This browser is no longer supported.
Upgrade to Microsoft Edge to take advantage of the latest features, security updates, and technical support.

Azure Policy assignment structure
- 9 contributors
Policy assignments are used by Azure Policy to define which resources are assigned which policies or initiatives. The policy assignment can determine the values of parameters for that group of resources at assignment time, making it possible to reuse policy definitions that address the same resource properties with different needs for compliance.
For more information on Azure Policy scope, see Understand scope in Azure Policy .
You use JavaScript Object Notation (JSON) to create a policy assignment. The policy assignment contains elements for:
- display name
- description
- resource selectors
- enforcement mode
- excluded scopes
- policy definition
- non-compliance messages
For example, the following JSON shows a policy assignment in DoNotEnforce mode with dynamic parameters:
All Azure Policy samples are at Azure Policy samples .
Display name and description
You use displayName and description to identify the policy assignment and provide context for its use with the specific set of resources. displayName has a maximum length of 128 characters and description a maximum length of 512 characters.
The optional metadata property stores information about the policy assignment. Customers can define any properties and values useful to their organization in metadata . However, there are some common properties used by Azure Policy. Each metadata property has a limit of 1,024 characters.
Common metadata properties
assignedBy (string): The friendly name of the security principal that created the assignment.
createdBy (string): The GUID of the security principal that created the assignment.
createdOn (string): The Universal ISO 8601 DateTime format of the assignment creation time.
parameterScopes (object): A collection of key-value pairs where the key matches a strongType configured parameter name and the value defines the resource scope used in Portal to provide the list of available resources by matching strongType . Portal sets this value if the scope is different than the assignment scope. If set, an edit of the policy assignment in Portal automatically sets the scope for the parameter to this value. However, the scope isn't locked to the value and it can be changed to another scope.
The following example of parameterScopes is for a strongType parameter named backupPolicyId that sets a scope for resource selection when the assignment is edited in the Portal.
updatedBy (string): The friendly name of the security principal that updated the assignment, if any.
updatedOn (string): The Universal ISO 8601 DateTime format of the assignment update time, if any.
evidenceStorages (object): The recommended default storage account that should be used to hold evidence for attestations to policy assignments with a manual effect. The displayName property is the name of the storage account. The evidenceStorageAccountID property is the resource ID of the storage account. The evidenceBlobContainer property is the blob container name in which you plan to store the evidence.
Resource selectors
The optional resourceSelectors property facilitates safe deployment practices (SDP) by enabling you to gradually roll out policy assignments based on factors like resource location, resource type, or whether a resource has a location. When resource selectors are used, Azure Policy will only evaluate resources that are applicable to the specifications made in the resource selectors. Resource selectors can also be used to narrow down the scope of exemptions in the same way.
In the following example scenario, the new policy assignment is evaluated only if the resource's location is either East US or West US .
When you're ready to expand the evaluation scope for your policy, you just have to modify the assignment. The following example shows our policy assignment with two more Azure regions added to the SDPRegions selector. Note, in this example, SDP means to Safe Deployment Practice :
Resource selectors have the following properties:
name : The name of the resource selector.
selectors : (Optional) The property used to determine which subset of resources applicable to the policy assignment should be evaluated for compliance.
kind : The property of a selector that describes which characteristic narrows down the set of evaluated resources. Each kind can only be used once in a single resource selector. Allowed values are:
resourceLocation : This property is used to select resources based on their type. Can't be used in the same resource selector as resourceWithoutLocation .
resourceType : This property is used to select resources based on their type.
resourceWithoutLocation : This property is used to select resources at the subscription level that don't have a location. Currently only supports subscriptionLevelResources . Can't be used in the same resource selector as resourceLocation .
in : The list of allowed values for the specified kind . Can't be used with notIn . Can contain up to 50 values.
notIn : The list of not-allowed values for the specified kind . Can't be used with in . Can contain up to 50 values.
A resource selector can contain multiple selectors . To be applicable to a resource selector, a resource must meet requirements specified by all its selectors. Further, up to 10 resource selectors can be specified in a single assignment. In-scope resources are evaluated when they satisfy any one of these resource selectors.
The optional overrides property allows you to change the effect of a policy definition without modifying the underlying policy definition or using a parameterized effect in the policy definition.
The most common use case for overrides is policy initiatives with a large number of associated policy definitions. In this situation, managing multiple policy effects can consume significant administrative effort, especially when the effect needs to be updated from time to time. Overrides can be used to simultaneously update the effects of multiple policy definitions within an initiative.
Let's take a look at an example. Imagine you have a policy initiative named CostManagement that includes a custom policy definition with policyDefinitionReferenceId corpVMSizePolicy and a single effect of audit . Suppose you want to assign the CostManagement initiative, but don't yet want to see compliance reported for this policy. This policy's 'audit' effect can be replaced by 'disabled' through an override on the initiative assignment, as shown in the following sample:
Overrides have the following properties:
kind : The property the assignment will override. The supported kind is policyEffect .
value : The new value that overrides the existing value. The supported values are effects .
selectors : (Optional) The property used to determine what scope of the policy assignment should take on the override.
kind : The property of a selector that describes what characteristic will narrow down the scope of the override. Allowed value for kind: policyEffect is:
- policyDefinitionReferenceId : This specifies which policy definitions within an initiative assignment should take on the effect override.
Note that one override can be used to replace the effect of many policies by specifying multiple values in the policyDefinitionReferenceId array. A single override can be used for up to 50 policyDefinitionReferenceIds, and a single policy assignment can contain up to 10 overrides, evaluated in the order in which they're specified. Before the assignment is created, the effect chosen in the override is validated against the policy rule and parameter allowed value list (in cases where the effect is parameterized ).
Enforcement mode
The enforcementMode property provides customers the ability to test the outcome of a policy on existing resources without initiating the policy effect or triggering entries in the Azure Activity log .
This scenario is commonly referred to as "What If" and aligns to safe deployment practices. enforcementMode is different from the Disabled effect, as that effect prevents resource evaluation from happening at all.
This property has the following values:
If enforcementMode isn't specified in a policy or initiative definition, the value Default is used. Remediation tasks can be started for deployIfNotExists policies, even when enforcementMode is set to DoNotEnforce .
Excluded scopes
The scope of the assignment includes all child resource containers and child resources. If a child resource container or child resource shouldn't have the definition applied, each can be excluded from evaluation by setting notScopes . This property is an array to enable excluding one or more resource containers or resources from evaluation. notScopes can be added or updated after creation of the initial assignment.
An excluded resource is different from an exempted resource. For more information, see Understand scope in Azure Policy .
Policy definition ID
This field must be the full path name of either a policy definition or an initiative definition. policyDefinitionId is a string and not an array. The latest content of the assigned policy definition or initiative is retrieved each time the policy assignment is evaluated. It's recommended that if multiple policies are often assigned together, to use an initiative instead.
Non-compliance messages
To set a custom message that describes why a resource is non-compliant with the policy or initiative definition, set nonComplianceMessages in the assignment definition. This node is an array of message entries. This custom message is in addition to the default error message for non-compliance and is optional.
Custom messages for non-compliance are only supported on definitions or initiatives with Resource Manager modes definitions.
If the assignment is for an initiative, different messages can be configured for each policy definition in the initiative. The messages use the policyDefinitionReferenceId value configured in the initiative definition. For details, see policy definitions properties .
This segment of the policy assignment provides the values for the parameters defined in the policy definition or initiative definition . This design makes it possible to reuse a policy or initiative definition with different resources, but check for different business values or outcomes.
In this example, the parameters previously defined in the policy definition are prefix and suffix . This particular policy assignment sets prefix to DeptA and suffix to -LC . The same policy definition is reusable with a different set of parameters for a different department, reducing the duplication and complexity of policy definitions while providing flexibility.
For policy assignments with effect set to deployIfNotExist or modify , it's required to have an identity property to do remediation on non-compliant resources. When using identity, the user must also specify a location for the assignment.
A single policy assignment can be associated with only one system- or user-assigned managed identity. However, that identity can be assigned more than one role if necessary.
- Learn about the policy definition structure .
- Understand how to programmatically create policies .
- Learn how to get compliance data .
- Learn how to remediate non-compliant resources .
- Review what a management group is with Organize your resources with Azure management groups .
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback .
Submit and view feedback for
Additional resources
Assignment in Insurance Policy | Meaning | Explanation | Types
Table of Contents
- 1 What is Assignment in an Insurance Policy?
- 2 Who can make an assignment?
- 3 What happens to the ownership of the policy upon Assignment?
- 4 Can assignment be changed or cancelled?
- 5 What happens if the assignment dies?
- 6 What is the procedure to make an assignment?
- 7 Is it necessary to Inform the insurer about assignment?
- 8 Can a policy be assigned to a minor person?
- 9 Who pays premium when a policy is assigned?
- 10.1 1. Conditional Assignment
- 10.2 2. Absolute Assignment
What is Assignment in an Insurance Policy?
Assignment means a complete transfer of the ownership of the policy to some other person. Usually assignment is done for the purpose of raising a loan from a bank or a financial institution .

Assignment is governed by Section 38 of the Insurance Act 1938 in India. Assignment can also be done in favour of a close relative when the policyholder wishes to give a gift to that relative. Such an assignment is done for “natural love and affection”. An example, a policyholder may assign his policy to his sister who is handicapped.
Who can make an assignment?
A policyholder who has policy on his own life can assign the policy to another person. However, a person to whom a policy has been assigned can reassign the policy to the policyholder or assign it to any other person. A nominee cannot make an assignment of the policy. Similarly, an assignee cannot make a nomination on the policy which is assigned to him.
What happens to the ownership of the policy upon Assignment?
When a policyholder assign a policy, he loses all control on the policy. It is no longer his property. It is now the assignee’s property whether the policyholder is alive or dead, the assignee alone will get the policy money from the insurance company.
If the assignee dies, then his (assignee’s) legal heirs will be entitled to the policy money.
Can assignment be changed or cancelled?
An assignment cannot be changed or cancelled. The assignee can of course, reassign the policy to the policyholder who assigned it to him. He can also assign the policy to any other person because it is now his property. We can think of a bank reassigning the policy to the policyholder when their loan is repaid.
What happens if the assignment dies?
If the assignee dies, the assignment does not get cancelled. The legal heirs of the assignee become entitled to the policy money. Assignment is a legal transfer of all the interests the policyholder has in the policy to the assignee.
What is the procedure to make an assignment?
Assignment can be made only after issue of the policy bond. The policyholder can either write out the wording on the policy bond (endorsement) or write it on a separate paper and get it stamped. (Stamp value is the same, as the stamp required for the policy — Twenty paise per one thousand sum assured). When assignment is made by an endorsement on the policy bond, there is no need for stamp because the policy is already stamped.
Is it necessary to Inform the insurer about assignment?
Yes, it is necessary to give information about assignment to the insurance company. The insurer will register the assignment in its records and from then on recognize the assignee as the owner of the policy. If someone has made more than one assignment, then the date of the notice will decide which assignment has priority. In the case of reassignment also, notice is necessary.
Can a policy be assigned to a minor person?
Assignment can be made in favour of a minor person. But it would be advisable to appoint a guardian to receive the policy money if it becomes due during the minority of the assignee.
Who pays premium when a policy is assigned?
When a policy is assigned normally, the assignee should pay the premium, because the policy is now his property. In practice, however, premium is paid by the assignor (policyholder) himself. When a bank gives a loan and takes the assignment of a policy a security, it will ask the assignor himself to pay the premium and keep it in force. In the case of an assignment as a gift, the assignor would like to pay the premium because he has gifted the policy.
Types of assignment
Assignment may take two forms:
- Conditional Assignment.
- Absolute Assignment.
1. Conditional Assignment
It would be useful where the policyholder desires the benefit of the policy to go to a near relative in the event of his earlier death. It is usually effected for consideration of natural love and affection. It generally provides for the right to revert the policyholder in the event of the assignee predeceasing the policyholder or the policyholder surviving to the date of maturity.
2. Absolute Assignment
This assignment is generally made for valuable consideration. It has the effect of passing the title in the policy absolutely to the assignee and the policyholder in no way retains any interest in the policy. The absolute assignee can deal with the policy in any manner he likes and may assign or transfer his interest to another person.
Related Posts

Can a policy be assigned during the minority of the life assured?
Can a general insurance policy(say fire/motor) under agreed bank clause should be assigned as the stock/motor is hypo/mortgaged to a bank

- Privacy Policy

- Peterborough

How to Write a Policy Assignment
What is a policy assignment, policy critique.
- Policy Brief/Briefing Note
Reading and Analyzing Policy
Writing policy assignments, research and writing process.
Understanding, evaluating, and writing policy documents are important competencies to develop as undergraduate students in a wide range of fields, spanning from Health Care to Environmental Science to Education. Policy is informed by strong research and accurate evidence, often compiled and presented by government and non-governmental organizations. Public policies include formal legislation, official plans, and regulations created by various levels of government. Each of these can act as guiding principles for governmental decision making and program delivery. Non-governmental and para-governmental organizations publish policy briefs, commission reports, and fact sheets to inform policy makers and recommend policy change.
Course instructors often ask students to analyze policy documents to better understand issues and policy alternatives, and students in many disciplines must write policy documents, including critiques and briefs or briefing notes. This guide offers steps to reading policy and keys for effective policy writing.
Types of Policy Assignments
In a policy critique, students are expected to read and critically analyze one or more policy documents that address a common issue. The goal of this assignment is to present an overall assessment of current or proposed policies and their efficacy or potential considering both scholarly theory and real-world, practical application with consideration of environmental, social, or economic contexts.
Proposed structure
- Issue: what is the policy in question?
- Background: where did it emerge? What problem does it try to address?
- Application: so far, based on evidence, how effective has it been?
- Limits: what are limits with the policy? How has it been adapted? What questions remain?
- Evaluation/potential: based on concepts and theories from course materials, what is the potential for this policy to address particular issue/problem?
Policy Brief (Briefing Note)
Policy briefs or briefing notes are documents written by governmental and non-governmental organizations to propose evidence-based policy solutions to a well-defined social, environmental, or economic issue. Briefs present findings from academic and grey literature to demonstrate the scope of an issue and to analyze its context and background. The brief is organized with clear headings and short sections, which are supported by figures or tables.
- Executive Summary: similar to an abstract, briefly explains the goal, findings, and recommendations. Although it is placed first in the document, it is written last.
- Issue Definition: identify and explain the key issue and its scope and significance.
- Policy Background: synthesize evidence to explain the context of the issue – its origins, key stakeholders, overlapping issues, and potential barriers – and any existing policy.
- Best Practices: describe relevant policies from other jurisdictions and introduce specific examples of policy and best practices that reinforce the argument your briefing note presents.
- Policy Options: synthesize your research to present a few policy options; for each option, describe the approach and present advantages, challenges, and potential barriers. Present one policy recommendation from these options.
- References: divide references into sections (e.g., academic sources, grey literature, policy documents etc.)
Each policy document is focused on a specific issue and establishes particular goals; when you read any policy document, you are working to understand and analyze the issue and how the policy addresses the issue. These messages are often presented in different ways. Policy briefs are, well, brief, but other policy documents or commissioned reports can be quite lengthy, so it is important to develop a reading strategy for each new document. Generally, it is best to follow this process: preview, plan, read and take notes, and assess within course context.
Because policy documents vary significantly in form and purpose, it is essential to preview the document prior to reading it: identify its author, its purpose, and its form. Take time to read the executive summary, which presents a short explanation of the issue and purpose of the document. Understand its authorship and the interests of the individual or organizational author.
Make a plan
Identify your goal in reading the document: do you wish to better understand the issue, to identify policy alternatives, to appreciate broader context, or to determine efficacy of policy? How will this document inform your understanding of the issue you are studying? What sections will be most useful or relevant?
Read and take notes
Your preview and plan can direct your reading and notetaking. Read closely to understand the policy or issue, its context, and the evidence used to support it. Identify stakeholders and their interests, the goals of the policy and how those goals are measurable and actionable. You may find it helpful to refer to the table of contents or index (or to use the ‘find’ tool in your browser) to seek out sections that contain relevant keywords in documents spanning more than 100 pages.
Assess policy within course context
Refer to theories, frameworks, and indices that you have discussed in class to assess a policy. Consider whether it follows a particular conceptual framework or achieves particular numerical targets. Compare it to other policies in similar contexts and analyze its parts to assess its adaptability to different contexts. Evaluate its fit to the specific issue and its relevance for various stakeholder needs or values.
Reading an Official Plan
An official plan is often a lengthy document that covers many topics and issues within a set of overarching goals for an organization, like a university, hospital, or municipality. Your aim should be to understand the overarching goals of the plan and its broader context, which are likely laid out in the executive summary and introductory sections. Then you may need to seek out references to a particular topic, issue, or stakeholder; the index, table of contents, or “find” tool can be helpful for this.
Reading a Policy Brief
The goal of a policy brief is to inform and persuade policy makers, so your aim should be to understand the issue the brief identifies and to analyze the policy it proposes. The structure and design of the policy brief will guide your reading. Take time to understand the context of the issue and the policy: who are the stakeholders, what are the goals, what is the process, and what are the barriers? Analyze the policy within the disciplinary concepts you’re learning in class; how does the policy fit particular frameworks, theories, or indices you’ve discussed? What is unique about this policy? How can this policy be adapted to different contexts? What is its potential to address the issue?
Successful policy assignments are focused, well-researched, analytical, organized, and concise. Therefore, it is important to take time to define the issue, understand the context of the issue, and seek out policy alternatives prior to identifying a recommended course of action.
- Focused Issue
- Using Research
- Demonstrating Analysis
- Organized, Concise, and Clear Writing
Focused issue
It is essential that you present a focused and clear issue, and that issue must be at the scale of policy action. For example, policy briefs can address ER wait times or agricultural pesticide use, but issues such as access to health care or the sustainability of food production are too complex for you to address in a short policy assignment. Often, course material and core concepts provide useful direction for you to narrow your issue.
In policy assignments, an issue is clearly defined and contextualized with evidence from scholarly and grey literature. It is important for you to explain how scholars, governments, or NGOs have discussed the issue, and numerical data or figures can demonstrate the scale of an issue or its projected trajectory. Provide details about the issue in its context: be specific about place, time, and stakeholders, and acknowledge any overlapping economic, environmental, or social issues.
Example: Effective issue definition 1
Age-friendly municipalities foster solidarity among generations within communities and reach out to older people at risk of isolation by making them feel socially included and involved (WHO, 2007). It is well documented that these trends are happening across Canada, and evidence suggests that local governments have a key role in enabling older people to live longer. It is unclear to what degree Aurora’s municipal government is prepared to support its expanding ageing population. It is essential to continue to examine new approaches to housing and transportation infrastructure within Aurora in order to improve public policy matters in regards to their ageing population.
- Issue is grounded by focused concept and evidence; writer demonstrates value of municipal policy to address the issue
- Writer precisely identifies the issue to be discussed in brief and the goals of the report
Example: Ineffective issue definition 1
In addition to the infrastructure issue in Peterborough, there is also an issue regarding how spread out the community is. The city is too big for residents to be able to walk the entire city. Amenities are also very spread out; it is unlikely that pedestrians would be able to access the required amenities within walking distance from their house. Ultimately, the main issues surrounding the walkability in the City of Peterborough are the lack of infrastructure and maintenance, as well as the lack of available activities near to peoples’ residences.
- Not grounded in conceptual framework or theory; writer needs to explain why walkability is an issue that a municipality should address
- Lack of precision or evidence to support claims about the size of the city or accessibility to amenities
Using research
Policy is informed by evidence from scholarly literature, government data, and research by various stakeholder organizations. Effective policy assignments synthesize evidence from academic and grey literature to create an accurate account of the issue and policy options. Common forms of evidence in policy writing include numerical and financial data, figures such as graphs and maps, excerpts from existing policies, recommendations from NGOs, and conceptual frameworks.
In policy writing, your goal is to present research both accurately and accessibly, as decision-makers in government and business may not be familiar with terminology or concepts presented by scholars. Make efforts to paraphrase the evidence you use and be sure to include citations in the form requested by your professor (footnotes or author-date systems are common).
One of the key factors in Municipal Cultural Planning is increasing cross-sectoral strategies by building new partnerships “…between the municipality and its community and business partners” (Municipal Cultural Plan, toolkit, 2011, p.21) for long term sustainability. Therefore, municipal cultural planning “…does not look at policy sectorally” (Gollmitzer, 2008, p.18), but instead strengthens and integrates “…cultural resources across all facets of government planning and decision making” (Municipal Cultural Plan Toolkit, 2011, p.21). Building new networks are supported by leveraging the sense of place within a community. Adopting a place-based planning approach allows “…government, community organizations and citizens to explore, measure and asses the values, resources and assets of the community” (Huhtala, 2016, p.66), in order to leverage them for economic prosperity.
- Writer synthesizes academic and grey literature to demonstrate how concepts are applied in policy.
- Writer also demonstrates analysis of evidence and its relevance to the brief’s focused issue.
- Use of direct quotation can feature the language of a policy if the writer wishes to analyze discourse; however, this excerpt relies too heavily on direct quotation, and it would be stronger if this evidence was paraphrased.
Demonstrating analysis
The quality of your policy assignment is closely tied to your analysis of the issue and the policy options you present. It is important to evaluate policy options as you research and to critically analyze how those options address the issue within its particular context. Take time to examine specific factors and parties involved in an issue and consider how these factors may facilitate or challenge each policy option; furthermore, you should also assess the advantages and disadvantages of each policy option and its impacts on these factors or parties.
You may find it valuable to consider theories, concepts, or frameworks from your course to develop your argument and to establish coherence throughout your assignment. If you assess all policy options through the same critical lens or theory, then your message will be clear and consistent throughout your document.
Integrating senior housing into the fabric of the inner core communities could make housing developments viable and situate seniors in settings where they can access these services by foot or nearby transit (Fang, 2013). This concept can allow seniors, who may be considering downsizing, to remain within their community where they can keep active, live within easy access to medical and community services, and stay close to their support network that they have spent their lives establishing. However, the growing demand for these developments could put major pressure on the municipality. City officials would have to amend current zoning by-laws to allow commercial and residential uses to be a part of mixed-use development and appropriate provisions need to be provided to ensure compatibility and to minimize potential negative impacts.
- Writer presents both advantages and challenges of policy option within common concept of healthy aging communities.
- Writer also includes potential impacts and barriers of policy option, which demonstrates their consideration of the issue and its context.
Organized, concise, and clear writing
Policy writing should be well-organized and easy to follow. Use headings and subheadings to create structure and to support your reader. It is common to number sections and subsections to further clarify the order of your ideas. In addition, good paragraph structure also supports organization and clarity, so we encourage you to use specific topic sentences to introduce the main idea of a paragraph.
Well-written policy assignments employ a formal writing style and use third-person voice (e.g., they) rather than first-person (e.g., I, we) or second-person (e.g., you) voice. Further, they avoid jargon, but use specific and clear language. When you revise your draft, take time to consider each sentence and remove repetitive or redundant phrases and words.
Finally, it is important to pay attention to the details. Label any figures or tables in your document; make reference to these figures or tables in the text of your work (e.g., see Figure 1). Also be sure to follow assignment instructions for referencing evidence in your text (e.g., footnotes or author-date system) and in your list of sources, which is often categorized by type of source (e.g., academic, government, NGOs).
There are many ways to approach a policy assignment, but it is important to take time to research and analyze issues and policy options thoroughly prior to writing. Consider the following steps to complete your policy assignment:
- Read assignment instructions closely
- Preliminary research: review course materials, brainstorm, conduct environmental scan or site visit, consider current issues relevant to course concepts
- Define issue: consider questions and frameworks
- Research issue and context
- Research and evaluate policy alternatives in other places
- Analyze policy alternatives and consider fit for current issue and context; select policy options to present
- Outline sections: what evidence goes where? How does evidence work together?
- Write sections (leave Executive Summary until last)
- Revise for organization, analysis, and use of evidence. See Strategies for Revision and Proofreading.
- Edit for clarity, concision, and grammar
- Complete final proof of document
- These examples are not to be reproduced in whole or part. Use of the ideas or words in this example is an act of plagiarism, which is subject to academic integrity policy at Trent University and other academic institutions.
Assignment of insurance policies and claims | Practical Law

Assignment of insurance policies and claims
Practical law uk practice note w-031-6021 (approx. 19 pages).
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
- Life Insurance
- Definitions
What Is a Collateral Assignment of Life Insurance?
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Group1805-3b9f749674f0434184ef75020339bd35.jpg)
Charlene Rhinehart is a CPA , CFE, chair of an Illinois CPA Society committee, and has a degree in accounting and finance from DePaul University.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/CharleneRhinehartHeadshot-CharleneRhinehart-ca4b769506e94a92bc29e4acc6f0f9a5.jpg)
A collateral assignment of life insurance is a conditional assignment appointing a lender as an assignee of a policy. Essentially, the lender has a claim to some or all of the death benefit until the loan is repaid. The death benefit is used as collateral for a loan.
The advantage to using a collateral assignee over naming the lender as a beneficiary is that you can specify that the lender is only entitled to a certain amount, namely the amount of the outstanding loan. That would allow your beneficiaries still be entitled to any remaining death benefit.
Lenders commonly require that life insurance serve as collateral for a business loan to guarantee repayment if the borrower dies or defaults. They may even require you to get a life insurance policy to be approved for a business loan.
Key Takeaways
- The borrower of a business loan using life insurance as collateral must be the policy owner, who may or may not be the insured.
- The collateral assignment helps you avoid naming a lender as a beneficiary.
- The collateral assignment may be against all or part of the policy's value.
- If any amount of the death benefit remains after the lender is paid, it is distributed to beneficiaries.
- Once the loan is fully repaid, the life insurance policy is no longer used as collateral.
How a Collateral Assignment of Life Insurance Works
Collateral assignments make sure the lender gets paid only what they are due. The borrower must be the owner of the policy, but they do not have to be the insured person. And the policy must remain current for the life of the loan, with the policy owner continuing to pay all premiums . You can use either term or whole life insurance policy as collateral, but the death benefit must meet the lender's terms.
A permanent life insurance policy with a cash value allows the lender access to the cash value to use as loan payment if the borrower defaults. Many lenders don't accept term life insurance policies as collateral because they do not accumulate cash value.
Alternately, the policy owner's access to the cash value is restricted to protect the collateral. If the loan is repaid before the borrower's death, the assignment is removed, and the lender is no longer the beneficiary of the death benefit.
Insurance companies must be notified of the collateral assignment of a policy. However, other than their obligation to meet the terms of the contract, they are not involved in the agreement.
Example of Collateral Assignment of Life Insurance
For example, say you have a business plan for a floral shop and need a $50,000 loan to get started. When you apply for the loan, the bank says you must have collateral in the form of a life insurance policy to back it up. You have a whole life insurance policy with a cash value of $65,000 and a death benefit of $300,000, which the bank accepts as collateral.
So, you then designate the bank as the policy's assignee until you repay the $50,000 loan. That way, the bank can ensure it will be repaid the funds it lent you, even if you died. In this case, because the cash value and death benefit is more than what you owe the lender, your beneficiaries would still inherit money.
Alternatives to Collateral Assignment of Life Insurance
Using a collateral assignment to secure a business loan can help you access the funds you need to start or grow your business. However, you would be at risk of losing your life insurance policy if you defaulted on the loan, meaning your beneficiaries may not receive the money you'd planned for them to inherit.
Consult with a financial advisor to discuss whether a collateral assignment or one of these alternatives may be most appropriate for your financial situation.
Life insurance loan (policy loan) : If you already have a life insurance policy with a cash value, you can likely borrow against it. Policy loans are not taxed and have less stringent requirements such as no credit or income checks. However, this option would not work if you do not already have a permanent life insurance policy because the cash value component takes time to build.
Surrendering your policy : You can also surrender your policy to access any cash value you've built up. However, your beneficiaries would no longer receive a death benefit.
Other loan types : Finally, you can apply for other loans, such as a personal loan, that do not require life insurance as collateral. You could use loans that rely on other types of collateral, such as a home equity loan that uses your home equity.
What Are the Benefits of Collateral Assignment of Life Insurance?
A collateral assignment of a life insurance policy may be required if you need a business loan. Lenders typically require life insurance as collateral for business loans because they guarantee repayment if the borrower dies. A policy with cash value can guarantee repayment if the borrower defaults.
What Kind of Life Insurance Can Be Used for Collateral?
You can typically use any type of life insurance policy as collateral for a business loan, depending on the lender's requirements. A permanent life insurance policy with a cash value allows the lender a source of funds to use if the borrower defaults. Some lenders may not accept term life insurance policies, which have no cash value. The lender will typically require the death benefit be a certain amount, depending on your loan size.
Is Collateral Assignment of Life Insurance Irrevocable?
A collateral assignment of life insurance is irrevocable. So, the policyholder may not use the cash value of a life insurance policy dedicated toward collateral for a loan until that loan has been repaid.
What is the Difference Between an Assignment and a Collateral Assignment?
With an absolute assignment , the entire ownership of the policy would be transferred to the assignee, or the lender. Then, the lender would be entitled to the full death benefit. With a collateral assignment, the lender is only entitled to the balance of the outstanding loan.
The Bottom Line
If you are applying for life insurance to secure your own business loan, remember you do not need to make the lender the beneficiary. Instead you can use a collateral assignment. Consult a financial advisor or insurance broker who can walk you through the process and explain its pros and cons as they apply to your situation.
Progressive. " Collateral Assignment of Life Insurance ."
Fidelity Life. " What Is a Collateral Assignment of a Life Insurance Policy? "
Kansas Legislative Research Department. " Collateral Assignment of Life Insurance Proceeds ."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/GettyImages-1465621717-5f131bf876c043898c13e6c471acf50f.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
Select Language

Find the right insurance for you
Switch to the Simpler Insurance
Hi There, We are working on our product and launching this soon.
Enter your Details
Submit your details and we will notify you once we launch our Product.
Hello, our Product is launching soon. Please share your details, and we will notify you once we are live.
- {{itemType}}
Thank you for showing interest.
Once we launch our product, we'll let you know.
What Is Assignment in Life Insurance Policy?

While purchasing a life insurance plan, you might encounter several unfamiliar terms, which can make this process even harder to follow. However, understanding these terms and their functions is essential to make an error-free decision while handling your policy.
Assignment is one such necessary process associated with life insurance, dealing with the transfer of ownership of your policy. It is often confused with a nomination, which refers to naming beneficiaries of your contract. Therefore, you must understand the aspects of assignment in a life insurance policy.
What Is Assignment and Assignee in Life Insurance Policy?
Assignment refers to the process of transferring your privileges as a policyholder to another person or entity such as the bank. Once the ownership is transferred, the former policyholder will have no further authority over it. You can assign your policy for various reasons, for instance to someone you love or to your bank in case you owe debt repayment.
Two other terms related to the assignment process are – assignor and assignee.
Assignor: An assignor is the one who is transferring their policy rights to someone else.
Assignee: An assignee is a person or an institution that receives the policy rights and now has complete control over it.
In many cases where people assign their policies to the bank, they remain the life insured, whereas the bank receives the claim benefit after their demise.
What Are the Types of Assignment in Life Insurance Policy?
Absolute assignment.
In an absolute assignment, you can transfer your life insurance policy ownership to another being without any terms and conditions. Here, the assignor can sign over the entire policy as a gift to their loved ones or if they owe an outstanding debt.
After the transfer procedure is complete, the assignee will be responsible for all policy-related decisions, including paying the outstanding premiums and designating nominees.
For Example,
Suppose you have purchased a ULIP plan to secure your family after you pass away. Now, within a few years, you are in need of urgent financing to support your child’s education.
So, instead of surrendering your policy, you can use it as collateral to seek help from someone. Now you have assigned your insurance plan to a friend (assignee) through an absolute assignment by which your friend can take over all the rights of your policy including paying future premiums.
Conditional Assignment
Condition assignment is a policy where you transfer the life insurance policy rights to an assignee under specific terms and conditions. Therefore, the transfer will only be valid if those conditions are met.
Furthermore, it can also be a temporary transfer, where the policy is transferred back to the assignor once they fulfil the predetermined conditions.
The transfer takes place through a form that mentions the reason and condition of the assignment along with an assigned percentage of the sum assured and who will pay the future premiums.
For Example:
Suppose you have assigned your life insurance policy under conditional assignment to a bank for which you secured a loan. If you repay the loan within the set time, the bank will transfer the policy rights back to you. However, if you fail to repay the EMIs, the bank can surrender your policy and get their money back.
An assignment is a legal process through which policy ownership transfers from an assignor to an assignee. It can be beneficial under multiple circumstances, especially in a financial emergency. Therefore, before you buy a life insurance plan, understand these features since they can help you in the future.
In addition, the assignment of a life insurance policy can also be used as a present to your loved ones. While nomination is where you directly assign beneficiaries to ensure that your loved ones are protected in your absence.
FAQs about Assignment in Life Insurance Policy:
Does the policy risk get transferred in the assignment process, what is an endorsement in an assignment, what are the liabilities and rights of the assignee, other important features of life insurance.
- This is an informative article provided on 'as is' basis for awareness purpose only and not intended as a professional advice. The content of the article is derived from various open sources across the Internet. Digit Life Insurance is not promoting or recommending any aspect in the article or its correctness. Please verify the information and your requirement before taking any decisions.
- All the figures reflected in the article are for illustrative purposes. The premium for Coverage that one buys depends on various factors including customer requirements, eligibility, age, demography, insurance provider, product, coverage amount, term and other factors
- Tax Benefits, if applicable depend on the Tax Regime opted by the individual and the applicable tax provision. Please consult your Tax consultant before making any decision.
- Digit Insurance
- ']" itemprop="itemListElement" itemscope itemtype="http://schema.org/ListItem"> Life Insurance
- ']" itemprop="itemListElement" itemscope itemtype="http://schema.org/ListItem"> Features
- ']" itemprop="itemListElement" itemscope itemtype="http://schema.org/ListItem"> Assignment in Life Insurance Policy
Last updated: 2024-03-28

Absolute Assignment of a Life Insurance Policy
Absolute Assignment means complete Transfer of Rights. The person who transfers the rights is called the Assignor and the person to whom the rights are being transferred is called the Assignee.

The process of transferring rights of a Life Insurance Policy is called Assignment. There are 2 types of Assignment.
- Absolute Assignment
- Conditional Assignment
Hence Absolute Assignment means completely transferring whole and sole rights of the policy from the Assignor to the Assignee without any further terms and conditions applicable.
The process of assignment is complete only when the original Policy Document has been endorsed or a fresh Policy Document has been issued in favour of the Assignee.
Let’s take an example:
Rahul owns a Life Insurance policy of value Rs 5 lakhs. He would like to gift it to his best friend Ajay.
Thus, in that case, he would like to perform Absolute Assignment of the policy in Ajay’s name such that the death or maturity proceeds are directly paid to him. Rahul’s family members or nominee does not have any right on the policy money.
After the assignment is executed, Ajay becomes the absolute owner of the policy. If he wishes, he may again transfer it to someone else for any other reason. This type of Assignment without any further clauses attached to it is called Absolute Assignment.

Example in real life of Absolute Assignment happens in case of an Insurance Policy being taken by the employer as a perquisite for the employee. Once the policy is purchased, it is transferred to the employee’s name under Absolute Assignment clause. Hence the employee becomes the owner of the policy, but the employer pays for it till the end. Thus, instead of paying the employee cash, they purchase an insurance policy in their name and add it to their Annual Income Package.

Deepak Yohannan is the Founder & CEO of MyInsuranceClub. He enjoys writing on Personal Finance and focusses on explaining the basic concepts of insurance in simple language.

- Practical Law
Assignment of insurance policies and claims
Practical law uk practice note w-031-6021 (approx. 19 pages).
- Construction and engineering
- Construction insurance
- Credit, terrorism and political risks
- Cyber insurance
- Directors and officers
- Disputes, investigations and enforcement
- Insurance in commercial transactions
- Insurance intermediaries
- Legal expenses
- Making and dealing with claims
- Reinsurance
- Security, risk management and business continuity
- Submit Article for Publication
Nomination and Assignment under Insurance Contracts
Published by siri k reddy on 30/01/2021 30/01/2021, introduction:.
The term assignment itself means you assign something to someone else. In term life insurance, the assignment of the policy describes the action of assigning legal rights as well as policy ownership to someone else. The person who assigns the policy is known as an Assignor and the person who has been assigned the policy is known as an Assignee.
Nomination under the insurance contract refers to nominate someone on your behalf in order to collect the benefit in your absence. A person who is trustworthy can be nominated upon the death of a person. The trustworthy person could be from the dead person’s family or close friends. Then that person is the nominee of the policy.
However in most of the cases, people choose their family member as the nominee of the policy but as per the insurance act of 1938, under section 39, the nomination of a particular person is not restricted to a family only. Any person who is considered as trustworthy and any person who will not misuse the policy are considered to be an ideal nominee of that particular policy.
Types of Assignment
There are two types of assignment of policies:
- Absolute assignment: under this particular type of assignment, the assignor is bound to transfer the ownership, title, legal interests and all the rights of the policy to the assignee. This type of transfer of the policy does not include the terms and conditions on the part of the assignee. The exact purpose of the absolute assignment is to repay the debts or to show affection to loved ones.
- Collateral assignment: collateral assignment refers to that particular assignment in which the policyholder assigns the policy on terms and conditions, and the assignee is restricted to avail the benefits of all the terms and conditions. The main purpose of the collateral assignment is to repay loans and liabilities.
Types of Nomination
There are three types of nominations, such as:
- Beneficiary nominee: in this particular nomination a particular person can be made beneficiary to the immediate family members like parents, children, and spouse. The beneficiary will be entitled to receive all the benefits of the policy legally only in case of unfavourable conditions.
- Minor nominee: since it is considered that a minor cannot deal with financial conditions, the guardian of that particular minor has to give the details of their selves only when the policyholder chooses his/her child as the nominee.
- Non-family nominee: a non-family member is that person who does not have blood relation with the policyholder such as close friends, a distant relative, a neighbour, etc. under section 39 of the insurance act of 1938; any trustworthy person can be a policy nominee.
Nomination and Assignment in Life Insurance Plans
As it is already known that insurance is a legal contract between the insurance company who is also called the insurer and the policyholder. An assignee is a person to whom the rights have been transverse to. An example of an absolute assignment is as follows: Mr Bharath owns a life insurance policy of 1 crore and he wants to gift this particular policy to his wife as ‘absolute assignment’ to her name. Once this absolute assignment is made to his wife’s name, she will be the owner of the policy. She also has the right to transfer this policy to someone else.
An example of a conditional assignment is as follows: Ms Supriya owns a term insurance policy of 900,000. She wants a home loan of the same amount. Hence her banker asked her to assign the term policy in their name in order to get the loan. If Supriya meets an untimely death the banker is entitled to enjoy their money. An assignment deed or deed of assignment [DOA] is that deed through which rights can be transferred from one person to another.

Sections and Policies
SECTION 38- ASSIGNMENT AND TRANSFER OF INSURANCE POLICIES
The provisions under section 38 of the Insurance Law Act, 2015. The provisions of this particular section are as follows:
- This policy allows itself to be transferred with or without consideration.
- An assignment has a high chance of being affected by an endorsement upon the policy or by a separate instrument to the insurer.
- The instruments should reflect the assignment and the reasons for the transfer.
- An authorized agent or the transferor should sign the assignment.
- The transferor of the assignment should not be operative against an insurer until prior notice is issued
- The authority has the right to specify the fees that is paid for the transfer
- The insurer is also expected to give a written acknowledgement of receipt of the notice. Such notice acts as evidence for the future.
- The notices shall be delivered only at one place where the policy is being served in order to avoid confusions. This arrangement is made as the insurer is involved in managing more than one business place.
- The insurer has the right to accept or deny acting upon any transfer or endorsement only if it is not bonafide or not in the public interest.
- Before denying the endorsement, the insurer should make a note of the reasons for the same.
SECTION 39- NOMINATION BY POLICYHOLDER
The provisions of this particular section are as follows:
- The policyholder can nominate a person to whom money secured by the policy shall be paid during the death.
- When in case of a minor, the policyholder can appoint any person to receive the money in the event of policyholder’s death during the minority of the nominee.
- Nomination can be made at any time before the maturity of the policy.
- The nomination can be incorporated or endorsed to the insurer.
- The provisions of section 39 are not applicable to any life insurance policy to which section 6 of the Married Women’s Property Act, 1874 applies.
- If the nominee dies before the policyholder, the money is payable to the legal representatives or the holder of succession certificate.
SECTION 45- Policy shall not be called in question on the ground of misstatement after three years
Provisions of this section are as follow:
- Any policy of life insurance shall not be called in question after the expiry of three years from the date of issuance of the policy, the date of commencement of risk, the date of revival, the date rider coming to the policy.
- Silence is not considered to be fraud unless it depends on the circumstances of the case.
- The insurer can call for age proof at any time only if he is entitled.
- No insurer can reject a life insurance policy on the grounds of fraud if the beneficiary can prove that the fraud was true to the best of his knowledge.
Difference between Nomination and Assignment
Assignment of policies- impact on existing nomination.
- According to section 39(4) of the insurance act, 938, the assignment of an insurance policy automatically cancels the nomination.
- Here are the few circumstances under which the assignment does not automatically cancel nomination :
When the policy loan is taken from the life insurer who issues the policy, the policy has to be assigned in favour of the life insurer. Under such circumstances, assignments in favour of the life insurer do not automatically cancel the nomination.
On the other hand, where the policy is assigned by a debtor to creditor acts as collateral security for the loan taken by the policyholder from the assignee.
The nomination and assignments have their own uses and benefits as a separate topic under the insurance contracts. I have gained in-depth knowledge of what exactly is nomination and assignment along with minute differences between them. The differences between them have helped me gain much more understanding of the topic. Nomination protects the interests of the insured and the insurer. Whereas the assignment strives to protect the interests of the assignee in availing all the benefits.
References:
- INSURANCE LAWS IN INDIA- VARDHAMAN MAHAVEER, pg. 32. 54.
- RAJIV JAIN: INSURANCE LAW AND PRACTICE, pg. 44
- https://m.economictimes.com/nomination-and-assignment/articleshow/3320189.cms
- https://accountlearning.com/difference-nomination-assignment/
- https://accountlearning.com/assignment-in-insurance-policy-meaning-explanation-types/
- https://life.futuregenerali.in/life-insurance-made-simple/life-insurance/change-nominee-in-term-insurance
Share this:
Leave a reply cancel reply.

Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Related Posts

Common Law Principles
Utmost good faith under english insurance law.
Importance of “utmost” good faith is not to be ignored as it gives the doctrine a pillar of necessity to be followed in insurance contracts.

Case Law Analysis
Tukeshwari devi vs royal sundaram alliance insurance company ltd & ors.
The deceased Shashi Kumar Mahato was killed in an accident by an unnamed Omni van which was driven by the negligent driving.

Insurance Law
Hospital management and medical insurance laws.
Health is a part of the State List with each state retaining sole jurisdiction over the formulation of policies in this regard.
To join our WhatsApp community
- 1800 102 2355
- Download the APP
- 1800 102 2355 [9:30AM-6:30PM]
- Branch Locator
- Customer Portal Login
- Advisor Portal Login

What is Assignment and Nomination in Life Insurance?
‘Assignment’ and ‘Nomination’ are two most common terms used in a life insurance policy document. Let us understand the importance of these two terms in-detail.
By Future Generali Updated On Oct 06, 2022

Your life insurance policy is a contract between you (insured) and the insurance company (insurer). The contract is filled with jargon. To the extent possible, we must understand all the terms mentioned in the policy bond (certificate). ‘Assignment’ and ‘Nomination’ are two most common terms used in the insurance world.
For instance, in the event that you plan to apply for a home loan, your home loan provider will surely use these terms. Hence, it is best to be sure and understand exactly what the terms mean before you make a decision to buy the policy.
What is assignment in life insurance?
A life insurance policy can be assigned when rights of one person are transferred to another. The rights to your insurance policy can be transferred to someone else for various reasons. The process is known as assignment.
An “assignor” (policyholder) is the person who assigns the insurance policy. An “assignee” is the person to whom the policy rights have been transferred, i.e. the person to whom the policy has been assigned.
In the event rights are transferred from an Assignor to an Assignee, the rights of the policyholder are canceled, and the Assignee becomes the owner of the insurance policy.
People often assign their life insurance policies to banks. A bank becomes the policy owner in this case, while the original policyholder continues to be the life assured whose death may be claimed by either the bank or the policy owner.
Types of Assignment
There are two ways to assign an insurance policy. They are as follows:
1. Absolute Assignment
During this process, the rights of the assignor (policyholder) will be completely transferred to the assignee (person to whom the policy rights have been transferred). It is not subject to any conditions.
As an example, Mr. Rajiv Tripathi owns a Rs 1 Crore life insurance policy. Mr. Tripathi wants to gift his wife this policy. Specifically, he wants to make “absolute assignment” of the policy in his wife's name, so that the death benefit (or maturity proceeds) can be paid directly to her. After the absolute assignment has been made, Mrs. Tripathi will own this policy, and she will be able to transfer it to someone else again.
2. Conditional Assignment
As part of this type of assignment, certain conditions must be met before the transfer of rights occurs from the Assignor to the Assignee. The Policy will only be transferred to the Assignee if all conditions are met.
For instance, a term insurance policy of Rs 50 Lakh is owned by Mr. Dinesh Pujari. Mr. Pujari is applying for a home loan of Rs 50 Lakh. For the loan, the banker asked him to assign the term policy in their name. To acquire a home loan, Mr. Pujari can assign the insurance policy to the home loan company. In the event of Mr. Pujari’s death (during the loan tenure), the bank can collect the death benefit and get their money back from the insurance company.
Mr. Pujari can get back his term insurance policy if he repays the entire amount of his home loan. As soon as the loan is repaid, the policy will be transferred to Mr. Pujari.
In the event that the insurer receives a death benefit that exceeds the outstanding loan balance, the bank will be paid from the difference between the death benefit and the loan and the balance will be paid directly to the nominee. In the above example, the remaining amount (if any) will be paid to Mr. Pujari’s beneficiaries (legal heirs/nominee).
Key Points to know Note About Assignment
In regards to the assignment, the following points should be noted:
- A policy assignment transfers/changes only the ownership, not the risk associated with it. The person assured thus becomes the insured.
- The assignment may lead to cancellation of the nomination in the policy only when it is done in favour of the insurance company due to a policy loan.
- Assignment for all insurance plans except for the pension plan and the Married Women's Property Act (MWP), can be done.
- A policy contract endorsement is required to effect the assignment.
What is nomination in life insurance?
Upon the death of the life assured, the nominee/ beneficiary (generally a close relative) receives the benefits. Policyholders appoint nominees to receive benefits. Under the Insurance Act, 1938, Section 39 governs the nomination process.
Types of Nominees
In a life insurance policy, the policyholder names someone who will receive the benefits in the event of the life assured's death. Here are a few types of nominees:
1. Beneficial Nominees
In accordance with the law, the beneficiary of the claimed benefits will be any immediate family member nominated by the policyholder (like a spouse, children, or parents). Beneficiary nominees are limited to immediate family members of the beneficiary.
2. Minor Nominees
It is common for individuals to name their children as beneficiaries of their life insurance policies. Minor nominees (under the age of 18) are not allowed to handle claim amounts. Hence, the policyholder needs to designate a custodian or appointee. Payments are made to the appointee until the minor reaches the age of 18.
3. Non-family Nominees
Nominees can include distant relatives or even friends as beneficiaries of a life insurance policy.
4. Changing Nominees
It is okay for policyholders to change their nominees as often as they wish, but the latest nominee should take priority over all previous ones.
Key Points to Note About Nomination
In regards to the nomination, the following points should be noted:
- In order to nominate, the policyholder and life assured must be the same.
- In the case of a different policyholder and life assured, the claim benefits will be paid to the policyholder.
- Nominations cannot be changed or modified.
- The policy can have more than one nominee.
- As part of successive nominations, if the life assured appoints person “A” as the first person to receive benefits. Now, in the event of the life assured’s death after person “A” dies, the claim benefits will be given to person “B”. The benefits will be available to Nominee “C” if Nominee “A” and Nominee “B” have passed away.
What is the difference between nomination and assignment?
Let's talk about the differences between assignment and nomination.
Nomination and Assignment serve different purposes. The nomination protects the interests of the insured as well as an insurer in offering claim benefits under the life insurance policy. On the other hand, assignment protects the interests of an assignee in availing the monetary benefits under the policy. The policyholder should be aware of both of them before buying life insurance.
Connect with our trusted financial advisors right away!
Fill in below details to get a call back
One of our associate will connect with you soon.
Latest Articles

Life Insurance 4 min What is Investment? A Complete guide to start your investment journey.
By Future Generali Dec 06, 2023

Life Insurance 5 min Endowment Policy: Returns, Benefits & Requirement
By Future Generali Sep 06, 2023

Life Insurance 4 min Understanding Sum Assured: Significance & Calculation
By Future Generali Jul 28, 2023
Couldn't find what you are looking for? TRY SEARCH
ARN No.: Comp-April-2022_534.

Absolute Assignment
What does absolute assignment mean.
Absolute assignment refers to a policyholder transferring his or her ownership of a policy to another party. That transfer means that all of the coverage within that policy will now go to the newly named party. The original owner of the policy does not have to state his or her reasons for doing so nor does he or she need to stipulate any conditions for the transfer.
Insuranceopedia Explains Absolute Assignment
There are a number of reasons why a policyholder transfers all of their rights to a policy to another person or entity. They might think of it as a gift to someone else. It could be the sole means of paying off a loan. Even if the insured has now given up their rights to all of the claims and privileges, they are still responsible for payments for the policy. The new owner might have been asked by the original owner to pay the insurer after the transfer is completed, but if the newly named party fails to do so, the negligence will not be blamed on that person but on the original policyholder.
Related Definitions
Managing general agent (mga), inland marine policy, multiple indemnity, policy reserve, position schedule bond, qualified pension plan, refund annuity, refund life income option, rental value insurance, related terms, transfer by endorsement, noninsurance transfer, risk transfer, insurable interest, non-insurable risk, direct billing, related articles, 5 types of crime insurance policies businesses should consider, choosing the right kind of mortgage, 10 things you need to know about health insurance in the united states, insurance self-service portal: the future of customer experience, blockchain’s impact on transforming the insurance landscape, what every college student should know about renters insurance, related reading, trending articles.
- Life Insurance
- Assignment Vs Nomination In Life Insurance Know The Difference
- Understanding Nomination and its Types
- Understanding Assignment and its Types
- Key Differences Between Nomination and Assignment

Buy Policy in just 2 mins
2 lakh + Happy Customers

Free Comparison
Customized Term Insurance Plan for you.
Get upto 10% Online Discount*

Select Your City
Popular Cities
Delhi Gurgaon Noida Bengaluru Chennai Ahmedabad Hyderabad Kolkata Mumbai
Select Your Annual Income Your life insurance cover limit will be calculated based on your income. You may be asked to provide income proof at the time of purchase.
15 Lacs+ P.A. 10-15 Lacs P.A. 7-10 Lacs P.A. 5-7 Lacs P.A. 3-5 Lacs P.A. Upto 3 Lacs P.A.
Enter Your Name
Mobile Number
By proceeding you are accepting our T&C and privacy policy
Confused? No Worries, We Are Here To Help!
Health offer, invest offer.

Assignment vs Nomination in Life Insurance
In life insurance plans, Nomination and Assignment are the two important terms that are frequently used. Acknowledging these terms helps the policyholder to extract the benefits available under the life insurance policy without making a hole in his/her pocket.
Policyholders should know the exact difference between the two before making any decision to purchase the policy. It is required that individuals should read terms and conditions carefully so that one doesn't make any mistake and use the policy in the right way.
What is the Nomination?
The nomination is a right given to the policyholder that authorizes him/her to appoint a person (usually a close family member) to receive the benefits in the event of the death of the life assured. The person who is appointed by the policyholder to receive the benefit is called a Nominee. The nomination is governed under Section 39 of the Insurance Act, 1938.
Types of Nominees
Under the life insurance policy , the policyholder nominates a person who is entitled to receive the benefits in case something happens to the life assured. Some of the different types of nominees given below:
Beneficial Nominees
As per the law, any immediate family member (like spouse, children or parents) nominated by the policyholder is entitled to receive the monetary benefits and will be the beneficial owner of the claim benefits. It is important to note that only immediate family members can be termed as Beneficial Nominees.
Minor Nominees
Many individuals appoint their children as beneficiaries of their life insurance policies. Minor nominees (who are less than 18 years of age) are not considered eligible to handle claim amounts. For this, the policyholder needs to assign an appointee or custodian. The claim amount is paid to the appointee until the minor turns 18.
Non-family Nominees
These types of nominees can be distant relatives or even friends as the beneficiary of the life insurance policy.
Changing Nominees
Policyholders can change their nominees as many times as they want, but the latest nominee should supersede all previous ones.
Life Insurance Companies
Compare and buy the most suitable Life Insurance Plan from the below-mentioned IRDAI-approved Life Insurance companies.
- Term Insurance
LIC Of India
Hdfc life insurance, icici prudential life insurance, sbi life insurance, max life insurance, tata aia life insurance, pnb metlife india insurance, bajaj allianz life insurance, aegon life insurance, kotak mahindra life insurance, canara hsbc life insurance, bharti axa life insurance, aviva life insurance, indiafirst life insurance, exide life insurance, edelweiss tokio life insurance, ageas federal life insurance, future generali life insurance, birla sun life insurance, reliance life insurance, pramerica life insurance limited, shri ram life insurance, sahara india life insurance.
Know More About Life Insurance Companies
LIC Term Insurance
Hdfc term insurance, icici term insurance, sbi life term insurance, max life term insurance, tata aia term insurance, pnb metlife term insurance, bajaj allianz term insurance, aegon life term insurance, kotak life term insurance, canara hsbc obc term insurance, bharti axa term insurance, aviva term insurance, indiafirst term insurance, exide life term insurance, edelweiss tokio term life insurance, ageas federal term insurance, future generali term insurance, birla sun life term insurance, reliance term insurance, pramerica term insurance.
Know More About Term Insurance Companies
Key Points to Know Regarding Nomination
- The nomination is possible only when the policyholder and life assured are the same. In case, the policyholder and life assured are different, the claim benefits will be availed by the policyholder only.
- The nominee cannot ask for changes/modifications to the policy.
- There can be more than one nominee in the policy.
- In the successive nomination, if the life assured appoints person A to be the first person to receive the claim benefits in case of assured's death and person A is no more, then the claim benefits will be passed to person B. However, if Nominee A and Nominee B have passed away, later Nominee C will be appointed to avail the benefits and so on.
What is Assignment?
Assignment of the policy refers to the transfer of rights, title, and policy ownership from the policyholder to another person or entity. The person involved in assigning/transferring the policy is called assignor, and the person/institution to which it is assigned is called the assignee. The assignment is regulated under Section 38 of the Insurance Act, 1938.
The assignment is categorized under two different types, i.e. Absolute Assignment and Conditional Assignment.
Absolute Assignment
Under the absolute assignment, all rights, title and interest are transferred by the assignor to an assignee without reversion to the assignor (in case of any event). It shifts the ownership of the insurance policy to other parties without any terms and conditions. This assignment is usually done for money consideration such as raising a loan, out of love or affection towards family members.

Conditional Assignment
It means that the transfer of rights will happen from the Assignor to the Assignee subject to certain terms and conditions. If the conditions are fulfilled, only then the policy will be transferred.
Key Points to know Regarding Assignment
- Under the assignment, only the ownership is transferred/changed, not the risk of the policy. This means the life assured is/will be considered as the person insured.
- The assignment may lead to cancellation of the nomination in the policy only when it is done in favour of the insurance company due to a policy loan.
- The assignment applies to all the insurance plans except Pensions Plan and Married Women's Property Act (MWP).
- The assignment is effected through an endorsement on the policy contract.
Difference Between Assignment and Nomination
Let's discuss how assignment differs from nomination.
Nomination and Assignment serve different purposes. The nomination protects the interests of the insured as well as an insurer in offering claim benefits under the life insurance policy. On the other hand, assignment protects the interests of an assignee in availing the monetary benefits under the policy. The policyholder should be aware of both of them before buying life insurance.
Life Insurance Articles

Top 5 Benefits of Life Insurance Jan, 2024

GST On Life Insurance Aug, 2023

Importance of Life Insurance Aug, 2023
Factors That Affect Life Insurance Premiums July, 2023

Life Insurance For Cancer Patients July, 2023

Difference Between ULIP and Traditional Plans July, 2023
Grace Period In Life Insurance Policy July, 2023

Life Insurance With Maturity Benefits July, 2023
Difference Between Life Insurance and Health July, 2023
Benefits of Life Insurance July, 2023

Advantages and Disadvantages Of Life July, 2023

Life Insurance Premium June, 2023

Cash Value Of Life Insurance June, 2023

Free Look Period in Life Insurance June, 2023

Ladli Laxmi Yojana Policy May, 2023

Group Term Life Insurance March, 2023

Bima Sugam Life Insurance December, 2022

Whole Life Insurance Policy September, 2022

Sabse Pehle Life Insurance April, 2022

Life Insurance FAQs September, 2021

Pandemic Challenges in Life Insurance May, 2021
Term Life vs. Traditional Life Insurance- Which Is Better? January, 2021

How to Get Duplicate LIC Policy Bond? October, 2020

How To Check ICICI Prudential Life Insurance Policy Status? May, 2020

What Are Late Payment Charges For LIC Premiums? September, 2020

How To Check SBI Life Insurance Policy Status? April, 2020
Life Insurance Claim Process & Requirements July, 2020

SBI Life Insurance Premium Payment April, 2020

Guaranteed Income Plan June, 2020

ICICI Prudential Life Insurance Login and Registration April, 2020

ICICI Prudential Premium Payment May, 2020

Revival of Lapsed LIC Policy - Steps to Revive It Online December, 2019
See More Life Insurance Articles
Top 10 Indian Life Insurance Companies Jan, 2024

How To Download LIC Premium Receipt Online? December, 2019

Top 10 Pension Plans in India December, 2019

How To Check HDFC Life Policy Status? November, 2019

Sukanya Samriddhi Yojana Vs LIC Kanyadan Policy September, 2019

Best Single Premium Insurance Plans in India December, 2019

How To Update HDFC Life Insurance Policy Online? November, 2019

Max Life Premium Payment November, 2019
What our customers have to say.

Shreya Chaudhary
April 8, 2024
I am very grateful to the insurance experts of PolicyX and Mr. Ankur, who kindly helped me settle the claim of Aegon Life Insurance. Thanks again, I& 039;ll always remember this favor.
Prerna Negi
I bought a Bajaj Allianz Life Insurance through PolicyX, and I must say the level of communication and assistance I have received has been truly impressive.
Preety Kamat
Got ICICI Pru iProtect Smart term insurance plan via PolicyX; so far, I& 039;ve hassle-free renewal service and have not faced any kind of nuisance.
Sahani Kaur
Gandhinagar
The PNB MetLife Mera Term Plan Plus I& 039;ve bought it at a low premium, and it is fully satisfactory to me. The insurance expert of PolicyX is too polite, and their online buying facility red...
March 28, 2024
I would like to inform you that my maturity claims have been settled by SBI Life Insurance on 04.15.2024 and thanks all of you for helping me throughout the claim process.
Khushi Kaur
I& 039;m writing this review to let you all know that I& 039;m very satisfied because I got my kotak mahindra life insurance policy today as a result of your team effort.
kartik saxena
March 18, 2024
I had to add some riders to my Sbi life insurance, policy.com team helps to me to understand which rider is more important and which is not. Resulting helps me to save lots of money. Happy with...
Anoop srivastva
No hidden fees or charges! I have some doubts regarding my PNB MetLife insurance premiums. So I decided to visit policyx.com. Within in couple of minutes, they resolved all of my queries. I am ...

Reviewed By: Naval Goel
Naval Goel is the CEO & founder of PolicyX.com. Naval has an expertise in the insurance sector and has professional experience of more than a decade in the Industry and has worked in companies like AIG, New York doing valuation of insurance subsidiaries. He is also an Associate Member of the Indian Institute of Insurance, Pune. He has been authorized by IRDAI to act as a Principal Officer of PolicyX.com Insurance Web Aggregator.
Talk to our Trusted Insurance Advisors for Best Plans

Search Anything
Most Searched:

- Tax Planning

What is ‘Assignment’ of Life Insurance Policy?
Insurance is a contract between the insurance company (insurer) and you (policyholder) . It is a contract with full of jargon. As much as possible, we must try to understand all the insurance terms mentioned in the policy bond (certificate) . One such insurance jargon which is mostly used is Assignment .
If you are planning to apply for a home loan, your home loan provider may surely use this term. So, what is Assignment? Why assignment of a life insurance policy is required? What are different types of assignment? What are the differences between Assignment & Nomination?
What is Assignment?
Assignment of a life insurance policy means transfer of rights from one person to another. You can transfer the rights on your insurance policy to another person / entity for various reasons. This process is referred to as ‘ Assignment ’.
The person who assigns the insurance policy is called the Assignor (policyholder) and the one to whom the policy has been assigned, i.e. the person to whom the policy rights have been transferred is called the Assignee .
Once the rights have been transferred from the Assignor to the Assignee, the rights of the policyholder stands cancelled and the assignee becomes the owner of the insurance policy.
Assigning one’s life insurance policy to a bank is fairly common. In this case, the bank becomes the policy owner whereas the original policyholder continues to be the life assured on whose death the bank or the policy owner is entitled to receive the insurance money.
Types of Assignment
The assignment of an insurance policy can be made in two ways;
- Example : Mr. PK Khan owns a life insurance policy of Rs 1 Crore. He would like to gift this policy to his wife. He wants to make ‘absolute assignment’ of this policy in his wife’s name, so that the death benefit (or) maturity proceeds can be directly paid to her. Once the absolute assignment is made, Mrs. Khan will be the owner of the policy and she may again transfer this policy to someone else.
- Example : Mr. Mallya owns a term insurance policy of Rs 50 Lakh. He wants to apply for a home loan of Rs 50 Lakh. His banker has asked him to assign the term policy in their name to get the loan. Mallya can conditionally assign the policy to the home loan provider to acquire a home loan. If Mallya meets an untimely death ( during the loan tenure) , the banker can receive the death benefit under this policy and get their money back from the insurance company.
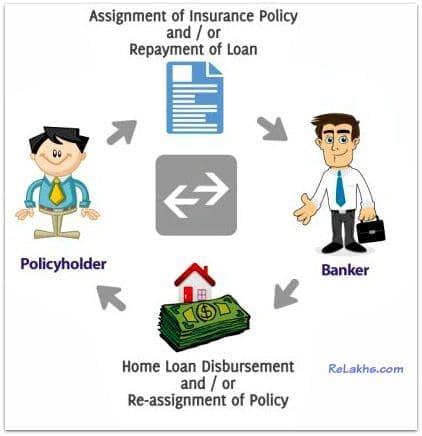
- In case if the death benefit received by the banker is more than the outstanding loan amount, the insurer will pay the bank the outstanding dues and pay the balance to the nominee directly. The balance amount (if any) will be paid to Mallya’s beneficiaries ( legal heirs / nominee) .
How to assign a life insurance policy?
The Assignment must be in writing and a notice to that effect must be given to the insurer. Assignment of a life insurance policy may be made by making an endorsement to that effect in the policy document (or) by executing a separate ‘ Assignment Deed ’. In case of assignment deed, stamp duty has to be paid. An Assignment should be signed by the assignor and attested by at least one witness.
Download absolute assignment deed sample format / conditional assignment deed format.

Nomination Vs Assignment
Nomination is a right given to the policyholder to appoint a person(s) to receive the death benefit (death claim) . The person in whose favor the nomination is effected is termed as ‘nominee’. The nominee comes into picture only after the death of the life assured (policy holder) . The nominee will not have the absolute right over the money (claim proceeds) . The other legal heirs of the policy holder can also recover money from the nominee.
(However, as per Insurance Laws (Amendment) Act, 2015 – If an immediate family member such as spouse / parent / child is made as the nominee, then the death benefit will be paid to that person and other legal heirs will not have a claim on the money)
Under nomination, the rights of the policyholder are not transferred. But, assignment is transfer of rights, interest and title of the policy to some other person (or) entity. To make assignment, consent of the insurer is also required.
Important Points
- Assignment of policies can be done even when a loan is not required or for some special purposes.
- If you assign the policy for other purpose other than taking a loan, the nomination stands cancelled.
- If the policy is assigned, then the assignee will receive the policy benefit. Death benefit will be paid to the Nominee, in case the policy is not assigned.
- The policy would be reassigned to you on the repayment of the loan (under conditional assignment) .
- Types of insurance policies used for assignment purpose to get business loans, generally include an endowment plan, money back policy or a ULIP. Home loan providers generally ask for the assignment of Term insurance plans on their names. (The term plan tenure should be more than the home loan tenure)
- An assignment of a life insurance policy once validly executed, cannot be cancelled or rendered in effectual by the assignor. The only way to cancel such assignment would be to get it re-assigned by the assignee in favor of the assignor.
- You can also raise a loan against your policy from your insurance company itself. In this case, your policy would have to be assigned to insurance company.
- An insurer may accept the assignment or decline. (The insurer shall, before refusing to act upon the endorsement, record in writing the reasons for such refusal and communicate the same to the policy-holder not later than thirty days from the date of the policy-holder giving notice of such transfer or assignment)
- In case of death of the absolute Assignee (to whom the policy rights have been transferred under absolute assignment) , the rights under the policy will be transferred to the legal heirs of the assignee.
- You can also assign a life insurance policy under Married Women’s Property Act . (At the time of making the application (buying a policy), a separate MWPA form has to be filled by the proposer for it to be covered under MWP Act. Do note that the existing life insurance policies cannot be assigned under MWP Act)
- Partial assignment or transfer of a policy can also be made. But banks will accept any of your life insurance policies as long as the sum assured is equal to or greater than the loan amount.
Hope you find this post informative and do share your comments.
(Image courtesy of Stuart Miles at FreeDigitalPhotos.net)
About The Author
Sreekanth Reddy
Can a LIC policy be assigned to someone not related by blood??
Dear Chowdhury, Yes, it is possible. However, Assignment is not permitted on all life insurance policies issued under How to buy Term Life Insurance under Married Women’s Property Act?
Very useful and gathered more knowledge
Hi, I got a question in CFP EXAM 5( case study paper) with regard to assignment of money back policy to a minor. I would like to know can a conditional assignment be made to a minor and if yes what about the premium that is yet to be paid? and would a guardian need to be appointed till the minor attains majority? and is it possible that an absolute assignment can be made?
Dear Dhaarini,
Where an assignment is made in favour of minor, the policy can not be dealt with during the minority of the assignee, even with consent of natural guardian or appointed guardian. This means minor assignee cannot raise loan, surrender or further assign the policy during his/her minority.
If the assignment is in favour of a minor, in the event of claim, policy money cannot be paid to him, as he cannot give valid discharge. It is therefore desirable that where the assignee is minor, testamentary guardian should be appointed in respect of all the properties of such minor including the policy moneys. The father i.e. natural guardian of the minor can only appoint the testamentary guardian. The appointment can be done by a separate instrument or on the back of the policy.
What if a wife has taken a policy in the name of his husband and put the nominee herself and also pays all the premiums herself, and now they are taking divorce. So, now can husband assign the policy to her and what benefits she can receive after assignment. Can she withdraw tha amount of the policy??
Dear Monika, Yes, he can make an Absolute assignment in the name of Wife..
Under Life Assurance one can assign a policy only if that policy is a policy of his/her own life. Here wife has taken a policy on her husband life and hence assignment does not arise. In the event of death of her husband she receives the death benefit irrespective of her relationship at the time of death. This is because under Life Assurance the Insurable Interest is required at the proposal stage and needs not be present at the claim stage.
I wanna give my policy to new owner
A assigned his policy to his brother B and B is paying premiums. A’s nominee is his father. What will happen if B dies?
Dear Mr Naidu, May I know what type of Assignment is this??
A assigned his policy to his brother B, out of love and affection as absolute assignment. Whose life is covered?. What happens if B dies?
Dear Mr Naidu, If the assignee (Mr B) dies, then his/her legal heirs will be entitled to the policy money. Kindly note that an assignee cannot make a nomination on the policy which is assigned to him.
“Absolute assignment is generally made for valuable consideration e.g. raising of loan from an individual / institution. This assignment has the effect of passing the title in the policy absolutely to the assignee and the policyholder in no way retains any interest in the policy. The absolute assignee can deal with the policy in any manner he likes and may even transfer his interest to another person or surrender the policy. Under absolute assignment when the assignee (Mr B) dies the benefits go to the legal heirs of the assignee and not to the heirs of the life assured.”
What is the procedure to get the policy assigned? How much time does it take?
Thanks for this. I always like to use study materials by Indians in preparing for my professional exams. The contents here are superb and easy to understand.
Once assignment is done, on whose name Renewal receipts and PPC will be generated.
Dear Gayu ..in the name of Policyholder only.
My colleagues were looking for USPS PS 1000 this month and were informed of an online platform that hosts a ton of fillable forms . If people are wanting USPS PS 1000 too , here’s https://goo.gl/Qqo6in .
Dear Sreekanth, I am having an LIC policy for the past 10 year. now i would like to assign the same to my mother. Now after the assignment, whose life is covered and who gets all the benefit? Do i have to appoint a new nominee after the assignment?
Dear Bhavik ..Life cover will be in your name only. Your mother can get the benefits. You can make her as the nominee.
If policy assigned to absolute assignment from A to B. B is the assignee of the policy and he have all rights of the policy. After assignment who will have a life cover A or B. Who will get the death benefits
Dear Senthil, Life cover – A. Beneficiary – B.
Thanks for this information, Let me know who will pay the remaining premium after assignment.and what are the other reasons for assignment except loan and gift. Manish
Dear Manish ..The policy holder only has to pay the premium.
I have a ULIP assigned to my home loan. I have paid two annual premiums till now. If I dont pay the next premium, will it have any impact on my home loan ? I know that my ulip will get discontinued in this case but can the bank force me to pay the premium legally ?
Dear Kalis, If sum assured falls below the outstanding loan amount then you banker may ask you to assign another policy or pay the premiums on this one.
Thanks. Sum assured is already below the loan amount. In this case, can bank take any legal action against me if I don’t pay the premium?
Dear Kalis..Why do you want to take this risk?
Who will have to pay tax if single premium ULIP where premium is >20% of sum assured is assgned to spouse & she then sureender it.
Dear Vishal ..The insured (policyholder)..
my father aged 72 has taken a ULIP policy on my Child with coverage 10 lakhs .But now he would like to Assign the policy to my mother’s Name aged 67.
Please Clarify weather the life coverage and policy benefits will be transferred to my Mother or will it continue with my son.
Dear Nisha, May I know who is the ‘insured’ in this policy? Is the child just a nominee to the policy? “If he assigns the policy for other purpose other than taking a loan, the nomination stands cancelled. If the policy is assigned, then the assignee will receive the policy benefit. “
Hi.. Really nice blog.very informative and useful. I liked the way You explained very briefly about Assignment’ of Life Insurance Policy.
Hi Srikanth,
Nice article on Assignment!
I Just wanted to know If i nominate my spouse for the life insurance or nominate my child and appoint my spouse how these to things are different in terms claim settlement of life insurance.
Ideally I may want my spouse to look-after my child education until they turn major and they do not misuse the claim amount.
Please let me know if possible your contact number so that we discuss further..
Please suggest.
Thanks, Shravan
Dear Shravan, If you are planning to buy a new Term plan, you can assign the policy under MWP Act by mentioning the Percentages (share in death benefits) among your legal heirs (spouse & kids). You also have the option to write a WILL and give detailed instructions about how the claim amount (if any, on such policy) should be used or allocated.
Dear Sreekant, Thanks for such valuable information. Please do correction on your post that the existing life insurance policies cannot be assigned under MWP Act. Pl correct me if I am wrong. Please let me know that even if I assign the policy unconditionally to the bank for home loan purpose, after repaying the home loan successfully, the bank should re-assign the policy to me. If it does not do this, what options do I have? Thanks again.
Dear Vivek, Yes, only new insurance policies can be assigned (while purchasing new ones) under MWP. I should have written the sentence as ‘You can also assign a new life insurance policy under….’ Thank you for pointing this out. (I have provided all the details about MWP act in another article).
If a policy is assigned with absolute assignment, it cannot be cancelled. It can be done only by another valid re-assignment. So, the banker has to re-assign it after the repayment of loan. When you do not wish to give away your complete control over policy, do not go in for absolute assignment.
thanks for prompt response.

ReLakhs.com is a blog on personal finances. The main aim of this blog is to help you make INFORMED financial decisions by presenting the content on money matters in a simple, unbiased and easy to understand manner.
Popular Posts
Latest court judgements on women’s property rights, who gets the joint bank account monies if one account holder dies, income tax deductions list fy 2023-24 | under old & new tax regimes, top 5 best aggressive hybrid equity mutual funds | equity-oriented balanced funds, useful links.
- Community (Forum) - SignUp
- Forum (Old)
- Privacy Policy
Viewsletter
Cared by T-Square Cloud
Session expired
Please log in again. The login page will open in a new tab. After logging in you can close it and return to this page.
- Share on WhatsApp
- Share on Facebook
- Share on Twitter
- Share on LinkedIn
- Share on Email

Assignment under Insurance Policies
By J Mandakini, NUALS
Editor’s Note: This paper attempts to explore the concept of assignment under Indian law especially Contract Act, Insurance Act and Transfer of Property Act. It seeks to appreciate why the assignment is made use of for securities of a facility sanctioned by ICICI Bank. Also, it explains how ICICI Bank faces certain problems in executing the same.
INTRODUCTION
For any facility sanctioned by a lender, collateral is always deposited to secure the same. Such mere deposition will not suffice, the borrower has to explicitly permit the lender to recover from the borrower, such securities in case of his default.
This is done by the concept of assignment, dealt with adequately in Indian law. Assignment of obligations is always a tricky matter and needs to be dealt with carefully. The Bank should not fall short of any legally permitted lengths to ensure the same. This is why ambiguity in its security documents have to be rectified.
This paper attempts to explore the concept of assignment in contract law. It seeks to appreciate why the assignment is made use of for securities of a facility sanctioned by ICICI Bank. The next section will deal with how ICICI Bank faces certain problems in executing the same. The following sections will talk about possible risks involved, as well as defenses and solutions to the same.
WHAT IS ASSIGNMENT?
Assignment refers to the transfer of certain or all (depending on the agreement) rights to another party. The party which transfers its rights is called an assignor, and the party to whom such rights are transferred is called an assignee. Assignment only takes place after the original contract has been made. As a general rule, assignment of rights and benefits under a contract may be done freely, but the assignment of liabilities and obligations may not be done without the consent of the original contracting party.
The liability on a contract cannot be transferred so as to discharge the person or estate of the original contractor unless the creditor agrees to accept the liability of another person instead of the first. [i]
Illustration
P agrees to sell his car to Q for Rs. 100. P assigns the right to receive the Rs. 100 to S. This may be done without the consent of Q. This is because Q is receiving his car, and it does not particularly matter to him, to whom the Rs. 100 is being handed as long as he is being absolved of his liability under the contract. However, notice may still be required to be given. Without such notice, Q would pay P, in spite of the fact that such right has been assigned to S. S would be a sufferer in such case.
In this case, that condition is being fulfilled since P has assigned his right to S. However, P may not assign S to be the seller. P cannot just transfer his duties under the contract to another. This is because Q has no guarantee as to the condition of S’s car. P entered into the contract with Q on the basis of the merits of P’s car, or any other personal qualifications of P. Such assignment may be done with the consent of all three parties – P, Q, S, and by doing this, P is absolved of his liabilities under the contract.
1.1. Effect of Assignment
Immediately on the execution of an assignment of an insurance policy, the assignor forgoes all his rights, title and interest in the policy to the assignee. The premium or loan interest notices etc. in such cases will be sent to the assignee. [ii] However, the existence of obligations must not be assumed, when it comes to the assignment. It must be accompanied by evidence of the same. The party asserting such a personal obligation must prove the existence of an express assumption by clear and unequivocal proof. [iii]

Assignment of a contract to a third party destroys the privity of contract between the initial contracting parties. New privity is created between the assignee and the original contracting party. In the illustration mentioned above, the original contracting parties were P and Q. After the assignment, the new contracting parties are Q and S.
1.2. Revocation of Assignment
Assignment, once validly executed, can neither be revoked nor canceled at the option of the assignor. To do so, the insurance policy will have to be reassigned to the original assignor (the insured).
1.3. Exceptions to Assignment
There are some instances where the contract cannot be assigned to another.
- Express provisions in the contract as to its non-assignability – Some contracts may include a specific clause prohibiting assignment. If that is so, then such a contract cannot be assigned. Assignability is the rule and the contrary is an exception. [iv]
Pensions, PFs, military benefits etc. Illustration
1.4. enforcing a contract of assignment.
From the day on which notice is given to the insurer, the assignee becomes the beneficiary of the policy even though the assignment is not registered immediately. It does not wait until the giving of notice of the transfer to the insurer. [vi] However, no claims may lie against the insurer until and unless notice of such assignment is delivered to the insurer.
If notice of assignment is not provided to the obligor, he is discharged if he pays to the assignor. Assignee would have to recover from the assignor. However, if the obligor pays the assignor in spite of the notice provided to him, he would still be liable to the assignee.
The following two illustrations make the point amply clear:
Illustrations
1. Seller A assigns its right to payment from buyer X to bank B. Neither A nor B gives notice to X. When payment is due, X pays A. This payment is fully valid and X is discharged. It will be up to B to recover it from A
2. Seller A assigns to bank B its right to payment from buyer X. B immediately gives notice of the assignment to X. When payment is due, X still pays A. X is not discharged and B is entitled to oblige X to pay a second time.
An assignee doesn’t stand in better shoes than those of his assignor. Thus, if there is any breach of contract by the obligor to the assignee, the latter can recover from the former only the same amount as restricted by counter claims, set offs or liens of the assignor to the obligor.
The acknowledgment of notice of assignment is conclusive proof of, and evidence enough to entertain a suit against an assignor and the insurer respectively who haven’t honoured the contract of assignment.
1.5. Assignment under various laws in India
There is no separate law in India which deals with the concept of assignment. Instead, several laws have codified it under different laws. Some of them have been discussed as follows:
1.5.1. Under the Indian Contract Act
There is no express provision for the assignment of contracts under the Indian Contract Act. Section 37 of the Act provides for the duty of parties of a contract to honour such contract (unless the need for the same has been done away with). This is how the Act attempts to introduce the concept of assignment into Indian commercial law. It lays down a general responsibility on the “representatives” of any parties to a contract that may have expired before the completion of the contract. (Illustrations to Section 37 in the Act).
An exception to this may be found from the contract, e.g. contracts of a personal nature. Representatives of a deceased party to a contract cannot claim privity to that contract while refusing to honour such contract. Under this Section, “representatives” would also include within its ambit, transferees and assignees. [vii]
Section 41 of the Indian Contract Act applies to cases where a contract is performed by a third party and not the original parties to the contract. It applies to cases of assignment. [viii] A promisee accepting performance of the promise from a third person cannot afterwards enforce it against the promisor. [ix] He cannot attain double satisfaction of its claim, i.e., from the promisor as well as the third party which performed the contract. An essential condition for the invocation of this Section is that there must be actual performance of the contract and not of a substituted promise.
1.5.2. Under the Insurance Act
The creation of assignment of life insurance policies is provided for, under Section 38 of the Insurance Act, 1938.
- When the insurer receives the endorsement or notice, the fact of assignment shall be recorded with all details (date of receipt of notice – also used to prioritise simultaneous claims, the name of assignee etc). Upon request, and for a fee of an amount not exceeding Re. 1, the insurer shall grant a written acknowledgment of the receipt of such assignment, thereby conclusively proving the fact of his receipt of the notice or endorsement. Now, the insurer shall recognize only the assignee as the legally valid party entitled to the insurance policy.
1.5.3. Under the Transfer of Property Act
Indian law as to assignment of life policies before the Insurance Act, 1938 was governed by Sections 130, 131, 132 and 135 of the Transfer of Property Act 1882 under Chapter VIII of the Act – Of Transfers of Actionable Claims. Section 130 of the Transfer of Property Act states that nothing contained in that Section is to affect Section 38 of the Insurance Act.
I) Section 130 of the Transfer of Property Act
An actionable claim may be transferred only by fulfilling the following steps:
- Signed by a transferor (or his authorized agent)
The transfer will be complete and effectual as soon as such an instrument is executed. No particular form or language has been prescribed for the transfer. It does not depend on giving notice to the debtor.
The proviso in the section protects a debtor (or other person), who, without knowledge of the transfer pays his creditor instead of the assignee. As long as such payment was without knowledge of the transfer, such payment will be a valid discharge against the transferee. When the transfer of any actionable claim is validly complete, all rights and remedies of transferor would vest now in the transferee. Existence of an instrument in writing is a sine qua non of a valid transfer of an actionable claim. [x]
II) Section 131 of the Transfer Of Property Act
This Section requires the notice of transfer of actionable claim, as sent to the debtor, to be signed by the transferor (or by his authorized agent), and if he refuses to sign it, a signature by the transferee (or by his authorized agent). Such notice must state both the name and address of the transferee. This Section is intended to protect the transferee, to receive from the debtor. The transfer does not bind a debtor unless the transferor (or transferee, if transferor refuses) sends him an express notice, in accordance with the provisions of this Section.
III) Section 132 of the Transfer Of Property Act
This Section addresses the issue as to who should undertake the obligations under the transfer, i.e., who will discharge the liabilities of the transferor when the transfer has been made complete – would it be the transferor himself or the transferee, to whom the rest of the surviving contract, so to speak, has been transferred.
This Section stipulates, that the transferee himself would fulfill such obligations. However, where an actionable claim is transferred with the stipulation in the contract that transferor himself should discharge the liability, then such a provision in the contract will supersede Ss 130 and 132 of this Act. Where the insured hypothecates his life insurance policies and stipulates that he himself would pay the premiums, the transferee is not bound to pay the premiums. [xi]
FACILITIES SECURED BY INSURANCE POLICIES – HOW ASSIGNMENT COMES INTO THE PICTURE
Many banks require the borrower to take out or deposit an insurance policy as security when they request a personal loan or a business loan from that institution. The policy is used as a way of securing the loan, ensuring that the bank will have the facility repaid in the event of either the borrower’s death or his deviations from the terms of the facility agreement.
Along with the deposit of the insurance policy, the policyholder will also have to assign the benefits of the policy to the financial institution from which he proposes to avail a facility. The mere deposit, without writing, or passing of any document of title to such a claim, does not create any equitable charge. [xii]
ETHICS OF ASSIGNING LIFE INSURANCE POLICY TO LENDERS
The purpose of taking out a life insurance policy on oneself, is that in the event of an untimely death, near and dear ones of the deceased are not left high and dry, and that they would have something to fall back on during such traumatic times. Depositing and assigning the rights under such policy document to another, would mean that there is a high chance that benefits of life insurance would vest in such other, in the event of unfortunate death and the family members are prioritized only second. These are not desirable circumstances where the family would be forced to cope with the death of their loved one coupled with the financial crisis.
Thus, there is a need to examine the ethics of:
- The bank accepting such assignment
The customer should be cautious before assigning his rights under life insurance policies. By “cautious”, it is only meant that he and his dependents and/or legal heirs should be aware of the repercussions of the act of assigning his life insurance policy. It is conceded that no law prohibits the assignment of life insurance policies.
In fact, Section 38 of the Insurance Act, 1938 , provides for such assignments. Judicial cases have held life insurance policies as property more than a social welfare measure. [xiii] Further, the bank has no personal relationship with any customer and thus has no moral obligation to not accept such assignments of life insurance.
However, the writer is of the opinion that, in dealing with the assignment of life insurance policies, utmost care and caution must be taken by the insured when assigning his life insurance policy to anyone else.
CURRENT STAND OF ICICI REGARDING FACILITIES SECURED BY INSURANCE POLICY, WITH SPECIFIC REFERENCE TO ASSIGNMENT OF OBLIGATIONS
This Section seeks to address and highlight the manner in which ICICI Bank drafts its security documents with regard to the assignment of obligations. The texts placed in quotes in the subsequent paragraphs are verbatim extracts from the security document as mentioned.
Composite Document for Corporate and Realty Funding
“ 8 . CHARGING CLAUSE
The Mortgagor doth hereby:
iii) Assign and transfer unto the Mortgagee all the Bank Accounts and all rights, title, interest, benefits, claims and demands whatsoever of the Mortgagor in, to, under and in respect of the Bank Accounts and all monies including all cash flows and receivables and all proceeds arising from Projects and Other Projects_______________, insurance proceeds, which have been deposited / credited / lying in the Bank Accounts, all records, investments, assets, instruments and securities which represent all amounts in the Bank Accounts, both present and future (the “Account Assets”, which expression shall, as the context may permit or require, mean any or each of such Account Assets) to have and hold the same unto and to the use of the Mortgagee absolutely and subject to the powers and provisions herein contained and subject also to the proviso for redemption hereinafter mentioned;
(v) Assign and transfer unto the Mortgagee all right, title, interest, benefit, claims and demands whatsoever of the Mortgagors, in, to, under and/or in respect of the Project Documents (including insurance policies) including, without limitation, the right to compel performance thereunder, and to substitute, or to be substituted for, the Mortgagor thereunder, and to commence and conduct either in the name of the Mortgagor or in their own names or otherwise any proceedings against any persons in respect of any breach of, the Project Documents and, including without limitation, rights and benefits to all amounts owing to, or received by, the Mortgagor and all claims thereunder and all other claims of the Mortgagor under or in any proceedings against all or any such persons and together with the right to further assign any of the Project Documents, both present and future, to have and to hold all and singular the aforesaid assets, rights, properties, etc. unto and to the use of the Mortgagee absolutely and subject to the powers and provisions contained herein and subject also to the proviso for redemption hereinafter mentioned.”
ICICI Bank’s Standard Terms and Conditions Governing Consumer Durable Loans
“ insurance.
The Borrower further agrees that upon any monies becoming due under the policy, the same shall be paid by the Insurance Company to ICICI Bank without any reference / notice to the Borrower, but not exceeding the principal amount outstanding under the Insurance Policy. The Borrower specifically acknowledges that in all cases of claim, the Insurance Company will be solely liable for settlement of the claim, and he/she will not hold ICICI Bank responsible in any manner whether for compensation, recovery of compensation, processing of claims or for any reason whatsoever.
Reference has been made only to assignment of assets, rights, benefits, interests, properties etc. No specific reference has been made to the assignment of obligations of the assignor under such insurance contract.
THE ISSUE FACED BY ICICI BANK
Where ICICI Bank accepts insurance policy documents of customers as security for a loan, in the light of the fact that the documents are silent about the question of assignment of obligations, are they assigned to ICICI Bank? Where there is hypothecation of a life insurance policy, with a stipulation that the mortgagor (assignor) should pay the premiums, and that the mortgagee (assignee) is not bound to pay the same, Sections 130 and 132 do not apply to such cases. [xiv] With rectification of this issue, ICICI Bank can concretize its hold over the securities with no reservations about its legality.
RISKS INVOLVED
This section of the paper attempts to explore the many risks that ICICI Bank is exposed to, or other factors which worsen the situation, due to the omission of a clause detailing the assignment of obligations by ICICI Bank.
Practices of Other Companies
The practices of other companies could be a risk factor for ICICI Bank in the light of the fact that some of them expressly exclude assignment of obligations in their security documents.
There are some companies whose notice of assignment forms contain an exclusive clause dealing with the assignment of obligations. It states that while rights and benefits accruing out of the insurance policy are to be assigned to the bank, obligations which arise out of such policy documents will not be liable to be performed by the bank. Thus, they explicitly provide for the only assignment of rights and benefits and never the assignment of obligations.
Possible Obligation to Insurance Companies
By not clearing up this issue, ICICI Bank could be held to be obligated to the insurance company from whom the assignor took the policy, for example, with respect to insurance premiums which were required to be paid by the assignor. This is not a desirable scenario for ICICI Bank. In case of default by the assignor in the terms of the contract, the right of ICICI Bank over the security deposited (insurance policy in question) could be fraught in the legal dispute.
Possible litigation
Numerous suits may be instituted against ICICI Bank alleging a violation of the Indian Contract Act. Some examples include allegations of concealment of fact, fraud etc. These could be enough to render the existing contract of assignment voidable or even void.
Contra Proferentem
This doctrine applies in a situation when a provision in the contract can be interpreted in more than one way, thereby creating ambiguities. It attempts to provide a solution to interpreting vague terms by laying down, that a party which drafts and imposes an ambiguous term should not benefit from that ambiguity. Where there is any doubt or ambiguity in the words of an exclusion clause, the words are construed more forcibly against the party putting forth the document, and in favour of the other party. [xv]
The doctrine of contra proferentem attempts to protect the layman from the legally knowledgeable companies which draft standard forms of contracts, in which the former stands on a much weaker footing with regard to bargaining power with the latter. This doctrine has been used in interpreting insurance contracts in India. [xvi]
If litigation ensues as a result of this uncertainty, there are high chances that the Courts will tend to favour the assignor and not the drafter of the documents.
POSSIBLE DEFENSES AGAINST DISPUTES FOR THE SECURITY DOCUMENTS AS THEY ARE NOW
This section of the paper attempts to give defences which the Bank may raise in case of any disputes arising out of silence on the matter of assignability of obligations.
Interpretation of the Security Documents
UNIDROIT principles expressly provide a method for interpretation of contracts. [xvii] The method consists of utilizing the following factors:
This defence relates to the concept of estoppel embodied in Section 115 of the Indian Evidence Act, 1872. According to the Section, when one person has, by his declaration, act or omission, intentionally caused or permitted another person to believe a thing to be true and to act upon such belief, neither he nor his representative shall be allowed, in any suit or proceeding between himself and such person or his representatives, to deny the truth of that thing.
If a man either by words or by conduct has intimated that he consents to an act which has been done and that he will not offer any opposition to it, and he thereby induces others to do that which they otherwise might have abstained from, he cannot question legality of the act he had sanctioned to the prejudice of those who have so given faith to his words or to the fair inference to be drawn from his conduct. [xviii] Subsequent conduct may be relevant to show that the contract exists, or to show variation in the terms of the contract, or waiver, or estoppel. [xix]
Where the meaning of the instrument is ambiguous, a statement subsequently interpreting such instrument is admissible. [xx] In the present case, where the borrower has never raised any claims with regard to non assignability of obligations on him, and has consented to the present conditions and relations with ICICI Bank, he cannot he cannot be allowed to raise any claims with respect to the same.
Internationally, the doctrine of post contractual conduct is invoked for such disputes. It refers to the acts of parties to a contract after the commencement of the contract. It stipulates that where a party has behaved in a particular manner, so as to induce the other party to discharge its obligations, even if there has been a variation from the terms of the contract, the first party cannot cite such variation as a reason for its breach of the contract.
Where the parties to a contract are both under a common mistake as to the meaning or effect of it, and therefore embark on a course of dealing on the footing of that mistake, thereby replacing the original terms of the contract by a conventional basis on which they both conduct their affairs, then the original contract is replaced by the conventional basis. The parties are bound by the conventional basis. Either party can sue or be sued upon it just as if it had been expressly agreed between them. [xxi]
The importance of consensus ad idem has been concretized by various case laws in India. Further, if the stipulations and terms are uncertain and the parties are not ad idem there can be no specific performance, for there was no contract at all. [xxii]
In the present case, the minds of the assignor and assignee can be said to have not met while entering into the assignment. The assignee never had any intention of undertaking any obligations of the assignor. In Hartog v Colin & Shields, [xxiii] the defendants made an offer to the plaintiffs to sell hare skins, offering to a pay a price per pound instead of per piece.
AVOIDING THESE RISKS
To concretize ICICI Bank’s stand on the assignment of obligations in the matter of loans secured by insurance policies, the relevant security documents could be amended to include such a clause.
For instances where loans are secured by life insurance policies, a standard set by the American Banker’s Association (ABA) has been followed by many Indian commercial institutions as well. [xxvi] The ABA is a trade association in the USA representing banks ranging from the smallest community bank to the largest bank holding companies. ABA’s principal activities include lobbying, professional development for member institutions, maintenance of best practices and industry standards, consumer education, and distribution of products and services. [xxvii]
There are several ICICI security documents which have included clauses denying any assignment of obligations to it. An extract of the deed of hypothecation for vehicle loan has been reproduced below:
“ 3. In further pursuance of the Loan Terms and for the consideration aforesaid, the Hypothecator hereby further agrees, confirms, declares and undertakes with the Bank as follows:
(i)(a) The Hypothecator shall at its expenses keep the Assets in good and marketable condition and, if stipulated by the Bank under the Loan Terms, insure such of the Assets which are of insurable nature, in the joint names of the Hypothecator and the Bank against any loss or damage by theft, fire, lightning, earthquake, explosion, riot, strike, civil commotion, storm, tempest, flood, erection risk, war risk and such other risks as may be determined by the Bank and including wherever applicable, all marine, transit and other hazards incidental to the acquisition, transportation and delivery of the relevant Assets to the place of use or installation. The Hypothecator shall deliver to the Bank the relevant policies of insurance and maintain such insurance throughout the continuance of the security of these presents and deliver to the Bank the renewal receipts / endorsements / renewed policies therefore and till such insurance policies / renewal policies / endorsements are delivered to the Bank, the same shall be held by the Hypothecator in trust for the Bank. The Hypothecator shall duly and punctually pay all premia and shall not do or suffer to be done or omit to do or be done any act, which may invalidate or avoid such insurance. In default, the Bank may (but shall not be bound to) keep in good condition and render marketable the relevant Assets and take out / renew such insurance. Any premium paid by the Bank and any costs, charges and expenses incurred by the Bank shall forthwith on receipt of a notice of demand from the Bank be reimbursed by the Hypothecator and/or Borrower to the Bank together with interest thereon at the rate for further interest as specified under the Loan Terms, from the date of payment till reimbursement thereof and until such reimbursement, the same shall be a charge on the Assets…”
The inclusion of such a clause in all security documents of the Bank can avoid the problem of assignability of obligations in insurance policies used as security for any facility sanctioned by it.
An assignment of securities is of utmost importance to any lender to secure the facility, without which the lender will not be entitled to any interest in the securities so deposited.
In this paper, one has seen the need for assignment of securities of a facility. Risks involved in not having a separate clause dealing with non assignability of obligations have been discussed. Certain defences which ICICI Bank may raise in case of the dispute have also been enumerated along with solutions to the same.
Formatted by March 2nd, 2019.
BIBLIOGRAPHY
[i] J.H. Tod v. Lakhmidas , 16 Bom 441, 449
[ii] http://www.licindia.in/policy_conditions.htm#12, last visited 30 th June, 2014
[iii] Headwaters Construction Co. Ltd. v National City Mortgage Co. Ltd., 720 F. Supp. 2d 1182 (D. Idaho 2010)
[iv] Indian Contract Act and Specific Relief Act, Mulla, Vol. I, 13 th Edn., Reprint 2010, p 968
[v] Khardah Co. Ltd. v. Raymond & Co ., AIR 1962 SC 1810: (1963) 3 SCR 183
[vi] Principles of Insurance Law, M.N. Srinivasan, 8 th Edn., 2006, p. 857
[vii] Ram Baran v Ram Mohit , AIR 1967 SC 744: (1967) 1 SCR 293
[viii] Sri Sarada Mills Ltd. v Union of India, AIR 1973 SC 281
[ix] Lala Kapurchand Godha v Mir Nawah Himayatali Khan, [1963] 2 SCR 168
[x] Velayudhan v Pillaiyar, 9 Mad LT 102 (Mad)
[xi] Hindustan Ideal Insurance Co. Ltd. v Satteya, AIR 1961 AP 183
[xii] Mulraj Khatau v Vishwanath, 40 IA 24 – Respondent based his claim on a mere deposit of the policy and not under a written transfer and claimed that a charge had thus been created on the policy.
[xiii] Insure Policy Plus Services (India) Pvt. Ltd. v The Life Insurance Corporation of India, 2007(109)BOMLR559
[xiv] Transfer of Property Act, Sanjiva Row, 7 th Edn., 2011, Vol II, Universal Law Publishing Company, New Delhi
[xv] Ghaziabad Development Authority v Union of India, AIR 2000 SC 2003
[xvi] United India Insurance Co. Ltd. v M/s. Pushpalaya Printers, [2004] 3 SCR 631, General Assurance Society Ltd. v Chandumull Jain & Anr., [1966 (3) SCR 500]
[xvii] UNIDROIT Principles, Art 4.3
[xviii] B.L.Sreedhar & Ors. v K.M. Munireddy & Ors., 2002 (9) SCALE 183
[xix] James Miller & Partners Ltd. v Whitworth Street Estates (Manchester) Ltd., [1970] 1 All ER 796 (HL)
[xx] Godhra Electricity Co. Ltd. v State of Gujarat, AIR 1975 SC 32
[xxi] Amalgamated Investment & Property Co. Ltd. v Texas Commerce International Bank Ltd., [1981] 1 All ER 923
[xxii] Smt. Mayawanti v Smt. Kaushalya Devi, 1990 SCR (2) 350
[xxiii] [1939] 3 All ER 566
[xxiv] Terrell v Alexandria Auto Co., 12 La.App. 625
[xxv] http://www.uncitral.org/pdf/english/CISG25/Pamboukis.pdf, last visited on 30 th June, 2014
[xxvi] https://www.phoenixwm.phl.com/shared/eforms/getdoc.jsp?DocId=525.pdf, last visited on 30 th June, 2014
[xxvii] http://www.aba.com/About/Pages/default.aspx, last visited on 30 th June, 2014

Related Posts:

Leave a Comment Cancel reply

Give it a try, you can unsubscribe anytime :)
Thanks, I’m not interested
Policygenius does not allow the submission of personal information by users located within the EU or the UK. If you believe this action is in error, or have any questions, please contact us at [email protected]
- MyNewMarkets.com
- Claims Journal
- Insurance Journal TV
- Academy of Insurance
- Carrier Management

Featured Stories
- Progressive Records 5-Fold Increase in Q1 Net Income
- Zurich to Halt Coverage of New Fossil-Fuel Exposures
Current Magazine

- Read Online
Post-Loss Assignments of Claims Under Insurance Policies
In the settlement of lawsuits involving insured claims, it is not uncommon that one condition of the settlement is that the defendant assign his or her claims under all applicable insurance policies to the party that filed suit.
Indeed, it is frequently the case that the defendant, particularly when the defendant is an individual, has a limited ability to pay a judgment and insurance coverage offers the best opportunity for a recovery by the suing party. Usually, such settlements are made without any serious thought being given to whether the defendant’s claim against its insurer is assignable; the assumption being that it is assignable.
However, insurance policies generally have anti-assignment clauses which prohibit the assignment of the policy, or an interest in the policy, without the insurer’s consent. These clauses come into play in determining the validity or enforceability of the assignment of a claim under an insurance policy and should be considered when such an assignment is part of a settlement.
When considering the enforceability of anti-assignment clauses in insurance policies, the courts generally draw a distinction between an assignment made prior to the occurrence of a covered loss (a “pre-loss” assignment) and an assignment made after the occurrence of a covered loss (a “post-loss” assignment).
In analyzing pre-loss assignments, the courts recognize that requiring an insurer to provide coverage to an assignee of its policy prior to the occurrence of a covered loss would place the insurer in the position of covering a party with whom it had not contracted nor been allowed to properly underwrite to assess the risks posed by that potential insured, and, accordingly, determine the appropriate premium to charge for the risks being undertaken or choose to decline coverage.
Post-loss assignments, on the other hand, take place after the insurer’s obligations under its policy have become fixed by the occurrence of a covered loss, thus the risk factors applicable to the assignee are irrelevant with regard to the covered loss in question. For these reasons, the majority of the courts enforce anti-assignment clauses to prohibit or restrict pre-loss assignments, but refuse to enforce anti-assignment clauses to prohibit or restrict post-loss assignments.
Katrina Cases
The Louisiana Supreme Court, which had not previously addressed the enforceability of anti-assignment clauses for post-loss assignments, was recently confronted with this issue in the In re: Katrina Canal Breaches Litigation, litigation involving consolidated cases arising out of Hurricane Katrina. The issue arose as a result of a lawsuit brought by the State of Louisiana as the assignee of claims under numerous insurance policies as part of the “Road Home” Program. The Road Home Program was set up following Hurricanes Katrina and Rita to distribute federal funds to homeowners suffering damage from the hurricanes. In return for receiving a grant of up to $150,000, homeowners were required to execute a Limited Subrogation/Assignment agreement, which provided in pertinent part:
Pursuant to these Limited Subrogation/Assignments, the State of Louisiana brought suit against more than 200 insurance companies to recover funds dispensed under the Road Home Program. The suit was removed to Federal Court under the Class Action Fairness Act and the insurers filed motions to dismiss, arguing that the assignments to the State of Louisiana were invalid under the anti-assignment clauses in the homeowner policies at issue.
On appeal, the United States Fifth Circuit Court of Appeals certified the following question to the Louisiana Supreme Court: “Does an anti-assignment clause in a homeowner’s insurance policy, which by its plain terms purports to bar any assignment of the policy or an interest therein without the insurer’s consent, bar an insured’s post-loss assignment of the insured’s claims under the policy when such an assignment transfers contractual obligations, not just the right to money due?”
In answering this question, the Louisiana Supreme Court began by noting that, as a general matter, contractual rights are assignable unless the law, the contract terms or the nature of the contract preclude assignment. Specific to the certified question, Louisiana Civil Code article 2653 provides that a right “cannot be assigned when the contract from which it arises prohibits the assignment of that right.” The Louisiana Supreme Court observed that the language of article 2653 is broad and, on its face, applies to all assignments, including post-loss assignments of insurance claims. The Court, therefore, construed the issue confronting it as whether Louisiana public policy would enforce an anti-assignment clause to preclude post-loss assignments of claims under insurance policies.
In addressing the public policy question, the Louisiana Supreme Court recognized the distinction between pre-loss assignments and post-loss assignments discussed by courts from other states and noted that the prevailing view was that anti-assignment clauses were invalid and/or unenforceable when applied to post-loss assignments. Notwithstanding this weight of authority, the Louisiana Supreme Court stated:
“[W]hile the Louisiana legislature has clearly indicated an intent to allow parties freedom to assign contractual rights, by enacting La. C.C. art. 2653, it has also clearly indicated an intent to allow parties freedom to contractually prohibit assignment of rights. We recognize the vast amount of national jurisprudence distinguishing between pre-loss and post-loss assignments and rejecting restrictions on post-loss assignments, however we find no public policy in Louisiana favoring assignability of claims over freedom of contract.”
Thus, Court refused to invalidate the enforceability of the anti-assignment clauses to the post-loss assignments before it based on public policy, adding that public policy determinations are better suited to the legislature.
Nonetheless, after having recognized the general enforceability of anti-assignment clauses to post-loss assignments, the Court immediately placed limits on when those clauses would be applicable, stating that to be applicable, they “must clearly and unambiguously express that the non-assignment clause applies to post-loss assignments.” The Court refused “to formulate a test consisting of specific terms or words,” which would satisfy this condition and remanded the case to the federal courts to determine whether the individual anti-assignment clauses in the various policies were sufficiently clear and explicit to be enforced with respect to post-loss assignments at issue.
A Broad Application
It should be noted that the Court’s opinion appears to apply broadly to all post-loss assignments irrespective of what specific rights are being assigned, despite the fact that the certified question was narrower and asked only about the applicability of a post-loss assignment where the assignment “transfers contractual obligations, not just the right to money due.”
In a footnote at the beginning of its opinion, the Louisiana Supreme Court observed that in certifying the question to it, the Fifth Circuit “disclaimed any intent” that the Court “confine its reply to the precise form or scope of the legal questions certified.” The footnote indicates that the Court’s opinion was not intended to be limited to only those post-loss assignments involving the assignment of contractual obligations.
Louisiana has departed from the majority view in holding that as a matter of general law, anti-assignment clauses are not inherently void with regard to post-loss assignments. However, it may be that in practical application, the results of individual cases may well be consistent with the majority rule of not enforcing anti-assignment clauses with regard to post-loss assignments because Louisiana courts may be reluctant to find that the anti-assignment clauses are sufficiently “clear and explicit” unless they specifically state that they apply to post-loss assignments, notwithstanding the Louisiana Supreme Court’s unwillingness to “formulate a test consisting of specific terms or words.”
Topics Lawsuits Carriers Profit Loss Claims Louisiana Hurricane Homeowners
Was this article valuable?
Thank you! Please tell us what we can do to improve this article.
Thank you! % of people found this article valuable. Please tell us what you liked about it.
Here are more articles you may enjoy.

Written By Robert Redfearn, Jr.
From this issue.

Excess, Surplus & Specialty Markets Directory Vol. II – The Industry’s Leading Coverage Placement Directory
Interested in carriers .
Get automatic alerts for this topic.
- Categories: Legal Beat
- Have a hot lead? Email us at [email protected]
Insurance Jobs
- Director, Medical Claim Audits - New York, NY
- Work and Rewards Director - San Francisco, CA
- Auto Design Business Process Lead Consultant – Remote - Chicago, IL
- Software Development Engineer in Test - Denver, CO
- Client Advocate - Tempe, AZ

- Squeezed from All Sides: Restaurants Pressured by Labor, Food, Insurance Costs
- Extreme Weather, Cyber Risks Top Concerns When Insuring Farms
- 3 Areas for Agents to Focus Growth Efforts in 2024 As the Hard Market Continues
- Majority of Underwriters Predict Cyber Risks Grow 'Greatly' in 2024: Survey
- What's to Come in 2024: AI Expansion, More Catastrophes, Network Consolidation

- 200 Patients Sue, Alleging Sexual Abuse, Unnecessary Exams by Boston Doctor
- St. Louis Contractor Faces $276K in Fines Over Deadly Fall Hazards
- Oregon Schools Sued for $9M After Young Girl Allegedly Raped
- Probe Underway of Fatal Crash Inolving Ford Mustang With Assisted Driver System
- Europe's Wildfires in 2023 Were Among Worst This Century: Report

- April 11 (Free) Artificial Intelligence and Insurance Agents - Panic or Promise?
- April 18 Waiting on the Grand Reopening: Business Income Essentials
- April 25 Getting Back to Work: Workers' Comp and the Social Determinants of Health
- May 2 Rules of Engagement in Selling
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
- Building Your Business
What Is an Anti-Assignment Clause?
Anti-Assignment Clauses Explained
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/ScreenShot2020-03-23at2.04.43PM-59de96b153e540c498f1f1da8ce5c965.png)
- Definition and Example
How Anti-Assignment Clauses Work
- State Laws and Anti-Assignment Clauses
Extreme Media / Getty Images
An anti-assignment clause is a provision in an insurance policy that bars the policyholder from transferring their rights under the policy to another party. The clause prohibits the insured from authorizing someone else to file claims, make changes, or take other actions under the policy.
Many small businesses purchase insurance policies that contain an anti-assignment clause, which may affect their ability to conduct certain routine business transactions. For instance, if your property is damaged and you hire a contractor to make repairs, the clause may bar you from allowing the contractor to collect loss payments directly from your insurer. In addition, some restrictions found in anti-assignment clauses may be overridden by state laws. Below, we’ll explore further what an anti-assignment clause is and how it works.
Definition and Example of an Anti-Assignment Clause
An anti-assignment clause is language found in an insurance policy that forbids the policyholder from assigning their rights and interests under the policy to someone else without the insurer’s consent. The clause is usually found in the policy conditions section.
Alternate name : Assignment clause, Non-assignment clause
An example of an anti-assignment clause is wording contained in the standard Insurance Services Office (ISO) business owners policy (BOP) . You can find it in the Common Policy Conditions (Section III) under the heading “Transfer of Your Rights and Duties Under This Policy.” The clause states that your rights and duties under the policy may not be transferred without the insurer’s written consent. However, if you are an individual named on the policy and you die, your rights will be transferred to your legal representative.
An anti-assignment clause may not include the word “assignment” but instead refer to a transfer of rights under the policy.
Anti-assignment clauses prevent policyholders from transferring their rights under the policy to someone else without the insurer’s permission. The clauses are designed to protect insurers from unknown risks. Insurers evaluate insurance applicants carefully before they agree to provide coverage. They consider an applicant’s business experience, loss history, and other factors to gauge their susceptibility to claims. When an insurer issues a policy, the premium reflects the insurer’s assessment of the applicant’s risks. If the policyholder transfers their rights under the policy to another party, the insurer’s risk increases. This is because the insurer hasn’t had an opportunity to evaluate the new party’s risks.
The following example demonstrates how an anti-assignment clause in an insurance policy can affect a business.
Theresa is the owner of Tasty Tidbits, a pastry shop she operates out of a commercial building she owns. She has insured her business for liability and property under a business owners policy. Theresa decides to take a one-year sabbatical from her business and asks her friend Ted to manage Tasty Treats during her absence. Theresa signs a contract assigning her rights under Tasty Tidbits’ BOP to Ted.
If a loss occurs, Ted may have no right to file a claim or collect benefits under the policy on Tasty Treats’ behalf. The assignment is barred by the anti-assignment clause in the BOP.
Effect of State Laws on Anti-Assignment Clauses
Many states have enacted laws via a statute or court ruling that override anti-assignment clauses in insurance policies. These laws may invalidate all or a portion of a policy’s anti-assignment provision. While the laws vary, many bar pre-loss assignments but permit assignments made after a loss has occurred. Assignments made before any losses have occurred are prohibited because they increase the insurer’s risks. Post-loss assignments don’t increase the insurer’s risks, so they generally are permitted.
Some states prohibit any assignment of benefits made without the insurer’s consent, whether the assignment occurred before or after a loss.
Here's an example of how a state law can impact an anti-assignment clause in an insurance policy. Suppose that Theresa (in the previous scenario) has returned from her sabbatical and is again operating her business. Tasty Treats is located in a state that bars pre-loss assignments but allows assignments made after a loss has occurred.
Late one night, a fire breaks out in the pastry shop and a portion of the building is damaged. Theresa files a property damage claim under her BOP and hires Rapid Reconstruction, a construction company, to repair the building. At the contractor’s suggestion, Theresa assigns her rights to receive benefits for the claim under the BOP to Rapid Reconstruction. Because Theresa has assigned her rights after a loss has occurred, the assignment is permitted by law and should be accepted by Theresa’s insurer.
Key Takeaways
- Many policies purchased by small businesses contain an anti-assignment clause.
- An anti-assignment clause bars the policyholder from assigning their rights and interests under the policy to someone else without the insurer’s consent.
- Many states have a statute or court ruling that overrides anti-assignment clauses in insurance policies.
- State laws vary, but many prohibit pre-loss assignments yet permit assignments made after a loss has occurred.
Canopy Claims. " Business Owners Coverage Form ," Page 53.
Penn State Law Review. " If You Give a Shop a Claim: The Unsustainable Inequity of Pennsylvania’s Unbridled Post-Loss Assignments ."
Stahl, Davies, Sewell, Chavarria & Friend. " Buyers and Sellers Beware - Assignment of Hurricane Claims May Be Invalid in Texas ."
Assignment of Benefits: What It Is, and How It Can Affect your Property Insurance Claim

Table of Contents
What is an Assignment of Benefits?
In the context of insured property claims, an assignment of benefits (AOB) is an agreement between you and a contractor in which you give the contractor your right to insurance payments for a specific scope of work . In exchange, the contractor agrees that it will not seek payment from you for that scope of work, except for the amount of any applicable deductible. In other words, you give part of your insurance claim to your contractor, and your contractor agrees not to collect from you for part of its work.
The most important thing to know about an assignment of benefits is that it puts your contractor in control your claim , at least for their scope of work. Losing that control can significantly affect the direction and outcome of your claim, so you should fully understand the implications of an AOB (sometimes called an assignment of claims or AOC) before signing one.
How Does an Assignment of Benefits Work in Practice?
Let’s say you’re an insured homeowner, and Hurricane Ian significantly damaged your roof. Let’s also assume your homeowner’s policy covers that damage. A roofer, after inspecting your roof and reviewing your insurance policy, might conclude that your insurer is probably going to pay for a roof replacement under your insurance policy. The only problem is that it’s early in the recovery process, and your insurer hasn’t yet stated whether it will pay for the roof replacement proposed by your contractor. So if you want your roof replaced now, you would ordinarily agree to pay your roofer for the replacement, and wait in hopes that your insurer reimburses you for the work. This means that if your insurance company refuses to pay or drags out payment, you’re on the hook to your roofer for the cost of the replacement.
As an alternative to agreeing to pay your roofer for the full cost of the work, you could sign an assignment of benefits for the roof replacement. In this scenario, your roofer owns the part of your insurance claim that pertains to the roof replacement. You might have to pay your roofer for the amount of your deductible, but you probably don’t have to pay them for the rest of the cost of the work. And if your insurance company refuses to pay or drags out payment for the roof replacement, it’s your roofer, and not you, who would be on the hook for that shortfall.
So should you sign an AOB? Not necessarily. Read below to understand the pros and cons of an assignment of benefits.
Are There any Downsides to Signing an Assignment of Benefits?
Yes.
You lose control of your claim . This is the most important factor to understand when considering whether to sign an AOB. An AOB is a formal assignment of your legal rights to payment under your insurance contract. Unless you’re able to cancel the AOB, your contractor will have full control over your claim as it relates to their work.
To explain why that control could matter, let’s go back to the roof replacement example. When you signed the AOB, the scope of work you agreed on was to replace the roof. But you’re not a roofing expert, so you don’t know whether the costs charged or the materials used by the roofer in its statement of work are industry appropriate or not. In most cases, they probably are appropriate, and there’s no problem. But if they’re not – if, for instance, the roofer’s prices are unreasonably high – then the insurer may not approve coverage for the replacement. At that point, the roofer could lower its prices so the insurer approves the work, but it doesn’t have to, because it controls the claim . Instead it could hold up work and threaten to sue your insurer unless it approves the work at the originally proposed price. Now the entire project is insnared in litigation, leaving you in a tough spot with your insurer for your other claims and, most importantly, with an old leaky roof.
Misunderstanding the Scope of Work. Another issue that can arise is that you don’t understand the scope of the assignment of benefits. Contractor estimates and scopes of work are often highly technical documents that can be long on detail but short on clarity. Contractors are experts at reading and writing them. You are not. That difference matters because the extent of your assignment of benefits is based on that technical, difficult-to-understand scope of work. This can lead to situations where your understanding of what you’re authorizing the contractor to do is very different from what you’ve actually authorized in the AOB agreement.
In many cases, it’s not necessary . Many contractors will work with you and your insurer to provide a detailed estimate of their work, and will not begin that work until your insurer has approved coverage for it. This arrangement significantly reduces the risk of you being on the hook for uninsured repairs, without creating any of the potential problems that can occur when you give away your rights to your claim.
Do I have to sign an Assignment of Benefits?
No. You are absolutely not required to sign an AOB if you do not want to.
Are There any Benefits to Signing an Assignment of Benefits?
Potentially, but only if you’ve fully vetted your contractor and your claim involves complicated and technical construction issues that you don’t want to deal with.
First, you must do your homework to fully vet your contractor! Do not just take their word for it or be duped by slick ads. Read reviews, understand their certificate of insurance, know where they’re located, and, if possible, ask for and talk to references. If you’ve determined that the contractor is highly competent at the work they do, is fully insured, and has a good reputation with customers, then that reduces the risk that they’ll abuse their rights to your claim.
Second, if your claim involves complicated reconstruction issues, a reputable contractor may be well equipped to handle the claim and move it forward. If you don’t want to deal with the hassle of handling a complicated claim like this, and you know you have a good contractor, one way to get rid of that hassle is an AOB.
Another way to get rid of the hassle is to try Claimly, the all-in-one claims handling tool that get you results but keeps you in control of your claim.
Can my insurance policy restrict the use of AOBs?
Yes, it’s possible that your Florida insurance policy restricts the use of AOBs, but only if all of the following criteria are met:
- When you selected your coverage, your insurer offered you a different policy with the same coverage, only it did not restrict the right to sign an AOB.
- Your insurer made the restricted policy available at a lower cost than the unrestricted policy.
- If the policy completely prohibits AOBs, then it was made available at a lower cost than any policy partially prohibiting AOBs.
- The policy includes on its face the following notice in 18-point uppercase and boldfaced type:
THIS POLICY DOES NOT ALLOW THE UNRESTRICTED ASSIGNMENT OF POST-LOSS INSURANCE BENEFITS. BY SELECTING THIS POLICY, YOU WAIVE YOUR RIGHT TO FREELY ASSIGN OR TRANSFER THE POST-LOSS PROPERTY INSURANCE BENEFITS AVAILABLE UNDER THIS POLICY TO A THIRD PARTY OR TO OTHERWISE FREELY ENTER INTO AN ASSIGNMENT AGREEMENT AS THE TERM IS DEFINED IN SECTION 627.7153 OF THE FLORIDA STATUTES.
627.7153.
Pro Tip : If you have an electronic copy of your complete insurance policy (not just the declaration page), then search for “policy does not allow the unrestricted assignment” or another phrase from the required language above to see if your policy restricts an AOB. If your policy doesn’t contain this required language, it probably doesn’t restrict AOBs.
Do I have any rights or protections concerning Assignments of Benefits?
Yes, you do. Florida recently enacted laws that protect consumers when dealing with an AOB.
Protections in the AOB Contract
To be enforceable, a Assignments of Benefits must meet all of the following requirements:
- Be in writing and executed by and between you and the contractor.
- Contain a provision that allows you to cancel the assignment agreement without a penalty or fee by submitting a written notice of cancellation signed by the you to the assignee:
- at least 30 days after the date work on the property is scheduled to commence if the assignee has not substantially performed, or
- at least 30 days after the execution of the agreement if the agreement does not contain a commencement date and the assignee has not begun substantial work on the property.
- Contain a provision requiring the assignee to provide a copy of the executed assignment agreement to the insurer within 3 business days after the date on which the assignment agreement is executed or the date on which work begins, whichever is earlier.
- Contain a written, itemized, per-unit cost estimate of the services to be performed by the assignee .
- Relate only to work to be performed by the assignee for services to protect, repair, restore, or replace a dwelling or structure or to mitigate against further damage to such property.
- Contain the following notice in 18-point uppercase and boldfaced type:
YOU ARE AGREEING TO GIVE UP CERTAIN RIGHTS YOU HAVE UNDER YOUR INSURANCE POLICY TO A THIRD PARTY, WHICH MAY RESULT IN LITIGATION AGAINST YOUR INSURER. PLEASE READ AND UNDERSTAND THIS DOCUMENT BEFORE SIGNING IT. YOU HAVE THE RIGHT TO CANCEL THIS AGREEMENT WITHOUT PENALTY WITHIN 14 DAYS AFTER THE DATE THIS AGREEMENT IS EXECUTED, AT LEAST 30 DAYS AFTER THE DATE WORK ON THE PROPERTY IS SCHEDULED TO COMMENCE IF THE ASSIGNEE HAS NOT SUBSTANTIALLY PERFORMED, OR AT LEAST 30 DAYS AFTER THE EXECUTION OF THE AGREEMENT IF THE AGREEMENT DOES NOT CONTAIN A COMMENCEMENT DATE AND THE ASSIGNEE HAS NOT BEGUN SUBSTANTIAL WORK ON THE PROPERTY. HOWEVER, YOU ARE OBLIGATED FOR PAYMENT OF ANY CONTRACTED WORK PERFORMED BEFORE THE AGREEMENT IS RESCINDED. THIS AGREEMENT DOES NOT CHANGE YOUR OBLIGATION TO PERFORM THE DUTIES REQUIRED UNDER YOUR PROPERTY INSURANCE POLICY.
- Contain a provision requiring the assignee to indemnify and hold harmless the assignor from all liabilities, damages, losses, and costs, including, but not limited to, attorney fees.
Contractor Duties
Under Florida law, a contractor (or anyone else) receiving rights to a claim under an AOB:
- Must provide you with accurate and up-to-date revised estimates of the scope of work to be performed as supplemental or additional repairs are required.
- Must perform the work in accordance with accepted industry standards.
- May not seek payment from you exceeding the applicable deductible under the policy unless asked the contractor to perform additional work at the your own expense.
- Must, as a condition precedent to filing suit under the policy, and, if required by the insurer, submit to examinations under oath and recorded statements conducted by the insurer or the insurer’s representative that are reasonably necessary, based on the scope of the work and the complexity of the claim, which examinations and recorded statements must be limited to matters related to the services provided, the cost of the services, and the assignment agreement.
- Must, as a condition precedent to filing suit under the policy, and, if required by the insurer, participate in appraisal or other alternative dispute resolution methods in accordance with the terms of the policy.
- If the contractor is making emergency repairs, the assignment of benefits cannot exceed the greater of $3,000 or 1% of your Coverage A limit.
Recommended Posts
New legislation alert: 2022 changes to florida property insurance laws and how they affect you, what is a public adjuster an overview of this important profession, property coverages in homeowners insurance: everything you need to know..
Brelly’s tools and resources are your secret weapon to getting your insurance claim filed right, moving fast, and paid fully .
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser to improve your experience.
The Policy Assignment workspace displays all the policies available in your environment.
Where You Assign Policies
To create and modify policy assignments, from the left menu, click Configure > Policies , and then click Policy Assignment .
How the Policy Assignment Workspace Works

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The policy assignment can determine the values of parameters for that group of resources at assignment time, making it possible to reuse policy definitions that address the same resource properties with different needs for compliance. Note. For more information on Azure Policy scope, see Understand scope in Azure Policy.
Assignment means a complete transfer of the ownership of the policy to some other person. Usually assignment is done for the purpose of raising a loan from a bank or a financial institution. Assignment is governed by Section 38 of the Insurance Act 1938 in India. Assignment can also be done in favour of a close relative when the policyholder ...
Writing Policy Assignments. Successful policy assignments are focused, well-researched, analytical, organized, and concise. Therefore, it is important to take time to define the issue, understand the context of the issue, and seek out policy alternatives prior to identifying a recommended course of action. Focused Issue.
An overview of the legal principles that apply when assigning an insurance policy or the right to receive the insurance monies due under the policy to a third party. It considers the requirements that must be met for the assignment to be valid and explains the difference between assignment, co-insurance, noting of interest and loss payee clauses.
A collateral assignment of life insurance is a conditional assignment appointing a lender as an assignee of a policy. Essentially, the lender has a claim to some or all of the death benefit until ...
An assignment is a legal process through which policy ownership transfers from an assignor to an assignee. It can be beneficial under multiple circumstances, especially in a financial emergency. Therefore, before you buy a life insurance plan, understand these features since they can help you in the future. In addition, the assignment of a life ...
Assignment of a Life Insurance Policy simply means transfer of rights from one person to another. The policyholder can transfer the rights of his insurance policy to another for various reasons and this process is called Assignment. The person who assigns the policy, i.e. transfers the rights, is called the Assignor and the one to whom the ...
The process of transferring rights of a Life Insurance Policy is called Assignment. There are 2 types of Assignment. Absolute Assignment. Conditional Assignment. Absolute Assignment means complete Transfer of Rights. The person who transfers the rights is called the Assignor and the person to whom the rights are being transferred is called the ...
Assignment of insurance policies and claims. An overview of the legal principles that apply when assigning an insurance policy or the right to receive the insurance monies due under the policy to a third party. It considers the requirements that must be met for the assignment to be valid and explains the difference between assignment, co ...
The term assignment itself means you assign something to someone else. In term life insurance, the assignment of the policy describes the action of assigning legal rights as well as policy ownership to someone else. The person who assigns the policy is known as an Assignor and the person who has been assigned the policy is known as an Assignee.
The assignment may lead to cancellation of the nomination in the policy only when it is done in favour of the insurance company due to a policy loan. Assignment for all insurance plans except for the pension plan and the Married Women's Property Act (MWP), can be done. A policy contract endorsement is required to effect the assignment.
Absolute assignment refers to a policyholder transferring his or her ownership of a policy to another party. That transfer means that all of the coverage within that policy will now go to the newly named party. The original owner of the policy does not have to state his or her reasons for doing so nor does he or she need to stipulate any ...
With collateral assignment of life insurance, ownership of an asset transfers from the borrower to the lender. This transfer only remains in place until the loan is paid in full. In this situation, the transferred asset is your life insurance policy. The goal is only to satisfy your loan obligation. Once that debt is repaid, you'll end the ...
The assignment may lead to cancellation of the nomination in the policy only when it is done in favour of the insurance company due to a policy loan. The assignment applies to all the insurance plans except Pensions Plan and Married Women's Property Act (MWP). The assignment is effected through an endorsement on the policy contract.
Assignment of a life insurance policy may be made by making an endorsement to that effect in the policy document (or) by executing a separate ' Assignment Deed '. In case of assignment deed, stamp duty has to be paid. An Assignment should be signed by the assignor and attested by at least one witness.
The creation of assignment of life insurance policies is provided for, under Section 38 of the Insurance Act, 1938. Endorsement has to be made on the policy or on a separate document, signed by assignor (or agent authorized by him), attested by at least one witness specifying the fact of the assignment. The assignment is complete and effectual ...
Collateral assignment of life insurance is an arrangement where you agree to give a lender the first claim to the payout from your life insurance policy. This allows your life insurance to serve as the collateral that many loans — especially small business loans or Small Business Administration (SBA) loans — require before they can lend you money you need.
The endorsement is the Assignment of Title Insurance Policy Endorsement (ATG Form 2089), which carries a special risk premium to ATG of $200. For insureds in the process of conveying their property to an estate planning vehicle, this endorsement may be issued at the time of the conveyance to ensure that the coverage under an original ATG Owner ...
Post-loss assignments, on the other hand, take place after the insurer's obligations under its policy have become fixed by the occurrence of a covered loss, thus the risk factors applicable to ...
An anti-assignment clause is a provision in an insurance policy that bars the policyholder from transferring their rights under the policy to another party. The clause prohibits the insured from authorizing someone else to file claims, make changes, or take other actions under the policy.
this policy does not allow the unrestricted assignment of post-loss insurance benefits. BY SELECTING THIS POLICY, YOU WAIVE YOUR RIGHT TO FREELY ASSIGN OR TRANSFER THE POST-LOSS PROPERTY INSURANCE BENEFITS AVAILABLE UNDER THIS POLICY TO A THIRD PARTY OR TO OTHERWISE FREELY ENTER INTO AN ASSIGNMENT AGREEMENT AS THE TERM IS DEFINED IN SECTION 627 ...
Type the name of the policy in the search box to filter by policy name. Policies: All the policies available in your environment are displayed in the left pane. Expand the policy card to view the priority, direct assignments, custom groups, affected objects, default assignment, and hierarchy of the policy.
The U.S. Coast Guard Academy held 55 Second Class cadets accountable after cadets distributed answers for two separate homework assignments via electronic means, in clear violation of Academy policy. The details of each cadet's involvement in this unauthorized collaboration were investigated and reviewed during a series of cadet disciplinary ...
teaching ChatGPT best practices in her writing workshop class at the University of Lynchburg in Virginia, said she sees the advantages for teachers using AI tools but takes issue with how it can ...
Join us at Texas' breakout politics and policy event as we dig into the 2024 elections, state and national politics, the state of democracy, and so much more. When tickets go on sale this spring ...