
- Tutoring Coming Soon

3CO01 Assignment Example
- October 6, 2022
- Posted by: Harry King
- Category: CIPD Level 3

What is meant by workplace culture, and why it is important to foster an appropriate and effective workplace culture? (AC 2.1)
Workplace culture refers to the environment created for employees, translating to the organisation’s personality or character, determining employees’ relationships and career progression (Rosenbaum et al., 2018). Consequently, a positive workplace culture fosters engagement, attracts talent, achieves job satisfaction and happiness, and impacts performance. Many factors influence the personality of an organisation, including workplace practices, management, leadership, policies and people (Hayes, 2018). Influential workplace culture is crucial for several reasons:
- It attracts and retains talent.
As employees spend more time working than at home, they naturally prioritise working in an environment in which they enjoy spending time. Culture and engagement are the highest priorities on the corporate agenda, with organisations that demonstrate the most robust cultures having a higher capacity to attract and retain talent (Dzwigol et al., 2019).
- It fosters engagement and retention.
Replacing talent comes at a high cost, and thus, the organisation must prioritise its workplace culture, which is instrumental in keeping these employees engaged at work. Workplace culture provides employees with a better understanding of what is expected of them and how to attain their professional goals; it allows employers to keep talented employees on board longer (Hayes, 2018).
- It cultivates an environment for healthy development
A strong workplace culture allows all stakeholders to initiate change and develop from a professional and personal standpoint. Moreover, it encourages employees to communicate their opinions and pursue values that they find essential (Rosenbaum et al., 2018).
- It yields satisfied employees and fosters productivity
A positive workplace culture generates happy employees, increasing their interest in their day-to-day tasks and responsibilities. A positive work environment is conducive for employees’ concentration, and therefore, translates to increased productivity levels (Hayes, 2018).
How organisations are whole systems, and how work and actions as a people professional could impact elsewhere. (AC 2.2)
How organisations are whole systems in which different areas and aspects such as structure, systems, and culture are interrelated.
Organisations comprise smaller, interconnected entities that perform specialised functions. Specialised functions are ultimately reintegrated into an effective organisational whole in various ways. The importance of viewing organisations as complex systems is that systems concepts provide insight into how they operate. Understanding the organisation as a whole is critical for adequately determining information specifications and designing suitable information systems (Dzwigol et al., 2019). Organisation units may be viewed as adaptive whole sub-systems with their emergent properties (Hayes, 2018). These components share a common purpose and resources and are primarily driven by organisational culture. Ultimately, understanding the purpose and mission of the system and its relationship to its environment is critical for adequately determining certain sub-system specifications and designing an optimal organisational structure, functions, and sub-systems.
An example of how good people practice and an example of how bad people practice can impact other parts of the organisation or beyond the organisation.
All systems and sub-systems are interconnected and interdependent. This fact has significant consequences for both organisations and the systems analysts who work to assist them in achieving their objectives. When one aspect of a system is altered or removed, this significantly impacts the rest of the system’s elements and sub-systems. For instance, an organisation’s management may decide to stop recruiting administrative assistants and instead substitute them with networked PCs. This decision may tremendously impact administrative assistants and supervisors and all organisational stakeholders who established communication networks with the now-departed administrative assistants. This organisational change amounts to a bad people practice. On the other hand, the management may introduce new technology to enhance operations and employee retention. This practice translates to HR learning and development policy changes, yielding career development opportunities for junior employees through new training courses.
How individuals may learn and develop in different ways in organisations and how this might be accommodated in assessing and developing skills and capabilities. (AC 2.3)
Employees’ learning and development entail working with the staff to enhance, improve, refine, and hone existing skills while cultivating new ones in organisational goals, mission, and vision (Rosenbaum et al., 2018). Despite significant costs featuring in employee learning and development, these efforts yield long-term employee retention. Individuals may learn and develop in several ways:
- Blended learning
Specific skills can only be learned in person. This group includes skills that require physical action, e.g., running hardware equipment, and skills that rely on personal contact, e.g., sales techniques. The organisation’s training curriculum encompasses such skills, learning, and development that may be improved by adopting a blended training, Instructor-Led Training (ILT), alongside standard eLearning (Rosenbaum et al., 2018). ILT can include both teleconference sessions and traditional lectures. A modern eLearning platform, e.g., TalentLMS, allows combining these learning and development alternatives by seamlessly scheduling, managing, and monitoring ILT sessions with standard online training programs.
- Soft Skills Training
An effective learning and development program must balance hard technical skills training and cultivate soft skills such as time management, conflict resolution, and leadership (Jayatilleke and Lai, 2018). Soft skills training aligns with a blended learning approach, as various soft skills training entail cross-personal interaction and are challenging to implement in a standard online learning program. ILT tools such as teleconferences and in-person training are suitable for learning and development in a realistic context.
- Learning Paths
A learning path amounts to a collection of training courses. An effective learning and development program must offer multiple learning paths based on the skills and future career goals at hand (Rosenbaum et al., 2018). When designing an employee learning and development program, the organisations should begin with the job positions that require staff training and combine courses in ways that allow employees of varying learning levels to advance to higher roles (Jayatilleke and Lai, 2018). Here, it is critical to incorporate employee feedback. Learning paths may be accommodated in assessing and developing skills and capabilities by gathering input from regular employees via an organisation-wide survey and sitting with line managers and leaders to discuss mid-and long-term skill needs.
Why it is important for an organisation that change is predicted, planned and effectively managed? (AC 3.1)
The organisational change affects programs, structures, and procedures; it typically involves a significant shift in its strategy (Rosenbaum et al., 2018). The new strategy establishes how tasks, skills, and behaviours or working models will be redefined. Predicting change entails using relevant tools and techniques to forecast areas of organisational change such as industrial directions, operational expenditures, profits and losses, and sales. Predicting change aims to foster better strategies based on informed predictions (Hayes, 2018). Predicting change is critical as it offers the ability to make informed decisions and devise data-driven approaches. Therefore, financial and operational decisions are derivatives of current market conditions and predictions of the future.
The type of change in question and the reason for it informs how the organisation plans the change process. Developing a business case to outline and describe business changes explains changes to employees and keeps planning on track (Jayatilleke and Lai, 2018). A compelling business case for change is critical for navigating the change process and yields better time management once the process begins. Key elements to consider while planning for change include testing the change argument, listing the steps needed, setting and clarifying project goals, determining change management objectives, and identifying critical milestones.
Managing organisational change fosters increased employee morale and is a crucial driver of positive team building. Also, effective change management enables job satisfaction and, by extension, employee retention (Rosenbaum et al., 2018). These factors have a positive and direct impact on productivity and quality of work. Ultimately, effective change management shortens production cycles and minimises costs.
How change can impact people in organisations, such as changing their role or status or financial situation, and the different ways people may respond to change. (AC 3.3)
In any change situation, employees often experience challenges adjusting to the new norm. Thus, organisational change may impact people in several ways:
- Life changes resulting from restructuring
Some organisational changes translate to significant restructuring, yielding sweeping changes such as salary cuts, lost benefits, job downgrades, job loss, and relocation. These changes may have devastating effects, especially for employees who have dependents.
- Impeding social relations
Various elements of change implementation may impede social relations at the workplace. For instance, rearranging the collegial composition may translate to employees losing or being introduced to new co-workers, increased competition for the same positions during the restructuring process, or getting a new line manager. Thus, structural change may hamper workplace social cohesion and unity of direction (Jayatilleke and Lai, 2018).
- Decreased sense of job predictability
Employees’ sense of job predictability and future employability often decreases after specific organisational changes. Reduced job predictability means an attenuated ability to form reasonable expectations about the future concerning short-term job characteristics versus long-term employment prospects (Rosenbaum et al., 2018). Reduced job predictability is, thus, synonymous with job insecurity.
People may respond to change in three fundamental ways:
- Being non-active
This category of people is opposed to change and remains in denial. These people choose not to address the issue at hand and develop negative attitudes around change. For example, an employee may perceive a change as unfair, resisting the process by failing to undertake procedures that drive change forward.
- Being reactive
This category of people acts in response to the effects of change. For example, an employee may discover that they may lose their job through restructuring and visit various placement agencies but end up in a new job that does not fit their skills set.
- Being proactive and positive
This category of people embraces change as a necessary and inevitable process, actively planning to adapt to a new norm. People in this category have better control of the situation at hand as they are involved in predicting, planning, and managing change.
The nature and importance of different roles that people can play practice professionals concerning change agendas. You might consider roles such as gatekeeper, champion, facilitator, critical friend or record-keeper. (AC 3.2)
To manage change effectively, various people practice professionals must participate:
- Change Practitioners
Change practitioners employ a structured change management methodology, formulate strategy, design role-based and activity plans, and support other roles (Jayatilleke and Lai, 2018). This role is critical in providing focus and monitoring change management activities. This role serves to cultivate responsibility and accountability.
Sponsors visibly and actively participate throughout the project cycle, establish a support coalition, and communicate directly with employees (Rosenbaum et al., 2018). Effective sponsorship is critical in predicting the project’s success or failure. This role’s commitment to change inspires acceptance of change in employees and gives authority to the rest of the change management roles.
- People managers
People managers act as communicators, liaisons, advocates, resistance managers, and coaches (Jayatilleke and Lai, 2018). This role is critical as it comprises the members who must change how they execute their jobs to ensure successful change. People managers offer support to employees, and their attitudes and actions are depicted in their people.
- Project manager
A project manager designs the actual change, manages the technical part, engages the change practitioner, and integrates change management plans with the project plan (Rosenbaum et al., 2018). This role is critical as it concentrates on the project’s design, development, and implementation. In the absence of direction and management, the technical aspect of the project may not advance.
Reference List
Dzwigol, H., Shcherbak, S., Semikina, M., Vinichenko, O. and Vasiuta, V., 2019. Formation of Strategic Change Management System at an Enterprise. Academy of Strategic Management Journal, 18, pp.1-8.
Hayes, J., 2018. The theory and practice of change management. Palgrave.
Jayatilleke, S. and Lai, R., 2018. A systematic review of requirements change management. Information and Software Technology, 93, pp.163-185.
Rosenbaum, D., More, E. and Steane, P., 2018. Planned organisational change management: Forward to the past? An exploratory literature review. Journal of Organizational Change Management.

CIPD Level 3 Past Papers
Table of contents.
We can provide you with general guidance on how to prepare for your exams. Here are some tips that may help you:
- Review the CIPD Level 3 syllabus: Make sure you are familiar with the topics and modules covered in your course. This will help you focus your study efforts on the areas that are most important.
- Use the CIPD Level 3 learning resources: CIPD provides a range of resources, including textbooks, online learning materials, and webinars, which can help you prepare for your exams. Make use of these resources to reinforce your learning.
- Practice exam questions: Try to find past exam papers or practice questions that cover the topics you have studied. This will help you get a feel for the types of questions you can expect and give you an opportunity to practice your exam technique.
- Study regularly: Don’t wait until the last minute to start studying. Make a study plan and stick to it, reviewing your notes and reading materials regularly to reinforce your understanding.
- Seek support: If you are struggling with any of the topics, don’t hesitate to seek support from your tutors or fellow students. You can also join online discussion forums or study groups to share ideas and get feedback.
Remember, preparation is key to success in your exams. Good luck!
3CO01 Business, Culture and Change in Context
Task – information sheet.
In recent years, the environment in which organisations operate has been turbulent. People professionals have a key role in supporting and enabling the organisation to achieve its goals at time of greater or lesser stability. To ensure the people team have sufficient knowledge and understanding to do this, your manager has decided the team should have good knowledge of the external business environment, the organisation’s goals, its products/services and customers, organisational culture, and the importance of change management. Your manager has asked you to undertake some research, then share your learning with the rest of the team through an information sheet.
Your information sheet can be based on your own organisation or one(s) that you are familiar with, and should include the following:
- An examination of the key external influences impacting or likely to impact the organisation’s activities. (AC 1.1)
- A discussion of the organisation’s business goals and why it is important for organisations to plan for how they will achieve these. (AC 1.2)
- A discussion of the organisation’s products and/or services and main customers. (AC 1.3)
- A short review of different technologies available to people professionals and how these can be, or are, used to improve working practices and collaboration. You might consider for example, technologies relating to communications, information sharing, record keeping, learning, wellbeing, productivity, or security. (AC 1.4)
- What is meant by organisational culture and why it is important to foster an appropriate and effective workplace culture. (AC 2.1)
- How organisations are whole systems, in which different areas and aspects such as structure, systems and culture, are all inter-related, and how people professionals work and actions could impact elsewhere in the organisation. (AC 2.2)
- Why it is important that organisational change is planned, and effectively managed. (AC 3.1)
- The nature and importance of different roles that can be played by people practice professionals, in relation to change agendas. You might consider roles such as: gatekeeper, champion, facilitator, critical friend or record-keeper. (AC 3.2)
- How organisational change can impact people in different ways, such as changing their role or status or financial situation, and the different ways people may respond to change. (AC 3.3)
3CO02 Principles of Analytics
The presentation must provide knowledge and understanding of how evidence-based practice informs organisational measures and outcomes and how creating value benefits employees, customers and wider stakeholders. Ensure that you:
- define what is meant by evidence-based practice and how it is applied within organisations, providing three examples of different types of evidence-based practice that can be used to inform principle-led judgements and outcomes for an organisation. (1.1),
- explain the reasons why it is important to use data to help assist organisational improvements and why this data need to be timely, ethical and accurate. (1.2)
- explain two different types of data measurements and information that can be used by people professionals, and how they are each used to collect and collate information to support effective decision making. (1.3)
- explain how organisational policies, procedures and other forms of evidence can be used to support appropriate choices and decisions. (1.5)
- explain the range of internal and external customers and stakeholders, that people professionals work with, and the part that influencing plays within the relationships (2.1)
- explain what is meant by creating value as a people professional, and identify benefits of providing value to customers and stakeholders (2.2)
- drawing on good practice examples, explain how the work that people professionals perform benefits others within an organisation in supporting good practice, open cultures, commitment and engagement. (2.4)
- explain how social media can be used internally and externally in workplaces to improve communication and organisational practices, highlighting the risks in a work context. (2.3)
- outline how you can, in your own work or a voluntary role, achieve and maintain a customer focused attitude to ensure consistent high standards and customer satisfaction. (2.5)
Task Two Example of Analysis of Data to Inform Practice
A mini survey on the quality of work has recently been carried out as a pilot and the raw data from the first three departments, Research & Design, Administration and Marketing has just been collected. The People Practice manager has asked you to represent the data as percentages and analyse the survey results.
- Review the sets of raw numerical data that have been provided in the tables below and convert them to percentages to illustrate the results.
- Provide an analysis of these, identifying themes, patterns and trends that appear to be occurring. As a part of this analysis, consider the possible issues that have been revealed by the data.
Absence rates for each department over a three-month period as a total of hours based on a contractual week of 37.5 hours are as follows:
- Calculate how many working days are lost in a three-month period for each department based on the above figures.
- Estimate the projected average loss of working days over a 12-month period if these rates were to continue.
- Calculate the costs of pay assuming all absentees are contractually paid full remuneration whilst off sick during the three-month period. (1.4)
3CO03 Core Behaviours for People Professionals
Task one – ethical practice paper.
You are currently studying for your CIPD qualification at a local study centre. Your study group has been asked to provide information about the role of a People Practice Professional, for a careers platform, and you and your fellow learners have decided to each write about a different aspect of the role.
For your contribution, you have decided to write about ethics and how a people practice professional would demonstrate and promote ethical practice at work. Having discussed this idea with your tutor you have agreed to write a short paper, covering all 4 points below.
- Explain what is meant by ‘ethical principles’ and ‘professional values’, and how these might inform the way people approach their work. (AC 1.1)
- Identify a piece of legislation and a Code of Practice that support ethical and professional practice, with examples of how a people professional would conform to these. (AC 1.2)
- contributing views and opinions
- clarifying problems or issues
- working effectively as part of a team
- Summarise different ways a people professional would stay up-to-date with people practice and world of work issues and developments, highlighting 2 ways in particular, that you have personally found effective. (AC 2.2)
Task Two – Professional Development Record
A crucial aspect of being a People Practice professional is staying up to date with issues and developments and ensuring professional currency by regularly upgrading knowledge and skills. This task is about how you, personally, do this.
The task requires you to provide a record of how you have maintained and upgraded your own knowledge and skills, along with your reflections on how effective this has been. Your ‘record’ can be presented as a simple written account or as a formal CPD Record and should cover at least 3 activities undertaken within the last year. (AC 2.3)
To complete the task, provide a written account/CPD Record, in which you:
- Describe (at least 3) activities you have undertaken to develop your knowledge, skills, and experience over the last year. Activities may be, for example, formal development activities such as planned learning events or programmes, informal activities such as researching online or reading a book, work-based activities such as participating in a particular work project or simply putting yourself in a work role or position that you knew would stretch and develop you. The activities may have been in response to an identified performance issue or problem or may reflect a new area of interest for you. Your record should explain the reasons for your choice of activity as well as what the activity involved. (This is the WHY and the WHAT of your CPD Record.)
- Reflect on the outcomes of each activity and their impact on your practice. For example: did you gain a greater understanding of, or more knowledge about, something and if so, how has that actually impacted your behaviour? How are you, or is your performance, different because of the learning undertaken? Was the activity worth doing in terms of its impact on your behaviour or performance? Did the activity make you aware of, or maybe generate, other development needs? What conclusions did you draw from this for further activities? (This is the SO WHAT ! of your CPD Record.)
3CO04 Essentials of People Practice
Task one – briefing paper.
The People Manager asks you to prepare a briefing paper that will be used when they meet with line managers and introduce the services the new team will provide. The briefing paper should explain:
- the different stages of the employee lifecycle and the role of the people professionals in the lifecycle. (AC 1.1)
- different ways in which information for specified roles can be prepared. (AC 1.2)
- different recruitment methods and when is it appropriate to use them. (AC 1.3)
- factors to consider when deciding on the content of copy used in recruitment methods. (AC 1.4)
- different selection methods and when it is appropriate to use them. (AC 2.1)
- the selection records that need to be retained. (AC 2.4)
In addition, your manager is keen that standard letters of appointment and non-appointment are used going forward. Your manager has asked you to draft a copy of each of these letters.
- Write letters of appointment and non-appointment for an identified role. (AC 2.5)
Task Two – Simulated interview
Appointment to the newly formed people team is not yet complete and your manager is keen to involve you in the selection of a People Assistant and has asked you to work as part of a team to:
- Devise selection criteria for the post of People Assistant using the job description (Appendix A). Use the selection shortlisting matrix (Appendix B) to shortlist applications against the selection criteria to determine candidates to be interviewed. (AC 2.2)
- Interview one applicant and decide whether they meet the criteria for the post. The interview could be a panel or one-to-one interview. The interview could be conducted face-to-face, by telephone or by web conferencing. (AC 2.3)
If working as a panel, it is essential that each member of the team actively takes part in devising the criteria, shortlisting, interviews and decision-making and that your contributions are clearly included in your submission. A copy of CIPD STARR Model Interview Questions (Appendix C) has been included that can be used when developing interview questions.
Task Three – Guidance document
As a healthcare organisation, the owners of Healthcare on Hand are keen to support well-being at work. They have some concerns about work-life balance as their employees start work early, work evenings and weekends, in addition to providing healthcare support during weekdays. The owners are keen to comply with relevant legislation and aim to provide their employees with a work-life balance. The clients of Healthcare on Hand are diverse, and the owners feel the diversity of their workforce should also reflect their client population but think there might be more to diversity than this.
Now the organisation has grown and the owners cannot be involved in all day-to-day issues, line managers will take more responsibility for employment relations matters. Your manager asks you to produce a guidance document to provide the owners and managers at Healthcare on Hand with a fundamental understanding of employment legislation and organisational practices.
The guidance document must include:
- An explanation of the importance of achieving work-life balance within the employment relationship with an overview of the regulations relevant to work-life balance. (AC 3.1)
- An explanation of what is meant by, and the importance of, wellbeing in the workplace. (AC 3.2)
- A summary of the main points of discrimination legislation. (AC 3.3)
- An explanation of what diversity and inclusion mean and why they are important. (AC 3.4)
- An explanation of the difference between fair and unfair dismissal. (AC 3.5)
Task Four – Briefing paper
Prepare a briefing paper, aimed at providing Healthcare on Hand’s management team with essential knowledge and understanding of performance management and reward. You need to ensure that you include an explanation of:
- the purpose and components of performance management. (AC 4.1)
- the main factors that need to be considered when managing performance. (AC 4.2)
- different methods of performance review. (AC 4.3)
- key components (financial and non-financial) that are required to achieve an effective total reward system. (AC 5.1)
- the relationship between reward and performance, and the links to motivation. (AC 5.2), and provide
- at least two reasons for treating employees fairly in relation to pay. (AC 5.3)
Task Five – Fact sheet
Employee development is important for both existing employees and new starters at Healthcare on Hand and falls under the remit of the People Team. To date, learning and development (L&D) has been limited to training courses that were necessary to ensure legal compliance. You have been asked to develop a fact sheet for managers to raise awareness of the benefits of L&D, different types of learning needs, L&D approaches, individual requirements and preferences and how L&D can be evaluated.
Your factsheet should:
- Explain why learning and development activities are of benefit to individuals and organisations. (AC 6.1)
- Describe different types of learning needs and reasons why they arise for individuals and organisations. (AC 6.2)
- Summarise different face-to-face and blended learning and development approaches, including: facilitation, training, coaching, and mentoring. (AC 6.3)
- Explain how, in the design and delivery of learning and development initiatives, individual requirements and preferences must be accommodated. (AC 6.4)
- Discuss at least two methods of evaluating learning and development and its impact (AC 6.5).


3CO01 Business, Culture and Change in Context CIPD Level 3 Assignment Example, UK
The CIPD Level 3 in Business, Culture and Change is a mandatory unit for all students studying for their CIPD qualification at Level 3. The aim of this unit is to provide students with the knowledge and understanding necessary to deal with a range of business change issues, and to apply this knowledge in a practical way. The unit covers a wide range of topics, including organisational change, change management, organisational development, human resources management and business strategy.
Pay & Get Instant Solution of this Assignment of Essay by UK Writers
Here we offer you the 3CO01 assignment example for your reference to get a high mark in this unit. Our cipd level 3 assessment answers are fully referenced and meet the CIPD required standard. Following are the assignment solutions of 3CO01 Business, Culture and Change in Context:
CIPD Level 3 3CO01 Assignment Task 1: Understand the business environment in which the people profession operates, including the key issues that affect it.
1.1 examine the key external influences that impact on business environments..
There are a variety of external factors that can impact businesses, including political, economic, social and technological trends.
- Political factors can include things like government regulation, tax policy and trade restrictions.
- Economic factors can include inflation, interest rates and exchange rates.
- Social trends can encompass everything from demographic shifts to consumer spending habits.
- And technological advancements can lead to changes in the way products are produced or distributed.
Obviously, not every business is equally susceptible to all of these different types of trends and it’s important for companies to identify which factors are most likely to affect their particular operations. But by understanding the key external influences on business environments, organizations can be better prepared to adapt and respond to change.
1.2 Discuss organisational goals and why it is important for organisations to plan.
Organisational goals are essential for guiding the direction of an organisation and providing a framework for employees to make decisions. They provide a sense of purpose and help to motivate employees. In order to be effective, goals must be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant and time-bound.
A well-planned organisation is one that is able to efficiently achieve its objectives. Employees need clarity on what is expected of them in order to work towards the common goal. Planning also helps to identify potential problems and strategise solutions. It allows organisations to track their progress and make necessary adjustments along the way. Effective planning is critical for success and should be regularly revisited to ensure alignment with organisational goals.
Please Write Fresh Non Plagiarized Assignment on this Topic
1.3 Discuss the products and/or services the organisation delivers, including who the main customers are.
Our main customers are businesses who want to outsource their social media marketing. We offer a suite of services that includes content creation, community management, and paid advertising.
We work with a variety of businesses, from small mom-and-pop shops to large corporations. We specialize in creating engaging content that resonates with our clients’ target audiences.
And we have a lot of experience managing social media communities for clients who want to connect with their customers on a more personal level.
Lastly, we’re experts in paid advertising, and we can help businesses reach more people through targeted campaigns.
1.4 Review the range of technology available within the people profession, including how it can be utilised to improve working practices and collaboration.
Technology plays a big role in the people profession, from recruitment and performance management to learning and development.
Recruitment software can help organisations to post job listings, track applications and schedule interviews.
Performance management systems can be used to set goals, give feedback and measure progress.
Learning management systems can be used to deliver training and development programmes.
And there are a number of collaborative tools available to help employees work together, such as video conferencing and project management software.
Technology can improve working practices by making processes more efficient and effective. It can also help to facilitate collaboration and knowledge sharing. By utilising the latest technology, organisations can give their employees the tools they need to be successful.
CIPD 3CO01 Assignment Activity 2: Understand how people’s behaviour in the workplace affects and shapes culture.
2.1 define workplace culture in organisational settings and the importance of fostering positive approaches towards it..
Workplace culture can be defined as the shared values, attitudes, and behaviors of employees within an organisation. It is often shaped by the company’s history, structure, and leadership.
There are many different types of workplace cultures, but some common ones include a results-oriented culture, a people-oriented culture, and a process-oriented culture. Each type of culture has its own set of values and norms that dictate how employees should behave when they’re at work.
Workplace culture is important because it can impact employee morale, productivity, and engagement. A positive workplace culture can lead to happier employees who are more productive and engaged with their work. A negative workplace culture, on the other hand, can lead to lower morale and higher turnover rates.
When creating or trying to change a workplace culture, it is important to consider the company’s history, mission, and values. For example, a company that values innovation and creativity may want to foster a culture that encourages employees to think outside the box. A company that values customer service may want to create a culture that is focused on providing excellent service.
2.2 Explain how organisations are whole systems, and how work and actions as a people professional could impact elsewhere in the organisation.
An organisation can be thought of as a whole system, made up of many different parts that work together to achieve the company’s goals. Each part of the organisation plays a specific role and contributes to the overall functioning of the organisation.
The people professionals in an organisation play a vital role in shaping the culture and climate of the workplace. They can impact the organisation in a number of ways, including through their work in human resources, organizational development, and employee relations.
Human resources professionals are responsible for recruiting, hiring, and training employees. They also play a role in managing employee benefits and compensation. Organizational development professionals help to create and implement strategies for improving the efficiency and effectiveness of the organisation. Employee relations professionals work to maintain positive relationships between employees and management, and they also handle disputes and grievances.
CIPD Level 3 3CO01 Learning Outcome 3 : Understand the importance of effective management of change.
3.1 explain the importance of planning and managing change within the workplace..
In order to ensure the successful implementation of change within a organisation, it is essential that a plan is put in place. This plan should be designed to meet the specific needs of the organisation and its employees, and should take into account any potential risks. Without effective management, change can often lead to negative consequences such as increased stress levels, decreased morale and even redundancies.
It is therefore essential that managers are aware of the importance of planning and managing change within the workplace, and are able to put in place the necessary measures to ensure its success.
3.2 Consider the importance and role that people professionals play within change.
People professionals play a vital role in the successful implementation of change within an organisation. They are responsible for ensuring that employees are kept informed of any changes that are taking place, and for providing support during the transition period.
They also need to be able to identify any potential issues that may arise as a result of the change, and put in place measures to mitigate these. Without the help of people professionals, it is often very difficult for organisations to successfully implement change.
3.3 Discuss how change can impact people in different ways.
Change can impact people in different ways because different people respond differently to change. Some people are very resistant to change and find it difficult to adapt, while others are more open to change and find it easier to adapt.
Some people also handle change better than others. For example, some people may be able to quickly adapt to a new work situation, while others may take a longer time to adjust. The amount of time it takes for someone to adjust to change also depends on the person’s background, experience, and personality.
Some people also find that they need more time than others to recover from a major life change such as a death in the family or a divorce. Again, this varies from person to person. So basically, change can impact people in different ways, and it really depends on the individual.
Buy Non Plagiarized & Properly Structured Assignment Solution
Pay To Get 3CO01 Assignment Answers Online In UK For CIPD Level 3
Want to write business, culture, and change in context assignment for CIPD Level 3? Here is the one-stop solution for you. We have professional writers who have years of experience in writing assignments at all levels of CIPD. So, if you want to pay for CIPD assignment help online , you can pay us to get instant help.
Providing best coursework writing services is our aim to help every single student of graduation, under-graduation and PhD, so that they can submit their papers perfectly. We have been writing essays, dissertion, thesis, case study etc in the highest quality. Students who get our services always feel satisfied when they find our UK writer for essay writing or for any other assignments. Therefore, when you choose us, you are assured to get plagiarism free results in your academic writing papers. We offer CIPD Level 3 assignment answers for free, so if you need plage free assignment solutions contact us now!
Moreover, we pledge to serve every college student. if you are student of UK university then you can check out our writing services for UK University courses at cheap rates. So, don’t waste your time by asking your friends do my assignemnt for me and place your order here to do your assignment cheaply, quickly and error-free.
Related Answers
- Kotter’s 8-Step Model of Change Management: CIPD Assignment Sample, UK
- CIPD Level 7OS06 Well-Being At Work Assignment Example UK
- CIPD Level 7OS05 Managing People In An International Context Assignment Example UK
- CIPD Level 7OS04 Advance Diversity And Inclusion Assignment Example UK
- CIPD Level 7OS03 Technology-Enhanced Learning Assignment Example, UK
- CIPD Level 7OS02 Learning And Development Practice Assignment Example UK
- CIPD Level 7OS01 Advanced Employment Law In Practice Assignment Example UK
- CIPD Level 7LD01 Organizational Design Development Assignment Example UK
- CIPD Level 7HR03 Strategic Reward Management Assignment Example UK
- CIPD Level 7HR02 Resource And Talent Management To Sustain Success Assignment Example UK
- CIPD Level 7HR01 Strategic Employment Relations Assignment Example UK
- CIPD Level 7CO04 Business Research In People Practice Assignment Example UK
- CIPD Level 7CO03 Personal Effectiveness, Ethics & Business Acumen Assignment Example UK
- CIPD Level 7CO02 People Management & Development Strategies For Performance Assignment Example, UK
- CIPD Level 7CO01 Work And Working Lives In A Changing Business Environment Assignment Example, UK
- CIPD Level 5OS07 Well-Being At Work Assignment Example, UK
- CIPD Level 5OS06 Leadership And Management Development Assignment Example UK
- CIPD Level 5OS05 Diversity And Inclusion Assignment Example, UK
- CIPD Level 5OS04 People Management In An International Context Assignment Example, UK
- CIPD Level 5OS03 Learning And Development Essentials Assignment Example, UK

Get Free Assignment Quote
Enter Discount Code If You Have, Else Leave Blank

do you want plagiarism free & researched assignment solution!
UPTO 15 % DISCOUNT
Get Your Assignment Completed At Lower Prices

3CO01 Business Culture and Change in Context Assignment Guideline
Task one – slide deck for team day.
Students will prepare a presentation on “The Business Environment” to help HR team understand issues affecting the business environment.
AC 1.1 Application of an analysis tool (such as PESTLE) to examine the key external forces impacting or likely to impact an organisation’s activities
Students analyse the external forces using PESTLE, SWOT, Porter’s Five Forces model and BMC, which guide professionals understand how the organisation operates.
Battista (2021) explains the need to carry out a PESTLE analysis to examine the political, economic, social, technological, legal and environmental factors. Professionals collect information and explore the risks that might affect the business environment. PESTLE analysis is an effective tool that supports organisational strategic business planning, helps in workforce planning, marketing, product development and organisation change.
SWOT analysis tool examines the organisational Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities and Threats (Wilson, 2021). Students when analysing these tools should explain the advantages and disadvantages of each of the analysis tool, and explain how the tools influence decision-making within the organisation.
AC 1.2 An explanation of an organisation’s business goals and why it is important for organisations to plan for how they will achieve these. Your explanation should include examples of planning, such as how a business has been structured or specific policies introduced or people practices followed, in order for business goals to be achieved
To answer this question, students may identify a specific company in their country. For instance, Unilever is a British multinational company that students may refer to when answering the question.
Business goals determine organisation progress and enhance successful running of the business. Business goals motivate employees and other organisation stakeholders to realise the organistaion vision. Unilever goals are to improve people’s health and wellbeing, improve people’s livelihood and provide products sufficient to halve the environmental footprint.
Businesses engage in planning to develop a positive employment climate for the employees, ensure that they develop policies that link to organisation practices and strategies. To achieve business goals, people professionals and managers should plan to enhance business continuity.
AC 1.3 An explanation of an organisation’s products and/or services and main customers
Students identify the products and services that the organisation offers to the market. Unilever offers food products beauty products and personal care products to the customers. Unilever has a large customer target with customers ranging from small children to the elderly.
Students should provide a specific presentation on what each customer segment receives from the company.
AC 1.4 A short review of different technologies available to people professionals and how these can be used to improve working practices and collaboration. You might consider for example, technologies relating to communications, information sharing, record keeping, learning, wellbeing, productivity or security
According to Mohdzaini (2021), technology highly affects the future of work and employees’ involvement to completing future roles and responsibilities. Students should identify different types of technologies such as-
- Electronic forms of communication such as social media and use of smart phones
- Use of technologies on file management and document sharing
- Students further explain how technology improve working practices
- Technology approaches to communication, efficiency improvement, security and productivity.
Task two – Guidance leaflet on organisation culture and impact of change
AC 2.1 What is meant by workplace (organisation) culture
According to Young (2021), organistaion culture refers to the norms, behaviours and values that determine people’s characteristics, interactions and relationships. Students further explain the positive and negative cultures and the role of people professionals in developing cultures that create meaning to work.
AC 2.1 Why it is important to foster an appropriate and effective workplace culture
Culture helps employees understand the organisation and its operations, gives employees an opportunity to voice their views and develops connections with the employers.
An appropriate workforce culture values diversity and inclusion, promotes employee engagement, motivation and retention. Additionally, culture affects people and organisation performance.
AC 2.2 How organisations are whole systems in which different areas and aspects such as structure, systems and culture, are all inter-related
Students explain the different types of organisational structures and systems (hierarchical, divisional functional and matrix). Students explain the significance of value-driven organisations. Students explain how people professionals strive to achieve holistic systems that influence people behaviours and organisation cultures.
AC 2.2 An example of how good people practice, and an example of how bad people practice can impact other parts of the organisation or beyond the organisation (for example through developing new and better ways of doing things or through poor practice stimulating new legislation)
Students provide a scenario of how good people practice impacts the organisation. For instance, people professionals explain the value of learning and development and its significance in improving employees’ skills and knowledge. Students then provide a scenario of how bad people practice impacts the organisation. For example, lack of support to people’s mental and physical health is a bad people practice in the organisation. Managing the issue would require people professionals to develop practices that support good health. This involves developing counselling programmes to reduce stress and improve wellbeing.
It is crucial for students to note that they can use different examples depending on their engagements and experiences in an organistaion.
AC 2.3 How individuals may learn and develop in different ways in organisations and how this might be accommodated in assessing and developing skills and capabilities
According to Hayden (2021), people professionals should develop learning policies to create a culture where people value learning for skills and knowledge development. Students may consider the following learning concepts when answering the question-
- Learning and competitiveness
- Importance of workplace learning
- Significance of learning to achieve high performance
- Learning trends (identifying employee learning gaps and causes of underperformance)
AC 3.1 Why it is important for an organisation’s business that change is predicted, planned and effectively managed
George (2021) acknowledge that change in an organisation is essential and professionals should be keen to plan and manage change for positive outcomes. Concepts that students should consider include-
- Change triggers (for example;- competition, change in technology, discontinuity)
- How change impacts the business
- Planning for change (role and purpose of introduction change)
BATTISTA, M. (2021) PESTLE analysis. Available at https://www.cipd.co.uk/knowledge/strategy/organisational-development/pestle-analysis-factsheet [Accessed 18th July 2022]
GEORGE, S. (2021) Change management. Available at https://www.cipd.co.uk/knowledge/strategy/change/management-factsheet [Accessed 18th July 2022]
HAYDEN, D. (2021) Learning and development strategy and policy, available from https://www.cipd.co.uk/knowledge/strategy/development/factsheet [Accessed 18th July 2022]
MOHDZAINI, H. (2021) Technology and the future of work. Available at: https://www.cipd.co.uk/knowledge/work/technology/emerging-future-work-factsheet [Accessed 18th July 2022]
WILSON, M. (2021) SWOT analysis. Available at https://www.cipd.co.uk/knowledge/strategy/organisational-development/swot-analysis-factsheet [Accessed 18th July 2022]
YOUNG, J. (2021) Organisational culture and cultural change, available from https://www.cipd.co.uk/knowledge/culture/working-environment/organisation-culture-change-factsheet [Accessed 18th July 2022]
Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
- CIPD LEVEL 3
- CIPD LEVEL 5
- CIPD Level 5_New Brief
- CIPD LEVEL 7
Latest Posts
Quick links.
Privacy Policy
Refund Policy
Terms of Service
Terms - Privacy Policy & Safety
© 2021 All Rights Reserved

- Username or email *
- Password *
Remember me
Lost your password?
- Email address *
- Username *
- Confirm Password *
Want to become an instructor?
3CO01 Business, Culture and Change in Context

The task assigned to students is to create a presentation on “The Business Environment” to assist the HR team in understanding the various factors that impact the business environment.
AC 1.1 Application of an analysis tool (such as PESTLE) to examine the key external forces impacting or likely to impact an organisation’s activities
The students conduct a comprehensive analysis of external forces using various strategic models such as PESTLE, SWOT, Porter’s Five Forces, and BMC. These models serve as guides for professionals, assisting them in understanding the organisational operational dynamics.
The importance of conducting a PESTLE analysis, according to Battista (2021), lies in its ability to thoroughly examine political, economic, social, technological, legal, and environmental factors. Professionals diligently collect pertinent information and assess potential risks to the business environment. The PESTLE analysis is a highly effective tool for facilitating workforce planning, marketing strategies, product development, and organisational change.
Additionally, Wilson (2021) clarifies that the SWOT analysis tool assesses the organisation’s Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats. Students are expected to elaborate on the benefits and drawbacks of each model when performing analyses using these tools. They must also clarify how these analytical tools affect organisational decision-making procedures.
AC 1.2 An explanation of an organisation’s business goals and why it is important for organisations to plan for how they will achieve these. Your explanation should include examples of planning, such as how a business has been structured or specific policies introduced or people practices followed, in order for business goals to be achieved
Students are urged to pick a specific company from their nation to respond to this inquiry. A British multinational corporation named Unilever might be used as an example when responding to the question.
An organisation’s business objectives have a significant impact on its development and effective operation. These goals not only help the organisation grow, but they also inspire workers and other stakeholders by helping them to align with the organisation’s vision. In the case of Unilever, their objectives center on enhancing livelihoods, enhancing people’s health and wellbeing, and providing goods that actively lessen their impact on the environment.
In order to create a favorable work environment for their employees, businesses engage in strategic planning. They work hard to create policies that complement the practices and overarching goals of the organization. In order to ensure that the business makes steady progress in achieving its goals, professionals and managers play a critical role in planning for business continuity.
AC 1.3 An explanation of an organisation’s products and/or services and main customers
Students are given the distinct task of evaluating the variety of goods and services that the company offers to the market. For instance, Unilever offers a wide variety of products to a wide range of customers, including food, beauty, and personal care items. This clientele includes people of all ages, including babies and the elderly.
Students are expected to detail the specific benefits that each customer segment receives from the business in their presentation, emphasising the distinctive value propositions and benefits catered to the various needs and preferences of various customer demographics.
AC 1.4 A short review of different technologies available to people professionals and how these can be used to improve working practices and collaboration. You might consider for example, technologies relating to communications, information sharing, record keeping, learning, wellbeing, productivity or security
According to Mohdzaini’s research (2021), technology has a significant impact on how engaged employees are in fulfilling their future roles and responsibilities. Students are encouraged to identify and investigate various types of technologies in light of this, such as:
- Internet: The global network that has transformed information access, research, and communication.
- Electronic communication: Social media platforms and smartphone use, which enable frictionless connectivity and cooperation.
- Technologies for managing files and sharing documents: Programs that facilitate data organisation and encourage effective information sharing and retrieval.
- Additionally, students should focus on the following areas as they delve deeper into how technology improves working practices:
- Communication: Technological developments that result in better internal and external communication channels for the organisation.
- Efficiency improvement: How technology streamlines operations and streamlines processes, resulting in higher productivity.
- Security is the application of technological solutions to protect against cyber threats and safeguard data.
- Productivity: The degree to which technology empowers workers and enables them to perform better in their individual roles.
Students can develop a thorough understanding of the advantages of technology on the future of work and organisational performance by examining these technological aspects.
AC 2.1 What is meant by workplace (organisation) culture
According to Young’s findings (2021), organisational culture is the collection of norms, behaviors, and values that influence how people behave, interact, and relate to one another within an organisation. Students are urged to go into detail about both positive and negative cultural aspects as well as the part that human resources professionals play in creating cultures that give work meaning.
An environment with a positive culture promotes teamwork, creativity, and employee happiness, which increases productivity and fosters a sense of belonging. On the other hand, toxic behaviors, poor communication, and resistance to change are all signs of a negative culture and can lead to low morale and potential organisational problems.
Professionals in human resources must be involved in creating meaningful cultures. These individuals can have an impact on the company’s values, promote open communication, support diversity and inclusion, and put policies in place that promote employee growth and well-being. People managers contribute to a work environment where people can find meaning and fulfillment in their jobs by actively shaping the culture. This fosters improved performance and the success of the organisation as a whole.
AC 2.1 Why it is important to foster an appropriate and effective workplace culture
Employees need to understand how the organisation works in order to be able to express their ideas and forge close relationships with their employers. Culture plays a crucial role in this process.
A workplace culture that prioritises diversity and inclusion is one that is successful. It encourages worker retention, motivation, and engagement, which helps build strong teamwork. Additionally, culture has a big impact on how well people perform both individually and as an organisation, which shapes the company’s overall success and accomplishments.
AC 2.2 How organisations are whole systems in which different areas and aspects such as structure, systems and culture, are all inter-related
Students explore various organisational systems and structures, including hierarchical, divisional, functional, and matrix systems. They emphasise the significance of aligning an organisation’s values with its strategic goals and operations, emphasising the significance of value-driven organisations. Students also describe the efforts made by human resources professionals to create extensive systems that influence both individual behaviors and the culture of the entire organisation with the goal of creating a setting that promotes development, productivity, and fulfillment.
AC 2.2 An example of how good people practice, and an example of how bad people practice can impact other parts of the organisation or beyond the organisation (for example through developing new and better ways of doing things or through poor practice stimulating new legislation)
Students demonstrate how employing good people practices has a positive effect on an organisation in one scenario. Professionals in the human resources field emphasise the value of learning and development by providing examples of how investing in employees’ knowledge and skills improves their capabilities and overall performance. A skilled and motivated workforce, for instance, is cultivated through the implementation of regular training programs and the provision of opportunities for professional growth, which boosts productivity, enhances decision-making, and improves employee retention.
Students, however, draw attention to an instance in which unethical behaviour has a negative impact on the organisation. Insufficient support for employees’ mental and physical health, for instance, can result in increased stress, decreased productivity, and low morale among staff members. Professionals in the human resources field intervene to solve this problem by establishing procedures that put employees’ welfare first. To reduce stress and enhance general health, they might develop counselling services, mental health assistance networks, and wellness programs.
Students must understand that these scenarios can change based on their experiences and interactions within an organisation. A variety of examples can be used to highlight the effects of both good and bad people practices, underscoring the crucial role that human resources professionals play in establishing a positive and effective organisational culture.
AC 2.3 How individuals may learn and develop in different ways in organisations and how this might be accommodated in assessing and developing skills and capabilities
In creating learning policies that support a culture where learning is highly valued for the development of skills and knowledge, Hayden (2021) emphasises the critical role of people professionals. The learning concepts listed below may be investigated by students when studying this subject:
- Learning and Competitiveness: Describe how a culture of ongoing learning helps to increase an organisation’s ability to compete. Organisations that place a high priority on learning are better able to innovate, adapt to changes, and maintain a competitive edge in the market.
- In order to develop a skilled and adaptable workforce, consider the importance of workplace learning. Employees are empowered by workplace learning to pick up new skills, stay current, and make valuable contributions to the expansion of the company.
- Learning’s Importance for High Performance: Explain the specific ways that learning affects both individual and organisational performance. Continuous learning among employees tends to boost performance, which boosts the efficiency of the entire organisation.
- Learning Trends: Describe the most recent developments in employee education, including techniques for locating knowledge gaps and addressing reasons for poor performance. Organisations can better meet the unique needs of their employees by customising their learning initiatives by analysing learning trends.
Students can gain a thorough understanding of the crucial role that learning policies play in forming a culture of continuous development and growth within an organisation by exploring these learning concepts.
AC 3.1 Why it is important for an organisation’s business that change is predicted, planned and effectively managed
George’s work from 2021 emphasises the importance of change as a component of organisational progress and exhorts professionals to actively plan and manage change for successful results. The following ideas should be investigated by students as they study this subject:
- Investigate the various catalysts for organisational change, such as heightened competition, technological advancements, or unsettling occurrences like market discontinuity. Professionals who are aware of these triggers are better able to anticipate and handle change.
- Change’s Effect on Business: Analyse how the change will affect the organisation’s operations, structure, and workforce. Students should consider how change will impact various aspects of the business because it can both present challenges and opportunities.
- Making Change Plans: Explain the role and motivation for bringing change to an organisation. Planning effectively is necessary to guarantee that change is effectively managed, effectively communicated, and in line with the objectives and vision of the organisation.
By taking into account these ideas, students can learn important lessons about the significance of change management and the proactive approach necessary to successfully navigate change, ultimately resulting in favourable outcomes for the organisation.
BATTISTA, M. (2021) PESTLE analysis. Available at https://www.cipd.co.uk/knowledge/strategy/organisational-development/pestle-analysis-factsheet [Accessed 18th July 2022]
GEORGE, S. (2021) Change management. Available at https://www.cipd.co.uk/knowledge/strategy/change/management-factsheet [Accessed 18th July 2022]
HAYDEN, D. (2021) Learning and development strategy and policy, available from https://www.cipd.co.uk/knowledge/strategy/development/factsheet [Accessed 18th July 2022]
MOHDZAINI, H. (2021) Technology and the future of work. Available at: https://www.cipd.co.uk/knowledge/work/technology/emerging-future-work-factsheet [Accessed 18th July 2022]
WILSON, M. (2021) SWOT analysis. Available at https://www.cipd.co.uk/knowledge/strategy/organisational-development/swot-analysis-factsheet [Accessed 18th July 2022]
YOUNG, J. (2021) Organisational culture and cultural change, available from https://www.cipd.co.uk/knowledge/culture/working-environment/organisation-culture-change-factsheet [Accessed 18th July 2022]
- 3CO01 Assignment Example

- CIPD Level 3
- CIPD Level 5
- CIPD Level 7
+44 2871140060
Image Disclaimer:
The images used on this website are not our own and are solely utilised for research purposes. Any credit for these images belongs to their rightful copyright owners. We do not claim ownership or authorship of any images displayed on this website. If you believe that any image used here infringes upon your copyright, please contact us immediately, and we will promptly remove it or provide proper attribution as per your request.
Content Disclaimer:
The papers shared on this platform are provided for reference purposes only. Users are strictly advised against submitting these papers to any educational institution or academic platform for grading or assessment purposes.
© 2024 CIPD Modules. All rights Reserved.
- Privacy policy
- Refund and Returns Policy
- +44 7456185486


3CO01 Assignment Example
- January 17, 2022
- Posted by: Assignment Help Gurus
- Category: CIPD LEVEL 3 CIPD CIPD EXAMPLES HUMAN RESOURCE
3CO01 Business Culture and Change in Context

You work in the HR Team of a medium sized organisation and are studying for your people practice qualification. In a recent discussion with your manager, you expressed how important you thought it was for employees to understand the business environment. You feel this is especially important for people practice professionals as their roles impact on the policies, processes and values of the organisation, which in turn impact on all the people within the organisation.
Inspired by this discussion, your manager has asked you to help prepare development day. A team-based learning needs analysis has shown that as well as more knowledge about the business environment, the team would benefit from a deeper understanding of organisational culture and how humans behave in organisations. The team would also like to build their knowledge and skills in relation to change management.
Preparation for the Tasks:
- At the start of your assignment, you are encouraged to plan your assessment work with your Assessor, and, where appropriate, agree milestones, so that they can help you monitor your progress.
- Refer to the indicative content in the unit to guide and support your evidence.
- Pay attention to how your evidence is presented, remember you are working in the People Practice Team.
- Ensure that the evidence generated for this assessment remains your own work.
You will also benefit from:
- Completing and acting on formative feedback from your Assessor.
- Reflecting on your own experiences of learning opportunities and continuing professional development.
- Reading the CIPD Insight, Fact Sheets and related online materials on these topics.
Task One-Slide Deck for Team Day
Your manager has asked you to prepare a presentation (slide deck and brief presenter notes) in readiness for delivery to the HR Team at the next Team day. The aim of the presentation, entitled
is for team members to gain a general understanding of their business environment and the key issues that can affect this.
Your presentation (which you are not required to deliver) can be based on your own organisation or one(s) that you are familiar with, and should include the following:
- Application of an analysis tool (such as PESTLE) to examine the key external forces impacting or likely to impact an ties. (AC 1.1)
- An explanation of business goals and why it is important for organisations to plan for how they will achieve these. Your explanation should include examples of planning, such as how a business has been structured or specific policies introduced or people practices followed, in order for business goals to be achieved. (AC 1.2)
- An explanation of an organisation s products and/or services and main customers. (AC 1.3)
- A short review of different technologies available to people professionals and how these can be used to improve working practices and collaboration. You might consider for example, technologies relating to communications, information sharing, record keeping, learning, wellbeing, productivity or security. (AC 1.4)
Task Two Guidance Leaflet
In line with the team learning need analysis and knowing that they will be required to support a number of change initiatives soon, your manager has also asked you to prepare a guidance leaflet for the team. The guidance leaflet should cover two main themes and include
- information about organisational culture and how people behave in organisations
- guidance about the impact of change and how organisational change can most effectivelybe managed.
Your guidance leaflet should explain (in any sequence):
- What is meant by workplace (organisation) culture (AC 2.1)
- Why it is important to foster an appropriate and effective workplace culture. (AC 2.1)
- How organisations are whole systems in which different areas and aspects such as structure, systems and culture, are all inter-related. (AC 2.2)
- An example of how good people practice, and an example of how bad people practice can impact other parts of the organisation or beyond the organisation (for example through developing new and better ways of doing things or through poor practice stimulating new legislation). (AC 2.2)
- How individuals may learn and develop in different ways in organisations and how this might be accommodated in assessing and developing skills and capabilities. (AC 2.3)
- Why it is important for an organisation that change is predicted, planned and effectively managed. (AC 3.1)
- How change can impact people in organisations, such as changing their role or status or financial situation, and the different ways people may respond to change. (AC 3.3)
- The nature and importance of different roles that can be played by people practice professionals, in relation to change agendas. You might consider roles such as: gatekeeper, champion, facilitator, critical friend or record-keeper. (AC 3.2)
Solution Task One
AC 1.1 Examine the key external influences that impact on business environments

Organisations do not operate in a vacuum rather their operations are influenced by external forces in their business worlds. To this end, there exists several tools that help in the analysis of external factors that affect business in all sectors including the hospitality industry that forms the core of our business. Among such tools is the PESTLE analysis that is an acronym for Political, Economic, Sociological, Technological, Legal and Environmental. Cipd (2021) defines the PESTLE analysis as a strategic, broad fact finding activity of the external factors that potentially influence the decisions of companies by assisting to minimise the threats and subsequently maximise on the available opportunities. The following is analysis of the factors within the hospitality industry
- Political factors that influence the industry include environmental regulations, tax policy, trade restrictions, political stability and tariffs. This has been evidence during the Covid19 pandemic period as many governments imposed travel bans that negatively affected the industry Frue (2019). Similarly, the hospitality industry operates in fear during presidential elections as new governments could introduce new ideas and policies that impact on the industry and disrupts the operations.
- Economic factors that influence the industry include economic growth or decline, inflation, interest, wage rates, exchange rate, minimum wage, working hours, cost of living, availability of credit and unemployment. In this regard, the strength or weakness if a currency can affect the attractiveness of a vacation destination. The short term impact of Brexit was loss of a substantial number of employees from other EU countries (James, 2021).
- Sociological factors include cultural norms, health consciousness, career attitudes, age distribution population growth rates, health and safety. For example, consumers have become more health conscious during the Covid19 pandemic period and hence the industry investment on sanitising procedures for their facilities.
- Technological factors include new technologies for example robotics and rate of change (Cipd, 2021). To this end, some hotels have adopted robotics in sanitising their facilities which is faster and more efficient. The industry is also investing in social media and working towards getting positive reviews on travelling websites ( Frue, 2019)
- Legal factors include changes to legislations such as employment, imports/exports, access to quotas, materials and taxation (Cipd, 2021)
- Environmental factors include ethical sourcing, global warming, pandemics and other emergencies. Frue (2019) noted that the industry have to understand the seasonal or weather differences to competitively price their rooms.
AC 2.1 Discuss organisational goals and why it is important for organisations to plan.

According to Hill (2019) planning is a process that charts a course for attainment of defined business goals. The process entails conducting a review of operations of the organisation and subsequently identifying what needs to be improved in the next year. As such planning necessitates forecasting of the results that an organisation desires to achieve and identifying the measures to be taken in order to attain the set goals. The results can be can be in financial terms or other measures such as consumer satisfaction (Hill, 2019).
Scott (2010) explained that human resources personnel have different functions in organisations including ensuring that there policies put in place to ensure that employees are responsible for the attainment of organisational objectives and goals. Giving reference to the hospitality industry, it is broadly structured into food and beverages, travel and tourism, lodging and recreation (Novak, 2017). Their ultimate goal is to create a positive customer experience so as retain the consumer in future or even gain a referral.
In line with this, the HR department training and development plans within the hospitality industry seeks to invest in imparting the right knowledge and skills to the employees who are the direct link between an organisation and the company. Scott (2010) detailed that HR professionals are charged with responsibility of developing training and development programs that strengthen the quality of work in a company. This proceed upon evaluating the training needs, developing manuals, facilitating instruction and ascertaining that training objectives align to the business goals. Scott (2010) highlight the findings of the Bureau of Labor statistics denoting that imparting employees with skills can enhance organisational performance and help achieve business results.
AC 1.3 Discuss the products and/or services the organisation delivers, including who the main customers are

Bansal, Gaulum, Anbardar and Kumar (n.d.) cited Philip Kotler’s definition of a product as a bundle of a physical service and symbolic particulars that are anticipated to be beneficial to the buyer or yield satisfaction to a consumer.
The hospitality industry has five components of hospitality products including core products that refers to the basic benefit accorded to a guest such as a place to eat. The second is facilitating products that refers to those products that are provided to a guest in order to utilise the core product such as food in case of restaurants. Consequently, there are tangible products that refer to physical products of hospitality such as television and air conditioning in a standard room. There are supporting products that are provided to increase the value of the basic product with the intention of making it unique. Last but not least are augmented products refers to the products that are essential in enhancing the quality of products devoid of additional charges.
On the other hand, Bansal et al. (n.d.) defined services as the intangible activities that provide want satisfaction. It is also defined as any activity that one party offers to another and does not yield to ownership. Services can also be articulated as intangible economic products that involves human beings serving the provider and the recipient. They have several traits such as they are perishable, they lack physical identity, they are inseparable, have high fixed costs and are interdependent.
Capozzi (2020) argued that consumers in the hospitality industry can be categorised into backpackers and solo travellers that enjoy exploring cities and spending time in hotels and thus choose low prices over services and amenities. The other category is couples that involves romantic partners seeking quiet premises and high quality bedding. The other group is families that have more specific needs such as on site play areas, discounts for kids’ rooms, entertainment and additional amenities such as booster chairs. Business travellers is the final category and requires fast internet access, electronics such as printers and are usually willing to pay a higher price for rooms.
AC 1.4 Review the range of technology available within the people profession, including how it can be utilised to improve working practices and collaboration

As the world and the workplace become increasingly digitised HR managers are also forced to adapt to new technology that has enhanced their work. Technology is utilised in managing information on the cloud, engaging with people on social media sites and working on the go through tablets and mobiles (Barcelos, 2018).the following are some of the technology pieces required by people professionals
- Social media platforms such as Facebook, twitter and LinkedIn and are used for posting vacant positions, communicate on upcoming events to the public and helps in making decisions on the right fit for a company
- Human Resources Information Software (HRIS) helps in streamlining several HR processes and tasks that diminish manual errors. Besides automating HR functions it also helps in easier management of HR documents
- Cloud technology that assists in centralisation of business and HR data from payroll to feedback, enhances transparency within the organisation and boosts consistency.
- Gamification techniques that are utilised in recruitment to enhance talent acquisition. It is also used to enhance learning and development through knowledge sharing and simulation of real life contexts.
(Adapted from Bercelos, 2018).
Bibliography
Barcelos, K. (2018). Top 6 Technology Skills Every HR Professional Needs Today . [online] AIHR. Available at: https://www.aihr.com/blog/technology-skills-every-hr-professional-needs/.
Capozzi, C. (2020). Service Marketing vs. Product Marketing in Hotels . [online] Small Business – Chron.com. Available at: https://smallbusiness.chron.com/service-marketing-vs-product-marketing-hotels-23637.html.
Frue, K. (2019). PESTLE Analysis for Hotel Industry . [online] PESTLE Analysis. Available at: https://pestleanalysis.com/pestle-analysis-for-hotel-industry/.
Hill, B. (2019). How to Analyze the Key Success Factors for Plan Implementation . [online] Small Business – Chron.com. Available at: https://smallbusiness.chron.com/analyze-key-success-factors-plan-implementation-47365.html.
James, W. (2021). The impact of Brexit on the hospitality sector; what’s the post-Brexit outlook? [online] Stint. Available at: https://stint.co/learning-hub/the-impact-of-brexit-on-the-hospitality-sector/.
Novak, P. (2017). What Are The 4 Segments Of The Hospitality Industry . [online] Hospitality Net. Available at: https://www.hospitalitynet.org/opinion/4082318.html.
Scott, S. (2010). Role of HR in Achieving Business Goals . [online] Chron.com. Available at: https://smallbusiness.chron.com/role-hr-achieving-business-goals-1767.html.
Solution Task Two
AC 2.1 Define workplace culture in organisational settings and the importance of fostering positive approaches towards it.
Workplace culture in organisations can be defined as the set of underlying beliefs, principles and values that serve as the cornerstone of a company’s management system. It is also inclusive of the management behaviours and practices adopted in reinforcing the basic beliefs (Cipd, 2020). Tarver (2021) defined corporate culture as the beliefs and behaviours that guide how employees and the management interact and conduct business transactions. Tarver (2021) emphasized that corporate culture though not expressly defined it is implied and organically develops over time as an organisation hires people that represent it. The culture at the workplace is demonstrated by business hours, hiring decisions, dress code, and treatment of consumers, office set up, consumer satisfaction, employee benefits and turnover.
Workplace culture offers employee a way to understand the company, develop a network and common purpose as well as voice their views in reference to the mission of the organisation (Cipd, 2020). Workplace culture is also important as it impacts the standards of customer service and influence the retention of employees. Further, workplace culture affects the general performance of the organisation and thus the need to cultivate a positive work culture (Cipd, 2020). There are some common traits or values that are associated with healthy workplace culture including accountability, expression, equity, communication and recognition (Indeed Editorial Team, 2021). Consequently, healthy workplace culture is associated with better hiring choices, performance quality, organisational reputation and employee happiness (Indeed Editorial Team, 2021).
AC 2.2 Explain how organisations are whole systems, and how work and actions as a people professional could impact elsewhere.
Organisations are equated to whole systems as they compromise of several departments that conduct different functions but are united by a common organisational goal and function. Levinson (2018) explained that organisational systems simply refer to the general set up of a company. In this regard, organisations as a whole system defines the structure of the company in cognizance of each division or department and the hierarchy structure that determines who reports to who and what is expected of each of the divisions (Levinson, 2018).
Irrespective of size, all organisations require a solid and well defined system that outline simple processes that employees should adhere and thus avoid confusion at the workplace. The lack of a concrete and functional system the workplace becomes chaotic (Levinson, 2018). The organisational system ensure that all employee are assigned to the correct department and thus contribute towards the growth of the company.
The Human resource department plays a significant role in building a robust organisational system. Bianca (2019) indicated that human resource managers are in charge of the most significant of component of a successful business which is to recruit a productive and thriving workforce for each of the departments in an organisation. To this end, people professionals view people as assets as opposed to cost in an organisation. The human resource department develop good practice by recruiting and hiring people with certain skills-set that meet organisational current and future goals, coordinate employee benefits as well as flexibly shift employee around in different departments depending on employee abilities and business priorities (Bianca, 2019). When people professionals are able build a concrete organisational system they eliminate challenges such as work duplication, employee frustration and conflict between different departments or positions
AC2.3 Discuss how people learn and develop in different ways relating this to organisational assessment of people’s skills and capabilities
Learning and development are terms that are often used interchangeably at the workplace Learning can be defined as work-based self-directed process that increased adaptive potential while development refers to a broader and long term process of acquiring knowledge and skills (Cipd, 2021). The main goal of learning and development is to change the behaviour of groups or individuals for the better such that they are able deliver their mandate more efficiently.
There are several methods through which individuals and groups learn and develop at the workplace including formal or informal techniques, digital or face to face, internal or external provision, direct learning at the workplace or away from the workplace and created or curated resources (Cipd, 2021). Some of the workplace learning and developments methods are onjob training, in house development programmes, coaching and mentoring, job rotation, secondment, project work and shadowing (Cipd, 2021).
Vulpen (2020) that one of the popular approach to organisation learning is the 70/20/10 model that denotes that seventy percent of learning is work-based and occurs informally through hand on experience through daily work routines. Subsequently, twenty percent of learning occurs through developmental relationships through peer feedback, coaching, collaboration and peer mentoring. Finally en percent of learning occurs through professional development courses or formal training techniques in an educational setting. This is demonstrated in figure one below
Fig 1: the 70/20/10 Model of Organisational Learning
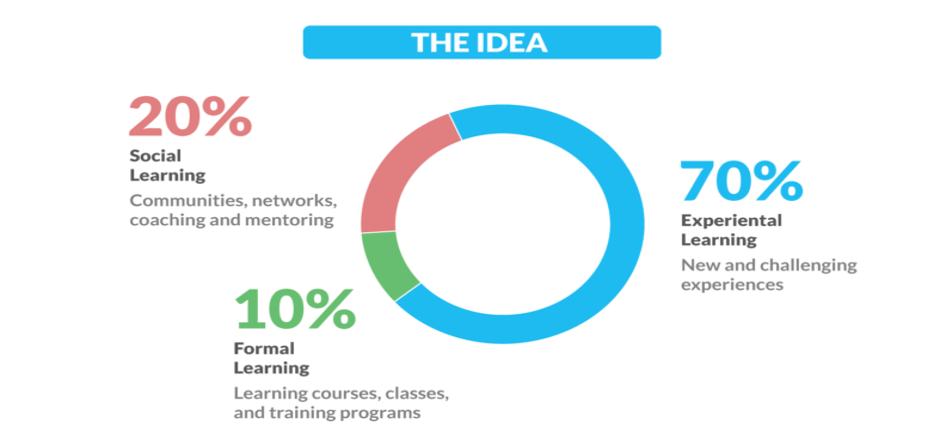
Prior to an organisation deciding on the learning and development method to use the organisation shoul evaluate the employees skills and competencies which can proceed through conducting of tests, getting feedback from teams, through self-assessment exercises, feedback from clients and engaging employees in a business game (Menshikov, 2017).
AC3.1 Explain the importance of planning and managing change within the workplace.
Business environments are regularly changing especially in today’s technological world. To this end, change management has been adopted by many organisations across the globe. Change management broadly defines the several ways that organisations prepare and implement simple or complex changes (Indeed Editorial Team, 2021). Michigan State University (2019) asserted that change management can be incremental that is evolutionary and internally driven or discontinuous that is revolutionary and externally driven.
Change management in organisations is important as any change that occurs impacts on all the employees. In addition, effective change management increases employee morale and drives team work among the employees. It also creates a positive environment for consistent evolution and thus facilitate general business change that allows the company to easily adopt new procedures and technologies (Michigan State University, 2019).
Change management is important as it assists each division of a company to succeed amidst major and minor adjustments within the company or business environment. Change management further allows employees to understand their new roles and thus execute their mandate efficiently and as per expectation. In general, change management in organisations ensures that businesses remain viable and thus continue to grow and align to the changing market trends (Indeed Editorial Team, 2021).
Change management is also attributed to reduce stress and anxiety with change, minimise resistance to change, enhances cooperation and collaboration in the business, responds to challenges more efficiently as well manages the diverse costs of change (Migrator, 2000).
AC3.2 Consider the importance and role that people professionals play within change.
According to Cipd (2020) people professionals have an important role in managing the change process in an organisations. This is because they are equated to stage directors of change serving behind the scenes and thus appreciated by all. The people professionals serve as the change agents in organisations due to their proximity to the people thus making it easy to influence leadership and provide an adequate framework that supports change within the workplace (Perrin, 2017).
In most organisations, the Human Resource department serves the role of a watchdog in change in management as it facilitates the implementation of new processes. In this regard, the HR takes up a monitoring role and also ensure that the change processes are harmonious, coherent and uphold integrity (Perrin, 2017).
People professionals also execute the role of communication in the change process as they clarify messages of change and ensure that people understand the process and comprehend the multiple avenues available to transmit the crucial messages. To this end, the HR utilises their knowledge and skills to minimise rumours by communicating through channels such as emails, formal briefs, podcasts and newsletter (Changeboard Team, 2016).
People professionals also have the role of diagnosing and planning change given that they are equipped with knowledge on the structure of change and thus have the skills to ask the right questions and diagnose the problems that might arise in the quest for change. Moreover, people professionals can assist in setting of expectations and ensuring that a comprehensive plan is laid out and thus creating an opportunity for the change architecture to be interrogated (Changeboard Team, 2019).
AC3.3 Discuss how change can impact people in different ways
Different people process and react to change differently. This is well captured by Owen (2018) who articulated that people react to change in different ways owing to their individual reasons giving cognizance to how that change impacts on their wellbeing. Owen (2018) indicated that some people thrive on change as they easily embrace new procedures and products while others initially resist change as the status quo is disrupted. In reference to a team, change can negatively affect employees as they are separated from each other and thus affect the efficiency of the team.
Additionally, change can creates uncertainty and anxiety which may be manifested through excessive worrying and changes in personal behaviours such as restlessness irritability and difficulty in concentrating. Other physical symptoms associated with anxiety include fidgeting, tiredness and trouble sleeping that are inevitably detrimental to employee productivity and performance (Owen, 2018). Change can also impact people financially as team restructuring for example may result in less overtime thus less money.
Change also positively or negatively affects employees trust and loyalty to the employer or organisation and thus impact on their job satisfaction, job attitude and organisational attitude (Owen, 2018). This can result in employees lacking confidence with the management and thus causing some of the employees to exit the organisation while others remain physically present but mentally searching for opportunities in other organisations thus diminishing their levels of productivity and involvement (Owen, 2018).
Wickford (2019) summarised the impacts of change to employees into increase in levels of stress due to fear of change, increased turnover as people exit the company in search of more stable organisations, diminished loyalty and increased time away from work as some employees avoid the office while looking for new jobs while other take longer lunch hours and leave the office earlier. However there are some employees who react by increasing their productivity as strategy of getting noticed and thus hoping that they will be retained amidst the change.
Bianca, A. (2019). The Components of Employee Retention & Career Development Processes . [online] Small Business – Chron.com. Available at: https://smallbusiness.chron.com/components-employee-retention-career-development-processes-12191.html.
Changeboard Team (2016). The role of HR in change . [online] Changeboard. Available at: https://www.changeboard.com/article-details/14013/the-role-of-hr-in-change/.
CIPD (2020a). Change Management | Factsheets . [online] CIPD. Available at: https://www.cipd.co.uk/knowledge/strategy/change/management-factsheet#gref.
CIPD (2020b). Organisational Culture and Cultural Change | Factsheets . [online] CIPD. Available at: https://www.cipd.co.uk/knowledge/culture/working-environment/organisation-culture-change-factsheet#gref.
CIPD (2021). Learning Methods | Factsheets . [online] CIPD. Available at: https://www.cipd.co.uk/knowledge/fundamentals/people/development/learning-methods-factsheet#gref.
Indeed Editorial Team (2021a). Change Management: What It Is and Why It’s Important . [online] Indeed Career Guide. Available at: https://www.indeed.com/career-advice/career-development/change-management.
Indeed Editorial Team (2021b). What Is Work Culture? [online] Indeed Career Guide. Available at: https://www.indeed.com/career-advice/career-development/work-culture.
Levinson, C. (2018). The Structure of a Bureaucratic Organization . [online] Bizfluent. Available at: https://bizfluent.com/facts-6877710-structure-bureaucratic-organization.html.
Menshikov, S. (2017). Top 6 Ways To Assess Employee Skills And Competencies . [online] eLearning Industry. Available at: https://elearningindustry.com/top-6-ways-assess-employee-skills-and-competencies.
Michigan State University (2019). Organizational Change Management . [online] Michiganstateuniversityonline.com. Available at: https://www.michiganstateuniversityonline.com/resources/leadership/organizational-change-management/.
Migrator (2000). Benefits of change management . [online] nibusinessinfo.co.uk. Available at: https://www.nibusinessinfo.co.uk/content/benefits-change-management.
Owen, C. (2018). Explain possible human effects of innovation and change upon people and teams in an organisation . [online] Skills for Leadership. Available at: https://www.skillsforleadership.co.uk/explain-possible-human-effects-of-innovation-and-change-upon-people-and-teams-in-an-organisation/.
Perrin, O. (2017). The Role of HR in Managing Change in the Workplace . [online] EmployeeConnect HRIS. Available at: https://www.employeeconnect.com/blog/hr-role-change-management/.
Tarver, E. (2020). How to Tell If Your Corporate Culture Is Healthy . [online] Investopedia. Available at: https://www.investopedia.com/terms/c/corporate-culture.asp.
Vulpen, E.V. (2020). Learning and Development: A Comprehensive Guide . [online] AIHR. Available at: https://www.aihr.com/blog/learning-and-development/.
3CO01 Assignment PPT

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
[vc_row full_width=”” parallax=”” parallax_image=””][vc_column width=”1/1″][vc_widget_sidebar sidebar_id=”default”][/vc_column][/vc_row]
CIPD Level 3 Assignment Help & Example
In pursuit of CIPD Level 3 qualification, individuals will acquire a diverse range of fundamental HR skills and knowledge. This program delves into HR’s crucial role in organizational success, equips learners with the ability to navigate complex employment laws, and fosters expertise in recruitment and talent selection.
Moreover, it imparts strategies for effective employee learning and development, guides in cultivating harmonious employee relations, and enhances skills in managing and improving employee performance.
Additionally, the curriculum emphasizes research skills for data-driven decision-making, ethical conduct, professionalism, and effective communication within HR. Practical CIPD assignment help is also available to reinforce these concepts and prepare students for success in the dynamic HR field.”
What are the key Learning Objectives of CIPD Level 3?
The CIPD Level 3 qualification encompasses a set of core concepts, each designed to equip you with essential HR skills and knowledge. The following are the key attributes of CIPD Level 3.
- Understanding HR – Delve into the heart of HR and grasp its significance in organizational success.
- Employment Law – Navigate the complex world of employment laws, contracts, and regulations.
- Recruitment and Selection- Master the art of attracting, assessing, and selecting top talent.
- Learning and Development – Discover effective strategies for employee growth and training.
- Employee Relations- Learn to foster harmonious workplace relationships and resolve conflicts.
- Performance Management- Understand how to motivate, evaluate, and enhance employee performance.
- Reward Management- Design compensation and benefits packages that attract and retain talent.
- HR in Context – Explore how HR fits into an organization’s broader strategy and goals.
- Research Skills- Develop the ability to gather and analyze HR data for informed decision-making.
- Ethics and Professionalism – Embrace ethical standards and professionalism as the cornerstones of your HR career.
- Communication Skills- Hone your communication skills for effective HR practice.
- Business Acumen : Gain insight into how HR contributes to an organization’s bottom
CIPD Level 3 Assignment Examples
In this section, we will explore a selection of CIPD Level 3 assignment examples, offering you valuable insights into the practical applications and diverse topics covered within the Chartered Institute of Personnel and Development (CIPD) Level 3 curriculum. These assignments serve as illustrative guides to help you better understand the depth and breadth of knowledge essential for HR professionals at this certification level.
CIPD 3CO01 Example
This CIPD 5CO01 assignment example, titled “Organizational Performance and Culture in Practice,” provides a comprehensive insight into the critical aspects of managing and improving organizational performance and culture. It delves into the practical application of theories and strategies discussed within the Chartered Institute of Personnel and Development (CIPD) Level 5 curriculum, making it an invaluable resource for students aiming to grasp the complexities of HR management in real-world contexts. Whether you’re a CIPD candidate seeking guidance or an HR practitioner looking to refine your skills, this example offers a practical illustration of how to navigate the intricacies of organizational culture and performance management. 3CO01 Assignment Example
CIPD 3CO02 Example
The CIPD 3CO02 module, “Principles of Analytics,” is a pivotal component of the Chartered Institute of Personnel and Development (CIPD) Level 3 curriculum, offering a comprehensive exploration of the fundamental principles and practical applications of HR analytics. This module equips students with a solid foundation in data-driven decision-making within the realm of human resource management. It covers key topics such as data collection, analysis, and interpretation, providing essential skills and knowledge for harnessing the power of data to inform HR strategies and drive organizational success. Whether you are a student aspiring to excel in HR analytics or an HR professional looking to enhance your analytical capabilities, this module serves as a crucial stepping stone in understanding and applying analytics in the field of human resources 3CO02 Assignment Example
CIPD 3CO03 Example
The CIPD 3CO03 module, “Core Behaviors for People Professionals,” plays a pivotal role in shaping the competencies and ethical standards of individuals pursuing a career in human resources. This module explores the essential behaviors and attributes required for success in the field, emphasizing the importance of professionalism, integrity, and ethical decision-making. It provides students with a deep understanding of the ethical dilemmas and challenges faced by HR professionals and equips them with the tools to navigate these situations responsibly. Whether you are a student aspiring to enter the HR profession or a seasoned practitioner looking to reinforce your core behaviors, this module serves as a valuable guide to becoming a skilled and principled people professional in today’s dynamic workplace 3CO03 Assignment Example.
CIPD 3CO04 Example
The CIPD 3CO04 module, “Essentials of People Practice,” represents a foundational cornerstone in the Chartered Institute of Personnel and Development (CIPD) Level 3 curriculum, designed to equip individuals with the fundamental knowledge and skills required for success in the field of human resources. This module covers a wide array of essential topics, ranging from HR policies and procedures to employee relations and workforce planning. It provides students with a comprehensive understanding of the core functions and responsibilities of HR professionals, preparing them to navigate the dynamic challenges of modern workplaces effectively. Whether you are a novice looking to embark on an HR career or a seasoned practitioner seeking to enhance your foundational expertise, this module serves as a crucial stepping stone in establishing a strong foothold in the field of people practice 3CO04 Assignment Example
What is the role of HR in organizations?
The role of HR in organizations, particularly within the context of a CIPD qualification, is multifaceted and critical to an organization’s success. HR professionals are responsible for managing various aspects of the employee lifecycle, including recruitment, training and development, employee relations, and performance management. They ensure compliance with employment laws and regulations, support organizational strategy by aligning HR practices with business goals, and contribute to fostering a positive workplace culture. In the context of CIPD Level 3, individuals gain a foundational understanding of these HR functions, preparing them to make meaningful contributions to their organizations by effectively managing human resources to drive performance and meet organizational objectives.
Why is understanding employment law important in HR?
Understanding employment law is of paramount importance in HR, as it forms the cornerstone of ethical and legally compliant HR practices. CIPD Level 3 coursework equips individuals with the knowledge and skills needed to navigate the complex landscape of employment legislation. This understanding is crucial as HR professionals are responsible for ensuring that their organizations operate within the boundaries of the law when it comes to recruitment, employment contracts, workplace policies, and employee rights. Compliance with employment law not only mitigates legal risks and potential liabilities for an organization but also fosters a fair and equitable work environment, essential for maintaining employee trust and contributing to overall organizational success.
How do you create effective job descriptions?
The creation of effective job descriptions is a skill honed to align with best HR practices. CIPD Level 3 equips individuals with the knowledge and tools needed to craft job descriptions that serve as valuable HR documents. This process involves collaborating with key stakeholders to clearly outline job roles, responsibilities, and qualifications, using precise and inclusive language. Effective job descriptions are crucial not only for successful recruitment but also for guiding performance management, employee development, and compliance with employment regulations. Furthermore, within a CIPD framework, students learn to ensure that job descriptions promote diversity and inclusivity while fostering a positive workplace culture, addressing the broader ethical considerations of HR practice.
What are the key steps in the recruitment process?
Understanding the key steps in the recruitment process is fundamental to HR expertise. At the CIPD Level 3, individuals are equipped with comprehensive knowledge of the recruitment process, which typically includes stages such as job analysis and description, sourcing and attracting candidates, screening and interviewing, and ultimately selecting the right candidate for the role. Moreover, CIPD emphasizes the importance of adhering to legal and ethical standards throughout the recruitment process, promoting fairness, diversity, and equal opportunity. Understanding these key steps not only ensures successful talent acquisition but also contributes to organizational effectiveness and compliance, aligning HR practices with best industry standards and ethical considerations.
What are the elements of a fair interview process?
A fair interview process is founded on principles of ethics and inclusivity. CIPD Level 3 equips individuals with a comprehensive understanding of the elements that constitute a fair interview process, which includes clear and consistent communication with candidates, unbiased questioning and evaluation, adherence to equal opportunity and anti-discrimination laws, and the use of structured assessment criteria to fairly evaluate each candidate’s qualifications and potential. Moreover, it emphasizes the importance of providing feedback to candidates and maintaining transparency throughout the process, ensuring that all individuals are given a fair and equal chance to demonstrate their suitability for the role. In essence, within the CIPD framework, a fair interview process not only selects the best candidates but also upholds ethical standards, diversity, and the organization’s reputation for fairness in talent acquisition.
How can you assess training needs for employees?
In the context of a CIPD qualification, assessing training needs for employees is a critical skill that involves a systematic approach. At the CIPD Level 3, individuals learn various methods and techniques to conduct a comprehensive training needs analysis. This process typically includes gathering input from employees and managers, conducting performance evaluations, identifying skill gaps, and considering future organizational goals and industry trends. The CIPD framework emphasizes the importance of aligning training needs with business objectives to ensure that investments in employee development contribute directly to organizational success. Moreover, students are guided to consider various assessment tools and approaches, promoting a holistic understanding of employee development requirements. By mastering these skills, HR professionals can effectively tailor training programs to address specific needs, foster employee growth, and enhance overall organizational performance.
What strategies can be used for employee development?
Strategies for employee development are a vital aspect of HR expertise. At the CIPD Level 3, individuals gain insights into a range of effective employee development strategies, including formal training programs, mentorship and coaching, job rotation, on-the-job learning, and e-learning platforms. The curriculum emphasizes the importance of aligning these strategies with both individual and organizational goals, ensuring that employees acquire the skills and knowledge necessary for career growth and to meet the evolving needs of the business. Moreover, ethical considerations, inclusivity, and diversity are integral elements, highlighting the significance of promoting equal access to development opportunities for all employees. By mastering these strategies, HR professionals can contribute to a motivated and skilled workforce, enhancing organizational agility and competitiveness.
How do you handle workplace conflicts effectively?
Effectively handling workplace conflicts is a crucial skill emphasized within the curriculum. At the CIPD Level 3, individuals learn a comprehensive approach that involves conflict prevention, early intervention, and resolution. This includes promoting open communication, active listening, and empathy to understand the root causes of conflicts. CIPD emphasizes the importance of adhering to ethical and legal standards while facilitating mediation, negotiation, and conflict resolution techniques. Additionally, the curriculum encourages HR professionals to create a supportive and inclusive workplace culture that fosters conflict resolution skills among employees, ultimately contributing to a harmonious work environment and enhanced organizational performance. By mastering conflict resolution strategies within the CIPD framework, HR practitioners can play a pivotal role in mitigating disputes and promoting a positive workplace atmosphere.
What is the process for addressing employee grievances?
The process for addressing employee grievances is a critical component of HR knowledge. At the CIPD Level 3, individuals learn a structured approach that includes various steps, such as encouraging open communication, providing multiple channels for employees to voice their concerns, and ensuring confidentiality and impartiality throughout the grievance process. CIPD emphasizes adherence to legal and ethical standards while conducting thorough investigations, involving relevant stakeholders, and seeking mutually agreeable resolutions. Additionally, the curriculum underscores the significance of maintaining detailed records and feedback mechanisms to continually improve the grievance-handling process. By mastering these procedures within the CIPD framework, HR professionals can effectively address employee grievances, promote fairness, and contribute to a positive workplace culture that values employee feedback and well-being.
What is the importance of setting performance goals?
In the context of a CIPD qualification, recognizing the importance of setting performance goals is integral to effective human resource management. At the CIPD Level 3, individuals learn that well-defined performance goals provide employees with clear expectations and objectives, which are essential for enhancing motivation and engagement. These goals also serve as benchmarks for measuring employee performance, aiding in the identification of strengths and areas for improvement. Moreover, aligning individual goals with organizational objectives ensures that employees’ efforts contribute directly to the achievement of broader business goals, promoting overall organizational success. Within the CIPD framework, setting performance goals is not only a tool for performance management but also a means to cultivate a culture of accountability, continuous improvement, and professional development, all of which are crucial for HR professionals to master.
What is the purpose of conducting performance appraisals?
At the CIPD Level 3, individuals learn that performance appraisals are instrumental in providing employees with feedback on their performance, recognizing their achievements, and identifying areas for improvement. These appraisals also facilitate the setting of clear performance goals and expectations, fostering alignment with organizational objectives. Additionally, performance appraisals offer opportunities for career development discussions, enhancing employee engagement and retention. Moreover, they serve as a basis for making decisions related to compensation, promotions, and training needs. In essence, within the CIPD framework, conducting performance appraisals is a strategic and comprehensive approach to managing and optimizing employee performance while contributing to organizational success and employee well-being.
How can you provide constructive feedback to employees?
Providing constructive feedback to employees is a skill that embodies principles of effective human resource management. At the CIPD Level 3, individuals learn to deliver feedback that is specific, timely, and actionable. This feedback should focus on behaviors and outcomes rather than personality traits, fostering a growth-oriented mindset. Moreover, the CIPD curriculum emphasizes the importance of maintaining a supportive and open communication environment, where employees are encouraged to ask questions and engage in a constructive dialogue about their performance. Feedback sessions are approached with empathy and active listening, ensuring that employees feel valued and motivated to implement improvements. By mastering these techniques within the CIPD framework, HR professionals can provide feedback that contributes to individual growth, enhances job performance, and promotes a positive workplace culture.
What factors should be considered in reward management?
At the CIPD Level 3, individuals learn to consider a multitude of factors, including market benchmarks to ensure competitive salaries, internal pay equity to maintain fairness within the organization, and alignment with the organization’s strategic goals to motivate and retain talent effectively. CIPD underscores the importance of considering diverse reward elements, such as financial incentives, non-monetary rewards, and recognition programs, all of which contribute to a comprehensive and motivating reward strategy. Moreover, ethical considerations, legal compliance, and the organization’s culture and values are integral aspects of reward management, ensuring that employees are fairly compensated while supporting the organization’s broader objectives. Within the CIPD framework, mastering reward management is key to attracting, retaining, and motivating a high-performing workforce while adhering to ethical and legal standards.
How does HR contribute to an organization’s strategy?
HR plays a pivotal role in shaping and executing an organization’s strategy. At the CIPD Level 3, individuals learn that HR professionals contribute to strategy formulation by aligning HR practices with the organization’s goals and objectives. This involves workforce planning, talent acquisition, and development strategies that ensure the right talent is in place to execute the strategy effectively. HR also helps in creating a supportive and inclusive culture that fosters innovation and employee engagement, critical for strategy execution. Additionally, HR ensures compliance with legal and ethical standards, mitigating risks that may hinder strategic progress. Through these multifaceted contributions within the CIPD framework, HR professionals become strategic partners, enabling the organization to achieve its mission and long-term success by leveraging its most valuable asset—its people.
Why is ethical behavior important in HR?
Individuals learn that ethical conduct is essential because HR professionals are entrusted with sensitive employee data, confidential information, and critical decisions that impact individuals’ livelihoods and well-being. Upholding ethical standards ensures fairness, equity, and transparency in HR processes, such as recruitment, performance management, and compensation. Moreover, ethics in HR promotes a positive workplace culture, trust among employees, and organizational reputation. By adhering to ethical principles and CIPD’s Code of Conduct, HR practitioners demonstrate integrity, promote diversity and inclusivity, and contribute to a workplace that values ethical behavior, which is vital for the organization’s long-term success and sustainability.
What are the key components of a job contract?
Individuals learn that a job contract typically includes several fundamental elements, such as the job title, a clear and concise job description outlining roles and responsibilities, terms of employment including working hours and location, salary and benefits details, and notice periods for termination. Additionally, HR practitioners are taught to consider legal and ethical aspects, ensuring compliance with employment laws and regulations, as well as principles of fairness and equity in contractual agreements. By mastering the creation and management of job contracts within the CIPD framework, HR professionals can help establish clear and mutually beneficial employment relationships while mitigating potential disputes or legal issues.
What is the concept of workplace discrimination?
Individuals learn that workplace discrimination refers to the unfair and unjust treatment of employees or job applicants based on certain protected characteristics, such as age, gender, race, religion, disability, or sexual orientation. Discrimination can take various forms, including direct discrimination, indirect discrimination, harassment, and victimization, all of which are illegal and unethical. HR practitioners are trained to recognize and prevent discrimination, ensuring that all employees have equal opportunities and are treated with dignity and respect. Moreover, CIPD underscores the importance of creating inclusive workplace policies and fostering a culture that values diversity, promoting a fair and equitable work environment that complies with legal requirements and aligns with best HR practices.
How can HR professionals address workplace harassment?
At the CIPD Level 3, individuals learn a comprehensive approach that involves establishing clear anti-harassment policies and procedures within organizations. HR practitioners are trained to create a safe environment for reporting harassment, conduct thorough investigations, and take appropriate corrective actions in accordance with legal and ethical standards. Additionally, CIPD emphasizes the importance of providing support to victims and raising awareness through training and education programs to prevent harassment. HR professionals within the CIPD framework play a pivotal role in fostering a culture of respect, dignity, and inclusivity, ensuring that all employees are protected from harassment and promoting a positive workplace environment conducive to organizational success.
What is the role of HR in resolving disputes?
At the CIPD Level 3, individuals learn that HR professionals act as mediators and facilitators, helping to identify, address, and resolve workplace disputes through open communication and conflict resolution techniques. They play a pivotal role in ensuring that disputes are managed impartially, ethically, and in compliance with legal standards, safeguarding the rights and well-being of all parties involved. HR practitioners are trained to conduct thorough investigations, gather relevant information, and propose fair and equitable solutions to conflicts, promoting a harmonious work environment. Moreover, they work proactively to implement preventive measures and policies that reduce the occurrence of disputes. By mastering dispute resolution within the CIPD framework, HR professionals contribute to a positive workplace culture and mitigate potential legal and organizational risks.
How does HR align with an organization’s mission?
Within the context of a CIPD qualification, aligning HR with an organization’s mission is fundamental to HR professionals. At the CIPD Level 3, individuals learn that HR plays a crucial role in ensuring that an organization’s mission, values, and strategic goals are reflected in its HR policies, practices, and workforce planning. This involves aligning recruitment and talent development strategies to secure the right talent that embodies the organization’s mission and values. HR professionals also contribute to fostering a culture that supports and reinforces the mission through employee engagement, communication, and leadership development. Moreover, HR ensures that HR metrics and key performance indicators (KPIs) are tied to organizational objectives, enabling the measurement of progress toward fulfilling the mission. By mastering the alignment of HR with an organization’s mission within the CIPD framework, HR practitioners contribute to the organization’s long-term success and sustainability by ensuring that its people practices are in harmony with its overarching purpose and goals.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Automated page speed optimizations for fast site performance
- +44 2871140060

- Terms of Service
3CO01 BUSINESS, CULTURE AND CHANGE IN CONTEXT
- October 14, 2022
- Posted by: Fletcher Samuel
- Category: CIPD Level 3

Table of Contents
Introduction to 3co01 new assessment brief.
The first unit in the Level 3 Foundation Certificate in People Practice is 3CO01. The new brief investigates the internal influences that shape the business and the culture in which it operates. The unit investigates the behaviours of people professionals in managing change. The new brief asks students to answer the following questions in an estimated 2500 words. Students base their responses on their organization or a familiar organization. I’ll use McDonald’s as an example in this guideline.
Are you a busy manager?
Secure your future with our high-quality paper—order now!
You can talk to the writer using our messaging system and keep track of how your assignment is going.
Assessment questions
1.1 An examination of the key external influences impacting or likely to impact the organisation’s activities
The guideline
Students will explain three external factors and their impact on the organization (positive or negative). Students can use the PESTLE analysis tool to identify and discuss the factors (political, economic, social, technological, legal, and environmental) that affect McDonald’s business operations. As an example:
- Political factor: Brexit.
- Economic factor: Covid-19 pandemic
- Legal Factor: Changing employment regulations laws
Students will explain how the factors listed above help them understand the business market environment.
1.2 A discussion of the organisation’s business goals and why organisations need to plan for how they will achieve these
A business goal is a target that the company intends to achieve within a certain time frame. McDonald’s business goal is to provide a welcoming environment for customers as well as nutritious food. Students detail the other organizational goals as well as the objectives that support business within the external environment.
Students will then discuss why professionals must plan how they will achieve business objectives. The reasons should be thoroughly discussed to ensure that HR is aligned with the organization’s goals and objectives.
1.3 A discussion of the organisation’s products and/or services and main customers
The students will describe the core products, the actual products, and the augmented products.
Students will also explain the customer characteristics and demographics, as well as the efforts made by the company to ensure that customers’ needs are met.
McDonald’s main products are fast food, beverages, and desserts. Among the services offered are improved dining experiences and a strong emphasis on customer service.
McDonald’s caters to low and middle-income customers, the majority of whom are students, employees, and parents with young children.
1.4 A short review of different technologies available to people professionals and how these can be, or are, used to improve working practices and collaboration. You might consider, for example, technologies relating to communications, information sharing, record keeping, learning, well-being, productivity, or security
Students provide three examples of workplace technology used by professionals. Here are some examples:
- Social media technology
- Artificial intelligence
- Cloud automation
Students go on to describe how each technology improves work practices and collaboration. Social media technology, for example, improves communication, artificial intelligence improves service, learning, and productivity, and automation improves the automation of manual processes to speed up functions, particularly record-keeping.
Finally, students explain the benefits and drawbacks of the technologies discussed.
2.1 What is meant by organisational culture and why it is important to foster an appropriate and effective workplace culture
Students define workplace culture as the concept that describes how things are done in the organization. The underlying beliefs, values, patterns, and principles that comprise an organization’s work system are referred to as its culture.
Students can refer to Charles Handy’s model of organizational culture, which describes the following elements:
- Task culture
- Person culture
- Role culture
Students explain why it is critical to cultivating a positive culture. Some of the reasons are as follows:
- Increase employee involvement
- Accept diversity and inclusion.
- Improve internal consistency
Finally, students will provide one example of positive workplace culture and one example of negative workplace culture. Here are some examples:
- A culture that encourages employee learning to improve growth and career development.
- Employee competition that is unhealthy and harms the employees
2.2 How organisations are whole systems, in which different areas and aspects such as structure, systems and culture, are all inter-related, and how people professionals work and actions could impact elsewhere in the organisation
Students describe various organizational structures, such as the flat or tail structure. Students may also include an organizational chart to demonstrate the roles of various professionals in various fields of work.
Students explain how various areas of the organization interact with one another to achieve holistic systems. For instance, a discussion about how the innovative development sector connects with the government and the international market to form a holistic organization.
Finally, students give one example of a good people practice, such as providing employees with safe and healthy working conditions, and one example of a bad people practice, such as failing to comply with employment laws.
3.1 Why it is important that organisational change is planned, and effectively managed
Organizations must adapt to change. Change should be planned and managed by people professionals to have a positive impact on the organization. Change agents at work include:
- Change in structure
- Technology advancement
- Introduction of new educational programs
- Organizational Process Change
By referencing project planning, students further explain why it is important to plan and manage change. To achieve project goals and objectives, explain the role and purpose of planning.
PESTLE and SWOT tools are used to predict change in organizations.
3.2 The nature and importance of different roles that can be played by people practice professionals, concerning change agendas. You might consider roles such as gatekeeper, champion, facilitator, critical friend or record-keeper
For instance, people professionals advocate for employee rights by following change agendas.
When implementing change agendas, students explain the support that people professionals provide.
3.3 How organisational change can impact people in different ways, such as changing their role or status or financial situation, and the different ways people may respond to change
Examples of change:
- An upgrade, regrade, or downgrade in the financial sector
- Loss of employment
- Changes in the family
- Competitor relationships
In this lesson, students examine how people respond to change using a model or theory. Here are some examples:
- Kubler-Ross model
- Fisher curve
- BATTISTA, M. (2021) PESTLE Analysis. Available at https://www.cipd.co.uk/knowledge/strategy/organisational-development/pestle-analysis-factsheet
- GEORGE, S. (2021) Change Management. Available at https://www.cipd.co.uk/knowledge/strategy/change/management-factsheet
- MOHDZAINI, H. (2021) Technology and the future of work. Available at https://www.cipd.co.uk/knowledge/work/technology/emerging-future-work-factsheet
- YOUNG, J. (2020) Organisational culture and cultural change. Available at https://www.cipd.co.uk/knowledge/culture/working-environment/organisation-culture-change-factsheet
- 3CO01 Assignment Example
Comments are closed.
Our writing service is available in the UK, USA, Ireland, Canada, Australia, Saudi Arabia, Singapore, and other countries around the world.

- WordPress.org
- Documentation
- Learn WordPress
- Always Online
- +44 2871140060

- CIPD Level 3 Course
- CIPD Level 5
- CIPD Level 7 Courses
- ILM Assignment Help
- CMI Assignment Help
3CO01 Business, Culture and Change in Context
- November 12, 2021
- Posted by: admin
- Category: CIPD Level 3

Introduction to 3CO01
This unit examines the importance of digital, commercial, and external influence in shaping business within an organisation’s culture, the impact of people’s behaviour on culture, and an organisation’s ability to manage change effectively.
Learning outcomes
Students will be able to:
- Recognise that external influences impact businesses. These include legal influences, social, economic, technological, and competitive influences.
- Understanding how the culture of the workshop is influenced by the culture of the people in it.
- Identify how one’s actions affect others and how an organisation as a whole function.
- Identify the diverse ways in which employees can learn, adapt, and develop in an organisation.
- Develop an understanding of the concept of change in an organisation as a whole. In addition, students will learn about the impact of people professions on employees.
The unit is designed to help learners understand;
The business environment and significant issues affecting it
Each organisation operates in a different environment and faces a unique set of challenges. These can be analysed by:-
- Analysing the primary external influences that have an impact on the environment of an organisation.
Different external forces affect the current and future activities of an organisation. These factors include the market an organisation operates in and the steeple. Therefore, an organisation needs to conduct a SWOT analysis to understand better the market it operates in.
- Analysing an organisation’s goals and discussing the importance of planning.
The organisation’s vision and objectives, business structure, documentation of the business, and employment climate should be included in each business’s short-term and long-term goals. Organisations use different methods of informing their customers and staff, determining their goals, planning, and linking these to their policies and people practices. Business continuity planning provides insight into potential disruptions and enables an organisation to continue operating during a crisis. Additionally, it helps maintain an organisation’s reputation and saves time and resources.
- Assessing an organisation’s products and services and their target customers.
In order to analyse the market, analyse consumer needs, analyse features and benefits of products or services an organisation offers, and to create market segments based on consumer needs, consumer priorities, demographics and consumer interests, learners will need to discuss the products or services that an organisation offers and their primary customers.
- Examine the importance of technology within people’s professions and examine how it can improve collaboration and working practices.
Learners should be aware of the different technologies used within organisations, such as the internet, email, and electronic communications. For example, electronic communication includes smartphones; social media, such as Twitter, Google, Facebook, Instagram, and YouTube; cloud-based communication methods; dashboards; cloud hosting; Bluetooth; voice command software; facial recognition software; fingertips; artificial intelligence; file management; autoresponders, and synchronising software. The course also teaches the capabilities of collective and individual technologies that are essential to change, improvement, and can influence working practices; the social and technological approaches that are utilised to enhance communication in organisations, digital marketing of products and services, customer service, improving work efficiency in organisations, and improving productivity and security.
The impact of people’s behaviour on an organisation’s culture
In an organisation, people’s behaviours influence and shape its culture by;-
- Determining the organisational culture at the workplace and highlighting the importance of promoting positive changes.
Understanding what culture is and describing its different types is essential to understanding culture in an organisational context; positive and negative cultures; impacts of culture; subcultures; norms and values; cultural diversity. Learners should also be able to comprehend and describe: the role people professionals play in facilitating relevant and effective organisational culture; an organisation as a holistic system; how to create diversity and inclusion principles in organisational practices; the importance of creating a diverse and inclusive environment in an organisation.
- Understanding how organisations operate as a whole system and how people professionals work and how their actions influence other areas.
The learners should be able to explain the type, structure, design and system of organisations. Furthermore, they should be able to identify the various approaches taken in order to achieve a productive holistic system approach, understand organisations as organic living systems, and determine how government influence, dissemination and communication, national and international, innovative developments, record keeping, changes in laws, legality and compliance are addressed.
- Assessment of employee skills and capabilities using organisational assessments of employees’ learning and development.
Students should be able to understand how learning can be transferred in order to achieve high performance and competitiveness within an organisation; the importance of learning; how to fill skill gaps, critical incidents and underperformance in organisations; how to capture and interpret learning trends; theories and factors affecting learning; The importance of managing change effectively in an organisation Each business must have effective management of change. Here are some ways to do this:
- Outlining the importance of managing change within an organisation.
Various factors trigger organisational change, such as competitive innovation, which is essential to beating competitors, technological change, which increases business opportunities, environmental turbulence, market demands, government policies, failure or divergence in the business community, and social and economic factors. In addition, the business can be affected by changes in initiatives and situations within an organisation. Therefore, several components of project planning need to be clearly defined, including roles, purposes, goals, and objectives.
- Defining the role and importance of people professionals in change.
Different types of people professionals play different roles in organisational change. People professionals play a significant role in facilitating the agendas of change, such as: being the gatekeepers to the process of change; taking on the role of the representatives of the change; they act as the catalysts for the change; they act as witnesses to the change; they act as change consultants; they actively participate and offer positive changes perspectives to non-participants; they provide legal guidelines and compliance; they disseminate information, and they keep records.
- Explaining how the change impacts people in different ways.
Individuals respond to change in different ways, including behavioural responses, personal responses and professional responses. To understand how change impacts learners, learners should explain how it impacts them. Job loss, demotion in position, promotion, relocation, degrading, and salary increment or decrease are among these impacts. For example, if someone is demoted, they may suffer from low self-esteem and mental health issues. In addition, customers report improved welfare, teamwork formation, and career advancement.


IMAGES
COMMENTS
3CO01 Assignment Example. This unit examines the impact of external factors and how the digital and commercial environments shape businesses and the cultures in which they operate. It also explores the significance of people's behaviour on organisational culture and its capacity to manage change effectively.
Project manager. A project manager designs the actual change, manages the technical part, engages the change practitioner, and integrates change management plans with the project plan (Rosenbaum et al., 2018). This role is critical as it concentrates on the project's design, development, and implementation.
CIPD 3CO01 Business, Culture, and Change in Context. An examinationof the key external influences impacting or likely to impact the organisation's activities. (AC 1.1) The education institution I work is a university chartered in a foreign country. As such, much of the funding comes from the mother country.
3CO01 Business, Culture and Change in Context. Task - Information sheet ... 3CO01 Assignment Example. 3CO02 Principles of Analytics. The presentation must provide knowledge and understanding of how evidence-based practice informs organisational measures and outcomes and how creating value benefits employees, customers and wider stakeholders. ...
Following are the assignment solutions of 3CO01 Business, Culture and Change in Context: 1 CIPD Level 3 3CO01 Assignment Task 1: Understand the business environment in which the people profession operates, including the key issues that affect it. 1.1 1.1 Examine the key external influences that impact on business environments.
For example, Apple has embraced a high-performance work culture that also prioritises accountability (PerformYard, 2022). The aforementioned ensures employees have a good understanding of their goals and responsibilities and are focused on creating the best products and delivering on the organisation's goals.
This comprehensive analysis examines three key external influences that impact, or are likely to impact, an organisation's activities: economic factors, technological advancements, and the regulatory and legal environment. A discussion of the organisation's products and/or services and main customers. (AC 1.3)
3CO01 is the first unit in Level 3 Foundation Certificate in People Practice. The new brief examines the internal influences shaping the business and the ... 5OS02 Advances in digital learning and development Assignment Example Guideline. 6 May, 2024 5OS02 Advances in Digital Learning and Development Assessment Brief Guidance. 5 Jul, 2023 Quick ...
3co01 Assignment Example Recent Posts. 7CO03 Assignment Example; 7OS06 Well-Being at Work; 7OS05 Managing People in an International Context ... allowing you to stay updated on the progress of your assignment. Click the button below to place your order and receive a high-quality paper. Order Now. TASK.
Guideline. George (2021) acknowledge that change in an organisation is essential and professionals should be keen to plan and manage change for positive outcomes. Concepts that students should consider include-. Change triggers (for example;- competition, change in technology, discontinuity) How change impacts the business.
Admin August 2, 2023 CIPD LEVEL 3. Task One. AC 1.1 Application of an analysis tool (such as PESTLE) to examine the key external forces impacting or likely to impact an organisation's activities. AC 1.2 An explanation of an organisation's business goals and why it is important for organisations to plan for how they will achieve these.
Fig 1: the 70/20/10 Model of Organisational Learning. 3CO01 Assignment Example. Prior to an organisation deciding on the learning and development method to use the organisation shoul evaluate the employees skills and competencies which can proceed through conducting of tests, getting feedback from teams, through self-assessment exercises ...
3CO01 Assignment Example. CIPD 3CO02 Example. The CIPD 3CO02 module, "Principles of Analytics," is a pivotal component of the Chartered Institute of Personnel and Development (CIPD) Level 3 curriculum, offering a comprehensive exploration of the fundamental principles and practical applications of HR analytics. This module equips students ...
The first unit in the Level 3 Foundation Certificate in People Practice is 3CO01. The new brief investigates the internal influences that shape the business and the culture in which it operates. The unit investigates the behaviours of people professionals in managing change. The new brief asks students to answer the following questions in an ...
Introduction to 3CO01. This unit examines the importance of digital, commercial, and external influence in shaping business within an organisation's culture, the impact of people's behaviour on culture, and an organisation's ability to manage change effectively.. Learning outcomes. Students will be able to: Recognise that external influences impact businesses.