducted on various aspects of starting a business.
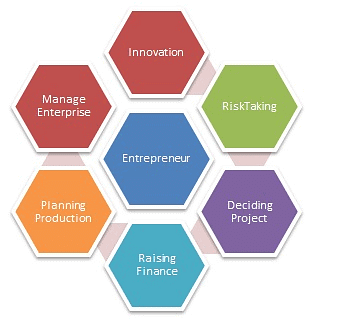
- A broad-level plan is laid down in terms of organizational structure, operational and production, financial, marketing, etc.
- In this chapter, we will discuss in detail various aspects of enterprise planning.
What are different forms of Business Entities?
Different forms of Business Entities are Sole Proprietorship Joint Hindu Family Business Partnership Cooperative Societies Joint Stock Company etc.
1. Sole Proprietorship
Sole proprietorship is a form of business, which is owned, managed, and controlled by an individual.
- It is the oldest and simplest form of business, established with the limited resources, ability, and capital.
- The business, if it is legal can be started anywhere, anytime at the sweet will of the individual. As such, a sole proprietorship is the form of business organization in which an individual introduces his own capital, uses his own skill in managing the affairs of the business, and is solely responsible for the result of the business operations.
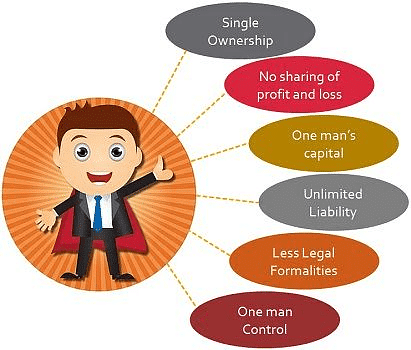
- The law does not make any distinction between the firm and the proprietor. The business and the businessmen are one and the same thing. In other words, the owner's personal property is also liable for business liabilities.
- If the business earns profit, the sole proprietor enjoys all the profit alone and if the business suffers a loss, it has to be borne by the sole trader himself. In the words of Peterson and Plowman , "A sole proprietorship has no legal existence apart from the proprietor himself. He is the firm". It means that he has unlimited liability and even his personal property is always at stake for the payment of business debts and loans.
- The sole proprietorship is also called sole trade, single ownership, single proprietorship, individual ownership and proprietorship, one-man business, etc. It has got the following important features.
2. Joint Hindu Family Business
Joint Hindu Family business is a form of business, which is owned by the members of a Joint Hindu family. It is also known as the Hindu undivided family business (HUF).

- It is a unique Indian business institution, governed by the provisions of Hindu law. It is managed by the head of the family, known as Karta, whose liability is unlimited.
- The liability of other members is limited. The male child attains the membership of the family business, since his birth in the family. It has the following special features.
3. Partnership
Sole proprietorship, as we know suffers from unlimited liability, limited resources, hasty decisions and temporary existence etc., so we tried to search for such a form of business organisation which could dispense with these demerits of sole proprietorship.
- As a remedy partnership emerged as a form of business organization.
- Definition of Partnership: Partnership as such is an agreement between two or more persons to carry on legal business with a profit motive, carried on by all or any one of them acting for all.
- According to the Indian Partnership Act, 1932 "Partnership is a relation between persons who have agreed to share the profit of the business carried on by all or any one of them acting for all".
4. Cooperative Societies
It was felt in the early nineteenth century that economic conditions of the weaker sections of the people can improve by cooperation not by competition.
- As such persons living in the same locality and having common needs join together in the form of association, known as the cooperative organization for mutual benefit.
- As this is a cooperative organization, the profit motive is missing and it is replaced by a service motive.
- In case there is surplus, it is distributed among members equitably honoring the principle of distributive justice.
- The dividend is paid on the basis of per member, not per share.
- Definition of Cooperative Societies: In the words of Saligman , "Cooperation in its technical sense means the abandonment of competition in distribution and production and elimination of middlemen of all kinds". In the words of Sir Horace Plankatte , "Cooperation is self-help made effective by the organization".
- According to International Labour Organization , "Cooperative is an association of persons usually of limited means, who have voluntarily joined together to achieve a common economic end through the formation of a democratically controlled business organization".
- As such cooperative societies are a voluntary association of persons having common needs joining together for mutual benefit.
The industrial revolution brought significant changes in the size of business structure. The unlimited liability and smaller size of business units could not meet the huge financial requirements of the modern business and provide limited liability to its individuals.
- The joint-stock company as a modern form of business emerged to meet the requirements of the large-sized business.
- Meaning of a Joint Stock Company: A joint-stock company is an artificial person, created by law with fixed capital, divisible into transferable shares, with perpetual succession and a common seal.
- The company has a separate legal entity. It must be compulsorily registered. The company is owned by shareholders, who subscribe to its shares.
- It is managed by the board of directors, the elected representatives of shareholders. In this way, the management and ownership are practically different. The company has permanent life, not at all affected by the death, insolvency, or lunacy of its members. The liability of the shareholders is limited to the face value of shares held by a particular shareholder.
- Definition of Company: According to Haney , "A joint-stock company is a voluntary association of persons for profit, whose capital is divided into transferable shares and ownership is required for its membership".
- In the opinion of Kimbal and Kimbel "Corporation by nature is an artificial person, which is created by law for a specific purpose."
What is a Business Plan?
A business plan may be defined as a written document of the business's future in terms of what you plan to do and how you plan to do it.
- In simple words, it is a broad-level strategy to start a business. There are 3 to 5 years of time horizons for preparing a business plan.
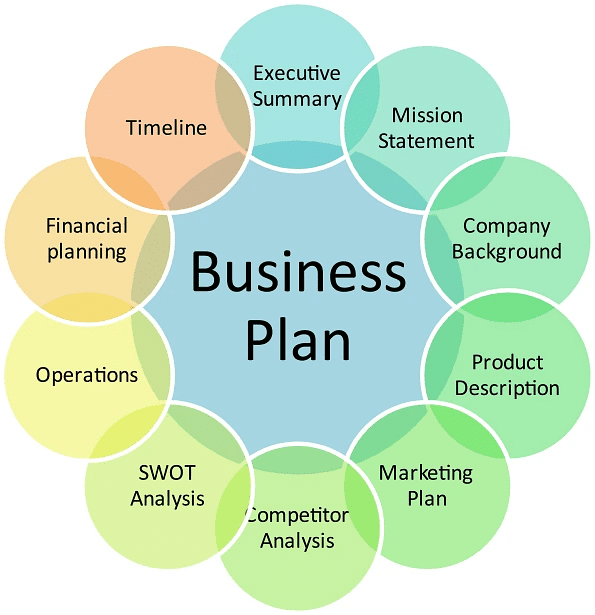
- Basically, detailed steps are put on a piece of paper in terms of where you intend to start and where you intend to reach after three to five years with a given level of resources and abilities.
- A business plan should be precise and lean and not necessarily be accurate. Instead of planning too much, a broad level structure should be laid down and changes be made as the entrepreneur progresses in implementing the plan.
However, in order to meet the challenges of carrying business and growing it, a good business plan is required which should have the following components:
- It should lay down the financial need of the business in terms of investment required for the business and expected return out of it year on a year basis.
- Strategy for business operation should be developed to give a firm direction to the business plan.
- A customer-oriented strategy should be in place in terms of what are the customer requirements and how it is going to be achieved.
- An effective monitoring plan should be prepared to identify the areas where achievements are less than expected and corrective steps can be taken.
- A business plan includes meticulous planning pertaining to organizational, operational and production, financial, marketing, and human resource planning. We will study each of them in detail in the coming paragraphs.
What is Organizational Planning?
Organizational planning depends on the forms of business selected by the entrepreneur.
- However, we need to understand that the initial phase of most entrepreneurs is to remain a low-cost organization.
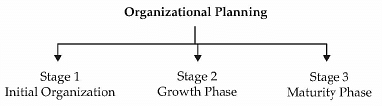
Stage 1: Initial Organization
This means that the initial organizational structure will be simple and decentralized.
- The entrepreneurs will most of the functions himself or herself with a bare minimum managerial and executive staff.
- There is also reluctance on part of the entrepreneur to delegate functions to others. Hence, the initial organization structure will be simple and centralized where most of the decision-making powers remain with the entrepreneur.
- This is also the first stage of the organization planning for an entrepreneur. In this phase, mostly the organization works as a proprietorship with one person managing and controlling most aspects of the business.
Stage 2: Growth Phase
The next stage comes when the business grows and the entrepreneur needs more managers and executives in the form of a helping hand to meet the demand of the growing business.
- Sub managers are hired to coordinate, organize and control the aspects of the business.
- Measurement, evaluation, rewards, training also becomes necessary at this stage. An entrepreneur needs to decentralize the organization at this stage in terms of delegating the authority to sub managers and tactical decision making and retaining the strategic decision making to himself or herself.
- An entrepreneur should put a formal structure of the organization with clear-cut authority and responsibility for each and every role. At this phase, the organization may change its form to either partnership or private limited company to give it a more formal structure as compared to a proprietorship.

Stage 3: Maturity Phase
This phase is reached when the firm is large enough to have a third level of managers.
- In this phase, the role of managers becomes important as he or she is required to adapt to changes in the environment.
- They have to evolve with new ideas and help entrepreneurs to achieve broad-level strategic objectives.
- The manager is also required to undertake the role of allocation of resources and handling pressures while maintaining the organization's progress in the right direction.
How to Build Organization Plan?
- A structure needs to be built for broad-level organization where the roles and responsibilities are clearly defined.
- Job analysis should be done for each role to have the right candidate available for the job.
- An analysis should be performed to see what is the workload and how many people required to complete the organization structure already planned.
What is Production and Operational Planning?
Operational and production planning is one of the key components of business plan. We will study this in two parts namely production planning and operational planning.
Production Planning
The areas which need attention for production planning are the manufacturing process, physical plant, machinery and equipment, and names of suppliers of materials.
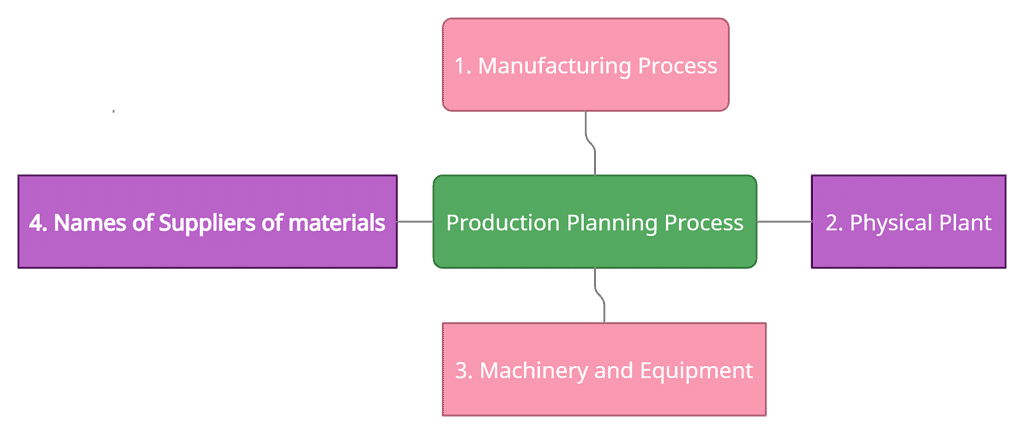
- Manufacturing Process: Under the manufacturing process, a key decision needs to be taken in terms of what should be manufactured by the entrepreneur himself or herself and what needs to be sub-contracted or outsourced. Generally, key processes like assembling; finishing, key components of the product are kept by the entrepreneur while ancillary items or components are sub-contracted. It also depends on the entrepreneur's willingness to keep full control of the manufacturing process or partial control. In a car manufacturing company, we see that the component manufacturing like steering, break, etc is subcontracted while the assembling, designing, finishing is done by the company itself.
- Physical Plant: Depending on the decision on sub-contracting and self-manufacturing, the entrepreneur has to devise a plan for setting up the physical plant. The plant capacity, location, layout, etc should be taken into consideration. Initially, the capacity should be low saved on the cost of managing a huge setup. However, the plant setup should be such that it is scalable to achieve higher production in case of surge in demand for the product in the market.
- Machinery and Equipment: The physical plant will consist of machinery and equipment which constitute the major part of plant infrastructure. An entrepreneur should plan as to which machinery in terms of technology should be installed in the plant. Installation of the machine will also depend on the decision that how much labor intensive or capital intensive plant is going to be. An entrepreneur may decide to go for capital intensive in which case the requirement of machines and equipment will be more as against labor-intensive where more labor is required than machines.
- Names of Suppliers of Materials: The suppliers of raw material needs to be identified. A competitive selection process should be applied in terms of the supplier who is ready to supply better quality raw material at competitive rates. It should also be seen that the supplier should have scalable infrastructure to increase supply if the demand for an entrepreneur's product rises in the market.
Operational Planning
- Operational planning mainly consists of defining the workflow and processes. A process may be defined as the list of activities that are required to be carried out to achieve an output of the products carried in the plant.
- These activities are interconnected to each other and there are separate roles and responsibilities assigned to the people in the organization. A workflow refers to the approval and authorization routes for the activities to be undertaken at a different stage of the production process.
- For example, if the raw material is required for the production process then a material requisition note is approved with the approval of the production manager to the store department for a specified quantity of material to be issued to the production department.
- In this case, we can see that raw material requirement has gone through the workflow of approvals which needs to be defined in the production process. This is what is called operational planning. An entrepreneur should devise an effective operational plan to aid in the production process.
- From the above points, it is clear that production and operational planning sets the business plan in the right direction. This plan requires a very careful thought process on the part of the entrepreneur and his organizational team to ensure the successful journey of the venture to be started.
- An accurate projection of the demand of the product is key to the operational strategy. For example, a plan to sell a woolen sweater for ^100 will fall flat if there is no strategy to have a good amount of stock as the demand soars in the market. Similarly, there should also not be an excessive investment in the inventory which blocks the working capital of the entrepreneur.
Financial Planning
A financial plan is prepared to assess the requirement of funds for starting the venture and also a plan pertaining to future income flows, cash flows, break-even analysis, and sources and application of funds.
Marketing Plan
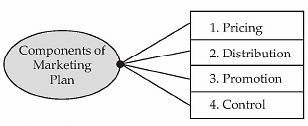
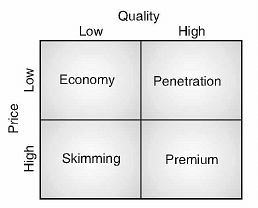
- Pricing: Pricing refers to the monetary value of the product which a consumer is willing to pay as per the product use and specification. Pricing plays an important role in pushing up or down the product's demand. It is impacted by the level of competition in the market, the cost of manufacturing the product, brand value of the product etc. An entrepreneur should set a competitive price of the product to ensure that the twin objective of higher demand and profit margin is achieved. The easiest way to determine product price is to add a profit margin to the product cost. However, there are other factors in terms of marketing strategy which affect the product price. The strategy may be in the form of Economy, penetration, skimming and premium pricing. Economy Pricing: Economy pricing is done where the product is of good quality but sold at lower price to achieve high volume of sales at lower profit margin. A very basic low cost approach is taken where the consumers are offered with bare minimum requirement. This strategy is adopted to attract a specific segment of the market that is very price sensitive. Penetration Pricing: This strategy is designed to capture market share by keeping low product price. It will help the entrepreneur to attract more customers for his entry level product. This strategy works well in a competitive environment where already a lot of sellers are available for the product. Although this strategy results in loss to the entrepreneur initially but it creates hope that more buyers will buy the product make it profitable at the later stage. Skimming Pricing: An entrepreneur who has a competitive advantage in the market sells the product at higher price. This pricing strategy is followed to make more money initially before competitors enter the market. Premium Pricing: It establishes a price higher than the competitors. This strategy is used when the product has some unique feature and has better quality than the competitors. Entrepreneur can earn more revenue at the early stage of the product life cycle and to establish a brand value in the premium range of the product.
- Distribution: Marketing plan also determines the distribution strategy of the entrepreneur. It will decide which territory to be covered for product supply and what channels of distribution will be taken up. The decision regarding territory depend on the factors like connectivity to the place of production, demographic profile of the territory like population, income distribution etc. Generally, entrepreneurs chose less territory and expand it as the product demand goes up. Channels of distribution may be through wholesalers, retailers, dealers, online selling etc. The entrepreneur has decided which channel of distribution is the most cost effective and has the widest reach to the customers.
- Promotion: Product promotion strategy covers the advertising, discount schemes, lucky draw etc. In today's age, promotion has to be good to overcome the competitive pressure of the market. Entrepreneur has to make a detailed plan pertaining to promotional schemes keeping in view that the product profitability is maintained. Advertising can be done through print media, TV, radio etc. The choice of advertising media will depend on the target segment of the market and its effectiveness in spreading the desired message to the potential customers. Generally, discount schemes, lucky draw etc is clubbed with the product advertising effort to educate consumers about the product and the scheme.
- Control: Market plan is prepared but it has to be effectively controlled to achieve the desired results as per the plan. A periodic review needs to take place to ensure that the planned targets are met and any adverse deviation is identified and its reasons investigated. Those reasons to be corrected to ensure that the plan is met by the end of its applicable period. Control mechanism determines the success of the plan. Entrepreneur should take interest in the progress of the plan to achieve the desired results.
Human Resource Planning
Business plan should include a description of organizational structure. The organization structure should include management and human resources capabilities, philosophy and needs, the number of employees an entrepreneur intends to hire, how he or she will manage them and estimated personnel costs. An entrepreneur has to begin human resource planning by outlining his/her own managerial experience and skills as well as that of his/her team. It should also be what roles each member will play also determine any particular strength or deficiency in the team. Entrepreneur should not worry if he/she doesn't yet have a complete team in place when the plan is being written. The objective of the human resource plan is to:
- Outline the organizational structure
- Complete with job descriptions
- How you plan to recruit key team members, and
- What their respective responsibilities will be.
Entrepreneur should consider recruiting a human resources manager or at least use an HR consulting firm. The reason is that human resource management requires an immense amount of time and paperwork. An experienced HR consultant should be able to quickly get payroll and benefits running, giving entrepreneur more time to concentrate on growing the business. Human resource strategy is another component of human resource planning. The strategy will outline the kind of corporate culture that needs to be nurtured in the organization. It will also help the investors to understand the philosophy of the organization towards its employees and the cost of administering employee related matters. Some of the important aspect of HR strategy may be pay scale, leaves, employee insurance and additional benefits to employees.
Creating the Plan
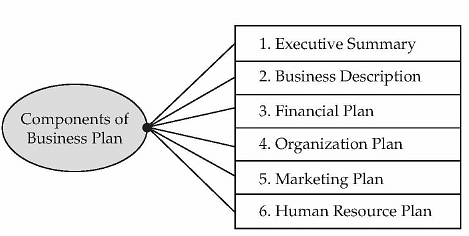
- Executive Summary: The executive summary will follow the title page. The summary should tell the reader what entrepreneur wants from the project he or she is planning to undertake.
- Business Description: It usually begins with a short description of the industry in terms present outlook as well as future possibilities. Entrepreneur should also provide information on various market segments within the industry including any new products or developments that will benefit or adversely affect his or her business. Business description should help the readers to understand the business idea of the entrepreneur.
- Financial Plan: Financial plan should spell out the plan for projected financial statements of the business. Financial statement includes income statement, balance sheet and cash flow. It should also indicate the sources and application of funds for smooth operation of the business. It should be noted that the financial plan is dependent on the other components of the business plan like production, operation, marketing and human resource plan.
- Organization Plan: Organization plan is prepared to define the roles and responsibilities of various organizational hierarchies. Job analysis is done to hire the right person for the predefined job role.
- Marketing plan: Marketing plan is the result of a meticulous market analysis. A market analysis forces the entrepreneur to become familiar with all aspects of the market so that the target market can be defined and the company can be positioned in order to garner its share of sales.
- Human Resource Plan: A description of organizational structure should be given which should include management and human resources capabilities, philosophy and needs, the number of employees an entrepreneur intends to hire, how he or she will manage them and estimated personnel costs.
Formalities of Starting a Business
Once business plan is created covering majorly all aspects of the business operations, the formalities for starting the business should be undertaken. It requires all the procedures to be completed so that the business operations can be started. These procedures include obtaining all necessary licenses and permits and completing any required notifications, verifications or inscriptions for the company and employees with relevant authorities. Internal processes, policies and procedures for the conduct of the business should be ready. Employee orientation should be conducted to ensure that everyone is aware of the organizational culture and values to be exhibited while dealing with day to day business affairs.
| |60 docs|12 tests |
Top Courses for Commerce
FAQs on Entrepreneurial Planning: Notes - Entrepreneurship Class 12 - Commerce
| 1. What is entrepreneurial planning? |
| 2. What are the different forms of business entities? |
| 3. What is a business plan? |
| 4. What is organizational planning? |
| 5. What is production and operational planning? |
| Rating | |
| Last updated |
Previous Year Questions with Solutions
Past year papers, entrepreneurial planning: notes | entrepreneurship class 12 - commerce, video lectures, semester notes, objective type questions, sample paper, important questions, viva questions, practice quizzes, study material, mock tests for examination, extra questions, shortcuts and tricks.

Entrepreneurial Planning: Notes Free PDF Download
Importance of entrepreneurial planning: notes, entrepreneurial planning: notes, entrepreneurial planning: notes commerce questions, study entrepreneurial planning: notes on the app.
| cation olution |
| Join the 10M+ students on EduRev |
Welcome Back
Create your account for free.
Forgot Password
Change country.

Project On Business Plan And Market Survey For Class 12 CBSE
Table of Contents
Introduction
In the realm of entrepreneurship, the path to triumph lies in the art of meticulous planning and a deep grasp of market intricacies. This project zooms in on two indispensable cornerstones of entrepreneurial ventures: the Business Plan and the Market Survey. In this initial section, let’s take a moment to underscore the profound importance of these pivotal elements for ambitious entrepreneurs.
Business Plan
Executive summary.
The Executive Summary provides a concise yet all-encompassing glimpse into the entirety of the business plan, encapsulating its vital components, objectives, and noteworthy highlights. This section is designed to offer a swift overview for our stakeholders and potential investors.
Noteworthy Highlights and Objectives:
Contained within this business plan is the vision for [Your Business Name], an innovative and dynamic endeavor poised to [briefly allude to our primary goal, such as “reshape the tech landscape” or “address the surging demand for sustainable solutions”]. Our overarching objectives comprise:
Market Dominance: To emerge as a distinguished frontrunner in [your specific industry or niche] by reaching a notable milestone, such as “capturing a 10% market share within three years.”
Customer-Centric Innovation: To consistently exceed customer expectations by fostering innovation, quality, and the delivery of unparalleled customer experiences.
Sustainability: To operate with unwavering dedication to environmental and social responsibility, making a positive impact on our communities and the planet.
Lucrative Expansion: To attain continuous and profitable growth, ensuring a robust return on investment for our valued stakeholders.
Team Empowerment: To cultivate a diverse and empowered team, driven by unyielding passion and commitment in advancing our mission.

Business Description
In this section, we delve into the very essence of [Your Business Name], elucidating its fundamental facets.
Business Concept and Products/Services:
Vision and Mission:
Vision: At [Your Business Name], our vision unfolds as we aspire to [depict the aspirational future we seek to create, like “trailblazing transformative technologies that reshape entire industries” or “becoming the ultimate destination for eco-conscious consumers”].
Mission: Our mission stands firm: [expressing our business’s fundamental purpose and the means by which it shall realize its vision, e.g., “delivering innovative, sustainable solutions that enrich lives” or “empowering businesses to thrive through strategic counsel and steadfast support”]. We are unwaveringly committed to upholding the loftiest standards of excellence, ethics, and environmental stewardship while concurrently delivering value to our cherished customers and stakeholders.

Market Analysis
In this section, we dive deep into an exhaustive market analysis, shedding light on its vast dimensions, growth potential, the demographics of our target audience, and the competition landscape.
Market Size and Growth Prospects:
The market for [insert your product or service category] stands robust, teeming with promise for substantial expansion. Current market intelligence pinpoints a market size of . Moreover, this sector is poised for impressive growth, with a projected annual escalation rate of [mention the anticipated growth rate] over the ensuing [mention the time horizon, like five years]. This upward trajectory finds its roots in factors such as [identify the key market propellers, such as a burgeoning appetite for sustainable solutions among consumers].
Target Customer Demographics and Personas:
Our sights are set on a precise target audience, consisting of individuals who share particular demographic attributes, including [outline the demographic specifics like age, gender, income bracket, etc., pertinent to our ideal customers]. These individuals, united by their shared characteristics, embody traits such as [list the common attributes, e.g., tech-savvy millennials with a penchant for eco-conscious solutions]. We’ve painstakingly crafted detailed customer personas, enriching our comprehension of their inclinations, pain points, and purchasing behaviors.
Competitor Appraisal:
A comprehensive scrutiny of the competitive panorama unveils several key contenders, prominently including [enumerate notable competitors in our sector]. Our scrutiny illuminates their prowess in domains such as [underscore their strengths, e.g., an entrenched brand presence, expansive distribution networks]. However, it also spotlights avenues where we can carve out our niche, such as .
Marketing Strategy
The marketing strategy segment delineates our blueprint for reaching our target audience with precision. It unravels the intricacies of pricing, promotion, distribution tactics, and lays bare our marketing expenditure.

Marketing Stratagems:
Our marketing maneuvers orbit around [expound upon our fundamental marketing approach, for example, “leveraging the digital realm to engage discerning tech-savvy millennials”]. We’ll orchestrate an orchestrated symphony of digital and real-world marketing gambits, encompassing content curation, social media immersion, the fine art of search engine optimization (SEO), and orchestrated email campaigns. Furthermore, forging strategic alliances with [mention potential partners, if germane] promises to broaden our reach.
Pricing, Promotion, and Distribution Strategies:
Our pricing strategy straddles the fine line between affordability and perceived value. We adopt a competitive pricing paradigm to beckon initial customers while safeguarding profitability. Promotion endeavors pivot around accentuating our unique value propositions, encompassing [emphasize our key differentiators, such as sustainability attributes or unmatched product prowess]. Our distribution blueprint entails [detail how and where our products or services shall find their way to consumers, whether through online sales, savvy retail collaborations, or other avenues].
Marketing Budget:
We’ve earmarked a budget of [designate the budget sum] to fuel our marketing exploits. This fiscal allocation will be prudently dispensed across a melange of marketing conduits and campaigns, with a keen eye on monitoring and optimizing the return on investment (ROI) for each conduit.
Operations Blueprint
In this juncture, we unfurl an exhaustive exposé of the quotidian operations underpinning our enterprise, delving into the intricacies of production, logistics, and the personnel imperative.
Day-to-Day Operations:
Our daily undertakings encompass a symphony of operational cadences, spanning [provide a glimpse into the core activities and processes that animate our business, whether it’s product development, customer concierge, or order orchestration]. We will harness [invoke relevant technologies or systems] to streamline and finesse these operations, rendering them efficient and synonymous with excellence.
Production and Logistics:
The theater of production unfurls within the hallowed precincts of our [reveal the location of our production hub]. We have cultivated partnerships with suppliers [where pertinent] to ensure the uninterrupted flow of our supply chain. Our logistical choreography shall be choreographed through [outline the methodologies and partners involved, be it third-party logistics virtuosos or in-house logistical dexterity].
Staffing Requisites:
Our human capital needs necessitate a cast of [indicate the headcount of professionals] adept in various domains, including [enumerating the pivotal roles, whether it’s product prodigies, marketing maestros, or customer care virtuosos]. Our commitment is unwavering – to nurture a workplace that pulsates with diversity and empowerment, propelling our mission forward with verve and dedication.
These operational blueprints are the architectural scaffolding of [Your Business Name], engineered to orchestrate the seamless symphony that delivers remarkable products/services to our esteemed patrons.
Financial Blueprint
The Financial Plan segment unveils an all-encompassing forecast for our business, casting a wide net over pivotal financial facets, including sales forecasts, income statements, cash flow delineations, and a break-even analysis.
Sales Projections:
Grounded in astute market analysis and our astute marketing stratagems, we foretell a continuous crescendo in sales. In the inaugural year, we envisage revenues scaling the summit of [reveal the anticipated revenue figure], with a projected annual surge of [declare the growth rate] in the subsequent [outline the time horizon].
Income Statements:
Our income statements lay bare the contours of anticipated revenues and expenditures, ultimately yielding a forecasted profit panorama. The intricate income statement for the nascent triennium is available in the appended financial dossier.
Cash Flow Statements:
Cash flow foresight unveils our financial fluidity and capacity to meet fiscal commitments. Projections for cash flow over the next triennium are presented in the attached financial documents.
Break-Even Analysis:
Our break-even scrutiny foretells the auspicious juncture when we attain financial equilibrium – an event slated for [specify the precise month/year], factoring in our sales prognostications and expense appraisals. This milestone signifies a threshold of financial sustainability and growth potential.
Risk Appraisal
Discerning latent perils and sketching blueprints for their aegis is a pivotal facet of our business stratagem.
Potential Perils:
Market Frenzy: The [insert your industry/niche] arena stands as a crucible of cutthroat competition, with venerable stalwarts reigning supreme. To temper this tempest, we shall ardently trumpet our unique value propositions and channel resources into perpetual market vigilance.
Economic Vicissitudes: Economic tides can sway consumer expenditure. We pledge to maintain fiscal reserves, sailing steadfastly through economic ebbs, and, when requisite, invoking austerity measures.
Supply Chain Turbulence: Ripples in the supply chain can shroud our production. Our defensive arsenal shall involve supplier diversification and the stewardship of emergency stockpiles, shoring up against such tempests.
Regulatory Flux: Legislative shifts in the [invoke pertinent regulations] sphere may influence our modus operandi. We shall be the vigilant sentinels, perpetually tracking legislative undertows and adapting our operational compass accordingly.
Peril Mitigation Stratagems:
To subdue these latent perils, we pledge to:
Maintain unwavering vigilance over the competitive terrain, flexing our strategies in tune with the market’s dynamic cadences. Carve a financial bulwark, equal to [specify a precise percentage] of annual operational expenses, to weather economic squalls. Forge robust partnerships with pivotal suppliers, while weaving in contingency blueprints to tame the supply chain’s capriciousness. Reside on the forefront of legislative flux, upholding compliance via recurring assessments and nimble adaptations.
In conclusion, this exhaustive business blueprint for [Your Business Name] unfurls our vision, stratagems, and the skeletal framework of our operations. We march forth with unwavering confidence that our diligently etched business stratagem, with its attendant fortifications against potential hazards, will not solely bear fruit in terms of our objectives but also usher in a transformative era in the [underscore your industry/niche]. We stand poised for the journey ahead, eager to transmute our vision into reality, and ardently dedicated to serving our cherished patrons and stakeholders.
Introduction to Market Survey
The Market Survey serves as a pivotal pillar in the edifice of our business plan, an indispensable instrument that unveils the nuances of the market’s ebb and flow, customer predilections, and the theater of competition.
The Rationale Behind Our Market Survey:
The primary motive behind conducting this market survey is to illuminate the intricate contours of the market milieu within which [Your Business Name] is poised to make its mark. Through the meticulous collection and astute analysis of market data, our objectives are as follows:
- Discerning Customer Desires: The compass of our market survey is aimed at unearthing the unspoken desires, needs, and pain points of our prospective clientele.
- Navigating Market Currents: Our survey serves as a radar, honed to detect the prevailing market trends and anticipate the tides that shall carry us forward.
- Charting the Competitive Terrain: Within the labyrinth of competitors, our market survey acts as a torchlight, casting light on their strengths and weaknesses.
- Fostering Informed Strategies: Armed with empirical data, our business strategies can be calibrated with precision, ensuring that every move is underpinned by knowledge.
The Imperative of Market Data Aggregation:
The process of gathering market data is invested with profound significance for a multitude of compelling reasons:
- Strategic Prowess: Market data stands as the bedrock upon which we erect our strategic edifice. It provides the compass points for aligning our products and services with the ever-shifting landscape of customer demand.
- Risk Safeguard: Market dynamics are the crucible in which potential risks and challenges are forged. An intimate understanding of these dynamics empowers us to proactively erect bulwarks against adversity.
- Competitive Vigor: Staying attuned to customer preferences and market trends allows us to craft offerings that emerge as beacons of distinction in the competitive tumult, endowing us with a resounding competitive advantage.
Methodology
The data collection ensemble:.
Our market survey was orchestrated with a multifaceted approach to data collection, casting a wide net to ensnare the insights we sought:
- Surveys: We orchestrated surveys, canvassing the viewpoints of a representative sample comprising [specify the sample size] respondents. This quantitative treasure trove unraveled the intricacies of customer preferences and behavioral patterns.
- Interviews: Delving deeper into the labyrinth of insights, we embarked on in-depth interviews. These conversations, shared with both industry luminaries and prospective customers, offered a qualitative tapestry rich with market trends and the poignant pain points experienced by stakeholders.
- Online Reconnaissance: The digital frontier was our hunting ground for secondary data, where we scoured the vast expanse of online resources. These virtual excavations unearthed nuggets of market trends, competitive benchmarks, and industry standards.
The Craft of Sample Selection:
The selection of our survey participants was a meticulously executed symphony, orchestrated with precision and purpose. Our sample size was calibrated to exude statistical significance, a requisite for the attainment of an accurate reflection of our target market. The criteria for participant selection were hinged upon [mention the selection criteria, e.g., demographic relevance, geographic dispersion, etc.], ensuring not only diversity but also relevance in our pursuit of profound insights.
Survey Findings
The fruits of our market survey have unveiled a treasure trove of insights across the diverse dimensions of the market:
- Customer Predilections: The survey has shone a spotlight on the fact that [insert key customer preferences, e.g., eco-conscious choices] loom large in the realm of customer priorities, signifying a harmonious alignment with our product spectrum.
- Market Zeitgeist: The prevailing winds in the market have whispered to us, foretelling a crescendo in the demand for [mention prevailing market trends, e.g., sustainable solutions], marking a defining moment in our industry’s evolution.
- Competitor Scrutiny: Our meticulous analysis has laid bare the titans of our field, accentuating their strengths and beckoning toward fertile grounds where we can cultivate our differentiation and innovation.
Analysis of Findings
The findings drawn from our survey underwent a thoroughgoing process of interpretation, culminating in the following cogent conclusions:
- Synergy of Customer Preferences: The survey results resonate harmoniously with our product portfolio, echoing the resonance of our business concept with the preferences of our prospective customers. This alignment validates the bedrock upon which we’ve erected our business concept.
- Echoes of Market Trends: The survey findings echo the prevailing market trends, thus validating and bolstering the strategic path charted within our business plan. Our unwavering commitment to sustainability, as substantiated by these trends, positions us as torchbearers in the industry’s evolution.
- Opportunities Amidst Competition: The analysis of our competitors has revealed both their strengths and the fertile grounds where we can cultivate innovation and differentiation. This insight equips us with the wisdom to forge our distinct path in the marketplace.
These conclusions emerge as the compass points that shall guide our strategic deliberations, reinforcing our conviction in the robustness of our business concept and igniting the beacon of innovation as we march forward.
In summation, the meticulous execution of our market survey has bequeathed us with a trove of market intelligence that shall unfailingly steer the ship of [Your Business Name] toward success. These findings, synergizing harmoniously with the comprehensive business plan we’ve etched, fortify our stance in the [underscore your industry/niche]. The interplay between the astutely crafted business plan and the sagacious insights garnered through our market survey promises an exciting voyage ahead, replete with excellence and innovation in serving our cherished patrons and stakeholders.
Certificate of Completion
This is to certify that I, [Student’s Name], a [Class/Grade Level] student, have successfully completed the project on “Business Plan And Market Survey For Class 12 CBSE.” The project explores the fundamental principles and key aspects of the chosen topic, providing a comprehensive understanding of its significance and implications.
In this project, I delved into in-depth research and analysis, investigating various facets and relevant theories related to the chosen topic. I demonstrated dedication, diligence, and a high level of sincerity throughout the project’s completion.
Key Achievements:
Thoroughly researched and analyzed Project On Business Plan And Market Survey For Class 12 CBSE. Examined the historical background and evolution of the subject matter. Explored the contributions of notable figures in the field. Investigated the key theories and principles associated with the topic. Discussed practical applications and real-world implications. Considered critical viewpoints and alternative theories, fostering a well-rounded understanding. This project has significantly enhanced my knowledge and critical thinking skills in the chosen field of study. It reflects my commitment to academic excellence and the pursuit of knowledge.
In order to download the PDF, You must follow on Youtube. Once done, Click on Submit
Subscribed? Click on Confirm
Download Project On Business Plan And Market Survey For Class 12 CBSE PDF
Related articles.

Automated Roti and Puri Maker Press project

The Oil Skimmer RC Boat

Secure Digi Locker Application Project

Software Piracy Protection Project
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Please Enable JavaScript in your Browser to Visit this Site.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Entrepreneurship project ( Business Plan ) on Wireless Earphone for class -12th (English - MY MOTHER AT SIXTY SIX)https://drive.google.com/file/d/1PAW6bNFAUX...
Watch Video🎥. The following formats are available to design a successful business plan. 1. Elevator pitch: It is a precise summary of the business plan's execution. 2. Oral/In person presentation: The presentation containing the key elements of the business plan is presented to the potential investors. 3.
CBSE Class 12 Entrepreneurship Syllabus 2024-25 Course Structure Theory Paper. Time: 3 hours Maximum marks: 70. S.No. Unit. No. of Periods. Marks. Unit 1. Entrepreneurial Opportunity. 40. 30. ... TOPICS FOR THE PROJECT: Business Plan; Market Survey; 10 Marks each for 02 Projects; 5 Marks for Numerical Assessment; 5 Marks for Viva;
Full syllabus notes, lecture and questions for Entrepreneurial Planning, Entrepreneurship, Class 12 Revision Notes - Class 12 ... The business plan projects. The business goals; The factors that favor the achievement of these goals ... OR Your friend has decided to start a production plant for manufacturing leather cases for mobile phones and ...
In this article, we will explore 10 exciting business plan project ideas for students in Entrepreneurship Class 12. 1. E-commerce Startup: Students can create a business plan for an e-commerce startup. They can choose a niche, identify target customers, and outline the marketing strategy. The project can include designing a website, setting up ...
Business Plan | Soap | Entrepreneurship Project | Class 12 | 2021-22 | CBSE | Nitesh Sharma Background music credit : https://youtu.be/C5fLxtJH2QsPROJECT WOR...
Business plans are crucial for entrepreneurial ventures. It helps businesses to identify possible problems and design practical solutions. It helps in critical decision-making. This is a pragmatic approach and helps the business in the long run. Another critical aspect of a business plan is it helps in identifying short-term goals and long-term ...
Entrepreneurial Planning - CBSE Notes for Class 12 Entrepreneurship 1. Entrepreneurial activities are of three major categories: Manufacturing, trading and service providing. 2. Business is 'A state of being busy or occupied'. 3. Activities undertaken to earn monetary benefits are called economic activities. 4. Activities done out of love and affection and not to earn […]
EduRev's Entrepreneurship Class 12 Course for Commerce is a comprehensive program that equips students with the knowledge and skills required to be successful entrepreneurs. The course covers various aspects of entrepreneurship, including idea generation, market research, business planning, funding, and marketing. It also provides students with real-world examples and case studies to help them ...
Ans. Entrepreneurial planning refers to the process of creating a strategic roadmap for an entrepreneur or business owner to achieve their goals and objectives. It involves identifying opportunities, setting objectives, formulating strategies, and allocating resources to effectively manage and grow a business. 2.
#businessstudies #class12project #businessplanEntrepreneurship Class 12 Business Plan Project on Wireless Earphones.Guys, it's my humble request to y'all to ...
SHIP CLASS XI-XII (2024-25) (CODE NO. 0. 6) RationaleSchool curriculum is a dynamic process. It continuously evolves i. self reflecting the needs and aspirations of learners. In recent times, our society is influence. by knowledge creation and technological advancements. Competencies affecting Innovation and creativity have become impo.
Get free entrepreneurship project list for class 12 CBSE. we also provide free downloadable pdf's. Here's a list of 60+ awesome ideas that you can use for Class 12 CBSE projects. Entrepreneurship Project Business Plan- CBSE Class 12. Entrepreneurship Project On Market Survey On Bisleri Class 12th CBSE. Marketing Management Project On ...
There are various components of a business plan which is prepared to depend upon the entrepreneur's enterprise and knowledge. CERTIFICATE This is to certify that the project is an authentic record of the work done by ROHITH S. BOBBY , class XII.D during 2017-2018 towards the partial fulfillment of the AISSCE course prescribed by the Central ...
Entrepreneurship Business plan on Chocolate Project for Class 12 CBSE 2022-23/Business plan project Please LIKE, COMMENT & SUBSCRIBE to my Channel to see mor...
This is to certify that I, [Student's Name], a [Class/Grade Level] student, have successfully completed the project on "Business Plan And Market Survey For Class 12 CBSE.". The project explores the fundamental principles and key aspects of the chosen topic, providing a comprehensive understanding of its significance and implications.