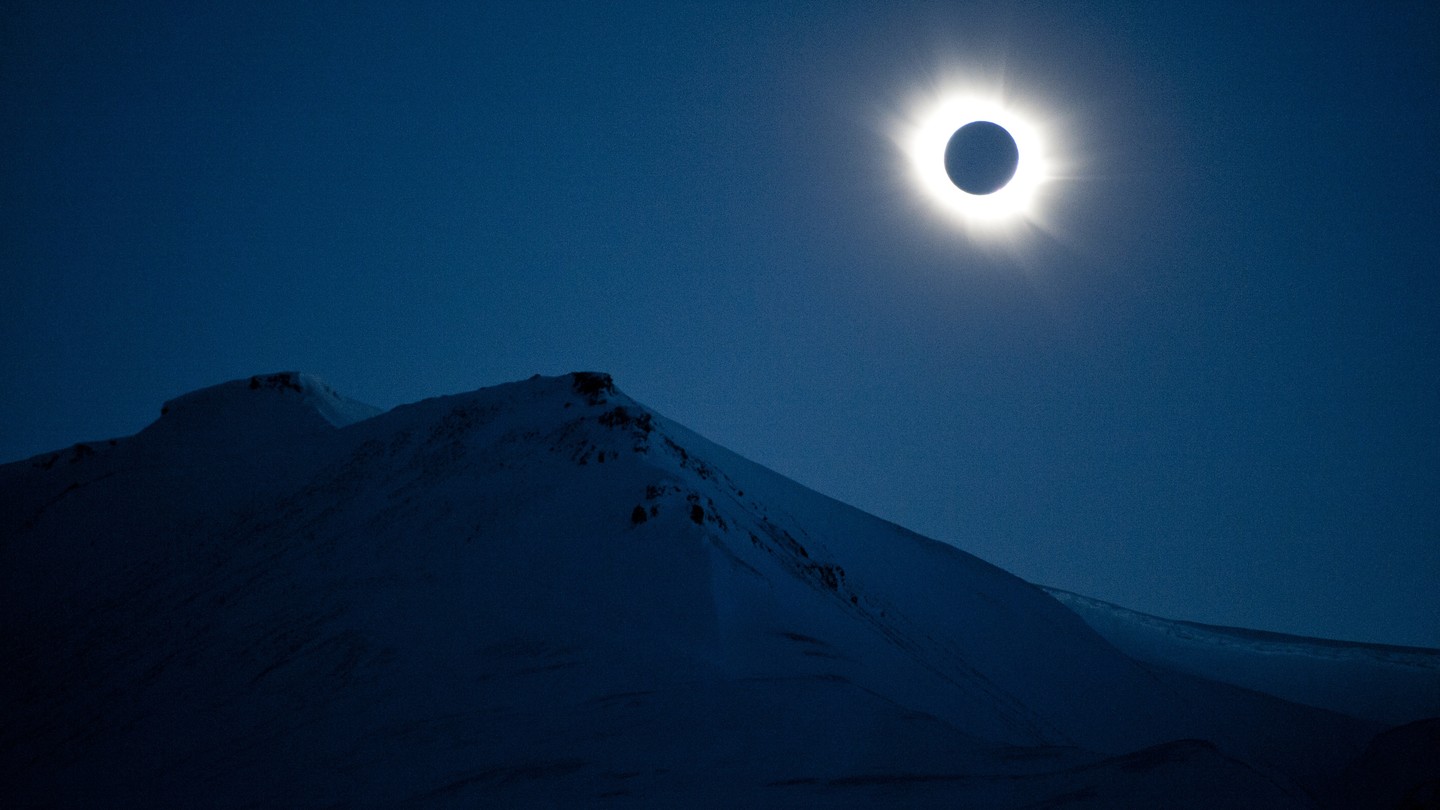


Total Eclipse
“Seeing a partial eclipse bears the same relation to seeing a total eclipse as kissing a man does to marrying him.”
Ever since the essay was first published in 1982, readers—including this one—have thrilled to “Total Eclipse,” Annie Dillard’s masterpiece of literary nonfiction, which describes her personal experience of a solar eclipse in Washington State. It first appeared in Dillard’s landmark collection, Teaching a Stone to Talk , and was recently republished in The Abundance , a new anthology of her work. The Atlantic is pleased to offer the essay in full. — Ross Andersen
It had been like dying, that sliding down the mountain pass. It had been like the death of someone, irrational, that sliding down the mountain pass and into the region of dread. It was like slipping into fever, or falling down that hole in sleep from which you wake yourself whimpering. We had crossed the mountains that day, and now we were in a strange place—a hotel in central Washington, in a town near Yakima. The eclipse we had traveled here to see would occur early in the next morning.
I lay in bed. My husband, Gary, was reading beside me. I lay in bed and looked at the painting on the hotel-room wall. It was a print of a detailed and lifelike painting of a smiling clown’s head, made out of vegetables. It was a painting of the sort that you do not intend to look at, and that, alas, you never forget. Some tasteless fate presses it upon you; it becomes part of the complex interior junk you carry with you wherever you go. Two years have passed since the total eclipse of which I write. During those years I have forgotten, I assume, a great many things I wanted to remember—but I have not forgotten that clown painting or its lunatic setting in the old hotel. The clown was bald. Actually, he wore a clown’s tight rubber wig, painted white; this stretched over the top of his skull, which was a cabbage. His hair was bunches of baby carrots. Inset in his white clown makeup, and in his cabbage skull, were his small and laughing human eyes. The clown’s glance was like the glance of Rembrandt in some of the self-portraits: lively, knowing, deep, and loving. The crinkled shadows around his eyes were string beans. His eyebrows were parsley. Each of his ears was a broad bean. His thin, joyful lips were red chili peppers; between his lips were wet rows of human teeth and a suggestion of a real tongue. The clown print was framed in gilt and glassed.
To put ourselves in the path of the total eclipse, that day we had driven five hours inland from the Washington coast, where we lived. When we tried to cross the Cascades range, an avalanche had blocked the pass.
A slope’s worth of snow blocked the road; traffic backed up. Had the avalanche buried any cars that morning? We could not learn. This highway was the only winter road over the mountains. We waited as highway crews bulldozed a passage through the avalanche. With two-by-fours and walls of plywood, they erected a one-way, roofed tunnel through the avalanche. We drove through the avalanche tunnel, crossed the pass, and descended several thousand feet into central Washington and the broad Yakima Valley, about which we knew only that it was orchard country. As we lost altitude, the snows disappeared; our ears popped; the trees changed, and in the trees were strange birds. I watched the landscape innocently, like a fool, like a diver in the rapture of the deep who plays on the bottom while his air runs out.
The hotel lobby was a dark, derelict room, narrow as a corridor, and seemingly without air. We waited on a couch while the manager vanished upstairs to do something unknown to our room. Beside us on an overstuffed chair, absolutely motionless, was a platinum-blond woman in her 40s wearing a black silk dress and a strand of pearls. Her long legs were crossed; she supported her head on her fist. At the dim far end of the room, their backs toward us, sat six bald old men in their shirtsleeves, around a loud television. Two of them seemed asleep. They were drunks. “Number six!” cried the man on television. “Number six!”
On the broad lobby desk, lit and bubbling, was a 10-gallon aquarium containing one large fish; the fish tilted up and down in its water. Against the long opposite wall sang a live canary in its cage. Beneath the cage, among spilled millet seeds on the carpet, were a decorated child’s sand bucket and matching sand shovel.
Now the alarm was set for six. I lay awake remembering an article I had read downstairs in the lobby, in an engineering magazine. The article was about gold mining.
In South Africa, in India, and in South Dakota, the gold mines extend so deeply into the Earth’s crust that they are hot. The rock walls burn the miners’ hands. The companies have to air-condition the mines; if the air conditioners break, the miners die. The elevators in the mine shafts run very slowly, down, and up, so the miners’ ears will not pop in their skulls. When the miners return to the surface, their faces are deathly pale.
Early the next morning we checked out. It was February 26, 1979, a Monday morning. We would drive out of town, find a hilltop, watch the eclipse, and then drive back over the mountains and home to the coast. How familiar things are here; how adept we are; how smoothly and professionally we check out! I had forgotten the clown’s smiling head and the hotel lobby as if they had never existed. Gary put the car in gear and off we went, as off we have gone to a hundred other adventures.
It was dawn when we found a highway out of town and drove into the unfamiliar countryside. By the growing light we could see a band of cirrostratus clouds in the sky. Later the rising sun would clear these clouds before the eclipse began. We drove at random until we came to a range of unfenced hills. We pulled off the highway, bundled up, and climbed one of these hills.
The hill was 500 feet high. Long winter-killed grass covered it, as high as our knees. We climbed and rested, sweating in the cold; we passed clumps of bundled people on the hillside who were setting up telescopes and fiddling with cameras. The top of the hill stuck up in the middle of the sky. We tightened our scarves and looked around.
East of us rose another hill like ours. Between the hills, far below, 13 was the highway that threaded south into the valley. This was the Yakima Valley; I had never seen it before. It is justly famous for its beauty, like every planted valley. It extended south into the horizon, a distant dream of a valley, a Shangri-la. All its hundreds of low, golden slopes bore orchards. Among the orchards were towns, and roads, and plowed and fallow fields. Through the valley wandered a thin, shining river; from the river extended fine, frozen irrigation ditches. Distance blurred and blued the sight, so that the whole valley looked like a thickness or sediment at the bottom of the sky. Directly behind us was more sky, and empty lowlands blued by distance, and Mount Adams. Mount Adams was an enormous, snow-covered volcanic cone rising flat, like so much scenery.
Now the sun was up. We could not see it; but the sky behind the band of clouds was yellow, and, far down the valley, some hillside orchards had lit up. More people were parking near the highway and climbing the hills. It was the West. All of us rugged individualists were wearing knit caps and blue nylon parkas. People were climbing the nearby hills and setting up shop in clumps among the dead grasses. It looked as though we had all gathered on hilltops to pray for the world on its last day. It looked as though we had all crawled out of spaceships and were preparing to assault the valley below. It looked as though we were scattered on hilltops at dawn to sacrifice virgins, make rain, set stone stelae in a ring. There was no place out of the wind. The straw grasses banged our legs.
Up in the sky where we stood, the air was lusterless yellow. To the west the sky was blue. Now the sun cleared the clouds. We cast rough shadows on the blowing grass; freezing, we waved our arms. Near the sun, the sky was bright and colorless. There was nothing to see.
It began with no ado. It was odd that such a well advertised public event should have no starting gun, no overture, no introductory speaker. I should have known right then that I was out of my depth. Without pause or preamble, silent as orbits, a piece of the sun went away. We looked at it through welders’ goggles. A piece of the sun was missing; in its place we saw empty sky.
I had seen a partial eclipse in 1970. A partial eclipse is very interesting. It bears almost no relation to a total eclipse. Seeing a partial eclipse bears the same relation to seeing a total eclipse as kissing a man does to marrying him, or as flying in an airplane does to falling out of an airplane. Although the one experience precedes the other, it in no way prepares you for it. During a partial eclipse the sky does not darken—not even when 94 percent of the sun is hidden. Nor does the sun, seen colorless through protective devices, seem terribly strange. We have all seen a sliver of light in the sky; we have all seen the crescent moon by day. However, during a partial eclipse the air does indeed get cold, precisely as if someone were standing between you and the fire. And blackbirds do fly back to their roosts. I had seen a partial eclipse before, and here was another.
What you see in an eclipse is entirely different from what you know. It is especially different for those of us whose grasp of astronomy is so frail that, given a flashlight, a grapefruit, two oranges, and 15 years, we still could not figure out which way to set the clocks for daylight saving time. Usually it is a bit of a trick to keep your knowledge from blinding you. But during an eclipse it is easy. What you see is much more convincing than any wild-eyed theory you may know.
You may read that the moon has something to do with eclipses. I have never seen the moon yet. You do not see the moon. So near the sun, it is as completely invisible as the stars are by day. What you see before your eyes is the sun going through phases. It gets narrower and narrower, as the waning moon does, and, like the ordinary moon, it travels alone in the simple sky. The sky is of course background. It does not appear to eat the sun; it is far behind the sun. The sun simply shaves away; gradually, you see less sun and more sky.
The sky’s blue was deepening, but there was no darkness. The sun was a wide crescent, like a segment of tangerine. The wind freshened and blew steadily over the hill. The eastern hill across the highway grew dusky and sharp. The towns and orchards in the valley to the south were dissolving into the blue light. Only the thin river held a trickle of sun.
Now the sky to the west deepened to indigo, a color never seen. A dark sky usually loses color. This was a saturated, deep indigo, up in the air. Stuck up into that unworldly sky was the cone of Mount Adams, and the alpenglow was upon it. The alpenglow is that red light of sunset that holds out on snowy mountaintops long after the valleys and tablelands are dimmed. “Look at Mount Adams,” I said, and that was the last sane moment I remember.
I turned back to the sun. It was going. The sun was going, and the world was wrong. The grasses were wrong; they were platinum. Their every detail of stem, head, and blade shone lightless and artificially distinct as an art photographer’s platinum print. This color has never been seen on Earth. The hues were metallic; their finish was matte. The hillside was a 19th-century tinted photograph from which the tints had faded. All the people you see in the photograph, distinct and detailed as their faces look, are now dead. The sky was navy blue. My hands were silver. All the distant hills’ grasses were finespun metal that the wind laid down. I was watching a faded color print of a movie filmed in the Middle Ages; I was standing in it, by some mistake. I was standing in a movie of hillside grasses filmed in the Middle Ages. I missed my own century, the people I knew, and the real light of day.
I looked at Gary. He was in the film. Everything was lost. He was a platinum print, a dead artist’s version of life. I saw on his skull the darkness of night mixed with the colors of day. My mind was going out; my eyes were receding the way galaxies recede to the rim of space. Gary was light-years away, gesturing inside a circle of darkness, down the wrong end of a telescope. He smiled as if he saw me; the stringy crinkles around his eyes moved. The sight of him, familiar and wrong, was something I was remembering from centuries hence, from the other side of death: Yes, that is the way he used to look, when we were living. When it was our generation’s turn to be alive. I could not hear him; the wind was too loud. Behind him the sun was going. We had all started down a chute of time. At first it was pleasant; now there was no stopping it. Gary was chuting away across space, moving and talking and catching my eye, chuting down the long corridor of separation. The skin on his face moved like thin bronze plating that would peel.
The grass at our feet was wild barley. It was the wild einkorn wheat that grew on the hilly flanks of the Zagros Mountains, above the Euphrates valley, above the valley of the river we called River. We harvested the grass with stone sickles, I remember. We found the grasses on the hillsides; we built our shelter beside them and cut them down. That is how he used to look then, that one, moving and living and catching my eye, with the sky so dark behind him, and the wind blowing. God save our life.
From all the hills came screams. A piece of sky beside the crescent sun was detaching. It was a loosened circle of evening sky, suddenly lit from the back. It was an abrupt black body out of nowhere; it was a flat disk; it was almost over the sun. That is when there were screams. At once this disk of sky slid over the sun like a lid. The sky snapped over the sun like a lens cover. The hatch in the brain slammed. Abruptly it was dark night, on the land and in the sky. In the night sky was a tiny ring of light. The hole where the sun belongs is very small. A thin ring of light marked its place. There was no sound. The eyes dried, the arteries drained, the lungs hushed. There was no world. We were the world’s dead people rotating and orbiting around and around, embedded in the planet’s crust, while the Earth rolled down. Our minds were light-years distant, forgetful of almost everything. Only an extraordinary act of will could recall to us our former, living selves and our contexts in matter and time. We had, it seems, loved the planet and loved our lives, but could no longer remember the way of them. We got the light wrong. In the sky was something that should not be there. In the black sky was a ring of light. It was a thin ring, an old, thin silver wedding band, an old, worn ring. It was an old wedding band in the sky, or a morsel of bone. There were stars. It was all over.
It is now that the temptation is strongest to leave these regions. We have seen enough; let’s go. Why burn our hands any more than we have to? But two years have passed; the price of gold has risen. I return to the same buried alluvial beds and pick through the strata again.
I saw, early in the morning, the sun diminish against a backdrop of sky. I saw a circular piece of that sky appear, suddenly detached, blackened, and backlit; from nowhere it came and overlapped the sun. It did not look like the moon. It was enormous and black. If I had not read that it was the moon, I could have seen the sight a hundred times and never thought of the moon once. (If, however, I had not read that it was the moon—if, like most of the world’s people throughout time, I had simply glanced up and seen this thing—then I doubtless would not have speculated much, but would have, like Emperor Louis of Bavaria in 840, simply died of fright on the spot.) It did not look like a dragon, although it looked more like a dragon than the moon. It looked like a lens cover, or the lid of a pot. It materialized out of thin air—black, and flat, and sliding, outlined in flame.
Seeing this black body was like seeing a mushroom cloud. The heart screeched. The meaning of the sight overwhelmed its fascination. It obliterated meaning itself. If you were to glance out one day and see a row of mushroom clouds rising on the horizon, you would know at once that what you were seeing, remarkable as it was, was intrinsically not worth remarking. No use running to tell anyone. Significant as it was, it did not matter a whit. For what is significance? It is significance for people. No people, no significance. This is all I have to tell you.
In the deeps are the violence and terror of which psychology has warned us. But if you ride these monsters deeper down, if you drop with them further over the world’s rim, you find what our sciences cannot locate or name, the substrate, the ocean or matrix or ether that buoys the rest, that gives goodness its power for good, and evil. Its power for evil, the unified field: our complex and inexplicable caring for one another, and for our life together here. This is given. It is not learned.
The world that lay under darkness and stillness following the closing of the lid was not the world we know. The event was over. Its devastation lay around about us. The clamoring mind and heart stilled, almost indifferent, certainly disembodied, frail, and exhausted. The hills were hushed, obliterated. Up in the sky, like a crater from some distant cataclysm, was a hollow ring.
You have seen photographs of the sun taken during a total eclipse. The corona fills the print. All of those photographs were taken through telescopes. The lenses of telescopes and cameras can no more cover the breadth and scale of the visual array than language can cover the breadth and simultaneity of internal experience. Lenses enlarge the sight, omit its context, and make of it a pretty and sensible picture, like something on a Christmas card. I assure you, if you send any shepherds a Christmas card on which is printed a three-by-three photograph of the angel of the Lord, the glory of the Lord, and a multitude of the heavenly host, they will not be sore afraid. More fearsome things can come in envelopes. More moving photographs than those of the sun’s corona can appear in magazines. But I pray you will never see anything more awful in the sky.
You see the wide world swaddled in darkness; you see a vast breadth of hilly land, and an enormous, distant, blackened valley; you see towns’ lights, a river’s path, and blurred portions of your hat and scarf; you see your husband’s face looking like an early black-and-white film; and you see a sprawl of black sky and blue sky together, with unfamiliar stars in it, some barely visible bands of cloud, and over there, a small white ring. The ring is as small as one goose in a flock of migrating geese—if you happen to notice a flock of migrating geese. It is one-360th part of the visible sky. The sun we see is less than half the diameter of a dime held at arm’s length.
The Crab Nebula, in the constellation Taurus, looks, through binoculars, like a smoke ring. It is a star in the process of exploding. Light from its explosion first reached the Earth in 1054; it was a supernova then, and so bright it shone in the daytime. Now it is not so bright, but it is still exploding. It expands at the rate of 70 million miles a day. It is interesting to look through binoculars at something expanding 70 million miles a day. It does not budge. Its apparent size does not increase. Photographs of the Crab Nebula taken 15 years ago seem identical to photographs of it taken yesterday. Some lichens are similar. Botanists have measured some ordinary lichens twice, at 50-year intervals, without detecting any growth at all. And yet their cells divide; they live.
The small ring of light was like these things—like a ridiculous lichen up in the sky, like a perfectly still explosion 4,200 light-years away: It was interesting, and lovely, and in witless motion, and it had nothing to do with anything.
It had nothing to do with anything. The sun was too small, and too cold, and too far away, to keep the world alive. The white ring was not enough. It was feeble and worthless. It was as useless as a memory; it was as off-kilter and hollow and wretched as a memory.
When you try your hardest to recall someone’s face, or the look of a place, you see in your mind’s eye some vague and terrible sight such as this. It is dark; it is insubstantial; it is all wrong.
The white ring and the saturated darkness made the Earth and the sky look as they must look in the memories of the careless dead. What I saw, what I seemed to be standing in, was all the wrecked light that the memories of the dead could shed upon the living world. We had all died in our boots on the hilltops of Yakima, and were alone in eternity. Empty space stoppered our eyes and mouths; we cared for nothing. We remembered our living days wrong. With great effort we had remembered some sort of circular light in the sky—but only the outline. Oh, and then the orchard trees withered, the ground froze, the glaciers slid down the valleys and overlapped the towns. If there had ever been people on Earth, nobody knew it. The dead had forgotten those they had loved. The dead were parted one from the other and could no longer remember the faces and lands they had loved in the light. They seemed to stand on darkened hilltops, looking down.
We teach our children one thing only, as we were taught: to wake up. We teach our children to look alive there, to join by words and activities the life of human culture on the planet’s crust. As adults we are almost all adept at waking up. We have so mastered the transition we have forgotten we ever learned it. Yet it is a transition we make a hundred times a day, as, like so many will-less dolphins, we plunge and surface, lapse and emerge. We live half our waking lives and all of our sleeping lives in some private, useless, and insensible waters we never mention or recall. Useless, I say. Valueless, I might add—until someone hauls their wealth up to the surface and into the wide-awake city, in a form that people can use.
I do not know how we got to the restaurant. Like Roethke, “I take my waking slow.” Gradually I seemed more or less alive, and already forgetful. It was now almost 9 in the morning. It was the day of a solar eclipse in central Washington, and a fine adventure for everyone. The sky was clear; there was a fresh breeze out of the north.
The restaurant was a roadside place with tables and booths. The other eclipse-watchers were there. From our booth we could see their cars’ California license plates, their University of Washington parking stickers. Inside the restaurant we were all eating eggs or waffles; people were fairly shouting and exchanging enthusiasms, like fans after a World Series game. Did you see ... ? Did you see ... ? Then somebody said something that knocked me for a loop.
A college student, a boy in a blue parka who carried a Hasselblad, said to us, “Did you see that little white ring? It looked like a Life Saver. It looked like a Life Saver up in the sky.”
And so it did. The boy spoke well. He was a walking alarm clock. I myself had at that time no access to such a word. He could write a sentence, and I could not. I grabbed that Life Saver and rode it to the surface. And I had to laugh. I had been dumbstruck on the Euphrates River, I had been dead and gone and grieving, all over the sight of something that, if you could claw your way up to that level, you would grant looked very much like a Life Saver. It was good to be back among people so clever; it was good to have all the world’s words at the mind’s disposal, so the mind could begin its task. All those things for which we have no words are lost. The mind—the culture—has two little tools, grammar and lexicon: a decorated sand bucket and a matching shovel. With these we bluster about the continents and do all the world’s work. With these we try to save our very lives.
There are a few more things to tell from this level, the level of the restaurant. One is the old joke about breakfast. “It can never be satisfied, the mind, never.” Wallace Stevens wrote that, and in the long run he was right. The mind wants to live forever, or to learn a very good reason why not. The mind wants the world to return its love, or its awareness; the mind wants to know all the world, and all eternity, and God. The mind’s sidekick, however, will settle for two eggs over easy.
The dear, stupid body is as easily satisfied as a spaniel. And, incredibly, the simple spaniel can lure the brawling mind to its dish. It is everlastingly funny that the proud, metaphysically ambitious, clamoring mind will hush if you give it an egg.
Further: While the mind reels in deep space, while the mind grieves or fears or exults, the workaday senses, in ignorance or idiocy, like so many computer terminals printing out market prices while the world blows up, still transcribe their little data and transmit them to the warehouse in the skull. Later, under the tranquilizing influence of fried eggs, the mind can sort through the data. The restaurant was a halfway house, a decompression chamber. There I remembered a few things more.
The deepest, and most terrifying, was this: I have said that I heard screams. (I have since read that screaming, with hysteria, is a common reaction even to expected total eclipses.) People on all the hillsides, including, I think, myself, screamed when the black body of the moon detached from the sky and rolled over the sun. But something else was happening at that same instant, and it was this, I believe, that made us scream.
The second before the sun went out we saw a wall of dark shadow come speeding at us. We no sooner saw it than it was upon us, like thunder. It roared up the valley. It slammed our hill and knocked us out. It was the monstrous swift shadow cone of the moon. I have since read that this wave of shadow moves at 1,800 miles an hour. Language can give no sense of this sort of speed—1,800 miles an hour. It was 195 miles wide. No end was in sight—you saw only the edge. It rolled at you across the land at 1,800 miles an hour, hauling darkness like plague behind it. Seeing it, and knowing it was coming straight for you, was like feeling a slug of anesthetic shoot up your arm. If you think very fast, you may have time to think, “Soon it will hit my brain.” You can feel the deadness race up your arm; you can feel the appalling, inhuman speed of your own blood. We saw the wall of shadow coming, and screamed before it hit.
This was the universe about which we have read so much and never before felt: the universe as a clockwork of loose spheres flung at stupefying, unauthorized speeds. How could anything moving so fast not crash, not veer from its orbit amok like a car out of control on a turn?
Less than two minutes later, when the sun emerged, the trailing edge of the shadow cone sped away. It coursed down our hill and raced eastward over the plain, faster than the eye could believe; it swept over the plain and dropped over the planet’s rim in a twinkling. It had clobbered us, and now it roared away. We blinked in the light. It was as though an enormous, loping god in the sky had reached down and slapped the Earth’s face.
Something else, something more ordinary, came back to me along about the third cup of coffee. During the moments of totality, it was so dark that drivers on the highway below turned on their cars’ headlights. We could see the highway’s route as a strand of lights. It was bumper-to-bumper down there. It was 8:15 in the morning, Monday morning, and people were driving into Yakima to work. That it was as dark as night, and eerie as hell, an hour after dawn apparently meant that in order to see to drive to work, people had to use their headlights. Four or five cars pulled off the road. The rest, in a line at least five miles long, drove to town. The highway ran between hills; the people could not have seen any of the eclipsed sun at all. Yakima will have another total eclipse in 2086. Perhaps, in 2086, businesses will give their employees an hour off.
From the restaurant we drove back to the coast. The highway crossing the Cascades range was open. We drove over the mountain like old pros. We joined our places on the planet’s thin crust; it held. For the time being, we were home free.
Early that morning at six, when we had checked out, the six bald men were sitting on folding chairs in the dim hotel lobby. The television was on. Most of them were awake. You might drown in your own spittle, God knows, at any time; you might wake up dead in a small hotel, a cabbage head watching TV while snows pile up in the passes, watching TV while the chili peppers smile and the moon passes over the sun and nothing changes and nothing is learned because you have lost your bucket and shovel and no longer care. What if you regain the surface and open your sack and find, instead of treasure, a beast that jumps at you? Or you may not come back at all. The winches may jam, the scaffolding buckle, the air-conditioning collapse. You may glance up one day and see by your headlamp the canary keeled over in its cage. You may reach into a cranny for pearls and touch a moray eel. You yank on your rope; it is too late.
Apparently people share a sense of these hazards, for when the total eclipse ended, an odd thing happened.
When the sun appeared as a blinding bead on the ring’s side, the eclipse was over. The black lens cover appeared again, backlit, and slid away. At once the yellow light made the sky blue again; the black lid dissolved and vanished. The real world began there. I remember now: We all hurried away. We were born and bored at a stroke. We rushed down the hill. We found our car; we saw the other people streaming down the hillsides; we joined the highway traffic and drove away.
We never looked back. It was a general vamoose, and an odd one, for when we left the hill, the sun was still partially eclipsed—a sight rare enough, and one which, in itself, we would probably have driven five hours to see. But enough is enough. One turns at last even from glory itself with a sigh of relief. From the depths of mystery, and even from the heights of splendor, we bounce back and hurry for the latitudes of home.
This post is excerpted from Dillard’s book The Abundance: Narrative Essays Old and New . Copyright © 2016 by Annie Dillard. Published by arrangement with Ecco, an imprint of HarperCollins Publishers.
When you buy a book using a link on this page, we receive a commission. Thank you for supporting The Atlantic.
Science Essay
Learn How to Write an A+ Science Essay
11 min read

People also read
150+ Engaging Science Essay Topics To Hook Your Readers
8 Impressive Science Essay Examples for Students
Science Fiction Essay: Examples & Easy Steps Guide
Essay About Science and Technology| Tips & Examples
Essay About Science in Everyday Life - Samples & Writing Tips
Check Out 5 Impressive Essay About Science Fair Examples
Did you ever imagine that essay writing was just for students in the Humanities? Well, think again!
For science students, tackling a science essay might seem challenging, as it not only demands a deep understanding of the subject but also strong writing skills.
However, fret not because we've got your back!
With the right steps and tips, you can write an engaging and informative science essay easily!
This blog will take you through all the important steps of writing a science essay, from choosing a topic to presenting the final work.
So, let's get into it!
- 1. What Is a Science Essay?
- 2. How To Write a Science Essay?
- 3. How to Structure a Science Essay?
- 4. Science Essay Examples
- 5. How to Choose the Right Science Essay Topic
- 6. Science Essay Topics
- 7. Science Essay Writing Tips
What Is a Science Essay?
A science essay is an academic paper focusing on a scientific topic from physics, chemistry, biology, or any other scientific field.
Science essays are mostly expository. That is, they require you to explain your chosen topic in detail. However, they can also be descriptive and exploratory.
A descriptive science essay aims to describe a certain scientific phenomenon according to established knowledge.
On the other hand, the exploratory science essay requires you to go beyond the current theories and explore new interpretations.
So before you set out to write your essay, always check out the instructions given by your instructor. Whether a science essay is expository or exploratory must be clear from the start. Or, if you face any difficulty, you can take help from a science essay writer as well.
Moreover, check out this video to understand scientific writing in detail.
Now that you know what it is, let's look at the steps you need to take to write a science essay.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job!
How To Write a Science Essay?
Writing a science essay is not as complex as it may seem. All you need to do is follow the right steps to create an impressive piece of work that meets the assigned criteria.
Here's what you need to do:
Choose Your Topic
A good topic forms the foundation for an engaging and well-written essay. Therefore, you should ensure that you pick something interesting or relevant to your field of study.
To choose a good topic, you can brainstorm ideas relating to the subject matter. You may also find inspiration from other science essays or articles about the same topic.
Conduct Research
Once you have chosen your topic, start researching it thoroughly to develop a strong argument or discussion in your essay.
Make sure you use reliable sources and cite them properly . You should also make notes while conducting your research so that you can reference them easily when writing the essay. Or, you can get expert assistance from an essay writing service to manage your citations.
Create an Outline
A good essay outline helps to organize the ideas in your paper. It serves as a guide throughout the writing process and ensures you don’t miss out on important points.
An outline makes it easier to write a well-structured paper that flows logically. It should be detailed enough to guide you through the entire writing process.
However, your outline should be flexible, and it's sometimes better to change it along the way to improve your structure.
Start Writing
Once you have a good outline, start writing the essay by following your plan.
The first step in writing any essay is to draft it. This means putting your thoughts down on paper in a rough form without worrying about grammar or spelling mistakes.
So begin your essay by introducing the topic, then carefully explain it using evidence and examples to support your argument.
Don't worry if your first draft isn't perfect - it's just the starting point!
Proofread & Edit
After finishing your first draft, take time to proofread and edit it for grammar and spelling mistakes.
Proofreading is the process of checking for grammatical mistakes. It should be done after you have finished writing your essay.
Editing, on the other hand, involves reviewing the structure and organization of your essay and its content. It should be done before you submit your final work.
Both proofreading and editing are essential for producing a high-quality essay. Make sure to give yourself enough time to do them properly!
After revising the essay, you should format it according to the guidelines given by your instructor. This could involve using a specific font size, page margins, or citation style.
Most science essays are written in Times New Roman font with 12-point size and double spacing. The margins should be 1 inch on all sides, and the text should be justified.
In addition, you must cite your sources properly using a recognized citation style such as APA , Chicago , or Harvard . Make sure to follow the guidelines closely so that your essay looks professional.
Following these steps will help you create an informative and well-structured science essay that meets the given criteria.
Tough Essay Due? Hire Tough Writers!
How to Structure a Science Essay?
A basic science essay structure includes an introduction, body, and conclusion.
Let's look at each of these briefly.
- Introduction
Your essay introduction should introduce your topic and provide a brief overview of what you will discuss in the essay. It should also state your thesis or main argument.
For instance, a thesis statement for a science essay could be,
"The human body is capable of incredible feats, as evidenced by the many athletes who have competed in the Olympic games."
The body of your essay will contain the bulk of your argument or discussion. It should be divided into paragraphs, each discussing a different point.
For instance, imagine you were writing about sports and the human body.
Your first paragraph can discuss the physical capabilities of the human body.
The second paragraph may be about the physical benefits of competing in sports.
Similarly, in the third paragraph, you can present one or two case studies of specific athletes to support your point.
Once you have explained all your points in the body, it’s time to conclude the essay.
Your essay conclusion should summarize the main points of your essay and leave the reader with a sense of closure.
In the conclusion, you reiterate your thesis and sum up your arguments. You can also suggest implications or potential applications of the ideas discussed in the essay.
By following this structure, you will create a well-organized essay.
Check out a few example essays to see this structure in practice.
Science Essay Examples
A great way to get inspired when writing a science essay is to look at other examples of successful essays written by others.
Here are some examples that will give you an idea of how to write your essay.
Science Essay About Genetics - Science Essay Example
Environmental Science Essay Example | PDF Sample
The Science of Nanotechnology
Science, Non-Science, and Pseudo-Science
The Science Of Science Education
Science in our Daily Lives
Short Science Essay Example
Let’s take a look at a short science essay:
Want to read more essay examples? Here, you can find more science essay examples to learn from.
How to Choose the Right Science Essay Topic
Choosing the right science essay topic is a critical first step in crafting a compelling and engaging essay. Here's a concise guide on how to make this decision wisely:
- Consider Your Interests: Start by reflecting on your personal interests within the realm of science. Selecting a topic that genuinely fascinates you will make the research and writing process more enjoyable and motivated.
- Relevance to the Course: Ensure that your chosen topic aligns with your course or assignment requirements. Read the assignment guidelines carefully to understand the scope and focus expected by your instructor.
- Current Trends and Issues: Stay updated with the latest scientific developments and trends. Opting for a topic that addresses contemporary issues not only makes your essay relevant but also demonstrates your awareness of current events in the field.
- Narrow Down the Scope: Science is vast, so narrow your topic to a manageable scope. Instead of a broad subject like "Climate Change," consider a more specific angle like "The Impact of Melting Arctic Ice on Global Sea Levels."
- Available Resources: Ensure that there are sufficient credible sources and research materials available for your chosen topic. A lack of resources can hinder your research efforts.
- Discuss with Your Instructor: If you're uncertain about your topic choice, don't hesitate to consult your instructor or professor. They can provide valuable guidance and may even suggest specific topics based on your academic goals.
Science Essay Topics
Choosing an appropriate topic for a science essay is one of the first steps in writing a successful paper.
Here are a few science essay topics to get you started:
- How space exploration affects our daily lives?
- How has technology changed our understanding of medicine?
- Are there ethical considerations to consider when conducting scientific research?
- How does climate change affect the biodiversity of different parts of the world?
- How can artificial intelligence be used in medicine?
- What impact have vaccines had on global health?
- What is the future of renewable energy?
- How do we ensure that genetically modified organisms are safe for humans and the environment?
- The influence of social media on human behavior: A social science perspective
- What are the potential risks and benefits of stem cell therapy?
Important science topics can cover anything from space exploration to chemistry and biology. So you can choose any topic according to your interests!
Need more topics? We have gathered 100+ science essay topics to help you find a great topic!
Continue reading to find some tips to help you write a successful science essay.
Science Essay Writing Tips
Once you have chosen a topic and looked at examples, it's time to start writing the science essay.
Here are some key tips for a successful essay:
- Research thoroughly
Make sure you do extensive research before you begin writing your paper. This will ensure that the facts and figures you include are accurate and supported by reliable sources.
- Use clear language
Avoid using jargon or overly technical language when writing your essay. Plain language is easier to understand and more engaging for readers.
- Referencing
Always provide references for any information you include in your essay. This will demonstrate that you acknowledge other people's work and show that the evidence you use is credible.
Make sure to follow the basic structure of an essay and organize your thoughts into clear sections. This will improve the flow and make your essay easier to read.
- Ask someone to proofread
It’s also a good idea to get someone else to proofread your work as they may spot mistakes that you have missed.
These few tips will help ensure that your science essay is well-written and informative!
You've learned the steps to writing a successful science essay and looked at some examples and topics to get you started.
Make sure you thoroughly research, use clear language, structure your thoughts, and proofread your essay. With these tips, you’re sure to write a great science essay!
Do you still need expert help writing a science essay? Our science essay writing service is here to help. With our team of professional writers, you can rest assured that your essay will be written to the highest standards.
Contact our essay service now to get started!
Also, do not forget to try our essay typer tool for quick and cost-free aid with your essays!

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Betty is a freelance writer and researcher. She has a Masters in literature and enjoys providing writing services to her clients. Betty is an avid reader and loves learning new things. She has provided writing services to clients from all academic levels and related academic fields.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!
Keep reading
Browse Course Material
Course info.
- Karen Boiko
Departments
- Comparative Media Studies/Writing
As Taught In
- Academic Writing
- Creative Writing
- Nonfiction Prose
Learning Resource Types
Science writing in contemporary society.
[AS] = The Best American Science and Nature Writing 2016 . Edited by Amy Stewart. Mariner Books, 2016. ISBN: 9780544748996.

You are leaving MIT OpenCourseWare
Scholar Blog
Classic papers: articles that have stood the test of time.
- March
- July
- April
- June
- January
- February
- September
- August
- October
- Classic Papers: Articles That Have Stood The Test ...
- November
- May
Essays About Science: Top 12 Examples and Prompts
Science can explain almost every aspect of our lives; if you want to write essays about science, start by reading our guide.
The word “science” comes from the Latin word Scientia or “knowledge,” It does indeed leave us with no shortage of knowledge as it advances to extraordinary levels. It is present in almost every aspect of our lives, allowing us to live the way we do today and helping us improve society.
In the 21st century, we see science everywhere. It has given us the technology we deem “essential” today, from our mobile phones to air conditioning units to lightbulbs and refrigerators. Yet, it has also allowed us to learn so much about the unknown, such as the endless vacuum of space and the ocean’s mysterious depths. It is, without a doubt, a vehicle for humanity to obtain knowledge and use this knowledge to flourish.
To start writing essays about science, look at some of our featured essay examples below.
1. The challenging environment for science in the 21st century by Nithaya Chetty
2. disadvantages of science by ella gray, 3. reflections from a nobel winner: scientists need time to make discoveries by donna strickland.
- 4. The fact of cloning by Cesar Hill
5. T. Rex Like You Haven’t Seen Him: With Feathers by Jason Farago
6. common, cheap ingredients can break down some ‘forever chemicals’ by jude coleman, 1. what is science, 2. a noteworthy scientist, 3. why is it important to study science, 4. are robots a net positive for society, 5. types of sciences, 6. science’s role in warfare.
“Open-ended, unfettered science in its purest form has, over the centuries, been pursued in the interests of understanding nature in a fundamental way, and long may that continue. Scientific ideas and discoveries have often been very successfully exploited for commercial gain and societal improvements, and much of the science system today the world over is designed to push scientists in the direction of more relevance.”
For South Africa to prosper, Chetty encourages cooperation and innovation among scientists. He discusses several problems the country faces, including the politicization of research, a weak economy, and misuse of scientific discoveries. These challenges, he believes, can be overcome if the nation works as one and with the international community and if the education system is improved.
“Technology can make people lazy. Many people are already dependent and embrace this technology. Like students playing computer games instead of going to school or study. Technology also brings us privacy issues. From cell phone signal interceptions to email hacking, people are now worried about their once private information becoming public knowledge and making profit out of video scandals.”
Gray discusses the adverse effects technology, a science product, has had on human life and society. These include pollution, the inability to communicate properly, and laziness.
She also acknowledges that technology has made life easier for almost everyone but believes that technology, as it is used now, is detrimental; more responsible use of technology is ideal.
“We must give scientists the opportunity through funding and time to pursue curiosity-based, long-term, basic-science research. Work that does not have direct ramifications for industry or our economy is also worthy. There’s no telling what can come from supporting a curious mind trying to discover something new.”
Strickland, a Nobel Prize winner, explains that a great scientific discovery can only come with ample time for scientists to research, using her work as an example. She describes her work on chirped pulse amplification and its possible applications, including removing brain tumors. Her Nobel-awarded work was done over a long time, and scientists must be afforded ample time and funding to make breakthroughs like hers.
4. The fact of cloning by Cesar Hill
“Any research into human cloning would eventually need to be tested on humans. Cloning might be used to create a “perfect human”. Cloning might have a detrimental effect family relationship. However the debate over cloning has more pros out weighting the cons, giving us a over site of the many advantages cloning has and the effects of it as well. Cloning has many ups and downs nevertheless there are many different ways in which it can be used to adapt and analyse new ways of medicine.”
Hill details both the pros and cons of cloning. It can be used for medical purposes and help us understand genetics more, perhaps even allowing us to prevent genetic diseases in children. However, it is expensive, and many oppose it on religious grounds. Regardless, Hill believes that the process has more advantages than disadvantages and is a net good.
“For the kids who will throng this new exhibition, and who will adore this show’s colorful animations and fossilized dino poop, T. rex may still appear to be a thrilling monster. But staring in the eyes of the feather-flecked annihilators here, adults may have a more uncanny feeling of identification with the beasts at the pinnacle of the food chain. You can be a killer of unprecedented savagery, but the climate always takes the coup de grâce.”
In his essay, Farago reviews an exhibition on the Tyrannosaurus Rex involving an important scientific discovery: it was a feathered dinosaur. He details the different displays in the exhibition, including models of other dinosaurs that helped scientists realize that the T-Rex had feathers.
“Understanding this mechanism is just one step in undoing forever chemicals, Dichtel’s team said. And more research is needed: There are other classes of PFAS that require their own solutions. This process wouldn’t work to tackle PFAS out in the environment, because it requires a concentrated amount of the chemicals. But it could one day be used in wastewater treatment plants, where the pollutants could be filtered out of the water, concentrated and then broken down.”
Coleman explains a discovery by which scientists were able to break down a perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substance, a “forever chemical” dangerous to the environment. He explains how they could break the chemical bond and turn the “forever chemical” into something harmless. This is important because pollution can be reduced significantly, particularly in the water.
Writing Prompts on Essays about Science
“Science” is quite a broad term and encompasses many concepts and definitions. Define science, explain what it involves and how we can use it, and give examples of how it is present in the world. If you want, you can also briefly discuss what science means to you personally.
Many individuals have made remarkable scientific discoveries, contributing to the wealth of knowledge we have acquired through science. For your essay, choose one scientist you feel has made a noteworthy contribution to their field. Then, give a brief background on the scientists and explain the discovery or invention that makes them essential.
Consider what it means to study science: how is it relevant now? What lessons can we learn from science? Then, examine the presence of science in today’s world and write about the importance of science in our day-to-day lives- be sure to give examples to support your points. Finally, in your essay, be sure to keep in mind the times we are living in today.

When we think of science, robots are often one of the first things that come to mind. However, there is much to discuss regarding safety, especially artificial intelligence. Discuss the pros and cons of robots and AI, then conclude whether or not the benefits outweigh the disadvantages. Finally, provide adequate evidence to reinforce your argument and explain it in detail.
From biology to chemistry to physics, science has many branches, each dealing with different aspects of the world and universe. Choose one branch of science and then explain what it is, define basic concepts under this science, and give examples of how it is applied: Are any inventions requiring it? How about something we know today thanks to scientific discovery? Answer these questions in your own words for a compelling essay.
Undoubtedly, technology developed using science has had devastating effects, from nuclear weapons to self-flying fighter jets to deadly new guns and tanks. Examine scientific developments’ role in the war: Do they make it more brutal? Or do they reduce the casualties? Make sure to conduct ample research before writing your essay; this topic is debatable.
For help with your essays, check out our round-up of the best essay checkers .
If you’re looking for inspiration, check out our round-up of essay topics about nature .

Martin is an avid writer specializing in editing and proofreading. He also enjoys literary analysis and writing about food and travel.
View all posts

Ideas That Created the Future : Classic Papers of Computer Science
Harry Lewis is Gordon McKay Research Professor of Computer Science at Harvard University. He is the coauthor of Blown to Bits: Your Life, Liberty, and Happiness after the Digital Explosion, coeditor of What Is College For? , and editor of Ideas That Created the Futur e (MIT Press).
Classic papers by thinkers ranging from Aristotle and Leibniz to Norbert Wiener and Gordon Moore that chart the evolution of computer science.
Ideas That Created the Future collects forty-six classic papers in computer science that map the evolution of the field. It covers all aspects of computer science: theory and practice, architectures and algorithms, and logic and software systems, with an emphasis on the period of 1936–1980 but also including important earlier work. Offering papers by thinkers ranging from Aristotle and Leibniz to Alan Turing and Nobert Wiener, the book documents the discoveries and inventions that created today's digital world. A brief essay by volume editor Harry Lewis, offering historical and intellectual context, accompanies each paper.
Readers will learn that we owe to Aristotle the realization that fixed rules of logic can apply to different phenomena—that logic provides a general framework for reasoning—and that Leibniz recognized the merits of binary notation. They can read Ada Lovelace's notes on L. F. Menabrea's sketch of an analytical engine, George Boole's attempt to capture the rules of reason in mathematical form, David Hilbert's famous 1900 address, “Mathematical Problems,” and Alan Turing's illumination of a metamathematical world. Later papers document the “Cambrian era” of 1950s computer design, Maurice Wilkes's invention of microcode, Grace Hopper's vision of a computer's “education,” Ivan Sutherland's invention of computer graphics at MIT, Whitfield Diffie and Martin Hellman's pioneering work on encryption, and much more. Lewis's guided tour of a burgeoning field is especially welcome at a time when computer education is increasingly specialized.
- Permissions
- Cite Icon Cite
Ideas That Created the Future : Classic Papers of Computer Science Edited by: Harry R. Lewis https://doi.org/10.7551/mitpress/12274.001.0001 ISBN (electronic): 9780262363174 Publisher: The MIT Press Published: 2021
Download citation file:
- Ris (Zotero)
- Reference Manager
Table of Contents
- [ Front Matter ] Doi: https://doi.org/10.7551/mitpress/12274.003.0051 Open the PDF Link PDF for [ Front Matter ] in another window
- Preface By Harry Lewis Harry Lewis Search for other works by this author on: This Site Google Scholar Doi: https://doi.org/10.7551/mitpress/12274.003.0001 Open the PDF Link PDF for Preface in another window
- Introduction: The Roots and Growth of Computer Science Doi: https://doi.org/10.7551/mitpress/12274.003.0002 Open the PDF Link PDF for Introduction: The Roots and Growth of Computer Science in another window
- 1: Prior Analytics (~350 BCE) By Aristotle Aristotle Search for other works by this author on: This Site Google Scholar Doi: https://doi.org/10.7551/mitpress/12274.003.0003 Open the PDF Link PDF for 1: Prior Analytics (~350 BCE) in another window
- 2: The True Method (1677) By Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz Search for other works by this author on: This Site Google Scholar Doi: https://doi.org/10.7551/mitpress/12274.003.0004 Open the PDF Link PDF for 2: The True Method (1677) in another window
- 3: Sketch of the Analytical Engine (1843) By L. F. Menabrea L. F. Menabrea Search for other works by this author on: This Site Google Scholar Doi: https://doi.org/10.7551/mitpress/12274.003.0005 Open the PDF Link PDF for 3: Sketch of the Analytical Engine (1843) in another window
- 4: An Investigation of the Laws of Thought on Which Are Founded the Mathematical Theories of Logic and Probabilities (1854) By George Boole George Boole Search for other works by this author on: This Site Google Scholar Doi: https://doi.org/10.7551/mitpress/12274.003.0006 Open the PDF Link PDF for 4: An Investigation of the Laws of Thought on Which Are Founded the Mathematical Theories of Logic and Probabilities (1854) in another window
- 5: Mathematical Problems (1900) By David Hilbert David Hilbert Search for other works by this author on: This Site Google Scholar Doi: https://doi.org/10.7551/mitpress/12274.003.0007 Open the PDF Link PDF for 5: Mathematical Problems (1900) in another window
- 6: On Computable Numbers, with an Application to the Entscheidungsproblem (1936) By Alan Mathison Turing Alan Mathison Turing Search for other works by this author on: This Site Google Scholar Doi: https://doi.org/10.7551/mitpress/12274.003.0008 Open the PDF Link PDF for 6: On Computable Numbers, with an Application to the Entscheidungsproblem (1936) in another window
- 7: A Proposed Automatic Calculating Machine (1937) By Howard Hathaway Aiken Howard Hathaway Aiken Search for other works by this author on: This Site Google Scholar Doi: https://doi.org/10.7551/mitpress/12274.003.0009 Open the PDF Link PDF for 7: A Proposed Automatic Calculating Machine (1937) in another window
- 8: A Symbolic Analysis of Relay and Switching Circuits (1938) By Claude Shannon Claude Shannon Search for other works by this author on: This Site Google Scholar Doi: https://doi.org/10.7551/mitpress/12274.003.0010 Open the PDF Link PDF for 8: A Symbolic Analysis of Relay and Switching Circuits (1938) in another window
- 9: A Logical Calculus of the Ideas Immanent in Nervous Activity (1943) By Warren McCulloch , Warren McCulloch Search for other works by this author on: This Site Google Scholar Walter Pitts Walter Pitts Search for other works by this author on: This Site Google Scholar Doi: https://doi.org/10.7551/mitpress/12274.003.0011 Open the PDF Link PDF for 9: A Logical Calculus of the Ideas Immanent in Nervous Activity (1943) in another window
- 10: First Draft of a Report on the EDVAC (1945) By John von Neumann John von Neumann Search for other works by this author on: This Site Google Scholar Doi: https://doi.org/10.7551/mitpress/12274.003.0012 Open the PDF Link PDF for 10: First Draft of a Report on the EDVAC (1945) in another window
- 11: As We May Think (1945) By Vannevar Bush Vannevar Bush Search for other works by this author on: This Site Google Scholar Doi: https://doi.org/10.7551/mitpress/12274.003.0013 Open the PDF Link PDF for 11: As We May Think (1945) in another window
- 12: A Mathematical Theory of Communication (1948) By Claude Shannon Claude Shannon Search for other works by this author on: This Site Google Scholar Doi: https://doi.org/10.7551/mitpress/12274.003.0014 Open the PDF Link PDF for 12: A Mathematical Theory of Communication (1948) in another window
- 13: Error Detecting and Error Correcting Codes (1950) By R. W. Hamming R. W. Hamming Search for other works by this author on: This Site Google Scholar Doi: https://doi.org/10.7551/mitpress/12274.003.0015 Open the PDF Link PDF for 13: Error Detecting and Error Correcting Codes (1950) in another window
- 14: Computing Machinery and Intelligence (1950) By Alan Mathison Turing Alan Mathison Turing Search for other works by this author on: This Site Google Scholar Doi: https://doi.org/10.7551/mitpress/12274.003.0016 Open the PDF Link PDF for 14: Computing Machinery and Intelligence (1950) in another window
- 15: The Best Way to Design an Automatic Calculating Machine (1951) By Maurice Wilkes Maurice Wilkes Search for other works by this author on: This Site Google Scholar Doi: https://doi.org/10.7551/mitpress/12274.003.0017 Open the PDF Link PDF for 15: The Best Way to Design an Automatic Calculating Machine (1951) in another window
- 16: The Education of a Computer (1952) By Grace Murray Hopper Grace Murray Hopper Search for other works by this author on: This Site Google Scholar Doi: https://doi.org/10.7551/mitpress/12274.003.0018 Open the PDF Link PDF for 16: The Education of a Computer (1952) in another window
- 17: On the Shortest Spanning Subtree of a Graph and the Traveling Salesman Problem (1956) By Joseph B. Kruskal, Jr. Joseph B. Kruskal, Jr. Search for other works by this author on: This Site Google Scholar Doi: https://doi.org/10.7551/mitpress/12274.003.0019 Open the PDF Link PDF for 17: On the Shortest Spanning Subtree of a Graph and the Traveling Salesman Problem (1956) in another window
- 18: The Perceptron: A Probabilistic Model for Information Storage and Organization (1958) By Frank Rosenblatt Frank Rosenblatt Search for other works by this author on: This Site Google Scholar Doi: https://doi.org/10.7551/mitpress/12274.003.0020 Open the PDF Link PDF for 18: The Perceptron: A Probabilistic Model for Information Storage and Organization (1958) in another window
- 19: Some Moral and Technical Consequences of Automation (1960) By Norbert Wiener Norbert Wiener Search for other works by this author on: This Site Google Scholar Doi: https://doi.org/10.7551/mitpress/12274.003.0021 Open the PDF Link PDF for 19: Some Moral and Technical Consequences of Automation (1960) in another window
- 20: Man–Computer Symbiosis (1960) By J. C. R. Licklider J. C. R. Licklider Search for other works by this author on: This Site Google Scholar Doi: https://doi.org/10.7551/mitpress/12274.003.0022 Open the PDF Link PDF for 20: Man–Computer Symbiosis (1960) in another window
- 21: Recursive Functions of Symbolic Expressions and Their Computation by Machine (1960) By John McCarthy John McCarthy Search for other works by this author on: This Site Google Scholar Doi: https://doi.org/10.7551/mitpress/12274.003.0023 Open the PDF Link PDF for 21: Recursive Functions of Symbolic Expressions and Their Computation by Machine (1960) in another window
- 22: Augmenting Human Intellect: A Conceptual Framework (1962) By Douglas C. Engelbart Douglas C. Engelbart Search for other works by this author on: This Site Google Scholar Doi: https://doi.org/10.7551/mitpress/12274.003.0024 Open the PDF Link PDF for 22: Augmenting Human Intellect: A Conceptual Framework (1962) in another window
- 23: An Experimental Time-Sharing System (1962) By Fernando Corbató , Fernando Corbató Search for other works by this author on: This Site Google Scholar Marjorie Merwin Daggett , Marjorie Merwin Daggett Search for other works by this author on: This Site Google Scholar Robert C. Daley Robert C. Daley Search for other works by this author on: This Site Google Scholar Doi: https://doi.org/10.7551/mitpress/12274.003.0025 Open the PDF Link PDF for 23: An Experimental Time-Sharing System (1962) in another window
- 24: Sketchpad (1963) By Ivan E. Sutherland Ivan E. Sutherland Search for other works by this author on: This Site Google Scholar Doi: https://doi.org/10.7551/mitpress/12274.003.0026 Open the PDF Link PDF for 24: Sketchpad (1963) in another window
- 25: Cramming More Components onto Integrated Circuits (1965) By Gordon Moore Gordon Moore Search for other works by this author on: This Site Google Scholar Doi: https://doi.org/10.7551/mitpress/12274.003.0027 Open the PDF Link PDF for 25: Cramming More Components onto Integrated Circuits (1965) in another window
- 26: Solution of a Problem in Concurrent Program Control (1965) By Edsger Dijkstra Edsger Dijkstra Search for other works by this author on: This Site Google Scholar Doi: https://doi.org/10.7551/mitpress/12274.003.0028 Open the PDF Link PDF for 26: Solution of a Problem in Concurrent Program Control (1965) in another window
- 27: ELIZA—A Computer Program for the Study of Natural Language Communication between Man and Machine (1966) By Joseph Weizenbaum Joseph Weizenbaum Search for other works by this author on: This Site Google Scholar Doi: https://doi.org/10.7551/mitpress/12274.003.0029 Open the PDF Link PDF for 27: ELIZA—A Computer Program for the Study of Natural Language Communication between Man and Machine (1966) in another window
- 28: The Structure of the “THE”-Multiprogramming System (1968) By Edsger Dijkstra Edsger Dijkstra Search for other works by this author on: This Site Google Scholar Doi: https://doi.org/10.7551/mitpress/12274.003.0030 Open the PDF Link PDF for 28: The Structure of the “THE”-Multiprogramming System (1968) in another window
- 29: Go To Statement Considered Harmful (1968) By Edsger Dijkstra Edsger Dijkstra Search for other works by this author on: This Site Google Scholar Doi: https://doi.org/10.7551/mitpress/12274.003.0031 Open the PDF Link PDF for 29: Go To Statement Considered Harmful (1968) in another window
- 30: Gaussian Elimination is Not Optimal (1969) By Volker Strassen Volker Strassen Search for other works by this author on: This Site Google Scholar Doi: https://doi.org/10.7551/mitpress/12274.003.0032 Open the PDF Link PDF for 30: Gaussian Elimination is Not Optimal (1969) in another window
- 31: An Axiomatic Basis for Computer Programming (1969) By C. A. R. Hoare C. A. R. Hoare Search for other works by this author on: This Site Google Scholar Doi: https://doi.org/10.7551/mitpress/12274.003.0033 Open the PDF Link PDF for 31: An Axiomatic Basis for Computer Programming (1969) in another window
- 32: A Relational Model of Large Shared Data Banks (1970) By Edgar F. Codd Edgar F. Codd Search for other works by this author on: This Site Google Scholar Doi: https://doi.org/10.7551/mitpress/12274.003.0034 Open the PDF Link PDF for 32: A Relational Model of Large Shared Data Banks (1970) in another window
- 33: Managing the Development of Large Software Systems (1970) By Winston W. Royce Winston W. Royce Search for other works by this author on: This Site Google Scholar Doi: https://doi.org/10.7551/mitpress/12274.003.0035 Open the PDF Link PDF for 33: Managing the Development of Large Software Systems (1970) in another window
- 34: The Complexity of Theorem-Proving Procedures (1971) By Stephen A. Cook Stephen A. Cook Search for other works by this author on: This Site Google Scholar Doi: https://doi.org/10.7551/mitpress/12274.003.0036 Open the PDF Link PDF for 34: The Complexity of Theorem-Proving Procedures (1971) in another window
- 35: A Statistical Interpretation of Term Specificity and Its Application in Retrieval (1972) By Karen Spärck Jones Karen Spärck Jones Search for other works by this author on: This Site Google Scholar Doi: https://doi.org/10.7551/mitpress/12274.003.0037 Open the PDF Link PDF for 35: A Statistical Interpretation of Term Specificity and Its Application in Retrieval (1972) in another window
- 36: Reducibility among Combinatorial Problems (1972) By Richard Karp Richard Karp Search for other works by this author on: This Site Google Scholar Doi: https://doi.org/10.7551/mitpress/12274.003.0038 Open the PDF Link PDF for 36: Reducibility among Combinatorial Problems (1972) in another window
- 37: The Unix Time-Sharing System (1974) By Dennis Ritchie , Dennis Ritchie Search for other works by this author on: This Site Google Scholar Kenneth Thompson Kenneth Thompson Search for other works by this author on: This Site Google Scholar Doi: https://doi.org/10.7551/mitpress/12274.003.0039 Open the PDF Link PDF for 37: The Unix Time-Sharing System (1974) in another window
- 38: A Protocol for Packet Network Intercommunication (1974) By Vinton Cerf , Vinton Cerf Search for other works by this author on: This Site Google Scholar Robert Kahn Robert Kahn Search for other works by this author on: This Site Google Scholar Doi: https://doi.org/10.7551/mitpress/12274.003.0040 Open the PDF Link PDF for 38: A Protocol for Packet Network Intercommunication (1974) in another window
- 39: Programming with Abstract Data Types (1974) By Barbara Liskov , Barbara Liskov Search for other works by this author on: This Site Google Scholar Stephen Zilles Stephen Zilles Search for other works by this author on: This Site Google Scholar Doi: https://doi.org/10.7551/mitpress/12274.003.0041 Open the PDF Link PDF for 39: Programming with Abstract Data Types (1974) in another window
- 40: The Mythical Man-Month (1975) By Frederick C. Brooks Frederick C. Brooks Search for other works by this author on: This Site Google Scholar Doi: https://doi.org/10.7551/mitpress/12274.003.0042 Open the PDF Link PDF for 40: The Mythical Man-Month (1975) in another window
- 41: Ethernet: Distributed Packet Switching for Local Computer Networks (1976) By Robert Metcalfe , Robert Metcalfe Search for other works by this author on: This Site Google Scholar David R. Boggs David R. Boggs Search for other works by this author on: This Site Google Scholar Doi: https://doi.org/10.7551/mitpress/12274.003.0043 Open the PDF Link PDF for 41: Ethernet: Distributed Packet Switching for Local Computer Networks (1976) in another window
- 42: New Directions in Cryptography (1976) By Whitfield Diffie , Whitfield Diffie Search for other works by this author on: This Site Google Scholar Martin Hellman Martin Hellman Search for other works by this author on: This Site Google Scholar Doi: https://doi.org/10.7551/mitpress/12274.003.0044 Open the PDF Link PDF for 42: New Directions in Cryptography (1976) in another window
- 43: Big Omicron and Big Omega and Big Theta (1976) By Donald E. Knuth Donald E. Knuth Search for other works by this author on: This Site Google Scholar Doi: https://doi.org/10.7551/mitpress/12274.003.0045 Open the PDF Link PDF for 43: Big Omicron and Big Omega and Big Theta (1976) in another window
- 44: Social Processes and Proofs of Theorems and Programs (1977) By Richard DeMillo , Richard DeMillo Search for other works by this author on: This Site Google Scholar Richard Lipton , Richard Lipton Search for other works by this author on: This Site Google Scholar Alan Perlis Alan Perlis Search for other works by this author on: This Site Google Scholar Doi: https://doi.org/10.7551/mitpress/12274.003.0046 Open the PDF Link PDF for 44: Social Processes and Proofs of Theorems and Programs (1977) in another window
- 45: A Method for Obtaining Digital Signatures and Public-Key Cryptosystems (1978) By Ronald Rivest , Ronald Rivest Search for other works by this author on: This Site Google Scholar Adi Shamir , Adi Shamir Search for other works by this author on: This Site Google Scholar Len Adleman Len Adleman Search for other works by this author on: This Site Google Scholar Doi: https://doi.org/10.7551/mitpress/12274.003.0047 Open the PDF Link PDF for 45: A Method for Obtaining Digital Signatures and Public-Key Cryptosystems (1978) in another window
- 46: How to Share a Secret (1979) By Adi Shamir Adi Shamir Search for other works by this author on: This Site Google Scholar Doi: https://doi.org/10.7551/mitpress/12274.003.0048 Open the PDF Link PDF for 46: How to Share a Secret (1979) in another window
- Bibliography Doi: https://doi.org/10.7551/mitpress/12274.003.0049 Open the PDF Link PDF for Bibliography in another window
- Index Doi: https://doi.org/10.7551/mitpress/12274.003.0050 Open the PDF Link PDF for Index in another window
- Open Access
A product of The MIT Press
Mit press direct.
- About MIT Press Direct
Information
- Accessibility
- For Authors
- For Customers
- For Librarians
- Direct to Open
- Media Inquiries
- Rights and Permissions
- For Advertisers
- About the MIT Press
- The MIT Press Reader
- MIT Press Blog
- Seasonal Catalogs
- MIT Press Home
- Give to the MIT Press
- Direct Service Desk
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Statement
- Crossref Member
- COUNTER Member
- The MIT Press colophon is registered in the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
Science Essay Examples

Best Science Essay Examples to Learn From
Published on: May 3, 2023
Last updated on: Jan 31, 2024

Share this article
Are you struggling to write a science essay that stands out?
Are you tired of feeling overwhelmed by scientific jargon and complicated concepts?
You're not alone.
Science essays can be a challenge for even the most dedicated students. It's no wonder that so many students struggle to produce top-notch papers.
But fear not!
In this blog post, we'll provide you with some science essay examples and tips. We will help you write a top-notch paper that impresses your professor and earns you a high grade.
So buckle up and get ready to tackle science essays like a pro!
On This Page On This Page -->
Science Essay Examples for Students
Writing a science essay can be a daunting task for students. However, with the right guidance and examples, it can also be a rewarding and enlightening experience.
Here, we'll provide you with examples so you can elevate your own writing.
Science Essay Example SPM
Scientific Essay Example Pdf (Insert
Science Paper Example
Science Project Essay Example
Science Essay Examples for Different Subjects
Science is a vast field that encompasses many different subjects, from biology to physics to chemistry. As a student, you may find yourself tasked with writing a science essay on a subject that you're not particularly familiar with.
We have provided you with science essay examples for different subjects to help you get started.
Social Science Essay Example
Political Science Essay Example
Environmental Science Essay Example
Health Science Essay Example
Computer Science Essay Example
University Science Essay Examples
Science essays are important part of university-level education. However, different universities may have different requirements and expectations when it comes to writing these essays.
That's why we've compiled some science essay examples for different universities. You can see what works and what doesn't, and tailor your own writing accordingly.
Scientific Essay Example University
Mcmaster Health Science Essay Example
Cornell Arts And Science Essay Example

Tough Essay Due? Hire Tough Writers!
Structure of a Science Essay
Science essays are a crucial part of many subjects, and learning to structure them effectively is essential for achieving academic success.
Letâs explore scientific essay structure.
Introduction
The introduction of a science essay should introduce the topic and provide some context for the reader.
You should explain the purpose of the essay and provide a thesis statement that outlines the main argument you will make in the essay. A good introduction should also capture the reader's interest and motivate them to read on.
Check out these how to start a science essay examples for better understanding:
Body Paragraphs
The body paragraphs of a science essay should provide evidence to support the thesis statement. You should use scientific evidence, research, and data to support your argument.
Each paragraph should focus on one key point, and the points should be organized logically to create a coherent argument. It is essential to provide citations for all sources you use in your essay.
Here is an example for you:
The conclusion of a science essay should summarize the main points of the essay and restate the thesis statement in a compelling manner.
You should also provide some final thoughts or recommendations based on the evidence presented in the essay.
The conclusion should be concise and leave a lasting impression on the reader.
Natural Science Essay Topics
There are countless interesting, thought-provoking and problem solving essay topics in science.
Explore some compelling natural science essay topics to inspire your writing.
Science Essay Topics for 5th Graders
- The importance of recycling for our environment
- The different types of clouds and how they form
- How animals hibernate during the winter months
- The different types of rocks and how they are formed
- The role of bees in pollination and food production
- How light travels and how we see objects
- The properties of magnets and how they work
- The different stages of stem cell research
- The human digestive system and how it works
- The effects of pollution on our environment and health
Science Essay Topics for 6th Graders
- The impact of climate change on the planet
- The different types of energy and how they are produced
- The importance of water conservation and management
- The role of artificial intelligence in human life
- The structure and function of the human respiratory system
- The properties and uses of acids and bases
- The effect of light on plant growth and development
- The differences between renewable and non-renewable energy sources
- The process of photosynthesis and its importance for life on Earth
- The impact of technology on the environment and society
Science Essay Topics for 7th Graders
- The structure and function of the human circulatory system
- The different types of fossils and how they are formed
- The impact of natural disasters on the environment and human life
- The pros and cons of bacteria in our bodies and in the environment
- The physics of sound and how it travels
- The effects of air pollution in United States
- The properties and uses of different types of waves (sound, light, etc.)
- The process of cell division and its role in growth and repair
- The structure and function of the human nervous system
- The different types of ecosystems and their unique characteristics
Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job!
Tips for Writing a Science Essay
Writing a science essay can be challenging, especially if you don't have much experience in writing academic papers.
However, with the right approach and strategies, you can produce a high-quality science essays.
Here are some tips to help you write a successful science essay:
Understand the assignment requirements: Before you start writing your essay, make sure you understand the assignment requirements. Read the prompt carefully and make note of any specific guidelines or formatting requirements.
Choose a topic that interests you: Writing about a topic that you find interesting and engaging can make the process enjoyable and rewarding. Consider topics that you have studied in class or that you have a personal interest in.
Conduct thorough research: To write a successful science essay, you need to have a deep understanding of the topic you are writing about. Conduct thorough research using reliable sources such as academic journals, textbooks, and reputable websites.
Develop a clear and concise thesis statement: Your thesis statement should clearly state your argument or position on the topic you are writing about. It should be concise and specific, and should be supported by evidence throughout your essay.
Use evidence to support your claims: When writing a science essay, it's important to use evidence to support your claims and arguments. This can include scientific data, research findings, and expert opinions.
Edit and proofread your essay: Before submitting your essay, make sure to edit and proofread it carefully. Check for spelling and grammatical errors. Ensure that your essay is formatted correctly according to the assignment requirements.
In conclusion, this blog has provided a comprehensive guide to writing a successful science essay.
By following the tips, students can produce high-quality essays that showcase their understanding of science.
If you're struggling to write a science essay or need additional assistance, CollegeEssay.org is one of the best online essay services to help you out,
Our expert writers have extensive experience in writing science essays for students of all levels.
So why wait? Contact our science essay writing service today!
Frequently Asked Questions
What are some common mistakes to avoid when writing a science essay.
Some common mistakes to avoid include:
- Plagiarizing content
- Using incorrect or unreliable sources
- Failing to clearly state your thesis
- Using overly complex language
How can I make my science essay stand out?
To make your science essay stand out, consider choosing a unique or controversial topic. Using relevant and up-to-date sources, and present your information in a clear and concise manner. You can also consider using visuals such as graphs or charts to enhance your essay.
What should I do if I'm struggling to come up with a topic for my science essay?
If you're struggling to come up with a topic for your science essay, consider discussing potential topics with your instructor or classmates. You can also conduct research online or in academic journals to find inspiration.
How important is research when writing a science essay?
Research is an essential component of writing a science essay. Your essay should be grounded in accurate and reliable scientific information. That is why it's important to conduct thorough research using reputable sources.
Can I use personal anecdotes or experiences in my science essay?
While personal anecdotes or experiences can be engaging, they may not always be relevant to a science essay. It's important to focus on presenting factual information and scientific evidence to support your argument or position.
Caleb S. (Law, Literature)
Caleb S. has extensive experience in writing and holds a Masters from Oxford University. He takes great satisfaction in helping students exceed their academic goals. Caleb always puts the needs of his clients first and is dedicated to providing quality service.
Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!

Legal & Policies
- Privacy Policy
- Cookies Policy
- Terms of Use
- Refunds & Cancellations
- Our Writers
- Success Stories
- Our Guarantees
- Affiliate Program
- Referral Program
- AI Essay Writer
Disclaimer: All client orders are completed by our team of highly qualified human writers. The essays and papers provided by us are not to be used for submission but rather as learning models only.
Essay on Science for Students and Children
500+ words essay on science.
Essay on science: As we look back in our ancient times we see so much development in the world. The world is full of gadgets and machinery . Machinery does everything in our surroundings. How did it get possible? How did we become so modern? It was all possible with the help of science. Science has played a major role in the development of our society. Furthermore, Science has made our lives easier and carefree.

Science in our Daily Lives
As I have mentioned earlier Science has got many changes in our lives. First of all, transportation is easier now. With the help of Science it now easier to travel long distances . Moreover, the time of traveling is also reduced. Various high-speed vehicles are available these days. These vehicles have totally changed. The phase of our society. Science upgraded steam engines to electric engines. In earlier times people were traveling with cycles. But now everybody travels on motorcycles and cars. This saves time and effort. And this is all possible with the help of Science.
Secondly, Science made us reach to the moon. But we never stopped there. It also gave us a glance at Mars. This is one of the greatest achievements. This was only possible with Science. These days Scientists make many satellites . Because of which we are using high-speed Internet. These satellites revolve around the earth every day and night. Even without making us aware of it. Science is the backbone of our society. Science gave us so much in our present time. Due to this, the teacher in our schools teaches Science from an early age.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
Science as a Subject
In class 1 only a student has Science as a subject. This only tells us about the importance of Science. Science taught us about Our Solar System. The Solar System consists of 9 planets and the Sun. Most Noteworthy was that it also tells us about the origin of our planet. Above all, we cannot deny that Science helps us in shaping our future. But not only it tells us about our future, but it also tells us about our past.
When the student reaches class 6, Science gets divided into three more subcategories. These subcategories were Physics, Chemistry, and Biology. First of all, Physics taught us about the machines. Physics is an interesting subject. It is a logical subject.
Furthermore, the second subject was Chemistry . Chemistry is a subject that deals with an element found inside the earth. Even more, it helps in making various products. Products like medicine and cosmetics etc. result in human benefits.
Last but not least, the subject of Biology . Biology is a subject that teaches us about our Human body. It tells us about its various parts. Furthermore, it even teaches the students about cells. Cells are present in human blood. Science is so advanced that it did let us know even that.
Leading Scientists in the field of Science
Finally, many scientists like Thomas Edison , Sir Isaac Newton were born in this world. They have done great Inventions. Thomas Edison invented the light bulb. If he did not invent that we would stay in dark. Because of this Thomas Edison’s name marks in history.
Another famous Scientist was Sir Isaac Newton . Sir Isaac Newton told us about Gravity. With the help of this, we were able to discover many other theories.
In India Scientists A..P.J Abdul was there. He contributed much towards our space research and defense forces. He made many advanced missiles. These Scientists did great work and we will always remember them.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App


40 Best Essays of All Time (Including Links & Writing Tips)
I wanted to improve my writing skills. I thought that reading the forty best essays of all time would bring me closer to my goal.
I had little money (buying forty collections of essays was out of the question) so I’ve found them online instead. I’ve hacked through piles of them, and finally, I’ve found the great ones. Now I want to share the whole list with you (with the addition of my notes about writing). Each item on the list has a direct link to the essay, so please click away and indulge yourself. Also, next to each essay, there’s an image of the book that contains the original work.
About this essay list:
Reading essays is like indulging in candy; once you start, it’s hard to stop. I sought out essays that were not only well-crafted but also impactful. These pieces genuinely shifted my perspective. Whether you’re diving in for enjoyment or to hone your writing, these essays promise to leave an imprint. It’s fascinating how an essay can resonate with you, and even if details fade, its essence remains. I haven’t ranked them in any way; they’re all stellar. Skim through, explore the summaries, and pick up some writing tips along the way. For more essay gems, consider “Best American Essays” by Joyce Carol Oates or “101 Essays That Will Change The Way You Think” curated by Brianna Wiest.

40 Best Essays of All Time (With Links And Writing Tips)
1. david sedaris – laugh, kookaburra.

A great family drama takes place against the backdrop of the Australian wilderness. And the Kookaburra laughs… This is one of the top essays of the lot. It’s a great mixture of family reminiscences, travel writing, and advice on what’s most important in life. You’ll also learn an awful lot about the curious culture of the Aussies.
Writing tips from the essay:
- Use analogies (you can make it funny or dramatic to achieve a better effect): “Don’t be afraid,” the waiter said, and he talked to the kookaburra in a soothing, respectful voice, the way you might to a child with a switchblade in his hand”.
- You can touch a few cognate stories in one piece of writing . Reveal the layers gradually. Intertwine them and arrange for a grand finale where everything is finally clear.
- Be on the side of the reader. Become their friend and tell the story naturally, like around the dinner table.
- Use short, punchy sentences. Tell only as much as is required to make your point vivid.
- Conjure sentences that create actual feelings: “I had on a sweater and a jacket, but they weren’t quite enough, and I shivered as we walked toward the body, and saw that it was a . . . what, exactly?”
- You may ask a few tough questions in a row to provoke interest and let the reader think.
2. Charles D’Ambrosio – Documents

Do you think your life punches you in the face all too often? After reading this essay, you will change your mind. Reading about loss and hardships often makes us sad at first, but then enables us to feel grateful for our lives . D’Ambrosio shares his documents (poems, letters) that had a major impact on his life, and brilliantly shows how not to let go of the past.
- The most powerful stories are about your family and the childhood moments that shaped your life.
- You don’t need to build up tension and pussyfoot around the crux of the matter. Instead, surprise the reader by telling it like it is: “The poem was an allegory about his desire to leave our family.” Or: “My father had three sons. I’m the eldest; Danny, the youngest, killed himself sixteen years ago”.
- You can use real documents and quotes from your family and friends. It makes it so much more personal and relatable.
- Don’t cringe before the long sentence if you know it’s a strong one.
- At the end of the essay, you may come back to the first theme to close the circuit.
- Using slightly poetic language is acceptable, as long as it improves the story.
3. E. B. White – Once more to the lake

What does it mean to be a father? Can you see your younger self, reflected in your child? This beautiful essay tells the story of the author, his son, and their traditional stay at a placid lake hidden within the forests of Maine. This place of nature is filled with sunshine and childhood memories. It also provides for one of the greatest meditations on nature and the passing of time.
- Use sophisticated language, but not at the expense of readability.
- Use vivid language to trigger the mirror neurons in the reader’s brain: “I took along my son, who had never had any fresh water up his nose and who had seen lily pads only from train windows”.
- It’s important to mention universal feelings that are rarely talked about (it helps to create a bond between two minds): “You remember one thing, and that suddenly reminds you of another thing. I guess I remembered clearest of all the early mornings when the lake was cool and motionless”.
- Animate the inanimate: “this constant and trustworthy body of water”.
- Mentioning tales of yore is a good way to add some mystery and timelessness to your piece.
- Using double, or even triple “and” in one sentence is fine. It can make the sentence sing.
4. Zadie Smith – Fail Better

Aspiring writers feel tremendous pressure to perform. The daily quota of words often turns out to be nothing more than gibberish. What then? Also, should the writer please the reader or should she be fully independent? What does it mean to be a writer, anyway? This essay is an attempt to answer these questions, but its contents are not only meant for scribblers. Within it, you’ll find some great notes about literary criticism, how we treat art , and the responsibility of the reader.
- A perfect novel ? There’s no such thing.
- The novel always reflects the inner world of the writer. That’s why we’re fascinated with writers.
- Writing is not simply about craftsmanship, but about taking your reader to the unknown lands. In the words of Christopher Hitchens: “Your ideal authors ought to pull you from the foundering of your previous existence, not smilingly guide you into a friendly and peaceable harbor.”
- Style comes from your unique personality and the perception of the world. It takes time to develop it.
- Never try to tell it all. “All” can never be put into language. Take a part of it and tell it the best you can.
- Avoid being cliché. Try to infuse new life into your writing .
- Writing is about your way of being. It’s your game. Paradoxically, if you try to please everyone, your writing will become less appealing. You’ll lose the interest of the readers. This rule doesn’t apply in the business world where you have to write for a specific person (a target audience).
- As a reader, you have responsibilities too. According to the critics, every thirty years, there’s just a handful of great novels. Maybe it’s true. But there’s also an element of personal connection between the reader and the writer. That’s why for one person a novel is a marvel, while for the other, nothing special at all. That’s why you have to search and find the author who will touch you.
5. Virginia Woolf – Death of the Moth

Amid an ordinary day, sitting in a room of her own, Virginia Woolf tells about the epic struggle for survival and the evanescence of life. This short essay is truly powerful. In the beginning, the atmosphere is happy. Life is in full force. And then, suddenly, it fades away. This sense of melancholy would mark the last years of Woolf’s life.
- The melody of language… A good sentence is like music: “Moths that fly by day are not properly to be called moths; they do not excite that pleasant sense of dark autumn nights and ivy-blossom which the commonest yellow- underwing asleep in the shadow of the curtain never fails to rouse in us”.
- You can show the grandest in the mundane (for example, the moth at your window and the drama of life and death).
- Using simple comparisons makes the style more lucid: “Being intent on other matters I watched these futile attempts for a time without thinking, unconsciously waiting for him to resume his flight, as one waits for a machine, that has stopped momentarily, to start again without considering the reason of its failure”.
6. Meghan Daum – My Misspent Youth

Many of us, at some point or another, dream about living in New York. Meghan Daum’s take on the subject differs slightly from what you might expect. There’s no glamour, no Broadway shows, and no fancy restaurants. Instead, there’s the sullen reality of living in one of the most expensive cities in the world. You’ll get all the juicy details about credit cards, overdue payments, and scrambling for survival. It’s a word of warning. But it’s also a great story about shattered fantasies of living in a big city. Word on the street is: “You ain’t promised mañana in the rotten manzana.”
- You can paint a picture of your former self. What did that person believe in? What kind of world did he or she live in?
- “The day that turned your life around” is a good theme you may use in a story. Memories of a special day are filled with emotions. Strong emotions often breed strong writing.
- Use cultural references and relevant slang to create a context for your story.
- You can tell all the details of the story, even if in some people’s eyes you’ll look like the dumbest motherfucker that ever lived. It adds to the originality.
- Say it in a new way: “In this mindset, the dollars spent, like the mechanics of a machine no one bothers to understand, become an abstraction, an intangible avenue toward self-expression, a mere vehicle of style”.
- You can mix your personal story with the zeitgeist or the ethos of the time.
7. Roger Ebert – Go Gentle Into That Good Night

Probably the greatest film critic of all time, Roger Ebert, tells us not to rage against the dying of the light. This essay is full of courage, erudition, and humanism. From it, we learn about what it means to be dying (Hitchens’ “Mortality” is another great work on that theme). But there’s so much more. It’s a great celebration of life too. It’s about not giving up, and sticking to your principles until the very end. It brings to mind the famous scene from Dead Poets Society where John Keating (Robin Williams) tells his students: “Carpe, carpe diem, seize the day boys, make your lives extraordinary”.
- Start with a powerful sentence: “I know it is coming, and I do not fear it, because I believe there is nothing on the other side of death to fear.”
- Use quotes to prove your point -”‘Ask someone how they feel about death’, he said, ‘and they’ll tell you everyone’s gonna die’. Ask them, ‘In the next 30 seconds?’ No, no, no, that’s not gonna happen”.
- Admit the basic truths about reality in a childlike way (especially after pondering quantum physics) – “I believe my wristwatch exists, and even when I am unconscious, it is ticking all the same. You have to start somewhere”.
- Let other thinkers prove your point. Use quotes and ideas from your favorite authors and friends.
8. George Orwell – Shooting an Elephant

Even after one reading, you’ll remember this one for years. The story, set in British Burma, is about shooting an elephant (it’s not for the squeamish). It’s also the most powerful denunciation of colonialism ever put into writing. Orwell, apparently a free representative of British rule, feels to be nothing more than a puppet succumbing to the whim of the mob.
- The first sentence is the most important one: “In Moulmein, in Lower Burma, I was hated by large numbers of people — the only time in my life that I have been important enough for this to happen to me”.
- You can use just the first paragraph to set the stage for the whole piece of prose.
- Use beautiful language that stirs the imagination: “I remember that it was a cloudy, stuffy morning at the beginning of the rains.” Or: “I watched him beating his bunch of grass against his knees, with that preoccupied grandmotherly air that elephants have.”
- If you’ve ever been to war, you will have a story to tell: “(Never tell me, by the way, that the dead look peaceful. Most of the corpses I have seen looked devilish.)”
- Use simple words, and admit the sad truth only you can perceive: “They did not like me, but with the magical rifle in my hands I was momentarily worth watching”.
- Share words of wisdom to add texture to the writing: “I perceived at this moment that when the white man turns tyrant it is his freedom that he destroys.”
- I highly recommend reading everything written by Orwell, especially if you’re looking for the best essay collections on Amazon or Goodreads.
9. George Orwell – A Hanging

It’s just another day in Burma – time to hang a man. Without much ado, Orwell recounts the grim reality of taking another person’s life. A man is taken from his cage and in a few minutes, he’s going to be hanged. The most horrible thing is the normality of it. It’s a powerful story about human nature. Also, there’s an extraordinary incident with the dog, but I won’t get ahead of myself.
- Create brilliant, yet short descriptions of characters: “He was a Hindu, a puny wisp of a man, with a shaven head and vague liquid eyes. He had a thick, sprouting mustache, absurdly too big for his body, rather like the mustache of a comic man on the films”.
- Understand and share the felt presence of a unique experience: “It is curious, but till that moment I had never realized what it means to destroy a healthy, conscious man”.
- Make your readers hear the sound that will stay with them forever: “And then when the noose was fixed, the prisoner began crying out on his god. It was a high, reiterated cry of “Ram! Ram! Ram! Ram!”
- Make the ending original by refusing the tendency to seek closure or summing it up.
10. Christopher Hitchens – Assassins of The Mind

In one of the greatest essays written in defense of free speech, Christopher Hitchens shares many examples of how modern media kneel to the explicit threats of violence posed by Islamic extremists. He recounts the story of his friend, Salman Rushdie, author of Satanic Verses who, for many years, had to watch over his shoulder because of the fatwa of Ayatollah Khomeini. With his usual wit, Hitchens shares various examples of people who died because of their opinions and of editors who refuse to publish anything related to Islam because of fear (and it was written long before the Charlie Hebdo massacre). After reading the essay, you realize that freedom of expression is one of the most precious things we have and that we have to fight for it. I highly recommend all essay collections penned by Hitchens, especially the ones written for Vanity Fair.
- Assume that the readers will know the cultural references. When they do, their self-esteem goes up – they are a part of an insider group.
- When proving your point, give a variety of real-life examples from eclectic sources. Leave no room for ambiguity or vagueness. Research and overall knowledge are essential here.
- Use italics to emphasize a specific word or phrase (here I use the underlining): “We live now in a climate where every publisher and editor and politician has to weigh in advance the possibility of violent Muslim reprisal. In consequence, several things have not happened.”
- Think about how to make it sound more original: “So there is now a hidden partner in our cultural and academic and publishing and the broadcasting world: a shadowy figure that has, uninvited, drawn up a chair to the table.”
11. Christopher Hitchens – The New Commandments

It’s high time to shatter the tablets and amend the biblical rules of conduct. Watch, as Christopher Hitchens slays one commandment after the other on moral, as well as historical grounds. For example, did you know that there are many versions of the divine law dictated by God to Moses which you can find in the Bible? Aren’t we thus empowered to write our version of a proper moral code? If you approach it with an open mind, this essay may change the way you think about the Bible and religion.
- Take the iconoclastic approach. Have a party on the hallowed soil.
- Use humor to undermine orthodox ideas (it seems to be the best way to deal with an established authority).
- Use sarcasm and irony when appropriate (or not): “Nobody is opposed to a day of rest. The international Communist movement got its start by proclaiming a strike for an eight-hour day on May 1, 1886, against Christian employers who used child labor seven days a week”.
- Defeat God on legal grounds: “Wise lawmakers know that it is a mistake to promulgate legislation that is impossible to obey”.
- Be ruthless in the logic of your argument. Provide evidence.
12. Phillip Lopate – Against Joie de Vivre

While reading this fantastic essay, this quote from Slavoj Žižek kept coming back to me: “I think that the only life of deep satisfaction is a life of eternal struggle, especially struggle with oneself. If you want to remain happy, just remain stupid. Authentic masters are never happy; happiness is a category of slaves”. I can bear the onus of happiness or joie de vivre for some time. But this force enables me to get free and wallow in the sweet feelings of melancholy and nostalgia. By reading this work of Lopate, you’ll enter into the world of an intelligent man who finds most social rituals a drag. It’s worth exploring.
- Go against the grain. Be flamboyant and controversial (if you can handle it).
- Treat the paragraph like a group of thoughts on one theme. Next paragraph, next theme.
- Use references to other artists to set the context and enrich the prose: “These sunny little canvases with their talented innocence, the third-generation spirit of Montmartre, bore testimony to a love of life so unbending as to leave an impression of rigid narrow-mindedness as extreme as any Savonarola. Their rejection of sorrow was total”.
- Capture the emotions in life that are universal, yet remain unspoken.
- Don’t be afraid to share your intimate experiences.
13. Philip Larkin – The Pleasure Principle

This piece comes from the Required Writing collection of personal essays. Larkin argues that reading in verse should be a source of intimate pleasure – not a medley of unintelligible thoughts that only the author can (or can’t?) decipher. It’s a sobering take on modern poetry and a great call to action for all those involved in it. Well worth a read.
- Write about complicated ideas (such as poetry) simply. You can change how people look at things if you express yourself enough.
- Go boldly. The reader wants a bold writer: “We seem to be producing a new kind of bad poetry, not the old kind that tries to move the reader and fails, but one that does not even try”.
- Play with words and sentence length. Create music: “It is time some of you playboys realized, says the judge, that reading a poem is hard work. Fourteen days in stir. Next case”.
- Persuade the reader to take action. Here, direct language is the most effective.
14. Sigmund Freud – Thoughts for the Times on War and Death

This essay reveals Freud’s disillusionment with the whole project of Western civilization. How the peaceful European countries could engage in a war that would eventually cost over 17 million lives? What stirs people to kill each other? Is it their nature, or are they puppets of imperial forces with agendas of their own? From the perspective of time, this work by Freud doesn’t seem to be fully accurate. Even so, it’s well worth your time.
- Commence with long words derived from Latin. Get grandiloquent, make your argument incontrovertible, and leave your audience discombobulated.
- Use unending sentences, so that the reader feels confused, yet impressed.
- Say it well: “In this way, he enjoyed the blue sea and the grey; the beauty of snow-covered mountains and green meadowlands; the magic of northern forests and the splendor of southern vegetation; the mood evoked by landscapes that recall great historical events, and the silence of untouched nature”.
- Human nature is a subject that never gets dry.
15. Zadie Smith – Some Notes on Attunement
“You are privy to a great becoming, but you recognize nothing” – Francis Dolarhyde. This one is about the elusiveness of change occurring within you. For Zadie, it was hard to attune to the vibes of Joni Mitchell – especially her Blue album. But eventually, she grew up to appreciate her genius, and all the other things changed as well. This top essay is all about the relationship between humans, and art. We shouldn’t like art because we’re supposed to. We should like it because it has an instantaneous, emotional effect on us. Although, according to Stansfield (Gary Oldman) in Léon, liking Beethoven is rather mandatory.
- Build an expectation of what’s coming: “The first time I heard her I didn’t hear her at all”.
- Don’t be afraid of repetition if it feels good.
- Psychedelic drugs let you appreciate things you never appreciated.
- Intertwine a personal journey with philosophical musings.
- Show rather than tell: “My friends pitied their eyes. The same look the faithful give you as you hand them back their “literature” and close the door in their faces”.
- Let the poets speak for you: “That time is past, / And all its aching joys are now no
- more, / And all its dizzy raptures”.
- By voicing your anxieties, you can heal the anxieties of the reader. In that way, you say: “I’m just like you. I’m your friend in this struggle”.
- Admit your flaws to make your persona more relatable.
16. Annie Dillard – Total Eclipse

My imagination was always stirred by the scene of the solar eclipse in Pharaoh, by Boleslaw Prus. I wondered about the shock of the disoriented crowd when they saw how their ruler could switch off the light. Getting immersed in this essay by Annie Dillard has a similar effect. It produces amazement and some kind of primeval fear. It’s not only the environment that changes; it’s your mind and the perception of the world. After the eclipse, nothing is going to be the same again.
- Yet again, the power of the first sentence draws you in: “It had been like dying, that sliding down the mountain pass”.
- Don’t miss the extraordinary scene. Then describe it: “Up in the sky, like a crater from some distant cataclysm, was a hollow ring”.
- Use colloquial language. Write as you talk. Short sentences often win.
- Contrast the numinous with the mundane to enthrall the reader.
17. Édouard Levé – When I Look at a Strawberry, I Think of a Tongue

This suicidally beautiful essay will teach you a lot about the appreciation of life and the struggle with mental illness. It’s a collection of personal, apparently unrelated thoughts that show us the rich interior of the author. You look at the real-time thoughts of another person, and then recognize the same patterns within yourself… It sounds like a confession of a person who’s about to take their life, and it’s striking in its originality.
- Use the stream-of-consciousness technique and put random thoughts on paper. Then, polish them: “I have attempted suicide once, I’ve been tempted four times to attempt it”.
- Place the treasure deep within the story: “When I look at a strawberry, I think of a tongue, when I lick one, of a kiss”.
- Don’t worry about what people might think. The more you expose, the more powerful the writing. Readers also take part in the great drama. They experience universal emotions that mostly stay inside. You can translate them into writing.
18. Gloria E. Anzaldúa – How to Tame a Wild Tongue

Anzaldúa, who was born in south Texas, had to struggle to find her true identity. She was American, but her culture was grounded in Mexico. In this way, she and her people were not fully respected in either of the countries. This essay is an account of her journey of becoming the ambassador of the Chicano (Mexican-American) culture. It’s full of anecdotes, interesting references, and different shades of Spanish. It’s a window into a new cultural dimension that you’ve never experienced before.
- If your mother tongue is not English, but you write in English, use some of your unique homeland vocabulary.
- You come from a rich cultural heritage. You can share it with people who never heard about it, and are not even looking for it, but it is of immense value to them when they discover it.
- Never forget about your identity. It is precious. It is a part of who you are. Even if you migrate, try to preserve it. Use it to your best advantage and become the voice of other people in the same situation.
- Tell them what’s really on your mind: “So if you want to hurt me, talk badly about my language. Ethnic identity is twin skin to linguistic identity – I am my language”.
19. Kurt Vonnegut – Dispatch From A Man Without a Country

In terms of style, this essay is flawless. It’s simple, conversational, humorous, and yet, full of wisdom. And when Vonnegut becomes a teacher and draws an axis of “beginning – end”, and, “good fortune – bad fortune” to explain literature, it becomes outright hilarious. It’s hard to find an author with such a down-to-earth approach. He doesn’t need to get intellectual to prove a point. And the point could be summed up by the quote from Great Expectations – “On the Rampage, Pip, and off the Rampage, Pip – such is Life!”
- Start with a curious question: “Do you know what a twerp is?”
- Surprise your readers with uncanny analogies: “I am from a family of artists. Here I am, making a living in the arts. It has not been a rebellion. It’s as though I had taken over the family Esso station.”
- Use your natural language without too many special effects. In time, the style will crystalize.
- An amusing lesson in writing from Mr. Vonnegut: “Here is a lesson in creative writing. First rule: Do not use semicolons. They are transvestite hermaphrodites representing absolutely nothing. All they do is show you’ve been to college”.
- You can put actual images or vignettes between the paragraphs to illustrate something.
20. Mary Ruefle – On Fear

Most psychologists and gurus agree that fear is the greatest enemy of success or any creative activity. It’s programmed into our minds to keep us away from imaginary harm. Mary Ruefle takes on this basic human emotion with flair. She explores fear from so many angles (especially in the world of poetry-writing) that at the end of this personal essay, you will look at it, dissect it, untangle it, and hopefully be able to say “f**k you” the next time your brain is trying to stop you.
- Research your subject thoroughly. Ask people, have interviews, get expert opinions, and gather as much information as possible. Then scavenge through the fields of data, and pull out the golden bits that will let your prose shine.
- Use powerful quotes to add color to your story: “The poet who embarks on the creation of the poem (as I know by experience), begins with the aimless sensation of a hunter about to embark on a night hunt through the remotest of forests. Unaccountable dread stirs in his heart”. – Lorca.
- Writing advice from the essay: “One of the fears a young writer has is not being able to write as well as he or she wants to, the fear of not being able to sound like X or Y, a favorite author. But out of fear, hopefully, is born a young writer’s voice”.
21. Susan Sontag – Against Interpretation

In this highly intellectual essay, Sontag fights for art and its interpretation. It’s a great lesson, especially for critics and interpreters who endlessly chew on works that simply defy interpretation. Why don’t we just leave the art alone? I always hated it when at school they asked me: “What did the author have in mind when he did X or Y?” Iēsous Pantocrator! Hell if I know! I will judge it through my subjective experience!
- Leave the art alone: “Today is such a time, when the project of interpretation is reactionary, stifling. Like the fumes of the automobile and heavy industry which befoul the urban atmosphere, the effusion of interpretations of art today poisons our sensibilities”.
- When you have something really important to say, style matters less.
- There’s no use in creating a second meaning or inviting interpretation of our art. Just leave it be and let it speak for itself.
22. Nora Ephron – A Few Words About Breasts

This is a heartwarming, coming-of-age story about a young girl who waits in vain for her breasts to grow. It’s simply a humorous and pleasurable read. The size of breasts is a big deal for women. If you’re a man, you may peek into the mind of a woman and learn many interesting things. If you’re a woman, maybe you’ll be able to relate and at last, be at peace with your bosom.
- Touch an interesting subject and establish a strong connection with the readers (in that case, women with small breasts). Let your personality shine through the written piece. If you are lighthearted, show it.
- Use hyphens to create an impression of real talk: “My house was full of apples and peaches and milk and homemade chocolate chip cookies – which were nice, and good for you, but-not-right-before-dinner-or-you’ll-spoil-your-appetite.”
- Use present tense when you tell a story to add more life to it.
- Share the pronounced, memorable traits of characters: “A previous girlfriend named Solange, who was famous throughout Beverly Hills High School for having no pigment in her right eyebrow, had knitted them for him (angora dice)”.
23. Carl Sagan – Does Truth Matter – Science, Pseudoscience, and Civilization

Carl Sagan was one of the greatest proponents of skepticism, and an author of numerous books, including one of my all-time favorites – The Demon-Haunted World . He was also a renowned physicist and the host of the fantastic Cosmos: A Personal Voyage series, which inspired a whole generation to uncover the mysteries of the cosmos. He was also a dedicated weed smoker – clearly ahead of his time. The essay that you’re about to read is a crystallization of his views about true science, and why you should check the evidence before believing in UFOs or similar sorts of crap.
- Tell people the brutal truth they need to hear. Be the one who spells it out for them.
- Give a multitude of examples to prove your point. Giving hard facts helps to establish trust with the readers and show the veracity of your arguments.
- Recommend a good book that will change your reader’s minds – How We Know What Isn’t So: The Fallibility of Human Reason in Everyday Life
24. Paul Graham – How To Do What You Love

How To Do What You Love should be read by every college student and young adult. The Internet is flooded with a large number of articles and videos that are supposed to tell you what to do with your life. Most of them are worthless, but this one is different. It’s sincere, and there’s no hidden agenda behind it. There’s so much we take for granted – what we study, where we work, what we do in our free time… Surely we have another two hundred years to figure it out, right? Life’s too short to be so naïve. Please, read the essay and let it help you gain fulfillment from your work.
- Ask simple, yet thought-provoking questions (especially at the beginning of the paragraph) to engage the reader: “How much are you supposed to like what you do?”
- Let the readers question their basic assumptions: “Prestige is like a powerful magnet that warps even your beliefs about what you enjoy. It causes you to work not on what you like, but what you’d like to like”.
- If you’re writing for a younger audience, you can act as a mentor. It’s beneficial for younger people to read a few words of advice from a person with experience.
25. John Jeremiah Sullivan – Mister Lytle

A young, aspiring writer is about to become a nurse of a fading writer – Mister Lytle (Andrew Nelson Lytle), and there will be trouble. This essay by Sullivan is probably my favorite one from the whole list. The amount of beautiful sentences it contains is just overwhelming. But that’s just a part of its charm. It also takes you to the Old South which has an incredible atmosphere. It’s grim and tawny but you want to stay there for a while.
- Short, distinct sentences are often the most powerful ones: “He had a deathbed, in other words. He didn’t go suddenly”.
- Stay consistent with the mood of the story. When reading Mister Lytle you are immersed in that southern, forsaken, gloomy world, and it’s a pleasure.
- The spectacular language that captures it all: “His French was superb, but his accent in English was best—that extinct mid-Southern, land-grant pioneer speech, with its tinges of the abandoned Celtic urban Northeast (“boned” for burned) and its raw gentility”.
- This essay is just too good. You have to read it.
26. Joan Didion – On Self Respect

Normally, with that title, you would expect some straightforward advice about how to improve your character and get on with your goddamn life – but not from Joan Didion. From the very beginning, you can feel the depth of her thinking, and the unmistakable style of a true woman who’s been hurt. You can learn more from this essay than from whole books about self-improvement . It reminds me of the scene from True Detective, where Frank Semyon tells Ray Velcoro to “own it” after he realizes he killed the wrong man all these years ago. I guess we all have to “own it”, recognize our mistakes, and move forward sometimes.
- Share your moral advice: “Character — the willingness to accept responsibility for one’s own life — is the source from which self-respect springs”.
- It’s worth exploring the subject further from a different angle. It doesn’t matter how many people have already written on self-respect or self-reliance – you can still write passionately about it.
- Whatever happens, you must take responsibility for it. Brave the storms of discontent.
27. Susan Sontag – Notes on Camp

I’ve never read anything so thorough and lucid about an artistic current. After reading this essay, you will know what camp is. But not only that – you will learn about so many artists you’ve never heard of. You will follow their traces and go to places where you’ve never been before. You will vastly increase your appreciation of art. It’s interesting how something written as a list could be so amazing. All the listicles we usually see on the web simply cannot compare with it.
- Talking about artistic sensibilities is a tough job. When you read the essay, you will see how much research, thought and raw intellect came into it. But that’s one of the reasons why people still read it today, even though it was written in 1964.
- You can choose an unorthodox way of expression in the medium for which you produce. For example, Notes on Camp is a listicle – one of the most popular content formats on the web. But in the olden days, it was uncommon to see it in print form.
- Just think about what is camp: “And third among the great creative sensibilities is Camp: the sensibility of failed seriousness, of the theatricalization of experience. Camp refuses both the harmonies of traditional seriousness and the risks of fully identifying with extreme states of feeling”.
28. Ralph Waldo Emerson – Self-Reliance

That’s the oldest one from the lot. Written in 1841, it still inspires generations of people. It will let you understand what it means to be self-made. It contains some of the most memorable quotes of all time. I don’t know why, but this one especially touched me: “Every true man is a cause, a country, and an age; requires infinite spaces and numbers and time fully to accomplish his design, and posterity seems to follow his steps as a train of clients”. Now isn’t it purely individualistic, American thought? Emerson told me (and he will tell you) to do something amazing with my life. The language it contains is a bit archaic, but that just adds to the weight of the argument. You can consider it to be a meeting with a great philosopher who shaped the ethos of the modern United States.
- You can start with a powerful poem that will set the stage for your work.
- Be free in your creative flow. Do not wait for the approval of others: “What I must do is all that concerns me, not what the people think. This rule, equally arduous in actual and in intellectual life, may serve for the whole distinction between greatness and meanness”.
- Use rhetorical questions to strengthen your argument: “I hear a preacher announce for his text and topic the expediency of one of the institutions of his church. Do I not know beforehand that not possibly say a new and spontaneous word?”
29. David Foster Wallace – Consider The Lobster

When you want simple field notes about a food festival, you needn’t send there the formidable David Foster Wallace. He sees right through the hypocrisy and cruelty behind killing hundreds of thousands of innocent lobsters – by boiling them alive. This essay uncovers some of the worst traits of modern American people. There are no apologies or hedging one’s bets. There’s just plain truth that stabs you in the eye like a lobster claw. After reading this essay, you may reconsider the whole animal-eating business.
- When it’s important, say it plainly and stagger the reader: “[Lobsters] survive right up until they’re boiled. Most of us have been in supermarkets or restaurants that feature tanks of live lobster, from which you can pick out your supper while it watches you point”.
- In your writing, put exact quotes of the people you’ve been interviewing (including slang and grammatical errors). It makes it more vivid, and interesting.
- You can use humor in serious situations to make your story grotesque.
- Use captions to expound on interesting points of your essay.
30. David Foster Wallace – The Nature of the Fun

The famous novelist and author of the most powerful commencement speech ever done is going to tell you about the joys and sorrows of writing a work of fiction. It’s like taking care of a mutant child that constantly oozes smelly liquids. But you love that child and you want others to love it too. It’s a very humorous account of what it means to be an author. If you ever plan to write a novel, you should read that one. And the story about the Chinese farmer is just priceless.
- Base your point on a chimerical analogy. Here, the writer’s unfinished work is a “hideously damaged infant”.
- Even in expository writing, you may share an interesting story to keep things lively.
- Share your true emotions (even when you think they won’t interest anyone). Often, that’s exactly what will interest the reader.
- Read the whole essay for marvelous advice on writing fiction.
31. Margaret Atwood – Attitude

This is not an essay per se, but I included it on the list for the sake of variety. It was delivered as a commencement speech at The University of Toronto, and it’s about keeping the right attitude. Soon after leaving university, most graduates have to forget about safety, parties, and travel and start a new life – one filled with a painful routine that will last until they drop. Atwood says that you don’t have to accept that. You can choose how you react to everything that happens to you (and you don’t have to stay in that dead-end job for the rest of your days).
- At times, we are all too eager to persuade, but the strongest persuasion is not forceful. It’s subtle. It speaks to the heart. It affects you gradually.
- You may be tempted to talk about a subject by first stating what it is not, rather than what it is. Try to avoid that.
- Simple advice for writers (and life in general): “When faced with the inevitable, you always have a choice. You may not be able to alter reality, but you can alter your attitude towards it”.
32. Jo Ann Beard – The Fourth State of Matter

Read that one as soon as possible. It’s one of the most masterful and impactful essays you’ll ever read. It’s like a good horror – a slow build-up, and then your jaw drops to the ground. To summarize the story would be to spoil it, so I recommend that you just dig in and devour this essay in one sitting. It’s a perfect example of “show, don’t tell” writing, where the actions of characters are enough to create the right effect. No need for flowery adjectives here.
- The best story you will tell is going to come from your personal experience.
- Use mysteries that will nag the reader. For example, at the beginning of the essay, we learn about the “vanished husband” but there’s no explanation. We have to keep reading to get the answer.
- Explain it in simple terms: “You’ve got your solid, your liquid, your gas, and then your plasma”. Why complicate?
33. Terence McKenna – Tryptamine Hallucinogens and Consciousness

To me, Terence McKenna was one of the most interesting thinkers of the twentieth century. His many lectures (now available on YouTube) attracted millions of people who suspect that consciousness holds secrets yet to be unveiled. McKenna consumed psychedelic drugs for most of his life and it shows (in a positive way). Many people consider him a looney, and a hippie, but he was so much more than that. He dared to go into the abyss of his psyche and come back to tell the tale. He also wrote many books (the most famous being Food Of The Gods ), built a huge botanical garden in Hawaii , lived with shamans, and was a connoisseur of all things enigmatic and obscure. Take a look at this essay, and learn more about the explorations of the subconscious mind.
- Become the original thinker, but remember that it may require extraordinary measures: “I call myself an explorer rather than a scientist because the area that I’m looking at contains insufficient data to support even the dream of being a science”.
- Learn new words every day to make your thoughts lucid.
- Come up with the most outlandish ideas to push the envelope of what’s possible. Don’t take things for granted or become intellectually lazy. Question everything.
34. Eudora Welty – The Little Store

By reading this little-known essay, you will be transported into the world of the old American South. It’s a remembrance of trips to the little store in a little town. It’s warm and straightforward, and when you read it, you feel like a child once more. All these beautiful memories live inside of us. They lay somewhere deep in our minds, hidden from sight. The work by Eudora Welty is an attempt to uncover some of them and let you get reacquainted with some smells and tastes of the past.
- When you’re from the South, flaunt it. It’s still good old English but sometimes it sounds so foreign. I can hear the Southern accent too: “There were almost tangible smells – licorice recently sucked in a child’s cheek, dill-pickle brine that had leaked through a paper sack in a fresh trail across the wooden floor, ammonia-loaded ice that had been hoisted from wet Croker sacks and slammed into the icebox with its sweet butter at the door, and perhaps the smell of still-untrapped mice”.
- Yet again, never forget your roots.
- Childhood stories can be the most powerful ones. You can write about how they shaped you.
35. John McPhee – The Search for Marvin Gardens

The Search for Marvin Gardens contains many layers of meaning. It’s a story about a Monopoly championship, but also, it’s the author’s search for the lost streets visible on the board of the famous board game. It also presents a historical perspective on the rise and fall of civilizations, and on Atlantic City, which once was a lively place, and then, slowly declined, the streets filled with dirt and broken windows.
- There’s nothing like irony: “A sign- ‘Slow, Children at Play’- has been bent backward by an automobile”.
- Telling the story in apparently unrelated fragments is sometimes better than telling the whole thing in a logical order.
- Creativity is everything. The best writing may come just from connecting two ideas and mixing them to achieve a great effect. Shush! The muse is whispering.
36. Maxine Hong Kingston – No Name Woman

A dead body at the bottom of the well makes for a beautiful literary device. The first line of Orhan Pamuk’s novel My Name Is Red delivers it perfectly: “I am nothing but a corpse now, a body at the bottom of a well”. There’s something creepy about the idea of the well. Just think about the “It puts the lotion in the basket” scene from The Silence of the Lambs. In the first paragraph of Kingston’s essay, we learn about a suicide committed by uncommon means of jumping into the well. But this time it’s a real story. Who was this woman? Why did she do it? Read the essay.
- Mysterious death always gets attention. The macabre details are like daiquiris on a hot day – you savor them – you don’t let them spill.
- One sentence can speak volumes: “But the rare urge west had fixed upon our family, and so my aunt crossed boundaries not delineated in space”.
- It’s interesting to write about cultural differences – especially if you have the relevant experience. Something normal for us is unthinkable for others. Show this different world.
- The subject of sex is never boring.
37. Joan Didion – On Keeping A Notebook

Slouching Towards Bethlehem is one of the most famous collections of essays of all time. In it, you will find a curious piece called On Keeping A Notebook. It’s not only a meditation about keeping a journal. It’s also Didion’s reconciliation with her past self. After reading it, you will seriously reconsider your life’s choices and look at your life from a wider perspective.
- When you write things down in your journal, be more specific – unless you want to write a deep essay about it years later.
- Use the beauty of the language to relate to the past: “I have already lost touch with a couple of people I used to be; one of them, a seventeen-year-old, presents little threat, although it would be of some interest to me to know again what it feels like to sit on a river levee drinking vodka-and-orange-juice and listening to Les Paul and Mary Ford and their echoes sing ‘How High the Moon’ on the car radio”.
- Drop some brand names if you want to feel posh.
38. Joan Didion – Goodbye To All That

This one touched me because I also lived in New York City for a while. I don’t know why, but stories about life in NYC are so often full of charm and this eerie-melancholy-jazz feeling. They are powerful. They go like this: “There was a hard blizzard in NYC. As the sound of sirens faded, Tony descended into the dark world of hustlers and pimps.” That’s pulp literature but in the context of NYC, it always sounds cool. Anyway, this essay is amazing in too many ways. You just have to read it.
- Talk about New York City. They will read it.
- Talk about the human experience: “It did occur to me to call the desk and ask that the air conditioner be turned off, I never called, because I did not know how much to tip whoever might come—was anyone ever so young?”
- Look back at your life and reexamine it. Draw lessons from it.
39. George Orwell – Reflections on Gandhi
George Orwell could see things as they were. No exaggeration, no romanticism – just facts. He recognized totalitarianism and communism for what they were and shared his worries through books like 1984 and Animal Farm . He took the same sober approach when dealing with saints and sages. Today, we regard Gandhi as one of the greatest political leaders of the twentieth century – and rightfully so. But did you know that when asked about the Jews during World War II, Gandhi said that they should commit collective suicide and that it: “would have aroused the world and the people of Germany to Hitler’s violence.” He also recommended utter pacifism in 1942, during the Japanese invasion, even though he knew it would cost millions of lives. But overall he was a good guy. Read the essay and broaden your perspective on the Bapu of the Indian Nation.
- Share a philosophical thought that stops the reader for a moment: “No doubt alcohol, tobacco, and so forth are things that a saint must avoid, but sainthood is also a thing that human beings must avoid”.
- Be straightforward in your writing – no mannerisms, no attempts to create ‘style’, and no invocations of the numinous – unless you feel the mystical vibe.
40. George Orwell – Politics and the English Language
Let Mr. Orwell give you some writing tips. Written in 1946, this essay is still one of the most helpful documents on writing in English. Orwell was probably the first person who exposed the deliberate vagueness of political language. He was very serious about it and I admire his efforts to slay all unclear sentences (including ones written by distinguished professors). But it’s good to make it humorous too from time to time. My favorite examples of that would be the immortal Soft Language sketch by George Carlin or the “Romans Go Home” scene from Monty Python’s Life of Brian. Overall, it’s a great essay filled with examples from many written materials. It’s a must-read for any writer.
- Listen to the master: “This mixture of vagueness and sheer incompetence is the most marked characteristic of modern English prose.” Do something about it.
- This essay is all about writing better, so go to the source if you want the goodies.

Other Essays You May Find Interesting
The list that I’ve prepared is by no means complete. The literary world is full of exciting essays and you’ll never know which one is going to change your life. I’ve found reading essays very rewarding because sometimes, a single one means more than reading a whole book. It’s almost like wandering around and peeking into the minds of the greatest writers and thinkers that ever lived. To make this list more comprehensive, below I included more essays you may find interesting.
Oliver Sacks – On Libraries
One of the greatest contributors to the knowledge about the human mind, Oliver Sacks meditates on the value of libraries and his love of books.
Noam Chomsky – The Responsibility of Intellectuals
Chomsky did probably more than anyone else to define the role of the intelligentsia in the modern world . There is a war of ideas over there – good and bad – intellectuals are going to be those who ought to be fighting for the former.

Sam Harris – The Riddle of The Gun
Sam Harris, now a famous philosopher and neuroscientist, takes on the problem of gun control in the United States. His thoughts are clear of prejudice. After reading this, you’ll appreciate the value of logical discourse overheated, irrational debate that more often than not has real implications on policy.
Tim Ferriss – Some Practical Thoughts on Suicide
This piece was written as a blog post , but it’s worth your time. The author of the NYT bestseller The 4-Hour Workweek shares an emotional story about how he almost killed himself, and what can you do to save yourself or your friends from suicide.
Edward Said – Reflections on Exile
The life of Edward Said was a truly fascinating one. Born in Jerusalem, he lived between Palestine and Egypt and finally settled down in the United States, where he completed his most famous work – Orientalism. In this essay, he shares his thoughts about what it means to be in exile.
Richard Feynman – It’s as Simple as One, Two, Three…
Richard Feynman is one of the most interesting minds of the twentieth century. He was a brilliant physicist, but also an undeniably great communicator of science, an artist, and a traveler. By reading this essay, you can observe his thought process when he tries to figure out what affects our perception of time. It’s a truly fascinating read.
Rabindranath Tagore – The Religion of The Forest
I like to think about Tagore as my spiritual Friend. His poems are just marvelous. They are like some of the Persian verses that praise love, nature, and the unity of all things. By reading this short essay, you will learn a lot about Indian philosophy and its relation to its Western counterpart.
Richard Dawkins – Letter To His 10-Year-Old Daughter
Every father should be able to articulate his philosophy of life to his children. With this letter that’s similar to what you find in the Paris Review essays , the famed atheist and defender of reason, Richard Dawkins, does exactly that. It’s beautifully written and stresses the importance of looking at evidence when we’re trying to make sense of the world.
Albert Camus – The Minotaur (or, The Stop In Oran)
Each person requires a period of solitude – a period when one’s able to gather thoughts and make sense of life. There are many places where you may attempt to find quietude. Albert Camus tells about his favorite one.
Koty Neelis – 21 Incredible Life Lessons From Anthony Bourdain
I included it as the last one because it’s not really an essay, but I just had to put it somewhere. In this listicle, you’ll find the 21 most original thoughts of the high-profile cook, writer, and TV host, Anthony Bourdain. Some of them are shocking, others are funny, but they’re all worth checking out.
Lucius Annaeus Seneca – On the Shortness of Life
It’s similar to the Rubaiyat of Omar Khayyam because it praises life. Seneca shares some of his stoic philosophy and tells you not to waste your time on stupidities. Drink! – for once dead you shall never return.
Bertrand Russell – In Praise of Idleness
This old essay is a must-read for modern humans. We are so preoccupied with our work, our phones, and all the media input we drown in our business. Bertrand Russell tells you to chill out a bit – maybe it will do you some good.
James Baldwin – Stranger in the Village
It’s an essay on the author’s experiences as an African-American in a Swiss village, exploring race, identity, and alienation while highlighting the complexities of racial dynamics and the quest for belonging.
Bonus – More writing tips from two great books
The mission to improve my writing skills took me further than just going through the essays. I’ve come across some great books on writing too. I highly recommend you read them in their entirety. They’re written beautifully and contain lots of useful knowledge. Below you’ll find random (but useful) notes that I took from The Sense of Style and On Writing.
The Sense of Style – By Steven Pinker
- Style manuals are full of inconsistencies. Following their advice might not be the best idea. They might make your prose boring.
- Grammarians from all eras condemn students for not knowing grammar. But it just evolves. It cannot be rigid.
- “Nothing worth learning can be taught” – Oscar Wilde. It’s hard to learn to write from a manual – you have to read, write, and analyze.
- Good writing makes you imagine things and feel them for yourself – use word pictures.
- Don’t fear using voluptuous words.
- Phonesthetics – or how the words sound.
- Use parallel language (consistency of tense).
- Good writing finishes strong.
- Write to someone. Never write for no one in mind. Try to show people your view of the world.
- Don’t tell everything you are going to say in summary (signposting) – be logical, but be conversational.
- Don’t be pompous.
- Don’t use quotation marks where they don’t “belong”. Be confident about your style.
- Don’t hedge your claims (research first, and then tell it like it is).
- Avoid clichés and meta-concepts (concepts about concepts). Be more straightforward!
- Not prevention – but prevents or prevented – don’t use dead nouns.
- Be more vivid while using your mother tongue – don’t use passive where it’s not needed. Direct the reader’s gaze to something in the world.
- The curse of knowledge – the reader doesn’t know what you know – beware of that.
- Explain technical terms.
- Use examples when you explain a difficult term.
- If you ever say “I think I understand this” it probably means you don’t.
- It’s better to underestimate the lingo of your readers than to overestimate it.
- Functional fixedness – if we know some object (or idea) well, we tend to see it in terms of usage, not just as an object.
- Use concrete language instead of an abstraction.
- Show your work to people before you publish (get feedback!).
- Wait for a few days and then revise, revise, revise. Think about clarity and the sound of sentences. Then show it to someone. Then revise one more time. Then publish (if it’s to be serious work).
- Look at it from the perspective of other people.
- Omit needless words.
- Put the heaviest words at the end of the sentence.
- It’s good to use the passive, but only when appropriate.
- Check all text for cohesion. Make sure that the sentences flow gently.
- In expository work, go from general to more specific. But in journalism start from the big news and then give more details.
- Use the paragraph break to give the reader a moment to take a breath.
- Use the verb instead of a noun (make it more active) – not “cancellation”, but “canceled”. But after you introduce the action, you can refer to it with a noun.
- Avoid too many negations.
- If you write about why something is so, don’t spend too much time writing about why it is not.
On Writing Well – By William Zinsser
- Writing is a craft. You need to sit down every day and practice your craft.
- You should re-write and polish your prose a lot.
- Throw out all the clutter. Don’t keep it because you like it. Aim for readability.
- Look at the best examples of English literature . There’s hardly any needless garbage there.
- Use shorter expressions. Don’t add extra words that don’t bring any value to your work.
- Don’t use pompous language. Use simple language and say plainly what’s going on (“because” equals “because”).
- The media and politics are full of cluttered prose (because it helps them to cover up for their mistakes).
- You can’t add style to your work (and especially, don’t add fancy words to create an illusion of style). That will look fake. You need to develop a style.
- Write in the “I” mode. Write to a friend or just for yourself. Show your personality. There is a person behind the writing.
- Choose your words carefully. Use the dictionary to learn different shades of meaning.
- Remember about phonology. Make music with words .
- The lead is essential. Pull the reader in. Otherwise, your article is dead.
- You don’t have to make the final judgment on any topic. Just pick the right angle.
- Do your research. Not just obvious research, but a deep one.
- When it’s time to stop, stop. And finish strong. Think about the last sentence. Surprise them.
- Use quotations. Ask people. Get them talking.
- If you write about travel, it must be significant to the reader. Don’t bother with the obvious. Choose your words with special care. Avoid travel clichés at all costs. Don’t tell that the sand was white and there were rocks on the beach. Look for the right detail.
- If you want to learn how to write about art, travel, science, etc. – read the best examples available. Learn from the masters.
- Concentrate on one big idea (“Let’s not go peeing down both legs”).
- “The reader has to feel that the writer is feeling good.”
- One very helpful question: “What is the piece really about?” (Not just “What the piece is about?”)
Now immerse yourself in the world of essays
By reading the essays from the list above, you’ll become a better writer , a better reader, but also a better person. An essay is a special form of writing. It is the only literary form that I know of that is an absolute requirement for career or educational advancement. Nowadays, you can use an AI essay writer or an AI essay generator that will get the writing done for you, but if you have personal integrity and strong moral principles, avoid doing this at all costs. For me as a writer, the effect of these authors’ masterpieces is often deeply personal. You won’t be able to find the beautiful thoughts they contain in any other literary form. I hope you enjoy the read and that it will inspire you to do your writing. This list is only an attempt to share some of the best essays available online. Next up, you may want to check the list of magazines and websites that accept personal essays .

Get your free PDF report: Download your guide to 100+ AI marketing tools and learn how to thrive as a marketer in the digital era.

Rafal Reyzer
Hey there, welcome to my blog! I'm a full-time entrepreneur building two companies, a digital marketer, and a content creator with 10+ years of experience. I started RafalReyzer.com to provide you with great tools and strategies you can use to become a proficient digital marketer and achieve freedom through online creativity. My site is a one-stop shop for digital marketers, and content enthusiasts who want to be independent, earn more money, and create beautiful things. Explore my journey here , and don't miss out on my AI Marketing Mastery online course.
- Craft and Criticism
- Fiction and Poetry
- News and Culture
- Lit Hub Radio
- Reading Lists

- Literary Criticism
- Craft and Advice
- In Conversation
- On Translation
- Short Story
- From the Novel
- Bookstores and Libraries
- Film and TV
- Art and Photography
- Freeman’s
- The Virtual Book Channel
- Behind the Mic
- Beyond the Page
- The Cosmic Library
- The Critic and Her Publics
- Emergence Magazine
- Fiction/Non/Fiction
- First Draft: A Dialogue on Writing
- The History of Literature
- I’m a Writer But
- Lit Century
- Tor Presents: Voyage Into Genre
- Windham-Campbell Prizes Podcast
- Write-minded
- The Best of the Decade
- Best Reviewed Books
- BookMarks Daily Giveaway
- The Daily Thrill
- CrimeReads Daily Giveaway

The 10 Best Essay Collections of the Decade
Ever tried. ever failed. no matter..
Friends, it’s true: the end of the decade approaches. It’s been a difficult, anxiety-provoking, morally compromised decade, but at least it’s been populated by some damn fine literature. We’ll take our silver linings where we can.
So, as is our hallowed duty as a literary and culture website—though with full awareness of the potentially fruitless and endlessly contestable nature of the task—in the coming weeks, we’ll be taking a look at the best and most important (these being not always the same) books of the decade that was. We will do this, of course, by means of a variety of lists. We began with the best debut novels , the best short story collections , the best poetry collections , and the best memoirs of the decade , and we have now reached the fifth list in our series: the best essay collections published in English between 2010 and 2019.
The following books were chosen after much debate (and several rounds of voting) by the Literary Hub staff. Tears were spilled, feelings were hurt, books were re-read. And as you’ll shortly see, we had a hard time choosing just ten—so we’ve also included a list of dissenting opinions, and an even longer list of also-rans. As ever, free to add any of your own favorites that we’ve missed in the comments below.
The Top Ten
Oliver sacks, the mind’s eye (2010).
Toward the end of his life, maybe suspecting or sensing that it was coming to a close, Dr. Oliver Sacks tended to focus his efforts on sweeping intellectual projects like On the Move (a memoir), The River of Consciousness (a hybrid intellectual history), and Hallucinations (a book-length meditation on, what else, hallucinations). But in 2010, he gave us one more classic in the style that first made him famous, a form he revolutionized and brought into the contemporary literary canon: the medical case study as essay. In The Mind’s Eye , Sacks focuses on vision, expanding the notion to embrace not only how we see the world, but also how we map that world onto our brains when our eyes are closed and we’re communing with the deeper recesses of consciousness. Relaying histories of patients and public figures, as well as his own history of ocular cancer (the condition that would eventually spread and contribute to his death), Sacks uses vision as a lens through which to see all of what makes us human, what binds us together, and what keeps us painfully apart. The essays that make up this collection are quintessential Sacks: sensitive, searching, with an expertise that conveys scientific information and experimentation in terms we can not only comprehend, but which also expand how we see life carrying on around us. The case studies of “Stereo Sue,” of the concert pianist Lillian Kalir, and of Howard, the mystery novelist who can no longer read, are highlights of the collection, but each essay is a kind of gem, mined and polished by one of the great storytellers of our era. –Dwyer Murphy, CrimeReads Managing Editor
John Jeremiah Sullivan, Pulphead (2011)
The American essay was having a moment at the beginning of the decade, and Pulphead was smack in the middle. Without any hard data, I can tell you that this collection of John Jeremiah Sullivan’s magazine features—published primarily in GQ , but also in The Paris Review , and Harper’s —was the only full book of essays most of my literary friends had read since Slouching Towards Bethlehem , and probably one of the only full books of essays they had even heard of.
Well, we all picked a good one. Every essay in Pulphead is brilliant and entertaining, and illuminates some small corner of the American experience—even if it’s just one house, with Sullivan and an aging writer inside (“Mr. Lytle” is in fact a standout in a collection with no filler; fittingly, it won a National Magazine Award and a Pushcart Prize). But what are they about? Oh, Axl Rose, Christian Rock festivals, living around the filming of One Tree Hill , the Tea Party movement, Michael Jackson, Bunny Wailer, the influence of animals, and by god, the Miz (of Real World/Road Rules Challenge fame).
But as Dan Kois has pointed out , what connects these essays, apart from their general tone and excellence, is “their author’s essential curiosity about the world, his eye for the perfect detail, and his great good humor in revealing both his subjects’ and his own foibles.” They are also extremely well written, drawing much from fictional techniques and sentence craft, their literary pleasures so acute and remarkable that James Wood began his review of the collection in The New Yorker with a quiz: “Are the following sentences the beginnings of essays or of short stories?” (It was not a hard quiz, considering the context.)
It’s hard not to feel, reading this collection, like someone reached into your brain, took out the half-baked stuff you talk about with your friends, researched it, lived it, and represented it to you smarter and better and more thoroughly than you ever could. So read it in awe if you must, but read it. –Emily Temple, Senior Editor
Aleksandar Hemon, The Book of My Lives (2013)
Such is the sentence-level virtuosity of Aleksandar Hemon—the Bosnian-American writer, essayist, and critic—that throughout his career he has frequently been compared to the granddaddy of borrowed language prose stylists: Vladimir Nabokov. While it is, of course, objectively remarkable that anyone could write so beautifully in a language they learned in their twenties, what I admire most about Hemon’s work is the way in which he infuses every essay and story and novel with both a deep humanity and a controlled (but never subdued) fury. He can also be damn funny. Hemon grew up in Sarajevo and left in 1992 to study in Chicago, where he almost immediately found himself stranded, forced to watch from afar as his beloved home city was subjected to a relentless four-year bombardment, the longest siege of a capital in the history of modern warfare. This extraordinary memoir-in-essays is many things: it’s a love letter to both the family that raised him and the family he built in exile; it’s a rich, joyous, and complex portrait of a place the 90s made synonymous with war and devastation; and it’s an elegy for the wrenching loss of precious things. There’s an essay about coming of age in Sarajevo and another about why he can’t bring himself to leave Chicago. There are stories about relationships forged and maintained on the soccer pitch or over the chessboard, and stories about neighbors and mentors turned monstrous by ethnic prejudice. As a chorus they sing with insight, wry humor, and unimaginable sorrow. I am not exaggerating when I say that the collection’s devastating final piece, “The Aquarium”—which details his infant daughter’s brain tumor and the agonizing months which led up to her death—remains the most painful essay I have ever read. –Dan Sheehan, Book Marks Editor
Robin Wall Kimmerer, Braiding Sweetgrass (2013)
Of every essay in my relentlessly earmarked copy of Braiding Sweetgrass , Dr. Robin Wall Kimmerer’s gorgeously rendered argument for why and how we should keep going, there’s one that especially hits home: her account of professor-turned-forester Franz Dolp. When Dolp, several decades ago, revisited the farm that he had once shared with his ex-wife, he found a scene of destruction: The farm’s new owners had razed the land where he had tried to build a life. “I sat among the stumps and the swirling red dust and I cried,” he wrote in his journal.
So many in my generation (and younger) feel this kind of helplessness–and considerable rage–at finding ourselves newly adult in a world where those in power seem determined to abandon or destroy everything that human bodies have always needed to survive: air, water, land. Asking any single book to speak to this helplessness feels unfair, somehow; yet, Braiding Sweetgrass does, by weaving descriptions of indigenous tradition with the environmental sciences in order to show what survival has looked like over the course of many millennia. Kimmerer’s essays describe her personal experience as a Potawotami woman, plant ecologist, and teacher alongside stories of the many ways that humans have lived in relationship to other species. Whether describing Dolp’s work–he left the stumps for a life of forest restoration on the Oregon coast–or the work of others in maple sugar harvesting, creating black ash baskets, or planting a Three Sisters garden of corn, beans, and squash, she brings hope. “In ripe ears and swelling fruit, they counsel us that all gifts are multiplied in relationship,” she writes of the Three Sisters, which all sustain one another as they grow. “This is how the world keeps going.” –Corinne Segal, Senior Editor
Hilton Als, White Girls (2013)
In a world where we are so often reduced to one essential self, Hilton Als’ breathtaking book of critical essays, White Girls , which meditates on the ways he and other subjects read, project and absorb parts of white femininity, is a radically liberating book. It’s one of the only works of critical thinking that doesn’t ask the reader, its author or anyone he writes about to stoop before the doorframe of complete legibility before entering. Something he also permitted the subjects and readers of his first book, the glorious book-length essay, The Women , a series of riffs and psychological portraits of Dorothy Dean, Owen Dodson, and the author’s own mother, among others. One of the shifts of that book, uncommon at the time, was how it acknowledges the way we inhabit bodies made up of variously gendered influences. To read White Girls now is to experience the utter freedom of this gift and to marvel at Als’ tremendous versatility and intelligence.
He is easily the most diversely talented American critic alive. He can write into genres like pop music and film where being part of an audience is a fantasy happening in the dark. He’s also wired enough to know how the art world builds reputations on the nod of rich white patrons, a significant collision in a time when Jean-Michel Basquiat is America’s most expensive modern artist. Als’ swerving and always moving grip on performance means he’s especially good on describing the effect of art which is volatile and unstable and built on the mingling of made-up concepts and the hard fact of their effect on behavior, such as race. Writing on Flannery O’Connor for instance he alone puts a finger on her “uneasy and unavoidable union between black and white, the sacred and the profane, the shit and the stars.” From Eminem to Richard Pryor, André Leon Talley to Michael Jackson, Als enters the life and work of numerous artists here who turn the fascinations of race and with whiteness into fury and song and describes the complexity of their beauty like his life depended upon it. There are also brief memoirs here that will stop your heart. This is an essential work to understanding American culture. –John Freeman, Executive Editor
Eula Biss, On Immunity (2014)
We move through the world as if we can protect ourselves from its myriad dangers, exercising what little agency we have in an effort to keep at bay those fears that gather at the edges of any given life: of loss, illness, disaster, death. It is these fears—amplified by the birth of her first child—that Eula Biss confronts in her essential 2014 essay collection, On Immunity . As any great essayist does, Biss moves outward in concentric circles from her own very private view of the world to reveal wider truths, discovering as she does a culture consumed by anxiety at the pervasive toxicity of contemporary life. As Biss interrogates this culture—of privilege, of whiteness—she interrogates herself, questioning the flimsy ways in which we arm ourselves with science or superstition against the impurities of daily existence.
Five years on from its publication, it is dismaying that On Immunity feels as urgent (and necessary) a defense of basic science as ever. Vaccination, we learn, is derived from vacca —for cow—after the 17th-century discovery that a small application of cowpox was often enough to inoculate against the scourge of smallpox, an etymological digression that belies modern conspiratorial fears of Big Pharma and its vaccination agenda. But Biss never scolds or belittles the fears of others, and in her generosity and openness pulls off a neat (and important) trick: insofar as we are of the very world we fear, she seems to be suggesting, we ourselves are impure, have always been so, permeable, vulnerable, yet so much stronger than we think. –Jonny Diamond, Editor-in-Chief
Rebecca Solnit, The Mother of All Questions (2016)
When Rebecca Solnit’s essay, “Men Explain Things to Me,” was published in 2008, it quickly became a cultural phenomenon unlike almost any other in recent memory, assigning language to a behavior that almost every woman has witnessed—mansplaining—and, in the course of identifying that behavior, spurring a movement, online and offline, to share the ways in which patriarchal arrogance has intersected all our lives. (It would also come to be the titular essay in her collection published in 2014.) The Mother of All Questions follows up on that work and takes it further in order to examine the nature of self-expression—who is afforded it and denied it, what institutions have been put in place to limit it, and what happens when it is employed by women. Solnit has a singular gift for describing and decoding the misogynistic dynamics that govern the world so universally that they can seem invisible and the gendered violence that is so common as to seem unremarkable; this naming is powerful, and it opens space for sharing the stories that shape our lives.
The Mother of All Questions, comprised of essays written between 2014 and 2016, in many ways armed us with some of the tools necessary to survive the gaslighting of the Trump years, in which many of us—and especially women—have continued to hear from those in power that the things we see and hear do not exist and never existed. Solnit also acknowledges that labels like “woman,” and other gendered labels, are identities that are fluid in reality; in reviewing the book for The New Yorker , Moira Donegan suggested that, “One useful working definition of a woman might be ‘someone who experiences misogyny.'” Whichever words we use, Solnit writes in the introduction to the book that “when words break through unspeakability, what was tolerated by a society sometimes becomes intolerable.” This storytelling work has always been vital; it continues to be vital, and in this book, it is brilliantly done. –Corinne Segal, Senior Editor
Valeria Luiselli, Tell Me How It Ends (2017)
The newly minted MacArthur fellow Valeria Luiselli’s four-part (but really six-part) essay Tell Me How It Ends: An Essay in Forty Questions was inspired by her time spent volunteering at the federal immigration court in New York City, working as an interpreter for undocumented, unaccompanied migrant children who crossed the U.S.-Mexico border. Written concurrently with her novel Lost Children Archive (a fictional exploration of the same topic), Luiselli’s essay offers a fascinating conceit, the fashioning of an argument from the questions on the government intake form given to these children to process their arrivals. (Aside from the fact that this essay is a heartbreaking masterpiece, this is such a good conceit—transforming a cold, reproducible administrative document into highly personal literature.) Luiselli interweaves a grounded discussion of the questionnaire with a narrative of the road trip Luiselli takes with her husband and family, across America, while they (both Mexican citizens) wait for their own Green Card applications to be processed. It is on this trip when Luiselli reflects on the thousands of migrant children mysteriously traveling across the border by themselves. But the real point of the essay is to actually delve into the real stories of some of these children, which are agonizing, as well as to gravely, clearly expose what literally happens, procedural, when they do arrive—from forms to courts, as they’re swallowed by a bureaucratic vortex. Amid all of this, Luiselli also takes on more, exploring the larger contextual relationship between the United States of America and Mexico (as well as other countries in Central America, more broadly) as it has evolved to our current, adverse moment. Tell Me How It Ends is so small, but it is so passionate and vigorous: it desperately accomplishes in its less-than-100-pages-of-prose what centuries and miles and endless records of federal bureaucracy have never been able, and have never cared, to do: reverse the dehumanization of Latin American immigrants that occurs once they set foot in this country. –Olivia Rutigliano, CrimeReads Editorial Fellow
Zadie Smith, Feel Free (2018)
In the essay “Meet Justin Bieber!” in Feel Free , Zadie Smith writes that her interest in Justin Bieber is not an interest in the interiority of the singer himself, but in “the idea of the love object”. This essay—in which Smith imagines a meeting between Bieber and the late philosopher Martin Buber (“Bieber and Buber are alternative spellings of the same German surname,” she explains in one of many winning footnotes. “Who am I to ignore these hints from the universe?”). Smith allows that this premise is a bit premise -y: “I know, I know.” Still, the resulting essay is a very funny, very smart, and un-tricky exploration of individuality and true “meeting,” with a dash of late capitalism thrown in for good measure. The melding of high and low culture is the bread and butter of pretty much every prestige publication on the internet these days (and certainly of the Twitter feeds of all “public intellectuals”), but the essays in Smith’s collection don’t feel familiar—perhaps because hers is, as we’ve long known, an uncommon skill. Though I believe Smith could probably write compellingly about anything, she chooses her subjects wisely. She writes with as much electricity about Brexit as the aforementioned Beliebers—and each essay is utterly engrossing. “She contains multitudes, but her point is we all do,” writes Hermione Hoby in her review of the collection in The New Republic . “At the same time, we are, in our endless difference, nobody but ourselves.” –Jessie Gaynor, Social Media Editor
Tressie McMillan Cottom, Thick: And Other Essays (2019)
Tressie McMillan Cottom is an academic who has transcended the ivory tower to become the sort of public intellectual who can easily appear on radio or television talk shows to discuss race, gender, and capitalism. Her collection of essays reflects this duality, blending scholarly work with memoir to create a collection on the black female experience in postmodern America that’s “intersectional analysis with a side of pop culture.” The essays range from an analysis of sexual violence, to populist politics, to social media, but in centering her own experiences throughout, the collection becomes something unlike other pieces of criticism of contemporary culture. In explaining the title, she reflects on what an editor had said about her work: “I was too readable to be academic, too deep to be popular, too country black to be literary, and too naïve to show the rigor of my thinking in the complexity of my prose. I had wanted to create something meaningful that sounded not only like me, but like all of me. It was too thick.” One of the most powerful essays in the book is “Dying to be Competent” which begins with her unpacking the idiocy of LinkedIn (and the myth of meritocracy) and ends with a description of her miscarriage, the mishandling of black woman’s pain, and a condemnation of healthcare bureaucracy. A finalist for the 2019 National Book Award for Nonfiction, Thick confirms McMillan Cottom as one of our most fearless public intellectuals and one of the most vital. –Emily Firetog, Deputy Editor
Dissenting Opinions
The following books were just barely nudged out of the top ten, but we (or at least one of us) couldn’t let them pass without comment.
Elif Batuman, The Possessed (2010)
In The Possessed Elif Batuman indulges her love of Russian literature and the result is hilarious and remarkable. Each essay of the collection chronicles some adventure or other that she had while in graduate school for Comparative Literature and each is more unpredictable than the next. There’s the time a “well-known 20th-centuryist” gave a graduate student the finger; and the time when Batuman ended up living in Samarkand, Uzbekistan, for a summer; and the time that she convinced herself Tolstoy was murdered and spent the length of the Tolstoy Conference in Yasnaya Polyana considering clues and motives. Rich in historic detail about Russian authors and literature and thoughtfully constructed, each essay is an amalgam of critical analysis, cultural criticism, and serious contemplation of big ideas like that of identity, intellectual legacy, and authorship. With wit and a serpentine-like shape to her narratives, Batuman adopts a form reminiscent of a Socratic discourse, setting up questions at the beginning of her essays and then following digressions that more or less entreat the reader to synthesize the answer for herself. The digressions are always amusing and arguably the backbone of the collection, relaying absurd anecdotes with foreign scholars or awkward, surreal encounters with Eastern European strangers. Central also to the collection are Batuman’s intellectual asides where she entertains a theory—like the “problem of the person”: the inability to ever wholly capture one’s character—that ultimately layer the book’s themes. “You are certainly my most entertaining student,” a professor said to Batuman. But she is also curious and enthusiastic and reflective and so knowledgeable that she might even convince you (she has me!) that you too love Russian literature as much as she does. –Eleni Theodoropoulos, Editorial Fellow
Roxane Gay, Bad Feminist (2014)
Roxane Gay’s now-classic essay collection is a book that will make you laugh, think, cry, and then wonder, how can cultural criticism be this fun? My favorite essays in the book include Gay’s musings on competitive Scrabble, her stranded-in-academia dispatches, and her joyous film and television criticism, but given the breadth of topics Roxane Gay can discuss in an entertaining manner, there’s something for everyone in this one. This book is accessible because feminism itself should be accessible – Roxane Gay is as likely to draw inspiration from YA novels, or middle-brow shows about friendship, as she is to introduce concepts from the academic world, and if there’s anyone I trust to bridge the gap between high culture, low culture, and pop culture, it’s the Goddess of Twitter. I used to host a book club dedicated to radical reads, and this was one of the first picks for the club; a week after the book club met, I spied a few of the attendees meeting in the café of the bookstore, and found out that they had bonded so much over discussing Bad Feminist that they couldn’t wait for the next meeting of the book club to keep discussing politics and intersectionality, and that, in a nutshell, is the power of Roxane. –Molly Odintz, CrimeReads Associate Editor
Rivka Galchen, Little Labors (2016)
Generally, I find stories about the trials and tribulations of child-having to be of limited appeal—useful, maybe, insofar as they offer validation that other people have also endured the bizarre realities of living with a tiny human, but otherwise liable to drift into the musings of parents thrilled at the simple fact of their own fecundity, as if they were the first ones to figure the process out (or not). But Little Labors is not simply an essay collection about motherhood, perhaps because Galchen initially “didn’t want to write about” her new baby—mostly, she writes, “because I had never been interested in babies, or mothers; in fact, those subjects had seemed perfectly not interesting to me.” Like many new mothers, though, Galchen soon discovered her baby—which she refers to sometimes as “the puma”—to be a preoccupying thought, demanding to be written about. Galchen’s interest isn’t just in her own progeny, but in babies in literature (“Literature has more dogs than babies, and also more abortions”), The Pillow Book , the eleventh-century collection of musings by Sei Shōnagon, and writers who are mothers. There are sections that made me laugh out loud, like when Galchen continually finds herself in an elevator with a neighbor who never fails to remark on the puma’s size. There are also deeper, darker musings, like the realization that the baby means “that it’s not permissible to die. There are days when this does not feel good.” It is a slim collection that I happened to read at the perfect time, and it remains one of my favorites of the decade. –Emily Firetog, Deputy Editor
Charlie Fox, This Young Monster (2017)
On social media as in his writing, British art critic Charlie Fox rejects lucidity for allusion and doesn’t quite answer the Twitter textbox’s persistent question: “What’s happening?” These days, it’s hard to tell. This Young Monster (2017), Fox’s first book,was published a few months after Donald Trump’s election, and at one point Fox takes a swipe at a man he judges “direct from a nightmare and just a repulsive fucking goon.” Fox doesn’t linger on politics, though, since most of the monsters he looks at “embody otherness and make it into art, ripping any conventional idea of beauty to shreds and replacing it with something weird and troubling of their own invention.”
If clichés are loathed because they conform to what philosopher Georges Bataille called “the common measure,” then monsters are rebellious non-sequiturs, comedic or horrific derailments from a classical ideal. Perverts in the most literal sense, monsters have gone astray from some “proper” course. The book’s nine chapters, which are about a specific monster or type of monster, are full of callbacks to familiar and lesser-known media. Fox cites visual art, film, songs, and books with the screwy buoyancy of a savant. Take one of his essays, “Spook House,” framed as a stage play with two principal characters, Klaus (“an intoxicated young skinhead vampire”) and Hermione (“a teen sorceress with green skin and jet-black hair” who looks more like The Wicked Witch than her namesake). The chorus is a troupe of trick-or-treaters. Using the filmmaker Cameron Jamie as a starting point, the rest is free association on gothic decadence and Detroit and L.A. as cities of the dead. All the while, Klaus quotes from Artforum , Dazed & Confused , and Time Out. It’s a technical feat that makes fictionalized dialogue a conveyor belt for cultural criticism.
In Fox’s imagination, David Bowie and the Hydra coexist alongside Peter Pan, Dennis Hopper, and the maenads. Fox’s book reaches for the monster’s mask, not really to peel it off but to feel and smell the rubber schnoz, to know how it’s made before making sure it’s still snugly set. With a stylistic blend of arthouse suavity and B-movie chic, This Young Monster considers how monsters in culture are made. Aren’t the scariest things made in post-production? Isn’t the creature just duplicity, like a looping choir or a dubbed scream? –Aaron Robertson, Assistant Editor
Elena Passarello, Animals Strike Curious Poses (2017)
Elena Passarello’s collection of essays Animals Strike Curious Poses picks out infamous animals and grants them the voice, narrative, and history they deserve. Not only is a collection like this relevant during the sixth extinction but it is an ambitious historical and anthropological undertaking, which Passarello has tackled with thorough research and a playful tone that rather than compromise her subject, complicates and humanizes it. Passarello’s intention is to investigate the role of animals across the span of human civilization and in doing so, to construct a timeline of humanity as told through people’s interactions with said animals. “Of all the images that make our world, animal images are particularly buried inside us,” Passarello writes in her first essay, to introduce us to the object of the book and also to the oldest of her chosen characters: Yuka, a 39,000-year-old mummified woolly mammoth discovered in the Siberian permafrost in 2010. It was an occasion so remarkable and so unfathomable given the span of human civilization that Passarello says of Yuka: “Since language is epically younger than both thought and experience, ‘woolly mammoth’ means, to a human brain, something more like time.” The essay ends with a character placing a hand on a cave drawing of a woolly mammoth, accompanied by a phrase which encapsulates the author’s vision for the book: “And he becomes the mammoth so he can envision the mammoth.” In Passarello’s hands the imagined boundaries between the animal, natural, and human world disintegrate and what emerges is a cohesive if baffling integrated history of life. With the accuracy and tenacity of a journalist and the spirit of a storyteller, Elena Passarello has assembled a modern bestiary worthy of contemplation and awe. –Eleni Theodoropoulos, Editorial Fellow
Esmé Weijun Wang, The Collected Schizophrenias (2019)
Esmé Weijun Wang’s collection of essays is a kaleidoscopic look at mental health and the lives affected by the schizophrenias. Each essay takes on a different aspect of the topic, but you’ll want to read them together for a holistic perspective. Esmé Weijun Wang generously begins The Collected Schizophrenias by acknowledging the stereotype, “Schizophrenia terrifies. It is the archetypal disorder of lunacy.” From there, she walks us through the technical language, breaks down the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual ( DSM-5 )’s clinical definition. And then she gets very personal, telling us about how she came to her own diagnosis and the way it’s touched her daily life (her relationships, her ideas about motherhood). Esmé Weijun Wang is uniquely situated to write about this topic. As a former lab researcher at Stanford, she turns a precise, analytical eye to her experience while simultaneously unfolding everything with great patience for her reader. Throughout, she brilliantly dissects the language around mental health. (On saying “a person living with bipolar disorder” instead of using “bipolar” as the sole subject: “…we are not our diseases. We are instead individuals with disorders and malfunctions. Our conditions lie over us like smallpox blankets; we are one thing and the illness is another.”) She pinpoints the ways she arms herself against anticipated reactions to the schizophrenias: high fashion, having attended an Ivy League institution. In a particularly piercing essay, she traces mental illness back through her family tree. She also places her story within more mainstream cultural contexts, calling on groundbreaking exposés about the dangerous of institutionalization and depictions of mental illness in television and film (like the infamous Slender Man case, in which two young girls stab their best friend because an invented Internet figure told them to). At once intimate and far-reaching, The Collected Schizophrenias is an informative and important (and let’s not forget artful) work. I’ve never read a collection quite so beautifully-written and laid-bare as this. –Katie Yee, Book Marks Assistant Editor
Ross Gay, The Book of Delights (2019)
When Ross Gay began writing what would become The Book of Delights, he envisioned it as a project of daily essays, each focused on a moment or point of delight in his day. This plan quickly disintegrated; on day four, he skipped his self-imposed assignment and decided to “in honor and love, delight in blowing it off.” (Clearly, “blowing it off” is a relative term here, as he still produced the book.) Ross Gay is a generous teacher of how to live, and this moment of reveling in self-compassion is one lesson among many in The Book of Delights , which wanders from moments of connection with strangers to a shade of “red I don’t think I actually have words for,” a text from a friend reading “I love you breadfruit,” and “the sun like a guiding hand on my back, saying everything is possible. Everything .”
Gay does not linger on any one subject for long, creating the sense that delight is a product not of extenuating circumstances, but of our attention; his attunement to the possibilities of a single day, and awareness of all the small moments that produce delight, are a model for life amid the warring factions of the attention economy. These small moments range from the physical–hugging a stranger, transplanting fig cuttings–to the spiritual and philosophical, giving the impression of sitting beside Gay in his garden as he thinks out loud in real time. It’s a privilege to listen. –Corinne Segal, Senior Editor
Honorable Mentions
A selection of other books that we seriously considered for both lists—just to be extra about it (and because decisions are hard).
Terry Castle, The Professor and Other Writings (2010) · Joyce Carol Oates, In Rough Country (2010) · Geoff Dyer, Otherwise Known as the Human Condition (2011) · Christopher Hitchens, Arguably (2011) · Roberto Bolaño, tr. Natasha Wimmer, Between Parentheses (2011) · Dubravka Ugresic, tr. David Williams, Karaoke Culture (2011) · Tom Bissell, Magic Hours (2012) · Kevin Young, The Grey Album (2012) · William H. Gass, Life Sentences: Literary Judgments and Accounts (2012) · Mary Ruefle, Madness, Rack, and Honey (2012) · Herta Müller, tr. Geoffrey Mulligan, Cristina and Her Double (2013) · Leslie Jamison, The Empathy Exams (2014) · Meghan Daum, The Unspeakable (2014) · Daphne Merkin, The Fame Lunches (2014) · Charles D’Ambrosio, Loitering (2015) · Wendy Walters, Multiply/Divide (2015) · Colm Tóibín, On Elizabeth Bishop (2015) · Renee Gladman, Calamities (2016) · Jesmyn Ward, ed. The Fire This Time (2016) · Lindy West, Shrill (2016) · Mary Oliver, Upstream (2016) · Emily Witt, Future Sex (2016) · Olivia Laing, The Lonely City (2016) · Mark Greif, Against Everything (2016) · Durga Chew-Bose, Too Much and Not the Mood (2017) · Sarah Gerard, Sunshine State (2017) · Jim Harrison, A Really Big Lunch (2017) · J.M. Coetzee, Late Essays: 2006-2017 (2017) · Melissa Febos, Abandon Me (2017) · Louise Glück, American Originality (2017) · Joan Didion, South and West (2017) · Tom McCarthy, Typewriters, Bombs, Jellyfish (2017) · Hanif Abdurraqib, They Can’t Kill Us Until they Kill Us (2017) · Ta-Nehisi Coates, We Were Eight Years in Power (2017) · Samantha Irby, We Are Never Meeting in Real Life (2017) · Alexander Chee, How to Write an Autobiographical Novel (2018) · Alice Bolin, Dead Girls (2018) · Marilynne Robinson, What Are We Doing Here? (2018) · Lorrie Moore, See What Can Be Done (2018) · Maggie O’Farrell, I Am I Am I Am (2018) · Ijeoma Oluo, So You Want to Talk About Race (2018) · Rachel Cusk, Coventry (2019) · Jia Tolentino, Trick Mirror (2019) · Emily Bernard, Black is the Body (2019) · Toni Morrison, The Source of Self-Regard (2019) · Margaret Renkl, Late Migrations (2019) · Rachel Munroe, Savage Appetites (2019) · Robert A. Caro, Working (2019) · Arundhati Roy, My Seditious Heart (2019).

Emily Temple
Previous article, next article.

- RSS - Posts
Literary Hub
Created by Grove Atlantic and Electric Literature
Sign Up For Our Newsletters
How to Pitch Lit Hub
Advertisers: Contact Us
Privacy Policy
Support Lit Hub - Become A Member
Become a Lit Hub Supporting Member : Because Books Matter
For the past decade, Literary Hub has brought you the best of the book world for free—no paywall. But our future relies on you. In return for a donation, you’ll get an ad-free reading experience , exclusive editors’ picks, book giveaways, and our coveted Joan Didion Lit Hub tote bag . Most importantly, you’ll keep independent book coverage alive and thriving on the internet.

Become a member for as low as $5/month

The 25 Greatest Essay Collections of All Time
Today marks the release of Aleksandar Hemon’s excellent book of personal essays, The Book of My Lives , which we loved, and which we’re convinced deserves a place in the literary canon. To that end, we were inspired to put together our list of the greatest essay collections of all time, from the classic to the contemporary, from the personal to the critical. In making our choices, we’ve steered away from posthumous omnibuses (Michel de Montaigne’s Complete Essays , the collected Orwell, etc.) and multi-author compilations, and given what might be undue weight to our favorite writers (as one does). After the jump, our picks for the 25 greatest essay collections of all time. Feel free to disagree with us, praise our intellect, or create an entirely new list in the comments.

The Book of My Lives , Aleksandar Hemon
Hemon’s memoir in essays is in turns wryly hilarious, intellectually searching, and deeply troubling. It’s the life story of a fascinating, quietly brilliant man, and it reads as such. For fans of chess and ill-advised theme parties and growing up more than once.

Slouching Towards Bethlehem , Joan Didion
Well, obviously. Didion’s extraordinary book of essays, expertly surveying both her native California in the 1960s and her own internal landscape with clear eyes and one eyebrow raised ever so slightly. This collection, her first, helped establish the idea of journalism as art, and continues to put wind in the sails of many writers after her, hoping to move in that Didion direction.

Pulphead , John Jeremiah Sullivan
This was one of those books that this writer deemed required reading for all immediate family and friends. Sullivan’s sharply observed essays take us from Christian rock festivals to underground caves to his own home, and introduce us to 19-century geniuses, imagined professors and Axl Rose. Smart, curious, and humane, this is everything an essay collection should be.

The Boys of My Youth , Jo Ann Beard
Another memoir-in-essays, or perhaps just a collection of personal narratives, Jo Ann Beard’s award-winning volume is a masterpiece. Not only does it include the luminous, emotionally destructive “The Fourth State of the Matter,” which we’ve already implored you to read , but also the incredible “Bulldozing the Baby,” which takes on a smaller tragedy: a three-year-old Beard’s separation from her doll Hal. “The gorgeous thing about Hal,” she tells us, “was that not only was he my friend, he was also my slave. I made the majority of our decisions, including the bathtub one, which in retrospect was the beginning of the end.”

Consider the Lobster , David Foster Wallace
This one’s another “duh” moment, at least if you’re a fan of the literary essay. One of the most brilliant essayists of all time, Wallace pushes the boundaries (of the form, of our patience, of his own brain) and comes back with a classic collection of writing on everything from John Updike to, well, lobsters. You’ll laugh out loud right before you rethink your whole life. And then repeat.

Notes of a Native Son , James Baldwin
Baldwin’s most influential work is a witty, passionate portrait of black life and social change in America in the 1940s and early 1950s. His essays, like so many of the greats’, are both incisive social critiques and rigorous investigations into the self, told with a perfect tension between humor and righteous fury.

Naked , David Sedaris
His essays often read more like short stories than they do social criticism (though there’s a healthy, if perhaps implied, dose of that slippery subject), but no one makes us laugh harder or longer. A genius of the form.

Against Interpretation , Susan Sontag
This collection, Sontag’s first, is a dazzling feat of intellectualism. Her essays dissect not only art but the way we think about art, imploring us to “reveal the sensuous surface of art without mucking about in it.” It also contains the brilliant “Notes on ‘Camp,'” one of our all-time favorites.

The Common Reader , Virginia Woolf
Woolf is a literary giant for a reason — she was as incisive and brilliant a critic as she was a novelist. These witty essays, written for the common reader (“He is worse educated, and nature has not gifted him so generously. He reads for his own pleasure rather than to impart knowledge or correct the opinions of others. Above all, he is guided by an instinct to create for himself, out of whatever odds and ends he can come by, some kind of whole- a portrait of a man, a sketch of an age, a theory of the art of writing”), are as illuminating and engrossing as they were when they were written.

Teaching a Stone to Talk , Annie Dillard
This is Dillard’s only book of essays, but boy is it a blazingly good one. The slender volume, filled with examinations of nature both human and not, is deft of thought and tongue, and well worth anyone’s time. As the Chicago Sun-Times ‘s Edward Abbey gushed, “This little book is haloed and informed throughout by Dillard’s distinctive passion and intensity, a sort of intellectual radiance that reminds me both Thoreau and Emily Dickinson.”

Thirteen Ways of Looking at a Black Man , Henry Louis Gates Jr.
In this eloquent volume of essays, all but one of which were originally published in the New Yorker , Gates argues against the notion of the singularly representable “black man,” preferring to represent him in a myriad of diverse profiles, from James Baldwin to Colin Powell. Humane, incisive, and satisfyingly journalistic, Gates cobbles together the ultimate portrait of the 20th-century African-American male by refusing to cobble it together, and raises important questions about race and identity even as he entertains.

Otherwise Known As the Human Condition , Geoff Dyer
This book of essays, which won the National Book Critics Circle Award in the year of its publication, covers 25 years of the uncategorizable, inimitable Geoff Dyer’s work — casually erudite and yet liable to fascinate anyone wandering in the door, witty and breathing and full of truth. As Sam Lipsyte said, “You read Dyer for his caustic wit, of course, his exquisite and perceptive crankiness, and his deep and exciting intellectual connections, but from these enthralling rants and cultural investigations there finally emerges another Dyer, a generous seeker of human feeling and experience, a man perhaps closer than he thinks to what he believes his hero Camus achieved: ‘a heart free of bitterness.'”

Art and Ardor , Cynthia Ozick
Look, Cynthia Ozick is a genius. One of David Foster Wallace’s favorite writers, and one of ours, Ozick has no less than seven essay collections to her name, and we could have chosen any one of them, each sharper and more perfectly self-conscious than the last. This one, however, includes her stunner “A Drugstore in Winter,” which was chosen by Joyce Carol Oates for The Best American Essays of the Century , so we’ll go with it.

No More Nice Girls , Ellen Willis
The venerable Ellen Willis was the first pop music critic for The New Yorker , and a rollicking anti-authoritarian, feminist, all-around bad-ass woman who had a hell of a way with words. This collection examines the women’s movement, the plight of the aging radical, race relations, cultural politics, drugs, and Picasso. Among other things.

The War Against Cliché , Martin Amis
As you know if you’ve ever heard him talk , Martin Amis is not only a notorious grouch but a sharp critical mind, particularly when it comes to literature. That quality is on full display in this collection, which spans nearly 30 years and twice as many subjects, from Vladimir Nabokov (his hero) to chess to writing about sex. Love him or hate him, there’s no denying that he’s a brilliant old grump.

Cultural Amnesia: Necessary Memories From History and the Arts , Clive James
James’s collection is a strange beast, not like any other essay collection on this list but its own breed. An encyclopedia of modern culture, the book collects 110 new biographical essays, which provide more than enough room for James to flex his formidable intellect and curiosity, as he wanders off on tangents, anecdotes, and cultural criticism. It’s not the only who’s who you need, but it’s a who’s who you need.

I Feel Bad About My Neck: And Other Thoughts on Being a Woman , Nora Ephron
Oh Nora, we miss you. Again, we could have picked any of her collections here — candid, hilarious, and willing to give it to you straight, she’s like a best friend and mentor in one, only much more interesting than any of either you’ve ever had.

Arguably , Christopher Hitchens
No matter what you think of his politics (or his rhetorical strategies), there’s no denying that Christopher Hitchens was one of the most brilliant minds — and one of the most brilliant debaters — of the century. In this collection, packed with cultural commentary, literary journalism, and political writing, he is at his liveliest, his funniest, his exactingly wittiest. He’s also just as caustic as ever.

The Solace of Open Spaces , Gretel Ehrlich
Gretel Ehrlich is a poet, and in this collection, you’ll know it. In 1976, she moved to Wyoming and became a cowherd, and nearly a decade later, she published this lovely, funny set of essays about rural life in the American West.”Keenly observed the world is transformed,” she writes. “The landscape is engorged with detail, every movement on it chillingly sharp. The air between people is charged. Days unfold, bathed in their own music. Nights become hallucinatory; dreams, prescient.”

The Braindead Megaphone , George Saunders
Saunders may be the man of the moment, but he’s been at work for a long while, and not only on his celebrated short stories. His single collection of essays applies the same humor and deliciously slant view to the real world — which manages to display nearly as much absurdity as one of his trademark stories.

Against Joie de Vivre , Phillip Lopate
“Over the years,” the title essay begins, “I have developed a distaste for the spectacle of joie de vivre , the knack of knowing how to live.” Lopate goes on to dissect, in pleasantly sardonic terms, the modern dinner party. Smart and thought-provoking throughout (and not as crotchety as all that), this collection is conversational but weighty, something to be discussed at length with friends at your next — oh well, you know.

Sex and the River Styx , Edward Hoagland
Edward Hoagland, who John Updike deemed “the best essayist of my generation,” has a long and storied career and a fat bibliography, so we hesitate to choose such a recent installment in the writer’s canon. Then again, Garrison Keillor thinks it’s his best yet , so perhaps we’re not far off. Hoagland is a great nature writer (name checked by many as the modern Thoreau) but in truth, he’s just as fascinated by humanity, musing that “human nature is interstitial with nature, and not to be shunned by a naturalist.” Elegant and thoughtful, Hoagland may warn us that he’s heading towards the River Styx, but we’ll hang on to him a while longer.

Changing My Mind , Zadie Smith
Smith may be best known for her novels (and she should be), but to our eyes she is also emerging as an excellent essayist in her own right, passionate and thoughtful. Plus, any essay collection that talks about Barack Obama via Pygmalion is a winner in our book.

My Misspent Youth , Meghan Daum
Like so many other writers on this list, Daum dives head first into the culture and comes up with meat in her mouth. Her voice is fresh and her narratives daring, honest and endlessly entertaining.

The White Album , Joan Didion
Yes, Joan Didion is on this list twice, because Joan Didion is the master of the modern essay, tearing at our assumptions and building our world in brisk, clever strokes. Deal.
Classic British and American Essays and Speeches
English Prose From Jack London to Dorothy Parker
U.S. National Archives and Records Administration / Wikimedia Commons / Public Domain
- An Introduction to Punctuation
- Ph.D., Rhetoric and English, University of Georgia
- M.A., Modern English and American Literature, University of Leicester
- B.A., English, State University of New York
From the works and musings of Walt Witman to those of Virginia Woolf, some of the cultural heroes and prolific artists of prose are listed below--along with some of the world's greatest essays and speeches ever composed by these British and American literary treasures.
George Ade (1866-1944)
George Ade was an America playwright, newspaper columnist and humorist whose greatest recognition was "Fables in Slang" (1899), a satire that explored the colloquial vernacular of America. Ade eventually succeeded in doing what he set out to do: Make America laugh.
- The Difference Between Learning and Learning How : "In due time the Faculty gave the Degree of M.A. to what was left of Otis and still his Ambition was not satisfied."
- Luxuries: "About sixty-five per cent of all the people in the world think they are getting along great when they are not starving to death."
- Vacations: "The planet you are now visiting may be the only one you ever see."
Susan B. Anthony (1820-1906)
American activist Susan B. Anthony crusaded for the women's suffrage movement, making way for the Nineteenth Amendment to the US Constitution in 1920, giving women the right to vote. Anthony is principally known for the six-volume "History of Woman Suffrage."
- On Women's Right to Vote : "The only question left to be settled now is: Are women persons?"
Robert Benchley (1889-1945)
The writings of American humorist, actor and drama critic Robert Benchley are considered his best achievement. His socially awkward, slightly confused persona allowed him to write about the inanity of the world to great effect.
- Advice to Writers : "A terrible plague of insufferably artificial and affected authors"
- Business Letters : "As it stands now things are pretty black for the boy."
- Christmas Afternoon : "Done in the Manner, If Not in the Spirit of Dickens"
- Do Insects Think? : "It really was more like a child of our own than a wasp, except that it looked more like a wasp than a child of our own."
- The Most Popular Book of the Month: "In practice, the book is not flawless. There are five hundred thousand names, each with a corresponding telephone number."
Joseph Conrad (1857-1924)
British novelist and short-story writer Joseph Conrad rendered about the "tragedy of loneliness" at sea and became known for his colorful, rich descriptions about the sea and other exotic places. He is regarded as one of the greatest English novelists of all time.
- Outside Literature : "A sea voyage would have done him good. But it was I who went to sea--this time bound to Calcutta."
Frederick Douglass (1818-1895)
American Frederick Douglass' great oratory and literary skills helped him to become the first African American citizen to hold high office in the US government. He was one of the 19th century's most prominent human rights activist, and his autobiography, "Life and Times of Frederick Douglass" (1882), became an American literary classic.
- The Destiny of Colored Americans : "Slavery is the peculiar weakness of America, as well as its peculiar crime."
- A Glorious Resurrection: "My long-crushed spirit rose."
W.E.B. Du Bois (1868-1963)
W.E.B. Du Bois was an American scholar and human rights activist, a respected author and historian of literature. His literature and studies analyzed the unreachable depths of American racism. Du Bois' seminal work is a collection of 14 essays titled "The Souls of Black Folk" (1903).
- Of Mr. Booker T. Washington and Others : "Mr. Washington represents in Negro thought the old attitude of adjustment and submission."
- Of the Passing of the First-Born : "He knew no color-line, poor dear--and the Veil, though it shadowed him, had not yet darkened half his sun."
F. Scott Fitzgerald (1896-1940)
Known foremost for his novel "The Great Gatsby," American novelist and short-story writer F. Scott Fitzgerald was also a renown playboy and had a tumultuous life compounded by alcoholism and depression. Only after his death did he become known as a preeminent American literary author.
- What I Think and Feel at 25: "The main thing is to be your own kind of a darn fool."
Ben Hecht (1894-1964)
American novelist, short-story writer and playwright Ben Hecht is remembered as one of Hollywood's greatest screenplay writers and may best be remembered for "Scarface," Wuthering Heights" and "Guys and Dolls."
- Fog Patterns : "Yes, we are all lost and wandering in the thick mists. We have no destinations."
- Letters: "You would see a procession of mysterious figures flitting through the streets, an unending swarm of dim ones, queer ones."
Ernest Hemingway (1899-1961)
American novelist Ernest Hemingway won the 1954 Nobel Prize in Literature for "his mastery of the art of narrative ... and for the influence he has exerted on contemporary style" as demonstrated in his brilliant novel "The Old Man and the Sea."
- American Bohemians in Paris: "The scum of Greenwich Village, New York, has been skimmed off and deposited in large ladles on that section of Paris adjacent to the Café Rotonde."
- Camping Out : "Any man of average office intelligence can make at least as good a pie as his wife."
Martin Luther King Jr. (1929-1968)
Civil rights activist and minister Martin Luther King Jr., winner of the Nobel Peace Prize in 1964, may be best known for "I Have A Dream," in which he wrote about love, peace, nonviolent activism and equality between all races.
- I Have a Dream : "Now is the time to make justice a reality for all of God's children."
- Reading Quiz on "I Have a Dream"
- Ten Things You Should Know About Dr. King's "I Have a Dream" Speech
Jack London (1876-1916)
Nineteenth-century American author and journalist Jack London is best known for his adventures "White Fang" and "The Call of the Wild." London published more than 50 books over the last 16 years of his life, including "John Barleycorn," which was somewhat of a memoir about his lifelong battle with alcohol.
- The Somnambulists : "[T]his archdeceiver believes all that they tell him. He reads only the newspapers and magazines that tell him what he wants to be told."
- The Story of an Eyewitness: The San Francisco Earthquake : "Not in history has a modern imperial city been so completely destroyed."
- Reading Quiz on "The San Francisco Earthquake"
- What Life Means to Me : "I accepted that up above me was all that was fine and noble and gracious, all that gave decency and dignity to life."
H.L. Mencken (1880-1956)
American journalist, activist and editor H.L. Mencken was also a very influential literary critic. His columns were popular not only for their literary criticism, but also for their questioning of popular political, social and cultural views.
- The Hills of Zion : "Dayton was having a roaring time. It was better than the circus."
- The Libido for the Ugly : "Out of the melting pot emerges a race which hates beauty."
- Literature and the Schoolma'm : "The essence of a sound style is that it cannot be reduced to rules."
- The Lower Depths : "The worst idiots, even among pedagogues, are the teachers of English."
- Portrait of an Ideal World : "All the great villainies of history have been perpetrated by sober men, and chiefly by teetotalers."
Christopher Morley (1890-1957)
American writer Christopher Morley was popular for his literary columns in the "New York Evening Post," among other literary magazines. His many collections of essays and columns were "lighthearted, vigorous displays of the English language."
- 1100 Words : "Let us be brief, crisp, packed with thought."
- The Art of Walking : "Sometimes it seems as though literature were a co-product of legs and head."
- A Morning in Marathon: "[W]e flashed onto the Hackensack marshes and into the fully minted gold of superb morning."
- On Going to Bed : "The happier creatures ... take the tide of sleep at the flood and are borne calmly and with gracious gentleness out to great waters of nothingness."
George Orwell (1903-1950)
This British novelist, essayist and critic is best known for his novels "1984" and "Animal Farm." George Orwell's disdain for imperialism (he considered himself an anarchist) guided him in his life as well as through some of his writings.
- A Hanging : "We all began laughing again. ... The dead man was a hundred yards away."
- Why Are Beggars Despised? : "A beggar, looked at realistically, is simply a businessman, getting his living."
Dorothy Parker (1893-1967)
Witty American poet and short-story writer Dorothy Parker began as an editorial assistant at "Vogue" and eventually became the book reviewer known as the "Constant Reader" for "The New Yorker." Among her hundreds of works, Parker won the 1929 O. Henry Award for her short story "Big Blond."
- Good Souls: "They are fated to go through life, congenial pariahs. They live out their little lives, mingling with the world, yet never a part of it."
- Mrs. Post Enlarges on Etiquette : "As one delves deeper and deeper into Etiquette , disquieting thoughts come."
Bertrand Russell (1872-1970)
British philosopher and social reformer Bertrand Russell won the Nobel Prize in Literature in 1950 "in recognition of his varied and significant writings in which he champions humanitarian ideals and freedom of thought." Russell was one of the foremost philosophers of the 20th century.
- In Praise of Idleness : "The road to happiness and prosperity lies in an organized diminution of work."
Margaret Sanger (1879-1966)
American activist Margaret Sanger was a sex educator, nurse and women's rights advocate. She began the first feminist publication, "The Woman Rebel," in 1914.
- The Turbid Ebb and Flow of Misery: "My own cozy and comfortable family existence was becoming a reproach to me."
George Bernard Shaw (1856-1950)
An Irish dramatist and critic, George Bernard Shaw was also a socialist propagandist and winner of the 1925 Nobel Prize in Literature (which he didn't receive until 1926) for "his work which is marked by both idealism and beauty." Shaw wrote more than 60 plays during his lifetime.
- Preface to Pygmalion: "It is impossible for an Englishman to open his mouth without making some other Englishman hate or despise him."
- She Would Have Enjoyed It: "Why does a funeral always sharpen one's sense of humor?"
- Why Law Is Indispensable: "Laws deaden the conscience of individuals by relieving them of responsibility."
- The Art of Political Lying : "Considering that natural disposition in many men to lie, and in multitudes to believe, I have been perplexed what to do with that maxim so frequent in everybody's mouth, that truth will at last prevail."
- Hints Toward an Essay on Conversation : "This degeneracy of conversation ... hath been owing, among other causes, to the custom arisen, for sometime past, of excluding women from any share in our society."
- A Meditation Upon a Broomstick : "But a broomstick is an emblem of a tree standing on its head."
Henry David Thoreau (1817-1862)
American essayist, poet and philosopher Henry David Thoreau is most known for his masterful work, "Walden," about living a life close to nature. He was a dedicated abolitionist and a strong practitioner of civil disobedience.
- The Battle of the Ants : "I never learned which party was victorious, nor the cause of the war."
- The Landlord: "If we do not look up to the Landlord, we look round for him on all emergencies, for he is a man of infinite experience, who unites hands with wit."
- The Last Days of John Brown : "[T]he one great rule of composition--and if I were a professor of rhetoric I should insist on this--is, to speak the truth ."
James Thurber (1894-1961)
American author and illustrator James Thurber is best known for his contributions to "The New Yorker." Via his contributions to the magazine, his cartoons became some of the most popular in the United States.
- The Subjunctive Mood : "Husbands are suspicious of all subjunctives. Wives should avoid them."
- Which: "Never monkey with 'which.'"
Anthony Trollope (1815-1882)
British author Anthony Trollope is best known for his writing in the Victorian Era--some of his work includes a series of novels known as "The Chronicles of Barsetshire." Trollope also wrote on political, social and gender issues.
- The Plumber : "The plumber is doubtless aware that he is odious. He feels himself, like Dickens's turnpike-man, to be the enemy of mankind."
Mark Twain (1835-1910)
Mark Twain was an American humorist, journalist, lecturer and novelist best known for his classic American novels "The Adventures of Tom Sawyer" and "Adventures of Huckleberry Finn." With his wit and grand telling of tales, Twain is nothing short of an American national treasure.
- Advice to Youth : "Always obey your parents, when they are present."
- Corn-Pone Opinions : "Tell me whar a man gits his corn pone, en I'll tell you what his 'pinions is."
- The Danger of Lying in Bed : "The danger isn't in traveling by rail, but in trusting to those deadly beds."
- A Fable : "You can find in a text whatever you bring."
- Fenimore Cooper's Literary Offences : " Deerslayer is just simply a literary delirium tremens."
- The Lowest Animal : "[W]e have descended and degenerated ... till we have reached the bottom stage of development."
- On the Decay of the Art of Lying: "Lying is universal: we all do it; we all must do it."
- Two Ways of Seeing a River : "All the grace, the beauty, the poetry had gone out of the majestic river!"
- Unconscious Plagiarism : "[P]ride protects a man from deliberately stealing other people's ideas."
H.G. Wells (1866-1944)
British author and historian H.G. Wells is best known for his works of science fiction, including "The Time Machine," "The First Men in the Moon" and "The War of the Worlds." Wells wrote an astounding 161 full-length books.
- For Freedom of Spelling: The Discovery of an Art: "Why should correct spelling be the one absolutely essential literary merit?"
- Of Conversation: An Apology: "I am no blowfly to buzz my way through the universe."
- The Pleasure of Quarrelling : "Without quarreling you have not fully appreciated your fellow-man."
- The Possible Collapse of Civilisation: "Modern warfare is an insanity, not a sane business proposition."
- The Writing of Essays: "The art of the essayist ... may be learnt in a brief ten minutes or so."
Walt Whitman (1819-1892)
American poet and journalist Walt Whitman's verse collection "Leaves of Grass" is an American literature landmark. Ralph Waldo Emerson praised the collection as "the most extraordinary piece of wit and wisdom" America had yet contributed.
- A Glimpse of War's Hell Scenes: "There was no exultation, very little said, almost nothing, yet every man there contributed his shot."
- Slang in America : "Language in the largest sense ... is really the greatest of studies."
- Street Yarn: "Come and walk in New York streets."
Virginia Woolf (1882-1941)
British author Virginia Woolf may be best known for her modernist classics "Mrs. Dalloway" and "To the Lighthouse." But she also produced feminist texts such as "A Room of One's Own" and "Three Guineas" and wrote pioneering essays on the politics of power, artistic theory and literary history.
- The Decay of Essay Writing : "Under the decent veil of print one can indulge one's egoism to the full."
- The Modern Essay : "The essay must lap us about and draw its curtain across the world."
- The Patron and the Crocus : "Be sure you choose your patron wisely."
- Street Haunting: A London Adventure : "Into each of these lives one could penetrate a little way."
- Writing for My Eye Only: "I can trace some increase of ease in my professional writing which I attribute to my casual half hours after tea."
- A List of Every Nobel Prize Winner in Literature
- 42 Must-Read Feminist Female Authors
- Biography of John Updike, Pulitzer Prize Winning American Author
- Complete List of John Steinbeck's Books
- 27 Black American Women Writers You Should Know
- 6 Speeches by American Authors for Secondary ELA Classrooms
- 10 Important Contemporary and Late-20th-Century Authors
- Notable Authors of the 19th Century
- Sinclair Lewis, First American to Win Nobel Prize for Literature
- A Brief Overview of American Literary Periods
- American Author Maps: Informational Texts in the English Classroom
- Mark Twain: His Life and His Humor
- Jack London: His Life and Work
- Top 100 Women of History
- What is a Familiar Essay in Composition?
- Biography of Ernest Hemingway, Pulitzer and Nobel Prize Winning Writer
Classics of Science Fiction
The best science fiction short stories.

[The project mentioned in this essay to create an all-time list of classic science fiction short stories has been completed. Jump to the Introduction to read how we created it or to Classics of Science Fiction Short Stories to see the ranked list.]
I’ve always wanted to identify the best science fiction short stories by the same method we used for the novels. Still, there are just not that many lists devoted to identifying the best science fiction short stories of all time. There are some though:
- Most Viewed Short Fiction Since 2005 ISFDB
- ISFDB older lists
- Top 100 SF Short Fiction 1-100
- Next 100 SF Short Fiction 101-200
- Anthology & Collection References
- Top 10 Reprinted Stories (see bottom of page)
This essay is for anyone who has thought about collecting science fiction short stories. First, let me thank P. F. Nel for sending me a spreadsheet of most of the annual best-of-the-year anthologies . Second, I’d like to thank all the folks at ISFDB.org for their magnificent database work. Clicking on the links below will take you to the table of contents and cover images at ISFDB. Piet and I have discussed the various ways to collect SF short stories:
- Collect the original magazines (thousands of magazines)
- Collect the annual anthologies (100-200 volumes)
- Collect the very best retrospective anthologies (2-25 volumes)
I’ve always considered stories appearing in science fiction magazines to be the heart of the genre. Anyone who reads the magazines as they came out would sense the evolution of science fiction, especially by reading the most famous titles: Amazing Stories , Wonder Stories , Astounding Stories , Astounding/Analog , F&SF , Galaxy , IF , and Asimov’s . Gideon Marcus over at Galactic Journey even started blogging by jumping back 55 years to read the science fiction mags in order. It’s possible to find scans of old SF magazines on the internet, but that’s far more reading than I want to do. The easier and quicker method of getting an overview of short science fiction is to collect the major retrospective anthologies. Some of my favorites have been:
- Adventures in Time and Space (1946)
- The Science Fiction Hall of Fame (1970)
- The Science Fiction Hall of Fame Volume 2 A (1973)
- The Science Fiction Hall of Fame Volume 2 B (1973)
- Before the Golden Age (1974)
- The Road to Science Fiction (1977-1998)
- The Arbor House Treasury of Modern Science Fiction (1980)
- The Ascent of Wonder (1994)
- Visions of Wonder (1996)
- The Science Fiction Century (1997)
- The Prentice Hall Anthology of Science Fiction and Fantasy (2000)
- The Best of the Best (2005)
- The Wesleyan Anthology of Science Fiction (2010)
- The Big Book of Science Fiction (2016)
Piet and I and a few others have an online discussion group where we read the best retrospective anthologies and discuss which stories we’d collect if we were editing our own anthology. We use a Google spreadsheet to track our favorite stories. We figure it will take us years to find the best stories published between 1939 and 1964. We’re using The Great SF Stories 1-26 (1939-1964) edited by Asimov/Greenberg/Silverberg, and the best of the year anthologies edited by Bleiler & Dikty, and Judith Merril as our guidebooks, supplemented with other retrospective anthologies.
Somewhere in the middle of collecting pulps and buying the best retrospective anthologies, would be to collect all the annual anthologies. I’ve listed below some of the most popular annual anthologies for the 20th century and added in a few retrospective anthologies to cover the years before 1939. Piet’s list is much more extensive , so there’s a good deal to collect if you want to be a completest.
The column for year(s) is meant for when the stories were first published. The tradition for the annual anthologies is to put the year the anthology was published in the title, but collect stories from the previous year. I’ve always hated that tradition.
Share this:

- Already have a WordPress.com account? Log in now.
- Subscribe Subscribed
- Copy shortlink
- Report this content
- View post in Reader
- Manage subscriptions
- Collapse this bar
- School Guide
- English Grammar Free Course
- English Grammar Tutorial
- Parts of Speech
- Figure of Speech
- Tenses Chart
- Essay Writing
- Email Writing
- NCERT English Solutions
- English Difference Between
- SSC CGL English Syllabus
- SBI PO English Syllabus
- SBI Clerk English Syllabus
- IBPS PO English Syllabus
- IBPS CLERK English Syllabus
- Essay on Science in English: Check 200, 300 & 500 Words Essay
- Essay on My House in English: Check 300, 500 & 800 Words Essay
- Essay on My Father in English: 300, 500 & 800 Words Essay
- My Aim in Life Essay For Students: 100, 200 & 500 Words Essay
- 500+Words Essay on My Hobby in English
- 500+ Words Essay on Importance of Education in English
- 500+ Words Essay on Newspaper in English For Students
- Essay on My Mother: 10 lines, 100 Words and 200 words essay
- Essay on My Family: Short, 10 Lines, 100 Words Essay
- 200+ Action Words in English: Know How to Use
- Essay on My Favourite Teacher (10 Lines, 100 Words, 200 Words)
- Grade 5 English Worksheet 2: Synonyms Worksheet
- Essay on Summer Vacation For Students in English: Samples Class 3 to 5
- 500+ Words Essay on Air Pollution
- 50+ Words That Start With R: Check their Meaning
- 1000 Most Common Words in the English Language
- 70+ New Words in English With Their Meaning
- Grade 5 English Worksheet 1: Reading Comprehension Worksheet
- CBSE Class 9 Science Notes 2023-2024
- CBSE Class 8 Science Notes 2023-24
Essay on Science in English: Check 200, 300 & 500 Words Essay
Science is the study of logic. It explains why the world is round, why stars twinkle, why light travels faster than sound, why hawks soar higher than crows, why sunflowers face the sun and other phenomena. Science answers every question logically rather than offering mystical interpretations. Students are very interested in science as a topic. This subject is indeed crucial for those hoping to pursue careers in science and related professions.
People who are knowledgeable in science are more self-assured and aware of their environment. Knowing the cause and origin of natural events, a person knowledgeable in science will not be afraid of them.
However, science also has a big impact on a country’s technological advancement and illiteracy.
Table of Content
English-language Long and Short Science Essay
Essay on science (200 words), essay on science (300 words), essay on science (400 words), essay on science (500 words), essay on science (600 words).
We have included a brief and lengthy English essay on science below for your knowledge and convenience. The writings have been thoughtfully crafted to impart to you the relevance and meaning of science. You will understand what science is, why it matters in daily life, and how it advances national progress after reading the writings. These science essays can be used for essay writing, debate, and other related activities at your institution or school.
Science entails a thorough examination of the behavior of the physical and natural world. Research, experimentation, and observation are used in the study.
The scientific disciplines are diverse. The social sciences, formal sciences, and natural sciences are some of them. Subcategories and sub-sub-categories have been created from these basic categories. The natural sciences include physics, chemistry, biology, earth science, and astronomy; the social sciences include history, geography, economics, political science, sociology, psychology, social studies, and anthropology; and the formal sciences include computer science, logic, statistics, decision theory, and mathematics.
The world has positively transformed because of science. Throughout history, science has produced several inventions that have improved human convenience. We cannot fathom our lives without several of these inventions since they have become essential parts of them.
Global scientists persist in their experiments and occasionally produce more advanced innovations, some of which spark global revolutions. Even if science is helpful, some people have abused knowledge, usually those in positions of authority, to drive an arms race and destroy the environment.
There is no common ground between the ideologies of science and religion. These seeming opposite viewpoints have historically led to a number of confrontations and still do.
Science is a way to learn about, comprehend, examine, and experiment with the physical and natural features of the world in order to apply it to the development of newer technologies that improve human convenience. In science, observation and experimentation are broad and not restricted to a specific concept or area of study.
Applications of Science
Science has given us almost everything we use on a daily basis. Everything, from laptops to washing machines, microwaves to cell phones, and refrigerators to cars, is the result of scientific experimentation. Here are some ways that science affects our daily lives:
Not only are refrigerators, grills, and microwaves examples of scientific inventions, but gas stoves, which are frequently used for food preparation, are as well.
Medical Interventions
Scientific advancements have made it feasible to treat a number of illnesses and conditions. Thus, science encourages healthy living and has helped people live longer.
Interaction
These days, mobile phones and internet connections are necessities in our life and were all made possible by scientific advancements. These innovations have lowered barriers to communication and widened global connections.
E nergy Source
The creation and application of numerous energy forms have been facilitated by the discovery of atomic energy. One of its greatest innovations is electricity, and everyone is aware of the effects it has on daily life.
Variety in Cuisine
There has also been an increase in food diversity. These days, a wide variety of fruits and vegetables are available year-round. It’s not necessary to wait for a given season to enjoy a certain meal. This modification is the result of scientific experimentation.
So, science is a part of our daily existence. Without scientific advancements, our lives would have been considerably more challenging and varied. Nonetheless, we cannot ignore the fact that a great deal of scientific innovation has contributed to environmental deterioration and a host of health issues for humankind.
There are essentially three main disciplines of science. The Natural Sciences, Social Sciences, and Formal Sciences are some of them. To examine different aspects, these branches are further divided into subcategories. This is a thorough examination of these groups and their subgroups.
Scientific Subdisciplines
Natural Science
This is the study of natural phenomena, as the name implies. It investigates how the cosmos and the world function. Physical science and life science are subcategories of natural science.
a) Science of Physics
The subcategories of physical science comprise the following:
- Physics is the study of matter’s and energy’s properties.
- Chemistry is the study of the materials that make up matter.
- The study of space and celestial bodies is called astronomy.
- Ecology is the study of how living things interact with their natural environments and with one another.
- Geology: It studies the composition and physical makeup of Earth.
- Earth science is the study of the atmosphere and the physical makeup of the planet.
- The study of the physical and biological components and phenomena of the ocean is known as oceanography.
- Meteorology: It studies the atmospheric processes.
The subcategories of life science include the following:
- The study of living things is called biology.
- The study of plants is known as botany.
- The study of animals is known as zoology.
c) Social Science
This includes examining social patterns and behavioral patterns in people. It is broken down into more than one subcategory. Among them are:
- History: The examination of past occurrences
- Political science is the study of political processes and governmental structures.
- Geographic: Study of the atmospheric and physical characteristics of Earth.
- Human society is studied in social studies.
- Sociology: The study of how societies form and operate.
Academic Sciences
It is the area of study that examines formal systems like logic and mathematics. It encompasses the subsequent subcategories:
- Numbers are studied in mathematics.
- Reasoning is the subject of logic.
- Statistics: It is the study of numerical data analysis.
- Mathematical analysis of decision-making in relation to profit and loss is known as decision theory.
- The study of abstract organization is known as systems theory.
- Computer science is the study of engineering and experimentation as a foundation for computer design and use.
Scientists from several fields have been doing in-depth research and testing numerous facets of the subject matter in order to generate novel ideas, innovations, and breakthroughs. Although these discoveries and technologies have made life easier for us, they have also permanently harmed both the environment and living things.
Introduction
Science is the study of various physical and natural phenomena’ structures and behaviors. Before drawing any conclusions, scientists investigate these factors, make extensive observations, and conduct experiments. In the past, science has produced a number of inventions and discoveries that have been beneficial to humanity.
I deas in Religion and Science
In science, new ideas and technologies are developed through a methodical and rational process; in religion, however, beliefs and faith are the only factors considered. In science, conclusions are reached by careful observation, analysis, and experimentation; in religion, however, conclusions are rarely reached through reason. As a result, they have very different perspectives on things.
Science and Religion at Odds
Because science and religion hold different opinions on many issues, they are frequently perceived as being at odds. Unfortunately, these disputes occasionally cause social unrest and innocent people to suffer. These are a few of the most significant disputes that have happened.
The World’s Creation
The world was formed in six days, according to many conservative Christians, sometime between 4004 and 8000 BCE. However, cosmologists assert that the Earth originated about 4.5 billion years ago and that the cosmos may be as old as 13.7 billion years.
The Earth as the Universe’s Center
Among the most well-known clashes is this one. Earth was considered to be the center of the universe by the Roman Catholic Church. They say that it is surrounded by the Sun, Moon, stars, and other planets. Famous Italian mathematician and astronomer Galileo Galilei’s discovery of the heliocentric system—in which the Sun is at the center of the solar system and the Earth and other planets orbit it—led to the conflict.
Eclipses of the Sun and Moon
Iraq was the scene of one of the first wars. The locals were informed by the priests that the moon eclipse was caused by the gods’ restlessness. These were seen as foreboding and intended to overthrow the kings. When the local astronomers proposed a scientific explanation for the eclipse, a disagreement arose.
There are still many myths and superstitions concerning solar and lunar eclipses around the world, despite astronomers providing a compelling and rational explanation for their occurrence.
In addition to these, there are a number of other fields in which religious supporters and scientists hold divergent opinions. While scientists, astronomers, and biologists have evidence to support their claims, the majority of people adhere closely to religious beliefs.
Not only do religious activists frequently oppose scientific methods and ideas, but many other facets of society have also taken issue with science since its discoveries are leading to a host of social, political, environmental, and health problems. Nuclear weapons are one example of a scientific invention that threatens humanity. In addition, the processes involved in preparation and the utilization of the majority of scientifically created equipment contribute to pollution, making life more difficult for all.
In the previous few decades, a number of scientific advancements and discoveries have greatly eased people’s lives. The previous ten years were not an anomaly. A good number of important scientific discoveries were acknowledged. The top ten most amazing recent scientific inventions are shown below.
New Developments and Findings in Science
Amputee Gains Control of Biomechanical Hand via Mental After a tragic accident took away his forearm, Pierpaolo Petruzziello, an Italian, used his mind to control a biomechanical hand attached to his arm. The hand used wires and electrodes to connect to the nerves in his arm. He became the first to become skilled at doing motions like gripping objects, wriggling his fingers, and moving.
The Global Positioning System
In 2005, the Global Positioning System, or GPS as it is more often known, went into commercial use. It was incorporated into mobile devices and worked wonders for tourists all over the world. Traveling to more recent locations and needing instructions couldn’t be simpler.
The Self-Driving Car Toyota debuted Prius shortly after Google launched its own self-driving car experiment in 2008. The accelerator, steering wheel, and brake pedals are absent from this vehicle. It runs without the need for user input because it is driven by an electric motor. To guarantee that the driverless experience is seamless and secure, it is integrated with specialized software, a collection of sensors, and precise digital maps.
Android, widely regarded as one of the most significant innovations of the decade, revolutionized the market by flooding it with devices running Java and Symbian earlier on. These days, Android is the operating system used by the majority of smartphones. Millions of applications are supported by it.
c) Computer Vision
A number of sub-domains fall under the umbrella of computer vision, including learning, video tracking, object recognition, object pose estimation, event detection, indexing, picture restoration, and scene reconstruction. In order to produce symbolic information, the field includes methods for processing, analyzing, obtaining, and understanding images in high-dimensional data from the real world.
d) Touch Screen Technology
It appears that touch screen technology has taken over the planet. The popularity of touch screen gadgets can be attributed to their ease of use. These gadgets are becoming quite popular everywhere.
e) Method of 3D Printing
The 3D printer is capable of producing a wide range of items, such as lamps, cookware, accessories, and much more. Alternatively referred to as additive manufacturing, this process uses digital model data from electronic data sources like Additive Manufacturing Files (AMF) to construct three-dimensional items of any shape.
Git Hub is an online hosting service and version control repository that was founded in 2008. It provides features including bug tracking, task management, feature requests, and the sharing of codes, apps, and other materials. The GitHub platform was first developed in 2007, and the website went live in 2008.
f) Smart Timepieces
The market for smart watches has been around for a while. The more recent models, like the one introduced by Apple, have garnered enormous popularity and come with a number of extra capabilities. Nearly all of the functionality found on smartphones are included in these watches, which are also more convenient to wear and use.
g) Websites for Crowdfunding
The emergence of crowdsourcing websites like Indiegogo, Kickstarter, and GoFundMe has been a blessing for innovators. Inventors, artists, and other creative people can share their ideas and gain the funding they need to put them into action by using these websites.
Global scientists constantly observe and experiment to develop new scientific discoveries that improve people’s lives. Not only do they consistently create new technologies, but they also adapt the ones that already exist whenever there is an opportunity. Even while these innovations have made life easier for humans, you are all aware of the numerous environmental, social, and political risks they have brought about.
500+ Words Essay on Mother Teresa in English For Students 500+ Words Essay on Swami Vivekananda in English for Students Rabindranath Tagore Essay in English For Students APJ Abdul Kalam Essay For Students: Check 500 Words Essay
Essay on Science- FAQs
Who is father of science.
Galileo is the father of science.
Why is it called science?
The word “scientia” has Latin origins and originally meant “knowledge,” “an expertness,” or “experience.”
What is science for students?
Science is the study of the world by observation, recording, listening, and watching. Science is the application of intellectual inquiry into the nature of the world and its behavior. Think like a scientist, anyone can.
What is science’s primary goal or objective?
Science’s primary goal is to provide an explanation for the facts. Moreover, science does not prohibit the explanation of facts in an arbitrary manner. Additionally, science organizes the data and develops theories to explain the data.
Describe what a scientific fact is.
Repeatable, meticulous observations or measurements made through experiments or other methods are referred to as scientific facts. Furthermore, empirical evidence is another name for a scientific fact. Most importantly, the development of scientific hypotheses depends on scientific facts.
Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.
- English Blogs
- School English
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?

10 of the Best Science-Fiction Short Stories Everyone Should Read
By Dr Oliver Tearle (Loughborough University)
What are the best places to begin exploring the wonderful world of science fiction? Some of the classic novels of the genre, from Frank Herbert’s Dune to Asimov’s Foundation series (which eventually stretched to seven volumes), might appear daunting because of their sheer size and scope.
Below, we introduce ten short science fiction stories which offer the perfect way in to the imaginative wonders of science fiction.
1. H. G. Wells, The Time Machine .
Wells stands at the beginning of science fiction in the English language. Although he wasn’t the very first English science fiction author, his contemporaries, such as George Griffith, have long since been forgotten.
The Time Machine is technically more of a novella than a short story, but it heads Wells’s big, fat complete short stories collection, so we reckon that qualifies it for inclusion here. Published in 1895, this tale centres on a Time Traveller who invents a machine that enables him to travel far into the future.
He ends up in the world of AD 802,701, in a London that has been transformed into a vast garden, and where humankind has evolved into two distinct subspecies: the above-ground Eloi and the sinister subterranean Morlocks …
We have discussed this remarkable novella in more detail here .
2. E. M. Forster, ‘ The Machine Stops ’.
Is this the most prophetic story of the twentieth century? Published in 1909 and showing Forster’s disdain for technological advancement and the way it would make our lives poorer, this story attracted plenty of new readers in 2020 when so many people’s lives ‘went virtual’.
It’s all here: Zoom, self-isolation, and even the fear of other human beings. Controlling everything is ‘the Machine’, a mysterious technological entity worshipped as a god by many of the inhabitants of this future Earth.
You can read our analysis of this prescient short story here.
3. Shirley Jackson, ‘ The Lottery ’.
This 1948 story is among the most acclaimed short stories of the twentieth century, and earns its place on this list because of the speculative nature of its scenario (recalling, perhaps, Borges’ ‘The Lottery in Babylon’) and the ambiguous setting.
The story is set in a fictional town. Every year an event known as ‘the lottery’ takes place. This lottery involves a member of the community being selected at random – but the fate of the person selected is truly chilling. Jackson’s story, like Le Guin’s (see below) is about the concept of the scapegoat and the dynamic between the individual and the collective in society.
The story initially attracted much negative reaction from readers of the New Yorker (where it was first published), with many readers cancelling their subscriptions, horrified and disgusted by the story. It is now regarded as a classic.
4. Isaac Asimov, ‘ Nightfall ’.
This 1941 short story, written while Asimov was still only in his early twenties, is widely regarded as one of the greatest science-fiction short stories of all time. Indeed, in 1968 the Science Fiction Writers of America voted it the best science fiction short story written before 1965.
The story is about a planet which doesn’t experience nightfall, except once in every 2,049 years, because it is normally lit by six suns. Since every human being alive will find nightfall a terrifying experience when that rare eclipse occurs, scientists worry about their chaos that will ensue when night falls …
5. Ray Bradbury, ‘ A Sound of Thunder ’.
This is another classic time travel story, this time involving a journey back into the distant past rather than the far-flung future. The story was first published in Collier’s magazine in 1952 and then collected a year later in Bradbury’s short-story collection, The Golden Apples of the Sun .
The story begins in the future, sometime around 2055. A time-travel safari company in the United States, Time Safari Inc., allows animal-hunters to travel back in time in a Time Machine and kill a long-extinct animal, such as a dinosaur. A man named Eckels turns up ready to undertake his safari … with disastrous results.
You can read more about this story in a separate post .
6. Arthur C. Clarke, ‘ The Nine Billion Names for God ’.
This 1953 story is another which, like Asimov’s ‘Nightfall’, is often given the title of ‘one of the best short stories written before the Nebula Awards were created in the mid-1960s’.
A group of Buddhist monks think that, once every single name by which ‘God’ is known has been listed, the world – indeed, the whole universe – will end. They predict there are 9 billion different names in total, which new technology will allow them to itemise. Two men are hired to be the computer programmers for the monks’ task. What happens when all nine billion names are printed out? Well, that would be telling …
7. Ursula K. Le Guin, ‘ The Ones Who Walk Away from Omelas ’.
This story, like Jackson’s ‘The Lottery’, is perhaps more correctly labelled ‘speculative fiction’: it’s set in the fictional town of Omelas, in which everyone is happy and prosperous. But such happiness and prosperity has come at a terrible cost, for the success and contentment of everyone’s life is dependent on the suffering of a small child which is kept in miserable conditions in a room in the town.
Le Guin raises some deeply unsettling but important ethical questions in this classic story, which is told in the beautiful, eloquent prose for which Le Guin’s work is rightly famed.
We tease out some of the elements of this story in a separate post .
8. Philip K. Dick, ‘ We Can Remember It For You Wholesale ’.
Dick (1928-82) has attracted a devoted cult following since his untimely death, and his work fuses Kafkan paranoia and fear over police states and totalitarianism with an interest in psychedelia, drugs, altered consciousness, and related paraphernalia of the 1960s.
In this story, which formed the basis of the 1990 film Total Recall , a man named Douglas Quail learns of a special ‘holiday’ to Mars that can be implanted into the brain so one can experience a trip to another planet without having to go anywhere. We discuss the story in more detail in a separate article .
9. J. G. Ballard, ‘ Billennium ’.
This 1962 story from one of the most original authors of the twentieth century is a dystopian tale set in a vastly overpopulated future, in which the world’s population is around 20 billion. As a result, people live in extraordinarily cramped rooms in vast cities. The story focuses on two friends, Ward and Rossiter, who find new living quarters and then discover a whole new room behind one of their cupboards.
10. William Gibson, ‘Burning Chrome’.
Often credited with coining the term ‘cyberspace’ (a word he certainly helped to popularise), William Gibson (born 1948) is perhaps the greatest living science-fiction author, and one of the most prophetic. His early novels of the 1980s helped to establish ‘cyberpunk’ as a new branch of science fiction, and no writer has engaged so imaginatively and prophetically with our new world of the internet and digital communication as Gibson.
Like many science fiction writers, Gibson started out writing short fiction such as ‘Johnny Mnemonic’ and ‘Burning Chrome’. The latter story prefigures Gibson’s debut novel, Neuromancer , from two years later, in focusing on a computer hacker: a startlingly new character type in the early 1980s.
This story is not available online, but is the title story of the William Gibson collection Burning Chrome .
Discover more from Interesting Literature
Subscribe to get the latest posts to your email.
Type your email…
1 thought on “10 of the Best Science-Fiction Short Stories Everyone Should Read”
The last line of Clarke’s “Nine Billion Names for God” sticks with you like the last line of some poems.
Comments are closed.
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Continue reading
MIT Technology Review
- Newsletters
Google helped make an exquisitely detailed map of a tiny piece of the human brain
A small brain sample was sliced into 5,000 pieces, and machine learning helped stitch it back together.
- Cassandra Willyard archive page
A team led by scientists from Harvard and Google has created a 3D, nanoscale-resolution map of a single cubic millimeter of the human brain. Although the map covers just a fraction of the organ—a whole brain is a million times larger—that piece contains roughly 57,000 cells, about 230 millimeters of blood vessels, and nearly 150 million synapses. It is currently the highest-resolution picture of the human brain ever created.
To make a map this finely detailed, the team had to cut the tissue sample into 5,000 slices and scan them with a high-speed electron microscope. Then they used a machine-learning model to help electronically stitch the slices back together and label the features. The raw data set alone took up 1.4 petabytes. “It’s probably the most computer-intensive work in all of neuroscience,” says Michael Hawrylycz, a computational neuroscientist at the Allen Institute for Brain Science, who was not involved in the research. “There is a Herculean amount of work involved.”
Many other brain atlases exist, but most provide much lower-resolution data. At the nanoscale, researchers can trace the brain’s wiring one neuron at a time to the synapses, the places where they connect. “To really understand how the human brain works, how it processes information, how it stores memories, we will ultimately need a map that’s at that resolution,” says Viren Jain, a senior research scientist at Google and coauthor on the paper, published in Science on May 9 . The data set itself and a preprint version of this paper were released in 2021 .
Brain atlases come in many forms. Some reveal how the cells are organized. Others cover gene expression. This one focuses on connections between cells, a field called “connectomics.” The outermost layer of the brain contains roughly 16 billion neurons that link up with each other to form trillions of connections. A single neuron might receive information from hundreds or even thousands of other neurons and send information to a similar number. That makes tracing these connections an exceedingly complex task, even in just a small piece of the brain..
To create this map, the team faced a number of hurdles. The first problem was finding a sample of brain tissue. The brain deteriorates quickly after death, so cadaver tissue doesn’t work. Instead, the team used a piece of tissue removed from a woman with epilepsy during brain surgery that was meant to help control her seizures.
Once the researchers had the sample, they had to carefully preserve it in resin so that it could be cut into slices, each about a thousandth the thickness of a human hair. Then they imaged the sections using a high-speed electron microscope designed specifically for this project.
Next came the computational challenge. “You have all of these wires traversing everywhere in three dimensions, making all kinds of different connections,” Jain says. The team at Google used a machine-learning model to stitch the slices back together, align each one with the next, color-code the wiring, and find the connections. This is harder than it might seem. “If you make a single mistake, then all of the connections attached to that wire are now incorrect,” Jain says.
“The ability to get this deep a reconstruction of any human brain sample is an important advance,” says Seth Ament, a neuroscientist at the University of Maryland. The map is “the closest to the ground truth that we can get right now.” But he also cautions that it’s a single brain specimen taken from a single individual.
The map, which is freely available at a web platform called Neuroglancer , is meant to be a resource other researchers can use to make their own discoveries. “Now anybody who’s interested in studying the human cortex in this level of detail can go into the data themselves. They can proofread certain structures to make sure everything is correct, and then publish their own findings,” Jain says. (The preprint has already been cited at least 136 times .)
The team has already identified some surprises. For example, some of the long tendrils that carry signals from one neuron to the next formed “whorls,” spots where they twirled around themselves. Axons typically form a single synapse to transmit information to the next cell. The team identified single axons that formed repeated connections—in some cases, 50 separate synapses. Why that might be isn’t yet clear, but the strong bonds could help facilitate very quick or strong reactions to certain stimuli, Jain says. “It’s a very simple finding about the organization of the human cortex,” he says. But “we didn’t know this before because we didn’t have maps at this resolution.”
The data set was full of surprises, says Jeff Lichtman, a neuroscientist at Harvard University who helped lead the research. “There were just so many things in it that were incompatible with what you would read in a textbook.” The researchers may not have explanations for what they’re seeing, but they have plenty of new questions: “That’s the way science moves forward.”
Biotechnology and health
How scientists traced a mysterious covid case back to six toilets.
When wastewater surveillance turns into a hunt for a single infected individual, the ethics get tricky.
An AI-driven “factory of drugs” claims to have hit a big milestone
Insilico is part of a wave of companies betting on AI as the "next amazing revolution" in biology
- Antonio Regalado archive page
The quest to legitimize longevity medicine
Longevity clinics offer a mix of services that largely cater to the wealthy. Now there’s a push to establish their work as a credible medical field.
- Jessica Hamzelou archive page
There is a new most expensive drug in the world. Price tag: $4.25 million
But will the latest gene therapy suffer the curse of the costliest drug?
Stay connected
Get the latest updates from mit technology review.
Discover special offers, top stories, upcoming events, and more.
Thank you for submitting your email!
It looks like something went wrong.
We’re having trouble saving your preferences. Try refreshing this page and updating them one more time. If you continue to get this message, reach out to us at [email protected] with a list of newsletters you’d like to receive.
Social-Science Genomics: Progress, Challenges, and Future Directions
Rapid progress has been made in identifying links between human genetic variation and social and behavioral phenotypes. Applications in mainstream economics are beginning to emerge. This review aims to provide the background needed to bring the interested economist to the frontier of social-science genomics. Our review is structured around a theoretical framework that nests many of the key methods, concepts and tools found in the literature. We clarify key assumptions and appropriate interpretations. After reviewing several significant applications, we conclude by outlining future advances in genetics that will expand the scope of potential applications, and we discuss the ethical and communication challenges that arise in this area of research.
For helpful comments and suggestions, we thank Peter M. Visscher and the University of Queensland Statistical Genomics Lab Meeting. For excellent research assistance, we are grateful to Matthew Howell and Moeen Nehzati. For financial support, we thank the NIA/NIH (grants R24-AG065184, R01-AG042568, R00-AG062787, and R01-AG081518) and Open Philanthropy. The views expressed herein are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of the National Bureau of Economic Research.
MARC RIS BibTeΧ
Download Citation Data
Mentioned in the News
More from nber.
In addition to working papers , the NBER disseminates affiliates’ latest findings through a range of free periodicals — the NBER Reporter , the NBER Digest , the Bulletin on Retirement and Disability , the Bulletin on Health , and the Bulletin on Entrepreneurship — as well as online conference reports , video lectures , and interviews .


25,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today
Meet top uk universities from the comfort of your home, here’s your new year gift, one app for all your, study abroad needs, start your journey, track your progress, grow with the community and so much more.

Verification Code
An OTP has been sent to your registered mobile no. Please verify

Thanks for your comment !
Our team will review it before it's shown to our readers.

- School Education /
Essay on Science: Sample for Students in 100,200 Words

- Updated on
- Oct 28, 2023

Science, the relentless pursuit of knowledge and understanding, has ignited the flames of human progress for centuries. It’s a beacon guiding us through the uncharted realms of the universe, unlocking secrets that shape our world. In this blog, we embark on an exhilarating journey through the wonders of science. We’ll explore the essence of science and its profound impact on our lives. With this we will also provide you with sample essay on science in 100 and 200 words.
Must Read: Essay On Internet
What Is Science?
Science is a systematic pursuit of knowledge about the natural world through observation, experimentation, and analysis. It aims to understand the underlying principles governing the universe, from the smallest particles to the vast cosmos. Science plays a crucial role in advancing technology, improving our understanding of life and the environment, and driving innovation for a better future.
Branches Of Science
The major branches of science can be categorized into the following:
- Physical Science: This includes physics and chemistry, which study the fundamental properties of matter and energy.
- Biological Science : Also known as life sciences, it encompasses biology, genetics, and ecology, focusing on living organisms and their interactions.
- Earth Science: Geology, meteorology, and oceanography fall under this category, investigating the Earth’s processes, climate, and natural resources.
- Astronomy : The study of celestial objects, space, and the universe, including astrophysics and cosmology.
- Environmental Science : Concentrating on environmental issues, it combines aspects of biology, chemistry, and Earth science to address concerns like climate change and conservation.
- Social Sciences : This diverse field covers anthropology, psychology, sociology, and economics, examining human behavior, society, and culture.
- Computer Science : Focused on algorithms, data structures, and computing technology, it drives advancements in information technology.
- Mathematics : A foundational discipline, it underpins all sciences, providing the language and tools for scientific analysis and modeling.
Wonders Of Science
Science has numerous applications that profoundly impact our lives and society: Major applications of science are stated below:
- Medicine: Scientific research leads to the development of vaccines, medicines, and medical technologies, improving healthcare and saving lives.
- Technology: Science drives technological innovations, from smartphones to space exploration.
- Energy: Advances in physics and chemistry enable the development of renewable energy sources, reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
- Agriculture: Biology and genetics improve crop yields, while chemistry produces fertilizers and pesticides.
- Environmental Conservation : Scientific understanding informs efforts to protect ecosystems and combat climate change.
- Transportation : Physics and engineering create efficient and sustainable transportation systems.
- Communication : Physics and computer science underpin global communication networks.
- Space Exploration : Astronomy and physics facilitate space missions, expanding our understanding of the cosmos.
Must Read: Essay On Scientific Discoveries
Sample Essay On Science in 100 words
Science, the bedrock of human progress, unveils the mysteries of our universe through empirical investigation and reason. Its profound impact permeates every facet of modern life. In medicine, it saves countless lives with breakthroughs in treatments and vaccines. Technology, a child of science, empowers communication and innovation. Agriculture evolves with scientific methods, ensuring food security. Environmental science guides conservation efforts, preserving our planet. Space exploration fuels dreams of interstellar travel.
Yet, science requires responsibility, as unchecked advancement can harm nature and society. Ethical dilemmas arise, necessitating careful consideration. Science, a double-edged sword, holds the potential for both salvation and destruction, making it imperative to harness its power wisely for the betterment of humanity.
Sample Essay On Science in 250 words
Science, often regarded as humanity’s greatest intellectual endeavor, plays an indispensable role in shaping our world and advancing our civilization.
At its core, science is a methodical pursuit of knowledge about the natural world. Through systematic observation, experimentation, and analysis, it seeks to uncover the underlying principles that govern our universe. This process has yielded profound insights into the workings of the cosmos, from the subatomic realm to the vastness of space.
One of the most remarkable contributions of science is to the field of medicine. Through relentless research and experimentation, scientists have discovered vaccines, antibiotics, and groundbreaking treatments for diseases that once claimed countless lives.
Furthermore, science has driven technological advancements that have reshaped society. The rapid progress in computing, for instance, has revolutionized communication, industry, and research. From the ubiquitous smartphones in our pockets to the complex algorithms that power our digital lives, science, and technology are inseparable partners in progress.
Environmental conservation is another critical arena where science is a guiding light. Climate change, a global challenge, is addressed through rigorous scientific study and the development of sustainable practices. Science empowers us to understand the impact of human activities on our planet and to make informed decisions to protect it.
In conclusion, science is not just a field of study; it is a driving force behind human progress. As we continue to explore the frontiers of knowledge, science will remain the beacon guiding us toward a brighter future.
Science is a boon due to innovations, medical advancements, and a deeper understanding of nature, improving human lives exponentially.
Galileo Galilei is known as the Father of Science.
Science can’t address questions about personal beliefs, emotions, ethics, or matters of subjective experience beyond empirical observation and measurement.
We hope this blog gave you an idea about how to write and present an essay on science that puts forth your opinions. The skill of writing an essay comes in handy when appearing for standardized language tests. Thinking of taking one soon? Leverage Edu provides the best online test prep for the same via Leverage Live . Register today to know more!
Amisha Khushara
Hey there! I'm a content writer who turns complex ideas into clear, engaging stories. Think of me as your translator, taking expert knowledge and making it interesting and relatable for everyone.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Contact no. *

Connect With Us

25,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today.

Resend OTP in

Need help with?
Study abroad.
UK, Canada, US & More
IELTS, GRE, GMAT & More
Scholarship, Loans & Forex
Country Preference
New Zealand
Which English test are you planning to take?
Which academic test are you planning to take.
Not Sure yet
When are you planning to take the exam?
Already booked my exam slot
Within 2 Months
Want to learn about the test
Which Degree do you wish to pursue?
When do you want to start studying abroad.
January 2024
September 2024
What is your budget to study abroad?

How would you describe this article ?
Please rate this article
We would like to hear more.
Have something on your mind?

Make your study abroad dream a reality in January 2022 with
India's Biggest Virtual University Fair

Essex Direct Admission Day
Why attend .

Don't Miss Out
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Letter of Recommendation
What I’ve Learned From My Students’ College Essays
The genre is often maligned for being formulaic and melodramatic, but it’s more important than you think.

By Nell Freudenberger
Most high school seniors approach the college essay with dread. Either their upbringing hasn’t supplied them with several hundred words of adversity, or worse, they’re afraid that packaging the genuine trauma they’ve experienced is the only way to secure their future. The college counselor at the Brooklyn high school where I’m a writing tutor advises against trauma porn. “Keep it brief , ” she says, “and show how you rose above it.”
I started volunteering in New York City schools in my 20s, before I had kids of my own. At the time, I liked hanging out with teenagers, whom I sometimes had more interesting conversations with than I did my peers. Often I worked with students who spoke English as a second language or who used slang in their writing, and at first I was hung up on grammar. Should I correct any deviation from “standard English” to appeal to some Wizard of Oz behind the curtains of a college admissions office? Or should I encourage students to write the way they speak, in pursuit of an authentic voice, that most elusive of literary qualities?
In fact, I was missing the point. One of many lessons the students have taught me is to let the story dictate the voice of the essay. A few years ago, I worked with a boy who claimed to have nothing to write about. His life had been ordinary, he said; nothing had happened to him. I asked if he wanted to try writing about a family member, his favorite school subject, a summer job? He glanced at his phone, his posture and expression suggesting that he’d rather be anywhere but in front of a computer with me. “Hobbies?” I suggested, without much hope. He gave me a shy glance. “I like to box,” he said.
I’ve had this experience with reluctant writers again and again — when a topic clicks with a student, an essay can unfurl spontaneously. Of course the primary goal of a college essay is to help its author get an education that leads to a career. Changes in testing policies and financial aid have made applying to college more confusing than ever, but essays have remained basically the same. I would argue that they’re much more than an onerous task or rote exercise, and that unlike standardized tests they are infinitely variable and sometimes beautiful. College essays also provide an opportunity to learn precision, clarity and the process of working toward the truth through multiple revisions.
When a topic clicks with a student, an essay can unfurl spontaneously.
Even if writing doesn’t end up being fundamental to their future professions, students learn to choose language carefully and to be suspicious of the first words that come to mind. Especially now, as college students shoulder so much of the country’s ethical responsibility for war with their protest movement, essay writing teaches prospective students an increasingly urgent lesson: that choosing their own words over ready-made phrases is the only reliable way to ensure they’re thinking for themselves.
Teenagers are ideal writers for several reasons. They’re usually free of preconceptions about writing, and they tend not to use self-consciously ‘‘literary’’ language. They’re allergic to hypocrisy and are generally unfiltered: They overshare, ask personal questions and call you out for microaggressions as well as less egregious (but still mortifying) verbal errors, such as referring to weed as ‘‘pot.’’ Most important, they have yet to put down their best stories in a finished form.
I can imagine an essay taking a risk and distinguishing itself formally — a poem or a one-act play — but most kids use a more straightforward model: a hook followed by a narrative built around “small moments” that lead to a concluding lesson or aspiration for the future. I never get tired of working with students on these essays because each one is different, and the short, rigid form sometimes makes an emotional story even more powerful. Before I read Javier Zamora’s wrenching “Solito,” I worked with a student who had been transported by a coyote into the U.S. and was reunited with his mother in the parking lot of a big-box store. I don’t remember whether this essay focused on specific skills or coping mechanisms that he gained from his ordeal. I remember only the bliss of the parent-and-child reunion in that uninspiring setting. If I were making a case to an admissions officer, I would suggest that simply being able to convey that experience demonstrates the kind of resilience that any college should admire.
The essays that have stayed with me over the years don’t follow a pattern. There are some narratives on very predictable topics — living up to the expectations of immigrant parents, or suffering from depression in 2020 — that are moving because of the attention with which the student describes the experience. One girl determined to become an engineer while watching her father build furniture from scraps after work; a boy, grieving for his mother during lockdown, began taking pictures of the sky.
If, as Lorrie Moore said, “a short story is a love affair; a novel is a marriage,” what is a college essay? Every once in a while I sit down next to a student and start reading, and I have to suppress my excitement, because there on the Google Doc in front of me is a real writer’s voice. One of the first students I ever worked with wrote about falling in love with another girl in dance class, the absolute magic of watching her move and the terror in the conflict between her feelings and the instruction of her religious middle school. She made me think that college essays are less like love than limerence: one-sided, obsessive, idiosyncratic but profound, the first draft of the most personal story their writers will ever tell.
Nell Freudenberger’s novel “The Limits” was published by Knopf last month. She volunteers through the PEN America Writers in the Schools program.

Growth Mindset
What is manifestation science-based ways to manifest, here's what the research says about manifestation..
Updated December 3, 2023 | Reviewed by Jessica Schrader

What is manifestation?
The word " manifestation " means to turn an idea into a reality. Usually, we want to manifest things that improve our happiness and well-being (take this well-being quiz to check your current level of well-being). People generally talk about manifestation as the process of using thoughts, feelings, and beliefs to bring something into reality, but given the science behind manifestation, it seems important to also include actions as a key part of the manifestation process.
What does manifestation really mean?
Manifestation has become popular thanks to books like The Secret and The Law of Attraction . Unfortunately, most psychological scientists will tell you that these books are based on pseudoscience—they claim to be scientific and factual, but they're not actually based on scientific evidence.
So as a psychological scientist I can't, in good conscience , recommend these books. However, I feel like many psychologists throw out the baby with the bathwater when it comes to the idea of "manifestation." They'll often say it's junk science. But I say: Of course we can manifest positive things in our lives—if we couldn't then what would be the point of therapy , wellness interventions, or any of the tools we use to help people?
So what does the science actually say about manifestation ? How can we take a goal or idea we have in our heads and make it real?
What is the science behind manifestation?
There actually is science behind the idea of manifestation—that is, turning an idea into a real thing. Here are some areas of research and how they lend support to manifestation:
A growth mindset can help you manifest your dreams and reach your goals
Research by Dr. Carol Dweck clearly shows that believing you can do something makes it more likely that you'll successfully do it. That means that our beliefs about our ability to learn, grow, and succeed—our growth mindset —can indeed affect whether we effectively manifest what we desire.
Importantly, this research suggests that if we truly believe we can achieve something, we are willing to do the hard work to achieve it. This is in contrast to law-of-attraction style manifestation which suggests that belief alone is enough to bring about manifestation. Ultimately, the science suggests that our beliefs bring about behaviors (and responses from others) that lead to the outcomes we desire.
Self-fulfilling prophecies may explain manifestation
Research shows that our expectations, positive or negative, tend to be confirmed. This is what is known as a self-fulfilling prophecy. So if we expect to bring our idea to life or reach our goal, we're more likely to.
For example, if you don't think you can succeed in some goal, let's say getting your dream job, you'll set in motion events that will actually make it more likely that you won't get your dream job. Maybe you'll be cold or grumpy during a job interview. Maybe you'll engage in negative self-talk with someone who could help you. Or maybe you'll just feel angry and not spend the necessary time required to reach your goal. Your beliefs set in motion circumstances that affect your ability to manifest an outcome.
Negativity bias may explain perceptions about manifestation
Research shows that if we're already feeling bad, we're more likely to interpret neutral circumstances in a negative way. It may be that someone with a more positive attitude just pays more attention to the ways in which they have successfully manifested parts of their dreams. Another person with a more negative outlook may experience the exact same things and only see where they failed to manifest what they desired. That's how bias may affect manifestation .
Upward spirals of positive emotion may explain manifestation success
Dr. Barbara Fredrickson's research has also shown that positive emotions enable us to think more creatively. Similarly, Dr. Sonja Lyubomirsky has shown that happiness leads to success and not the other way around. People who are generally happy and positive attract more opportunities, have better relationships, and seem to be able to manifest what they set their minds to more easily.
It makes sense when you think about it, right? We prefer to be around positive, optimistic people. And being around people with a negative attitude? It's off-putting and doesn't lead us to want to help these people.
How do we use science to manifest what we want?
1. Get clear on what you want to manifest

What do you actually want? Spend some time focusing to get clarity on your manifestation goal. Mindful meditation can be a useful tool for this—it quiets the mind and helps increase self-awareness . Or, you could talk to a friend. Sometimes just talking can help you gain the clarity you need to manifest something.
2. Manifest what matters to you
When deciding what to manifest, ask yourself a few reflection questions:
- Will this make me happy and fulfilled?
- Does it feel right for me? (Or is there something or someone influencing me?)
- Will this do any harm to myself or others?
By asking yourself these questions you can choose the right things to manifest—things that you will be more likely to believe in, things that you have positive expectations about, and things that make you feel more positive. As a result, you'll be more likely to manifest them.
3. Visualize your manifestation to generate positive emotions
Visualizing what you desire can help you feel positive emotions related to it more strongly. And those emotions can help you believe in yourself more. Just close your eyes, take a few deep breaths, and imagine a scene from your future life as you desire it. Here's a future visualization exercise if you need more help.
Created with content from The Berkeley Well-Being Institute.

Tchiki Davis, Ph.D. , is a consultant, writer, and expert on well-being technology.
- Find a Therapist
- Find a Treatment Center
- Find a Psychiatrist
- Find a Support Group
- Find Online Therapy
- United States
- Brooklyn, NY
- Chicago, IL
- Houston, TX
- Los Angeles, CA
- New York, NY
- Portland, OR
- San Diego, CA
- San Francisco, CA
- Seattle, WA
- Washington, DC
- Asperger's
- Bipolar Disorder
- Chronic Pain
- Eating Disorders
- Passive Aggression
- Personality
- Goal Setting
- Positive Psychology
- Stopping Smoking
- Low Sexual Desire
- Relationships
- Child Development
- Therapy Center NEW
- Diagnosis Dictionary
- Types of Therapy

Understanding what emotional intelligence looks like and the steps needed to improve it could light a path to a more emotionally adept world.
- Emotional Intelligence
- Gaslighting
- Affective Forecasting
- Neuroscience
Jump to navigation
Feminisms in the 21st-Century Science Fiction Novel; PAMLA (Nov. 7-10, 2024)
The 121st annual conference of the Pacific Ancient and Modern Language Association (PAMLA) will be held from Thursday, November 7, to Sunday, November 10, 2024, at the Margaritaville Resort, Palm Springs, California.
Feminisms in the 21st-Century Science Fiction Novel:
Much scholarship has been produced on the foundational works of science fiction and speculative fiction that address feminist themes, such as those by Margaret Cavendish, Rokeya Sakhawat Hossain, Ursula K. LeGuin, James Tiptree, Jr., Joanna Russ, Marge Piercy, Margaret Atwood, Octavia Butler, et al., and these texts continue to influence more recent contributions to SF and speculative fiction. For example, in the past couple of decades, one may well have lost count of the number of novels whose editorial reviews have declared them to be “the heir to The Handmaid’s Tale .”
This session will ask, in what ways do science fiction and speculative novels of the past 24 years borrow from, build upon, expand, and / or challenge earlier feminist science fiction and speculative texts? More broadly, how do more recent novels address themes of gender, sexuality, race, ethnicity, class, migration, ability, religion, ageism, bodily autonomy, reproduction, parenting, labor, economics, power, violence, technology, environmental destruction and equity, or other aspects that can be considered through the lenses of feminist and gender theories?
Submissions might consider recent contributions by authors such as Naomi Alderman, Alexandra Almeida, Madeline Ashby, Virginia Bergin, Jessamine Chan, Charlotte Nicole Davis, Christina Dalcher, Louise Erdrich, Sarah Hall, Nalo Hopkinson, Kameron Hurley, N.K. Jemisin, Alaya Dawn Johnson, Laura Lam, Ann Leckie, Sophie Mackintosh, Jennie Melamed, Mary Anne Mohanraj, Annalee Newitz, Nnedi Okorafor, Louise O’Neill, Joanne Ramos, Sabrina Vourvoulias, Martha Wells, Colleen Winter, or Leni Zumas, among many others -- as well as, of course, the actual sequel to The Handmaid’s Tale, Margaret Atwood’s The Testaments , published in 2019.
Please submit a 250-500 word proposal and a brief bio by June 1, 2024. To submit a proposal for this session, please go to https://pamla.ballastacademic.com to login or create an account first. Then go to https://pamla.ballastacademic.com/Home/S/19264 to submit your proposal.
Once you have created an account, you will be able to use the online system to submit a proposal. The deadline for proposals is June 1, 2024. If you have any questions, please contact Mary Cummins ( [email protected] ).

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Here at Science we love ranking things, so we were thrilled with this list of the top 100 most-cited scientific papers, courtesy of Nature.Surprisingly absent are many of the landmark discoveries you might expect, such as the discovery of DNA's double helix structure. Instead, most of these influential manuscripts are slightly more utilitarian in nature.
This guide was inspired by Joshua Schimel's Writing Science: How to Write Papers that Get Cited and Proposals that Get Funded—an excellent book about scientific writing for graduate students and professional scientists—but designed to address undergraduate students. While the guide was written by a group of ecologists and evolutionary ...
The science essay uses science to think about the human condition; it uses humanistic thinking to reflect on the possibilities and limits of science and technology. In this class we read and practice writing science essays of varied lengths and purposes. We will read a wide variety of science essays, ranging across disciplines, both to learn more about this genre and to inspire your own writing.
Ever since the essay was first published in 1982, readers—including this one—have thrilled to "Total Eclipse," Annie Dillard's masterpiece of literary nonfiction, which describes her ...
PNAS Classics are landmark papers from the archives of PNAS—significant scientific reports that have withstood the test of time. The authors of PNAS Classics opened new avenues of research within their respective fields. These groundbreaking discoveries offer insights into how the best science is practiced. Each Classic article is accompanied ...
Dr Peter Judge | Tutorial Essays for Science Subjects 1 Tutorial Essays for Science Subjects This guide is designed to provide help and advice on scientific writing. Although students studying Medical and Life Sciences are most likely to have to write essays for tutorials at Oxford, it is important all scientists ...
Most science essays are written in Times New Roman font with 12-point size and double spacing. The margins should be 1 inch on all sides, and the text should be justified. In addition, you must cite your sources properly using a recognized citation style such as APA, Chicago, or Harvard. Make sure to follow the guidelines closely so that your ...
The classic science essay No assigned readings 21 Preparing for Book Review Essay No assigned readings 22 Workshop Book Review Essays For Assignment #22: Levenson, Thomas. "Doubting climate change is not enough." The Boston Globe. April 17, 2016. Fitts, Alexis Sobel. "Of Science, Activism, and Journalism." Undark. March 20, 2016. Song ...
History of science, the development of science over time. Humankind has long observed regularities in nature, from the movements of the Sun and Moon during day and night to the seasonal migrations of animals. Learn how science advanced from the observation of these natural phenomena to modern understanding.
This release of classic papers consists of articles that were published in 2006 and is based on our index as it was in May 2017. To browse classic papers, select one of the broad areas and then select the specific research field of your interest. For example, Agronomy & Crop Science, Oil, Petroleum & Natural Gas, and African Studies & History.
Look for the paper (using the title or authors) in a science database, like those listed below, in Table 2. These databases contain free, full-text versions of scientific papers, as well as other relevant information, like publicly accessible data sets. Table 2: List of databases containing free, full-text scientific papers and data sets.
3. Reflections from a Nobel winner: Scientists need time to make discoveries by Donna Strickland. "We must give scientists the opportunity through funding and time to pursue curiosity-based, long-term, basic-science research. Work that does not have direct ramifications for industry or our economy is also worthy.
Classic papers by thinkers ranging from Aristotle and Leibniz to Norbert Wiener and Gordon Moore that chart the evolution of computer science. Ideas That Created the Future collects forty-six classic papers in computer science that map the evolution of the field. It covers all aspects of computer science: theory and practice, architectures and ...
The properties and uses of acids and bases. The effect of light on plant growth and development. The differences between renewable and non-renewable energy sources. The process of photosynthesis and its importance for life on Earth. The impact of technology on the environment and society.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas. Science as a Subject. In class 1 only a student has Science as a subject. This only tells us about the importance of Science. Science taught us about Our Solar System. The Solar System consists of 9 planets and the Sun. Most Noteworthy was that it also tells us about the origin of our ...
1. David Sedaris - Laugh, Kookaburra. A great family drama takes place against the backdrop of the Australian wilderness. And the Kookaburra laughs…. This is one of the top essays of the lot. It's a great mixture of family reminiscences, travel writing, and advice on what's most important in life.
Robin Wall Kimmerer, Braiding Sweetgrass (2013) Of every essay in my relentlessly earmarked copy of Braiding Sweetgrass, Dr. Robin Wall Kimmerer's gorgeously rendered argument for why and how we should keep going, there's one that especially hits home: her account of professor-turned-forester Franz Dolp.When Dolp, several decades ago, revisited the farm that he had once shared with his ex ...
After the jump, our picks for the 25 greatest essay collections of all time. Feel free to disagree with us, praise our intellect, or create an entirely new list in the comments. The Book of My ...
The Destiny of Colored Americans : "Slavery is the peculiar weakness of America, as well as its peculiar crime." A Glorious Resurrection: "My long-crushed spirit rose." W.E.B. Du Bois (1868-1963) W.E.B. Du Bois was an American scholar and human rights activist, a respected author and historian of literature.
Be sure and play with our new database query tool to create your own lists of classic short stories. [The project mentioned in this essay to create an all-time list of classic science fiction short stories has been completed. Jump to the Introduction to read how we created it or to Classics of Science Fiction Short Stories to see the ranked list.]
These science essays can be used for essay writing, debate, and other related activities at your institution or school. Essay On Science (200 words) Science entails a thorough examination of the behavior of the physical and natural world. Research, experimentation, and observation are used in the study. The scientific disciplines are diverse.
4. Isaac Asimov, ' Nightfall '. This 1941 short story, written while Asimov was still only in his early twenties, is widely regarded as one of the greatest science-fiction short stories of all time. Indeed, in 1968 the Science Fiction Writers of America voted it the best science fiction short story written before 1965.
A massive suite of papers offers a high-res view of the human and non-human primate brain. Many other brain atlases exist, but most provide much lower-resolution data. ... published in Science on ...
DOI 10.3386/w32404. Issue Date May 2024. Rapid progress has been made in identifying links between human genetic variation and social and behavioral phenotypes. Applications in mainstream economics are beginning to emerge. This review aims to provide the background needed to bring the interested economist to the frontier of social-science ...
Sample Essay On Science in 100 words. Science, the bedrock of human progress, unveils the mysteries of our universe through empirical investigation and reason. Its profound impact permeates every facet of modern life. In medicine, it saves countless lives with breakthroughs in treatments and vaccines. Technology, a child of science, empowers ...
May 14, 2024. Most high school seniors approach the college essay with dread. Either their upbringing hasn't supplied them with several hundred words of adversity, or worse, they're afraid ...
The word "manifestation" means to turn an idea into a reality. Usually, we want to manifest things that improve our happiness and well-being (take this well-being quiz to check your current level ...
Call for Papers. a service provided by www.english.upenn.edu. FAQ changelog: 2024/05/03. flag as inappropriate. Feminisms in the 21st-Century Science Fiction Novel; PAMLA (Nov. 7-10, 2024) deadline for submissions: June 1, 2024. full name / name of organization: Pacific Ancient and Modern Language Association (PAMLA) contact email:
Computational Humanities, Arts & Social Sciences ( CHASS) hosted a variety of tutorials ranging from "An Analysis on Emerson's Work" to large language model discussions throughout the Spring 2024 semester. These sessions are a great way to learn about the data science industry and how your skills will be used in the real world.
The number of active studies per month was greatest between 2016 and 2019, with 88 ongoing studies in May 2017. We found evidence of data integrity concerns in 130 (49%) papers, 43 (33%) of which contained concerns sufficient to suggest that they could not be based on data reliably collected from human participants.