You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser or activate Google Chrome Frame to improve your experience.


Gr. 12 HISTORY T3 W1:The end of the Cold War and a new world order 1989 to the present
This essay focus on Gorbachev's reforms in the Soviet Union in 1989 and its impact on South Africa
Do you have an educational app, video, ebook, course or eResource?
Contribute to the Western Cape Education Department's ePortal to make a difference.

Home Contact us Terms of Use Privacy Policy Western Cape Government © 2024. All rights reserved.


The Cold War
The end of the cold war.

Three events heralded the end of the Cold War: the fall of the Berlin Wall , the reunification of Germany and the dissolution of the Soviet Union. All came at the end of a tumultuous decade where ordinary people challenged the viability of socialism and socialist governments. The pressures they applied undermined and eroded political authority in Soviet bloc nations. With Moscow no longer demanding adherence to socialist policies, these governments relented, allowing political reforms or relaxing restrictions such as border controls. In East Germany , the epicentre of Cold War division, popular unrest brought about a change in leadership and the collapse of the Berlin Wall (November 1989). Within a few months, the two Germanys were rejoined after 45 years of division. Meanwhile, the Soviet Union was also in its death throes. After two decades of economic stagnation , the USSR was weakening internally. As the historian John Lewis Gaddis put it, the USSR was a “troubled triceratops”: it remained powerful and intimidating but on the inside its “digestive, circulatory and respiratory systems were slowly clogging up then shutting down”. Mikhail Gorbachev ‘s twin reforms, glasnost and perestroika , failed to save the beast.
The demise of the Berlin Wall cleared the road to the reunification of Germany. Internal borders between East and West Germany, as well as those within the divided city of Berlin, were quickly removed. West German chancellor Helmut Kohl seized the moment by drafting a ten-point plan for German reunification, without consulting NATO allies or members of his own party. While most Germans welcomed the move, the prospect of a reunified Germany did not please everyone. It was particularly troubling for older Europeans with lingering memories of Nazism and World War II. British prime minister Margaret Thatcher was privately concerned about it, as were many French, Italians and indeed the Soviets. Israel, now home to thousands of Holocaust survivors, was the most vocal opponent of German reunification.
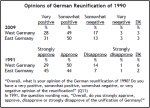
In March 1990, East Germany held its first free elections, producing a resounding defeat for the communists. The two German states stepped up their political and economic co-operation, agreeing to a single currency (the Deutschmark ) in July 1990. Work was already underway on the formalities of reunification and the composition of a new German state. These questions were finalised by the Unification Treaty , which was signed in August 1990 and came into effect on October 3rd. A general election – the first all-German free election since 1932 – was held in December 1990. A coalition of Christian conservative parties won almost half the seats in the Bundestag (parliament), while Helmut Kohl was endorsed as chancellor. In the years that followed, Germany would dispel concerns about its wartime past by becoming one of the most prosperous and progressive states in Europe.
The Soviet Union passes into history

The Soviet Union remained the last bastion of socialism in Europe – but it too was rapidly changing. Gorbachev’s reforms of the mid-1980s failed to arrest critical problems in the Soviet economy. Soviet industries faced critical shortages of resources, leading to a decline in productivity. Meanwhile, Soviet citizens endured shortages of state-provided food items and consumer goods, giving rise to a thriving black market. Moscow’s big-ticket spending on the military, space exploration and propping up satellite states further drained the stagnating Soviet economy. More reforms in 1988 allowed private ownership in many sectors, though this came too late to achieve any reversal. It became clear that the Soviet economy could not recover on its own: it needed access to Western markets and emerging technologies.
The political dissolution of the Soviet Union unfolded gradually in the late 1980s. A series of reforms in 1987-88 loosened Communist Party control of elections, released political prisoners and expanded freedom of speech under glasnost . Outside Russia, the Baltic states (Latvia, Lithuania and Estonia) agitated for independence while separatist-driven violence was reported in Azerbaijan and Armenia. In early 1990, the Communist Party accepted Gorbachev’s recommendation that Soviet bloc nations be permitted to hold free elections and referendums on independence. By the end of 1990, the citizens in six states – Latvia, Lithuania, Estonia, Armenia, Georgia and Moldova – had voted to leave the Soviet Union. Ukraine, a region of considerable economic value, also declared its independence in July 1990. The Soviet republics that remained were given greater political and economic autonomy.
The August 1991 coup
“Many Russians sympathised with the plotters… because they approved of their motivation, that of preventing the Soviet Union from unravelling. After the initial euphoria… had died down, and people began to face the realities of a disbanded Soviet empire, disenchantment set in. Within a couple of years, the Yeltsin administration was itself pushing for a ‘reintegration’ of the former Soviet republics.” Amy Knight, historian In 1991 Gorbachev attempted to restructure and decentralise the Soviet Union by granting its member-states greater autonomy. Under Gorbachev’s proposed model, the USSR would become the “Union of Soviet Sovereign Republics”, a confederation of independent nations sharing a military force, foreign policy and economic ties. These proposed changes angered some Communist Party leaders, who feared they would erode Soviet power and bringing about the collapse of the USSR. In August 1991 a group of hardliners including Gorbachev’s vice-president, prime minister, defence minister and KGB chief, decided to act. With Gorbachev at his dacha in Crimea, the group ordered his arrest, shut down the media and attempted to seize control of the government. The coup leaders misread the mood of the public, however, which came out in support of Gorbachev. The coup collapsed after three days and Gorbachev was returned to office, though with his authority reduced. By Christmas 1991, the Soviet Union had passed into history. It was formally dissolved and replaced by a looser confederation called the Commonwealth of Independent States. The death of the Soviet Union marked the curtain call of the Cold War. While communist regimes remained in China , North Korea and Cuba , the perceived threat of Soviet imperialism had been lifted from the world. Debate raged among commentators and historians about who was responsible for ending the Cold War. Some hailed Gorbachev and other Soviet bloc reformers as the architects of change and reform. Others credited strong-minded Western leaders like Ronald Reagan and Thatcher with bringing down the Soviet empire. Some believed communism was defeated by its own false promises: it was an unsustainable economic system that had collapsed from within. There was some truth in all three perspectives. In the tumultuous 1980s, however, ordinary people were the true engine of change. For decades citizens in the Soviet bloc had lived under oppressive one-party regimes and had little or no say in government. They were forced to work, denied the right to protest or speak and denied the choices available to their neighbours in the West. The final years of the Cold War were defined by these ordinary people, who risked their lives to rejoin the free world. Their determination and heroism were noted by novelist John Le Carre: “It was man who ended the Cold War, in case you didn’t notice. It wasn’t weaponry, or technology, or armies or campaigns. It was just man. Not even Western man either, as it happened, but our sworn enemy in the East, who went into the streets, faced the bullets and the batons and said: ‘We’ve had enough’. It was their emperor, not ours, who had the nerve to mount the rostrum and declare he had no clothes. And the ideologies trailed after these impossible events like condemned prisoners, as ideologies do when they’ve had their day.”

1. Three significant events heralded the end of the Cold War: the fall of the Berlin Wall, the reunification of Germany and the dissolution of the Soviet Union.
2. The fall of the Berlin Wall prompted the removal of borders between East and West Germany, while West German chancellor Helmut Kohl began pushing for the reunification of the two states.
3. Despite opposition from some quarters, reunification proceeded during 1990. It was finalised by the Reunification Treaty (October) and free elections for a single Germany (December).
4. Beset by internal economic and political problems, the Soviet Union weakened during the late 1980s. After an unsuccessful coup attempt by hardliners, the USSR was dissolved in 1991.
5. There is much debate about the factors that brought the Cold War to an end. Some attribute it to Gorbachev’s reforms, strong leadership in the West or the unsustainability of socialist economic systems. The role of ordinary people in the late 1980s is also undeniable.

US intelligence paper: ‘The Soviet system in crisis’ (November 1989) The German Unification Treaty (August 1990) Communist hardliners justify their attempted coup to unseat Mikhail Gorbachev (August 1991) The Minsk Agreement dissolves the Soviet Union (December 1991)
Content on this page is © Alpha History 2018. This content may not be republished or distributed without permission. For more information please refer to our Terms of Use . This page was written by Jennifer Llewellyn, Jim Southey and Steve Thompson. To reference this page, use the following citation: J. Llewellyn et al, “The end of the Cold War”, Alpha History, accessed [today’s date], https://alphahistory.com/coldwar/end-of-the-cold-war/.
- Society and Politics
- Art and Culture
- Biographies
- Publications

Grade 12 - Topic 4 - The end of the Cold War and a new global world order 1989 to present
There were many reasons why apartheid collapsed. You can read about the crisis of Apartheid in the 1980s in section 5 of the grade 12 material. The collapse of communism in the Soviet Union was another major cause of the end of apartheid.
Under apartheid, South Africa was a fascist state with a capitalist economy. The National Party was strongly anti-communist and said they were faced with a ' Rooi Gevaar' or a 'Red Threat'. The apartheid state used the label 'communist' to justify its repressive actions against anyone who disagreed with their policies.
During the Cold War, there was a contest for influence in Africa, between the US and Western powers on the one hand, and the Soviet Union and Eastern bloc countries on the other. Most of newly independent ex-colonies in Africa received military and economic support from one of the Superpowers.
Despite its racist policies, the South African government was supported by many governments in the West, particularly Britain and the USA. This was because the South African government was anti-communist. The British and American governments used political rhetoric and economic sanctions against apartheid, but continued to supply the South African regime with military expertise and hardware.
The collapse of the USSR in 1989 meant that the National Party could no longer use communism as a justification for their oppression. The ANC could also no longer rely on the Soviet Union for economic and military support. By the end of the 1980s, the Soviet Union was in political and economic crisis, and it was increasingly difficult for the Soviet Government to justify spending money in Africa.
In 1989, President F.W de Klerk , the last apartheid Head of State, unbanned the African National Congress , the South African Communist Party and the Pan Africanist Congress . He states that the collapse of the Soviet Union was decisive in persuading him to take this step:
"The collapse of the Soviet Union helped to remove our long-standing concern regarding the influence of the South African Communist Party within the ANC Alliance. By 1990 classic socialism had been thoroughly discredited throughout the world and was no longer a serious option, even for revolutionary parties like the ANC.
At about the same time, the ANC was reaching a similar conclusion that it could not achieve a revolutionary victory within the foreseeable future. The State of Emergency, declared by the South African Government in 1986, and the collapse of the Soviet Union - which had traditionally been one the ANC's main allies and suppliers - led the organisation to adopt a more realistic view of the balance of forces. It concluded that its interests could be best secured by accepting negotiations rather than by committing itself to a long and ruinous civil war." - Quote source: www.fwdklerk.org.za
Suggested activities and links:
- " End of the Cold War " at www.schoolhistory.co.uk (provides additional information from an international perspective. Includes activities)
- " The Cold War Museum " at www.coldwar.org (This link gives a decade by decade breakdown of all major developments in the Cold War from an American perspective. This is helpful for general understanding. Also includes a trivia game and timeline) *needs Windows IE browser for quiz
- " Learning Curve " at www.learningcurve.gov.uk (This resource has some interesting clips and worksheets from a British perspective)
- " Cartoon Stock " at www.cartoonstock.com (This site has a range of Cold War cartoons that could be used to practise cartoon analysis.)
To reflect on the impact of the collapse of the USSR in 1989 on the re-imagining of African nations in the 1990s the curriculum requires that certain countries are examined in detail.
The case studies for the examination are as follows:
Central Africa: Congo and Angola to be examined in 2009 (below)
West Africa: Benin and Guinea: to be examined in 2010
North Africa: Egypt: to be examined in 2011
Colonialism in the Congo
The present day Democratic Republic of Congo was formerly the Belgian Congo. The capital under colonial rule was Leopoldville (now Kinshasa).
The area was colonised in 1885 as a personal possession of the Belgian King Leopold II as the Congo Free State. It is one of the largest countries in Africa and one of the richest.
Leopold ideas reflected the racist ideas of most of his European counterparts at the time. He thought that Africa was "stagnant, primitive and dark", and that his rule would bring "progress, civilisation and light."
Belgium's brutal exploitation of the Congo is infamous. Leopold accumulated a vast personal fortune from ivory and rubber using Congolese forced labour. In 1891, the price of rubber began to increase following the invention of the inflatable rubber tyre, which increased his profits even further.
He was known locally as 'Bula Matadi' (He Who Breaks Rocks) to indicate the brutality of his regime. During Leopold's rule the population of the Congo declined from an estimated 20-30 million to less than nine million.
In 1907, administration of the colony shifted from the king to the Belgian Government, which renamed the country the Belgian Congo.
Independence in the Congo
Independence was granted in 1960, and the country was named the Republic of the Congo. The African elite in the colony was very small, and this suited the financial interests of Belgium, which planned to maintain its economic grip on the Congo's mineral resources and raw materials.
Elections were held, and Patrice Lumumba became Prime Minister. Joseph Kasavubu became Head of State.
During the Cold War, there was a contest for influence in Africa, between the US and Western powers on the one hand, and the Soviet Union and Eastern bloc countries on the other. The Cold War spread outside Europe to every region of the world. Most of newly independent ex-colonies in Africa got military and economic support from one of the Superpowers. The Congo was important because of its wealth and its size.
Lumumba followed a policy of "positive neutralism," - a return to African values and the rejection of foreign non-African ideologies, including that of the Soviet Union.
The West feared the consequences of a Lumumba's Congo government for its position in Africa. The USA had recently witnessed Fidel Castro's victorious revolution in Cuba, and Castro's friendship with Moscow.
The CIA quickly became involved in destabilising Lumumba's government. US President Eisenhower's government said Lumumba was a "very difficult if not impossible person to deal with, and was dangerous to the peace and safety of the world."
Within weeks of independence, the Katanga Province, which was rich in copper, led by Moise Tshombe, broke away from the new republic. Belgium sent in troops. It said the troops were to protect Belgian nationals. However, the Belgian troops mainly landed in Katanga, where they helped keep the regime of Moise Tshombe in power with the help of the USA.
Lumumba appealed to the United Nations to expel the Belgians and help restore internal order. The United Nations forces refused to help suppress the Katangese revolt.
Having been rejected by the West, Lumumba appealed to the Soviet Union for planes to assist in transporting his troops to Katanga. The Western powers were alarmed. Moreover, in the context of the Cold War, the Soviet Union's support for Lumumba appeared at the time as a threat to the West.
On 5 September 1960, President Kasavubu dismissed Lumumba, and Lumumba contested the move. There were therefore two groups now claiming to be the legal central government. On 14 September 1960, power was seized by the Congolese army leader Colonel Joseph Mobutu (president of Zaire as Mobutu Sese Seko), who later reached a working agreement with Kasavubu.
The assassination of Lumumba
In November 1960, Lumumba wanted to travel from Leopoldville, where the United Nations had provided him with protection, to Stanleyville where his supporters had control. With the secret help of the CIA, Joseph Mobutu sent his soldiers after Lumumba. Lumumba was caught, and spent three months in prison, while his enemies tried in vain to consolidate their power.
In January 1961, Lumumba was handed over to the Katanga secessionist regime, where he was executed. Documents from the USA which were released in 2000 revealed that President Eisenhower gave direct orders for the CIA to assassinate Lumumba. You can read an interesting article about Lumumba's assassination on this external link: www.wsws.org
Mobutu seizes power
In 1965, army leader Joseph Mobutu seized control as the dictator of the Congo. Mobutu renamed the country, and called it the Republic of Zaire. All citizens had to adopt African names. He called himself Mobutu Sese Seko. He had the backing of the USA government, as he was willing to turn Zaire into a springboard for operations against Soviet-backed Angola. You can read about Angola in another section.
The USA considered Mobutu Sese Seko as a safeguard against Soviet-sponsored Communism in Africa. Mobutu received American support, including military aid, throughout his ruthless dictatorship. He was even received by American presidents at the White House. The Cold War support of Mobutu by the USA put Mobutu in a position to loot his country's riches and he became one of history's most corrupt dictators. He funnelled the wealth of the Congo into his own pockets.
Lumumba had wanted to reform the Congo and use its riches to lift the Congolese out of poverty. In contrast, Mobutu chose King Leopold II as his role model. Leopold ran the Congo as his private rubber plantation. Mobutu outdid even Leopold, as he sold off the Congo's resources and stashed billions of dollars in Swiss bank accounts. Mobutu built himself a refuge on the French Riviera.
The Congolese continued to live in poverty.
Zaire and the Cold War
President Ford's American administration opposed the Soviet-backed Popular Movement for the Liberation of Angola (MPLA). Mobutu helped the USA against the MPLA. He supported his brother-in-law, Jonas Savimbi, who led UNITA.
In the 1980s, the Reagan administration called Savimbi a "freedom fighter" worthy of CIA support. Thankful for the use of Zaire as a supply route to Savimbi's forces, Reagan praised Mobutu as "a voice of good sense and good will."
Between 1962 and 1991, the U.S. directly supported Mobutu and his government with more than $1.03 billion in development aid and $227.4 million in military assistance.
Reviewing America's support for Mobutu, the former US Assistant Secretary of State, Chester Crocker said: "I think we have no apologies to make. We were in a state of global rivalry with a global adversary."
The end of the Cold War
Soviet leader Mikhail Gorbachev introduced reform policies in the USSR - called perestroika (restructuring of the Soviet economy) and glasnost (openness and transparency). After more than four decades, in December 1989, Gorbachev and President George H.W. Bush Sr. declared the Cold War officially over.
With the Cold War ended, Zaire ceased to be of interest to the US, and US aid to Mobutu began to dry up.
There had been simmering anger and discontent with Mobutu's rule in Zaire for a long time. Mobutu could not stay in power without US help. The Zairian liberation movement led by Laurent Kabila overthrew Mobutu's dictatorship in 1997. It quickly reinstated the country's name, the Democratic Republic of the Congo (D.R.C.) and appointed a new government. Laurent Kabila declared himself President.
Mobutu went into exile in Togo and then in Morocco, and died of cancer in 1997. He had seventeen children. The accounts held by Swiss institutions containing the assets of the late Mobutu Sese Seko were frozen in 1997. Swiss authorities have repeatedly denied Mobutu's heirs access to the money, and in May 2009 the funds remained frozen.
Laurent Kabila banned all political parties except his own, and elections were never held. Kabila's policies differed little from his Mobutu's as he ran a dictatorship that was corrupt and rampant with human rights abuses. He was assassinated in 2001, and succeeded by his son, Joseph Kabila.
Case Study: Congo
The sources that appear in the Grade 12 examination are often quite long and difficult. The sources in this task on the Congo are taken from the Supplementary History Paper Two that was written in March 2009. It is good practice for you to try to answer all the questions, and then check your answers.
There are four sources A, B, C and D. Each source has a separate set of questions and answers.
Examine the sources and then answer the questions that follow.
The following extract is adapted from In the Footsteps of Mr Kurtz: Living on the Brink of Disaster in the Congo :
The US played a major role in converting the newly independent Congo into a Cold War battleground. The US administration in the 1960s authorised the murder of Prime Minister Patrice Lumumba, who had been voted into office just months earlier in the territory's first-ever democratic election. Washington, who was instrumental in helping Mobutu Seso Seko to power and kept him there for more than 30 years, bears heavy responsibility for the disastrous economic conditions, massive corruption, and suppression of human rights in the Congo.
Mobutu was regarded as a particularly valuable asset by the United States of America and they were determined to keep him in power at all costs so that the Congo remained a pro-Western defence against Soviet ambitions in Africa. When Mobutu visited Washington for the first time in May 1963, President Kennedy stated: 'General if it hadn't been for you, the whole thing would have collapsed and the Communists would have taken over...'
Subsequent US presidents believed that Mobutu was the only alternative to communism and continued to support him financially and militarily. The US, using Congo's bases as the conduit (pipeline) for arms destined for Angola's rebels, was determined to keep Mobutu on board. This despite having substantial knowledge that he was highly corrupt and an inefficient leader.
According to Roger Morris, US representative responsible for African affairs in the 1970s, keeping Mobutu on the US side was not cheap. It is argued that the CIA prolonged Mobutu's rule by providing more than $300 million in weapons and $100 million in military training ...
Look at Source A and answer the following questions:
1. Why do you think the US administration 'authorised the murder' of Lumumba?
2. Explain to what extent the USA was responsible for the installation of Mobutu as leader of the Congo.
3. How did the various US presidents continue to keep Mobutu's regime in power?
4. Why was the Congo important to the USA in the Cold War context?
The following has been taken from World History, A New Perspective . It focuses on Mikhail Gorbachev's reform measures.
Gorbachev, a reformist communist, became general secretary of the Soviet Communist Party in March 1985. He introduced reforms called Perestroika and Glasnost which allowed greater openness and freedom of speech.
When Gorbachev addressed the United Nations in 1988, he committed himself to ending the Cold War with the United States. He decided to abandon the Brezhnev Doctrine, renounced the Communist Party's emphasis on a world revolution dating back to 1917 and was intent on cutting back on nuclear weapons. With Russia's conservative and ailing economy, Gorbachev was no longer prepared to support Soviet dominated governments in Europe and Africa. By doing this Gorbachev effectively withdrew his support from hard-line communist regimes of Europe and Africa and he encouraged the leaders of these regimes to seek new ways of gaining support. By doing so, Gorbachev opened the way for political and economic reforms in Europe and Africa.
Look at Source B and answer the following questions:
1. Using the information in the source and your own knowledge, define the following concepts: (a) Perestroika (b) Glasnost. Explain how the concepts differ from each other.
2. Explain why Gorbachev wanted to end Russia's participation in the Cold War.
3. List some of the criticism of Gorbachev's reforms.
4. Using the information in the source and your own knowledge, explain how African countries (such as the Congo) responded to Gorbachev's decision?
The following extract focuses on the impact of Gorbachev's reforms on Mobutu's regime. Taken from A History of Fifty Years of Independence .
With Mikhail Gorbachev's perestroika transforming the Soviet Union, the Cold War priorities were fading. Democracy was sweeping across Africa and Mobutu was moving from useful US ally to an embarrassment. In the 1990s the World Bank noted that Congo's economy had shrunk to the level of 1958, while the population had tripled. Average life expectancy was fifty-two years, illiteracy was growing, Aids was rife and diseases such as bubonic plague and sleeping sickness were enjoying a vibrant comeback. It further noted that by the end of the century one of Africa's richest states was dipping below the daily takings of the US super store Wal-Mart.
Western self-interest made indulging Mobutu worthwhile, in fact Chester Crocker, the former US assistant secretary of state for Africa, stated that 'If we tried to attach 1990's governance conditionalities to Mobutu, we would have been calling for his overthrow and if we asked him to turn off the taps, his own people would have toppled him. We would, in effect, have been calling for a coup. I'm sure of that'.
However, when the Cold War ended, the US gradually stopped supporting Mobutu. On 29 April 1997 American negotiators met Mobutu, bearing a letter from President Clinton, trying to persuade him to leave 'with honour and dignity' and spare the capital from looting and destruction that seemed likely to accompany his downfall.
He was overthrown in 1997 and went into exile. A new government, under Laurent Kabila, took over and changed Zaire's name to the Democratic Republic of Congo.
Look at Source C and answer the following questions:
1. Why, according to the source, did Mobutu prove to be an embarrassment to the USA?
2. Explain how Chester Crocker justified the US's support of Mobutu.
3. What factors contributed to Mobutu being overthrown as the leader of the Congo?
The following is a Cuban cartoon showing American arms pushing Mobutu over the cliff with the words 'the time for change has arrived' and putting Laurent Kabila in his place. Kabila and Mobutu both hold skulls as sceptres (symbol of a ruler).
Look at Source D and answer the following questions:
1. Identify the man on the left and the right and explain what is happening to both of them.
2. Who is 'the boss' being referred to by the man on the right?
3. What does the cartoonist suggest about the nature of the change of leadership?
4. Why do you think the USSR is not involved?
5. The cartoonist is Cuban. What is the cartoonist opinion of the USA?
Case Study: Angola
The following extract is from The Post Cold War Diplomacy in Angola: The Emergence of New Foci of Power by Dr. Skyne Uku-Wertimer.
Angola is potentially one of the richest countries in sub-Saharan Africa with extensive petroleum reserves, rich agricultural land and valuable mineral resources. Few countries in the world have experienced as well as sustained the degree of violent conflict seen in Angola.
Intervention has diminished but has not disappeared. Angola's abundant natural resources continue to attract outside interests from industrialized nations globally. In the competition for oil, diamonds and other precious resources in Angola, interests external to Angola continue to play a large and decisive role, both in suppressing conflict and in sustaining it.
The end of the Cold War changed the political landscape of Africa since the 1990s and opened new vistas for the continent, it helped in reshaping international relations as well as the emergence of new concepts of security and self interest. It eliminated the division of Africa into two ideological camps and eliminated a source of external support that was taken for granted.
1. What were the Cold War ideological camps referred to in the source? Lists some of the countries that belonged in both ideological camps.
2. What other reason does the source suggest is a reason for the violent conflict in Angola?
The Civil War has ended in Angola, but most of the country is still in chaos. Almost half of the land in Angola is considered too dangerous to walk on. Nobody knows how many landmines lie beneath the soil of Angola. Some say it may be somewhere between 500,000 and one million, others say there may be as many as six million landmines.
A child bearing the effects of conflict and landmines in civil war torn Angola. Source: www.emine.org
1. What does Source B suggest about one of the legacies of the Civil War?
2. What impact would the image in Source B have on Angola's economy?
1. What four images in the cartoon tell you about the state of Angola?
2. Explain the play on words the cartoon is using.
This cartoon shows the USSR releasing its control of Africa. (Source unknown)
1. What message does the source convey?
2. Using the information from the source and your own knowledge, explain the accuracy of the cartoonist's portrayal of events in Africa.
3. Why is this cartoon a reflection of the history of Africa that goes beyond its presence in the Cold War?
Collections in the Archives
Know something about this topic.
Towards a people's history
- Political Science
- International History and Politics
The Fall of the Berlin Wall, the Collapse of the USSR and the End of Cold War. A Chain of Surprises 'Too Big' to Be Predicted
- January 2021

- Università Ca' Foscari Venezia
Discover the world's research
- 25+ million members
- 160+ million publication pages
- 2.3+ billion citations
- Robert Legvold
- Bill Tompson
- Archie Brown
- FOREIGN AFF
- John C. Campbell
- Seweryn Bialer
- Robert Bothwell
- John Lewis Gaddis
- Robert Latham
- Deborah Welch Larson
- Robert I. Rotberg
- Theodore K. Rabb
- Fred Halliday
- AM POLIT SCI REV
- Wolfram F. Handrieder
- Hans J. Morgenthau
- DAEDALUS-US
- John F. Naylor
- Sean Greenwood
- Recruit researchers
- Join for free
- Login Email Tip: Most researchers use their institutional email address as their ResearchGate login Password Forgot password? Keep me logged in Log in or Continue with Google Welcome back! Please log in. Email · Hint Tip: Most researchers use their institutional email address as their ResearchGate login Password Forgot password? Keep me logged in Log in or Continue with Google No account? Sign up
This website uses cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website. Without cookies your experience may not be seamless.

- Journal of Cold War Studies
Explaining the End of the Cold War: A New Historical Consensus?
- Jeremi Suri
- The MIT Press
- Volume 4, Number 4, Fall 2002
- View Citation
Additional Information
Despite the many books and articles written about the end of the Cold War, scholars have not produced a truly international history of this seminal event. This article shows how some of the most important monographs on the end of the Cold War can be synthesized to yield a preliminary account. In particular, the article outlines an interpretation that connects the immediate crisis of the early 1980s, long-term ideological and institutional trends, and transformational choices made from 1985 to 1991. No single decision or variable brought the Cold War to an end. Personalities, trends, and institutions interacted to create an outcome that few predicted.
Project MUSE Mission
Project MUSE promotes the creation and dissemination of essential humanities and social science resources through collaboration with libraries, publishers, and scholars worldwide. Forged from a partnership between a university press and a library, Project MUSE is a trusted part of the academic and scholarly community it serves.

2715 North Charles Street Baltimore, Maryland, USA 21218
+1 (410) 516-6989 [email protected]
©2024 Project MUSE. Produced by Johns Hopkins University Press in collaboration with The Sheridan Libraries.
Now and Always, The Trusted Content Your Research Requires

Built on the Johns Hopkins University Campus
- DOI: 10.1162/15203970260209518
- Corpus ID: 57567541
Explaining the End of the Cold War: A New Historical Consensus?
- Published in Journal of Cold War Studies 1 September 2002
- History, Political Science
38 Citations
Norms, heresthetics, and the end of the cold war, continuing debate and new approaches in cold war history, the end of the cold war: a battle or bridging ground between rationalist and ideational approaches in international relations.
- Highly Influenced
Another Transatlantic Split? American and European Narratives and the End of the Cold War
The war scare that wasn't: able archer 83 and the myths of the second cold war, still out in the cold russia's place in a globalizing world, human rights activism and the end of the cold war: a transnational history of the helsinki network, between political rhetoric and realpolitik calculations: western diplomacy and the baltic independence struggle in the cold war endgame, a theory of nuclear disarmament: cases, analogies, and the role of the non-proliferation regime, the promise and failure of ‘developed socialism’: the soviet ‘thaw’ and the crucible of the prague spring, 1964–1972, 123 references, the united states and the end of the cold war: implications, reconsiderations, provocations, ideology and the cold war, we now know: rethinking cold war history, witnesses to the end of the cold war, realism, ideology, and the end of the cold war: a reply to william wohlforth, the long peace, the end of the cold war, and the failure of realism, world politics, power, globalization, and the end of the cold war: reevaluating a landmark case for ideas, the great transition: american-soviet relations and the end of the cold war, related papers.
Showing 1 through 3 of 0 Related Papers
- History Classics
- Your Profile
- Find History on Facebook (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on Twitter (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on YouTube (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on Instagram (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on TikTok (Opens in a new window)
- This Day In History
- History Podcasts
- History Vault
Cold War History
By: History.com Editors
Updated: June 26, 2023 | Original: October 27, 2009

The Cold War was a period of geopolitical tension marked by competition and confrontation between communist nations led by the Soviet Union and Western democracies including the United States. During World War II , the United States and the Soviets fought together as allies against Nazi Germany . However, U.S./Soviet relations were never truly friendly: Americans had long been wary of Soviet communism and Russian leader Joseph Stalin ’s tyrannical rule. The Soviets resented Americans’ refusal to give them a leading role in the international community, as well as America’s delayed entry into World War II, in which millions of Russians died.
These grievances ripened into an overwhelming sense of mutual distrust and enmity that never developed into open warfare (thus the term “cold war”). Soviet expansionism into Eastern Europe fueled many Americans’ fears of a Russian plan to control the world. Meanwhile, the USSR came to resent what they perceived as U.S. officials’ bellicose rhetoric, arms buildup and strident approach to international relations. In such a hostile atmosphere, no single party was entirely to blame for the Cold War; in fact, some historians believe it was inevitable.

Containment
By the time World War II ended, most American officials agreed that the best defense against the Soviet threat was a strategy called “containment.” In his famous “Long Telegram,” the diplomat George Kennan (1904-2005) explained the policy: The Soviet Union, he wrote, was “a political force committed fanatically to the belief that with the U.S. there can be no permanent modus vivendi [agreement between parties that disagree].” As a result, America’s only choice was the “long-term, patient but firm and vigilant containment of Russian expansive tendencies.”
“It must be the policy of the United States,” he declared before Congress in 1947, “to support free peoples who are resisting attempted subjugation…by outside pressures.” This way of thinking would shape American foreign policy for the next four decades.
Did you know? The term 'cold war' first appeared in a 1945 essay by the English writer George Orwell called 'You and the Atomic Bomb.'
The Cold War: The Atomic Age
The containment strategy also provided the rationale for an unprecedented arms buildup in the United States. In 1950, a National Security Council Report known as NSC–68 had echoed Truman’s recommendation that the country use military force to contain communist expansionism anywhere it seemed to be occurring. To that end, the report called for a four-fold increase in defense spending.
In particular, American officials encouraged the development of atomic weapons like the ones that had ended World War II. Thus began a deadly “ arms race .” In 1949, the Soviets tested an atom bomb of their own. In response, President Truman announced that the United States would build an even more destructive atomic weapon: the hydrogen bomb, or “superbomb.” Stalin followed suit.
As a result, the stakes of the Cold War were perilously high. The first H-bomb test, in the Eniwetok atoll in the Marshall Islands, showed just how fearsome the nuclear age could be. It created a 25-square-mile fireball that vaporized an island, blew a huge hole in the ocean floor and had the power to destroy half of Manhattan. Subsequent American and Soviet tests spewed radioactive waste into the atmosphere.
The ever-present threat of nuclear annihilation had a great impact on American domestic life as well. People built bomb shelters in their backyards. They practiced attack drills in schools and other public places. The 1950s and 1960s saw an epidemic of popular films that horrified moviegoers with depictions of nuclear devastation and mutant creatures. In these and other ways, the Cold War was a constant presence in Americans’ everyday lives.

HISTORY Vault: Nuclear Terror
Now more than ever, terrorist groups are obtaining nuclear weapons. With increasing cases of theft and re-sale at dozens of Russian sites, it's becoming more and more likely for terrorists to succeed.
The Cold War and the Space Race
Space exploration served as another dramatic arena for Cold War competition. On October 4, 1957, a Soviet R-7 intercontinental ballistic missile launched Sputnik (Russian for “traveling companion”), the world’s first artificial satellite and the first man-made object to be placed into the Earth’s orbit. Sputnik’s launch came as a surprise, and not a pleasant one, to most Americans.
In the United States, space was seen as the next frontier, a logical extension of the grand American tradition of exploration, and it was crucial not to lose too much ground to the Soviets. In addition, this demonstration of the overwhelming power of the R-7 missile–seemingly capable of delivering a nuclear warhead into U.S. air space–made gathering intelligence about Soviet military activities particularly urgent.
In 1958, the U.S. launched its own satellite, Explorer I, designed by the U.S. Army under the direction of rocket scientist Wernher von Braun, and what came to be known as the Space Race was underway. That same year, President Dwight Eisenhower signed a public order creating the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), a federal agency dedicated to space exploration, as well as several programs seeking to exploit the military potential of space. Still, the Soviets were one step ahead, launching the first man into space in April 1961.
That May, after Alan Shepard become the first American man in space, President John F. Kennedy (1917-1963) made the bold public claim that the U.S. would land a man on the moon by the end of the decade. His prediction came true on July 20, 1969, when Neil Armstrong of NASA’s Apollo 11 mission , became the first man to set foot on the moon, effectively winning the Space Race for the Americans.
U.S. astronauts came to be seen as the ultimate American heroes. Soviets, in turn, were pictured as the ultimate villains, with their massive, relentless efforts to surpass America and prove the power of the communist system.
The Cold War and the Red Scare
Meanwhile, beginning in 1947, the House Un-American Activities Committee ( HUAC ) brought the Cold War home in another way. The committee began a series of hearings designed to show that communist subversion in the United States was alive and well.
In Hollywood , HUAC forced hundreds of people who worked in the movie industry to renounce left-wing political beliefs and testify against one another. More than 500 people lost their jobs. Many of these “blacklisted” writers, directors, actors and others were unable to work again for more than a decade. HUAC also accused State Department workers of engaging in subversive activities. Soon, other anticommunist politicians, most notably Senator Joseph McCarthy (1908-1957), expanded this probe to include anyone who worked in the federal government.
Thousands of federal employees were investigated, fired and even prosecuted. As this anticommunist hysteria spread throughout the 1950s, liberal college professors lost their jobs, people were asked to testify against colleagues and “loyalty oaths” became commonplace.
The Cold War Abroad
The fight against subversion at home mirrored a growing concern with the Soviet threat abroad. In June 1950, the first military action of the Cold War began when the Soviet-backed North Korean People’s Army invaded its pro-Western neighbor to the south. Many American officials feared this was the first step in a communist campaign to take over the world and deemed that nonintervention was not an option. Truman sent the American military into Korea, but the Korean War dragged to a stalemate and ended in 1953.
In 1955, the United States and other members of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) made West Germany a member of NATO and permitted it to remilitarize. The Soviets responded with the Warsaw Pact , a mutual defense organization between the Soviet Union, Albania, Poland, Romania, Hungary, East Germany, Czechoslovakia and Bulgaria that set up a unified military command under Marshal Ivan S. Konev of the Soviet Union.
Other international disputes followed. In the early 1960s, President Kennedy faced a number of troubling situations in his own hemisphere. The Bay of Pigs invasion in 1961 and the Cuban missile crisis the following year seemed to prove that the real communist threat now lay in the unstable, postcolonial “Third World.”
Nowhere was this more apparent than in Vietnam , where the collapse of the French colonial regime had led to a struggle between the American-backed nationalist Ngo Dinh Diem in the south and the communist nationalist Ho Chi Minh in the north. Since the 1950s, the United States had been committed to the survival of an anticommunist government in the region, and by the early 1960s it seemed clear to American leaders that if they were to successfully “contain” communist expansionism there, they would have to intervene more actively on Diem’s behalf. However, what was intended to be a brief military action spiraled into a 10-year conflict .
The End of the Cold War and Effects
Almost as soon as he took office, President Richard Nixon (1913-1994) began to implement a new approach to international relations. Instead of viewing the world as a hostile, “bi-polar” place, he suggested, why not use diplomacy instead of military action to create more poles? To that end, he encouraged the United Nations to recognize the communist Chinese government and, after a trip there in 1972, began to establish diplomatic relations with Beijing.
At the same time, he adopted a policy of “détente”—”relaxation”—toward the Soviet Union. In 1972, he and Soviet premier Leonid Brezhnev (1906-1982) signed the Strategic Arms Limitation Treaty (SALT I), which prohibited the manufacture of nuclear missiles by both sides and took a step toward reducing the decades-old threat of nuclear war.
Despite Nixon’s efforts, the Cold War heated up again under President Ronald Reagan (1911-2004). Like many leaders of his generation, Reagan believed that the spread of communism anywhere threatened freedom everywhere. As a result, he worked to provide financial and military aid to anticommunist governments and insurgencies around the world. This policy, particularly as it was applied in the developing world in places like Grenada and El Salvador, was known as the Reagan Doctrine .
Even as Reagan fought communism in Central America, however, the Soviet Union was disintegrating. In response to severe economic problems and growing political ferment in the USSR, Premier Mikhail Gorbachev (1931-2022) took office in 1985 and introduced two policies that redefined Russia’s relationship to the rest of the world: “glasnost,” or political openness, and “ perestroika ,” or economic reform.
Soviet influence in Eastern Europe waned. In 1989, every other communist state in the region replaced its government with a noncommunist one. In November of that year, the Berlin Wall –the most visible symbol of the decades-long Cold War–was finally destroyed, just over two years after Reagan had challenged the Soviet premier in a speech at Brandenburg Gate in Berlin: “Mr. Gorbachev, tear down this wall.” By 1991, the Soviet Union itself had fallen apart. The Cold War was over.

‘Blood in the Water’: The Cold War Olympic Showdown Between Hungary and the USSR
Just weeks before the match, Soviet tanks and troops brutally crushed the short‑lived Hungarian Revolution.
How the Cold War Space Race Led to US Students Doing Tons of Homework
In the first half of the 20th century, U.S. educators shunned homework. The Soviet Union’s launch of Sputnik 1 changed that.
Why the Berlin Airlift Was the First Major Battle of the Cold War
American and British pilots ferried some 2.3 million tons of supplies into West Berlin on a total of 277,500 flights, in what would be the largest air relief operation in history.

Sign up for Inside History
Get HISTORY’s most fascinating stories delivered to your inbox three times a week.
By submitting your information, you agree to receive emails from HISTORY and A+E Networks. You can opt out at any time. You must be 16 years or older and a resident of the United States.
More details : Privacy Notice | Terms of Use | Contact Us
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

The end of the Cold War

Related Papers
Abraham Nyuon
Jurnal Hubungan Internasional, 2015 - journal.umy.ac.id
Ahmad Fuad Fanani
Abstrak Tulisan ini akan membahas berakhirnya Perang Dingin dan factor kritis yang mempengaruhi keberakhiran tersebut. Telah dikemukakan bahwa Perang Dingain merupakan konflik ideologi antara Uni Soviet dan Amerika Serikat. Namun, konflik antara negara adi kuasa telah memicu konfrontasi militer dan pendekatan keamanan di dunia setelah berakirnya Perang Dunia Kedua. Akibatnya, banyak Negara, terutama negara dunia ketiga menjadi korban persaingan ideologi antara Amerika Serikat dan Uni Soviet. Kata kunci: pendekatan antar-sistemik, konflik ideologi, runtuhnya komunisme, kebijakan luar negeri Abstract This essay will discuss the end of the Cold War and the critical factors which influenced its ending. It has been suggested that the Cold War actually was the ideological conflict between the Soviet Union and the United States. However, the conflict between the superpowers has triggered the military confrontation and security approach in the world after the end of the Second World War. As a result, many countries, especially the Third World countries became victims of the ideological rivalry between the United States and the Soviet Union.
COLD WAR. GEOPOLITICS
Patrick Kyanda
Background to the Study The Cold War was essentially a period of time that was characterized by political, military and economic tensions between the major powers of the Eastern Bloc and the Western Bloc following the end of World War II. The Eastern powers were the Soviet Union and other powers in the Warsaw Pact. The Western Bloc, on the other hand, consisted of the United States of America (US) and its NATO allies (Fousek, 2000). It is not clearly known when the Cold War officially started; and different dates have been given. However, the most commonly cited date for the commencement of the Cold War is 1947. The War ended in 1991. This happened following the disintegration of the Soviet Union. The Cold War was simply a period of intense political and military tensions between the world’s major powers; but did not involve any direct military confrontations. Instead, the confrontations often took place in the form of proxy wars fought in other countries and places. The Vietnam War, the Korean War, and the first Afghanistan War are notable proxy wars between these two sides. The Eastern Bloc and the Western Bloc supported different sides in these wars; and this was the closest that they came to confronting each other (Gaddis, 1989). The Cold War, therefore, can be said to have been a supremacy and hegemonic battle to determine the greatest power in the world after the end of World War II and the devastating defeat of Japan and East Germany (Gaddis, 1997). Although the US and the Soviet Union had been allies against Nazi Germany during World War II, they were split by the Cold War. This split would prove to be quite disastrous for both sides both economically and politically. The major differences were that the Soviet Union pursued a Marxist-Leninist political ideology while the US and its allies pursued a capitalist ideology (Fousek, 2000). Although there was no full-scale armed combat between the two superpowers, they nonetheless armed themselves heavily in anticipation for a possible real war. With both sides owning nuclear and other lethal weapons, there was an expectation that a worldwide nuclear war might erupt (Grenville, 2005; Nalebuff, 1988). However, it was largely because of their possession of nuclear weapons that each side was able to deter the other. Both the US and the Soviet Union were not willing to initiate a direct nuclear confrontation for fear that the nuclear weapons held by the other would be used. The state of tension between two continued until 1991 when the Soviet Union disintegrated (Freedman, 2004).
Carmen Ioana
Diplomatic History
Robert Jervis
Rinashree Khound
Paolo Arnoldi
Vladislav B . Sotirović
The official end of the Cold War era in 1989 brought during the first coming years a kind of international optimism that the idea of the " end of history " really can be realized as it was a belief in no reason for the geopolitical struggles between the most powerful states. The New World Order, spoken out firstly by M. Gorbachev in his address to the UN on December 7th, 1988 was originally seen as the order of equal partnership in the world politics reflecting " radically different international circumstances after the Cold War ". 1 Unfortunately, the Cold War era finished without the " end of history " as the US continues the same policy from the time of the Cold War against Moscow – now not against the USSR but against its successor Russia. Therefore, for the Pentagon, the Cold War era in fact never ended as the fundamental political task to eliminate Russia from the world politics still is not accomplished. Regardless the fact that in 1989 Communism collapsed in the East Europe, followed by the end of the USSR in 1991, that brought a real possibility for creation of a new international system and global security 2 , the eastward enlargement of the NATO from March 1999 (the Fourth enlargement) onward is a clear proof of the continuation of the US Cold War time policy toward Moscow which actually creates uncertainty about the future of the global security. After the end of the USSR and the Cold War, there were many Western public workers and academicians who questioned firstly why the NATO has to exist at all and secondly why this officially defensive military alliance is enlarging its membership when the more comprehensive Conference on Security and Cooperation in Europe (the CSCE, today the OSCE) could provide the necessary framework for security cooperation in Europe including and Russia. 3 However, the NATO was not dissolved, but quite contrary adopted the same policy of the further (eastward) enlargement likewise the EU. The Kosovo crisis in 1998−1999 became a formal excuse for the enlargement of both these US client organizations for the " better security of Europe ". The EU Commission President, Romano Prodi, in his speech before the EU Parliament on October 13th, 1999 was quite clear on this matter. 4 However, if we know that the Kosovo crisis followed by the NATO military intervention (aggression) against Serbia and Montenegro was fully fuelled exactly by the US administration, it is not far from the truth that the Kosovo crisis was provoked and maintained by Washington, among other purposes, for the sake to give a formal excuse for the further eastward enlargement of both the EU and the NATO. However, can we speak at all about the end of the Cold War in 1989/1990 taking into account probably the focal counterargument: the NATO existence and even its further enlargement? As a matter of fact, the NATO is the largest and longest-surviving military alliance in contemporary history (est. 1949, i.e., six years before the Warsaw Pact came into existence). No doubts today that the NATO was established and still is operating as a fundamental instrument of the US policy of global imperialistic unilateralism that is, however, primarily directed against Russia. The deployment of the US missiles in West Europe in the 1980s, regardless on achieved détente in the 1970s in the US-USSR relations, became a clear indicator of a real nature of Pentagon's geopolitical game with the East in which the NATO is misused for the realization of the US foreign policy objectives under the pretext that the NATO is allegedly the dominant international organization in the field of West European security. Although the NATO was formally founded specifically to " protect and
Journal of Contemporary History, 55(3)
Dionysios Chourchoulis
Angelique LOUIS
Loading Preview
Sorry, preview is currently unavailable. You can download the paper by clicking the button above.
RELATED PAPERS
International Affairs (Royal Institute of International Affairs 1944-)
Phil Williams
WHY DÉTENTE FAILED?
CARLOS DOMINGOS
Interstate - Journal of International Affairs
Jittipat Poonkham
Bryan R Jackson A.A., BFA, M.Ed.
War, Peace and International Security
Jan Eichler
Jyotishman Bhagawati
Academia Letters
Diana Clark Gill
Gary K Busch
Bazil Cunningham 'student'
Sydney Mupeta
abidemi adedeji
Review of International Studies
Jason Ralph
Michelle Paranzino
Robert T Osborne
Seungjoon Kim
Felix Collado
Esen Ermiş Ertürk
Gar Alperovitz
cosmin mihail coatu
Hadrian Gorun
Robert J Bunker
Priscilla Roberts
IR Theory, Historical Analogy, and Major Power War
Hall Gardner
Position Paper
Levan Zosiashvili
Giles Scott-Smith
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024

IMAGES
COMMENTS
This research paper premises on the thesis statement that, 'the end of the cold war actually happened in 1989 and was an ideological conflict which was made possible by the appointment of Mikhail Gorbachev'. Communism in the Soviet Union. The rise of Mikhail Gorbachev as Soviet leader led marked the Cold War period of 1985-1991.
This essay focus on Gorbachev's reforms in the Soviet Union in 1989 and its impact on South Africa. ... The end of the Cold War and a new world order 1989 to the present ... pdf . Size: 1.38MB . Share this content. This essay focus on Gorbachev's reforms in the Soviet Union in 1989 and its impact on South Africa. Language: English.
eh so 164 Seee 2016 he so ssoo 59 Melvyn Leffler and Odd Arne Westad (eds) (2011) The Cambridge History of the Cold War (3 vols), Cambridge: Cambridge University Press - a mine of useful, succinct essays. Reynolds, David (2000) One World Divisible: a global history since 1945, London: Penguin - the end of the Cold War within the explosion of globalisation.
1. Three significant events heralded the end of the Cold War: the fall of the Berlin Wall, the reunification of Germany and the dissolution of the Soviet Union. 2. The fall of the Berlin Wall prompted the removal of borders between East and West Germany, while West German chancellor Helmut Kohl began pushing for the reunification of the two ...
The End of the Cold War, 1985-1991 ... "A British historian and author investigates the final years of the Cold War from both sides of the Iron Curtain, discussing the relationship between Reagan and Gorbachev whose unprecedented, historic cooperation worked against the odds to end the arms race."-- ... Pdf_module_version 0.0.15 Ppi 360 Rcs_key ...
The end of the Cold War. Soviet leader Mikhail Gorbachev introduced reform policies in the USSR - called perestroika (restructuring of the Soviet economy) and glasnost (openness and transparency). After more than four decades, in December 1989, Gorbachev and President George H.W. Bush Sr. declared the Cold War officially over.
the meaning of, the end of the Cold War (Cox, 2007: 128). Likewise, there is no consensus, among the scholars, o n the date of the end of the Cold War:
This article shows how some of the most important monographs on the end of the Cold War can be synthesized to yield a preliminary account. In particular, the article outlines an interpretation that connects the immediate crisis of the early 1980s, long-term ideological and institutional trends, and transformational choices made from 1985 to 1991.
The United States and the End of the Cold War: Implications, Reconsiderations, Provocations. J. Gaddis. Political Science, History. 1992. This collection of eleven essays provides one of the first explanations of how and why the United States forty year struggle with the former Soviet Union has finally ended.
The Post-Cold War Era:: A View from the South Download; XML; The United Nations in a Post-Cold War Order Download; XML; Challenge and Opportunity in the Post-Cold War Era:: Building an International Environment Supportive of Democracy Download; XML; The Post-Cold War Era:: "Facts and Prospects" Download; XML
Konferenz über Sicherheit und Zusammenarbeit in Europa, Cold War, World politics -- 1985-1995, ... In The End of the Cold War, acclaimed Russian historian Robert Service examines precisely how that change came about. ... Pdf_module_version 0.0.7 Ppi 300 Rcs_key 24143 Republisher_date 20210131062735 ...
The abrupt collapse of the Cold War system caused a popular surge of enthusiasm among IR scholars regarding the reasons behind the USSRs downfall. One group of scholars argue that it was Reagans SDI that exhausted the Soviet Unions local remedies, ultimately bankrupting the Kremlin. Another group of scholars suggest that the Soviet Union had ...
the end of the Cold War, or the passing of a particular period of postwar history, but the end of history as such: that is, the end point of mankind's ideological evolution and the universalization of Western liberal democracy as the final form of human government. This is not to say that there will no longer be events
European integration and the end of the Cold War / Pierre-Henri Laurent -- The military aftermath of the Cold War / Ian Clark -- The United Nations / Alan James -- The end of the Cold War and the international system / R.J. Vincent -- A chronology of the Cold War / Erik Goldstein ... Pdf_module_version 0.0.18 Ppi 360 Rcs_key 24143 Republisher ...
Cold War historiography, discussing the underlying issues, sketching out the positions that have dominated the literature, and placing Leffler's argument in context. In the final sections of this essay, I compare Leffler's work with an approach grounded in domestic political economy and domestic conflict. I conclude with suggestions for future ...
What Was the Main Cause of the end of the Cold War? This essay is about the end of Cold War emphasizing the main factors which have contributed to the termination of the Cold War. It should be comprehend that the end Cold War was a multifarious event with back-and-forth factors involved over a decade. This essay will therefore focus on the main factors which have played a major in speeding up ...
The term 'cold war' first appeared in a 1945 essay by the English writer George Orwell called 'You and the Atomic Bomb.' The Cold War: The Atomic Age ... The End of the Cold War and Effects.
The Bibliography of New Cold War History (second enlarged edition) 2018 •. Tsotne Tchanturia, Aigul Kazhenova, Khatia Kardava. This bibliography attempts to present the publications on the history of the Cold War published after 1989, the beginning of the „archival revolution" in the former Soviet bloc countries. Download Free PDF.
the note on which individual authors greet its end varies greatly: as I read him, a perhaps excessive judiciousness on the part of Melvyn Leffler as opposed to ... Piero Gleijeses's essay, "Cuba and the Cold War, 1959-1980," begins with a surprising claim, whose significance the rest of the essay demonstrates in detail. ...
West of the Wall, Berliners reveled in the growing prosperity of a new, democratic Germany. East of it they labored under the apparatus of a new dictatorship, still overshadowed by the ruins. of the old. This dichotomy defined life in Berlin. The longer the Cold War lasted, the more.
Topics include among others the origins of the Cold War, cultural competition, technology and science, the division of Germany, the space race, spies, tourism, sport, the power of media, social protest, counter-cultures, and the end of the Cold War. There are no prerequisites for this class; familiarity with the broader outlines of postwar ...
View PDF. The end of the Cold War The Cold War had seen more than four decades of tension between the two superpowers, the USA and the USSR. There had been a number of crises, and a whole generation had grown up with the fear of nuclear war. However, by the early 1990s the Cold War had officially ended.