
Cover Story

What makes teams work?
Psychologists are pinpointing the factors that make teams gel—research that has far-reaching implications for health care, education, research, industry and more
By Kirsten Weir
September 2018, Vol 49, No. 8
Print version: page 46
15 min read

- Healthy Workplaces
The lone wolf is becoming an endangered species. In fields from health care to hospitality, startups to big business, teamwork has become the favored way to get things done. "The world is so complex, no one person has the skills or knowledge to accomplish all that we want to accomplish," says Susan McDaniel, PhD, a psychologist at the University of Rochester Medical Center and 2016 APA president known for her dedication to team-based work. "Interdisciplinary teams are the way to make that happen."
While humans have always joined forces with one another to achieve shared goals, psychologists are zeroing in on the methods and processes that make those collaborations more efficient and successful. "What's changing is the understanding and appreciation that there is a science behind how to manage teams," says Suzanne Bell, PhD, an associate professor of industrial/organizational (I/O) psychology at DePaul University in Chicago.
Now, a special issue of American Psychologist (Vol. 73, No. 4, 2018) details what psychologists have learned—and need to learn—about working in teams. "The Science of Teamwork," co-edited by McDaniel and colleague Eduardo Salas, PhD, of Rice University in Houston, in cooperation with American Psychologist editor-in-chief Anne E. Kazak, PhD, offers 21 articles that delve into the theory, research and applications of team science.
Here, we look at some of the most significant findings in the special issue, particularly the ways that team processes matter for psychologists, whether they're working in health care, research, industry, the military or education.
Building a dream team
Sometimes teams seem to click without too much effort, working together seamlessly and producing great work as a result. Other collaborations crash and burn. A team's success often depends on its composition, as Bell and her co-authors describe in their contribution to the special issue.
Surface-level attributes of individual team members—such as age, gender and reputation—can be important to the team's overall function, but they aren't necessarily the factors that matter most, Bell says. Instead, it's the "deep-level" factors you can't see at a glance, such as the members' personality traits, values and abilities, that tend to have a much bigger impact on work teams, studies suggest.
Those deep-level factors shape what researchers call the ABCs of teamwork: the attitudes, behaviors and cognitive states that collectively influence whether a team achieves its goals. Those elements depend to some degree on the context and on the team's objectives, Bell says. If the goal is to design an innovative new digital device, it's a good idea to build a team with diverse thinkers who bring a range of knowledge, skills and abilities to the project. But if a team's goal is to be more efficient, diverse attitudes might be less critical.
Team success also hinges on some basic tenets of team composition, say Bell and her co-authors. One person's mood and outlook can spread within a team, so a pessimistic team member could negatively influence the way the whole group views its goals. Individuals who value working in groups tend to be both more confident and more cooperative in a team setting. When team members are high in conscientiousness, they are better at self-regulating their teamwork. And groups composed of high-ability members who are able to learn, reason, adapt and solve problems are more likely to work well together.
Researchers are working to design algorithms that help organizations create effective teams for specific goals. In a project with NASA, for instance, Bell and colleagues are developing algorithms to identify crew members suited to working together on long-distance space missions.
Ultimately, such tools can help organizations create the best possible teams from the outset and tailor interventions for the unique needs of a team with a specific composition. "Teams are complex systems," Bell says. "The more you can manage them using a scientific basis, the better your teams will be."
The secret sauce: Cooperation in the military
Using scientific methods to understand teams isn't a new trend. Military researchers have been studying teamwork systematically for more than half a century, as Gerald F. Goodwin, PhD, of the U.S. Army Research Institute for the Behavioral and Social Sciences, and colleagues describe in an article in the special issue. "The military has been really central in supporting and executing research on teams since the 1950s," he says. "That support has been critical to moving this science forward."

That distinction might seem obvious, says Goodwin, but understanding the elements that allow teams to function well—team cohesion and shared mental models, for example—is important for training teams as well as evaluating their performance. "How well people work together may be more important than how well they work on the tasks," he says. "The secret sauce comes from the teamwork."
Research from military settings has also clarified the importance of team cognition—what teams think, how they think together and how well synchronized their beliefs and perceptions are. Team cognition is what allows team members to understand intuitively how their teammates will think and act, whether on the battlefield, in a surgical suite or on a basketball court. "Team cognition is really important for teams that have to quickly adapt to dynamic circumstances without having the opportunity to communicate a lot," Goodwin says.
Many of the empirical findings from military research apply to civilian teams as well. From the earliest studies, military and civilian researchers have openly shared findings and worked together to grow the science of teamwork, Goodwin says. The military, for instance, has made use of results from team research in aviation. Meanwhile, findings from military-funded research have informed processes in many industries, health care in particular.
Teaming up for better health
Teams in the military and in health care share an important commonality: They can be operating in situations in which team coordination can be a matter of life or death. Some of the earlier research on health-care teams focused on hospital settings, where teamwork failures can lead to patient harms such as misdiagnoses, medication mistakes, surgical errors and hospital-acquired infections. In a paper for the special issue, Michael Rosen, PhD, an associate professor of anesthesiology and critical care medicine at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, and colleagues describe how medical team coordination affects patient safety and the quality of patient care.
Unlike teams in a business setting that might collaborate with one another for months at a time, health-care teams are often fluid, especially in hospitals. Medical personnel including physicians, nurses, surgical assistants and pharmacists might have to jump into a new care team at each shift change or for each new patient. The fundamentals of good collaboration are the same no matter how transient the team, Rosen says: "It's about having clear roles, clear goals and a clear plan of care."

Teams are also becoming increasingly important in primary-care settings. "I think the industry is recognizing that we don't have a choice. Health care has become too complex, and the current model isn't working very well," says Kevin Fiscella, MD, a professor of family medicine at the University of Rochester Medical Center who co-authored a special issue article with McDaniel on the science of primary-care teams. "It's not a question of whether we adopt teamwork [in primary care], but how we do it—and how we begin addressing the barriers to teams."
Unfortunately, those barriers are not insignificant, Fiscella adds. One challenge is simply changing the way that many physicians think about primary care. "I graduated from medical school in 1980, and our whole training was that care is about me and the patient, and everybody else is there to support that relationship," he says. While that mentality is changing, it's not dead yet. "That unfortunate mental model of what it means to provide primary care can make it difficult" to move toward team thinking, he adds.
Systemic challenges also make collaboration difficult in primary-care settings. Clinicians such as family physicians, specialists and mental health professionals might be spread out in different locations. "It makes it harder to support other team members who are making important contributions," Fiscella says.
The traditional fee-for-service payment model also makes it difficult for medical professionals to prioritize teamwork, Fiscella and McDaniel add. Research has shown, for example, that when primary-care teams have short "huddles" before a visit to coordinate their care plans, they routinely report better teamwork and more supportive practice climates. Similarly, short team debriefings at the end of the day to hash out what worked and what didn't can boost learning and performance among team members and improve outcomes for patients.
Yet due to scheduling challenges, it can be tough for primary-care teams to find even a few minutes to come together for huddles or debriefings. "Time is money. If you take time out for a team meeting, that's lost revenue," Fiscella says.
Teamwork in the lab
Academia is famous for its departmental silos, but that, too, is changing as multidisciplinary research becomes the norm across all fields of science. Team science is gaining momentum for good reason, says Kara Hall, PhD, director of the Science of Team Science Team at the National Cancer Institute and co-author of a special issue article about collaboration in science.
Globalization and technology have made the pressing problems of society ever more complex, Hall says. Take the public health problem of reducing tobacco use, for instance. To address that challenge, you need an understanding of the genetic, neural, psychological and behavioral factors related to tobacco dependence, not to mention related social forces and the public policy context. "If you want to solve an applied global health problem, you need people who can bring their specialized knowledge to bear," she says. "Multidisciplinary teams can really [create] movement on these big problems."
Research on team science has found that collaborating across organizational and geographic boundaries increases productivity and scientific impact. And cross-disciplinary teams produce more academic publications and publish in more diverse outlets, Hall and her colleagues report.
Despite proven benefits, it can be hard for a researcher to wrap his or her head around team science. Most scientists were trained in an apprenticeship model, learning the ropes from a single mentor. "Historically, our scientists haven't been trained to work in teams or to lead teams," Hall says.
Even if scientists are prepared to take the leap to team-based research, their institutions might not be. Tenure and promotion are usually based on outputs such as academic publications, with more weight given to a paper's lead author and to articles published in journals in a researcher's own discipline. That model rewards competition, with the potential for tension as team members hash out who should be credited as first author. Team science is built instead on interdisciplinary cooperation—but so far, only a few academic institutions reward those cooperative efforts.
Because of the lack of team training and the institutional hurdles, Hall says, a research project may be technically and scientifically well-conceived yet fail to yield anticipated outcomes. If a cross-disciplinary team fails to meet its goals, was it because the topic was better suited to intradisciplinary science? Was it a problem with the way the team was composed? Or could the team have succeeded if members had received more institutional support and training?
Still, some early patterns are emerging to guide the way toward improved science teams, Hall and her co-authors report. Some studies have found that small teams are best for generating ideas that shake up the status quo, for instance, while larger teams are better at further developing those big ideas. And while cultural diversity can increase a science team's impact, diverse teams might benefit from more team science principles to head off challenges such as miscommunication.
Multicutural questions
The role of diversity in teamwork is a topic that needs a lot more attention, not just for scientific teams but in all areas of teamwork, says Jennifer Feitosa, PhD, an assistant professor of I/O psychology at the City University of New York, Brooklyn College. In the special issue, Feitosa and her co-authors describe the ways in which multicultural teams may function differently from teams in which all members share the same cultural background.

Yet it can take longer for a diverse team to find its groove than a team with similar backgrounds and mindsets. Individuals in multicultural teams are more likely to have different ways of doing things and might not understand where their fellow team members are coming from. "If you take a snapshot of a multicultural team at the beginning, it doesn't look so promising. They often need more time to all get on the same page," Feitosa says.
In both multicultural teams and more homogenous teams, trust is a key component for effective collaboration, Feitosa and her colleagues reported. But because of their differences, members of multicultural teams might have difficulty trusting each other at first.
"Focusing on shared goals can really help to develop that trust," she says.
In other ways, diverse teams operate quite differently from teams with cultural similarities. In the general teamwork literature, for example, research suggests that it's important to address and manage team conflict head-on. But when team members come from cultures that emphasize harmony and avoid conflict, calling out the elephant in the room can make people extremely uncomfortable and interfere with the teamwork dynamic, Feitosa says.
Differences in leadership style can also hinder multicultural teams. In North America, organizations are moving toward giving individuals greater autonomy and opportunities for self-management, Feitosa notes. "In very collectivistic and high power-distance cultures, people might rely more heavily on direction from team leaders and might rather be told what to do."
Fortunately, teams can prevent cultural differences from becoming obstacles by creating a "hybrid" culture, the authors report. "It's about establishing team norms that aren't entirely your culture or entirely my culture, but a little bit of everyone's," Feitosa says.
The research on multicultural teams can guide those looking to create collaborations that are both diverse and high-functioning. But to fully harness the value of cross-cultural perspectives and talents, Feitosa and her colleagues conclude, much more needs to be done to integrate findings from research on single-culture teams and multicultural teams. "Teamwork is a complex phenomenon, so we need to get more creative in how we look at this," she says.
Intervening to improve teamwork
Although researchers have more work to do to fully understand team processes, especially in multicultural contexts, it's not too early to apply what we know, Salas says. For the special issue, Salas and colleagues described evidence-based approaches for improving teamwork.
Organizations are clamoring for tools to make their teams more effective. "Team building is probably the No. 1 human resources intervention in the world," Salas says. Yet the results of such programs are mixed. If you send a group of executives into the wilderness for two days, they might have fun and learn something about one another—but it doesn't mean they'll magically develop new teamwork skills.
Put them into evidence-based team trainings, however, and the story is different. "Team training works," Salas says. "We know how to design, develop and evaluate it."
In particular, Salas and his colleagues describe four types of team development interventions that have been shown to benefit team performance: team training, team building, leadership training and debriefing.
Team training describes formalized learning experiences that aim to improve specific team skills or competencies. Structured team training has been shown to improve teamwork functioning and outcomes in industries such as education, engineering and health care. A prime example is TeamSTEPPS , an intervention to reduce medical errors by improving communication and teamwork skills among health-care professionals (see sidebar). Team-building interventions, meanwhile, aim to better teams by improving interpersonal relationships, clarifying roles and improving problem-solving. Such interventions might focus on increasing trust or setting challenging yet specific goals, for example. Leadership training targets a team leader's knowledge, skills and abilities, and improvements to these areas have been shown to support effective overall team processes. When leaders are trained in occupational safety, for instance, their teams exhibit safer behaviors on the job. Finally, team debriefings of the sort used in primary-care settings have been shown to improve performance in a variety of settings, including aviation and military teams.
There's power in numbers, and high-performing teams can be more than the sum of their parts. It's fortunate, then, that teamwork processes can be measured and improved with targeted interventions. But to keep sharpening the science, psychologists must continue exploring the conditions that allow teams to succeed, Salas says.
There's certainly no shortage of demand, he adds. "There's a tremendous amount of interest in trying to understand collaboration and teamwork—in health care, aviation, academia, the military, space exploration, the corporate world. I hope this special issue will inspire people to improve their teams, and to look for new ways of motivating their teams using psychological science."
To read the full American Psychologist special issue on teamwork, go to http://psycnet.apa.org/PsycARTICLES/journal/amp/73/4 .
Further resources
APA: A Curriculum for an Interprofessional Seminar on Integrated Primary Care www.apa.org/education/grad/curriculum-seminar
National Cancer Institute: Team Science Toolkit www.teamsciencetoolkit.cancer.gov
Related Articles
- Team building in health care
Letters to the Editor
- Send us a letter

ESSAY SAUCE
FOR STUDENTS : ALL THE INGREDIENTS OF A GOOD ESSAY
Essay: Working in a Group: Analyzing Benefits and Drawbacks
Essay details and download:.
- Subject area(s): Management essays
- Reading time: 3 minutes
- Price: Free download
- Published: 26 January 2020*
- Last Modified: 2 August 2024
- File format: Text
- Words: 902 (approx)
- Number of pages: 4 (approx)
Text preview of this essay:
This page of the essay has 902 words.
The debate on whether working alone or in a group is more beneficial has been a long-standing one. While personal preference plays a significant role in this decision, working in a group often proves to be more advantageous due to the diversity of ideas, the variety of skills that members bring, and the potential for higher productivity and better outcomes. This essay will delve deeper into the benefits of group work, supported by academic theories, and will also address the reasons why some individuals may prefer working alone.
The Benefits of Group Work
One of the primary advantages of group work is the plethora of ideas generated. According to Lynda Moultry Belcher , “This type of collaboration benefits the project and gives team members an outlet to bounce around ideas to find the best fit.” The concept of brainstorming, introduced by Alex Osborn in the 1940s, supports this view. Brainstorming in groups facilitates a wide range of ideas that might not emerge when individuals work in isolation. The collective intelligence of a group often surpasses that of an individual, leading to more innovative and effective solutions.
Moreover, working in a group brings together people with different skills and expertise, which enhances the quality of the work produced. Chitra Reddy states, “To solve complex problems and to complete difficult tasks, team works better than an individual.” This is supported by Belbin’s Team Roles theory , which emphasizes that effective teams are composed of individuals who fulfill various roles, such as the Plant (creative problem solver), the Monitor Evaluator (analytical thinker), and the Implementer (practical organizer). Each member contributes their unique strengths, leading to a more comprehensive and well-rounded approach to problem-solving.
Another significant benefit of group work is increased productivity and creativity. Belcher emphasizes that, “Another key advantage of group work in the office is that it can increase efficiency.” Research on social facilitation, which refers to the tendency for people to perform better on tasks when in the presence of others, supports this claim. When individuals work in groups, they are often motivated to perform better due to peer pressure and the desire to not let their team down. This can lead to higher levels of productivity and more creative outputs.
The Challenges of Group Work
Despite the numerous benefits, working in a group can also present challenges. One common issue is the potential for conflicts and disagreements among group members. Tuckman’s stages of group development (forming, storming, norming, performing, and adjourning) highlight that groups often go through a “storming” phase where conflicts arise. While this can be a healthy part of group development, it requires effective conflict resolution skills and strong leadership to navigate.
Another challenge is the risk of social loafing, where some group members may contribute less effort, relying on others to carry the workload. This phenomenon was identified by Latane, Williams, and Harkins (1979) , who found that individuals tend to exert less effort when working in a group compared to when they work alone. To mitigate this, it is crucial to establish clear roles, responsibilities, and accountability within the group.
The Appeal of Working Alone
While working in a group has its advantages, some individuals find working alone more convenient and productive. Sam Ashe-Edmunds argues, “If you own your own business, you only answer to your clients, who have little say over how you do your work.” This autonomy can be highly appealing as it allows individuals to work at their own pace, make independent decisions, and avoid the potential frustrations of group dynamics.
Working alone can also lead to higher levels of concentration and focus. Without the distractions and interruptions that often accompany group work, individuals can immerse themselves fully in their tasks. This is particularly beneficial for complex or creative work that requires deep thought and sustained attention.
Balancing Individual and Group Work
The decision to work alone or in a group often depends on the nature of the task and the individual’s personal preferences. For tasks that require a wide range of skills, diverse perspectives, and collective problem-solving, group work is usually more effective. However, for tasks that require deep concentration, creativity, and independent decision-making, working alone may be more beneficial.
In modern workplaces, a balance between individual and group work is often the most effective approach. Organizations can foster environments that allow for both collaborative and independent work, recognizing the strengths and preferences of their employees. This approach aligns with the Job Characteristics Model (JCM) developed by Hackman and Oldham, which suggests that providing employees with a variety of tasks and the autonomy to choose how they work can lead to higher job satisfaction and productivity.
In conclusion, while working alone and in a group each have their distinct advantages, the benefits of group work often outweigh those of working independently. The diversity of ideas, the combination of various skills, and the potential for increased productivity and creativity make group work particularly effective for complex and multifaceted tasks. However, it is important to acknowledge and address the challenges that can arise in group settings, such as conflicts and social loafing, to ensure successful collaboration. Balancing individual and group work based on the task at hand and the preferences of the individuals involved can lead to the most effective outcomes. As we navigate the complexities of modern work environments, fostering a culture that values both collaboration and autonomy can help individuals and organizations thrive.
About this essay:
If you use part of this page in your own work, you need to provide a citation, as follows:
Essay Sauce, Working in a Group: Analyzing Benefits and Drawbacks . Available from:<https://www.essaysauce.com/management-essays/working-in-a-group/> [Accessed 18-10-24].
These Management essays have been submitted to us by students in order to help you with your studies.
* This essay may have been previously published on EssaySauce.com and/or Essay.uk.com at an earlier date than indicated.
Essay Categories:
- Accounting essays
- Architecture essays
- Business essays
- Computer science essays
- Criminology essays
- Economics essays
- Education essays
- Engineering essays
- English language essays
- Environmental studies essays
- Essay examples
- Finance essays
- Geography essays
- Health essays
- History essays
- Hospitality and tourism essays
- Human rights essays
- Information technology essays
- International relations
- Leadership essays
- Linguistics essays
- Literature essays
- Management essays
- Marketing essays
- Mathematics essays
- Media essays
- Medicine essays
- Military essays
- Miscellaneous essays
- Music Essays
- Nursing essays
- Philosophy essays
- Photography and arts essays
- Politics essays
- Project management essays
- Psychology essays
- Religious studies and theology essays
- Sample essays
- Science essays
- Social work essays
- Sociology essays
- Sports essays
- Types of essay
- Uncategorised
- Zoology essays
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
Teamwork Makes the Dream Work: The Importance of Working Together
Sanjana is a health writer and editor. Her work spans various health-related topics, including mental health, fitness, nutrition, and wellness.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/SanjanaGupta-d217a6bfa3094955b3361e021f77fcca.jpg)
Rachel Goldman, PhD FTOS, is a licensed psychologist, clinical assistant professor, speaker, wellness expert specializing in eating behaviors, stress management, and health behavior change.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Rachel-Goldman-1000-a42451caacb6423abecbe6b74e628042.jpg)
Luis Alvarez / Getty Images
Why Teamwork Makes the Dream Work
Characteristics of good teamwork, how to foster good teamwork, how to be a good team player.
You’ve probably seen the phrase “Teamwork makes the dream work” printed on office mugs and motivational posters. But what exactly does it mean and what does good teamwork look like?
Teamwork Makes the Dream Work
The phrase “Teamwork makes the dream work” essentially means that dividing tasks and responsibilities among a team can lead to better outcomes than a single person doing the same task, says Sabrina Romanoff , PsyD, a clinical psychologist and professor at Yeshiva University.
The saying was initially coined by American clergyman John C. Maxwell. Maxwell published an eponymous book in 2002, in which he wrote, “Teamwork makes the dream work, but a vision becomes a nightmare when the leader has a big dream and a bad team.” In his book, Maxwell discusses the importance of working together collaboratively and shares some principles for building a strong team.
The phrase caught on and has become popular over the years. In this article, we explore the benefits of teamwork, the characteristics of good teamwork, as well as some steps to help you be a good team player and build a strong team.
Below, Dr. Romanoff explains why teamwork is important and the benefits it can offer:
- Improves efficiency and output: Teamwork is important because much more can be accomplished as part of a team than a single person working alone. Successful teams are much more efficient and effective at completing tasks than individuals.
- Produces better solutions: Teamwork allows the opportunity for diverse perspectives to tackle problems and find solutions that are more resourceful and effective than one person’s input alone. When multiple people are contributing, more knowledge, viewpoints, and feedback are incorporated, helping teammates arrive at more holistic solutions.
- Offers a larger pool of resources: Each member of the team can contribute their efforts, knowledge, abilities, and strengths to the task at hand. The team can tap into the resources each member provides to tackle new challenges.
- Promotes growth and learning: When people work together, there is an opportunity for each member of the team to learn and grow, both personally and professionally.
- Creates strong bonds among teammates: Collaborating on shared tasks, helping others, and working together helps teammates foster strong connections. People bond when they work together toward a common goal in an encouraging and supportive environment.
- Fosters a feeling of belonging: Teamwork also taps into our human need for belonging to a community or group and feeling like we are working towards something that is bigger than ourselves.
- Reduces stress: People tend to feel more supported when they’re part of a team. They often experience less perceived stress because they’re not facing the problem alone.
According to Dr. Romanoff, these are some of the characteristics of good teamwork:
- Shared goal: A successful team articulates and agrees on a common goal that has meaning to its members. Shared understanding of the goal the team is working toward is crucial so that everyone is on the same page and the team can operate as a cohesive unit.
- Cooperation: It’s important for teammates to actively listen to one another, cooperate with each other, and help one other out when required. A collaborative approach leads to more efficient and effective output.
- Respect: When people feel respected by their teammates, they are able to freely share ideas and opinions without fear of rejection or judgment. This level of safety sets the stage for greater commitment among teammates, originality, and novelty.
- Trust: There is trust that each member will deliver on their role for the team and meet their commitments. Team members take their responsibilities seriously and commit to following through on behalf of the individual members but also for the collective group. Each member is also trusted with placing the team’s interests above their own.
- Coordination: The team is well-organized so everyone is systematically and efficiently working together toward deadlines and shared goals. Effective communication and coordination are the bedrock of good teamwork.
- Strong interpersonal relationships: There are strong relationships among teammates. Team members care about each other and relationships are deeper than just their roles in the team. For instance, there is knowledge and sharing about people’s personal lives, and interest in other’s talents, skills, and interests. Team members take the time to celebrate achievements or have social outings outside of work to get to know each other as people.
- Effective conflict-resolution: Members of the team understand that conflict is inevitable but they are able to successfully manage and resolve them, by prioritizing the team’s goal over individual differences and conflicts. This means addressing issues among team members as they come up instead of pushing them under the rug, while also keeping differences among members in perspective so they don’t override the group’s mission.
Dr. Romanoff shares some strategies that can help you foster good teamwork:
- Define the goal: Define the mission and goal of the team. These can be co-constructed with your teammates, as team members are likely to have more buy-in when they have a role in choosing goals that are personally meaningful to them.
- Regularly ask for and provide feedback: Checking in with team members is the best way to implement needed change. This doesn’t have to be a formal process. Instead, openly discussing how team members are feeling can be normalized as part of the team’s culture.
- Maintain transparency: Be transparent, not just about the goal of the team but the goal of smaller tasks and mandates. This helps people understand how each job and agenda item is contributing to the overall mission of the organization.
- Making learning a continuous priority: Offer trainings, reading material, and resources to team members. Bring in people to teach on new topics and host events where members can share new information and passions with their teammates.
- Recognize accomplishments: Give team members kudos for a job well done and have their good work acknowledged by their peers and managers.
- Foster a culture of gratitude: It can be helpful to foster a culture of gratitude by having members consider what they are grateful for within the team or in their day, to help them reflect on what they appreciate in another.
If you’re wondering how to be a good team player, Dr. Romanoff has some suggestions that can help:
- Commit to the goal: Commit to the group process and the team’s goal.
- Take ownership: Take your tasks and responsibilities seriously. Be accountable to yourself and your teammates. Be cognizant of how your actions impact the team.
- Be flexible: Be flexible , open to change, and willing to take on new challenges or responsibilities to help your team.
- Work with your peers, not against them: Don’t compete with your peers. Instead try to work together toward a common goal and help each other out.
- Maintain a positive mindset: Be positive and optimistic. This mindset is contagious and will draw other team members towards you.
- Stay true to your values: Have integrity and speak your mind to advocate for the greater good and values of the group, even if it means going against what other group members are saying.
If you’ve ever been part of a team that just clicked, you know that being part of a team can be engaging and gratifying. Whether it’s at home, at work, on a playground, or in a relationship, working together as part of a team offers several benefits.
Clark W. Teamwork: A multidisciplinary review . Child Adolesc Psychiatr Clin N Am. 2021;30(4):685-695. doi:10.1016/j.chc.2021.05.003
Rosen MA, DiazGranados D, Dietz AS, et al. Teamwork in healthcare: Key discoveries enabling safer, high-quality care . Am Psychol . 2018;73(4):433-450. doi:10.1037/amp0000298
By Sanjana Gupta Sanjana is a health writer and editor. Her work spans various health-related topics, including mental health, fitness, nutrition, and wellness.
Eberly Center
Teaching excellence & educational innovation, what are the benefits of group work.
“More hands make for lighter work.” “Two heads are better than one.” “The more the merrier.”
These adages speak to the potential groups have to be more productive, creative, and motivated than individuals on their own.
Benefits for students
Group projects can help students develop a host of skills that are increasingly important in the professional world (Caruso & Woolley, 2008; Mannix & Neale, 2005). Positive group experiences, moreover, have been shown to contribute to student learning, retention and overall college success (Astin, 1997; Tinto, 1998; National Survey of Student Engagement, 2006).
Properly structured, group projects can reinforce skills that are relevant to both group and individual work, including the ability to:
- Break complex tasks into parts and steps
- Plan and manage time
- Refine understanding through discussion and explanation
- Give and receive feedback on performance
- Challenge assumptions
- Develop stronger communication skills.
Group projects can also help students develop skills specific to collaborative efforts, allowing students to...
- Tackle more complex problems than they could on their own.
- Delegate roles and responsibilities.
- Share diverse perspectives.
- Pool knowledge and skills.
- Hold one another (and be held) accountable.
- Receive social support and encouragement to take risks.
- Develop new approaches to resolving differences.
- Establish a shared identity with other group members.
- Find effective peers to emulate.
- Develop their own voice and perspectives in relation to peers.
While the potential learning benefits of group work are significant, simply assigning group work is no guarantee that these goals will be achieved. In fact, group projects can – and often do – backfire badly when they are not designed , supervised , and assessed in a way that promotes meaningful teamwork and deep collaboration.
Benefits for instructors
Faculty can often assign more complex, authentic problems to groups of students than they could to individuals. Group work also introduces more unpredictability in teaching, since groups may approach tasks and solve problems in novel, interesting ways. This can be refreshing for instructors. Additionally, group assignments can be useful when there are a limited number of viable project topics to distribute among students. And they can reduce the number of final products instructors have to grade.
Whatever the benefits in terms of teaching, instructors should take care only to assign as group work tasks that truly fulfill the learning objectives of the course and lend themselves to collaboration. Instructors should also be aware that group projects can add work for faculty at different points in the semester and introduce its own grading complexities .
Astin, A. (1993). What matters in college? Four critical years revisited. San Francisco: Jossey-Bass.
Caruso, H.M., & Wooley, A.W. (2008). Harnessing the power of emergent interdependence to promote diverse team collaboration. Diversity and Groups. 11, 245-266.
Mannix, E., & Neale, M.A. (2005). What differences make a difference? The promise and reality of diverse teams in organizations. Psychological Science in the Public Interest, 6(2), 31-55.
National Survey of Student Engagement Report. (2006). http://nsse.iub.edu/NSSE_2006_Annual_Report/docs/NSSE_2006_Annual_Report.pdf .
Tinto, V. (1987). Leaving college: Rethinking the causes and cures of student attrition. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
The Power of Teamwork
- Maggie Craddock
Few people realize that a group can accomplish what an individual alone cannot do — even when it comes to individual advancement. If you want the next promotion, you have to elbow that hardworking colleague next to you out of the way, right? Wrong. Here’s a true story that shows you why. It started when […]
Few people realize that a group can accomplish what an individual alone cannot do — even when it comes to individual advancement. If you want the next promotion, you have to elbow that hardworking colleague next to you out of the way, right? Wrong. Here’s a true story that shows you why.
- MC Maggie Craddock is the president and founder of Workplace Relationships . She is the author of Power Genes: Understanding Your Power Persona — and How to Wield It at Work .
Partner Center
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Group work as an incentive for learning – students’ experiences of group work.

- Division of Psychology, Department of Behavioural Sciences and Learning, Linköping University, Linköping, Sweden
Group work is used as a means for learning at all levels in educational systems. There is strong scientific support for the benefits of having students learning and working in groups. Nevertheless, studies about what occurs in groups during group work and which factors actually influence the students’ ability to learn is still lacking. Similarly, the question of why some group work is successful and other group work results in the opposite is still unsolved. The aim of this article is to add to the current level of knowledge and understandings regarding the essence behind successful group work in higher education. This research is focused on the students’ experiences of group work and learning in groups, which is an almost non-existing aspect of research on group work prior to the beginning of the 21st century. A primary aim is to give university students a voice in the matter by elucidating the students’ positive and negative points of view and how the students assess learning when working in groups. Furthermore, the students’ explanations of why some group work ends up being a positive experience resulting in successful learning, while in other cases, the result is the reverse, are of interest. Data were collected through a study-specific questionnaire, with multiple choice and open-ended questions. The questionnaires were distributed to students in different study programs at two universities in Sweden. The present result is based on a reanalysis and qualitative analysis formed a key part of the study. The results indicate that most of the students’ experiences involved group work that facilitated learning, especially in the area of academic knowledge. Three important prerequisites (learning, study-social function, and organization) for group work that served as an effective pedagogy and as an incentive for learning were identified and discussed. All three abstractions facilitate or hamper students’ learning, as well as impact their experiences with group work.
Introduction
Group work is used as a means for learning at all levels in most educational systems, from compulsory education to higher education. The overarching purpose of group work in educational practice is to serve as an incentive for learning. For example, it is believed that the students involved in the group activity should “learn something.” This prerequisite has influenced previous research to predominantly focus on how to increase efficiency in group work and how to understand why some group work turns out favorably and other group work sessions result in the opposite. The review of previous research shows that in the 20th century, there has been an increase in research about students’ cooperation in the classroom ( Lou et al., 1996 ; Gillies and Boyle, 2010 , 2011 ). This increasing interest can be traced back to the fact that both researchers and teachers have become aware of the positive effects that collaboration might have on students’ ability to learn. The main concern in the research area has been on how interaction and cooperation among students influence learning and problem solving in groups ( Hammar Chiriac, 2011a , b ).
Two approaches concerning learning in group are of interest, namely cooperative learning and collaborative learning . There seems to be a certain amount of confusion concerning how these concepts are to be interpreted and used, as well as what they actually signify. Often the conceptions are used synonymously even though there are some differentiations. Cooperative group work is usually considered as a comprehensive umbrella concept for several modes of student active working modes ( Johnson and Johnson, 1975 ; Webb and Palincsar, 1996 ), whereas collaboration is a more of an exclusive concept and may be included in the much wider concept cooperation ( Hammar Chiriac, 2011a , b ). Cooperative learning may describe group work without any interaction between the students (i.e., the student may just be sitting next to each other; Bennet and Dunne, 1992 ; Galton and Williamson, 1992 ), while collaborative learning always includes interaction, collaboration, and utilization of the group’s competences ( Bennet and Dunne, 1992 ; Galton and Williamson, 1992 ; Webb and Palincsar, 1996 ).
At the present time, there is strong scientific support for the benefits of students learning and working in groups. In addition, the research shows that collaborative work promotes both academic achievement and collaborative abilities ( Johnson and Johnson, 2004 ; Baines et al., 2007 ; Gillies and Boyle, 2010 , 2011 ). According to Gillies and Boyle (2011) , the benefits are consistent irrespective of age (pre-school to college) and/or curriculum. When working interactively with others, students learn to inquire, share ideas, clarify differences, problem-solve, and construct new understandings. Gillies (2003a , b ) also stresses that students working together are more motivated to achieve than they would be when working individually. Thus, group work might serve as an incentive for learning, in terms of both academic knowledge and interpersonal skills. Nevertheless, studies about what occur in groups during group work and which factors actually influence the students’ ability to learn is still lacking in the literature, especially when it comes to addressing the students’ points of view, with some exceptions ( Cantwell and Andrews, 2002 ; Underwood, 2003 ; Peterson and Miller, 2004 ; Hansen, 2006 ; Hammar Chiriac and Granström, 2012 ). Similarly, the question of why some group work turns out successfully and other work results in the opposite is still unsolved. In this article, we hope to contribute some new pieces of information concerning the why some group work results in positive experiences and learning, while others result in the opposite.
Group Work in Education
Group work is frequently used in higher education as a pedagogical mode in the classroom, and it is viewed as equivalent to any other pedagogical practice (i.e., whole class lesson or individual work). Without considering the pros and cons of group work, a non-reflective choice of pedagogical mode might end up resulting in less desirable consequences. A reflective choice, on the other hand, might result in positive experiences and enhanced learning ( Galton et al., 2009 ; Gillies and Boyle, 2011 ; Hammar Chiriac and Granström, 2012 ).
Group Work as Objective or Means
Group work might serve different purposes. As mentioned above, the overall purpose of the group work in education is that the students who participate in group work “learn something.” Learning can be in terms of academic knowledge or “group knowledge.” Group knowledge refers to learning to work in groups ( Kutnick and Beredondini, 2009 ; Gillies and Boyle, 2010 , 2011 ; Hammar Chiriac, 2011a , b ). Affiliation, fellowship, and welfare might be of equal importance as academic knowledge, or they may even be prerequisites for learning. Thus, the group and the group work serve more functions than just than “just” being a pedagogical mode. Hence, before group work is implemented, it is important to consider the purpose the group assignment will have as the objective, the means, or both.
From a learning perspective, group work might function as both an objective (i.e., learning collaborative abilities) and as the means (i.e., a base for academic achievement) or both ( Gillies, 2003a , b ; Johnson and Johnson, 2004 ; Baines et al., 2007 ). If the purpose of the group work is to serve as an objective, the group’s function is to promote students’ development of group work abilities, such as social training and interpersonal skills. If, on the other hand, group work is used as a means to acquire academic knowledge, the group and the collaboration in the group become a base for students’ knowledge acquisition ( Gillies, 2003a , b ; Johnson and Johnson, 2004 ; Baines et al., 2007 ). The group contributes to the acquisition of knowledge and stimulates learning, thus promoting academic performance. Naturally, group work can be considered to be a learning environment, where group work is used both as an objective and as the means. One example of this concept is in the case of tutorial groups in problem-based learning. Both functions are important and might complement and/or even promote each other. Albeit used for different purposes, both approaches might serve as an incentive for learning, emphasizing different aspect knowledge, and learning in a group within an educational setting.
Working in a Group or as a Group
Even if group work is often defined as “pupils working together as a group or a team,” ( Blatchford et al., 2003 , p. 155), it is important to bear in mind that group work is not just one activity, but several activities with different conditions ( Hammar Chiriac, 2008 , 2010 ). This implies that group work may change characteristics several times during a group work session and/or during a group’s lifetime, thus suggesting that certain working modes may be better suited for different parts of a group’s work and vice versa ( Hammar Chiriac, 2008 , 2010 ). It is also important to differentiate between how the work is accomplished in the group, whether by working in a group or working as a group.
From a group work perspective, there are two primary ways of discussing cooperation in groups: working in a group (cooperation) or working as a group (collaboration; Underwood, 2003 ; Hammar Chiriac and Granström, 2012 ). Situations where students are sitting together in a group but working individually on separate parts of a group assignment are referred to as working in a group . This is not an uncommon situation within an educational setting ( Gillies and Boyle, 2011 ). Cooperation between students might occur, but it is not necessary to accomplish the group’s task. At the end of the task, the students put their separate contributions together into a joint product ( Galton and Williamson, 1992 ; Hammar Chiriac, 2010 , 2011a ). While no cooperative activities are mandatory while working in a group, cooperative learning may occur. However, the benefits in this case are an effect of social facilitation ( Zajonc, 1980 ; Baron, 1986 ; Uziel, 2007 ) and are not caused by cooperation. In this situation, social facilitation alludes to the enhanced motivational effect that the presence of other students have on individual student’s performance.
Working as a group, on the other hand, causes learning benefits from collaboration with other group members. Working as a group is often referred to as “real group work” or “meaningful group work,” and denotes group work in which students utilizes the group members’ skills and work together to achieve a common goal. Moreover, working as a group presupposes collaboration, and that all group members will be involved in and working on a common task to produce a joint outcome ( Bennet and Dunne, 1992 ; Galton and Williamson, 1992 ; Webb and Palincsar, 1996 ; Hammar Chiriac, 2011a , b ). Working as a group is characterized by common effort, the utilization of the group’s competence, and the presence of problem solving and reflection. According to Granström (2006) , working as a group is a more uncommon activity in an educational setting. Both approaches might be useful in different parts of group work, depending on the purpose of the group work and type of task assigned to the group ( Hammar Chiriac, 2008 ). Working in a group might lead to cooperative learning, while working as group might facilitate collaborative learning. While there are differences between the real meanings of the concepts, the terms are frequently used interchangeably ( Webb and Palincsar, 1996 ; Hammar Chiriac, 2011a , b ; Hammar Chiriac and Granström, 2012 ).
Previous Research of Students’ Experiences
As mentioned above, there are a limited number of studies concerning the participants’ perspectives on group work. Teachers often have to rely upon spontaneous viewpoints and indications about and students’ experiences of group work in the form of completed course evaluations. However, there are some exceptions ( Cantwell and Andrews, 2002 ; Underwood, 2003 ; Peterson and Miller, 2004 ; Hansen, 2006 ; Hammar Chiriac and Einarsson, 2007 ; Hammar Chiriac and Granström, 2012 ). To put this study in a context and provide a rationale for the present research, a selection of studies focusing on pupils’ and/or students’ experiences and conceptions of group work will be briefly discussed below. The pupils’ and/or students inside knowledge group work may present information relevant in all levels of educational systems.
Hansen (2006) conducted a small study with 34 participating students at a business faculty, focusing on the participants’ experiences of group work. In the study different aspects of students’ positive experiences of group work were identified. For example, it was found to be necessary that all group members take part and make an effort to take part in the group work, clear goals are set for the work, role differentiation exists among members, the task has some level of relevance, and there is clear leadership. Even though Hansen’s (2006) study was conducted in higher education, these findings may be relevant in other levels in educational systems.
To gain more knowledge and understand about the essence behind high-quality group work, Hammar Chiriac and Einarsson (2007) turned their focus toward students’ experiences and conceptions of group work in higher education. A primary aim was to give university students a voice in the matter by elucidating their students’ points of view and how the students assess working in groups. Do the students’ appreciate group projects or do they find it boring and even as a waste of time? Would some students prefer to work individually, or even in “the other group?” The study was a part of a larger research project on group work in education and only a small part of the data corpus was analyzed. Different critical aspects were identified as important incitements for whether the group work turned out to be a success or a failure. The students’ positive, as well as negative, experiences of group work include both task-related (e.g., learning, group composition, participants’ contribution, time) and socio-emotional (e.g., affiliation, conflict, group climate) aspects of group work. The students described their own group, as well as other groups, in a realistic way and did not believe that the grass was greener in the other group. The same data corpus is used in this article (see under Section The Previous Analysis). According to Underwood (2003) and Peterson and Miller (2004) , the students’ enthusiasm for group work is affected by type of task, as well as the group’s members. One problem that recurred frequently concerned students who did not contribute to the group work, also known as so-called free-riders ( Hammar Chiriac and Hempel, 2013 ). Students are, in general, reluctant to punish free-riders and antipathy toward working in groups is often associated with a previous experience of having free-riders in the group ( Peterson and Miller, 2004 ). To accomplish a favorable attitude toward group work, the advantages of collaborative activities as a means for learning must be elucidated. Furthermore, students must be granted a guarantee that free-riders will not bring the group in an unfavorable light. The free-riders, on the other hand, must be encouraged to participate in the common project.
Hammar Chiriac and Granström (2012) were also interested in students’ experiences and conceptions of high-quality and low-quality group work in school and how students aged 13–16 describe good and bad group work? Hammar Chiriac and Granström (2012) show that the students seem to have a clear conception of what constitutes group work and what does not. According to the students, genuine group work is characterized by collaboration on an assignment given by the teacher. They describe group work as working together with their classmates on a common task. The students are also fully aware that successful group work calls for members with appropriate skills that are focused on the task and for all members take part in the common work. Furthermore, the results disclose what students consider being important requisites for successful versus more futile group work. The students’ inside knowledge about classroom activities ended up in a taxonomy of crucial conditions for high-quality group work. The six conditions were: (a) organization of group work conditions, (b) mode of working in groups, (c) tasks given in group work, (d) reporting group work, (e) assessment of group work, and (f) the role of the teacher in group work. The most essential condition for the students seemed to be group composition and the participants’ responsibilities and contributions. According to the students, a well-organized group consists of approximately three members, which allows the group to not be too heterogeneous. Members should be allotted a reasonable amount of time and be provided with an environment that is not too noisy. Hence, all six aspects are related to the role of the teacher’s leadership since the first five points concern the framework and prerequisites created by the teacher.
Näslund (2013) summarized students’ and researchers’ joint knowledge based on experience and research on in the context of shared perspective for group work. As a result, Näslund noticed a joint apprehension concerning what constitutes “an ideal group work.” Näslund (2013) highlighted the fact that both students and researchers emphasized for ideal group work to occur, the following conditions were important to have: (a) the group work is carried out in supportive context, (b) cooperation occurs, (c) the group work is well-structured, (d) students come prepared and act as working members during the meetings, and (e) group members show respect for each other.
From this brief exposition of a selection of research focusing on students’ views on group work, it is obvious that more systematic studies or documentations on students’ conceptions and experiences of group work within higher education are relevant and desired. The present study, which is a reanalysis of a corpus of data addressing the students’ perspective of group, is a step in that direction.
Aim of the Study
The overarching knowledge interest of this study is to enhance the body of knowledge regarding group work in higher education. The aim of this article is to add knowledge and understanding of what the essence behind successful group work in higher education is by focusing on the students’ experiences and conceptions of group work and learning in groups , an almost non-existing aspect of research on group work until the beginning of the 21st century. A primary aim is to give university students a voice in the matter by elucidating the students’ positive and negative points of view and how the students assess learning when working in groups. Furthermore, the students’ explanations of why some group work results in positive experiences and learning, while in other cases, the result is the opposite, are of interest.
Materials and Methods
To capture university students’ experiences and conceptions of group work, an inductive qualitative approach, which emphasizes content and meaning rather than quantification, was used ( Breakwell et al., 2006 ; Bryman, 2012 ). The empirical data were collected through a study-specific, semi-structured questionnaire and a qualitative content analysis was performed ( Mayring, 2000 ; Graneheim and Lundman, 2003 ; Elo and Kyngäs, 2007 ).
Participants
All participating students attended traditional university programs where group work was a central and frequently used pedagogical method in the educational design. In addition, the participants’ programs allowed the students to be allocated to the same groups for a longer period of time, in some cases during a whole semester. University programs using specific pedagogical approaches, such as problem-based learning or case method, were not included in this study.
The participants consisted of a total of 210 students, 172 female and 38 male, from two universities in two different cities (approximately division: 75 and 25%). The students came from six different populations in four university programs: (a) The Psychologist Program/Master of Science in Psychology, (b) The Human Resource Management and Work Sciences Program, (c) Social Work Program, and (d) The Bachelor’s Programs in Biology. The informants were studying in their first through eighth terms, but the majority had previous experiences from working in other group settings. Only 2% of the students had just started their first term when the study was conducted, while the vast majority (96%) was participating in university studies in their second to sixth semester.
The teacher most frequently arranged the group composition and only a few students stated that they have had any influence on the group formation. There were, with a few exceptions, between 6 and 10 groups in each of the programs included in this study. The groups consisted of between four to eight members and the differences in sizes were almost proportionally distributed among the research group. The groups were foremost heterogeneous concerning gender, but irrespective of group size, there seems to have been a bias toward more women than men in most of the groups. When there was an underrepresented sex in the group, the minority mostly included two students of the same gender. More than 50% of the students answered that in this particularly group, they worked solely with new group members, i.e., students they had not worked with in previous group work during the program.
To collect data about students’ experiences and conceptions of group work, a study-specific, semi-structured questionnaire was constructed. The questionnaire approached the students’ experiences regarding the specific group work they were working in at the time of the data collection (spring 2006), not their experiences of group work in general. The questionnaire contained a total of 18 questions, including both multiple choice and open-ended questions. The multiple choice questions concerned background variables and information about the present group. The seven open-ended questions were designed to gather data about the students’ experiences and perceptions of group work in higher education. The questionnaires were distributed to the different populations of students (some populations studied at the same program) at two universities in Sweden. During the time the questionnaires were completed, the researcher or an assistant was present to answer possible questions. In all, 210 students answered the questionnaire.

The previous analysis
As described above (Section Previous Research of Students’ Experiences) a previous analysis based on the same data corpus revealed that most of the students included in the study found group work to be an enjoyable and stimulating working method ( Hammar Chiriac and Einarsson, 2007 ). The data were analyzed using a qualitative content analysis based on three different research questions. There were two main criticisms of the previous study presented from other researchers. The criticism conveyed applied mostly to the question of whether we could assemble these groups into a joint research group and second to the fact that the results were mostly descriptive. To counter this criticism and to elaborate on the analysis, a further analysis was conducted.
The present analysis
The present analysis (or reanalysis) was conducted by using an inductive qualitative content analysis based on three open-ended research questions:
(1) In what ways does group work contribute to your learning?
(2) What positive experiences have you had while working in your present group?
(3) What negative experiences have you had while working in your present group?
Each question corresponds to one aspect of the research’s objective, but together, they might support and enrich each other and unravel new information based on the students’ experiences and conceptions of group work. Research question 1, listed above, was not included in the first analysis and is being investigated for the first time in this study, while the other two questions are being reanalyzed. An inductive, qualitative content analysis is applicable when the aim of the research is a description of the meaning or of a phenomenon in conceptual form ( Mayring, 2000 ; Graneheim and Lundman, 2003 ; Elo and Kyngäs, 2007 ).
The analysis was carried out over several steps, following the basic principles of an inductive, qualitative content analysis ( Mayring, 2000 ; Graneheim and Lundman, 2003 ; Elo and Kyngäs, 2007 ). The steps included three phases: preparation, organizing, and reporting ( Elo and Kyngäs, 2007 ). Each question was treated as a unit of analysis and was thus analyzed separately. In the preparation phase, the researcher tried to make sense of the data by becoming familiar with the data corpus. In the current study, this included transcription and thorough reading of the answers. An open coding system composed of marginal notes and headings began the second phase, which included organizing the data. This second phase, in turn, included open coding, creating categories, and abstraction. The notes and the headings from the open coding were transferred to coding sheets and then grouped into categories. Categories were formed through the interpretation of the codes that described the same meaning or phenomenon. Finally, an abstraction process began, where a general description of the grouped categories formed an abstraction (see Table 1 ). An abstraction was denominated using the content-characteristic words for this paper: learning, study-social function, and organization . The third phase, reporting , addressed the presentation of the process of analysis and the results.
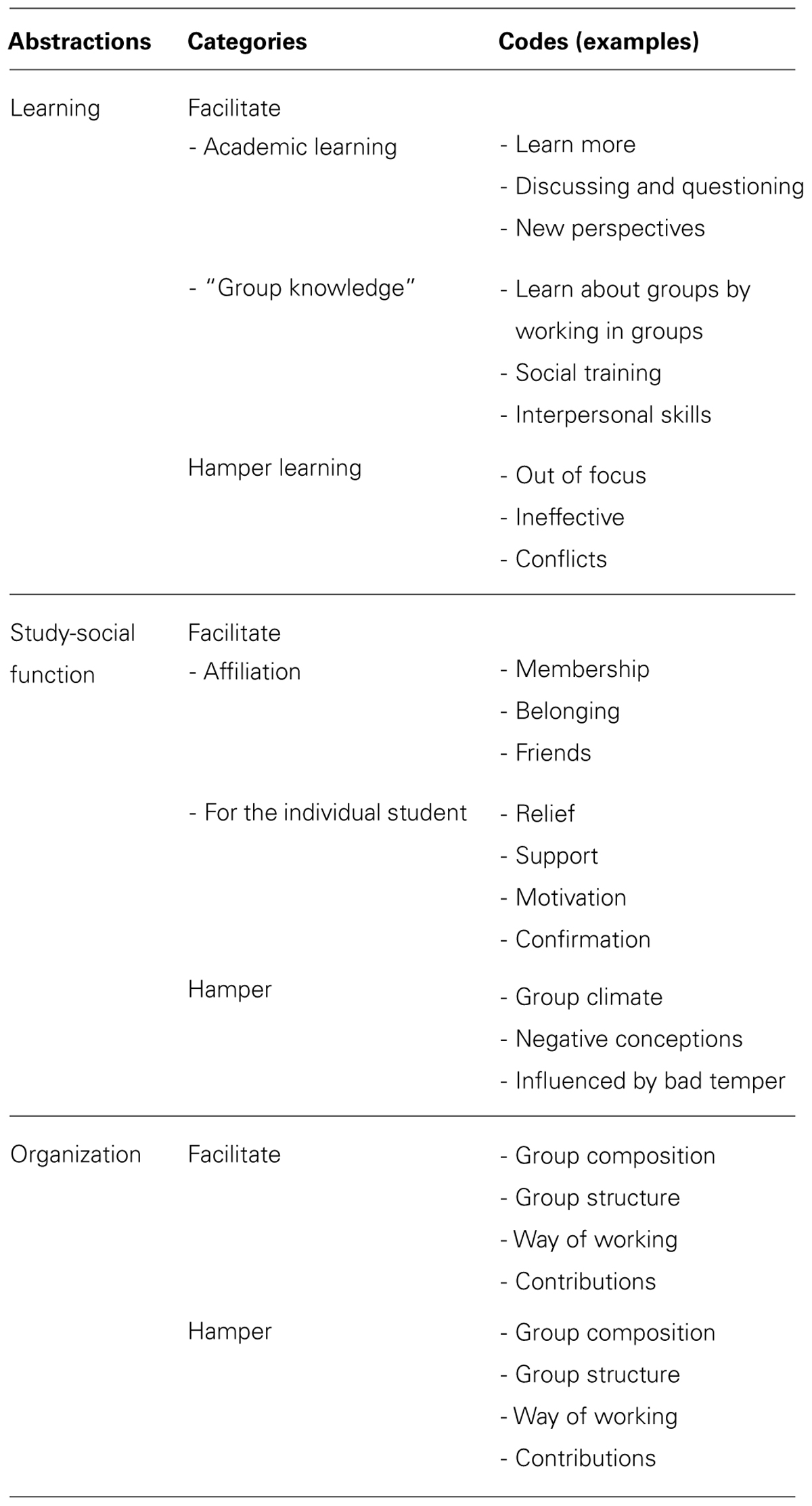
TABLE 1. Examples from the organization phase of the coding process.
The final aim of this study is to present the phenomenon studied in a model or conceptual map of the categories ( Elo and Kyngäs, 2007 ). In following these procedures, we aim to expand our understanding of the existing work and to counter the second part of the criticisms, which included criticisms stating that the results were mostly descriptive in nature. To counter the criticisms regarding the question of whether we could assemble these groups into a joint research group, the qualitative abstraction that emerged from the qualitative content analysis was compared to background information by using SPSS. Three background variables were used: gender, cities, and programs.
Ethics and Quality
The ethical principles provided by the British Psychology Society have formed a guideline [ British Psychology Society (BPS), 2006 ] for the present study. The ethical principles, which emphasize the concern for participants’ interest, have been applied throughout the study [ American Psychological Association (APA), 2002 ; British Psychology Society (BPS), 2004 ; Barett, 2007 ]. To facilitate trustworthiness, a thorough description of the analysis process has been presented ( Graneheim and Lundman, 2003 ; Elo and Kyngäs, 2007 ). Translated citations are also included to increase trustworthiness.
As described above, the analysis resulted in three abstraction emerging: learning, study-social function , and organization . Each abstraction includes both a positive variant (i.e., facilitating learning, study-social function, and/or organization) as well as a negative alternative (i.e., hampering learning, study-social function, and/or organization). The results will be presented in three different sections, with each section corresponding to one abstraction. However, we would like to call attention to the fact that one fifth (20%, including missing value 8%) of the students included in this study did not perceive and/or mention any negative experiences at all in their present group. From a general point of view, there is no difference with respect to gender or city regarding the distribution of positive and negative experiences concerning the abstractions, neither concerning different programs nor the distribution of negative experiences (all p > 0.05). In contrast, there is a difference between the various programs and the distribution of positive experiences (χ 2 = 14.474; df: 6; p < 0.025). The students from the social work program display a higher amount of positive experiences in connection with a study-social function and organizing in comparison with the other programs.
The majority of the students (97%) responded that working in group somehow facilitated learning, academic knowledge, collaborative abilities or both. They learned more or different things when working in groups than they would have if working alone. By discussing and questioning each other’s points of view and listening to their fellow students’ contributions, thus obtaining different perspectives, the participants experienced an enhanced academic learning, compared to working alone. “I learn much more by working in groups than working individually. I obtain more through interaction with the other group members.” Academic knowledge is not the only type of knowledge learned through group work. In addition to academic knowledge, students also gain advanced knowledge about how groups work, how the students function as individual members of groups and how other members behave and work in groups. Some of the respondents also argued that group work in group courses strengthen the combination between empirical and theoretical learning, thus learning about groups by working in groups. “Through practical knowledge demonstrate several of the phenomena we read about in theory (group psychology and sociology).”
The results show no difference when considering either gender or city. However, when comparing the four programs included in the study and the types of learning, a difference occurs (χ 2 = 14.474; df: 6; p < 0.025). A division into two parts seems to generate the difference. On the one hand, the students from the Bachelor’s Program in Biology and the students from the Human Resource Management and Work Sciences Program emphasize academic knowledge. On the other hand, students from the Psychologist Program/Master of Science in Psychology and Social Work Program more often mentioned learning collaborative abilities single handed, as well as a combination of academic knowledge and group learning.
Even though the participants did not expressly report that group work hampered learning, they often mentioned that they perceived group work as being ineffective due to loss of focus and the presence of conflicts, thereby hampering conceivable learning. One respondent stated, “that you sometimes are out of focus in the discussion and get side-tracked instead of considering the task.” Another offered the following perspective: “Occasionally, it is too little task related and feels unnecessary sometimes. Individual work is, in certain situations, preferable.” Group work might be perceived as ineffective and time consuming considering long working periods with tedious discussions. One participant stated, “The time aspect, everything is time consuming.” The absence or presence of conflicts in the group affects students’ experiences, and conflicts not handled may influence learning in a negative way. The students perceived that it was difficult to come to an agreement and experience those conflicts and the need to compromise hampered individual learning. Accordingly, the absence of conflicts seemed to be an important incitement for learning. However, fear of conflicts can lead to reduced learning and cause negative experiences, but to a considerably lesser extent than does the presence of actual conflicts. “A great fear of conflicts sometimes raises an oppressive atmosphere.” “Fear of conflicts leads to much not made known.”
A Study-Social Function
Group work also has an important study - social function according to the students. They describe their membership in groups as an important aspect of affiliation. In general, the total number of students at a program is approximately 60–80 or more. In contexts with a large population of students, the smaller group gives the participants an opportunity to feel affiliated with the group and to each other. “Feels safe to have a certain group to prepare oneself together with before, for instance, an upcoming seminar.” The group gives the individual student a platform of belonging, which might serve as an important arena for learning ( facilitate ) and finding friends to spend leisure time with. Many of the participants also reported feeling a positive atmosphere in the group, which is important for the satisfaction of being in the group together with the fellow students.
To be a member of a group may also serve as a function of relief, both academically and socially, for the individual student. The participants reported that many of the tasks assigned by the university teachers are difficult to handle on their own. “The others explain to me. We help one another.” However, the students reported that they helped and supported each other, even if the task did not demand cooperation. “As a student, you get more active. You help one another to extract the groups’ common knowledge. Forward info if somebody is missing.” Being a member of a group also affects students’ motivation to study. They prepare themselves by reading texts and other material before the next group session. Group work may also have positive effects on achievement. Students’ total amount of time and effort on their work may also increase. Through group work, the participants also get confirmation of who they are and what their capacities are.
Being a member of a group also has its downside, which often has to do with the group climate and/or group processes, both of which have multiple and complex features. Many students reported that both the group climate and group processes might be the source of negative conceptions of the group and hamper learning. “Process losses.” The respondents described negative conceptions based on the feeling of not having enough time to get to know each other in the group or being in situations where no cooperation occurred. Other students referred to the fact that the group’s life is too long, which may lead to group members not only wearing each other out, but also having a negative effect on each other’s mood. “Influenced by each other’s mood.” Examples of negative experiences are process losses in general, including insufficient communication, unclear roles, and problems with one group member. As mentioned above, the students from the Social Work Program display a higher number of positive experiences in connection with a study-social function and organizing in comparison with students from the other programs.
Organization
O rganization concerns the structure of group work and includes different aspects, all describing group work from different angles. The aspects are relevant no matter how the participants perceive the group work, whether as positive or negative. Unlike the other two abstractions (learning and study-social function), organization includes the same aspects no matter what the experiences are, namely group composition , group structure , way of working and contributions.
Whether the group is composed in a homogeneous or heterogeneous way seems to be experienced in both a positive and negative sense. A well-thought-out group composition , including both group size and mix of members, is essential. A just large-enough group for the task, consisting of a population of members that is not too heterogeneous, facilitates a joyful experience and learning. A homogeneous mix of members might be perceived as positive, as the students feel that they have similar life situations, opinions, and skills, thereby causing positive conditions for collaboration within the group. Conversely, in a group with a heterogeneous mix, different members contribute with different knowledge and/or prior experiences, which can be used in the group for collective and collaborative learning. “Good group composition, distribution of age groups that leads to fruitful discussions.”
An additional facilitating prerequisite is that the group develops adequate ways of working together, which includes a well-organized group structure . Well-working groups are characterized as having developed adequate ways of working together, while groups that work less well together lack a developed way of cooperation. “Well-organized working group with clear and distinct rules and structure.” Preparation and attendance for group work are aspects mentioned as facilitating (and hampering) incitements. Group work in educational settings sometimes entails that you, as a student, are forced to read and learn within a certain period of time that is beyond your control. Some participants find the pressure positive, hence “increase the pressure to read chapters in time.” The members’ contribution to the group is also a central factor for the students’ apprehension of how the group works. This is, in short, about how much each member ought to contribute to the group and to the work. Groups considered to be well-working are ones where all members contribute to the group’s work, but the content of the contribution may vary according to the single member’s qualifications. “We work well together (most of us). Everybody participates in different ways and seems committed.” “Good, everybody participates the same amount. We complement each other well.”
The same prerequisites can lead to the reverse result, i.e., hampering learning and stirring up negative experiences. If the group members are too identical (a homogeneous group composition ), it might lead to a lack of opinions, which several participants perceived as being negative. “That we do not get a male perspective about the subject. We are all girls, at the age of 20, which also means that we have pretty much the same experiences that may be seen as both positive and negative. The negative is the lack of opinion.” If the group is considered to be too small, students seems to find it troublesome, as the relationships are few, but there are also few people who are available to handle the workload allotted to the group. Nevertheless, a group that is too large could also lead to negative experiences. “It is far too large a group.”
A lack of group structure might lead to a lower degree of satisfaction with the group’s way of working . A commonly expressed point of view seen in the students’ answers involved the occurrences of when all members did not attend the meetings (absence). In these cases, it was also viewed that the work in the group often was characterized as unstructured. “Sometimes a bit unclear structures, some students have difficulties with coming in time.” Not attending or coming unprepared or badly prepared to the group work is other aspect that is commented on. “Low degree of fellowship, punctuality is a problem, an insecure group.” Some students find it frustrating to prepare for a certain time decided that is beyond their control. “A necessity to read certain chapters within a specific period of time is never stimulating.”
One characteristic of groups that are not working well is that contribution varies among the members. In group work, students with different levels of ambition are assembled, which may result in different levels of interest and commitment, as well as differences in the willingness to take on responsibilities or part of the workload of the group’s work. Some members are active and do much of the work, while others barely contribute at all. “Some don’t do anything while others pull the heaviest burden. Two out of three prepare before the meeting, the rest think that they are able to read during the group work and do not supply the group with anything else other than delays and frustration.” A common answer seen in the questionnaires that concerns negative experiences of group work as they relate to contribution is: “Everybody does not contribute just as much.” or “There is always someone who just glides along and doesn’t take part.”
Summary of the Results
The results are summarized in a model illustrating the relationship between abstractions (i.e., learning, study-social function, and organization) and result (i.e., enhanced or reduced learning), as well as positive or negative experiences (see Figure 1 ).
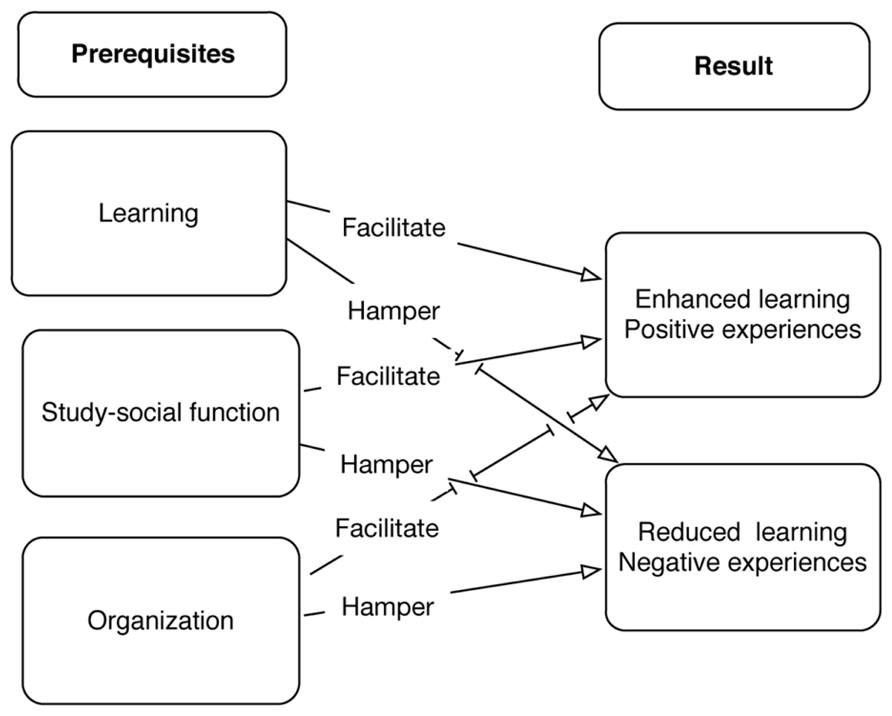
FIGURE 1. A model illustrating the relationship between abstractions and result .
The figure shows that all three abstractions may facilitate or hamper learning as well as the experiences of group work. To piece together, the difficult and extensive jigsaw puzzle concerning why some group work result in positive experiences and learning, while in other cases the result is the reverse is still not solved. In this article, we propose that the prerequisites learning, study-social function, and organization influence learning and experiences of working in group, thus, providing additional pieces of information to the jigsaw puzzle (Figure 2 ).
FIGURE 2. Pieces of jigsaw puzzle influence learning and experiences.
The current study focuses on university students’ experiences and conceptions of group work and learning in groups. A primary aim was to give university students a voice in the matter by elucidating the students’ positive and negative points of view, as well as how the students’ assess learning when working in groups. The analysis resulted in the emergence of three different abstractions: learning, study-social function, and organizations. Each abstraction also included a positive and a negative variant. In other words, all three abstractions either facilitated or hampered university students’ learning, as well as their experiences of group work.
Learning in Group Work
The result shows that the majority of the students (97%) experience that working in group facilitated learning, either academic knowledge, collaborative abilities or both, accordingly confirming previous research ( Johnson and Johnson, 2004 ; Baines et al., 2007 ; Gillies and Boyle, 2010 , 2011 ). According to the students, they learn more or different things when working in groups compared with working individually. Academic knowledge was not the only type of knowledge learned through group work. In addition to academic knowledge, students also gained advanced knowledge about how groups work, how the students function as individual members of groups and how other members behave and work in groups. Some of the respondents also argued that group work might strengthen the combination between empirical and theoretical learning, thus the students were learning about groups by working in groups. This implies that group work, from a learning perspective, serves several functions for the students ( Kutnick and Beredondini, 2009 ; Gillies and Boyle, 2010 , 2011 ; Hammar Chiriac, 2011a , b ). Group work also seems to have an important study-social function for the university students, hence confirming that group work serves more functions than just being a pedagogical mode.
Affiliation, fellowship, and welfare seem to be highly important, and may even be essential prerequisites for learning. Accordingly, group work functions as both as an objective (i.e., learning collaborative abilities), and as the means (i.e., a base for academic achievement), or both, for the students ( Gillies, 2003a , b ; Johnson and Johnson, 2004 ; Baines et al., 2007 ). Moreover, the students from the Bachelor’s Program in Biology and the students from the Program for Human Resources seem to use group work more as means for obtaining academic knowledge. In contrast, students from the Psychologist Program/Master of Science in Psychology and Social Work Program more often mentioned learning collaborative abilities alone, as well as a combination of academic knowledge and group learning, thus using group work as an objective, as a means, or as a combination of both. One interpretation might be that the type of task assigned to the students differs in various programs. This can be valid both concerning the purpose of group work (group work as objective or as the means), but also arrangement (working in a group or as a group; Underwood, 2003 ; Hammar Chiriac and Granström, 2012 ). Another possible explanation might be that the main emphasis in the Bachelor’s Program in Biology and the Program for Human Resources is on product and academic knowledge, while in the Psychologist Program/Master of Science in Psychology and Social Work Program, the process is more articulated and demanded. However, this is only speculation and further research is needed.
Even though the participants did not explicitly state that group work hampered learning, they mentioned that they perceived group work to be ineffective due to the loss of focus and/or the presence of conflicts with other group members, thereby hampering conceivable learning. This may also be an effect of the purpose or arrangement of the group work ( Cantwell and Andrews, 2002 ; Underwood, 2003 ; Peterson and Miller, 2004 ; Hansen, 2006 ; Hammar Chiriac and Granström, 2012 ; Hammar Chiriac and Hempel, 2013 ).
Experiences of Group Work
The results revealed that several aspects of group work are important incentives for learning. In addition, this study revealed students’ experiences of group work (i.e., facilitating or hampering positive/negative experiences), which is in line with the previous studies on students’ experiences of working in groups ( Cantwell and Andrews, 2002 ; Underwood, 2003 ; Peterson and Miller, 2004 ; Hansen, 2006 ; Hammar Chiriac and Granström, 2012 ; Hammar Chiriac and Hempel, 2013 ). Group composition, group structure, ways of working, and participants’ contributions are aspects put forward by the university students as either facilitating or hampering the positive experience of group work ( Underwood, 2003 ; Peterson and Miller, 2004 ; Hansen, 2006 ; Hammar Chiriac and Granström, 2012 ; Hammar Chiriac and Hempel, 2013 ).
Several of the aspects bear reference to whether the group members work in a group or as a group ( Underwood, 2003 ; Hammar Chiriac and Granström, 2012 ). Working as a group is characterized by common effort, utilization of the group’s competence, and includes problem solving and reflection. All group members are involved in and working on a common task to produce a joint outcome ( Bennet and Dunne, 1992 ; Galton and Williamson, 1992 ; Webb and Palincsar, 1996 ; Hammar Chiriac, 2011a , b ). According to the results, not all groups are working as a group but rather working in a group, which, according to Granström (2006) , is common in an educational setting.
Due to problems with group composition, members’ contributions, and group structure, including rules and ways of cooperation, some students end up with negative experiences of group work. Additionally, the university students allude to the fact that a well-functioning supportive study-social context is an essential prerequisite not only for positive experiences of group work, but also for learning ( Hammar Chiriac and Hempel, 2013 ). Both working in a group and working as group might be useful in different parts of the group work ( Hammar Chiriac, 2008 ) and cause learning. Hence working in a group causes cooperative learning based on social facilitation ( Zajonc, 1980 ; Baron, 1986 ; Uziel, 2007 ) while working as group causes learning benefits through collaboration with other group members. Although both approaches might cause positive or negative experiences, a conceivable interpretation is that working as a group has a greater potential to enhance positive experiences. The findings suggest a need for further research to fully understand why some group work causes positive experiences and other instances of group work cause negative experiences.
The findings in the current study develop the findings from Hammar Chiriac and Einarsson (2007) . First, it shows that it is possible to assemble all groups in to a joint research group (see below). Second, a thorough reanalysis, using an inductive qualitative content analysis, resulted in the emergence of three different abstractions: learning, study-social function, and organizations as either facilitating or hampering learning, and experiences.
Methodological Considerations
There are some limitations in the current study and most of them have to do with the construction of the study-specific, semi-structured questionnaire. First, the questions do not discriminate between (a) the type of group work, (b) the purpose with the group work, (c) the structure of the group work (i.e., extent and/or time); or (d) ways of working in the group (i.e., cooperation or collaboration). Second, the design of the questionnaire does not facilitate comparison between the populations included in the group. The questionnaire treated group work as one activity and did not acknowledge that group work can serve different functions and include various activities ( Hammar Chiriac, 2008 ). This simplification of the phenomena group work causes criticism concerning whether or not it is possible to assemble these populations into a joint research group. An elaborated description of the analysis process and the comparison to three background variables has been used to counter this criticism. The thin results from the comparison, indicate that based on the question used in the study-specific questionnaire, it is possible to assemble the results into a corpus of joint results.
Conclusion/Concluding Remarks
The results indicate that most of the students’ experienced that group work facilitated learning, especially concerning academic knowledge. Three important prerequisites (learning, study-social function, and organization) for group work that serve as an effective pedagogy and as an incentive for learning were identified and discussed. All three abstractions either facilitated or hampered university students’ learning, as well as their experiences of group work. By listening to the university students’ voices and elucidating their experiences and conceptions, we have been able to add new knowledge and understanding of what the essence is behind successful group work in higher education. Furthermore, the students’ explanations of why some group work results in positive experiences and learning, while in other cases, the result is the opposite, can be of use for further development of group work as a pedagogical practice.
Conflict of Interest Statement
The author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
The author acknowledges Ph.D. Faculty Program Director, Charlotta Einarsson, for her contribution to the design of this study and contribution to early stages of the data analysis and manuscript.
American Psychological Association (APA). (2002). The Ethical Principles of Psychologists and Code of Conduct . Available at: http://www.apa.org/ethics/code2002.html
Baines, E., Blatchford, P., and Chowne, A. (2007). Improving the effectiveness of collaborative group work in primary schools: effects on science attainment. Br. Educ. Res. J. 33, 663–680. doi: 10.1080/01411920701582231
CrossRef Full Text
Barett, M. (2007). “Practical and ethical issues in planning research,” in Research Methods in Psychology , eds G. Breakell, S. Hammond, C. Fife-Schaw, and J. A. Smith (London: Sage Publications), 24–48.
Baron, R. S. (1986). Distraction-conflict theory: progress and problems. Adv. Exp. Soc. Psychol. 19, 1–40. doi: 10.1016/S0065-2601(08)60211-7
Bennet, N., and Dunne, E. (1992). Managing Classroom Groups. Hemel Hempstead: Simon & Schuster Education.
Blatchford, P., Kutnick, P., Baines, E., and Galton, M. (2003). Toward a social pedagogy of classroom group work. Int. J. Educ. Res. 39, 153–172. doi: 10.1016/S0883-0355(03)00078-8
Breakwell, G. M., and Hammond, F., Fife-Schaw, C., and Smith, J. A. (eds). (2006). Research Methods in Psychology . London: Sage Publications.
British Psychology Society (BPS). (2004). Code of Conduct, Ethical Principles, and Guidelines . Available at: http://www.bps.org.uk/document-download-area/document-download.cfm?file_uuid=6D0645CC-7E96-C67F-D75E2648E5580115&ext=pdf
British Psychology Society (BPS). (2006). Code of Ethics and Conduct . Available at: http://www.bps.org.uk/the-society/code-of-conduct/code-of-conduct_home.cfm
Bryman, A. (2012). Social Research Methods . Oxford: University Press.
Cantwell, R. H., and Andrews, B. (2002). Cognitive and psychological factors underlying secondary school students’ feeling towards group work. Educ. Psychol. 22, 75–91. doi: 10.1080/01443410120101260
Elo, S., and Kyngäs, H. (2007). The qualitative content analysis process. J. Adv. Nurs. 62, 107–115. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2648.2007.04569.x
Pubmed Abstract | Pubmed Full Text | CrossRef Full Text
Galton, M., and Williamson, J. (1992). Group Work in the Primary Classroom . London: Routledge.
Galton, M. J., Hargreaves, L., and Pell, T. (2009). Group work and whole-class teaching with 11–14-years-old compared. Cambridge J. Educ . 39, 119–147. doi: 10.1080/03057640802701994
Gillies, R. M. (2003a). The behaviours, interactions, and perceptions of junior high school students during small-group learning. J. Educ. Psychol. 95, 137–147. doi: 10.1037/0022-0663.95.1.137
Gillies, R. M. (2003b). Structuring cooperative group work in classrooms. Int. J. Educ. Res. 39, 35–49. doi: 10.1016/S0883-0355(03)00072-7
Gillies, R. M., and Boyle, M. (2010). Teachers’ reflections on cooperative learning: Issues of implementation. Teach. Teach. Educ. 26, 933–940. doi: 10.1016/j.tate.2009.10.034
Gillies, R. M., and Boyle, M. (2011). Teachers’ reflections on cooperative learning (CL): a two-year follow-up. Teach. Educ. 1, 63–78. doi: 10.1080/10476210.2010.538045
Graneheim, U. H., and Lundman, B. (2003). Qualitative content analysis in nursing research: concepts, procedures and measures to achieve trustworthiness. Nurse Educ. Today 24, 105–112. doi: 10.1016/j.nedt.2003.10.001
Granström, K. (2006). “Group phenomena and classroom management in Sweden,” in Handbook of Classroom Management: Research, Practice, and Contemporary Issues , eds C. M. Evertson and C. S. Weinstein (Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum), 1141–1160.
Hammar Chiriac, E. (2008). A scheme for understanding group processes in problem-based learning. High. Educ. 55, 505–518. doi: 10.1007/s10734-007-9071-7
Hammar Chiriac, E. (2010). “Group work is not one, but a great many processes – understanding group work dynamics,” in Group Theory: Classes, Representation and Connections, and Applications , ed. C. W. Danellis (New York: Nova Science Publishers, Inc.), 153–166.
Hammar Chiriac, E. (2011a). Research on Group Work in Education . New York: Nova Science Publishers, Inc.
Hammar Chiriac, E. (2011b). “Research on group work in education,” in Emerging Issues in Compulsory Education [Progress in Education. Volume 20 ], ed R. Nata (New York: Nova Science Publishers, Inc.), 25–44.
Hammar Chiriac, E., and Einarsson, C. (2007). “Is the grass greener in the other group? Students’ experiences of group-work” [“Är gräset grönare i den andra gruppen? Studenters erfarenheter av grupparbete”] [Published in Swedish], in Interaction on the Edge 2. Proceedings from the 5th GRASP Conference , ed. J. Näslund (Linköping: Linköping University).
Hammar Chiriac, E., and Granström, K. (2012). Teachers’ leadership and students’ experience of group work. Teach. Teach. Theor. Pract. 3, 345–363. doi: 10.1080/13540602.2012.629842
Hammar Chiriac, E., and Hempel, A. (2013), Handbook for Group Work [Published in Swedish: Handbok för grupparbete – att skapa fungerande grupper i undervisningen] . Lund: Studentlitteratur.
Hansen, R. S. (2006). Benefits and problems with student teams: suggestions for improving team projects. J. Educ. Bus. 82, 11–19. doi: 10.3200/JOEB.82.1.11-19
Johnson, D. W., and Johnson, R. T. (1975). Learning Together and Alone. Cooperative, Competitive and Individualistic Learning (Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall).
Johnson, D. W., and Johnson, R. T. (2004). Assessing Students in Groups: Promoting Group Responsibility and Individual Accountability . Thousand Oaks: Sage.
Kutnick, P., and Beredondini, L. (2009). Can the enhancement of group work in classrooms provide a basis for effective communication in support of school-based cognitive achievement in classrooms of young learners? Cambridge J. Educ . 39, 71–94. doi: 10.1080/03057640902836880
Lou, Y., Abrami, P. C., Spence, J. C., Poulsen, C., Chambers, B., and d’Apllonia, S. (1996). Within-class grouping: a meta analysis. Rev. Educ. Res. 66, 423–458. doi: 10.3102/00346543066004423
Mayring, P. (2000). Qualitative Content Analysis. Forum: Qualitative Social Research 1:2. Available at: http://qualitative-research.net/fqs/fqs-e/2-00inhalt-e.htm_140309
Näslund, J. (2013). “Pupils’ and students’ view on group work” [Published in Swedish: Elevers och studenters syn på grupparbete] in Handbook for Group Work [Published in Swedish: Handbok för grupparbete – att skapa fungerande grupper i undervisningen] , eds E. Hammar Chiriac and A. Hempel (Lund: Studentlitteratur), 233–242.
Peterson, S, and Miller, J. A. (2004). Quality of college students’ experiences during cooperative learning. Soc. Psychol. Learn. 7, 161–183.
Underwood, J. D. M. (2003). Student attitudes towards socially acceptable and unacceptable group working practices. Br. J. Psychol. 94, 319–337. doi: 10.1348/000712603767876253
Uziel, L. (2007). Individual differences in the social facilitation effect: a review and meta-analysis. J. Res. Person. 41, 579–601. doi: 10.1016/j.jrp.2006.06.008
Webb, N. M., and Palincsar, A. S. (1996). “Group processes in the classroom,” in Handbook of Educational Psychology , eds D. C. Berliner and R. C. Calfee (New York: Macmillan), 841–873.
Zajonc, R. B. (1980). “Compresence,” in Psychology of Group Influence , ed. P. B. Paulus (New York, NY: Lawrence Erlbaum), 35–60.
Keywords : group work, collaborative learning, cooperative learning, higher education, students’ perspectives, qualitative research
Citation: Hammar Chiriac E (2014) Group work as an incentive for learning – students’ experiences of group work. Front. Psychol. 5 :558. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2014.00558
Received: 30 Mar 2014; Accepted: 20 May 2014; Published online: 05 June 2014.
Reviewed by:
Copyright © 2014 Hammar Chiriac. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY) . The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) or licensor are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Eva Hammar Chiriac, Division of Psychology, Department of Behavioural Sciences and Learning, Linköping University, SE-581 83 Linköping, Sweden e-mail: [email protected]
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
- Entertainment
- Environment
- Information Science and Technology
- Social Issues
Home Essay Samples Business Teamwork
My Experience Working in a Group: a Reflection
Table of contents, challenges of group work, benefits and learning opportunities, lessons learned.
- Johnson, D. W., & Johnson, R. T. (2009). An educational psychology success story: Social interdependence theory and cooperative learning. Educational researcher, 38(5), 365-379.
- Belbin, R. M. (2012). Team roles at work. Taylor & Francis.
- Tuckman, B. W. (1965). Developmental sequence in small groups. Psychological Bulletin, 63(6), 384-399.
- Forsyth, D. R. (2014). Group dynamics (6th ed.). Cengage Learning.
- Katzenbach, J. R., & Smith, D. K. (2015). The wisdom of teams: Creating the high-performance organization. Harvard Business Review Press.
*minimum deadline
Cite this Essay
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing style below

- New Product Development
- Strategic Planning
- Democratic Leadership
- Management By Objectives
Related Essays
Need writing help?
You can always rely on us no matter what type of paper you need
*No hidden charges
100% Unique Essays
Absolutely Confidential
Money Back Guarantee
By clicking “Send Essay”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement. We will occasionally send you account related emails
You can also get a UNIQUE essay on this or any other topic
Thank you! We’ll contact you as soon as possible.
The Psychology of Teamwork: 7 Habits of Highly Effective Teams

These are the outcomes of working as a team, whether in business or on the sports field. Yet teamwork comes with its own set of challenges.
Would you like to know how to leverage the many benefits of teamwork?
Yet avoid its pitfalls, such as lack of communication, poor trust, and personality clashes among team members?
Then this article is for you, as we explore the psychology of teamwork and share actionable habits that can build highly effective teams.
Before you continue, we thought you might like to download our three Work & Career Coaching Exercises for free . These detailed, science-based exercises will help you or your clients identify opportunities for professional growth and create a more meaningful career.
This Article Contains:
The psychology of teamwork: what makes an effective team, 7 habits of highly effective teams, 2 real-life examples of effective teamwork, 10 barriers to teamwork, 10 team-building skills for successful teams, resources from positivepsychology.com, a take-home message.
Psychological theory, research, and models provide valuable insights and guidance into effective team building and maintenance in various workplace settings, including schools, hospitals, corporate offices, oil rigs, power plants, and the military (Salas et al., 2018).
Psychology has come a long way in understanding such complex groups—as recognized by a special issue on the “ Science of Teamwork ” in the American Psychological Association’s flagship journal American Psychologist in 2018.
Teams are vital and commonplace. Because of their prevalence and impact, “our safety, security, comfort, and innovation depend on good teamwork and collaboration” (Salas et al., 2018, p. 593).
Innovation is often the result of constant communication and side-by-side work and takes place “when collaboration translates each person’s creativity into group genius” and conflict is avoided (Sawyer, 2007, p. 13).
But then, what are teams exactly, and how do we define them?
Teamwork definition
We must begin by understanding what defines a “group.” Within an organization, a group is more than simply a collection of people. Members recognize themselves as a social entity that (Davenport, 2009):
- Interacts with each of its members
- Is psychologically aware of each of its members
- Perceives itself as a group
And yet, teams go further. They share a common goal. With the modern workplace demanding successful partnering across functional and geographical divides, fostering collaborative team working cultures becomes increasingly vital (Davenport, 2009).
Therefore, an effective team has the following attributes (Davenport, 2009):
- Clear understanding of the team’s objectives and goals
- Range of skills and know-how among team members to handle tasks effectively
- Variety of personality types and strengths among its team members
- High degree of respect and trust, both individually and for each other’s contributions to team performance
- An effective recognition and reward system
The points above are helpful because they enable us to distinguish between people working together in groups and those forming effective teams.
When considered together, it’s possible to arrive at the following teamwork definition: “Teamwork can be defined as the ability of team members to work together, communicate effectively, anticipate and meet each other’s demands, and inspire confidence, resulting in a coordinated collective action” (Salas & Cannon-Bowers, 2001, extract).
And a definition of team building might arise as follows:
“Team building is an ongoing process that helps a work group evolve into a cohesive unit. The team members not only share expectations for accomplishing group tasks, but trust and support one another and respect one another’s individual differences” (Team building: Introduction, n.d., para. 1).
Understanding the psychology of group dynamics
“We know what effective teams do, think, and feel. We know what influences team dynamics, and some interventions that help develop teamwork” (Salas et al., 2018, p. 593).
Psychological research has confirmed that the following elements are the minimum prerequisites for an effective team:
- Strong team leadership
- Role clarity
- Mutual trust
- Sound information exchange protocols
- A compelling reason to be a team
Team psychology in the workplace
Several psychological and organizational models and frameworks have grown out of the need to understand and explain how teams form, grow, develop, maintain, and change in the workplace.
The following three early models are valuable for our current understanding of how effective teams evolve (Davenport, 2009).
Bass and Ryterband’s model
Bass and Ryterband’s (1979) model of team development includes four stages and areas of focus:
- First stage: Building trust among team members
- Second stage: Open communication, problem-solving, and decision-making
- Third stage: Motivation and productivity of the team
- Fourth stage: Control and organization where members can work independently
Woodcock’s model
Woodcock’s (1979) model of team development also has four stages:
- The undeveloped team: Unclear objectives, established policies, and a lack of shared understanding prevail. Mistakes are used to blame others.
- The experimenting team: The team is willing to take risks and includes more active listening and short periods of group introspection.
- The consolidating team: The team adopts a systematic approach. Rules and procedures are agreed upon, and improved relationships and methods from the previous stage are maintained.
- The mature team: The team achieves high flexibility and appropriate leadership for different situations, and prioritizes development for continued success. Trust, openness, honesty, cooperation, confrontation, and reviewing results become the norm.
Tuckman’s model
Tuckman’s (1965) model of team development includes five stages:
- Forming During the initial stage, team members come together. They may be anxious and unsure, and there are few rules.
- Storming This is the stage of disagreement, including frustration and potential confrontation, where team members are more confident to express themselves and challenge each other.
- Norming This is when group identity, guidelines, and norms are established. Emotions are expressed constructively.
- Performing The team has created structure and cohesiveness to work effectively and can now concentrate on achieving its objectives.
- Adjourning In this final stage, the team reflects on their time together and may disband.
Sports psychology
As with individuals, team performance in sports can benefit from time spent building psychological capital , which comprises four key elements (Luthans et al., 2015):
- Self-efficacy
Furthermore, according to positive psychology consultant and performance coach John Yeager, sports teams collectively benefit from coaching focused on each element to build the psychological capital required to boost their combined performance.
Once achieved, they “maintain a healthy culture and find an effective balance between holding athletes accountable and supporting each other” (Yeager, 2021, p. 223).
Recommended read: Positive Psychology in the Workplace

Keith Sawyer (2007, p. 13), a psychologist at Washington University, says that his research shows “the secret to understanding what makes a collaboration successful lies inside the box, in moment-to-moment interactional dynamics.”
This understanding led him to rethink group innovation and creativity, identifying the following seven key characteristics (or habits) of effective, creative teams along with suggested actions for moving innovation forward (Sawyer, 2007):
- Innovation emerges over time. Successful innovation requires its members to combine the right ideas in an appropriate structure, bit by bit.
ACTION: Encourage team members to take time each day/week to brainstorm and share new ideas and establish a structure for combining and building on those ideas over time .
- Successful collaborative teams practice deep listening. Team members often spend too much time planning what they will say and how to respond in meetings and too little time listening to and observing others.
ACTION: Prioritize active listening and observation during team meetings and discussions. And provide opportunities for team members to practice deep listening skills .
- Team members build on their collaborators’ ideas. Through deep listening, team members take on and evolve each idea further.
ACTION: Recognize the potential of other team members’ ideas and accept the importance of collective ownership to drive forward problem-solving .
- Only afterward does the meaning of each idea become clear. While it’s tempting to attribute an idea to one person, its full importance results from being taken up, reinterpreted, and applied by the whole team. “Participants are willing to allow other people to give their action meaning by building on it later” (Sawyer, 2007, p. 15).
ACTION: Emphasize the importance of evolving and adapting ideas as a team, rather than attributing them to one individual .
- Surprising questions emerge. “The most transformative creativity results when a group either thinks of a new way to frame a problem or finds a new problem that no one has noticed before” (Sawyer, 2007, p. 16).
ACTION: Encourage team members to question assumptions and think outside the box by regularly posing surprising or unconventional questions during meetings and discussions .
- Innovation is inefficient. Improvised innovation will make more mistakes, but it can be phenomenal when the team gets a hit.
ACTION: Recognize that innovation can be inefficient and messy but emphasize the potential for breakthroughs .
- Innovation emerges from the bottom up. Teams start with the detail, improvise innovation, then work up to the big picture.
ACTION: Foster a bottom-up approach to innovation, starting with small details and building toward the bigger picture .
While all seven are characteristics of an effective team, they are also actionable tasks within the process where team members play off each other (Sawyer, 2007).

The New Low-Effort, High-Impact Wellbeing Program.
Wellbeing X© is a seven-session, science-based training template. It contains everything you need to position yourself as a wellbeing expert and deliver a scalable, high-impact program to help others develop sustainable wellbeing.
The following are two high-profile examples of the immense potential of effective teamwork, especially when the stakes are high (Keup, 2022; Allen, 2022).
One giant leap for humankind
The Apollo 11 mission in 1969 is a prime example of teamwork at its finest.
While the world celebrated the achievement of Neil Armstrong, Buzz Aldrin, and Michael Collins, the success of the mission resulted from the efforts of a much larger team.
The mission planners, scientists, engineers, and technicians, numbering around 400,000, worked tirelessly for years to make the moon landing a reality. The team’s cohesion was strengthened by the astronauts’ close collaboration with these groups, emphasizing the importance of human connection in any team.

World’s Largest Positive Psychology Resource
The Positive Psychology Toolkit© is a groundbreaking practitioner resource containing over 500 science-based exercises , activities, interventions, questionnaires, and assessments created by experts using the latest positive psychology research.
Updated monthly. 100% Science-based.
“The best positive psychology resource out there!” — Emiliya Zhivotovskaya , Flourishing Center CEO
Wikipedia is the epitome of teamwork in the digital age. It’s a collaborative engine of knowledge that is constantly evolving, thanks to the efforts of an army of volunteer writers and editors.
Unlike traditional encyclopedias, Wikipedia is constantly updated and open to debate and challenge, making it a dynamic and accurate source of information.
While the scale of this teamwork is almost incomprehensible, the site runs smoothly, with errors quickly discovered and corrected. Everyone who has landed on the site is considered a part of the team, making Wikipedia a perfect example of how teamwork can achieve great things in the digital age.
5 Traits of high performing teams
Understanding what stops or limits individual and group performance can help us build and maintain motivated, resilient, and highly effective teams.
The following 10 barriers can present themselves in real-world team environments (Haas & Mortensen, 2016):
- Poor understanding of roles and responsibilities Team members may not fully understand their roles and responsibilities, leading to confusion and lack of accountability.
- Insufficiently defined goals and objectives Team members may not clearly identify what they are working toward, leading to uncertainty and lack of motivation.
- Poor decision-making processes Teams may lack effective decision-making techniques and strategies, leading to delays and suboptimal outcomes.
- Resistance to change Team members may resist change, leading to a lack of flexibility and stagnation.
- Lack of accountability and ownership Team members may not feel accountable for their work and the team’s success.
- Lack of resources or support Teams may not have the necessary resources and support from leadership to achieve their goals effectively.
- Inadequate leadership Teams may not have effective leadership, leading to a lack of direction and guidance.
- Groupthink Team members may be reluctant to challenge the opinions and ideas of others, leading to poor decision-making and an absence of creative thinking.
- Lack of trust and psychological safety among team members Team members may be hesitant to share their ideas and concerns due to a lack of trust in their colleagues or fear of being judged and rejected.
- Inadequate communication Team members may not be effectively communicating with each other, leading to misunderstandings and conflicting priorities.

- Clear communication Encourage team members to speak openly and honestly and actively listen to one another’s ideas and perspectives. Provide training and resources to help team members improve their communication skills.
- Trust and accountability Create an environment where team members feel safe to take risks and be vulnerable with one another. Hold team members accountable for their actions and decisions and provide them with the support and resources they need to succeed.
- Adaptability and flexibility Encourage team members to be open to new ideas and ways of working. Be willing to pivot and change course when necessary.
- Emotional intelligence Provide training and resources to help team members better understand and manage their own emotions and those of others.
- Active listening Encourage team members to fully engage, pay attention to what others are saying, and respond thoughtfully.
- Conflict resolution Teach team members how to navigate and resolve conflicts constructively and effectively.
- Goal alignment Ensure that individual goals align with the team’s overall objectives and that everyone works toward a common purpose.
- Delegation Teach team members how to assign tasks and responsibilities to one another effectively to maximize their strengths and capabilities.
- Problem-solving Teach team members how to identify problems and develop practical solutions.
- Empowerment and autonomy Give team members the freedom and support they need to take ownership of their work and make decisions. Provide regular feedback and coaching to help them improve their skills and advance in their careers.
We have many practical resources for you as a manager or leader supporting your team as they form, develop, and attempt to avoid some challenges of group dynamics.
Our free resources include the following:
- GROW model Use the power of the GROW model to define team goals and boost motivation and cohesion.
- Do the Hula In this novel and fun exercise , the group learns the value of team cooperation.
- Stepping Forward Use this activity to begin and end team building by clarifying expectations for the day.
Our Emotional Intelligence Masterclass© helps boost teamwork by teaching staff to handle emotions better. The training improves communication, relationships, decision-making, job satisfaction, motivation, and overall wellbeing. It also enhances the emotional intelligence of the coach, making them better equipped to lead teams.
The Positive Relationships Masterclass© strengthens teamwork using the “Six Pillars of Positive Relationships.” It offers practical techniques to enhance communication and maintain healthy relationships, leading to improved coaching skills and a thriving workplace.
You will learn the key aspects of positive relationships and explore science-based ways to categorize the different types of positive network members and grow social capital.
Not only that, but we also have specific articles that delve into team-building topics; for example:
- 15 Communication Exercises and Games for the Workplace
- Active Listening: The Art of Empathetic Conversation
- The Importance, Benefits, and Value of Goal Setting
And lastly, if you’re looking for more science-based ways to help your team develop their strengths, check out this collection of 17 strength-finding tools . Use them to help others better understand and harness their strengths in life-enhancing ways.
Research in the psychology of teamwork has shown that effective collaboration can lead to improved productivity, creativity, and job satisfaction among team members (Sawyer, 2007; Salas et al., 2018).
When teams experience a sense of belonging and purpose in their work, they are more likely to achieve their goals and be motivated to perform at their best. It can also lead to improved organizational outcomes, such as achieving goals, making better decisions, and providing higher levels of customer service.
Great teamwork relies on successful team building—the process of creating a cohesive, high-performing team capable of working together successfully. Effective team building can reduce conflicts, turnover, and absenteeism among its members by fostering a positive culture and improving overall morale.
As a manager, you can encourage the best out of your teams by creating a supportive and inclusive environment, encouraging clear communication, and promoting trust, accountability, and active listening.
Additionally, you can provide training and resources to help team members develop the skills they need to work well together, such as problem-solving, conflict resolution , and emotional intelligence. In our resources section, we provide a recommended selection of free and paid resources—all well worth it to build your own highly effective team.
We hope you enjoyed reading this article. Don’t forget to download our three Work & Career Coaching Exercises for free .
- Allen, V. (2022). Teams that changed the world . WorkStyle. Retrieved January 20, 2023, from https://www.workstyle.io/top-performing-team-case-studies.
- Bass, B. M., & Ryterband, E. C. (1979). Organizational psychology (2nd ed.). Allyn & Bacon.
- Boogaard, K. (2022). 7 essential teamwork skills . Work Life by Atlassian. Retrieved January 23, 2023, from https://www.atlassian.com/blog/teamwork/teamwork-skills-accelerate-career/amp
- Davenport, H. (2009). Groups and teams. In I. Brooks (Ed.), Organisational behaviour: Individuals, groups and organisation (pp. 111–155). Essay, Pearson.
- Haas, M., & Mortensen, M. (2016). The secrets of great teamwork . Harvard Business Review. Retrieved January 20, 2023, from https://hbr.org/2016/06/the-secrets-of-great-teamwork.
- Keup, M. (2022). 9 inspirational teamwork examples . ProjectManager. Retrieved January 20, 2023, from https://www.projectmanager.com/blog/teamwork-examples.
- Luthans, F., Youssef, C. M., & Avolio, B. J. (2015). Psychological capital and beyond . Oxford University Press.
- Sawyer, K. (2007). Group genius . Basic Books.
- Salas, E., & Cannon-Bowers, J. A. (2001). Teamwork and team training. In N. J. Smelser & P. B. Baltes (Eds.), International encyclopedia of the social & behavioral sciences (pp. 15487–15492). Elsevier.
- Salas, E., Reyes, D. L., & McDaniel, S. H. (2018). The science of teamwork: Progress, reflections, and the road ahead. American Psychologist , 73 (4), 593–600.
- Steps to building an effective team. (n.d.). Retrieved January 23, 2023, from https://hr.berkeley.edu/hr-network/central-guide-managing-hr/managing-hr/interaction/team-building/steps.
- Team building: Introduction. (n.d.). Retrieved January 24, 2023, from https://hr.berkeley.edu/hr-network/central-guide-managing-hr/managing-hr/interaction/team-building/introduction.
- Tuckman, B. W. (1965.) Development sequence in small groups. Psychological Bulletin , 63, 384–399.
- Woodcock, M. (1979). Team development manual . Gower.
- Yeager, J. (2021). The coaching zone: Next level leadership in sports . Yeager Leadership Press.
Share this article:
Article feedback
What our readers think.
interesting and well organized food for thought
Some practical examples of effective teams- Love the 7 habits links
Nice article, thank you! Well, I think a strong team consists of strong individuals that are aware of their impact on the company.
Very helpful with the work I do dealing with grief counseling.
Going to use with my sporting team as a new coach
Let us know your thoughts Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Related articles

Company Culture: How to Create a Flourishing Workplace
Company culture has become a buzzword, particularly in the post-COVID era, with more organizations recognizing the critical importance of a healthy workplace. During the Great [...]

Integrity in the Workplace (What It Is & Why It’s Important)
Integrity in the workplace matters. In fact, integrity is often viewed as one of the most important and highly sought-after characteristics of both employees and [...]

Neurodiversity in the Workplace: A Strengths-Based Approach
Promoting diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI) in the workplace is a priority for ethical employers who want to optimize productivity and leverage the full potential [...]
Read other articles by their category
- Body & Brain (52)
- Coaching & Application (40)
- Compassion (23)
- Counseling (41)
- Emotional Intelligence (22)
- Gratitude (18)
- Grief & Bereavement (18)
- Happiness & SWB (40)
- Meaning & Values (26)
- Meditation (16)
- Mindfulness (40)
- Motivation & Goals (41)
- Optimism & Mindset (29)
- Positive CBT (28)
- Positive Communication (23)
- Positive Education (36)
- Positive Emotions (33)
- Positive Leadership (16)
- Positive Parenting (14)
- Positive Psychology (21)
- Positive Workplace (35)
- Productivity (16)
- Relationships (46)
- Resilience & Coping (39)
- Self Awareness (21)
- Self Esteem (37)
- Strengths & Virtues (30)
- Stress & Burnout Prevention (33)
- Theory & Books (43)
- Therapy Exercises (38)
- Types of Therapy (55)

Save 60% for a limited time only →
[New!] Wellbeing X©. The low-effort, high-impact wellbeing program.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Individuals who value working in groups tend to be both more confident and more cooperative in a team setting. When team members are high in conscientiousness, they are better at self-regulating their teamwork.
This essay will delve deeper into the benefits of group work, supported by academic theories, and will also address the reasons why some individuals may prefer working alone. The Benefits of Group Work. One of the primary advantages of group work is the plethora of ideas generated.
Below, Dr. Romanoff explains why teamwork is important and the benefits it can offer: Improves efficiency and output: Teamwork is important because much more can be accomplished as part of a team than a single person working alone. Successful teams are much more efficient and effective at completing tasks than individuals.
In this article, I reflect on the impetus, strategy, key features, and scientific contribution of “Enhancing the Effectiveness of Work Groups and Teams,” by Kozlowski and Ilgen, a review monograph published in Psychological Science in the Public Interest in 2006.
What are the benefits of group work? “More hands make for lighter work.” “Two heads are better than one.” “The more the merrier.” These adages speak to the potential groups have to be more productive, creative, and motivated than individuals on their own.
The Power of Teamwork. Few people realize that a group can accomplish what an individual alone cannot do — even when it comes to individual advancement.
When you’re trying to get something done, working in a group promises many positive possibilities, among them being the following: The group will most likely have access to much more information than any member possesses. The group can focus multiple attentions and diverse energy on a topic.
There is strong scientific support for the benefits of having students learning and working in groups. Nevertheless, studies about what occurs in groups during group work and which factors actually influence the students’ ability to learn is still lacking.
Group work is a ubiquitous aspect of education, professional settings, and even social engagements. In this essay, I will delve into the various facets of group work based on my own encounters, highlighting its challenges, benefits, and lessons that can be gleaned from such experiences. Challenges of Group Work
7 Habits of Highly Effective Teams. 2 Real-Life Examples of Effective Teamwork. 10 Barriers to Teamwork. 10 Team-Building Skills for Successful Teams. Resources From PositivePsychology.com. A Take-Home Message. References. The Psychology of Teamwork: What Makes an Effective Team?