- Privacy Policy

Home » Ethical Considerations – Types, Examples and Writing Guide

Ethical Considerations – Types, Examples and Writing Guide
Table of Contents

Ethical Considerations
Ethical considerations in research refer to the principles and guidelines that researchers must follow to ensure that their studies are conducted in an ethical and responsible manner. These considerations are designed to protect the rights, safety, and well-being of research participants, as well as the integrity and credibility of the research itself
Some of the key ethical considerations in research include:
- Informed consent: Researchers must obtain informed consent from study participants, which means they must inform participants about the study’s purpose, procedures, risks, benefits, and their right to withdraw at any time.
- Privacy and confidentiality : Researchers must ensure that participants’ privacy and confidentiality are protected. This means that personal information should be kept confidential and not shared without the participant’s consent.
- Harm reduction : Researchers must ensure that the study does not harm the participants physically or psychologically. They must take steps to minimize the risks associated with the study.
- Fairness and equity : Researchers must ensure that the study does not discriminate against any particular group or individual. They should treat all participants equally and fairly.
- Use of deception: Researchers must use deception only if it is necessary to achieve the study’s objectives. They must inform participants of the deception as soon as possible.
- Use of vulnerable populations : Researchers must be especially cautious when working with vulnerable populations, such as children, pregnant women, prisoners, and individuals with cognitive or intellectual disabilities.
- Conflict of interest : Researchers must disclose any potential conflicts of interest that may affect the study’s integrity. This includes financial or personal relationships that could influence the study’s results.
- Data manipulation: Researchers must not manipulate data to support a particular hypothesis or agenda. They should report the results of the study objectively, even if the findings are not consistent with their expectations.
- Intellectual property: Researchers must respect intellectual property rights and give credit to previous studies and research.
- Cultural sensitivity : Researchers must be sensitive to the cultural norms and beliefs of the participants. They should avoid imposing their values and beliefs on the participants and should be respectful of their cultural practices.
Types of Ethical Considerations
Types of Ethical Considerations are as follows:
Research Ethics:
This includes ethical principles and guidelines that govern research involving human or animal subjects, ensuring that the research is conducted in an ethical and responsible manner.
Business Ethics :
This refers to ethical principles and standards that guide business practices and decision-making, such as transparency, honesty, fairness, and social responsibility.
Medical Ethics :
This refers to ethical principles and standards that govern the practice of medicine, including the duty to protect patient autonomy, informed consent, confidentiality, and non-maleficence.
Environmental Ethics :
This involves ethical principles and values that guide our interactions with the natural world, including the obligation to protect the environment, minimize harm, and promote sustainability.
Legal Ethics
This involves ethical principles and standards that guide the conduct of legal professionals, including issues such as confidentiality, conflicts of interest, and professional competence.
Social Ethics
This involves ethical principles and values that guide our interactions with other individuals and society as a whole, including issues such as justice, fairness, and human rights.
Information Ethics
This involves ethical principles and values that govern the use and dissemination of information, including issues such as privacy, accuracy, and intellectual property.
Cultural Ethics
This involves ethical principles and values that govern the relationship between different cultures and communities, including issues such as respect for diversity, cultural sensitivity, and inclusivity.
Technological Ethics
This refers to ethical principles and guidelines that govern the development, use, and impact of technology, including issues such as privacy, security, and social responsibility.
Journalism Ethics
This involves ethical principles and standards that guide the practice of journalism, including issues such as accuracy, fairness, and the public interest.
Educational Ethics
This refers to ethical principles and standards that guide the practice of education, including issues such as academic integrity, fairness, and respect for diversity.
Political Ethics
This involves ethical principles and values that guide political decision-making and behavior, including issues such as accountability, transparency, and the protection of civil liberties.
Professional Ethics
This refers to ethical principles and standards that guide the conduct of professionals in various fields, including issues such as honesty, integrity, and competence.
Personal Ethics
This involves ethical principles and values that guide individual behavior and decision-making, including issues such as personal responsibility, honesty, and respect for others.
Global Ethics
This involves ethical principles and values that guide our interactions with other nations and the global community, including issues such as human rights, environmental protection, and social justice.
Applications of Ethical Considerations
Ethical considerations are important in many areas of society, including medicine, business, law, and technology. Here are some specific applications of ethical considerations:
- Medical research : Ethical considerations are crucial in medical research, particularly when human subjects are involved. Researchers must ensure that their studies are conducted in a way that does not harm participants and that participants give informed consent before participating.
- Business practices: Ethical considerations are also important in business, where companies must make decisions that are socially responsible and avoid activities that are harmful to society. For example, companies must ensure that their products are safe for consumers and that they do not engage in exploitative labor practices.
- Environmental protection: Ethical considerations play a crucial role in environmental protection, as companies and governments must weigh the benefits of economic development against the potential harm to the environment. Decisions about land use, resource allocation, and pollution must be made in an ethical manner that takes into account the long-term consequences for the planet and future generations.
- Technology development : As technology continues to advance rapidly, ethical considerations become increasingly important in areas such as artificial intelligence, robotics, and genetic engineering. Developers must ensure that their creations do not harm humans or the environment and that they are developed in a way that is fair and equitable.
- Legal system : The legal system relies on ethical considerations to ensure that justice is served and that individuals are treated fairly. Lawyers and judges must abide by ethical standards to maintain the integrity of the legal system and to protect the rights of all individuals involved.
Examples of Ethical Considerations
Here are a few examples of ethical considerations in different contexts:
- In healthcare : A doctor must ensure that they provide the best possible care to their patients and avoid causing them harm. They must respect the autonomy of their patients, and obtain informed consent before administering any treatment or procedure. They must also ensure that they maintain patient confidentiality and avoid any conflicts of interest.
- In the workplace: An employer must ensure that they treat their employees fairly and with respect, provide them with a safe working environment, and pay them a fair wage. They must also avoid any discrimination based on race, gender, religion, or any other characteristic protected by law.
- In the media : Journalists must ensure that they report the news accurately and without bias. They must respect the privacy of individuals and avoid causing harm or distress. They must also be transparent about their sources and avoid any conflicts of interest.
- In research: Researchers must ensure that they conduct their studies ethically and with integrity. They must obtain informed consent from participants, protect their privacy, and avoid any harm or discomfort. They must also ensure that their findings are reported accurately and without bias.
- In personal relationships : People must ensure that they treat others with respect and kindness, and avoid causing harm or distress. They must respect the autonomy of others and avoid any actions that would be considered unethical, such as lying or cheating. They must also respect the confidentiality of others and maintain their privacy.
How to Write Ethical Considerations
When writing about research involving human subjects or animals, it is essential to include ethical considerations to ensure that the study is conducted in a manner that is morally responsible and in accordance with professional standards. Here are some steps to help you write ethical considerations:
- Describe the ethical principles: Start by explaining the ethical principles that will guide the research. These could include principles such as respect for persons, beneficence, and justice.
- Discuss informed consent : Informed consent is a critical ethical consideration when conducting research. Explain how you will obtain informed consent from participants, including how you will explain the purpose of the study, potential risks and benefits, and how you will protect their privacy.
- Address confidentiality : Describe how you will protect the confidentiality of the participants’ personal information and data, including any measures you will take to ensure that the data is kept secure and confidential.
- Consider potential risks and benefits : Describe any potential risks or harms to participants that could result from the study and how you will minimize those risks. Also, discuss the potential benefits of the study, both to the participants and to society.
- Discuss the use of animals : If the research involves the use of animals, address the ethical considerations related to animal welfare. Explain how you will minimize any potential harm to the animals and ensure that they are treated ethically.
- Mention the ethical approval : Finally, it’s essential to acknowledge that the research has received ethical approval from the relevant institutional review board or ethics committee. State the name of the committee, the date of approval, and any specific conditions or requirements that were imposed.
When to Write Ethical Considerations
Ethical considerations should be written whenever research involves human subjects or has the potential to impact human beings, animals, or the environment in some way. Ethical considerations are also important when research involves sensitive topics, such as mental health, sexuality, or religion.
In general, ethical considerations should be an integral part of any research project, regardless of the field or subject matter. This means that they should be considered at every stage of the research process, from the initial planning and design phase to data collection, analysis, and dissemination.
Ethical considerations should also be written in accordance with the guidelines and standards set by the relevant regulatory bodies and professional associations. These guidelines may vary depending on the discipline, so it is important to be familiar with the specific requirements of your field.
Purpose of Ethical Considerations
Ethical considerations are an essential aspect of many areas of life, including business, healthcare, research, and social interactions. The primary purposes of ethical considerations are:
- Protection of human rights: Ethical considerations help ensure that people’s rights are respected and protected. This includes respecting their autonomy, ensuring their privacy is respected, and ensuring that they are not subjected to harm or exploitation.
- Promoting fairness and justice: Ethical considerations help ensure that people are treated fairly and justly, without discrimination or bias. This includes ensuring that everyone has equal access to resources and opportunities, and that decisions are made based on merit rather than personal biases or prejudices.
- Promoting honesty and transparency : Ethical considerations help ensure that people are truthful and transparent in their actions and decisions. This includes being open and honest about conflicts of interest, disclosing potential risks, and communicating clearly with others.
- Maintaining public trust: Ethical considerations help maintain public trust in institutions and individuals. This is important for building and maintaining relationships with customers, patients, colleagues, and other stakeholders.
- Ensuring responsible conduct: Ethical considerations help ensure that people act responsibly and are accountable for their actions. This includes adhering to professional standards and codes of conduct, following laws and regulations, and avoiding behaviors that could harm others or damage the environment.
Advantages of Ethical Considerations
Here are some of the advantages of ethical considerations:
- Builds Trust : When individuals or organizations follow ethical considerations, it creates a sense of trust among stakeholders, including customers, clients, and employees. This trust can lead to stronger relationships and long-term loyalty.
- Reputation and Brand Image : Ethical considerations are often linked to a company’s brand image and reputation. By following ethical practices, a company can establish a positive image and reputation that can enhance its brand value.
- Avoids Legal Issues: Ethical considerations can help individuals and organizations avoid legal issues and penalties. By adhering to ethical principles, companies can reduce the risk of facing lawsuits, regulatory investigations, and fines.
- Increases Employee Retention and Motivation: Employees tend to be more satisfied and motivated when they work for an organization that values ethics. Companies that prioritize ethical considerations tend to have higher employee retention rates, leading to lower recruitment costs.
- Enhances Decision-making: Ethical considerations help individuals and organizations make better decisions. By considering the ethical implications of their actions, decision-makers can evaluate the potential consequences and choose the best course of action.
- Positive Impact on Society: Ethical considerations have a positive impact on society as a whole. By following ethical practices, companies can contribute to social and environmental causes, leading to a more sustainable and equitable society.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Background of The Study – Examples and Writing...

Purpose of Research – Objectives and Applications

Institutional Review Board – Application Sample...

Research Recommendations – Examples and Writing...

Thesis Outline – Example, Template and Writing...

Thesis – Structure, Example and Writing Guide

What Are the Ethical Considerations in Research Design?
When I began my work on the thesis I was always focused on my research. However, once I began to make my way through research, I realized that research ethics is a core aspect of the research work and the foundation of research design.
Research ethics play a crucial role in ensuring the responsible conduct of research. Here are some key reasons why research ethics matter:

Let us look into some of the major ethical considerations in research design.
Ethical Issues in Research
There are many organizations, like the Committee on Publication Ethics , dedicated to promoting ethics in scientific research. These organizations agree that ethics is not an afterthought or side note to the research study. It is an integral aspect of research that needs to remain at the forefront of our work.
The research design must address specific research questions. Hence, the conclusions of the study must correlate to the questions posed and the results. Also, research ethics demands that the methods used must relate specifically to the research questions.
Voluntary Participation and Consent
An individual should at no point feel any coercion to participate in a study. This includes any type of persuasion or deception in attempting to gain an individual’s trust.
Informed consent states that an individual must give their explicit consent to participate in the study. You can think of consent form as an agreement of trust between the researcher and the participants.
Sampling is the first step in research design . You will need to explain why you want a particular group of participants. You will have to explain why you left out certain people or groups. In addition, if your sample includes children or special needs individuals, you will have additional requirements to address like parental permission.
Confidentiality
The third ethics principle of the Economic and Social Research Council (ESRC) states that: “The confidentiality of the information supplied by research subjects and the anonymity of respondents must be respected.” However, sometimes confidentiality is limited. For example, if a participant is at risk of harm, we must protect them. This might require releasing confidential information.
Risk of Harm
We should do everything in our power to protect study participants. For this, we should focus on the risk to benefit ratio. If possible risks outweigh the benefits, then we should abandon or redesign the study. Risk of harm also requires us to measure the risk to benefit ratio as the study progresses.
Research Methods
We know there are numerous research methods. However, when it comes to ethical considerations, some key questions can help us find the right approach for our studies.
i. Which methods most effectively fit the aims of your research?
ii. What are the strengths and restrictions of a particular method?
iii. Are there potential risks when using a particular research method?
For more guidance, you can refer to the ESRC Framework for Research Ethics .
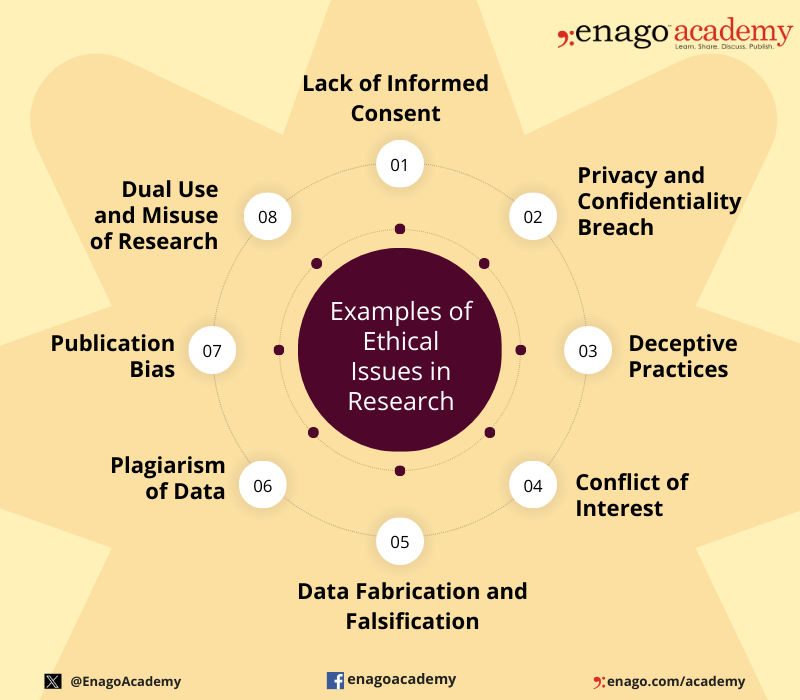
Ethical issues in research can arise at various stages of the research process and involve different aspects of the study. Here are some common examples of ethical issues in research:
Institutional Review Boards
The importance of ethics in research cannot be understated. Following ethical guidelines will ensure your study’s validity and promote its contribution to scientific study. On a personal level, you will strengthen your research and increase your opportunities to gain funding.
To address the need for ethical considerations, most institutions have their own Institutional Review Board (IRB). An IRB secures the safety of human participants and prevents violation of human rights. It reviews the research aims and methodologies to ensure ethical practices are followed. If a research design does not follow the set ethical guidelines, then the researcher will have to amend their study.
Applying for Ethical Approval
Applications for ethical approval will differ across institutions. Regardless, they focus on the benefits of your research and the risk to benefit ratio concerning participants. Therefore, you need to effectively address both in order to get ethical clearence.
Participants
It is vital that you make it clear that individuals are provided with sufficient information in order to make an informed decision on their participation. In addition, you need to demonstrate that the ethical issues of consent, risk of harm, and confidentiality are clearly defined.
Benefits of the Study
You need to prove to the panel that your work is essential and will yield results that contribute to the scientific community. For this, you should demonstrate the following:
i. The conduct of research guarantees the quality and integrity of results.
ii. The research will be properly distributed.
iii. The aims of the research are clear and the methodology is appropriate.
Integrity and transparency are vital in the research. Ethics committees expect you to share any actual or potential conflicts of interest that could affect your work. In addition, you have to be honest and transparent throughout the approval process and the research process.
The Dangers of Unethical Practices
There is a reason to follow ethical guidelines. Without these guidelines, our research will suffer. Moreover, more importantly, people could suffer.
The following are just two examples of infamous cases of unethical research practices that demonstrate the importance of adhering to ethical standards:
- The Stanford Prison Experiment (1971) aimed to investigate the psychological effects of power using the relationship between prisoners and prison officers. Those assigned the role of “prison officers” embraced measures that exposed “prisoners” to psychological and physical harm. In this case, there was voluntary participation. However, there was disregard for welfare of the participants.
- Recently, Chinese scientist He Jiankui announced his work on genetically edited babies . Over 100 Chinese scientists denounced this research, calling it “crazy” and “shocking and unacceptable.” This research shows a troubling attitude of “do first, debate later” and a disregard for the ethical concerns of manipulating the human body Wang Yuedan, a professor of immunology at Peking University, calls this “an ethics disaster for the world” and demands strict punishments for this type of ethics violation.
What are your experiences with research ethics? How have you developed an ethical approach to research design? Please share your thoughts with us in the comments section below.
I love the articulation of reasoning and practical examples of unethical research
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles

- AI in Academia
- Trending Now
6 Leading AI Detection Tools for Academic Writing — A comparative analysis
The advent of AI content generators, exemplified by advanced models like ChatGPT, Claude AI, and…

- Reporting Research
Choosing the Right Analytical Approach: Thematic analysis vs. content analysis for data interpretation
In research, choosing the right approach to understand data is crucial for deriving meaningful insights.…

- Industry News
China’s Ministry of Education Spearheads Efforts to Uphold Academic Integrity
In response to the increase in retractions of research papers submitted by Chinese scholars to…

Comparing Cross Sectional and Longitudinal Studies: 5 steps for choosing the right approach
The process of choosing the right research design can put ourselves at the crossroads of…

- Publishing Research
- Understanding Ethics
Understanding the Difference Between Research Ethics and Compliance
Ethics refers to the principles, values, and moral guidelines that guide individual or group behavior…
Unlocking the Power of Networking in Academic Conferences
Avoiding the AI Trap: Pitfalls of relying on ChatGPT for PhD applications
10 Ways to Help Students Restore Focus on Learning
Switching Your Major As a Researcher: Things to Consider Before Making the Decision

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
Ethical considerations in research: Best practices and examples

Doing responsible research means keeping ethics considerations front and center. Ethical practices not only safeguard research participant welfare but also ensures the integrity of your findings. By rigorously applying ethical principles throughout the research process, you not only enhance the methodological robustness of your study but also amplify its potential for meaningful societal impact.
But what does good ethics in research look like?
From best practices to conducting ethical and impactful research, we explore the meaning and importance of research ethics in modern-day research.

Examples of ethical considerations in research
As a researcher, you're responsible for ethical research alongside your organization. Fulfilling ethical guidelines is critical. Organizations must see to it that employees follow best practices to protect participants' rights and well-being.
Keep the below considerations in mind when it comes to ethical considerations in research.
Voluntary participation
Nobody should feel like they're being forced to participate or pressured into doing anything they don't want to. That means giving people a choice and the ability to opt out at any time, even if they've already agreed to take part in the study.
Researchers must clearly communicate this right to participants. It's necessary for creating an environment where people feel comfortable declining or withdrawing without fear of negative consequences.
Informed consent
Informed consent isn't just an ethical consideration. It's a legal requirement as well. Participants must fully understand what they're agreeing to, including potential risks and benefits.
The best way to go about this is by using a consent form. Make sure you include:
Brief description of the study and research methods
Provide a clear, concise overview of your research goals and how you'll conduct the study. Use simple language so participants understand the nature of their involvement and what they'll be asked to do.
Potential benefits and risks of participating
Outline any possible advantages or drawbacks of taking part in the study. Be honest about potential risks, no matter how small. You’ll allow participants to make an informed decision about their involvement.
Length of the study
Specify how long the study will take. If it involves multiple sessions, provide details on timing and frequency. It means participants will be able to plan their commitment and decide if they can fully engage.
Contact information for the researcher and/or sponsor
Include your name, institution, and contact details. If there's a study sponsor, provide their information too so participants can reach out with questions or concerns before, during, or after the study.
Participant's right to withdraw
Clearly state that participants can leave the study at any time without consequences. Emphasize that withdrawal won't affect their relationship with the researcher or institution to reinforce the voluntary nature of participation.
Cultural sensitivity
Consider cultural differences when conducting research across diverse populations. It will increase the chance that your study is respectful, inclusive, and produces valid results. Understanding cultural context, adapting research methods, and using appropriate language are central steps in this process.
Include team members from various cultural backgrounds on your research team. They can provide valuable insights and help interpret results within the appropriate cultural context. Be mindful of cultural practices that might affect participation, such as scheduling around religious observances or respecting dietary restrictions.
Prioritizing cultural sensitivity will help you conduct more ethical research and likely obtain more accurate, meaningful results from diverse populations. As a result, you can build trust with participants and enhance the overall quality and applicability of your research findings.
Anonymity means that participants aren't identifiable in any way and includes:
- Email address
- Photographs
- Video footage
You need a way to anonymize research data so that it can't be traced back to individual participants. This may involve creating a new digital ID for participants that can’t be linked back to their original identity using numerical codes.
Confidentiality
Information gathered during a study must be kept confidential. Confidentiality helps to protect the privacy of research participants and also ensures that their information isn't disclosed to unauthorized individuals.
Here are some ways to ensure confidentiality.
Use a secure server to store data
Store all research data on encrypted servers with strong access controls. Regularly update security measures to protect against potential breaches. Doing so safeguards participant information from unauthorized access or cyber threats.
Remove identifying information from databases
Create separate databases for participant identifiers and research data. Use coded identifiers to link the two, as it prevents direct association between sensitive data and individual participants.
Use a third-party company for data management
Consider partnering with specialized data management firms. They often have advanced security protocols and expertise in handling sensitive information, which can add an extra layer of protection for your research data.
Limit record retention periods
Establish clear timelines for data retention. Delete or destroy participant records once they're no longer needed for research purposes to reduce the risk of accidental disclosure or unauthorized access over time.
Avoid public discussion of findings
Be cautious when discussing research in public settings. Refrain from sharing specific details that could potentially identify participants. Focus on aggregate results and general insights to maintain confidentiality.
Conflict of interest
Researchers must disclose any potential conflicts of interest that could influence their study or its outcomes. Such transparency is important for maintaining the integrity and credibility of scientific research. Conflicts of interest can arise from financial relationships, personal connections, or professional affiliations.
Key considerations for managing conflicts of interest include:
- Full disclosure : Openly declare any potential conflicts in research proposals, publications, and presentations.
- Mitigation strategies : Develop plans to minimize the impact of conflicts on research conduct and outcomes.
- Independent review : Seek evaluation from unbiased third parties to ensure objectivity in research design and analysis.
Addressing conflicts of interest proactively means you can maintain public trust and uphold the ethical standards of their field.
Potential for harm
The potential for harm is a major factor in deciding whether a research study should proceed. It can manifest in various forms, such as:
Psychological harm
Research may unintentionally cause stress, anxiety, or emotional distress. Carefully consider the psychological impact of your study design, questions, or tasks. Provide support resources if needed.
Social harm
Some studies might affect participants' relationships or social standing, so think about potential stigma or social consequences. Guarantee confidentiality to minimize risks to participants' social well-being.
Physical harm
While rare in many fields, some studies involve physical risks. Assess all potential physical dangers thoroughly. Implement safety measures and have emergency protocols in place.
Research findings or participation could sometimes lead to legal issues for subjects. Be aware of legal implications. Protect participants from potential legal consequences through careful study design and data handling.
Conduct an ethical review to identify possible harms. Be prepared to explain how you’ll minimize these harms and what support is available in case they do happen.
Ethical use of technology
As research increasingly moves online and incorporates emerging technologies, new ethical challenges arise. Researchers must carefully consider the implications of using digital tools for data collection and analysis. This includes addressing concerns about privacy, data security, and the potential for unintended consequences.
Key considerations for the ethical use of technology in research include:
- Data protection: Implement robust security measures to safeguard participant information collected through digital platforms
- Informed consent: Clearly explain how technology will be used in the study and any potential risks associated with digital data collection
- Algorithmic bias: Be aware of and mitigate potential biases in AI-driven data analysis tools to ensure fair and accurate results
With these issues addressed, you can benefit from technology while upholding ethical standards and protecting participants' rights.
Fair payment
One of the most important aspects of setting up a research study is deciding on fair compensation for your participants. Underpayment is a common ethical issue that shouldn't be overlooked. Properly rewarding participants' time is necessary for boosting engagement and obtaining high-quality data. While Prolific requires a minimum payment of £6.00 / $8.00 per hour, there are other factors you need to consider when deciding on a fair payment.
Institutional guidelines and minimum wage
Check your institution's reimbursement guidelines to see if they already have a minimum or maximum hourly rate. You can also use the national minimum wage as a reference point.
Level of effort and task complexity
Think about the amount of work you're asking participants to do. The level of effort required for a task, such as producing a video recording versus a short survey, should correspond with the reward offered.
Target population considerations
You also need to consider the population you're targeting. You may need to offer more as an incentive to attract research subjects with specific characteristics or high-paying jobs,
We recommend a minimum payment of £9.00 / $12.00 per hour, but we understand that payment rates can vary depending on a range of factors. Whatever payment you choose should reflect the amount of effort participants are required to put in and be fair to everyone involved.
Ethical research made easy with Prolific
At Prolific, we believe in making ethical research easy and accessible. The findings from the Fairwork Cloudwork report speak for themselves. Prolific was given the top score out of all competitors for minimum standards of fair work.
With over 25,000 researchers in our community, we're leading the way in revolutionizing the research industry. If you're interested in learning more about how we can support your research journey, sign up free to get started now .
You might also like

Building a better world with better data.

Follow us on
All Rights Reserved Prolific 2024
A guide to ethical considerations in research
Last updated
12 March 2023
Reviewed by
Miroslav Damyanov
Whether you are conducting a survey, running focus groups , doing field research, or holding interviews, the chances are participants will be a part of the process.
Taking ethical considerations into account and following all obligations are essential when people are involved in your research. Upholding academic integrity is another crucial ethical concern in all research types.
So, how can you protect your participants and ensure that your research is ethical? Let’s take a closer look at the ethical considerations in research and the best practices to follow.
Make research less tedious
Dovetail streamlines research to help you uncover and share actionable insights
- The importance of ethical research
Research ethics are integral to all forms of research. They help protect participants’ rights, ensure that the research is valid and accurate, and help minimize any risk of harm during the process.
When people are involved in your research, it’s particularly important to consider whether your planned research method follows ethical practices.
You might ask questions such as:
Will our participants be protected?
Is there a risk of any harm?
Are we doing all we can to protect the personal data and information we collect?
Does our study include any bias?
How can we ensure that the results will be accurate and valid?
Will our research impact public safety?
Is there a more ethical way to complete the research?
Conducting research unethically and not protecting participants’ rights can have serious consequences. It can discredit the entire study. Human rights, dignity, and research integrity should all be front of mind when you are conducting research.
- How to conduct ethical research
Before kicking off any project, the entire team must be familiar with ethical best practices. These include the considerations below.
Voluntary participation
In an ethical study, all participants have chosen to be part of the research. They must have voluntarily opted in without any pressure or coercion to do so. They must be aware that they are part of a research study. Their information must not be used against their will.
To ensure voluntary participation, make it clear at the outset that the person is opting into the process.
While participants may agree to be part of a study for a certain duration, they are allowed to change their minds. Participants must be free to leave or withdraw from the study at any time. They don’t need to give a reason.
Informed consent
Before kicking off any research, it’s also important to gain consent from all participants. This ensures participants are clear that they are part of a research study and understand all of the information related to it.
Gaining informed consent usually involves a written consent form—physical or digital—that participants can sign.
Best practice informed consent generally includes the following:
An explanation of what the study is
The duration of the study
The expectations of participants
Any potential risks
An explanation that participants are free to withdraw at any time
Contact information for the research supervisor
When obtaining informed consent, you should ensure that all parties truly understand what they are signing and their obligations as a participant. There should never be any coercion to sign.
Anonymity is key to ensuring that participants cannot be identified through their data. Personal information includes things like participants’ names, addresses, emails, phone numbers, characteristics, and photos.
However, making information truly anonymous can be challenging, especially if personal information is a necessary part of the research.
To maintain a degree of anonymity, avoid gathering any information you don’t need. This will minimize the risk of participants being identified.
Another useful tool is data pseudonymization, which makes it harder to directly link information to a real person. Data pseudonymization means giving participants fake names or mock information to protect their identity. You could, for example, replace participants’ names with codes.
Confidentiality
Keeping data confidential is a critical aspect of all forms of research. You should communicate to all participants that their information will be protected and then take active steps to ensure that happens.
Data protection has become a serious topic in recent years and should be taken seriously. The more information you gather, the more important it is to heavily protect that data.
There are many ways to protect data, including the following:
Restricted access: Information should only be accessible to the researchers involved in the project to limit the risk of breaches.
Password protection : Information should not be accessible without access via a password that complies with secure password guidelines.
Encrypted data: In this day and age, password protection isn’t usually sufficient. Encrypting the data can help ensure its security.
Data retention: All organizations should uphold a data retention policy whereby data gathered should only be held for a certain period of time. This minimizes the risk of breaches further down the line.
In research where participants are grouped together (such as in focus groups), ask participants not to pass on what has been discussed. This helps maintain the group’s privacy.
Data falsification
Regardless of what your study is about or whether it involves humans, it’s always unethical to falsify data or information. That means editing or changing any data that has been gathered or gathering data in ways that skew the results.
Bias in research is highly problematic and can significantly impact research integrity. Data falsification or misrepresentation can have serious consequences.
Take the case of Korean researcher Hwang Woo-suk, for example. Woo-suk, once considered a scientific leader in stem-cell research, was found guilty of fabricating experiments in the field and making ethical violations. Once discovered, he was fired from his role and sentenced to two years in prison.
All conflicts of interest should be declared at the outset to avoid any bias or risk of fabrication in the research process. Data must be collected and recorded accurately, and analysis must be completed impartially.
If conflicts do arise during the study, researchers may need to step back to maintain the study’s integrity. Outsourcing research to neutral third parties is necessary in some cases.
Potential for harm
Another consideration is the potential for harm. When completing research, it’s important to ensure that your participants will be safe throughout the study’s duration.
Harm during research could occur in many forms.
Physical harm may occur if your participants are asked to perform a physical activity, or if they are involved in a medical study.
Psychological harm can occur if questions or activities involve triggering or sensitive topics, or if participants are asked to complete potentially embarrassing tasks.
Harm can be caused through a data breach or privacy concern.
A study can cause harm if the participants don’t feel comfortable with the study expectations or their supervisors.
Maintaining the physical and mental well-being of all participants throughout studies is an essential aspect of ethical research.
- Gaining ethical approval
Gaining ethical approval may be necessary before conducting some types of research.
The US Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) and the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) advise that approval is likely required for studies involving people.
To gain approval, it’s necessary to submit a proposal to an Institutional Review Board (IRB). The board will check the proposal and ensure that the research aligns with ethical practices. It will allow the project to proceed if it meets requirements.
Not gaining appropriate approval could invalidate your study, so it’s essential to pay attention to all local guidelines and laws.
- The dangers of unethical practices
Not maintaining ethical standards in research isn’t just questionable—it can be dangerous too. Many historical cases show just how widespread the ramifications can be.
The case of Korean researcher Hwang Woo-suk shows just how critical it is to obtain information ethically and accurately represent findings.
A case in 1998, which involved fraudulent data reporting, further proves this point.
The study, now debunked, was completed by Andrew Wakefield. It suggested there may be a link between the measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR) vaccine and autism in children. It was later found that the data was manipulated to show a causal link when there wasn’t one. Wakefield’s medical license was removed as a result, but the fraudulent study was still widely cited and continues to cause vaccine hesitancy among many parents.
Large organizational bodies have also been a part of unethical research. The alcohol industry, for example, was found to be highly influential in a major public health study in an attempt to prove that moderate alcohol consumption had health benefits. Five major alcohol companies pledged approximately $66 million to fund the study.
However, the World Health Organization (WHO) is clear that research shows there is no safe level of alcohol consumption. After pressure from many organizations, the study was eventually pulled due to biasing by the alcohol industry. Despite this, the idea that moderate alcohol consumption is better than abstaining may still appear in public discourse.
In more extreme cases, unethical research has led to medical studies being completed on people without their knowledge and against their will. The atrocities committed in Nazi Germany during World War II are an example.
Unethical practices in research are not just problematic or in conflict with academic integrity; they can seriously harm public health and safety.
- The ethical way to research
Considering ethical concerns and adopting best practices throughout studies is essential when conducting research.
When people are involved in studies, it’s important to consider their rights. They must not be coerced into participating, and they should be protected throughout the process.
Accurate reporting, unbiased results, and a genuine interest in answering questions rather than confirming assumptions are all essential aspects of ethical research.
Ethical research ultimately means producing true and valuable results for the benefit of everyone impacted by your study.
What are ethical considerations in research?
Ethical research involves a series of guidelines and considerations to ensure that the information gathered is valid and reliable. These guidelines ensure that:
People are not harmed during research
Participants have data protection and anonymity
Academic integrity is upheld
Not maintaining ethics in research can have serious consequences for those involved in the studies, the broader public, and policymakers.
What are the most common ethical considerations?
To maintain integrity and validity in research, all biases must be removed, data should be reported accurately, and studies must be clearly represented.
Some of the most common ethical guidelines when it comes to humans in research include avoiding harm, data protection, anonymity, informed consent, and confidentiality.
What are the ethical issues in secondary research?
Using secondary data is generally considered an ethical practice. That’s because the use of secondary data minimizes the impact on participants, reduces the need for additional funding, and maximizes the value of the data collection.
However, secondary research still has risks. For example, the risk of data breaches increases as more parties gain access to the information.
To minimize the risk, researchers should consider anonymity or data pseudonymization before the data is passed on. Furthermore, using the data should not cause any harm or distress to participants.
Should you be using a customer insights hub?
Do you want to discover previous research faster?
Do you share your research findings with others?
Do you analyze research data?
Start for free today, add your research, and get to key insights faster
Editor’s picks
Last updated: 30 January 2024
Last updated: 11 January 2024
Last updated: 17 January 2024
Last updated: 12 December 2023
Last updated: 30 April 2024
Last updated: 4 July 2024
Last updated: 12 October 2023
Last updated: 5 March 2024
Last updated: 6 March 2024
Last updated: 31 January 2024
Last updated: 23 January 2024
Last updated: 13 May 2024
Last updated: 20 December 2023
Latest articles
Related topics, decide what to build next, log in or sign up.
Get started for free

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Ethical considerations in research refer to the principles and guidelines that researchers must follow to ensure that their studies are conducted in an ethical and responsible manner.
Ethical considerations in research are a set of principles that guide your research designs and practices. These principles include voluntary participation, informed consent, anonymity, confidentiality, potential for harm, and results communication.
Ethical Considerations in Research. January 2015. DOI: 10.1007/978-94-6300-112-0_4. In book: The Praxis of English Language Teaching and Learning (PELT) (pp.61-79) Authors: Marcelle...
In this paper, we discuss core ethical and methodological considerations in the design and implementation of qualitative research in the COVID-19 era, and in pivoting to virtual methods—online interviews and focus groups; internet-based archival research and netnography, including social media; participatory video methods, including photo ...
Research ethics protect the rights and well-being of participants, uphold the integrity of research findings, and contribute to the positive impact of research on individuals and society. Let us look into some of the major ethical considerations in research design.
In an age where technology is rapidly advancing and societal values and roles are changing dramatically, ethical issues are becoming increasingly more complex. This is evidenced when human beings are used as subjects of research investigations. What does the conduct of research eth ically involve?
From an ethical viewpoint, conducting research with vulnerable populations requires protection for them because data collection methods, such as in-depth interviews with sensible themes, can delve into interpersonally and politically charged matters, which can create potentially conflicting situations (Peter, 2015).
This book takes up ethical (and some etiquette) issues. These issues usu-ally are addressed in only a few pages in typical introductory research methods texts that are aimed at those learning how to conduct research with human subjects.
Explore key ethical considerations in research, from informed consent to fair compensation. Learn how to conduct responsible studies that protect participants.
Accurate reporting, unbiased results, and a genuine interest in answering questions rather than confirming assumptions are all essential aspects of ethical research. Ethical research ultimately means producing true and valuable results for the benefit of everyone impacted by your study.