- Grades 6-12
- School Leaders
Have You Seen Our List of Favorite Graphic Novels?

50 of the Best Quotes About Education
Learn as if you were to live forever.

Being an educator is not always the easiest job, but knowing you have made an impact on students’ lives can be so rewarding. Through all of the good times and bad, you continue to persevere and provide education to students of all backgrounds and abilities. We collected 50 of the best quotes about education to celebrate the best parts of teaching, learning, and the impact they have on the world.
Our Favorite Quotes About Education
“education is our passport to the future, for tomorrow belongs only to the people who prepare for it today.” — malcolm x.

“Education is one thing no one can take away from you.” — Elin Nordegren

“Education’s purpose is to replace an empty mind with an open one.” — Malcolm Forbes

“The whole purpose of education is to turn mirrors into windows.” — Sydney J. Harris

“Learning is not attained by chance, it must be sought for with ardor and attended to with diligence.” — Abigail Adams

“An investment in knowledge pays the best interest.” — Benjamin Franklin

“Education is the most powerful weapon which you can use to change the world.” — Nelson Mandela

“The function of education is to teach one to think intensively and to think critically. … Intelligence plus character—that is the goal of true education.” — Martin Luther King Jr.

“A person who won’t read has no advantage over a person who can’t read.” — Mark Twain

“Education is not the filling of a pail but the lighting of a fire.” — Unknown

“Education is the key to unlock a golden door of freedom.” — George Washington Carver

“The great aim of education is not knowledge but action.” — Herbert Spencer

“The goal of education is the advancement of knowledge and the dissemination of truth.” — John F. Kennedy

“The great difficulty in education is to get experience out of ideas.” — George Santayana

“The roots of education … are bitter, but the fruit is sweet.” — Aristotle

“Education must not simply teach work, it must teach Life.” — W.E.B Du Bois

“Education then, beyond all other devices of human origin, is the great equalizer of the conditions of men, the balance-wheel of the social machinery.” — Horace Mann

“I believe that education is all about being excited about something. Seeing passion and enthusiasm helps push an educational message.” — Steve Irwin

“Everyone who remembers his own education remembers teachers, not methods and techniques. The teacher is the heart of the educational system.” — Sidney Hook

“All real education is the architecture of the soul.” — William Bennett

“Education is the key which will unlock the door of opportunity for you.” — Gordon B. Hinckley

“I did then what I knew how to do. Now that I know better, I do better.” — Maya Angelou

“Everyone you will ever meet knows something you don’t.” — Bill Nye

“The highest result of education is tolerance.” — Helen Keller

“Educating the mind without educating the heart is no education at all.” — Aristotle

“To teach is to learn twice.” — Joseph Joubert

“The mind is not a vessel to be filled, but a fire to be kindled.” — Plutarch

“Tell me and I forget. Teach me and I remember. Involve me and I learn.” — Benjamin Franklin

“Education breeds confidence. Confidence breeds hope. Hope breeds peace.” — Confucius

“The art of teaching is the art of assisting discovery.” — Mark Van Doren

“Children must be taught how to think, not what to think.” — Margaret Mead

“Anyone who stops learning is old, whether at twenty or eighty. Anyone who keeps learning stays young.” — Henry Ford

“A teacher affects eternity; he can never tell where his influence stops.” — Henry Brooks Adams

“They may forget what you said but they will never forget how you made them feel.” — Carl W. Buehner

“A good teacher must be able to put himself in the place of those who find learning hard.” — Eliphas Levi

“One child, one teacher, one book, and one pen can change the world.” — Malala Yousafzai

“Teachers are the one and only people who save nations.” — Mustafa Kemal Atatürk

“Self-education is, I firmly believe, the only kind of education there is.” — Isaac Asimov

“Real education must ultimately be limited to one who INSISTS on knowing, the rest is mere sheep-herding.” — Ezra Pound

“Education is for improving the lives of others and for leaving your community and world better than you found it.” — Marian Wright Edelman

“It is only the ignorant who despise education.” — Publilius Syrus

“A writer should get as much education as possible, but just going to school is not enough; if it were, all owners of doctorates would be inspired writers.” — Gwendolyn Brooks

“I do not want art for a few, any more than education for a few, or freedom for a few.” — William Morris

“Real education should educate us out of self into something far finer; into a selflessness which links us with all humanity.” — Nancy Astor

“It makes little difference how many university courses or degrees a person may own. If he cannot use words to move an idea from one point to another, his education is incomplete.” — Norman Cousins

“The child who desires education will be bettered by it; the child who dislikes it disgraced.” — John Ruskin

“Education is our only political safety. Outside of this ark all is deluge.” — Horace Mann

“Education is learning what you didn’t even know you didn’t know.” — Daniel J. Boorstin
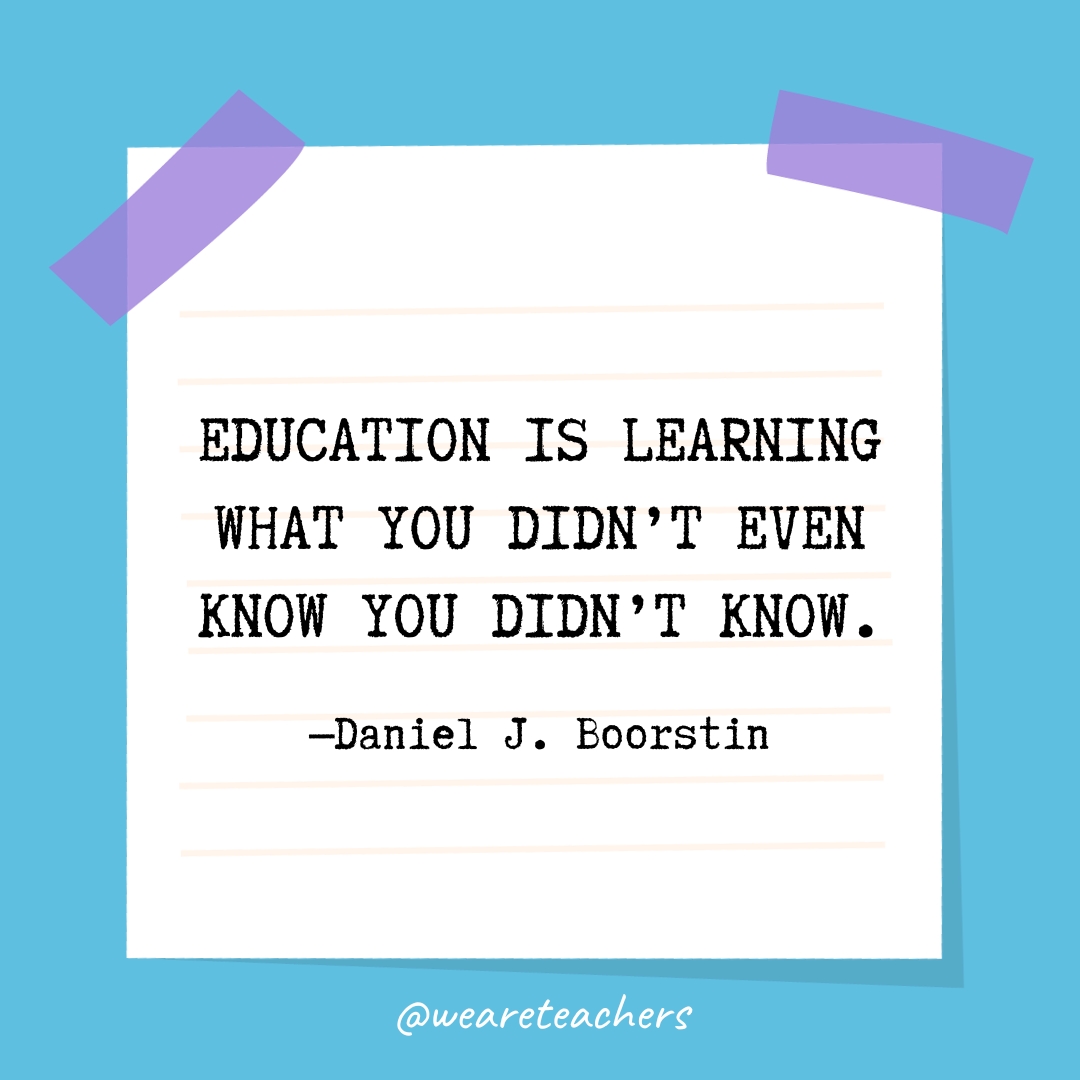
“Instruction ends in the schoolroom, but education ends only with life. A child is given to the universe to be educated.” — Frederick William Robertson

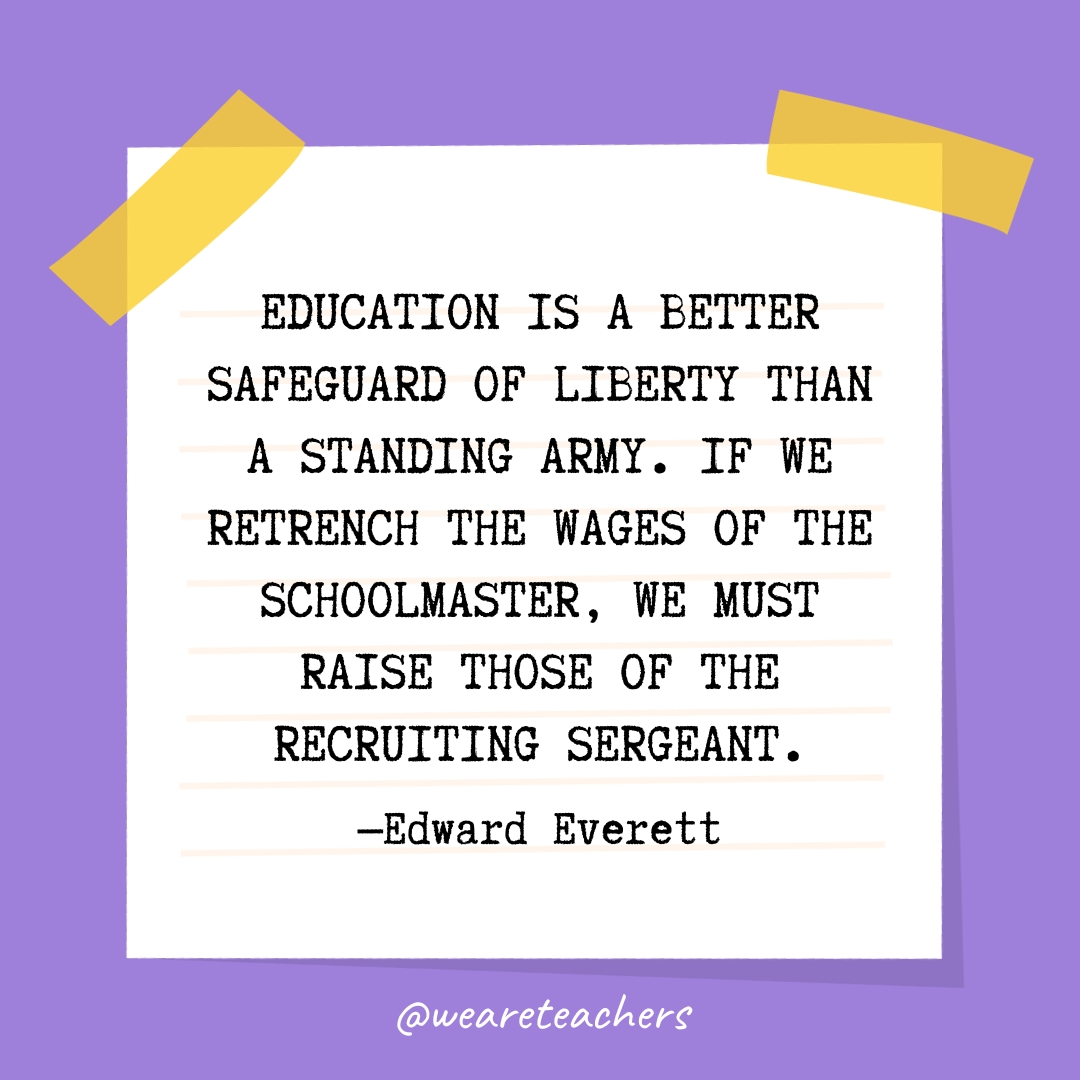
“Education is a better safeguard of liberty than a standing army. If we retrench the wages of the schoolmaster, we must raise those of the recruiting sergeant.” — Edward Everett
Like these quotes about education? Check out these team-building quotes for classrooms and schools .
Come share your favorite motivational quotes about education in the we are teachers helpline group on facebook .

You Might Also Like

64 Inspirational Quotes for Teachers To Brighten Your Day
Because teachers make the world a better place. Continue Reading
Copyright © 2024. All rights reserved. 5335 Gate Parkway, Jacksonville, FL 32256

Home > Blog > Tips for Online Students > Top 8 Reasons Why Education is the Key to Success
Higher Education News , Tips for Online Students , Tips for Students
Top 8 Reasons Why Education is the Key to Success
Updated: June 19, 2024
Published: April 19, 2019

You may have heard the saying that education is the key to success, but it’s really true. In fact, there are eight solid reasons to believe that pursuing education beyond your high school degree in the 21st century will make you more attractive to potential employers and ultimately become more successful.


1. Education gives you the skills that companies are looking for
As you progress through a college degree, you’ll learn how to manage your time; how to juggle several tasks at the same time, how to interact with all kinds of people, and new skills that companies are looking for now. At the University of the People (UoPeople), for example, faculty come from all over the globe and are prepared to teach those cutting-edge skills that companies are seeking as they look for new hires who will carry their businesses forward through the 21st century. In short, a real education today means that the institution offering a program of study provides skills that can be applied immediately once the student graduates and becomes part of the workforce
2. You’ll form networks and meet new people
Attending college isn’t just about completing courses and meeting other students. A successful, viable institution of higher learning has partners, affiliates, alumni, and other entities that can become a part of your professional network once you join a university community. Nowadays, when you pursue your education, most universities will show you how to become part of an online community where you have plenty of opportunities to engage with other students, thinkers, degree-seekers, and problem-solvers like yourself.
As you proceed, you’ll gain a clearer sense of your own ideas and values. And when you’re finished with school, you’ll find that businesses in today’s global society are looking for people who know how to be a part of an online community and can communicate the company brand to their clients.

3. You’ll keep up with changing technologies
When you enroll in an academic program offered by University of the People or another accredited university, you engage in learning while using technologies that hiring companies are looking for. You gain valuable digital experience, allowing your education to provide you with the key to success.
4. You’ll define your career interests.
When you pursue an education in a particular degree, you’ll find that you’ll learn more about your professional interests, what you plan to do with your degree, and what the career options are. For instance, your choice of higher education provides you with resources, contacts, networks, and many other influences that allow you to explore the details of your career choice. You’ll have a much clearer notion of what you want to do, what you are capable of doing, and how to get a actually get a job in your field after completing your education.
5. You’ll develop time management skills.
Even if you are pursuing an education full-time, you may still need to work and manage the household budget, along with many other challenges. In short, because life requires that we wear many hats even under the best of circumstances, the process of getting an education automatically makes you focus on honing those coveted time management skills one of the sure-fire keys to success desired by top hiring companies all over the world.
6. You won’t be left out
Up until the first half of the 20th century, societies across the globe were vastly more rural and much less interconnected. Many people only received a minimal education without pursuing a high school degree. Today, times have changed. Digital technologies dominate virtually every aspect of our lives, making it essential to have the basic high school requirements for working with various technologies, communicating with written and verbal skills, and reaching out to others around the globe. However, a high school degree these days is just the minimum you need to consider entering the workforce in most instances. In fact, between 2019 and 2029, most of the jobs available will require a bachelor’s degree .

For all these reasons, acquiring education beyond the high school level is the key to success. We live in an ever-connected society where opportunities and expectations for knowledge and performance increase every day. And that’s why you don’t want to be left behind when there are real resources available to help you succeed. University of the People understands these growing needs and opportunities, and that’s why it makes learning tuition-free and accessible.
To go back to school through a completely online program offered by a US-accredited institution, check out the University of the People’s academic programs ! University of the People offers associate, bachelor, and master’s programs, all of which are online and tuition-free. When it comes to receiving a quality education without the huge price tag, University of the People is for people like you!
In this article
At UoPeople, our blog writers are thinkers, researchers, and experts dedicated to curating articles relevant to our mission: making higher education accessible to everyone. Read More
Why education is the key to development

.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo{-webkit-transition:all 0.15s ease-out;transition:all 0.15s ease-out;cursor:pointer;-webkit-text-decoration:none;text-decoration:none;outline:none;color:inherit;}.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo:hover,.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo[data-hover]{-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;}.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo:focus,.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo[data-focus]{box-shadow:0 0 0 3px rgba(168,203,251,0.5);} Børge Brende
.chakra .wef-9dduvl{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-size:1.25rem;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-9dduvl{font-size:1.125rem;}} Explore and monitor how .chakra .wef-15eoq1r{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-size:1.25rem;color:#F7DB5E;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-15eoq1r{font-size:1.125rem;}} Infrastructure is affecting economies, industries and global issues

.chakra .wef-1nk5u5d{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;color:#2846F8;font-size:1.25rem;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-1nk5u5d{font-size:1.125rem;}} Get involved with our crowdsourced digital platform to deliver impact at scale
Stay up to date:, infrastructure.
Education is a human right. And, like other human rights, it cannot be taken for granted. Across the world, 59 million children and 65 million adolescents are out of school . More than 120 million children do not complete primary education.
Behind these figures there are children and youth being denied not only a right, but opportunities: a fair chance to get a decent job, to escape poverty, to support their families, and to develop their communities. This year, decision-makers will set the priorities for global development for the next 15 years. They should make sure to place education high on the list.
The deadline for the Millennium Development Goals is fast approaching. We have a responsibility to make sure we fulfill the promise we made at the beginning of the millennium: to ensure that boys and girls everywhere complete a full course of primary schooling.
The challenge is daunting. Many of those who remain out of school are the hardest to reach, as they live in countries that are held back by conflict, disaster, and epidemics. And the last push is unlikely to be accompanied by the double-digit economic growth in some developing economies that makes it easier to expand opportunities.
Nevertheless, we can succeed. Over the last 15 years, governments and their partners have shown that political will and concerted efforts can deliver tremendous results – including halving the number of children and adolescents who are out of school. Moreover, most countries are closing in on gender parity at the primary level. Now is the time to redouble our efforts to finish what we started.
But we must not stop with primary education. In today’s knowledge-driven economies, access to quality education and the chances for development are two sides of the same coin. That is why we must also set targets for secondary education, while improving quality and learning outcomes at all levels. That is what the Sustainable Development Goal on education, which world leaders will adopt this year, aims to do.
Addressing the fact that an estimated 250 million children worldwide are not learning the basic skills they need to enter the labor market is more than a moral obligation. It amounts to an investment in sustainable growth and prosperity. For both countries and individuals, there is a direct and indisputable link between access to quality education and economic and social development.
Likewise, ensuring that girls are not kept at home when they reach puberty, but are allowed to complete education on the same footing as their male counterparts, is not just altruism; it is sound economics. Communities and countries that succeed in achieving gender parity in education will reap substantial benefits relating to health, equality, and job creation.
All countries, regardless of their national wealth, stand to gain from more and better education. According to a recent OECD report , providing every child with access to education and the skills needed to participate fully in society would boost GDP by an average 28% per year in lower-income countries and 16% per year in high-income countries for the next 80 years.
Today’s students need “twenty-first-century skills,” like critical thinking, problem solving, creativity, and digital literacy. Learners of all ages need to become familiar with new technologies and cope with rapidly changing workplaces.
According to the International Labour Organization, an additional 280 million jobs will be needed by 2019. It is vital for policymakers to ensure that the right frameworks and incentives are established so that those jobs can be created and filled. Robust education systems – underpinned by qualified, professionally trained, motivated, and well-supported teachers – will be the cornerstone of this effort.
Governments should work with parent and teacher associations, as well as the private sector and civil-society organizations, to find the best and most constructive ways to improve the quality of education. Innovation has to be harnessed, and new partnerships must be forged.
Of course, this will cost money. According to UNESCO, in order to meet our basic education targets by 2030, we must close an external annual financing gap of about $22 billion. But we have the resources necessary to deliver. What is lacking is the political will to make the needed investments.
This is the challenge that inspired Norway to invite world leaders to Oslo for a Summit on Education for Development , where we can develop strategies for mobilizing political support for increasing financing for education. For the first time in history, we are in the unique position to provide education opportunities for all, if only we pull together. We cannot miss this critical opportunity.
To be sure, the responsibility for providing citizens with a quality education rests, first and foremost, with national governments. Aid cannot replace domestic-resource mobilization. But donor countries also have an important role to play, especially in supporting least-developed countries. We must reverse the recent downward trend in development assistance for education, and leverage our assistance to attract investments from various other sources. For our part, we are in the process of doubling Norway’s financial contribution to education for development in the period 2013-2017.
Together, we need to intensify efforts to bring the poorest and hardest to reach children into the education system. Education is a right for everyone. It is a right for girls, just as it is for boys. It is a right for disabled children, just as it is for everyone else. It is a right for the 37 million out-of-school children and youth in countries affected by crises and conflicts. Education is a right regardless of where you are born and where you grow up. It is time to ensure that the right is upheld.
This article is published in collaboration with Project Syndicate . Publication does not imply endorsement of views by the World Economic Forum.
To keep up with the Agenda subscribe to our weekly newsletter .
Author: Erna Solberg is Prime Minister of Norway. Børge Brende is Norway’s Minister of Foreign Affairs.
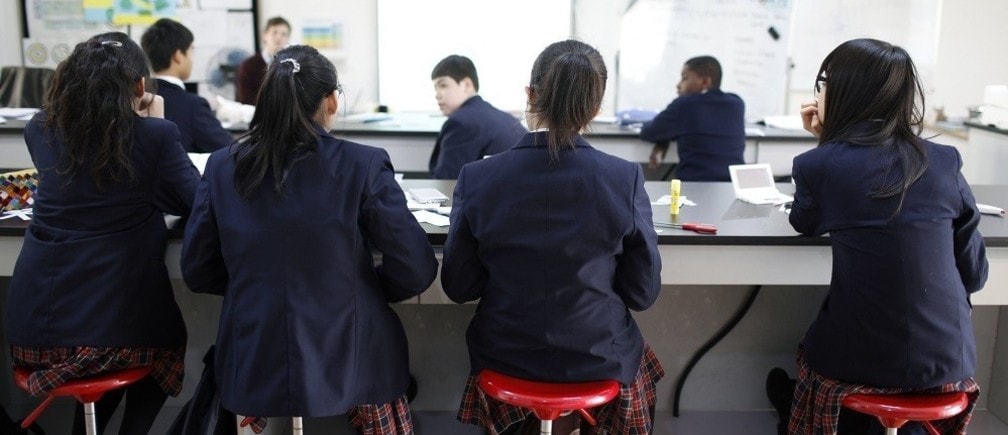
Image: Students attend a class at the Oxford International College in Changzhou. REUTERS/Aly Song.
Share this:
- Share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
Don't miss any update on this topic
Create a free account and access your personalized content collection with our latest publications and analyses.
License and Republishing
World Economic Forum articles may be republished in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International Public License, and in accordance with our Terms of Use.
The views expressed in this article are those of the author alone and not the World Economic Forum.
Related topics:
The agenda .chakra .wef-n7bacu{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-weight:400;} weekly.
A weekly update of the most important issues driving the global agenda
.chakra .wef-1dtnjt5{display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;-webkit-flex-wrap:wrap;-ms-flex-wrap:wrap;flex-wrap:wrap;} More on Economic Growth .chakra .wef-17xejub{-webkit-flex:1;-ms-flex:1;flex:1;justify-self:stretch;-webkit-align-self:stretch;-ms-flex-item-align:stretch;align-self:stretch;} .chakra .wef-zh0r2a{display:-webkit-inline-box;display:-webkit-inline-flex;display:-ms-inline-flexbox;display:inline-flex;white-space:normal;vertical-align:middle;padding-left:0px;padding-right:0px;text-transform:uppercase;font-size:0.75rem;border-radius:0.25rem;font-weight:700;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;line-height:1.2;-webkit-letter-spacing:1.25px;-moz-letter-spacing:1.25px;-ms-letter-spacing:1.25px;letter-spacing:1.25px;background:none;padding:0px;color:#B3B3B3;-webkit-box-decoration-break:clone;box-decoration-break:clone;-webkit-box-decoration-break:clone;}@media screen and (min-width:37.5rem){.chakra .wef-zh0r2a{font-size:0.875rem;}}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-zh0r2a{font-size:1rem;}} See all

Global public debt to exceed $100 trillion, says IMF - plus other economy stories to read this week
Rebecca Geldard
October 21, 2024

Can the European Union get it together on capital markets? This is what’s at stake
John Letzing
October 17, 2024

How the Maldives can revive its economy through sustainable growth
Kanni Wignaraja and Enrico Gaveglia

Can the IMF and World Bank autumn meetings drive global economic recovery?
Alem Tedeneke
October 16, 2024

A framework for advancing data equity in a digital world
JoAnn Stonier, Lauren Woodman, Stephanie Teeuwen and Karla Yee Amezaga

Do we have the workforce for the growth we want?
Mohammad Ali Rashed Lootah, Roselyne Chambrier and Kumi Kitamori
October 15, 2024

- Progress towards quality education was already slower than required before the pandemic, but COVID-19 has had devastating impacts on education, causing learning losses in four out of five of the 104 countries studied.
Without additional measures, an estimated 84 million children and young people will stay out of school by 2030 and approximately 300 million students will lack the basic numeracy and literacy skills necessary for success in life.
In addition to free primary and secondary schooling for all boys and girls by 2030, the aim is to provide equal access to affordable vocational training, eliminate gender and wealth disparities, and achieve universal access to quality higher education.
Education is the key that will allow many other Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) to be achieved. When people are able to get quality education they can break from the cycle of poverty.
Education helps to reduce inequalities and to reach gender equality. It also empowers people everywhere to live more healthy and sustainable lives. Education is also crucial to fostering tolerance between people and contributes to more peaceful societies.
- To deliver on Goal 4, education financing must become a national investment priority. Furthermore, measures such as making education free and compulsory, increasing the number of teachers, improving basic school infrastructure and embracing digital transformation are essential.
What progress have we made so far?
While progress has been made towards the 2030 education targets set by the United Nations, continued efforts are required to address persistent challenges and ensure that quality education is accessible to all, leaving no one behind.
Between 2015 and 2021, there was an increase in worldwide primary school completion, lower secondary completion, and upper secondary completion. Nevertheless, the progress made during this period was notably slower compared to the 15 years prior.
What challenges remain?
According to national education targets, the percentage of students attaining basic reading skills by the end of primary school is projected to rise from 51 per cent in 2015 to 67 per cent by 2030. However, an estimated 300 million children and young people will still lack basic numeracy and literacy skills by 2030.
Economic constraints, coupled with issues of learning outcomes and dropout rates, persist in marginalized areas, underscoring the need for continued global commitment to ensuring inclusive and equitable education for all. Low levels of information and communications technology (ICT) skills are also a major barrier to achieving universal and meaningful connectivity.
Where are people struggling the most to have access to education?
Sub-Saharan Africa faces the biggest challenges in providing schools with basic resources. The situation is extreme at the primary and lower secondary levels, where less than one-half of schools in sub-Saharan Africa have access to drinking water, electricity, computers and the Internet.
Inequalities will also worsen unless the digital divide – the gap between under-connected and highly digitalized countries – is not addressed .
Are there groups that have more difficult access to education?
Yes, women and girls are one of these groups. About 40 per cent of countries have not achieved gender parity in primary education. These disadvantages in education also translate into lack of access to skills and limited opportunities in the labour market for young women.
What can we do?
Ask our governments to place education as a priority in both policy and practice. Lobby our governments to make firm commitments to provide free primary school education to all, including vulnerable or marginalized groups.

Facts and figures
Goal 4 targets.
- Without additional measures, only one in six countries will achieve the universal secondary school completion target by 2030, an estimated 84 million children and young people will still be out of school, and approximately 300 million students will lack the basic numeracy and literacy skills necessary for success in life.
- To achieve national Goal 4 benchmarks, which are reduced in ambition compared with the original Goal 4 targets, 79 low- and lower-middle- income countries still face an average annual financing gap of $97 billion.
Source: The Sustainable Development Goals Report 2023
4.1 By 2030, ensure that all girls and boys complete free, equitable and quality primary and secondary education leading to relevant and Goal-4 effective learning outcomes
4.2 By 2030, ensure that all girls and boys have access to quality early childhood development, care and preprimary education so that they are ready for primary education
4.3 By 2030, ensure equal access for all women and men to affordable and quality technical, vocational and tertiary education, including university
4.4 By 2030, substantially increase the number of youth and adults who have relevant skills, including technical and vocational skills, for employment, decent jobs and entrepreneurship
4.5 By 2030, eliminate gender disparities in education and ensure equal access to all levels of education and vocational training for the vulnerable, including persons with disabilities, indigenous peoples and children in vulnerable situations
4.6 By 2030, ensure that all youth and a substantial proportion of adults, both men and women, achieve literacy and numeracy
4.7 By 2030, ensure that all learners acquire the knowledge and skills needed to promote sustainable development, including, among others, through education for sustainable development and sustainable lifestyles, human rights, gender equality, promotion of a culture of peace and non-violence, global citizenship and appreciation of cultural diversity and of culture’s contribution to sustainable development
4.A Build and upgrade education facilities that are child, disability and gender sensitive and provide safe, nonviolent, inclusive and effective learning environments for all
4.B By 2020, substantially expand globally the number of scholarships available to developing countries, in particular least developed countries, small island developing States and African countries, for enrolment in higher education, including vocational training and information and communications technology, technical, engineering and scientific programmes, in developed countries and other developing countries
4.C By 2030, substantially increase the supply of qualified teachers, including through international cooperation for teacher training in developing countries, especially least developed countries and small island developing states
UN Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization
UN Children’s Fund
UN Development Programme
Global Education First Initiative
UN Population Fund: Comprehensive sexuality education
UN Office of the Secretary General’s Envoy on Youth
Fast Facts: Quality Education

Infographic: Quality Education

Related news

‘Education is a human right,’ UN Summit Adviser says, urging action to tackle ‘crisis of access, learning and relevance’
Masayoshi Suga 2022-09-15T11:50:20-04:00 14 Sep 2022 |
14 September, NEW YORK – Education is a human right - those who are excluded must fight for their right, Leonardo Garnier, Costa Rica’s former education minister, emphasized, ahead of a major United Nations [...]
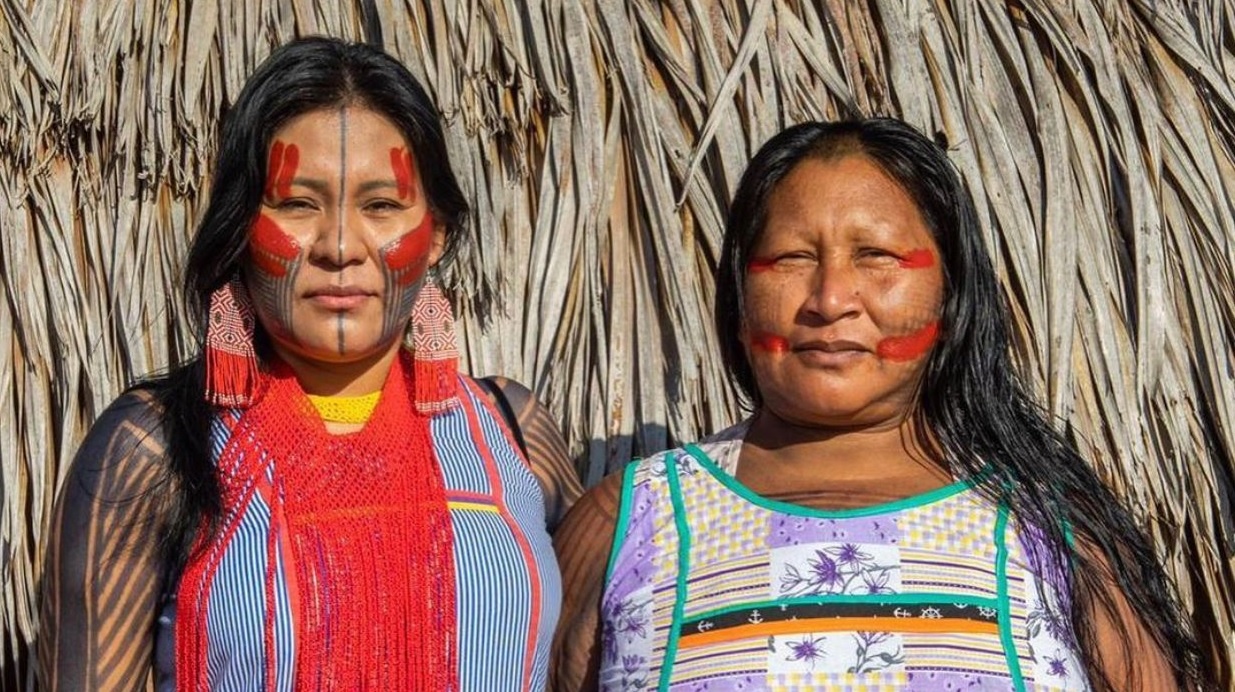

Showcasing nature-based solutions: Meet the UN prize winners
Masayoshi Suga 2022-08-13T22:16:45-04:00 11 Aug 2022 |
NEW YORK, 11 August – The United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) and partners have announced the winners of the 13th Equator Prize, recognizing ten indigenous peoples and local communities from nine countries. The winners, selected from a [...]

UN and partners roll out #LetMeLearn campaign ahead of Education Summit
Yinuo 2022-08-10T09:27:23-04:00 01 Aug 2022 |
New York, 1 August – Amid the education crisis exacerbated by the COVID-19 pandemic, the United Nations is partnering with children's charity Theirworld to launch the #LetMeLearn campaign, urging world leaders to hear the [...]
Related videos
Malala yousafzai (un messenger of peace) on “financing the future: education 2030”.
VIDEO: Climate education at COP22
From the football field to the classrooms of Nepal | UNICEF
Share this story, choose your platform!
George Washington Carver: 'Education is the key to unlock the golden door of freedom.'
Education is the key to unlock the golden door of freedom.
Education is the key to unlock the golden door of freedom, as famously said by George Washington Carver. This profound quote encapsulates the transformative power of education in unlocking the doors to freedom, both individually and collectively. It emphasizes the crucial role that education plays in empowering individuals to break free from the constraints of ignorance, prejudice, and systemic inequalities. Education opens up a world of possibilities, providing individuals with the knowledge, skills, and understanding necessary to lead fulfilling lives, make informed choices, and actively participate in society.Imagine a world where education was accessible to all, regardless of socio-economic status or geographic location. In such a world, the golden door of freedom would be open to everyone, offering endless opportunities to elevate oneself and contribute to the betterment of society. Education serves as a catalyst for social and economic mobility, enabling individuals to rise above their circumstances and pursue their dreams, breaking the cycle of poverty and oppression.Not only does education empower individuals, but it also strengthens the very fabric of society. When people are educated, they are more likely to engage in critical thinking, promote inclusivity, and foster social harmony. A well-informed and educated citizenry forms the foundation of a democratic society, capable of making informed decisions and actively participating in the governance of their communities. By unlocking the minds of individuals, education unlocks the doors to social progress, equality, and justice.However, while education is undoubtedly a powerful tool, it is important to recognize that it alone cannot guarantee freedom. An unexpected philosophical concept, existentialism, sheds light on this contrast. According to existentialism, freedom comes not from external factors but from an individual's own choices and actions. In this context, education serves as a guide, providing individuals with the knowledge and critical thinking abilities to make informed choices about their own lives, values, and beliefs.Existentialism challenges the notion that education alone can unlock the golden door of freedom. It argues that freedom ultimately lies in the hands of individuals, who must take responsibility for their own existence and create meaning within a seemingly chaotic and indifferent world. Education, therefore, becomes not just a means to unlock the door of freedom but a tool to equip individuals with the capacity for self-reflection, introspection, and personal growth.In the convergence of ideas between Carver's quote and existentialism lies an important lesson. Education may not be the magical key that guarantees freedom, but it is an essential component in the journey towards it. Both ideas converge on the belief that education empowers individuals to take charge of their own lives and make choices that align with their values, aspirations, and desires.In conclusion, George Washington Carver's quote, "Education is the key to unlock the golden door of freedom," resonates deeply with the transformative power of education in bringing about personal and societal liberation. Education opens doors to opportunities, dismantles barriers, and enables individuals to break free from ignorance and prejudice. However, it is crucial to acknowledge that education alone cannot guarantee freedom; it is the individual's responsibility to use education as a tool in the pursuit of personal growth, self-reflection, and the creation of meaning. By embracing this holistic perspective, we can fully appreciate the profound impact education has on freedom and the immense potential it holds for a more equitable and inclusive society.
George Washington Carver: 'I love to think of nature as an unlimited broadcasting station, through which God speaks to us every hour, if we will only tune in.'
Friedrich engels: 'look at the paris commune. that was the dictatorship of the proletariat.'.

The World Bank Group is the largest financier of education in the developing world, working in 94 countries and committed to helping them reach SDG4: access to inclusive and equitable quality education and lifelong learning opportunities for all by 2030.
Education is a human right, a powerful driver of development, and one of the strongest instruments for reducing poverty and improving health, gender equality, peace, and stability. It delivers large, consistent returns in terms of income, and is the most important factor to ensure equity and inclusion.
For individuals, education promotes employment, earnings, health, and poverty reduction. Globally, there is a 9% increase in hourly earnings for every extra year of schooling . For societies, it drives long-term economic growth, spurs innovation, strengthens institutions, and fosters social cohesion. Education is further a powerful catalyst to climate action through widespread behavior change and skilling for green transitions.
Developing countries have made tremendous progress in getting children into the classroom and more children worldwide are now in school. But learning is not guaranteed, as the 2018 World Development Report (WDR) stressed.
Making smart and effective investments in people’s education is critical for developing the human capital that will end extreme poverty. At the core of this strategy is the need to tackle the learning crisis, put an end to Learning Poverty , and help youth acquire the advanced cognitive, socioemotional, technical and digital skills they need to succeed in today’s world.
In low- and middle-income countries, the share of children living in Learning Poverty (that is, the proportion of 10-year-old children that are unable to read and understand a short age-appropriate text) increased from 57% before the pandemic to an estimated 70% in 2022.
However, learning is in crisis. More than 70 million more people were pushed into poverty during the COVID pandemic, a billion children lost a year of school , and three years later the learning losses suffered have not been recouped . If a child cannot read with comprehension by age 10, they are unlikely to become fluent readers. They will fail to thrive later in school and will be unable to power their careers and economies once they leave school.
The effects of the pandemic are expected to be long-lasting. Analysis has already revealed deep losses, with international reading scores declining from 2016 to 2021 by more than a year of schooling. These losses may translate to a 0.68 percentage point in global GDP growth. The staggering effects of school closures reach beyond learning. This generation of children could lose a combined total of US$21 trillion in lifetime earnings in present value or the equivalent of 17% of today’s global GDP – a sharp rise from the 2021 estimate of a US$17 trillion loss.
Action is urgently needed now – business as usual will not suffice to heal the scars of the pandemic and will not accelerate progress enough to meet the ambitions of SDG 4. We are urging governments to implement ambitious and aggressive Learning Acceleration Programs to get children back to school, recover lost learning, and advance progress by building better, more equitable and resilient education systems.
Last Updated: Mar 25, 2024
The World Bank’s global education strategy is centered on ensuring learning happens – for everyone, everywhere. Our vision is to ensure that everyone can achieve her or his full potential with access to a quality education and lifelong learning. To reach this, we are helping countries build foundational skills like literacy, numeracy, and socioemotional skills – the building blocks for all other learning. From early childhood to tertiary education and beyond – we help children and youth acquire the skills they need to thrive in school, the labor market and throughout their lives.
Investing in the world’s most precious resource – people – is paramount to ending poverty on a livable planet. Our experience across more than 100 countries bears out this robust connection between human capital, quality of life, and economic growth: when countries strategically invest in people and the systems designed to protect and build human capital at scale, they unlock the wealth of nations and the potential of everyone.
Building on this, the World Bank supports resilient, equitable, and inclusive education systems that ensure learning happens for everyone. We do this by generating and disseminating evidence, ensuring alignment with policymaking processes, and bridging the gap between research and practice.
The World Bank is the largest source of external financing for education in developing countries, with a portfolio of about $26 billion in 94 countries including IBRD, IDA and Recipient-Executed Trust Funds. IDA operations comprise 62% of the education portfolio.
The investment in FCV settings has increased dramatically and now accounts for 26% of our portfolio.
World Bank projects reach at least 425 million students -one-third of students in low- and middle-income countries.
The World Bank’s Approach to Education
Five interrelated pillars of a well-functioning education system underpin the World Bank’s education policy approach:
- Learners are prepared and motivated to learn;
- Teachers are prepared, skilled, and motivated to facilitate learning and skills acquisition;
- Learning resources (including education technology) are available, relevant, and used to improve teaching and learning;
- Schools are safe and inclusive; and
- Education Systems are well-managed, with good implementation capacity and adequate financing.
The Bank is already helping governments design and implement cost-effective programs and tools to build these pillars.
Our Principles:
- We pursue systemic reform supported by political commitment to learning for all children.
- We focus on equity and inclusion through a progressive path toward achieving universal access to quality education, including children and young adults in fragile or conflict affected areas , those in marginalized and rural communities, girls and women , displaced populations, students with disabilities , and other vulnerable groups.
- We focus on results and use evidence to keep improving policy by using metrics to guide improvements.
- We want to ensure financial commitment commensurate with what is needed to provide basic services to all.
- We invest wisely in technology so that education systems embrace and learn to harness technology to support their learning objectives.
Laying the groundwork for the future
Country challenges vary, but there is a menu of options to build forward better, more resilient, and equitable education systems.
Countries are facing an education crisis that requires a two-pronged approach: first, supporting actions to recover lost time through remedial and accelerated learning; and, second, building on these investments for a more equitable, resilient, and effective system.
Recovering from the learning crisis must be a political priority, backed with adequate financing and the resolve to implement needed reforms. Domestic financing for education over the last two years has not kept pace with the need to recover and accelerate learning. Across low- and lower-middle-income countries, the average share of education in government budgets fell during the pandemic , and in 2022 it remained below 2019 levels.
The best chance for a better future is to invest in education and make sure each dollar is put toward improving learning. In a time of fiscal pressure, protecting spending that yields long-run gains – like spending on education – will maximize impact. We still need more and better funding for education. Closing the learning gap will require increasing the level, efficiency, and equity of education spending—spending smarter is an imperative.
- Education technology can be a powerful tool to implement these actions by supporting teachers, children, principals, and parents; expanding accessible digital learning platforms, including radio/ TV / Online learning resources; and using data to identify and help at-risk children, personalize learning, and improve service delivery.
Looking ahead
We must seize this opportunity to reimagine education in bold ways. Together, we can build forward better more equitable, effective, and resilient education systems for the world’s children and youth.
Accelerating Improvements
Supporting countries in establishing time-bound learning targets and a focused education investment plan, outlining actions and investments geared to achieve these goals.
Launched in 2020, the Accelerator Program works with a set of countries to channel investments in education and to learn from each other. The program coordinates efforts across partners to ensure that the countries in the program show improvements in foundational skills at scale over the next three to five years. These investment plans build on the collective work of multiple partners, and leverage the latest evidence on what works, and how best to plan for implementation. Countries such as Brazil (the state of Ceará) and Kenya have achieved dramatic reductions in learning poverty over the past decade at scale, providing useful lessons, even as they seek to build on their successes and address remaining and new challenges.
Universalizing Foundational Literacy
Readying children for the future by supporting acquisition of foundational skills – which are the gateway to other skills and subjects.
The Literacy Policy Package (LPP) consists of interventions focused specifically on promoting acquisition of reading proficiency in primary school. These include assuring political and technical commitment to making all children literate; ensuring effective literacy instruction by supporting teachers; providing quality, age-appropriate books; teaching children first in the language they speak and understand best; and fostering children’s oral language abilities and love of books and reading.
Advancing skills through TVET and Tertiary
Ensuring that individuals have access to quality education and training opportunities and supporting links to employment.
Tertiary education and skills systems are a driver of major development agendas, including human capital, climate change, youth and women’s empowerment, and jobs and economic transformation. A comprehensive skill set to succeed in the 21st century labor market consists of foundational and higher order skills, socio-emotional skills, specialized skills, and digital skills. Yet most countries continue to struggle in delivering on the promise of skills development.
The World Bank is supporting countries through efforts that address key challenges including improving access and completion, adaptability, quality, relevance, and efficiency of skills development programs. Our approach is via multiple channels including projects, global goods, as well as the Tertiary Education and Skills Program . Our recent reports including Building Better Formal TVET Systems and STEERing Tertiary Education provide a way forward for how to improve these critical systems.
Addressing Climate Change
Mainstreaming climate education and investing in green skills, research and innovation, and green infrastructure to spur climate action and foster better preparedness and resilience to climate shocks.
Our approach recognizes that education is critical for achieving effective, sustained climate action. At the same time, climate change is adversely impacting education outcomes. Investments in education can play a huge role in building climate resilience and advancing climate mitigation and adaptation. Climate change education gives young people greater awareness of climate risks and more access to tools and solutions for addressing these risks and managing related shocks. Technical and vocational education and training can also accelerate a green economic transformation by fostering green skills and innovation. Greening education infrastructure can help mitigate the impact of heat, pollution, and extreme weather on learning, while helping address climate change.
Examples of this work are projects in Nigeria (life skills training for adolescent girls), Vietnam (fostering relevant scientific research) , and Bangladesh (constructing and retrofitting schools to serve as cyclone shelters).
Strengthening Measurement Systems
Enabling countries to gather and evaluate information on learning and its drivers more efficiently and effectively.
The World Bank supports initiatives to help countries effectively build and strengthen their measurement systems to facilitate evidence-based decision-making. Examples of this work include:
(1) The Global Education Policy Dashboard (GEPD) : This tool offers a strong basis for identifying priorities for investment and policy reforms that are suited to each country context by focusing on the three dimensions of practices, policies, and politics.
- Highlights gaps between what the evidence suggests is effective in promoting learning and what is happening in practice in each system; and
- Allows governments to track progress as they act to close the gaps.
The GEPD has been implemented in 13 education systems already – Peru, Rwanda, Jordan, Ethiopia, Madagascar, Mozambique, Islamabad, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Sierra Leone, Niger, Gabon, Jordan and Chad – with more expected by the end of 2024.
(2) Learning Assessment Platform (LeAP) : LeAP is a one-stop shop for knowledge, capacity-building tools, support for policy dialogue, and technical staff expertise to support student achievement measurement and national assessments for better learning.
Supporting Successful Teachers
Helping systems develop the right selection, incentives, and support to the professional development of teachers.
Currently, the World Bank Education Global Practice has over 160 active projects supporting over 18 million teachers worldwide, about a third of the teacher population in low- and middle-income countries. In 12 countries alone, these projects cover 16 million teachers, including all primary school teachers in Ethiopia and Turkey, and over 80% in Bangladesh, Pakistan, and Vietnam.
A World Bank-developed classroom observation tool, Teach, was designed to capture the quality of teaching in low- and middle-income countries. It is now 3.6 million students.
While Teach helps identify patterns in teacher performance, Coach leverages these insights to support teachers to improve their teaching practice through hands-on in-service teacher professional development (TPD).
Our recent report on Making Teacher Policy Work proposes a practical framework to uncover the black box of effective teacher policy and discusses the factors that enable their scalability and sustainability.
Supporting Education Finance Systems
Strengthening country financing systems to mobilize resources for education and make better use of their investments in education.
Our approach is to bring together multi-sectoral expertise to engage with ministries of education and finance and other stakeholders to develop and implement effective and efficient public financial management systems; build capacity to monitor and evaluate education spending, identify financing bottlenecks, and develop interventions to strengthen financing systems; build the evidence base on global spending patterns and the magnitude and causes of spending inefficiencies; and develop diagnostic tools as public goods to support country efforts.
Working in Fragile, Conflict, and Violent (FCV) Contexts
The massive and growing global challenge of having so many children living in conflict and violent situations requires a response at the same scale and scope. Our education engagement in the Fragility, Conflict and Violence (FCV) context, which stands at US$5.35 billion, has grown rapidly in recent years, reflecting the ever-increasing importance of the FCV agenda in education. Indeed, these projects now account for more than 25% of the World Bank education portfolio.
Education is crucial to minimizing the effects of fragility and displacement on the welfare of youth and children in the short-term and preventing the emergence of violent conflict in the long-term.
Support to Countries Throughout the Education Cycle
Our support to countries covers the entire learning cycle, to help shape resilient, equitable, and inclusive education systems that ensure learning happens for everyone.
The ongoing Supporting Egypt Education Reform project , 2018-2025, supports transformational reforms of the Egyptian education system, by improving teaching and learning conditions in public schools. The World Bank has invested $500 million in the project focused on increasing access to quality kindergarten, enhancing the capacity of teachers and education leaders, developing a reliable student assessment system, and introducing the use of modern technology for teaching and learning. Specifically, the share of Egyptian 10-year-old students, who could read and comprehend at the global minimum proficiency level, increased to 45 percent in 2021.
In Nigeria , the $75 million Edo Basic Education Sector and Skills Transformation (EdoBESST) project, running from 2020-2024, is focused on improving teaching and learning in basic education. Under the project, which covers 97 percent of schools in the state, there is a strong focus on incorporating digital technologies for teachers. They were equipped with handheld tablets with structured lesson plans for their classes. Their coaches use classroom observation tools to provide individualized feedback. Teacher absence has reduced drastically because of the initiative. Over 16,000 teachers were trained through the project, and the introduction of technology has also benefited students.
Through the $235 million School Sector Development Program in Nepal (2017-2022), the number of children staying in school until Grade 12 nearly tripled, and the number of out-of-school children fell by almost seven percent. During the pandemic, innovative approaches were needed to continue education. Mobile phone penetration is high in the country. More than four in five households in Nepal have mobile phones. The project supported an educational service that made it possible for children with phones to connect to local radio that broadcast learning programs.
From 2017-2023, the $50 million Strengthening of State Universities in Chile project has made strides to improve quality and equity at state universities. The project helped reduce dropout: the third-year dropout rate fell by almost 10 percent from 2018-2022, keeping more students in school.
The World Bank’s first Program-for-Results financing in education was through a $202 million project in Tanzania , that ran from 2013-2021. The project linked funding to results and aimed to improve education quality. It helped build capacity, and enhanced effectiveness and efficiency in the education sector. Through the project, learning outcomes significantly improved alongside an unprecedented expansion of access to education for children in Tanzania. From 2013-2019, an additional 1.8 million students enrolled in primary schools. In 2019, the average reading speed for Grade 2 students rose to 22.3 words per minute, up from 17.3 in 2017. The project laid the foundation for the ongoing $500 million BOOST project , which supports over 12 million children to enroll early, develop strong foundational skills, and complete a quality education.
The $40 million Cambodia Secondary Education Improvement project , which ran from 2017-2022, focused on strengthening school-based management, upgrading teacher qualifications, and building classrooms in Cambodia, to improve learning outcomes, and reduce student dropout at the secondary school level. The project has directly benefited almost 70,000 students in 100 target schools, and approximately 2,000 teachers and 600 school administrators received training.
The World Bank is co-financing the $152.80 million Yemen Restoring Education and Learning Emergency project , running from 2020-2024, which is implemented through UNICEF, WFP, and Save the Children. It is helping to maintain access to basic education for many students, improve learning conditions in schools, and is working to strengthen overall education sector capacity. In the time of crisis, the project is supporting teacher payments and teacher training, school meals, school infrastructure development, and the distribution of learning materials and school supplies. To date, almost 600,000 students have benefited from these interventions.
The $87 million Providing an Education of Quality in Haiti project supported approximately 380 schools in the Southern region of Haiti from 2016-2023. Despite a highly challenging context of political instability and recurrent natural disasters, the project successfully supported access to education for students. The project provided textbooks, fresh meals, and teacher training support to 70,000 students, 3,000 teachers, and 300 school directors. It gave tuition waivers to 35,000 students in 118 non-public schools. The project also repaired 19 national schools damaged by the 2021 earthquake, which gave 5,500 students safe access to their schools again.
In 2013, just 5% of the poorest households in Uzbekistan had children enrolled in preschools. Thanks to the Improving Pre-Primary and General Secondary Education Project , by July 2019, around 100,000 children will have benefitted from the half-day program in 2,420 rural kindergartens, comprising around 49% of all preschool educational institutions, or over 90% of rural kindergartens in the country.
In addition to working closely with governments in our client countries, the World Bank also works at the global, regional, and local levels with a range of technical partners, including foundations, non-profit organizations, bilaterals, and other multilateral organizations. Some examples of our most recent global partnerships include:
UNICEF, UNESCO, FCDO, USAID, Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation: Coalition for Foundational Learning
The World Bank is working closely with UNICEF, UNESCO, FCDO, USAID, and the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation as the Coalition for Foundational Learning to advocate and provide technical support to ensure foundational learning. The World Bank works with these partners to promote and endorse the Commitment to Action on Foundational Learning , a global network of countries committed to halving the global share of children unable to read and understand a simple text by age 10 by 2030.
Australian Aid, Bernard van Leer Foundation, Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, Canada, Echida Giving, FCDO, German Cooperation, William & Flora Hewlett Foundation, Conrad Hilton Foundation, LEGO Foundation, Porticus, USAID: Early Learning Partnership
The Early Learning Partnership (ELP) is a multi-donor trust fund, housed at the World Bank. ELP leverages World Bank strengths—a global presence, access to policymakers and strong technical analysis—to improve early learning opportunities and outcomes for young children around the world.
We help World Bank teams and countries get the information they need to make the case to invest in Early Childhood Development (ECD), design effective policies and deliver impactful programs. At the country level, ELP grants provide teams with resources for early seed investments that can generate large financial commitments through World Bank finance and government resources. At the global level, ELP research and special initiatives work to fill knowledge gaps, build capacity and generate public goods.
UNESCO, UNICEF: Learning Data Compact
UNESCO, UNICEF, and the World Bank have joined forces to close the learning data gaps that still exist and that preclude many countries from monitoring the quality of their education systems and assessing if their students are learning. The three organizations have agreed to a Learning Data Compact , a commitment to ensure that all countries, especially low-income countries, have at least one quality measure of learning by 2025, supporting coordinated efforts to strengthen national assessment systems.
UNESCO Institute for Statistics (UIS): Learning Poverty Indicator
Aimed at measuring and urging attention to foundational literacy as a prerequisite to achieve SDG4, this partnership was launched in 2019 to help countries strengthen their learning assessment systems, better monitor what students are learning in internationally comparable ways and improve the breadth and quality of global data on education.
FCDO, Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation: EdTech Hub
Supported by the UK government’s Foreign, Commonwealth & Development Office (FCDO), in partnership with the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, the EdTech Hub is aimed at improving the quality of ed-tech investments. The Hub launched a rapid response Helpdesk service to provide just-in-time advisory support to 70 low- and middle-income countries planning education technology and remote learning initiatives.
MasterCard Foundation
Our Tertiary Education and Skills global program, launched with support from the Mastercard Foundation, aims to prepare youth and adults for the future of work and society by improving access to relevant, quality, equitable reskilling and post-secondary education opportunities. It is designed to reframe, reform, and rebuild tertiary education and skills systems for the digital and green transformation.

Choosing Our Future: Education for Climate Action

From chalkboards to chatbots in Nigeria: 7 lessons to pioneer generative AI for education

Common challenges and tailored solutions: How policymakers are strengthening early learning systems across the world
Areas of focus.
Data & Measurement
Early Childhood Development
Financing Education
Foundational Learning
Fragile, Conflict & Violent Contexts
Girls’ Education
Inclusive Education
Skills Development
Technology (EdTech)
Tertiary Education
Initiatives
- Show More +
- Invest in Childcare
- Global Education Policy Dashboard
- Global Education Evidence Advisory Panel
- Show Less -
Collapse and Recovery: How the COVID-19 Pandemic Eroded Human Capital and What to Do About It
BROCHURES & FACT SHEETS
Flyer: Education Factsheet - May 2024
Publication: Realizing Education's Promise: A World Bank Retrospective – August 2023
Flyer: Education and Climate Change - November 2022
Brochure: Learning Losses - October 2022
STAY CONNECTED

Human Development Topics
Around the bank group.
Find out what the Bank Group's branches are doing in education

Global Program for Safer Schools
The Roadmap for Safer and Resilient Schools (RSRS) supports strategies and investment plans to make schools safer and resilient at scale.
- Teachers brief on safe schools

Global Education Newsletter - September 2024
What's happening in the World Bank Education Global Practice? Read to learn more.

Learning Can't Wait: A commitment to education in Latin America and the ...
An IDB-World Bank report describes challenges and priorities to address the educational crisis.

Impact Evaluations
Research that measures the impact of education policies to improve education in low and middle income countries.
- Compendium of World Bank Supported Impact Evaluations
- Strategic Impact Evaluation Fund (SIEF)

Human Capital Project
The Human Capital Project is a global effort to accelerate more and better investments in people for greater equity and economic growth.

Education Videos
Watch our latest videos featuring our projects across the world
Additional Resources
Skills & Workforce Development
Technology (EdTech)
This site uses cookies to optimize functionality and give you the best possible experience. If you continue to navigate this website beyond this page, cookies will be placed on your browser. To learn more about cookies, click here .

Why is education more important today than ever? Innovation
Eduardo velez bustillo, harry a. patrinos.

The competitiveness of an economy depends a lot on technological progress, but recent data in some countries, including not only high-income but also middle-income countries, suggests that innovation is getting harder, and the pace of growth is slowing down. A new challenge, then, is to understand what conditions are most effective in supporting innovation, so countries can support their best and brightest to advance technology and lead innovative work that helps boost economies.
Education and mobility
The main findings of status attainment research—which studies how an individual’s family background relates to her educational and occupational attainment and income—show that an individual’s status originates in the education, occupation, and income of his or her parents, in particular fathers. At the same time, the individual’s income is also explained by his or her level of education and occupation status, as described many years ago in the seminal book The American Occupational Structure by Blau and Duncan. On the other hand, economists studying human capital theory have emphasized for decades how education correlates to income and have concluded that education increases the productivity of individuals by increasing their skills, as was proposed by Gary Becker . This can be done by investing in people.
This basic model describes the process by which family status and education were converted into occupational status through educational attainment even after controlling by ability, and has implications for how we develop and implement education policy. The results of many studies show that education has a significant positive influence on the occupational and income attainment process . These findings are consistent with human capital theory, where education explains individual productivity after ability is controlled, showing that it has an independent effect on productivity . The results have been similar in developed and developing countries where access to education, including higher education, for example, still is restricted to people with low socioeconomic status.
Education, innovation and technology
Today, there is agreement that education, independent of innate ability, helps spur innovation and technology, and it contributes to productivity and economic growth. A key element in this process is that education is important to adopt the technology that produces innovation. Parental education and a person’s education affect productivity, directly or indirectly, and independently of many other characteristics. In consequence, policymakers in countries that want to remain competitive in the globalized economy need to make sure that the education system takes this into account and supports quantitative indicators (enrollments) and qualitative ones, including the number of Ph.D. graduates , the strongest education indicator of technology and innovation. In the long term, when it comes to spurring innovation, it is more important subsidize PhD students than R&D. This would help produce the sort of technology and innovation that could give us the next generation of mRNA vaccines or medicines to treat intractable diseases. It could produce the next generation of AI tools or maybe the next generation of IBM Watson .
Without fair access to education, we are constraining the possibilities for a country to develop. All countries need to ensure that everybody starts with the right steps early on and moves thru the education cycles according to their capabilities. To do this, countries should equalize opportunities so that individuals, their families, and communities will benefit. Some countries like Finland, Singapore, and Korea, for example, have done it. In a generation, they were able to break the parent-child cycle in terms of access to quality education and access to higher education.
Investing in education boosts innovation
This is important because the findings relate to how innovation and education policy affect individual career choices and aggregate productivity. Emerging studies indicate that subsidies to R&D, a typical policy to support technology/innovation, have a clear strong impact in the short term, but its effect tends to decrease in the longer term. Subsidies to education , however, have a stronger effect on technology and innovation in the long term . A challenge is how to support students to successfully complete Ph.D. programs. These students will be more successful in developing technology and innovation. The literature indicates that expanding access to basic skills, improving the quality of education, and investing in universities may do the trick. These policies help individuals who would have been innovators anyway to become more successful; and allow creative individuals who would otherwise not have become inventors to reach their potential, widening the talent pipeline .
The World Bank is contributing towards improvements in technology and by expanding support to experiences that have been successful in increasing access to higher education, such as the projects that support loans for low-income students so that they can attend higher education in certified institutions. It also supports improving research capacity at the university level, including a series of projects that supported the Millennium Science Initiative. This initiative—initially in Latin America and the Caribbean, but most recently in sub-Saharan Africa—expands doctoral and post-doctoral training to promote scientific excellence and produce better and more qualified science and engineering graduates. It also aims to produce higher quality and more relevant research for firms to utilize these outputs to improve productivity, such as the Millennium Science Initiative project in Uganda . The World Bank is also investing in highly sophisticated technology to strengthen higher education and research universities, including with the Higher Education and Research for Innovation and Competitiveness (HERIC) project in Montenegro .
Get updates from Education for Global Development
Thank you for choosing to be part of the Education for Global Development community!
Your subscription is now active. The latest blog posts and blog-related announcements will be delivered directly to your email inbox. You may unsubscribe at any time.

Consultant, Education Sector, World Bank

Senior Adviser, Education
Join the Conversation
- Share on mail
- comments added

- Our mission
- Our structure
- Annual reports
- Nominations
- Our community
- Collaborations
Education is our most powerful force for change
For the first time in history, we have 70 years of research at our fingertips that shows the impact of education—as well as modelling our future to the end of the 21st century. So while the idea of education as the bedrock of human progress goes back centuries, we now have decades of data to prove that’s exactly what it is.
That’s the focus of a paper we’ve developed with the Wittgenstein Centre for Demography and Global Human Capital. In Education: The key to global sustainable development , we explore the evidence that places education at the centre of human life. And we show how it’s the key to making our world healthier, fairer, richer—and more resilient to global threats like climate change.
The research tells us that education helps us live longer and more productive lives. It physically moulds our minds, changing our behaviour for the better. And we can now see that—although education is a long game—we can make progress, fast.
Literacy gaps prevent global progress—so we must close them.
The gap between the world’s most and least skilled adult populations is growing. When we look at the difference between countries where people emerge from education with strong literacy skills, and places where they don’t, it’s equivalent to an extra ten years in school. And we know that skilled populations lead to economic growth.
So if we want people, countries, and our globalized world to develop and thrive, we need to make sure that every learner has access to quality education in essential skills. That means investing in more, better trained, and properly supported teachers.
But it’s an investment we can prove pays off in the long term. We all know about the correlation between greater wealth and longer life expectancy. But when we lay out the data visually—as in our paper—we can see that it’s education that actually maps most closely with living longer, healthier lives. Finally, we have an answer to the chicken-and-egg problem: education comes first, and longevity and prosperity follow.
Education literally changes our minds.
We now have research that shows the effect education has on our brains. It makes us more capable of abstract thinking, and more able to calculate risk. And we know it’s not simply genetic: how we interact with the world around us shapes our brains, so identical twins raised differently show very different behaviour.
That’s because we learn from experience, and repetition: familiar faces stay with us, while we quickly forget strangers. We lay down neural networks that get faster and faster at processing similar experiences and combining information. With every new thing we learn, we are, literally, different people than we were before. And those people are better at making the kinds of choices that lead to healthier, longer, more productive lives.
We have a blueprint for building a better world.
The report concludes that there are five policy areas where we can take action, now. We can:
Invest in early years support that gets children primed to learn. Like the Finnish neuvola (‘advisory’) system that offers free medical care, mental development check-ups and education counselling long before formal schooling starts.
Give every child at least ten years of education. Even better, 12. The evidence shows universal primary education alone isn’t enough to pull countries out of poverty—but investing in quality secondary education can.
- Train more, and better, teachers. Nothing makes a bigger difference than confident, motivated teachers that empower and inspire their students.
- Use all the technology at hand . With a grounding in basic literacy and critical thinking skills—and especially the guidance of a good teacher—technology means students can navigate their own learning, and broaden their horizons.
- Set ourselves up for lifelong learning. Our world is changing—as are the skills we need to thrive. We can’t expect that what children learn in school now will still be relevant at work in 30 years. And opportunities for adult learning keep people healthier and more active into old age.
At the Yidan Prize Foundation, we bring together people and ideas that are already changing the world for the better. We’re building networks of the world’s brightest thinkers—including educators, economists, statisticians, and neuroscientists. With this increasing wealth of information showing us that education is the fundamental force for change, we inform and influence policymakers to invest in all our tomorrows.

Search by subject
More to explore, share the blog with others.
Nominate now
Get the latest news in your inbox
Sign up for regular news about our work and the most exciting ideas in education
We look forward to sharing the latest news about our work with you.
- Rukmini Banerji
- Foundation background
We use cookies on this site. Please let us know if you agree to that. You can find out more here .

IMAGES
VIDEO