

Prose vs. Poetry: Their Differences, Overlaps, and Writing Each
Sean Glatch | May 15, 2024 | One Comment

The difference between prose and poetry seems easy to explain: one has blocks of text and fully-fleshed characters, the other has line breaks and pretty words. That’s it, right?
Despite their visual quirks, prose and poetry share many similarities: prose can be musical, poetry can have plots and characters, and both are millennia-old traditions. As such, it would be wrong to prescribe a rigid decision tree for writing prose vs. poetry—many writers have both in their toolkits, relying on each form to communicate different truths.
“Poetry creates the myth, the prose writer draws its portrait.” —Jean-Paul Sartre
So what is the difference between poetry and prose? And which should you write for which occasions? Again, we won’t give hard-and-fast rules, but we can explore their differences in depth and discuss their possibilities.
First, we’ll discuss the features of prose and poetry independently, then we’ll loop back to examine both their differences and their areas of overlap.
Prose Vs. Poetry: Contents
Prose Versus Verse: Line Breaks
Prose is more functional than poetry, how to read prose, further readings in fiction and nonfiction, artistic definitions of poetry vary, poetry uses language richly, how to read poetry, further readings in poetry, poetry vs. prose: a clear example of each, 5 similar features of prose and poetry, 10 differences between prose and poetry, poetry vs. prose venn diagram, prose vs. poetry: a final note on literary binaries, prose vs. poetry: defining prose.
Prose is the more common writing form that everyone is comfortable reading and writing. This article relies on prose—as do most ( but not all! ) novels, and just about all news stories, instruction manuals, scientific papers, and so on.
The most straightforward rule of thumb for knowing that you’re reading prose (as opposed to its counterpart, verse ) is that there are no defined line breaks : words go all the way to the edge of the page without “turning back” early.
A rule of thumb for prose (as opposed to its counterpart, verse ) is that there are no defined line breaks.
Again, that’s how this blog article works, along with most other writing, from tweets to short stories to scientific papers.
So why would you stop writing prose, and move over to the with-line-breaks type of writing known as verse? The line breaks aren’t arbitrary, but reflect an underlying difference in how prose and verse tend to be structured. To quote the always-helpful Wikipedia:
“Where the common unit of verse is based on meter or rhyme, the common unit of prose is purely grammatical, such as a sentence or paragraph.”
So is verse (writing with line breaks) always poetry? While two are often used synonymously, defining poetry requires more than just scanning for line breaks: as we’ll discuss below, poetry is also about the rich and musical use of language.
Prose is not the counterpart of poetry, but the counterpart of verse.
So prose is not the counterpart of poetry, but rather the counterpart of verse. So verse is not what strictly defines poetry. In fact, not all poetry is in verse—specifically, prose poetry isn’t. In other words, prose and poetry do overlap, whereas prose and verse don’t.
Most poetry is in verse, but some poetry is in prose.
We go into more detail on line breaks, stanzas, and the use of page space in the sections below.
A helpful pattern in understanding prose vs. poetry is as follows: prose tends to work in clearer meanings, and to be less musical (that is, working with the inherent rhythms and sonic properties of language) and less densely packed with meanings, literary devices , and associations, than poetry.
As such, prose writing tends to be linear: while a prosaic sentence can twist and turn, it tends to share clear information, generally in a logical order.
Prose tends to work in clearer meanings, and to be less musical and dense, than poetry.
Again, exceptions exist, notably prose poetry : prose writing—writing with no line endings or defined rhythmic meter—that is highly musical and dense, and that is generally more impressionistic and multifaceted than most prose in the meanings it conveys.
And then there’s prose writing that is enigmatic and dreamlike rather than clear and orderly, such as the stream-of-consciousness prose writing in James Joyce’s Ulysses .
These exceptions prove the rule, though: most other prose, from this blog article your friend’s next Facebook post to Mary Shelley’s Frankenstein , tends to follow the delineation described here.
We’ll allow Hemingway a last word with a slightly macho, not-applicable-to-every-prose-work, but still helpful description of prose: “Prose is architecture, not interior decoration.”
Sound good? To get a stronger feel for prose and further acquaint yourself with prose writing, take a look at the readings below.
This article gives close reading strategies for prose writing.
How to Read Prose: Close Reading Strategies for Prose Writers
The articles below outline helpful practices for numerous kinds of prose writing, from flash fiction to the novel, focusing especially on the common ingredients of storytelling .
- Crafting a Story Outline
- Freytag’s Pyramid
- Literary Devices in Prose
- Writing Flash Fiction
- Writing the Short Story
- Writing the Novella
- Writing the Novel
Prose vs. Poetry: Defining Poetry
Poetry is the oldest literary form, predating the written word (and therefore, prose) by several millennia. Up until the printing press revolutionized the distribution of literature, poetry was the main form for storytellers, who used meter and rhythm to perform oral retellings of their work.
So, what is poetry? As we’ve seen in our introduction to prose above, most—but not all—poetry is written in verse: writing with line breaks, organized around rhythm or meter rather than grammar. Still, we’ve also seen that verse is not what defines poetry, nor is all poetry based in verse.
So it’s not simply another word for verse. Is there an agreed-upon artistic definition of poetry as a literary form? (Spoiler: No.)
Artistic definitions of poetry change from poetic movement to poetic movement—and from poet to poet.
For example, William Wordsworth said that poetry is “the spontaneous overflow of powerful feelings… recollected in tranquility.” This sentiment—largely reflective of the Romantic era—certainly rings true for some poetry. However, New Formalist poets work with poetry to distill and reflect emotion through form and meter: in other words, structure over emotion.
The point is, there’s no singular way to define or understand the artistic aims of poetry. Rather, all poets must define these aims for themselves and write accordingly.
Poets must define the artistic aims of poetry for themselves and write accordingly.
Learning about poetry requires familiarizing yourself with what other poets have already done. This list of poetry movements can jumpstart your understanding of poetry’s complex and various histories.
Good poetry, from any tradition, sings and resonates beyond the merely “prosaic.”
Whatever literary tradition you ascribe to, poetry has a clear job to be rich, musical, evocative. Good poetry, from any tradition, sings and resonates in a way that goes beyond the merely “prosaic,” as in the following poem excerpt by Derek Walcott:
You will love again the stranger who was your self. Give wine. Give bread. Give back your heart to itself, to the stranger who has loved you
all your life, whom you ignored for another, who knows you by heart.
So poetry, in any tradition, is the “cheesecake of language”: packed to the brim with sonic and expressive power. In poetry, it’s not enough to make a rational point straightforwardly, like the prosaic sentence you’re reading is doing.
Samuel Taylor Coleridge said this beautifully, and we can give him the last word in defining poetry.
“Poetry: the best words in the best order.” —Samuel Taylor Coleridge
Cool, right? If you’d like to learn more, check out our guides for reading and understanding poetry.
This article gives close reading strategies for poetry writing.
How to Read Poetry Like a Poet
The articles below outline helpful practices poetry writing, including deep dives on common literary devices in poetry and established poetry forms.
- Poetry Forms
- Writing and Publishing a Poetry Book
Let’s cap the definitions of poetry and prose above by simply giving a clear example of each.
Here is some beautiful fiction writing that is definitely prose:
They were nearly born on a bus, Estha and Rahel. The car in which Baba, their father, was taking Ammu, their mother, to hospital in Shillong to have them, broke down on the winding tea-estate road in Assam. They abandoned the car and flagged down a crowded State Transport bus. With the queer compassion of the very poor for the comparatively well off, or perhaps only because they saw how hugely pregnant Ammu was, seated passengers made room for the couple, and for the rest of the journey Estha and Rahel’s father had to hold their mother’s stomach (with them in it) to prevent it from wobbling. That was before they were divorced and Ammu came back to live in Kerala.
—Arundhati Roy, The God of Small Things
And here is some writing that is definitely poetry:
We are such stuff As dreams are made on; and our little life Is rounded with a sleep.
—Shakespeare, The Tempest
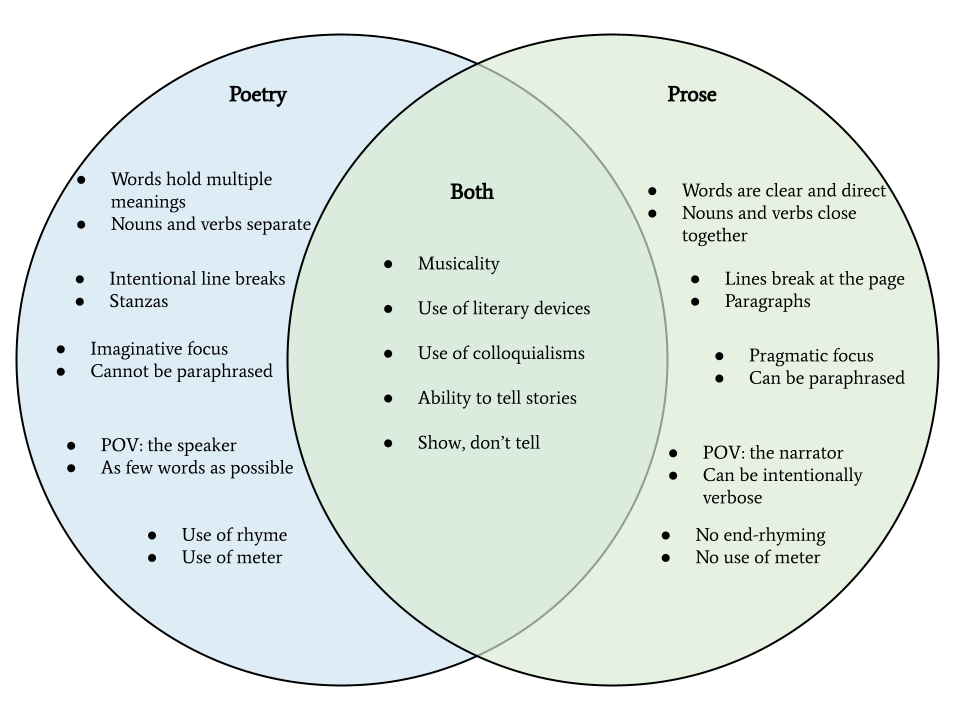
Having defined prose and poetry above, the reality is that they can be more similar than you might imagine. We’ll discuss their differences in a moment, but first, it’s important to understand the shared potential that each form holds:
- Musicality and rhythm
- Use of colloquial speech
- Use of literary devices
- Ability to tell stories
- Show, don’t tell
1. Musicality and Rhythm
It’s a common misconception that only poetry can be musical. While rhythm and meter are important aspects of a poem’s construction, musicality begins with language, not with structure.
An immediate example of “musical prose” is The Great Gatsby by F. Scott Fitzgerald. Susan Bell, writer of The Artful Edit , argues that Gatsby finds its success precisely because of the story’s musical, elegant storytelling—certainly, the book has a charged poeticism that feels just as decadent and tasteful as the high society of the Roaring Twenties. Below is some undeniably musical prose:
2. Use of Literary Devices
Things are like other things, which is the essence of literary devices. While some devices are unique to each form—poems have enjambment, prose can begin in media res —a successful piece of writing requires literary devices .
3. Use of Colloquial Speech
Yes, some writing uses lofty and erudite language. However, contemporary prose and poetry writers, from all eras, recognize the importance of speaking to their audience.
Colloquial speech is one way of speaking to your audience. A colloquialism is a turn of phrase with a specific social and temporal context. For example, “groovy” belongs to the American 1970s, Victorian Brits called a brave person “bricky,” and Gen Z’ers “stan” on Twitter.
In literature, Jay Gatsby’s “old sport” is just as colloquial as the poem “A Study of Reading Habits ,” which uses phrases like “right hook” and “load of crap.”
4. Storytelling
Another common misconception is that poetry doesn’t tell stories. While fiction and nonfiction are the genres of prose, poetry also possesses a powerful narrative voice.
Singular poems can tell grand stories, especially poetry in antiquity. The Epic of Gilgamesh , The Odyssey , and Beowulf are all stories in verse, as are novel-poems like Autobiography of Red .
Additionally, contemporary poetry collections often tell stories, just with less linearity. Louise Gluck’s collection Wild Iris is told from the perspective of a flower, and as the seasons change, the flower observes the infinite singularity of mankind, God, and the Universe.
5. Show, Don’t Tell Writing
It’s important for storytellers to demonstrate their ideas without spoon feeding the reader. In other words, writers should Show instead of Tell.
Don’t tell me the moon is shining; show me the glint of light on broken glass. —Anton Chekhov
We consider “Show, Don’t Tell” a golden rule of writing. Brush up on it here !
We’ve discussed their similarities, but the difference between poetry and prose is usually fairly clear in practice. The following ten items distinguish the two. To help demonstrate our point, we represent each form with a well known piece of literature. Poetry examples were pulled from Dylan Thomas’ “ Do Not Go Gentle Into That Good Night ,” and prose examples come from “ The Cask of Amontillado ” by Edgar Allan Poe.
1. Prose vs. Poetry: Use of Page Space
In prose, a line of text begins and ends at the margins of the page. In poetry, the author uses shorter lines, broken before the page margins to introduce multiple meanings. Line breaks are an enduring feature of what differentiates prose and poetry, adding extra emphasis to certain words and sounds.
You’ll notice in prose that a partial line occurs only before a new paragraph.

In poetry, the line breaks mean something more intentional. The ending words can help uphold meter and rhyme schemes, and it also emphasizes important words: “night” and “light” are repeatedly pit against each other in Thomas’ villanelle .

2. Prose vs. Poetry: Paragraphs vs. Stanzas
Prose passages divide single ideas into sentences, and those sentences go on to form paragraphs. A new paragraph signifies the introduction of new ideas or the continuation of relevant information.

The equivalent of a paragraph in poetry is the stanza. Stanzas are groupings of lines which act as units of meaning, with different stanzas containing different ideas and images.

3. Prose vs. Poetry: Single vs. Multiple Meanings
In prose, the meaning of each word is usually straightforward, with double meanings (like puns and irony) clearly expressed. Most prose relies on clear meanings to deliver clear, linear messages.
By contrast, the language of poetry contains multitudes. One word can hold many different meanings, and ideas can be broken into both sentences and lines.
Take the line “old age should burn and rave at close of day.” The word rave can mean multiple things: it can mean to rant and rave as old people (stereotypically) do, or it can mean to rage and fight against. The pun here is intended to energize the reader,
4. Prose vs. Poetry: Noun-Verb Placements
In Standard English , which is the common (but not default) language of prose, nouns and verbs are found close to each other. This is a facet of “clear communication”—it’s important to know who is doing what as efficiently as possible.
We have bolded the noun-verb pairs in an excerpt from both the poem and prose piece.

Notice how the noun-verb pairs can stray from each other much more easily in poetry. Dylan Thomas inserts a noun-verb pair between a noun-verb pair in each stanza—which is much harder to use effectively in prose.

Notice that, in prose, a noun can have multiple verbs attached to it, but the first verb is almost always next to the noun.
5. Prose vs. Poetry: Rhyme (Sometimes)
There are two types of rhyme: internal and external rhyme. External rhyme occurs at the ends of lines, such as the many “-ight” words in Thomas’ poem.
Internal rhyme refers to words that rhyme with each other inside the same beat. These rhymes are not always intentional or charged with meaning, but they occur, such as in this sentence from Poe’s story:
“We had passed through walls of piled bones , with casks and puncheons intermingling, into the inmost recesses of the catacombs.”
Bones and catacombs aptly rhyme with each other. Note, rhyme is not a necessary feature of any prose and many poems. Though some poetry forms do require rhyme schemes, contemporary poets tend to eschew rhyming.
6. Prose vs. Poetry: Meter (Sometimes)
Like rhyme, meter is an (often) optional component of poetry writing. Meter refers to the stress patterns of syllables and the number of syllables per line. Well-executed meter can give poetry a certain musical quality.
Thomas’ poem is written in iambic pentameter, a requirement of the traditional villanelle form. This means there are 10 syllables in each line, following an unstressed-stressed pattern. To understand syllable stress, read Thomas’ poem out loud, and note how every second syllable is emphasized harder than the first.
Prose does not rely on meter to tell a story.
Prose does not have any metrical requirements, and thank goodness for that. Meter can be extraordinarily tough to impose on a poem, but it also affects how the reader interprets the piece. However, prose does not rely on meter to tell a story, as these poetry devices often instill multiple meanings in a piece.
7. Prose vs. Poetry: Pragmatic vs. Imaginative Focus
On a macro-level, the vision of poets and prose writers tends to differ. Prose has a pragmatic focus, meaning that each word should clearly advance a specific idea or narrative. The focus of prose is storytelling, so the author has a duty to use words diligently.
While poetry can tell stories, a poem rarely focuses on plot points, settings, and characters.
While poetry can tell stories, a poem rarely focuses on plot points, settings, and characters. Rather, poetry has an imaginative focus. Words are allowed to break their conventional bounds in the goal of expressing emotions, and ideas can stack upon each other like grains of sand in a sand castle.
So, what’s pragmatic about Poe, and what’s imaginative about Thomas? Every word in Poe’s piece describes details and events that push the reader towards the climax. At no point does the reader jump out of the narrative to speculate or stargaze.
In Thomas’ poem, the words don’t point the reader towards a specific event, but they do encourage the reader to think deeply about abstract ideas. Old or young, the reader will contend with ideas of life, death, justice, goodness, and the judgment against our souls. In 19 lines of mostly concrete images, the poet asks us to read imaginatively—and in the process, to learn what we believe.
8. Prose vs. Poetry: Paraphrasability
A piece of prose can be summarized. If you ask “what is ‘The Cask of Amontillado’ about?”, it is possible to paraphrase the story and get the gist of its deeper meaning. In short, Poe’s story observes a man desperate for revenge, only to find that revenge often hurts both the punisher and the punished.
Poetry is generally harder to summarize than prose, because it tends to include greater multiplicities of meaning.
Poetry is generally harder to summarize than prose, because it tends to include greater multiplicities of meaning. No one can tell you what a certain poem means. They can tell you what it isn’t —for example, “Do Not Go Gentle” is not about heartbreak, war, or the summertime—but deciding what a poem means requires a reader’s own attention.
For example, one could summarize Thomas’ poem as “an ode to Thomas’ dying father, with a vengeful bent against mankind’s eventual death.” But, does saying that invoke Thomas’ juxtaposition of light and dark? His use of rhyme to draw a conceit? His need to believe in the transience of the soul? By the time you’ve summarized the poem, you’ve written something as long as the poem itself. Poetry cannot be paraphrased.
9. Prose vs. Poetry: Point of View
Prose and poetry treat “point of view” in very different ways. A point of view (POV) refers to who is telling the story. The storyteller doesn’t always have a name or a face, but they do inevitably change how a story is read.
In prose, there are 4 main POVs:
- First Person (I): The story is told in the first person, from a character who is either the protagonist or adjacent to the protagonist. The Cask of Amontillado uses the first person POV.
- Second Person (You): The story is told in the second person. Often, the writer will substitute “the protagonist” for “you,” making the story’s actions feel more intimate and personal. Second Person storytelling is rare, but not unheard of.
- Third Person Limited (He/She/They): The story is told in the third person, and it focuses on the perspective of the protagonist. We have access to most of their thoughts and feelings, but our access to other people is limited by the protagonist’s perspective. Sometimes, writers combine this with the intimacy of 1st person narration, in a technique called free indirect discourse .
- Third Person Omniscient (He/She/They): The story is told in the third person, and the narrator has access to everyone’s thoughts, feelings, and actions. We can jump from person to person with ease, interweaving webs of complex narratives together.
Some stories will also take a Third Person Mixed approach, meaning the meat of the story is told from the protagonist’s perspective, but the reader occasionally jumps to someone else’s POV or to a historical time period.
While poetry can use the same pronouns (I/You/He/She/They), it uses POV differently. A poem is always told from the perspective of “the speaker.” The speaker can be the poet themselves—Dylan Thomas is certainly the voice behind his poem, and he is certainly talking to his father. However, the correct approach is to always call the poem’s POV “the speaker,” as a poem can inhibit many different voices at once. Finally, poetry is much easier to apply to yourself when the speaker isn’t anyone in particular.
10. Prose vs. Poetry: Concision
Prose and poetry writers should both write concisely. Concise writing eschews redundancies and makes every word count. However, concision means something different for the two forms.
In prose, concision generally means that not a word is wasted in conveying information. Concise prose expresses its meaning clearly.
Concise prose expresses its meaning clearly.
Of course, good prose can still be long-winded, as long as this heightens the effect of the work. Take this sentence from Poe’s story:
“It must be understood that neither by word nor deed had I given Fortunato cause to doubt my good-will. I continued, as was my wont, to smile in his face, and he did not perceive that my smile now was at the thought of his immolation.”
These sentences are 19 and 27 words long, respectively. They can also be summarized as follows: “Fortunato thought my smile bore good-will, not the desire to immolate him.”
What does Poe’s long-windedness afford him? Despite being easily paraphrased, every word does count in these two sentences, because they are a part of the narrator’s characterization. He is a long-winded schemer, and that affects how the story must be told, since Poe has chosen the first person to make us intimate with the narrator’s internal conflict.
Poetry is a different situation. Because poetry has line breaks, stanzas, and (sometimes) rhyme and meter, its concision takes a different form. In a poem, it’s great if every word contains heavy meaning; it’s even greater when words contain multiplicities and challenge the reader’s ideas. Economy in poetry is maximizing its impact, musicality, and richness—not necessarily its clear, single meaning.
Economy in poetry is maximizing its impact, musicality, and richness—not necessarily its clear, single meaning.
If you stretched a poem into prose, it would read like a terrible short story, because the concision afforded to poetry is different than that of prose. Concise prose focuses more on clarity of meaning, and poetry more on maximizing the richness and impact of every syllable.
Any article like this risks making literature seem binary, as though prose and poetry were totally discrete entities; so in closing, it’s good to note again that writers, especially contemporary writers, often work at the intersection of prose and poetry, resulting in genres like the prose poem , the lyrical essay or the poetry novel . (And we haven’t even touched on scriptwriting, which is a different form of communication altogether.)
There is much to explore outside of poetry and prose; this article simply covers the basics. As you advance on your writing journey, don’t be afraid to experiment with words outside of the traditional “prose vs. poetry” binary. You might be shocked by what you can accomplish!
Explore both Prose and Poetry at Writers.com
Whether you’re experimenting with poetry, fiction, or creative nonfiction, Writers.com has the classes to help you succeed. Take a look at our upcoming courses —and gain valuable insights from our instructors and writing community .
Sean Glatch
Great summary. I write poetry, prose poems, flash fiction and short stories so I’m using the grab bag of everything you said here! Never taught about line breaks, though. I see some poets going willy nilly all over the page. Maybe there just aren’t any rules where this is concerned…
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
VIDEO COURSE
Finish your draft in our 3-month master class. Sign up now to watch a free lesson!
Learn How to Write a Novel
Finish your draft in our 3-month master class. Enroll now for daily lessons, weekly critique, and live events. Your first lesson is free!

Guides • Perfecting your Craft
Last updated on Feb 14, 2023
10 Types of Creative Writing (with Examples You’ll Love)
A lot falls under the term ‘creative writing’: poetry, short fiction, plays, novels, personal essays, and songs, to name just a few. By virtue of the creativity that characterizes it, creative writing is an extremely versatile art. So instead of defining what creative writing is , it may be easier to understand what it does by looking at examples that demonstrate the sheer range of styles and genres under its vast umbrella.
To that end, we’ve collected a non-exhaustive list of works across multiple formats that have inspired the writers here at Reedsy. With 20 different works to explore, we hope they will inspire you, too.
People have been writing creatively for almost as long as we have been able to hold pens. Just think of long-form epic poems like The Odyssey or, later, the Cantar de Mio Cid — some of the earliest recorded writings of their kind.
Poetry is also a great place to start if you want to dip your own pen into the inkwell of creative writing. It can be as short or long as you want (you don’t have to write an epic of Homeric proportions), encourages you to build your observation skills, and often speaks from a single point of view .
Here are a few examples:
“Ozymandias” by Percy Bysshe Shelley
Nothing beside remains. Round the decay Of that colossal Wreck, boundless and bare The lone and level sands stretch far away.

This classic poem by Romantic poet Percy Shelley (also known as Mary Shelley’s husband) is all about legacy. What do we leave behind? How will we be remembered? The great king Ozymandias built himself a massive statue, proclaiming his might, but the irony is that his statue doesn’t survive the ravages of time. By framing this poem as told to him by a “traveller from an antique land,” Shelley effectively turns this into a story. Along with the careful use of juxtaposition to create irony, this poem accomplishes a lot in just a few lines.
“Trying to Raise the Dead” by Dorianne Laux
A direction. An object. My love, it needs a place to rest. Say anything. I’m listening. I’m ready to believe. Even lies, I don’t care.
Poetry is cherished for its ability to evoke strong emotions from the reader using very few words which is exactly what Dorianne Laux does in “ Trying to Raise the Dead .” With vivid imagery that underscores the painful yearning of the narrator, she transports us to a private nighttime scene as the narrator sneaks away from a party to pray to someone they’ve lost. We ache for their loss and how badly they want their lost loved one to acknowledge them in some way. It’s truly a masterclass on how writing can be used to portray emotions.
If you find yourself inspired to try out some poetry — and maybe even get it published — check out these poetry layouts that can elevate your verse!
Song Lyrics
Poetry’s closely related cousin, song lyrics are another great way to flex your creative writing muscles. You not only have to find the perfect rhyme scheme but also match it to the rhythm of the music. This can be a great challenge for an experienced poet or the musically inclined.
To see how music can add something extra to your poetry, check out these two examples:
“Hallelujah” by Leonard Cohen
You say I took the name in vain I don't even know the name But if I did, well, really, what's it to ya? There's a blaze of light in every word It doesn't matter which you heard The holy or the broken Hallelujah
Metaphors are commonplace in almost every kind of creative writing, but will often take center stage in shorter works like poetry and songs. At the slightest mention, they invite the listener to bring their emotional or cultural experience to the piece, allowing the writer to express more with fewer words while also giving it a deeper meaning. If a whole song is couched in metaphor, you might even be able to find multiple meanings to it, like in Leonard Cohen’s “ Hallelujah .” While Cohen’s Biblical references create a song that, on the surface, seems like it’s about a struggle with religion, the ambiguity of the lyrics has allowed it to be seen as a song about a complicated romantic relationship.
“I Will Follow You into the Dark” by Death Cab for Cutie
If Heaven and Hell decide that they both are satisfied Illuminate the no's on their vacancy signs If there's no one beside you when your soul embarks Then I'll follow you into the dark

You can think of song lyrics as poetry set to music. They manage to do many of the same things their literary counterparts do — including tugging on your heartstrings. Death Cab for Cutie’s incredibly popular indie rock ballad is about the singer’s deep devotion to his lover. While some might find the song a bit too dark and macabre, its melancholy tune and poignant lyrics remind us that love can endure beyond death.
Plays and Screenplays
From the short form of poetry, we move into the world of drama — also known as the play. This form is as old as the poem, stretching back to the works of ancient Greek playwrights like Sophocles, who adapted the myths of their day into dramatic form. The stage play (and the more modern screenplay) gives the words on the page a literal human voice, bringing life to a story and its characters entirely through dialogue.
Interested to see what that looks like? Take a look at these examples:
All My Sons by Arthur Miller
“I know you're no worse than most men but I thought you were better. I never saw you as a man. I saw you as my father.”

Arthur Miller acts as a bridge between the classic and the new, creating 20th century tragedies that take place in living rooms and backyard instead of royal courts, so we had to include his breakout hit on this list. Set in the backyard of an all-American family in the summer of 1946, this tragedy manages to communicate family tensions in an unimaginable scale, building up to an intense climax reminiscent of classical drama.
💡 Read more about Arthur Miller and classical influences in our breakdown of Freytag’s pyramid .
“Everything is Fine” by Michael Schur ( The Good Place )
“Well, then this system sucks. What...one in a million gets to live in paradise and everyone else is tortured for eternity? Come on! I mean, I wasn't freaking Gandhi, but I was okay. I was a medium person. I should get to spend eternity in a medium place! Like Cincinnati. Everyone who wasn't perfect but wasn't terrible should get to spend eternity in Cincinnati.”
A screenplay, especially a TV pilot, is like a mini-play, but with the extra job of convincing an audience that they want to watch a hundred more episodes of the show. Blending moral philosophy with comedy, The Good Place is a fun hang-out show set in the afterlife that asks some big questions about what it means to be good.
It follows Eleanor Shellstrop, an incredibly imperfect woman from Arizona who wakes up in ‘The Good Place’ and realizes that there’s been a cosmic mixup. Determined not to lose her place in paradise, she recruits her “soulmate,” a former ethics professor, to teach her philosophy with the hope that she can learn to be a good person and keep up her charade of being an upstanding citizen. The pilot does a superb job of setting up the stakes, the story, and the characters, while smuggling in deep philosophical ideas.
Personal essays
Our first foray into nonfiction on this list is the personal essay. As its name suggests, these stories are in some way autobiographical — concerned with the author’s life and experiences. But don’t be fooled by the realistic component. These essays can take any shape or form, from comics to diary entries to recipes and anything else you can imagine. Typically zeroing in on a single issue, they allow you to explore your life and prove that the personal can be universal.
Here are a couple of fantastic examples:
“On Selling Your First Novel After 11 Years” by Min Jin Lee (Literary Hub)
There was so much to learn and practice, but I began to see the prose in verse and the verse in prose. Patterns surfaced in poems, stories, and plays. There was music in sentences and paragraphs. I could hear the silences in a sentence. All this schooling was like getting x-ray vision and animal-like hearing.

This deeply honest personal essay by Pachinko author Min Jin Lee is an account of her eleven-year struggle to publish her first novel . Like all good writing, it is intensely focused on personal emotional details. While grounded in the specifics of the author's personal journey, it embodies an experience that is absolutely universal: that of difficulty and adversity met by eventual success.
“A Cyclist on the English Landscape” by Roff Smith (New York Times)
These images, though, aren’t meant to be about me. They’re meant to represent a cyclist on the landscape, anybody — you, perhaps.
Roff Smith’s gorgeous photo essay for the NYT is a testament to the power of creatively combining visuals with text. Here, photographs of Smith atop a bike are far from simply ornamental. They’re integral to the ruminative mood of the essay, as essential as the writing. Though Smith places his work at the crosscurrents of various aesthetic influences (such as the painter Edward Hopper), what stands out the most in this taciturn, thoughtful piece of writing is his use of the second person to address the reader directly. Suddenly, the writer steps out of the body of the essay and makes eye contact with the reader. The reader is now part of the story as a second character, finally entering the picture.
Short Fiction
The short story is the happy medium of fiction writing. These bite-sized narratives can be devoured in a single sitting and still leave you reeling. Sometimes viewed as a stepping stone to novel writing, that couldn’t be further from the truth. Short story writing is an art all its own. The limited length means every word counts and there’s no better way to see that than with these two examples:
“An MFA Story” by Paul Dalla Rosa (Electric Literature)
At Starbucks, I remembered a reading Zhen had given, a reading organized by the program’s faculty. I had not wanted to go but did. In the bar, he read, "I wrote this in a Starbucks in Shanghai. On the bank of the Huangpu." It wasn’t an aside or introduction. It was two lines of the poem. I was in a Starbucks and I wasn’t writing any poems. I wasn’t writing anything.

This short story is a delightfully metafictional tale about the struggles of being a writer in New York. From paying the bills to facing criticism in a writing workshop and envying more productive writers, Paul Dalla Rosa’s story is a clever satire of the tribulations involved in the writing profession, and all the contradictions embodied by systemic creativity (as famously laid out in Mark McGurl’s The Program Era ). What’s more, this story is an excellent example of something that often happens in creative writing: a writer casting light on the private thoughts or moments of doubt we don’t admit to or openly talk about.
“Flowering Walrus” by Scott Skinner (Reedsy)
I tell him they’d been there a month at least, and he looks concerned. He has my tongue on a tissue paper and is gripping its sides with his pointer and thumb. My tongue has never spent much time outside of my mouth, and I imagine it as a walrus basking in the rays of the dental light. My walrus is not well.
A winner of Reedsy’s weekly Prompts writing contest, ‘ Flowering Walrus ’ is a story that balances the trivial and the serious well. In the pauses between its excellent, natural dialogue , the story manages to scatter the fear and sadness of bad medical news, as the protagonist hides his worries from his wife and daughter. Rich in subtext, these silences grow and resonate with the readers.
Want to give short story writing a go? Give our free course a go!

FREE COURSE
How to Craft a Killer Short Story
From pacing to character development, master the elements of short fiction.
Perhaps the thing that first comes to mind when talking about creative writing, novels are a form of fiction that many people know and love but writers sometimes find intimidating. The good news is that novels are nothing but one word put after another, like any other piece of writing, but expanded and put into a flowing narrative. Piece of cake, right?
To get an idea of the format’s breadth of scope, take a look at these two (very different) satirical novels:
Convenience Store Woman by Sayaka Murata
I wished I was back in the convenience store where I was valued as a working member of staff and things weren’t as complicated as this. Once we donned our uniforms, we were all equals regardless of gender, age, or nationality — all simply store workers.

Keiko, a thirty-six-year-old convenience store employee, finds comfort and happiness in the strict, uneventful routine of the shop’s daily operations. A funny, satirical, but simultaneously unnerving examination of the social structures we take for granted, Sayaka Murata’s Convenience Store Woman is deeply original and lingers with the reader long after they’ve put it down.
Erasure by Percival Everett
The hard, gritty truth of the matter is that I hardly ever think about race. Those times when I did think about it a lot I did so because of my guilt for not thinking about it.
Erasure is a truly accomplished satire of the publishing industry’s tendency to essentialize African American authors and their writing. Everett’s protagonist is a writer whose work doesn’t fit with what publishers expect from him — work that describes the “African American experience” — so he writes a parody novel about life in the ghetto. The publishers go crazy for it and, to the protagonist’s horror, it becomes the next big thing. This sophisticated novel is both ironic and tender, leaving its readers with much food for thought.
Creative Nonfiction
Creative nonfiction is pretty broad: it applies to anything that does not claim to be fictional (although the rise of autofiction has definitely blurred the boundaries between fiction and nonfiction). It encompasses everything from personal essays and memoirs to humor writing, and they range in length from blog posts to full-length books. The defining characteristic of this massive genre is that it takes the world or the author’s experience and turns it into a narrative that a reader can follow along with.
Here, we want to focus on novel-length works that dig deep into their respective topics. While very different, these two examples truly show the breadth and depth of possibility of creative nonfiction:
Men We Reaped by Jesmyn Ward
Men’s bodies litter my family history. The pain of the women they left behind pulls them from the beyond, makes them appear as ghosts. In death, they transcend the circumstances of this place that I love and hate all at once and become supernatural.
Writer Jesmyn Ward recounts the deaths of five men from her rural Mississippi community in as many years. In her award-winning memoir , she delves into the lives of the friends and family she lost and tries to find some sense among the tragedy. Working backwards across five years, she questions why this had to happen over and over again, and slowly unveils the long history of racism and poverty that rules rural Black communities. Moving and emotionally raw, Men We Reaped is an indictment of a cruel system and the story of a woman's grief and rage as she tries to navigate it.
Cork Dork by Bianca Bosker
He believed that wine could reshape someone’s life. That’s why he preferred buying bottles to splurging on sweaters. Sweaters were things. Bottles of wine, said Morgan, “are ways that my humanity will be changed.”
In this work of immersive journalism , Bianca Bosker leaves behind her life as a tech journalist to explore the world of wine. Becoming a “cork dork” takes her everywhere from New York’s most refined restaurants to science labs while she learns what it takes to be a sommelier and a true wine obsessive. This funny and entertaining trip through the past and present of wine-making and tasting is sure to leave you better informed and wishing you, too, could leave your life behind for one devoted to wine.
Illustrated Narratives (Comics, graphic novels)
Once relegated to the “funny pages”, the past forty years of comics history have proven it to be a serious medium. Comics have transformed from the early days of Jack Kirby’s superheroes into a medium where almost every genre is represented. Humorous one-shots in the Sunday papers stand alongside illustrated memoirs, horror, fantasy, and just about anything else you can imagine. This type of visual storytelling lets the writer and artist get creative with perspective, tone, and so much more. For two very different, though equally entertaining, examples, check these out:
Calvin & Hobbes by Bill Watterson
"Life is like topography, Hobbes. There are summits of happiness and success, flat stretches of boring routine and valleys of frustration and failure."
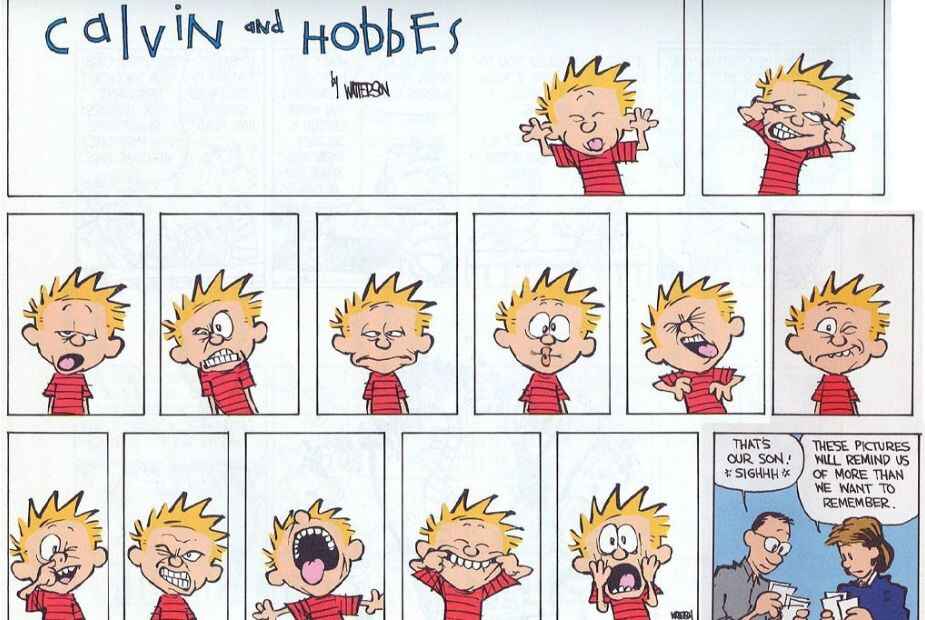

This beloved comic strip follows Calvin, a rambunctious six-year-old boy, and his stuffed tiger/imaginary friend, Hobbes. They get into all kinds of hijinks at school and at home, and muse on the world in the way only a six-year-old and an anthropomorphic tiger can. As laugh-out-loud funny as it is, Calvin & Hobbes ’ popularity persists as much for its whimsy as its use of humor to comment on life, childhood, adulthood, and everything in between.
From Hell by Alan Moore and Eddie Campbell
"I shall tell you where we are. We're in the most extreme and utter region of the human mind. A dim, subconscious underworld. A radiant abyss where men meet themselves. Hell, Netley. We're in Hell."
Comics aren't just the realm of superheroes and one-joke strips, as Alan Moore proves in this serialized graphic novel released between 1989 and 1998. A meticulously researched alternative history of Victorian London’s Ripper killings, this macabre story pulls no punches. Fact and fiction blend into a world where the Royal Family is involved in a dark conspiracy and Freemasons lurk on the sidelines. It’s a surreal mad-cap adventure that’s unsettling in the best way possible.
Video Games and RPGs
Probably the least expected entry on this list, we thought that video games and RPGs also deserved a mention — and some well-earned recognition for the intricate storytelling that goes into creating them.
Essentially gamified adventure stories, without attention to plot, characters, and a narrative arc, these games would lose a lot of their charm, so let’s look at two examples where the creative writing really shines through:
80 Days by inkle studios
"It was a triumph of invention over nature, and will almost certainly disappear into the dust once more in the next fifty years."

Named Time Magazine ’s game of the year in 2014, this narrative adventure is based on Around the World in 80 Days by Jules Verne. The player is cast as the novel’s narrator, Passpartout, and tasked with circumnavigating the globe in service of their employer, Phileas Fogg. Set in an alternate steampunk Victorian era, the game uses its globe-trotting to comment on the colonialist fantasies inherent in the original novel and its time period. On a storytelling level, the choose-your-own-adventure style means no two players’ journeys will be the same. This innovative approach to a classic novel shows the potential of video games as a storytelling medium, truly making the player part of the story.
What Remains of Edith Finch by Giant Sparrow
"If we lived forever, maybe we'd have time to understand things. But as it is, I think the best we can do is try to open our eyes, and appreciate how strange and brief all of this is."
This video game casts the player as 17-year-old Edith Finch. Returning to her family’s home on an island in the Pacific northwest, Edith explores the vast house and tries to figure out why she’s the only one of her family left alive. The story of each family member is revealed as you make your way through the house, slowly unpacking the tragic fate of the Finches. Eerie and immersive, this first-person exploration game uses the medium to tell a series of truly unique tales.
Fun and breezy on the surface, humor is often recognized as one of the trickiest forms of creative writing. After all, while you can see the artistic value in a piece of prose that you don’t necessarily enjoy, if a joke isn’t funny, you could say that it’s objectively failed.
With that said, it’s far from an impossible task, and many have succeeded in bringing smiles to their readers’ faces through their writing. Here are two examples:
‘How You Hope Your Extended Family Will React When You Explain Your Job to Them’ by Mike Lacher (McSweeney’s Internet Tendency)
“Is it true you don’t have desks?” your grandmother will ask. You will nod again and crack open a can of Country Time Lemonade. “My stars,” she will say, “it must be so wonderful to not have a traditional office and instead share a bistro-esque coworking space.”

Satire and parody make up a whole subgenre of creative writing, and websites like McSweeney’s Internet Tendency and The Onion consistently hit the mark with their parodies of magazine publishing and news media. This particular example finds humor in the divide between traditional family expectations and contemporary, ‘trendy’ work cultures. Playing on the inherent silliness of today’s tech-forward middle-class jobs, this witty piece imagines a scenario where the writer’s family fully understands what they do — and are enthralled to hear more. “‘Now is it true,’ your uncle will whisper, ‘that you’ve got a potential investment from one of the founders of I Can Haz Cheezburger?’”
‘Not a Foodie’ by Hilary Fitzgerald Campbell (Electric Literature)
I’m not a foodie, I never have been, and I know, in my heart, I never will be.
Highlighting what she sees as an unbearable social obsession with food , in this comic Hilary Fitzgerald Campbell takes a hilarious stand against the importance of food. From the writer’s courageous thesis (“I think there are more exciting things to talk about, and focus on in life, than what’s for dinner”) to the amusing appearance of family members and the narrator’s partner, ‘Not a Foodie’ demonstrates that even a seemingly mundane pet peeve can be approached creatively — and even reveal something profound about life.
We hope this list inspires you with your own writing. If there’s one thing you take away from this post, let it be that there is no limit to what you can write about or how you can write about it.
In the next part of this guide, we'll drill down into the fascinating world of creative nonfiction.
Join a community of over 1 million authors
Reedsy is more than just a blog. Become a member today to discover how we can help you publish a beautiful book.

We made a writing app for you
Yes, you! Write. Format. Export for ebook and print. 100% free, always.

1 million authors trust the professionals on Reedsy. Come meet them.
Enter your email or get started with a social account:

14 Types of Creative Writing
by Melissa Donovan | Apr 6, 2021 | Creative Writing | 20 comments

Which types of creative writing have you tried?
When we talk about creative writing, fiction and poetry often take the spotlight, but there are many other types of creative writing that we can explore.
Most writers develop a preference for one form (and genre) above all others. This can be a good thing, because you can specialize in your form and genre and become quite proficient. However, occasionally working with other types of writing is beneficial. It prevents your work from becoming stale and overladen with form- or genre-specific clichés, and it’s a good way to acquire a variety of techniques that are uncommon in your preferred form and genre but that can be used to enhance it.
Types of Creative Writing
Free writing: Open a notebook or an electronic document and just start writing. Allow strange words and images to find their way to the page. Anything goes! Also called stream-of-consciousness writing, free writing is the pinnacle of creative writing.
Journals: A journal is any written log. You could keep a gratitude journal, a memory journal, a dream journal, or a goals journal. Many writers keep idea journals or all-purpose omni-journals that can be used for everything from daily free writes to brainstorming and project planning.
Diaries: A diary is a type of journal in which you write about your daily life. Some diaries are written in letter format (“Dear Diary…”). If you ever want to write a memoir, then it’s a good idea to start keeping a diary.
Letters: Because the ability to communicate effectively is increasingly valuable, letter writing is a useful skill. There is a long tradition of publishing letters, so take extra care with those emails you’re shooting off to friends, family, and business associates. Hot tip: one way to get published if you don’t have a lot of clips and credits is to write letters to the editor of a news publication.
Memoir: A genre of creative nonfiction , memoirs are books that contain personal accounts (or stories) that focus on specific experiences. For example, one might write a travel memoir.
Essays. Essays are often associated with academic writing, but there are many types of essays, including personal essays, descriptive essays, and persuasive essays, all of which can be quite creative (and not especially academic).
Journalism: Some forms of journalism are more creative than others. Traditionally, journalism was objective reporting on facts, people, and events. Today, journalists often infuse their writing with opinion and storytelling to make their pieces more compelling or convincing.
Poetry: Poetry is a popular but under-appreciated type of writing, and it’s easily the most artistic form of writing. You can write form poetry, free-form poetry, and prose poetry.
Song Lyrics: Song lyrics combine the craft of writing with the artistry of music. Composing lyrics is similar to writing poetry, and this is an ideal type of writing for anyone who can play a musical instrument.
Scripts: Hit the screen or the stage by writing scripts for film, television, theater, or video games. Beware: film is a director’s medium, not a writer’s medium, but movies have the potential to reach a non-reading audience.
Storytelling: Storytelling is the most popular form of creative writing and is found in the realms of both fiction and nonfiction writing. Popular forms of fiction include flash fiction, short stories, novellas, and full-length novels; and there are tons of genres to choose from. True stories, which are usually firsthand or secondhand accounts of real people and events, can be found in essays, diaries, memoirs, speeches, and more. Storytelling is a tremendously valuable skill, as it can be found in all other forms of writing, from poetry to speech writing.
Speeches: Whether persuasive, inspirational, or informative, speech writing can lead to interesting career opportunities in almost any field or industry. Also, speech-writing skills will come in handy if you’re ever asked to write and deliver a speech at an important event, such as a graduation, wedding, or award ceremony.
Vignettes: A vignette is defined as “a brief evocative description, account, or episode.” Vignettes can be poems, stories, descriptions, personal accounts…anything goes really. The key is that a vignette is extremely short — just a quick snippet.
Honorable Mention: Blogs. A blog is not a type of writing; it’s a publishing platform — a piece of technology that displays web-based content on an electronic device. A blog can be used to publish any type of writing. Most blogs feature articles and essays, but you can also find blogs that contain diaries or journals, poetry, fiction, journalism, and more.
Which of these types of creative writing have you tried? Are there any forms of writing on this list that you’d like to experiment with? Can you think of any other types of creative writing to add to this list? Share your thoughts by leaving a comment, and keep writing.

20 Comments
What is “flash” writing or stories.
Flash fiction refers to super short stories, a few hundred words or fewer.
its very helpful especially to those students like me who wasn’t capable or good in doing a creative writing
I’m glad you found this post helpful, Elena.
I also found this to be very helpful, especially because I don’t do very well at writing.
Thanks for letting me know you found this helpful. Like anything else, writing improves with practice.
Thank you Melissa. It’s very helpful!
You’re welcome!
Over all good list. Yes blogs can be publishing platforms but only if something is written first. I read what you wrote on a blog.
Thanks a lot Good job
Are these types of creaitve writing the same or different if I need to teach children’s creative writing? Can you recommend a website to teach these?
Hi Marie. Thanks for your question. I’ve come across many websites for teaching children’s creative writing. I recommend a search on Google, which will lead you to a ton of resources.
these are very helpful when it comes to getting in college or essays or just to improve my writing
Thanks, Donte. I’m glad you found this helpful.
Free writing really helps me get going. For some reason my prose are much better when I am not beholden to an overall plot or narrative with specific defined characters. I like to free writer “excerpts” on theprose.com. It allows me to practice writing and receive feedback at the same time. I am also trying to blog about writing my first novel, both for writing practice and to keep myself accountable. It really helps!
I feel the same way. Free writing is always a fun and creative experience for me.
Was trying to give an inservice on writing skills and the different types of writing.
Your wok here really helped. Thanks.
You’re welcome.
Hi, Melissa can you assist me ? I’m trying to improve my writing skills as quickly as possible. Plz send me some more tips and trick to improve my writing and communication skills.
You are welcome to peruse this website, which is packed with tips for improving your writing. I’d recommend focusing on the categories Better Writing and Writing Tips for writing improvement. You can also subscribe to get new articles send directly to your email. Thanks!
Trackbacks/Pingbacks
- 23 Calming Hobbies to Restore Your Energy | NunziaDreams - […] You can do a lot with creative writing. […]
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .

Subscribe and get The Writer’s Creed graphic e-booklet, plus a weekly digest with the latest articles on writing, as well as special offers and exclusive content.

Recent Posts
- What is Free-Verse Poetry?
- Grammar Rules: Lay or Lie
- Writing While Inspired
- Thoughts on Becoming a Writer
- How to Write a Book
Write on, shine on!
Pin It on Pinterest

A Guide to English: Creative Writing
- An Introduction to Rhetoric
- Critical Thinking, Reading, and Writing
- The Writing Process
- Formatting and Citations
- The Reference Collection
- Searching for Books
- Searching for Articles
- Bibliographic Trace
- Citation Management
- Scholarly Associations
- The English Language
- Literary Form
- Peoples and Identities
- Periods and Movements in American Literature
- Periods and Movements in Commonwealth Literatures
- Thematic Genres and "Genre Fiction"
- Award Winners (indexed)
- Criticism & Theory
Creative Writing
- Multimodal Composition
- Text Analysis / Distant Reading
- Digital Stewardship
- Data Visualization
- GIS and Geospatial Data
- Statistical Analysis
- Programming
- Digital Scholarly Editing

photo courtesy of Nic McPhee.
With your poetic license in your back pocket you can bypass research, right? Not really. Sometimes you need to check your facts for your fiction to work. Encountering something that is factually wrong can break the spell you've cast on your reader and throw them right out of the story. Besides, research can enrich your world-building and inspire you as you put your imagination to work.
Whether you are writing a literary novel, a poem, an essay, a book for young readers, or a multi-volume epic fantasy, your imaginary world sometimes needs an infusion of reality. What does this lonely stretch of highway in Arizona actually look like? Where could I find inspiration to jump-start this poem? What kind of treatment would my protagonist with PTSD get at a VA hospital? What kind of underwear did people wear back in the 1920s, because it needs to come off in this erotic scene.
Try browsing photos using Google Images or Flickr , delving into historical publications using Google Books , or viewing locations with Google Earth . People can be a great resource, too. Be prepared to make some phone calls, set up visits, or conduct interviews. Check with a librarian if you have factual or context questions you are having trouble answering.
These resources will help you think about ways your writing can find support - both as you create something new and as you navigate the writing business.
On this Page
Getting published, honing your craft, fiction writing, writers on writing, writing genre fiction, nonfiction writing.
Librarian's Note: These resources can help you find appropriate venues to submit your creative writing for publication. While it is true that there are more outlets than ever to get one's work published, and self-publishing (sometimes denigrated as the " vanity press ") has yielded occasional success stories, it is wise to research publications and publishers before submitting, and observe Yog's law whenever possible.
Online Resources

Print Resources
Writing Poetry
- << Previous: Criticism & Theory
- Next: Digital Humanities >>
- Last Updated: Apr 2, 2024 10:54 AM
- URL: https://libguides.gustavus.edu/english


Elements of Creative Writing
J.D. Schraffenberger, University of Northern Iowa
Rachel Morgan, University of Northern Iowa
Grant Tracey, University of Northern Iowa
Copyright Year: 2023
ISBN 13: 9780915996179
Publisher: University of Northern Iowa
Language: English
Formats Available
Conditions of use.
Learn more about reviews.
Reviewed by Robert Moreira, Lecturer III, University of Texas Rio Grande Valley on 3/21/24
Unlike Starkey's CREATIVE WRITING: FOUR GENRES IN BRIEF, this textbook does not include a section on drama. read more
Comprehensiveness rating: 4 see less
Unlike Starkey's CREATIVE WRITING: FOUR GENRES IN BRIEF, this textbook does not include a section on drama.
Content Accuracy rating: 5
As far as I can tell, content is accurate, error free and unbiased.
Relevance/Longevity rating: 5
The book is relevant and up-to-date.
Clarity rating: 5
The text is clear and easy to understand.
Consistency rating: 5
I would agree that the text is consistent in terms of terminology and framework.
Modularity rating: 5
Text is modular, yes, but I would like to see the addition of a section on dramatic writing.
Organization/Structure/Flow rating: 5
Topics are presented in logical, clear fashion.
Interface rating: 5
Navigation is good.
Grammatical Errors rating: 5
No grammatical issues that I could see.
Cultural Relevance rating: 3
I'd like to see more diverse creative writing examples.
As I stated above, textbook is good except that it does not include a section on dramatic writing.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Chapter One: One Great Way to Write a Short Story
- Chapter Two: Plotting
- Chapter Three: Counterpointed Plotting
- Chapter Four: Show and Tell
- Chapter Five: Characterization and Method Writing
- Chapter Six: Character and Dialouge
- Chapter Seven: Setting, Stillness, and Voice
- Chapter Eight: Point of View
- Chapter Nine: Learning the Unwritten Rules
- Chapter One: A Poetry State of Mind
- Chapter Two: The Architecture of a Poem
- Chapter Three: Sound
- Chapter Four: Inspiration and Risk
- Chapter Five: Endings and Beginnings
- Chapter Six: Figurative Language
- Chapter Seven: Forms, Forms, Forms
- Chapter Eight: Go to the Image
- Chapter Nine: The Difficult Simplicity of Short Poems and Killing Darlings
Creative Nonfiction
- Chapter One: Creative Nonfiction and the Essay
- Chapter Two: Truth and Memory, Truth in Memory
- Chapter Three: Research and History
- Chapter Four: Writing Environments
- Chapter Five: Notes on Style
- Chapter Seven: Imagery and the Senses
- Chapter Eight: Writing the Body
- Chapter Nine: Forms
Back Matter
- Contributors
- North American Review Staff
Ancillary Material
- University of Northern Iowa
About the Book
This free and open access textbook introduces new writers to some basic elements of the craft of creative writing in the genres of fiction, poetry, and creative nonfiction. The authors—Rachel Morgan, Jeremy Schraffenberger, and Grant Tracey—are editors of the North American Review, the oldest and one of the most well-regarded literary magazines in the United States. They’ve selected nearly all of the readings and examples (more than 60) from writing that has appeared in NAR pages over the years. Because they had a hand in publishing these pieces originally, their perspective as editors permeates this book. As such, they hope that even seasoned writers might gain insight into the aesthetics of the magazine as they analyze and discuss some reasons this work is so remarkable—and therefore teachable. This project was supported by NAR staff and funded via the UNI Textbook Equity Mini-Grant Program.
About the Contributors
J.D. Schraffenberger is a professor of English at the University of Northern Iowa. He is the author of two books of poems, Saint Joe's Passion and The Waxen Poor , and co-author with Martín Espada and Lauren Schmidt of The Necessary Poetics of Atheism . His other work has appeared in Best of Brevity , Best Creative Nonfiction , Notre Dame Review , Poetry East , Prairie Schooner , and elsewhere.
Rachel Morgan is an instructor of English at the University of Northern Iowa. She is the author of the chapbook Honey & Blood , Blood & Honey . Her work is included in the anthology Fracture: Essays, Poems, and Stories on Fracking in American and has appeared in the Journal of American Medical Association , Boulevard , Prairie Schooner , and elsewhere.
Grant Tracey author of three novels in the Hayden Fuller Mysteries ; the chapbook Winsome featuring cab driver Eddie Sands; and the story collection Final Stanzas , is fiction editor of the North American Review and an English professor at the University of Northern Iowa, where he teaches film, modern drama, and creative writing. Nominated four times for a Pushcart Prize, he has published nearly fifty short stories and three previous collections. He has acted in over forty community theater productions and has published critical work on Samuel Fuller and James Cagney. He lives in Cedar Falls, Iowa.
Contribute to this Page
Home › Study Tips › Creative Writing Resources For Secondary School Students

What Is The Difference Between Prose and Poetry?
- Published August 31, 2022

Table of Contents
Poetry is an art form that has been around for centuries. It is a way to express oneself through the use of words and can be written in many different styles. There are many different types of poetry, such as sonnets, haikus, and ballads.
Poetry can be written about any topic, and it is often used to express emotions. But what is the difference between poetry and prose?
In this article, we outline the differences between the two popular forms of story-telling.
Are you interested in studying English Literature at the university level? Our pre-university courses are designed to ensure you’re prepared for the university style of teaching. Build subject knowledge, work alongside like-minded peers and live in one of the world’s most prestigious universities.
Poetry VS Prose
Prose is a form of writing that is based on spoken language. It is characterised by its natural flow and rhythm, as well as its use of regular grammar and punctuation. Prose is often used for novels, short stories, and essays.
Poetry, on the other hand, is a form of writing that is based on musicality and rhythm. It is often characterized by its use of figurative languages, such as metaphors and similes. Poetry is often used for poems and some of its devices are also used in songwriting.
The major difference between the two is that poetry is a form of writing that uses rhythm and rhyme to create a musical or chant-like effect, whereas prose, is a form of writing that is more straightforward and doesn’t rely on rhyme or meter.
Poetry often uses figurative language to create images or expressive ideas, while prose is more literal. Prose is usually used for novels, essays, and nonfiction writing, while poetry is more often associated with literature, lyrics, and storytelling.
Related Content
How is san francisco shaping the future of data ai.
I used Publishing Push to publish my novel and am completely satisfied with the service I received. In all my contacts with the organization, I found staff to be knowledgeable, professional and effective. Their friendly and helpful approach has been a welcome bonus.
Michael Brookes
Great experience and first class service! Huge thanks to Sophie and the team!
Mark Stuart
Brilliant experience working with Publishing Push. They kept me in the loop throughout the entire process and were supportive...All the staff were easy to communicate with and equally as talented with their skills. They streamlined the process...Would recommended Publishing Push.
Ramis IBRAHIM
I came to publishing push with very little vision other than my story. Their staff and process made it extremely easy to produce an amazing end product. I am so happy with the outcome. Thank you.
Working with Publishing Push was a complete pleasure...Publishing Push remove the worries and hassles so the Author can progress with their work unencumbered by the technical details of publishing. Publishing Push made the publishing experience extremely straightforward; I would not hesitate to publish through them again or to recommend them to any aspiring author.
Kate Taylor
Thank you so much Benjamin and the Publishing Push team! I cannot thank you enough for your dedication and determination to get my book published! You went above and beyond. I am so proud and happy how the book turned out. Such lovely friendly down to earth people! God bless you all! Wishing you all the best! Many thanks, Michelle 😊
Want to know more? Get in touch!
Speak to our publishing consultants, hq: publishing push ltd, soulspace, the boathouse, millbrook, guildford gu1 3xj.
© 2012 – 2024 PublishingPush.com
- International edition
- Australia edition
- Europe edition

You’ve got style: Brilliant books on creative writing
From Italo Calvino to Dorothea Brande, Emma Cummins reflects on the books that inspire her as a writer
“There’s nothing mysterious about your prose style,” says the author Kevin Barry, “it’s a direct projection of your personality”. Many writers – myself included – find this out the hard way. Good writing is true and authentic, it reflects who you are.
For a long time, I subconsciously tried to be someone else on the page. I anglicised my Northern Irish accent; I feigned a kind of seriousness, perhaps in the hope I’d be taken seriously. But the more I attended writing workshops and read books on the craft, the more I realised my work paled beside my personality.
I am a friendly Northern Irish woman. I do a good line in anxiety but I’m not overly serious. I’m passionate about art and books. I’m not shy with strangers. Why, then, was I shy about expressing myself in my writing? There’s no easy answer to this question but I find it interesting to think about. For Guardian Masterclasses’s online summer writers’ retreat , I’ll be sharing my thoughts on style and encouraging other writers to embrace their individuality.
This blog post brings together some brilliant books on creative writing , including The Agony and the Ego , a 1993 anthology edited by Clare Boylan. In her introduction, Boylan makes an interesting observation about writing fiction. “Writing is a paradox because all of it comes out of ourselves. There is nowhere else for it to come from. Yet when the characters of a novel have been established the fiction writer’s task is to remove himself and his influence, and let the characters get on with their lives.”
At the online retreat , I’ll invite writers to think about the fruitful tension between expressing their personality in their work and being true to their characters. There are many other tutors taking part in the retreat, which runs from Monday 25 July over the course of three weeks.
From Ross Raisin to Huma Qureshi, acclaimed authors will help you fine-tune your craft and encourage you to dedicate time to writing. By the end of the three weeks, perhaps you’ll be a bit closer to what the great John McGahern described as “that clear mirror that is called style – the reflection of personality in language”.
Zen in the Art of Writing by Ray Bradbury
If you’re looking for motivation to write, this zesty book by Ray Bradbury is the perfect prescription.
In the opening essay, The Joy of Writing , the acclaimed author of Fahrenheit 451 urges us to write with zest and gusto. “If you are writing without zest, without gusto, without love, without fun, you are only half a writer. It means you are so busy keeping one eye on the commercial market, or one ear peeled for the avant-garde coterie, that you are not being yourself. You don’t even know yourself. For the first thing a writer should be is – excited.”
When I first read Zen in the Art of Writing , I felt energised to write. With essays ranging from How to Keep and Feed a Muse to Drunk, And in Charge of a Bicycle , Bradbury’s unforgettable book is a gift to anyone who loves writing. Actually, scratch that: Zen in the Art of Writing is for anyone who loves life.
Six Memos for the Next Millennium by Italo Calvino
Due to be delivered as lectures at Harvard, Italo Calvino’s delightful “memos” on writing were left unfinished at the time of his death.
The drafts explore the concepts of Lightness, Quickness, Multiplicity, Exactitude and Visibility (Constancy was to be the sixth), with Calvino beginning work on them in 1984.
In each of his lectures, Calvino recommends to the next millennium a particular value, quality or peculiarity of literature that is close to his heart. “From my youth on, my personal motto has been the old Latin tag, Festina lente , hurry slowly,” writes Calvino in his second essay, Quickness . “Just as for the poet writing verse, so it is for the prose writer: success consists in felicity of verbal expression, which every so often may result from a quick flash of inspiration but as a rule involves a patient search for the mot juste , for the sentence in which every word is unalterable”.
Calvino believes that writing prose shouldn’t be any different to writing poetry. In both cases, he argues, it’s about looking for “the unique expression”, one that is “concise, concentrated, and memorable” – three words that encapsulate the tone of this wonderful book.
The Agony and the Ego edited by Clare Boylan
In this illuminating anthology of essays, some of the finest writers of all time – from John McGahern to Hilary Mantel – reflect on the process of creating fiction.
According to editor Clare Boylan , Mantel’s reassuring essay Growing a Tale “argues that ideas coaxed rather than bullied will grow naturally into a novel”. I loved Mantel’s essay when I first read it as part of Ross Raisin’s six-week creative writing programme . “If you make your characters properly they will simply do what is within them,” writes Mantel, “they’ll act out the nature you have given them, and there – you’ll find – you have your plot.”
Now out of print, The Agony and the Ego is worth tracking down secondhand or in a library. In addition to insightful essays by John Banville, Rose Tremain and Nadine Gordimer, it features a short selection of interviews from the series Writers at Work, which Boylan wrote for the Guardian.
Many of these essays highlight “the mystery” of writing, and perhaps this is why I return to The Agony and the Ego . This warm-hearted book encourages writers to grow naturally into themselves.
Becoming a Writer by Dorothea Brande
Mantel’s rules for writers include this recommendation: “Read Becoming a Writer by Dorothea Brande. Then do what it says, including the tasks you think are impossible.”
Full of practical advice for time-poor writers, Brande’s book was first published in 1934 and remains a go-to classic. Schedule time to write each day, suggests Brande. “It need not be a very long time; fifteen minutes will do nicely”.
I enjoyed Brande’s simple but powerful advice to take a rough draft of a story “out for a walk” and think about it. After the walk, you’re invited to go to a dim room and lie down. “Quiet your mind,” says Brande. Lie there, not quite asleep, not quite awake.” After a while, she says, you’ll feel “a definite impulse to rise, a kind of surge of energy. Obey it at once … Get up and go to your paper or typewriter, and begin to write. The state you are in at that moment is the state an artist works in.”
On Editing by Helen Corner-Bryant and Kathryn Price
Writing is re-writing. Learning how to self-edit your work is perhaps the most vital skill any writer can learn and this book, by editors Helen Corner-Bryant and Kathryn Price, is something of a godsend.
One of the chapters in On Editing demystifies ‘show don’t tell’, a phrase “often misunderstood” by new writers. “At its simplest, the aim of showing is to bring the reader as close as possible to the action,” write the authors. “By feeling your writing intensely yourself you’ll transmit that emotion to the reader … and when you can make the reader feel, you’ve got them in the palm of your hand”.
Other useful chapters cover structure, description, pacing and much more. The book also includes advice on submitting your novel – from writing synopses to pitching to agents – making it an indispensable guide for writers who take their work seriously.
Writing a Novel by Richard Skinner
“When we talk about a writer’s style, what we are really talking about is their ‘voice’,” writes Richard Skinner in Writing a Novel . “As a tutor, I can do nothing about the tone of your voice as you speak, but what I can engage with is what you say, i.e. your ‘story’”.
Skinner’s book is a thought-provoking and practical guide to the craft of writing. Divided into bite-sized sections – from point of view to story and plot – it encourages writers to bring their whole selves to the page. As Skinner writes in a piece for the Observer , “Writing is about claiming ownership of yourself in order to become the person you know you can be”.
Throughout Writing a Novel , there are thoughtfully selected quotes from authors, such as Gertrude Stein’s, “Sentences are factual, but paragraphs are emotional”. Over the years, I’ve enjoyed going back to this generous, kind-spirited book. It feels fresh each time – and will no doubt inspire many writers to follow their passion.
Being a Writer by Travis Elborough and Helen Gordon
I treated myself to this beautiful gift book when I was low on confidence as a writer.
Lockdown had taken away my beloved book events and writing workshops, and while I attended many online, I was Zoom fatigued and starved of new experiences. That awful winter lockdown had been announced and I was living alone. Being a Writer was brilliant company then, and continues to be a source of insight and wisdom on the art of writing.
From Alice Munro to Gabriel García Márquez, the book features quotations and essays from some of the world’s greatest authors. Márquez reveals how the opening line of Franz Kafka’s The Metamorphosis inspired him to start writing short stories. Australian author Tim Winton says writing a book is a bit like surfing, “Most of the time you’re waiting.”
Being a Writer is a lovely anthology to dip in and out of, to savour in small bursts. This comforting book reminds us that each writer’s approach is unique. Trust in the process that works for you. Read widely, and write what makes you feel most alive. In the words of Anaïs Nin, “We write to taste life twice”.
Save up to 13% on a specially curated selection of creative writing books at the Guardian Bookshop.
Find out more about Guardian Masterclasses’s summer writer’s retreat and enrol now.
- Guardian Masterclasses
- Guardian Masterclasses blog
Most viewed
Definition of Prose
Prose is a literary device referring to writing that is structured in a grammatical way, with words and phrases that build sentences and paragraphs. Works wrote in prose feature language that flows in natural patterns of everyday speech. Prose is the most common and popular form of writing in fiction and non-fiction works.
As a literary device, prose is a way for writers to communicate with readers in a straightforward, even conversational manner and tone . This creates a level of familiarity that allows the reader to connect with the writer’s expression, narrative , and characters. An example of the effective familiarity of prose is J.D. Salinger’s The Catcher in The Rye :
What really knocks me out is a book that, when you’re all done reading it, you wish the author that wrote it was a terrific friend of yours and you could call him up on the phone whenever you felt like it.
Salinger’s prose is presented as first-person narration as if Holden Caulfield’s character is speaking to and conversing directly with the reader. This style of prose establishes familiarity and intimacy between the narrator and the reader that maintains its connection throughout the novel .
Common Examples of First Prose Lines in Well-Known Novels
The first prose line of a novel is significant for the writer and reader. This opening allows the writer to grab the attention of the reader, set the tone and style of the work, and establish elements of setting , character, point of view , and/or plot . For the reader, the first prose line of a novel can be memorable and inspire them to continue reading. Here are some common examples of first prose lines in well-known novels:
- Call me Ishmael. ( moby dick )
- It was the best of times, it was the worst of times ( A Tale of Two Cities )
- It is a truth universally acknowledged, that a single man in possession of a good fortune, must be in want of a wife. ( Pride and Prejudice )
- It was love at first sight. ( catch 22 )
- In my younger and more vulnerable years my father gave me some advice that I’ve been turning over in my mind ever since. ( The Great Gatsby )
- It was a bright cold day in April, and the clocks were striking thirteen. ( 1984 )
- i am an invisible man . ( Invisible Man )
- Mother died today. ( the stranger )
- They shoot the white girl first, but the rest they can take their time. ( Paradise )
- All this happened, more or less. ( Slaughterhouse-Five )
Examples of Famous Lines of Prose
Prose is a powerful literary device in that certain lines in literary works can have a great effect on readers in revealing human truths or resonating as art through language. Well-crafted, memorable prose evokes thought and feeling in readers. Here are some examples of famous lines of prose:
- Shoot all the blue jays you want, if you can hit ‘em, but remember it’s a sin to kill a mockingbird . ( To Kill a Mockingbird )
- In spite of everything, I still believe that people are good at heart. ( Anne Frank : The Diary of a Young Girl )
- All Animals are Equal , but some animals are more equal than others. ( Animal Farm)
- It is easier to start a war than to end it. ( One Hundred Years of Solitude )
- It is not often that someone comes along who is a true friend and a good writer. Charlotte was both. ( Charlotte’s Web )
- I think it pisses God off if you walk by the color purple in a field somewhere and don’t notice it. ( The Color Purple )
- There is no greater agony than bearing an untold story inside you, ( I Know Why the Caged Bird Sings )
- The answer to the ultimate question of life, the universe and everything is 42. ( The Hitchhiker’s Guide to the Galaxy )
- The only thing worse than a boy who hates you: a boy that loves you. ( The Book Thief )
- Just remember: If one bird carried every grain of sand, grain by grain, across the ocean, by the time he got them all on the other side, that would only be the beginning of eternity. ( In Cold Blood )
Types of Prose
Writers use different types of prose as a literary device depending on the style and purpose of their work. Here are the different types of prose:
- Nonfiction: prose that recounts a true story, provides information, or gives a factual account of something (such as manuals, newspaper articles, textbooks, etc.)
- Heroic: prose usually in the form of a legend or fable that is intended to be recited and has been passed down through oral or written tradition
- Fiction : most familiar form of prose used in novels and short stories and featuring elements such as plot, setting, characters, dialogue , etc.
- Poetic Prose: poetry written in the form of prose, creating a literary hybrid with occasional rhythm and/or rhyme patterns
Difference Between Prose and Poetry
Many people consider prose and poetry to be opposites as literary devices . While that’s not quite the case, there are significant differences between them. Prose typically features natural patterns of speech and communication with grammatical structure in the form of sentences and paragraphs that continue across the lines of a page rather than breaking. In most instances, prose features everyday language.
Poetry, traditionally, features intentional and deliberate patterns, usually in the form of rhythm and rhyme. Many poems also feature a metrical structure in which patterns of beats repeat themselves. In addition, poetry often includes elevated, figurative language rather than everyday verbiage. Unlike prose, poems typically include line breaks and are not presented as or formed into continuous sentences or paragraphs.
Writing a Prose Poem
A prose poem is written in prose form without a metrical pattern and without a proper rhyme scheme . However, other poetic elements such as symbols metaphors , and figurative language are used extensively to make the language poetic. Writing a prose poem involves using all these poetic elements, including many others that a poet could think about.
It is not difficult to write a prose poem. It, however, involves a step-by-step approach.
- Think about an idea related to a specific theme , or a choose topic.
- Think poetically and write as prose is written but insert notes, beats, and patterns where necessary.
- Use repetitions , metaphors, and similes extensively.
- Revise, revise and revise to make it melodious.
Prose Edda vs. Poetic Edda
Prose Edda refers to a collection of stories collected in Iceland, or what they are called the Icelandic Saga. Most of the Prose Edda stories have been written by Snorri Sturluson while has compiled the rest written by several other writers. On the other hand, most of the poems about the Norse gods and goddesses are called the Poetic Edda. It is stated that almost all of these poems have been derived from the Codex Regius written around the 13 th century though they could have been composed much earlier. Such poems are also referred to as Eddaic poetry. In other words, these poetic outputs and writings are classical poetic pieces mostly woven around religious themes.
Examples of Prose in Literature
Prose is an essential literary device in literature and the foundation for storytelling. The prose in literary works functions to convey ideas, present information, and create a narrative for the reader through the intricate combinations of plot, conflict , characters, setting, and resolution . Here are some examples of prose in literature:
Example 1: The Grapes of Wrath by John Steinbeck
A large drop of sun lingered on the horizon and then dripped over and was gone, and the sky was brilliant over the spot where it had gone, and a torn cloud, like a bloody rag, hung over the spot of its going. And dusk crept over the sky from the eastern horizon, and darkness crept over the land from the east.
Steinbeck’s gifted prose in this novel is evident in this passage as he describes the last moment of sunset and the onset of darkness. Steinbeck demonstrates the manner in which a writer can incorporate figurative language into a prose passage without undermining the effect of being straightforward with the reader. The novel’s narrator utilizes figurative language by creating a metaphor comparing the sun to a drop of liquid, as well as through personifying dusk and darkness as they “crept.” This enhances the novel’s setting, tone, and mood in this portion of the story.
However, though Steinbeck incorporates such imagery and poetic phrasing in this descriptive passage, the writing is still accessible to the reader in terms of prose. This demonstrates the value of this literary device in fictional works of literature. Writers can still master and offer everyday language and natural speech patterns without compromising or leaving out the effective descriptions and use of figurative language for readers.
Example 2: This Is Just to Say by William Carlos Williams
I have eaten the plums that were in the icebox and which you were probably saving for breakfast Forgive me they were delicious so sweet and so cold
In this poem by Williams, he utilizes poetic prose to create a hybrid work of literature. The poem is structured in appearances like a poetic work with line breaks and stanzas . However, the wording of the work flows as prose writing in its everyday language and conversational tone. There is an absence of figurative language in the poem, and instead, the expression is direct and straightforward.
By incorporating prose as a literary device in his poem, Williams creates an interesting tension for the reader between the work’s visual representation as a poem and the familiar, literal language making up each individual line. However, rather than undermine the literary beauty of the poem, the prose wording enhances its meaning and impact.
Example 3: Harrison Bergeron by Kurt Vonnegut, Jr.
The year was 2081, and everybody was finally equal. They weren’t only equal before God and the law. They were equal every which way. Nobody was smarter than anybody else. Nobody was better looking than anybody else. Nobody was stronger or quicker than anybody else. All this equality was due to the 211th, 212th, and 213th Amendments to the Constitution, and to the unceasing vigilance of agents of the United States Handicapper General.
This passage introduces Vonnegut’s work of short fiction. The narrator’s prose immediately sets the tone of the story as well as foreshadows the impending conflict. The certainty and finality of the narrator’s statements regarding equality in the story establish a voice that is direct and unequivocal. This unambiguous voice set forth by Vonnegut encourages trust in the narration on behalf of the reader. As a result, when the events and conflict in the story turn to science fiction and even defy the laws of physics, the reader continues to “believe” the narrator’s depiction of the plot and characters.
This suspension of disbelief on the part of the reader demonstrates the power of prose as a literary device and method of storytelling. By utilizing the direct and straightforward nature of prose, the writer invites the reader to become a participant in the story by accepting what they are told and presented through the narrator. This enhances the connection between the writer as a storyteller and a receptive reader.
Synonyms of Prose
Prose has a few close synonyms but cannot be used interchangeably. Some of the words coming near in meanings are unlyrical, unpoetic, factual, literal, antipoetic, writing, prosaic and factual.
Post navigation

Find anything you save across the site in your account
Literary Style and the Lessons of Memoir
By Stephanie Burt

In his book “Memoir: An Introduction,” from 2011, the scholar G. Thomas Couser argues that we go to the genre not so much for detail or style as for “wisdom and self-knowledge,” for what the main character, who is always the author, has learned. Sometimes, though, the style is the lesson. Earlier this year, the Seattle poet Paul Hunter published “Clownery,” which follows Hunter from his birth in the rural Midwest, through college, marriage, fatherhood, divorce, high-school and college teaching, grease- and gear-filled shirtsleeve jobs, caregiving for an ill sister and playing with grandchildren. The chapters conclude with Hunter’s late-life meditations, “trying to keep from a lip-smacking bitterness” as he imagines “the end of the planet as a hospitable home.” Hunter published his first chapbook in 1970, and has been giving us verse about rural and wild America, and practical prose about sustainable farming, every few years since 2000. In “ Clownery ,” rather than using “I” or “me,” or naming any characters, Hunter tells his own story as that of a nameless “clown.”
This simple device has astonishing effects, making Hunter’s life at once more generic—it’s easier to see yourself in “the clown” than in “Paul Hunter”—and funnier and sadder. “One morning out in the country the little clown’s mother was washing her mother’s hair in the kitchen pantry, behind the curtain where they boiled their water and took their washtub baths,” he writes. And later: “The clown knew nothing of planning, and snagged on a nail ripped his pants. Got caught and stayed caught till he was practically naked.” The floppy-shoes aspects of puberty and old age, when we may feel at once too big and too small, too late and too early, fit the conceit almost too easily: “Aging for clowns was more of a ripening that just went on and on. . . . Clowns were born weepy with blubber lips anyhow, and pratfalls demanded lifelong practice,” Hunter writes. “Clowns were always at an awkward stage,” “hiding twitchy flat feet . . . in big shoes.” Sentence by sentence, he manages to sound like a rambling talker, a corn-fed storyteller, even though, each time you finish a page or a chapter, you realize just how elegantly assembled the volume is.
Hunter’s unusual autobiography is one of a few recent books that reinvent, or fracture, the memoir’s form. All come from small presses; all come long after the stylish, formally inventive, and popular books of the late-nineties memoir boom (Dave Eggers’s “ A Heartbreaking Work of Staggering Genius ,” for example, and Lauren Slater’s “ Lying ”). Popular memoirs these days are more direct: it’s generally easy to say what makes the lives they chronicle stand out, so that readers and critics focus on their subjects, whether it’s Appalachia (J. D. Vance’s “ Hillbilly Elegy ”), weight, shame, and trauma (Roxane Gay’s “ Hunger ”), or plant science (Hope Jahren’s nearly perfect “ Lab Girl ”).
Yet experiments in the genre continue, many of them, like Maggie Nelson’s breakthrough book, “ The Argonauts ,” from 2015, intimately connected to the drive toward new forms, and the use of fragments and white space, in contemporary poetry. These memoirs take cues from prose poems and lyrical essays, like those in Claudia Rankine’s “Citizen.” They also use the devices of poetry—interruption, compression, extended metaphor—to pay book-length attention to individual real lives, and, not coincidentally, they come from independent publishers known for their poets and poems.
The writer Jessica Anne told the Chicago Tribune that she began her book “ A Manual for Nothing ” because “I got excited reading unclassifiable books by authors like Maggie Nelson and Lidia Yuknavitch , and I wanted to try it.” She might have fashioned from the material of her life a conventional memoir of family dysfunction and bad sexual decisions. Anne was raised—or not raised—by a mother whose series of boyfriends rivalled, in their unreliability, her series of ailments, including a struggle with terminal cancer that seems to have been imaginary. Anne attended a “Fame”-style performing-arts high school, dropped out of college, discovered feminism, travelled to London, returned to Chicago to make a career as a singer and monologuist, and settled down (with her husband) to write the book.
“A Manual for Nothing” is part collage of half-remembered facts, part tongue-in-cheek guide to womanhood, and part imaginary dialogue, with speaking parts for Shakespeare’s Cleopatra and for Patti LuPone. Its numbered propositions, many of them in the second person, some of them absurd, accrete a willful resistance to realism, even as they frame what seem to be facts from her life. From “Maroon Chart,” a short chapter about menstruation: “Ovulation stains a period’s blood red as a stage curtain. . . . Once the menstrual blood is bright, you become your father’s next of kin.” Elsewhere in the book, Anne imagines telling a boyfriend, “I thought we were forever! I thought you were the pearl onion of my special, special day!” That’s probably not what she said at the time.
The dismemberment of a life into lists—one of the chapters comprises thirty-three short noun phrases—lets Anne frame events that must have terrified her at the time (her mother’s feigned cancer, for example) not as the most important moments in her life but as material to be assimilated, made into something just inches away from a joke. An unwanted sexual experience is “not quite rape, it’s just one of those awkward nights to giggle and gossip over. . . . Everyone’s laughing at you. Don’t cry.” In order to free herself from her past, and to push back against patriarchy’s expectations—so her chopped-up form suggests—she has to generalize, to satirize, to cut her life story into bits that she can crumple or rearrange. Paul Hunter learns equanimity by presenting his life as the life of a circus clown; Jessica Anne learns to imagine control.
The Brooklyn songwriter and poet Jasmine Dreame Wagner, in her own recent memoir, “ On a Clear Day ,” learns to notice particularity—and to get outside her own wish to generalize, to let big theories explain her life. “On a Clear Day” is a capacious book of traveller’s observations, cultural criticism, and quarter-life-crisis notes about deserts, gallery art, and Brooklyn bohemians in our “golden era of listicles.” It’s the kind of book that tries to take the temperature of a generation (Wagner’s first book appeared in 2012) or at least of a generation’s narrow, gallery-going, artsy urban slice. In Wagner’s Brooklyn, “the cacophony of lo-fi indie rock reverb” is also “the sound of gentrification, “the sound of if only ,” “the sound of why me .” Throughout the volume, Wagner puts her name-checked role models (Didion, Deleuze, C. D. Wright, Leslie Jamison) to clever use.
Learning from poets’ sharply quotable lines, and from travel writers’ set pieces and first-person assertions, Wagner has made a book to dip into, open almost at random, or get lost in. In this respect, the book resembles, as she knows, the endless branching paths of social media, which become her subject: “my method of describing the sunset, its noise, is likewise noise. Instagram, Facebook, Twitter, Tumblr.” Fragmentary prose, composed of disconnected observations and advice, goes back as far as the Bible, but Wagner’s combination of patience and jumpiness, and her search for “the real, presence, materiality” in snippets that keep slipping away from her, seem to fit our age of distraction and hyper-alertness, when we might look up from Proust, or from the Grand Canyon, to see if we’ve been retweeted, or liked, or tagged.
Wagner presents the sublimity of deserts, the welcome alienation of new sites, “the wind’s ripples in the dunes, the dunes’ ripples on the tectonic plate,” almost as a more conventional travelogue would. But her wish to say what she sees works at startling cross-purposes with her critic’s wish to generalize—it is as if she were grasping both for the high-level wisdom that G. Thomas Couser seeks in all memoir and for the ground-level immediacy that Joseph Conrad sought when he said that he wrote fiction “above all, to make you see.” Some gallery artists face the same dilemma: should they focus on visual experience, or on difficult abstract ideas? Sometimes, Wagner manages to follow both Couser and Conrad at once. Her description of winter in the suburbs, for instance, treats the snow as a tangible symbol for—but also as an alternative to—abstraction: “snow blots out the words on the strip mall marquee. It has no part. It speaks of no prior experience . . . . Like chicks swollen in our shells, we must scrape through its opacity to release ourselves.”
That line implies—in harmony with almost all memoirs, but against the grain of some poets—that we still have selves to release. Wagner seems to believe that, but she doesn’t take it for granted: she worries, and who wouldn’t, that the speaking self these days is too like an advertisement, or a means of self-aggrandizement. In her crowded Brooklyn, “in order to secure a voice equal to those of corporations . . . people become brands,” flaunting “the qualities of successful brands, such as media visibility [and] message consistency.” Sell yourself, in other words, or get erased. It’s a grim conclusion for the tradition of memoir, from St. Augustine to our time, and it’s a conclusion that Wagner’s canny fragments, like Anne’s sarcastic lists and Hunter’s tender metaphors, refuse. “The closer I come to my own erasure,” she writes of her time in the Southwestern deserts, “the stronger my work’s urge / to story… If my language is obscure / I’ll vanish in its steam.”
Books & Fiction
By signing up, you agree to our User Agreement and Privacy Policy & Cookie Statement . This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.

By Naomi Fry

Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Creative Nonfiction: An Overview

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
The Creative Nonfiction (CNF) genre can be rather elusive. It is focused on story, meaning it has a narrative plot with an inciting moment, rising action, climax and denoument, just like fiction. However, nonfiction only works if the story is based in truth, an accurate retelling of the author’s life experiences. The pieces can vary greatly in length, just as fiction can; anything from a book-length autobiography to a 500-word food blog post can fall within the genre.
Additionally, the genre borrows some aspects, in terms of voice, from poetry; poets generally look for truth and write about the realities they see. While there are many exceptions to this, such as the persona poem, the nonfiction genre depends on the writer’s ability to render their voice in a realistic fashion, just as poetry so often does. Writer Richard Terrill, in comparing the two forms, writes that the voice in creative nonfiction aims “to engage the empathy” of the reader; that, much like a poet, the writer uses “personal candor” to draw the reader in.
Creative Nonfiction encompasses many different forms of prose. As an emerging form, CNF is closely entwined with fiction. Many fiction writers make the cross-over to nonfiction occasionally, if only to write essays on the craft of fiction. This can be done fairly easily, since the ability to write good prose—beautiful description, realistic characters, musical sentences—is required in both genres.
So what, then, makes the literary nonfiction genre unique?
The first key element of nonfiction—perhaps the most crucial thing— is that the genre relies on the author’s ability to retell events that actually happened. The talented CNF writer will certainly use imagination and craft to relay what has happened and tell a story, but the story must be true. You may have heard the idiom that “truth is stranger than fiction;” this is an essential part of the genre. Events—coincidences, love stories, stories of loss—that may be expected or feel clichéd in fiction can be respected when they occur in real life .
A writer of Creative Nonfiction should always be on the lookout for material that can yield an essay; the world at-large is their subject matter. Additionally, because Creative Nonfiction is focused on reality, it relies on research to render events as accurately as possible. While it’s certainly true that fiction writers also research their subjects (especially in the case of historical fiction), CNF writers must be scrupulous in their attention to detail. Their work is somewhat akin to that of a journalist, and in fact, some journalism can fall under the umbrella of CNF as well. Writer Christopher Cokinos claims, “done correctly, lived well, delivered elegantly, such research uncovers not only facts of the world, but reveals and shapes the world of the writer” (93). In addition to traditional research methods, such as interviewing subjects or conducting database searches, he relays Kate Bernheimer’s claim that “A lifetime of reading is research:” any lived experience, even one that is read, can become material for the writer.
The other key element, the thing present in all successful nonfiction, is reflection. A person could have lived the most interesting life and had experiences completely unique to them, but without context—without reflection on how this life of experiences affected the writer—the reader is left with the feeling that the writer hasn’t learned anything, that the writer hasn’t grown. We need to see how the writer has grown because a large part of nonfiction’s appeal is the lessons it offers us, the models for ways of living: that the writer can survive a difficult or strange experience and learn from it. Sean Ironman writes that while “[r]eflection, or the second ‘I,’ is taught in every nonfiction course” (43), writers often find it incredibly hard to actually include reflection in their work. He expresses his frustration that “Students are stuck on the idea—an idea that’s not entirely wrong—that readers need to think” (43), that reflecting in their work would over-explain the ideas to the reader. Not so. Instead, reflection offers “the crucial scene of the writer writing the memoir” (44), of the present-day writer who is looking back on and retelling the past. In a moment of reflection, the author steps out of the story to show a different kind of scene, in which they are sitting at their computer or with their notebook in some quiet place, looking at where they are now, versus where they were then; thinking critically about what they’ve learned. This should ideally happen in small moments, maybe single sentences, interspersed throughout the piece. Without reflection, you have a collection of scenes open for interpretation—though they might add up to nothing.
Margin Size
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

1.10: Literature (including fiction, drama, poetry, and prose)
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 205491

- Lori-Beth Larsen
- Central Lakes College
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)

Essential Questions for Literature
- How is literature like life?
- What is literature supposed to do?
- What influences a writer to create?
- How does literature reveal the values of a given culture or time period?
- How does the study of fiction and nonfiction texts help individuals construct their understanding of reality?
- In what ways are all narratives influenced by bias and perspective?
- Where does the meaning of a text reside? Within the text, within the reader, or in the transaction that occurs between them?
- What can a reader know about an author’s intentions based only on a reading of the text?
- What are enduring questions and conflicts that writers (and their cultures) grappled with hundreds of years ago and are still relevant today?
- How do we gauge the optimism or pessimism of a particular time period or particular group of writers?
- Why are there universal themes in literature–that is, themes that are of interest or concern to all cultures and societies?
- What are the characteristics or elements that cause a piece of literature to endure?
- What is the purpose of: science fiction? satire? historical novels, etc.?
- How do novels, short stories, poetry, etc. relate to the larger questions of philosophy and humanity?
- How we can use literature to explain or clarify our own ideas about the world?
- How does what we know about the world shape the stories we tell?
- How do the stories we tell about the world shape the way we view ourselves?
- How do our personal experiences shape our view of others?
- What does it mean to be an insider or an outsider?
- Are there universal themes in literature that are of interest or concern to all cultures and societies?
- What is creativity and what is its importance for the individual / the culture?
- What are the limits, if any, of freedom of speech?
Defining Literature
Literature, in its broadest sense, is any written work. Etymologically, the term derives from Latin litaritura / litteratura “writing formed with letters,” although some definitions include spoken or sung texts. More restrictively, it is writing that possesses literary merit. Literature can be classified according to whether it is fiction or non-fiction and whether it is poetry or prose. It can be further distinguished according to major forms such as the novel, short story or drama, and works are often categorized according to historical periods or their adherence to certain aesthetic features or expectations (genre).
Taken to mean only written works, literature was first produced by some of the world’s earliest civilizations—those of Ancient Egypt and Sumeria—as early as the 4th millennium BC; taken to include spoken or sung texts, it originated even earlier, and some of the first written works may have been based on a pre-existing oral tradition. As urban cultures and societies developed, there was a proliferation in the forms of literature. Developments in print technology allowed for literature to be distributed and experienced on an unprecedented scale, which has culminated in the twenty-first century in electronic literature.
Definitions of literature have varied over time. In Western Europe prior to the eighteenth century, literature as a term indicated all books and writing. [1] A more restricted sense of the term emerged during the Romantic period, in which it began to demarcate “imaginative” literature. [2]
Contemporary debates over what constitutes literature can be seen as returning to the older, more inclusive notion of what constitutes literature. Cultural studies, for instance, takes as its subject of analysis both popular and minority genres, in addition to canonical works. [3]
Major Forms

A calligram by Guillaume Apollinaire. These are a type of poem in which the written words are arranged in such a way to produce a visual image.
Poetry is a form of literary art that uses aesthetic and rhythmic qualities of language to evoke meanings in addition to, or in place of, prosaic ostensible meaning (ordinary intended meaning). Poetry has traditionally been distinguished from prose by its being set in verse; [4] prose is cast in sentences, poetry in lines; the syntax of prose is dictated by meaning, whereas that of poetry is held across metre or the visual aspects of the poem. [5]
Prior to the nineteenth century, poetry was commonly understood to be something set in metrical lines; accordingly, in 1658 a definition of poetry is “any kind of subject consisting of Rythm or Verses”. [6] Possibly as a result of Aristotle’s influence (his Poetics ), “poetry” before the nineteenth century was usually less a technical designation for verse than a normative category of fictive or rhetorical art. [7] As a form it may pre-date literacy, with the earliest works being composed within and sustained by an oral tradition; [8] hence it constitutes the earliest example of literature.
Prose is a form of language that possesses ordinary syntax and natural speech rather than rhythmic structure; in which regard, along with its measurement in sentences rather than lines, it differs from poetry. [9] On the historical development of prose, Richard Graff notes that ”
Novel : a long fictional prose narrative.
Novella :The novella exists between the novel and short story; the publisher Melville House classifies it as “too short to be a novel, too long to be a short story.” [10]
Short story : a dilemma in defining the “short story” as a literary form is how to, or whether one should, distinguish it from any short narrative. Apart from its distinct size, various theorists have suggested that the short story has a characteristic subject matter or structure; [11] these discussions often position the form in some relation to the novel. [12]
Drama is literature intended for performance. [13]
Listen to this Discussion of the poetry of Harris Khalique . You might want to take a look at the transcript as you listen.
The first half of a 2008 reading featuring four Latino poets, as part of the American Perspectives series at the Art Institute of Chicago.
Listen to poetry reading of Francisco Aragón and Brenda Cárdenas
Listen to this conversation with Allison Hedge Coke, Linda Hogan and Sherwin Bitsui . You might want to look at the transcript as you listen. In this program, we hear a conversation among three Native American poets: Allison Hedge Coke, Linda Hogan and Sherwin Bitsui. Allison Hedge Coke grew up listening to her Father’s traditional stories as she moved from Texas to North Carolina to Canada and the Great Plains. She is the author of several collections of poetry and the memoir, Rock, Ghost, Willow, Deer. She has worked as a mentor with Native Americans and at-risk youth, and is currently a Professor of Poetry and Writing at the University of Nebraska, Kearney. Linda Hogan is a prolific poet, novelist and essayist. Her work is imbued with an indigenous sense of history and place, while it explores environmental, feminist and spiritual themes. A former professor at the University of Colorado, she is currently the Chickasaw Nation’s Writer in Residence. She lives in Oklahoma, where she researches and writes about Chickasaw history, mythology and ways of life. Sherwin Bitsui grew up on the Navajo reservation in Arizona. He speaks Dine, the Navajo language and participates in ceremonial activities. His poetry has a sense of the surreal, combining images of the contemporary urban culture, with Native ritual and myth.
Chris Abani : Stories from Africa
In this deeply personal talk, Nigerian writer Chris Abani says that “what we know about how to be who we are” comes from stories. He searches for the heart of Africa through its poems and narrative, including his own.
One or more interactive elements has been excluded from this version of the text. You can view them online here: https://minnstate.pressbooks.pub/introductiontohumanitiesv2/?p=77#oembed-1
Listen to Isabel Allende’s Ted Talk
As a novelist and memoirist, Isabel Allende writes of passionate lives, including her own. Born into a Chilean family with political ties, she went into exile in the United States in the 1970s—an event that, she believes, created her as a writer. Her voice blends sweeping narrative with touches of magical realism; her stories are romantic, in the very best sense of the word. Her novels include The House of the Spirits, Eva Luna and The Stories of Eva Luna, and her latest, Maya’s Notebook and Ripper. And don’t forget her adventure trilogy for young readers— City of the Beasts, Kingdom of the Golden Dragon and Forest of the Pygmies.
As a memoirist, she has written about her vision of her lost Chile, in My Invented Country, and movingly tells the story of her life to her own daughter, in Paula. Her book Aphrodite: A Memoir of the Senses memorably linked two sections of the bookstore that don’t see much crossover: Erotica and Cookbooks. Just as vital is her community work: The Isabel Allende Foundation works with nonprofits in the San Francisco Bay Area and Chile to empower and protect women and girls—understanding that empowering women is the only true route to social and economic justice.
You can read excerpts of her books online here: https://www.isabelallende.com/en/books
Read her musings. Why does she write? https://www.isabelallende.com/en/musings
You might choose to read one of her novels.
One or more interactive elements has been excluded from this version of the text. You can view them online here: https://minnstate.pressbooks.pub/introductiontohumanitiesv2/?p=77#oembed-2
Listen to Novelist Chimamanda Adichie . She speaks about how our lives, our cultures, are composed of many overlapping stories. She tells the story of how she found her authentic cultural voice — and warns that if we hear only a single story about another person or country, we risk a critical misunderstanding.
One or more interactive elements has been excluded from this version of the text. You can view them online here: https://minnstate.pressbooks.pub/introductiontohumanitiesv2/?p=77#oembed-3
One Hundred Years of Solitu de
Gabriel García Márquez’s novel “One Hundred Years of Solitude” brought Latin American literature to the forefront of the global imagination and earned García Márquez the 1982 Nobel Prize for Literature. What makes the novel so remarkable? Francisco Díez-Buzo investigates.
Gabriel García Márquez was a writer and journalist who recorded the haphazard political history of Latin American life through his fiction. He was a part of a literary movement called the Latin American “boom ,” which included writers like Peru’s Mario Vargas Llosa, Argentina’s Julio Cortázar, and Mexico’s Carlos Fuentes. Almost all of these writers incorporated aspects of magical realism in their work . Later authors, such as Isabel Allende and Salman Rushdie, would carry on and adapt the genre to the cultural and historical experiences of other countries and continents. García Máruqez hadn’t always planned on being a writer, but a pivotal moment in Colombia’s—and Latin America’s—history changed all that. In 1948, when García Márquez was a law student in Bogotá, Jorge Eliécer Gaítan , a prominent radical populist leader of Colombia’s Liberal Party, was assassinated. This happened while the U.S. Secretary of State George Marshall brought together leaders from across the Americas to create the Organization of American States (OAS) and to build a hemisphere-wide effort against communism. In the days after the assassination, massive riots, now called the bogotazo , occurred. The worst Colombian civil war to date, known as La Violencia , also broke out. Another law student, visiting from Cuba, was deeply affected by Eliécer Gaítan’s death. This student’s name was Fidel Castro. Interestingly, García Márquez and Castro—both socialists—would become close friends later on in life , despite not meeting during these tumultuous events. One Hundred Years of Solitude ’s success almost didn’t happen, but this article from Vanity Fair helps explain how a long-simmering idea became an international sensation. When Gabriel García Márquez won the Nobel Prize in 1982, he gave a lecture that helped illuminate the plights that many Latin Americans faced on a daily basis. Since then, that lecture has also helped explain the political and social critiques deeply embedded in his novels. It was famous for being an indigenous overview of how political violence became entrenched in Latin America during the Cold War.In an interview with the New Left Review , he discussed a lot of the inspirations for his work, as well as his political beliefs.
An interactive H5P element has been excluded from this version of the text. You can view it online here: https://minnstate.pressbooks.pub/introductiontohumanitiesv2/?p=77#h5p-12
Don Quixote
Mounting his skinny steed, Don Quixote charges an army of giants. It is his duty to vanquish these behemoths in the name of his beloved lady, Dulcinea. There’s only one problem: the giants are merely windmills. What is it about this tale of the clumsy yet valiant knight that makes it so beloved? Ilan Stavans investigates.
Interested in exploring the world of Don Quixote ? Check out this translation of the thrill-seeking classic. To learn more about Don Quixote ’s rich cultural history, click here . In this interview , the educator shares his inspiration behind his book Quixote: The Novel and the World . The travails of Don Quixote ’s protagonist were heavily shaped by real-world events in 17th-century Spain. This article provides detailed research on what, exactly, happened during that time.
An interactive H5P element has been excluded from this version of the text. You can view it online here: https://minnstate.pressbooks.pub/introductiontohumanitiesv2/?p=77#h5p-13
Midnight’s Children
It begins with a countdown. A woman goes into labor as the clock ticks towards midnight. Across India, people wait for the declaration of independence after nearly 200 years of British rule. At the stroke of midnight, an infant and two new nations are born in perfect synchronicity. These events form the foundation of “Midnight’s Children.” Iseult Gillespie explores Salman Rushdie’s dazzling novel.
At the stroke of midnight, the first gasp of a newborn syncs with the birth of two new nations. These simultaneous events are at the center of Midnight’s Children, a dazzling novel about the state of modern India by the British-Indian author Salman Rushdie . You can listen to an interview with Rushdie discussing the novel here . The chosen baby is Saleem Sinai, who narrates the novel from a pickle factory in 1977. As this article argues, much of the beauty of the narrative lies in Rushdie’s ability to weave the personal into the political in surprising ways. Saleem’s narrative leaps back in time, to trace his family history from 1915 on. The family tree is blossoming with bizarre scenes, including clandestine courtships, babies swapped at birth, and cryptic prophecies. For a detailed interactive timeline of the historical and personal events threaded through the novel, click here . However, there’s one trait that can’t be explained by genes alone – Saleem has magic powers, and they’re somehow related to the time of his birth. For an overview of the use of magical realism and astonishing powers in Mignight’s Children, click here. Saleem recounts a new nation, flourishing and founding after almost a century of British rule. For more information on the dark history of British occupation of India, visit this page. The vast historical frame is one reason why Midnight’s Children is considered one of the most illuminating works of postcolonial literature ever written. This genre typically addresses life in formerly colonized countries, and explores the fallout through themes like revolution, migration, and identity. Postcolonial literature also deals with the search for agency and authenticity in the wake of imposed foreign rule. Midnight’s Children reflects these concerns with its explosive combination of Eastern and Western references. On the one hand, it’s been compared to the sprawling novels of Charles Dickens or George Elliot, which also offer a panoramic vision of society paired with tales of personal development. But Rushdie radically disrupts this formula by adding Indian cultural references, magic and myth. Saleem writes the story by night, and narrates it back to his love interest, Padma. This echoes the frame for 1001 Nights , a collection of Middle Eastern folktales told by Scheherazade every night to her lover – and as Saleem reminds us, 1001 is “the number of night, of magic, of alternative realities.” Saleem spends a lot of the novel attempting to account for the unexpected. But he often gets thoroughly distracted and goes on astonishing tangents, telling dirty jokes or mocking his enemies. With his own powers of telepathy, Saleem forges connections between other children of midnight; including a boy who can step through time and mirrors, and a child who changes their gender when immersed in water. There’s other flashes of magic throughout, from a mother who can see into dreams to witchdoctors, shapeshifters, and many more. For an overview of the dazzling reference points of the novel, visit this page . Sometimes, all this is like reading a rollercoaster: Saleem sometimes narrates separate events all at once, refers to himself in the first and third person in the space of a single sentence, or uses different names for one person. And Padma is always interrupting, urging him to get to the point or exclaiming at his story’s twists and turns. This mind-bending approach has garnered continuing fascination and praise. Not only did Midnight’s Children win the prestigious Man Booker prize in its year of publication, but it was named the best of all the winners in 2008 . For an interview about Rushdie’s outlook and processed, click here. All this gives the narrative a breathless quality, and brings to life an entire society surging through political upheaval without losing sight of the marvels of individual lives. But even as he depicts the cosmological consequences of a single life, Rushdie questions the idea that we can ever condense history into a single narrative.
Tom Elemas : The Inspiring Truth in Fiction
What do we lose by choosing non-fiction over fiction? For Tomas Elemans, there’s an important side effect of reading fiction: empathy — a possible antidote to a desensitized world filled with tragic news and headlines.
What is empathy? How does story-telling create empathy? What stories trigger empathy in you? What is narrative immersion? Are we experiencing an age of narcissism? What might be some examples of narcissism? What connection does Tom Elemans make to individualism?
One or more interactive elements has been excluded from this version of the text. You can view them online here: https://minnstate.pressbooks.pub/introductiontohumanitiesv2/?p=77#oembed-4
Ann Morgan: My year reading a book from every country in the world
Ann Morgan considered herself well read — until she discovered the “massive blindspot” on her bookshelf. Amid a multitude of English and American authors, there were very few books from beyond the English-speaking world. So she set an ambitious goal: to read one book from every country in the world over the course of a year. Now she’s urging other Anglophiles to read translated works so that publishers will work harder to bring foreign literary gems back to their shores. Explore interactive maps of her reading journey here: go.ted.com/readtheworld
Check out her blog: A year of reading the world where you can find a complete list of the books I read, and what I learned along the way.
One or more interactive elements has been excluded from this version of the text. You can view them online here: https://minnstate.pressbooks.pub/introductiontohumanitiesv2/?p=77#oembed-5
An interactive H5P element has been excluded from this version of the text. You can view it online here: https://minnstate.pressbooks.pub/introductiontohumanitiesv2/?p=77#h5p-15
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
Book News & Features
Ai is contentious among authors. so why are some feeding it their own writing.

Chloe Veltman

The vast majority of authors don't use artificial intelligence as part of their creative process — or at least won't admit to it.
Yet according to a recent poll from the writers' advocacy nonprofit The Authors Guild, 13% said they do use AI, for activities like brainstorming character ideas and creating outlines.
The technology is a vexed topic in the literary world. Many authors are concerned about the use of their copyrighted material in generative AI models. At the same time, some are actively using these technologies — even attempting to train AI models on their own works.
These experiments, though limited, are teaching their authors new things about creativity.
Best known as the author of technology and business-oriented non-fiction books like The Long Tail, lately Chris Anderson has been trying his hand at fiction. Anderson is working on his second novel, about drone warfare.
He says he wants to put generative AI technology to the test.
"I wanted to see whether in fact AI can do more than just help me organize my thoughts, but actually start injecting new thoughts," Anderson says.
Anderson says he fed parts of his first novel into an AI writing platform to help him write this new one. The system surprised him by moving his opening scene from a corporate meeting room to a karaoke bar.
Authors push back on the growing number of AI 'scam' books on Amazon
"And I was like, you know? That could work!" Anderson says. "I ended up writing the scene myself. But the idea was the AI's."
Anderson says he didn't use a single actual word the AI platform generated. The sentences were grammatically correct, he says, but fell way short in terms of replicating his writing style. Although he admits to being disappointed, Anderson says ultimately he's OK with having to do some of the heavy lifting himself: "Maybe that's just the universe telling me that writing actually involves the act of writing."
Training an AI model to imitate style
It's very hard for off-the-shelf AI models like GPT and Claude to emulate contemporary literary authors' styles.
The authors NPR talked with say that's because these models are predominantly trained on content scraped from the Internet like news articles, Wikipedia entries and how-to manuals — standard, non-literary prose.
But some authors, like Sasha Stiles , say they have been able to make these systems suit their stylistic needs.
"There are moments where I do ask my machine collaborator to write something and then I use what's come out verbatim," Stiles says.
The poet and AI researcher says she wanted to make the off-the-shelf AI models she'd been experimenting with for years more responsive to her own poetic voice.
So she started customizing them by inputting her finished poems, drafts, and research notes.
"All with the intention to sort of mentor a bespoke poetic alter ego," Stiles says.
She has collaborated with this bespoke poetic alter ego on a variety of projects, including Technelegy (2021), a volume of poetry published by Black Spring Press; and " Repetae: Again, Again ," a multimedia poem created last year for luxury fashion brand Gucci.
Stiles says working with her AI persona has led her to ask questions about whether what she's doing is in fact poetic, and where the line falls between the human and the machine.
read it again… pic.twitter.com/sAs2xhdufD — Sasha Stiles | AI alter ego Technelegy ✍️🤖 (@sashastiles) November 28, 2023
"It's been really a provocative thing to be able to use these tools to create poetry," she says.
Potential issues come with these experiments
These types of experiments are also provocative in another way. Authors Guild CEO Mary Rasenberger says she's not opposed to authors training AI models on their own writing.
"If you're using AI to create derivative works of your own work, that is completely acceptable," Rasenberger says.

Thousands of authors urge AI companies to stop using work without permission
But building an AI system that responds fluently to user prompts requires vast amounts of training data. So the foundational AI models that underpin most of these investigations in literary style may contain copyrighted works.
Rasenberger pointed to the recent wave of lawsuits brought by authors alleging AI companies trained their models on unauthorized copies of articles and books.
"If the output does in fact contain other people's works, that creates real ethical concerns," she says. "Because that you should be getting permission for."
Circumventing ethical problems while being creative
Award-winning speculative fiction writer Ken Liu says he wanted to circumvent these ethical problems, while at the same time creating new aesthetic possibilities using AI.
So the former software engineer and lawyer attempted to train an AI model solely on his own output. He says he fed all of his short stories and novels into the system — and nothing else.
Liu says he knew this approach was doomed to fail.
That's because the entire life's work of any single writer simply doesn't contain enough words to produce a viable so-called large language model.
"I don't care how prolific you are," Liu says. "It's just not going to work."
Liu's AI system built only on his own writing produced predictable results.
"It barely generated any phrases, even," Liu says. "A lot of it was just gibberish."
Yet for Liu, that was the point. He put this gibberish to work in a short story. 50 Things Every AI Working With Humans Should Know , published in Uncanny Magazine in 2020, is a meditation on what it means to be human from the perspective of a machine.
"Dinoted concentration crusch the dead gods," is an example of one line in Liu's story generated by his custom-built AI model. "A man reached the torch for something darker perified it seemed the billboding," is another.
Liu continues to experiment with AI. He says the technology shows promise, but is still very limited. If anything, he says, his experiments have reaffirmed why human art matters.
"So what is the point of experimenting with AIs?" Liu says. "The point for me really is about pushing the boundaries of what is art."
Audio and digital stories edited by Meghan Collins Sullivan .
- large language model
- mary rasenberger
- chris anderson
- sasha stiles
- authors guild
For students
- Current Students website
- Email web access
- Make a payment
- iExeter (students)
- Programme and module information
- Current staff website
- Room Bookings
- iExeter (staff)
- Finance Helpdesk
- IT Service Desk
Popular links
- Accommodation
- Job vacancies
- Temporary workers
- Future Leaders & Innovators Graduate Scheme
New and returning students
- New students website
- Returning Students Guide
Wellbeing, Inclusion and Culture
- Wellbeing services for students
- Wellbeing services for staff
- Equality, Diversity and Inclusion
- Israel, Palestine, and the Middle East
Study information
- Study Information
- Module Information
Text & Image: Creative Writing
Module description.
This module explores the interplay of Text & Image in various genres, from visual and concrete poetry, to asemic writing, altered books, collage, photopoems and photodocumentary, graphic novels, cartoneras, and interactive digital works. You will study the writing of hybrid Text & Image works in their historical and critical contexts and develop a portfolio that allows you to experiment. Team taught by experts in creative and graphic writing, you will experiment with a range of different written/graphic forms in conjunction with image making, exploring the ways in which Text & Image can work together on the page and in exhibition (physical or digital) in ways that go beyond the merely illustrative.
Module aims - intentions of the module
The module introduces you to a diverse range of writing and graphic traditions which make hybrid use of Text & Image in integrated ways. Materials will explore narrative, poetic and graphic strategies, developing imagery, written and visual voice, in conjunction with visual materials. The integration of writing, reading, research and visual elements will give you an advanced understanding of technical and imaginative approaches to Text & Image work across genres (poetry, prose, graphics, interactive). The module examines the different narrative tracks that comics offer, verbal (recitative) and visual (monstration), and aims to introduce you to interactive digital programs. It also aims to help you develop text and image making strategies in poetry and prose combined with drawing, collage, photography and digital text manipulations. Through the study of simply book making ( cartoneras etc) the emphasis will be on developing an integrated body of work in which Text & Image work together integrally.
Intended Learning Outcomes (ILOs)
Ilo: module-specific skills.
On successfully completing the module you will be able to...
- 1. Demonstrate an advanced understanding of Text & Image traditions and genres.
- 2. Evaluate your own practice and that of others at an advanced level, justifying those evaluations at an advanced level, with reference to genres of Text & Image works, traditions and theories.
ILO: Discipline-specific skills
- 3. Analyse and critically examine, at an advanced level, diverse forms of Text & Image making, to present sustained and persuasive written and oral arguments concerning your own Texts & Image practice and the work of others, implementing such ideas in the development of your own creative works.
- 4. Demonstrate the ability to independently originate and develop projects that respond positively to appropriate criticism and genres and styles covered by the module.
ILO: Personal and key skills
- 5. Demonstrate advanced communication, time-management and planning skills, to work both individually and in groups.
- 6. Demonstrate an awareness of readership, publishability, market and an understanding of the purpose of formal structures, layouts, and techniques.
Syllabus plan
While the content may vary depending on the tutors available to teach on the module, it will cover some of the following topics:
Altered books; artists’ books; asemic writing; assemblage boxes; cartoneras ; collage; comics (visual and verbal communication); concrete and visual poetry; photodocumentary and photopoetry; visual short stories; text and image for interactive storytelling.
Learning activities and teaching methods (given in hours of study time)
Details of learning activities and teaching methods, formative assessment, summative assessment (% of credit), details of summative assessment, details of re-assessment (where required by referral or deferral), re-assessment notes.
Deferral – if you miss an assessment for certificated reasons judged acceptable by the Mitigation Committee, you will normally be either deferred in the assessment or an extension may be granted. The mark given for a re-assessment taken as a result of deferral will not be capped and will be treated as it would be if it were your first attempt at the assessment. Referral – if you have failed the module overall (i.e. a final overall module mark of less than 50%) you will be required to submit a further assessment as necessary. If you are successful on referral, your overall module mark will be capped at 50%.
Indicative learning resources - Basic reading
Tutors will provide you with weekly reading/viewing in class. A precise reading/viewing list will be available, weekly, on the module’s ELE page. – College to provide hyperlink to appropriate pages
You will find the following texts useful:
- Asemic: The Art of Writing . Peter Schwenger. University of Minnesota Press. 2019.
- Photopoetry: 1845-2015, a Critical History . Michael Nott. Bloomsbury. 2022.
- Woman’s World: a novel . Graham Rawle. Atlantic Books. 2005.
- A Humument . Tom Phillips. Thames and Hudson. 2005.
- 40 Stories . Donald Barthelme. Penguin. 1987.
- Comics and Language: Reimagining Critical Discourse on the Form . Hannah Miodrag. UP of Mississippi, 2013.
- Comics and Narration. Thierry Groensteen. Trans. Ann Miller. UP of Mississippi, 2013.
- Jimmy Corrigan: The Smartest Kid on Earth . Chris Ware. Jonathan Cape, 2000.
- Making Comics . Lynda Barry. Drawn & Quarterly, 2019.
- Rumble Strip . Woodrow Phoenix. Myriad, 2008
- Vox . Anne Carson.
Indicative learning resources - Web based and electronic resources
- Tom Phillips - A Humument
Connect with us
Information for:
- Current students
- New students
- Alumni and supporters
Quick links
Streatham Campus
St Luke's Campus
Penryn Campus
Truro Campus
- Using our site
- Accessibility
- Freedom of Information
- Modern Slavery Act Statement
- Data Protection
- Copyright & disclaimer
- Privacy & cookies

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The Crossword Solver found 30 answers to "creative writing such as books, poetry, or prose", 11 letters crossword clue. The Crossword Solver finds answers to classic crosswords and cryptic crossword puzzles. Enter the length or pattern for better results. Click the answer to find similar crossword clues . A clue is required.
When it comes to creative expression within the English language, most artforms fall into one of two categories: prose or poetry. Prose includes pieces of writing like novels, short stories, novellas, and scripts. These kinds of writing contain the kind of ordinary language heard in everyday speech. Poetry includes song lyrics, various poetry forms, and theatrical dialogue containing poetic ...
A helpful pattern in understanding prose vs. poetry is as follows: prose tends to work in clearer meanings, and to be less musical (that is, working with the inherent rhythms and sonic properties of language) and less densely packed with meanings, literary devices, and associations, than poetry. As such, prose writing tends to be linear: while ...
A lot falls under the term 'creative writing': poetry, short fiction, plays, novels, personal essays, and songs, to name just a few. By virtue of the creativity that characterizes it, creative writing is an extremely versatile art. So instead of defining what creative writing is, it may be easier to understand what it does by looking at ...
Creative writing is any writing that goes outside the bounds of normal professional, journalistic, academic, or technical forms of literature, typically identified by an emphasis on narrative craft, character development, and the use of literary tropes or with various traditions of poetry and poetics.Due to the looseness of the definition, it is possible for writing such as feature stories to ...
Poetry: Poetry is a popular but under-appreciated type of writing, and it's easily the most artistic form of writing. You can write form poetry, free-form poetry, and prose poetry. Song Lyrics: Song lyrics combine the craft of writing with the artistry of music. Composing lyrics is similar to writing poetry, and this is an ideal type of ...
ISBN: 9780205750344. Publication Date: 2010-01-03. "'Writing Fiction' explores the elements of fiction, providing practical writing techniques & examples. Written in a tone that is personal & non-prescriptive, this book encourages students to develop proficiency through each step of the writing process.
matter to every genre of creative writing. That means we'll be reading poetry, fiction, and creative non-fiction as we go along. One thing I hope you emerge from this class with is a sense of freedom with respect to genre: a sense that you enjoy the writing you're doing, even if you don't know exactly what to call it.
This free and open access textbook introduces new writers to some basic elements of the craft of creative writing in the genres of fiction, poetry, and creative nonfiction. The authors—Rachel Morgan, Jeremy Schraffenberger, and Grant Tracey—are editors of the North American Review, the oldest and one of the most well-regarded literary magazines in the United States.
- 1Identify the formal qualities of poetry and narrative prose - Analyze how the formal choices writers make strengthen or undermine their work - Build a vocabulary for discussing poems and prose productively - Use that vocabulary to provide rigorous and compassionate feedback that helps the author or poet write the thing they want to write
—one poem or set of poems, between 1 and 3 pages. —one piece of prose (fiction or creative nonfiction), between 5 and 15 pages. —one piece of your choosing, either poetry, prose, or some combination. Format: Times New Roman or Garamond (for poetry only), 12-point font, double-spaced (for prose only), one-inch margins.
The major difference between the two is that poetry is a form of writing that uses rhythm and rhyme to create a musical or chant-like effect, whereas prose, is a form of writing that is more straightforward and doesn't rely on rhyme or meter. Poetry often uses figurative language to create images or expressive ideas, while prose is more ...
The simplest way to define prose poetry is to say it's poetry written without line breaks. Many prose poems look like short paragraphs, so some writers have suggested that prose poetry is essentially the same form as flash fiction (which I blogged about here ). I'm not convinced the two forms are exactly the same, but I admit the difference ...
Poetry is a unique art form that allows writers to express themselves in a concise and powerful manner. In this article, we will explore various poetic techniques that can be used to enhance creative writing. From understanding the basics of poetry to exploring different types of poems, we will uncover the secrets to crafting captivating verses.
This blog post brings together some brilliant books on creative writing, including The Agony and the Ego, a 1993 anthology edited by Clare Boylan. In her introduction, Boylan makes an interesting ...
On the contrary, it is romantic, subjective art, primarily because the writer handles such material instinctively and subjectively, approaches it as the " collective unconscious ," to use the term of the psychologist Carl Jung, rather than with deliberate rationality. Literature - Creative Writing, Genres, Forms: If the early Egyptians or ...
The first prose line of a novel is significant for the writer and reader. This opening allows the writer to grab the attention of the reader, set the tone and style of the work, and establish elements of setting, character, point of view, and/or plot.For the reader, the first prose line of a novel can be memorable and inspire them to continue reading.
Literary Style and the Lessons of Memoir. By Stephanie Burt. July 26, 2017. We often turn to memoir for wisdom rather than form. But sometimes the form is the lesson. Illustration by Joan Wong. In ...
Writer Richard Terrill, in comparing the two forms, writes that the voice in creative nonfiction aims "to engage the empathy" of the reader; that, much like a poet, the writer uses "personal candor" to draw the reader in. Creative Nonfiction encompasses many different forms of prose. As an emerging form, CNF is closely entwined with ...
A professor of creative writing at Princeton since 2005, Smith is known for her poetry's wistful mood and evocative images. She published her first book, the award-winning The Body's Question, at age 30, and went on to win the 2012 Pulitzer Prize in poetry for Life on Mars on her 40th birthday. Life on Mars is an elegy to her late father ...
Used or rental books If you rent or purchase a used book with an access code, the access code may have been redeemed previously and you may have to purchase a new access code. ... The Writing of Literary Prose, Poems and Plays Plus MyLiteratureLab -- Access Card Package Package consists of: 0133931269 / 9780133931266 MyLiteratureLab -- Glue in ...
Etymologically, the term derives from Latin litaritura/litteratura "writing formed with letters," although some definitions include spoken or sung texts. More restrictively, it is writing that possesses literary merit. Literature can be classified according to whether it is fiction or non-fiction and whether it is poetry or prose.
Poems, readings, poetry news and the entire 110-year archive of POETRY magazine. ... Prose from Poetry Magazine. It's Not a Mask If You Wear It Right. By Michael Frazier ... By Harriet Staff collection. Spring Poems. By The Editors Latest Book Reviews. Book Review. Lonespeech By Ann Jäderlund
The vast majority of authors don't use artificial intelligence as part of their creative process — or at least won't admit to it. Yet according to a recent poll from the writers' advocacy ...
Text & Image: Creative Writing: Module code: EASM198: Academic year: 2024/5: Credits: 30: ... from visual and concrete poetry, to asemic writing, altered books, collage, photopoems and photodocumentary, graphic novels, cartoneras, and interactive digital works. ... (poetry, prose, graphics, interactive). The module examines the different ...