Got any suggestions?
We want to hear from you! Send us a message and help improve Slidesgo
Top searches
Trending searches


dia de muertos
24 templates

day of the dead
13 templates

9 templates

supreme court
29 templates

16 templates
Computer Presentation templates
Use these google slides themes or download our ppt files for powerpoint or keynote to give a presentation about a computer-related topic, including information technology..
- Calendar & Weather
- Infographics
- Marketing Plan
- Project Proposal
- Social Media
- Thesis Defense
- Black & White
- Craft & Notebook
- Floral & Plants
- Illustration
- Interactive & Animated
- Professional
- Instagram Post
- Instagram Stories

It seems that you like this template!

Register for free and start downloading now
Computer science degree for college.
Computer science degrees prepare students for the jobs of the future (and the present!). If you are interested in getting an education about coding, math, computers, and robots, this is the degree for you! Speak about it with this futuristic template that will take the viewers to another digital dimension....

Create your presentation Create personalized presentation content
Writing tone, number of slides, web project proposal.
We live in the internet era, which means that web design is currently one of the most demanded skills. This free template is perfect for those designers who want to present their web project proposal to their clients and see a preview of the final work.

Virtual Slides for Education Day
Digital learning is making its way into the world of education. For this reason, we've designed this new template so that the slides look like the screen of a laptop (complete with reflections!). Apart from graphs and infographics, the font is quite "computer-esque" and a perfect fit for this theme....

Soft Colors UI Design for Agencies
Agencies have the most creative employees, so having boring meetings with traditional Google Slides & PowerPoint presentations would be a waste. Make the most out of this potential with this creative design full of editable resources and beautiful decorations in calming, pastel tones. Let the creativity of your agency be...

Premium template
Unlock this template and gain unlimited access
Videogames Lesson!
Download the Videogames Lesson! presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides. The education sector constantly demands dynamic and effective ways to present information. This template is created with that very purpose in mind. Offering the best resources, it allows educators or students to efficiently manage their presentations and engage audiences. With...

Multimedia Software Pitch Deck
Download the "Multimedia Software Pitch Deck" presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides. Whether you're an entrepreneur looking for funding or a sales professional trying to close a deal, a great pitch deck can be the difference-maker that sets you apart from the competition. Let your talent shine out thanks to...

All About Programming in Java
Download the All About Programming in Java presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides. High school students are approaching adulthood, and therefore, this template’s design reflects the mature nature of their education. Customize the well-defined sections, integrate multimedia and interactive elements and allow space for research or group projects—the possibilities of...

Software Testing Company
Software testing might not be the sexiest part of coding, but that doesn't mean it lacks intrigue or importance. After all, who wants to use a buggy app? It's software testing that ensures smooth operation and prevents annoying glitches from making it into the final product. Without it, our lives...

Interactive Classroom Icebreakers
Download the Interactive Classroom Icebreakers presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides and easily edit it to fit your own lesson plan! Designed specifically for elementary school education, this eye-catching design features engaging graphics and age-appropriate fonts; elements that capture the students' attention and make the learning experience more enjoyable and...

Computer Science & Mathematics Major For College: Computer Science & Programming
Show future students the wonders of computer science and what they can achieve if they join a career in this incredible degree. With these slides you can speak about both technical and simple concepts and they will all be quickly understood! Editing them is as easy as printing Hello world!...

Tech Startup Newsletter
Download the "Tech Startup Newsletter" presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides. Attention all marketers! Are you looking for a way to make your newsletters more creative and eye-catching for your target audience? This amazing template is perfect for creating the perfect newsletter that will capture your audience's attention from the...

AI Tech Types and Tools
Download the AI Tech Types and Tools presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides. The world of business encompasses a lot of things! From reports to customer profiles, from brainstorming sessions to sales—there's always something to do or something to analyze. This customizable design, available for Google Slides and PowerPoint, is...

Software Engineering Business Plan
Download the "Software Engineering Business Plan" presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides. Conveying your business plan accurately and effectively is the cornerstone of any successful venture. This template allows you to pinpoint essential elements of your operation while your audience will appreciate the clear and concise presentation, eliminating any potential...

Global Technology Investments Project Proposal Infographics
Download the "Global Technology Investments Project Proposal Infographics" template for PowerPoint or Google Slides to get the most out of infographics. Whether you want to organize your business budget in a table or schematically analyze your sales over the past year, this set of infographic resources will be of great...
Silicon Valley Programmer Portfolio
Download the "Silicon Valley Programmer Portfolio" presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides. When a potential client or employer flips through the pages of your portfolio, they're not just looking at your work; they're trying to get a sense of who you are as a person. That's why it's crucial to...

Software Development Business Plan
People in the IT sector will be glad to know that Slidesgo has created a new template especially for them! Describe in these slides your software development business plan and try to convince possible partners of the viability of your idea. The palette is composed of cool colors, which are...

Data Analysis for Business
Download the Data Analysis for Business presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides and start impressing your audience with a creative and original design. Slidesgo templates like this one here offer the possibility to convey a concept, idea or topic in a clear, concise and visual way, by using different graphic...

Soft Palette Consulting
Download the "Soft Palette Consulting" presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides. Your business demands smart solutions, and this consulting toolkit template is just that! This versatile and ingenious toolkit will provide you with the essential tools you need to shape your strategies and make informed decisions. Whether you are devising...
- Page 1 of 37
Register for free and start editing online

- My presentations
Auth with social network:
Download presentation
We think you have liked this presentation. If you wish to download it, please recommend it to your friends in any social system. Share buttons are a little bit lower. Thank you!
Presentation is loading. Please wait.
Basic Introduction to Computers
Published by Siv Sundberg Modified over 6 years ago
Similar presentations
Presentation on theme: "Basic Introduction to Computers"— Presentation transcript:

Discovering Computers Fundamentals, 2012 Edition
Professor Michael J. Losacco CIS 1110 – Using Computers Introduction to Computers Chapter 1.

Chapter 1 Introduction to Computers

Your Interactive Guide to the Digital World Discovering Computers 2012.

Your Interactive Guide to the Digital World Discovering Computers Fundamentals, 2012 Edition.

Objectives Overview Explain why computer literacy is vital to success in today’s world Define the term, computer, and describe the relationship between.

Chp 1 – Introduction to Computers

Objectives Overview Differentiate among laptops, tablets, and servers Describe the purpose and uses of smartphones, digital cameras, portable media players,

Chp 1 – Introduction to Computer Section 1-3. A World of Computers What is computer literacy (digital literacy)? p. 4-5 Fig. 1-1 Next Current knowledge.

Discovering Computers Chapter 1 Discovering Computers & Microsoft Office 2010.

Lecture # 1 M.Sc / BS(CS)/ BS(I.T) DPT www. Shahid Rasul.com.

Introduction to Information Technology

DC Chp 1 Jeopardy Review Section 1Section 2Section 3Section 4Section

Introduction to Computers

Chapter 1 Introduction to Computers. Chapter 1 Objectives Recognize the importance of computer literacy Identify the components of a computer Discuss.
About project
© 2024 SlidePlayer.com Inc. All rights reserved.

Introduction to computer fundamentals
Nov 06, 2014
9.91k likes | 20.23k Views
Introduction to computer fundamentals. The Computer Defined. A computer is an electronic device that processes data, converting it into information that is useful to people. Analog and Digital Computer. Analog systems represent data as variable points along a continuous spectrum of values.
Share Presentation
- personal computer
- computer system
- personal computers
- computer perform tasks
- standard desktop personal computer

Presentation Transcript
The Computer Defined • A computer is an electronic device that processes data, converting it into information that is useful to people.
Analog and Digital Computer • Analog systems represent data as variable points along a continuous spectrum of values. • Early analog computers were mechanically devices, weighing several tons and using motors and gears to perform calculations.
Digital systems represents data as having one distinct value or another with no other possibilities. • Digital computers are so called because they work by the numbers.That is they break all types of information into tiny units and use numbers to represent those pieces of information.
Computers for individual users • Most computers are meant to be used by only one person at a time.Such computers are shared by several people,but only one user can work with the machine at any given moment.
Six primary types of computers • Desktop computers • Workstations • Notebook computers • Tablet computers • Handheld computers • Smart phones These systems are all examples of Personal Computers Personal computers are also called micro computers
Desktop Computers • The most common type of personal computer is the desktop computer…………….a PC that is designed to sit on a desk or table. • These computers you see in schools ,homes, offices. • These computers are used to communicate, produce music, edit photographs and videos, play sophisticated games and much more.
Workstations • A workstation is a speacialized,single user computer that typically has more power and features than a standard desktop personal computer. • These machines are popular among scientists,engineer who need a system with grater than average speed and the power to perform sophisticated tasks. • Workstations often have large high resolutions monitors and accelerated graphics handling capabilities.
Notebook Computer • Notebook computers as their name implies approximate the shape of an 8.5 by 11 inch notebook and easily fit inside a briefcase. • People frequently use these devices on their lap they are also called laptop computers.
Tablet PCs • The tablet PC is the newest development in portable , full featured computers. • Tablet PCs offer all the functionality of a notebook PC • They are lighter and can accept input from a special pen called a stylus or a digital pen.
Handheld PCs • Handheld personal computers are computing devices small enough to fit in your hands. • Personal digital assistant (PDA) is the type of handheld computers. • Size of PDA is no larger than small appointment book and is normally used for special applications • Displaying telephone numbers and addresses • Taking notes • Keeping track of dates or agendas
Smart phones • Some cellular phones double as miniature PCs • These phones offer advanced features ,that’s way they are called smart phones • These features can include • Web service • E-mail services • Special software such as personal organizers • Special hardware such as digital cameras or music players etc.
Computer for Organizations • Some computers handle the need of many users at the same time. • The largest organizational computers support thousands of individual users at the same time, from thousands of miles away.
Network servers • Today,most organization’s network are based on personal computer • Individual users have their own desktop computers which are connected to one or more centralized computers,called network servers. • Large organizations may have dozens or hundreds of individual servers working together at the heart of their network • When set up in such groups sometimes called clusters or server farms
In these large networks different group of servers may have different purposes • Handling printing tasks • Enabling internet communications • Accounting tasks • Word processing • Database management tasks
Mainframe computres • Mainframe computers are used in large organizations such as insurance companies and banks, where many people frequently need to use the same data. • In a traditional mainframe environment,each user access the mainframe’s resources through a device called a terminal
Types of terminal • A dumb terminal • An intelligent terminal
A dumb terminal • A dumb terminal does not process or store data • It is simply an input/output device that function as a window into a computer located somewhere else.
An intelligent terminal • An intelligent terminal can perform some processing operations but it usually does not have any storage.
The Parts of a Computer System • A complete computer system consists of four parts • Hardware • Software • Data • User
Hardware • The mechanical devices that make up the computer are called hardware • Hardware is any part of the computer you touch
Software • Software is a set of instructions that makes the computer perform tasks • The term program refers to any piece of software.
Data • Data consists of individual facts or pieces of information that by themselves may not make much sense to a person. • Tiny pieces of data in various form is actually the useful information.
Users • People are the computer operators, also known as users • No computer is totally autonomous
The information processing cycle • A computer converts data into information by performing various action. • During performing a mathematical operation on two numbers,then display the result.This is called the information processing cycle.
The information processing cycle has four parts • Input • Processing • Output • storage
Essential Computer hardware • A computer’s hardware devices fall into one of four categories • Processor • Memory • Input and Output • Storage
Processing devices • The processor is like the brain of the computer • It organizes and carries out instructions that come from either the user or software. • Processor usually consists of one or more speacialized chips called microprocessors. • Microprocessor is plugged into the computer’s motherboard • Motherboard is an example of circuit board • Many internal devices like sound card,videocard,disk controller are attached to the mother board.
Memory devices • In a computer, memory is one or more sets of chips that store data and program instructions either temporarily or permanently.
Random Access Memory • The most common type of memory is called random access memory(RAM) • RAM is like an electronic scratch pad inside the computer. • RAM holds data and program instructions while the CPU works with them. • When a program is launched it is loaded into and run from memory • RAM is also called read/write memory • RAM is made up of a set of chips mounted on a small circuit board. • RAM is also volatile ,meaning that it lost its contents when computer is shut off.
Read Only Memory • Unlike RAM ,read only memory (ROM) permanently stores its data, even when the computer is off. • RAM is called non volatile memory because it never lost its contents • ROM holds instructions that the computer needs to operate.
Input and Output devices • Input devices accept data and instructions from the user or from another computer • Out put devices return processed data to the user or to another system. • The most common input device is the keyboard,which accept letters,numbers and commands from the user. • Another type is mouse
Examples of input devices • The trackball and touchpad • The joystick • A scanner • A digital Camera • A microphone
The function of an output device is to present processed data to the user • The most common output devices are monitor and the printer
Storage Devices • The purpose of storage is to hold data permanently ,even when the computer is turned off. • Storage as an electronic file cabinet and RAM as an electronic worktable. • When you work with a program or set of data,the computer locates it in the file cabinet and puts a copy on the table.
What is storage and memory • There are three major distinctions between storage and memory • There is more room in storage than in memory • Contents are retained in storage but not in memory • Storage devices operate much slower than memory chips
Two types of storage • Magnetic storage • Optical storage
Magnetic storage • There are many types of computer storage but the most common is magnetic disk. • A disk is round, flat object that spins around its center.
Optical storage • Every computer sold today includes at least one form of optical storage • Devices that use lasers to read data from or write data to the reflective surface of an optical disc • The CD-ROM DRIVE is the most common type of optical storage device • An increasingly popular data storage technology is the digital video disc (DVD)
- More by User

Computer Fundamentals
Computer Fundamentals. Types Of Memories. Introduction.
444 views • 20 slides

Introduction to Computer
Introduction to Computer . Waqas Ali Sahito Lecturer Department of Computer Science. Subject Distribution. Theory 100 Marks Paper marks = 75 Sessional Marks = 25 Practical 50 Marks Objective = 10 Viva = 20 Sessional Marks = 20 Sessional Marks.
730 views • 41 slides

By Kiramat Rahman Department of Computer & Software Technology. Introduction to Computer. Input / Output (I/O) devices Commonly used input devices Commonly used output devices Other concepts related to I/O devices. Outline. Provide means of communication between a computer
959 views • 61 slides

INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER
INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER. EVOLUTION OF THE COMPUTER. EVOLUTION OF THE COMPUTER. The history and evolution of computer are divided into two eras : before 1940 after 1940. BEFORE 1940. In the beginning, human do calculation by fingers, stones, small woods etc.
587 views • 8 slides

Introduction to computer
Introduction to computer. Submitted by : aashish.c ashish.m Abhijeet.g Ankit.j abhay.j . CONTENT. WHAT IS COMPUTER? WHY COMPUTER? COMPUTER COMPONENT DATA & INFORMATION
879 views • 32 slides

INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER. Lecture #15 ARRAYS. By Shahid Naseem (Lecturer). ARRAYS DEFINITION. An array is a sequence of objects of same data type. The objects in an array are also called “elements of array”.
368 views • 16 slides

INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER. Lecture #9 OPERATING SYSTEM. By Shahid Naseem (Lecturer). LECTURE OUTLINES. DATA. A collection of raw (unprepared or unprocessed) facts ( things, people, objects, events) and figures, collected for a specific purpose is called data.
393 views • 19 slides

Computer Fundamentals. MSCH 233 Lecture 1. What is a computer?. A computer is an electronic machine which can accept data in a certain form, process the data and give the results of the process on a specific format as information. Where can computers be found and what are they used for ?.
576 views • 11 slides
Computer Fundamentals. Multimedia MSCH 233 Lecture 10. Who Use Multimedia Applications:. Teachers: To make video projects or to teach subjects Companies: To make Business Presentations Museums Banks Web designers Singers Movie maker. Etc. Types of multimedia. Audio Graphics Video.
302 views • 7 slides

Introduction to 7 Fundamentals
Introduction to 7 Fundamentals. PROSPECTING APPOINTMENT SETTING PRESENTATION OVERCOMING OBJECTIONS CLOSING RECRUITING & GETTING REFERRALS GETTING A LIST & GET NEW ASSOCIATE OFF TO FAST START. WHAT, WHY, HOW. Our Training System. The 7 Fundamentals Classes – 9 Weeks Total
902 views • 38 slides

Chapter-1. Computer Fundamentals. By: Mr. Birbal Jat PGT-Computer Sc . Kendriya Vidyalaya No 3 Jaipur. COMPUTER MEANS. C : Commonly O : Operator M : Machine P: Particular U: User T : Trade E : Education R: Research. The First in Computer World.
2.53k views • 35 slides

Computer Fundamentals. Input. Processing. Output. A Computer Is a System. Data is entered into the computer. The data is processed by adding, subtracting, and sorting. Becomes useful information. Input. Processing. Output. Example. Data for student registration.
1.32k views • 18 slides

Computer Science Fundamentals Course Introduction
Computer Science Fundamentals Course Introduction. How to learn stuff from Mr. Kramer. Class Flow. Lecture time I talk, you listen I demonstrate something raise hand for questions Open time Do the work I give help each other understand I’m wandering – raise hand or call me for help
383 views • 15 slides
Computer Fundamentals. MSCH 233 Lecture 7. Magnetic Drives. Types of Magnetic Drives: Floppy drive Hard disk Removable hard drive Tape drive Pocket-sized drive Microdrive. Floppy drive. Uses a high density floppy disk The floppy disk can store 1.44 MB of data It’s called drive A.
602 views • 17 slides

Computer Fundamentals. Northern College Diploma Philip Bird. Processor Architecture. Virtually every computer that has been built shares the same common layout. Von Neumann – programs and data both exist in the computers memory.
295 views • 9 slides

Computer Fundamentals. MDCS 134 Lecture 1. What is a computer?. A computer is an electronic machine which can accept data in a certain form, process the data and give the results of the process on a specific format as information. Where can computers be found and what are they used for ?.

Computer Fundamentals is not only useful topic for students it is also a must learn topic for all students. After the invention of computers life become more flexible for all human being. There are many computer languages for students to learn but before that they should learn all the simple Basic computer knowledge questions and answers from Mydearstudent website. Basic computer knowledge of anybody is a measure for today's job oppurtunities. For more details go through the website http://www.mydearstudent.com/basic-computers
299 views • 8 slides

14. Computer Fundamentals. Advanced Automotive Electricity and Electronics James D. Halderman. FIGURE 14.1 All computer systems perform four basic functions: input, processing, storage, and output.
404 views • 15 slides

COMPUTER FUNDAMENTALS
COMPUTER FUNDAMENTALS. Instructor: Fatima Naseem Lecture # 02 [email protected] http://web.uettaxila.edu.pk/CMS/AUT2010/cpCFbs/index.asp. Chapter 1B. Looking Inside the Computer System. Overview. Parts of Computer System > Hardware > Software
3.85k views • 58 slides

71. COMPUTER FUNDAMENTALS. Figure 71-1 All computer systems perform four basic functions: input, processing, storage, and output. Figure 71-2 A potentiometer uses a movable contact to vary resistance and send an analog voltage right to the PCM.
313 views • 14 slides

COMPUTER FUNDAMENTALS. Instructor: Fatima Naseem Lecture # 01 [email protected] http://web.uettaxila.edu.pk/CMS/AUT2010/cpCFbs/index.asp. Course Book. “Introduction to Computers” by Peter Norton, 6th Edition. Contact. Fatima Naseem Room # 17, CED.
950 views • 45 slides
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

Download Free PDF
lesson 1-Introduction to computers.pptx

Related papers
There are a lot of terms used to describe computers. To put it in simple words a computer can be defined as an electronic device that processes instructions and produces an output to the user. To unveil the secret behind this process, understanding of individual components is important. Starting with the case, we'll discuss the role and functionalities of the various peripherals and hardware which are integral parts of the computer. What is a Computer? A machine that can be programmed to : Receive information. Process the information according to a set of suitable instructions. Display desired result information. A computer can also be used to store information whenever required It is a device capable of performing arithmetic and logical operations Computer-The Framework Types of computers Analog-An analog computer represents data as physical quantities and operates on the data by manipulating the quantities Digital-A computer that stores data in terms of digits (numbers) and proceeds in discrete steps from one state to the next Hybrid-Hybrid computers are made by combining features of analog computers and digital computers
Zenodo, 2018
Computer, any of a class of devices capable of solving problems by processing information in discrete form. It operates on data, including magnitudes, letters, and symbols, that are expressed in binary code — i.e., using only the two digits 0 and 1. By counting, comparing, and manipulating these digits or their combinations according to a set of instructions held in its memory, a digital computer can perform such tasks as to control industrial processes and regulate the operations of machines; analyze and organize vast amounts of business data; and simulate the behaviour of dynamic systems (e.g., global weather patterns and chemical reactions) in scientific research. A typical computer system has four basic functional elements : (1) Input-output equipment, (2) Main memory, (3) Control unit, and (4) Arithmetic-logic unit.
Ken Trotman Publishing, 2024
This volume follows our critically acclaimed Vilnius 1812 - Ghosts of Napoleon's Grande Armée through their artefacts. Few campaigns in the history of warfare have been impacted by poor logistics, weather and the resulting attrition as much as the ill-fated invasion of Russia by Emperor Napoleon in 1812. His troops and their horses succumbed to extremes of heat and cold, incessant marching, illnesses, warfare at close-quarters and brutal guerrilla tactics. They were physically worn down by lack of nutrition, medical care, and finally psychological trauma. This is their story from the data and artefacts found. It explores areas that are rarely covered by histories of the campaign. Napoleon collected an army of well over half a million men with most of his veterans involved in the Peninsular War. The exact numbers are still impossible to quantify with certainty. The estimates range from 450,000 to 720,000. Chapter 1 looks at the structure and nationality of the Grande Armée. The French lost 13 Eagles captured and 5 burnt. It is uncertain as to the number of French flags that were burnt on Napoleon’s orders at the Berezina but at least 33 eagles survived. The flags were replaced for the 1813 campaign. The Bavarians and Saxons lost the most flags in Russia. Interestingly, the large number of Polish flags and standards in Russian hands were removed from Poland to Razan Cathedral in St Petersburg after the Polish-Russian War of 1830-31 rather than when captured in 1812. [Chapter 2] The nationality and branch of service whether infantry, cavalry or artillery has been grouped together into separate chapters so the proportion and attrition rates can be appreciated. The French only contributed a third of the Army. The majority was concentrated in the Army Headquarters [Chapter 3], the Imperial Guard [Chapter 4-6], French 1er-4e Corps [Chapter 7-8], French 1er-3e Cavalry Corps [Chapter 9], and the French Artillery [Chapter 10]. The Wurttemberg, Swiss, Italian and Bavarian Cavalry contingents of the French 2e-4e Corps are detailed in Chapter 11. The minor foreign contingents were from Illyria, Croatia, Portugal, Spain and the Vistula Legion [Chapter 12]. The French allies provided complete Corps from Bavaria (6e Corps), Polish (5e Corps), Saxony (7e Corps), and Westphalia (8e Corps) [Chapter 13-14]. The second line troops of 9e (Victor) Corps [Chapter 15] were destroyed in a few weeks from when they joined the remnants of the Grande Armée at the Berezina. The Northern flank of 10e (MacDonald) Corps contained the majority of the reluctant allied division of the Prussians [Chapter 16]. Few of the third line troops of 11e (Augereau) Corps entered Russia [Chapter 17]. The Austrian Auxiliary did not penetrate deeply into Russian [Chapter 18]. Chapter 19 gives parallels from history for Agincourt (1415), Afghanistan (1842), the German invasion of Russia in Operation Barbarossa (1941) and the Falklands War (1982). Chapter 20 tells the stories and data upon the sad fate of the huge number of prisoners of war. Those captured would suffer murderous conditions at the hands of the Cossacks and Russian partisans. Chapter 21 attempts to bring together the data on the Corps and officer attrition. In just six months, the Grande Armée had been completely destroyed by strategic mistakes and complete logistic failure. The data has derived from many sources and is not consistent. The returns reproduced by Fabry’s (1903) Campagne de Russie 1812 was an immense undertaking but were not recorded on the same day. The earliest was 25 June and the latest was mid-August 1812. These were later reproduced by Digby Smith (1977 and 2002). The later returns for the December 1812-February 1813 in the main are derived from the two volumes by Frederic Reboul (1910 and 1913). The following have been excluded because they are rarely included in the returns for men under arms. 1. The numbers of officers and men that entered Russia excludes replacements, therefore attrition rates, especially among the men, were even higher. 2. In in a few occurrences, the number of men in hospital. 3. The engineers, sappers, pontoniers and train etc. have been excluded as the numbers are rarely or consistently available and underwent numerous re-organisations. 4. Where possible, the number for the artillerymen is included. Officer casualty tables were derived from Martinien (1899 and 1909) who compiled the battle casualties. Although not perfect data, it gives an insight into the severity of the actions. Martinien did not record deaths from disease. He recorded officer casualties for engagements and some officers have multiple entries.
Lo spazio dei possibili, scrive Pierre Bourdieu nelle Regole dell’arte, è uno spazio definito e continuamente ridefinito dal lavoro collettivo di scrittori e critici: «un insieme di cose “da fare”, “movimenti” da lanciare, riviste da fondare, avversari da combattere, prese di posizione affermate da “superare”». Questo libro presenta tredici saggi ispirati alla teoria e alla prassi del sociologo francese che nell’insieme delineano una nuova prospettiva sulla storia della letteratura italiana del Novecento e dei primi anni Duemila. Ogni capitolo contribuisce a comporre un quadro inedito e pionieristico delle relazioni e delle forze costitutive del campo letterario italiano focalizzandosi di volta in volta su un differente oggetto di studio: la traiettoria di un autore o un’autrice, l’organizzazione materiale e simbolica di riviste e blog letterari, la formazione e dissoluzione delle avanguardie, i rapporti di forza transnazionali, l’intervento dei letterati in altri campi artistici e le loro relazioni con il campo politico, i flussi dell’import-export letterario, la centralità della traduzione per la creazione di poetiche innovative, il ruolo cruciale dell’editoria come porta di accesso e consacrazione del mondo letterario. Anna Baldini, Michele Sisto, Teoria dei campi e storia letteraria. Sviluppi della ricerca in Italia e all’estero Anna Baldini, «Alleati e nemici» dell’avanguardia fiorentina. Le riviste come strumenti di lotta Anna Boschetti, Il Futurismo dall’Italia all’Europa. Pratiche e rappresentazioni dell’avanguardia Fabio Andreazza, La conversione di Pirandello al cinema. Campo letterario e campo cinematografico Rosario Gennaro, Il doppio legame di Massimo Bontempelli. Traduzione e legittimazione letteraria tra Parigi e il fascismo Daniela La Penna, Alberto Carocci fra «Solaria» e «La Riforma letteraria». Habitus e embeddedness nel campo letterario fiorentino Flavia Di Battista, L’ermetismo fiorentino e i suoi “ismi”. Traiettoria di un’avanguardia Cecilia Benaglia, Carlo Emilio Gadda prima e dopo il 1945. Guerra di Liberazione e apertura dei possibili letterari Riccardo Bonavita, La traiettoria di Franco Fortini da Éluard a Brecht. Tradurre per creare una nuova posizione Salvatore Spampinato, L’età dello straniamento, da Pasolini alla Neoavanguardia. Appropriazioni di Brecht nel sottocampo della poesia Gisèle Sapiro, Le traduzioni di Elsa Morante in Francia. Il ruolo delle case editrici nella produzione della World Literature Michele Sisto, Il web letterario italiano. Genesi e struttura di un sottocampo Luca Pareschi, L’editor e l’esordiente. La selezione di narrativa nel campo editoriale contemporaneo Barbara Julieta Bellini, Il romanzo francese in Italia. Tradurre l’extrême contemporain Bibliografia essenziale degli studi sul campo letterario italiano
Loading Preview
Sorry, preview is currently unavailable. You can download the paper by clicking the button above.
Inteligencia artificial para un futuro sostenible. Desafíos jurídicos y éticos, 2024
“Salamina di Cipro: il Foro di Granito”, Marmora. An International Journal for Archaeology, History and Archaeometry of Marbles and Stones 19 (2023), 87-102., 2024
BRICS Journal of Educational Research, 2024
Handbook of Translation Studies, 2010
Religious Studies and Theology, 2022
Academy of Strategic Management Journal, 2019
ILCEA, 2020
HAL (Le Centre pour la Communication Scientifique Directe), 2009
Hydrological Processes, 2020
WATERING THE NEIGHBOUR'S …
The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2020
Journal of Hydrologic Engineering, 2000
Investigaciones Sociales, 2017
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
151+ Computer Presentation Topics [Updated 2024]

For both professionals and fans, keeping up with the most recent developments and trends in the rapidly evolving field of technology is essential. One effective way to share and acquire knowledge is through computer presentations.
Whether you are a seasoned presenter or someone looking to enhance your tech presentation skills, choosing the right topics is key to delivering a compelling and informative session.
In this blog, we’ll explore various computer presentation topics, their relevance, and provide insights into tailoring presentations for different audiences and occasions.
How do you Tailor Topics According to Audience and Occasion?
Table of Contents
Tailoring topics according to the audience and occasion is a crucial aspect of delivering an effective and engaging presentation. Here are some strategies and considerations to help you customize your computer presentation topics based on your audience and the specific occasion:
- Know Your Audience
- Assess Knowledge Levels: Understand the expertise of your audience. Are they beginners, intermediate users, or experts in the field? This assessment will guide you in selecting the appropriate depth and complexity of your topics.
- Consider Backgrounds: Take into account the professional backgrounds, interests, and industries of your audience. Tailor your examples and case studies to resonate with their experiences.
- Identify Audience Needs and Goals:
- Address Pain Points: If possible, research or survey your audience to identify their challenges and pain points. Tailor your presentation to address these concerns, providing practical solutions and insights.
- Align with Goals: Understand the goals and objectives of your audience. Tailor your topics to align with their aspirations, whether it’s professional development, problem-solving, or staying updated on industry trends.
- Adapt to the Occasion:
- Event Type: Consider the type of event you are presenting at. Is it a conference, workshop, seminar, or a more informal gathering? The format and expectations of the event will influence your choice of topics.
- Time Constraints: Be mindful of the time allotted for your presentation. Tailor the scope and depth of your topics to fit within the designated time frame.
- Customize Content:
- Relevance to Industry: If your audience belongs to a specific industry, tailor your topics to address challenges and innovations relevant to that industry. Provide concrete examples and case studies that resonate with their professional experiences.
- Localize Examples: Consider the cultural context and geographic location of your audience. If possible, use examples and references that are familiar to them, making the content more relatable.
- Engage in Interactivity:
- Q&A Sessions: Plan for interactive sessions, allowing the audience to ask questions. This helps you gauge their interests and tailor your responses to address specific concerns.
- Polls and Surveys: Incorporate interactive elements such as polls or surveys to gather real-time feedback. Use the results to adjust your presentation on the fly if necessary.
- Provide Actionable Takeaways:
- Practical Applications: Tailor your topics to include practical applications and actionable takeaways. Ensure that your audience can apply the knowledge gained from your presentation in their professional or personal endeavors.
- Workshops and Demos: For hands-on sessions, tailor your topics to include workshops or live demonstrations. This enhances the learning experience and allows the audience to see practical implementations.
- Be Adaptable:
- Read the Room: Pay attention to the audience’s reactions during the presentation. Be adaptable and ready to adjust your approach based on their engagement levels and feedback.
- Flexibility in Content: Have backup content or supplementary materials that can be introduced based on audience interest or questions.
Software Development and Programming
- Trends in Programming Languages : A Comprehensive Overview
- Introduction to Python: Basics and Beyond
- Exploring the World of JavaScript Frameworks
- Best Practices in Software Development Methodologies
- The Evolution of Mobile App Development
- Low-Code Platforms: Revolutionizing Software Development
- The Impact of Microservices Architecture on Modern Applications
- DevOps Practices: Streamlining Development and Operations
- Code Review Techniques for Quality Assurance
- GUI vs. Command Line Interfaces: Pros and Cons
Emerging Technologies
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): An Introduction and Applications
- Machine Learning Algorithms: A Deep Dive
- The Role of Natural Language Processing (NLP) in AI
- Computer Vision: Applications and Challenges
- Internet of Things (IoT) and its Transformative Power
- Blockchain Technology: Beyond Cryptocurrencies
- Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) in Computing
- Edge Computing: Enhancing Network Performance
- Quantum Computing: A Glimpse into the Future
- 6G Technology: Enabling the Next Generation of Connectivity
Cybersecurity
- Cyber Threats: Types, Trends, and Prevention Strategies
- Ethical Hacking: Unveiling Security Vulnerabilities
- Biometric Security Systems: Enhancing Authentication
- Cryptography: Ensuring Secure Communication
- Security Measures for Computer Networks: A Practical Guide
- Privacy Concerns in the Digital Age: Safeguarding Information
- Incident Response Planning for Cybersecurity
- Cloud Security Best Practices
- Cybersecurity Awareness Training for Employees
- The Future of Cybersecurity: Emerging Challenges
Data Science and Big Data
- Introduction to Data Science: Concepts and Applications
- Data Analysis Techniques: From Descriptive to Predictive Analytics
- Big Data Technologies: Hadoop, Spark, and Beyond
- Data Warehousing: Storing and Retrieving Massive Datasets
- Data Visualization Tools : Making Sense of Complex Data
- Predictive Modeling in Business: Leveraging Data Insights
- Internet of Things (IoT) and Big Data Integration
- Real-Time Analytics: Turning Data into Actionable Insights
- Data Ethics: Navigating the Challenges of Responsible Data Use
- Data-driven Decision Making in Organizations
Computer Hardware and Networking
- Latest Advancements in Computer Hardware
- The Role of Graphics Processing Units (GPUs) in Modern Computing
- Networking Protocols: A Deep Dive into TCP/IP, UDP, and More
- Wireless Technologies: Wi-Fi 6 and Beyond
- Cloud Computing Models : IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS Explained
- Edge Computing vs. Cloud Computing: Choosing the Right Approach
- Green Computing: Sustainable Practices in IT
- Quantum Computing and its Potential Impact on Industry
- 5G Technology: Revolutionizing Mobile Communication
- Wearable Technology: Integrating Computing into Everyday Life
Artificial Intelligence (AI) Applications
- AI in Healthcare: Transforming Diagnosis and Treatment
- AI in Finance: Applications and Risk Management
- AI in Customer Service: Enhancing User Experience
- AI in Education: Personalized Learning and Assessment
- AI in Autonomous Vehicles: Navigating the Future
- AI in Agriculture: Precision Farming and Crop Monitoring
- AI in Cybersecurity: Detecting and Preventing Threats
- AI in Natural Language Processing (NLP) : Conversational Interfaces
- AI in Robotics: Innovations and Challenges
- AI in Retail: Personalized Shopping Experiences
Internet and Web Technologies
- Evolution of the Internet: From ARPANET to the Present
- Web Development Trends: Responsive Design and Progressive Web Apps
- Content Management Systems (CMS): Choosing the Right Platform
- E-commerce Platforms: Building Successful Online Stores
- Search Engine Optimization (SEO) Strategies for Web Visibility
- Cloud-based Web Hosting Solutions: Comparisons and Best Practices
- Web Accessibility: Designing Inclusive and User-Friendly Websites
- Social Media Integration: Enhancing Online Presence
- Web Security Best Practices: SSL, HTTPS, and Beyond
- The Future of the Internet: Trends and Predictions
Mobile Technologies
- Mobile Operating Systems: A Comparison of iOS and Android
- Mobile App Monetization Strategies: Ads, Subscriptions, and Freemium Models
- Cross-platform Mobile Development: Pros and Cons
- Mobile Payment Technologies: From NFC to Cryptocurrencies
- Mobile Health (mHealth) Applications: Improving Healthcare Access
- Location-based Services in Mobile Apps: Opportunities and Challenges
- Mobile Gaming Trends: Augmented Reality and Multiplayer Experiences
- The Impact of 5G on Mobile Applications
- Mobile App Testing: Ensuring Quality User Experiences
- Mobile Security: Protecting Devices and User Data
Human-Computer Interaction (HCI)
- User Experience (UX) Design Principles: Creating Intuitive Interfaces
- Usability Testing Methods: Evaluating the User-Friendliness of Products
- Interaction Design Patterns: Enhancing User Engagement
- Accessibility in Design: Designing for All Users
- Virtual Reality (VR) and User Experience: Design Considerations
- Gamification in User Interface Design: Enhancing Engagement
- Voice User Interface (VUI) Design: Building Natural Interactions
- Biometric User Authentication: Balancing Security and Convenience
- The Evolution of Graphical User Interfaces (GUIs)
- Wearable Technology Design: Integrating Fashion and Functionality

Cloud Computing
- Cloud Service Models: IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS Explained
- Cloud Deployment Models: Public, Private, and Hybrid Clouds
- Cloud Security Best Practices: Protecting Data in the Cloud
- Serverless Computing: Streamlining Application Development
- Cloud Computing in Business: Cost Savings and Scalability
- Cloud-Native Technologies: Containers and Orchestration
- Microservices Architecture in the Cloud: Breaking Down Monoliths
- Cloud Computing Trends: Edge Computing and Multi-cloud Strategies
- Cloud Migration Strategies: Moving Applications to the Cloud
- Cloud Computing in Healthcare: Enhancing Patient Care
Robotics and Automation
- Robotics in Manufacturing: Increasing Efficiency and Precision
- Autonomous Robots: Applications and Challenges
- Humanoid Robots: Advancements in AI-driven Robotics
- Robotic Process Automation (RPA): Streamlining Business Processes
- Drones in Industry: Surveillance, Delivery, and Beyond
- Surgical Robotics: Innovations in Medical Procedures
- Robotic Exoskeletons: Assisting Human Mobility
- Social Robots: Interacting with Humans in Various Settings
- Ethical Considerations in Robotics and AI
- The Future of Robotics: Trends and Predictions
Ethical Considerations in Technology
- Responsible AI: Ethical Considerations in Artificial Intelligence
- Data Privacy Laws: Navigating Compliance and Regulations
- Bias in Algorithms: Addressing and Mitigating Unintended Consequences
- Ethical Hacking: Balancing Security Testing and Privacy Concerns
- Technology and Mental Health: Addressing Digital Well-being
- Environmental Impact of Technology: Green Computing Practices
- Open Source Software: Community Collaboration and Ethical Licensing
- Technology Addiction: Understanding and Combating Dependencies
- Social Media Ethics: Privacy, Fake News, and Cyberbullying
- Ethical Considerations in Biometric Technologies
Future Trends in Technology
- The Future of Computing: Quantum Computing and Beyond
- Edge AI: Bringing Intelligence to the Edge of Networks
- Biocomputing: Merging Biology and Computing
- Neurotechnology: Brain-Computer Interfaces and Cognitive Enhancement
- Sustainable Technologies: Innovations in Green Computing
- 7G and Beyond: Envisioning the Next Generation of Connectivity
- Space Technology and Computing: Exploring the Final Frontier
- Biohacking and DIY Tech: A Look into Citizen Science
- Tech for Social Good: Using Technology to Address Global Challenges
- The Convergence of Technologies: AI, IoT, Blockchain, and More
Miscellaneous Topics
- Technology and Education: Transforming Learning Experiences
- Digital Transformation: Strategies for Modernizing Businesses
- Tech Startups: Navigating Challenges and Achieving Success
- Women in Technology: Empowering Diversity and Inclusion
- The History of Computing: Milestones and Innovations
- Tech and Art: Exploring the Intersection of Creativity and Technology
- Hackathons: Fostering Innovation in Tech Communities
- The Role of Technology in Disaster Management
- Exploring Careers in Technology: Opportunities and Challenges
Tips for Effective Computer Presentations
- Mastering the Art of Public Speaking in the Tech Industry
- Designing Engaging Visuals for Technical Presentations
- The Dos and Don’ts of Live Demonstrations in Tech Presentations
- Building a Compelling Narrative: Storytelling Techniques in Tech Talks
- Handling Q&A Sessions: Tips for Addressing Audience Questions
- Time Management in Tech Presentations: Balancing Content and Interaction
- Incorporating Humor in Technical Presentations: Dos and Don’ts
- Creating Interactive Workshops: Engaging Audiences in Hands-on Learning
- Leveraging Social Media for Tech Presentations: Tips for Promotion
- Continuous Learning in the Tech Industry: Strategies for Staying Informed
Case Studies and Real-World Applications
Real-world examples and case studies add practical relevance to computer presentations. Showcase successful projects, discuss challenges faced, and share lessons learned.
Analyzing the impact of technology in real-world scenarios provides valuable insights for the audience and encourages a deeper understanding of the subject matter.
Future Trends in Computer Presentation Topics
Predicting future trends in technology is both exciting and challenging. Presenters can offer insights into upcoming technological developments, anticipate challenges and opportunities, and encourage continuous learning in the rapidly evolving tech landscape.
Discussing the potential impact of technologies like 6G, augmented reality, or advancements in quantum computing sparks curiosity and keeps the audience abreast of the latest innovations.
In conclusion, computer presentations serve as powerful tools for knowledge sharing and skill development in the tech industry. Whether you’re presenting to novices or seasoned professionals, the choice of topics, presentation skills, and a thoughtful approach to ethical considerations can elevate the impact of your presentation.
As technology continues to evolve, staying informed and exploring diverse computer presentation topics will be instrumental in fostering a culture of continuous learning and innovation.
Embrace the dynamic nature of technology and embark on a journey of exploration and enlightenment through engaging computer presentations.
Related Posts

Step by Step Guide on The Best Way to Finance Car

The Best Way on How to Get Fund For Business to Grow it Efficiently
28 Free Technology PowerPoint Templates for Presentations from the Future
- Share on Facebook
- Share on Twitter
By Lyudmil Enchev
in Freebies
3 years ago
Viewed 282,420 times
Spread the word about this article:
If you’re amongst the science and technology teachers, students, or businesses in the field; we have something for you. We deep-dived to find the best free technology PowerPoint templates for your presentation, so today’s collection has 28 amazing designs to choose from.
The following selection has templates related to science, technology, cybersecurity, search engines, bitcoin, networking, programming, and engineering, so there’s something for everyone.
1. Computer Hardware Free Technology PowerPoint Template
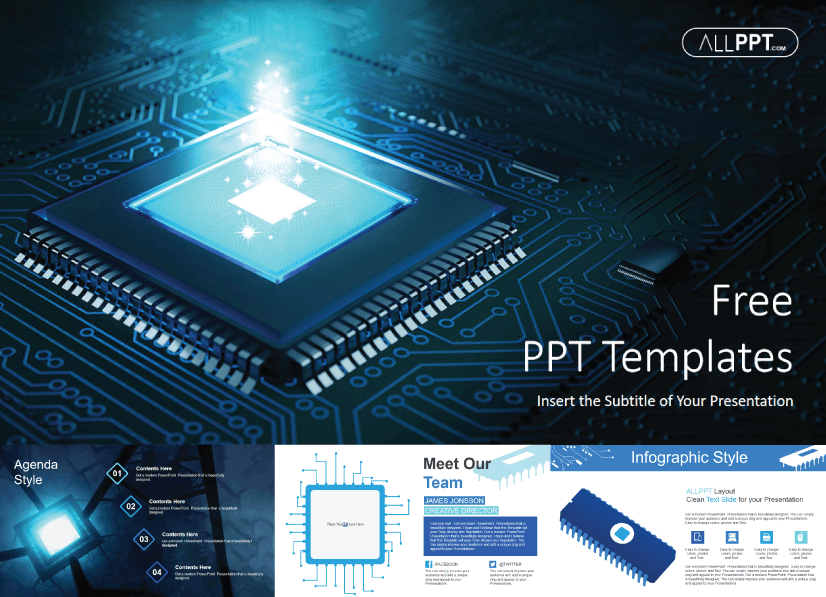
This template sports a cool design with a bright light of a microchip processor and a blue background. Ideal for explaining concepts such as semiconductors, databases, and central computer processors.
- Theme : Technology, Hardware
- Slides : 48
- Customization : Fully editable + 136 editable icons
- Graphics : Vector
- Aspect Ratio : 16:9
- License : Free for Personal and Commercial Use │ Do Not Redistribute Any Components of the Template
2. Space Science Free Technology Powerpoint Templates
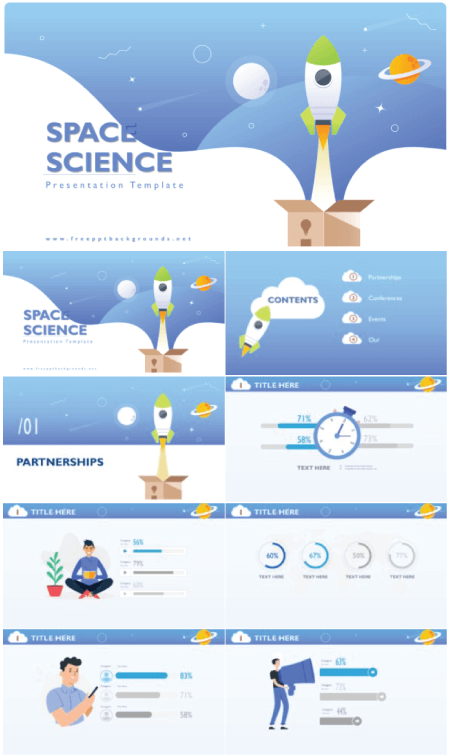
This free template has 3D spaceship graphics and blue background color. It’s great for presentations on astronomy.
- Theme : Technology, Cosmos
- Slides : 25
- Customization : Fully editable
- Resolution : 1920×1080
3. 5G Technology Speed Free Powerpoint Templates

Design with twinkling rays of geometric shapes is perfect for presentations on technology topics such as internet networking, intranet, and communication technology.
- Theme : Technology, Networking, 5G
- Customization : Editable
4. Start-Up Tech Corporation Free Powerpoint Template
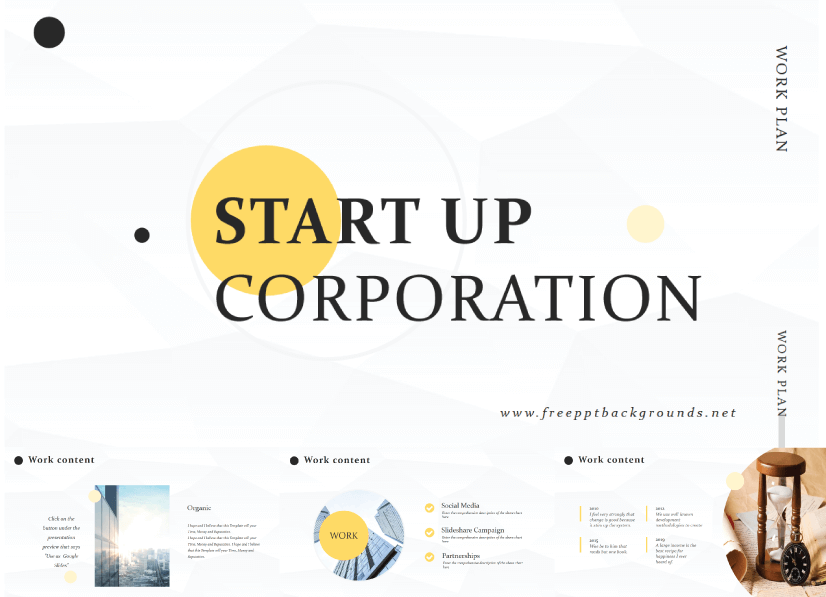
This free tech corporation template is great for presentations on tech business startups.
- Theme : Technology, Tech Business, Start-Up Companies
5. App Startup Free Powerpoint Technology Template
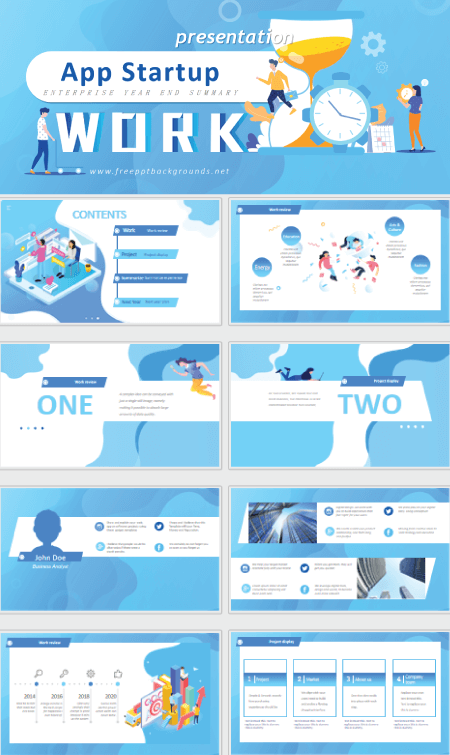
This design is great for presentations on communication, mobile technology, and other digital devices used for the PPT presentations.
- Theme : Technology, Apps, Software
6. Cloud Technology Free Powerpoint Template
A technology template with a clean and modern design for your presentations about cloud computing and other computing services.
- Theme : Cloud Technlogy
7. Artificial Intelligence High Technology Free PowerPoint Template
This template represents artificial intelligence as an illustration . It also includes related shapes to allow for a variety of expressions.
- Theme : Technology, Artificial Intelligence
8. Search Engine Optimization PowerPoint Template
The template is SEO-themed but you can adapt it to any presentation related to marketing and search engines.
- Theme : Technology, Marketing, SEO
9. Binary Code Free PowerPoint Template
The cool binary code design makes this template perfect for any presentation on computer science.
- Theme : Computer Science, Programming
10. Network Free Technology PowerPoint Template

Sporting design with crags and electric rays in many angles are representing networking around the globe, the template is suitable for presentations on communication, networking, technology, and crag wheels.
- Theme : Technology, Networking
11. Hexagonal Design Free PowerPoint Template

Here we have a free template with hexagons and icons pattern for techy content. Its dark background and bright blue color palette give a professional look.
- Theme : Technology
12. Technology Pixels Free PowerPoint Template

A technology-themed template for presentations on consulting, IT, software, and other related subjects. The pixel pattern is grouped by tones which you can change from the master slides.
13. Connections and Networking Free PowerPoint Template

This free Powerpoint template is perfect for a presentation about the internet, blockchain, machine learning, cybersecurity, or cloud computing.
14. Isometric Free Technology PowerPoint Template

Here we have an amazing isometric design and high-tech background with gradients. Ideal for subjects like cloud computing, SaaS development, servers, and networks, or cybersecurity.
- Theme : Networking, Programming
15. Free PowerPoint Template with Techy Contour Lines
This design has an abstract contour lines background in a dark green color. Ideal for subjects like geography, technology, video games, or even military affairs.
- Theme : Technology, Gaming

16. Marketing and Technology Free PowerPoint Template
The isometric design has illustrations on business, marketing, and technology topics that will make every slide stand out.
- Theme : Technology, Marketing
17. Purple Hexagons Free PowerPoint Template

For presentations related to scientific or technological topics, with professional hexagonal design.
- Theme : Technology, Science
18. Rockets Taking Off Free PowerPoint Template

Rockets taking off is a great metaphor for growing businesses. It’s also a symbol of progress and technology.
- Slides : 35
19. IOT Smart City Free PowerPoint Template
Smart City offers a futuristic design for subjects such as internet communication, smart city concepts, and tech innovation.
- Theme : Technology, Smart City
20. Cyber Security Free PowerPoint Template

The perfect template for presentations on cybersecurity, antivirus software, and other related topics.
- Theme : Technology, Cyber Security
21. BlockChain Free PowerPoint Templates
This template is a 3D rendering design of blockchain technology and you can use it for a variety of purposes.
Presentation Design Tips You Wish You Knew Earlier:
The shorter you keep the text, the better. In fact, some specialists suggest that you shouldn’t use more than 5-6 words per slide . And sometimes, a single word combined with a powerful visual is enough to nail the attention of the people sitting in front of you and make them listen to what you have to say.
22. BitCoin Themed Free PowerPoint Template

A very versatile template that includes 20 semi-transparent illustrations of different concepts: security, social networks, programming, bitcoin.
- Theme : Technology, Bitcoin
23. Technical Blueprint Free Technology PowerPoint Template

This template uses a blueprint style and a monospaced font to emulate the technical drawings used in construction and industry.
- Theme : Technology, Engineering
24. Blue Connections Free PowerPoint Template

The design of this free template fits social media, connection, internet, cloud computing, and science-related topics.
- Theme : Technology, Social Media
25. Cute Robots Free PowerPoint Template

Here we have a colorful design with beautifully illustrated robots for presentation on technology, science, and physics.
- Theme : Technology, Physics
26. Green Circuit Free PowerPoint Template

This is a free template with futuristic vibes that you can use for your tech presentations both in PowerPoint and Google Slides.
27. Data Particles Free Technology PowerPoint Template

The design with particle lines gives it a modern and slightly technological look.
28. Science Hexagons Free Technology PowerPoint Template

The background gradients highlight the white text, and the hexagons give it a techie style.
Final Words
That’s it. Today’s collection covered the best free technology PowerPoint templates that you can download and adapt to your presentations related to science, technology, programming, engineering, and physics. Now all you need to do is open your PowerPoint and make the most amazing presentation your viewers have ever seen.
For more freebies, you can check the Best Free Powerpoint Templates of 2022 or see these related articles:
- 36 Free Food PowerPoint Templates For Delicious Presentations
- 31 Free Modern Powerpoint Templates for Your Presentation
- 25 Free Education PowerPoint Templates For Lessons, Thesis, and Online Lectures

Add some character to your visuals
Cartoon Characters, Design Bundles, Illustrations, Backgrounds and more...
Like us on Facebook
Subscribe to our newsletter
Be the first to know what’s new in the world of graphic design and illustrations.
- [email protected]
Browse High Quality Vector Graphics
E.g.: businessman, lion, girl…
Related Articles
81 impressive free presentation backgrounds for outstanding presentations, 16 free vector infographic design templates: on different themes in different styles, the best free photoshop brushes, textures and patterns on the web, 100+ free food vector graphics and characters for tasty projects, free clipart for teachers: top 12 sources to find what you need, 500+ free and paid powerpoint infographic templates:, enjoyed this article.
Don’t forget to share!
- Comments (0)

Lyudmil Enchev
Lyudmil is an avid movie fan which influences his passion for video editing. You will often see him making animations and video tutorials for GraphicMama. Lyudmil is also passionate for photography, video making, and writing scripts.

Thousands of vector graphics for your projects.
Hey! You made it all the way to the bottom!
Here are some other articles we think you may like:

60 Free Medical Background Resources with Modern Design
by Al Boicheva
![computer information presentation 100+ PowerPoint Graphics For Better Presentations [Free PPT]](https://i.graphicmama.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2020/08/10085624/Free-PowerPoint-Graphics-Free-PPT.png)
100+ Free PowerPoint Graphics For Better Presentations [Free PPT]
by Lyudmil Enchev

Free Vectors
200 of the best free logo templates to grab now, looking for design bundles or cartoon characters.
A source of high-quality vector graphics offering a huge variety of premade character designs, graphic design bundles, Adobe Character Animator puppets, and more.

COMMENTS
Download ppt "Chapter 1: Introduction to Computer". Computer A computer is an electronic device, operating under the control of instructions stored in its own memory that can accept data (input), process the data according to specified rules, produce information (output), and store the information for future use.
Download the Videogames Lesson! presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides. The education sector constantly demands dynamic and effective ways to present information. This template is created with that very purpose in mind. Offering the best resources, it allows educators or students to efficiently manage their presentations and engage audiences.
37 Basic Introduction to Computers. Chapter 1 Complete. Download ppt "Basic Introduction to Computers". Objectives Overview Explain why computer literacy is vital to success in today's world Define the term, computer, and describe the relationship between data and information Describe the five components of a computer Discuss the advantages ...
Computer Basics 1. Computer Basic 1 includes two lessons: Lesson 1: Introduction to Computers Lesson 2: Common Computer Terminology. Lesson 1 - Introduction to Computer Objectives. After completing lesson 1, you will be able to: Describe the importance of computers in today's world. Download Presentation.
Presentation Transcript. Introduction to computer fundamentals. The Computer Defined • A computer is an electronic device that processes data, converting it into information that is useful to people. Analog and Digital Computer • Analog systems represent data as variable points along a continuous spectrum of values.
Computer, any of a class of devices capable of solving problems by processing information in discrete form. It operates on data, including magnitudes, letters, and symbols, that are expressed in binary code — i.e., using only the two digits 0 and 1. By counting, comparing, and manipulating these digits or their combinations according to a set ...
computer, device for processing, storing, and displaying information. Computer once meant a person who did computations, but now the term almost universally refers to automated electronic machinery. The first section of this article focuses on modern digital electronic computers and their design, constituent parts, and applications.
151+ Computer Presentation Topics [Updated 2024] General / By StatAnalytica / 4th January 2024. For both professionals and fans, keeping up with the most recent developments and trends in the rapidly evolving field of technology is essential. One effective way to share and acquire knowledge is through computer presentations.
The following selection has templates related to science, technology, cybersecurity, search engines, bitcoin, networking, programming, and engineering, so there's something for everyone. 1. Computer Hardware Free Technology PowerPoint Template. This template sports a cool design with a bright light of a microchip processor and a blue background.
19. Scrum Process PowerPoint Presentation Template - Illustrate the Future of Software Development: Scrum using this Premium Information Technology PowerPoint Template. The Scrum Process PPT Presentation Template is a great way to present your company's unique process for delivering products and services.