How to Write a Thesis Statement For a Rhetorical Analysis
Table of contents
- 1 Rhetorical Analysis Thesis Statement
- 2.1 Doing Proper Analysis
- 2.2 Find Concrete Examples
- 2.3 Determine the Author’s Purpose
- 2.4 The Effect on the Audience
- 2.5 Take a Position
- 3.1 Do’s
- 3.2 Don’ts
- 4.1 Elements of a STRONG Thesis
- 4.2 Elements of a WEAK Thesis
- 5 Formula for Thesis Statement
Because of its convoluted name, rhetorical analysis thesis statements might sound like a daunting thing to write. However, it is not that difficult to create as long as you can acknowledge all of its different components and form a proper thesis sentence. In this article, we will cover everything you need to construct a compelling rhetorical analysis statement for your essay. So let’s begin!

Rhetorical Analysis Thesis Statement
Rhetorical analysis thesis statements present a main argument about how a particular text (usually non-fiction) uses rhetorical devices to achieve a desired purpose. They can generally be found in rhetorical analysis essays or academic research papers used in college classes such as English, Political Science, or History. It is best to place it at the end of your introduction paragraph.
A thesis statement for rhetorical analysis has three main objectives:
- Give the name of the text being analyzed, as well as the author and genre
- Take note of the different rhetoric being used by said author
- Determine the overall effect these strategies have on the reader
Rhetorical analysis thesis statements are necessary for keeping you focused while you are writing your essay. It also benefits the reader because they can read it in the introduction and know exactly what the paper will be about.
Now we will cover the best practices for creating a proper argument needed for your thesis.
Tips to Compose a Thesis Statement for Rhetorical Analysis

Doing Proper Analysis
Before you begin writing, it is important to remember that it must be defensible. This means that it must be proven with evidence and you should not simply use your own opinion. It might be a good idea to write a rhetorical analysis essay outline to jot down ideas and sources that you will use in your paper. A thorough analysis should be done for your thesis. While you are reading the passage, take note of the rhetorical devices and strategies that the author uses. What specific choice did the author decide on in terms of rhetoric? You can include the names of the devices such as juxtaposition, alliteration, etc.
Find Concrete Examples
Once you have determined the different techniques utilized by the author, your next step is to find solid cases of those techniques within the text. This will serve as evidence for your thesis. The more evidence you can find to back up your claim, the better. While doing research, take note of how the example illustrates the rhetorical technique you are trying to prove.
Determine the Author’s Purpose
After you have found sufficient evidence, start thinking about WHY the author decided to use them in the first place. Why did the author make these particular choices? What point was she trying to make?
The Effect on the Audience
One of the goals of the rhetorical thesis is to take apart an essay or literary work and break it down into its smaller components. You then determine how the parts come together to create a particular effect for the reader. What is going through your mind? Was the author trying to persuade you of something? Or was the purpose only to entertain?
Take a Position
Before you start a rhetorical analysis essay, you must take a firm position if you want your thesis statement to be effective. Of course, the reason why we even read literary works in the first place is because they can be interpreted in a myriad of ways. There might be several rhetorical methods the author uses in their work, but your job is to focus on ONE of them. You cannot convince the reader of your position if your ideas are all over the place. Choose what you think is the strongest point and stick with it.

Do’s and Don’ts when Writing a Thesis Statement
Use this list as a guide when you begin to write. This way, you can remain on task and create a thesis sentence that is coherent and clear to the reader.
- Make it very clear which techniques you will be analyzing and their effectiveness within the text.
- Take a firm position on the issue you will be discussing. Resist the urge to bloat your thesis statement with different rhetorical devices. Choosing one will keep you organized while you are presenting your argument.
- Keep in mind that this will serve as a guide to the reader on what you will be covering in your essay. Always keep the reader in mind while you are writing so that they do not get lost. This is why having a specific focus is so important.
- Try to use your credentials, reputation, or personal stories to establish yourself as an expert on the topic.
Don’ts
- This is not an opinion piece. Avoid using phrases like “I believe” or “I think”. How you personally feel about the topic being discussed is irrelevant. By the time you write your thesis statement, you should have ample proof to validate your position.
- Do not write a simple, flat statement about the topic. This type of thesis statement has a certain structure that you can find below.
- Don’t make your piece either too vague or too convoluted. Keep the reader in mind when you are stating your argument. Your words should be something they can clearly follow and understand.

Examples of Strong and Weak Rhetorical Analysis Thesis
Now that we have determined what goes into creating a thesis statement for a rhetorical essay, we can now discuss what is needed to write the argument itself.
Elements of a STRONG Thesis
A strong rhetorical essay thesis utilizes appeals. Appeals are tools that the author uses to earn the approval of the reader by playing to common experiences that we all have. The three types of appeals are pathos, ethos, and logos.
The pathos appeal uses language to conjure strong emotions in the reader like sympathy, anger, compassion, or sadness.
The ethos appeal uses the writer’s character and credibility to convince the reader that they are an expert on the topic being discussed.
Finally, the logos appeal calls to the reader’s logic and reasoning. You can employ evidence, statistics, and testimonies from other experts in the field to convince the reader of your position.
Utilizing all three types of appeals will guarantee that you create a rock-solid argument for your essay.
Elements of a WEAK Thesis
This should go without saying, but avoid plagiarism when writing a thesis for rhetorical analysis and be sure to properly cite your source.
You should also avoid bias when writing your rhetorical analysis essay thesis. The purpose of this type of essay writing is to be objective and to present evidence to convey the most logical argument possible. Lastly, you should try your best not to merely summarize a thesis for a rhetorical analysis essay . If you want to establish yourself as an expert on the topic, use facts and reasoning to your advantage to arrive at a believable conclusion.

Formula for Thesis Statement
Use the template below to help you get started and to give you ideas on how to proceed. Remember to place it after your introduction.
In his/her (ADJECTIVE) speech/article/letter, (WRITER’S NAME) uses (RHET. TECHNIQUE) and (RHET. TECHNIQUE) to persuade (AUDIENCE or READER) to (DESCRIBE THE AUTHOR’S PURPOSE)
Readers also enjoyed

WHY WAIT? PLACE AN ORDER RIGHT NOW!
Just fill out the form, press the button, and have no worries!
We use cookies to give you the best experience possible. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy.
- College Essay
- Argumentative Essay
- Expository Essay
- Narrative Essay
- Descriptive Essay
- Scholarship Essay
- Admission Essay
- Reflective Essay
- Nursing Essay
- Economics Essay
Assignments
- Term Papers
- Research Papers
- Case Studies
- Dissertation
- Presentation
- Editing Help
- Cheap Essay Writing
- How to Order
Rhetorical Analysis Essay
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example - Free Samples
11 min read

People also read
Rhetorical Analysis Essay - A Complete Guide With Examples
320+ Best Rhetorical Analysis Essay Topics
Crafting an Effective Rhetorical Analysis Essay Outline - Free Samples!
Ethos, Pathos, and Logos - Structure, Usage & Examples
Many students find themselves confused by rhetorical strategies, which often leads to essays that miss the mark. The good news is there's an easy fix: using great examples.
By looking at high-quality rhetorical analysis essay examples, you can learn what works and improve your own writing.
That’s why we’ve compiled some top-notch rhetorical analysis essay examples to boost your understanding of how to write a compelling and well-structured essay.
So, let’s explore these examples!
- 1. Good Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example
- 2. Rhetorical Analysis Essay Examples for Students
- 3. Writing a Visual Rhetorical Analysis Essay with Example
- 4. Rhetorical Analysis Essay Writing Tips
Good Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example
The step-by-step writing process of a rhetorical analysis essay is far more complicated than ordinary academic essays. This essay type critically analyzes the rhetorical means used to persuade the audience and their efficiency.
The example provided below is the best rhetorical analysis essay example:
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Sample
In this essay type, the author uses rhetorical approaches such as ethos, pathos, and logos . These approaches are then studied and analyzed deeply by the essay writers to weigh their effectiveness in delivering the message.
Let’s take a look at the following example to get a better idea;
The outline and structure of a rhetorical analysis essay are important.
According to the essay outline, the essay is divided into three sections:
- Introduction
- Ethos
- Logos
A rhetorical analysis essay outline follows a traditional essay outline. Here’s how each part is typically written:
Rhetorical Analysis Introduction Example
An introduction for a rhetorical essay is drafted by:
- Stating an opening sentence known as the hook . This catchy sentence is prepared to grab the audience’s attention to the paper.
- After the opening sentence, the background information of the author and the original text are provided.
For example, a rhetorical analysis essay written by Lee Jennings on“The Right Stuff” by David Suzuki. Lee started the essay by providing the introduction in the following way:
Analysis of the Example:
- Suzuki stresses the importance of high school education. He prepares his readers for a proposal to make that education as valuable as possible.
- A rhetorical analysis can show how successful Suzuki was in using logos, pathos, and ethos. He had a strong ethos because of his reputation.
- He also used pathos to appeal to parents and educators. However, his use of logos could have been more successful.
- Here Jennings stated the background information about the text and highlighted the rhetorical techniques used and their effectiveness.
Thesis Statement Example for Rhetorical Analysis Essay
A thesis statement of a rhetorical analysis essay is the writer’s stance on the original text. It is the argument that a writer holds and proves it using the evidence from the original text.
A thesis statement for a rhetorical essay is written by analyzing the following elements of the original text:
- Diction - It refers to the author’s choice of words and the tone
- Imagery - The visual descriptive language that the author used in the content.
- Simile - The comparison of things and ideas
In Jennings's analysis of “The Right Stuff,” the thesis statement was:
Example For Rhetorical Analysis Thesis Statement
Rhetorical Analysis Body Paragraph Example
In the body paragraphs of your rhetorical analysis essay, you dissect the author's work. Each body paragraph opens with a topic sentence that shows the main point of that paragraph.
This is where you present the main analysis of their rhetorical techniques, and provide evidence to support your analysis.
Let's look at an example that analyzes the use of ethos in David Suzuki's essay:
Rhetorical Analysis Conclusion Example
All the body paragraphs lead the audience towards the essay’s conclusion .
Here is the conclusion for rhetorical analysis essay example by Jennings:
In the conclusion section, Jennings summarized the major points and restated the thesis statement to prove them.
Rhetorical Essay Example For The Right Stuff by David Suzuki
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Examples for Students
Writing a rhetorical analysis for AP Language and Composition courses can be challenging. Here are some AP English language rhetorical analysis essay examples:
AP Language Rhetorical Essay Sample
AP Rhetorical Analysis Essay Template
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example AP Lang
AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example
Here are a few more rhetorical analysis essay examples pdfs to help students:
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example Ethos, Pathos, Logos
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example Outline
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example College
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example APA Format
Compare and Contrast Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example
Comparative Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example
How to Start Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example High School
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example APA Sample
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example Of a Song
Florence Kelley Speech Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example MLA
Writing a Visual Rhetorical Analysis Essay with Example
The visual rhetorical analysis essay determines how pictures and images communicate messages and persuade the audience.
Usually, visual rhetorical analysis papers are written for advertisements. This is because they use strong images to convince the audience to behave in a certain way.
To draft a perfect visual rhetorical analysis essay, follow the tips below:
- Analyze the advertisement deeply and note every minor detail.
- Notice objects and colors used in the image to gather every detail.
- Determine the importance of the colors and objects and analyze why the advertiser chose the particular picture.
- See what you feel about the image.
- Consider the objective of the image. Identify the message that the image is portraying.
- Identify the targeted audience and how they respond to the picture.
An example is provided below to give students a better idea of the concept.
Simplicity Breeds Clarity Visual Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Writing Tips
Follow the tips provided below to make your rhetorical writing compelling.
- Choose an engaging topic for your essay. The rhetorical analysis essay topic should be engaging to grab the reader’s attention.
- Thoroughly read the original text.
- Identify the SOAPSTone. From the text, determine the speaker, occasions, audience, purpose, subject, and tone.
- Develop a thesis statement to state your claim over the text.
- Draft a rhetorical analysis essay outline.
- Write an engaging essay introduction by giving a hook statement and background information. At the end of the introductory paragraph, state the thesis statement.
- The body paragraphs of the rhetorical essay should have a topic sentence. Also, in the paragraph, a thorough analysis should be presented.
- For writing a satisfactory rhetorical essay conclusion, restate the thesis statement and summarize the main points.
- Proofread your essay to check for mistakes in the content. Make your edits before submitting the draft.
All in all,
Following the tips and the correct writing procedure will guarantee success in your academics.
We’ve provided plenty of examples of a rhetorical analysis essay. But if you’re still struggling to draft a great rhetorical analysis essay, it’s a good idea to seek professional help.
MyPerfectWords.com can assist with all your academic assignments. Our analytical essay writing service is ready to help if you’re confused about your writing assignments or struggling to meet a deadline.
Feel free to place your ' Just do my essay ' request and hire our serivces today at the most reasonable prices.

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Nova Allison is a Digital Content Strategist with over eight years of experience. Nova has also worked as a technical and scientific writer. She is majorly involved in developing and reviewing online content plans that engage and resonate with audiences. Nova has a passion for writing that engages and informs her readers.
Struggling With Your Paper?
Get a custom paper written at
With a FREE Turnitin report, and a 100% money-back guarantee
LIMITED TIME ONLY!
Keep reading

OFFER EXPIRES SOON!
AP ® Lang teachers: looking to help your students improve their rhetorical analysis essays?
Coach Hall Writes
clear, concise rhetorical analysis instruction.
How to Write a Rhetorical Analysis Thesis
November 20, 2021 by Beth Hall
One of the first steps of writing a rhetorical analysis essay is knowing how to write a rhetorical analysis thesis.
Rhetorical analysis thesis statements can seem intimidating, but they do not have to be.
While the thesis is a small portion of an essay, it carries significant weight and impact, especially on the AP® Lang exam. For example, on AP® Lang rubric, a defensible thesis is one out of six possible points.
So, what is a defensible thesis and how do you write one for a rhetorical analysis essay?
A defensible thesis means that the thesis or position can be justified, proven, or defended.
You can craft a rhetorical analysis thesis statement with the following steps:
Step 1: As you are reading the passage, look for strategies or choices the author utilizes. Ask: What rhetorical choices does the writer/speaker make? (ie. juxtaposition, allusion, etc) This will be the basis of your thesis statement.
Step 2: Mention the author’s purpose in the thesis. Ask: Why did he/she make these choices? Why did he/she write this?
Step 3: Consider the effect on the audience. This step is not mandatory or always appropriate, but it can strengthen the thesis. The effect is looking at the author’s call to action. Ask: How does he/she want the audience to think/act?

Now that you understand the basis of a thesis statement, let’s talk about where this thesis goes in the essay.
The thesis is best placed in the introductory paragraph. By placing it in the introduction, it gives you a direction for your writing (and often where readers go looking for the thesis). The introduction contains the hook, context, and thesis statement. Often, the context and the thesis are combined together (look at the example below). The context identifies the specific passage you are talking about in your essay.
You can write only a thesis statement for an introductory paragraph if you are short on time, but it is better to have a well-developed introduction. If you want to know more about writing an introduction, you can watch the video here.
Let’s put this information together and look at an example of a thesis statement.
In Leonid Fridman’s passionate article “America Needs its Nerds,” ← context
he defines “geek” and contrasts America with other industrialized nations to develop his argument that America values athletes more than intellectuals. ← thesis
By doing so, Fridman urges readers to reprioritize the current social hierarchy. ← Effect
If you are feeling unsure about thesis statements or need a place to start, sentence frames are a great way to begin a thesis statement. Below are several sentence frames and examples to help you navigate thesis statements.
In SPEAKER/WRITER’S (tone) speech/letter/article (to AUDIENCE), he/she uses ___ and ____ to PURPOSE.
Note: The blanks in this sentence frame should be choices or strategies (nouns). For example, “he uses repetition and juxtaposition to…” Saying “uses” and then a device is rather simple. However, this sentence frame can lead to a defensible thesis. Once you understand this style of thesis writing, you can try more advanced styles.
In SPEAKER/WRITER’S (tone) speech/letter/article (to AUDIENCE), he/she ____ and ____ to PURPOSE.
Example: In his patriotic speech to Congress, President Roosevelt repeats “attacked” and “deliberate” as well as appeals to patriotism in order to convince Congress to declare war on Japan.
Example: In his patriotic speech to Congress, President Roosevelt repeatedly emphasizes the deliberate nature of the attack on Pearl Harbor and appeals to patriotism in order to convince Congress to declare war on Japan.
When you are ready to begin writing thesis statements on your own, remember to keep the following items in mind:
- A thesis identifies the strategies / choices AND purpose. Without both of these, it is not a defensible thesis.
- A thesis does not restate the prompt. Use the prompt as a guide, not as a thesis.
- A thesis answers the prompt. This may seem obvious, but it can be easy to get caught up in writing and lose track of your goal
Looking for more tips about how to write a rhetorical analysis essay, check out this post here.
AP® Lang Teachers
Looking to help your students improve their rhetorical analysis essays?
Latest on Instagram

Shop My TPT Store
How to Write a Thesis Statement for a Rhetorical Analysis in 10 Steps

The cornerstone of any successful rhetorical analysis essay is its thesis statement. This essential sentence guides both you, the writer, and your reader through the author's strategies for persuasion. But how can you create a thesis that's clear, concise, and insightful? Don't worry - here are some of the writing steps which we'll break down in this detailed guide:
Step 1: Understand the purpose of a rhetorical analysis
Step 2: Identify the author's main argument
Step 3: Examine the rhetorical strategies used
Step 4: Analyze the effectiveness of the strategies
Step 5: Determine the author's intentions
A rhetorical analysis thesis statement captures the main argument you'll explore in your essay. It explains how the author uses different tools – things like word choices, descriptive language, or even how sentences are structured – to achieve a specific outcome with their audience.
When writing one, you should consider the three key components.
- Your thesis should identify the specific text you're analyzing, including the author and the type of work (such as a speech, essay, or advertisement).
- It should pinpoint the specific methods of persuasion the author uses.
- Your thesis should explain the overall impact these strategies have on the reader.
Having a strong thesis benefits not only the reader by providing a clear roadmap for the essay but also keeps you, the writer, focused throughout the writing process. Now that we have the foundation laid let's learn the best practices for crafting powerful rhetorical analysis thesis statements. While you're at it, you can always pay for essay online using our expert help!

Wednesday Addams
Mysterious, dark, and sarcastic
You’re the master of dark humor and love standing out with your unconventional style. Your perfect costume? A modern twist on Wednesday Addams’ gothic look. You’ll own Halloween with your unapologetically eerie vibe. 🖤🕸️
Is Your Rhetorical Analysis Thesis Stuck in "The Author Uses...?"
Let us ditch the generic and use the power of a truly insightful thesis!
How to Write a Thesis Statement for a Rhetorical Analysis
In the below sections, we'll break down the writing process into simple, actionable steps. Follow these 10 steps to create a clear and effective thesis statement for rhetorical analysis.
.webp)
Understand the Purpose of a Rhetorical Analysis
To focus on how the author's choices affect the audience, first, you should understand the purpose. By recognizing the main strategies, you can better articulate how the author's methods contribute to the overall message.
For instance, does the author use emotional appeals to evoke sympathy? Do they use logical arguments to convince the audience of their point? Or do they rely on their credibility and authority to persuade the readers? Identify these elements to develop a strong thesis statement that reflects the core of your analysis.
Identify the Author's Main Argument
The next step is to identify the author's main argument or central claim since your analysis will revolve around how effectively the author supports and communicates this point. This is the primary point the author is trying to convey to the audience.
To identify the main argument, ask yourself:
- What is the author trying to persuade the audience to believe or do?
- What is the central message of the text?
By pinpointing the author's main argument, you can then examine the specific rhetorical strategies used to support this argument.
Examine the Rhetorical Strategies Used
Once you have identified the author's main argument, the next step is to examine the rhetorical strategies used to support it. Rhetorical strategies are the techniques the author uses to persuade the audience, and they often include ethos (credibility), pathos (emotional appeal), and logos (logical argument).
Ethos: Look for how the author establishes credibility. Do they mention their qualifications, use reliable sources, or demonstrate knowledge of the subject?
Pathos: Identify emotional appeals. Does the author use vivid language, personal anecdotes, or emotional stories to connect with the audience on an emotional level?
Logos: Analyze logical arguments. Does the author use facts, statistics, logical reasoning, or evidence to support their claims?
By closely examining these strategies, you can understand how the author builds their argument, and you will form the basis of your thesis statement for rhetorical analysis.
Analyze the Effectiveness of the Strategies
After identifying the rhetorical strategies used by the author, the effectiveness of the strategies is analyzed. This means evaluating how well these strategies work in persuading the audience and supporting the author's main argument.
Consider the following questions:
- Do the strategies enhance the author's credibility? Does the use of ethos make the author appear knowledgeable and trustworthy?
- Are the emotional appeals impactful? Does the use of pathos resonate with the audience and evoke the intended emotions?
- Is the logical argument convincing? Does the use of logos provide strong evidence and clear reasoning that support the author's claims?
This evaluation will highlight not only the strategies used but also your judgment on how well they work to persuade the audience.
Determine the Author's Intentions
Sometimes, figuring out the author's goals can be difficult. They might have more than one reason for writing, or they might try to be subtle about their main point. This is where careful reading comes in. So, while you're working on your rhetorical analysis thesis statement, pay close attention to the words the author uses, how they organize their ideas, and the feelings they try to create. This way, you can figure out what the author was really trying to accomplish.
Ask yourself why the author wrote the text. What are they hoping to achieve? The author's intentions might include persuading the audience to adopt a certain viewpoint, inspiring action, informing about an issue, or entertaining. Knowing the author's goal helps you understand the choices they made in their writing and whether those choices were effective.
Consider the Audience and Context
The audience and context are critical components in a rhetorical analysis. Consider who the intended audience is and how the author tailors their message to appeal to that audience. Different audiences respond to different rhetorical strategies, so identifying the audience helps you understand why the author chose specific techniques.
Also, think about the context in which the text was created and received. Context includes the time period, cultural background, and circumstances surrounding the text. This information can influence how the audience interprets the message and how effective the rhetorical strategies are.
Craft a Clear and Specific Claim
Now that you have a thorough understanding of the author's main argument, rhetorical strategies, their effectiveness, and the context, it's time to craft rhetorical analysis thesis statements.
Your statement should:
- Identify the text, author, and genre : Clearly state the work you are analyzing.
- Mention the main argument : Summarize the author's primary claim.
- Highlight the rhetorical strategies : Specify the key strategies used by the author.
- Evaluate their effectiveness : Include your judgment on how well these strategies support the author's argument.
Example of a clear and specific thesis statement:
"In her essay 'Why We Should Protect Rainforests,' Dr. Jane Goodall uses vivid descriptions and statistics to persuade readers of the environmental dangers of deforestation and the importance of rainforest conservation."
This thesis statement clearly identifies the text, author, and genre. It also mentions the main argument ("persuade readers") and highlights a specific rhetorical strategy ("vivid descriptions and statistics"). Finally, it evaluates the effectiveness of those strategies ("persuade readers").
Incorporate the Key Elements of the Analysis
Here's what to include in your analysis:
- Appeals: Logos, pathos, and ethos.
- Figurative Language: Similes, metaphors, personification, etc.
- Structure and Organization: How the text is arranged, use of transitions, and emphasis on certain points.
- Diction (Word Choice): Formal vs. informal language, technical jargon, and the use of specific words to evoke emotions.
- Logos: Did the logical arguments convince the reader?
- Pathos: Did the emotional appeals stir the reader's feelings?
- Ethos: Did the author come across as trustworthy and knowledgeable?
Ensure Conciseness and Clarity
For a strong thesis statement for rhetorical analysis remember to keep it specific and don't use generic terms. Also, be analytical, not descriptive - don't simply summarize the content, instead focus on the author's choices and their impact.
Focus on the essentials:
- Briefly mention the text (e.g., essay, speech) and author.
- State the author's goal.
- Mention a few of the main rhetorical strategies used.
- Briefly state your judgment on the effectiveness of these strategies.
Example (reworked for conciseness):
"Dr. King, in his 'Letter from Birmingham Jail,' employs powerful appeals to pathos and logos to persuade clergymen of the moral urgency of the civil rights movement."
Here's what we removed for conciseness:
- Unnecessary introductory phrases ("In his essay..." or "This essay argues that...")
- Redundant information ("effectively" - already implied by "persuade").
Revise and Refine Your Thesis Statement
Lastly, revise your thesis statement iteratively to ensure it acts as a strong foundation for your essay. Here's a formula you can use to write a concise statement:
The author of [text title], [author's name], uses [specific tools] to [author's purpose].
Some tips to consider:
- Avoid unnecessary words: Focus on the core purpose and tools.
- Specificity is key: Mention specific tools the author uses, not just general categories.
- Active voice is stronger: "The author uses..." is more impactful than "It is shown that...".
Bonus Tip: Read your thesis out loud. Does it sound clear and focused?
Tips for Writing a Rhetorical Analysis Thesis Statement
Strong rhetorical analysis thesis statement example.
In her scathing editorial titled 'A Needless War,' journalist Sarah Carter employs a relentless barrage of statistics, expert testimonials, and hypothetical scenarios to expose the devastating human cost of a potential military intervention and ultimately sway public opinion toward a diplomatic resolution.
This thesis breaks down the key elements effectively:
- Author and Text: Identifies the author (Sarah Carter) and the specific text ("A Needless War").
- Author's Purpose: Clearly states the author's goal: to sway public opinion against war.
- Rhetorical Choices: Highlights specific techniques used (statistics, expert testimonials, hypothetical scenarios).
- Impact on Audience: Explains how these choices influence the reader (expose human cost, encourage diplomacy).
This thesis is strong because it's specific, claims a clear effect on the audience, and avoids simply summarizing the text. It prepares the reader for an analysis focused on Carter's persuasive strategies and their impact on the anti-war message.
By juxtaposing nostalgic imagery of the American West with harsh statistics on environmental degradation, filmmaker John Ford subtly critiques the destructive impact of unchecked expansionism in his classic western, The Searchers, prompting viewers to question the romanticized narrative of American frontier conquest.
This example analyzes a different type of text (a film) and focuses on a more nuanced strategy:
- Author and Text: Identifies the filmmaker (John Ford) and the specific film ( The Searchers ).
- Author's Purpose: Suggests a hidden message: critiquing expansionism.
- Rhetorical Choices: Highlights the technique used (the juxtaposition of contrasting imagery and statistics).
- Impact on Audience: Explains how this technique makes viewers question a romanticized view.
This thesis is strong because it goes beyond the film's surface story, revealing a deeper message and the use of a subtle technique to deliver it. It prepares the reader for an analysis of how Ford uses imagery and data to challenge a traditional perspective.
Weak Rhetorical Analysis Thesis Statement Example
.webp)
While the author uses strong emotional appeals, their argument on gun control lacks depth in its consideration of opposing viewpoints.
This thesis statement is weak for a couple of reasons:
- It Summarizes Instead of Analyzes: It simply states that the author uses emotional appeals and doesn't analyze how effectively they are used or how they impact the argument.
- It Lacks Specificity: It doesn't specify which emotional appeals are used or how the argument on gun control lacks depth.
Here's how we can improve it:
A stronger version: By relying heavily on personal anecdotes and neglecting to address counterarguments, the author's emotional plea for stricter gun control fails to persuade a well-informed audience.
This revised thesis is stronger because:
- It Analyzes: It identifies specific tactics (anecdotes) and explains their impact (emotional plea).
- It's Specific: It mentions the neglected counterarguments and the target audience (well-informed).
The advertisement uses colors and images to persuade viewers.
This statement is weak for similar reasons as the previous ones:
- It's Vague: It doesn't specify which colors or images are used or how they persuade viewers.
- It Lacks Analysis: It simply states a fact about advertising without analyzing the specific choices made.
A stronger version: By employing a warm color palette and nostalgic imagery, the advertisement subtly evokes a sense of comfort and familiarity, encouraging viewers to associate the product with positive emotions.
- It's Specific: It mentions the color palette (warm) and imagery (nostalgic).
- It Analyzes: It explains how these choices create a specific emotional response (comfort, familiarity) and its connection to persuasion (positive association with the product).
As we wrap up this article, let's recap the key points for writing your thesis statement:
- Analyze the "how" : Don't just state methods; explain how they're used.
- Be specific : Name devices (metaphors, facts) and their effects (emotion, trust).
- Connect choices to goals : Show how strategies help the author's aim (persuade, inform).
- Consider the audience : Who is the author trying to reach?
- Effectiveness : Did the author's approach work?
And always remember to use our custom thesis writing service for any writing endeavor - we're always ready to help!
Tired of Bland Summaries?
Let's write a thesis that gets noticed!
What is an Example of an Analysis Thesis Statement?
What is a good thesis statement example, how to write a thesis statement for a rhetorical analysis.

Daniel Parker
is a seasoned educational writer focusing on scholarship guidance, research papers, and various forms of academic essays including reflective and narrative essays. His expertise also extends to detailed case studies. A scholar with a background in English Literature and Education, Daniel’s work on EssayPro blog aims to support students in achieving academic excellence and securing scholarships. His hobbies include reading classic literature and participating in academic forums.

is an expert in nursing and healthcare, with a strong background in history, law, and literature. Holding advanced degrees in nursing and public health, his analytical approach and comprehensive knowledge help students navigate complex topics. On EssayPro blog, Adam provides insightful articles on everything from historical analysis to the intricacies of healthcare policies. In his downtime, he enjoys historical documentaries and volunteering at local clinics.
- Created by the Virginia Wesleyan College Learning Center . (n.d.). https://www.vwu.edu/academics/academic-support/learning-center/pdfs/Rhetorical-Analysis-Thesis.pdf
- Adapted from a worksheet by Bethany Ekle Gray . (n.d.). Retrieved July 6, 2024, from https://ttu1301.wordpress.com/wp-content/uploads/2011/09/thesis-statements-handout.pdf
%20(1).webp)
Writers Workshop
Rhetorical Analysis

A rhetorical analysis asks you to explain how writers or speakers within specific social situations attempt to influence others through discourse (including written or spoken language, images, gestures, and so on). A rhetorical analysis is not a summary. It also does not ask you to agree or disagree with the author’s argument. Instead, the purpose of a rhetorical analysis is to make an argument about how an author conveys their message to a particular audience: you’re exploring the author’s goals, describing the techniques or tools used and providing examples of those techniques, and analyzing the effectiveness of those techniques.
To write a rhetorical analysis, you’ll first break down the rhetorical situation and analyze the author’s rhetorical strategies.
Rhetorical Situation
The rhetorical situation is the communicative context of a text, which includes:
Audience : The specific or intended audience of a text.
Author/speaker/writer : The person or group of people who composed the text.
Purpose : To inform, persuade, entertain; what the author wants the audience to believe, know, feel, or do.
Exigence : The text’s reason for being, such as an event, situation, or position within an ongoing debate that the writer is responding to.
Message : The content of the text, the key point(s) the author is communicating to the audience.
Medium and genre : The delivery method, which includes broadly and narrowly defined categories of communication such as:
- Alphabetic text (newspaper editorials, peer-reviewed academic articles, magazine feature essays),
- Images (advertisements, photographs),
- Sound (speeches, radio commercials, songs),
- Multimodal texts (YouTube videos, performances, graphic novels).
Rhetorical Strategies
After breaking down the rhetorical situation, you need to analyze how the author uses rhetorical techniques to convey the message. As you analyze the text, consider:
- How effectively does the author use the ethos appeal to accomplish their intended purpose? In other words, how does the author convince the audience of their credibility, authority, or trustworthiness? What qualifications do they have to address this topic? How does the author demonstrate shared values with the audience?
- How effectively does the author use the pathos appeal to accomplish their intended purpose? In other words, how does the author evoke emotions of pity, sympathy, anger, courage, happiness, sorrow, etc. in the audience? How does the author establish a bond with the audience? What kinds of images, colors, words, sounds does the author use to evoke these feelings?
- How effectively does the author use the logos appeal to accomplish their intended purpose? What evidence and types of reasoning does the author use? How does the author arrange their ideas or order their main points? Does the author use repetition, inductive logic, or deductive logic? Does the author refer to precedents? Address alternative arguments or viewpoints?
Writing a Thesis for Your Rhetorical Analysis
After you’ve analyzed the rhetorical situation and rhetorical strategies, you’ll need to create a thesis for your rhetorical analysis. Often, the thesis statement will assess the author’s effectiveness in accomplishing their purpose with the intended audience through the use of rhetorical strategies.
You might adapt a template like this one: “In [text], [author] effectively convinces [audience] of [message] by [rhetorical strategies].”
Here’s an example: The webpage “Rhetorical Analysis,” written by the Writers Workshop, effectively informs students about how to write a rhetorical analysis by breaking down the elements of the rhetorical situation in an easy-to-read list, posing a series of questions about rhetorical strategies, and capitalizing on the Workshop’s ethos as the campus writing center.
Related Links
Understanding Assignments
Reading Scholarly Sources
Integrating Sources
Copyright University of Illinois Board of Trustees Developed by ATLAS | Web Privacy Notice
*** Enter the $2,000 College Transitions No Essay Scholarship Contest ***
How to Write the AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay (With Example)
November 27, 2023
Feeling intimidated by the AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay? We’re here to help demystify. Whether you’re cramming for the AP Lang exam right now or planning to take the test down the road, we’ve got crucial rubric information, helpful tips, and an essay example to prepare you for the big day. This post will cover 1) What is the AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay? 2) AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Rubric 3) AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis: Sample Prompt 4) AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example 5)AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example: Why It Works
What is the AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay?
The AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay is one of three essays included in the written portion of the AP English Exam. The full AP English Exam is 3 hours and 15 minutes long, with the first 60 minutes dedicated to multiple-choice questions. Once you complete the multiple-choice section, you move on to three equally weighted essays that ask you to synthesize, analyze, and interpret texts and develop well-reasoned arguments. The three essays include:
Synthesis essay: You’ll review various pieces of evidence and then write an essay that synthesizes (aka combines and interprets) the evidence and presents a clear argument. Read our write up on How to Write the AP Lang Synthesis Essay here.
Argumentative essay: You’ll take a stance on a specific topic and argue your case.
Rhetorical essay: You’ll read a provided passage, then analyze the author’s rhetorical choices and develop an argument that explains why the author made those rhetorical choices.
AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Rubric
The AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay is graded on just 3 rubric categories: Thesis, Evidence and Commentary, and Sophistication . At a glance, the rubric categories may seem vague, but AP exam graders are actually looking for very particular things in each category. We’ll break it down with dos and don’ts for each rubric category:
Thesis (0-1 point)
There’s nothing nebulous when it comes to grading AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay thesis. You either have one or you don’t. Including a thesis gets you one point closer to a high score and leaving it out means you miss out on one crucial point. So, what makes a thesis that counts?
- Make sure your thesis argues something about the author’s rhetorical choices. Making an argument means taking a risk and offering your own interpretation of the provided text. This is an argument that someone else might disagree with.
- A good test to see if you have a thesis that makes an argument. In your head, add the phrase “I think that…” to the beginning of your thesis. If what follows doesn’t logically flow after that phrase (aka if what follows isn’t something you and only you think), it’s likely you’re not making an argument.
- Avoid a thesis that merely restates the prompt.
- Avoid a thesis that summarizes the text but does not make an argument.
Evidence and Commentary (0-4 points)
This rubric category is graded on a scale of 0-4 where 4 is the highest grade. Per the AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis rubric, to get a 4, you’ll want to:
- Include lots of specific evidence from the text. There is no set golden number of quotes to include, but you’ll want to make sure you’re incorporating more than a couple pieces of evidence that support your argument about the author’s rhetorical choices.
- Make sure you include more than one type of evidence, too. Let’s say you’re working on your essay and have gathered examples of alliteration to include as supporting evidence. That’s just one type of rhetorical choice, and it’s hard to make a credible argument if you’re only looking at one type of evidence. To fix that issue, reread the text again looking for patterns in word choice and syntax, meaningful figurative language and imagery, literary devices, and other rhetorical choices, looking for additional types of evidence to support your argument.
- After you include evidence, offer your own interpretation and explain how this evidence proves the point you make in your thesis.
- Don’t summarize or speak generally about the author and the text. Everything you write must be backed up with evidence.
- Don’t let quotes speak for themselves. After every piece of evidence you include, make sure to explain your interpretation. Also, connect the evidence to your overarching argument.
Sophistication (0-1 point)
In this case, sophistication isn’t about how many fancy vocabulary words or how many semicolons you use. According to College Board , one point can be awarded to AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis essays that “demonstrate sophistication of thought and/or a complex understanding of the rhetorical situation” in any of these three ways:
- Explaining the significance or relevance of the writer’s rhetorical choices.
- Explaining the purpose or function of the passage’s complexities or tensions.
- Employing a style that is consistently vivid and persuasive.
Note that you don’t have to achieve all three to earn your sophistication point. A good way to think of this rubric category is to consider it a bonus point that you can earn for going above and beyond in depth of analysis or by writing an especially persuasive, clear, and well-structured essay. In order to earn this point, you’ll need to first do a good job with your thesis, evidence, and commentary.
- Focus on nailing an argumentative thesis and multiple types of evidence. Getting these fundamentals of your essay right will set you up for achieving depth of analysis.
- Explain how each piece of evidence connects to your thesis.
- Spend a minute outlining your essay before you begin to ensure your essay flows in a clear and cohesive way.
- Steer clear of generalizations about the author or text.
- Don’t include arguments you can’t prove with evidence from the text.
- Avoid complex sentences and fancy vocabulary words unless you use them often. Long, clunky sentences with imprecisely used words are hard to follow.
AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis: Sample Prompt
The sample prompt below is published online by College Board and is a real example from the 2021 AP Exam. The prompt provides background context, essay instructions, and the text you need to analyze. For sake of space, we’ve included the text as an image you can click to read. After the prompt, we provide a sample high scoring essay and then explain why this AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis essay example works.
Suggested time—40 minutes.
(This question counts as one-third of the total essay section score.)
On February 27, 2013, while in office, former president Barack Obama delivered the following address dedicating the Rosa Parks statue in the National Statuary Hall of the United States Capitol building. Rosa Parks was an African American civil rights activist who was arrested in 1955 for refusing to give up her seat on a segregated bus in Montgomery, Alabama. Read the passage carefully. Write an essay that analyzes the rhetorical choices Obama makes to convey his message.
In your response you should do the following:
- Respond to the prompt with a thesis that analyzes the writer’s rhetorical choices.
- Select and use evidence to support your line of reasoning.
- Explain how the evidence supports your line of reasoning.
- Demonstrate an understanding of the rhetorical situation.
- Use appropriate grammar and punctuation in communicating your argument.
AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example
In his speech delivered in 2013 at the dedication of Rosa Park’s statue, President Barack Obama acknowledges everything that Parks’ activism made possible in the United States. Telling the story of Parks’ life and achievements, Obama highlights the fact that Parks was a regular person whose actions accomplished enormous change during the civil rights era. Through the use of diction that portrays Parks as quiet and demure, long lists that emphasize the extent of her impacts, and Biblical references, Obama suggests that all of us are capable of achieving greater good, just as Parks did.
Although it might be a surprising way to start to his dedication, Obama begins his speech by telling us who Parks was not: “Rosa Parks held no elected office. She possessed no fortune” he explains in lines 1-2. Later, when he tells the story of the bus driver who threatened to have Parks arrested when she refused to get off the bus, he explains that Parks “simply replied, ‘You may do that’” (lines 22-23). Right away, he establishes that Parks was a regular person who did not hold a seat of power. Her protest on the bus was not part of a larger plan, it was a simple response. By emphasizing that Parks was not powerful, wealthy, or loud spoken, he implies that Parks’ style of activism is an everyday practice that all of us can aspire to.
AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example (Continued)
Even though Obama portrays Parks as a demure person whose protest came “simply” and naturally, he shows the importance of her activism through long lists of ripple effects. When Parks challenged her arrest, Obama explains, Martin Luther King, Jr. stood with her and “so did thousands of Montgomery, Alabama commuters” (lines 27-28). They began a boycott that included “teachers and laborers, clergy and domestics, through rain and cold and sweltering heat, day after day, week after week, month after month, walking miles if they had to…” (lines 28-31). In this section of the speech, Obama’s sentences grow longer and he uses lists to show that Parks’ small action impacted and inspired many others to fight for change. Further, listing out how many days, weeks, and months the boycott lasted shows how Parks’ single act of protest sparked a much longer push for change.
To further illustrate Parks’ impact, Obama incorporates Biblical references that emphasize the importance of “that single moment on the bus” (lines 57-58). In lines 33-35, Obama explains that Parks and the other protestors are “driven by a solemn determination to affirm their God-given dignity” and he also compares their victory to the fall the “ancient walls of Jericho” (line 43). By of including these Biblical references, Obama suggests that Parks’ action on the bus did more than correct personal or political wrongs; it also corrected moral and spiritual wrongs. Although Parks had no political power or fortune, she was able to restore a moral balance in our world.
Toward the end of the speech, Obama states that change happens “not mainly through the exploits of the famous and the powerful, but through the countless acts of often anonymous courage and kindness” (lines 78-81). Through carefully chosen diction that portrays her as a quiet, regular person and through lists and Biblical references that highlight the huge impacts of her action, Obama illustrates exactly this point. He wants us to see that, just like Parks, the small and meek can change the world for the better.
AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example: Why It Works
We would give the AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis essay above a score of 6 out of 6 because it fully satisfies the essay’s 3 rubric categories: Thesis, Evidence and Commentary, and Sophistication . Let’s break down what this student did:
The thesis of this essay appears in the last line of the first paragraph:
“ Through the use of diction that portrays Parks as quiet and demure, long lists that emphasize the extent of her impacts, and Biblical references, Obama suggests that all of us are capable of achieving greater good, just as Parks did .”
This student’s thesis works because they make a clear argument about Obama’s rhetorical choices. They 1) list the rhetorical choices that will be analyzed in the rest of the essay (the italicized text above) and 2) include an argument someone else might disagree with (the bolded text above).
Evidence and Commentary:
This student includes substantial evidence and commentary. Things they do right, per the AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis rubric:
- They include lots of specific evidence from the text in the form of quotes.
- They incorporate 3 different types of evidence (diction, long lists, Biblical references).
- After including evidence, they offer an interpretation of what the evidence means and explain how the evidence contributes to their overarching argument (aka their thesis).
Sophistication
This essay achieves sophistication according to the AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis essay rubric in a few key ways:
- This student provides an introduction that flows naturally into the topic their essay will discuss. Before they get to their thesis, they tell us that Obama portrays Parks as a “regular person” setting up their main argument: Obama wants all regular people to aspire to do good in the world just as Rosa Parks did.
- They organize evidence and commentary in a clear and cohesive way. Each body paragraph focuses on just one type of evidence.
- They explain how their evidence is significant. In the final sentence of each body paragraph, they draw a connection back to the overarching argument presented in the thesis.
- All their evidence supports the argument presented in their thesis. There is no extraneous evidence or misleading detail.
- They consider nuances in the text. Rather than taking the text at face value, they consider what Obama’s rhetorical choices imply and offer their own unique interpretation of those implications.
- In their final paragraph, they come full circle, reiterate their thesis, and explain what Obama’s rhetorical choices communicate to readers.
- Their sentences are clear and easy to read. There are no grammar errors or misused words.
AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay—More Resources
Looking for more tips to help your master your AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay? Brush up on 20 Rhetorical Devices High School Students Should Know and read our Tips for Improving Reading Comprehension . If you’re ready to start studying for another part of the AP English Exam, find more expert tips in our How to Write the AP Lang Synthesis blog post.
Considering what other AP classes to take? Read up on the Hardest AP Classes .
- High School Success

Christina Wood
Christina Wood holds a BA in Literature & Writing from UC San Diego, an MFA in Creative Writing from Washington University in St. Louis, and is currently a Doctoral Candidate in English at the University of Georgia, where she teaches creative writing and first-year composition courses. Christina has published fiction and nonfiction in numerous publications, including The Paris Review , McSweeney’s , Granta , Virginia Quarterly Review , The Sewanee Review , Mississippi Review , and Puerto del Sol , among others. Her story “The Astronaut” won the 2018 Shirley Jackson Award for short fiction and received a “Distinguished Stories” mention in the 2019 Best American Short Stories anthology.
- 2-Year Colleges
- ADHD/LD/Autism/Executive Functioning
- Application Strategies
- Best Colleges by Major
- Best Colleges by State
- Big Picture
- Career & Personality Assessment
- College Essay
- College Search/Knowledge
- College Success
- Costs & Financial Aid
- Data Visualizations
- Dental School Admissions
- Extracurricular Activities
- General Knowledge
- Graduate School Admissions
- High Schools
- Homeschool Resources
- Law School Admissions
- Medical School Admissions
- Navigating the Admissions Process
- Online Learning
- Outdoor Adventure
- Private High School Spotlight
- Research Programs
- Summer Program Spotlight
- Summer Programs
- Teacher Tools
- Test Prep Provider Spotlight
“Innovative and invaluable…use this book as your college lifeline.”
— Lynn O'Shaughnessy
Nationally Recognized College Expert
$2,000 No Essay Scholarship
Presented by College Transitions
- Win $2,000 for college • 1 minute or less to enter • No essay required • Open to students and parents in the U.S.
Create your account today and easily enter all future sweepstakes!
Enter to Win $2,000 Today!
- Affiliate Program

- UNITED STATES
- 台灣 (TAIWAN)
- TÜRKIYE (TURKEY)
- Academic Editing Services
- - Research Paper
- - Journal Manuscript
- - Dissertation
- - College & University Assignments
- Admissions Editing Services
- - Application Essay
- - Personal Statement
- - Recommendation Letter
- - Cover Letter
- - CV/Resume
- Business Editing Services
- - Business Documents
- - Report & Brochure
- - Website & Blog
- Writer Editing Services
- - Script & Screenplay
- Our Editors
- Client Reviews
- Editing & Proofreading Prices
- Wordvice Points
- Partner Discount
- Plagiarism Checker
- APA Citation Generator
- MLA Citation Generator
- Chicago Citation Generator
- Vancouver Citation Generator
- - APA Style
- - MLA Style
- - Chicago Style
- - Vancouver Style
- Writing & Editing Guide
- Academic Resources
- Admissions Resources
How to Write a Rhetorical Analysis Essay–Examples & Template
What is a Rhetorical Analysis Essay?
A rhetorical analysis essay is, as the name suggests, an analysis of someone else’s writing (or speech, or advert, or even cartoon) and how they use not only words but also rhetorical techniques to influence their audience in a certain way. A rhetorical analysis is less interested in what the author is saying and more in how they present it, what effect this has on their readers, whether they achieve their goals, and what approach they use to get there.
Its structure is similar to that of most essays: An Introduction presents your thesis, a Body analyzes the text you have chosen, breaks it down into sections and explains how arguments have been constructed and how each part persuades, informs, or entertains the reader, and a Conclusion section sums up your evaluation.
Note that your personal opinion on the matter is not relevant for your analysis and that you don’t state anywhere in your essay whether you agree or disagree with the stance the author takes.
In the following, we will define the key rhetorical concepts you need to write a good rhetorical analysis and give you some practical tips on where to start.
Key Rhetorical Concepts
Your goal when writing a rhetorical analysis is to think about and then carefully describe how the author has designed their text so that it has the intended effect on their audience. To do that, you need to consider a number of key rhetorical strategies: Rhetorical appeals (“Ethos”, “Logos”, and “Pathos”), context, as well as claims, supports, and warrants.
Ethos, Logos, and Pathos were introduced by Aristotle, way back in the 4th century BC, as the main ways in which language can be used to persuade an audience. They still represent the basis of any rhetorical analysis and are often referred to as the “rhetorical triangle”.
These and other rhetorical techniques can all be combined to create the intended effect, and your job as the one analyzing a text is to break the writer’s arguments down and identify the concepts they are based on.
Rhetorical Appeals
Rhetorical appeal #1: ethos.
Ethos refers to the reputation or authority of the writer regarding the topic of their essay or speech and to how they use this to appeal to their audience. Just like we are more likely to buy a product from a brand or vendor we have confidence in than one we don’t know or have reason to distrust, Ethos-driven texts or speeches rely on the reputation of the author to persuade the reader or listener. When you analyze an essay, you should therefore look at how the writer establishes Ethos through rhetorical devices.
Does the author present themselves as an authority on their subject? If so, how?
Do they highlight how impeccable their own behavior is to make a moral argument?
Do they present themselves as an expert by listing their qualifications or experience to convince the reader of their opinion on something?
Rhetorical appeal #2: Pathos
The purpose of Pathos-driven rhetoric is to appeal to the reader’s emotions. A common example of pathos as a rhetorical means is adverts by charities that try to make you donate money to a “good cause”. To evoke the intended emotions in the reader, an author may use passionate language, tell personal stories, and employ vivid imagery so that the reader can imagine themselves in a certain situation and feel empathy with or anger towards others.
Rhetorical appeal #3: Logos
Logos, the “logical” appeal, uses reason to persuade. Reason and logic, supported by data, evidence, clearly defined methodology, and well-constructed arguments, are what most academic writing is based on. Emotions, those of the researcher/writer as well as those of the reader, should stay out of such academic texts, as should anyone’s reputation, beliefs, or personal opinions.
Text and Context
To analyze a piece of writing, a speech, an advertisement, or even a satirical drawing, you need to look beyond the piece of communication and take the context in which it was created and/or published into account.
Who is the person who wrote the text/drew the cartoon/designed the ad..? What audience are they trying to reach? Where was the piece published and what was happening there around that time?
A political speech, for example, can be powerful even when read decades later, but the historical context surrounding it is an important aspect of the effect it was intended to have.
Claims, Supports, and Warrants
To make any kind of argument, a writer needs to put forward specific claims, support them with data or evidence or even a moral or emotional appeal, and connect the dots logically so that the reader can follow along and agree with the points made.
The connections between statements, so-called “warrants”, follow logical reasoning but are not always clearly stated—the author simply assumes the reader understands the underlying logic, whether they present it “explicitly” or “implicitly”. Implicit warrants are commonly used in advertisements where seemingly happy people use certain products, wear certain clothes, accessories, or perfumes, or live certain lifestyles – with the connotation that, first, the product/perfume/lifestyle is what makes that person happy and, second, the reader wants to be as happy as the person in the ad. Some warrants are never clearly stated, and your job when writing a rhetorical analysis essay is therefore to identify them and bring them to light, to evaluate their validity, their effect on the reader, and the use of such means by the writer/creator.

What are the Five Rhetorical Situations?
A “rhetorical situation” refers to the circumstance behind a text or other piece of communication that arises from a given context. It explains why a rhetorical piece was created, what its purpose is, and how it was constructed to achieve its aims.
Rhetorical situations can be classified into the following five categories:
Asking such questions when you analyze a text will help you identify all the aspects that play a role in the effect it has on its audience, and will allow you to evaluate whether it achieved its aims or where it may have failed to do so.
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Outline
Analyzing someone else’s work can seem like a big task, but as with every assignment or writing endeavor, you can break it down into smaller, well-defined steps that give you a practical structure to follow.
To give you an example of how the different parts of your text may look when it’s finished, we will provide you with some excerpts from this rhetorical analysis essay example (which even includes helpful comments) published on the Online Writing Lab website of Excelsior University in Albany, NY. The text that this essay analyzes is this article on why one should or shouldn’t buy an Ipad. If you want more examples so that you can build your own rhetorical analysis template, have a look at this essay on Nabokov’s Lolita and the one provided here about the “Shitty First Drafts” chapter of Anne Lamott’s writing instruction book “Bird by Bird”.
Analyzing the Text
When writing a rhetorical analysis, you don’t choose the concepts or key points you think are relevant or want to address. Rather, you carefully read the text several times asking yourself questions like those listed in the last section on rhetorical situations to identify how the text “works” and how it was written to achieve that effect.
Start with focusing on the author : What do you think was their purpose for writing the text? Do they make one principal claim and then elaborate on that? Or do they discuss different topics?
Then look at what audience they are talking to: Do they want to make a group of people take some action? Vote for someone? Donate money to a good cause? Who are these people? Is the text reaching this specific audience? Why or why not?
What tone is the author using to address their audience? Are they trying to evoke sympathy? Stir up anger? Are they writing from a personal perspective? Are they painting themselves as an authority on the topic? Are they using academic or informal language?
How does the author support their claims ? What kind of evidence are they presenting? Are they providing explicit or implicit warrants? Are these warrants valid or problematic? Is the provided evidence convincing?
Asking yourself such questions will help you identify what rhetorical devices a text uses and how well they are put together to achieve a certain aim. Remember, your own opinion and whether you agree with the author are not the point of a rhetorical analysis essay – your task is simply to take the text apart and evaluate it.
If you are still confused about how to write a rhetorical analysis essay, just follow the steps outlined below to write the different parts of your rhetorical analysis: As every other essay, it consists of an Introduction , a Body (the actual analysis), and a Conclusion .
Rhetorical Analysis Introduction
The Introduction section briefly presents the topic of the essay you are analyzing, the author, their main claims, a short summary of the work by you, and your thesis statement .
Tell the reader what the text you are going to analyze represents (e.g., historically) or why it is relevant (e.g., because it has become some kind of reference for how something is done). Describe what the author claims, asserts, or implies and what techniques they use to make their argument and persuade their audience. Finish off with your thesis statement that prepares the reader for what you are going to present in the next section – do you think that the author’s assumptions/claims/arguments were presented in a logical/appealing/powerful way and reached their audience as intended?
Have a look at an excerpt from the sample essay linked above to see what a rhetorical analysis introduction can look like. See how it introduces the author and article , the context in which it originally appeared , the main claims the author makes , and how this first paragraph ends in a clear thesis statement that the essay will then elaborate on in the following Body section:
Cory Doctorow ’s article on BoingBoing is an older review of the iPad , one of Apple’s most famous products. At the time of this article, however, the iPad was simply the latest Apple product to hit the market and was not yet so popular. Doctorow’s entire career has been entrenched in and around technology. He got his start as a CD-ROM programmer and is now a successful blogger and author. He is currently the co-editor of the BoingBoing blog on which this article was posted. One of his main points in this article comes from Doctorow’s passionate advocacy of free digital media sharing. He argues that the iPad is just another way for established technology companies to control our technological freedom and creativity . In “ Why I Won’t Buy an iPad (and Think You Shouldn’t, Either) ” published on Boing Boing in April of 2010, Cory Doctorow successfully uses his experience with technology, facts about the company Apple, and appeals to consumer needs to convince potential iPad buyers that Apple and its products, specifically the iPad, limit the digital rights of those who use them by controlling and mainstreaming the content that can be used and created on the device .
Doing the Rhetorical Analysis
The main part of your analysis is the Body , where you dissect the text in detail. Explain what methods the author uses to inform, entertain, and/or persuade the audience. Use Aristotle’s rhetorical triangle and the other key concepts we introduced above. Use quotations from the essay to demonstrate what you mean. Work out why the writer used a certain approach and evaluate (and again, demonstrate using the text itself) how successful they were. Evaluate the effect of each rhetorical technique you identify on the audience and judge whether the effect is in line with the author’s intentions.
To make it easy for the reader to follow your thought process, divide this part of your essay into paragraphs that each focus on one strategy or one concept , and make sure they are all necessary and contribute to the development of your argument(s).
One paragraph of this section of your essay could, for example, look like this:
One example of Doctorow’s position is his comparison of Apple’s iStore to Wal-Mart. This is an appeal to the consumer’s logic—or an appeal to logos. Doctorow wants the reader to take his comparison and consider how an all-powerful corporation like the iStore will affect them. An iPad will only allow for apps and programs purchased through the iStore to be run on it; therefore, a customer must not only purchase an iPad but also any programs he or she wishes to use. Customers cannot create their own programs or modify the hardware in any way.
As you can see, the author of this sample essay identifies and then explains to the reader how Doctorow uses the concept of Logos to appeal to his readers – not just by pointing out that he does it but by dissecting how it is done.
Rhetorical Analysis Conclusion
The conclusion section of your analysis should restate your main arguments and emphasize once more whether you think the author achieved their goal. Note that this is not the place to introduce new information—only rely on the points you have discussed in the body of your essay. End with a statement that sums up the impact the text has on its audience and maybe society as a whole:
Overall, Doctorow makes a good argument about why there are potentially many better things to drop a great deal of money on instead of the iPad. He gives some valuable information and facts that consumers should take into consideration before going out to purchase the new device. He clearly uses rhetorical tools to help make his case, and, overall, he is effective as a writer, even if, ultimately, he was ineffective in convincing the world not to buy an iPad .
Frequently Asked Questions about Rhetorical Analysis Essays
What is a rhetorical analysis essay.
A rhetorical analysis dissects a text or another piece of communication to work out and explain how it impacts its audience, how successfully it achieves its aims, and what rhetorical devices it uses to do that.
While argumentative essays usually take a stance on a certain topic and argue for it, a rhetorical analysis identifies how someone else constructs their arguments and supports their claims.
What is the correct rhetorical analysis essay format?
Like most other essays, a rhetorical analysis contains an Introduction that presents the thesis statement, a Body that analyzes the piece of communication, explains how arguments have been constructed, and illustrates how each part persuades, informs, or entertains the reader, and a Conclusion section that summarizes the results of the analysis.
What is the “rhetorical triangle”?
The rhetorical triangle was introduced by Aristotle as the main ways in which language can be used to persuade an audience: Logos appeals to the audience’s reason, Ethos to the writer’s status or authority, and Pathos to the reader’s emotions. Logos, Ethos, and Pathos can all be combined to create the intended effect, and your job as the one analyzing a text is to break the writer’s arguments down and identify what specific concepts each is based on.
Let Wordvice help you write a flawless rhetorical analysis essay!
Whether you have to write a rhetorical analysis essay as an assignment or whether it is part of an application, our professional proofreading services feature professional editors are trained subject experts that make sure your text is in line with the required format, as well as help you improve the flow and expression of your writing. Let them be your second pair of eyes so that after receiving paper editing services or essay editing services from Wordvice, you can submit your manuscript or apply to the school of your dreams with confidence.
And check out our editing services for writers (including blog editing , script editing , and book editing ) to correct your important personal or business-related work.
What Is a Rhetorical Analysis and How to Write a Great One

By Helly Douglas

Do you have to write a rhetorical analysis essay? Fear not! We’re here to explain exactly what rhetorical analysis means, how you should structure your essay, and give you some essential “dos and don’ts.”
What is a Rhetorical Analysis Essay?
How do you write a rhetorical analysis, what are the three rhetorical strategies, what are the five rhetorical situations, how to plan a rhetorical analysis essay, creating a rhetorical analysis essay, examples of great rhetorical analysis essays, final thoughts.
A rhetorical analysis essay studies how writers and speakers have used words to influence their audience. Think less about the words the author has used and more about the techniques they employ, their goals, and the effect this has on the audience.

In your analysis essay, you break a piece of text (including cartoons, adverts, and speeches) into sections and explain how each part works to persuade, inform, or entertain. You’ll explore the effectiveness of the techniques used, how the argument has been constructed, and give examples from the text.
A strong rhetorical analysis evaluates a text rather than just describes the techniques used. You don’t include whether you personally agree or disagree with the argument.
Structure a rhetorical analysis in the same way as most other types of academic essays . You’ll have an introduction to present your thesis, a main body where you analyze the text, which then leads to a conclusion.
Think about how the writer (also known as a rhetor) considers the situation that frames their communication:
- Topic: the overall purpose of the rhetoric
- Audience: this includes primary, secondary, and tertiary audiences
- Purpose: there are often more than one to consider
- Context and culture: the wider situation within which the rhetoric is placed
Back in the 4th century BC, Aristotle was talking about how language can be used as a means of persuasion. He described three principal forms —Ethos, Logos, and Pathos—often referred to as the Rhetorical Triangle . These persuasive techniques are still used today.
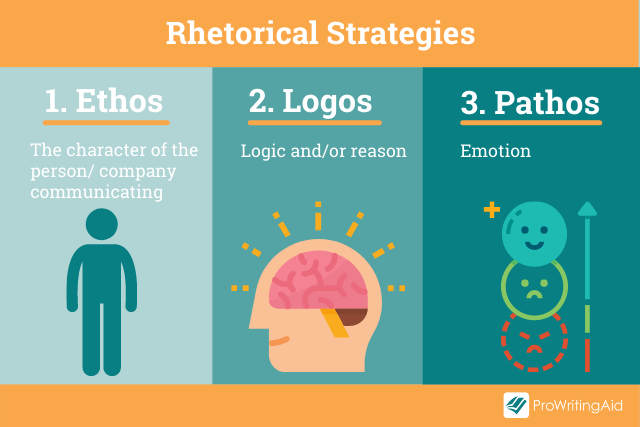
Rhetorical Strategy 1: Ethos
Are you more likely to buy a car from an established company that’s been an important part of your community for 50 years, or someone new who just started their business?
Reputation matters. Ethos explores how the character, disposition, and fundamental values of the author create appeal, along with their expertise and knowledge in the subject area.
Aristotle breaks ethos down into three further categories:
- Phronesis: skills and practical wisdom
- Arete: virtue
- Eunoia: goodwill towards the audience
Ethos-driven speeches and text rely on the reputation of the author. In your analysis, you can look at how the writer establishes ethos through both direct and indirect means.
Rhetorical Strategy 2: Pathos
Pathos-driven rhetoric hooks into our emotions. You’ll often see it used in advertisements, particularly by charities wanting you to donate money towards an appeal.
Common use of pathos includes:
- Vivid description so the reader can imagine themselves in the situation
- Personal stories to create feelings of empathy
- Emotional vocabulary that evokes a response
By using pathos to make the audience feel a particular emotion, the author can persuade them that the argument they’re making is compelling.
Rhetorical Strategy 3: Logos
Logos uses logic or reason. It’s commonly used in academic writing when arguments are created using evidence and reasoning rather than an emotional response. It’s constructed in a step-by-step approach that builds methodically to create a powerful effect upon the reader.
Rhetoric can use any one of these three techniques, but effective arguments often appeal to all three elements.
The rhetorical situation explains the circumstances behind and around a piece of rhetoric. It helps you think about why a text exists, its purpose, and how it’s carried out.
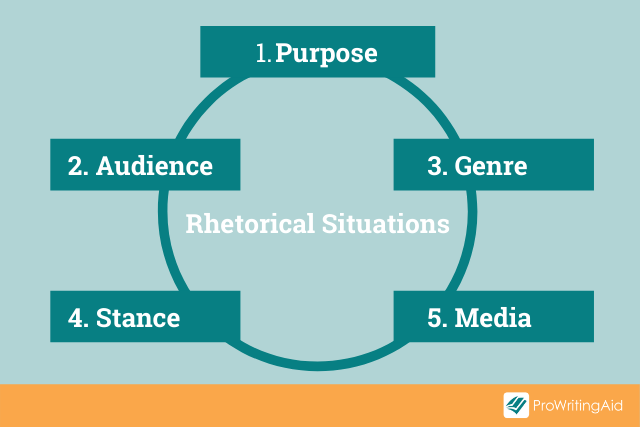
The rhetorical situations are:
- 1) Purpose: Why is this being written? (It could be trying to inform, persuade, instruct, or entertain.)
- 2) Audience: Which groups or individuals will read and take action (or have done so in the past)?
- 3) Genre: What type of writing is this?
- 4) Stance: What is the tone of the text? What position are they taking?
- 5) Media/Visuals: What means of communication are used?
Understanding and analyzing the rhetorical situation is essential for building a strong essay. Also think about any rhetoric restraints on the text, such as beliefs, attitudes, and traditions that could affect the author's decisions.
Before leaping into your essay, it’s worth taking time to explore the text at a deeper level and considering the rhetorical situations we looked at before. Throw away your assumptions and use these simple questions to help you unpick how and why the text is having an effect on the audience.

1: What is the Rhetorical Situation?
- Why is there a need or opportunity for persuasion?
- How do words and references help you identify the time and location?
- What are the rhetoric restraints?
- What historical occasions would lead to this text being created?
2: Who is the Author?
- How do they position themselves as an expert worth listening to?
- What is their ethos?
- Do they have a reputation that gives them authority?
- What is their intention?
- What values or customs do they have?
3: Who is it Written For?
- Who is the intended audience?
- How is this appealing to this particular audience?
- Who are the possible secondary and tertiary audiences?
4: What is the Central Idea?
- Can you summarize the key point of this rhetoric?
- What arguments are used?
- How has it developed a line of reasoning?
5: How is it Structured?
- What structure is used?
- How is the content arranged within the structure?
6: What Form is Used?
- Does this follow a specific literary genre?
- What type of style and tone is used, and why is this?
- Does the form used complement the content?
- What effect could this form have on the audience?
7: Is the Rhetoric Effective?
- Does the content fulfil the author’s intentions?
- Does the message effectively fit the audience, location, and time period?
Once you’ve fully explored the text, you’ll have a better understanding of the impact it’s having on the audience and feel more confident about writing your essay outline.
A great essay starts with an interesting topic. Choose carefully so you’re personally invested in the subject and familiar with it rather than just following trending topics. There are lots of great ideas on this blog post by My Perfect Words if you need some inspiration. Take some time to do background research to ensure your topic offers good analysis opportunities.

Remember to check the information given to you by your professor so you follow their preferred style guidelines. This outline example gives you a general idea of a format to follow, but there will likely be specific requests about layout and content in your course handbook. It’s always worth asking your institution if you’re unsure.
Make notes for each section of your essay before you write. This makes it easy for you to write a well-structured text that flows naturally to a conclusion. You will develop each note into a paragraph. Look at this example by College Essay for useful ideas about the structure.
1: Introduction
This is a short, informative section that shows you understand the purpose of the text. It tempts the reader to find out more by mentioning what will come in the main body of your essay.
- Name the author of the text and the title of their work followed by the date in parentheses
- Use a verb to describe what the author does, e.g. “implies,” “asserts,” or “claims”
- Briefly summarize the text in your own words
- Mention the persuasive techniques used by the rhetor and its effect
Create a thesis statement to come at the end of your introduction.
After your introduction, move on to your critical analysis. This is the principal part of your essay.
- Explain the methods used by the author to inform, entertain, and/or persuade the audience using Aristotle's rhetorical triangle
- Use quotations to prove the statements you make
- Explain why the writer used this approach and how successful it is
- Consider how it makes the audience feel and react
Make each strategy a new paragraph rather than cramming them together, and always use proper citations. Check back to your course handbook if you’re unsure which citation style is preferred.
3: Conclusion
Your conclusion should summarize the points you’ve made in the main body of your essay. While you will draw the points together, this is not the place to introduce new information you’ve not previously mentioned.
Use your last sentence to share a powerful concluding statement that talks about the impact the text has on the audience(s) and wider society. How have its strategies helped to shape history?
Before You Submit
Poor spelling and grammatical errors ruin a great essay. Use ProWritingAid to check through your finished essay before you submit. It will pick up all the minor errors you’ve missed and help you give your essay a final polish. Look at this useful ProWritingAid webinar for further ideas to help you significantly improve your essays. Sign up for a free trial today and start editing your essays!
You’ll find countless examples of rhetorical analysis online, but they range widely in quality. Your institution may have example essays they can share with you to show you exactly what they’re looking for.
The following links should give you a good starting point if you’re looking for ideas:
Pearson Canada has a range of good examples. Look at how embedded quotations are used to prove the points being made. The end questions help you unpick how successful each essay is.
Excelsior College has an excellent sample essay complete with useful comments highlighting the techniques used.
Brighton Online has a selection of interesting essays to look at. In this specific example, consider how wider reading has deepened the exploration of the text.

Writing a rhetorical analysis essay can seem daunting, but spending significant time deeply analyzing the text before you write will make it far more achievable and result in a better-quality essay overall.
It can take some time to write a good essay. Aim to complete it well before the deadline so you don’t feel rushed. Use ProWritingAid’s comprehensive checks to find any errors and make changes to improve readability. Then you’ll be ready to submit your finished essay, knowing it’s as good as you can possibly make it.
Try ProWritingAid's Editor for Yourself

Be confident about grammar
Check every email, essay, or story for grammar mistakes. Fix them before you press send.
Helly Douglas
Helly Douglas is a UK writer and teacher, specialising in education, children, and parenting. She loves making the complex seem simple through blogs, articles, and curriculum content. You can check out her work at hellydouglas.com or connect on Twitter @hellydouglas. When she’s not writing, you will find her in a classroom, being a mum or battling against the wilderness of her garden—the garden is winning!
Get started with ProWritingAid
Drop us a line or let's stay in touch via:
Rhetorical Analysis Sample Essay
Harriet Clark
Ms. Rebecca Winter
13 Feb. 2015
Not Quite a Clean Sweep: Rhetorical Strategies in
Grose's "Cleaning: The Final Feminist Frontier”
A woman’s work is never done: many American women grow up with this saying and feel it to be true. 1 One such woman, author Jessica Grose, wrote “Cleaning: The Final Feminist Frontier,” published in 2013 in the New Republic, 2 and she argues that while the men recently started taking on more of the childcare and cooking, cleaning still falls unfairly on women. 3 Grose begins building her credibility with personal facts and reputable sources, citing convincing facts and statistics, and successfully employing emotional appeals; however, toward the end of the article, her attempts to appeal to readers’ emotions weaken her credibility and ultimately, her argument. 4
In her article, Grose first sets the stage by describing a specific scenario of house-cleaning with her husband after being shut in during Hurricane Sandy, and then she outlines the uneven distribution of cleaning work in her marriage and draws a comparison to the larger feminist issue of who does the cleaning in a relationship. Grose continues by discussing some of the reasons that men do not contribute to cleaning: the praise for a clean house goes to the woman; advertising and media praise men’s cooking and childcare, but not cleaning; and lastly, it is just not fun. Possible solutions to the problem, Grose suggests, include making a chart of who does which chores, dividing up tasks based on skill and ability, accepting a dirtier home, and making cleaning more fun with gadgets. 5
Throughout her piece, Grose uses many strong sources that strengthen her credibility and appeal to ethos, as well as build her argument. 6 These sources include, “sociologists Judith Treas and Tsui-o Tai,” “a 2008 study from the University of New Hampshire,” and “P&G North America Fabric Care Brand Manager, Matthew Krehbiel” (qtd. in Grose). 7 Citing these sources boosts Grose’s credibility by showing that she has done her homework and has provided facts and statistics, as well as expert opinions to support her claim. She also uses personal examples from her own home life to introduce and support the issue, which shows that she has a personal stake in and first-hand experience with the problem. 8
Adding to her ethos appeals, Grose uses strong appeals to logos, with many facts and statistics and logical progressions of ideas. 9 She points out facts about her marriage and the distribution of household chores: “My husband and I both work. We split midnight baby feedings ...but ... he will admit that he’s never cleaned the bathroom, that I do the dishes nine times out of ten, and that he barely knows how the washer and dryer work in the apartment we’ve lived in for over eight months.” 10 These facts introduce and support the idea that Grose does more household chores than her husband. Grose continues with many statistics:
[A]bout 55 percent of American mothers employed full time do some housework on an average day, while only 18 percent of employed fathers do. ... [W]orking women with children are still doing a week and a half more of “second shift” work each year than their male partners. ... Even in the famously gender-neutral Sweden, women do 45 minutes more housework a day than their male partners. 11
These statistics are a few of many that logically support her claim that it is a substantial and real problem that men do not do their fair share of the chores. The details and numbers build an appeal to logos and impress upon the reader that this is a problem worth discussing. 12
Along with strong logos appeals, Grose effectively makes appeals to pathos in the beginning and middle sections. 13 Her introduction is full of emotionally-charged words and phrases that create a sympathetic image; Grose notes that she “was eight months pregnant” and her husband found it difficult to “fight with a massively pregnant person.” 14 The image she evokes of the challenges and vulnerabilities of being so pregnant, as well as the high emotions a woman feels at that time effectively introduce the argument and its seriousness. Her goal is to make the reader feel sympathy for her. Adding to this idea are words and phrases such as, “insisted,” “argued,” “not fun,” “sucks” “headachey,” “be judged,” “be shunned” (Grose). All of these words evoke negative emotions about cleaning, which makes the reader sympathize with women who feel “judged” and shunned”—very negative feelings. Another feeling Grose reinforces with her word choice is the concept of fairness: “fair share,” “a week and a half more of ‘second shift’ work,” “more housework,” “more gendered and less frequent.” These words help establish the unfairness that exists when women do all of the cleaning, and they are an appeal to pathos, or the readers’ feelings of frustration and anger with injustice. 15
However, the end of the article lacks the same level of effectiveness in the appeals to ethos. 16 For example, Grose notes that when men do housework, they are considered to be “’enacting “small instances of gender heroism,” or ‘SIGH’s’—which, barf.” 17 The usage of the word “barf” is jarring to the reader; unprofessional and immature, it is a shift from the researched, intelligent voice she has established and the reader is less likely to take the author seriously. This damages the strength of her credibility and her argument. 18
Additionally, her last statement in the article refers to her husband in a way that weakens the argument. 19 While returning to the introduction’s hook in the conclusion is a frequently-used strategy, Grose chooses to return to her discussion of her husband in a humorous way: Grose discusses solutions, and says there is “a huge, untapped market ... for toilet-scrubbing iPods. I bet my husband would buy one.” 20 Returning to her own marriage and husband is an appeal to ethos or personal credibility, and while that works well in the introduction, in the conclusion, it lacks the strength and seriousness that the topic deserves and was given earlier in the article. 21
Though Grose begins the essay by effectively persuading her readers of the unfair distribution of home-maintenance cleaning labor, she loses her power in the end, where she most needs to drive home her argument. Readers can see the problem exists in both her marriage and throughout the world; however, her shift to humor and sarcasm makes the reader not take the problem as seriously in the end. 22 Grose could have more seriously driven home the point that a woman’s work could be done: by a man. 23
Works Cited
Grose, Jessica. “Cleaning: The Final Feminist Frontier.” New Republic. The New Republic, 19 Mar. 2013. Web. 28 Mar. 2014.
- Article author's claim or purpose
- Summary of the article's main point in the second paragraph (could also be in the introduction)
- Third paragraph begins with a transition and topic sentence that reflects the first topic in the thesis
- Quotes illustrate how the author uses appeals to ethos
- Analysis explains how the quotes show the effective use of ethos as noted in the thesis
- Transition and topic sentence about the second point from the thesis
- Quote that illustrates appeals to logos
- Analysis explains how the quotes show the effective use of logos, as noted in the thesis
- Transition and topic sentence about the third point from the thesis
- Quotes that illustrate appeals to pathos
- Analysis explains how the quotes show the effective use of pathos, as noted in the thesis
- Transition and topic sentence about fourth point from the thesis
- Quote illustrates how the author uses appeal to ethos
- Analysis explains how quote supports thesis
- Transition and topic sentence about fourth point from thesis
- Conclusion returns to the ideas in the thesis and further develops them
- Last sentence returns to the hook in the introduction
Learn more about the " Rhetorical Analysis Graphic Organizer ."
Learn more about " Pathos, Logos, and Ethos ."
Rhetorical Analysis Essay
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example

Top 15+ Rhetorical Analysis Essay Examples for Students
Published on: Mar 10, 2023
Last updated on: Jan 29, 2024

People also read
How To Write A Rhetorical Analysis Essay That Stands Out
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Topics & Ideas for Students
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Outline - Tips & Examples
Understanding Ethos, Pathos, Logos - The Three Rhetorical Appeals
Share this article
Writing a rhetorical analysis essay can be tough. You want to engage your reader, but you also need to provide clear and concise analysis of the text.
It's hard to know where to start, what information is important, and how to make your argument clear.
Don't fret! We've got you covered.
In this blog post, we'll give you 15+ Rhetorical analysis essay examples to help you craft a winning essay. Plus, we'll give you some tips on how to make your essay stand out.
So without a further delay, let's start!
On This Page On This Page -->
Good Rhetorical Analysis Essay Examples
Examples help the readers to understand things in a better way. They also help a writer to compose an essay just like professionals.
Here are some amazing rhetorical analysis examples on different topics. Use them as a helping hand to understand the concept and write a good essay.
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example: AP Language
Rhetorical analysis done in AP Language and Composition is one of the biggest tasks a student can ever get. On the same hand, drafting it in a proper way is also necessary to get good grades.
Look at these rhetorical analysis essay example AP language given below to see how a well-written rhetorical essay is written.
AP Rhetorical analysis essay example
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example Ap Lang 2020
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example Ap Lang 2021
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example AP Lang 2022
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example AP Lang 2023
These rhetorical analysis essay example college board will help you to win over your panel in no time!
Want to start from the basics? Head over to our Rhetorical essay guide to solidify your base.
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example: Ted Talk
A rhetorical analysis can be done on nearly anything. Here is a good example of a rhetorical essay in which a ted talk is being analyzed.
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example: Ethos, Pathos, Logos
The first impression of these three terms sounds just like a conjuration in some kind of a magical story. But in fact, these elements of persuasion were created by Aristotle and have been used for a very long time.
According to Aristotle, they were the primary persuasive strategies that authors should use in their papers. These elements are further elaborated as follows:
- The ethos appeals to ethics.
- Pathos appeals to emotions.
- Logos mean the use of rational thinking.
Here is an example of a rhetorical essay written using these elements.
Understand Ethos,Pathos and Logos to write a compelling essay.
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example for College
College students often get to write a rhetorical analysis essay. They find it hard to write such an essay because it is a bit more technical than other essay types.
Here is an example of a well-written rhetorical essay for college students.
Comparative Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example
A rhetorical analysis essay can be written to show a comparison between two objects. Here is a compare-and-contrast rhetorical analysis essay example.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job!
Visual Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example
The visual rhetorical essay determines how pictures and images communicate messages and persuade the audience. Usually, visual rhetorical essays are written for advertisements. They use strong images to convince the audience to behave in a certain way.
Visual Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example Pdf
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example: Letter from Birmingham Jail
Here is another good example of a rhetorical essay. Most of us know about the history of âletter from a Birmingham jailâ. Read the given example to see how rhetorical analysis is done on it.
Struggling for a similar good topic? Check out our amazing rhetorical essay topics to select the perfect theme for your essay.
Great Influenza: Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example
Influenza has been one of the scariest pandemics the world has faced in history. Here is a rhetorical essay on great influenza.
Great influenza: Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example
Condoleezza Rice Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example
The speech given by Condoleezza Rice has become a classic example of effective oratory. Here is an example of a rhetorical analysis essay on the speech given by Condoleezza Rice at a commencement ceremony.
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example: Condoleezza Riceâs Commencement Speech
This example explores the effectiveness of Rice's speech and features an in-depth analysis.
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example High School
High school essays involve the analysis of different texts and the application of rhetorical tools to those texts. Here is an example that focuses on a high school essay about the effects of television on society.
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example (Pdf)
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example MLA
MLA format is one of the most commonly used formats for essays. Here is an example of a rhetorical essay written in MLA format that focuses on the effectiveness of advertisements.
MLA Rhetorical Analysis Essay PDF
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example Outline
Outline helps to organize the ideas and arguments that you want to present in your essay. Here is a sample outline that can help you write an effective rhetorical analysis essay.
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example Outline sample
Hop on to our rhetorical essay outline guide to learn the step-by-step process of crafting an exemplary outline.
How to Start a Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example
When starting a rhetorical analysis essay, it is important to provide a brief overview of the topic that you are analyzing. This should include the overall message being conveyed, the target audience and the rhetorical devices used in the text.
Here is a rhetorical analysis introduction example for your ease.
Thesis Statement Example for Rhetorical Analysis Essay
The thesis statement of a rhetorical analysis essay should explain the primary argument being made in the text. Here is an example of a thesis statement for a rhetorical analysis essay for your ease.
Example of Rhetorical Analysis Thesis Statement
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example Conclusion
The conclusion of a rhetorical analysis essay is an important part of the overall essay. It should summarize your main points and provide some final thoughts on the topic.
Here is an example of conclusion for a rhetorical analysis essay for your ease.
Download this Rhetorical Analysis Essay Writing Manual to help gather all the relevant guidance for your rhetorical essay.
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Writing Manual (PDF)
Watch this video to understand how to select Rhetorical analysis essay evidences.
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Writing Tips
To write a rhetorical analysis essay, you must have good writing skills. Writing a rhetorical essay is a technical task to do. This is why many students find it really difficult.
There are the following things that you should do to write a good rhetorical analysis essay. Those important things are as follows:
- Determine the Rhetorical Strategy
To write a rhetorical essay, the writer needs to follow a specific method for research. The typical research methods used for this particular essay are as follows:
- Choose a Topic
For any essay type, it is very important to have a good topic. A good topic seeks the readers of attention and convinces them to read the complete essay.
- Create a Rhetorical Analysis Outline
An outline is an essential part of essay writing. The outline provides a definite structure to the essay and also guides the reader throughout the essay. A rhetorical analysis outline has the following elements in it:
- Introduction
- Body paragraphs
These three elements let you describe the entire idea of your rhetorical analysis essay. These three elements are further written with the help of sub-elements.
- Develop a Thesis Statement
The thesis statement is yet another important part of essay writing. It is the essence of the entire essay. It may be a sentence or two explaining the whole idea of your essay. However, not give background information about the topic.
- Proofread and Edit
The formal terminology used for essay revision is known as proofreading. To make sure that your essay is error-free, repeat this process more than once.
Now let's wrap up , shall we?
So far we have provided you with the best rhetorical analysis examples that are sure to win over your panel. With our help, you can surely sfe guard your academic success journey in no time!
In case you think you can not write such an essay on your own, consult an essay writing service.
At CollegeEssay.org , we provide the best rhetorical analysis essay writing service to every student. We have an extensive team of professional writers who can handle all your essay writing assignments.
We make sure that the content we provide you is 100% unique and help you get the best grade.
So why delay when our essay writer can provide you with a top-notch rhetorical essay right away?
Hire our essay service and avail yourself 50% OFF on your first order today!
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the 3 parts of rhetorical analysis.
The three parts of rhetorical analysis are:
- Ethos
- Logos
- Pathos
What are the elements of a rhetorical analysis?
The main elements of a rhetorical analysis essay are:
- Situation
- Audience
- Purpose
- Medium
- Context
Is there any difference between AP lang rhetorical analysis essay example 2020 and AP lang rhetorical analysis essay example 2021?
Yes, there are differences between 2020 and 2021 AP Language and Composition rhetorical analysis essay examples.
- In 2020 the essay prompts revolved around various social issues related to public discourse. In 2021 they mainly focused on the ideas of justice or progress.
- In 2020 students were encouraged to write a multi-paragraph essay shifting back and forth between creative devices of rhetoric. While in 2021 more emphasis was placed on analyzing how well an author's argument is structured.
Cathy A. (Literature, Marketing)
For more than five years now, Cathy has been one of our most hardworking authors on the platform. With a Masters degree in mass communication, she knows the ins and outs of professional writing. Clients often leave her glowing reviews for being an amazing writer who takes her work very seriously.
Need Help With Your Essay?
Also get FREE title page, Turnitin report, unlimited revisions, and more!
Keep reading

OFF ON CUSTOM ESSAYS
Legal & Policies
- Privacy Policy
- Cookies Policy
- Terms of Use
- Refunds & Cancellations
- Our Writers
- Success Stories
- Our Guarantees
- Affiliate Program
- Referral Program
- AI Essay Writer
Disclaimer: All client orders are completed by our team of highly qualified human writers. The essays and papers provided by us are not to be used for submission but rather as learning models only.

Analytical Essay Thesis
Analytical essay thesis statement generator.
Analytical essays delve deep into the intricacies of a subject, offering insightful interpretations and evaluations. At the heart of these essays lies the analytical thesis statement – a crucial element that encapsulates the analytical perspective you’ll explore. This guide explores a range of analytical thesis statement examples, guiding you through the process of creating thought-provoking statements. Learn to dissect complex subjects, develop critical arguments, and master the art of crafting compelling analytical thesis statements.
What is an Analytical Thesis Statement? – Definition
An analytical thesis statement is a concise declaration that outlines the main focus of an analytical essay. It presents the central argument or analysis the essay will explore, providing a roadmap for readers to understand the specific perspective, interpretation, or evaluation the writer intends to present. Unlike other types of thesis statements, an analytical thesis statement does not simply present a fact but delves into the “how” and “why” of a subject.
What is an Example of an Analytical Thesis Statement?
Example: “In F. Scott Fitzgerald’s novel ‘The Great Gatsby,’ Jay Gatsby’s excessive pursuit of wealth and social status serves as a commentary on the illusory nature of the American Dream, highlighting the emptiness and moral decay that often accompany unchecked ambition.”
In this analytical thesis statement, the focus is on analyzing the character of Jay Gatsby and his actions as a reflection of larger themes within the novel. The strong thesis statement goes beyond a surface-level observation and delves into the deeper analysis of Gatsby’s character and its symbolic significance in relation to the American Dream.
100 Analytical Thesis Statement Examples

Size: 264 KB
- “In Shakespeare’s ‘Hamlet,’ the protagonist’s internal conflict reflects the complex interplay between duty, morality, and personal desires.”
- “Through symbolic imagery and character development, ‘The Scarlet Letter’ by Nathaniel Hawthorne explores the destructive power of guilt on individuals and society.”
- “Analyzing the juxtaposition of innocence and corruption in ‘To Kill a Mockingbird,’ Harper Lee critiques the pervasive societal biases that perpetuate injustice.”
- “The film ‘Eternal Sunshine of the Spotless Mind’ employs nonlinear narrative structure to delve into the complexities of memory, love, and human connection.”
- “Through the lens of Marxist theory, George Orwell’s ‘1984’ unveils a dystopian world that critiques totalitarianism and the manipulation of truth.”
- “In Emily Dickinson’s poetry, the recurring theme of death serves as a means of contemplating the transient nature of life and the human condition.”
- “Analyzing Frida Kahlo’s self-portraits reveals her use of visual symbolism to convey her physical and emotional pain as well as her feminist ideals.”
- “Through intricate narrative structure and character development, ‘One Hundred Years of Solitude’ by Gabriel García Márquez explores the cyclical nature of history and human experience.”
- “The painting ‘Starry Night’ by Vincent van Gogh conveys the artist’s emotional turmoil and inner conflict through its vivid color palette and swirling forms.”
- “Through the analysis of ‘The Catcher in the Rye,’ J.D. Salinger portrays the protagonist Holden Caulfield’s alienation as a manifestation of his fear of adulthood and societal conformity.
- “Exploring the use of metaphors and allegory in ‘Animal Farm,’ George Orwell satirizes political ideologies and the corruption of power.”
- “The poem ‘The Road Not Taken’ by Robert Frost delves into the concept of choices and regret, using a diverging path as a metaphor for life’s decisions.”
- “Analyzing the historical context and literary techniques in ‘The Grapes of Wrath,’ John Steinbeck critiques the exploitation of the working class during the Great Depression.”
- “In Mary Shelley’s ‘Frankenstein,’ the creature’s isolation and rejection serve as a commentary on the consequences of unchecked scientific ambition.”
- “Through visual elements and composition, Leonardo da Vinci’s ‘Mona Lisa’ conveys a sense of mystery and psychological depth, captivating viewers for centuries.”
- “Analyzing the use of irony and social commentary in Jonathan Swift’s ‘A Modest Proposal,’ one can understand his satirical critique of British colonialism.”
- “The play ‘Death of a Salesman’ by Arthur Miller explores the disillusionment of the American Dream through the tragic downfall of the protagonist Willy Loman.”
- “Through the lens of feminist theory, Charlotte Perkins Gilman’s ‘The Yellow Wallpaper’ critiques the societal constraints placed on women’s mental and emotional well-being.”
- “Analyzing the motifs of light and darkness in Joseph Conrad’s ‘Heart of Darkness,’ one can interpret them as representations of morality and the human psyche.”
- “Edgar Allan Poe’s ‘The Tell-Tale Heart’ uses unreliable narration and symbolism to delve into the narrator’s descent into madness and guilt.”
- “In the film ‘Citizen Kane,’ Orson Welles employs non-linear storytelling and deep focus cinematography to explore the enigmatic life of the titular character.”
- “Analyzing the use of repetition and imagery in Langston Hughes’ ‘Dream Deferred,’ one can interpret the poem as a commentary on the consequences of unfulfilled dreams.”
- “Through allegorical elements and character interactions, William Golding’s ‘Lord of the Flies’ examines the inherent capacity for savagery within human nature.”
- “The painting ‘Guernica’ by Pablo Picasso serves as a powerful anti-war statement, depicting the horrors of conflict and the suffering of innocent civilians.”
- “Analyzing the themes of identity and societal conformity in Jhumpa Lahiri’s ‘The Namesake,’ one can uncover the struggles faced by immigrant families in adapting to new cultures.”
- “In ‘The Picture of Dorian Gray’ by Oscar Wilde, the portrait serves as a symbol of the protagonist’s moral decay and the consequences of pursuing eternal youth.”
- “Analyzing the use of color symbolism in F. Scott Fitzgerald’s ‘The Great Gatsby,’ one can interpret colors as reflections of characters’ personalities and societal decadence.”
- “Through the examination of allegorical elements in George Orwell’s ‘Animal Farm,’ one can uncover the representation of historical events and political ideologies.”
- “In ‘Brave New World’ by Aldous Huxley, the dystopian society’s use of technology and conditioning raises questions about the cost of sacrificing individuality for stability.”
- “Analyzing the character of Lady Macbeth in Shakespeare’s ‘Macbeth,’ one can discern her ambition-driven transformation and the psychological toll of her actions.
- “In ‘Pride and Prejudice’ by Jane Austen, the social commentary and character interactions illuminate the societal norms and expectations of the Regency era.”
- “Analyzing the use of religious symbolism in Herman Melville’s ‘Moby-Dick,’ one can interpret the white whale as a representation of the unattainable and the divine.”
- “The film ‘The Shawshank Redemption’ explores themes of hope and redemption through the friendship between two inmates, offering a commentary on the human spirit.”
- “Analyzing the motif of the American Dream in ‘The Great Gatsby,’ F. Scott Fitzgerald critiques the pursuit of materialism and the illusion of social mobility.”
- “In ‘Othello’ by William Shakespeare, the tragic downfall of the titular character is driven by jealousy and manipulation, revealing the destructive power of unchecked emotions.”
- “Analyzing the use of symbolism in T.S. Eliot’s poem ‘The Waste Land,’ one can interpret various images and references as reflections of societal decay and spiritual desolation.”
- “The painting ‘American Gothic’ by Grant Wood conveys a complex narrative through the stern expressions and juxtaposition of the farmer and his daughter.”
- “Analyzing the character development in Jane Eyre’s journey, Charlotte Brontë examines themes of independence, feminism, and self-discovery.”
- “In ‘The Metamorphosis’ by Franz Kafka, the protagonist’s transformation into a giant insect serves as a metaphor for alienation and the absurdity of modern life.”
- “Analyzing the use of foreshadowing and symbolism in William Faulkner’s ‘A Rose for Emily,’ one can interpret the decayed mansion as a representation of the past and its lingering impact.”
- “Through allegorical elements in ‘The Alchemist’ by Paulo Coelho, one can uncover themes of personal legend and the transformative power of following one’s dreams.”
- “Analyzing the narrative structure in Gabriel García Márquez’s ‘Chronicle of a Death Foretold,’ one can discern the multi-perspective exploration of truth and collective guilt.”
- “The sculpture ‘The Thinker’ by Auguste Rodin captures the contemplative nature of human thought and the complexity of philosophical introspection.”
- “Analyzing the use of irony and satire in Voltaire’s ‘Candide,’ one can interpret the protagonist’s misadventures as a commentary on the irrationality of human behavior.”
- “Through the exploration of nature and human experience in Ralph Waldo Emerson’s essays, transcendentalism emerges as a celebration of individual intuition and connection.”
- “Analyzing the use of narrative structure in Vladimir Nabokov’s ‘Lolita,’ one can discern the unreliable narration that challenges readers’ perceptions of truth and morality.”
- “In ‘The Awakening’ by Kate Chopin, the protagonist’s journey towards self-discovery and liberation reflects the constraints placed on women in the 19th-century society.”
- “Analyzing the use of dramatic monologue in Robert Browning’s ‘My Last Duchess,’ one can uncover the psychological complexity and possessive nature of the speaker.”
- “Through allegorical elements and philosophical themes in Albert Camus’ ‘The Stranger,’ the protagonist’s indifference to societal norms questions the absurdity of existence.”
- “Analyzing the use of myth and symbolism in Toni Morrison’s ‘Beloved,’ one can interpret the haunting presence of the titular character as a representation of historical trauma.”
- “In ‘Crime and Punishment’ by Fyodor Dostoevsky, the psychological turmoil of the protagonist Raskolnikov reflects the tension between morality and rationality.”
- “Analyzing the narrative techniques in Salman Rushdie’s ‘Midnight’s Children,’ one can discern the blending of history and magical realism to explore India’s postcolonial identity.”
- “Through the examination of imagery and metaphor in Sylvia Plath’s poetry, themes of mental illness, identity, and gender roles come to the forefront.”
- “Analyzing the use of symbolism in E.M. Forster’s ‘A Passage to India,’ one can interpret the Marabar Caves as a metaphor for the complexity of cultural misunderstandings.”
- “The short story ‘The Lottery’ by Shirley Jackson employs irony and social commentary to critique blind adherence to tradition and the potential for collective cruelty.”
- “Analyzing the use of allegory in John Bunyan’s ‘The Pilgrim’s Progress,’ one can interpret the protagonist’s journey as a representation of spiritual enlightenment and salvation.”
- “In ‘Their Eyes Were Watching God’ by Zora Neale Hurston, the protagonist Janie’s journey towards self-discovery reflects her search for autonomy and empowerment.”
- “Analyzing the use of literary devices in Gabriel García Márquez’s ‘Love in the Time of Cholera,’ one can uncover the exploration of enduring love and the passage of time.”
- “Through allegorical elements in Franz Kafka’s ‘The Trial,’ one can interpret the absurdity of the bureaucratic legal system as a commentary on the human struggle for control.”
- “Analyzing the use of dramatic irony in Shakespeare’s ‘Romeo and Juliet,’ one can discern the tragic irony that underscores the lovers’ fate and the societal feud.”
- “In ‘The Road’ by Cormac McCarthy, the post-apocalyptic landscape serves as a metaphor for the fragility of human existence and the pursuit of hope.”
- “Analyzing the themes of colonization and cultural clash in Chinua Achebe’s ‘Things Fall Apart,’ one can interpret the protagonist Okonkwo’s downfall as a representation of societal upheaval.”
- “Through allegorical elements in Jack London’s ‘To Build a Fire,’ the protagonist’s struggle against nature serves as a reflection of human hubris and vulnerability.”
- “In ‘Invisible Man’ by Ralph Ellison, the protagonist’s invisibility becomes a metaphor for social marginalization and the dehumanizing effects of racial prejudice.”
- “Analyzing the use of motifs and symbolism in Kate Chopin’s ‘The Story of an Hour,’ one can interpret the protagonist’s liberation as a commentary on societal expectations.”
- “Through allegorical elements in Franz Kafka’s ‘Metamorphosis,’ one can interpret the protagonist’s transformation as a representation of alienation and the absurdity of modern life.”
- “In ‘Gulliver’s Travels’ by Jonathan Swift, the protagonist’s encounters with different societies serve as satirical commentaries on various aspects of human behavior.”
- “Analyzing the use of symbolism in William Faulkner’s ‘As I Lay Dying,’ one can interpret the journey to bury Addie Bundren’s body as a representation of family dynamics and individual motivations.”
- “Through allegorical elements in Herman Melville’s ‘Bartleby, the Scrivener,’ one can interpret the enigmatic character Bartleby as a representation of passive resistance and societal alienation.”
- “In ‘The Handmaid’s Tale’ by Margaret Atwood, the dystopian society serves as a critique of patriarchal control and the erosion of women’s rights.”
- “Analyzing the use of foreshadowing and symbolism in Shirley Jackson’s ‘The Haunting of Hill House,’ one can interpret the house itself as a representation of psychological trauma.”
- “Through allegorical elements in Albert Camus’ ‘The Plague,’ one can interpret the outbreak of plague as a metaphor for the absurdity of human existence and the inevitability of suffering.”
- “In ‘The Sun Also Rises’ by Ernest Hemingway, the Lost Generation’s disillusionment serves as a commentary on the aftermath of World War I.”
- “Analyzing the use of metaphors and allegory in John Milton’s ‘Paradise Lost,’ one can interpret Satan’s rebellion as a representation of the dangers of pride and ambition.”
- “Through allegorical elements in H.G. Wells’ ‘The Time Machine,’ one can interpret the protagonist’s journey to the distant future as a commentary on societal evolution and the consequences of unchecked progress.”
- “In ‘Wuthering Heights’ by Emily Brontë, the tumultuous relationship between Heathcliff and Catherine serves as a metaphor for the destructive power of passionate obsession.”
- “Analyzing the use of irony and satire in Mark Twain’s ‘The Adventures of Huckleberry Finn,’ one can interpret the river as a symbol of freedom and a commentary on the racial tensions of the time.”
- “Through allegorical elements in John Steinbeck’s ‘Of Mice and Men,’ one can interpret the dream of owning a piece of land as a representation of companionship and the American Dream.”
- “In ‘The Kite Runner’ by Khaled Hosseini, the protagonist’s journey towards redemption serves as a commentary on guilt, betrayal, and the complexities of friendship.”
- “Analyzing the use of symbolism in Aldous Huxley’s ‘Brave New World,’ one can interpret the conditioning and drug-induced happiness as a representation of societal control and the loss of individuality.”
- “Through allegorical elements in William Golding’s ‘Lord of the Flies,’ the descent into savagery among the stranded boys serves as a commentary on the inherent darkness within humanity.”
- “In Gabriel García Márquez’s ‘Love in the Time of Cholera,’ the protagonist’s enduring love and pursuit of lost opportunities serve as a reflection of the passage of time and the complexities of relationships.”
- “Analyzing the use of narrative structure in Leo Tolstoy’s ‘Anna Karenina,’ one can discern the parallel narratives of different characters as a commentary on societal norms and the consequences of personal choices.”
- “Through allegorical elements in Franz Kafka’s ‘The Castle,’ one can interpret the protagonist’s futile attempts to reach the inaccessible castle as a representation of the human struggle for meaning and belonging.”
- “In George Orwell’s ‘Down and Out in Paris and London,’ the protagonist’s experiences of poverty and social alienation serve as a commentary on the disparities within society.”
- “Analyzing the use of symbolism in E.E. Cummings’ poetry, one can interpret his innovative typography and language as a representation of individualism and breaking away from convention.”
- “Through allegorical elements in Jean-Paul Sartre’s play ‘No Exit,’ the characters’ confinement in a room becomes a metaphor for existential anguish and the consequences of human choices.”
- “In William Shakespeare’s ‘Julius Caesar,’ the manipulation of public opinion serves as a commentary on the dynamics of power, loyalty, and the consequences of political ambition.
Analytical Essay Thesis Statement Example for High School
An analytical essay’s thesis statement for high school sets the stage for the examination of a topic, delving into its complexities and drawing insights based on evidence.
- In Shakespeare’s “Romeo and Juliet,” the theme of fate challenges the power of free will as seen through the tragic end of the young lovers.
- The portrayal of friendship in “The Outsiders” demonstrates the significance of social class divides in the 1960s.
- Through symbolism and imagery, Emily Dickinson’s poems convey profound themes about life, death, and eternity.
- Atticus Finch’s moral integrity in “To Kill a Mockingbird” stands as a beacon of hope in a racially divided society.
- “Lord of the Flies” uses the island as a microcosm to examine the inherent evil in human nature.
- George Orwell’s “1984” delves deep into the dangers of totalitarian governments and the loss of individuality.
- The character development of Elizabeth Bennet in “Pride and Prejudice” sheds light on the societal constraints of women during the Regency era.
- “The Catcher in the Rye” critiques the phoniness of adulthood while highlighting the vulnerability of adolescence.
- The journey of Bilbo Baggins in “The Hobbit” is a testament to personal growth and the discovery of inner courage.
- In “Fahrenheit 451,” Bradbury warns about the consequences of censorship and the loss of intellectual freedom.
Analytical Essay Thesis Statement Example for Middle School
Middle school thesis statements for analytical essays examine topics in a straightforward manner, building critical thinking skills.
- “Bridge to Terabithia” shows that friendship can help overcome personal challenges and grief.
- The challenges faced by Percy Jackson highlight the complexities of growing up with a unique identity.
- Matilda uses her intellect and supernatural powers to combat negativity and find her place in the world.
- “The Giver” reveals the dangers of a seemingly perfect society devoid of memories and emotions.
- Through “The Lion, the Witch, and the Wardrobe,” the Pevensie siblings learn about bravery, sacrifice, and loyalty.
- In “Holes,” the interwoven stories demonstrate the impact of family legacies and the power of redemption.
- “Charlotte’s Web” uses the farm setting to explore themes of friendship, sacrifice, and the cycle of life.
- “Diary of a Wimpy Kid” humorously addresses the challenges and intricacies of middle school life.
- Through “Harry Potter and the Sorcerer’s Stone,” Rowling discusses the importance of choices in shaping one’s destiny.
- “A Wrinkle in Time” showcases the battle between good and evil, emphasizing the power of love.
Analytical Essay Thesis Statement Example for College
College-level thesis statements delve deeper into complex topics, offering nuanced insights and arguments.
- “Moby Dick” serves as a profound exploration of obsession, illustrating its destructive consequences and moral ambiguities.
- In “The Great Gatsby,” Fitzgerald critiques the American Dream, revealing its inherent flaws and the disillusionment of the Jazz Age.
- “One Hundred Years of Solitude” portrays the cyclical nature of history through the Buendía family’s experiences.
- Virginia Woolf’s “To the Lighthouse” delves into the human consciousness, capturing fleeting emotions and moments.
- In “Brave New World,” Huxley showcases the dehumanizing effects of technological advancements and societal uniformity.
- “Heart of Darkness” explores the impact of colonialism, presenting a dark reflection on human nature and moral corruption.
- Toni Morrison’s “Beloved” addresses the haunting legacy of slavery and its lasting psychological effects.
- Through “The Handmaid’s Tale,” Atwood critiques patriarchal societies, illustrating the dangers of religious extremism and loss of female agency.
- “Crime and Punishment” offers a deep psychological analysis of guilt and redemption through Raskolnikov’s actions and motivations.
- Franz Kafka’s “The Metamorphosis” provides an existential view of alienation and identity crisis in the modern world.
Analytical Essay Thesis Statement Example for Beginners
Beginner-level thesis statements offer clear and simple insights, setting the foundation for deeper analytical thinking.
- “The Little Prince” teaches readers about the importance of relationships and seeing with the heart.
- “Charlotte’s Web” illustrates the value of friendship and the inevitability of life’s cycles.
- “The Very Hungry Caterpillar” uses vibrant illustrations to show the process of metamorphosis in nature.
- In “Where the Wild Things Are,” Max learns about emotions and the comfort of home.
- “The Rainbow Fish” highlights the joy of sharing and the essence of true beauty.
- “Green Eggs and Ham” humorously emphasizes the idea of trying new things and overcoming initial hesitations.
- Through “The Cat in the Hat,” Dr. Seuss illustrates the fun and chaos that arise from breaking rules.
- “Goodnight Moon” uses repetitive structure and rhymes to convey the calming ritual of bedtime.
- “Brown Bear, Brown Bear, What Do You See?” introduces young readers to colors and animals through patterned text.
- “Corduroy” portrays the desire for belonging and the importance of friendship and acceptance.
How do you start an analytical thesis?
Starting an analytical thesis requires a clear understanding of the topic, a comprehensive evaluation of the relevant materials, and identifying the primary elements to be analyzed.
- Select a Topic: The first step in starting an analytical thesis is to select a specific topic or aspect you want to explore in-depth.
- Research the Topic: Before drafting your thesis, it’s important to delve into your topic. Familiarize yourself with the primary sources, secondary analyses, and any related discussions.
- Identify a Focus: Determine the specific aspect of the topic you want to analyze. This could be a character in a novel, a historical event’s cause and effect, or a particular trend in science.
- Ask Analytical Questions: Pose questions that will guide your analysis. For example, “What is the significance of this character’s actions?” or “How does this event influence the larger narrative?”
What makes a good analytical thesis?
A good analytical thesis possesses several characteristics:
- Clear and Concise: A thesis should clearly convey your main argument without being overly wordy.
- Specific: It should narrow down your topic to a specific aspect or element that can be thoroughly explored in your essay.
- Arguable: A good thesis presents an argument or an interpretation that could be challenged by others.
- Evidence-Based: It should be based on evidence from the source material.
- Relevant: The thesis should be pertinent to the assignment or topic at hand.
- Original: Your thesis should offer a fresh perspective or insight, rather than simply stating the obvious.
How do you write a thesis statement for an analytical essay? – Step by Step Guide
- Read Your Source Material: Engage with your primary source, noting key elements, themes, or patterns that emerge.
- Identify Your Main Argument: What primary message or insight do you wish to convey about your topic?
- Gather Supporting Evidence: List down the pieces of evidence from the source that support your main argument.
- Formulate a Working Thesis: Draft a tentative thesis statement that encapsulates your main argument and supporting evidence.
- Refine and Narrow: Make sure your thesis is specific and focuses on a particular aspect of your topic.
- Ensure It’s Debatable: Your thesis should present a perspective or interpretation that can be debated.
- Seek Feedback: Discuss your thesis with peers, instructors, or mentors to get feedback and further refine it.
- Finalize the Statement: Once refined, finalize your thesis statement, ensuring it accurately represents your analytical insights.
Tips for Writing an Analytical Thesis Statement Example
- Start Broad, then Narrow Down: Begin with a broad perspective on your topic and then hone in on the specific area you want to analyze.
- Avoid Subjectivity: While an analytical thesis represents your interpretation, it should be based on evidence and not personal biases.
- Stay Active: Use active voice for a more assertive and clear thesis.
- Revisit and Revise: As you write your essay, you might find more insights that can refine your thesis. Be open to revisiting and tweaking your statement.
- Avoid Vague Language: Words like “might,” “could,” or “possibly” can weaken your thesis. Be assertive in your statement.
- Test Your Thesis: A good practice is to try to counter-argue your thesis. If you can find valid counter-arguments, it might be too weak or broad.
- Keep it Focused: Your thesis should only cover what you will discuss in your essay, not introduce new topics.
- Practice Makes Perfect: Write multiple versions of your thesis before settling on the final one. This practice will help you refine your analytical skills over time.
An analytical essay thesis statement is the cornerstone of any analytical essay, offering a concise insight into the writer’s analysis. Crafting it requires a clear understanding of the topic, supporting evidence, and a focused approach. By adopting best practices and refining one’s skills, a writer can effectively convey their analytical insights, enhancing the overall impact of their essay.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
Write an Analytical Essay Thesis Statement on the symbolism in
Create an Analytical Essay Thesis Statement analyzing the effects of global warming.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A strong thesis statement for a rhetorical analysis is NOT… A simple statement of your topic A broad statement A statement of facts or statistics A summary of the author's essay you are analyzing A statement of what you're going to do in the essay Examples of weak rhetorical analysis thesis statements:
A strong thesis statement for a rhetorical analysis is NOT… A broad, simple statement of your topic A statement of facts or statistics A summary of the author's essay you are analyzing A statement of what you're going to do in the essay Examples of weak rhetorical analysis thesis statements:
100 Thesis Statement Examples for Rhetorical Analysis. Details. File Format. PDF. Size: 280 KB. Download. "Through her use of vivid imagery, Maya Angelou masterfully conveys the resilience of the human spirit in the face of adversity in her poem 'Still I Rise.'". "Through the skillful integration of statistics, personal anecdotes, and ...
1 Rhetorical Analysis Thesis Statement. 2 Tips to Compose a Thesis Statement for Rhetorical Analysis. 2.1 Doing Proper Analysis. 2.2 Find Concrete Examples. 2.3 Determine the Author's Purpose. 2.4 The Effect on the Audience. 2.5 Take a Position. 3 Do's and Don'ts when Writing a Thesis Statement. 3.1 Do's.
Good Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example. The step-by-step writing process of a rhetorical analysis essay is far more complicated than ordinary academic essays. This essay type critically analyzes the rhetorical means used to persuade the audience and their efficiency. The example provided below is the best rhetorical analysis essay example:
Step 1: As you are reading the passage, look for strategies or choices the author utilizes. Ask: What rhetorical choices does the writer/speaker make? (ie. juxtaposition, allusion, etc) This will be the basis of your thesis statement. Step 2: Mention the author's purpose in the thesis.
A rhetorical analysis is a type of essay that looks at a text in terms of rhetoric. This means it is less concerned with what the author is saying than with how they say it: their goals, techniques, and appeals to the audience. A rhetorical analysis is structured similarly to other essays: an introduction presenting the thesis, a body analyzing ...
Step 2: Identify the author's main argument. Step 3: Examine the rhetorical strategies used. Step 4: Analyze the effectiveness of the strategies. Step 5: Determine the author's intentions. A rhetorical analysis thesis statement captures the main argument you'll explore in your essay. It explains how the author uses different tools - things ...
5. State your thesis. Now that you've completed your analysis of the material, try to summarize it into one clear, concise thesis statement that will form the foundation of your essay. Your thesis statement should summarize: 1) the argument or purpose of the speaker; 2) the methods the speaker uses; and 3) the effectiveness of those methods ...
Outline - plan your essay. Like all other essays, your rhetorical analysis essay will have an introduction with a thesis, body paragraphs, and a conclusion. WRITE- write your essay. Asher AP ELAC Name: _____________________. Step 3: Organizing and Writing Your Essay: Some of this is redundant, but this breaks down some of the steps from MAD ...
After you've analyzed the rhetorical situation and rhetorical strategies, you'll need to create a thesis for your rhetorical analysis. Often, the thesis statement will assess the author's effectiveness in accomplishing their purpose with the intended audience through the use of rhetorical strategies. You might adapt a template like this ...
A Simplified Guide to Writing a Rhetorical Analysis RHETORICAL ANALYSIS Rhetoric studies how writers use words to influence a reader. Rhetorical analysis separates a work of non-fiction ... THE FINAL STEP: THESIS, BODY, AND CONCLUSION Your introduction should clearly state your argument about how the text's author persuades the reader. This is
The AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay is one of three essays included in the written portion of the AP English Exam. The full AP English Exam is 3 hours and 15 minutes long, with the first 60 minutes dedicated to multiple-choice questions. Once you complete the multiple-choice section, you move on to three equally weighted essays that ask you ...
A good rhetorical analysis does not try to address every element of a text; discuss just those aspects with the greatest [positive or negative] impact on the text's effectiveness. ... THESIS . A thesis for a rhetorical analysis does not address the content of the writer's argument. Instead, the thesis should be a
4. Summarizing Your Main Points. In your conclusion, sum up the main points of your analysis and restate your thesis. Without introducing any new points (such as topics or ideas you haven't already covered in the main body of your essay), summarize the overall impact that the author's rhetorical strategies likely had on their intended audience.
writer's position/issue, or explaining the issue. Instead, you are analyzing how the writer i. s in Creating a Rhetorical AnalysisPa. 1: AnalyzePick your text and read it thoroughly. Determine the speaker, audience, purpose, & genre.The spea. er refers to the first and last name of the writer. If the writer has credentials that len.
Rhetorical appeal #2: Pathos. The purpose of Pathos-driven rhetoric is to appeal to the reader's emotions. A common example of pathos as a rhetorical means is adverts by charities that try to make you donate money to a "good cause". To evoke the intended emotions in the reader, an author may use passionate language, tell personal stories ...
Name the author of the text and the title of their work followed by the date in parentheses. Use a verb to describe what the author does, e.g. "implies," "asserts," or "claims". Briefly summarize the text in your own words. Mention the persuasive techniques used by the rhetor and its effect.
Rhetorical Analysis Sample Essay. Harriet Clark. Ms. Rebecca Winter. CWC 101. 13 Feb. 2015. Not Quite a Clean Sweep: Rhetorical Strategies in. Grose's "Cleaning: The Final Feminist Frontier". A woman's work is never done: many American women grow up with this saying and feel it to be true. 1 One such woman, author Jessica Grose, wrote ...
Good Rhetorical Analysis Essay Examples. Examples help the readers to understand things in a better way. They also help a writer to compose an essay just like professionals. ... Thesis Statement Example for Rhetorical Analysis Essay. The thesis statement of a rhetorical analysis essay should explain the primary argument being made in the text.
An analytical thesis statement is a concise declaration that outlines the main focus of an analytical essay. It presents the central argument or analysis the essay will explore, providing a roadmap for readers to understand the specific perspective, interpretation, or evaluation the writer intends to present.