

1. Learn how clouds form
2. learn about types of clouds, 3. learn how to identify types of clouds, 4. make cloud (and weather) observations, 5. identify the types of clouds you see, 6. help nasa scientists, 7. look for patterns in the weather, 8. get creative.
Learning Space
Teachable Moments
Stay Connected

The Types of Clouds and What They Mean
Have you ever looked up at the clouds and wondered what gives them different shapes, sizes and colors? Put yourself in the shoes of NASA scientists as you learn about different cloud types and how they form. Then, make your own cloud observations and record what you see. You can even share your observations with NASA cloud scientists to help them with their research!
(Optional) Globe Observer smartphone app
(Optional) thermometer
(Optional) barometer
(Optional) graph paper (for graphing temperature and/or pressure measurements)
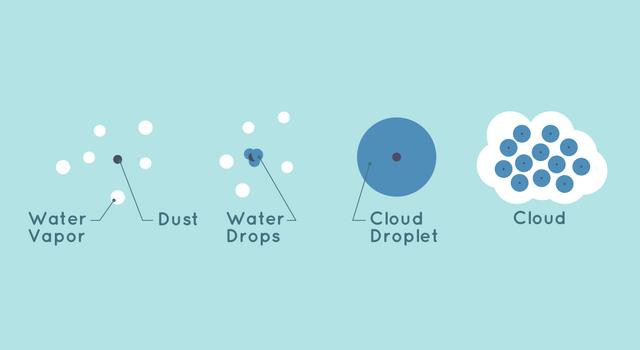
Looking up at the sky you’ve probably noticed clouds. While clouds are similar in many ways, there are lots of different types and they form in different ways. Learn more about clouds and how they form on NASA Climate Kids .

Read the list below to learn about the different types of clouds, what they look like and where they appear in the sky. Or download and print out this chart (also available en Español )
High Altitude
- Cirrocumulus – High clouds with a puffy, patchy appearance and small spaces between clouds. Often form wave-like patterns.
- Cirrostratus – High clouds, light gray or white, often thin with the Sun or Moon seen through them. Usually cover much of the sky.
- Cirrus – High clouds, thin wispy and feathery, composed of ice crystals.
Middle Altitude
- Altocumulus – Middle clouds with a puffy, patchy appearance, usually with spaces between clouds.
- Altostratus – Middle clouds, light gray and uniform in appearance, generally covering most of the sky.
Low Altitude
- Nimbostratus – Low and middle dark gray clouds with precipitation falling from them. Bases are diffuse and difficult to determine because of falling precipitation.
- Cumulus – Low clouds. Clouds appear puffy and look like cotton balls, popcorn or cauliflower.
- Stratus – Low clouds, light or dark gray and generally uniform in appearance and covering most of the sky. Fog is a stratus cloud.
- Stratocumulus – Low clouds with irregular masses of clouds, rolling or puffy in appearance, sometimes with space between the clouds.
- Cumulonimbus – Large clouds with dark bases and tall billowing towers. Can have sharp well defined edges or an anvil shape at the top. Precipitation can obscure the base of the clouds. Clouds can be accompanied by thunder.

A dichotomous key is a tool scientists (and you!) can use to identify things in nature by answering yes or no questions. You can use this dichotomous key to identify types of clouds .

Go outside or look out the window toward the sky to begin observations. If you have a thermometer, measure the temperature and write it down. If you have a barometer, measure the air pressure and write it down.

Answer the questions on this dichotomous key to identify what types of clouds are in the sky. Make a note about what kinds of clouds you see.

You can help NASA scientists studying clouds! Just complete this Cloud Observations Report Form . If you need help, ask an adult to join you in your observations.
Then, upload the information you collected to the Globe Observer App using the Clouds tool. Your observations will help scientists confirm similar measurements made by satellites orbiting Earth.
Repeat Steps 4 and 5 for several days in a row or throughout the year. You can learn even more about clouds and how they relate to the weather by tracking temperature, pressure and cloud data over time.

Head over the NASA Space Place website to find out how to make this cloud mobile !
- International
- Schools directory
- Resources Jobs Schools directory News Search

Cloud Types PowerPoint and Activity Sheets
Subject: Geography
Age range: 7-11
Resource type: Worksheet/Activity
Last updated
22 January 2024
- Share through email
- Share through twitter
- Share through linkedin
- Share through facebook
- Share through pinterest

A fully editable 16 slide PowerPoint presentation on different types of clouds. Includes a bonus activity sheet and word search.
Covers following topics: ➸ How clouds form. ➸ How clouds are classified. ➸ 8 different cloud types:
- altocumulus
- altostratus
- cirrocumulus
- stratocumulus
- cumulonimbus ➸ 2 Embedded videos cloud formation and cloud spotting.
Includes the following bonus resources: ➸ Activity sheet with word puzzle, labelling activity and gap fill. ➸ Cloud types word search.
Clipart by: Educlips
Ron Leishman Digital Toonage ToonClipart
Tes paid licence How can I reuse this?
Your rating is required to reflect your happiness.
It's good to leave some feedback.
Something went wrong, please try again later.
This resource hasn't been reviewed yet
To ensure quality for our reviews, only customers who have purchased this resource can review it
Report this resource to let us know if it violates our terms and conditions. Our customer service team will review your report and will be in touch.
Not quite what you were looking for? Search by keyword to find the right resource:
- Join for Free

- Back to Listing
- Current: Science
- Current: Weather

PowerPoint Presentation with Audio: PowerPoint: Different Types of Clouds
Powerpoint presentation with audio about the different types of clouds (upper elementary). includes 14 slides with colorful images, simple text and audio., resource tags, similar resources.

PowerPoint: Presentation with Audio: Soil 2: Dirt (multi-age)
/ Think Green PowerPoint
Media Type PPT

Common Core: Math Lesson Planner – Numbers and Operations in Base Ten (grade 2)
/ PowerPoint Templates
Media Type PPTX

Italian: PowerPoint Interactive–Colori
/ PowerPoint Interactive: Languages
New to abcteach?
Sign up to Download From 49,000+ Resources
TERMS OF SERVICE
1.1. The abcteach.com public and membership websites have been in operation since about 2000, providing access to downloadable materials for educators and parents.
1.2. The abcteach.com website is owned and operated by ABCTEACH LLC, a Michigan limited liability company. The names "abcteach" and "abctools" are registered trademarks. As used in this Terms of Service and Privacy Policy, "We" and "abcteach" and "Site" refer to all websites and services, whether public or membership, operated or offered by abcteach. Currently we operate under the following base urls: abcteach.com, and members.abcteach.com.
1.3. abcteach is for use by parents, educators, and others over the age of 18. The materials made available by abcteach are intended to be used with and for children and students, among others, at the discretion and under the control, supervision, and direction of the parents, educators, and other adults who are visitors, members, or subscribers to the Site. As used in this Terms of Service and Privacy Policy, "you" refers to such visitors, members, or subscribers.
1.4. By using the Site, you accept and agree to be bound by the following terms. We may, solely at our discretion, modify or revise these terms and conditions at any time by updating this web page, and you agree to be bound by these modifications or revisions. You should visit this page periodically to review the terms. From time to time, we will require that you confirm your agreement to the terms.
2.1. Sharing of password or login information is strictly prohibited. Suspension of account access may result from sharing of this information.
2.2. Worksheets and other materials available on abcteach, including clip art, may be printed or otherwise duplicated for use in your home or your classroom(s). Clip art on abcteach is intended as a resource for you in creating lessons and teaching materials and the like within your permitted usage of the Site. If you are a paid member, our clip art may be: placed on another publication as clip art, or distributed individually on a third-party authorship site, if you as a member give abcteach credit for any clip art intended to be redistributed. Giving credit to abcteach requires you to mention our name and website on any publications in which you use our clip art for redistribution. You may not use our clip art in the design or content of another website; or distribute our clip art electronically or by email or text or by any other media or social media. Furthermore, Members are prohibited from packaging our clip art into their own collections for sale, each clip art illustration used for resale, must be used individually, again giving credit to abcteach.com.
2.3. The abcteach copyright appears on every page; we require that this copyright remain in place on all reproductions.
2.4. Except as provided in section 2.7 below, all of the worksheets and other materials available on abcteach are intended for non-commercial educational purposes.
2.5. You may place links to abcteach from your own education website; however, copying or uploading abcteach resources and documents to your own site is a copyright violation and will be treated as such. Deep linking is not permitted. (A "deep link" is a hyperlink that bypasses a website's home page and takes the user directly to an internal page. For example, instead of linking to the home page of a newspaper, a deep link might take the user directly to a newspaper article within the site.) At abcteach, linking directly to a content page rather than the home page or a directory page is considered deep linking and is not permitted.
2.6. Under no circumstances may any of the documents, resources, clip art, worksheets, or other materials (including text, images, or website design) on abcteach be re-sold or re-distributed without the express permission of abcteach.
2.7. We may permit you to use abcteach materials in your creation and sale of educational materials produced by you individually, on sites such as Teachers Pay Teachers, upon your payment of a separate additional fee and your submission of an executed agreement as stated elsewhere on the Site. This would offer you a limited non-exclusive license to use abcteach materials within the scope of the separate agreement; such permission being terminable at any time by abcteach in our sole discretion; you agree that you will immediately cease the use, or offering for sale, or sale, of any such educational materials in the event we take such action. By using any materials, you acknowledge that other members may be acting under similar permissions and creating similar materials.
2.8. If you desire to use abcteach materials in any other manner, or if you have any questions about permissible uses that are not specifically addressed here, you should address your inquiry to support@abcteach.
3. Responsibility for User-Created Content
3.1. The Site has tools and other features, including but not limited to abctools, the abcWorkshop, and other applications, that facilitate the creation of user-generated word lists, puzzles, worksheets, and other resources. The user-selected content of such user-generated materials is your sole responsibility and not that of abcteach. If any other person, including children or students, uses your member account to access or use abctools or abcWorkshop or any other abcteach application, you agree to and assume responsibility for any such materials.
3.2. You are responsible for assuring that any materials, lists, documents or other documents created with this abcteach tools, resources, and applications, are appropriate, and you will not cause or permit the tool to be used to create harmful, vulgar, threatening, or otherwise inappropriate content.
3.3. If you share an abcteach document or user-generated document, by any means including any of the sharing features or applications or tools found on the Site, you are solely responsible for the content of the transmitted materials or documents.
3.4. If any sensitive materials or information or documents from the Site, or user-generated materials, are shared or provided to a child under the age of 13, you agree that you will first obtain express consent from the child’s parent or guardian(s) to share such documents with the child, and obtain permission and/or releases for the use of any user-generated information concerning the child or the child’s family that may be contained in such documents.
4. License Grant to abcteach
By posting information on or through our Sites, you automatically grant abcteach a royalty-free, perpetual, irrevocable, non-exclusive license to use, reproduce, modify, publish, edit, translate, distribute, perform, and display the information, alone or as part of other works, in any form, media, or technology, whether now known or hereafter developed, and to sublicense such rights through multiple tiers of sub-licensees.
5. Charges, Payments, and Subscription Charges and Cancellation
5.1. We currently offer one-year and two-year individual memberships for single payment, and a monthly plan with payment of an initial setup charge followed by monthly payments. We also offer group memberships to schools, districts, and groups, the details of which are described separately. The terms and prices of individual memberships as they may exist from time to time are stated on the Site. We may choose to offer different membership plans. By becoming an abcteach member, you agree that we may renew your subscription automatically for the same subscription terms on the day your previous subscription ends, and you authorize us to charge you for the subscription term, unless you cancel your account prior to its renewal date through the cancellation process, as provided in sections 5.4 – 5.6 below.
5.2. We use third-party payment providers (such as CyberSource and other providers) for all credit and debit card and PayPal and similar transactions. We do not collect or retain information about user’s credit or debit cards or PayPal accounts or other payment mechanism, all of which information is retained and used according to secure procedures of the third-party payment providers.
5.3. Depending on the plan you choose, you will be charged a fee automatically through our renewal system. By becoming an abcteach member, you are agreeing that we are authorized to charge you the membership fee associated with the type of membership (monthly, yearly, or bi-yearly) that you chose during registration. You agree that we are authorized to charge you the membership fee at the then-current rate to the payment method you provided during registration. Please note that prices and charges are subject to change without notice. Fees each month may be modified using credit card, debit card, PayPal, or other payment methods available through your account. This includes: promotional discounts advertised in our weekly member newsletters, or on-brand promotional ads. Each renewal payment will take place on or about the anniversary of the original date of account registration. If all eligible payments methods we have on file for you are declined, you must provide us a new payment method promptly or your membership will be canceled. If the renewal of your membership fails for any reason, we will attempt to process your renewal for a period up to thirty (10) days.
5.4. Membership Cancellation. You may cancel your membership any time by visiting Your Account and adjusting your settings. If you choose to cancel your subscription or fail to pay any fees, we may stop your membership. If you cancel your membership or are no longer a paid user, you have the option to continue use as a free user.
5.5. UNLESS YOU NOTIFY US BEFORE A SUBSCRIPTION PAYMENT THAT YOU WANT TO CANCEL OR DO NOT WANT TO AUTO RENEW, YOU UNDERSTAND THAT YOUR ABCTEACH MEMBERSHIP WILL AUTOMATICALLY CONTINUE AND YOU AUTHORIZE US TO COLLECT THE THEN-APPLICABLE MEMBERSHIP FEE AND ANY APPLICABLE TAXES, USING ANY/ ALL ELIGIBLE PAYMENT METHODS WE HAVE ON RECORD FOR YOUR ACCOUNT.
5.6. ALL FEES ARE NON-REFUNDABLE. Termination of your account may include removal of your access to all offerings of the website; including password, information, files, and user content associated with your account, and barring any further use of abcteach membership services and tools.
5.7. We may terminate your membership at our discretion without notice. If we do so, we will provide a prorated refund based on the number of days/months remaining in your membership. However, we will not give any refund for termination related to conduct that we determine, in our discretion, violates these terms or any applicable law, involves fraud or misuse of the membership agreement, or is harmful to our interests or another use.
5.8. By applying for membership, you represent that: you are over the age of 18; that you are competent to enter into a contract; that you are the owner of, or authorized by the owner, to utilize the credit or debit card or other payment mechanism used for the payments; that the information you submit about your location and contact information is correct; that you will promptly notify us of any change in your email address or payment mechanism; and that you have read and agree with the provision of these Terms of Service and Privacy Policy. We reserve the right to decline any application for membership, or to change the terms and/or conditions of any account at any time, for any reason or no reason.
5.9. We may offer, on the Site or through other means, and broadly or to limited groups of potential members, promotional prices, seasonal pricing, free trial memberships, or other special prices and terms. Such promotional activities do not affect existing memberships, and abcteach will not provide or offer such promotional prices to existing members or users, and will not provide refunds or rebates or other price protections.
PRIVACY POLICY
- This Privacy Policy applies to all websites, public and membership, operated by abcteach. By providing information to us or using the Site, you agree to the terms and conditions of this Privacy Policy.
- abcteach will not knowingly send marketing or other messages to children. Nor does abcteach knowingly permit children to communicate through the Site or to provide personal information to us.
- Member Registration Information. abcteach collects and stores certain information that members, subscribers, and users of the Site are required to provide in registering for or subscribing to the Site. Such information can vary depending on the nature of the account, and may include personal identifying information such as name, email address, school or district information, physical address, etc.
- Electronic Payment and Credit Card Information. abcteach currently utilizes third party providers to handle electronic and credit card payment transactions, and abcteach does not itself collect or store information concerning such payments. If you want to review the privacy policies of such third party service providers, please request contact information for those providers by contacting abcteach at the one of the addresses given below.
- Payments by Check or Bank Transfers. When abcteach receives payments by check or bank transfers, most often from schools and districts, we collect and maintain information about such payments.
- Information about Usage of the Site. We collect information on usage of the Site, which may include pages visited, and downloaded, time on site, identifying information about the uses, etc.
- "Cookies" and other Tracking and Technology Information. abcteach and our third party service providers may use cookies and other technologies to retrieve and store information about Site usage, browser type, IP addresses, pages visited, date and time of usage, etc.
- Information derived from use of ABCTOOLS and abcWorkshop and other abcteach services and products. If a member or others introduce information into the system by utilizing any of abcteach's services or products including ABCTOOLS or abcWorkshop, it is possible such information will be gathered or stored. You represent, by using or permitting such use of the Site by yourself or by others or by children, that any personal information that may be included in such usage is used with permission and authority, including parental consent, and that you represent to us and our service providers that we are permitted to use the information.
- Registration and use of the Site.
- Payment for membership or subscriptions or products or services.
- Internal business purposes.
- Newsletters distribution.
- Special offers and marketing relating to abcteach.
- Customer service and problem resolution.
- Enforcement of abcteach intellectual property rights and membership terms and conditions.
- Responding to legal process or governmental requests for information.
- As required under applicable law or regulations.
- In connection with possible future transactions affecting abcteach, such as the sale of the Site, or mergers, sales of assets, reorganizations, etc. , in which event all or a part of stored information including member and user information may be transferred to a successor business or website operator.
- As we may require in connection with specific services and products, current or future.
- Children's Privacy Notice Usage of the Site is limited to adults and children are not permitted to use the Site. Nor do we request that any personal information be provided by or about children including those in your family or classroom. Children under the age of 13 are not requested to provide any personal information while using the Site. However, to comply with the Children's Online Privacy Protection Act, if it is brought to our attention that children under 13 years of age intend to use the Site, we reserve the right to require you to seek the consent of Parents in order for children under 13 years of age to use the Site in any manner that could result in the submission of personal information, and to terminate your access to the Site if such consent(s) is not obtained or submitted timely. If a member, teacher, or parent uses the Site or any of its tools or products in a manner by which a child could disclose personal information to others, it shall be a representation by that member, teacher or parent that the child's parent has expressly authorized such use and has expressly authorized abcteach to collect, store, and distribute the child's personal information to other users of the Site. Additionally, such personal information may be collected or stored by the cookies and other technologies described above. Parents may contact abcteach at the addresses provided below.
- Security abcteach attempts to secure its information and that of others by using reasonable safeguards and procedures. However, no internet or electronic data communication, transmission or storage system can be guaranteed to be completely secure. For that reason, abcteach cannot and does not guaranty the security of information transmitted to or shared with us. You use the Site and provide and share information at your own risk. If you have questions or concerns, you should not submit or share personal information or other sensitive information.
- Links to Other Sites abcteach does not ordinarily link to other websites. If such links are used, those websites or applications will be not be covered by this Privacy Policy. Users should review privacy policies of such sites and applications.
- Consent to Transfer of Information to the United States and to the Application of U.S. Law and Jurisdiction. abcteach is operated and managed by ABCTEACH LLC from within the United States. Neither the Site nor its staff nor its owner intend to be governed or subjected to the laws or jurisdiction of any other country other than the United States. Information provided to abcteach or to its third party service providers will be processed, stored, and used in the United States and other countries where the service providers or abcteach or affiliates may have operations. By using the Site, you irrevocably consent to the transfer of information to the United States, or to other countries other than your country of residence, and to the storage and use of the information in the United States. You acknowledge and agree that, to the extent that the laws of the United States differ from those of your country of residence, you consent to the application of the laws of the United States to your information and to the relationship between yourself and us, and you covenant and agree that you will not assert that other law is applicable. Any litigation or court proceedings of any nature concerning the relationship between you and abcteach, or to these terms and conditions, or to the Privacy Policy, or to any other matter relating to abcteach, shall be only and exclusively in the Circuit Court for Oakland County, Michigan, or the United States District Court for the Eastern District of Michigan, and you irrevocably consent to personal jurisdiction in such forums for any such litigation or proceedings.
- Indemnification and Hold Harmless You agree to indemnify, defend, and hold harmless abcteach, and all related parties and services, from any and all liability, penalties, losses, damages, costs, expenses, attorneys' fees, causes of action, or claims caused by or resulting indirectly from your use of our Sites.
- No Warranties Use of this service is on an "as-is" basis. ALL WARRANTIES, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND MERCHANTABILITY, ARE SPECIFICALLY DISCLAIMED. Any contact with any agents of this service, either in person or through electronic means does not create a warranty.
- Changes to Our Terms of Service and Privacy Policy We may change these Terms of Service and Privacy Policy at any time and such changes will become effective when posted to the Site. Your use of the Site following such the posting of any revised Terms of Service and Privacy Policy means that you accept the revised terms and policy.
- Contact Information Regarding Terms of Service and Privacy Policy Legal questions and concerns should be directed to our General Counsel, whose email address is [email protected] . Alternatively, first class mail addressed to General Counsel, ABCTEACH LLC, c/o Bodman PLC, 1901 St. Antoine Street, Detroit, Michigan 48226. Other questions should be directed to Customer Support, whose email address is [email protected] .
REVISION DATE: August 1, 2017

Powerpoint Templates
Icon Bundle
Kpi Dashboard
Professional
Business Plans
Swot Analysis
Gantt Chart
Business Proposal
Marketing Plan
Project Management
Business Case
Business Model
Cyber Security
Business PPT
Digital Marketing
Digital Transformation
Human Resources
Product Management
Artificial Intelligence
Company Profile
Acknowledgement PPT
PPT Presentation
Reports Brochures
One Page Pitch
Interview PPT
All Categories

Cloud Computing Powerpoint Presentation Slides
Cloud computing service provides your organization with flexibility in the work by giving immense benefits to the company. Grab our insightfully designed Cloud Computing ppt templates. It provides a brief overview of the company, its core values, the types of businesses they assist, and the benefits of cloud storage. Our Cloud computing deck also includes an introduction to cloud storage architecture, including generic architecture, levels of architecture, cloud storage access methods, cloud scalability, and cloud storage models. Additionally, it incorporates the different types of cloud storage services and the various uses for cloud storage, such as data backup and recovery, software testing and development, compliance, big data, and data lakes. Lastly, the Cloud Storage PPT addresses data transfer to the cloud and data backup strategies. Get immediate access.

- Add a user to your subscription for free
You must be logged in to download this presentation.
Do you want to remove this product from your favourites?
PowerPoint presentation slides
Enthrall your audience with this Cloud Computing Powerpoint Presentation Slides. Increase your presentation threshold by deploying this well-crafted template. It acts as a great communication tool due to its well-researched content. It also contains stylized icons, graphics, visuals etc, which make it an immediate attention-grabber. Comprising sixty seven slides, this complete deck is all you need to get noticed. All the slides and their content can be altered to suit your unique business setting. Not only that, other components and graphics can also be modified to add personal touches to this prefabricated set.

People who downloaded this PowerPoint presentation also viewed the following :
- Complete Decks , All Decks , IT
- Cloud Storage In Healthcare ,
- Cloud Storage In Manufacturing ,
- Cloud Storage In Retail Industry ,
- Cloud Storage In Logistics ,
- Key Features Of Cloud Storage ,
- Pros And Cons Of Cloud Storage
Content of this Powerpoint Presentation
Slide 1 : This slide introduces Cloud Computing. Commence by stating Your Company Name. Slide 2 : This slide depicts the Agenda of the presentation. Slide 3 : This slide incorporates the Table of contents. Slide 4 : This is yet another slide continuing the Table of contents. Slide 6 : This slide presents the Overview of the cloud storage company. Slide 7 : This slide states the Core values of the organization. Slide 8 : This slide describes the types of business the company supports. Slide 9 : This slide depicts cloud storage benefits for businesses. Slide 10 : This slide elucidates the Heading for the Contents to be discussed next. Slide 11 : This slide describes why organizations choose cloud storage firm as their cloud storage service provider. Slide 12 : This slide showcases the cloud storage security by describing the various security measures taken by the company. Slide 13 : This slide shows the Open source cloud storage service. Slide 14 : This slide contains the Title for the Ideas to be covered further. Slide 15 : This slide displays the application of cloud storage in the healthcare industry and its various benefits. Slide 16 : This slide focuses on the Cloud storage in manufacturing. Slide 17 : This slide describes the application of cloud storage services in the retail industry and its benefits. Slide 18 : This slide talks about Cloud storage in logistics. Slide 19 : This slide mentions the Heading for the Ideas to be discussed in the following template. Slide 20 : This slide elucidates the Introduction to cloud storage. Slide 21 : This slide depicts the key features of cloud storage that include the easy switch to lower-cost classes, multiple backup options, etc. Slide 22 : This slide represents the working of the cloud storage and the components of cloud storage. Slide 23 : This slide showcases the pros of cloud storage services. Slide 24 : This slide exhibits the cons of the cloud storage services such as security issues, latency issues, etc. Slide 25 : This slide portrays the Heading for the Ideas to be covered further. Slide 26 : This slide describes the architecture of cloud storage, the technology it's built on, scalability, etc. Slide 27 : This slide highlights the different levels of cloud storage architecture. Slide 28 : This slide talks about the Generic cloud storage architecture. Slide 29 : This slide depicts the cloud storage access methods. Slide 30 : This slide represents the scalability of the company’s cloud storage, flexibility to scale up and down, etc. Slide 31 : This slide deals with the Distribution of cloud sites for data availability. Slide 32 : This slide shows the Models of cloud storage. Slide 33 : This slide indicates the Title for the Components to be discussed further. Slide 34 : This slide describes the public cloud storage service, its administrative method, and its various advantages. Slide 35 : This slide exhibits the Private cloud storage service. Slide 36 : This slide talks about the Hybrid cloud storage service. Slide 37 : This slide displays the community cloud storage service, its members, and advantages. Slide 38 : This slide reveals the Heading for the Topics to be covered next. Slide 39 : This slide focuses on the Cloud storage for backup and recovery. Slide 40 : This slide elucidates the Cloud storage for software test and development. Slide 41 : This slide provides information about the Cloud storage for cloud data migration. Slide 42 : This slide depicts the use of cloud storage services for data compliance through compliance controls, WORM restrictions, and audit log solutions. Slide 43 : This slide talks about the Cloud storage for big data and data lakes. Slide 44 : This slide presents the Title for the Topics to be covered further. Slide 45 : This slide represents the checklist for cloud storage setup for organizations. Slide 46 : This slide shows the Data storage plan for cloud storage. Slide 47 : This slide states the steps for smart cloud migration by including the checklist for cloud migration, estimate migration time, and data migration stages. Slide 48 : This slide outlines the Cloud backup and disaster recovery solutions. Slide 49 : This slide indicates the Title for the Idaes to be covered in the forth-coming template. Slide 50 : This slide represents the pricing for cloud storage services based on types, standard storage, nearline storage, etc. Slide 51 : This slide elucidates the Heading for the Ideas to be further discussed. Slide 52 : This is the 30-60-90 days plan slide for data migration. Slide 53 : This slide displays the Timeline for data migration to cloud storage. Slide 54 : This slide reveals the Timeline for data migration cloud storage. Slide 55 : This slide illustrates the Dashboard for cloud storage tracking. Slide 56 : This slide represents the dashboard for cloud storage tracking by covering details of users, available workspaces, shared files, etc. Slide 57 : This is the Icons slide containing all the Icons used in the plan. Slide 58 : This slide is used to showcase some Additional information. Slide 59 : This slide presents the Column chart. Slide 60 : This is the Idea Generation slide for encouraging fresh ideas. Slide 61 : This slide elucidates the Comapny Timeline. Slide 62 : This is the Puzzle slide with related imagery. Slide 63 : This slide contains the Post it notes for reminders and deadlines. Slide 64 : This slide is used for the purpose of Comparison. Slide 65 : This is the Venn Diagram slide. Slide 66 : This is Our goal slide. State your organizational goals here. Slide 67 : This is the Thank you slide for acknowledgement.
Cloud Computing Powerpoint Presentation Slides with all 72 slides:
Use our Cloud Computing Powerpoint Presentation Slides to effectively help you save your valuable time. They are readymade to fit into any presentation structure.

Cloud storage in the healthcare industry provides various benefits, including cost-effectiveness, improved accessibility to patient records, increased data security, and easy data backup and recovery.
Public cloud storage service offers advantages like cost savings, scalability, flexibility, easy access to resources, and reduced need for infrastructure maintenance.
The cons of cloud storage services include potential security issues, latency issues, dependency on internet connectivity, data privacy concerns, and limited control over data management.
The different models of cloud storage include public cloud, private cloud, hybrid cloud, and community cloud.
Cloud storage architecture works by using a network of servers that store and manage data. The architecture typically includes multiple layers, including the front-end, back-end, and storage layer, and it can be scaled up or down based on demand.
Ratings and Reviews
by Colton Fisher
March 10, 2023
by Chung Bennett
March 9, 2023


Types of Clouds
Apr 06, 2019
1.09k likes | 2.71k Views
Types of Clouds. What’s the Weather?. Cirrus, Cirrocumulus and Cirrostratus (high 5000-16,000 m). thin and often wispy composed of ice crystals that originate from the freezing of supercooled water droplets.
Share Presentation
- light precipitation
- supercooled water droplets
- wispy streamers
- cumulus clouds

Presentation Transcript
Types of Clouds What’s the Weather?
Cirrus, Cirrocumulus and Cirrostratus(high 5000-16,000 m) • thin and often wispy • composed of ice crystals that originate from the freezing of supercooled water droplets. • Generally occur in fair weather and point in the direction of air movement at their elevation.
Cirrus • They are made of ice crystals and have long, thin, wispy streamers. • Cirrus clouds are usually white and predict fair weather.
Cirrocumulus • They are small rounded puffs that usually appear in long rows. • Cirrocumulus are usually white, but sometimes appear gray. • Cirrocumulus are usually seen in the winter time and mean that there will be fair, but cold weather.
Cirrostratus • Sheetlike thin clouds that usually cover the entire sky. • Cirrostratus clouds usually come 12-24 hours before a rain or snow storm.
Altocumulus and Altostratus(middle 2,000 to 7, 000 m) • Middle clouds are made of ice crystals and water droplets. • The base of a middle cloud above the surface can be anywhere from 2000-8000m in the tropics to 2000-4000m in the polar regions. An
Altocumulus • They are grayish-white with one part of the cloud darker than the other. • Usually form in groups. • If you see altocumulus clouds on a warm sticky morning, then expect thunderstorms by late afternoon.
Altostratus • An altostratus cloud usually covers the whole sky. • The cloud looks gray or blue-gray. • Usually forms ahead of storms that have a lot of rain or snow. Sometimes, rain will fall from an altostratus cloud. • If the rain hits the ground, then the cloud is called a nimbostratus cloud.
Stratus, Nimbostratus and Stratocumulus(low surface to 2000 m) • Low clouds are made up of water droplets. The base of a low cloud is from the ground to 2000m.
Stratus • They are gray and can cover most or all of the sky (like a big blanket). • Stratus clouds sometimes produce light mist or drizzle.
Stratocumulus • Low, lumpy, and gray. • Only light precipitation, usually drizzle, occurs with stratocumulus clouds.
Nimbostratus • They are dark gray with a ragged base. • Produce rain or snow. • Sometimes they cover the whole sky and you can't see the edges of the cloud.
Clouds with Vertical DevelopmentCumulus and Cumulonimbus(surface to 13,000 m) • The clouds develop by warm air rising from the surface. Cumulus and Cumulonimbus clouds provide the most interesting and severe weather to our planet.
Cumulus • Puffy white or light gray clouds that look like floating cotton balls. • Cumulus clouds have sharp outlines and a flat base. • Seeing cumulus clouds in the sky can mean the weather will be good or bad.
Cumulonimbus • Known as thunderstorm clouds. • Can grow up to 10km high. • High winds make the top of the cloud flat. • Cumulonimbus clouds can produce heavy rain, hail, lightning, and tornadoes.
- More by User

Clouds Of Fire
Clouds Of Fire. What would be the most troubling thing your mind could imagine ? Are you concerned? If So, Why? Could it be a total financial collapse of the worlds markets? Could it be that famine and disease engulf our country & world?
240 views • 13 slides

Different Types of Clouds
Different Types of Clouds. Ms. Felicia Fratto Fifth Grade Science. Objectives. Students will understand how clouds form. Students will be able to identify the three basic cloud types. Students will understand the prefixes and suffixes used with cloud vocabulary. South Carolina Standards:
420 views • 12 slides

Clouds of Steel
Clouds of Steel. Clouds of Steel. Cloud application for offer requests for steel products Customers can enter the offer request and see what is in stock. Running on Microsoft Azure Cloud platform Accessible everywhere. Enter your requests.
171 views • 6 slides

Clouds of War
Clouds of War. Chapter 26. Foreign Affairs 1933-1936. Anti-Semite. Jews scapegoats. Austrian. Thugs and Bullies. Organized Nazi Party. Rise of Hitler. Wrote Mein Kampf. Preached Germans were Master Race. Nazi Bible. Great Speaker. Appealed to a discontented Germany.
1.07k views • 92 slides

Types of clouds
Types of clouds. Meera Mehtaji. CLOUDS. Four Types of Clouds. Cirrus Clouds Cumulonimbus Clouds Cumulus clouds Stratus Clouds. Cirrus Clouds . Cirrus clouds are the most common of the High Cloud (5000-13000m) group.
513 views • 11 slides

Types of Clouds. Kristian Diore 3 r d Grade Science. Click here to begin!. Click on each cloud to learn more about it!. Cumulus clouds. Cirrus clouds. Stratus clouds. Nimbus clouds. Click here for a review question. Cumulus Clouds. Puffy, white clouds
3.25k views • 16 slides

Types of Clouds. Vertical Clouds. Cumulus Clouds. Also called fair weather clouds and look like floating cotton Have very flat bases and are not very tall
674 views • 24 slides

Clouds: Types & Formation
Clouds: Types & Formation. Meteorology. Warm moist air rises, expands, and cools in a convection current Air reaches dew point, water vapor in air condenses around small particles in atmosphere (sea salt, dust) Millions of these droplets collect= form clouds
223 views • 7 slides

Types of Clouds QUIZ
Types of Clouds QUIZ. What is the Latin word meaning “layered”?. STRATUS. Name the cloud that Looks like cumulus clouds pressed in layers Found low in the sky. Stratocumulus. Name this cloud… A low, puffy cloud bringing heavy rain, thunder, lightening A “thunderhead”
598 views • 37 slides

Clouds of War. Section 1: Foreign Affairs, 1933-1939. Foreign Affairs, 1933-1939. Franklin Delano Roosevelt (FDR), shown right, came into office in march of 1933, when the outlook of civilization looked darker than ever.
418 views • 25 slides

Types of Clouds. Cirrus. Cirrus clouds can best be described as “ice-crystal” clouds that look like wispy curls of hair. These clouds are often the first signs of approaching weather changes. . Cirrus. Cirrocumulus.
2.61k views • 22 slides

Clouds, Clouds, and more Clouds!
Clouds, Clouds, and more Clouds!. By: Aidan Weston. Type: cumulus or cumulonimbus Date:12/12/12 Time:8:20 am Location: my house Group: Hard-to-see clouds. Type: cumulus Date: 11/3/12 Time:3:45 pm Where: New River trail state park Group: No-group clouds. Type: cumulus Date: 12/18/12
276 views • 11 slides


Objective: Create the three types of clouds.
Objective: Create the three types of clouds. DO NOW Pick up construction paper & rubric Open red textbook to pg. 487 INTRO What does the word nimbus mean in terms of clouds ? OUTRO Why are some clouds formed from water droplets, while others are made up of ice crystal?.
191 views • 3 slides

877 views • 43 slides

Clouds, Clouds, Clouds
Clouds, Clouds, Clouds. Let’s Sing!. Oh When the Clouds go Floating By (Sung to the tune of: When the Saints go Marching By) Written by: Mrs. Lovell (Myrtle Beach: Blue Ribbon Conference). Oh when the clouds go floating by Oh when the clouds go floating by
531 views • 7 slides
Formation of Clouds
Formation of Clouds. A cloud is composed of millions of little droplets of water (or ice crystals when temperature is very low) suspended in the air. There are several major processes for cloud formation. Convection Forceful Lifting Meeting air masses Horizontal motion. Convection :.
534 views • 15 slides
Types of Clouds. In the following slides, decide what type of cloud you see in the picture. Click in the box above the picture and type the name of the cloud. Contents of this web site are intended to be used for the enhancement of instruction only. By: Joy Lynn Cox Buckingham.
375 views • 12 slides

CLOUDS. How do clouds form?. Key words: evaporation, dew point, condensation, condensation nuclei. 4. All the water droplets form clouds. 2 . Temperature drops to dew point. 3 . Water condenses on condensation nuclei (dust). tiny water droplets. 1 . Water evaporates and rises.
180 views • 2 slides

Types of Clouds in Cloud Computing
Are you looking for best AWS Cloud Computing Online training Institute in Hyderabad? Visualpath provides AWS online classes with certification and placement. Learn AWS Cloud Computing and its business objects with real-time project work and test practice for more details call@9704455959. https://www.visualpath.in/amazon-web-services-aws-training.html
127 views • 8 slides

Types of Clouds. A fifth grade Powerpoint slide show. created by Mrs. Sheehan 1/07. Most clouds you see in the sky are based on these three basic cloud types:. Cumulus - puffy, like a cotton ball Stratus - flat, covers the sky like a blanket Cirrus - high, wispy clouds.
463 views • 30 slides

Types of Azure Clouds
We at Visualpath offers the finest MS Azure Training in Hyderabad. We have highly skilled as well as proficient trainers in our institute who have years of experience. All the class recordings, presentations will be shared with you for reference. Call Now 919989971070.
136 views • 8 slides
Published: 14 February 2024 Contributors: Stephanie Susnjara, Ian Smalley
Cloud computing is the on-demand access of computing resources—physical servers or virtual servers, data storage, networking capabilities, application development tools, software, AI-powered analytic tools and more—over the internet with pay-per-use pricing.
The cloud computing model offers customers greater flexibility and scalability compared to traditional on-premises infrastructure.
Cloud computing plays a pivotal role in our everyday lives, whether accessing a cloud application like Google Gmail, streaming a movie on Netflix or playing a cloud-hosted video game.
Cloud computing has also become indispensable in business settings, from small startups to global enterprises. Its many business applications include enabling remote work by making data and applications accessible from anywhere, creating the framework for seamless omnichannel customer engagement and providing the vast computing power and other resources needed to take advantage of cutting-edge technologies like generative AI and quantum computing .
A cloud services provider (CSP) manages cloud-based technology services hosted at a remote data center and typically makes these resources available for a pay-as-you-go or monthly subscription fee.
Read how Desktop as a service (DaaS) enables enterprises to achieve the same level of performance and security as deploying the applications on-premises.
Register for the guide on app modernization
Compared to traditional on-premises IT that involves a company owning and maintaining physical data centers and servers to access computing power, data storage and other resources (and depending on the cloud services you select), cloud computing offers many benefits, including the following:
Cloud computing lets you offload some or all of the expense and effort of purchasing, installing, configuring and managing mainframe computers and other on-premises infrastructure. You pay only for cloud-based infrastructure and other computing resources as you use them.
With cloud computing, your organization can use enterprise applications in minutes instead of waiting weeks or months for IT to respond to a request, purchase and configure supporting hardware and install software. This feature empowers users—specifically DevOps and other development teams—to help leverage cloud-based software and support infrastructure.
Cloud computing provides elasticity and self-service provisioning, so instead of purchasing excess capacity that sits unused during slow periods, you can scale capacity up and down in response to spikes and dips in traffic. You can also use your cloud provider’s global network to spread your applications closer to users worldwide.
Cloud computing enables organizations to use various technologies and the most up-to-date innovations to gain a competitive edge. For instance, in retail, banking and other customer-facing industries, generative AI-powered virtual assistants deployed over the cloud can deliver better customer response time and free up teams to focus on higher-level work. In manufacturing, teams can collaborate and use cloud-based software to monitor real-time data across logistics and supply chain processes.
The origins of cloud computing technology go back to the early 1960s when Dr. Joseph Carl Robnett Licklider (link resides outside ibm.com), an American computer scientist and psychologist known as the "father of cloud computing", introduced the earliest ideas of global networking in a series of memos discussing an Intergalactic Computer Network. However, it wasn’t until the early 2000s that modern cloud infrastructure for business emerged.
In 2002, Amazon Web Services started cloud-based storage and computing services. In 2006, it introduced Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2), an offering that allowed users to rent virtual computers to run their applications. That same year, Google introduced the Google Apps suite (now called Google Workspace), a collection of SaaS productivity applications. In 2009, Microsoft started its first SaaS application, Microsoft Office 2011. Today, Gartner predicts worldwide end-user spending on the public cloud will total USD 679 billion and is projected to exceed USD 1 trillion in 2027 (link resides outside ibm.com).
The following are a few of the most integral components of today’s modern cloud computing architecture.
CSPs own and operate remote data centers that house physical or bare metal servers , cloud storage systems and other physical hardware that create the underlying infrastructure and provide the physical foundation for cloud computing.
In cloud computing, high-speed networking connections are crucial. Typically, an internet connection known as a wide-area network (WAN) connects front-end users (for example, client-side interface made visible through web-enabled devices) with back-end functions (for example, data centers and cloud-based applications and services). Other advanced cloud computing networking technologies, including load balancers , content delivery networks (CDNs) and software-defined networking (SDN) , are also incorporated to ensure data flows quickly, easily and securely between front-end users and back-end resources.
Cloud computing relies heavily on the virtualization of IT infrastructure —servers, operating system software, networking and other infrastructure that’s abstracted using special software so that it can be pooled and divided irrespective of physical hardware boundaries. For example, a single hardware server can be divided into multiple virtual servers . Virtualization enables cloud providers to make maximum use of their data center resources.
IaaS (Infrastructure-as-a-Service), PaaS (Platform-as-a-Service), SaaS (Software-as-a-Service) and serverless computing are the most common models of cloud services, and it’s not uncommon for an organization to use some combination of all four.
IaaS (Infrastructure-as-a-Service) provides on-demand access to fundamental computing resources—physical and virtual servers, networking and storage—over the internet on a pay-as-you-go basis. IaaS enables end users to scale and shrink resources on an as-needed basis, reducing the need for high up-front capital expenditures or unnecessary on-premises or "owned" infrastructure and for overbuying resources to accommodate periodic spikes in usage.
According to a Business Research Company report (link resides outside ibm.com), the IaaS market is predicted to grow rapidly in the next few years, growing to $212.34 billion in 2028 at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 14.2%.
PaaS (Platform-as-a-Service) provides software developers with an on-demand platform—hardware, complete software stack, infrastructure and development tools—for running, developing and managing applications without the cost, complexity and inflexibility of maintaining that platform on-premises. With PaaS, the cloud provider hosts everything at their data center. These include servers, networks, storage, operating system software, middleware and databases. Developers simply pick from a menu to spin up servers and environments they need to run, build, test, deploy, maintain, update and scale applications.
Today, PaaS is typically built around container s , a virtualized compute model one step removed from virtual servers. Containers virtualize the operating system, enabling developers to package the application with only the operating system services it needs to run on any platform without modification and the need for middleware.
Red Hat® OpenShift ® is a popular PaaS built around Docker containers and Kubernetes , an open source container orchestration solution that automates deployment, scaling, load balancing and more for container-based applications.
SaaS (Software-as-a-Service) , also known as cloud-based software or cloud applications, is application software hosted in the cloud. Users access SaaS through a web browser, a dedicated desktop client or an API that integrates with a desktop or mobile operating system. Cloud service providers offer SaaS based on a monthly or annual subscription fee. They may also provide these services through pay-per-usage pricing.
In addition to the cost savings, time-to-value and scalability benefits of cloud, SaaS offers the following:
- Automatic upgrades: With SaaS, users use new features when the cloud service provider adds them without orchestrating an on-premises upgrade.
- Protection from data loss: Because SaaS stores application data in the cloud with the application, users don’t lose data if their device crashes or breaks.
SaaS is the primary delivery model for most commercial software today. Hundreds of SaaS solutions exist, from focused industry and broad administrative (for example, Salesforce) to robust enterprise database and artificial intelligence (AI) software. According to an International Data Center (IDC) survey (the link resides outside IBM), SaaS applications represent the largest cloud computing segment, accounting for more than 48% of the $778 billion worldwide cloud software revenue.
Serverless computing , or simply serverless, is a cloud computing model that offloads all the back-end infrastructure management tasks, including provisioning, scaling, scheduling and patching to the cloud provider. This frees developers to focus all their time and effort on the code and business logic specific to their applications.
Moreover, serverless runs application code on a per-request basis only and automatically scales the supporting infrastructure up and down in response to the number of requests. With serverless, customers pay only for the resources used when the application runs; they never pay for idle capacity.
FaaS, or Function-as-a-Service , is often confused with serverless computing when, in fact, it’s a subset of serverless. FaaS allows developers to run portions of application code (called functions) in response to specific events. Everything besides the code—physical hardware, virtual machine (VM) operating system and web server software management—is provisioned automatically by the cloud service provider in real-time as the code runs and is spun back down once the execution is complete. Billing starts when execution starts and stops when execution stops.
A public cloud is a type of cloud computing in which a cloud service provider makes computing resources available to users over the public internet. These include SaaS applications, individual virtual machines (VMs) , bare metal computing hardware, complete enterprise-grade infrastructures and development platforms. These resources might be accessible for free or according to subscription-based or pay-per-usage pricing models.
The public cloud provider owns, manages and assumes all responsibility for the data centers, hardware and infrastructure on which its customers’ workloads run. It typically provides high-bandwidth network connectivity to ensure high performance and rapid access to applications and data.
Public cloud is a multi-tenant environment where all customers pool and share the cloud provider’s data center infrastructure and other resources. In the world of the leading public cloud vendors, such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud, IBM Cloud®, Microsoft Azure and Oracle Cloud, these customers can number in the millions.
Most enterprises have moved portions of their computing infrastructure to the public cloud since public cloud services are elastic and readily scalable, flexibly adjusting to meet changing workload demands. The promise of greater efficiency and cost savings through paying only for what they use attracts customers to the public cloud. Still, others seek to reduce spending on hardware and on-premises infrastructure. Gartner predicts (link resides outside ibm.com) that by 2026, 75% of organizations will adopt a digital transformation model predicated on cloud as the fundamental underlying platform.
A private cloud is a cloud environment where all cloud infrastructure and computing resources are dedicated to one customer only. Private cloud combines many benefits of cloud computing—including elasticity, scalability and ease of service delivery—with the access control, security and resource customization of on-premises infrastructure.
A private cloud is typically hosted on-premises in the customer’s data center. However, it can also be hosted on an independent cloud provider’s infrastructure or built on rented infrastructure housed in an offsite data center.
Many companies choose a private cloud over a public cloud environment to meet their regulatory compliance requirements. Entities like government agencies, healthcare organizations and financial institutions often opt for private cloud settings for workloads that deal with confidential documents, personally identifiable information (PII), intellectual property, medical records, financial data or other sensitive data.
By building private cloud architecture according to cloud-native principles, an organization can quickly move workloads to a public cloud or run them within a hybrid cloud (see below) environment whenever ready.
A hybrid cloud is just what it sounds like: a combination of public cloud, private cloud and on-premises environments. Specifically (and ideally), a hybrid cloud connects a combination of these three environments into a single, flexible infrastructure for running the organization’s applications and workloads.
At first, organizations turned to hybrid cloud computing models primarily to migrate portions of their on-premises data into private cloud infrastructure and then connect that infrastructure to public cloud infrastructure hosted off-premises by cloud vendors. This process was done through a packaged hybrid cloud solution like Red Hat® OpenShift® or middleware and IT management tools to create a " single pane of glass ." Teams and administrators rely on this unified dashboard to view their applications, networks and systems.
Today, hybrid cloud architecture has expanded beyond physical connectivity and cloud migration to offer a flexible, secure and cost-effective environment that supports the portability and automated deployment of workloads across multiple environments. This feature enables an organization to meet its technical and business objectives more effectively and cost-efficiently than with a public or private cloud alone. For instance, a hybrid cloud environment is ideal for DevOps and other teams to develop and test web applications. This frees organizations from purchasing and expanding the on-premises physical hardware needed to run application testing, offering faster time to market. Once a team has developed an application in the public cloud, they may move it to a private cloud environment based on business needs or security factors.
A public cloud also allows companies to quickly scale resources in response to unplanned spikes in traffic without impacting private cloud workloads, a feature known as cloud bursting. Streaming channels like Amazon use cloud bursting to support the increased viewership traffic when they start new shows.
Most enterprise organizations today rely on a hybrid cloud model because it offers greater flexibility, scalability and cost optimization than traditional on-premises infrastructure setups. According to the IBM Transformation Index: State of Cloud , more than 77% of businesses and IT professionals have adopted a hybrid cloud approach.
To learn more about the differences between public, private and hybrid cloud, check out “ Public cloud vs. private cloud vs. hybrid cloud: What’s the difference? ”
Watch the IBM hybrid cloud architecture video series.
Multicloud uses two or more clouds from two or more different cloud providers. A multicloud environment can be as simple as email SaaS from one vendor and image editing SaaS from another. But when enterprises talk about multicloud, they typically refer to using multiple cloud services—including SaaS, PaaS and IaaS services—from two or more leading public cloud providers.
Organizations choose multicloud to avoid vendor lock-in, to have more services to select from and to access more innovation. With multicloud, organizations can choose and customize a unique set of cloud features and services to meet their business needs. This freedom of choice includes selecting “best-of-breed” technologies from any CSP, as needed or as they emerge, rather than being locked into offering from a single vendor. For example, an organization may choose AWS for its global reach with web-hosting, IBM Cloud for data analytics and machine learning platforms and Microsoft Azure for its security features.
A multicloud environment also reduces exposure to licensing, security and compatibility issues that can result from " shadow IT "— any software, hardware or IT resource used on an enterprise network without the IT department’s approval and often without IT’s knowledge or oversight.
Today, most enterprise organizations use a hybrid multicloud model. Apart from the flexibility to choose the most cost-effective cloud service, hybrid multicloud offers the most control over workload deployment, enabling organizations to operate more efficiently, improve performance and optimize costs. According to an IBM® Institute for Business Value study , the value derived from a full hybrid multicloud platform technology and operating model at scale is two-and-a-half times the value derived from a single-platform, single-cloud vendor approach.
Yet the modern hybrid multicloud model comes with more complexity. The more clouds you use—each with its own management tools, data transmission rates and security protocols—the more difficult it can be to manage your environment. With over 97% of enterprises operating on more than one cloud and most organizations running 10 or more clouds , a hybrid cloud management approach has become crucial. Hybrid multicloud management platforms provide visibility across multiple provider clouds through a central dashboard where development teams can see their projects and deployments, operations teams can monitor clusters and nodes and the cybersecurity staff can monitor for threats.
Learn more about hybrid cloud management.
Traditionally, security concerns have been the primary obstacle for organizations considering cloud services, mainly public cloud services. Maintaining cloud security demands different procedures and employee skillsets than in legacy IT environments. Some cloud security best practices include the following:
- Shared responsibility for security: Generally, the cloud service provider is responsible for securing cloud infrastructure, and the customer is responsible for protecting its data within the cloud. However, it’s also essential to clearly define data ownership between private and public third parties.
- Data encryption: Data should be encrypted while at rest, in transit and in use. Customers need to maintain complete control over security keys and hardware security modules.
- Collaborative management: Proper communication and clear, understandable processes between IT, operations and security teams will ensure seamless cloud integrations that are secure and sustainable.
- Security and compliance monitoring: This begins with understanding all regulatory compliance standards applicable to your industry and establishing active monitoring of all connected systems and cloud-based services to maintain visibility of all data exchanges across all environments, on-premises, private cloud, hybrid cloud and edge.
Cloud security is constantly changing to keep pace with new threats. Today’s CSPs offer a wide array of cloud security management tools, including the following:
- Identity and access management (IAM): IAM tools and services that automate policy-driven enforcement protocols for all users attempting to access both on-premises and cloud-based services.
- Data loss prevention (DLP): DLP services that combine remediation alerts data encryption and other preventive measures to protect all stored data, whether at rest or in motion.
- Security information and event management (SIEM) : SIEM is a comprehensive security orchestration solution that automates threat monitoring, detection and response in cloud-based environments. SIEM technology uses artificial intelligence (AI)-driven technologies to correlate log data across multiple platforms and digital assets. This allows IT teams to successfully apply their network security protocols, enabling them to react to potential threats quickly.
- Automated data compliance platforms: Automated software solutions provide compliance controls and centralized data collection to help organizations adhere to regulations specific to their industry. Regular compliance updates can be baked into these platforms so organizations can adapt to ever-changing regulatory compliance standards.
Learn more about cloud security.
Sustainability in business , a company’s strategy to reduce negative environmental impact from their operations in a particular market, has become an essential corporate governance mandate. Moreover, Gartner predicts (link resides outside ibm.com) that by 2025, the carbon emissions of hyperscale cloud services will be a top-three criterion in cloud purchase decisions.
As companies strive to advance their sustainability objectives, cloud computing has evolved to play a significant role in helping them reduce their carbon emissions and manage climate-related risks. For instance, traditional data centers require power supplies and cooling systems, which depend on large amounts of electrical power. By migrating IT resources and applications to the cloud, organizations only enhance operational and cost efficiencies and boost overall energy efficiency through pooled CSP resources.
All major cloud players have made net-zero commitments to reduce their carbon footprints and help clients reduce the energy they typically consume using an on-premises setup. For instance, IBM is driven by sustainable procurement initiatives to reach NetZero by 2030. By 2025, IBM Cloud worldwide data centers will comprise energy procurement drawn from 75% renewable sources .
According to an International Data Corporation (IDC) forecast (link resides outside ibm.com), worldwide spending on the whole cloud opportunity (offerings, infrastructure and services) will surpass USD 1 trillion in 2024 while sustaining a double-digit compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 15.7%. Here are some of the main ways businesses are benefitting from cloud computing:
- Scale infrastructure: Allocate resources up or down quickly and easily in response to changes in business demands.
- Enable business continuity and disaster recovery: Cloud computing provides cost-effective redundancy to protect data against system failures and the physical distance required to apply disaster recovery strategies and recover data and applications during a local outage or disaster. All of the major public cloud providers offer Disaster-Recovery-as-a-Service (DRaaS) .
- Build and test cloud-native applications : For development teams adopting Agile, DevOps or DevSecOps to streamline development, the cloud offers on-demand end-user self-service that prevents operations tasks, such as spinning up development and test servers, from becoming development bottlenecks.
- Support edge and IoT environments: Address latency challenges and reduce downtime by bringing data sources closer to the edge . Support Internet of Things (IoT) devices (for example, patient monitoring devices and sensors on a production line) to gather real-time data.
- Leverage cutting-edge technologies: Cloud computing supports storing and processing huge volumes of data at high speeds—much more storage and computing capacity than most organizations can or want to purchase and deploy on-premises. These high-performance resources support technologies like blockchain , quantum computing and large language models (LLMs ) that power generative AI platforms like customer service automation.
Create a no-charge IBM Cloud account and access more than 40 always-free products in cloud and AI.
IBM Cloud for VMware Solutions enables you to seamlessly migrate and modernize VMware workloads to the cloud, allowing you to leverage your existing investments for a consistent VMware experience—retaining the same level of access, security and control.
Let IBM Cloud manage your infrastructure while you manage your environment. Pay only for what you use.
Tackle large-scale, compute-intensive challenges and speed time to insight with hybrid cloud HPC solutions.
An industry-specific cloud, built to support your unique modernization and AI transformation needs.
Hybrid cloud integrates public cloud services, private cloud services and on-premises infrastructure into a single distributed computing environment.
DevOps speeds delivery of higher quality software by combining and automating the work of software development and IT operations teams.
Cloud migration is the process of relocating an organization’s data, applications, and workloads to a cloud infrastructure.
Although cloud computing is only a different way to deliver computer resources rather than a new technology, it has sparked a revolution in the way organizations provide information and service.
Determining the best cloud computing architecture for enterprise business is critical for overall success. That’s why it is essential to compare the different functionalities of private cloud versus public cloud versus hybrid cloud.
We're excited to introduce a three-part lightboarding video series that will delve into the world of hybrid cloud architecture. In this intro video, our guide, Sai Vennam, lays out the three major hybrid cloud architecture issues that we're going to cover: Connectivity, Modernization and Security.
Designed for industry, security and the freedom to build and run anywhere, IBM Cloud is a full stack cloud platform with over 170 products and services covering data, containers, AI, IoT and blockchain. Use IBM Cloud to build scalable infrastructure at a lower cost, deploy new applications instantly and scale up workloads based on demand.
Got any suggestions?
We want to hear from you! Send us a message and help improve Slidesgo
Top searches
Trending searches

11 templates

66 templates

teacher appreciation

9 templates

memorial day
12 templates

pediatrician
27 templates
Sky Clouds Presentation
Free google slides theme, powerpoint template, and canva presentation template.
Feel free as a bird plowing through the sky with this wonderful template! Learn the difference between the types of clouds and relax observing the beautiful design of this template!
This theme is based on a multi-purpose structure. The backgrounds look like a lilac sky, displaying clouds in purple, blue and orange hues. We have added flat illustrations of a hot air balloon, a skydiver and a light aircraft. The slab title typography is smart and shows round strokes, which combines with the softness of the template.
Features of this template
- A delicate template that looks like a dusk sky
- 100% editable and easy to modify
- 33 different slides to impress your audience
- Contains easy-to-edit graphics, maps and mockups
- Includes 500+ icons and Flaticon’s extension for customizing your slides
- Designed to be used in Google Slides, Canva, and Microsoft PowerPoint
- 16:9 widescreen format suitable for all types of screens
- Includes information about fonts, colors, and credits of the free resources used
How can I use the template?
Am I free to use the templates?
How to attribute?
Attribution required If you are a free user, you must attribute Slidesgo by keeping the slide where the credits appear. How to attribute?
Related posts on our blog.

How to Add, Duplicate, Move, Delete or Hide Slides in Google Slides

How to Change Layouts in PowerPoint

How to Change the Slide Size in Google Slides
Related presentations.

Premium template
Unlock this template and gain unlimited access

- Español – América Latina
- Português – Brasil
What is Cloud Storage?
Cloud Storage is a mode of computer data storage in which digital data is stored on servers in off-site locations. The servers are maintained by a third-party provider who is responsible for hosting, managing, and securing data stored on its infrastructure. The provider ensures that data on its servers is always accessible via public or private internet connections.
Cloud Storage enables organizations to store, access, and maintain data so that they do not need to own and operate their own data centers, moving expenses from a capital expenditure model to operational. Cloud Storage is scalable, allowing organizations to expand or reduce their data footprint depending on need.
Google Cloud provides a variety of scalable options for organizations to store their data in the cloud. Learn more about Cloud Storage at Google Cloud .
How does Cloud Storage work?
Cloud Storage uses remote servers to save data, such as files, business data, videos, or images. Users upload data to servers via an internet connection, where it is saved on a virtual machine on a physical server. To maintain availability and provide redundancy, cloud providers will often spread data to multiple virtual machines in data centers located across the world. If storage needs increase, the cloud provider will spin up more virtual machines to handle the load. Users can access data in Cloud Storage through an internet connection and software such as web portal, browser, or mobile app via an application programming interface (API).
Cloud Storage is available in four different models:
Public Cloud Storage is a model where an organization stores data in a service provider’s data centers that are also utilized by other companies. Data in public Cloud Storage is spread across multiple regions and is often offered on a subscription or pay-as-you-go basis. Public Cloud Storage is considered to be “elastic” which means that the data stored can be scaled up or down depending on the needs of the organization. Public cloud providers typically make data available from any device such as a smartphone or web portal.
Private Cloud Storage is a model where an organization utilizes its own servers and data centers to store data within their own network. Alternatively, organizations can deal with cloud service providers to provide dedicated servers and private connections that are not shared by any other organization. Private clouds are typically utilized by organizations that require more control over their data and have stringent compliance and security requirements.
A hybrid cloud model is a mix of private and public cloud storage models. A hybrid cloud storage model allows organizations to decide which data it wants to store in which cloud. Sensitive data and data that must meet strict compliance requirements may be stored in a private cloud while less sensitive data is stored in the public cloud. A hybrid cloud storage model typically has a layer of orchestration to integrate between the two clouds. A hybrid cloud offers flexibility and allows organizations to still scale up with the public cloud if need arises.
A multicloud storage model is when an organization sets up more than one cloud model from more than one cloud service provider (public or private). Organizations might choose a multicloud model if one cloud vendor offers certain proprietary apps, an organization requires data to be stored in a specific country, various teams are trained on different clouds, or the organization needs to serve different requirements that are not stated in the servicers’ Service Level Agreements. A multicloud model offers organizations flexibility and redundancy.
Advantages of Cloud Storage
Total cost of ownership.
Cloud Storage enables organizations to move from a capital expenditure to an operational expenditure model, allowing them to adjust budgets and resources quickly.
Cloud Storage is elastic and scalable, meaning that it can be scaled up (more storage added) or down (less storage needed) depending on the organization’s needs.
Flexibility
Cloud Storage offers organizations flexibility on how to store and access data, deploy and budget resources, and architect their IT infrastructure.
Most cloud providers offer robust security, including physical security at data centers and cutting edge security at the software and application levels. The best cloud providers offer zero trust architecture , identity and access management , and encryption .
Sustainability
One of the greatest costs when operating on-premises data centers is the overhead of energy consumption. The best cloud providers operate on sustainable energy through renewable resources.
Redundancy (replicating data on multiple servers in different locations) is an inherent trait in public clouds, allowing organizations to recover from disasters while maintaining business continuity.
Disadvantages of Cloud Storage
Certain industries such as finance and healthcare have stringent requirements about how data is stored and accessed. Some public cloud providers offer tools to maintain compliance with applicable rules and regulations.
Traffic to and from the cloud can be delayed because of network traffic congestion or slow internet connections.
Storing data in public clouds relinquishes some control over access and management of that data, entrusting that the cloud service provider will always be able to make that data available and maintain its systems and security.
While public cloud providers aim to ensure continuous availability, outages sometimes do occur, making stored data unavailable.
How to use Cloud Storage
Cloud Storage provides several use cases that can benefit individuals and organizations. Whether a person is storing their family budget on a spreadsheet, or a massive organization is saving years of financial data in a highly secure database, Cloud Storage can be used for saving digital data of all kinds for as long as needed.
Data backup is one of the simplest and most prominent uses of Cloud Storage. Production data can be separated from backup data, creating a gap between the two that protects organizations in the case of a cyber threat such as ransomware. Data backup through Cloud Storage can be as simple as saving files to a digital folder such as Google Drive or using block storage to maintain gigabytes or more of important business data.
The ability to archive old data has become an important aspect of Cloud Storage, as organizations move to digitize decades of old records, as well as hold on to records for governance and compliance purposes. Google Cloud offers several tiers of storage for archiving data, including coldline storage and archival storage , that can be accessed whenever an organization needs them.
Disaster recovery
A disaster—natural or otherwise— that wipes out a data center or old physical records needs not be the business-crippling event that it was in the past. Cloud Storage allows for disaster recovery so that organizations can continue with their business, even when times are tough.
Data processing
As Cloud Storage makes digital data immediately available, data becomes much more useful on an ongoing basis. Data processing, such as analyzing data for business intelligence or applying machine learning and artificial intelligence to large datasets, is possible because of Cloud Storage.
Content delivery
With the ability to save copies of media data, such as large audio and video files, on servers dispersed across the globe, media and entertainment companies can serve their audience low-latency, always available content from wherever they reside.
Types of Cloud Storage
Cloud Storage comes in three different types: object , file , and block .
Object storage is a data storage architecture for large stores of unstructured data. It designates each piece of data as an object, keeps it in a separate storehouse, and bundles it with metadata and a unique identifier for easy access and retrieval.
File storage organizes data in a hierarchical format of files and folders. File storage is common in personal computing where data is saved as files and those files are organized in folders. File storage makes it easy to locate and retrieve individual data items when they are needed. File storage is most often used in directories and data repositories.
Block storage breaks data into blocks, each with an unique identifier, and then stores those blocks as separate pieces on the server. The cloud network stores those blocks wherever it is most efficient for the system. Block storage is best used for large volumes of data that require low latency such as workloads that require high performance or databases.
Related products and services
Google Cloud offers a variety of products and services to help organizations make the most of cloud storage.
By using Google Cloud, organizations are using the most sustainable cloud in the business, with the most robust artificial intelligence and machine learning solutions.
Take the next step
Start building on Google Cloud with $300 in free credits and 20+ always free products.
Start your next project, explore interactive tutorials, and manage your account.
- Need help getting started? Contact sales
- Work with a trusted partner Find a partner
- Continue browsing See all products
- Get tips & best practices See tutorials

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
There are 3 main types of clouds: Cirrus or thin feathery clouds Stratus or layered clouds Cumulus or fluffy clouds Cirrus Clouds Are the most common of the high clouds. They are composed of ice and are thin, wispy clouds blown in high winds into long streamers. Cirrus clouds are usually white and predict fair to pleasant weather.
Let's take a quick look at the 4 main types of clouds. The four main types of clouds are: Cumulus clouds: These are white, fluffy clouds that often have flat bottoms and rounded tops. They are associated with fair weather but can also indicate a thunderstorm if they grow taller and darker. Stratus clouds: These are low-lying clouds that form ...
A cloud forms when air is heated by the sun. As it rises, it slowly cools it reaches the saturation point and water condenses, forming a cloud. As long as the cloud and the air that its made of is warmer than the outside air around it, it will float. Why do clouds float? 6 Clouds get their names in two ways: altitude and shape.
2. Learn about types of clouds. Read the list below to learn about the different types of clouds, what they look like and where they appear in the sky. Or download and print out this chart (also available en Español) High Altitude. Cirrocumulus - High clouds with a puffy, patchy appearance and small spaces between clouds. Often form wave ...
Well, now they can learn just what they're looking at with this brilliant Second Level, types of clouds PowerPoint! It's a great resource to support your people, place and environment teaching. In this resource, you'll find an introduction to cirrus, cumulus, stratus, nimbostratus and cumulonimbus clouds.
The main three types of cloud computing are public cloud, private cloud, and hybrid cloud. Within these deployment models, there are four main services: infrastructure as a service (IaaS), platform as a service (PaaS), software as a service (SaaS), and serverless computing. The type of cloud deployment model and cloud service model you choose ...
A fully editable 16 slide PowerPoint presentation on different types of clouds. Includes a bonus activity sheet and word search. How clouds form. How clouds are classified. 2 Embedded videos cloud formation and cloud spotting. Activity sheet with word puzzle, labelling activity and gap fill. Cloud types word search.
PowerPoint Presentation with Audio: PowerPoint: Different Types of Clouds Overview PowerPoint presentation with audio about the different types of clouds (upper elementary). Includes 14 slides with colorful images, simple text and audio. Media PPTX. Free Download Resource Tags.
This PowerPoint introduces children about the four main types of cloud: cirrus, cumulus, stratus and nimbus. Designed by teachers to make information about clouds more accessible to children, this PowerPoint shows kids how to recognise different cloud types. It includes photographs of each cloud type as well as an explanation of what they look ...
Well, now they can learn just what they're looking at with this brilliant Second Level, types of clouds PowerPoint! It's a great resource to support your people, place and environment teaching. In this resource, you'll find an introduction to cirrus, cumulus, stratus, nimbostratus and cumulonimbus clouds.
The four main types of clouds are: Cumulus clouds: These are white, fluffy clouds that often have flat bottoms and rounded tops. They are associated with fair weather but can also indicate a thunderstorm if they grow taller and darker. Stratus clouds: These are low-lying clouds that form a flat, uniform layer.
The 4 different types of clouds are: Cirrus - Made up of ice crystals, 18,000 feet in the sky there are the highest form of cloud and look like paintbrush strokes across the sky. Cumulus - A pile of fluffy clouds that do not produce any rain or snow and only appear on a sunny day.
Presentation Transcript. Different Types of Clouds Ms. Felicia Fratto Fifth Grade Science. Objectives • Students will understand how clouds form. • Students will be able to identify the three basic cloud types. • Students will understand the prefixes and suffixes used with cloud vocabulary.
Additionally, it incorporates the different types of cloud storage services and the various uses for cloud storage, such as data backup and recovery, software testing and development, compliance, big data, and data lakes. Lastly, the Cloud Storage PPT addresses data transfer to the cloud and data backup strategies. Get immediate access.
Cumulus • Puffy white or light gray clouds that look like floating cotton balls. • Cumulus clouds have sharp outlines and a flat base. • Seeing cumulus clouds in the sky can mean the weather will be good or bad. Cumulonimbus • Known as thunderstorm clouds. • Can grow up to 10km high.
Cloud computing defined. Cloud computing is the on-demand availability of computing resources (such as storage and infrastructure), as services over the internet. It eliminates the need for individuals and businesses to self-manage physical resources themselves, and only pay for what they use. The main cloud computing service models include ...
Cloud computing is the on-demand access of computing resources—physical servers or virtual servers, data storage, networking capabilities, application development tools, software, AI-powered analytic tools and more—over the internet with pay-per-use pricing. The cloud computing model offers customers greater flexibility and scalability ...
Canva is a cloud-based app. Presentations can be seen on any device. Available to Create on Multiple Devices. ... In this guide, you learned about 15 different types of presentation software and we gave you a checklist to help you decide.
Free Google Slides theme, PowerPoint template, and Canva presentation template. Feel free as a bird plowing through the sky with this wonderful template! Learn the difference between the types of clouds and relax observing the beautiful design of this template! This theme is based on a multi-purpose structure. The backgrounds look like a lilac ...
Cloud Storage comes in three different types: object, file, and block. Object . Object storage is a data storage architecture for large stores of unstructured data. It designates each piece of data as an object, keeps it in a separate storehouse, and bundles it with metadata and a unique identifier for easy access and retrieval.