Elementary Education Essays
Approaches to elementary education, popular essay topics.
- American Dream
- Artificial Intelligence
- Black Lives Matter
- Bullying Essay
- Career Goals Essay
- Causes of the Civil War
- Child Abusing
- Civil Rights Movement
- Community Service
- Cultural Identity
- Cyber Bullying
- Death Penalty
- Depression Essay
- Domestic Violence
- Freedom of Speech
- Global Warming
- Gun Control
- Human Trafficking
- I Believe Essay
- Immigration
- Importance of Education
- Israel and Palestine Conflict
- Leadership Essay
- Legalizing Marijuanas
- Mental Health
- National Honor Society
- Police Brutality
- Pollution Essay
- Racism Essay
- Romeo and Juliet
- Same Sex Marriages
- Social Media
- The Great Gatsby
- The Yellow Wallpaper
- Time Management
- To Kill a Mockingbird
- Violent Video Games
- What Makes You Unique
- Why I Want to Be a Nurse
- Send us an e-mail
Home — Essay Samples — Life — Childhood Lessons — My Experience in Elementary School

My Experience in Elementary School
- Categories: Childhood Lessons Elementary School
About this sample

Words: 521 |
Published: Mar 20, 2024
Words: 521 | Page: 1 | 3 min read

Cite this Essay
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing style below:
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Dr. Heisenberg
Verified writer
- Expert in: Life Education

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
1 pages / 649 words
5 pages / 2080 words
1 pages / 547 words
2 pages / 1131 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online
Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Childhood Lessons
Nabokov’s Speak, Memory is a work that focuses as much on the process of recollection of memories as on the memories that are being recollected. Nabokov’s patient and repetitive interrogation of his memories shows the [...]
Paul J. Flory was an activist, scientist, journalist, chemist, and educator all in one. He was born on June 19, 1910 in Sterling, Illinois, of Ezra Flory and Martha Brumbaugh. His father, Ezra Flory, was a Brethren [...]
The true meaning of the phrase “the American Dream” is a topic that could be debated by Americans all across the country. For some, it is accomplishing the goals they set for themselves as children or teenagers. For others, it [...]
Professionalism is something that is extremely important for any job a person may have, yet it comes into play even more so with the military. War is something that requires a large amount of discipline, respect, and commitment. [...]
In the past sixteen years I have faced various challenges that have molded my personality to as it is today. I went through a very tough stage in my social life when I was in grade seven and eight at the age of twelve and [...]
“Weather 72, or 88. 44 or 68. We will not let exam results decide our fate”. Spoken Words artist Suli Breaks seamlessly illustrates the tug of war game that is my life. Somehow we’ve come to believe that we’re only as good as [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
- Grades 6-12
- School Leaders
Have You Seen Our List of Favorite Graphic Novels?
40 Philosophy of Education Examples, Plus How To Write Your Own
Learn how to define and share your teaching philosophy.

These days, it’s become common for educators to be asked what their personal teaching philosophy is. Whether it’s for a job interview, a college class, or to share with your principal, crafting a philosophy of education can seem like a daunting task. So set aside some time to consider your own teaching philosophy (we’ll walk you through it), and be sure to look at philosophy of education examples from others (we’ve got those too!).
What is a philosophy of education?
Before we dive into the examples, it’s important to understand the purpose of a philosophy of education. This statement will provide an explanation of your teaching values and beliefs. Your teaching philosophy is ultimately a combination of the methods you studied in college and any professional experiences you’ve learned from since. It incorporates your own experiences (negative or positive) in education.
Many teachers have two versions of their teaching philosophy: a long form (a page or so of text) and a short form. The longer form is useful for job application cover letters or to include as part of your teacher portfolio. The short form distills the longer philosophy into a couple of succinct sentences that you can use to answer teacher job interview questions or even share with parents.
What’s the best teaching philosophy?
Here’s one key thing to remember: There’s no one right answer to “What’s your teaching philosophy?” Every teacher’s will be a little bit different, depending on their own teaching style, experiences, and expectations. And many teachers find that their philosophies change over time, as they learn and grow in their careers.
When someone asks for your philosophy of education, what they really want to know is that you’ve given thought to how you prepare lessons and interact with students in and out of the classroom. They’re interested in finding out what you expect from your students and from yourself, and how you’ll apply those expectations. And they want to hear examples of how you put your teaching philosophy into action.
What’s included in strong teaching philosophy examples?
Depending on who you ask, a philosophy of education statement can include a variety of values, beliefs, and information. As you build your own teaching philosophy statement, consider these aspects, and write down your answers to the questions.
Purpose of Education (Core Beliefs)
What do you believe is the purpose of teaching and learning? Why does education matter to today’s children? How will time spent in your classroom help prepare them for the future?
Use your answers to draft the opening statement of your philosophy of education, like these:
- Education isn’t just about what students learn, but about learning how to learn.
- A good education prepares students to be productive and empathetic members of society.
- Teachers help students embrace new information and new ways of seeing the world around them.
- A strong education with a focus on fundamentals ensures students can take on any challenges that come their way.
- I believe education is key to empowering today’s youth, so they’ll feel confident in their future careers, relationships, and duties as members of their community.
- Well-educated students are open-minded, welcoming the opinions of others and knowing how to evaluate information critically and carefully.
Teaching Style and Practices
Do you believe in student-led learning, or do you like to use the Socratic method instead? Is your classroom a place for quiet concentration or sociable collaboration? Do you focus on play-based learning, hands-on practice, debate and discussion, problem-solving, or project-based learning? All teachers use a mix of teaching practices and styles, of course, but there are some you’re likely more comfortable with than others. Possible examples:
- I frequently use project-based learning in my classrooms because I believe it helps make learning more relevant to my students. When students work together to address real-world problems, they use their [subject] knowledge and skills and develop communication and critical thinking abilities too.
- Play-based learning is a big part of my teaching philosophy. Kids who learn through play have more authentic experiences, exploring and discovering the world naturally in ways that make the process more engaging and likely to make a lasting impact.
- In my classroom, technology is key. I believe in teaching students how to use today’s technology in responsible ways, embracing new possibilities and using technology as a tool, not a crutch.
- While I believe in trying new teaching methods, I also find that traditional learning activities can still be effective. My teaching is mainly a mix of lecture, Socratic seminar, and small-group discussions.
- I’m a big believer in formative assessment , taking every opportunity to measure my students’ understanding and progress. I use tools like exit tickets and Kahoot! quizzes, and watch my students closely to see if they’re engaged and on track.
- Group work and discussions play a major role in my instructional style. Students who learn to work cooperatively at a young age are better equipped to succeed in school, in their future careers, and in their communities.
Students and Learning Styles
Why is it important to recognize all learning styles? How do you accommodate different learning styles in your classroom? What are your beliefs on diversity, equity, and inclusion? How do you ensure every student in your classroom receives the same opportunities to learn? How do you expect students to behave, and how do you measure success? ADVERTISEMENT
Sample teaching philosophy statements about students might sound like this:
- Every student has their own unique talents, skills, challenges, and background. By getting to know my students as individuals, I can help them find the learning styles that work best for them, now and throughout their education.
- I find that motivated students learn best. They’re more engaged in the classroom and more diligent when working alone. I work to motivate students by making learning relevant, meaningful, and enjoyable.
- We must give every student equal opportunities to learn and grow. Not all students have the same support outside the classroom. So as a teacher, I try to help bridge gaps when I see them and give struggling students a chance to succeed academically.
- I believe every student has their own story and deserves a chance to create and share it. I encourage my students to approach learning as individuals, and I know I’m succeeding when they show a real interest in showing up and learning more every day.
- In my classroom, students take responsibility for their own success. I help them craft their own learning goals, then encourage them to evaluate their progress honestly and ask for help when they need it.
- To me, the best classrooms are those that are the most diverse. Students learn to recognize and respect each other’s differences, celebrating what each brings to the community. They also have the opportunity to find common ground, sometimes in ways that surprise them.
How do I write my philosophy of education?
Think back to any essay you’ve ever written and follow a similar format. Write in the present tense; your philosophy isn’t aspirational, it’s something you already live and follow. This is true even if you’re applying for your first teaching job. Your philosophy is informed by your student teaching, internships, and other teaching experiences.
Lead with your core beliefs about teaching and learning. These beliefs should be reflected throughout the rest of your teaching philosophy statement.
Then, explain your teaching style and practices, being sure to include concrete examples of how you put those practices into action. Transition into your beliefs about students and learning styles, with more examples. Explain why you believe in these teaching and learning styles, and how you’ve seen them work in your experiences.
A long-form philosophy of education statement usually takes a few paragraphs (not generally more than a page or two). From that long-form philosophy, highlight a few key statements and phrases and use them to sum up your teaching philosophy in a couple of well-crafted sentences for your short-form teaching philosophy.
Still feeling overwhelmed? Try answering these three key questions:
- Why do you teach?
- What are your favorite, tried-and-true methods for teaching and learning?
- How do you help students of all abilities and backgrounds learn?
If you can answer those three questions, you can write your teaching philosophy!
Short Philosophy of Education Examples
We asked real educators in the We Are Teachers HELPLINE group on Facebook to share their teaching philosophy examples in a few sentences . Here’s what they had to say:
I am always trying to turn my students into self-sufficient learners who use their resources to figure it out instead of resorting to just asking someone for the answers. —Amy J.

My philosophy is that all students can learn. Good educators meet all students’ differentiated learning needs to help all students meet their maximum learning potential. —Lisa B.
I believe that all students are unique and need a teacher that caters to their individual needs in a safe and stimulating environment. I want to create a classroom where students can flourish and explore to reach their full potential. My goal is also to create a warm, loving environment, so students feel safe to take risks and express themselves. —Valerie T.
In my classroom, I like to focus on the student-teacher relationships/one-on-one interactions. Flexibility is a must, and I’ve learned that you do the best you can with the students you have for however long you have them in your class. —Elizabeth Y
I want to prepare my students to be able to get along without me and take ownership of their learning. I have implemented a growth mindset. —Kirk H.
My teaching philosophy is centered around seeing the whole student and allowing the student to use their whole self to direct their own learning. As a secondary teacher, I also believe strongly in exposing all students to the same core content of my subject so that they have equal opportunities for careers and other experiences dependent upon that content in the future. —Jacky B.

All children learn best when learning is hands-on. This works for the high students and the low students too, even the ones in between. I teach by creating experiences, not giving information. —Jessica R.
As teachers, it’s our job to foster creativity. In order to do that, it’s important for me to embrace the mistakes of my students, create a learning environment that allows them to feel comfortable enough to take chances, and try new methods. —Chelsie L.
I believe that every child can learn and deserves the best, well-trained teacher possible who has high expectations for them. I differentiate all my lessons and include all learning modalities. —Amy S.
All students can learn and want to learn. It is my job to meet them where they are and move them forward. —Holli A.
I believe learning comes from making sense of chaos. My job is to design work that will allow students to process, explore, and discuss concepts to own the learning. I need to be part of the process to guide and challenge perceptions. —Shelly G.

I want my students to know that they are valued members of our classroom community, and I want to teach each of them what they need to continue to grow in my classroom. —Doreen G.
Teach to every child’s passion and encourage a joy for and love of education and school. —Iris B.
I believe in creating a classroom culture of learning through mistakes and overcoming obstacles through teamwork. —Jenn B.
It’s our job to introduce our kids to many, many different things and help them find what they excel in and what they don’t. Then nurture their excellence and help them figure out how to compensate for their problem areas. That way, they will become happy, successful adults. —Haley T.
Longer Philosophy of Education Examples
Looking for longer teaching philosophy examples? Check out these selections from experienced teachers of all ages and grades.
- Learning To Wear the Big Shoes: One Step at a Time
- Nellie Edge: My Kindergarten Teaching Philosophy
- Faculty Focus: My Philosophy of Teaching
- Robinson Elementary School: My Teaching Philosophy
- David Orace Kelly: Philosophy of Education
- Explorations in Higher Education: My Teaching Philosophy Statement
- University of Washington Medical School Faculty Teaching Philosophy Statements
Do you have any philosophy of education examples? Share them in the We Are Teachers HELPLINE Group on Facebook!
Want more articles and tips like this be sure to subscribe to our newsletters to find out when they’re posted..

You Might Also Like
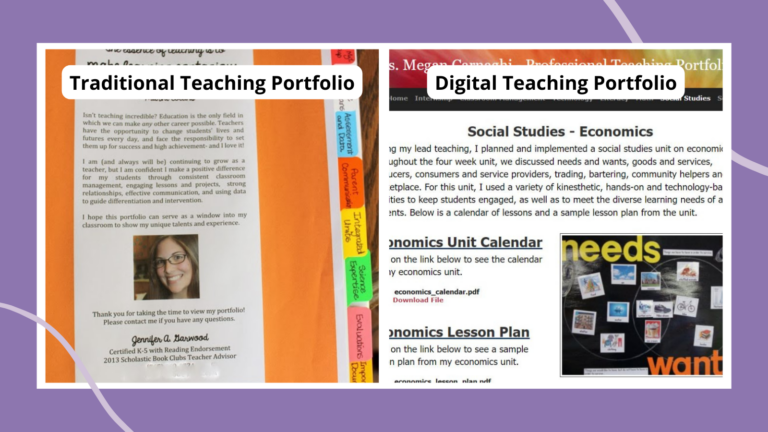
15 Inspiring Teaching Portfolio Examples (Plus How To Create Your Own)
Show them what you've got. Continue Reading
Copyright © 2024. All rights reserved. 5335 Gate Parkway, Jacksonville, FL 32256
Why is Elementary Education so Important?

It’s widely known that early education plays a critical role in how students perform in their later school years. Understanding just how crucial these early education years are is important.
According to The Annie E. Casey Foundation, the annual average learning gain for students in kindergarten through second grade is higher than at any time during a child’s years in school. And the ability to read proficiently by fourth grade is so important that not doing so often puts kids on track to drop out of high school.
For teachers considering a master’s degree in education, focusing on elementary education offers a chance to become a leader in this critical area.
The Power of Reading
While there are important aspects to elementary education across all subjects, almost all of it comes back to the ability to read. Reading is how students can be introduced to every educational subject presented to them. And although it’s a skill we learn at a young age, reading is complex. Students need the opportunity to ask questions, make predictions and grasp words they may not completely understand based on their contextual use.
Teachers of elementary education have to stretch their teaching skills to face the challenges of teaching children to read. Students in any given classroom possess a vast range of reading skills. Elementary school teachers must have strategies to help students interpret complex ideas, develop critical skills, synthesize information from diverse sources and use reading to learn about all subjects.
This requires a high level of teaching expertise in elementary education – something that the state of Massachusetts requires.
A Master of Education with a focus on elementary education can prepare teachers to become leaders both in the classroom and with their peers, helping them find strategies that will lead to better outcomes for students.
What You’ll Learn in a Master’s Degree Program
Because of the challenging nature of elementary education, quality master’s degree programs are designed to give graduates expertise in a range of areas.
In the Merrimack College Master of Education programs, students take classes on a variety of topics, including the following.
Teaching and Learning in the Inclusive Classroom
Teachers learn how to use different instructional strategies to accommodate students of varying backgrounds, learning styles and levels of academic readiness. They also learn how to create cooperative, orderly and motivational student environments.
Foundations of Language and Reading
Good reading skills are the foundation for academic achievement. Teachers taking this course learn the fundamental skills behind language and reading development.
Reading Strategies and Interventions
This course provides an introduction to the significant theories, practices, and programs for developing literacy skills in students with learning challenges. This includes students from diverse linguistic and cultural backgrounds, as well as students with limited experience in an educational environment.
Math Methods for the Elementary School
Students learn how to teach math skills to students from diverse backgrounds and experiences. This includes developing learning objectives, instructional methods, and assessment techniques. This course is designed with consideration for recommendations from the professional standards established by the Massachusetts Department of Elementary and Secondary Education, among other sources.
Curriculum, Instruction and Assessment in Social Studies and World Geography
This course focuses on teaching skills in three areas of social studies: the development of geography skills and global awareness, the development of history skills that include critical, creative and analytical thinking, and cooperative learning, vocabulary, and concept formation.
Curriculum, Instruction and Assessment in Science, Health and Physical Education
Students learn teaching methods that promote the development of cognitive and scientific reasoning, as well as strategies for teaching science and assessing students’ understanding. Other sections of the course deal with health education, laws and regulations on student health and safety, warning signs that students are experiencing issues and development of school physical education programs.
Massachusetts and Elementary Education
The Merrimack College degree program prepares teachers for the MTEL exams. Massachusetts requires these exams before teachers can earn the Initial License to teach in Massachusetts. Preparation for the exams is a part of the degree program. The MTEL exams required are:
- Communication and Literacy Skills
- Math and Multi-Subject subtests of the General Curriculum exam
- Foundations of Reading
Merrimack College provides a degree program that meets the state’s rigorous standards. The Elementary education years are some of the most important in the life of a student. They deserve teachers who have trained themselves to work at the highest possible level.
Request Information
- Resources ›
- For Educators ›
- Becoming A Teacher ›
How to Write a Philosophy of Education for Elementary Teachers
- Becoming A Teacher
- Assessments & Tests
- Elementary Education
- Secondary Education
- Special Education
- Homeschooling
- M.S., Education, Buffalo State College
- B.S., Education, Buffalo State College
A philosophy of education statement, sometimes called a teaching statement, should be a staple in every teacher's portfolio. For elementary school teachers, the statement is an opportunity to define what teaching means to you and allows you to describe how and why you teach as you do at the early stages of learning. The following tips and philosophy of education examples for elementary teachers can help you write an essay that you'll be proud to have.
A philosophy of education statement is an opportunity to define what teaching means to you, and to describe how and why you teach as you do. Articulating this statement in the first person and using a traditional essay format (introduction, body, conclusion) will help you craft an enduring and inspiring personal statement.
Structure of a Teaching Philosophy
Unlike other kinds of writing, educational statements are frequently written in the first person because these are personal essays on your chosen profession. In general, they should be one to two pages long, though they can be longer if you've had an extensive career. Like other essays, a good educational philosophy should have an introduction, a body, and a conclusion. Here is a sample structure.
Introduction
Use this paragraph to describe your views on teaching in a general sense. State your thesis (for example, "My philosophy of education is that every child should have the right to learn and get a quality education.") and discuss your ideals. Be brief; you'll use the following paragraphs to explain the details. Think about aspects of early education that are unique to elementary teachers, and introduce these ideals into your writing.
Use the following three to five paragraphs (or more, if needed) to elaborate on your introductory statement. For example, you could discuss the ideal elementary classroom environment and how it makes you a better teacher, addresses student needs, and facilitates parent/child interactions.
Build on these ideals in the following paragraphs by discussing how you keep your classes aware and engaged, how you facilitate age-appropriate learning , and how you involve students in the assessment process . Whatever your approach, remember to focus on what you value most as an educator and to cite examples of how you've put these ideals into practice.
Go beyond simply restating your educational philosophy in your closing. Instead, talk about your goals as a teacher, how you have been able to meet them in the past, and how you can build on these to meet future challenges.
Philosophy of education documents for elementary teachers are very personal and unique to the individual. While some may have similarities, your own philosophy should focus on your personal approach to pedagogy and classroom management. Focus on what makes you unique as an educator, and how you wish to advance your career to further support elementary education.
Writing Prompts
As with any writing, take the time to outline your ideas before you begin. The following tips can help you craft your teaching philosophy statement:
- Brainstorm about your educational philosophy and your views of education, making notes on those principles you value most. This can help you articulate your philosophy as you organize your essay.
- Demonstrate how you have put your educational philosophy into practice in the classroom by citing specific examples and outcomes with students, parents, or fellow teachers and administrators.
- Reflect on your experience over your career. Most likely, your teaching philosophy has changed over time. Reflect on the opportunities and challenges that lie ahead, and how you intend to meet them.
- Connect with others and talk to your peers in the field, as well as mentors. Ask them about how they crafted their essays and ask them to review yours once you complete it. Having people who know you and your teaching style well review your work can help you craft a truly representative statement.
- Review a few sample essays to help you as you begin writing your own.

Career Advancement
Applying for a brand new job isn't the only time you need an educational philosophy. If you're seeking a promotion or are applying for tenure, you'll need to craft or update your educational philosophy statement. As time goes on, your approach to education and classroom management will likely evolve, and so will your beliefs. Updating your philosophy allows you to articulate your professional motivations and goals, as well as your approach to educating others so that observers can have a better sense of who you are, even without observing you in the classroom. Consider reviewing your philosophy every few years.
- What Requirements Are Needed to Be an Elementary School Teacher?
- 4 Teaching Philosophy Statement Examples
- What Is the Role of a Teacher?
- 9 Things to Know About Becoming a Teacher
- Top Tips for Acing a Teacher Interview
- Common Interview Questions in Education
- 8 Signs You Should Become a Teacher
- What Is Student Teaching Really Like?
- 7 Reasons to Become a Teacher
- Learning the Basics of a Student Teacher Resume
- A Short Guide to Microteaching
- Weighing the Decision: To Teach or Not to Teach
- Landing Your First Teaching Job
- 24 Simple Rules All Teachers Should Live By
- Student Teacher Evaluation Criteria
- 10 Useful Skills Modern Teachers Need
Essay on Education for School Students and Children
500+ words essay on education.
Education is an important tool which is very useful in everybody’s life. Education is what differentiates us from other living beings on earth. It makes man the smartest creature on earth. It empowers humans and gets them ready to face challenges of life efficiently. With that being said, education still remains a luxury and not a necessity in our country. Educational awareness needs to be spread through the country to make education accessible. But, this remains incomplete without first analyzing the importance of education. Only when the people realize what significance it holds, can they consider it a necessity for a good life. In this essay on Education, we will see the importance of education and how it is a doorway to success.

Importance of Education
Education is the most significant tool in eliminating poverty and unemployment . Moreover, it enhances the commercial scenario and benefits the country overall. So, the higher the level of education in a country, the better the chances of development are.
In addition, this education also benefits an individual in various ways. It helps a person take a better and informed decision with the use of their knowledge. This increases the success rate of a person in life.
Subsequently, education is also responsible for providing with an enhanced lifestyle. It gives you career opportunities that can increase your quality of life.
Similarly, education also helps in making a person independent. When one is educated enough, they won’t have to depend on anyone else for their livelihood. They will be self-sufficient to earn for themselves and lead a good life.
Above all, education also enhances the self-confidence of a person and makes them certain of things in life. When we talk from the countries viewpoint, even then education plays a significant role. Educated people vote for the better candidate of the country. This ensures the development and growth of a nation.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
Doorway to Success
To say that education is your doorway to success would be an understatement. It serves as the key which will unlock numerous doors that will lead to success. This will, in turn, help you build a better life for yourself.
An educated person has a lot of job opportunities waiting for them on the other side of the door. They can choose from a variety of options and not be obligated to do something they dislike. Most importantly, education impacts our perception positively. It helps us choose the right path and look at things from various viewpoints rather than just one.

With education, you can enhance your productivity and complete a task better in comparison to an uneducated person. However, one must always ensure that education solely does not ensure success.
It is a doorway to success which requires hard work, dedication and more after which can you open it successfully. All of these things together will make you successful in life.
In conclusion, education makes you a better person and teaches you various skills. It enhances your intellect and the ability to make rational decisions. It enhances the individual growth of a person.
Education also improves the economic growth of a country . Above all, it aids in building a better society for the citizens of a country. It helps to destroy the darkness of ignorance and bring light to the world.

FAQs on Education
Q.1 Why is Education Important?
A.1 Education is important because it is responsible for the overall development of a person. It helps you acquire skills which are necessary for becoming successful in life.
Q.2 How does Education serve as a Doorway to Success?
A.2 Education is a doorway to success because it offers you job opportunities. Furthermore, it changes our perception of life and makes it better.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

A primer on elementary and secondary education in the United States
Editor’s Note: This report is an excerpt, with minor edits, from Addressing Inequities in the US K-12 Education System , which first appeared in Rebuilding the Pandemic Economy , published by the Aspen Economic Strategy Group in 2021.
This report reviews the basics of the American elementary and secondary education system: Who does what and how do we pay for it? While there are some commonalities across the country, the answers to both questions, it turns out, vary considerably across states. 1
Who does what?
Schools are the institution most visibly and directly responsible for educating students. But many other actors and institutions affect what goes on in schools. Three separate levels of government—local school districts, state governments, and the federal government—are involved in the provision of public education. In addition, non-governmental actors, including teachers’ unions, parent groups, and philanthropists play important roles.
Most 5- to 17-year-old children – about 88%– attend public schools. 2 (Expanding universal schooling to include up to two years of preschool is an active area of discussion which could have far-reaching implications, but we focus on grades K-12 here.) About 9% attend private schools; about a quarter of private school students are in non-sectarian schools, and the remaining three-quarters are about evenly split between Catholic and other religious schools. The remaining 3% of students are homeschooled.
Magnet schools are operated by local school districts but enroll students from across the district; magnet schools often have special curricula—for example, a focus on science or arts—and were sometimes designed specifically to encourage racial integration. Charter schools are publicly funded and operate subject to state regulations; private school regulations and homeschooling requirements are governed by state law and vary across states. Nationally, 6.8% of public school students are enrolled in charter schools; the remainder attend “traditional public schools,” where students are mostly assigned to schools based on their home address and the boundaries school districts draw. Washington, D.C. and Arizona have the highest rates of charter enrollment, with 43 and 19% of their public school students attending charter schools. Several states have little or no charter school enrollment. Prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, nearly all public schooling took place in person, with about 0.6% of students enrolled in virtual schools.
Local School Districts
Over 13,000 local education agencies (LEAs), also known as school districts, are responsible for running traditional public schools. The size and structure of local school districts, as well as the powers they have and how they operate, depend on the state. Some states have hundreds of districts, and others have dozens. District size is mostly historically determined rather than a reflection of current policy choices. But while districts can rarely “choose” to get smaller or larger, district size implicates important trade-offs . Having many school districts operating in a metropolitan area can enhance incentives for school and district administrators to run schools consistent with the preferences of residents, who can vote out leaders or vote with their feet by leaving the district. On the other hand, fragmentation can lead to more segregation by race and income and less equity in funding, though state laws governing how local districts raise revenue may address the funding issues. Larger districts can benefit from economies of scale as the fixed costs of operating a district are spread over more students and they are better able to operate special programs, but large districts can also be difficult to manage. And even though large districts have the potential to pool resources between more- and less-affluent areas, equity challenges persist as staffing patterns lead to different levels of spending at schools within the same district.
School boards can be elected or appointed, and they generally are responsible for hiring the chief school district administrator, the superintendent. In large districts, superintendent turnover is often cited as a barrier to sustained progress on long term plans, though the causation may run in the other direction: Making progress is difficult, and frustration with reform efforts leads to frequent superintendent departures. School districts take in revenue from local, state, and federal sources, and allocate resources—primarily staff—to schools. The bureaucrats in district “central offices” oversee administrative functions including human resources, curriculum and instruction, and compliance with state and federal requirements. The extent to which districts devolve authority over instructional and organizational decisions to the school level varies both across and within states.
State Governments
The U.S. Constitution reserves power over education for the states. States have delegated authority to finance and run schools to local school districts but remain in charge when it comes to elementary and secondary education. State constitutions contain their own—again, varying—language about the right to education, which has given rise to litigation over the level and distribution of school funding in nearly all states over the past half century. States play a major role in school finance, both by sending aid to local school districts and by determining how local districts are allowed to tax and spend, as discussed further below.
State legislatures and state education agencies also influence education through mechanisms outside the school finance system. For example, states may set requirements for teacher certification and high school graduation, regulate or administer retirement systems, determine the ages of compulsory schooling, decide how charter schools will (or will not) be established and regulated, set home-schooling requirements, establish curricular standards or approve specific instructional materials, choose standardized tests and proficiency standards, set systems for school accountability (subject to federal law), and create (or not) education tax credits or vouchers to direct public funds to private schools. Whether and how states approach these issues—and which functions they delegate to local school districts—varies considerably.
Federal Government
The authority of the federal government to direct schools to take specific actions is weak. Federal laws protect access to education for specific groups of students, including students with disabilities and English language learners. Title IX prohibits sex discrimination in education, and the Civil Rights Act prohibits discrimination on the basis of race. The U.S. Department of Education issues regulations and guidance on K-12 laws and oversees grant distribution and compliance. It also collects and shares data and funds research. The Bureau of Indian Education is housed in the Department of the Interior, not the Department of Education.
The federal government influences elementary and secondary education primarily by providing funding—and through the rules surrounding the use of those funds and the conditions that must be met to receive federal funding. Federal aid is typically allocated according to formulas targeting particular populations. The largest formula-aid federal programs are Title I of the Elementary and Secondary Education Act (ESEA), which provides districts funds to support educational opportunity, and the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA), for special education. Both allocate funding in part based on child poverty rates. State and school district fiscal personnel ensure that districts comply with rules governing how federal funds can be spent and therefore have direct influence on school environments. Since 1965, in addition to specifying how federal funds can be spent, Congress has required states and districts to adopt other policies as a condition of Title I receipt. The policies have changed over time, but most notably include requiring school districts to desegregate, requiring states to adopt test-based accountability systems, and requiring the use of “evidence-based” approaches.
IDEA establishes protections for students with disabilities in addition to providing funding. The law guarantees their right to a free and appropriate public education in the least restrictive setting and sets out requirements for the use of Individualized Educational Programs. Because of these guarantees, IDEA allows students and families to pursue litigation. Federal law prohibits conditioning funding on the use of any specific curriculum. The Obama Administration’s Race to the Top program was also designed to promote specific policy changes—many related to teacher policy—but through a competitive model under which only select states or districts “won” the funds. For the major formula funds, like Title I and IDEA, the assumption (nearly always true) is that states and districts will adopt the policies required to receive federal aid and all will receive funds; in some cases, those policy changes may have more impact than the money itself. The federal government also allocated significant funding to support schools during the Great Recession and during the COVID-19 pandemic through specially created fiscal stabilization or relief funds; federal funding for schools during the COVID crisis was significantly larger than during the Great Recession.
The federal tax code, while perhaps more visible in its influence on higher education, also serves as a K-12 policy lever. The controversial state and local tax deduction, now limited to $10,000, reduces federal tax collections and subsidizes progressive taxation for state and local spending, including for education. As of 2018, 529 plans, which historically allowed tax-preferred savings only for higher education expenses, can also be used for private K-12 expenses.
Non-Governmental Actors
Notable non-governmental actors in elementary and secondary education include teachers’ unions and schools of education, along with parents, philanthropists, vendors, and other advocates.The nation’s three million public school teachers are a powerful political force, affecting more than just teachers’ compensation. For example, provisions of collective bargaining agreements meant to improve teachers working conditions also limit administrator flexibility. Teachers unions are also important political actors; they play an active role in federal, state, and school board elections and advocate for (or, more often, against) a range of policies affecting education. Union strength varies considerably across U.S. states.
Both states and institutions of higher education play important roles in determining who teaches and the preparation they receive. Policies related to teacher certification and preparation requirements, ranging from whether teachers are tested on academic content to which teachers are eligible to supervise student teachers, vary considerably across states. 3 Meanwhile, reviews of teacher training programs reveal many programs do not do a good job incorporating consensus views of research-based best practices in key areas. To date, schools of education have not been the focus of much policy discussion, but they would be critical partners in any changes to how teachers are trained.
Parents play an important role, through a wide range of channels, in determining what happens in schools. Parents choose schools for their children, either implicitly when they choose where to live or explicitly by enrolling in a charter school, private school, participating in a school district choice program, or homeschooling, though these choices are constrained by income, information, and other factors. They may also raise money through Parent Teacher Associations (PTAs) or other foundations—and determine how it is spent. And they advocate for (or against) specific policies, curriculum, or other aspects of schooling through parent organizations, school boards, or other levels of government. Parents often also advocate for their children to receive certain teachers, placements, evaluation, or services; this is particularly true for parents of students with disabilities, who often must make sure their children receive legally required services and accommodations. Though state and federal policymakers sometimes mandate parent engagement , these mechanisms do not necessarily provide meaningful pathways for parental input and are often dominated by white and higher-SES parents .
Philanthropy also has an important influence on education policy, locally and nationally. Not only do funders support individual schools in traditional ways, but they are also increasingly active in influencing federal and state laws. Part of these philanthropic efforts happen through advocacy groups, including civil rights groups, religious groups, and the hard-to-define “education reform” movement. Finally, the many vendors of curriculum, assessment, and “edtech” products and services bring their own lobbying power.
Paying for school
Research on school finance might be better termed school district finance because districts are the jurisdictions generating and receiving revenue, and districts, not schools, are almost always responsible for spending decisions. School districts typically use staffing models to send resources to schools, specifying how many staff positions (full-time equivalents), rather than dollars, each school gets.
Inflation-adjusted, per-pupil revenue to school districts has increased steadily over time and averaged about $15,500 in 2018-19 (total expenditure, which includes both ongoing and capital expenditure, is similar but we focus on revenue because we are interested in the sources of revenue). Per-pupil revenue growth tends to stall or reverse in recessions and has only recently recovered to levels seen prior to the Great Recession (Figure 1). On average, school districts generated about 46% of their revenue locally, with about 80% of that from property taxes; about 47% of revenue came from state governments and about 8% from the federal government. The share of revenue raised locally has declined from about 56% in the early 1960s to 46% today, while the state and federal shares have grown. Local revenue comes from taxes levied by local school districts, but local school districts often do not have complete control over the taxes they levy themselves, and they almost never determine exactly how much they spend because that depends on how much they receive in state and federal aid. State governments may require school districts to levy certain taxes, limit how much local districts are allowed to tax or spend, or they may implicitly or explicitly redistribute some portion of local tax revenue to other districts.
Both the level of spending and distribution of revenue by source vary substantially across states (Figure 2), with New York, the highest-spending state, spending almost $30,000 per pupil, while Idaho, Utah, and Oklahoma each spent under $10,000 per pupil. (Some, but far from all, of this difference is related to higher labor costs in New York.) Similarly, the local share of revenue varies from less than 5% in Hawaii and Vermont to about 60% in New Hampshire and Nebraska. On average, high-poverty states spend less, but there is also considerable variation in spending among states with similar child poverty rates.
Discussions of school funding equity—and considerable legal action—focus on inequality of funding across school districts within the same state . While people often assume districts serving disadvantaged students spend less per pupil than wealthier districts within a state, per-pupil spending and the child poverty rate are nearly always uncorrelated or positively correlated, with higher-poverty districts spending more on average. Typically, disadvantaged districts receive more state and federal funding, offsetting differences in funding from local sources. Meanwhile, considerable inequality exists between states, and poorer states spend less on average. Figure 3 illustrates an example of this dynamic, showing the relationship between district-level per-pupil spending and the child poverty rate in North Carolina (a relatively low-spending state with county- and city-based districts) and Illinois (a higher-spending state with many smaller districts). In North Carolina, higher poverty districts spend more on average; Illinois is one of only a few states in which this relationship is reversed. But this does not mean poor kids get fewer resources in Illinois than in North Carolina. Indeed, nearly all districts in Illinois spend more than most districts in North Carolina, regardless of poverty rate.
Figure 4 gives a flavor of the wide variation in per-pupil school spending. Nationally, the district at the 10th percentile had per-pupil current expenditure of $8,800, compared to $18,600 at the 90th percentile (for these calculations we focus on current expenditure, which is less volatile year-to-year, rather than revenue). Figure 4 shows that this variation is notably not systematically related to key demographics. For example, on average, poor students attend school in districts that spent $13,023 compared to $13,007 for non-poor students. The average Black student attends school in a district that spent $13,485 per student, compared to $12,918 for Hispanic students and $12,736 for White students. 4 School districts in high-wage areas need to spend more to hire the same staff, but adjusting spending to account for differences in prevailing wages of college graduates (the second set of bars) does not change the picture much.
Does this mean the allocation of spending is fair? Not really. First, to make progress reducing the disparities in outcomes discussed above, schools serving more disadvantaged students will need to spend more on average. Second, these data are measured at the school district level, lumping all schools together. This potentially masks inequality across (as well as within) schools in the same district.
The federal government now requires states to report some spending at the school level; states have only recently released these data. One study using these new data finds that within districts, schools attended by students of color and economically-disadvantaged students tend to have more staff per pupil and to spend more per pupil. These schools also have more novice teachers. How could within-district spending differences systematically correlate with student characteristics, when property taxes and other revenues for the entire district feed into the central budget? Most of what school districts buy is staff, and compensation is largely based on credentials and experience. So schools with less-experienced teachers spend less per pupil than those with more experienced ones, even if they have identical teacher-to-student ratios. Research suggests schools enrolling more economically disadvantaged students, or more students of color, on average have worse working conditions for teachers and experience more teacher turnover. Together, this means that school districts using the same staffing rules for each school—or even allocating more staff to schools serving more economically disadvantaged students—would have different patterns in spending per pupil than staff per pupil.
[1] : For state-specific information, consult state agency websites (e.g., Maryland State Department of Education) for more details. You can find data for all 50 states at the U.S. Department of Education’s National Center for Education Statistics , and information on state-specific policies at the Education Commission of the States .
[2] : The numbers in this section are based on the most recent data available in the Digest of Education Statistics, all of which were collected prior to the COVID-19 pandemic.
[3] : See the not-for-profit National Council on Teacher Quality for standards and reviews of teacher preparation programs, and descriptions of state teacher preparation policies.
[4] : These statistics may be particularly surprising to people given the widely publicized findings of the EdBuild organization that, “ Nonwhite school districts get $23 billion less than white school districts. ” The EdBuild analysis estimates gaps between districts where at least 75% of students are non-White versus at least 75% of students are White. These two types of districts account for 53% of enrollment nationally. The $23 billion refers to state and local revenue (excluding federal revenue), whereas we focus on current expenditure (though patterns for total expenditure or total revenue are similar).
Disclosures: The Brookings Institution is financed through the support of a diverse array of foundations, corporations, governments, individuals, as well as an endowment. A list of donors can be found in our annual reports published online here . The findings, interpretations, and conclusions in this report are solely those of its author(s) and are not influenced by any donation .
About the Authors
Sarah reber, joseph a. pechman senior fellow – economic studies, nora gordon, professor – mccourt school of public policy, georgetown university.
Student Writing Samples
Annotated student writing samples illustrating the integration of content understanding and writing in the three types of writing expected by college- and career-ready standards, including the CCSS. The resources presented are from In Common: Effective Writing for All Students , authored by the Vermont Writing Collaborative with Student Achievement Partners and CCSSO. There are two types of resources available:
- On-Demand Writing provides a progression of writing across grades (K–5 and 6–12); students have written independently to the same text-based prompt across grades.
- Range of Writing provides multiple examples of student writing within a grade across a wide variety of content areas, curriculum units, conditions for writing, and purposes.
Learn more about In Common.
Resources specifically designed to support understanding and development of CCR-aligned writing
Filter by category
- Argument/Opinion Writing
- Informative/Explanatory Writing
- Narrative Writing
To find out how mini-assessment questions align to particular standards, use the Literacy Mini-Assessment Sorter Microsoft Excel file Learn More
Results (39)
- Most Downloaded Date Added Title (A-Z)
Narrative: Range of Writing
These pieces represent a wide variety of content areas, curriculum units, conditions for writing, and purposes. They reflect Comm…
Argument/Opinion: Range of Writing
Informative/explanatory: range of writing.
Grades 11–12
Grades 9–10
Informative/Explanatory Writing: On-Demand ©
The pieces in this On-Demand section represent one of the three types of writing named in the Common Core State Standards for Writing: …
Grades K–5
Informative/Explanatory Writing: On-Demand
Grades 6–12
Narrative Writing: On-Demand
Argument/opinion writing: on-demand, narrative writing: on-demand ©.

Essay on My School Life

Table of Contents
Essay on My School Life: School life is the best phase of a student’s life. It is a time when a student learns new things and explores his/her own potential. It is a time when a student discovers his/her own identity and develops a sense of self-confidence. School life is also a time when a student develops friendships and bonds with classmates. These friendships and bonds often last a lifetime.
Fill Out the Form for Expert Academic Guidance!
Please indicate your interest Live Classes Books Test Series Self Learning
Verify OTP Code (required)
I agree to the terms and conditions and privacy policy .
Fill complete details
Target Exam ---
We have always heard that school life is the best life, enjoy yourself till you are in school make as many mistakes as you can till you are in school, and many such phrases which make the kids who are still in school wonder that why are the elder people hyping this thing up. But as soon as the school life is over and people enter the real world they realize that how right the elders were.
Children should live their school life to the fullest. They will be missing these days later in life and would never be able to enjoy such carefree life again. School life lived well gives memories to cherish and friend to keep for a lifetime. Here are essays on My School Life of varying lengths to help you with the topic in your exam. You can select any My School Life Essay as per your interest and need:
Long and Short Essay on My School Life in English

Essay on My School Life 200 words
School is said to be a temple of knowledge, the very first place that introduced you to the world and more so your own self. My school life is all about the memories I deeply cherish. The memories of not only the fun, friendship and all the sport and extracurricular but also the way it helped me find my interests. I owe it all to my school life. It has made me who I am today.
My school life has been full of different experiences over the years. It gave various opportunities to develop not only my scholastic abilities but also the art and sport side. It supported me in my sports as well as exposed me to numerous types of people. All of this accounted to make me understand how to behave socially and in building a personality which I have today.
There are numerous things that make school life the best phase in one’s life. All of this eventually is because we are young to do mistakes again and again till we realize, dumb enough to not think about people and do what we feel like doing, curious to know everything we can and most importantly still not exposed and contaminated with the evil feelings of this world. And all of this makes us build a personality of our own.

Essay on My School Life Experience 300 words
In my school life, I’ve always been that ideal studious student so I typically don’t have that super amazing bunch of memories like the notorious back benchers except for ones that I remember when I was in my eighth grade.
My School Life Experience
It was a usual day at school until this incident took place. It was about the time of recess when I used to play football with my classmates. One day while I was out in the field suddenly a boy called Stephen Francis who was also the captain of our school football team kicked my brand new Liverpool FC soccer ball out of the school premises, to the narrow lane that passed just behind our school ground.
The walls of our school were a bit high and fenced and like every other school, going out of the premises was strictly prohibited. We partially climbed the wall so that we could have a look on the ball and waited for some genuine person to pass by so that we could ask him to return our ball.
We had to wait for quite long until a guy of almost same age as ours walked by. He was quite far however he saw the ball and went towards it. We saw that he tried to run away taking the ball. So, without thinking twice I and my friend jumped the school wall but till the time we could make it past the wall he was already running with our soccer ball.
We started running behind him and my friend bumped into a bike and was hurt badly. I probably had to let go off my soccer ball and see how she was hurt. She got three stitches from that injury. We were scolded by teachers and principal for this, as a punishment our parents were called to school the next day to discuss the seriousness of the trouble.
Since then me and this friend of mine have been partners in numerous mischief that have made my school life memorable.
Essay on School Life is the Best Life 400 words
Every phase in a person’s life holds special importance as it helps him grow and develop his personality. But one can never learn as much as he does from his school life because that is the time when we are doing everything for the first time. This is the time we can make mistakes and get away with them. We don’t care much about the people around and are curious to try everything out. We build our unique personality from our mistakes and experiences.
How School Life is the Best Life?
Here are some reasons that prove that school life is the best life:
- Uniform : One hates school uniform while in school but when we grow up we realize how difficult it is to figure out what to wear each day.
- Holidays : This is the major perk of school life which we crave the most after it ends. We got numerous holidays while in school and spent them in a carefree manner without any stress. We visited our cousins and extended family and also invited them over to our place. As we join jobs, we don’t get as many holidays to relax and enjoy.
- Friends : The longest known friendships are made during the school days. This is mainly because during this time we can trust people easily. We are also enthusiastic and curious to meet new people, try new things and build new friendships.
- Teachers : We realize how important it is to always have a guide who still thinks that we are immature for everything and makes us understand accordingly. We cannot get such a mentor/ guide after we have completed our schooling.
- Homework : A thing which we hate during our school life and tried hundreds of creative excuses to avoid was actually fun. School life would have been so incomplete without it.
- Punishments and rewards : Punishments used to come in the variety of standing whole period or getting out of the class or going to the principal’s office and the best reward was when someone was made the class monitor.
- First Experiences : It was the time when we are allowed to make mistakes as too many things were our firsts, whether it was our first crush, first heartbreak without even being in relationship, first fight or first kiss.
All of these experiences hold a special importance in our hearts even as we grow up. They have taught me a lot and have helped me become the person I am today.
Essay on My School Life Memories 500 words
A school is a building dedicated to provide learning space and environment to provide education. It is a building wherein your majority of childhood has passed, a building that everyone misses after they’ve finally left it, same is the scenario in my case. I’ve studied in Don Bosco High School Vadodara, an all-boys Christian missionary School. Hard for other people to admit but being in an all-boys school has got some perks that only those who study here can understand.
My Memories of Primary and Secondary Classes
I’ve been a part of Don Bosco institution since kindergarten until my tenth grade. After tenth in higher secondary I went to Rosary high school, which was more or less like an unofficial dummy school for the students in science stream so I barely have any school memories from higher secondary school. So, the story of my enchanting school memories revolves around my school from junior years.
Like a stereotypical school going kid I used to go to the school in a school van. I would wake up at quarter to six in the morning, get fresh, wear school uniform, arrange my school bag according to the time table for the day and have a quick breakfast by 6:40 am as at sharp quarter to seven my school van would be right in front of my house honking. Then, further half an hour until we reached school was a time for chit-chat and discussion about the homework assigned to us the earlier day.
Free Online Mock Tests For IIT-JEE, NEET And CBSE Exams
The Daily Activities at School
We would reach the school at around 7:30 am, approximately fifteen minutes prior to the school bell. We had to be in our respective classes before the bell rang. Then it was time for national song and school prayer that went on until eight which was a time for regular school periods to begin. This continued for four periods continuously until the recess bell rang at 10:30 am. Recess felt more of a games period then a lunch break. Everyone would be seen doing different activities during this time. The kind of activities one indulged in depended on the class he was in.
When we were in the primary classes we played different games in the school garden. Basketball, football, running and hide and seek were some of our favourite games. As we reached the secondary classes, we began to sit in the canteen to chit chat about the various things and enjoy delicious food. After the recess, we had to attend four more periods. Not every period was that boring though, art and craft, PT, value education and mathematics periods were interesting for me.
Apart from this formal schedule at school, those gossips with friends, hanging around at canteen, going to washroom to partially bunk the lecture, that fear of punishment when we’d forgotten to complete the homework, that note which the teacher wrote in the handbook when we’d done some mischief in the class, the ride in nervousness from home to school on the result day, from immature fights to the innocent laughs – everything from the school feels so dear now, maybe because the things were simple back then.

Essay on My High School Experience 600 words
It is said that entering the high school is the first step in the real world in any student’s life. It is the place where one gets experiences for life. So, one is obviously nervous while entering this phase, but over and above that, extremely excited as now they’ll be adults and will be able to take their decisions on their own. And it is well said that with great authority, comes greater responsibility, and with these responsibilities, comes social pressure. All of which we were unaware of from our childhood time because that is when we were allowed to do mistakes thinking that we are kids, but this doesn’t happen in high school as we are considered adults now.
My High School Experience
One cannot live a carefree life in the high school. There is a lot of study pressure. We need to balance between our academics and extra-curricular activities and also prepare for competitive examinations that lie ahead. Even as we have so much to do we don’t want to miss out on the fun we can have with our friends as this is also the time for blooming friendships and a lot of mischief.
The Day I Bunked My School
I had many bittersweet high school experiences. One of these was when I bunked a lecture, with two of my friends, for the first time. Not only did we bunk the lecture, but also we jumped through our school walls to get out of the school premises and watch a newly released movie. We had a class of 70 students, out of which, around 55 students were present that day.
Now coincidentally, 10 more students from my class also bunked the lecture which made the decreased class strength visible. Moreover, the bags of all of the 13 students, including us, were still there in the class, as we were not allowed to leave the class with bags during school hours. So, our teacher did the checking and found out about the students who bunked and so eventually we were suspended from our laboratory sessions for a week.
However, we didn’t stop bunking lectures post this. We became really smart in finding ways to bunk. We tried to strike a balance between being a good student and enjoying high school. During all those bunks, I realized how important it is to have friends to make your life worth living.
The Ups and Downs in My High School
Then, there came our first high school exam and I managed to be on the list of top 10 students of my class. I had always been a good student academically. So this time, even after all the shenanigans that I indulged in, I managed to score good marks. But this was the last time that I got good marks. My grades started degrading after that and this led to a lot of stress and anxiety. I lost interest in studies and indulged in gaming, watching movies or reading novels.
Thankfully, I didn’t do anything bad, but this normal stuff made the situation worse as I could not concentrate on my studies. So, I went through counselling which I never thought I’ll ever require. It was a difficult period for me but eventually I was able to get decent score in my finals. My parents stood as my pillar of strength during this time. They encouraged me to study and motivated me to lead the right path. I cannot thank them enough for their guidance and support.
All of such experiences from my high school gave me lessons to remember for a lifetime. They made me realize how everything wrong could turn right if only you believe so and have support from your loved ones.
Visit IL website for more study resource.
Essay on My School Life FAQs
How do i write an essay about my school.
To write an essay about your school, start with an introduction, describe the campus, mention teachers and friends, highlight activities, and conclude with your thoughts.
How to write 10 lines about our school?
Write about the school's name, location, facilities, teachers, subjects, friends, favorite spots, activities, why it's special, and how you feel about it.
What makes my school special essay?
Your school is special because of its caring teachers, fun activities, great friends, and a positive learning environment that makes you happy to go there.
What is the paragraph of my school?
My school is a wonderful place where I learn, play, and make friends. Teachers are kind, and I love my school because it feels like a second home.
Related content

Get access to free Mock Test and Master Class
Register to Get Free Mock Test and Study Material
Offer Ends in 5:00
Select your Course
Please select class.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Introduction Elementary education is the initial phase of formal schooling for children aged 5-12. Generally, it covers subjects including literacy and numeracy skills development, socialization, and building foundational knowledge and critical thinking abilities. Elementary classes often incorporate reading, writing, mathematics, science, and ...
This essay discusses the importance of elementary education. Education can be considered to be the most vital asset that the society has because knowledge is the priceless wealth that people will never mislay under any circumstances, and the further the knowledge gets shared, the further it will advance. Therefore, elementary education forms ...
Published: Mar 20, 2024. Elementary school is a crucial stage in a child's education. It is where young minds are shaped and molded, and where the foundation for future learning is laid. My experience in elementary school has had a profound impact on my academic journey and personal development. In this essay, I will share my experiences and ...
Elementary education is often preceded by some form of preschool for children age 3 to 5 or 6 and is often followed by secondary education. (Read Arne Duncan's Britannica essay on "Education: The Great Equalizer.") Despite the many cultural and political differences among nations, the objectives and curriculum at least of elementary ...
Play-based learning is a big part of my teaching philosophy. Kids who learn through play have more authentic experiences, exploring and discovering the world naturally in ways that make the process more engaging and likely to make a lasting impact. In my classroom, technology is key.
Foundations of Reading. Merrimack College provides a degree program that meets the state's rigorous standards. The Elementary education years are some of the most important in the life of a student. They deserve teachers who have trained themselves to work at the highest possible level. The elementary education years are the foundation for ...
The following tips and philosophy of education examples for elementary teachers can help you write an essay that you'll be proud to have. A philosophy of education statement is an opportunity to define what teaching means to you, and to describe how and why you teach as you do. Articulating this statement in the first person and using a ...
Elementary Education Essay. Thesis: Elementary teachers may not have highest income, but they have one of the most fulfilling careers. Introduction: When thinking back to elementary school, what most people remember the best, are the teachers they had along the way. Elementary teachers not only introduce their students to the basic concepts of ...
Essay Topics About Elementary Education #1: Should elementary students be allowed time for recess? Some schools are focusing so much on academics that they're sacrificing recess for additional classroom time. Others argue that play is an important part of development and that all elementary-age children deserve recess.
500+ Words Essay on Education. Education is an important tool which is very useful in everybody's life. Education is what differentiates us from other living beings on earth. It makes man the smartest creature on earth. It empowers humans and gets them ready to face challenges of life efficiently. With that being said, education still remains ...
Grade: 5. Download. Choosing a career is a significant aspect of someone's life because when choosing a career, the first stage ensures that someone is willing to commit themselves to pursue it. I chose to write "why did you choose elementary education" essay to argument why I chose career in elementary education. Do not use plagiarized ...
Browse essays about Elementary Education and find inspiration. Learn by example and become a better writer with Kibin's suite of essay help services. Essay Examples
A Career in Elementary Education Essay. Good Essays. 1211 Words. 5 Pages. 1 Works Cited. Open Document. So you want to be an elementary school teacher? It's a challenging career, requiring patience and social skills, as you have to be able to wrangle a room filled with rambunctious children. Once you get through the tough stuff, the career is ...
Washington, D.C. and Arizona have the highest rates of charter enrollment, with 43 and 19% of their public school students attending charter schools. Several states have little or no charter ...
ABOUT THE JOURNAL Frequency: 4 issues/year ISSN: 0013-5984 E-ISSN: 1554-8279 2023 CiteScore*: 2.6 Ranked #628 out of 1,543 "Education" journals. The Elementary School Journal has served researchers, teacher educators, and practitioners in the elementary and middle school education for more than one hundred years.ESJ publishes peer-reviewed articles that pertain to both education theory and ...
and followers created the comprehensive system of developmental education for elementary school. The Zankov education system is used now at public schools in Russia. Its main principles and properties are described. Keywords: Leonid Zankov, Lev Vygotsky, Pedagogical experiment, Developmental education, Elementary school, Zone of proximal ...
The resources presented are from In Common: Effective Writing for All Students, authored by the Vermont Writing Collaborative with Student Achievement Partners and CCSSO. There are two types of resources available: On-Demand Writing provides a progression of writing across grades (K-5 and 6-12); students have written independently to the ...
My School Life Essay for Class 1-12. Find essay on My School Life for Students in English in 100, 200, 300, 400, 500 and 600 words by Infinity Learn (IL) ... A school is a building dedicated to provide learning space and environment to provide education. It is a building wherein your majority of childhood has passed, a building that everyone ...
OSAT for Elementary Education: Sample Prompts. Sample Prompt #1. A fifth grade teacher reviews a recent autobiographical poem by a new student. An excerpt is provided below. Not much is known ...
Elementary Education. Russian children enter elementary education at six to seven years of age. This stage of education lasts four years and includes instruction in the subjects of Russian language (reading, writing, literature), mathematics, history, natural sciences, arts and crafts, physical education, and a foreign language starting in grade two.
For Sale - 130 Pear Ct, Moscow Mills, MO - $675,000. View details, map and photos of this single family property with 4 bedrooms and 4 total baths. MLS# 24067055.