Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- What is Secondary Research? | Definition, Types, & Examples

What is Secondary Research? | Definition, Types, & Examples
Published on January 20, 2023 by Tegan George . Revised on January 12, 2024.
Secondary research is a research method that uses data that was collected by someone else. In other words, whenever you conduct research using data that already exists, you are conducting secondary research. On the other hand, any type of research that you undertake yourself is called primary research .
Secondary research can be qualitative or quantitative in nature. It often uses data gathered from published peer-reviewed papers, meta-analyses, or government or private sector databases and datasets.
Table of contents
When to use secondary research, types of secondary research, examples of secondary research, advantages and disadvantages of secondary research, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions.
Secondary research is a very common research method, used in lieu of collecting your own primary data. It is often used in research designs or as a way to start your research process if you plan to conduct primary research later on.
Since it is often inexpensive or free to access, secondary research is a low-stakes way to determine if further primary research is needed, as gaps in secondary research are a strong indication that primary research is necessary. For this reason, while secondary research can theoretically be exploratory or explanatory in nature, it is usually explanatory: aiming to explain the causes and consequences of a well-defined problem.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

Secondary research can take many forms, but the most common types are:
Statistical analysis
Literature reviews, case studies, content analysis.
There is ample data available online from a variety of sources, often in the form of datasets. These datasets are often open-source or downloadable at a low cost, and are ideal for conducting statistical analyses such as hypothesis testing or regression analysis .
Credible sources for existing data include:
- The government
- Government agencies
- Non-governmental organizations
- Educational institutions
- Businesses or consultancies
- Libraries or archives
- Newspapers, academic journals, or magazines
A literature review is a survey of preexisting scholarly sources on your topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant themes, debates, and gaps in the research you analyze. You can later apply these to your own work, or use them as a jumping-off point to conduct primary research of your own.
Structured much like a regular academic paper (with a clear introduction, body, and conclusion), a literature review is a great way to evaluate the current state of research and demonstrate your knowledge of the scholarly debates around your topic.
A case study is a detailed study of a specific subject. It is usually qualitative in nature and can focus on a person, group, place, event, organization, or phenomenon. A case study is a great way to utilize existing research to gain concrete, contextual, and in-depth knowledge about your real-world subject.
You can choose to focus on just one complex case, exploring a single subject in great detail, or examine multiple cases if you’d prefer to compare different aspects of your topic. Preexisting interviews , observational studies , or other sources of primary data make for great case studies.
Content analysis is a research method that studies patterns in recorded communication by utilizing existing texts. It can be either quantitative or qualitative in nature, depending on whether you choose to analyze countable or measurable patterns, or more interpretive ones. Content analysis is popular in communication studies, but it is also widely used in historical analysis, anthropology, and psychology to make more semantic qualitative inferences.
Secondary research is a broad research approach that can be pursued any way you’d like. Here are a few examples of different ways you can use secondary research to explore your research topic .
Secondary research is a very common research approach, but has distinct advantages and disadvantages.
Advantages of secondary research
Advantages include:
- Secondary data is very easy to source and readily available .
- It is also often free or accessible through your educational institution’s library or network, making it much cheaper to conduct than primary research .
- As you are relying on research that already exists, conducting secondary research is much less time consuming than primary research. Since your timeline is so much shorter, your research can be ready to publish sooner.
- Using data from others allows you to show reproducibility and replicability , bolstering prior research and situating your own work within your field.
Disadvantages of secondary research
Disadvantages include:
- Ease of access does not signify credibility . It’s important to be aware that secondary research is not always reliable , and can often be out of date. It’s critical to analyze any data you’re thinking of using prior to getting started, using a method like the CRAAP test .
- Secondary research often relies on primary research already conducted. If this original research is biased in any way, those research biases could creep into the secondary results.
Many researchers using the same secondary research to form similar conclusions can also take away from the uniqueness and reliability of your research. Many datasets become “kitchen-sink” models, where too many variables are added in an attempt to draw increasingly niche conclusions from overused data . Data cleansing may be necessary to test the quality of the research.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
If you want to know more about statistics , methodology , or research bias , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Normal distribution
- Degrees of freedom
- Null hypothesis
- Discourse analysis
- Control groups
- Mixed methods research
- Non-probability sampling
- Quantitative research
- Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Research bias
- Rosenthal effect
- Implicit bias
- Cognitive bias
- Selection bias
- Negativity bias
- Status quo bias
A systematic review is secondary research because it uses existing research. You don’t collect new data yourself.
The research methods you use depend on the type of data you need to answer your research question .
- If you want to measure something or test a hypothesis , use quantitative methods . If you want to explore ideas, thoughts and meanings, use qualitative methods .
- If you want to analyze a large amount of readily-available data, use secondary data. If you want data specific to your purposes with control over how it is generated, collect primary data.
- If you want to establish cause-and-effect relationships between variables , use experimental methods. If you want to understand the characteristics of a research subject, use descriptive methods.
Quantitative research deals with numbers and statistics, while qualitative research deals with words and meanings.
Quantitative methods allow you to systematically measure variables and test hypotheses . Qualitative methods allow you to explore concepts and experiences in more detail.
Sources in this article
We strongly encourage students to use sources in their work. You can cite our article (APA Style) or take a deep dive into the articles below.
George, T. (2024, January 12). What is Secondary Research? | Definition, Types, & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved April 18, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/methodology/secondary-research/
Largan, C., & Morris, T. M. (2019). Qualitative Secondary Research: A Step-By-Step Guide (1st ed.). SAGE Publications Ltd.
Peloquin, D., DiMaio, M., Bierer, B., & Barnes, M. (2020). Disruptive and avoidable: GDPR challenges to secondary research uses of data. European Journal of Human Genetics , 28 (6), 697–705. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41431-020-0596-x
Is this article helpful?
Tegan George
Other students also liked, primary research | definition, types, & examples, how to write a literature review | guide, examples, & templates, what is a case study | definition, examples & methods, what is your plagiarism score.
Root out friction in every digital experience, super-charge conversion rates, and optimise digital self-service
Uncover insights from any interaction, deliver AI-powered agent coaching, and reduce cost to serve
Increase revenue and loyalty with real-time insights and recommendations delivered straight to teams on the ground
Know exactly how your people feel and empower managers to improve employee engagement, productivity, and retention
Take action in the moments that matter most along the employee journey and drive bottom line growth
Whatever they’re are saying, wherever they’re saying it, know exactly what’s going on with your people
Get faster, richer insights with qual and quant tools that make powerful market research available to everyone
Run concept tests, pricing studies, prototyping + more with fast, powerful studies designed by UX research experts
Track your brand performance 24/7 and act quickly to respond to opportunities and challenges in your market
Meet the operating system for experience management
- Free Account
- For Digital
- For Customer Care
- For Human Resources
- For Researchers
- Financial Services
- All Industries
Popular Use Cases
- Customer Experience
- Employee Experience
- Employee Exit Interviews
- Net Promoter Score
- Voice of Customer
- Customer Success Hub
- Product Documentation
- Training & Certification
- XM Institute
- Popular Resources
- Customer Stories
Market Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Partnerships
- Marketplace
The annual gathering of the experience leaders at the world’s iconic brands building breakthrough business results.
- English/AU & NZ
- Español/Europa
- Español/América Latina
- Português Brasileiro
- REQUEST DEMO
- Experience Management
- Ultimate Guide to Market Research
- Secondary Research
Try Qualtrics for free
Secondary research: definition, methods, & examples.
18 min read This ultimate guide to secondary research helps you understand changes in market trends, customers buying patterns and your competition using existing data sources.
In situations where you’re not involved in the data gathering process ( primary research ), you have to rely on existing information and data to arrive at specific research conclusions or outcomes. This approach is known as secondary research.
In this article, we’re going to explain what secondary research is, how it works, and share some examples of it in practice.
What is secondary research?
Secondary research, also known as desk research, is a research method that involves compiling existing data sourced from a variety of channels . This includes internal sources (e.g.in-house research) or, more commonly, external sources (such as government statistics, organisational bodies, and the internet).
Secondary research comes in several formats, such as published datasets, reports, and survey responses , and can also be sourced from websites, libraries, and museums.
The information is usually free — or available at a limited access cost — and gathered using surveys , telephone interviews, observation, face-to-face interviews, and more.
When using secondary research, researchers collect, verify, analyse and incorporate it to help them confirm research goals for the research period.
As well as the above, it can be used to review previous research into an area of interest. Researchers can look for patterns across data spanning several years and identify trends — or use it to verify early hypothesis statements and establish whether it’s worth continuing research into a prospective area.
How to conduct secondary research
There are five key steps to conducting secondary research effectively and efficiently:
1. Identify and define the research topic
First, understand what you will be researching and define the topic by thinking about the research questions you want to be answered.
Ask yourself: What is the point of conducting this research? Then, ask: What do we want to achieve?
This may indicate an exploratory reason (why something happened) or confirm a hypothesis. The answers may indicate ideas that need primary or secondary research (or a combination) to investigate them.
2. Find research and existing data sources
If secondary research is needed, think about where you might find the information. This helps you narrow down your secondary sources to those that help you answer your questions. What keywords do you need to use?
Which organisations are closely working on this topic already? Are there any competitors that you need to be aware of?
Create a list of the data sources, information, and people that could help you with your work.
3. Begin searching and collecting the existing data
Now that you have the list of data sources, start accessing the data and collect the information into an organised system. This may mean you start setting up research journal accounts or making telephone calls to book meetings with third-party research teams to verify the details around data results.
As you search and access information, remember to check the data’s date, the credibility of the source, the relevance of the material to your research topic, and the methodology used by the third-party researchers. Start small and as you gain results, investigate further in the areas that help your research’s aims.
4. Combine the data and compare the results
When you have your data in one place, you need to understand, filter, order, and combine it intelligently. Data may come in different formats where some data could be unusable, while other information may need to be deleted.
After this, you can start to look at different data sets to see what they tell you. You may find that you need to compare the same datasets over different periods for changes over time or compare different datasets to notice overlaps or trends. Ask yourself: What does this data mean to my research? Does it help or hinder my research?
5. Analyse your data and explore further
In this last stage of the process, look at the information you have and ask yourself if this answers your original questions for your research. Are there any gaps? Do you understand the information you’ve found? If you feel there is more to cover, repeat the steps and delve deeper into the topic so that you can get all the information you need.
If secondary research can’t provide these answers, consider supplementing your results with data gained from primary research. As you explore further, add to your knowledge and update your findings. This will help you present clear, credible information.
eBook: The ultimate guide to conducting market research
Primary vs secondary research
Unlike secondary research, primary research involves creating data first-hand by directly working with interviewees, target users, or a target market. Primary research focuses on the method for carrying out research, asking questions, and collecting data using approaches such as:
- Interviews (panel, face-to-face or over the phone)
- Questionnaires or surveys
- Focus groups
Using these methods, researchers can get in-depth, targeted responses to questions, making results more accurate and specific to their research goals. However, it does take time to do and administer.
Unlike primary research, secondary research uses existing data, which also includes published results from primary research. Researchers summarise the existing research and use the results to support their research goals.
Both primary and secondary research have their places. Primary research can support the findings found through secondary research (and fill knowledge gaps), while secondary research can be a starting point for further primary research. Because of this, these research methods are often combined for optimal research results that are accurate at both the micro and macro level.
Sources of Secondary Research
There are two types of secondary research sources: internal and external. Internal data refers to in-house data that can be gathered from the researcher’s organisation. External data refers to data published outside of and not owned by the researcher’s organization.
Internal data
Internal data is a good first port of call for insights and knowledge, as you may already have relevant information stored in your systems. Because you own this information — and it won’t be available to other researchers — it can give you a competitive edge. Examples of internal data include:
- Database information on sales history and business goal conversions
- Information from website applications and mobile site data
- Customer-generated data on product and service efficiency and use
- Previous research results or supplemental research areas
- Previous campaign results
External data
External data is useful when you: 1) need information on a new topic, 2) want to fill in gaps in your knowledge, or 3) want data that breaks down a population or market for trend and pattern analysis. Examples of external data include:
- Government, non-government agencies, and trade body statistics
- Company reports and research
- Competitor research
- Public library collections
- Textbooks and research journals
- Media stories in newspapers
- Online journals and research sites
Three examples of secondary research methods in action
How and why might you conduct secondary research? Let’s look at a few examples:
1. Collecting factual information from the internet on a specific topic or market
There are plenty of sites that hold data for people to view and use in their research. For example, Google Scholar, ResearchGate, or Wiley Online Library all provide previous research on a particular topic. Researchers can create free accounts and use the search facilities to look into a topic by keyword, before following the instructions to download or export results for further analysis.
This can be useful for exploring a new market that your organisation wants to consider entering. For instance, by viewing the U.K census data for that area, you can see what the demographics of your target audience are , and create compelling marketing campaigns accordingly.
2. Finding out the views of your target audience on a particular topic
If you’re interested in seeing the historical views on a particular topic, for example, attitudes to women’s rights in the US, you can turn to secondary sources.
Textbooks, news articles, reviews, and journal entries can all provide qualitative reports and interviews covering how people discussed women’s rights. There may be multimedia elements like video or documented posters of propaganda showing biased language usage.
By gathering this information, synthesising it, and evaluating the language, who created it and when it was shared, you can create a timeline of how a topic was discussed over time.
3. When you want to know the latest thinking on a topic
Educational institutions, such as schools and colleges, create a lot of research-based reports on younger audiences or their academic specialisms. Dissertations from students also can be submitted to research journals, making these places useful places to see the latest insights from a new generation of academics.
Information can be requested — and sometimes academic institutions may want to collaborate and conduct research on your behalf. This can provide key primary data in areas that you want to research, as well as secondary data sources for your research.
Advantages of secondary research
There are several benefits of using secondary research, which we’ve outlined below:
- Easily and readily available data – There is an abundance of readily accessible data sources that have been pre-collected for use, in person at local libraries and online using the internet. This data is usually sorted by filters or can be exported into spreadsheet format, meaning that little technical expertise is needed to access and use the data.
- Faster research speeds – Since the data is already published and in the public arena, you don’t need to collect this information through primary research. This can make the research easier to do and faster, as you can get started with the data quickly.
- Low financial and time costs – Most secondary data sources can be accessed for free or at a small cost to the researcher, so the overall research costs are kept low. In addition, by saving on preliminary research, the time costs for the researcher are kept down as well.
- Secondary data can drive additional research actions – The insights gained can support future research activities (like conducting a follow-up survey or specifying future detailed research topics) or help add value to these activities.
- Secondary data can be useful pre-research insights – Secondary source data can provide pre-research insights and information on effects that can help resolve whether research should be conducted. It can also help highlight knowledge gaps, so subsequent research can consider this.
- Ability to scale up results – Secondary sources can include large datasets (like Census data results across several states) so research results can be scaled up quickly using large secondary data sources.
Disadvantages of secondary research
The disadvantages of secondary research are worth considering in advance of conducting research :
- Secondary research data can be out of date – Secondary sources can be updated regularly, but if you’re exploring the data between two updates, the data can be out of date. Researchers will need to consider whether the data available provides the right research coverage dates, so that insights are accurate and timely, or if the data needs to be updated. Also, fast-moving markets may find secondary data expires very quickly.
- Secondary research needs to be verified and interpreted – Where there’s a lot of data from one source, a researcher needs to review and analyse it. The data may need to be verified against other data sets or your hypotheses for accuracy and to ensure you’re using the right data for your research.
- The researcher has had no control over the secondary research – As the researcher has not been involved in the secondary research, invalid data can affect the results. It’s therefore vital that the methodology and controls are closely reviewed so that the data is collected in a systematic and error-free way.
- Secondary research data is not exclusive – As data sets are commonly available, there is no exclusivity and many researchers can use the same data. This can be problematic where researchers want to have exclusive rights over the research results and risk duplication of research in the future.
When do we conduct secondary research?
Now that you know the basics of secondary research, when do researchers normally conduct secondary research?
It’s often used at the beginning of research, when the researcher is trying to understand the current landscape. In addition, if the research area is new to the researcher, it can form crucial background context to help them understand what information exists already. This can plug knowledge gaps, supplement the researcher’s own learning or add to the research.
Secondary research can also be used in conjunction with primary research. Secondary research can become the formative research that helps pinpoint where further primary research is needed to find out specific information. It can also support or verify the findings from primary research.
You can use secondary research where high levels of control aren’t needed by the researcher, but a lot of knowledge on a topic is required from different angles.
Secondary research should not be used in place of primary research as both are very different and are used for various circumstances.
Questions to ask before conducting secondary research
Before you start your secondary research, ask yourself these questions:
Is there similar internal data that we have created for a similar area in the past?
If your organisation has past research, it’s best to review this work before starting a new project. The older work may provide you with the answers, and give you a starting dataset and context of how your organisation approached the research before. However, be mindful that the work is probably out of date and view it with that note in mind. Read through and look for where this helps your research goals or where more work is needed.
What am I trying to achieve with this research?
When you have clear goals, and understand what you need to achieve, you can look for the perfect type of secondary or primary research to support the aims. Different secondary research data will provide you with different information – for example, looking at news stories to tell you a breakdown of your market’s buying patterns won’t be as useful as internal or external data e-commerce and sales data sources.
How credible will my research be?
If you are looking for credibility, you want to consider how accurate the research results will need to be, and if you can sacrifice credibility for speed by using secondary sources to get you started. Bear in mind which sources you choose — low-credibility data sites, like political party websites that are highly biased to favor their own party, would skew your results.
What is the date of the secondary research?
When you’re looking to conduct research, you want the results to be as useful as possible, so using data that is 10 years old won’t be as accurate as using data that was created a year ago. Since a lot can change in a few years, note the date of your research and look for earlier data sets that can tell you a more recent picture of results. One caveat to this is using data collected over a long-term period for comparisons with earlier periods, which can tell you about the rate and direction of change.
Can the data sources be verified? Does the information you have check out?
If you can’t verify the data by looking at the research methodology, speaking to the original team or cross-checking the facts with other research, it could be hard to be sure that the data is accurate. Think about whether you can use another source, or if it’s worth doing some supplementary primary research to replicate and verify results to help with this issue.
We created a front-to-back guide on conducting market research, The ultimate guide to conducting market research , so you can understand the research journey with confidence.
In it, you’ll learn more about:
- What effective market research looks like
- The use cases for market research
- The most important steps to conducting market research
- And how to take action on your research findings
Download the free guide for a clearer view on secondary research and other key research types for your business.
Related resources
Market intelligence 9 min read, qualitative research questions 11 min read, ethnographic research 11 min read, business research methods 12 min read, qualitative research design 12 min read, business research 10 min read, qualitative research interviews 11 min read, request demo.
Ready to learn more about Qualtrics?
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
- QuestionPro

- Solutions Industries Gaming Automotive Sports and events Education Government Travel & Hospitality Financial Services Healthcare Cannabis Technology Use Case NPS+ Communities Audience Contactless surveys Mobile LivePolls Member Experience GDPR Positive People Science 360 Feedback Surveys
- Resources Blog eBooks Survey Templates Case Studies Training Help center
Home Market Research
Secondary Research: Definition, Methods and Examples.
In the world of research, there are two main types of data sources: primary and secondary. While primary research involves collecting new data directly from individuals or sources, secondary research involves analyzing existing data already collected by someone else. Today we’ll discuss secondary research.
One common source of this research is published research reports and other documents. These materials can often be found in public libraries, on websites, or even as data extracted from previously conducted surveys. In addition, many government and non-government agencies maintain extensive data repositories that can be accessed for research purposes.
LEARN ABOUT: Research Process Steps
While secondary research may not offer the same level of control as primary research, it can be a highly valuable tool for gaining insights and identifying trends. Researchers can save time and resources by leveraging existing data sources while still uncovering important information.
What is Secondary Research: Definition
Secondary research is a research method that involves using already existing data. Existing data is summarized and collated to increase the overall effectiveness of the research.
One of the key advantages of secondary research is that it allows us to gain insights and draw conclusions without having to collect new data ourselves. This can save time and resources and also allow us to build upon existing knowledge and expertise.
When conducting secondary research, it’s important to be thorough and thoughtful in our approach. This means carefully selecting the sources and ensuring that the data we’re analyzing is reliable and relevant to the research question . It also means being critical and analytical in the analysis and recognizing any potential biases or limitations in the data.
LEARN ABOUT: Level of Analysis
Secondary research is much more cost-effective than primary research , as it uses already existing data, unlike primary research, where data is collected firsthand by organizations or businesses or they can employ a third party to collect data on their behalf.
LEARN ABOUT: Data Analytics Projects
Secondary Research Methods with Examples
Secondary research is cost-effective, one of the reasons it is a popular choice among many businesses and organizations. Not every organization is able to pay a huge sum of money to conduct research and gather data. So, rightly secondary research is also termed “ desk research ”, as data can be retrieved from sitting behind a desk.
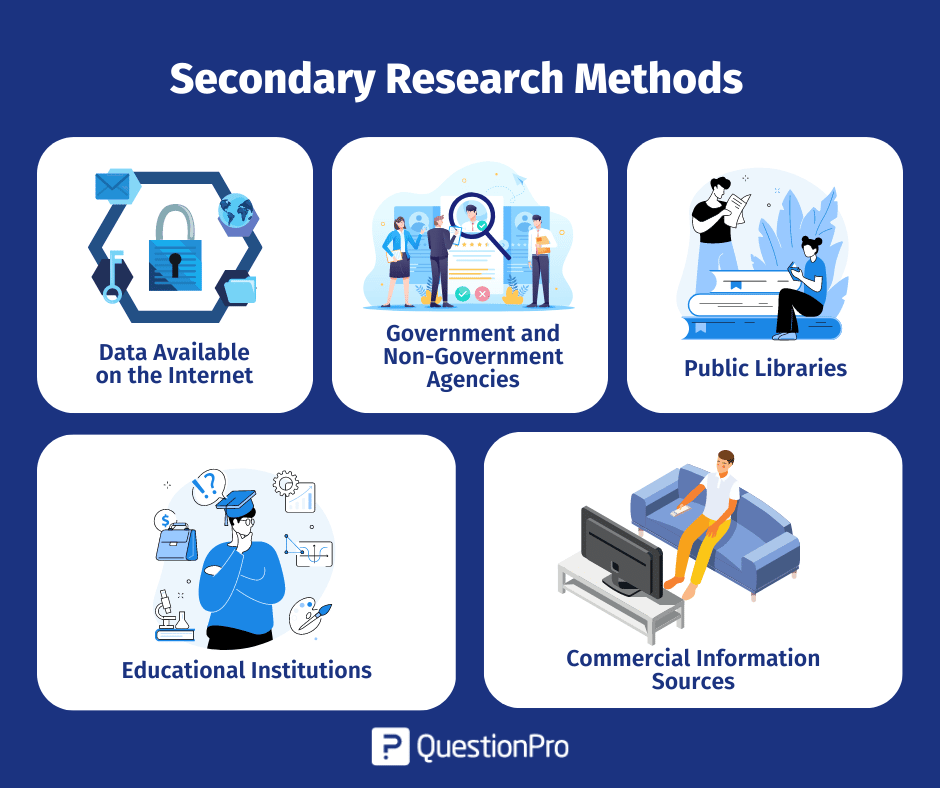
The following are popularly used secondary research methods and examples:
1. Data Available on The Internet
One of the most popular ways to collect secondary data is the internet. Data is readily available on the internet and can be downloaded at the click of a button.
This data is practically free of cost, or one may have to pay a negligible amount to download the already existing data. Websites have a lot of information that businesses or organizations can use to suit their research needs. However, organizations need to consider only authentic and trusted website to collect information.
2. Government and Non-Government Agencies
Data for secondary research can also be collected from some government and non-government agencies. For example, US Government Printing Office, US Census Bureau, and Small Business Development Centers have valuable and relevant data that businesses or organizations can use.
There is a certain cost applicable to download or use data available with these agencies. Data obtained from these agencies are authentic and trustworthy.
3. Public Libraries
Public libraries are another good source to search for data for this research. Public libraries have copies of important research that were conducted earlier. They are a storehouse of important information and documents from which information can be extracted.
The services provided in these public libraries vary from one library to another. More often, libraries have a huge collection of government publications with market statistics, large collection of business directories and newsletters.
4. Educational Institutions
Importance of collecting data from educational institutions for secondary research is often overlooked. However, more research is conducted in colleges and universities than any other business sector.
The data that is collected by universities is mainly for primary research. However, businesses or organizations can approach educational institutions and request for data from them.
5. Commercial Information Sources
Local newspapers, journals, magazines, radio and TV stations are a great source to obtain data for secondary research. These commercial information sources have first-hand information on economic developments, political agenda, market research, demographic segmentation and similar subjects.
Businesses or organizations can request to obtain data that is most relevant to their study. Businesses not only have the opportunity to identify their prospective clients but can also know about the avenues to promote their products or services through these sources as they have a wider reach.
Key Differences between Primary Research and Secondary Research
Understanding the distinction between primary research and secondary research is essential in determining which research method is best for your project. These are the two main types of research methods, each with advantages and disadvantages. In this section, we will explore the critical differences between the two and when it is appropriate to use them.
How to Conduct Secondary Research?
We have already learned about the differences between primary and secondary research. Now, let’s take a closer look at how to conduct it.
Secondary research is an important tool for gathering information already collected and analyzed by others. It can help us save time and money and allow us to gain insights into the subject we are researching. So, in this section, we will discuss some common methods and tips for conducting it effectively.
Here are the steps involved in conducting secondary research:
1. Identify the topic of research: Before beginning secondary research, identify the topic that needs research. Once that’s done, list down the research attributes and its purpose.
2. Identify research sources: Next, narrow down on the information sources that will provide most relevant data and information applicable to your research.
3. Collect existing data: Once the data collection sources are narrowed down, check for any previous data that is available which is closely related to the topic. Data related to research can be obtained from various sources like newspapers, public libraries, government and non-government agencies etc.
4. Combine and compare: Once data is collected, combine and compare the data for any duplication and assemble data into a usable format. Make sure to collect data from authentic sources. Incorrect data can hamper research severely.
4. Analyze data: Analyze collected data and identify if all questions are answered. If not, repeat the process if there is a need to dwell further into actionable insights.
Advantages of Secondary Research
Secondary research offers a number of advantages to researchers, including efficiency, the ability to build upon existing knowledge, and the ability to conduct research in situations where primary research may not be possible or ethical. By carefully selecting their sources and being thoughtful in their approach, researchers can leverage secondary research to drive impact and advance the field. Some key advantages are the following:
1. Most information in this research is readily available. There are many sources from which relevant data can be collected and used, unlike primary research, where data needs to collect from scratch.
2. This is a less expensive and less time-consuming process as data required is easily available and doesn’t cost much if extracted from authentic sources. A minimum expenditure is associated to obtain data.
3. The data that is collected through secondary research gives organizations or businesses an idea about the effectiveness of primary research. Hence, organizations or businesses can form a hypothesis and evaluate cost of conducting primary research.
4. Secondary research is quicker to conduct because of the availability of data. It can be completed within a few weeks depending on the objective of businesses or scale of data needed.
As we can see, this research is the process of analyzing data already collected by someone else, and it can offer a number of benefits to researchers.
Disadvantages of Secondary Research
On the other hand, we have some disadvantages that come with doing secondary research. Some of the most notorious are the following:
1. Although data is readily available, credibility evaluation must be performed to understand the authenticity of the information available.
2. Not all secondary data resources offer the latest reports and statistics. Even when the data is accurate, it may not be updated enough to accommodate recent timelines.
3. Secondary research derives its conclusion from collective primary research data. The success of your research will depend, to a greater extent, on the quality of research already conducted by primary research.
LEARN ABOUT: 12 Best Tools for Researchers
In conclusion, secondary research is an important tool for researchers exploring various topics. By leveraging existing data sources, researchers can save time and resources, build upon existing knowledge, and conduct research in situations where primary research may not be feasible.
There are a variety of methods and examples of secondary research, from analyzing public data sets to reviewing previously published research papers. As students and aspiring researchers, it’s important to understand the benefits and limitations of this research and to approach it thoughtfully and critically. By doing so, we can continue to advance our understanding of the world around us and contribute to meaningful research that positively impacts society.
QuestionPro can be a useful tool for conducting secondary research in a variety of ways. You can create online surveys that target a specific population, collecting data that can be analyzed to gain insights into consumer behavior, attitudes, and preferences; analyze existing data sets that you have obtained through other means or benchmark your organization against others in your industry or against industry standards. The software provides a range of benchmarking tools that can help you compare your performance on key metrics, such as customer satisfaction, with that of your peers.
Using QuestionPro thoughtfully and strategically allows you to gain valuable insights to inform decision-making and drive business success. Start today for free! No credit card is required.
LEARN MORE FREE TRIAL
MORE LIKE THIS

Top 7 Focus Group Software for Comprehensive Research
Apr 17, 2024

Top 7 DEI Software Solutions to Empower Your Workplace
Apr 16, 2024

The Power of AI in Customer Experience — Tuesday CX Thoughts

Employee Lifecycle Management Software: Top of 2024
Apr 15, 2024
Other categories
- Academic Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assessments
- Brand Awareness
- Case Studies
- Communities
- Consumer Insights
- Customer effort score
- Customer Engagement
- Customer Experience
- Customer Loyalty
- Customer Research
- Customer Satisfaction
- Employee Benefits
- Employee Engagement
- Employee Retention
- Friday Five
- General Data Protection Regulation
- Insights Hub
- Life@QuestionPro
- Market Research
- Mobile diaries
- Mobile Surveys
- New Features
- Online Communities
- Question Types
- Questionnaire
- QuestionPro Products
- Release Notes
- Research Tools and Apps
- Revenue at Risk
- Survey Templates
- Training Tips
- Uncategorized
- Video Learning Series
- What’s Coming Up
- Workforce Intelligence
Find Study Materials for
- Business Studies
- Combined Science
- Computer Science
- Engineering
- English Literature
- Environmental Science
- Human Geography
- Macroeconomics
- Microeconomics
- Social Studies
- Browse all subjects
- Read our Magazine
Create Study Materials
Market research can be overwhelming, but the good news is you don't have to start from scratch. Using secondary market research methods can save a lot of time and effort. Explore various methods and sources of secondary market research, and discover how to conduct secondary market research like a pro. Weigh the advantages and disadvantages, and learn from real-life secondary market research examples.

Explore our app and discover over 50 million learning materials for free.
- Secondary Market Research
- Explanations
- StudySmarter AI
- Textbook Solutions
- Customer Driven Marketing Strategy
- Digital Marketing
- Integrated Marketing Communications
- International Marketing
- Introduction to Marketing
- Marketing Campaign Examples
- Behavioral Targeting
- Customer Relationship Management
- Ethics in Marketing
- Experimental Research
- Focus Groups
- Interview in Research
- Market Calculations
- Market Mapping
- Market Research
- Marketing Analytics
- Marketing Information System
- Marketing KPIs
- Methods of Market Research
- Multi level Marketing
- Neuromarketing
- Observational Research
- Online Focus Groups
- PED and YED
- Primary Market Research
- Research Instrument
- Sampling Plan
- Survey Research
- Understanding Markets and Customers
- Marketing Management
- Strategic Marketing Planning
Lerne mit deinen Freunden und bleibe auf dem richtigen Kurs mit deinen persönlichen Lernstatistiken
Nie wieder prokastinieren mit unseren Lernerinnerungen.
Market research can be overwhelming, but the good news is you don't have to start from scratch. Using secondary market research methods can save a lot of time and effort. Explore various methods and sources of secondary market research, and discover how to conduct secondary market research like a pro. Weigh the advantages and disadvantages, and learn from real-life secondary market research examples.
Secondary Market Research Definition
Secondary market research is when a company uses existing information from other sources, like reports, articles, or surveys, to learn about its market and customers. It's like using someone else's research to help you make decisions for your business, without having to collect new data yourself.
Secondary market research, also known as desk research, is the process of gathering, analyzing, and interpreting data already collected by others, including industry reports, government publications, academic research, and competitor analysis, to inform business decisions.
Secondary market research is one of the two types of market research that businesses can employ to get necessary information/data about a target market. Market research refers to the process of studying a target market and determining the market value or viability of a new product or service in said market.
Imagine a world where everyone loves a specific type of fruit, but no one knows which is the most popular. A juice company wants to create a new drink that will be a hit with customers. Instead of conducting their own survey, they find a recent study on fruit preferences conducted by a well-known research firm. The study reveals that strawberry is the most popular fruit, so the juice company decides to launch a new strawberry-flavored drink based on the findings from the secondary market research.
While most secondary data is inexpensive to obtain, companies may have to pay a secondary data provider to access specialized data.
Nielsen and Gartner are two major global secondary data suppliers. Nielsen is a US-based company offering marketing and media information analytics for clients in over 100 countries. Here, researchers can retrieve plenty of data on customer behavior - where they buy their products, what they watch or listen to daily, etc. Gartner is a subscription-based service that provides access to on-demand published research content produced by over 2,300 research experts worldwide. 1
Secondary Market Research Methods
Secondary market research involves gathering data from existing sources to gain insights into a market, industry, or consumer behavior. The methods for secondary market research include:
Analyzing industry reports
Industry reports provide comprehensive information on a specific industry, including market size, growth trends, competitive landscape, and future prospects. For example, a company planning to enter the electric vehicle market can review industry reports to understand the current market situation, demand patterns, and major players.
Analyzing government publications
Government agencies publish a wide range of data and statistics on various industries, demographics, and economic indicators. For example, a startup looking to open a retail store in a new location can access census data to evaluate the area's population, income levels, and age distribution.

Reviewing academic research
Universities and research institutions often conduct studies and publish research papers on various topics, including consumer behavior, market trends, and emerging technologies. For instance, a pharmaceutical company can review academic research on the effectiveness of different drug delivery methods to inform their product development.
Reviewing trade publications
Trade publications are industry-specific magazines, journals, or newsletters that provide insights, news, and analysis relevant to a particular sector. A company in the solar energy sector can follow trade publications to stay informed about the latest technological advancements, regulations, and market trends.
Performing competitors analysis
Analyzing competitors' websites, press releases, marketing materials, and financial reports can provide valuable information about their strategies, product offerings, and performance. For example, a company looking to launch a new software-as-a-service platform can review competitors' websites to understand their pricing structures, features, and target audience.
Monitoring media coverage
News articles, blog posts, and social media can provide insights into public sentiment, emerging trends, and relevant events. A food industry company can monitor media coverage to identify popular diets or consumer preferences, helping them adjust their product offerings accordingly.
By using these secondary market research methods, businesses can gather valuable data to inform their decision-making and strategy development without the need for time-consuming and costly primary research.
Secondary Market Research Sources
The method of gathering secondary data is relatively straightforward. You simply go to reliable sources and search for secondary data relevant to your needs.
- Public sources: These are freely available resources such as government publications, websites, public libraries, and statistics bureaus. Examples include the U.S. Census Bureau, Eurostat, or the World Bank.
- Commercial sources: These are paid sources of information, such as industry reports, market research databases, and subscription-based publications. Examples include Statista, IBISWorld, or Gartner.
- Educational institutions: Academic research papers, dissertations, and theses can be valuable sources of secondary market research. University libraries, online academic databases, and research repositories like JSTOR, Google Scholar, or SSRN provide access to such resources.
- Trade associations and organizations: Industry-specific associations and organizations often publish relevant data, reports, and newsletters that can be useful for secondary market research. Examples include the National Retail Federation, the Consumer Technology Association, or the American Marketing Association.
- News and media outlets: Newspapers, magazines, news websites, and television networks provide information about current events, trends, and public sentiment. Examples include The New York Times, Forbes, or CNBC.
- Social media platforms: Social media platforms like Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn, or Instagram can be valuable sources for gathering insights on public opinion, consumer preferences, and emerging trends.
These sources of secondary market research can be accessed and utilized through the methods mentioned earlier, such as analyzing industry reports, reviewing academic research, or monitoring media coverage.
Like primary data, secondary data can be qualitative or quantitative. Qualitative data is descriptive and answers the question "why" or "how", whereas quantitative data is related to numbers and tell us "how many", "how much", and "how often". Qualitative data is acquired via interviews or observations, whereas quantitative data mainly comes from statistics or sales reports. Both types of data are essential to secondary research and help researchers analyze different angles of the research problem. 3
How to Conduct Secondary Market Research
The process of conducting secondary market research consists of five steps:
1. Define the research needs
Before doing any research, the researchers need to clarify the research objectives. Why are we conducting research? How can it contribute to the marketing effort?
2. Choose research sources
Once the research's purpose is identified, researchers need to choose the data sources. The sources can be internal, external, or both. One thing to note is that sources can vary widely in quality and credibility. For example, business magazines and published journals have a high-credibility score, whereas a random article or blog post on the Internet might be biased and unreliable.
How to evaluate research sources
To determine the quality of secondary data sources, the researcher needs to consider the following:
- Research purpose
- The audience
- Authority and creditability (Author's qualification, publisher)
- Accuracy and reliability (Citations and data collection methods).
- Currency (Date of publishing)
- Bias (Opinions or facts). 4
3. Collect secondary data
The next step is to select data based on the company's needs. The quickest way to source high-quality information is to look at online commercial databases or to buy from secondary data agencies. However, search engines and libraries are also a big help when the company is tight on budget.
4. Combine acquired data
The information collected should be grouped in the same categories or format. This grouping approach simplifies the secondary data analysis and cuts out content that does not contribute to research.
5. Analyze data
Finally, the data needs to be analyzed to answer the research question. If the research needs are unmet, researchers need to look for more secondary data or create their own. Researchers can also use secondary data to form a new perspective and help expand the understanding of a topic.
6. Provide conclusions and feedback
Once the data has been collected and analyzed, researchers must formulate and organize it to allow managers to draw feedback from it. Oftentimes a research report is created that outlines results, conclusions, implications, and recommendations.
Advantages of Secondary Market Research
Secondary market research can be an efficient and cost-effective way for businesses to gather information about their market, competitors, and customers using existing data sources.
Cost-effective
Secondary research is generally less expensive than primary research, as businesses can access existing data sources without spending resources on data collection. For example, a startup can use free government publications to analyze the demographics of their target market without incurring additional costs.
Time-saving
Secondary research provides businesses with immediate access to data, eliminating the need for planning and conducting time-consuming primary research. For example, a company can quickly gather industry insights from published reports instead of waiting for the results of a custom survey.
Broad scope
Secondary research can provide a comprehensive overview of market trends, historical data, and industry benchmarks. For example, a business can examine multiple years of financial reports from competitors to understand long-term growth patterns and financial stability.
Disadvantages of Secondary Market Research
While secondary market research offers several benefits, it's essential to be aware of the potential disadvantages as well. Here, we'll explore the disadvantages of secondary market research.
Lack of specificity
Secondary research may not address specific research questions or cater to unique business needs, as it wasn't collected for that purpose. For example, a company seeking information on customer preferences for a niche product may struggle to find relevant secondary data.
Potential outdated information
Since secondary research relies on existing data, it may be outdated or no longer relevant, limiting its usefulness for decision-making. For example, a business looking to enter a rapidly changing market may find that historical data is insufficient for understanding current trends.
Quality and reliability concerns
The accuracy and reliability of secondary research data may vary, as businesses have limited control over how the data is collected and analyzed. For example, a company using data from an unknown source might not be able to trust its accuracy or validity.
To address the disadvantages of secondary research, researchers should accompany it with primary research - collecting original data through interviews, observations, etc. Using high-quality sources to minimize biases and incorrect information is also crucial.
Secondary Market Research Examples
Examples of secondary market research include a nalyzing industry reports, r eviewing academic research and trade publications as well as p erforming competitors analysis or monitoring media coverage. Let' see how companies can use them in action.
Market trend analysis for a fashion retailer
A fashion retailer wants to identify upcoming trends and preferences to inform their product line and marketing strategy. They conduct secondary market research by reviewing fashion magazines, blog posts, and social media influencers' content. This helps them identify popular colors, patterns, and styles, which they incorporate into their clothing designs and promotional campaigns.

Competitor pricing analysis for a new restaurant
A new restaurant wants to understand the pricing strategies of its local competitors to determine its own menu pricing. They gather secondary data by visiting competitors' websites and analyzing their menus. Based on this research, the restaurant can set competitive prices that appeal to customers and position themselves effectively in the market.
Industry growth projections for a renewable energy startup
A renewable energy startup is seeking investment and wants to demonstrate the potential for growth in its industry. They conduct secondary market research by examining government publications, industry reports, and academic research on renewable energy trends and projections. This data allows them to present a compelling case to potential investors, showcasing the promising growth trajectory of the renewable energy sector.
Secondary Market Research - Key Takeaways
- Secondary market researc h is the process of gathering, analyzing, and interpreting data already collected by others, including industry reports, government publications, academic research, and competitor analysis, to inform business decisions.
- The main benefit of secondary market research is saving research time and costs.
- Examples of secondary market research include a nalyzing industry reports, r eviewing academic research and trade publications as well as p erforming competitors analysis or monitoring media coverage
- There are five steps of primary market research : defining the research needs, choosing sources, collecting secondary data, combining the acquired data, and analyzing it.
- The main disadvantage of secondary research is that the data may be outdated, not specific or low quality.
- Software Testing Help, Top 10 Market Research Companies [2022 Review & Comparison], 2022.
- The-Definition, Commercial online database, 2022.
- Career Foundry, Quantitative vs Qualitative Data: What's the Difference?, 2022.
- Brock University Library, Evaluating Information Sources, n.d.
Frequently Asked Questions about Secondary Market Research
--> what is an example of gathering secondary data.
Online resources and resource banks such as Google Scholar, Research Gate, Euromonitor, and Statista provide relevant information and data on a target market for businesses. For example, data can be gathered from Statista to identify the services or products customers spent the most money on in a certain industry during a set period of time.
--> What are the 5 methods of collecting secondary data?
Some of the methods of collecting secondary data include buying them from a supplier, searching commercial online databases, using search engines, or using internal sources like sales reports, customer feedback, etc.
--> What is secondary research in marketing?
Secondary market research, also known as desk research, involves businesses using existing information or data. This type of data has already been collected by someone other than the researcher.
--> What should be in secondary marketing research?
To conduct secondary research marketers have to define the research needs, choose research sources, collect the data, combine the data, analyze the data, and come up with conclusions.
--> What is an example of secondary market research?
An example of secondary market research includes searching online commercial databases. These are archives of data from commercial sources on the Internet. Researchers can dig around these databases to find their secondary data sources.
--> What useful data can marketers gather from suppliers and distributors?
Marketers can gather useful data from suppliers and distributors on product availability, pricing, customer preferences, and emerging trends in the industry.
--> How does secondary research help a business?
Secondary research helps a business by providing cost-effective and time-saving access to existing data on market trends, competitors, and customer behavior to inform decision-making and strategy development.
--> Why is secondary market research important?
Secondary market research is important because it allows businesses to gain valuable insights and understanding of their market, competition, and customers without the need for resource-intensive primary research.
Test your knowledge with multiple choice flashcards
Primary research uses _________ while secondary uses ___________.
Companies can buy secondary data from a third-party provider.
Government censuses are an internal source of secondary data.
Your score:

Join the StudySmarter App and learn efficiently with millions of flashcards and more!
Learn with 13 secondary market research flashcards in the free studysmarter app.
Already have an account? Log in
Secondary data gathering involves using ___________ collected by someone else for another purpose.
existing data
original data, existing data
Secondary data can be obtained using __________, _________, or buying from a supplier.
search engines, commercial online databases
What is not an EXTERNAL source of secondary data?
Buyer personas

of the users don't pass the Secondary Market Research quiz! Will you pass the quiz?
How would you like to learn this content?
Free marketing cheat sheet!
Everything you need to know on . A perfect summary so you can easily remember everything.
Join over 22 million students in learning with our StudySmarter App
The first learning app that truly has everything you need to ace your exams in one place
- Flashcards & Quizzes
- AI Study Assistant
- Study Planner
- Smart Note-Taking

Sign up to highlight and take notes. It’s 100% free.
This is still free to read, it's not a paywall.
You need to register to keep reading, create a free account to save this explanation..
Save explanations to your personalised space and access them anytime, anywhere!
By signing up, you agree to the Terms and Conditions and the Privacy Policy of StudySmarter.
Entdecke Lernmaterial in der StudySmarter-App


Methods of market research

In this post
In order to make sure that it is doing the right things, a business will carry out market research. Now that we have looked at the purpose of this research, we will move on to explore how to carry out this research and the various methods that may be used. The two main types of research are primary and secondary, with the majority of businesses using a combination of the two in order to plan new activity.
Primary market research
Primary research is when you collect information yourself. It is called primary because it has not been collected previously by someone else . Types of primary research include:
- Observations – businesses will record the interactions they have with customers and look at ways that these can be improved. They may also observe the methods of other businesses and look for ways that they can work with customers in order to meet their needs.
- Surveys and questionnaires – asking existing or potential customers their opinion is very important when carrying out market research on customers’ needs. This will require the business to ask specific questions and gather feedback that will inform its decisions in the future.

- Focus groups – focus groups are small groups of people that are invited to discuss a potential new product or service. The researcher will then record the responses of each individual in order to understand if the product is understood and will be popular with the intended customer
- Experimentation and testing – testing and experiments are most popular as a form of research with innovative products. A small batch of goods might be created (these are called ‘prototypes’) which are then tested in a variety of situations. Products might be tested for their quality, durability, safety or features
Primary research can have many different advantages. Firstly, it can be done in any manner that the business sees as appropriate with questions and analysis specifically designed to test the individual products that a company offers. Some of the drawbacks are that it can be expensive, time-consuming and hard to ensure that answers are gathered fairly. Since a business is biased when it comes to its own products, questionnaires can often contain leading answers, focus groups made up of people that do not cover the whole population and observations interpreted in a way that is good for the business. All of these things can lead to research that is unreliable and expensive.
Secondary market research
Secondary research (also known as desk research) is when data that has already been collected is used to inform a decision. This means that information is gathered from sources (these can be inside the business or outside) that has been collected previously for a different purpose. This information has not been collected specifically for the market research currently being carried out but can still be vital when making decisions. Typical types of secondary research include:
- Using resources to gather data – the internet is one of the main resources now used in secondary research. This allows a business to research what is already on the market, the demand for products, what its competitors offer and the key features of other products or services. Some other resources that can be used include business directories, magazines, newspapers or reviews by customers
- Market reports – finding reports that contain information on different markets can be great sources of data. These can be free but can also be purchased and will help a business to understand the demand for goods and what companies already operate in the market.
- Financial data – information can be gathered about running and manufacturing costs for new ventures, returns that other companies have seen and the prices that are charged for similar items
- Information the business already has – many businesses will carry out primary research. In the future, this research may be used again for another purpose. Since the data was not specifically collected for this new purpose, it is now secondary research. However, this information can still be very useful to inform business decisions

Secondary research is usually easy to carry out and cheap (often it is free) for a business. The time taken to collect this type of research is often much less than with primary research. There are several drawbacks to consider though – one of the main ones being reliability. Because the research has not been conducted by the researcher personally, it is hard to know if the data is accurate, as there could be other factors that had an influence over results. Businesses can also run into issues with secondary research as the data that is needed might not be available. This will mean that the company might be unable to carry out this method of research or that it has to use data that is not right for the situation.
Collecting and using data
Data comes in many different styles. Understanding the types of data and how each should be used is key to getting the most from information that is gathered.
Qualitative and quantitative data
All data can be split down into two categories: qualitative and quantitative. The difference between the two is that qualitative data is information that cannot necessarily be counted. It includes opinions and attitudes that are hard to count and focuses on finding trends, since a number cannot be assigned to this type of information.
Quantitative data can be counted easily. This type of data will include a lot of numbers such as the number of people who answered ‘yes’ to a question, the breaking point of a prototype during product testing or the number of potential customers in a market. This type of data can be used to create graphs and charts; making it easier to spot trends and form opinions.
Customer contact when collecting data
When collecting data, a business must work with customers to ensure that information collected is accurate. It is customers that keep a business making money so they must be fully understood to ensure products are desirable. The way that customers work with companies changes over time and the rise of social media has changed the way data is collected massively. Using social media sites, businesses can generate reviews and collect data in a way that is quick and easy for customers. Doing this means that the amount of data collected is much wider and people are more likely to be honest since data is not collected face to face. However, since younger people use social media more, data collected can be skewed and not reflect the full range of customers that a company has.
Data reliability
When information is collected by a company, it simply must be accurate . If data is unreliable then business decisions could be made based on this information with catastrophic consequences. Basing a business decision on incorrect data will dramatically decrease the chances of the change being a success. Incorrect data that influences a business decision may include:
- Opinions from customers that have not been truthful
- Poor estimations of financial data
- Not accounting for all costs or possible earnings
- Using a data collection method that is biased
- Using data from secondary research that is incorrectly collected
All information that is collected should be thoroughly checked by a business to ensure it is valid. Many businesses have made errors in the past due to information being incorrect and invested heavily in something that seems like a good idea, only to find out later that the information they initially collected was incorrect.

Interested in business?
We offer a GCSE Business course that covers Methods of market research
Learn more about our GCSE business course
Read another one of our posts
Understanding dementia: types, symptoms, and care needs.

How GCSE Business Prepares You for Real-World Entrepreneurship

Preparing for a Career in Adult Social Care: What You Need to Know

Parent’s Guide to Supporting A-Level Students

The Importance of Compassion in Healthcare

The Role of Palliative Care in End of Life Care

Community Health Initiatives – Promoting Wellness Locally

Caring for Older People – Strategies for Providing Quality Senior Care

Save your cart?
This website works best with JavaScript switched on. Please enable JavaScript
- Centre Services
- Associate Extranet
- All About Maths
GCSE Business
- Specification
- Planning resources
- Teaching resources
- Assessment resources
- Introduction
- Specification at a glance
- 3.1 Business in the real world
- 3.2 Influences on business
- 3.3 Business operations
- 3.4 Human resources
- 3.5 Marketing
- 3.6 Finance
- Scheme of assessment
- General administration
- Appendix: quantitative skills in business

3.5.3 The purpose and methods of market research
- International
- Schools directory
- Resources Jobs Schools directory News Search

Primary and Secondary Research lessons
Subject: Business and finance
Age range: 14-16
Resource type: Lesson (complete)
Last updated
14 April 2021
- Share through email
- Share through twitter
- Share through linkedin
- Share through facebook
- Share through pinterest

This resource comprises of 2 lessons - one on primary research and one on secondary research. The lessons contain theory, examples and activities/tasks.
Tes paid licence How can I reuse this?
Your rating is required to reflect your happiness.
It's good to leave some feedback.
Something went wrong, please try again later.
This resource hasn't been reviewed yet
To ensure quality for our reviews, only customers who have purchased this resource can review it
Report this resource to let us know if it violates our terms and conditions. Our customer service team will review your report and will be in touch.
Not quite what you were looking for? Search by keyword to find the right resource:

- Teesside University Student & Library Services
- Learning Hub Group
Research Methods
Introduction to research methods, useful resources, using material on this page.
- Primary Research
- Secondary Research
- Quantitative Research This link opens in a new window
- Qualitative Research This link opens in a new window
- Being Critical This link opens in a new window
- Subject LibGuides This link opens in a new window

Research involves collecting information sources and data. Research methods are the tools which you use to carry out this research. They help you find, analyse and interpret the information.
As you conduct your searches, you might find quantitative , qualitative or mixed methods research. You might conduct primary or secondary research as part of your studies.
This guide has been created to help you navigate through this process and understand the differences between the research areas.
The video below discusses how to choose the most appropriate research method for your project. Professor Stephen Gorard explains how researchers should start by defining what they want to explore and then choose the research methods which are most suitable for this.

Click on the image below to access the reading list which includes resources used in this guide as well as some additional useful resources.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License .
- Next: Primary Research >>
- Last Updated: Aug 11, 2022 3:41 PM
- URL: https://libguides.tees.ac.uk/researchmethods
Final dates! Join the tutor2u subject teams in London for a day of exam technique and revision at the cinema. Learn more →
Reference Library
Collections
- See what's new
- All Resources
- Student Resources
- Assessment Resources
- Teaching Resources
- CPD Courses
- Livestreams
Study notes, videos, interactive activities and more!
Sociology news, insights and enrichment
Currated collections of free resources
Browse resources by topic
- All Sociology Resources
Resource Selections
Currated lists of resources
Quizzes & Activities
Research Methods | AQA GCSE Sociology
Last updated 22 Dec 2023
- Share on Facebook
- Share on Twitter
- Share by Email
This quiz tests GCSE Sociology students' knowledge and understanding of Research methods - a key theme in both the Paper 1 and Paper 2 exams.
Click here for the quiz: Research Methods | AQA GCSE Sociology
- Research Methods
You might also like
Research methods - "card drop" activity.
26th November 2018
Example Answer for Q5 Paper 1 (2019) AQA A Level Sociology
Exam Support
Example Answer for Q6 Paper 1 (2019) AQA A Level Sociology
Screen time.
3rd June 2019
Methods in Context: Researching In-School Factors
Topic Videos
Research Methods: Interpretivism
Methods in context: researching home factors, our subjects.
- › Criminology
- › Economics
- › Geography
- › Health & Social Care
- › Psychology
- › Sociology
- › Teaching & learning resources
- › Student revision workshops
- › Online student courses
- › CPD for teachers
- › Livestreams
- › Teaching jobs
Boston House, 214 High Street, Boston Spa, West Yorkshire, LS23 6AD Tel: 01937 848885
- › Contact us
- › Terms of use
- › Privacy & cookies
© 2002-2024 Tutor2u Limited. Company Reg no: 04489574. VAT reg no 816865400.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Learn about and revise how market research can influence the products or services a business offers with BBC Bitesize GCSE Business - Edexcel. ... Methods of market research - secondary research.
It involves constructing suitable research questions, collecting appropriate primary and secondary data and analysing information for a written report. Part of National: Foundation KS4 Individual ...
Learn about and revise how market research can influence the products or services a business offers with BBC Bitesize GCSE Business - Edexcel. ... Methods of market research - secondary ...
Secondary research is a research method that uses data that was collected by someone else. In other words, whenever you conduct research using data that already exists, you are conducting secondary research. On the other hand, any type of research that you undertake yourself is called primary research. Example: Secondary research.
Watch this video if you want to understand the role of Secondary Market Research in Business and the common methods used. SUBSCRIBE: https://www.youtube.com...
Secondary research comes in several formats, such as published datasets, reports, and survey responses, and can also be sourced from websites, libraries, and museums. The information is usually free — or available at a limited access cost — and gathered using surveys, telephone interviews, observation, face-to-face interviews, and more.
What Is Secondary Market Research?This video will give an insight into Secondary Market Research - GCSE and A Level Business revision video to support revisi...
Students are shown undertaking secondary research using books and postcards from museums, to explore different techniques and interpret artists' inspiration related to their study themes. One student researches textile artist Rachel Howard using the internet and watching a video entitled 'Indian Embroidery Factory'. Another student visits the ...
So, rightly secondary research is also termed " desk research ", as data can be retrieved from sitting behind a desk. The following are popularly used secondary research methods and examples: 1. Data Available on The Internet. One of the most popular ways to collect secondary data is the internet.
Understand the research process. Be able to collect appropriate primary and secondary data and analyse information in order to write a research report. BBC Homepage
Secondary market research, also known as desk research, is the process of gathering, analyzing, and interpreting data already collected by others, including industry reports, government publications, academic research, and competitor analysis, to inform business decisions. Secondary market research is one of the two types of market research ...
Market research data can be quantitative or qualitative ; Quantitative data is based on numbers and could include financial reports (e.g. sales, costs), market data (e.g. markets share) or summaries of data gained from primary research (e.g. on a scale of 1-10 rate our customer service); Qualitative data gathers descriptions or explanations based on conversations, discussions, impressions, and ...
Primary market research. Secondary market research. Collecting and using data. Qualitative and quantitative data. Customer contact when collecting data. Data reliability. In order to make sure that it is doing the right things, a business will carry out market research. Now that we have looked at the purpose of this research, we will move on to ...
Secondary research which goes beyond literature reviews. For some dissertations/major projects there might only be a literature review (discussed above).For others there could be a literature review followed by primary research and for others the literature review might be followed by further secondary research.. You may be asked to write a literature review which will form a background ...
Students should understand why businesses conduct market research, such as to identify market opportunities and to get a better insight into their customers and competitors. Methods of market research to include primary and secondary: questionnaires. surveys. interviews. focus groups. internet research.
Primary and Secondary Research lessons. Subject: Business and finance. Age range: 14-16. Resource type: Lesson (complete) File previews. pptx, 2.15 MB. pptx, 1.83 MB. This resource comprises of 2 lessons - one on primary research and one on secondary research. The lessons contain theory, examples and activities/tasks.
National 5; Market research Methods of market research. Businesses use market research to identify customers' needs and wants. Each method of market research has advantages and disadvantages for ...
Introduction to Research Methods. Research involves collecting information sources and data. Research methods are the tools which you use to carry out this research. They help you find, analyse and interpret the information. As you conduct your searches, you might find quantitative, qualitative or mixed methods research.
2) Explain the following different methods of Research; Primary Research Secondary Research According to BBC (2019), Primary research 'involves gathering new data that has not been collected before. ' It can also be known as field research.
This quiz tests GCSE Sociology students' knowledge and understanding of Research methods - a key theme in both the Paper 1 and Paper 2 exams. Final dates! Join the tutor2u subject teams in London for a day of exam technique and revision at the cinema.
There are a variety of research methods that you could use: interviews. surveys/questionnaires. letters/emails. internet - newspapers, magazines, political party websites, government reports ...
Planning and organisation. The research process is important. It involves constructing suitable research questions, collecting appropriate primary and secondary data and analysing information for ...
Andrew Marr describes how Mahatma Gandhi led India to independence during British led rule through a campaign of civil disobedience.Suitable for Key stage 3 and GCSE, National 5 and Higher
The six main tertiary colours. There are six main tertiary colours. Artists use what they know about colours to help them make their art. Image caption, Yellow and orange mix to make yellow-orange ...