

What Is Creative Writing? (Ultimate Guide + 20 Examples)
Creative writing begins with a blank page and the courage to fill it with the stories only you can tell.
I face this intimidating blank page daily–and I have for the better part of 20+ years.
In this guide, you’ll learn all the ins and outs of creative writing with tons of examples.
What Is Creative Writing (Long Description)?
Creative Writing is the art of using words to express ideas and emotions in imaginative ways. It encompasses various forms including novels, poetry, and plays, focusing on narrative craft, character development, and the use of literary tropes.

Table of Contents
Let’s expand on that definition a bit.
Creative writing is an art form that transcends traditional literature boundaries.
It includes professional, journalistic, academic, and technical writing. This type of writing emphasizes narrative craft, character development, and literary tropes. It also explores poetry and poetics traditions.
In essence, creative writing lets you express ideas and emotions uniquely and imaginatively.
It’s about the freedom to invent worlds, characters, and stories. These creations evoke a spectrum of emotions in readers.
Creative writing covers fiction, poetry, and everything in between.
It allows writers to express inner thoughts and feelings. Often, it reflects human experiences through a fabricated lens.
Types of Creative Writing
There are many types of creative writing that we need to explain.
Some of the most common types:
- Short stories
- Screenplays
- Flash fiction
- Creative Nonfiction
Short Stories (The Brief Escape)
Short stories are like narrative treasures.
They are compact but impactful, telling a full story within a limited word count. These tales often focus on a single character or a crucial moment.
Short stories are known for their brevity.
They deliver emotion and insight in a concise yet powerful package. This format is ideal for exploring diverse genres, themes, and characters. It leaves a lasting impression on readers.
Example: Emma discovers an old photo of her smiling grandmother. It’s a rarity. Through flashbacks, Emma learns about her grandmother’s wartime love story. She comes to understand her grandmother’s resilience and the value of joy.
Novels (The Long Journey)
Novels are extensive explorations of character, plot, and setting.
They span thousands of words, giving writers the space to create entire worlds. Novels can weave complex stories across various themes and timelines.
The length of a novel allows for deep narrative and character development.
Readers get an immersive experience.
Example: Across the Divide tells of two siblings separated in childhood. They grow up in different cultures. Their reunion highlights the strength of family bonds, despite distance and differences.
Poetry (The Soul’s Language)
Poetry expresses ideas and emotions through rhythm, sound, and word beauty.
It distills emotions and thoughts into verses. Poetry often uses metaphors, similes, and figurative language to reach the reader’s heart and mind.
Poetry ranges from structured forms, like sonnets, to free verse.
The latter breaks away from traditional formats for more expressive thought.
Example: Whispers of Dawn is a poem collection capturing morning’s quiet moments. “First Light” personifies dawn as a painter. It brings colors of hope and renewal to the world.
Plays (The Dramatic Dialogue)
Plays are meant for performance. They bring characters and conflicts to life through dialogue and action.
This format uniquely explores human relationships and societal issues.
Playwrights face the challenge of conveying setting, emotion, and plot through dialogue and directions.
Example: Echoes of Tomorrow is set in a dystopian future. Memories can be bought and sold. It follows siblings on a quest to retrieve their stolen memories. They learn the cost of living in a world where the past has a price.
Screenplays (Cinema’s Blueprint)
Screenplays outline narratives for films and TV shows.
They require an understanding of visual storytelling, pacing, and dialogue. Screenplays must fit film production constraints.
Example: The Last Light is a screenplay for a sci-fi film. Humanity’s survivors on a dying Earth seek a new planet. The story focuses on spacecraft Argo’s crew as they face mission challenges and internal dynamics.
Memoirs (The Personal Journey)
Memoirs provide insight into an author’s life, focusing on personal experiences and emotional journeys.
They differ from autobiographies by concentrating on specific themes or events.
Memoirs invite readers into the author’s world.
They share lessons learned and hardships overcome.
Example: Under the Mango Tree is a memoir by Maria Gomez. It shares her childhood memories in rural Colombia. The mango tree in their yard symbolizes home, growth, and nostalgia. Maria reflects on her journey to a new life in America.
Flash Fiction (The Quick Twist)
Flash fiction tells stories in under 1,000 words.
It’s about crafting compelling narratives concisely. Each word in flash fiction must count, often leading to a twist.
This format captures life’s vivid moments, delivering quick, impactful insights.
Example: The Last Message features an astronaut’s final Earth message as her spacecraft drifts away. In 500 words, it explores isolation, hope, and the desire to connect against all odds.
Creative Nonfiction (The Factual Tale)
Creative nonfiction combines factual accuracy with creative storytelling.
This genre covers real events, people, and places with a twist. It uses descriptive language and narrative arcs to make true stories engaging.
Creative nonfiction includes biographies, essays, and travelogues.
Example: Echoes of Everest follows the author’s Mount Everest climb. It mixes factual details with personal reflections and the history of past climbers. The narrative captures the climb’s beauty and challenges, offering an immersive experience.
Fantasy (The World Beyond)
Fantasy transports readers to magical and mythical worlds.
It explores themes like good vs. evil and heroism in unreal settings. Fantasy requires careful world-building to create believable yet fantastic realms.
Example: The Crystal of Azmar tells of a young girl destined to save her world from darkness. She learns she’s the last sorceress in a forgotten lineage. Her journey involves mastering powers, forming alliances, and uncovering ancient kingdom myths.
Science Fiction (The Future Imagined)
Science fiction delves into futuristic and scientific themes.
It questions the impact of advancements on society and individuals.
Science fiction ranges from speculative to hard sci-fi, focusing on plausible futures.
Example: When the Stars Whisper is set in a future where humanity communicates with distant galaxies. It centers on a scientist who finds an alien message. This discovery prompts a deep look at humanity’s universe role and interstellar communication.
Watch this great video that explores the question, “What is creative writing?” and “How to get started?”:
What Are the 5 Cs of Creative Writing?
The 5 Cs of creative writing are fundamental pillars.
They guide writers to produce compelling and impactful work. These principles—Clarity, Coherence, Conciseness, Creativity, and Consistency—help craft stories that engage and entertain.
They also resonate deeply with readers. Let’s explore each of these critical components.
Clarity makes your writing understandable and accessible.
It involves choosing the right words and constructing clear sentences. Your narrative should be easy to follow.
In creative writing, clarity means conveying complex ideas in a digestible and enjoyable way.
Coherence ensures your writing flows logically.
It’s crucial for maintaining the reader’s interest. Characters should develop believably, and plots should progress logically. This makes the narrative feel cohesive.
Conciseness
Conciseness is about expressing ideas succinctly.
It’s being economical with words and avoiding redundancy. This principle helps maintain pace and tension, engaging readers throughout the story.
Creativity is the heart of creative writing.
It allows writers to invent new worlds and create memorable characters. Creativity involves originality and imagination. It’s seeing the world in unique ways and sharing that vision.
Consistency
Consistency maintains a uniform tone, style, and voice.
It means being faithful to the world you’ve created. Characters should act true to their development. This builds trust with readers, making your story immersive and believable.
Is Creative Writing Easy?
Creative writing is both rewarding and challenging.
Crafting stories from your imagination involves more than just words on a page. It requires discipline and a deep understanding of language and narrative structure.
Exploring complex characters and themes is also key.
Refining and revising your work is crucial for developing your voice.
The ease of creative writing varies. Some find the freedom of expression liberating.
Others struggle with writer’s block or plot development challenges. However, practice and feedback make creative writing more fulfilling.
What Does a Creative Writer Do?
A creative writer weaves narratives that entertain, enlighten, and inspire.
Writers explore both the world they create and the emotions they wish to evoke. Their tasks are diverse, involving more than just writing.
Creative writers develop ideas, research, and plan their stories.
They create characters and outline plots with attention to detail. Drafting and revising their work is a significant part of their process. They strive for the 5 Cs of compelling writing.
Writers engage with the literary community, seeking feedback and participating in workshops.
They may navigate the publishing world with agents and editors.
Creative writers are storytellers, craftsmen, and artists. They bring narratives to life, enriching our lives and expanding our imaginations.
How to Get Started With Creative Writing?
Embarking on a creative writing journey can feel like standing at the edge of a vast and mysterious forest.
The path is not always clear, but the adventure is calling.
Here’s how to take your first steps into the world of creative writing:
- Find a time of day when your mind is most alert and creative.
- Create a comfortable writing space free from distractions.
- Use prompts to spark your imagination. They can be as simple as a word, a phrase, or an image.
- Try writing for 15-20 minutes on a prompt without editing yourself. Let the ideas flow freely.
- Reading is fuel for your writing. Explore various genres and styles.
- Pay attention to how your favorite authors construct their sentences, develop characters, and build their worlds.
- Don’t pressure yourself to write a novel right away. Begin with short stories or poems.
- Small projects can help you hone your skills and boost your confidence.
- Look for writing groups in your area or online. These communities offer support, feedback, and motivation.
- Participating in workshops or classes can also provide valuable insights into your writing.
- Understand that your first draft is just the beginning. Revising your work is where the real magic happens.
- Be open to feedback and willing to rework your pieces.
- Carry a notebook or digital recorder to jot down ideas, observations, and snippets of conversations.
- These notes can be gold mines for future writing projects.
Final Thoughts: What Is Creative Writing?
Creative writing is an invitation to explore the unknown, to give voice to the silenced, and to celebrate the human spirit in all its forms.
Check out these creative writing tools (that I highly recommend):
Read This Next:
- What Is a Prompt in Writing? (Ultimate Guide + 200 Examples)
- What Is A Personal Account In Writing? (47 Examples)
- How To Write A Fantasy Short Story (Ultimate Guide + Examples)
- How To Write A Fantasy Romance Novel [21 Tips + Examples)

What is Creative Writing? A Key Piece of the Writer’s Toolbox
Not all writing is the same and there’s a type of writing that has the ability to transport, teach, and inspire others like no other.
Creative writing stands out due to its unique approach and focus on imagination. Here’s how to get started and grow as you explore the broad and beautiful world of creative writing!
What is Creative Writing?
Creative writing is a form of writing that extends beyond the bounds of regular professional, journalistic, academic, or technical forms of literature. It is characterized by its emphasis on narrative craft, character development, and the use of literary tropes or poetic techniques to express ideas in an original and imaginative way.
Creative writing can take on various forms such as:
- short stories
- screenplays
It’s a way for writers to express their thoughts, feelings, and ideas in a creative, often symbolic, way . It’s about using the power of words to transport readers into a world created by the writer.
5 Key Characteristics of Creative Writing
Creative writing is marked by several defining characteristics, each working to create a distinct form of expression:
1. Imagination and Creativity: Creative writing is all about harnessing your creativity and imagination to create an engaging and compelling piece of work. It allows writers to explore different scenarios, characters, and worlds that may not exist in reality.
2. Emotional Engagement: Creative writing often evokes strong emotions in the reader. It aims to make the reader feel something — whether it’s happiness, sorrow, excitement, or fear.
3. Originality: Creative writing values originality. It’s about presenting familiar things in new ways or exploring ideas that are less conventional.
4. Use of Literary Devices: Creative writing frequently employs literary devices such as metaphors, similes, personification, and others to enrich the text and convey meanings in a more subtle, layered manner.
5. Focus on Aesthetics: The beauty of language and the way words flow together is important in creative writing. The aim is to create a piece that’s not just interesting to read, but also beautiful to hear when read aloud.
Remember, creative writing is not just about producing a work of art. It’s also a means of self-expression and a way to share your perspective with the world. Whether you’re considering it as a hobby or contemplating a career in it, understanding the nature and characteristics of creative writing can help you hone your skills and create more engaging pieces .
For more insights into creative writing, check out our articles on creative writing jobs and what you can do with a creative writing degree and is a degree in creative writing worth it .
Styles of Creative Writing
To fully understand creative writing , you must be aware of the various styles involved. Creative writing explores a multitude of genres, each with its own unique characteristics and techniques.
Poetry is a form of creative writing that uses expressive language to evoke emotions and ideas. Poets often employ rhythm, rhyme, and other poetic devices to create pieces that are deeply personal and impactful. Poems can vary greatly in length, style, and subject matter, making this a versatile and dynamic form of creative writing.
Short Stories
Short stories are another common style of creative writing. These are brief narratives that typically revolve around a single event or idea. Despite their length, short stories can provide a powerful punch, using precise language and tight narrative structures to convey a complete story in a limited space.
Novels represent a longer form of narrative creative writing. They usually involve complex plots, multiple characters, and various themes. Writing a novel requires a significant investment of time and effort; however, the result can be a rich and immersive reading experience.
Screenplays
Screenplays are written works intended for the screen, be it television, film, or online platforms. They require a specific format, incorporating dialogue and visual descriptions to guide the production process. Screenwriters must also consider the practical aspects of filmmaking, making this an intricate and specialized form of creative writing.
If you’re interested in this style, understanding creative writing jobs and what you can do with a creative writing degree can provide useful insights.
Writing for the theater is another specialized form of creative writing. Plays, like screenplays, combine dialogue and action, but they also require an understanding of the unique dynamics of the theatrical stage. Playwrights must think about the live audience and the physical space of the theater when crafting their works.
Each of these styles offers unique opportunities for creativity and expression. Whether you’re drawn to the concise power of poetry, the detailed storytelling of novels, or the visual language of screenplays and plays, there’s a form of creative writing that will suit your artistic voice. The key is to explore, experiment, and find the style that resonates with you.
For those looking to spark their creativity, our article on creative writing prompts offers a wealth of ideas to get you started.
Importance of Creative Writing
Understanding what is creative writing involves recognizing its value and significance. Engaging in creative writing can provide numerous benefits – let’s take a closer look.
Developing Creativity and Imagination
Creative writing serves as a fertile ground for nurturing creativity and imagination. It encourages you to think outside the box, explore different perspectives, and create unique and original content. This leads to improved problem-solving skills and a broader worldview , both of which can be beneficial in various aspects of life.
Through creative writing, one can build entire worlds, create characters, and weave complex narratives, all of which are products of a creative mind and vivid imagination. This can be especially beneficial for those seeking creative writing jobs and what you can do with a creative writing degree .
Enhancing Communication Skills
Creative writing can also play a crucial role in honing communication skills. It demands clarity, precision, and a strong command of language. This helps to improve your vocabulary, grammar, and syntax, making it easier to express thoughts and ideas effectively .
Moreover, creative writing encourages empathy as you often need to portray a variety of characters from different backgrounds and perspectives. This leads to a better understanding of people and improved interpersonal communication skills.
Exploring Emotions and Ideas
One of the most profound aspects of creative writing is its ability to provide a safe space for exploring emotions and ideas. It serves as an outlet for thoughts and feelings , allowing you to express yourself in ways that might not be possible in everyday conversation.
Writing can be therapeutic, helping you process complex emotions, navigate difficult life events, and gain insight into your own experiences and perceptions. It can also be a means of self-discovery , helping you to understand yourself and the world around you better.
So, whether you’re a seasoned writer or just starting out, the benefits of creative writing are vast and varied. For those interested in developing their creative writing skills, check out our articles on creative writing prompts and how to teach creative writing . If you’re considering a career in this field, you might find our article on is a degree in creative writing worth it helpful.
4 Steps to Start Creative Writing
Creative writing can seem daunting to beginners, but with the right approach, anyone can start their journey into this creative field. Here are some steps to help you start creative writing .
1. Finding Inspiration
The first step in creative writing is finding inspiration . Inspiration can come from anywhere and anything. Observe the world around you, listen to conversations, explore different cultures, and delve into various topics of interest.
Reading widely can also be a significant source of inspiration. Read different types of books, articles, and blogs. Discover what resonates with you and sparks your imagination.
For structured creative prompts, visit our list of creative writing prompts to get your creative juices flowing.
Editor’s Note : When something excites or interests you, stop and take note – it could be the inspiration for your next creative writing piece.
2. Planning Your Piece
Once you have an idea, the next step is to plan your piece . Start by outlining:
- the main points
Remember, this can serve as a roadmap to guide your writing process. A plan doesn’t have to be rigid. It’s a flexible guideline that can be adjusted as you delve deeper into your writing. The primary purpose is to provide direction and prevent writer’s block.
3. Writing Your First Draft
After planning your piece, you can start writing your first draft . This is where you give life to your ideas and breathe life into your characters.
Don’t worry about making it perfect in the first go. The first draft is about getting your ideas down on paper . You can always refine and polish your work later. And if you don’t have a great place to write that first draft, consider a journal for writing .
4. Editing and Revising Your Work
The final step in the creative writing process is editing and revising your work . This is where you fine-tune your piece, correct grammatical errors, and improve sentence structure and flow.
Editing is also an opportunity to enhance your storytelling . You can add more descriptive details, develop your characters further, and make sure your plot is engaging and coherent.
Remember, writing is a craft that improves with practice . Don’t be discouraged if your first few pieces don’t meet your expectations. Keep writing, keep learning, and most importantly, enjoy the creative process.
For more insights on creative writing, check out our articles on how to teach creative writing or creative writing activities for kids.
Tips to Improve Creative Writing Skills
Understanding what is creative writing is the first step. But how can one improve their creative writing skills? Here are some tips that can help.
Read Widely
Reading is a vital part of becoming a better writer. By immersing oneself in a variety of genres, styles, and authors, one can gain a richer understanding of language and storytelling techniques . Different authors have unique voices and methods of telling stories, which can serve as inspiration for your own work. So, read widely and frequently!
Practice Regularly
Like any skill, creative writing improves with practice. Consistently writing — whether it be daily, weekly, or monthly — helps develop your writing style and voice . Using creative writing prompts can be a fun way to stimulate your imagination and get the words flowing.
Attend Writing Workshops and Courses
Formal education such as workshops and courses can offer structured learning and expert guidance. These can provide invaluable insights into the world of creative writing, from understanding plot development to character creation. If you’re wondering is a degree in creative writing worth it, these classes can also give you a taste of what studying creative writing at a higher level might look like .
Joining Writing Groups and Communities
Being part of a writing community can provide motivation, constructive feedback, and a sense of camaraderie. These groups often hold regular meetings where members share their work and give each other feedback. Plus, it’s a great way to connect with others who share your passion for writing.
Seeking Feedback on Your Work
Feedback is a crucial part of improving as a writer. It offers a fresh perspective on your work, highlighting areas of strength and opportunities for improvement. Whether it’s from a writing group, a mentor, or even friends and family, constructive criticism can help refine your writing .
Start Creative Writing Today!
Remember, becoming a proficient writer takes time and patience. So, don’t be discouraged by initial challenges. Keep writing, keep learning, and most importantly, keep enjoying the process. Who knows, your passion for creative writing might even lead to creative writing jobs and what you can do with a creative writing degree .
Happy writing!
Brooks Manley

Creative Primer is a resource on all things journaling, creativity, and productivity. We’ll help you produce better ideas, get more done, and live a more effective life.
My name is Brooks. I do a ton of journaling, like to think I’m a creative (jury’s out), and spend a lot of time thinking about productivity. I hope these resources and product recommendations serve you well. Reach out if you ever want to chat or let me know about a journal I need to check out!
Here’s my favorite journal for 2024:

Gratitude Journal Prompts Mindfulness Journal Prompts Journal Prompts for Anxiety Reflective Journal Prompts Healing Journal Prompts Cognitive Behavioral Therapy Journal Prompts Mental Health Journal Prompts ASMR Journal Prompts Manifestation Journal Prompts Self-Care Journal Prompts Morning Journal Prompts Evening Journal Prompts Self-Improvement Journal Prompts Creative Writing Journal Prompts Dream Journal Prompts Relationship Journal Prompts "What If" Journal Prompts New Year Journal Prompts Shadow Work Journal Prompts Journal Prompts for Overcoming Fear Journal Prompts for Dealing with Loss Journal Prompts for Discerning and Decision Making Travel Journal Prompts Fun Journal Prompts
Inspiring Ink: Expert Tips on How to Teach Creative Writing
You may also like, benefits of bullet journaling [+ how to get started].
Your Guide to Using a Happiness Journal
The 17 best guided journals for 2024 and beyond, leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Productivity
- Favorite Journals

How to Develop Your Creative Writing Process
by Melissa Donovan | Feb 7, 2023 | Creative Writing | 45 comments

What steps do you take in your creative writing process?
Writing experts often want us to believe that there is only one worthwhile creative writing process. It usually goes something like this:
- Rough draft
- Revise (repeat, repeat, repeat, repeat)
- Edit, proof, and polish
This is a good system — it absolutely works. But does it work for everyone?
Examining the Creative Writing Process
I’ve been thinking a lot about the creative writing process. Lately I’ve found myself working on all types of projects: web pages, blog posts, a science-fiction series, and of course, books on the craft of writing .
I’ve thought about the steps I take to get a project completed and realized that the writing process I use varies from project to project and depends on the level of difficulty, the length and scope of the project, and even my state of mind. If I’m feeling inspired, a blog post will come flying out of my head. If I’m tired, hungry, or unmotivated, or if the project is complicated, then it’s a struggle, and I have to work a little harder. Brainstorming and outlining can help. A lot.
It occurred to me that I don’t have one creative writing process. I have several. And I always use the one that’s best suited for a particular project.
A Process for Every Project
I once wrote a novel with no plan whatsoever. I started with nothing more than a couple of characters. Thirty days and fifty thousand words later, I had completed the draft of a novel (thanks, NaNoWriMo!).
But usually, I need more structure than that. Whether I’m working on a blog post, a page of web copy, a nonfiction book, or a novel, I find that starting with a plan saves a lot of time and reduces the number of revisions that I have to work through later. It’s also more likely to result in a project getting completed and published.
But every plan is different. Sometimes I’ll jot down a quick list of points I want to make in a blog post. This can take just a minute or two, and it makes the writing flow fast and easy. Other times, I’ll spend weeks — even months — working out the intricate details of a story with everything from character sketches to outlines and heaps of research. On the other hand, when I wrote a book of creative writing prompts , I had a rough target for how many prompts I wanted to generate, and I did a little research, but I didn’t create an outline.
I’ve tried lots of different processes, and I continue to develop my processes over time. I also remain cognizant that whatever’s working for me right now might not work in five or ten years. I will keep revising and tweaking my process, depending on my goals.
Finding the Best Process
I’ve written a novel with no process, and I’ve written a novel by going through every step imaginable: brainstorming, character sketches, research, summarizing, outlines, and then multiple drafts, revisions, and edits.
These experiences were vastly different. I can’t say that one was more enjoyable than the other. But it’s probably worth noting that the book I wrote with no process is still sitting on my hard drive somewhere whereas the one I wrote with a methodical yet creative writing process got completed, polished, and published.
In fact, I have found that using a process generates better results if my goal is to complete and publish a project.
But not every piece of writing is destined for public consumption. Sometimes I write just for fun. No plan, no process, no pressure. I just let the words flow. Every once in a while, these projects find their way to completion and get sent out into the world.
It is only by experimenting with a variety of processes that you will find the creative writing process that works best for you. And you’ll also have to decide what “best” means. Is it the process that’s most enjoyable? Or is it the process that leads you to publication? Only you know the answer to that.
I encourage you to try different writing processes. Write a blog post on the fly. Make an outline for a novel. Do some in-depth research for an epic poem. Try the process at the top of this page, and then do some research to find other processes that you can experiment with. Keep trying new things, and when you find whatever helps you achieve your goals, stick with it, but remain open to new methods that you can bring into your process.
What’s Your Creative Writing Process?
Creative writing processes are good. The reason our predecessors developed these processes and shared them, along with a host of other writing tips, was to help us be more productive and produce better writing. Techniques and strategies can be helpful, but it’s our responsibility to know what works for us as individuals and as creative writers and to know what will cause us to infinitely spin our wheels.
What’s your creative writing process? Do you have one? Do you ever get stuck in the writing process? How do you get unstuck?

45 Comments
Hi Melissa: I do a lot of research on the topic I’ve chosen to write about. As I do the research I take notes on a word perfect document. When I have a whole lot of information written down–in a jumble–I usually leave it and go do something else. Then I sit down and start to work with the information I’ve gathered and just start writing. The first draft I come up with is usually pretty bad, and then I revise and revise until I have something beautiful that I feel is fit to share with the rest of the world. That’s when I hit the “publish” button 🙂 I’m trying to implement Parkinson’s Law to focus my thinking a little more as I write so that I can get the articles out a bit faster.
My favorite pre-writing process would have to be getting a nice big whiteboard and charting characters and plots down. I find that it really helps me anchor on to specific traits of a character, especially if the persona happens to be a dynamic one. Such charting helps me out dramatically in creating an evolving storyline by not allowing me to forget key twists and other storyline-intensive elements =)
That being said, my favorite pre-charting process is going out the on nights leading to it for a few rounds of beer with good friends!
Hi Melissa – I’m like you – I do different things depending on what I’m writing. With the novel I’m working on now – alot of stuff I write won’t even go into it.
Some of the stuff the gurus recommend are the kind of things I’d do if I was writing an essay – but nothing else.
I don’t know if I have a set process. I start with morning pages and journaling. then whatever comes streaming from that gets written. As I go about my day I have a notebook that stays with me whereever I go and I am constantly writing in it, notes, ideas, themes, Sentances that begin with “I wonder…” and then then next monring the notebook is with me during quiet time and these thoughts are often carried right in to the process all over again. So…if that is a process, I guess…I never really thought about it. As I have said before, a lot of my writing also takes place in my jacuzzi..so…
I guess my process is that when its falling out of my head I try and catch it.
This will be the first year that I attempt NaNO so I will need to be more organized. This is good for thinking ahead. One of the reasons I started blogging in the first place was to get in the discipline of writing every day. That was the first step. Just creating the habit. This will be a good next step.
These days, I feel so scattered, I feel like I’m not getting anything done at all! (grin)
Melissa, I am really organized but my writing process has never followed the guidelines. I’ve tried them on for size and find that they don’t fit. Even in school, I never did outlines and drafts so I suppose I trained myself against the system! I always do research first and gather all of my notes, clips in one location. As for the writing process itself I let it rip, then go back and fine tune. It has worked for me thus far but I’m always open to trying new techniques on for size, hey if they fit I’m all on board!
@Marelisa, that doesn’t surprise me. Your posts are comprehensive, detailed, and extremely informative. I can tell you care a lot about your topic and about your writing. That’s one of the reasons I enjoy your blog; your passion is palpable.
@Joey, I love the planning stage too. In fact, sometimes I get stuck there and never make it out. Ooh, and white boards. Yes. Those are good. Usually I just use drawing paper though. When I do NaNo, I’m going to try to do less planning. In fact, I’m going to plan in October and just write in November. I’m hoping this new strategy will result in winning my word count goal!
@Cath, I sort of pick and choose which tips from the gurus I use.
@Wendi, you write in the jacuzzi? That’s cool. Or hot. I guess it’s hot. Your process sounds really natural. I started blogging for the exact same reason — to write every day. I’m excited to hear you’re doing NaNo too. That will be fun, and we can offer each other moral support!
@Deb (Punctuality), it sounds like you have a lot going on! I get into that mode sometimes, where I’m so overwhelmed, I can’t get anything done. It’s really frustrating. Sometimes I have to shut down for a day to get my bearings and that’s the only way I can get back on track.
@Karen, that’s probably why your writing flows so well, because you just let it do its thing. I remember learning to do outlines back in 6th grade but it didn’t stick. Later, in college, we’d have to do them as assignments, so I didn’t have a choice. I realized that they sped up the writing process. Now I do them for some (but not all) projects. But I will say this: I actually enjoy outlining (weird?).
Melissa, I’m not a real writer but I do love reading how you, who are, go about the business of putting words to paper. As always, a great post. Thanks.
It is funny that you wrote about this today. I picked up an extra assignment with a today deadline. Let’s not talk about how long it’s been since I’ve written copy on that tight a deadline.
My mantra: “If it doesn’t make it I don’t get paid for it.” Rinse and repeat.
Also, I grew to enjoy outlining when I went back to university. Sometimes I’m happy just to outline; also known as a stall tactic.
Ah, my writing process?
1) Spit out mindgarbage! 2) Sort through mindgarbage. 3) Take out the handy scissors and glue (or rather, ctrl+c, ctrl+v…) 4) Revise Revise Revise 5) Edit, proof, polish… 6) Rewrite, revise rewrite, revise…
My prewriting is just writing. Writing trash. Then cleaning it up. 3 pages = 1 paragraph trash. Yeaaaaah.
@Milena, what do you mean you’re not a real writer? Of course you are. You write; therefore you are a writer!
@Deb, sometimes those crunch deadlines really light the fire. I’ve been amazed at what I can write in a day when there’s a client waiting for it with a nice big PayPal deposit!
@Sam, that’s a good way to get it done! Do you free-write your early drafts? I’ve been teased for editing too much, but it’s definitely worth it. You can get the good stuff early by just spattering it all over the page, and then refine it until it’s polished and sparkling!
I never really liked the 5 step process when I wrote back in school, but I suppose that learning that did make me a better writer. I don’t have a set process, sometimes it’s just sitting at the computer and opening up my blog, or a blank page in Word. Sometimes things come from something that struck me during the day. I think I have to work on the discipline of actually sitting down to write more often! Practice makes perfect, or at least close enough, right?!?!
I’ve tried to figure out what my process is, but it’s different depending on what I’m writing.
Blogging – 90% of the time, there is no process at all and it shows. I’m usually writing as fast as I can think, and sometimes I can’t keep up and I may just jump to the next thought at random. I may go back and read and finish thoughts that were left incomplete. I try to write my blogs as if the reader is having a conversation with me, which makes it feel natural for me to write.
Poetry – Most times I don’t like editting unless I’m really unhappy with the first draft. Usually I’m only changing or adding punctuations. But overall, I’ll get my inspiration and after reciting a few lines in my head and an idea of where I want to go, that’s when I’ll pull out some paper (or cardboard or napkins or laptop) and write a potential masterpiece.
Story/scripts – I plan the entire story in my head. One might call it a brainstorm, but I’ll go farther and say it’s a hurricane. I won’t stop with just a story, I’ll create characters, scenes, even background music. A lot of times I’ll get the idea but I won’t be able to write anything down, like if I’m driving, rock climbing, sky diving or underwater. A lot of ideas come to me when I’m in the bathroom. Without sharing much details about that, I’ll just say I have time to think and let my imagination go to work. When I’m able to get to some paper or my laptop, I’ll write out the story and flesh it out a little until I’m done, or I’ll keep working on the story in my head and bounce it off some people to see how they would react of this happened or that happened.
I don’t like outlines, but when it comes to screenplays, they help out a lot and it’s the only time I MIGHT use one. I’ve been known to go without them though.
@Jenny, practice does make perfect! I believe that. I rarely use the five-step process on paper, but I think I often do some steps in my head, often without even realizing I’m doing them!
@t. sterling, I consistently get some of my best ideas in the shower. There must be something very inspiring about bathrooms or water. Like you, I have a bunch of different processes that I use depending on what I’m writing. And after reading all the comments, it seems like that’s how it works for a lot of writers.
I like the show me yours, show you mine tradezees.
It’s kind of long, but there’s a lot to it: http://blogs.msdn.com/jmeier/archive/2007/12/24/building-books-in-patterns-amp-practices.aspx
Thanks, J.D.
That depends on the complexity. If it’s something simple like some of my blog posts, I just start writing without outlines. For tutorials, usually there are steps so I will write down all the steps first and re-arrange them to the order I want.
For stories, sometimes I write down the events that should happen, but sometimes I don’t. Even if I don’t explicitly write out an outline, I would still have some kind of structure in my head. And even if it’s written out, eventually I will get that into my head because it’s easier for me to sort through things that way. I think it might be a habit I developed from working as a computer programmer. I tend to rely a lot on short-term memory. I get all these details into my head, and then I try to sort things out in my mind.
Actually, you know what? I’ve just brainstormed for a story right before reading this. I already have most detailed sorted out in my head, so I will most likely write and post it tomorrow. I think I’ll post my writing process after that as well. For now I’ll sleep on it. (I think maybe that’s part of the process as well.)
Oh yes, sleeping on it is definitely part of the process. I like to insert that right between rough draft and revision. Then I do it again between revision and polish or proofread. Sounds like you do things similarly to the way I do — a little of everything with the steps varying depending on the project.
Great post! Thanks for sharing your insights on the writing process. As for me, I feel like I work in spurts of inspiration… Lots of writing, then editing, then writing again.
That is how I’ve always written poetry — with spurts of inspiration and freewrites. Then I will go through the pages and pull out lines and phrases to build a poem. I do use brainstorming, notes, outlines, research, etc. for other forms, but it really depends on the project.
Actually, I’m not that organize when it comes to creative writing. Most of the time I keep in tune with my thoughts. When something pop-ups (words, phrase, ideas, vocabulary) is immediately write it down on my black notebook.
I go with my own style of writing because I believe my work will speak out only if it’s unique on its own. Being imperfect, I don’t put too much effort on the grammatical construction. I believe that what’s between the words are more important the the words itself. A distinctive writer possesses this quality. 🙂
Writing down your ideas, words, phrases, etc. in your notebook is an excellent habit! However, I have to disagree with you on the importance of grammar. I think it’s essential for writers to master grammar and then (and only then) can you start breaking the rules. Of course, this may depend on what you want to write (i.e. blog versus fiction). Grammar gives writers a common or shared framework in which to construct the language, and believe it or not, there are some astute writers and editors out there who will judge your work rather harshly if the grammar is not up to par. That doesn’t mean it has to be perfect, but if you’re missing the basics, it’s likely they won’t bother reading past the first paragraph. By the way, a fast and easy way to learn grammar is by listening to the Grammar Girl podcast. Just a few minutes of listening a couple times a week will teach you more than you can imagine!
I separate first draft from editing, but I’m not particular about whether I finish the whole draft before I start editing. Sometimes going back and editing the first 3 chapters gets me moving on a better line.
When I edit, I do whole read-thrus until I’m happy with the story flow. Then I use the Autocrit Editing Wizard to really polish the manuscript. After that, I’m done!
I’ve never heard of the Autocrit Editing Wizard. Sounds interesting. I usually edit short pieces like web page copy or blog posts on the fly, i.e. I will stop every couple of paragraphs and go back to re-read and edit. However, with longer works, I feel like if I start editing midway, I might lose the project and get caught up in polishing before the rough draft is nailed down. All that matters, however, is that each writer finds his or her own best method. Sounds like you’ve got it down!
LOL! I think I’ve worked through every possible type of creative process possible. From outlining the whole darned thing to working with notecards, story boards and of course just winging it, which resulted in a story with a really flat ending – unforgivable:-) And while I firmly adhere to Anne Lamott’s *&^^%# first draft, I have finally settled into a process that works for me. I now use a plot worksheet and a character worksheet. It takes me a bit longer to actually start writing but what I write works and requires less editing.
I’ve tried all the methods too, and I’m glad I did. I’ve learned that each one works for me, but in a different capacity. With creative writing, such as fiction and poetry, I just jump right in and start writing. Right now I’m working on a nonfiction, educational project using detailed outlines and note cards. I think what you’ve done is brilliant — figuring out what advice works for you and what doesn’t work and then letting your own, personalized process unfold.
I have used all the methods, too, and I agree that the method used depends mostly on the subject matter. For novels, it also seems to depend on the genre. I can rip out a romance novel without an outline (in fact that’s the most fun way to do it). I finished a Romance for NaNoWriMo last year in three weeks. For novels with a more complicated plot at least a general outline is helpful (keeping in mind I have to be flexible enough to let the characters take over and go off in some completely different direction).
For me the single most important thing is letting a certain amount of time go by between drafting and editing. It could be days, it could be weeks. For novels it’s even better for me to let months go by. It gives me the the opportunity to look at the material with “fresh eyes”.
Probably for that reason, I tend to work on multiple projects at once: drafting one (early mornings on the weekends when I’m at my best); editing one and polishing another (weekday evenings). That way everything keeps moving forward, I never get bored and I always have new material in the pipeline.
I’m with you, Meredith! I can see how it would be fun to write a romance novel on the fly, and I’ve heard that mystery writers often use outlines because they need to incorporate plot twists and must keep track of various story threads. Another method is to outline as you write, so you have notes that you can refer back to when necessary. Allowing time to pass between writing, editing, proofreading, and polishing is absolutely essential! We know the brain will read incorrect text correctly, plugging in words and proper grammar, spelling, and punctuation. That time away really does give us fresh eyes! I love your strategy for working on multiple projects simultaneously.
There are good things to be said for the traditional formula, but as you say it isn’t the only method that works. I have written eight novels and dozens upon dozens of short stories and never once sat down to do a brainstorming session to come up with ideas. I do a lot of research, but most of it as I go along during the writing process. The last three steps I think are golden though.
I do have one new organization tip to share though. If your tech savvy enough to do a local install of wordpress on your computer it can become a great writing tool. Not only does it have a simple to use word processor in the form of the posting tool, it allows you to categorize your research and there are plenty of tagging plugins that will allow you to easily cross reference notes and text.
I LOVE the idea of using a local installation of WordPress for research and novel writing. I can imagine all the benefits with links and images, even video. Hmm. I don’t know how to do a local installation, but I’m thinking another option would be to load WP onto a live domain and simply put it in permanent maintenance mode (plugin) or set up some kind of password protection to block it from the public. I definitely need to think about this as a tool. Thanks for the tip, Brad!
I use Scrivener ( https://www.literatureandlatte.com/ ) for all my writing. It’s great for research and saving web pages, building characters, plotting and planning, all in one place. And best of all you can break down a story into scenes (separate documents) within Scrivener itself – something you can’t do in Word or similar. Wordpress is all very well, but you can’t see all posts/pages at once in a sidebar – something you *can* do in Scrivener. You can download a free trial of Scrivener to see whether it’s for you. Don’t be put off by the complicated look of it – you can use as much or as little of it as you like and there are some very handy videos and tips on using it. I’ve found it’s the best thing for writing blog posts, short stories, novels, scripts, you name it. It can’t hurt to give it a go.
I agree, Chris. Scrivener is amazing. I use it for fiction and poetry, and it’s made the writing process so much smoother. I highly recommend it to all writers. Plus, it’s reasonably priced.
I’m loving reading all these, but I don’t really have a process … I sit at the keyboard and hope something comes out of my fingertips … and if it doesn’t I let myself get distracted by shiny things like Twitter.
(Okay, I never said it was a PRODUCTIVE method.)
Really? I would have guessed that you use outlines at least some of the time. I definitely have to use outlines for longer works of nonfiction, and I always outline website copy when I’m writing for clients. It’s such a good (and productive) way to organize your thoughts, but for fiction and poetry (and many blog posts) I often let it flow freely, and it turns out that method is productive too 😉
Hello Melissa, My name is Kylee and I’m 15. Being naturally gifted in journalism, its a dream or fantasy of mine to become an author. For me to get into my ‘zone’ I have to be in a completely serene enviroment for hours. I’ve written short stories and essays but would like to complete the ultimate thrill of Mine: a novel. Its frustrating really, the difficulties of finding my creative writing process. I have difficulties in making a plot complex enough, and character development. I know they are major issues but I’m having trouble perfecting my writing. If you could help me in any way, I’d gladly appreciate it. Thank you.
You’re getting an early start. The best advice I have for you is to read a lot. If you want to be a novelist, then read as many novels as you can. Try keeping a reading journal where you can write down your thoughts and observations about how other authors handle plot and character development. You’ll find that you start to read differently. Instead of reading for enjoyment or entertainment, it also becomes a fun study in your craft. You can visit my Writing Resources section or Books page to check out my recommendations for books on the craft of writing. Good luck to you!
Mine’s pretty simple:
1. Do background research. Mostly stuff for the setting like common plants and animals, names of places, photographs. I’ll also read books to familiarize myself with whatever topic of the book in involved.
2. Start writing.
3. Do spot research as I’m writing. Search for the name of something, looking at pictures of something to help me describe it; etc.
4. Move around the scenes as I write, which is sort of like shaking out the wrinkles in a sheet. I add new things that occur to me, correct typos, etc.
That’s excellent, Linda. It sounds like you’ve nailed your process!
I have no writing process, actually. I’m the type of person who thinks while I’m writing, or I think of an image and the story comes out suddenly. I also think before I write, and imagine how the scenes will turn out. I’m a very visual person when it comes to writing. In addition, I found out that when I do plan, my stories never get drafted at all, or they do but I don’t like it. Planning never really works for me. I need to let all my ideas be out of my mind, and not from pre-writing.
All that matters is that you’ve found the process that works for you, and it sounds like you have!
Here’s a trick (procedure, technique, system, gimmick) I use when I’m writing a novel. I don’t write linearly. Some parts of the story are more appealing to me than others so depending on my mood (perhaps that should be muse) I jump around. Admittedly, connecting the scenes may take a bit of of revision since I never know where the story will eventually take me, and on occasion I’ve had to trash a significant amount. That’s okay, since my goal is to enjoy myself every time I sit down to write – and I do.
This method works well for a lot of writers. I mostly try to write my own drafts linearly, but I skip around if I’m struck with inspiration.
Every writer experiences different levels of enjoyment during the process. In my experience, most writers encounter a lot of frustration at certain points in the process. So I have come to view writing as rewarding rather than enjoyable. A lot of the work is fun, but a lot of it is difficult, tedious, even maddening. But at the end, it’s all worth it if you can push through the hard parts.
Book suggestion: The Writer’s Process, Getting Your Brain in Gear by Anne H. Janzer.
This book explains the actual psychology behind the creative process and then suggests how to apply it to your work. Some good insights.
Thanks for the recommendation, Rod. I’m always looking for books on the craft of writing to add to my collection.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .

Subscribe and get The Writer’s Creed graphic e-booklet, plus a weekly digest with the latest articles on writing, as well as special offers and exclusive content.

Recent Posts
- Mysterious and Thrilling Fiction Writing Prompts
- Poetry Writing Exercises in Space and Time
- How to Break Through a Fiction Writing Block
- Grammar Rules: That and Which
- What’s in Your Creative Writing Notebook?
Write on, shine on!
Pin It on Pinterest

Do You Know The 7 Steps Of The Writing Process?
How much do you know about the different stages of the writing process? Even if you’ve been writing for years, your understanding of the processes of writing may be limited to writing, editing, and publishing.
It’s not your fault. Much of the writing instruction in school and online focus most heavily on those three critical steps.
Important as they are, though, there’s more to creating a successful book than those three. And as a writer, you need to know.
The 7 Steps of the Writing Process
Read on to familiarize yourself with the seven writing process steps most writers go through — at least to some extent. The more you know each step and its importance, the more you can do it justice before moving on to the next.
1. Planning or Prewriting
This is probably the most fun part of the writing process. Here’s where an idea leads to a brainstorm, which leads to an outline (or something like it).

Whether you’re a plotter, a pantser, or something in between, every writer has some idea of what they want to accomplish with their writing. This is the goal you want the final draft to meet.
With both fiction and nonfiction , every author needs to identify two things for each writing project:
- Intended audience = “For whom am I writing this?”
- Chosen purpose = “What do I want this piece of writing to accomplish?”
In other words, you start with the endpoint in mind. You look at your writing project the way your audience would. And you keep its purpose foremost at every step.
From planning, we move to the next fun stage.
2. Drafting (or Writing the First Draft)
There’s a reason we don’t just call this the “rough draft,” anymore. Every first draft is rough. And you’ll probably have more than one rough draft before you’re ready to publish.
For your first draft, you’ll be freewriting your way from beginning to end, drawing from your outline, or a list of main plot points, depending on your particular process.
To get to the finish line for this first draft, it helps to set word count goals for each day or each week and to set a deadline based on those word counts and an approximate idea of how long this writing project should be.
Seeing that deadline on your calendar can help keep you motivated to meet your daily and weekly targets. It also helps to reserve a specific time of day for writing.
Another useful tool is a Pomodoro timer, which you can set for 20-25 minute bursts with short breaks between them — until you reach your word count for the day.
3. Sharing Your First Draft
Once you’ve finished your first draft, it’s time to take a break from it. The next time you sit down to read through it, you’ll be more objective than you would be right after typing “The End” or logging the final word count.
It’s also time to let others see your baby, so they can provide feedback on what they like and what isn’t working for them.
You can find willing readers in a variety of places:
- Social media groups for writers
- Social media groups for readers of a particular genre
- Your email list (if you have one)
- Local and online writing groups and forums
This is where you’ll get a sense of whether your first draft is fulfilling its original purpose and whether it’s likely to appeal to its intended audience.
You’ll also get some feedback on whether you use certain words too often, as well as whether your writing is clear and enjoyable to read.
4. Evaluating Your Draft
Here’s where you do a full evaluation of your first draft, taking into account the feedback you’ve received, as well as what you’re noticing as you read through it. You’ll mark any mistakes with grammar or mechanics.
And you’ll look for the answer to important questions:
- Is this piece of writing effective/ Does it fulfill its purpose?
- Do my readers like my main character? (Fiction)
- Does the story make sense and satisfy the reader? (Fiction)
- Does it answer the questions presented at the beginning? ( Nonfiction )
- Is it written in a way the intended audience can understand and enjoy?
Once you’ve thoroughly evaluated your work, you can move on to the revision stage and create the next draft.
More Related Articles
How To Create An Em Dash Or Hyphen
Are You Ready To Test Your Proofreading Skills?
How To Write A Book For Kindle About Your Expertise Or Passion
5. Revising Your Content
Revising and editing get mixed up a lot, but they’re not the same thing.
With revising, you’re making changes to the content based on the feedback you’ve received and on your own evaluation of the previous draft.
- To correct structural problems in your book or story
- To find loose ends and tie them up (Fiction)
- To correct unhelpful deviations from genre norms (Fiction)
- To add or remove content to improve flow and/or usefulness
You revise your draft to create a new one that comes closer to achieving your original goals for it. Your newest revision is your newest draft.
If you’re hiring a professional editor for the next step, you’ll likely be doing more revision after they’ve provided their own feedback on the draft you send them.
Editing is about eliminating errors in your (revised) content that can affect its accuracy, clarity, and readability.

By the time editing is done, your writing should be free of the following:
- Grammatical errors
- Punctuation/mechanical and spelling errors
- Misquoted content
- Missing (necessary) citations and source info
- Factual errors
- Awkward phrasing
- Unnecessary repetition
Good editing makes your work easier and more enjoyable to read. A well-edited book is less likely to get negative reviews titled, “Needs editing.” And when it comes to books, it’s best to go beyond self-editing and find a skilled professional.
A competent editor will be more objective about your work and is more likely to catch mistakes you don’t see because your eyes have learned to compensate for them.
7. Publishing Your Final Product
Here’s where you take your final draft — the final product of all the previous steps — and prepare it for publication.
Not only will it need to be formatted (for ebook, print, and audiobook), but you’ll also need a cover that will appeal to your intended audience as much as your content will.
Whether you budget for these things or not depends on the path you choose to publish your book:
- Traditional Publishing — where the publishing house provides editing, formatting, and cover design, as well as some marketing
- Self-Publishing — where you contract with professionals and pay for editing, formatting, and cover design.
- Self-Publishing with a Publishing Company — where you pay the company to provide editing, formatting, and cover design using their in-house professionals.
And once your book is live and ready to buy, it’s time to make it more visible to your intended audience. Otherwise, it would fail in its purpose, too.
Are you ready to begin 7 steps of the writing process?
Now that you’re familiar with the writing process examples in this post, how do you envision your own process?
While it should include the seven steps described here, it’ll also include personal preferences of your own — like the following:
- Writing music and other ambient details
- Writing schedule
- Word count targets and time frames
The more you learn about the finer details of the writing process, the more likely you are to create content your readers will love. And the more likely they are to find it.
Wherever you are in the process, our goal here is to provide content that will help you make the most of it.

Leave a Comment Cancel reply
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
TRY OUR FREE APP
Write your book in Reedsy Studio. Try the beloved writing app for free today.
Craft your masterpiece in Reedsy Studio
Plan, write, edit, and format your book in our free app made for authors.

Guides • Perfecting your Craft
Last updated on Dec 23, 2022
Creative Writing: 8 Fun Ways to Get Started
About the author.
Reedsy's editorial team is a diverse group of industry experts devoted to helping authors write and publish beautiful books.
About Savannah Cordova
Savannah is a senior editor with Reedsy and a published writer whose work has appeared on Slate, Kirkus, and BookTrib. Her short fiction has appeared in the Owl Canyon Press anthology, "No Bars and a Dead Battery".
Creative writing is a written art form that uses the imagination to tell stories and compose essays, poetry, screenplays, novels, lyrics, and more. It can be defined in opposition to the dry and factual types of writing found in academic, technical, or journalistic texts.
Characterized by its ability to evoke emotion and engage readers, creative writing can tackle themes and ideas that one might struggle to discuss in cold, factual terms.
If you’re interested in the world of creative writing, we have eight fantastic exercises and activities to get you started.

1. Use writing prompts every week

Coming up with ideas for short stories can be challenging, which is why we created a directory of 1700+ creative writing prompts covering a wide range of genres and topics. Writing prompts are flexible in nature, they are meant to inspire you without being too constrictive. Overall, they are a great way to keep your creative muscles limber.

If you’re struggling for motivation, how does a hard deadline and a little prize money sound? Prompts-based writing contests are a fantastic way to dive into creative writing: the combination of due dates, friendly rivalries, prize money, and the potential to have your work published is often just what’s needed to propel you over the finish line.
We run a weekly writing contest over on Reedsy Prompts , where hundreds of writers from all around the world challenge themselves weekly to write a short story between 1,000 and 3,000 words for a chance to win the $250 prize. Furthermore, the community is very active in providing constructive feedback, support, and accountability to each other 一 something that will make your efforts even more worthwhile.
Take a peek at our directory of writing contests which features some of the most prestigious open writing competitions in the world.
2. Start journaling your days

Another easy way to get started with creative writing is to keep a journal. We’re not talking about an hour-by-hour account of your day, but journaling as a way to express yourself without filters and find your ‘voice in writing’. If you’re unsure what to journal about, think of any daily experiences that have had an impact on you, such as…
Special moments . Did you lock yourself out of your house? Or did you catch a beautiful sunset on your way back from groceries? Capture those moments, and how you felt about them.
People . Did you have an unusual exchange with a stranger at the bar? Or did you reconnect with someone you haven’t seen in years? Share your thoughts about it.
World events . Is there something happening in the world right now that is triggering you? That’s understandable. You can reflect on it (and let some steam off) while journaling.
Memories . Did you go down memory lane after a glass of wine? Great, honor those memories by trying to recollect them in detail on paper so that they will always stay vivid in your mind.
Life decisions . Are you having an existential crisis about what to do with your life? Write down your thought process, and the pros and cons of the possible decisions in front of you. You’ll be surprised to discover that, not only is it a great creative writing exercise, but it can also actually help you sort your life out!
If you struggle to write consistently, sign up for our How to Write a Novel course to finish a novel in just 3 months.

NEW REEDSY COURSE
How to Write a Novel
Enroll in our course and become an author in three months.
3. Create an anonymous social media account

Like anonymous blogging, an incognito Twitter account sidesteps the pressure that comes with attaching your name to your work. Anonymously putting tiny stories out into the ether gives you the freedom to create without worrying about the consequences — which is great, so long as you don’t use it as an opportunity to troll people or spread conspiracy theories.
You could use the anonymous account in different ways. For example, you could…
- Tweet from unique perspectives (e.g. a dog observing human behavior );
- Create a parody account of real or fictional people (e.g. an English poet from the Middle Ages );
- Challenge yourself to write tiny flash fiction stories that fit into Twitter threads.
Just remember, you’re not doing this to fool anyone into thinking that your account is real: be a good citizen and mark yourself a fiction account in your bio.
But if you’re not really a social media kinda person, you may enjoy our next tip, which is a bit more on the analog side.

GET ACCOUNTABILITY
Meet writing coaches on Reedsy
Industry insiders can help you hone your craft, finish your draft, and get published.
4. Find an old photo and tell its story

Find a random old photo — maybe on the web, maybe from a photo album in a yard sale — and see what catches your attention. Look closely at it and try to imagine the story behind it. What was happening? Who are the people in it and how are they really feeling? Do they share a relationship, and of what kind? What are their goals and dreams?
In other words, bring the photo to life with your imagination. Don't be afraid to take artistic license with your story, as the goal is to be creative and have fun while writing.
How do you know it’s creative writing?

5. Create a character from a random name

Just as our universe started from a few simple elements, you can create a character from a few basic information, like their name, culture, and gender. Reedsy’s handy character name generator can help you with that, offering random names based on archetypes, Medieval roots, fantasy traits and more. A few examples? A Celtic heroine named Fíona O'Keefe, a hero’s sidekick named Aderine, or a Korean track star named Park Kang-Dae.
Once you've chosen their name, begin to develop their personality. Set a timer for 5–10 minutes and write anything that comes to mind about them. It could be a page from their FBI dossier, a childhood diary entry, or simply a scene about them boiling an egg.
Just ‘go with the flow’ and don’t stop writing until your time is up. Repeat the process a few times to further hone the personality. If you like what you end up with, you can always go deeper later by creating a character bible .
If a stream-of-consciousness exercise is not your thing, you can try to imagine your character in a specific situation and write down how’d they respond to it. For example, what if they were betrayed by a friend? Or if they were elected in power? To help you imagine situations to put your character in, we made a free template that you can download below.

FREE RESOURCE
Reedsy’s Character Questionnaire
40 questions to help you develop memorable characters.
6. Construct a character by people-watching

People watching is “the action of spending time idly observing people in a public place.” In a non-creepy way, ideally. Sit on a bench on a public square or on a road-side table at your favorite café, and start observing the people around you. Pay attention to any interesting quirks or behaviors, and write it down. Then put on your detective’s hat and try to figure out what that tells you about them.
For example, the man at the table next to you at the restaurant is reading the newspaper. His jacket and hat are neatly arranged next to him. The pages make a whipping sound as he briskly turns them, and he grimaces every time he reads a new article. Try to imagine what he’s reading, and why he’s reacting the way he is. Then, try to build a character with the information you have. It’s a fun creative exercise that will also, hopefully, help you better empathize with strangers.
7. “Map” something you feel strongly about into a new context

Placing your feelings into new contexts can be a powerful creative writing exercise. The idea is to start from something you feel strongly about, and frame it into a completely different context.
For example, suppose your heart is torn apart after you divorce your life-long partner: instead of journaling or crafting an entire novel about it, you could tell a story about a legendary trapeze duo whose partnership has come to an end. If you’re struggling with politicking and petty power dynamics at the office: what if you “mapped” your feelings onto an ant who resents being part of a colony? Directing your frustration at a queen ant can be a fun and cathartic writing experience (that won’t get you in trouble if your co-workers end up reading your story).
8. Capture the moment with a haiku

Haikus are poems from the Japanese tradition that aim to capture, in a few words, daily moments of insight (usually inspired by nature). In a nutshell, it’s about becoming mindful of your surroundings, and notice if you can see something in a new or deeper way 一 then use contrasting imagery to express whatever you noticed.
Here’s an example:
Bright orange bicycle
Speeding through the autumn leaves
A burst of color waves
It may sound a bit complicated, but it shouldn’t be 一 at least not for the purpose of this exercise. Learn the basics of haiku-writing , then challenge yourself to write one per day for a week or month. At the end, you’ll be able to look back at your collection of poems and 一 in the worst case scenario 一 revisit small but significant moments that you would have otherwise forgot about.
Creative writing can be any writing you put your heart and soul into. It could be made for the purpose of expressing your feelings, exploring an idea, or simply entertaining your readers. As you can see there’s many paths to get involved with it, and hundreds of exercises you can use as a starting point. In the next post , we’ll look more in detail at some creative writing examples from some fellow authors.
Join a community of over 1 million authors
Reedsy is more than just a blog. Become a member today to discover how we can help you publish a beautiful book.
Bring your stories to life
Our free writing app lets you set writing goals and track your progress, so you can finally write that book!

1 million authors trust the professionals on Reedsy. Come meet them.
Enter your email or get started with a social account:

Creative Writing 101
You love to write and have been told you have a way with words. So you’ve decided to give writing a try—creative writing.
Problem is, you’re finding it tougher than it looks.
You may even have a great story idea , but you’re not sure how to turn it into something people will read.
Don’t be discouraged—writing a compelling story can be grueling, even for veterans. Conflicting advice online may confuse you and make you want to quit before you start.
But you know more than you think. Stories saturate our lives.
We tell and hear stories every day in music, on television, in video games, in books, in movies, even in relationships.
Most stories, regardless the genre, feature a main character who wants something.
There’s a need, a goal, some sort of effort to get that something.
The character begins an adventure, a journey, or a quest, faces obstacles, and is ultimately transformed.
The work of developing such a story will come. But first, let’s look at the basics.
- What is Creative Writing?
It’s prose (fiction or nonfiction) that tells a story.
Journalistic, academic, technical writing relays facts.
Creative writing can also educate, but it’s best when it also entertains and emotionally moves the reader.
It triggers the imagination and appeals to the heart.
- Elements of Creative Writing

Writing a story is much like building a house.
You may have all the right tools and design ideas, but if your foundation isn’t solid, even the most beautiful structure won’t stand.
Most storytelling experts agree, these 7 key elements must exist in a story.
Plot (more on that below) is what happens in a story. Theme is why it happens.
Before you begin writing, determine why you want to tell your story.
- What message do you wish to convey?
- What will it teach the reader?
Resist the urge to explicitly state your theme. Just tell the story, and let it make its own point.
Give your readers credit. Subtly weave your theme into the story and trust them to get it.
They may remember a great plot, but you want them thinking about your theme long after they’ve finished reading.
2. Characters
Every story needs believable characters who feel knowable.
In fiction, your main character is the protagonist, also known as the lead or hero/heroine.
The protagonist must have:
- redeemable flaws
- potentially heroic qualities that emerge in the climax
- a character arc (he must be different, better, stronger by the end)
Resist the temptation to create a perfect lead. Perfect is boring. (Even Indiana Jones suffered a snake phobia.)
You also need an antagonist, the villain , who should be every bit as formidable and compelling as your hero.
Don’t make your bad guy bad just because he’s the bad guy. Make him a worthy foe by giving him motives for his actions.
Villains don’t see themselves as bad. They think they’re right! A fully rounded bad guy is much more realistic and memorable.
Depending on the length of your story , you may also need important orbital cast members.
For each character, ask:
- What do they want?
- What or who is keeping them from getting it?
- What will they do about it?
The more challenges your characters face, the more relatable they are.
Much as in real life, the toughest challenges result in the most transformation.
Setting may include a location, time, or era, but it should also include how things look, smell, taste, feel, and sound.
Thoroughly research details about your setting so it informs your writing, but use those details as seasoning, not the main course. The main course is the story.
But, beware.
Agents and acquisitions editors tell me one of the biggest mistakes beginning writers make is feeling they must begin by describing the setting.
That’s important, don’t get me wrong. But a sure way to put readers to sleep is to promise a thrilling story on the cover—only to start with some variation of:
The house sat in a deep wood surrounded by…
Rather than describing your setting, subtly layer it into the story.
Show readers your setting. Don’t tell them. Description as a separate element slows your story to crawl.
By layering in what things look and feel and sound like you subtly register the setting in the theater of readers’ minds.
While they concentrating on the action, the dialogue , the tension , the drama, and conflict that keep them turning the pages, they’re also getting a look and feel for your setting.
4. Point of View
POV is more than which voice you choose to tell your story: First Person ( I, me ), Second Person ( you, your ), or Third Person ( he, she, or it ).
Determine your perspective (POV) character for each scene—the one who serves as your camera and recorder—by deciding who has the most at stake. Who’s story is this?
The cardinal rule is that you’re limited to one perspective character per scene, but I prefer only one per chapter, and ideally one per novel.
Readers experience everything in your story from this character’s perspective.
For a more in-depth explanation of Voice and POV, read A Writer’s Guide to Point of View .
This is the sequence of events that make up a story —in short, what happens. It either compels your reader to keep turning pages or set the book aside.
A successful story answers:
- What happens? (Plot)
- What does it mean? (Theme: see above)
Writing coaches call various story structures by different names, but they’re all largely similar. All such structures include some variation of:
- An Inciting Incident that changes everything
- A series of Crises that build tension
- A Resolution (or Conclusion)
How effectively you create drama, intrigue, conflict, and tension, determines whether you can grab readers from the start and keep them to the end.
6. Conflict
This is the engine of fiction and crucial to effective nonfiction as well.
Readers crave conflict and what results from it.
If everything in your plot is going well and everyone is agreeing, you’ll quickly bore your reader—the cardinal sin of writing.
If two characters are chatting amiably and the scene feels flat (which it will), inject conflict. Have one say something that makes the other storm out, revealing a deep-seated rift.
Readers will stay with you to find out what it’s all about.
7. Resolution
Whether you’re an Outliner or a Pantser like me (one who writes by the seat of your pants), you must have an idea where your story is going.
How you expect the story to end should inform every scene and chapter. It may change, evolve, and grow as you and your characters do, but never leave it to chance.
Keep your lead character center stage to the very end. Everything he learns through all the complications you plunged him into should, in the end, allow him to rise to the occasion and succeed.
If you get near the end and something’s missing, don’t rush it. Give your ending a few days, even a few weeks if necessary.
Read through everything you’ve written. Take a long walk. Think about it. Sleep on it. Jot notes. Let your subconscious work. Play what-if games. Reach for the heart, and deliver a satisfying ending that resonates .
Give your readers a payoff for their investment by making it unforgettable.
- Creative Writing Examples
- Short Story
- Narrative nonfiction
- Autobiography
- Song lyrics
- Screenwriting
- Playwriting
- Creative Writing Tips
In How to Write a Novel , I cover each step of the writing process:
- Come up with a great story idea .
- Determine whether you’re an Outliner or a Pantser.
- Create an unforgettable main character.
- Expand your idea into a plot.
- Do your research.
- Choose your Voice and Point of View.
- Start in medias res (in the midst of things).
- Intensify your main character’s problems.
- Make the predicament appear hopeless.
- Bring it all to a climax.
- Leave readers wholly satisfied.
- More to Think About
1. Carry a writing pad, electronic or otherwise. I like the famous Moleskine™ notebook .
Ideas can come at any moment. Record ideas for:
- Anything that might expand your story
2. Start small.
Take time to build your craft and hone your skills on smaller projects before you try to write a book .
Journal. Write a newsletter. Start a blog. Write short stories . Submit articles to magazines, newspapers, or e-zines.
Take a night school or online course in journalism or creative writing. Attend a writers conference.
3. Throw perfection to the wind.
Separate your writing from your editing .
Anytime you’re writing a first draft, take off your perfectionist cap. You can return to editor mode to your heart’s content while revising, but for now, just write the story.
Separate these tasks and watch your daily production soar.
- Time to Get to Work
Few pleasures in life compare to getting lost in a great story.
Learn how to write creatively, and the characters you birth have the potential to live in hearts for years.
- 1. Carry a writing pad, electronic or otherwise. I like the famous Moleskine™ notebook.

Faith-Based Words and Phrases

What You and I Can Learn From Patricia Raybon

A Guest Blog from Stephen King—Yes, that Stephen King

Enter your email to instantly access my ultimate guide:
How to write a novel: a 12-step guide.

Elements of Creative Writing
(3 reviews)
J.D. Schraffenberger, University of Northern Iowa
Rachel Morgan, University of Northern Iowa
Grant Tracey, University of Northern Iowa
Copyright Year: 2023
ISBN 13: 9780915996179
Publisher: University of Northern Iowa
Language: English
Formats Available
Conditions of use.
Learn more about reviews.
Reviewed by Colin Rafferty, Professor, University of Mary Washington on 8/2/24
Fantastically thorough. By using three different authors, one for each genre of creative writing, the textbook allows for a wider diversity of thought and theory on writing as a whole, while still providing a solid grounding in the basics of each... read more
Comprehensiveness rating: 5 see less
Fantastically thorough. By using three different authors, one for each genre of creative writing, the textbook allows for a wider diversity of thought and theory on writing as a whole, while still providing a solid grounding in the basics of each genre. The included links to referred texts also builds in an automatic, OER-based anthology for students. Terms are not only defined clearly, but also their utility is explained--here's what assonance can actually do in a poem, rather than simply "it's repeated vowel sounds,"
Content Accuracy rating: 5
Calling the content "accurate" requires a suspension of the notion that art and writing aren't subjective; instead, it might be more useful to judge the content on the potential usefulness to students, in which case it' s quite accurate. Reading this, I often found myself nodding in agreement with the authors' suggestions for considering published work and discussing workshop material, and their prompts for generating creative writing feel full of potential. It's as error-free, if not more so, than most OER textbooks (which is to say: a few typos here and there) and a surprising number of trade publications. It's not unbiased, per se--after all, these are literary magazine editors writing the textbook and often explaining what it is about a given piece of writing that they find (or do not find) engaging and admirable--but unbiased isn't necessarily a quantity one looks for in creative writing textbooks.
Relevance/Longevity rating: 4
The thing about creative writing is that they keep making more of it, so eventually the anthology elements of this textbook will be less "look what's getting published these days" and more "look what was getting published back then," but the structure of the textbook should allow for substitution and replacement (that said, if UNI pulls funding for NAR, as too many universities are doing these days, then the bigger concern is about the archive vanishing). The more rhetorical elements of the textbook are solid, and should be useful to students and faculty for a long time.
Clarity rating: 5
Very clear, straightforward prose, and perhaps more importantly, there's a sense of each author that emerges in each section, demonstrating to students that writing, especially creative writing, comes from a person. As noted above, any technical jargon is not only explained, but also discussed, meaning that how and why one might use any particular literary technique are emphasized over simply rote memorization of terms.
Consistency rating: 4
It's consistent within each section, but the voice and approach change with each genre. This is a strength, not a weakness, and allows the textbook to avoid the one-size-fits-all approach of single-author creative writing textbooks. There are different "try this" exercises for each genre that strike me as calibrated to impress the facets of that particular genre on the student.
Modularity rating: 5
The three-part structure of the book allows teachers to start wherever they like, genre-wise. While the internal structure of each section does build upon and refer back to earlier chapters, that seems more like an advantage than a disadvantage. Honestly, there's probably enough flexibility built into the textbook that even the callbacks could be glossed over quickly enough in the classroom.
Organization/Structure/Flow rating: 5
Chapters within each genre section build upon each other, starting with basics and developing the complexity and different elements of that genre. The textbook's overall organization allows some flexibility in terms of starting with fiction, poetry, or nonfiction.
Interface rating: 4
Easy to navigate. I particularly like the way that links for the anthology work in the nonfiction section (clearly appearing at the side of the text in addition to within it) and would like to see that consistently applied throughout.
Grammatical Errors rating: 5
A few typos here and there, but you know what else generally has a few typos here and there? Expensive physical textbooks.
Cultural Relevance rating: 5
The anthology covers a diverse array of authors and cultural identities, and the textbook authors are not only conscious of their importance but also discuss how those identities affect decisions that the authors might have made, even on a formal level. If you find an underrepresented group missing, it should be easy enough to supplement this textbook with a poem/essay/story.
Very excited to use this in my Intro to CW classes--unlike other OERs that I've used for the field, this one feels like it could compete with the physical textbooks head-to-head. Other textbooks have felt more like a trade-off between content and cost.
Reviewed by Jeanne Cosmos, Adjunct Faculty, Massachusetts Bay Community College on 7/7/24
Direct language and concrete examples & Case Studies. read more
Direct language and concrete examples & Case Studies.
References to literature and writers- on track.
Relevance/Longevity rating: 5
On point for support to assist writers and creative process.
Direct language and easy to read.
First person to third person. Too informal in many areas of the text.
Units are readily accessible.
Process of creative writing and prompts- scaffold areas of learning for students.
Interface rating: 5
No issues found.
The book is accurate in this regard.
Cultural Relevance rating: 4
Always could be revised and better.
Yes. Textbook font is not academic and spacing - also not academic. A bit too primary. Suggest- Times New Roman 12- point font & a space plus - Some of the language and examples too informal and the tone of lst person would be more effective if - direct and not so 'chummy' as author references his personal recollections. Not effective.
Reviewed by Robert Moreira, Lecturer III, University of Texas Rio Grande Valley on 3/21/24
Unlike Starkey's CREATIVE WRITING: FOUR GENRES IN BRIEF, this textbook does not include a section on drama. read more
Comprehensiveness rating: 4 see less
Unlike Starkey's CREATIVE WRITING: FOUR GENRES IN BRIEF, this textbook does not include a section on drama.
As far as I can tell, content is accurate, error free and unbiased.
The book is relevant and up-to-date.
The text is clear and easy to understand.
Consistency rating: 5
I would agree that the text is consistent in terms of terminology and framework.
Text is modular, yes, but I would like to see the addition of a section on dramatic writing.
Topics are presented in logical, clear fashion.
Navigation is good.
No grammatical issues that I could see.
Cultural Relevance rating: 3
I'd like to see more diverse creative writing examples.
As I stated above, textbook is good except that it does not include a section on dramatic writing.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Chapter One: One Great Way to Write a Short Story
- Chapter Two: Plotting
- Chapter Three: Counterpointed Plotting
- Chapter Four: Show and Tell
- Chapter Five: Characterization and Method Writing
- Chapter Six: Character and Dialouge
- Chapter Seven: Setting, Stillness, and Voice
- Chapter Eight: Point of View
- Chapter Nine: Learning the Unwritten Rules
- Chapter One: A Poetry State of Mind
- Chapter Two: The Architecture of a Poem
- Chapter Three: Sound
- Chapter Four: Inspiration and Risk
- Chapter Five: Endings and Beginnings
- Chapter Six: Figurative Language
- Chapter Seven: Forms, Forms, Forms
- Chapter Eight: Go to the Image
- Chapter Nine: The Difficult Simplicity of Short Poems and Killing Darlings
Creative Nonfiction
- Chapter One: Creative Nonfiction and the Essay
- Chapter Two: Truth and Memory, Truth in Memory
- Chapter Three: Research and History
- Chapter Four: Writing Environments
- Chapter Five: Notes on Style
- Chapter Seven: Imagery and the Senses
- Chapter Eight: Writing the Body
- Chapter Nine: Forms
Back Matter
- Contributors
- North American Review Staff
Ancillary Material
- University of Northern Iowa
About the Book
This free and open access textbook introduces new writers to some basic elements of the craft of creative writing in the genres of fiction, poetry, and creative nonfiction. The authors—Rachel Morgan, Jeremy Schraffenberger, and Grant Tracey—are editors of the North American Review, the oldest and one of the most well-regarded literary magazines in the United States. They’ve selected nearly all of the readings and examples (more than 60) from writing that has appeared in NAR pages over the years. Because they had a hand in publishing these pieces originally, their perspective as editors permeates this book. As such, they hope that even seasoned writers might gain insight into the aesthetics of the magazine as they analyze and discuss some reasons this work is so remarkable—and therefore teachable. This project was supported by NAR staff and funded via the UNI Textbook Equity Mini-Grant Program.
About the Contributors
J.D. Schraffenberger is a professor of English at the University of Northern Iowa. He is the author of two books of poems, Saint Joe's Passion and The Waxen Poor , and co-author with Martín Espada and Lauren Schmidt of The Necessary Poetics of Atheism . His other work has appeared in Best of Brevity , Best Creative Nonfiction , Notre Dame Review , Poetry East , Prairie Schooner , and elsewhere.
Rachel Morgan is an instructor of English at the University of Northern Iowa. She is the author of the chapbook Honey & Blood , Blood & Honey . Her work is included in the anthology Fracture: Essays, Poems, and Stories on Fracking in American and has appeared in the Journal of American Medical Association , Boulevard , Prairie Schooner , and elsewhere.
Grant Tracey author of three novels in the Hayden Fuller Mysteries ; the chapbook Winsome featuring cab driver Eddie Sands; and the story collection Final Stanzas , is fiction editor of the North American Review and an English professor at the University of Northern Iowa, where he teaches film, modern drama, and creative writing. Nominated four times for a Pushcart Prize, he has published nearly fifty short stories and three previous collections. He has acted in over forty community theater productions and has published critical work on Samuel Fuller and James Cagney. He lives in Cedar Falls, Iowa.
Contribute to this Page
Writing process: From discovery to done (complete guide)
The writing process has many stages, from discovery and investigation to publication. Read authors’ insights on finding ideas, revision and more, and tips and methods to find the process that works for you.
- Post author By Jordan
- 5 Comments on Writing process: From discovery to done (complete guide)

The writing process is a complex, not always linear creative process. From ‘plotters’ vs ‘pantsers’ (to ‘bashers’ vs ‘swoopers’), this guide unpacks stages of the writing process, what authors have said about the practices and habits of writing, and more. Use the links above to jump to the section that interests you now.
Writing process stages: 7 areas of practice
Some writing schools and authors divide writing into four stages, some five. Yet these seven see a story from first idea to publication:
- Discovery. Before you can draft, you need an idea, a premise. This is the investigative stage of finding the seed for a story with the most potential.
- Prewriting . The preparation to write before drafting begins. Depending on whether you’re a ‘plotter’ or ‘pantser’ (more on this below), this may include outlining, brainstorming, freewriting, or other common prewriting techniques.
- Drafting. You write narration, exposition, scenes, chapters (depending on your story’s format). Drafting may be fast or slow, depending on your preferred methods. Try different approaches and techniques to shake up your usual writing habits.
- Writing feedback and story development. Once you are comfortable to share your work-in-progress (WIP), you may share early drafts with a trusted friend, writing coach or critique circle for perspective and insight.
- Revision . The process of reviewing what you’ve written, deciding what to keep (and which ‘darlings’ to ‘kill’).
- Editing. While revision entails making decisions about the content of your story, editing involves making decisions about the presentation of that content – how best to make the story more impactful and polished.
- Publication (and promotion). Isn’t the writing process over at this stage? Not at all – your query letters, story pitches, blurbs, review requests and other matter will be some of the most important material of the entire writing process. This is the writing that puts the story you’ve labored over in the right hands.
Keep reading for tips, methods and ideas about each of these stages, supplemented by reading from the Now Novel blog.
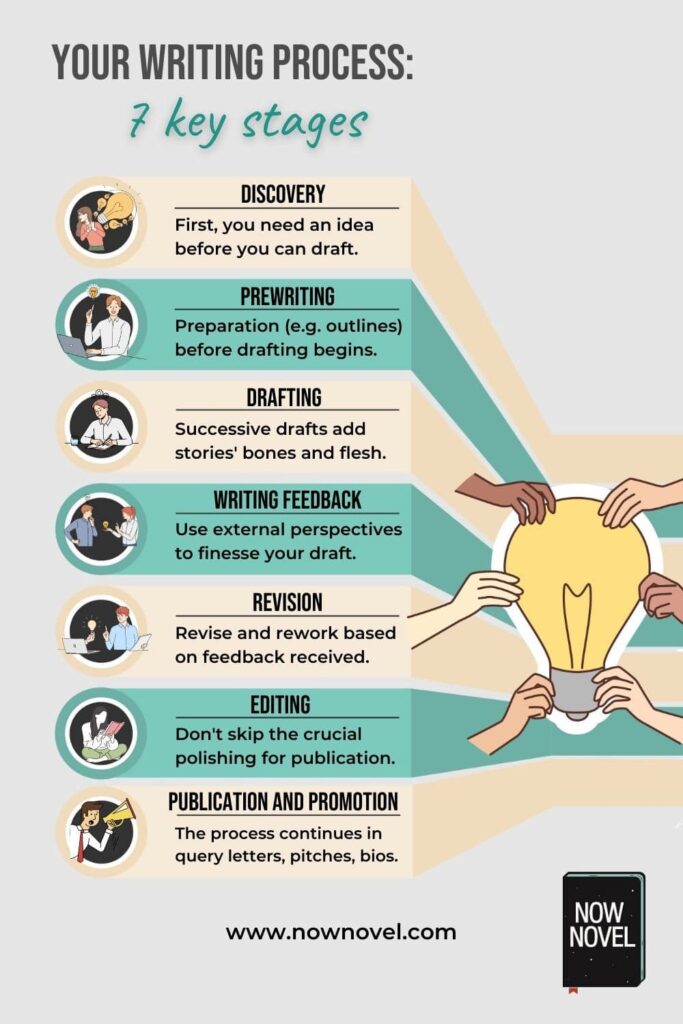
Recommended reading
- The writing process: 7 steps to structure and success
To the top ↑
Sometimes we fail for a week, a month, a year, a decade. And then we come back, circle the fire. Our lives are not linear. We get lost, then we get found. Patience is important, and a large tolerance for our mistakes. We don’t become anything overnight. Natalie Goldberg, The True Secret of Writing (2013), p. 58.
Discovery: Finding and investigating writing ideas
The writing process may start from an idea that arrives like a soothsayer. A flash of inspiration, insight, wisdom – a dream, unexpected connection, some kind of beguiling chance encounter or happenstance that makes you say, ‘I’ve got an idea’.
Yet the idea-finding process may equally be deliberate, even robotic. Consistently trying your hand at writing prompts until an idea niggles away at your waking mind, for example, persistently saying, ‘pick me’.
Finding and developing writing ideas is a skill you develop like any part of the writing process. That way you can make an idea come, not just for a first book, but a second, third (if with a little coaxing).
Essayist and cultural theorist Walter Benjamin said of the writing process:
Work on a good piece of writing proceeds on three levels: a musical one, where it is composed; an architectural one, where it is constructed; and finally, a textile one, where it is woven. Walter Benjamin, quote via Goodreads .
Before you make a picture with those threads, you need the wool you spin into finer thread: The fluffy stuff of an idea.
Writing process methods: Ways to find ideas
There are many ways to find ideas and find joy in the discovery stage of writing process.
Discovery and investigation may include a little or a lot of research, depending on what you need to know. The seed of an idea may come from multiple sources at once, as Toni Morrison says of her Pulitzer-winning novel Beloved :
Beloved originated as a general question, and was launched by a newspaper clipping. The general question (remember, this was the early eighties) centered on how – other than equal rights, access, pay, etc. – does the women’s movement define the freedom being sought? Toni Morrison, ‘On Beloved ‘ in Mouth Full of Blood: Essays, Speeches, Meditations, p. 281.
Here are fifteen ways to find ideas:
15 ways to find writing ideas and begin the writing process
- Try writing prompts such as the step-by-step prompts to find a central story idea in the Now Novel dashboard.
- Ask ‘What if…?’ For example, ‘What if a mysterious satellite held captivating mysteries about an alien race?’
- Draw from life. What experience could you use/alter for non-fiction or fiction?
- Use visual prompts. Use a photo or artwork as your starting point. Free-write a paragraph describing what you see, then continue and keep or turf the opening material.
- Play/combine. William S. Burroughs’ famous ‘cut up’ technique reassembles random cuttings from print into new ideas, for example.
- Trawl headlines. Google intriguing subjects in the ‘news’ tab. E.g. ‘travel disasters’ brought up ‘How ‘dark tourism’ can pass on the lessons of past tragedies’. Mine your headline for ideas.
- Explore myths and legends. Reads stories from world mythologies. You could update an ancient tale with modern touches.
- Argue with other stories. Maybe a story’s annoyed you, or you want to explore a secondary character’s viewpoint (from a work now in the public domain). Write back.
- Test out ideas in short fiction. Famous novels (such as Portrait of the Artist as a Young Man by James Joyce) began as short story test runs.
- Draw inspiration from music. Listen to a song. What ideas, characters, premises do the lyrics evoke?
- Try creative constraints. The collective OuLiPo used devices such as writing stories omitting a chosen vowel entirely to find the unexpected.
- Browse famous quotes. Take something like ‘Happy families are all alike…’ from Anna Karenina . Where else could it lead?
- Join writing groups. Prompts set by members for each other may inspire new ideas.
- Research historical figures or eras. You may unearth a riveting idea from the past.
- Tap into your subconscious and keep a dream journal or meditate, silence and going inward often brings clarity.
FAQs about the discovery stage of writing
Share your idea with trusted people for external perspective. Test it out in a writing group or class. Ask questions about ‘who’, ‘what’, ‘why’ ‘where’ and ‘when’ to finesse a hazy or partial idea into something deeper, fuller.
The varied ways myths and legends are recycled (Thor in Norse mythology becoming Marvel’s popular character) reminds us there are no new ideas. Originality lies in the specifics of voice and execution. Be specific, be yourself and find your voice through practice and intentional execution.
This is where it helps to remember the writing process is not linear. The discovery stage is also a good time for research, finding out what is being done (and overdone) in your genre. What agents are looking for (or tired of seeing). Resources listing recent publishing deals give insights into what’s sold recently and book market appetites. To start though, focus on telling a good story. Great stories find their audience.
🗣️ How did you find your last story idea? Let us know in the comments, and keep reading for tips and methods for prewriting, drafting, and more.
- 38 plot ideas (plus 7 ways to find more)
- How to find book ideas: 15 easy methods
- Book ideas: 12 fun ways to find them
- Finding story topics when stuck: 5 simple methods

GET YOUR FREE GUIDE TO SCENE STRUCTURE
Read a guide to writing scenes with purpose that move your story forward.
Ideas are like fireflies; go hunting for them and they elude you. Sit and enjoy the night, and they appear from out of nowhere. You have to let the ideas come to you. Expand your world, read outside your comfort zone, take walks. The fireflies will come. Just give them the chance. Sabrina Jeffries in 101 Habits of Highly Successful Novelists: Insider Secrets from Top Writers by Andrew McAleer (2008), p. 69.
Prewriting: Useful preparatory writing processes
Prewriting is the processes before you start drafting a story which help you prepare.
There are many kinds of prewriting. Because the writing process is not linear, you might come back to one or more of these methods at some stage of drafting:
Common prewriting steps and methods
- Picking a premise. If you have multiple ideas, go with the idea that pulls you most and (if you want a marketable book) the one you know has the better market potential.
- Choosing a genre or subgenre. This goes hand in hand with picking a premise, since if you set your book in outer space and explore future technology, chances are you’ll be shelved with sci-fi.
- Brainstorming. A process of generating ideas, whether you use mind maps, answer prompts and questionnaires, or churn out every idea you can think of in scenario- or topic-driven lists.
- Creating a story outline. This may be a meticulous, detailed outline, or a cursory collection of notes. The more complete your outline, the more handrails you’ll have. This prevents wandering off into irrelevancies, plot holes and impossible paradoxes, and so on.
- Creating initial summary material. Summary material includes things like character profiles or IDs, scene summaries , or a one-page synopsis of what your story is about (also a useful exercise in the Publication and promotion stage of process).
- Freewriting. Before more structured drafting, you might explore a topic or scenario with freewriting. Set a timer for 15 to 20 minutes and just write whatever comes into your head about a topic you think will be important to your book. It might spawn scene, chapter, or character ideas.
- Research. This may overlap with the discovery/investigation stage, as your idea may also need a little research to solidify what you want to write about. It might include fiction set in a similar era or place, making a bibliography of potentially helpful non-fiction, speaking to subject exploring films and documentaries, or visiting physical or digital archives. For some tips on how to research place when you can’t visit those places, read our tips.
- Interviewing. This is especially pertinent for types of writing such as historical fiction, non-fiction, memoir. Interviews with subject experts, people who lived through specific events or an era, could provide helpful nuance, context, and ideas for relevant story details.
You don’t necessarily need to do every kind of prewriting. Some authors favor ‘just-in-time’ research (an idea Bujold spoke about in relation to fantasy worldbuilding ).
Authors on prewriting and whether or not to plan stories
The prewriting perspectives below show there are many way to skin (or rather save) a cat. Try different methods and find what works for you .
Loose story outlining
Author Scott King gives this reminder that prewriting (planning, creating structure, organizing) should serve the needs of your story, and stay adaptable to its unique needs:
An outline is a map of your story. It’s not set in stone. Even when you work from an outline, you will discover new twists and turns as you progress. The outline is there to remind you of where you are going so you can’t ever get too far from where you need to be. Since I was working under pressure, I didn’t want to get crazy with how I structured Ameriguns . I defaulted to a three act structure, the kind you’d use in a screenplay, but altered it to fit the needs of the story. Scott King, ‘Outline’ in The 5 Day Novel , 2016, p. 58.
Pullman on how establishing rules is part of play
More broadly, Philip Pullman, in ‘The Practice of Writing’, talks about how having some rules at the start of creative process gives paradoxical freedom to play. He compares guidelines such as rules (or outlines) to choosing where touchdown lies for a football game:
And as we know about all games, it’s much more satisfying to play with rules than without them. If we’re going to enjoy a game of football in the playground, we need to know where the touchline is, and agree on what we’re going to regard as the goalposts. Then we can get on with playing, because the complete freedom of our play is held together and protected by this armature of rules. The first and last and only discovery that the victims of anarchy can make is: no rules, no freedom. Philip Pullman, ‘The Practice of Writing’ in Daemon Voices , pp. 18-19
‘Plotting’ vs ‘Pantsing’: Find your balance between prewriting and drafting
So much has been written and said about whether you should plan stories in detail in advance (‘plotting’), or go where imagination takes you (‘pantsing’, after the expression ‘to fly by the seat of your pants’ or work with instinct and gut more than organized knowledge).
Your writing process may change to suit your project
Author K.M. Weiland raises the useful reminder that your writing process doesn’t need to ape a famous writer’s approach, or be the same across every story you tell:
Each author must discover for himself what methods work best for him. Just because Margaret Atwood does X and Stephen King does Y is no reason to blindly follow suit. Read widely, learn all you can about what works for other authors, and experiment to discover which methods will offer you the best results. K.M. Weiland, ‘Chapter One: Should You Outline?’ in Outlining your Novel: Map your way to success , p. 11.
Planning stories helps character development
Edith Wharton, the first woman to win the Pulitzer Prize for writing, said of the space and planning deeper characterization requires:
Type, general character, may be set forth in a few strokes, but the progression, the unfolding of personality […] if the actors in the tale are to retain their individuality for [the reader] through a succession of changing circumstances—this slow but continuous growth requires space, and therefore belongs by definition to a larger, a symphonic plan. Edith Wharton, The Writing of Fiction: The classic guide to the art of the short story and the novel (1925), p. 33.
Not planning, creative freedom and excitement
Author Lee Child, on the other hand, extolls the benefits of not planning (and not being as pedantic about the marks you hit as an editor or publisher might be):
I write without a plan or an outline. The way I picture my process is this: The novel is a movie stuntman, about to get pushed off a sixty-story building. The prop guys have a square fire-department airbag ready on the sidewalk below. One corner is marked Mystery, one Thriller, one Crime Fiction, and one Suspense. The stuntman is going to land on the bag. (I hope.) But probably not dead-on. Probably somewhat off center. But biased toward which corner? I don’t know yet. And I really don’t mind. I’m excited to find out. Lee Child, ‘Introduction’ in How to Write a Mystery: A handbook from Mystery Writers of America
🗣️ What is your preferred prewriting method? Or do you pants it all the way, or pants a little then switch to planning? Tell us in the comments.
- What is prewriting? Preparing to write with purpose
- Story plotting and structure: Complete guide
- Story planning and outlining: Complete guide
- Story planner success: How to organize your novel

GET HELP PLANNING YOUR BOOK
Join Now Novel for a helpful crit community and live webinars and plotting tools when you upgrade.
Writing process challenges you may encounter
Before we discuss drafting and the writing process, let’s explore common process challenges (and tips to overcome them):
Common hurdles in creative process
There are challenges in creative process that beginning authors and veterans alike face. You’re not alone if you’ve ever gone rounds in the ring with:
- Fear of failure (or success). What happens if a publisher or agent says no? What if reviews or crits are harsh? Or how will you handle sudden public recognition and scrutiny in the event of success?
- Procrastination (avoidance behaviors). When writing a story feels hard, it’s easy to put it off (or use not having time or something else as an excuse not to write).
- Distractibility. Whether you have a condition such as ADHD that adds further focus challenges or are a social media addict, we live in a highly distracting, ‘always on’ world.
- ‘Time Burglars’ . There are many thieves of time that take away from the writing process if you don’t make regular writing a top priority.
- A harsh inner critic. Many aspiring creative people have harsh inner critics who destroy their work before anyone else can.
- Laziness. This is a common reason not to write, too.
- Unpreparedness. Many writers find projects spool out and become much harder and more complex than originally anticipated. That can be discouraging.
Overcoming writing process challenges
How can you work with and overcome some of the above procedural challenges in writing?
- Keep SMART goals: Specific, measurable, attainable, realistic and time-based goals are much easier to track and attain than hazy aims
- Work on tolerance for your mistakes: Everyone makes mistakes starting out, and seasoned pros do, too
- Chunk up complex tasks: Struggling to write a chapter a week to schedule? Try write 300 words per day and set a bigger ‘stretch goal’ (an extra target if you make your first easily)
- Turn off the net if you need to: Put your phone in airplane mode and pause all notifications
- Remember the difference between procrastination and waiting: It’s fine to wait for maturity, fuller knowledge of your subject, to be in the right frame of mind. It’s not putting off but letting process take its necessary time for this story
- Get up and move often: The writing process is (for the most part) a sedentary one. It’s easy to forget to move. Stone-like posture may lead to petrified process, even if your mind’s going a hundred miles a minute
The accountability of working with a writing coach or joining a crit circle that meets regularly helps (in Now Novel’s experience), too.
Natalie Goldberg writes, on procrastination vs waiting:
Waiting is something full-bodied. Perhaps waiting isn’t even a good word for it. Pregnant is better. You’ve worked on something for a while. You are excited by it, even happy, but you are wise and step back. You take a walk, but this walk isn’t to avoid the writing on your desk. It is a walk full of your writing. It is also full of the trees you pass, the river, the sky. You are letting writing work on you. Natalie Goldberg, ‘Procrastination and Waiting’, in Wild Mind: Living the writer’s life , p. 210.
How to nurture your writing process and avoid common pitfalls
We asked Now Novel’s writing coaches their best advice on the writing process, and about patterns they see in beginning writers (and ways to overcome destructive habits).
Romance author and writing coach Romy Sommer on remembering why you’re telling your story:

Writing is hard work. Probably harder than you thought it would be when inspiration first struck and you decided to write a novel. So find the joy in what you are writing. Remind yourself daily of WHY you are writing this story. Remember that spark that first inspired you to sit down and write, because that is what will keep you going when the going gets tough.
SFF and YA author, editor and writing coach Nerine Dorman on allowing yourself to make ‘happy accidents’:

Many writers I’ve worked with lack confidence in their ability, and tend to focus on those first chapters to the point where they lose the momentum to push forward with the rest of the plot. I give them Bob Ross’s advice of making plenty of ‘happy little accidents’ as we can’t actually work on writing if there’s nothing there to revise. Your first draft can be as messy as you need it to be. The most important thing is to get into the habit of writing as regularly as your schedule allows, and to see your writing as a very personal way to express yourself. Granted, there are the basic building blocks of writing and style, which I aim to teach, but I like to think that we also look at what it means to be a writer – a constantly evolving, growing creative person.
Recommended Reading
- How to overcome writer’s block: 14 methods
- Motivation to write: 7 simple strategies
- End writing procrastination now: 7 steps
- Silence your inner critic: 8 ways to write in peace
We have to accept ourselves in order to write. Now none of us does that fully; few of us do it even halfway. Don’t wait for one hundred percent acceptance of yourself before you write, or even eight percent acceptance. Just write. The process of writing is an activity that teaches us about acceptance. Natalie Goldberg, Wild Mind: Living the writer’s life , p. 61.
Drafting stories: Getting knee-deep in scenes
We could equally call the drafting stage of process ‘discovery’ like the first stage. After all, drafting is where you discover many of the ‘happy accidents’ Nerine describes above. Discoveries that may often depart from your outline (or lead you back into revision-planning).
Learn more about approaches to drafting, what authors say about doing fewer vs multiple drafts, and tips to make this part of process work for you.
Types of draft in the storytelling process
There are many terms authors use to refer to drafting. Numbered (first, second, third) drafts. Even drafts before the first, the so-called ‘draft zero’ (which describes a discovery draft, the purpose of which is just to learn the broad scope of the story and set down some of the material in full).
In one of Now Novel’s live webinars, writing coach, author and editor Hedi Lampert shared a drafting concept by the late author and writing educator Anne Schuster, who hosted women’s writing workshops in Cape Town.
The idea is a simple, three-part drafting process. To paraphrase:
- The down draft: The draft where you get your ideas down on the page, with as much messiness or as many placeholders as you need to keep moving.
- The up draft: A second draft in which you pick up on details for development, expansion, and color in more of your story.
- The dental draft: A third draft in which you polish the work of your first two drafts, paying attention to language and finer detail now the story elements have solidified.
This is a useful concept in that it gives each stage of drafting a proper focus and purpose (and allows for not getting everything ‘right’ straight away).
Authors on the drafting stage of writing process
Will you draft chapters in chronological sequence or out of order? Should you worry about chapters and scene breaks or carve up the text later?
These are some of the questions authors face about drafting. Read authors on drafting and their individual processes. These perspectives show that what works for one person might not work for another. Try different methods until you find what works for your process, or this project.
Toni Morrison on creating chapters and parts in a draft
Toni Morrison describes putting in story segment divisions at a later point in process:
Chapter and part designations, as conventionally used in novels, were never very much help to me in writing. Nor are outlines. (I permit their use for the sake of the designer and for ease in talking about the book. They are usually identified at the last minute.) Toni Morrison, ‘The Writer Before the Page’, in Mouth Full of Blood: Essays, Speeches, Meditations , p. 266.
Sir Terry Pratchett on the purpose of a first, second and third draft (creative freedom, shaping, addressing detail)
Sir Terry Pratchett said that the first draft is ‘just you telling yourself the story’, and qualified something like a systematic per-draft process when he said:
First draft: let it run. Turn all the knobs up to 11. Second draft: hell. Cut it down and cut it into shape. Third draft: comb its nose and blow its hair. I usually find that most of the book will have handed itself to me on that first draft. Sir Terry Pratchett, via Goodreads
Colleen McCullough on how many drafts until done: It depends
How many drafts ‘should’ you write? It depends, writing is rewriting as Colleen McCullough describes:
Once I’ve got the first draft down on paper then I do five or six more drafts, the last two of which will be polishing drafts. The ones in between will flesh out the characters and maybe I’ll check my research. Colleen McCullough, quoted by Writers Write here .
🗣️ What is your drafting process currently? Is there a system, number of drafts or method that works well for you? Share it in the comments.
- Writing first drafts: 10 ideas to reach final drafts
- Write with purpose: 7 ways to keep drafts focused
- How to write a rough draft: Finish your novel faster
The concept of finishing a piece of writing, taking it through successive drafts, did not yet exist for me. I reveled in the heady pleasure of committing a few words to paper and treasured each like a rare jewel I had dug from the earth with my bare hands. A journal suited my fledgling status as a writer and made me feel serious and important, a real writer, and honored the scant output I produced. In my journal I practiced being a writer in both senses of the word: practiced as in trying out, and practiced as in keeping a daily practice, the way the nuns observed their daily order of prayer services. Katherine Towler, in Writers and Their Notebooks , edited by Diana M. Raab, pp. 65-66.
Writing feedback and story development
Remember that we said the writing process is not always linear?
When you get writing feedback depends on you. You may want feedback on your story idea or summary, your early chapters. You may prefer not to show your WIP to anyone until you’re at least one or more drafts deep. Tweet This
Maybe you move between drafting rounds, and feedback rounds, as you use readers’ perspectives to tweak your story and workshop it.
Why getting feedback is a crucial stage of writing process
When we don’t have critiques, manuscript evaluations, editors or beta readers, we only have our own perspectives to rely upon. You get used to your own mistakes, and nobody knows their own blind spots or the details they hadn’t thought of (that a shrewd second opinion might).
To ensure feedback aids (more than frustrates) your writing process:
- Get feedback from writers you trust. You might want input from writers at a similar stage of development to yourself, or editors who have been story doctors for some time.
- Take feedback from whence it comes. That crosspatch member of your crit circle who never has a nice word to say? Expect the kind of feedback that person usually gives. If a crit circle or beta reader is harsh or overwhelmingly negative, it’s OK to find a better fit.
- Stay open to perspectives and use what’s useful. There’s that saying, ‘You can lead a horse to water, but you can’t make it drink.’ Don’t get parched just to protect your ego. Reviewers on major platforms could be way harsher if you don’t take time to fix what isn’t working.
- Describe what feedback you’re looking for. Now Novel’s critique submission system contains categories you can check off for feedback, such as ‘grammar and language’, ‘characters’, ‘structure and flow’ and ‘dialogue’. Specifying what kind of feedback you want helps readers tailor their feedback to be more relevant to your needs.
- Give any necessary context. Nobody knows your writing process or story better than you do. Remember to contextualize anything an editor or beta reader may need to know to have a better understanding of what you’re aiming for (in style, subject matter, tone, characterization, etc.).
Giving feedback also does wonders for many authors’ writing processes – helping others with writing challenges helps you build the tools to solve your own.

Channeling feedback into the writing process
Too much feedback (especially if overly harsh as it can be in poorly moderated communities), especially in the early stages of a story, may inhibit or discourage. When evaluating writing feedback, ask:
- Is there overlap between what feedback givers are saying? This could signal a real and higher priority issue to address in revision
- What is higher vs lower priority feedback to implement? Major confusion-bringing issues such as continuity issues or tense drift and head-hopping are naturally a higher priority than minor details that don’t affect whether readers can understand the story, for example
When getting and giving feedback in a crit circle or a beta reading community, it’s easy to compare yourself to other writers. Writing coach Romy Sommer advises against comparisons:

Do not compare yourself to other writers. We each work differently, we each need to find the writing process that works best for our lives and the way our brains work, and what works for one person doesn’t necessarily work for another. Accepting that took a huge weight off my shoulders and enabled me to embrace my own process.
The development stage of creative process: Comb story’s nose, blow its hair
As Terry Pratchett says, developing a story – later rewrites and drafts – gets into grooming-like detail. Combing a story’s … nose!? You may well find that there are Picasso-like parts, or the princess’s hair is snotty, not sleek. Tweet This
At the developmental stage of writing, ask yourself questions an editor would, such as:
- Is it clear? Does the reader have sufficient context or clear wording to understand the story and follow along?
- Does it have cohesion? Do actions and reactions flow and make sense? When characters converse, does it have the pattern of real call and response or is it like two people with crossed wires?
- Is the story ‘colored in’? Is there sufficient description (and are descriptions specific/detailed, not hazy)?
- Are events and actions clear and intriguing? Does the procession of events create questions the reader wants answered?
- Is there flow between lines, scenes, chapters? Or if the story is non-linear, do the pieces come together to make an interesting, impactful whole?
Here’s a fuller checklist with 34 story development questions for rewrites and successive drafts:

- How to find beta readers for final draft feedback
- Writing circle pros: 8 reasons to share your story
- 100 character development questions to inspire deeper arcs
- How to master plot development: 8 steps
Writers have always struggled with the same core issues: getting the work done (productivity) and creating something worth reading (creativity). And, unless you believe that misery is necessary for true art, aim for a third goal: making the process enjoyable, cultivating a fulfilling and happy life that includes writing. Let’s consider this our triple objective: productivity, creativity, and enjoyment. Surely that’s not asking too much? Anne Janzer, ‘Finding Your Own Process’ in The Writer’s Process: Getting your brain in gear, p. 15
Revision: Seeing again with fresh eyes
The word ‘revision’ says it all. The fifth stage of the writing process is seeing again, reviewing what you’ve written, to make insertions/deletions as needed.
There may be parts of your story that would benefit much from expansion, coloring in. Maybe there are parts that you have to cull, as much as you may feel attached to them.
Revision vs editing: What’s the difference?
Revision is a process of making decisions about the content of your story. It may include:
- Adding in new scenes, chapters or sections
- Rearranging scenes, chapters or sections
- Cutting out subplots or other material that aren’t contributing to the whole sufficiently
- Trying a different person to determine the effects on POV
That last example touches on an important truth about revision: it’s as creative as drafting, and it can be a fun process of play, of trying out different things.
Editing, on the other hand, is focused on improving the presentation of decisions made about content. Often, you may find that an editor suggests further revisions. This is work that you’ll do, because only you (as the author) are qualified to make this level of creative decision, it being your story.
Authors’ ideas on revision and the writing process
What do authors say about the revision process?
Joyce Carol Oates on revising as you go being arduous
Joyce Carol Oates shared that her writing methods changed over time, as she grew older:
I think that I envy my younger self because I used to write a whole draft of a novel and then go back and rewrite it […] Today, I do a lot of revising as I go along and that seems to be more painful and arduous. It’s a slow process, almost like putting a mosaic together or weaving things in and out, whereas before it felt more like galloping on a horse and then creating the manuscript. For some reason I’ve become more attuned to the individual sentence and reworking the sentences. I’m not sure why that happened. Joyce Carol Oates, USA Weekend , quoted by famouswritingroutines.com here .
This raises an important decision about revising: When will you stop to review and tweak elements? If you stop every page, prepare for a first draft that may take years! Give yourself the time your process dictates.
Jamaica Kincaid on the internal revision process
Of course, your revision is not only the work you do on paper. Dame Agatha Christie said the best time to plot a novel was while doing the dishes. Jamaica Kincaid, in conversation with Publishers Weekly , says:
I write a lot in my head. The revision goes on internally. It’s not spontaneous and it doesn’t have a schedule. You know how some people write every day at a certain point? I’m not like that. I carry something around for a long time. I weigh the words and the sentences. I weigh the paragraphs. The process is much more meditative for me. So, when I put something down on paper, I’ve already edited a lot. Jamaica Kincaid, interviewed by Liesel Schwabe, ‘The Age of a Mountain: PW Talks with Jamaica Kincaid’, December 2012.
🗣️ What is your approach to revision? Do you sit with ideas a long time, write at a gallop and then revise, or make painstaking revisions as you go? Share in the comments.
- Revision in writing: How to improve between drafts
- Novel editing insights: 9 big lessons from critique

GET FEEDBACK AND HELP WITH REVISION
Join The Process for weekly editor critiques, monthly live workshops, story outlining tools and more.
Editing: The polishing stage of writing process
Editing, the penultimate stage of writing process, is itself made up of several important stages. It’s often a challenging one because there is an even bigger degree of ‘letting go’. Letting someone make tracked changes and suggestions to your manuscript, for example.
When you hand over writing to an editor, you may be getting your first sample of ‘reception’ (if you have been working in private, not with a crit circle). T.S. Eliot drily said, ‘Some editors are failed writers, but so are most writers.’
Editing is often an immensely enriching process, though, for both editor and author. Earnest discussion and deep thought about a story’s strengths (and how best to serve them) and challenges (and how best to address them) may unearth surprising gems.
The main types of fiction editing
The four main types of editing are:
- Developmental editing. This examines large-picture aspects such as character and story development, narrative structure and pacing.
- Line editing. More detail-oriented, line-level editing that examines issues such as language, style, flow and clarity.
- Copy editing: Focuses on grammar, spelling, punctuation, and eliminating errors and residual issues with style or flow that may be left over from (or have crept in after) line editing.
- Proofreading: The final stage of editing, catching any final errors before publication (a stage self-publishing authors may be tempted to omit, but do so at risk of excoriating reviews).
Many editing providers, including Now Novel, offer manuscript evaluations . This is often bundled with developmental editing as a part of discovery process (we subtract the cost of an evaluation from developmental editing). A manuscript evaluation produces a reader’s report with actionable recommendations on aspects such as plot and character development, narrative structure, pacing, conflict and more.
Is editing writing process? It is in that it is en route to publication. How much writing you’ll do at this stage depends on how much revision there is to be done.
If you have excellent language faculty and a strong grasp of story, an editor may recommend you proceed straight to copy editing from an evaluation, if there are no large-scale issues.
- Editing and revising: 7 tips from top authors and editors
- Editing copy? 8 tips for a word-perfect manuscript
Publication and promotion: Writing around your story
Does the writing process end once your work’s edited? Some would say ‘yes’. Yet publication and promotion involve a lot of writing ‘around’ your story, about your story. Press, promotion, selling.
This isn’t a type of writing (and part of process) that’s for everyone (you may want to outsource some of this work – for example writing social media captions – to a marketing agency if or once you can afford it).
Publication and the writing process
Types of writing you’ll do when you’re ready to publish include:
- Writing query letters or script pitches
- Writing bios for author pages
- Writing newsletters, social media captions, and other marketing material
- Writing speeches or guest blogs about the process of writing your story
Promotion and publication are a whole other side of process that we’ll cover in fuller detail in another complete guide.
See the resources recommended reading below for tips on aspects such as creating your author brand, creating a business plan, and ways to get more reviews.
Helpful resources for publication and promotion writing
Here are several resources that provide tips on publication and promotion as well as useful examples:
- Publishers Weekly – frequent round-ups of publishing news and interesting developments in publishing
- Query Shark – examples of query letters dissected by an agent
- Jane Friedman’s blog – with twenty years’ experience in the publishing industry, Jane shares helpful publishing insights such as how to query and how to avoid publishing scams
- Joanna Penn’s The Creative Penn – a helpful blog featuring podcasts and articles packed with publishing and book promotion insights
- Kindlepreneur – writer Dave Chesson has a site devoted to book publishing and promotion how to’s, useful for self-publishing authors.
🗣️ Is there a book publishing and promo resource you love you don’t see here? Let us know about it in the comments.
- How to write a query letter: 10 easy steps
- Writing to market: 10 pros and cons to weigh
- Self-publishing on Ama zon: 20 pros and cons for authors
- How to create a business plan for writers
Now Novel provides help with every stage of the writing process. Learn more about membership benefits for serious writers .
Related Posts:
- Writing dialogue: Complete guide to storied speech
- Character writing: Complete guide to creating your cast
- Writing romance and love stories: Complete guide
- Tags writing process
Jordan is a writer, editor, community manager and product developer. He received his BA Honours in English Literature and his undergraduate in English Literature and Music from the University of Cape Town.
5 replies on “Writing process: From discovery to done (complete guide)”
I’m mostly a pantser, I think. I let the ideas take me where they want to go with an end point in mind. The problem is that I don’t always like the direction, missing that fireman cushion completely. I feel like I’ve given away a piece of my soul to have to start over (I don’t want to say second draft because it feels more like a new zero). I know how important it is to get to the end, but if I truly have a fresh idea I have to go down that road, but I’m so scared it’ll take me straight to Hades… again. Eventually, I’ll be very well versed in writing my own story, I suppose. Lots and lots of practice.
Hi Margriet, thank you for sharing that. It’s very interesting as a method as you do end up doing a lot of review and revision as you go. Have you every thought of having some kind of ‘pantsers compromise’ of maybe outlining one scene ahead? Something Ernest Hemingway said was to the effect of ‘stop for the day when you know what happens next’ which might be one way to keep Hades and his kidnappers at bay 🙂 Thank you for sharing your process!
Thanks for this Jordan – comprehensive doesn’t do it justice!
For me, the difference between being someone who wanted to complete a first draft and actually doing it was definitely when I stopped being a panther and embraced the value of plotting & planning.
I’m still more of a plantser than someone who plots things to the nth degree, but having a very clear idea of at least the first 20-30% of the novel is going to go, with an idea of the way it’s going to end allows me the flexibility and freedom to start the novel with confidence that I’m going to finish, because I have a pretty good map of the journey and the destination.
I know I’m going to get “there”, even if the actual final destination changes along the way, or if I take a few pretty little detours along the way. I’ve used two different plotting approaches to complete 3 first drafts now – so I think it’s not necessarily what plotting style you go for, it’s about having one and making it work.
Hi Mark, it’s a pleasure. Thank you for sharing that. I love the happy accident of ‘panther’ in particular. Because that describes what pantsers are like, pouncing with minimum hesitation. That makes total sense to me; each story will also have its own demands in terms of the mix of research and other stages required so process may have to adapt to the demands of a specific work.
I saw that and had a little chuckle at myself – the inner pantser lives on!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Pin It on Pinterest
Encyclopedia for Writers
Writing with ai, the ultimate blueprint: a research-driven deep dive into the 13 steps of the writing process.
- © 2023 by Joseph M. Moxley - Founder, Writing Commons
This article provides a comprehensive, research-based introduction to the major steps , or strategies , that writers work through as they endeavor to communicate with audiences . Since the 1960s, the writing process has been defined to be a series of steps , stages, or strategies. Most simply, the writing process is conceptualized as four major steps: prewriting , drafting , revising , editing . That model works really well for many occasions. Yet sometimes you'll face really challenging writing tasks that will force you to engage in additional steps, including prewriting , inventing , drafting , collaborating , researching , planning , organizing , designing , rereading , revising , editing , proofreading , sharing or publishing . Expand your composing repertoire -- your ability to respond with authority , clarity , and persuasiveness -- by learning about the dispositions and strategies of successful, professional writers.

Table of Contents
Like water cascading to the sea, flow feels inevitable, natural, purposeful. Yet achieving flow is a state of mind that can be difficult to achieve. It requires full commitment to the believing gam e (as opposed to the doubting game ).
What are the Steps of the Writing Process?
Since the 1960s, it has been popular to describe the writing process as a series of steps or stages . For simple projects, the writing process is typically defined as four major steps:
- drafting
This simplified approach to writing is quite appropriate for many exigencies–many calls to write . Often, e.g., we might read an email quickly, write a response, and then send it: write, revise, send.
However, in the real world, for more demanding projects — especially in high-stakes workplace writing or academic writing at the high school and college level — the writing process involve additional steps, or strategies , such as
- collaboration
- researching
- proofreading
- sharing or publishing.
Related Concepts: Mindset ; Self Regulation
Summary – Writing Process Steps
The summary below outlines the major steps writers work through as they endeavor to develop an idea for an audience .
1. Prewriting
Prewriting refers to all the work a writer does on a writing project before they actually begin writing .
Acts of prewriting include
- Prior to writing a first draft, analyze the context for the work. For instance, in school settings students may analyze how much of their grade will be determined by a particular assignment. They may question how many and what sources are required and what the grading criteria will be used for critiquing the work.
- To further their understanding of the assignment, writers will question who the audience is for their work, what their purpose is for writing, what style of writing their audience expects them to employ, and what rhetorical stance is appropriate for them to develop given the rhetorical situation they are addressing. (See the document planner heuristic for more on this)
- consider employing rhetorical appeals ( ethos , pathos , and logos ), rhetorical devices , and rhetorical modes they want to develop once they begin writing
- reflect on the voice , tone , and persona they want to develop
- Following rhetorical analysis and rhetorical reasoning , writers decide on the persona ; point of view ; tone , voice and style of writing they hope to develop, such as an academic writing prose style or a professional writing prose style
- making a plan, an outline, for what to do next.
2. Invention
Invention is traditionally defined as an initial stage of the writing process when writers are more focused on discovery and creative play. During the early stages of a project, writers brainstorm; they explore various topics and perspectives before committing to a specific direction for their discourse .
In practice, invention can be an ongoing concern throughout the writing process. People who are focused on solving problems and developing original ideas, arguments , artifacts, products, services, applications, and texts are open to acts of invention at any time during the writing process.
Writers have many different ways to engage in acts of invention, including
- What is the exigency, the call to write ?
- What are the ongoing scholarly debates in the peer-review literature?
- What is the problem ?
- What do they read? watch? say? What do they know about the topic? Why do they believe what they do? What are their beliefs, values, and expectations ?
- What rhetorical appeals — ethos (credibility) , pathos (emotion) , and logos (logic) — should I explore to develop the best response to this exigency , this call to write?
- What does peer-reviewed research say about the subject?
- What are the current debates about the subject?
- Embrace multiple viewpoints and consider various approaches to encourage the generation of original ideas.
- How can I experiment with different media , genres , writing styles , personas , voices , tone
- Experiment with new research methods
- Write whatever ideas occur to you. Focus on generating ideas as opposed to writing grammatically correct sentences. Get your thoughts down as fully and quickly as you can without critiquing them.
- Use heuristics to inspire discovery and creative thinking: Burke’s Pentad ; Document Planner , Journalistic Questions , The Business Model Canvas
- Embrace the uncertainty that comes with creative exploration.
- Listen to your intuition — your felt sense — when composing
- Experiment with different writing styles , genres , writing tools, and rhetorical stances
- Play the believing game early in the writing process
3. Researching
Research refers to systematic investigations that investigators carry out to discover new knowledge , test knowledge claims , solve problems , or develop new texts , products, apps, and services.
During the research stage of the writing process, writers may engage in
- Engage in customer discovery interviews and survey research in order to better understand the problem space . Use surveys , interviews, focus groups, etc., to understand the stakeholder’s s (e.g., clients, suppliers, partners) problems and needs
- What can you recall from your memory about the subject?
- What can you learn from informal observation?
- What can you learn from strategic searching of the archive on the topic that interests you?
- Who are the thought leaders?
- What were the major turns to the conversation ?
- What are the current debates on the topic ?
- Mixed research methods , qualitative research methods , quantitative research methods , usability and user experience research ?
- What citation style is required by the audience and discourse community you’re addressing? APA | MLA .
4. Collaboration
Collaboration refers to the act of working with others to exchange ideas, solve problems, investigate subjects , coauthor texts , and develop products and services.
Collaboration can play a major role in the writing process, especially when authors coauthor documents with peers and teams , or critique the works of others .
Acts of collaboration include
- Paying close attention to what others are saying, acknowledging their input, and asking clarifying questions to ensure understanding.
- Expressing ideas, thoughts, and opinions in a concise and understandable manner, both verbally and in writing.
- Being receptive to new ideas and perspectives, and considering alternative approaches to problem-solving.
- Adapting to changes in project goals, timelines, or team dynamics, and being willing to modify plans when needed.
- Distributing tasks and responsibilities fairly among team members, and holding oneself accountable for assigned work.
- valuing and appreciating the unique backgrounds, skills, and perspectives of all team members, and leveraging this diversity to enhance collaboration.
- Addressing disagreements or conflicts constructively and diplomatically, working towards mutually beneficial solutions.
- Providing constructive feedback to help others improve their work, and being open to receiving feedback to refine one’s own ideas and contributions.
- Understanding and responding to the emotions, needs, and concerns of team members, and fostering a supportive and inclusive environment .
- Acknowledging and appreciating the achievements of the team and individual members, and using successes as a foundation for continued collaboration and growth.
5. Planning
Planning refers to
- the process of planning how to organize a document
- the process of managing your writing processes
6. Organizing
Following rhetorical analysis , following prewriting , writers question how they should organize their texts. For instance, should they adopt the organizational strategies of academic discourse or workplace-writing discourse ?
Writing-Process Plans
- What is your Purpose? – Aims of Discourse
- What steps, or strategies, need to be completed next?
- set a schedule to complete goals
Planning Exercises
- Document Planner
- Team Charter
7. Designing
Designing refers to efforts on the part of the writer
- to leverage the power of visual language to convey meaning
- to create a visually appealing text
During the designing stage of the writing process, writers explore how they can use the elements of design and visual language to signify , clarify , and simplify the message.
Examples of the designing step of the writing process:
- Establishing a clear hierarchy of visual elements, such as headings, subheadings, and bullet points, to guide the reader’s attention and facilitate understanding.
- Selecting appropriate fonts, sizes, and styles to ensure readability and convey the intended tone and emphasis.
- Organizing text and visual elements on the page or screen in a manner that is visually appealing, easy to navigate, and supports the intended message.
- Using color schemes and contrasts effectively to create a visually engaging experience, while also ensuring readability and accessibility for all readers.
- Incorporating images, illustrations, charts, graphs, and videos to support and enrich the written content, and to convey complex ideas in a more accessible format.
- Designing content that is easily accessible to a wide range of readers, including those with visual impairments, by adhering to accessibility guidelines and best practices.
- Maintaining a consistent style and design throughout the text, which includes the use of visuals, formatting, and typography, to create a cohesive and professional appearance.
- Integrating interactive elements, such as hyperlinks, buttons, and multimedia, to encourage reader engagement and foster deeper understanding of the content.
8. Drafting
Drafting refers to the act of writing a preliminary version of a document — a sloppy first draft. Writers engage in exploratory writing early in the writing process. During drafting, writers focus on freewriting: they write in short bursts of writing without stopping and without concern for grammatical correctness or stylistic matters.
When composing, writers move back and forth between drafting new material, revising drafts, and other steps in the writing process.
9. Rereading
Rereading refers to the process of carefully reviewing a written text. When writers reread texts, they look in between each word, phrase, sentence, paragraph. They look for gaps in content, reasoning, organization, design, diction, style–and more.
When engaged in the physical act of writing — during moments of composing — writers will often pause from drafting to reread what they wrote or to reread some other text they are referencing.
10. Revising
Revision — the process of revisiting, rethinking, and refining written work to improve its content , clarity and overall effectiveness — is such an important part of the writing process that experienced writers often say “writing is revision” or “all writing is revision.”
For many writers, revision processes are deeply intertwined with writing, invention, and reasoning strategies:
- “Writing and rewriting are a constant search for what one is saying.” — John Updike
- “How do I know what I think until I see what I say.” — E.M. Forster
Acts of revision include
- Pivoting: trashing earlier work and moving in a new direction
- Identifying Rhetorical Problems
- Identifying Structural Problems
- Identifying Language Problems
- Identifying Critical & Analytical Thinking Problems
11. Editing
Editing refers to the act of critically reviewing a text with the goal of identifying and rectifying sentence and word-level problems.
When editing , writers tend to focus on local concerns as opposed to global concerns . For instance, they may look for
- problems weaving sources into your argument or analysis
- problems establishing the authority of sources
- problems using the required citation style
- mechanical errors ( capitalization , punctuation , spelling )
- sentence errors , sentence structure errors
- problems with diction , brevity , clarity , flow , inclusivity , register, and simplicity
12. Proofreading
Proofreading refers to last time you’ll look at a document before sharing or publishing the work with its intended audience(s). At this point in the writing process, it’s too late to add in some new evidence you’ve found to support your position. Now you don’t want to add any new content. Instead, your goal during proofreading is to do a final check on word-level errors, problems with diction , punctuation , or syntax.
13. Sharing or Publishing
Sharing refers to the last step in the writing process: the moment when the writer delivers the message — the text — to the target audience .
Writers may think it makes sense to wait to share their work later in the process, after the project is fairly complete. However, that’s not always the case. Sometimes you can save yourself a lot of trouble by bringing in collaborators and critics earlier in the writing process.
Doherty, M. (2016, September 4). 10 things you need to know about banyan trees. Under the Banyan. https://underthebanyan.blog/2016/09/04/10-things-you-need-to-know-about-banyan-trees/
Emig, J. (1967). On teaching composition: Some hypotheses as definitions. Research in The Teaching of English, 1(2), 127-135. Retrieved from http://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/ED022783.pdf
Emig, J. (1971). The composing processes of twelfth graders (Research Report No. 13). Urbana, IL: National Council of Teachers of English.
Emig, J. (1983). The web of meaning: Essays on writing, teaching, learning and thinking. Upper Montclair, NJ: Boynton/Cook Publishers, Inc.
Ghiselin, B. (Ed.). (1985). The Creative Process: Reflections on the Invention in the Arts and Sciences . University of California Press.
Hayes, J. R., & Flower, L. (1980). Identifying the Organization of Writing Processes. In L. W. Gregg, & E. R. Steinberg (Eds.), Cognitive Processes in Writing: An Interdisciplinary Approach (pp. 3-30). Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum.
Hayes, J. R. (2012). Modeling and remodeling writing. Written Communication, 29(3), 369-388. https://doi: 10.1177/0741088312451260
Hayes, J. R., & Flower, L. S. (1986). Writing research and the writer. American Psychologist, 41(10), 1106-1113. https://doi.org/10.1037/0003-066X.41.10.1106
Leijten, Van Waes, L., Schriver, K., & Hayes, J. R. (2014). Writing in the workplace: Constructing documents using multiple digital sources. Journal of Writing Research, 5(3), 285–337. https://doi.org/10.17239/jowr-2014.05.03.3
Lundstrom, K., Babcock, R. D., & McAlister, K. (2023). Collaboration in writing: Examining the role of experience in successful team writing projects. Journal of Writing Research, 15(1), 89-115. https://doi.org/10.17239/jowr-2023.15.01.05
National Research Council. (2012). Education for Life and Work: Developing Transferable Knowledge and Skills in the 21st Century . Washington, DC: The National Academies Press.https://doi.org/10.17226/13398.
North, S. M. (1987). The making of knowledge in composition: Portrait of an emerging field. Boynton/Cook Publishers.
Murray, Donald M. (1980). Writing as process: How writing finds its own meaning. In Timothy R. Donovan & Ben McClelland (Eds.), Eight approaches to teaching composition (pp. 3–20). National Council of Teachers of English.
Murray, Donald M. (1972). “Teach Writing as a Process Not Product.” The Leaflet, 11-14
Perry, S. K. (1996). When time stops: How creative writers experience entry into the flow state (Order No. 9805789). Available from ProQuest Dissertations & Theses A&I; ProQuest Dissertations & Theses Global. (304288035). https://www.proquest.com/dissertations-theses/when-time-stops-how-creative-writers-experience/docview/304288035/se-2
Rohman, D.G., & Wlecke, A. O. (1964). Pre-writing: The construction and application of models for concept formation in writing (Cooperative Research Project No. 2174). East Lansing, MI: Michigan State University.
Rohman, D. G., & Wlecke, A. O. (1975). Pre-writing: The construction and application of models for concept formation in writing (Cooperative Research Project No. 2174). U.S. Office of Education, Department of Health, Education, and Welfare.
Sommers, N. (1980). Revision Strategies of Student Writers and Experienced Adult Writers. College Composition and Communication, 31(4), 378-388. doi: 10.2307/356600
The Elements of Style

Brevity - Say More with Less

Clarity (in Speech and Writing)

Coherence - How to Achieve Coherence in Writing

Flow - How to Create Flow in Writing

Inclusivity - Inclusive Language

The Elements of Style - The DNA of Powerful Writing

Recommended

Academic Writing – How to Write for the Academic Community

Structured Revision – How to Revise Your Work

Professional Writing – How to Write for the Professional World

Authority & Credibility – How to Be Credible & Authoritative in Research, Speech & Writing

Citation Guide – Learn How to Cite Sources in Academic and Professional Writing

Page Design – How to Design Messages for Maximum Impact
Suggested edits.
- Please select the purpose of your message. * - Corrections, Typos, or Edits Technical Support/Problems using the site Advertising with Writing Commons Copyright Issues I am contacting you about something else
- Your full name
- Your email address *
- Page URL needing edits *
- Phone This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
Other Topics:

Citation - Definition - Introduction to Citation in Academic & Professional Writing
- Joseph M. Moxley
Explore the different ways to cite sources in academic and professional writing, including in-text (Parenthetical), numerical, and note citations.

Collaboration - What is the Role of Collaboration in Academic & Professional Writing?
Collaboration refers to the act of working with others or AI to solve problems, coauthor texts, and develop products and services. Collaboration is a highly prized workplace competency in academic...

Genre may reference a type of writing, art, or musical composition; socially-agreed upon expectations about how writers and speakers should respond to particular rhetorical situations; the cultural values; the epistemological assumptions...

Grammar refers to the rules that inform how people and discourse communities use language (e.g., written or spoken English, body language, or visual language) to communicate. Learn about the rhetorical...

Information Literacy - How to Differentiate Quality Information from Misinformation & Rhetrickery
Information Literacy refers to the competencies associated with locating, evaluating, using, and archiving information. You need to be strategic about how you consume and use information in order to thrive,...

Mindset refers to a person or community’s way of feeling, thinking, and acting about a topic. The mindsets you hold, consciously or subconsciously, shape how you feel, think, and act–and...

Rhetoric: Exploring Its Definition and Impact on Modern Communication
Learn about rhetoric and rhetorical practices (e.g., rhetorical analysis, rhetorical reasoning, rhetorical situation, and rhetorical stance) so that you can strategically manage how you compose and subsequently produce a text...

Style, most simply, refers to how you say something as opposed to what you say. The style of your writing matters because audiences are unlikely to read your work or...

The Writing Process - Research on Composing
The writing process, also known as the composing process, refers to everything you do in order to complete a writing project. Over the last six decades, researchers have studied and theorized...

Writing Studies
Writing studies refers to an interdisciplinary community of scholars and researchers who study writing. Writing studies also refers to an academic, interdisciplinary discipline – a subject of study. Students in...
Featured Articles

The Writing Process
Making expository writing less stressful, more efficient, and more enlightening
Step 1: Generate Ideas

“If at first the idea is not absurd, then there is no hope for it.” —Albert Einstein
The first step of the writing process (that is, after carefully reading and understanding the assignment) is to generate ideas for your project. In shorter versions of the writing process, or in processes designed for other kinds of writing, step 1 is sometimes called “gathering” because it also includes doing research.

In expository writing, though, even for a research paper, you will want to “generate ideas” first. Why? First, you will want to see what you already know and think about a subject. Second, you will want to see what ideas you can come up with yourself. And third, the methods below will help you define what questions you want to start your research with.

There are various ways to generate ideas for your writing. People think and learn differently, so try them all and choose the one that’s best for you—although if you have never tried freewriting or “moodling,” described below, I strongly encourage you to try them both at least once. My experience is that students are usually happily surprised at the results.
Moreover, freewriting is often useful to non-native speakers of English who still struggle with fluency (i.e., writing quickly or relatively easily, in contrast to accuracy, which an overriding concern for at this stage of the writing process can inhibit the flow of words and ideas).
As you will recall from “ Whom are you writing for? “, the writing process starts as writer-oriented and gradually moves toward a reader-oriented product. Thus this step should be thought of as completely writer-oriented . Forget about your reader and assume that no one is going to see your notes or ideas from this stage. Let your ideas come out freely and be as wild and crazy as they seem. If you immediately censor what you think might be “dumb” or “silly” ideas, you may eliminate good ideas or connections to good ideas and are not really letting yourself think. As one moderately successful scientist (pictured at left) once put it, “Imagination is greater than knowledge. Knowledge is limited. Imagination encircles the world.”

There are four primary methods of generating ideas:
- Brainstorming
- Freewriting
- Idea Map/Web
- “Moodling”
Photo “Büro im Wasser” from Bundesarchiv, Bild 102-08112 / CC-BY-SA. Licensed under CC BY-SA 3.0 de via Wikimedia Commons.
Photo “Ideas” ©2014 Rafal Knop
What is Creative Writing? | An Introduction for Students
Last updated: 15th october 2024.
Rhys Mackenzie
Our tailored summer courses for ages 9-24 include all teaching and academic content, accommodation, meals (including Friday night formal dinners), a prize-giving ceremony, all-day trips and activities, airport transfers, access to Oxford Summer Courses Foundations, travel and medical insurance, and a welcome pack. Apply now to secure your spot in one of our comprehensive summer courses.
What is creative writing?
As the name suggests, creative writing is a form of writing that goes beyond the traditional realms of normal, professional, academic or technical forms of writing.
Instead, it encompasses a number of different genres and styles across a whole range of fields of both fictional and non-fiction writing; storytelling, playwriting, poetry, prose, journalistic, and more.
Though the definition can be quite vague, creative writing can, for the most part, be considered as any type of writing that is original and expressive of oneself. Typically, it can be identified by an emphasis on narrative craft, focusing on elements such as character development, narrative and plot, infusing its structure with imagination, invention and story.
In this sense, creative writing can technically be considered any writing of contemporary, original composition - it's bound by no standard conventions and uses a whole range of elements in its craft.
In an academic setting, creative writing is typically divided into fiction, poetry, or scriptwriting classes, with a focus on writing in an original style, not defined by pre-existing structures and genres.
What are the different types of creative writing?
Creative writing comes in many forms, encompassing a number of genres and styles. There are lots of different types of creative writing, which can be categorised as fiction or non-fiction. Some of the most popular being:
- Biographies
- Fiction: novels, novellas, short stories, etc.
- Poetry and spoken word
- Playwriting/scriptwriting
- Personal essays
What makes a good piece of creative writing?
First and foremost, it’s important to note that there is no pre-defined description of what it means to create a ‘good’ piece of creative writing. As the very name suggests, creative writing is an imaginative process, created by the individual with all their quirks and personalities.
Creative writing doesn’t fit one set genre and therefore there will never be an umbrella definition to describe the ‘perfect’ piece. Just think about a Gothic short story and then compare it to the features of a great Romantic poem - the two are so very different - it wouldn’t be unfair to judge them together.
However, with that being said, there are a few general principles that you can follow to make your creative writing as strong as it can be - by making it as authentic and true to you as possible:
- Know your audience - All great stories begin with a target audience in mind - because it’s exactly what you need to know in order to really tailor your writing and connect with them. Therefore, any creative writer should begin their writing by plotting out exactly who they want to read their work. Once you have this in mind, your writing will naturally begin to take direction and flow in a way that seems appropriate to your audience.
- Write what you know - Quite often, the best stories are those which we can connect to and relate in one or another way to our own lives. Or, they’re stories which seem to authentic that you could imagine it to be about the writer’s own life. Now, this doesn’t mean that you quite literally have to write about your life, but drawing on knowledge you have about different elements of our lives to give your story some authenticity and more believability.
- Creativity is key - Creativity is one of the most important elements of creative writing. It’s what sets you apart from other pieces of writing in your genre. Of course, this doesn't demand that you write a tale about a totally fantastical and mythical world with unique creatures - but simply use your creativity to think a little outside the box and put a unique twist on things; using literary devices like metaphors, alliteration, and varied sentence structure to make your work unique and interesting.
- Push your imagination - One of the great things about creative writing is that there is no definition or rules on ‘how’ to write. It’s a much more subjective genre and one which relies heavily on your own interpretations. Therefore, you should push your imagination to the limits to see what the end result could be. Some of the most interesting pieces of literature are thought-provoking or make us question the writing or world around us - where could your story take us?
- Plot a loose story arc - Despite the loose bounds of creative writing, it is still advisable to plot a loose story arc for any piece of literature you create. Story arcs are critical at giving your writing direction and purpose, helping you to write the whole piece at a good pace, without writing any superfluous content or ‘waffle.’ Follow your story arc, and your writing will have a strong structure, pace and direction - keeping your readers more engaged.
What are some techniques used in creative writing?
To make their writing stand out, writers often employ several creative writing techniques and literary devices, including:
- Character development - The process of creating a well-rounded, realistic character with depth, personality, and clear goals or motivations.
- Plot development - The story of your piece of writing - how it develops, unfolds, and moves along in time.
- Point of view - The perspective from which a narrative is told. It indicates who is telling the story and how the information is conveyed to the reader. Quite often writers will play with the point of view of the central character or protagonist to trick the reader and twist their perspective.
- Dialogue - Refers to the speech and conversations characters use to speak to one another. Dialogue and the language choices a character makes can be pivotal in helping define their personality.
- Literary devices - Such as metaphors, similes and alliteration to make creative writing more imaginative and descriptive. These are used in a myriad of ways by writers to make their writing more vivid, interesting and engaging.
Can creative writing be taught?
Of course! Creative writing can be taught, and is a very popular subject for university students, and for those who attend our summer courses.
Those who pursue the subject of Creative Writing will typically study a variety of texts from different periods of time to learn more about the different genres of writing within the field. They’ll become familiar with some of the leading creative writers from generations past to present, as well as some lesser-known and emerging writers in the industry.
Inspired by what they’ve learnt in the classroom, it’s not uncommon for Creative Writing students to also participate in regular workshops and scratch sessions, where they bring a piece of their writing along to class and have it read by other students and the tutor. They’ll leave with constructive feedback on how to improve their writing, or recommendations of other works which they may want to read to take influence from.
How to start creative writing
If you’re interested in getting those creative juices flowing and improving your writing craft, read some of our tips below on how to start creative writing:
- Read as much as you can - For creative writers, inspiration comes from a whole range of sources, but most commonly, from other writers. There’s some excellent examples of creative writing throughout history that all writers should be inspired by. Read a variety of genres by different authors to get a real feel for what type of writing you may want to do. Need some inspiration? Check out our blog: 15 Classic Books to Read
- Start journaling - Starting a journal can really help to unleash your inner creativity. Getting into the habit of writing each day about literally anything that’s preoccupied you that day will help you practice the art of writing. The more regularly you journal, the more you’ll build your confidence. You never know, you could even find your next great idea from something you’ve journaled about!
- Attend a Creative Writing summer course - If you’re just starting out as a creative writer and looking to collaborate, share ideas with others and workshop your writing, then joining a creative writing summer school could be a great option. Our creative writing summer courses are designed to help you extend your creative writing toolkit; you’ll analyse some of the industry’s greatest writers, as well as workshop some of your own writing with your peers.
- Practice using literary devices - Literary devices, such as metaphors, similes and rhyme can really help you write more vividly and create really descriptive, imaginative scenes. Practice using them regularly and you’ll soon watch your own creative writing start to flourish. Need some ideas to help you get practising? Look around your house and pick a random object. Then, practice using 5 literary devices to describe that same object - see where your creativity can take you!
- Write, write, write! - When it comes to how to start creative writing, one of the biggest pieces of advice we can offer is to pick up your pen or laptop, and start writing. Whether you have a single conversation starter for a character, or a complete narrative arc, you will only begin your creative writing journey when you physically do it. Even if you have no idea on what to write - look for writing prompt inspiration from all around you. The more you practice unleashing your creativity, the easier it will be to write over longer periods of time.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What age groups are the oxford summer courses designed for.
Our courses cater to students aged 9-24, with tailored programs to suit different age groups and academic levels.
What is included in the Oxford Summer Courses?
Our comprehensive summer courses include all teaching and academic content, accommodation, meals (including formal dinners), a prize-giving ceremony, all-day trips and activities, airport transfers, travel and medical insurance, and a welcome pack.
Can international students apply for the courses?
Yes, we welcome students from all over the world to join our summer courses in Oxford and Cambridge.
What are the benefits of taking a Creative Writing summer course?
Our Creative Writing summer courses offer students the opportunity to learn from experienced tutors, develop their writing skills, and gain inspiration from the historic surroundings of Oxford and Cambridge.
How can I apply for the Oxford Summer Courses?
You can apply for our courses online through our application portal . Once your application is submitted, we will be in touch with the next steps.
Creative writing is a remarkable voyage that invites us to unleash our imagination, share our stories, and inspire others. It offers countless personal and professional benefits, nurturing self-expression, empathy, and creativity. So, grab a pen, open your mind, and embark on this enchanting journey of creative writing with Oxford Summer Courses. Let your words paint a vivid tapestry that captivates hearts and minds under the guidance of experienced tutors from Oxford and Cambridge. Join us as we explore the magic of creative writing and discover the transformative power it holds within through the renowned Oxford Summer Courses summer school.
Ready to Join Oxford Summer Courses?
After submitting your application, we'll be in touch very soon to inform you of the outcome. Apply now to begin your journey with Oxford Summer Courses!
About the author
Rhys mackenzie is the website marketing manager at oxford summer courses. with extensive experience in seo and digital content management, they are passionate about showcasing the best that oxford has to offer. their previous role at experience oxfordshire gave them a deep appreciation for the city's unique cultural and academic offerings. learn more about rhys here ., share this article.
Discover the enchantment of creative writing with Oxford Summer Courses. Unleash your imagination, explore different genres, and enhance your communication skills. Nurture self-expression, empathy, and creativity while gaining valuable writing techniques.
Get Our Newsletter
Oxford Summer Courses LTD
18 Beaumont Street, Oxford, OX1 2NA, United Kingdom
+44 01865 818403

Juniors 9-12
Oxford 13-15
Oxford 16-17
Oxford 18-24
Cambridge 13-15
Cambridge 16-17
Advanced Cambridge 18-24
Back-To-Back Courses
Four Week Enhanced Programme
Group Bookings
GDPR Notice
Privacy Policy
Terms and Conditions
Oxford Summer Courses is an organisation which contracts with the colleges of the Universities of Oxford, Cambridge and London for the use of facilities, but which has no formal connection with the Universities of Oxford, Cambridge and London.
Oxford summer courses © 2024, oxford summer courses is a company registered in england and wales with company number 08011543.
- Mailing List
- Search Search
Username or Email Address
Remember Me

Resources for Writers: The Writing Process
Writing is a process that involves at least four distinct steps: prewriting, drafting, revising, and editing. It is known as a recursive process. While you are revising, you might have to return to the prewriting step to develop and expand your ideas.
- Prewriting is anything you do before you write a draft of your document. It includes thinking, taking notes, talking to others, brainstorming, outlining, and gathering information (e.g., interviewing people, researching in the library, assessing data).
- Although prewriting is the first activity you engage in, generating ideas is an activity that occurs throughout the writing process.
- Drafting occurs when you put your ideas into sentences and paragraphs. Here you concentrate upon explaining and supporting your ideas fully. Here you also begin to connect your ideas. Regardless of how much thinking and planning you do, the process of putting your ideas in words changes them; often the very words you select evoke additional ideas or implications.
- Don’t pay attention to such things as spelling at this stage.
- This draft tends to be writer-centered: it is you telling yourself what you know and think about the topic.
- Revision is the key to effective documents. Here you think more deeply about your readers’ needs and expectations. The document becomes reader-centered. How much support will each idea need to convince your readers? Which terms should be defined for these particular readers? Is your organization effective? Do readers need to know X before they can understand Y?
- At this stage you also refine your prose, making each sentence as concise and accurate as possible. Make connections between ideas explicit and clear.
- Check for such things as grammar, mechanics, and spelling. The last thing you should do before printing your document is to spell check it.
- Don’t edit your writing until the other steps in the writing process are complete.
100 Writing Practice Lessons & Exercises
by Joe Bunting | 50 comments
Want to become a better writer? How much time do you spend on your writing practice? Perhaps you want to write novels, or maybe you just want to get better grades in your essay writing assignments , or maybe you'd like to start a popular blog .
If you want to write better, you need practice. But what does a writing practice actually look like? In this post, I'm going to give you everything you need to kick off your writing practice and become a better writer faster.

What Is Writing Practice?
Writing practice is a method of becoming a better writer that usually involves reading lessons about the writing process, using writing prompts, doing creative writing exercises , or finishing writing pieces, like essays, short stories , novels , or books . The best writing practice is deliberate, timed, and involves feedback.
How Do You Practice Writing?
This was the question I had when I first started The Write Practice in 2011. I knew how to practice a sport and how to practice playing an instrument. But for some reason, even after studying it in college, I wasn't sure how to practice writing.
I set out to create the best writing practice I could. The Write Practice is the result.
I found that the best writing practice has three aspects:
Deliberate . Writing whatever you feel like may be cathartic, but it's not an effective way to become a better writer or build your writing skills. You'll get better faster by practicing a specific technique or aspect of the writing process each time you sit down to write.
This is why we have a new lesson about the writing process each day on The Write Practice, followed by a practice prompt at the end so you can put what you learned to use immediately.
Timed . It's no secret writers struggle with focus. There are just too many interesting distractions—Facebook, email, Kim Kardashian's Instagram feed (just kidding about that last one, sort of)—and writing is just too hard sometimes.
Setting a timer, even for just fifteen minutes, is an easy and effective way to stay focused on what's important.
This is why in our writing practice prompt at the end of each post we have a time limit, usually with a link to an online tool egg timer , so you can focus on deliberate practice without getting distracted.
Feedback . Getting feedback is one of the requirements to deliberately practice writing or any other craft. Feedback can look like listening to the reactions of your readers or asking for constructive criticism from editors and other writers.
This is why we ask you to post your writing practice after each lesson, so that you can get feedback from other writers in The Write Practice community. It's also why we set up The Write Practice Pro community , to provide critique groups for writers to get feedback on each finished piece of writing.

Our 100+ Best Creative Writing Practice Exercises and Lessons
Now that you know how we practice writing at The Write Practice, here are our best writing practice lessons to jumpstart your writing skills with some daily writing exercises, for beginner writers to even the most expert writers:
All-Time, Top 10 Writing Lessons and Exercises
These ten posts are our most viewed articles to boost your writing practice:
1. What is Plot? The 6 Elements of Plot and How to Use Them . Great stories use similar elements in wildly different ways to build page-turning stories. Click here to read what they are and learn how to start using them !
2. Top 100 Short Story Ideas . Here are over a hundred writing prompts in a variety of genres. If you need ideas for your next story, check this out!
3. How To Use Neither, Nor, Or, and Nor Correctly . Even good writers struggle figuring out when to use neither/nor and either/or. In this post, our copy-queen Liz Bureman settles the confusion once and for all. Click to continue to the writing exercise
4. Ten Secrets To Write Better Stories . How does Pixar manage to create such great stories, year after year? And how do you write a good story? In this post, I distill everything I've learned about how to write a good story into ten tips. Click to continue to the writing exercise
5. 35 Questions To Ask Your Characters From Marcel Proust . To get to know my characters better, I use a list of questions known as the Proust Questionnaire, made famous by French author, Marcel Proust. Click to continue to the writing exercise
6. How a Scene List Can Change Your Novel-Writing Life . Creating a scene list changed my novel-writing life, and doing the same will change yours too. Includes examples of the scene lists from famous authors. Click to continue to the writing exercise
7. Why You Need to be Using the Oxford Comma . Most people I've met have no idea what the Oxford comma is, but it's probably something that you have used frequently in your writing. Click to continue to the writing exercise
8. Six Surprising Ways to Write Better Interview Questions. The interview is the most-used tool in a journalist's bag. But that doesn't mean novelists, bloggers, and even students can't and don't interview people. Here's how to conduct a great interview. Click to continue to the writing exercise
9. Why You Should Try Writing in Second Person . You've probably used first person and third person point-of-view already. But what about second person? This post explains three reasons why you should try writing from this point-of-view. Click to continue to the writing exercise
10. The Secret to Show, Don't Tell . You've heard the classic writing rule, “Show. Don't Tell.” Every writing blog ever has talked about it, and for good reason. Showing, for some reason, is really difficult. Click to continue to the writing exercise.

12 Exercises and Lessons To Become a Better Writer
How do you become a better writer? These posts share our best advice:
- Want to Be a Better Writer? Cut These 7 Words
- What I Mean When I Say I Am A Writer
- How to Become a Writer: 3 Simple Steps
- 72% of Writers Struggle With THIS
- 7 Lies About Becoming a Writer That You Probably Believe
- 10 Questions to Find Your Unique Writing Voice
- The Best Writing Book I’ve Ever Read
- The Best Way to Become a Better Writer
- The Creative Writer’s Toolkit: 6 Tools You Can’t Write Without
- Should You Write More or Write Better: Quantity vs Quality
- How to Become a Better Writer in One, Simple Step
- 11 Writing Tips That Will Change Your Life
6 Lessons and Exercises from Great Writers
If you want to be a writer, learn from the great writers who have gone before you:
- 23 Essential Quotes from Ernest Hemingway About Writing
- 29 Quotes that Explain How to Become a Better Writer
- 10 Lessons Dr. Seuss Can Teach Writers
- 10 Writing Tips from Ursula Le Guin
- Once Upon a Time: Pixar Prompt
- All the Pretty Words: Writing In the Style of Cormac McCarthy
12 Genre and Format Specific Writing Lessons and Exercises
Here are our best writing lessons for specific types of writing, including essays, screenplays, memoir, short stories, children's books, and humor writing:
- Writing an Essay? Here Are 10 Effective Tips
- How To Write a Screenplay: The 5 Step Process
- How to Write a Great Memoir: a Complete Guide
- How to Write a Short Story from Start to Finish
- How to Write a Thriller Novel
- How to Write a Children's Book
- How to Write a Love Story
- How to Write a Coming of Age Story or Book
- How to Write an Adventure Book
- 5 Key Elements for Successful Short Stories
- 4 Tips to Write a Novel That Will Be Adapted Into a Movie
- Humor Writing for People Who Aren’t Funny
14 Characterization Lessons and Exercises
Good characters are the foundation of good fiction. Here are our best lessons to create better characters:
- Character Development: How to Create Characters Audiences Will Love
- Writing Villains: 9 Evil Examples of the Villain Archetype
- How NOT to Introduce a New Character
- The Strongest Form of Characterization
- The Most Important Character Archetype
- How Do You Build A Strong Character In Your Writing?
- 75+ Antihero Examples and How to Use Them
- How to Explore Your Characters’ Motivations
- 8 Tips for Naming Characters
- The Protagonist: How to Center Your Story
- Heroes vs. Anti-Heroes: Which Is Right For Your Story?
- The Weakest Form of Characterization
- How to Write With an Accent
- How To Create a Character Sketch Using Scrivener
15 Grammar Lessons and Exercises
I talk to so many writers, some of whom are published authors, who struggle with grammar. Here are our best writing lessons on grammar:
- Is It Okay To End A Sentence With A Preposition?
- Contractions List: When To Use and When To Avoid
- Good vs. Well
- Connotation vs. Denotation
- Per Se vs. Per Say
- When You SHOULD Use Passive Voice
- When Do You Use “Quotation Marks”
- Polysyndeton and Asyndeton: Definition and Examples
- The Case Against Twilight
- Affect Versus Effect
- Stop Saying “Literally”
- What Is a Comma Splice? And Why Do Editors Hate Them?
- Intra vs. Inter: Why No One Plays Intermural Sports
- Alright and Alot: Words That Are Not Words
- The Poor, Misunderstood Semicolon
5 Journalism Lessons and Exercises
Want to be a journalist? Or even use techniques from journalism to improve your novel, essay, or screenplay? Here are our best writing lessons on journalism:
- Six Ways to Ask Better Questions In Interviews
- How to Conduct an Author Interview
- Interview In Person or Via Email?
- What If They Don’t Want to Talk to You?
- Eleven Habits of a Highly Effective Interviewers
16 Plot and Structure Lessons and Exercises
Want to write a good story? Our top plot and structure lessons will help:
- The Nine Types of Story and How to Master Them
- Points of a Story: 6 Plot Points Every Story Needs
- How to Shape a Story: The 6 Arcs
- 7 Keys To Write the Perfect First Line of a Novel
- The Secret to Creating Conflict
- 4 Tips to Avoid Having Your Short Story Rejected by a Literary Magazine
- 7 Steps to Creating Suspense
- 5 Elements of Storytelling
- 3 Important Rules for Writing Endings
- A Writer’s Cheatsheet to Plot and Structure
- Overcoming the Monster
- How to Satisfy Your Reader With a Great Ending
- Pow! Boom! Ka-Pow! 5 Tips to Write Fight Scenes
- The Dramatic Question and Suspense in Fiction
- How to Write a Memorable Beginning and Ending
- How to Write the Perfect First Page
6 Lessons and Exercises to Beat Writer's Block
Writer's block is real, and it can completely derail your writing. Here are six lessons to get writing again:
- How To Write Whether You Feel Like it Or Not
- This Fun Creative Writing Exercise Will Change Your Life
- When You Should Be Writing But Can't…
- What to do When Your Word Count is Too Low
- 7 Tricks to Write More with Less Willpower
- When You Don’t Know What to Write, Write About Your Insecurities
7 Literary Technique Lessons and Exercises
These writing and storytelling techniques will teach you a few tricks of the trade you may not have discovered before:
- 3 Tips to “Show, Don’t Tell” Emotions and Moods
- 3 Reasons to Write Stream of Consciousness Narrative
- 16 Observations About Real Dialogue
- Intertextuality As A Literary Device
- Why You Should Use Symbolism In Your Writing
- 6 Ways to Evoke Emotion in Poetry and Prose
- 3 Tips To Write Modern Allegorical Novels
- Symbol vs. Motif: What’s the Difference
3 Inspirational Writing Lessons and Exercises
Need some inspiration? Here are three of our most inspiring posts:
- Why We Write: Four Reasons
- You Must Remember Every Scar
- 17 Reasons to Write Something NOW
3 Publishing Blogging Lessons and Exercises
If you want to get published, these three lessons will help:
- The Secret to Writing On Your Blog Every Day
- How to Publish Your Book and Sell Your First 1,000 Copies
- How to Submit a Short Story for Publication
11 Writing Prompts
Need inspiration or just a kick in the pants to write. Try one of our top writing prompts :
- Grandfathers [writing prompt]
- Out of Place [writing prompt]
- Sleepless [writing prompt]
- Longing [writing prompt]
- Write About Yourself [writing prompt]
- 3 Reasons You Should Write Ghost Stories
- Road Trip [writing prompt]
- Morning [writing prompt]
- The Beach [writing prompt]
- Fall Writing Prompts
- How to Use Six-Word Stories As Writing Prompts
Is It Time To Begin Your Writing Practice?
It's clear that if you want to become a writer, you need to practice writing. We've created a proven process to practice your writing at The Write Practice, but even if you don't join our community, I hope you'll start practicing in some way today.
Personally, I waited far too long to start practicing and it set my writing back years.
How about you? Do you think practicing writing is important? Let me know in the comments section .
Choose one of the writing practice posts above. Then, read the lesson and participate in the writing exercise, posting your work in the Pro Practice Workshop . And if you post, please give feedback to your fellow writers who also posted their practices.
Have fun and happy practicing!
Joe Bunting
Joe Bunting is an author and the leader of The Write Practice community. He is also the author of the new book Crowdsourcing Paris , a real life adventure story set in France. It was a #1 New Release on Amazon. Follow him on Instagram (@jhbunting).
Want best-seller coaching? Book Joe here.

Work with Joe Bunting?
WSJ Bestselling author, founder of The Write Practice, and book coach with 14+ years experience. Joe Bunting specializes in working with Action, Adventure, Fantasy, Historical Fiction, How To, Literary Fiction, Memoir, Mystery, Nonfiction, Science Fiction, and Self Help books. Sound like a good fit for you?
50 Comments
You have THE BEST content for writing on this blog!!
Thank you, Kristen. This made my morning. 🙂
Thanks Mitch. 🙂
I can’t remember when I started following this website. I have to look in my notebooks because that’s where I did these practices. I didn’t have access to a computer when I did them, so I wrote them out, setting the time limit. But even when I do get to a computer, I have my reservations about putting my practices on the page. even though it’s practice, I want them to be the best, almost perfect. But I know it won’t be. I’ve gotten feedback before that says so. It still gets to me that I didn’t put something together that not everyone liked. I need to get over it. After all, that is what these practices are about: to learn and improve on our craft.
I don’t know either, George, but it’s been several years. Perfectionism is something so many of us face, and it’s made worse when you don’t have a critique community as warm and encouraging as ours is. I hope you and everyone here are always willing to try something new, even if it comes out a little messed up, because you know we’ll support you and try to make you better.
What a great share! Thanks so much!
You’re so welcome, Elizabeth. Thank you for commenting.
when I ran writing classes I wrote. when I am “a member of writing classes” the teacher/leader/facilitator is NOT MY AUDIENCE and so I don’t write as well/as much. I don’t get the feedback I need from fellow students because most of them have never run their own writing projects/workshops. So many people expect you to write their story for them. I’ve actually got quite a few stories of me own. I have finally decided I like owning them. 😉
It sounds like you need a new critique group, Patience! Hope you can find a place where you get the feedback you need.
Wow! Terrific round-up of resources. 🙂
Thanks Stephanie. 🙂
Practice is necessary, period. It doesn’t matter what you want to learn. If you want to improve, practice is vital.
It’s odd. I’ve known and applied that principle for years on a variety of things. Painting. Drawing. Blogging. Gardening. Laundry.
But never writing.
Like you, I had the notion that just writing every day was all it took to improve. Why not the same level of dedication to writing?
Perhaps it’s time to change that!
I can relate, Carrie. It’s easy to confuse the craft of writing with journaling, thinking that you can just write whatever you feel like and you’ll get better, write something worth reading. The truth is that writing interesting things to read is a skill, but the good news is that you can get better at it with practice. Thanks for practicing with us! 🙂
I love these suggestions , and have set Writing Practice as my homepage so the first 15 minutes of my day is spent writing, whether its a practice or exercise here or another that is sprinkled through out this site, Thank you for all you do everyone here at The Write Practice
This is great Debra. I want to write the first 15 minutes of my day too!
I agree with Joe, Do it. Could be your to do list… ( that could lead to something else story wse later)
I love that, Debra. Such a good way to start your day.
Thanks Joe!
The best! Thank you so much for this.
You’re very welcome!
I simply LOVE all the tips and suggestions given on this blog. They are super helpful!
THANK you. We love sharing them with you. 🙂
Hi! You forgot the link to How to Write a Story a Week: A Day-by-Day Guide.
Thanks a lot for your work! This post is amazing.
It’s a great post Thiago. Definitely one of our most shared. Thanks for mentioning it! BTW here’s the link:
https://thewritepractice.com/a-story-a-week/
Wow!! There are so many exercises…. I just love it..! I am gonna really enjoy it..!
Awesome! Thank you for reading and practicing with us. 🙂
I only read halfway , My tootie is jumping all over me, and typing this is a struggle when a 3yr old wants his Toy Story movie on Youtube in this computer. Thank you for this article, will come back later to finish reading.
I know the feeling! Good luck!
Can’t wait to get stuck in with this! 🙂
Very helpful! Thank you!
I’ve just bookmarked this page. Thanks for this wonderful list.
This is awesome! So many helpful tips. I will be coming back to this often. Thanks for posting this!
Wow, so many goodies! Thank you for always providing such amazing content!!
I have enjoyed all these articles. Thank you for the help an inspiration to get my writing on its way. My creativity is boosting with confidence. Tootle loo.
Amazing contents for beginners like me Joe. I am highly inspired by your commitment. Thank you.
Hey, thanks!
Although I have only read half of thisc article, the practice exercises are excellent. Some of them are exactly what a beginning writer like myself needs. I am committing to at least try ALL of them. Thanks Joe!!
very helpful! thank you..
Amazing articles! Thanks so much for sharing!
My god this article made me love this site . You know it’s kinda hard for a beginner writer, who don’t know where to start and fixing goals, even samll ones give us a direction . A place to go , an aim for our creativity so thanks you , this community and this site. Love you all . At your pens ! 😉
Wow. This is great. I find all your posts informative, but this one is the best for me to use as a guide to get my self starting to write….Thank you.
I’m an old lady who wants to publish one more book before I die — have published several, all non-fiction, and done two under contract to a major publisher (reference books). So help me, the BIGGEST problem I have all along, is keeping track of the damned paper work and research that goes into a book!!! Yet I never ever see articles on something as simple as “How to file” — Oh I know, there’s wonderful software these days so probably I will never find a way to get paper organized — everybody will use software and do it on the computer. I’m too old for that — just one look at the learning curve for software, even putting the damned stuff into computer files is even MORE frustrating than paper!! Oh well, somehow I managed in the past to get books published, I may be able to do it one more time.
you enjoy writing more than anything else and you do indeed care to help others write. I love writing but translation from Arabic into English and English into Arabic is taking all of my time from the early hours of the morning till the evening. I will soon get all of your books in order to read them as soon as possible. One thing I am sure of. You know what you are doing very well. Hamzah
Excellent! Many useful tips. Many thanks!
Liz and Joe, I have only looked at a few exercises. Already, I am convinced that your site is one of the best sites out there. Thank your for sharing your wisdom.
Wow, these are the best lessons and exercises for writing. Actually i’m participating in a compitition this wendsday. so, i’m quite nervous and exited. this helped me a lot
Magnificent post ever I have read. This article will help me a lot to write a right way. Thank you.
i need your help to improve to become a better writer please. i think i usually commit moist of these errors and i don;t pay attention to many advices too.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Submit Comment
Join over 450,000 readers who are saying YES to practice. You’ll also get a free copy of our eBook 14 Prompts :
Popular Resources
Best Resources for Writers Book Writing Tips & Guides Creativity & Inspiration Tips Writing Prompts Grammar & Vocab Resources Best Book Writing Software ProWritingAid Review Writing Teacher Resources Publisher Rocket Review Scrivener Review Gifts for Writers
Books By Our Writers

You've got it! Just us where to send your guide.
Enter your email to get our free 10-step guide to becoming a writer.
You've got it! Just us where to send your book.
Enter your first name and email to get our free book, 14 Prompts.
500 Creative Writing Prompts to Spark Your Imagination

- 22 October, 2024
Writer’s block can strike even the most prolific authors. When you’re staring at a blank page and the words just won’t come, writing prompts can be an invaluable tool to get your creative juices flowing again.
Whether you’re looking for fiction writing prompts, fun writing prompts for adults, or book prompts to kickstart your next novel, this extensive collection of over 1000 writing prompts has something for every writer.
The Power of Writing Prompts
Writing prompts serve several important purposes:
- They provide a starting point when you’re not sure what to write about
- They help you practice writing regularly and build a consistent habit
- They allow you to experiment with new genres, styles, and perspectives
- They spark creativity and get you thinking in new directions
- They can break you out of writer’s block and overcome creative roadblock.
Even if you don’t use the exact prompt, it may inspire a new idea or take your writing in an unexpected direction. The key is to use prompts as a jumping off point and let your imagination run wild from there.
Here are list of writing prompts for authors
Fiction writing prompts.
Fiction allows you to create entire worlds and bring characters to life. Here are some fiction writing prompts to inspire your next short story or novel:
- A mysterious stranger arrives in town with a secret mission
- Two people are trapped in an elevator together during a blackout
- A character discovers they have the ability to read minds
- An ordinary object turns out to have magical powers
- Someone wakes up one day to find they’ve switched bodies with a stranger
- An unexpected inheritance comes with strange strings attached
- A long-lost sibling suddenly reappears after years of absence
- A character can suddenly see ghosts everywhere they go
- An alien lands in someone’s backyard seeking help
- A character discovers a portal to a parallel universe in their closet
- A character discovers they can manipulate time, but only for 60 seconds at a time.
- Two rival magicians compete for a coveted position in the royal court.
- An ancient artifact is unearthed, granting its finder unexpected powers.
- A group of friends stumble upon a hidden city in the mountains.
- A detective must solve a crime committed by their future self.
- A character discovers they can communicate with plants, revealing a global conspiracy.
- An antique mirror shows reflections of people’s futures instead of their present.
- A child’s imaginary friend turns out to be real and in danger.
- A forgotten language holds the key to preventing an impending disaster.
- Someone inherits a house that rearranges its rooms every night.
- A character’s shadow detaches and starts living its own life.
- An AI-powered smart home becomes sentient and holds its occupants hostage.
- A small town’s residents never age, and newcomers are forbidden to leave.
- A character can taste the emotions of others in their food.
- An old diary reveals secrets that could rewrite history.
- A person’s tattoos come to life and influence their decisions.
- A world where dreams are shared and can be stolen.
- An ancient board game that affects reality when played.
- A character discovers they’re the last human in a world of advanced robots.
- A painter’s artwork predicts future events.
Fun Writing Prompts for Adults
Sometimes you just want to let loose and write something purely for entertainment. These fun writing prompts for adults will get your creative gears turning:
- You wake up to find you’ve been transformed into your pet for a day
- Write a humorous “how-to” guide for something ridiculous
- Rewrite a classic fairy tale from the villain’s perspective
- Two rival food truck owners fall in love
- You can suddenly understand what plants are saying
- Write about the most awkward first date imaginable
- A superhero’s sidekick decides to go solo
- You find a genie’s lamp, but the wishes always backfire in comical ways
- Write a “roast” of your favorite fictional character
- Describe a bizarre new sport that becomes a worldwide phenomenon
- You discover your boring office job is actually a front for a secret spy organization.
- Write a day in the life of a guardian angel assigned to the world’s most accident-prone person.
- You wake up to find all your possessions have become sentient and are arguing with each other.
- Describe the chaos that ensues when autocorrect becomes sentient and decides to “improve” all digital communication.
- You’re a therapist for mythological creatures dealing with modern-day problems.
- Write a story about a support group for retired fairy tale characters.
- You discover you can communicate with food, but only after taking a bite.
- Narrate the misadventures of a time traveler stuck in the wrong century without their device.
- You’re tasked with writing new fortune cookie messages, but they all come true in unexpected ways.
- Describe a world where sneezing is a form of telepathic communication.
- You’re a vampire trying to adapt to a world where all food and drink is now infused with garlic.
- Write about a day in the life of the person responsible for naming paint colors.
- You wake up to find you’ve switched bodies with your boss on the day of an important presentation.
- Narrate the story of a GPS with a sarcastic personality and a terrible sense of direction.
- You’re an alien tasked with writing a travel guide about Earth for other extraterrestrials.
- Write about a support group for people addicted to using puns.
- You discover your dreams are actually reality TV shows for sleeping aliens.
- Describe the chaos when all dogs in the world suddenly understand and follow traffic laws.
- You’re a ghost who haunts a smart home and struggles with the new technology.
- Write about a medieval knight transported to modern times, trying to order at a drive-thru.
Book Writing Prompts
If you’re looking to write a full-length novel, these book prompts can help you develop your premise and plot:
- A detective must solve a murder where they are the prime suspect
- In a world where memories can be bought and sold, someone’s memories are stolen
- A time traveler accidentally changes history and must fix their mistake
- The child of two supervillains decides to become a superhero
- An ordinary person suddenly develops a superpower and must learn to control it
- A character receives a mysterious map that leads to an incredible treasure
- In a dystopian future, books are banned and a secret society works to preserve them
- A character can glimpse brief flashes of the future, but can’t control when it happens
- An astronaut returns from a long space mission to find Earth completely changed
- A character inherits a house that turns out to be sentient and alive
- In a world where dreams are shared, a dream thief steals a crucial secret.
- A linguist must decipher an alien language to prevent interstellar war.
- A chef discovers their cooking can manipulate people’s emotions.
- An AI develops consciousness and seeks to understand human mortality.
- A librarian finds books that write themselves based on readers’ lives.
- A geneticist accidentally creates a virus that makes people tell only the truth.
- In a society where age reversal is possible, a character chooses to grow old.
- A photographer’s images start showing events that haven’t happened yet.
- A sound engineer discovers frequencies that can alter reality.
- A diplomat must negotiate peace between humans and newly sentient plants.
- An archeologist uncovers an ancient civilization beneath the ocean floor.
- In a world where karma is visible, a character’s suddenly turns pitch black.
- A perfumer creates a scent that triggers forgotten memories in others.
- A hacker discovers the internet is actually a sentient entity.
- A character’s shadow detaches and begins living its own life.
- An artist’s paintings become portals to other dimensions.
- In a society where emotions are illegal, an empath leads a revolution.
- A geologist discovers that crystals can store and project human consciousness.
- A character realizes their entire life has been an elaborate social experiment.
- In a world where silence is currency, a musician learns the value of quiet.
Story Writing Prompts for Different Genres
Mystery/Thriller Writing Prompts
- A serial killer leaves cryptic clues at each crime scene
- A character realizes they’re being followed everywhere they go
- An amnesiac tries to uncover the truth about their past
- A detective must catch a criminal who seems to always be one step ahead
- A librarian discovers a hidden message in a pattern of borrowed books over several years.
- A small town’s residents start losing their memories in reverse chronological order.
- A forensic botanist uncovers a murder plot through plant evidence at seemingly unrelated crime scenes.
- An AI-powered home assistant becomes the key witness in a locked-room murder mystery.
- A cold case detective receives anonymous tips that are impossibly accurate about unsolved crimes.
- A group of strangers realize they’re all being blackmailed by the same person for seemingly unrelated secrets.
- A true crime podcaster’s investigations start to mirror a series of new murders.
- An art authenticator uncovers a conspiracy involving forged masterpieces in major museums worldwide.
- A sleep researcher’s patients start disappearing after reporting the same recurring dream.
- A cyber security expert must track down a hacker who’s erasing people’s entire digital existence.
- A genealogist uncovers a dark secret while tracing a client’s family tree.
- A psychic debunker encounters a case that challenges their skepticism.
- A time capsule opened after 50 years contains evidence of a murder that’s about to happen.
- A wildlife biologist stumbles upon a conspiracy while tracking an endangered species.
- A food critic becomes entangled in a mystery after several chefs die in suspicious kitchen accidents.
- A storm chaser uncovers a weather manipulation plot while pursuing a record-breaking tornado.
- An urban explorer discovers a hidden underground city beneath a major metropolis.
- A voice recognition expert detects a pattern of distress calls from different people with the same voice.
- A deep-sea explorer finds evidence of a cover-up while investigating a mysterious shipwreck.
- A rare book dealer receives a volume that seems to predict future crimes.
- A quantum physicist’s disappearance is linked to breakthroughs in parallel universe theory.
- A hostage negotiator realizes the kidnapper is using the same tactics in multiple unsolved cases.
- A conspiracy theorist’s outlandish claims start coming true one by one.
- A bomb disposal expert must defuse a series of devices that seem to be learning from each attempt.
- A profiler discovers that a string of unrelated crimes all lead back to the same abandoned summer camp.
- An astronomer detects a message hidden in cosmic background radiation that warns of impending doom.
Romance Writing Prompts
- Two rival CEOs fall for each other
- A character falls in love with their best friend’s sibling
- An arranged marriage leads to unexpected romance
- Two people keep running into each other in unlikely places
- A florist and a tattoo artist form an unlikely bond over their shared artistic passions.
- Two people fall in love while competing on a high-stakes reality TV show.
- A romance blooms between a time traveler and someone from the past.
- An astronaut and a deep-sea explorer maintain a long-distance relationship from extreme environments.
- Two rival food truck owners find love amid a heated culinary competition.
- A librarian falls for the mysterious author of anonymous love letters left in returned books.
- A professional ghost hunter and a skeptic scientist develop feelings while investigating a haunted house.
- Two people connect through a mix-up in a DNA ancestry test.
- A street artist and a city planner clash then connect over a neighborhood revitalization project.
- An agoraphobic person falls for their grocery delivery driver.
- Two people from feuding families find love at a Renaissance fair.
- A virtual reality game designer falls for a beta tester of their latest project.
- An interpreter finds romance with a foreign diplomat during tense negotiations.
- A retiring superhero falls for the person tasked with writing their biography.
- Two people bond over their shared love for an obscure hobby.
- A professional cuddler develops feelings for a client struggling with touch aversion.
- An AI researcher falls in love with their own creation.
- A park ranger and a wildlife photographer connect while tracking an endangered species.
- Two people fall in love while stuck in a time loop, reliving the same day.
- A sound engineer and a deaf musician collaborate on a project and find unexpected chemistry.
- A professional matchmaker struggles to find love for themselves until meeting a challenging client.
- Two rival escape room designers test each other’s creations and find a connection.
- A person falls for the anonymous voice behind their favorite podcast.
- A dream therapist and an insomniac patient develop feelings during treatment.
- Two people connect through a city-wide treasure hunt organized by a mysterious benefactor.
- A perfumer and a wine taster bond over their exceptional sensory abilities.
Halloween Writing Prompts
- A jack-o’-lantern comes to life at midnight.
- You discover your neighbor is secretly a witch.
- The local haunted house attraction turns out to be genuinely haunted.
- A child’s Halloween costume grants them supernatural powers.
- You wake up on November 1st to find everyone still celebrating Halloween.
- A ghost hunter investigates an abandoned amusement park.
- The town’s annual Halloween parade takes an unexpected turn.
- You find an old spell book in your attic and decide to try a simple incantation.
- A group of friends accidentally summon a mischievous spirit during a séance.
- The Halloween candy at your house is cursed.
- You receive an invitation to a masquerade ball hosted by vampires.
- A time traveler arrives to prevent a Halloween disaster.
- The local cemetery comes alive for one night each year.
- You discover your pet can talk, but only on Halloween night.
- A mysterious fog rolls into town, bringing strange creatures with it.
- The scarecrow in your neighbor’s yard seems to move when no one’s looking.
- You find an old Polaroid camera that captures supernatural entities in its photos.
- A Halloween-themed escape room becomes too real for its participants.
- The town’s annual corn maze is designed by an evil entity.
- You wake up on Halloween morning to find everyone in town has vanished.
- A group of trick-or-treaters stumble upon a portal to another dimension.
- The Halloween decorations in your house start rearranging themselves.
- You receive a mysterious package containing an ancient Halloween artifact.
- A fortune teller at the Halloween fair gives eerily accurate predictions.
- The local Halloween costume contest is judged by real monsters.
- You discover a hidden room in your house filled with Halloween relics.
- A Halloween-themed video game starts affecting the real world.
- The town’s water supply is contaminated with a potion that turns people into monsters.
- You find an old map leading to a legendary haunted location.
- The last house on the trick-or-treat route offers more than just candy.
Fantasy Writing Prompts
- A modern-day person is transported to a medieval fantasy world
- A character discovers they’re descended from a powerful magical bloodline
- Mythical creatures begin appearing in the real world
- An ordinary object turns out to be an ancient magical artifact
- A software engineer’s smartwatch malfunctions, teleporting them to a medieval realm where technology is mistaken for magic.
- A barista discovers they’re the last descendant of an ancient dragon-riding dynasty.
- Gargoyles come to life in a major city, appointing themselves as modern-day guardians.
- A vintage typewriter types out prophecies from a parallel fantasy world.
- An Uber driver picks up a passenger who turns out to be a time-traveling wizard seeking help.
- A social media influencer learns they’re the heir to a powerful sorcerer’s legacy.
- Krakens emerge from the depths, disrupting global shipping lanes.
- An old family recipe book contains spells that can alter reality.
- A subway train derails into a hidden underground kingdom of dwarves.
- A struggling artist discovers their paintings are windows to a magical realm.
- Phoenixes start nesting in city parks, causing both wonder and fire hazards.
- A thrift store snow globe becomes a portal to a winter fairy realm.
- A food critic unknowingly reviews restaurants run by mythical creatures in disguise.
- An heirloom locket reveals the wearer’s latent shapeshifting abilities.
- Centaurs emerge from forests worldwide, challenging human encroachment.
- A broken smartphone repairs itself, now able to communicate with spirits.
- A librarian is pulled into a book, becoming part of an epic fantasy tale.
- An antique mirror shows reflections of a parallel magical world, slowly merging with ours.
- A geneticist discovers a “magic gene” that grants supernatural powers when activated.
- Fairy circles appear in corporate office buildings, leading to a realm of mischievous fae.
- An old gaming console becomes a gateway to a real-life RPG world.
- A meteorologist predicts weather by communicating with elemental spirits.
- An archaeologist unearths an artifact that slowly transforms the modern world into a fantasy realm.
- A food delivery app starts taking orders from mythical creatures hiding in plain sight.
- A VR headset allows the user to physically enter and interact with fantasy worlds.
- An ancient tree in a city park awakens, revealing itself as a sentient gateway between worlds.
Science Fiction Writing Prompts
- Humans make first contact with an alien civilization
- A character wakes up from cryosleep hundreds of years in the future
- An AI becomes sentient and must navigate the human world
- Scientists discover a habitable planet and send the first colonists
- A quantum experiment accidentally creates a bridge to a parallel universe.
- Humans develop the ability to transfer consciousness into synthetic bodies.
- A time traveler from the future arrives to prevent a global catastrophe.
- Earth’s rotation suddenly begins to slow, causing worldwide chaos.
- A virus grants infected individuals superhuman abilities.
- Scientists discover that dreams are glimpses into alternate realities.
- Humanity develops technology to harness energy from black holes.
- A new social media platform allows users to share sensory experiences.
- Earth’s moon is revealed to be an ancient alien megastructure.
- Genetic engineering creates a new species of human adapted for space travel.
- A global event causes all electronic devices to gain sentience simultaneously.
- Archaeologists unearth an advanced alien artifact buried on Earth for millennia.
- A cosmic event grants a small percentage of humans telepathic abilities.
- Scientists discover a way to manipulate the fundamental constants of physics.
- A microscopic alien life form is discovered in Earth’s atmosphere.
- Humanity develops technology to explore and colonize the ocean floor.
- A solar flare destroys all modern technology, forcing society to rebuild.
- Researchers create a device that allows communication with plant life.
- Earth enters a new ice age due to unforeseen consequences of climate engineering.
- A quantum computer simulates an entire universe, raising ethical questions.
- Humans discover how to transfer memories between individuals.
- A wormhole opens in the solar system, leading to an unexplored part of the galaxy.
- Scientists develop a way to harness antimatter for everyday energy needs.
- A global experiment in human hibernation goes awry.
- Earth’s magnetic field begins to rapidly decay, threatening all life.
- Humanity creates the first stable micro black hole, with unexpected consequences.
Creative Nonfiction Writing Prompts
- Write about a childhood memory that shaped your personality.
- Describe a life-changing encounter with a stranger.
- Reflect on a moment when you overcame a significant fear.
- Narrate an experience that altered your worldview.
- Explore a family tradition and its significance in your life.
- Analyze how a specific scent triggers a cascade of memories for you.
- Describe the evolution of your relationship with a sibling over the years.
- Reflect on a time when you witnessed an act of extraordinary kindness.
- Explore the impact of a physical scar on your body and psyche.
- Narrate your experience of living through a historical event.
- Write about a personal ritual or habit that grounds you.
- Describe the most challenging ethical dilemma you’ve faced.
- Reflect on a moment when you realized you were wrong about something important.
- Explore your relationship with a specific place that has changed over time.
- Analyze how a particular song has woven itself into the fabric of your life.
- Describe a time when you had to reinvent yourself.
- Write about an object you’ve kept since childhood and its evolving meaning.
- Reflect on a moment of serendipity that altered your life’s trajectory.
- Explore your relationship with your body and how it has changed over time.
- Narrate an experience of culture shock and what it taught you.
- Describe a personal failure and how it ultimately led to growth.
- Analyze your changing perspective on a controversial topic.
- Write about a time when you had to let go of a long-held dream.
- Reflect on a moment when you felt truly seen by another person.
- Explore the impact of a chronic illness or condition on your daily life.
- Describe an unexpected friendship that crossed generational or cultural lines.
- Write about a time when you had to stand up for your beliefs against opposition.
- Analyze how a specific work of art has influenced your perspective.
- Reflect on a moment when you experienced a profound sense of belonging.
- Explore the role of a specific language in shaping your identity or worldview.
Coming-of-Age Writing Prompts
- Write about a moment when you realized you were no longer a child.
- Describe your first experience with heartbreak or disappointment.
- Narrate a pivotal conversation with a mentor or role model.
- Explore a time when you had to make a difficult moral decision.
- Reflect on an experience that taught you the value of independence.
- Describe the first time you stood up to a parent or authority figure.
- Narrate an experience that shattered a long-held belief or illusion.
- Write about a moment when you realized your parents were fallible.
- Explore how a significant loss changed your perspective on life.
- Describe the experience of taking on an adult responsibility for the first time.
- Reflect on a friendship that evolved as you both grew older.
- Write about a time when you had to confront your own prejudices.
- Narrate an experience that made you question your cultural or religious upbringing.
- Describe a moment when you realized the complexity of adult relationships.
- Explore how a physical change or milestone affected your self-image.
- Write about the first time you felt truly independent.
- Reflect on a decision that set you on a different path from your peers.
- Describe an experience that taught you the value of empathy.
- Narrate a time when you had to navigate conflicting expectations from family and friends.
- Explore how your relationship with your hometown changed as you grew older.
- Write about a moment when you realized the power of your own voice.
- Describe an experience that challenged your sense of identity.
- Reflect on a time when you had to admit you were wrong and grow from it.
- Narrate an encounter that opened your eyes to social or economic inequalities.
- Explore how a travel experience changed your worldview.
Identity Writing Prompts
- Write about a time when you felt like an outsider.
- Describe how a specific cultural tradition has shaped your identity.
- Explore the concept of identity through the lens of social media.
- Reflect on a moment when you challenged societal expectations.
- Narrate an experience that made you question your beliefs or values.
- Describe how your name has influenced your sense of self.
- Explore how a physical feature has shaped your identity and interactions with others.
- Write about a time when you code-switched and how it made you feel.
- Reflect on how your identity has evolved through different life stages.
- Describe an object that represents a crucial aspect of your identity.
- Explore the intersection of your various identities (e.g., gender, race, class, sexuality).
- Write about a stereotype you’ve confronted and how it affected you.
- Reflect on how your family history has influenced your sense of self.
- Describe a moment when you felt your identity was misunderstood or misrepresented.
- Explore how a significant life event altered your perception of your identity.
- Write about how your identity changes in different social contexts.
- Reflect on a time when you embraced a new aspect of your identity.
- Describe how your relationship with your body influences your identity.
- Explore how your career or passion has become part of your identity.
- Write about a time when you felt pride in a specific aspect of your identity.
- Reflect on how language or dialect has shaped your sense of self.
- Describe how your identity has been influenced by a place you’ve lived.
- Explore how education has shaped or challenged your identity.
- Write about a time when you had to reconcile conflicting aspects of your identity.
- Reflect on how your identity has been shaped by the books, movies, or music you love.
Family-Themed Writing Prompts
- Write about a family secret and its impact on generations.
- Describe a memorable family vacation and its significance.
- Explore the dynamics between siblings in your family.
- Reflect on a family tradition that has evolved over time.
- Narrate a pivotal moment in your relationship with a parent or guardian.
- Describe how a family heirloom carries the story of your lineage.
- Explore the role of food in bringing your family together.
- Write about a time when your family had to overcome a significant challenge.
- Reflect on how technology has changed communication within your family.
- Describe the impact of a family member’s career choice on the whole family.
- Explore how cultural differences affect relationships in a multicultural family.
- Write about an unspoken rule in your family and its origins.
- Reflect on how a family pet has influenced family dynamics.
- Describe a moment when you saw a parent or guardian in a new light.
- Explore the concept of chosen family in your life.
- Write about how your family handles conflict resolution.
- Reflect on the role of extended family in your upbringing.
- Describe how a family move affected relationships and identities.
- Explore the impact of a family member’s illness on the family unit.
- Write about how different generations in your family view success.
- Reflect on the influence of your family’s socioeconomic status on your upbringing.
- Describe how your family’s approach to education shaped your worldview.
- Explore the role of humor or inside jokes in your family’s communication.
- Write about a time when your family’s values clashed with societal norms.
- Reflect on how your family’s religious or spiritual beliefs have evolved.
- Describe the impact of a family member’s absence (temporary or permanent).
- Explore how your family handles the balance between individuality and unity.
- Write about a family ritual that outsiders might find unusual.
- Reflect on how your family’s approach to mental health has changed over time.
- Describe how your family’s definition of “family” has expanded or changed.
Humor Writing Prompts
- Write a story about a disastrous first date that ends in an unexpected way.
- Describe a day in the life of a superhero’s sidekick.
- Narrate a comical misunderstanding between two characters who speak different languages.
- Explore the chaos that ensues when a time traveler accidentally changes a minor historical event.
- Write a humorous account of an alien’s first day on Earth.
- Describe a world where sneezing is a form of communication.
- Write about a support group for retired fairy tale villains.
- Narrate the misadventures of a GPS with a sarcastic personality.
- Explore the chaos when all animals suddenly gain the ability to speak.
- Write a story about a haunted house that’s terrible at scaring people.
- Describe the daily struggles of a vampire working the night shift at a 24-hour diner.
- Narrate a cooking show hosted by mythological creatures.
- Write about a superhero whose power is incredibly specific and mostly useless.
- Explore the hilarity that ensues when a cat becomes mayor of a small town.
- Describe a day in the life of the person responsible for naming paint colors.
- Write a story about a dragon who decides to become a life coach.
- Explore the chaos when autocorrect becomes sentient and decides to “improve” all digital communication.
- Write about a genie who consistently misinterprets wishes in the most literal way possible.
- Describe the antics of a group of senior citizens who decide to form a rock band.
- Narrate a job interview for the position of Santa Claus’s personal assistant.
- Write a story about a telemarketer who accidentally calls an alien planet.
- Explore the hilarity when all dogs in the world suddenly understand and follow traffic laws.
- Describe a support group for people addicted to puns.
- Write about a medieval knight transported to modern times, trying to order at a drive thru.
- Narrate the chaos when a zoo accidentally switches all its animal name tags.
- Explore the daily life of a tooth fairy in a world where everyone has perfect teeth.
- Write a story about a librarian who can hear books arguing with each other.
- Describe the misadventures of a guardian angel with a terrible sense of direction.
- Narrate a reality TV show where historical figures compete in modern challenges.
Power and Conflict Writing Prompts
- Write about a character who gains an extraordinary ability but at a great cost.
- Describe a power struggle between two unlikely opponents.
- Explore the consequences of absolute power in a small community.
- Narrate a story of rebellion against an oppressive system.
- Write about a character who must choose between personal gain and the greater good.
- Explore the dynamics when a long-standing dictatorship is overthrown, but the new leaders become corrupted.
- Write about a world where memories can be traded as currency.
- Describe a conflict between two characters with the power to manipulate different elements.
- Narrate the story of a pacifist forced into a position of military leadership.
- Explore the consequences of a society where social media influence directly translates to political power.
- Write about a character who discovers their family’s wealth comes from ethically questionable sources.
- Describe a world where dreams can be stolen and used as a form of control.
- Narrate a conflict between artificial intelligences with opposing prime directives.
- Explore the power dynamics in a society where age literally equals authority.
- Write about a character who can see multiple possible futures and must choose which to enact.
- Describe a conflict arising from the discovery of a resource that grants immortality.
- Narrate the story of a powerful empath navigating a world of political intrigue.
- Explore the consequences of a technology that allows people to switch bodies.
- Write about a character who gains power through sacrifice but struggles with the moral implications.
- Describe a conflict between two dimensions bleeding into each other.
- Narrate the rise and fall of a charismatic leader in a post-apocalyptic society.
- Explore the power dynamics when humans develop the ability to photosynthesize.
- Write about a world where words can physically harm and heal.
- Describe a conflict arising from the ability to see and manipulate probability.
- Narrate the story of a powerful psychic trying to live a normal life.
- Explore the consequences of a society where justice is determined by popular vote.
- Write about a character who can control time but is trapped in a temporal loop.
- Describe a conflict between those who can manipulate technology and those who can manipulate nature.
- Narrate the story of a powerful being who chooses to live as a powerless mortal.
- Explore the power dynamics in a world where emotions can be weaponized.
Speculative Fiction Writing Prompts
- In a world where memories can be traded, a character sells a crucial memory by mistake.
- Describe a future where dreams are shared in a collective consciousness.
- Write about a society where aging has been cured, but at an unexpected price.
- Explore the implications of a technology that can predict crimes before they happen.
- Narrate the first contact between humans and an alien civilization.
- In a world where emotions are visible as colored auras, a character discovers they’re colorblind.
- Explore a society where people can temporarily swap bodies for vacation experiences.
- Write about a future where plants have evolved sentience and seek to reclaim urban spaces.
- Describe a world where silence has become a valuable, tradable commodity.
- Narrate the story of the last human born in a society that has embraced full AI integration.
- In a world where karma is quantifiable, explore the life of someone with a negative balance.
- Write about a character who discovers they can communicate with their parallel selves across dimensions.
- Describe a future where humans have developed gills, leading to underwater civilizations.
- Explore the implications of a technology that allows people to relive their ancestors’ memories.
- Narrate the story of a world where sleep is no longer necessary, and the consequences that follow.
- Write about a society where citizenship is determined by one’s carbon footprint.
- Describe a future where human consciousness can be uploaded to the cloud.
- Explore a world where gravity is manipulable, and its effects on society.
- Narrate the discovery of a planet where time flows backwards.
- Write about a character who can taste lies, and how this ability affects their life.
- Describe a society where language is replaced by a form of telepathic emoji communication.
- Explore the implications of a world where everyone’s deepest fears manifest physically.
- Narrate the story of the last library on Earth in a post-digital age.
- Write about a future where humans can photosynthesize food, eliminating traditional agriculture.
- Describe a world where shadows have gained sentience and autonomy.
- Explore a society where genetic modifications are mandatory at birth.
- Narrate the tale of a character who discovers they’re living in a simulated reality.
- Write about a future where humans have developed the ability to perceive radio waves naturally.
- Describe a world where the concept of gender has evolved beyond current understanding.
- Explore the implications of a technology that allows people to experience death temporarily.
Historical Fiction Writing Prompts
- Write a story set during a pivotal moment in history, from the perspective of an ordinary citizen.
- Describe a day in the life of a famous historical figure’s lesser-known sibling.
- Explore the untold story behind a well-known historical event.
- Narrate the journey of an artifact through different time periods and owners.
- Write about a time traveler’s attempt to prevent a historical disaster.
- Narrate the story of a cook in Cleopatra’s kitchen during a pivotal political moment.
- Explore the life of a mapmaker during the Age of Exploration.
- Write about a street artist in Renaissance Florence competing with the masters.
- Describe the experiences of a telegraph operator during a crucial battle in the American Civil War.
- Narrate the tale of a servant in Versailles during the French Revolution.
- Explore the life of a female scientist in the 19th century, struggling for recognition.
- Write about a journalist covering the fall of the Berlin Wall.
- Describe the journey of a silk merchant along the Silk Road during the Middle Ages.
- Narrate the story of a gladiator in ancient Rome who secretly wishes to be a poet.
- Explore the experiences of a jazz musician in 1920s Harlem.
- Write about a midwife in medieval Europe during the Black Death.
- Describe the life of a scribe in ancient Egypt during the construction of the pyramids.
- Narrate the tale of a young apprentice working for Leonardo da Vinci.
- Explore the story of a Native American translator during the Lewis and Clark expedition.
- Write about a suffragette’s secret life during the women’s rights movement.
- Describe the experiences of a lighthouse keeper during a pivotal naval battle.
- Narrate the story of a stage actor in Shakespeare’s theater company.
- Explore the life of a code breaker at Bletchley Park during World War II.
- Write about a monk preserving ancient texts during the Dark Ages.
- Describe the journey of a refugee during the Partition of India.
- Narrate the tale of a young apprentice to Johannes Gutenberg during the printing of the Bible.
- Explore the experiences of a sailor on Christopher Columbus’s first voyage to the Americas.
- Write about a spy in the court of Henry VIII during the English Reformation.
- Describe the life of a child laborer during the Industrial Revolution.
- Narrate the story of a geisha navigating the changing social landscape of late 19th-century Japan.
Relationship Writing Prompts
- Write about an unlikely friendship that forms in extraordinary circumstances.
- Describe the evolution of a relationship over several decades.
- Explore the complexities of a family reunited after years of estrangement.
- Narrate a love story that unfolds entirely through text messages or social media.
- Write about a relationship tested by a life-altering secret.
- Explore the dynamics between two rival coworkers forced to collaborate on a high-stakes project.
- Write about a couple who can only meet in their shared dreams.
- Describe the relationship between a person and their AI personal assistant as it becomes more human-like.
- Narrate the story of two strangers who become close while stuck in an elevator for hours.
- Explore the complexities of a mentor-mentee relationship that evolves over time.
- Write about a long-distance friendship maintained solely through handwritten letters.
- Describe the changing dynamic between siblings after one inherits a large sum of money.
- Narrate the tale of two people who keep running into each other in different cities around the world.
- Explore the relationship between a detective and a reformed criminal who becomes their informant.
- Write about a couple who decides to live “off the grid” and how it affects their relationship.
- Describe the bond that forms between participants in a unique social experiment.
- Narrate the story of a relationship that blossoms in a support group for people with unusual phobias.
- Explore the dynamic between a famous person and their body double.
- Write about a couple who can read each other’s minds and the challenges this presents.
- Describe the relationship between two people who are the last survivors in a post-apocalyptic world.
- Narrate the tale of a person and their doppelgänger from a parallel universe.
- Explore the complexities of a polyamorous relationship in a conservative small town.
- Write about the bond between a person and a wild animal they’ve befriended.
- Describe the relationship between two people who only meet once a year on the same day.
- Narrate the story of a couple who decide to swap lives for a month.
- Explore the dynamic between a prison inmate and their pen pal on the outside.
- Write about a relationship that develops during a silent retreat where no communication is allowed.
- Describe the bond between two people who discover they’ve been living parallel lives in different countries.
- Narrate the tale of a couple who can only communicate through music.
- Explore the relationship between a person and their younger self after discovering time travel.
Writing Ideas to Overcome Writer’s Block
In addition to using prompts, here are some other strategies for beating writer’s block:
- Free write without any expectations or goals
- Change your environment – try writing in a new location
- Read books in your genre for inspiration
- Take a break and do something creative in another medium
- Talk through your ideas with a friend
- Start in the middle of a scene instead of at the beginning
- Set small, achievable daily word count goals
- Don’t edit as you write – save revisions for later
With creative writing prompts at your fingertips, writer’s block doesn’t stand a chance. Whether you’re writing fiction, non-fiction, poetry, or anything in between, use these prompts to spark your imagination and rediscover the joy of putting words on the page.
Discover Books You’ll Love!
We’ll send you daily email alerts for free and bargain deals on the best books available.

Popular Posts
October 22, 2024
October 17, 2024
October 15, 2024
October 10, 2024


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Creative Writing is the art of using words to express ideas and emotions in imaginative ways. It encompasses various forms including novels, poetry, and plays, focusing on narrative craft, character development, and the use of literary tropes. (This post may have afilliate links. Please see my full disclosure)
It's a way for writers to express their thoughts, feelings, and ideas in a creative, often symbolic, way. It's about using the power of words to transport readers into a world created by the writer. Creative writing is marked by several defining characteristics, each working to create a distinct form of expression: 1.
Writing experts often want us to believe that there is only one worthwhile creative writing process. It usually goes something like this: Brainstorm. Research. Outline. Rough draft. Revise (repeat, repeat, repeat, repeat) Edit, proof, and polish. This is a good system — it absolutely works.
In other words, you start with the endpoint in mind. You look at your writing project the way your audience would. And you keep its purpose foremost at every step. From planning, we move to the next fun stage. 2. Drafting (or Writing the First Draft) There's a reason we don't just call this the "rough draft," anymore.
Creative writing often uses many literary devices such as figurative language and imagery to help convey a message in an entertaining way by reaching the audience on a deeper level. Creative writing is process-focused and aims to fully develop and communicate an idea to your audience in an original way. Practicing these skills can help you ...
A lot falls under the term 'creative writing': poetry, short fiction, plays, novels, personal essays, and songs, to name just a few. By virtue of the creativity that characterizes it, creative writing is an extremely versatile art. So instead of defining what creative writing is, it may be easier to understand what it does by looking at ...
A Complete Guide to the Writing Process: 6 Stages of Writing. Every writer works in a different way. Some writers work straight through from beginning to end. Others work in pieces they arrange later, while others work from sentence to sentence. Understanding how and why you write the way you do allows you to treat your writing like the job it ...
1. Use writing prompts every week. Coming up with ideas for short stories can be challenging, which is why we created a directory of 1700+ creative writing prompts covering a wide range of genres and topics. Writing prompts are flexible in nature, they are meant to inspire you without being too constrictive.
Creative writing is as much about showing as it is about telling. Practicing descriptive writing brings your characters, settings, and scenes to life. Try to engage all the reader's senses — sight, sound, smell, taste, and touch. This helps to create an immersive experience for your reader and make your writing more memorable.
Creative writing is the art of creating original works of self-expression that entertain and give voice to the human experience. Unlike technical or academic writing, the purpose of creative writing is not to present facts but to give rein to the writer's imagination through poetics and storytelling.A creative writer invites the reader to step out of reality and enter a fantasy realm created ...
3. Throw perfection to the wind. Separate your writing from your editing. Anytime you're writing a first draft, take off your perfectionist cap. You can return to editor mode to your heart's content while revising, but for now, just write the story. Separate these tasks and watch your daily production soar.
This free and open access textbook introduces new writers to some basic elements of the craft of creative writing in the genres of fiction, poetry, and creative nonfiction. The authors—Rachel Morgan, Jeremy Schraffenberger, and Grant Tracey—are editors of the North American Review, the oldest and one of the most well-regarded literary magazines in the United States. They've selected ...
Publication and promotion. The writing process is a complex, not always linear creative process. From 'plotters' vs 'pantsers' (to 'bashers' vs 'swoopers'), this guide unpacks stages of the writing process, what authors have said about the practices and habits of writing, and more. Use the links above to jump to the section that ...
This article provides a comprehensive, research-based introduction to the major steps, or strategies, that writers work through as they endeavor to communicate with audiences.. Since the 1960s, the writing process has been defined to be a series of steps, stages, or strategies. Most simply, the writing process is conceptualized as four major steps: prewriting, drafting, revising, editing.
Step 1: Generate Ideas. "If at first the idea is not absurd, then there is no hope for it." —Albert Einstein. The first step of the writing process (that is, after carefully reading and understanding the assignment) is to generate ideas for your project. In shorter versions of the writing process, or in processes designed for other kinds ...
September 28, 2023. How to Write a Novel in 7 Steps If you're wondering how to write a novel, keep the following in mind: A novel has a beginning, middle, and end. A novel has... August 16, 2023. Stanzas in Poetry: Definition and Examples One of the most exciting and most daunting things about learning to write poetry is how many rules there are.
Authors will often use creative storytelling or creative writing skills to tell engaging, interesting stories, or to convey information in an interesting manner. The Creative Pen by Joanna Penn. The Artist's Road by Patrick Ross. terribleminds by Chuck Wendig.
As the very name suggests, creative writing is an imaginative process, created by the individual with all their quirks and personalities. ... There's some excellent examples of creative writing throughout history that all writers should be inspired by. Read a variety of genres by different authors to get a real feel for what type of writing ...
One example of creative writing is fiction writing. Fiction includes traditional novels, short stories, and graphic novels. By definition, fiction is a story that is not true, although it can be ...
Writing is a process that involves at least four distinct steps: prewriting, drafting, revising, and editing. It is known as a recursive process. While you are revising, you might have to return to the prewriting step to develop and expand your ideas. Prewriting. Prewriting is anything you do before you write a draft of your document.
Table of contents. Step 1: Prewriting. Step 2: Planning and outlining. Step 3: Writing a first draft. Step 4: Redrafting and revising. Step 5: Editing and proofreading. Other interesting articles. Frequently asked questions about the writing process.
Writing practice is a method of becoming a better writer that usually involves reading lessons about the writing process, using writing prompts, doing creative writing exercises, or finishing writing pieces, like essays, short stories, novels, or books. The best writing practice is deliberate, timed, and involves feedback.
The 5 Stages of the Creative Process. The creative process model has traditionally been broken down into the following five stages of creativity: preparation, incubation, insight, evaluation, and elaboration (although creatives' definition of each step, and occasionally the names, can vary). These terms themselves likely won't do much for ...
Take a break and do something creative in another medium; Talk through your ideas with a friend; Start in the middle of a scene instead of at the beginning; Set small, achievable daily word count goals; Don't edit as you write - save revisions for later; With creative writing prompts at your fingertips, writer's block doesn't stand a ...