
- Search Search Search …
- Search Search …

Best Careers for Problem Solving: Top Opportunities for Critical Thinkers

Problem-solving is a highly sought-after skill in today’s job market, as it plays a critical role in finding solutions to complex problems and driving innovation across various industries. Whether it’s science, technology, education, or healthcare, professionals with a knack for identifying issues and developing effective strategies to address them are invaluable assets in any organization. By pursuing a career that aligns with their natural strengths, individuals with strong problem-solving skills can have a fulfilling and successful career while making a significant impact in their chosen field.
To effectively navigate and excel in these careers, professionals must be able to adapt their thinking approach, utilize various methods and tools, and stay current with education and training opportunities. By having a solid foundation in problem-solving skills, an individual allows themselves to access a wide array of specific careers that not only demand these abilities but also provide a sense of accomplishment and satisfaction. In various industries, management and decision-making skills play an essential role in maximizing problem-solving capabilities and ensuring sustainable growth.
Key Takeaways
- Problem-solving skills are vital in various industries and can lead to fulfilling and successful careers.
- Continual education and training in problem-solving are crucial for personal growth and professional success in these fields.
- Management and decision-making skills play a significant role in maximizing one’s problem-solving capabilities and success in careers for problem solvers.
Understanding Problem Solving

Problem solving is a critical skill in many careers, as it involves the ability to identify, analyze, and resolve issues or challenges that one may encounter in their work. Problem-solving skills are closely related to analytical skills and analytical thinking, both of which involve breaking down complex information into simpler, more manageable components. This process often includes brainstorming, creativity, teamwork, and solid decision-making abilities.
In many job roles, employees are expected to exhibit strong problem-solving skills, as they contribute significantly to the company’s overall success. These skills enable them to tackle various challenges and develop innovative solutions. One key aspect of problem solving is the ability to think critically in order to assess the situation and determine the best course of action. This may involve weighing the pros and cons of different options, understanding the risks involved, and making a decision that will yield the best possible outcome.
Brainstorming, an essential component of problem-solving, involves generating multiple ideas in response to a given issue. This requires a high level of creativity and often benefits from collaboration with coworkers or team members. Through open and honest communication, team members can harness their collective creative power to explore a wider range of possibilities and potential solutions.
Strong problem solvers also exhibit flexibility in their thinking. They are open to various perspectives and approaches, and can adapt their strategies based on new information or changes in circumstances. This level of adaptability is essential for navigating the rapidly evolving workspaces of today, where new challenges continually emerge.
Moreover, effective problem solving often involves collaboration and teamwork. Working together with others enables individuals to leverage diverse skills and perspectives, which can lead to more well-rounded and innovative solutions. By embracing collaboration, professionals can also foster a productive work environment that encourages open communication, mutual respect, and shared responsibility for achieving successful outcomes.
In summary, problem-solving skills are crucial for success in many careers, and involve a range of abilities, including analytical thinking, brainstorming, creativity, teamwork, and decision-making. A strong problem solver is adaptive, open to new perspectives, and capable of working effectively with others, all of which contribute to their ability to navigate complex challenges and find viable solutions.
Role of Problem Solving in Careers
Problem solving is a crucial skill across a wide array of careers, as it enables professionals to tackle challenges, enhance efficiency, and drive innovation. Various occupations require a strong foundation in problem solving, and individuals who excel in this area enjoy a more successful and fulfilling work life.
Careers in actuarial science demand a keen ability to analyze data and develop models to predict future events. Actuaries play a significant role in the insurance and finance industries, where they help businesses navigate complex risk management scenarios. This occupation combines strong problem-solving, mathematical, and statistical skills, making it ideal for individuals who are critical thinkers and possess quantitative aptitude.
Another career that values problem-solving expertise is that of a judge . Judges are responsible for interpreting laws, assessing evidence presented in trials, and making impartial decisions. They use their problem-solving abilities to navigate complex legal disputes and ensure a just outcome for all parties involved.
In the field of computer science , problem-solving skills are critical to success. This includes roles such as software developers, who are responsible for designing and coding computer programs, as well as project managers, who oversee the development process. These individuals use their problem-solving abilities to troubleshoot issues, optimize system performance, and create innovative solutions to meet client needs.
Executives and chief executives are also required to possess strong problem-solving capabilities. As leaders of organizations, they face various challenges, from managing resources and personnel to developing strategic plans for growth. With excellent problem-solving skills, executives can make well-informed decisions, successfully manage crises, and foster a culture of continuous improvement.
Professionals in other fields, such as accounting , chemistry , law , radiology , financial analysis , and education administration , also depend on problem-solving skills to excel in their roles. Whether they are diagnosing medical conditions, crafting legal arguments, or managing budgets, these individuals apply critical thinking and problem-solving techniques to navigate complex situations and achieve success.
Several other careers, including respiratory therapy technicians , social and community-service managers , magistrates , ophthalmologists , anesthesiologists , detectives , statisticians , and air traffic controllers , require problem-solving as a core competency. In each of these professions, individuals rely on their critical thinking skills and practical problem-solving approach to address challenges effectively.
In conclusion, problem-solving is an essential element for success across various careers and industries. Professionals with strong problem-solving abilities can contribute positively to their organizations, innovate solutions, and drive growth.
Problem Solving in Science and Mathematics
In the realm of science and mathematics, problem solvers are in high demand. Professionals in this field typically possess strong analytical and critical thinking skills . They are adept at finding solutions to complex problems and overcoming challenges.
Engineering is one such career path that emphasizes problem solving. Engineers design, build, and maintain structures, systems, and devices to solve real-world issues. They apply mathematical and scientific principles to their work, and their goal is to improve the quality and efficiency of products, systems, and services. This field includes various branches, such as civil, electrical, and mechanical engineering, providing a diverse range of opportunities for problem solvers.
Mathematics is another field where problem-solving skills are highly valued. Careers in mathematics demand strong logical and analytical abilities to solve complex equations and models. Actuaries, for example, focus on assessing risk and uncertainty in various financial contexts. They evaluate the potential outcomes of different scenarios and make data-driven decisions to minimize risks. This profession is ideal for those who enjoy tackling challenges, and combining mathematical and statistical knowledge with practical applications.
The sciences offer multiple avenues for problem solvers, with chemists being particularly notable in this regard. Chemists conduct research and experimentation to develop new substances and materials, find solutions to environmental problems, and improve existing products. Their work involves analyzing data, synthesizing compounds, and assessing chemical reactions. These professionals often collaborate with colleagues from other disciplines, combining their expertise to address complex issues.
Overall, careers in science, engineering, and mathematics are ideally suited for individuals who enjoy problem solving. These fields offer a wide range of opportunities for critical thinkers to apply their skills and contribute to advancements in various industries. By pursuing a career in any of these domains, problem solvers can combine their passions with their professional aspirations, making a meaningful impact in the world around them.
Methods and Tools for Problem Solving
Effective problem-solving is a highly sought-after skill in today’s job market. Employees with strong problem-solving skills tend to be more productive, creative, and capable of working well in teams. There are several methods and tools available to help individuals and teams develop their problem-solving abilities and tackle complex issues.
The first step in any problem-solving process is to accurately define the problem. This involves gathering and analyzing information to identify the root cause of the issue. Once the problem is clearly defined, the next step is to approach it using various strategies and techniques.
Brainstorming is a popular technique for generating ideas and uncovering potential solutions. It encourages creativity by allowing individuals to freely share their thoughts and ideas without judgement. It is important for teams to create a comfortable environment where everyone feels encouraged to contribute.
For a more structured approach, consider using the “Six Thinking Hats” method. This technique, developed by Dr. Edward de Bono, encourages participants to consider various perspectives by wearing different “hats.” Each hat represents a distinct mode of thinking, such as analytical, creative, or emotional thinking. By exploring the problem from multiple angles, the team can develop a more comprehensive understanding and devise effective solutions.
In situations where data analysis is crucial, tools like root cause analysis, Pareto charts, or fishbone diagrams can be helpful. These tools allow teams to systematically analyze data and identify trends, patterns, or anomalies that may contribute to the problem.
Training is essential in developing strong problem-solving skills. Regularly investing in workshops, seminars, or online courses can help individuals stay up-to-date with the latest problem-solving strategies and tools. Additionally, encouraging a culture of learning and collaboration in the workplace can lead to more efficient problem-solving and a stronger team dynamic.
To conclude, there are numerous methods and tools available for problem-solving. The key is to identify the most appropriate strategy for the problem at hand, combining creativity with analytical thinking. With proper training and a collaborative mindset, individuals and teams can greatly enhance their problem-solving abilities, making them valuable assets in any workplace.
Significance of Education and Training
The significance of education and training in the realm of problem-solving careers cannot be overstated. Pursuing a career in this field generally requires a solid academic foundation along with specialized training to hone one’s skills. Educational administrators, for example, play a crucial role in shaping the education system and addressing issues related to equity and quality of education. 1
Education and training can be viewed as a fundamental stepping-stone in preparing individuals for a successful career in problem-solving. Academic backgrounds ranging from engineering and mathematics to social sciences and management provide diverse perspectives and tools for solving complex real-world problems. Furthermore, specialized training equips individuals with practical knowledge and technical expertise, making them more effective problem solvers in their respective fields.
The US Department of Labor highlights the importance of education and training in problem-solving careers by stating that higher-level positions often demand a stronger academic background, along with specialized training and certifications. 2 This demonstrates the correlation between proper education, training, and career success in problem-solving-based fields.
In conclusion, the importance of education and training in problem-solving careers should not be overlooked. A strong academic background, combined with practical training and experience, enables individuals to thrive in their chosen fields. Educational administrators and other key stakeholders play an essential role in shaping the education system and ensuring equitable access to valuable resources and training opportunities.
Using Occupational Information for Career Guidance
When seeking the best careers for problem-solving, one valuable resource is the Occupational Information Network (O*NET) . O*NET is a comprehensive database created by the US Department of Labor that compiles detailed information on hundreds of occupations. This network assists individuals in making informed decisions about their career paths based on their problem-solving skills and interests.
The O*NET database contains information on various aspects of each occupation, including required skills, knowledge, abilities, and job tasks. By utilizing this information, individuals can match their strengths in critical thinking, analysis, and creativity to suitable career opportunities.
Some of the careers for problem solvers identified on O*NET include positions in engineering, information technology, and the sciences. However, it’s important to recognize that there is a wide range of occupations that require two years or less of training and still utilize problem-solving skills, such as construction carpenters, computer user support specialists, and environmental engineering technicians.
While exploring O*NET, users can also examine related occupations and industries, providing further insight into potential career paths. By evaluating various aspects of each occupation and considering the required education and training, individuals can make informed decisions about pursuing a career that aligns with their problem-solving abilities.
Remember to use the O*NET database as a starting point for career guidance. It’s essential to do additional research, gather information from professionals working in the field, and consider personal preferences and goals when deciding on the best career path. Making use of the Occupational Information Network can lead to a fulfilling career that harnesses one’s natural problem-solving skills and abilities.
Specific Careers for Problem Solvers
If you have a knack for solving complicated issues and enjoy finding solutions to challenging tasks, then a career in problem-solving could be the ideal path for you. There are numerous professions that focus on analytical thinking and technical expertise, offering unique and exciting opportunities for those who thrive in such environments. Here, we will discuss some of the best careers for problem solvers across various fields.
Actuaries , for instance, are tasked with assessing and analyzing financial risks for insurance companies, and making data-driven decisions based on their calculations. Actuaries utilize their analytical skills and statistical knowledge on a daily basis, making it a natural fit for problem solvers.
In the legal realm, both judges and lawyers play critical roles in addressing complex disputes and resolving conflicts. Judges are responsible for impartially interpreting the law, while lawyers work to resolve their clients’ legal issues by navigating through intricate laws and regulations. Both professions demand strong analytical thinking and problem-solving abilities.
Computer science is another field where problem-solving skills are highly valued. Computer scientists develop algorithms, build software, and tackle challenges in artificial intelligence and machine learning. Similarly, software developers combine their technical expertise with creativity to design and create innovative solutions for various problems.
Other careers in the science field, such as chemists and statisticians , also involve problem-solving skills as they conduct research, analyze data, and develop models. Radiologists – who interpret medical imagery and diagnose diseases – and neurologists – who diagnose and treat neurological disorders – are examples of problem-solving careers in the medical field.
Financial analysts and accountants are essential in the world of business, as they are responsible for analyzing financial data and providing valuable advice on how to allocate resources and make sound decisions. Strong analytical skills are crucial for these roles.
Careers such as detective and air traffic controller involve keeping people safe by applying problem-solving abilities in high-stress situations. Detectives piece together clues and analyze evidence to resolve crimes, whereas air traffic controllers manage flight routes and prevent the likelihood of collisions.
In the realm of management, project managers and logistics managers tackle complex challenges by organizing resources, managing timelines, and ensuring smooth coordination of operations. Successful management professionals exhibit strong problem-solving skills, which are essential in navigating various scenarios and achieving goals.
Finally, chief executives are responsible for making high-level decisions for their organizations. They must have a strong grasp on the business landscape, innovative ideas, and excellent problem-solving abilities to lead their companies successfully through uncertain times.
It’s evident that there’s no shortage of problem-solving careers spanning a wide array of industries. Those with natural analytical thinking and a passion for resolving challenges will likely excel in these professions and find a fulfilling career path.

Importance of Management and Decision-Making Skills
In today’s competitive business world, management and decision-making skills play a crucial role in the success of an organization. For professionals like chief executives and project managers, these skills are essential to effectively handle various situations and challenges that arise in the workplace.
One of the primary responsibilities of managers and executives is making decisions . They need to determine the best course of action to achieve the organization’s objectives while considering various factors such as resources, constraints, and uncertainties. By making well-informed decisions, they can drive innovation, productivity, and growth.
In the context of project management , problem-solving and decision-making are intertwined. Project managers are responsible for planning, executing, and closing projects, which requires assessing risks, allocating resources, and addressing unexpected challenges. Effective problem-solving enables them to find creative solutions and make timely decisions that can positively impact the project’s outcome.
Moreover, decision-making in management often involves collaboration and teamwork. Managers need to communicate their vision and goals effectively, listen to inputs from team members, and be open to different perspectives and ideas . By fostering a collaborative environment, they can harness the collective intelligence of the team and achieve better results.
In conclusion, management and decision-making skills are essential in a variety of career paths, including chief executives and project managers. These professionals must demonstrate the ability to navigate complex situations, make well-informed choices, and collaborate effectively with their teams. By cultivating these skills, individuals can become successful leaders who drive positive change and growth in their organizations.
- https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10833-021-09437-z ↩
- https://www.bls.gov/careeroutlook/2014/spring/art02.pdf ↩
You may also like
Mastering Your Thought Process Using Critical Thinking Frameworks
People live their days dealing with all sorts of problems, from the awfully mundane to the considerably urgent. Oftentimes, a sound decision-making […]

Common Critical Thinking Fallacies
Critical thinking is the process of reaching a decision or judgment by analyzing, evaluating, and reasoning with facts and data presented. However, […]

Critical Thinking for Self-Improvement: A Guide to Unlocking Your Potential
Critical thinking plays a significant role in self-improvement as it allows individuals to analyze information, question assumptions, and make informed decisions. By […]

Critical Thinking Questions for your Boyfriend
There’s no denying that romantic relationships thrive on good communication. So what better way to communicate with your partner than with some […]
Filter by Keywords
Software Developers, Lawyers, and 11 Other Occupations That Demand Frequent Problem-Solving
May 4, 2023
Start using ClickUp today
- Manage all your work in one place
- Collaborate with your team
- Use ClickUp for FREE—forever
Only about 14% of civilian workers have to solve problems on a daily basis, according to the Bureau of Labor Statistics . But some jobs are all about problem-solving.
Looking at the BLS 2022 data, ClickUp found that software developers, executives, and lawyers are among the top 13 jobs that demand the most frequent problem-solving. Occupations on the list are ranked by the estimated percentage of workers in each job who had to solve problems more than once per day.
Over 100 jobs were reviewed in the analysis, and only those where more than half of the workers problem-solved multiple times daily made the rankings. Nearly half of the jobs on the list involve management responsibilities.
Management positions come with many problem-solving requirements because of the need to oversee people and processes; define goals and break them down into smaller, assignable tasks; and make resource management decisions based on theory and data.
Employers value problem-solving in the workplace because workers with these skills are better able to overcome challenges independently, suggest new ideas and improve processes , and save the company and its customers time and money.
Focusing on and developing advanced, nuanced, and quick-reaction problem-solving skills might even help insulate, to a degree, some knowledge-based professionals from the most disruptive effects of artificial intelligence and automation technologies.
The MIT Sloan Management Review found the most likely skills to be automated are those that can be “standardized and codified.” The research noted that tasks requiring physical or real-time resolution typically had lower automation rates. That was due to the fact that creating tools that can handle the unpredictability of those tasks is either too expensive, involves too much work, or may not yet be technologically achievable.
Problem-solving is a skill that can be practiced and honed. There is a wide array of literature and coursework available for learning established methods of problem-solving, with specialties in topics like parallel thinking, decomposition, research, and analysis. Even practicing word and logic puzzles as a leisure activity can help hone problem-solving skills.
A COMPLETE GUIDE TO RESOURCE ALLOCATION Understand the ins and outs of resource allocation to maximize productivity and efficiency with this handy guide.
13. Electrical engineers
12. transportation, storage, and distribution managers, 11. computer and information systems managers, 10. architectural and engineering managers, 9. k-12 education administrators, 8. natural sciences managers, 7. software developers, 6. physicists, 5. chief executives, 4. nurse practitioners, 3. personal financial advisors, 1. podiatrists, enhance your problem-solving skills and boost your management efficiency with clickup.
- Share of workers who problem-solve more than once per day : 51.7%
- Nationwide employment : 186,020 (1.32 per 1,000 jobs)
Electrical engineers design, develop, test, and maintain electrical systems and components. They may identify problems, design circuitry and other parts, and create prototypes to test their solutions. And they can encounter surprises.
For instance, in 1945, Percy Lebaron Spencer, an electrical engineer for Raytheon, was working on radar equipment and noticed a candy bar in his pocket melted. Applying critical thinking and problem-solving skills, he devised a series of tests, observations, and experiments, ultimately inventing the microwave oven.
Hands-on experience and professional development help electrical engineers develop their analytical and critical thinking skills. Participating in professional associations can also assist in the development of their communication and teamwork abilities, allowing them to collaborate effectively with their colleagues and clients .

- Share of workers who problem-solve more than once per day : 52.6%
- Nationwide employment : 144,640 (1.027 per 1,000 jobs)
Transportation, storage, and distribution managers are involved in the planning, directing, and coordinating of transportation, storage, and distribution activities.
These logistics professionals must organize and manage the work of subordinates, effectively use analytical and inventory software, evaluate and act on data and reports, and communicate and collaborate with other departments.
The COVID-19 pandemic has been a nonstop series of problems to solve for transportation, storage, and distribution managers, who have had to deal with demand spikes, driver shortages, and soaring warehouse costs. Now rising inflation and cooling demand are going to send their own series of problems through the pipeline in the reverse direction.
Staying on top of important data, such as changing regulations, weather, software innovations, and tariffs are some of the steps transportation, storage, and distribution managers take to be better prepared to problem-solve. Obtaining certificates and pursuing coursework in supply chain management and other related fields of study are also beneficial for practicing and developing key problem-solving skills.

- Share of workers who problem-solve more than once per day : 54.0%
- Nationwide employment : 485,190 (3.444 per 1,000 jobs)
Computer and information systems managers are responsible for the planning and coordinating of computer-related activities within their organization. High levels of technical expertise, as well as people management skills, are required to be effective.
Duties for computer and information systems managers can include managing all of the organization’s personnel who are relevant to its computer systems, as well as consulting with end users and stakeholders to ensure computing plans align with organizational goals.
Staying current with the latest research and technology is an important step in preparation for becoming a better problem-solver as a computer and information system manager so that you are up to speed on current best practices when it is time to make or advise a decision.
Another way to improve problem-solving skills is to hold routine meetings and solicit team feedback as a way to work on communication skills and ensure expectations and issues are being clearly understood and acted on.

- Share of workers who problem-solve more than once per day : 54.6%
- Nationwide employment : 187,100 (1.328 per 1,000 jobs)
Architectural and engineering managers plan, direct, and coordinate activities in the fields of architecture and engineering, according to the BLS Occupational Outlook Handbook . For instance, they might oversee a construction and renovation project, develop and present project proposals and bids, and oversee the recruiting of staff for design and engineering teams.
Architectural and engineering managers need to be able to effectively lead and inspire their teams. They must also strictly adhere to project deadlines and exhibit superior written and oral communication skills, all of which require advanced problem-solving abilities.
To be better prepared as a problem-solver, architectural and engineering managers attend design showcases to examine the work of other professionals, take advantage of continuing education opportunities, and seize opportunities to gain further field experience.
Bonus: Project Management Software for Engineering
SOFTWARE FOR MANAGING YOUR ARCHITECTURAL PROJECTS Discover the right project management software for architects to ensure smooth operation of your projects.

- Share of workers who problem-solve more than once per day : 54.8%
- Nationwide employment : 274,710 (1.95 per 1,000 jobs)
K-12 education administrators plan, direct, and coordinate the academic, administrative, or auxiliary activities of kindergarten, elementary, and secondary schools, according to the BLS Occupational Outlook Handbook.
Whether managing teachers, helping students navigate curriculum challenges, or overseeing facility improvements, elementary administrators are constantly solving problems. And they’re expected to create “accurate, rapid, effective and accepted solutions,” depending on their visions “and school development programs,” according to a 2010 study .
Being an effective school administrator requires practice in building positive relationships, putting colleagues and families first, and using strategies to diffuse conflict and stressful situations.
Participating in research opportunities, attending seminars and classes, and joining professional educational groups are all ways to stay current with the latest problem-solving tools and trends in the field.

- Share of workers who problem-solve more than once per day : 56.4%
- Nationwide employment : 74,760 (0.531 per 1,000 jobs)
Natural sciences managers are involved in supervising the work of scientists, including chemists, physicists, and biologists, according to the BLS Occupational Outlook Handbook. These workers are in charge of activities that relate to research and development and coordinate testing, quality control, and production.
Natural sciences managers must use their highly developed research and scientific observation skills, and harness those of their direct reports, to uncover answers to complex technical issues.
Workers in this role are expected to perform functions like developing strategies and research projects; interviewing, hiring, and directing scientists, technicians, and support personnel; and administrative duties.
Because science moves so rapidly, natural science managers must constantly read and stay current with the latest developments so they have the knowledge and latest best practices to apply to their work. Attending health fairs, publishing papers, and working with a scientific mentor are some ways natural sciences managers build the skills and knowledge needed to be successful problem-solvers.

- Share of workers who problem-solve more than once per day : 58.4%
- Nationwide employment : 1,364,180 (9.683 per 1,000 jobs)
Software developers are in charge of analyzing users’ needs and designing and developing software to meet those needs, according to the BLS Occupational Outlook Handbook. They design every part of an application or system and coordinate how each will work together.
Computer science itself is the study of problem-solving, so problem-solving skills are baked into all aspects of being a software developer. When designing and implementing code, troubleshooting and bug squashing, and communicating accurately and effectively within and between teams, software developers are problem-solving mavens.
Software developers hone their problem-solving skills through on-the-job experience, obtaining additional certifications and credentials, and staying current with rapid industry developments. Outside of their core job functions, they might contribute code to open source projects, participate in coding challenges and hackathons, or volunteer their time with nonprofit groups focused on building software solutions to civic challenges, such as Code for America.
EVERYTHING YOU NEED TO KNOW ABOUT AGILE Explore this hub of articles, guides and blueprints to understand Agile methodologies for software teams .

- Share of workers who problem-solve more than once per day : 60.3%
- Nationwide employment : 20,020 (0.142 per 1,000 jobs)
Physicists are scientists who study the interactions of matter and energy. Whether tackling climate change, hunting for new subatomic particles, or figuring out how to make a chocolate cake mix rise faster, physicists are solving problems all around us.
From the epic to the everyday, physicists use step-by-step approaches, apply past solutions to new problems, diagram procedures, and verify results.
Physicists prepare themselves to be problem-solvers by drilling into the fundamentals of their field, learning and practicing problem-solving strategies, and participating in professional organizations. They may also tackle physics word problems and brain teasers in their free time and then share solutions and strategies with colleagues.

- Share of workers who problem-solve more than once per day : 61.8%
- Nationwide employment : 200,480 (1.423 per 1,000 jobs)
Top executives plan strategies and policies to ensure an organization meets its goals, according to the BLS, which includes coordinating and directing the company and organization activities.
Recognizing gaps between where an organization is and its goals—and devising and implementing solutions, often in real time—is core to the role of an executive.
Putting structures in place to develop new products, overcoming budget shortfalls, keeping pace with the competition, navigating regulations, and managing the personalities and career growth of staff are all types of problems executives need to solve.
Executives take training and development programs to improve their problem-solving and management skills. They may volunteer their management expertise to a nonprofit or become a mentor to a more junior manager. Executives attend conferences and workshops and stay current on their industry news to expand their skills, including problem-solving.

- Share of workers who problem-solve more than once per day : 62.4%
- Nationwide employment : 234,690 (1.666 per 1,000 jobs)
Nurse practitioners diagnose and treat acute, episodic, or chronic illness, independently or as part of a health care team, according to the BLS, and may focus on health promotion and disease prevention. They may be involved with ordering, performing, or interpreting lab work and X-rays, and can prescribe medication.
Nurses are called upon to apply their diverse knowledge to handle various situations during their shifts in a constantly changing environment. They might apply a solution from one set of patients to another.
For example, one nurse described how a pain medication that worked for diabetic patients with neuropathy helped an amputation patient suffering from deep nerve pain who wasn’t responding well to traditional opioids.
Health care providers who stay on top of the most recent research report better patient outcomes. Nurse practitioners can use an evidence-based approach to apply a systematic process to review, analyze, and translate to the real world the latest health care and scientific evidence. Training, conferences, and social media also provide other sources of information to sharpen skills and knowledge.

- Share of workers who problem-solve more than once per day : 67.1%
- Nationwide employment : 263,030 (1.867 per 1,000 jobs)
Personal financial advisors assess their clients’ financial needs and advise them on investment decisions and navigating tax laws and insurance, according to the BLS. They help their clients with short- and long-term goals, like saving for college and retirement.
Saving for retirement in an environment with rising interest rates, coping with soaring college costs, and deciding what to do with the proceeds of a house sale are some of the issues that might come up for the clients of a personal financial advisor, which require tailored solutions.
In each case, personal financial advisors define their client’s problems, identify the causes, explore and decide on solutions , and implement them, according to Vesticor Advisors Managing Director Michael Sciortino.
Certifications—like certified financial planner, chartered financial analyst, or chartered financial consultant—or professional development courses can improve personal financial advisors’ hard skills and provide structured opportunities to learn and apply proven problem-solving strategies.
Participating in a pro bono program through a professional organization allows an advisor to apply their knowledge to help individuals, families, and communities in need while getting additional opportunities to practice tackling new and pressing problems.

- Share of workers who problem-solve more than once per day : 68.1%
- Nationwide employment : 681,010 (4.834 per 1,000 jobs)
Advising and representing individuals, businesses, and government agencies on legal issues and disputes are some of the main obligations of lawyers.
Lawyers must research and analyze legal problems and provide advice to their clients. They evaluate all manner of legal decisions—such as weighing the pros and cons of filing for a judgment versus offering a settlement in a case—negotiate contracts, and respond to cease and desist letters. Problem-solving is so key to the legal profession that it was placed at the top of an American Bar Association’s report on fundamental skills for lawyers, even before legal analysis.
Lawyers prepare to be problem-solvers by being active listeners, zeroing in on the details of a case, and reading up on the latest cases and legal strategies. Specialized problem-solving workshops, exercises, role-plays, and simulations— sometimes organized through professional societies —are other ways lawyers can develop their skills.
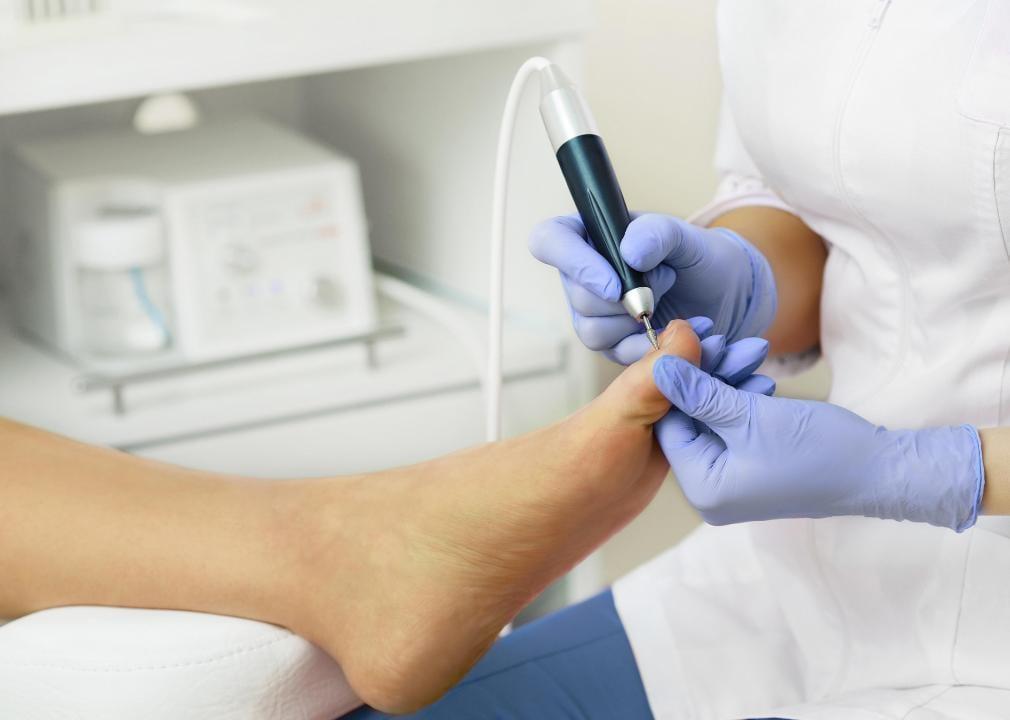
- Share of workers who problem-solve more than once per day : 85.5%
- Nationwide employment : 8,840 (0.063 per 1,000 jobs)
Podiatrists provide medical and surgical care for people with foot, ankle, and lower leg problems, according to the BLS Occupational Outlook Handbook.
Patients come to their podiatrists presenting problems such as heel pain, bunions, ingrown toenails, and issues with gait and walking. Podiatrists listen to and diagnose the issue and prescribe solutions depending on what’s needed, such as orthotics, medical creams, or physical therapy.
Podiatrists sharpen their problem-solving skills by practicing and learning new and established methodologies for diagnosis and attending training sessions and conferences. They also practice regularly and seek feedback from patients and colleagues to improve their techniques and patient outcomes.
In today’s fast-paced business world, being an effective problem-solver is crucial for any role, especially management or leadership. Fortunately, there are various tools available to help you streamline your work and manage your tasks efficiently.
ClickUp, in particular, is an exceptional project management tool that can help you stay organized and achieve your goals. With ClickUp, you can easily track your progress, collaborate with your team members, and take corrective action whenever necessary.
Give ClickUp a try for free and take your management efficiency to the next level!
Guest Writer: Ben Popken

Receive the latest WriteClick Newsletter updates.
Thanks for subscribing to our blog!
Please enter a valid email
- Free training & 24-hour support
- Serious about security & privacy
- 99.99% uptime the last 12 months

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Problem-solving jobs are ideal for critical thinkers who enjoy analyzing information and overcoming challenges. Many industries offer jobs that involve solving …
If you have a knack for solving complicated issues and enjoy finding solutions to challenging tasks, then a career in problem-solving could be the ideal path for you. There are numerous professions that focus on analytical thinking and …
Are you a critical thinker or a mastermind problem solver? Love unraveling complex situations and finding solutions? You’re in luck! Today, we’re delving into a list of dream jobs for thinkers …
In this article, we define complex problem-solving, discuss the key differences between complex and simple problem solving, talk about the necessary steps to solve …
Love puzzling out complex challenges? Then, you’re in for a thrill! Today, we’re exploring a list of ideal jobs for problem solvers. From operations analysts to data scientists. Each one, is a perfect fit for those who thrive on complexity …
But some jobs are all about problem-solving. Looking at the BLS 2022 data, ClickUp found that software developers, executives, and lawyers are among the top 13 jobs that demand the most frequent problem-solving.
Problem-Solving: Adept at solving complex problems and thinking outside the box to resolve challenging cases. Career Path and Growth: Detectives play a critical role in the criminal justice system.
50% of all employees will need reskilling by 2025, as adoption of technology increases, according the the World Economic Forum's Future of Jobs Report. Critical thinking and problem-solving top the list of skills employers …