- Resources Home 🏠
- Try SciSpace Copilot
- Search research papers
- Add Copilot Extension
- Try AI Detector
- Try Paraphraser
- Try Citation Generator
- April Papers
- June Papers
- July Papers


What is a thesis | A Complete Guide with Examples

Table of Contents
A thesis is a comprehensive academic paper based on your original research that presents new findings, arguments, and ideas of your study. It’s typically submitted at the end of your master’s degree or as a capstone of your bachelor’s degree.
However, writing a thesis can be laborious, especially for beginners. From the initial challenge of pinpointing a compelling research topic to organizing and presenting findings, the process is filled with potential pitfalls.
Therefore, to help you, this guide talks about what is a thesis. Additionally, it offers revelations and methodologies to transform it from an overwhelming task to a manageable and rewarding academic milestone.
What is a thesis?
A thesis is an in-depth research study that identifies a particular topic of inquiry and presents a clear argument or perspective about that topic using evidence and logic.
Writing a thesis showcases your ability of critical thinking, gathering evidence, and making a compelling argument. Integral to these competencies is thorough research, which not only fortifies your propositions but also confers credibility to your entire study.
Furthermore, there's another phenomenon you might often confuse with the thesis: the ' working thesis .' However, they aren't similar and shouldn't be used interchangeably.
A working thesis, often referred to as a preliminary or tentative thesis, is an initial version of your thesis statement. It serves as a draft or a starting point that guides your research in its early stages.
As you research more and gather more evidence, your initial thesis (aka working thesis) might change. It's like a starting point that can be adjusted as you learn more. It's normal for your main topic to change a few times before you finalize it.
While a thesis identifies and provides an overarching argument, the key to clearly communicating the central point of that argument lies in writing a strong thesis statement.
What is a thesis statement?
A strong thesis statement (aka thesis sentence) is a concise summary of the main argument or claim of the paper. It serves as a critical anchor in any academic work, succinctly encapsulating the primary argument or main idea of the entire paper.
Typically found within the introductory section, a strong thesis statement acts as a roadmap of your thesis, directing readers through your arguments and findings. By delineating the core focus of your investigation, it offers readers an immediate understanding of the context and the gravity of your study.
Furthermore, an effectively crafted thesis statement can set forth the boundaries of your research, helping readers anticipate the specific areas of inquiry you are addressing.
Different types of thesis statements
A good thesis statement is clear, specific, and arguable. Therefore, it is necessary for you to choose the right type of thesis statement for your academic papers.
Thesis statements can be classified based on their purpose and structure. Here are the primary types of thesis statements:
Argumentative (or Persuasive) thesis statement
Purpose : To convince the reader of a particular stance or point of view by presenting evidence and formulating a compelling argument.
Example : Reducing plastic use in daily life is essential for environmental health.
Analytical thesis statement
Purpose : To break down an idea or issue into its components and evaluate it.
Example : By examining the long-term effects, social implications, and economic impact of climate change, it becomes evident that immediate global action is necessary.
Expository (or Descriptive) thesis statement
Purpose : To explain a topic or subject to the reader.
Example : The Great Depression, spanning the 1930s, was a severe worldwide economic downturn triggered by a stock market crash, bank failures, and reduced consumer spending.
Cause and effect thesis statement
Purpose : To demonstrate a cause and its resulting effect.
Example : Overuse of smartphones can lead to impaired sleep patterns, reduced face-to-face social interactions, and increased levels of anxiety.
Compare and contrast thesis statement
Purpose : To highlight similarities and differences between two subjects.
Example : "While both novels '1984' and 'Brave New World' delve into dystopian futures, they differ in their portrayal of individual freedom, societal control, and the role of technology."
When you write a thesis statement , it's important to ensure clarity and precision, so the reader immediately understands the central focus of your work.
What is the difference between a thesis and a thesis statement?
While both terms are frequently used interchangeably, they have distinct meanings.
A thesis refers to the entire research document, encompassing all its chapters and sections. In contrast, a thesis statement is a brief assertion that encapsulates the central argument of the research.
Here’s an in-depth differentiation table of a thesis and a thesis statement.
Aspect | Thesis | Thesis Statement |
Definition | An extensive document presenting the author's research and findings, typically for a degree or professional qualification. | A concise sentence or two in an essay or research paper that outlines the main idea or argument. |
Position | It’s the entire document on its own. | Typically found at the end of the introduction of an essay, research paper, or thesis. |
Components | Introduction, methodology, results, conclusions, and bibliography or references. | Doesn't include any specific components |
Purpose | Provides detailed research, presents findings, and contributes to a field of study. | To guide the reader about the main point or argument of the paper or essay. |
Now, to craft a compelling thesis, it's crucial to adhere to a specific structure. Let’s break down these essential components that make up a thesis structure
15 components of a thesis structure
Navigating a thesis can be daunting. However, understanding its structure can make the process more manageable.
Here are the key components or different sections of a thesis structure:
Your thesis begins with the title page. It's not just a formality but the gateway to your research.

Here, you'll prominently display the necessary information about you (the author) and your institutional details.
- Title of your thesis
- Your full name
- Your department
- Your institution and degree program
- Your submission date
- Your Supervisor's name (in some cases)
- Your Department or faculty (in some cases)
- Your University's logo (in some cases)
- Your Student ID (in some cases)
In a concise manner, you'll have to summarize the critical aspects of your research in typically no more than 200-300 words.

This includes the problem statement, methodology, key findings, and conclusions. For many, the abstract will determine if they delve deeper into your work, so ensure it's clear and compelling.
Acknowledgments
Research is rarely a solitary endeavor. In the acknowledgments section, you have the chance to express gratitude to those who've supported your journey.

This might include advisors, peers, institutions, or even personal sources of inspiration and support. It's a personal touch, reflecting the humanity behind the academic rigor.
Table of contents
A roadmap for your readers, the table of contents lists the chapters, sections, and subsections of your thesis.

By providing page numbers, you allow readers to navigate your work easily, jumping to sections that pique their interest.
List of figures and tables
Research often involves data, and presenting this data visually can enhance understanding. This section provides an organized listing of all figures and tables in your thesis.

It's a visual index, ensuring that readers can quickly locate and reference your graphical data.
Introduction
Here's where you introduce your research topic, articulate the research question or objective, and outline the significance of your study.

- Present the research topic : Clearly articulate the central theme or subject of your research.
- Background information : Ground your research topic, providing any necessary context or background information your readers might need to understand the significance of your study.
- Define the scope : Clearly delineate the boundaries of your research, indicating what will and won't be covered.
- Literature review : Introduce any relevant existing research on your topic, situating your work within the broader academic conversation and highlighting where your research fits in.
- State the research Question(s) or objective(s) : Clearly articulate the primary questions or objectives your research aims to address.
- Outline the study's structure : Give a brief overview of how the subsequent sections of your work will unfold, guiding your readers through the journey ahead.
The introduction should captivate your readers, making them eager to delve deeper into your research journey.
Literature review section
Your study correlates with existing research. Therefore, in the literature review section, you'll engage in a dialogue with existing knowledge, highlighting relevant studies, theories, and findings.

It's here that you identify gaps in the current knowledge, positioning your research as a bridge to new insights.
To streamline this process, consider leveraging AI tools. For example, the SciSpace literature review tool enables you to efficiently explore and delve into research papers, simplifying your literature review journey.
Methodology
In the research methodology section, you’ll detail the tools, techniques, and processes you employed to gather and analyze data. This section will inform the readers about how you approached your research questions and ensures the reproducibility of your study.

Here's a breakdown of what it should encompass:
- Research Design : Describe the overall structure and approach of your research. Are you conducting a qualitative study with in-depth interviews? Or is it a quantitative study using statistical analysis? Perhaps it's a mixed-methods approach?
- Data Collection : Detail the methods you used to gather data. This could include surveys, experiments, observations, interviews, archival research, etc. Mention where you sourced your data, the duration of data collection, and any tools or instruments used.
- Sampling : If applicable, explain how you selected participants or data sources for your study. Discuss the size of your sample and the rationale behind choosing it.
- Data Analysis : Describe the techniques and tools you used to process and analyze the data. This could range from statistical tests in quantitative research to thematic analysis in qualitative research.
- Validity and Reliability : Address the steps you took to ensure the validity and reliability of your findings to ensure that your results are both accurate and consistent.
- Ethical Considerations : Highlight any ethical issues related to your research and the measures you took to address them, including — informed consent, confidentiality, and data storage and protection measures.
Moreover, different research questions necessitate different types of methodologies. For instance:
- Experimental methodology : Often used in sciences, this involves a controlled experiment to discern causality.
- Qualitative methodology : Employed when exploring patterns or phenomena without numerical data. Methods can include interviews, focus groups, or content analysis.
- Quantitative methodology : Concerned with measurable data and often involves statistical analysis. Surveys and structured observations are common tools here.
- Mixed methods : As the name implies, this combines both qualitative and quantitative methodologies.
The Methodology section isn’t just about detailing the methods but also justifying why they were chosen. The appropriateness of the methods in addressing your research question can significantly impact the credibility of your findings.
Results (or Findings)
This section presents the outcomes of your research. It's crucial to note that the nature of your results may vary; they could be quantitative, qualitative, or a mix of both.

Quantitative results often present statistical data, showcasing measurable outcomes, and they benefit from tables, graphs, and figures to depict these data points.
Qualitative results , on the other hand, might delve into patterns, themes, or narratives derived from non-numerical data, such as interviews or observations.
Regardless of the nature of your results, clarity is essential. This section is purely about presenting the data without offering interpretations — that comes later in the discussion.
In the discussion section, the raw data transforms into valuable insights.
Start by revisiting your research question and contrast it with the findings. How do your results expand, constrict, or challenge current academic conversations?
Dive into the intricacies of the data, guiding the reader through its implications. Detail potential limitations transparently, signaling your awareness of the research's boundaries. This is where your academic voice should be resonant and confident.
Practical implications (Recommendation) section
Based on the insights derived from your research, this section provides actionable suggestions or proposed solutions.
Whether aimed at industry professionals or the general public, recommendations translate your academic findings into potential real-world actions. They help readers understand the practical implications of your work and how it can be applied to effect change or improvement in a given field.
When crafting recommendations, it's essential to ensure they're feasible and rooted in the evidence provided by your research. They shouldn't merely be aspirational but should offer a clear path forward, grounded in your findings.
The conclusion provides closure to your research narrative.
It's not merely a recap but a synthesis of your main findings and their broader implications. Reconnect with the research questions or hypotheses posited at the beginning, offering clear answers based on your findings.

Reflect on the broader contributions of your study, considering its impact on the academic community and potential real-world applications.
Lastly, the conclusion should leave your readers with a clear understanding of the value and impact of your study.
References (or Bibliography)
Every theory you've expounded upon, every data point you've cited, and every methodological precedent you've followed finds its acknowledgment here.

In references, it's crucial to ensure meticulous consistency in formatting, mirroring the specific guidelines of the chosen citation style .
Proper referencing helps to avoid plagiarism , gives credit to original ideas, and allows readers to explore topics of interest. Moreover, it situates your work within the continuum of academic knowledge.
To properly cite the sources used in the study, you can rely on online citation generator tools to generate accurate citations!
Here’s more on how you can cite your sources.
Often, the depth of research produces a wealth of material that, while crucial, can make the core content of the thesis cumbersome. The appendix is where you mention extra information that supports your research but isn't central to the main text.

Whether it's raw datasets, detailed procedural methodologies, extended case studies, or any other ancillary material, the appendices ensure that these elements are archived for reference without breaking the main narrative's flow.
For thorough researchers and readers keen on meticulous details, the appendices provide a treasure trove of insights.
Glossary (optional)
In academics, specialized terminologies, and jargon are inevitable. However, not every reader is versed in every term.
The glossary, while optional, is a critical tool for accessibility. It's a bridge ensuring that even readers from outside the discipline can access, understand, and appreciate your work.

By defining complex terms and providing context, you're inviting a wider audience to engage with your research, enhancing its reach and impact.
Remember, while these components provide a structured framework, the essence of your thesis lies in the originality of your ideas, the rigor of your research, and the clarity of your presentation.
As you craft each section, keep your readers in mind, ensuring that your passion and dedication shine through every page.
Thesis examples
To further elucidate the concept of a thesis, here are illustrative examples from various fields:
Example 1 (History): Abolition, Africans, and Abstraction: the Influence of the ‘Noble Savage’ on British and French Antislavery Thought, 1787-1807 by Suchait Kahlon.
Example 2 (Climate Dynamics): Influence of external forcings on abrupt millennial-scale climate changes: a statistical modelling study by Takahito Mitsui · Michel Crucifix
Checklist for your thesis evaluation
Evaluating your thesis ensures that your research meets the standards of academia. Here's an elaborate checklist to guide you through this critical process.
Content and structure
- Is the thesis statement clear, concise, and debatable?
- Does the introduction provide sufficient background and context?
- Is the literature review comprehensive, relevant, and well-organized?
- Does the methodology section clearly describe and justify the research methods?
- Are the results/findings presented clearly and logically?
- Does the discussion interpret the results in light of the research question and existing literature?
- Is the conclusion summarizing the research and suggesting future directions or implications?
Clarity and coherence
- Is the writing clear and free of jargon?
- Are ideas and sections logically connected and flowing?
- Is there a clear narrative or argument throughout the thesis?
Research quality
- Is the research question significant and relevant?
- Are the research methods appropriate for the question?
- Is the sample size (if applicable) adequate?
- Are the data analysis techniques appropriate and correctly applied?
- Are potential biases or limitations addressed?
Originality and significance
- Does the thesis contribute new knowledge or insights to the field?
- Is the research grounded in existing literature while offering fresh perspectives?
Formatting and presentation
- Is the thesis formatted according to institutional guidelines?
- Are figures, tables, and charts clear, labeled, and referenced in the text?
- Is the bibliography or reference list complete and consistently formatted?
- Are appendices relevant and appropriately referenced in the main text?
Grammar and language
- Is the thesis free of grammatical and spelling errors?
- Is the language professional, consistent, and appropriate for an academic audience?
- Are quotations and paraphrased material correctly cited?
Feedback and revision
- Have you sought feedback from peers, advisors, or experts in the field?
- Have you addressed the feedback and made the necessary revisions?
Overall assessment
- Does the thesis as a whole feel cohesive and comprehensive?
- Would the thesis be understandable and valuable to someone in your field?
Ensure to use this checklist to leave no ground for doubt or missed information in your thesis.
After writing your thesis, the next step is to discuss and defend your findings verbally in front of a knowledgeable panel. You’ve to be well prepared as your professors may grade your presentation abilities.
Preparing your thesis defense
A thesis defense, also known as "defending the thesis," is the culmination of a scholar's research journey. It's the final frontier, where you’ll present their findings and face scrutiny from a panel of experts.
Typically, the defense involves a public presentation where you’ll have to outline your study, followed by a question-and-answer session with a committee of experts. This committee assesses the validity, originality, and significance of the research.
The defense serves as a rite of passage for scholars. It's an opportunity to showcase expertise, address criticisms, and refine arguments. A successful defense not only validates the research but also establishes your authority as a researcher in your field.
Here’s how you can effectively prepare for your thesis defense .
Now, having touched upon the process of defending a thesis, it's worth noting that scholarly work can take various forms, depending on academic and regional practices.
One such form, often paralleled with the thesis, is the 'dissertation.' But what differentiates the two?
Dissertation vs. Thesis
Often used interchangeably in casual discourse, they refer to distinct research projects undertaken at different levels of higher education.
To the uninitiated, understanding their meaning might be elusive. So, let's demystify these terms and delve into their core differences.
Here's a table differentiating between the two.
Aspect | Thesis | Dissertation |
Purpose | Often for a master's degree, showcasing a grasp of existing research | Primarily for a doctoral degree, contributing new knowledge to the field |
Length | 100 pages, focusing on a specific topic or question. | 400-500 pages, involving deep research and comprehensive findings |
Research Depth | Builds upon existing research | Involves original and groundbreaking research |
Advisor's Role | Guides the research process | Acts more as a consultant, allowing the student to take the lead |
Outcome | Demonstrates understanding of the subject | Proves capability to conduct independent and original research |
Wrapping up
From understanding the foundational concept of a thesis to navigating its various components, differentiating it from a dissertation, and recognizing the importance of proper citation — this guide covers it all.
As scholars and readers, understanding these nuances not only aids in academic pursuits but also fosters a deeper appreciation for the relentless quest for knowledge that drives academia.
It’s important to remember that every thesis is a testament to curiosity, dedication, and the indomitable spirit of discovery.
Good luck with your thesis writing!
Frequently Asked Questions
A thesis typically ranges between 40-80 pages, but its length can vary based on the research topic, institution guidelines, and level of study.
A PhD thesis usually spans 200-300 pages, though this can vary based on the discipline, complexity of the research, and institutional requirements.
To identify a thesis topic, consider current trends in your field, gaps in existing literature, personal interests, and discussions with advisors or mentors. Additionally, reviewing related journals and conference proceedings can provide insights into potential areas of exploration.
The conceptual framework is often situated in the literature review or theoretical framework section of a thesis. It helps set the stage by providing the context, defining key concepts, and explaining the relationships between variables.
A thesis statement should be concise, clear, and specific. It should state the main argument or point of your research. Start by pinpointing the central question or issue your research addresses, then condense that into a single statement, ensuring it reflects the essence of your paper.
You might also like

5 Tools zur Literaturrecherche für die optimale Recherche (+2 Bonustools)

5 outils de revue de littérature pour réussir vos recherches (+2 outils bonus)

人工智能在系统文献综述中的作用
- More from M-W
- To save this word, you'll need to log in. Log In
Definition of thesis
Did you know.
In high school, college, or graduate school, students often have to write a thesis on a topic in their major field of study. In many fields, a final thesis is the biggest challenge involved in getting a master's degree, and the same is true for students studying for a Ph.D. (a Ph.D. thesis is often called a dissertation ). But a thesis may also be an idea; so in the course of the paper the student may put forth several theses (notice the plural form) and attempt to prove them.
Examples of thesis in a Sentence
These examples are programmatically compiled from various online sources to illustrate current usage of the word 'thesis.' Any opinions expressed in the examples do not represent those of Merriam-Webster or its editors. Send us feedback about these examples.
Word History
in sense 3, Middle English, lowering of the voice, from Late Latin & Greek; Late Latin, from Greek, downbeat, more important part of a foot, literally, act of laying down; in other senses, Latin, from Greek, literally, act of laying down, from tithenai to put, lay down — more at do
14th century, in the meaning defined at sense 3a(1)
Dictionary Entries Near thesis
the sins of the fathers are visited upon the children
thesis novel
Cite this Entry
“Thesis.” Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary , Merriam-Webster, https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/thesis. Accessed 15 Oct. 2024.
Kids Definition
Kids definition of thesis, more from merriam-webster on thesis.
Nglish: Translation of thesis for Spanish Speakers
Britannica English: Translation of thesis for Arabic Speakers
Britannica.com: Encyclopedia article about thesis
Subscribe to America's largest dictionary and get thousands more definitions and advanced search—ad free!

Can you solve 4 words at once?
Word of the day.
See Definitions and Examples »
Get Word of the Day daily email!
Popular in Grammar & Usage
Plural and possessive names: a guide, every letter is silent, sometimes: a-z list of examples, the difference between 'i.e.' and 'e.g.', what's the difference between 'fascism' and 'socialism', more commonly misspelled words, popular in wordplay, weird words for autumn time, 8 words with fascinating histories, 8 words for lesser-known musical instruments, birds say the darndest things, 10 words from taylor swift songs (merriam's version), games & quizzes.

While Sandel argues that pursuing perfection through genetic engineering would decrease our sense of humility, he claims that the sense of solidarity we would lose is also important.
This thesis summarizes several points in Sandel’s argument, but it does not make a claim about how we should understand his argument. A reader who read Sandel’s argument would not also need to read an essay based on this descriptive thesis.
Broad thesis (arguable, but difficult to support with evidence)
Michael Sandel’s arguments about genetic engineering do not take into consideration all the relevant issues.
This is an arguable claim because it would be possible to argue against it by saying that Michael Sandel’s arguments do take all of the relevant issues into consideration. But the claim is too broad. Because the thesis does not specify which “issues” it is focused on—or why it matters if they are considered—readers won’t know what the rest of the essay will argue, and the writer won’t know what to focus on. If there is a particular issue that Sandel does not address, then a more specific version of the thesis would include that issue—hand an explanation of why it is important.
Arguable thesis with analytical claim
While Sandel argues persuasively that our instinct to “remake” (54) ourselves into something ever more perfect is a problem, his belief that we can always draw a line between what is medically necessary and what makes us simply “better than well” (51) is less convincing.
This is an arguable analytical claim. To argue for this claim, the essay writer will need to show how evidence from the article itself points to this interpretation. It’s also a reasonable scope for a thesis because it can be supported with evidence available in the text and is neither too broad nor too narrow.
Arguable thesis with normative claim
Given Sandel’s argument against genetic enhancement, we should not allow parents to decide on using Human Growth Hormone for their children.
This thesis tells us what we should do about a particular issue discussed in Sandel’s article, but it does not tell us how we should understand Sandel’s argument.
Questions to ask about your thesis
- Is the thesis truly arguable? Does it speak to a genuine dilemma in the source, or would most readers automatically agree with it?
- Is the thesis too obvious? Again, would most or all readers agree with it without needing to see your argument?
- Is the thesis complex enough to require a whole essay's worth of argument?
- Is the thesis supportable with evidence from the text rather than with generalizations or outside research?
- Would anyone want to read a paper in which this thesis was developed? That is, can you explain what this paper is adding to our understanding of a problem, question, or topic?
- picture_as_pdf Thesis
- Cambridge Dictionary +Plus
Meaning of thesis in English
Your browser doesn't support HTML5 audio
- I wrote my thesis on literacy strategies for boys .
- Her main thesis is that children need a lot of verbal stimulation .
- boilerplate
- composition
- corresponding author
- dissertation
- essay question
- peer review
You can also find related words, phrases, and synonyms in the topics:
thesis | Intermediate English
Examples of thesis, collocations with thesis.
These are words often used in combination with thesis .
Click on a collocation to see more examples of it.
Translations of thesis
Get a quick, free translation!

Word of the Day
to burn the surface of something with sudden very strong heat

Skimming through and writing up (Studying phrasal verbs)

Learn more with +Plus
- Recent and Recommended {{#preferredDictionaries}} {{name}} {{/preferredDictionaries}}
- Definitions Clear explanations of natural written and spoken English English Learner’s Dictionary Essential British English Essential American English
- Grammar and thesaurus Usage explanations of natural written and spoken English Grammar Thesaurus
- Pronunciation British and American pronunciations with audio English Pronunciation
- English–Chinese (Simplified) Chinese (Simplified)–English
- English–Chinese (Traditional) Chinese (Traditional)–English
- English–Dutch Dutch–English
- English–French French–English
- English–German German–English
- English–Indonesian Indonesian–English
- English–Italian Italian–English
- English–Japanese Japanese–English
- English–Norwegian Norwegian–English
- English–Polish Polish–English
- English–Portuguese Portuguese–English
- English–Spanish Spanish–English
- English–Swedish Swedish–English
- Dictionary +Plus Word Lists
- English Noun
- Intermediate Noun
- Collocations
- Translations
- All translations
To add thesis to a word list please sign up or log in.
Add thesis to one of your lists below, or create a new one.
{{message}}
Something went wrong.
There was a problem sending your report.

How To Write A Dissertation Or Thesis
8 Straightforward Steps + Examples
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) Expert Reviewed By: Dr Eunice Rautenbach | June 2020

How To Write A Dissertation: 8 Steps
- Clearly understand what a dissertation (or thesis) is
- Find a unique and valuable research topic
- Craft a convincing research proposal
- Write up a strong introduction chapter
- Review the existing literature and compile a literature review
- Design a rigorous research strategy and undertake your own research
- Present the findings of your research
- Draw a conclusion and discuss the implications

Step 1: Understand exactly what a dissertation is
This probably sounds like a no-brainer, but all too often, students come to us for help with their research and the underlying issue is that they don’t fully understand what a dissertation (or thesis) actually is.
So, what is a dissertation?
At its simplest, a dissertation or thesis is a formal piece of research , reflecting the standard research process . But what is the standard research process, you ask? The research process involves 4 key steps:
- Ask a very specific, well-articulated question (s) (your research topic)
- See what other researchers have said about it (if they’ve already answered it)
- If they haven’t answered it adequately, undertake your own data collection and analysis in a scientifically rigorous fashion
- Answer your original question(s), based on your analysis findings

In short, the research process is simply about asking and answering questions in a systematic fashion . This probably sounds pretty obvious, but people often think they’ve done “research”, when in fact what they have done is:
- Started with a vague, poorly articulated question
- Not taken the time to see what research has already been done regarding the question
- Collected data and opinions that support their gut and undertaken a flimsy analysis
- Drawn a shaky conclusion, based on that analysis
If you want to see the perfect example of this in action, look out for the next Facebook post where someone claims they’ve done “research”… All too often, people consider reading a few blog posts to constitute research. Its no surprise then that what they end up with is an opinion piece, not research. Okay, okay – I’ll climb off my soapbox now.
The key takeaway here is that a dissertation (or thesis) is a formal piece of research, reflecting the research process. It’s not an opinion piece , nor a place to push your agenda or try to convince someone of your position. Writing a good dissertation involves asking a question and taking a systematic, rigorous approach to answering it.
If you understand this and are comfortable leaving your opinions or preconceived ideas at the door, you’re already off to a good start!

Step 2: Find a unique, valuable research topic
As we saw, the first step of the research process is to ask a specific, well-articulated question. In other words, you need to find a research topic that asks a specific question or set of questions (these are called research questions ). Sounds easy enough, right? All you’ve got to do is identify a question or two and you’ve got a winning research topic. Well, not quite…
A good dissertation or thesis topic has a few important attributes. Specifically, a solid research topic should be:
Let’s take a closer look at these:
Attribute #1: Clear
Your research topic needs to be crystal clear about what you’re planning to research, what you want to know, and within what context. There shouldn’t be any ambiguity or vagueness about what you’ll research.
Here’s an example of a clearly articulated research topic:
An analysis of consumer-based factors influencing organisational trust in British low-cost online equity brokerage firms.
As you can see in the example, its crystal clear what will be analysed (factors impacting organisational trust), amongst who (consumers) and in what context (British low-cost equity brokerage firms, based online).
Need a helping hand?
Attribute #2: Unique
Your research should be asking a question(s) that hasn’t been asked before, or that hasn’t been asked in a specific context (for example, in a specific country or industry).
For example, sticking organisational trust topic above, it’s quite likely that organisational trust factors in the UK have been investigated before, but the context (online low-cost equity brokerages) could make this research unique. Therefore, the context makes this research original.
One caveat when using context as the basis for originality – you need to have a good reason to suspect that your findings in this context might be different from the existing research – otherwise, there’s no reason to warrant researching it.
Attribute #3: Important
Simply asking a unique or original question is not enough – the question needs to create value. In other words, successfully answering your research questions should provide some value to the field of research or the industry. You can’t research something just to satisfy your curiosity. It needs to make some form of contribution either to research or industry.
For example, researching the factors influencing consumer trust would create value by enabling businesses to tailor their operations and marketing to leverage factors that promote trust. In other words, it would have a clear benefit to industry.
So, how do you go about finding a unique and valuable research topic? We explain that in detail in this video post – How To Find A Research Topic . Yeah, we’ve got you covered 😊
Step 3: Write a convincing research proposal
Once you’ve pinned down a high-quality research topic, the next step is to convince your university to let you research it. No matter how awesome you think your topic is, it still needs to get the rubber stamp before you can move forward with your research. The research proposal is the tool you’ll use for this job.
So, what’s in a research proposal?
The main “job” of a research proposal is to convince your university, advisor or committee that your research topic is worthy of approval. But convince them of what? Well, this varies from university to university, but generally, they want to see that:
- You have a clearly articulated, unique and important topic (this might sound familiar…)
- You’ve done some initial reading of the existing literature relevant to your topic (i.e. a literature review)
- You have a provisional plan in terms of how you will collect data and analyse it (i.e. a methodology)
At the proposal stage, it’s (generally) not expected that you’ve extensively reviewed the existing literature , but you will need to show that you’ve done enough reading to identify a clear gap for original (unique) research. Similarly, they generally don’t expect that you have a rock-solid research methodology mapped out, but you should have an idea of whether you’ll be undertaking qualitative or quantitative analysis , and how you’ll collect your data (we’ll discuss this in more detail later).
Long story short – don’t stress about having every detail of your research meticulously thought out at the proposal stage – this will develop as you progress through your research. However, you do need to show that you’ve “done your homework” and that your research is worthy of approval .
So, how do you go about crafting a high-quality, convincing proposal? We cover that in detail in this video post – How To Write A Top-Class Research Proposal . We’ve also got a video walkthrough of two proposal examples here .
Step 4: Craft a strong introduction chapter
Once your proposal’s been approved, its time to get writing your actual dissertation or thesis! The good news is that if you put the time into crafting a high-quality proposal, you’ve already got a head start on your first three chapters – introduction, literature review and methodology – as you can use your proposal as the basis for these.
Handy sidenote – our free dissertation & thesis template is a great way to speed up your dissertation writing journey.
What’s the introduction chapter all about?
The purpose of the introduction chapter is to set the scene for your research (dare I say, to introduce it…) so that the reader understands what you’ll be researching and why it’s important. In other words, it covers the same ground as the research proposal in that it justifies your research topic.
What goes into the introduction chapter?
This can vary slightly between universities and degrees, but generally, the introduction chapter will include the following:
- A brief background to the study, explaining the overall area of research
- A problem statement , explaining what the problem is with the current state of research (in other words, where the knowledge gap exists)
- Your research questions – in other words, the specific questions your study will seek to answer (based on the knowledge gap)
- The significance of your study – in other words, why it’s important and how its findings will be useful in the world
As you can see, this all about explaining the “what” and the “why” of your research (as opposed to the “how”). So, your introduction chapter is basically the salesman of your study, “selling” your research to the first-time reader and (hopefully) getting them interested to read more.

Step 5: Undertake an in-depth literature review
As I mentioned earlier, you’ll need to do some initial review of the literature in Steps 2 and 3 to find your research gap and craft a convincing research proposal – but that’s just scratching the surface. Once you reach the literature review stage of your dissertation or thesis, you need to dig a lot deeper into the existing research and write up a comprehensive literature review chapter.
What’s the literature review all about?
There are two main stages in the literature review process:
Literature Review Step 1: Reading up
The first stage is for you to deep dive into the existing literature (journal articles, textbook chapters, industry reports, etc) to gain an in-depth understanding of the current state of research regarding your topic. While you don’t need to read every single article, you do need to ensure that you cover all literature that is related to your core research questions, and create a comprehensive catalogue of that literature , which you’ll use in the next step.
Reading and digesting all the relevant literature is a time consuming and intellectually demanding process. Many students underestimate just how much work goes into this step, so make sure that you allocate a good amount of time for this when planning out your research. Thankfully, there are ways to fast track the process – be sure to check out this article covering how to read journal articles quickly .
Literature Review Step 2: Writing up
Once you’ve worked through the literature and digested it all, you’ll need to write up your literature review chapter. Many students make the mistake of thinking that the literature review chapter is simply a summary of what other researchers have said. While this is partly true, a literature review is much more than just a summary. To pull off a good literature review chapter, you’ll need to achieve at least 3 things:
- You need to synthesise the existing research , not just summarise it. In other words, you need to show how different pieces of theory fit together, what’s agreed on by researchers, what’s not.
- You need to highlight a research gap that your research is going to fill. In other words, you’ve got to outline the problem so that your research topic can provide a solution.
- You need to use the existing research to inform your methodology and approach to your own research design. For example, you might use questions or Likert scales from previous studies in your your own survey design .
As you can see, a good literature review is more than just a summary of the published research. It’s the foundation on which your own research is built, so it deserves a lot of love and attention. Take the time to craft a comprehensive literature review with a suitable structure .
But, how do I actually write the literature review chapter, you ask? We cover that in detail in this video post .
Step 6: Carry out your own research
Once you’ve completed your literature review and have a sound understanding of the existing research, its time to develop your own research (finally!). You’ll design this research specifically so that you can find the answers to your unique research question.
There are two steps here – designing your research strategy and executing on it:
1 – Design your research strategy
The first step is to design your research strategy and craft a methodology chapter . I won’t get into the technicalities of the methodology chapter here, but in simple terms, this chapter is about explaining the “how” of your research. If you recall, the introduction and literature review chapters discussed the “what” and the “why”, so it makes sense that the next point to cover is the “how” –that’s what the methodology chapter is all about.
In this section, you’ll need to make firm decisions about your research design. This includes things like:
- Your research philosophy (e.g. positivism or interpretivism )
- Your overall methodology (e.g. qualitative , quantitative or mixed methods)
- Your data collection strategy (e.g. interviews , focus groups, surveys)
- Your data analysis strategy (e.g. content analysis , correlation analysis, regression)
If these words have got your head spinning, don’t worry! We’ll explain these in plain language in other posts. It’s not essential that you understand the intricacies of research design (yet!). The key takeaway here is that you’ll need to make decisions about how you’ll design your own research, and you’ll need to describe (and justify) your decisions in your methodology chapter.
2 – Execute: Collect and analyse your data
Once you’ve worked out your research design, you’ll put it into action and start collecting your data. This might mean undertaking interviews, hosting an online survey or any other data collection method. Data collection can take quite a bit of time (especially if you host in-person interviews), so be sure to factor sufficient time into your project plan for this. Oftentimes, things don’t go 100% to plan (for example, you don’t get as many survey responses as you hoped for), so bake a little extra time into your budget here.
Once you’ve collected your data, you’ll need to do some data preparation before you can sink your teeth into the analysis. For example:
- If you carry out interviews or focus groups, you’ll need to transcribe your audio data to text (i.e. a Word document).
- If you collect quantitative survey data, you’ll need to clean up your data and get it into the right format for whichever analysis software you use (for example, SPSS, R or STATA).
Once you’ve completed your data prep, you’ll undertake your analysis, using the techniques that you described in your methodology. Depending on what you find in your analysis, you might also do some additional forms of analysis that you hadn’t planned for. For example, you might see something in the data that raises new questions or that requires clarification with further analysis.
The type(s) of analysis that you’ll use depend entirely on the nature of your research and your research questions. For example:
- If your research if exploratory in nature, you’ll often use qualitative analysis techniques .
- If your research is confirmatory in nature, you’ll often use quantitative analysis techniques
- If your research involves a mix of both, you might use a mixed methods approach
Again, if these words have got your head spinning, don’t worry! We’ll explain these concepts and techniques in other posts. The key takeaway is simply that there’s no “one size fits all” for research design and methodology – it all depends on your topic, your research questions and your data. So, don’t be surprised if your study colleagues take a completely different approach to yours.

Step 7: Present your findings
Once you’ve completed your analysis, it’s time to present your findings (finally!). In a dissertation or thesis, you’ll typically present your findings in two chapters – the results chapter and the discussion chapter .
What’s the difference between the results chapter and the discussion chapter?
While these two chapters are similar, the results chapter generally just presents the processed data neatly and clearly without interpretation, while the discussion chapter explains the story the data are telling – in other words, it provides your interpretation of the results.
For example, if you were researching the factors that influence consumer trust, you might have used a quantitative approach to identify the relationship between potential factors (e.g. perceived integrity and competence of the organisation) and consumer trust. In this case:
- Your results chapter would just present the results of the statistical tests. For example, correlation results or differences between groups. In other words, the processed numbers.
- Your discussion chapter would explain what the numbers mean in relation to your research question(s). For example, Factor 1 has a weak relationship with consumer trust, while Factor 2 has a strong relationship.
Depending on the university and degree, these two chapters (results and discussion) are sometimes merged into one , so be sure to check with your institution what their preference is. Regardless of the chapter structure, this section is about presenting the findings of your research in a clear, easy to understand fashion.
Importantly, your discussion here needs to link back to your research questions (which you outlined in the introduction or literature review chapter). In other words, it needs to answer the key questions you asked (or at least attempt to answer them).
For example, if we look at the sample research topic:
In this case, the discussion section would clearly outline which factors seem to have a noteworthy influence on organisational trust. By doing so, they are answering the overarching question and fulfilling the purpose of the research .

Step 8: The Final Step Draw a conclusion and discuss the implications
Last but not least, you’ll need to wrap up your research with the conclusion chapter . In this chapter, you’ll bring your research full circle by highlighting the key findings of your study and explaining what the implications of these findings are.
What exactly are key findings? The key findings are those findings which directly relate to your original research questions and overall research objectives (which you discussed in your introduction chapter). The implications, on the other hand, explain what your findings mean for industry, or for research in your area.
Sticking with the consumer trust topic example, the conclusion might look something like this:
Key findings
This study set out to identify which factors influence consumer-based trust in British low-cost online equity brokerage firms. The results suggest that the following factors have a large impact on consumer trust:
While the following factors have a very limited impact on consumer trust:
Notably, within the 25-30 age groups, Factors E had a noticeably larger impact, which may be explained by…
Implications
The findings having noteworthy implications for British low-cost online equity brokers. Specifically:
The large impact of Factors X and Y implies that brokers need to consider….
The limited impact of Factor E implies that brokers need to…
As you can see, the conclusion chapter is basically explaining the “what” (what your study found) and the “so what?” (what the findings mean for the industry or research). This brings the study full circle and closes off the document.

Let’s recap – how to write a dissertation or thesis
You’re still with me? Impressive! I know that this post was a long one, but hopefully you’ve learnt a thing or two about how to write a dissertation or thesis, and are now better equipped to start your own research.
To recap, the 8 steps to writing a quality dissertation (or thesis) are as follows:
- Understand what a dissertation (or thesis) is – a research project that follows the research process.
- Find a unique (original) and important research topic
- Craft a convincing dissertation or thesis research proposal
- Write a clear, compelling introduction chapter
- Undertake a thorough review of the existing research and write up a literature review
- Undertake your own research
- Present and interpret your findings
Once you’ve wrapped up the core chapters, all that’s typically left is the abstract , reference list and appendices. As always, be sure to check with your university if they have any additional requirements in terms of structure or content.

You Might Also Like:

How To Choose A Tutor For Your Dissertation
Hiring the right tutor for your dissertation or thesis can make the difference between passing and failing. Here’s what you need to consider.

5 Signs You Need A Dissertation Helper
Discover the 5 signs that suggest you need a dissertation helper to get unstuck, finish your degree and get your life back.

Writing A Dissertation While Working: A How-To Guide
Struggling to balance your dissertation with a full-time job and family? Learn practical strategies to achieve success.

How To Review & Understand Academic Literature Quickly
Learn how to fast-track your literature review by reading with intention and clarity. Dr E and Amy Murdock explain how.

Dissertation Writing Services: Far Worse Than You Think
Thinking about using a dissertation or thesis writing service? You might want to reconsider that move. Here’s what you need to know.
📄 FREE TEMPLATES
Research Topic Ideation
Proposal Writing
Literature Review
Methodology & Analysis
Academic Writing
Referencing & Citing
Apps, Tools & Tricks
The Grad Coach Podcast
20 Comments
thankfull >>>this is very useful
Thank you, it was really helpful
unquestionably, this amazing simplified way of teaching. Really , I couldn’t find in the literature words that fully explicit my great thanks to you. However, I could only say thanks a-lot.
Great to hear that – thanks for the feedback. Good luck writing your dissertation/thesis.
This is the most comprehensive explanation of how to write a dissertation. Many thanks for sharing it free of charge.
Very rich presentation. Thank you
Thanks Derek Jansen|GRADCOACH, I find it very useful guide to arrange my activities and proceed to research!
Thank you so much for such a marvelous teaching .I am so convinced that am going to write a comprehensive and a distinct masters dissertation
It is an amazing comprehensive explanation
This was straightforward. Thank you!
I can say that your explanations are simple and enlightening – understanding what you have done here is easy for me. Could you write more about the different types of research methods specific to the three methodologies: quan, qual and MM. I look forward to interacting with this website more in the future.
Thanks for the feedback and suggestions 🙂
Hello, your write ups is quite educative. However, l have challenges in going about my research questions which is below; *Building the enablers of organisational growth through effective governance and purposeful leadership.*
Very educating.
Just listening to the name of the dissertation makes the student nervous. As writing a top-quality dissertation is a difficult task as it is a lengthy topic, requires a lot of research and understanding and is usually around 10,000 to 15000 words. Sometimes due to studies, unbalanced workload or lack of research and writing skill students look for dissertation submission from professional writers.
Thank you 💕😊 very much. I was confused but your comprehensive explanation has cleared my doubts of ever presenting a good thesis. Thank you.
thank you so much, that was so useful
Hi. Where is the excel spread sheet ark?
could you please help me look at your thesis paper to enable me to do the portion that has to do with the specification
my topic is “the impact of domestic revenue mobilization.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Submit Comment
- Print Friendly
Thesis and Purpose Statements
Use the guidelines below to learn the differences between thesis and purpose statements.
In the first stages of writing, thesis or purpose statements are usually rough or ill-formed and are useful primarily as planning tools.
A thesis statement or purpose statement will emerge as you think and write about a topic. The statement can be restricted or clarified and eventually worked into an introduction.
As you revise your paper, try to phrase your thesis or purpose statement in a precise way so that it matches the content and organization of your paper.
Thesis statements
A thesis statement is a sentence that makes an assertion about a topic and predicts how the topic will be developed. It does not simply announce a topic: it says something about the topic.
Good: X has made a significant impact on the teenage population due to its . . . Bad: In this paper, I will discuss X.
A thesis statement makes a promise to the reader about the scope, purpose, and direction of the paper. It summarizes the conclusions that the writer has reached about the topic.
A thesis statement is generally located near the end of the introduction. Sometimes in a long paper, the thesis will be expressed in several sentences or an entire paragraph.
A thesis statement is focused and specific enough to be proven within the boundaries of the paper. Key words (nouns and verbs) should be specific, accurate, and indicative of the range of research, thrust of the argument or analysis, and the organization of supporting information.
Purpose statements
A purpose statement announces the purpose, scope, and direction of the paper. It tells the reader what to expect in a paper and what the specific focus will be.
Common beginnings include:
“This paper examines . . .,” “The aim of this paper is to . . .,” and “The purpose of this essay is to . . .”
A purpose statement makes a promise to the reader about the development of the argument but does not preview the particular conclusions that the writer has drawn.
A purpose statement usually appears toward the end of the introduction. The purpose statement may be expressed in several sentences or even an entire paragraph.
A purpose statement is specific enough to satisfy the requirements of the assignment. Purpose statements are common in research papers in some academic disciplines, while in other disciplines they are considered too blunt or direct. If you are unsure about using a purpose statement, ask your instructor.
This paper will examine the ecological destruction of the Sahel preceding the drought and the causes of this disintegration of the land. The focus will be on the economic, political, and social relationships which brought about the environmental problems in the Sahel.
Sample purpose and thesis statements
The following example combines a purpose statement and a thesis statement (bold).
The goal of this paper is to examine the effects of Chile’s agrarian reform on the lives of rural peasants. The nature of the topic dictates the use of both a chronological and a comparative analysis of peasant lives at various points during the reform period. . . The Chilean reform example provides evidence that land distribution is an essential component of both the improvement of peasant conditions and the development of a democratic society. More extensive and enduring reforms would likely have allowed Chile the opportunity to further expand these horizons.
For more tips about writing thesis statements, take a look at our new handout on Developing a Thesis Statement.

Writing Process and Structure
This is an accordion element with a series of buttons that open and close related content panels.
Getting Started with Your Paper
Interpreting Writing Assignments from Your Courses
Generating Ideas for Your Paper
Creating an Argument
Thesis vs. Purpose Statements
Developing a Thesis Statement
Architecture of Arguments
Working with Sources
Quoting and Paraphrasing Sources
Using Literary Quotations
Citing Sources in Your Paper
Drafting Your Paper
Introductions
Paragraphing
Developing Strategic Transitions
Conclusions
Revising Your Paper
Peer Reviews
Reverse Outlines
Revising an Argumentative Paper
Revision Strategies for Longer Projects
Finishing Your Paper
Twelve Common Errors: An Editing Checklist
How to Proofread your Paper
Writing Collaboratively
Collaborative and Group Writing
- Privacy Policy

Home » Thesis – Structure, Example and Writing Guide
Thesis – Structure, Example and Writing Guide
Table of contents.

Definition:
Thesis is a scholarly document that presents a student’s original research and findings on a particular topic or question. It is usually written as a requirement for a graduate degree program and is intended to demonstrate the student’s mastery of the subject matter and their ability to conduct independent research.
History of Thesis
The concept of a thesis can be traced back to ancient Greece, where it was used as a way for students to demonstrate their knowledge of a particular subject. However, the modern form of the thesis as a scholarly document used to earn a degree is a relatively recent development.
The origin of the modern thesis can be traced back to medieval universities in Europe. During this time, students were required to present a “disputation” in which they would defend a particular thesis in front of their peers and faculty members. These disputations served as a way to demonstrate the student’s mastery of the subject matter and were often the final requirement for earning a degree.
In the 17th century, the concept of the thesis was formalized further with the creation of the modern research university. Students were now required to complete a research project and present their findings in a written document, which would serve as the basis for their degree.
The modern thesis as we know it today has evolved over time, with different disciplines and institutions adopting their own standards and formats. However, the basic elements of a thesis – original research, a clear research question, a thorough review of the literature, and a well-argued conclusion – remain the same.
Structure of Thesis
The structure of a thesis may vary slightly depending on the specific requirements of the institution, department, or field of study, but generally, it follows a specific format.
Here’s a breakdown of the structure of a thesis:
This is the first page of the thesis that includes the title of the thesis, the name of the author, the name of the institution, the department, the date, and any other relevant information required by the institution.
This is a brief summary of the thesis that provides an overview of the research question, methodology, findings, and conclusions.
This page provides a list of all the chapters and sections in the thesis and their page numbers.
Introduction
This chapter provides an overview of the research question, the context of the research, and the purpose of the study. The introduction should also outline the methodology and the scope of the research.
Literature Review
This chapter provides a critical analysis of the relevant literature on the research topic. It should demonstrate the gap in the existing knowledge and justify the need for the research.
Methodology
This chapter provides a detailed description of the research methods used to gather and analyze data. It should explain the research design, the sampling method, data collection techniques, and data analysis procedures.
This chapter presents the findings of the research. It should include tables, graphs, and charts to illustrate the results.
This chapter interprets the results and relates them to the research question. It should explain the significance of the findings and their implications for the research topic.
This chapter summarizes the key findings and the main conclusions of the research. It should also provide recommendations for future research.
This section provides a list of all the sources cited in the thesis. The citation style may vary depending on the requirements of the institution or the field of study.
This section includes any additional material that supports the research, such as raw data, survey questionnaires, or other relevant documents.
How to write Thesis
Here are some steps to help you write a thesis:
- Choose a Topic: The first step in writing a thesis is to choose a topic that interests you and is relevant to your field of study. You should also consider the scope of the topic and the availability of resources for research.
- Develop a Research Question: Once you have chosen a topic, you need to develop a research question that you will answer in your thesis. The research question should be specific, clear, and feasible.
- Conduct a Literature Review: Before you start your research, you need to conduct a literature review to identify the existing knowledge and gaps in the field. This will help you refine your research question and develop a research methodology.
- Develop a Research Methodology: Once you have refined your research question, you need to develop a research methodology that includes the research design, data collection methods, and data analysis procedures.
- Collect and Analyze Data: After developing your research methodology, you need to collect and analyze data. This may involve conducting surveys, interviews, experiments, or analyzing existing data.
- Write the Thesis: Once you have analyzed the data, you need to write the thesis. The thesis should follow a specific structure that includes an introduction, literature review, methodology, results, discussion, conclusion, and references.
- Edit and Proofread: After completing the thesis, you need to edit and proofread it carefully. You should also have someone else review it to ensure that it is clear, concise, and free of errors.
- Submit the Thesis: Finally, you need to submit the thesis to your academic advisor or committee for review and evaluation.
Example of Thesis
Example of Thesis template for Students:
Title of Thesis
Table of Contents:
Chapter 1: Introduction
Chapter 2: Literature Review
Chapter 3: Research Methodology
Chapter 4: Results
Chapter 5: Discussion
Chapter 6: Conclusion
References:
Appendices:
Note: That’s just a basic template, but it should give you an idea of the structure and content that a typical thesis might include. Be sure to consult with your department or supervisor for any specific formatting requirements they may have. Good luck with your thesis!
Application of Thesis
Thesis is an important academic document that serves several purposes. Here are some of the applications of thesis:
- Academic Requirement: A thesis is a requirement for many academic programs, especially at the graduate level. It is an essential component of the evaluation process and demonstrates the student’s ability to conduct original research and contribute to the knowledge in their field.
- Career Advancement: A thesis can also help in career advancement. Employers often value candidates who have completed a thesis as it demonstrates their research skills, critical thinking abilities, and their dedication to their field of study.
- Publication : A thesis can serve as a basis for future publications in academic journals, books, or conference proceedings. It provides the researcher with an opportunity to present their research to a wider audience and contribute to the body of knowledge in their field.
- Personal Development: Writing a thesis is a challenging task that requires time, dedication, and perseverance. It provides the student with an opportunity to develop critical thinking, research, and writing skills that are essential for their personal and professional development.
- Impact on Society: The findings of a thesis can have an impact on society by addressing important issues, providing insights into complex problems, and contributing to the development of policies and practices.
Purpose of Thesis
The purpose of a thesis is to present original research findings in a clear and organized manner. It is a formal document that demonstrates a student’s ability to conduct independent research and contribute to the knowledge in their field of study. The primary purposes of a thesis are:
- To Contribute to Knowledge: The main purpose of a thesis is to contribute to the knowledge in a particular field of study. By conducting original research and presenting their findings, the student adds new insights and perspectives to the existing body of knowledge.
- To Demonstrate Research Skills: A thesis is an opportunity for the student to demonstrate their research skills. This includes the ability to formulate a research question, design a research methodology, collect and analyze data, and draw conclusions based on their findings.
- To Develop Critical Thinking: Writing a thesis requires critical thinking and analysis. The student must evaluate existing literature and identify gaps in the field, as well as develop and defend their own ideas.
- To Provide Evidence of Competence : A thesis provides evidence of the student’s competence in their field of study. It demonstrates their ability to apply theoretical concepts to real-world problems, and their ability to communicate their ideas effectively.
- To Facilitate Career Advancement : Completing a thesis can help the student advance their career by demonstrating their research skills and dedication to their field of study. It can also provide a basis for future publications, presentations, or research projects.
When to Write Thesis
The timing for writing a thesis depends on the specific requirements of the academic program or institution. In most cases, the opportunity to write a thesis is typically offered at the graduate level, but there may be exceptions.
Generally, students should plan to write their thesis during the final year of their graduate program. This allows sufficient time for conducting research, analyzing data, and writing the thesis. It is important to start planning the thesis early and to identify a research topic and research advisor as soon as possible.
In some cases, students may be able to write a thesis as part of an undergraduate program or as an independent research project outside of an academic program. In such cases, it is important to consult with faculty advisors or mentors to ensure that the research is appropriately designed and executed.
It is important to note that the process of writing a thesis can be time-consuming and requires a significant amount of effort and dedication. It is important to plan accordingly and to allocate sufficient time for conducting research, analyzing data, and writing the thesis.
Characteristics of Thesis
The characteristics of a thesis vary depending on the specific academic program or institution. However, some general characteristics of a thesis include:
- Originality : A thesis should present original research findings or insights. It should demonstrate the student’s ability to conduct independent research and contribute to the knowledge in their field of study.
- Clarity : A thesis should be clear and concise. It should present the research question, methodology, findings, and conclusions in a logical and organized manner. It should also be well-written, with proper grammar, spelling, and punctuation.
- Research-Based: A thesis should be based on rigorous research, which involves collecting and analyzing data from various sources. The research should be well-designed, with appropriate research methods and techniques.
- Evidence-Based : A thesis should be based on evidence, which means that all claims made in the thesis should be supported by data or literature. The evidence should be properly cited using appropriate citation styles.
- Critical Thinking: A thesis should demonstrate the student’s ability to critically analyze and evaluate information. It should present the student’s own ideas and arguments, and engage with existing literature in the field.
- Academic Style : A thesis should adhere to the conventions of academic writing. It should be well-structured, with clear headings and subheadings, and should use appropriate academic language.

Advantages of Thesis
There are several advantages to writing a thesis, including:
- Development of Research Skills: Writing a thesis requires extensive research and analytical skills. It helps to develop the student’s research skills, including the ability to formulate research questions, design and execute research methodologies, collect and analyze data, and draw conclusions based on their findings.
- Contribution to Knowledge: Writing a thesis provides an opportunity for the student to contribute to the knowledge in their field of study. By conducting original research, they can add new insights and perspectives to the existing body of knowledge.
- Preparation for Future Research: Completing a thesis prepares the student for future research projects. It provides them with the necessary skills to design and execute research methodologies, analyze data, and draw conclusions based on their findings.
- Career Advancement: Writing a thesis can help to advance the student’s career. It demonstrates their research skills and dedication to their field of study, and provides a basis for future publications, presentations, or research projects.
- Personal Growth: Completing a thesis can be a challenging and rewarding experience. It requires dedication, hard work, and perseverance. It can help the student to develop self-confidence, independence, and a sense of accomplishment.
Limitations of Thesis
There are also some limitations to writing a thesis, including:
- Time and Resources: Writing a thesis requires a significant amount of time and resources. It can be a time-consuming and expensive process, as it may involve conducting original research, analyzing data, and producing a lengthy document.
- Narrow Focus: A thesis is typically focused on a specific research question or topic, which may limit the student’s exposure to other areas within their field of study.
- Limited Audience: A thesis is usually only read by a small number of people, such as the student’s thesis advisor and committee members. This limits the potential impact of the research findings.
- Lack of Real-World Application : Some thesis topics may be highly theoretical or academic in nature, which may limit their practical application in the real world.
- Pressure and Stress : Writing a thesis can be a stressful and pressure-filled experience, as it may involve meeting strict deadlines, conducting original research, and producing a high-quality document.
- Potential for Isolation: Writing a thesis can be a solitary experience, as the student may spend a significant amount of time working independently on their research and writing.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Thesis Statement – Examples, Writing Guide

Research Recommendations – Examples and Writing...

Limitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Ethical Considerations – Types, Examples and...

Research Report – Example, Writing Guide and...
- Dictionaries home
- American English
- Collocations
- German-English
- Grammar home
- Practical English Usage
- Learn & Practise Grammar (Beta)
- Word Lists home
- My Word Lists
- Recent additions
- Resources home
- Text Checker
Definition of thesis noun from the Oxford Advanced Learner's Dictionary
- Students must submit a thesis on an agreed subject within four years.
- He presented this thesis for his PhD.
- a thesis for a master's degree
- He's doing a doctoral thesis on the early works of Shostakovich.
- Many departments require their students to do a thesis defense.
- She completed an MSc by thesis.
- her thesis adviser at MIT
- in a/the thesis
- thesis about
Take your English to the next level
The Oxford Learner’s Thesaurus explains the difference between groups of similar words. Try it for free as part of the Oxford Advanced Learner’s Dictionary app

Thesis Meaning: Here’s What It Means and How To Use It
Your writing, at its best
Compose bold, clear, mistake-free, writing with Grammarly's AI-powered writing assistant
Understanding what a thesis is can help you improve your written and spoken communication.
There are countless different contexts where this word is used, and knowing how to properly use it can help you communicate effectively in your field. If you want to be the most effective and successful communicator possible, feel free to read and learn about this essential word !
This is everything you need to know about what this word means, where it comes from in etymology, and how it is used.
What Is a Thesis?
The definition of thesis (ˈθi sɪs, ˈθiːsɪs, the-sis, plural theses) in American English is the main idea presented in an essay. In other words, the central message of the piece. Behind every literary device and rhetorical strategy stands a thesis. Thesis statements don’t just appear at the beginning of your paper; they should be woven into every sentence you write.
Your thesis statement will probably be one of two things: an assertion that something is true or an argument for why something should be done (or not done).
What Is a Thesis Statement?
A Thesis statement is a sentence that contains the main idea of a written work.
All other sentences in a paper should explain, prove, or describe this main idea. Thesis statements are often used in reports to express a central message of an essay or article. Researchers commonly use them to propose a hypothesis and then test it with evidence from their study.
What Are Some Synonyms of Thesis?
If you look in a thesaurus for word lists of synonyms for the word thesis, you’ll likely find words including:
- Point of View
- Proposition
- Dissertation
What Is a Thesis in the Academic World?
When it comes to the world of academics, the word thesis has another similar yet different meaning.
A thesis is a long-form piece of writing, often a research paper, that is used as the final project of a university degree, like a master’s degree.
What Is a Master’s Thesis?
A master’s thesis is a project that contains lots of original research and is used to cap off an academic degree. It is how a student takes an unproved statement and then proves it through extensive writing.
When Would You Write a Thesis?
If you’re studying a language like Greek, Spanish, Arabic, or Late Latin, you’ll likely have to do an extensive study — and write a thesis — to prove your knowledge of the language. The main goal of a thesis is to establish the synthesis of knowledge that a student is capable of and ensure that they can operate well in the academic world.
How Do You Start Writing a Thesis?
Before a student or researcher begins writing a paper, they must have a thesis statement. This thesis statement is one sentence that describes how you will support your argument and what evidence you will provide in your paper. In many cases, it is the last sentence of your introduction paragraph and appears again as the first sentence of the body paragraph:
A thesis statement usually evolves only after considerable reading, writing, and thinking has been done on your topic. Your thesis changes and develops as you write it, so by the time you arrive at the end, you will know what your paper is about and should be able to sum it up clearly in a sentence or two.
What Is the Etymology of the Word Thesis?
The word thesis comes from the Greek word θέσις (thésis), which means “placement” or “setting.” The term was first used in English in 1632 by William Lilly. As time has progressed, the word has entered into many different languages, including Latin tithenai , French, and Middle English.
Throughout its different stages of development, the word has remained relatively the same. However, this word’s collocations and more specific meanings have gradually changed over the years.
Luckily, as long as you’re only sticking to English, thesis is a word with meanings that are relatively consistent and easy to understand!
What Are Some Example Sentences Using the Word Thesis?
One of the best ways to learn how to use a word is by seeing it in use in the context of actual-world sentences and conversations.
Here are some excellent examples of thesis being used in everyday sentences, so you can start using the word for yourself!
As he started his conversation, the lowering of his voice enticed everyone to listen intently to his thesis presentation.
The first research stage for her doctoral thesis meant studying the Hegelian people.
Mr. Tese’s master’s thesis primarily focused on a tiny part of a metrical foot in poetry, which was reasonably interesting for many poets.
My entire paper’s central thesis was based on how the downbeat is not the most crucial part of music — the backbeat is.
My professor keeps telling me that the thesis statement is, by far, the most critical part of any essay, and I’m starting to believe her.
It took nearly six months to write the first draft of my thesis, which was really exhausting.
We’re willing to bet that you have some writing skills if you’re reading this. However, everyone has room to improve when it comes to writing. If you feel like you need to brush up your vocabulary or learn a few additional techniques on writing clearly and effectively, look no further — we are here to help! Let us show you how to get the most out of your communication skills with our resources here on The Word Counter website.
The Word Counter is a living body of content that will continue to be updated with new and exciting lessons on language, communication, grammar, and writing. We believe everyone can continue to grow in their ability to communicate effectively, and we’ve created this blog as a stepping-stone for precisely that goal.
Check out our latest articles right here !
Sources:
Thesis Definition & Meaning | Merriam-Webster
Thesis definition and meaning | Collins English Dictionary
Thesis – Definition, Meaning & Synonyms | Vocabulary.com
Kevin Miller is a growth marketer with an extensive background in Search Engine Optimization, paid acquisition and email marketing. He is also an online editor and writer based out of Los Angeles, CA. He studied at Georgetown University, worked at Google and became infatuated with English Grammar and for years has been diving into the language, demystifying the do's and don'ts for all who share the same passion! He can be found online here.
Recent Posts

Dreams Meaning: Here’s What It Means and How To Use It

Chutzpah Meaning: Here’s What It Means and How To Use It

White Roses Meaning: Here’s What It Means and How To Use It

7777 Angel Number Meaning: Here’s What It Means and How to Use It?
The Thesis Process
The thesis is an opportunity to work independently on a research project of your own design and contribute to the scholarly literature in your field. You emerge from the thesis process with a solid understanding of how original research is executed and how to best communicate research results. Many students have gone on to publish their research in academic or professional journals.
To ensure affordability, the per-credit tuition rate for the 8-credit thesis is the same as our regular course tuition. There are no additional fees (regular per-credit graduate tuition x 8 credits).
Below are the steps that you need to follow to fulfill the thesis requirement. Please know that through each step, you will receive guidance and mentorship.
1. Meet with Your Research Advisor
Upon admission to the program, set up an introductory meeting with your Research Advisor to discuss potential thesis topics as well as course selections that can support your thesis path.
When you have completed between 24 and 32 credits, you work more intensively with your assigned Research Advisor to determine a specific thesis topic.
Log in to MyDCE , then ALB/ALM Community to schedule an appointment with your assigned Research Advisor via the Degree Candidate Portal.
Failure to work with your Research Advisor initially and then more intensively may result in your Crafting the Thesis Proposal (CTP) Application not being approved (see below) and/or the selection of a different thesis topic.
Thesis Topic Selection Guidelines
Every effort is made to support research interests that are grounded in your ALM course work, but faculty guidance is not available for all possible projects. Therefore, revision or a change of thesis topic may be necessary.
- The above point about topic selection is particularly pertinent to scientific research (e.g., biology) that is dependent upon laboratory space, project funding, and access to private databases.
- This point is also critical for our candidates in ALM, liberal arts fields (i.e., anthropology, English, government, history, international relations, psychology, and religion) who are required to have Harvard faculty direct their thesis projects. Review Harvard’s course catalog online ( My.Harvard.edu ) to be sure that there are faculty teaching courses related to your thesis topic. If faculty are not available, you will need to choose an alternative topic.
- Your topic choice must be a new area of research for you. You cannot re-purpose prior research. If you want to draw or expand upon your own previously written scholarship for a small portion of your thesis, you need to obtain the explicit permission of your research advisor and cite the work in both the proposal and thesis. Violations of this policy will be referred to the Administrative Board.
We’ve put together this guide to help frame your thinking about thesis topic selection.
While it is natural to follow your interests in selecting a thesis topic, it is important to avoid choosing a topic where your own passions might produce insurmountable biases and assumptions. A thesis is not a piece of advocacy work where you are out to prove something that you already believe. Thesis projects must take a fair and balanced stance by bringing in differing points of view from respected scholars in the field.
2. Prepare Your Crafting the Thesis Proposal Application
Once you and your Research Advisor have confirmed your thesis topic, the next step in the process is to prepare and submit the CTP Application in order to gain registration approval for the Crafting the Thesis Proposal (CTP) tutorial or course.
The CTP Application process confirms that you have done enough prior reading and thinking about your thesis topic to generate a pertinent and answerable research question. Pre-CTP preparation is critical as it helps to ensure that you will benefit from and succeed in the CTP.
Application Approvals and Denials. Your Research Advisor will provide feedback on your CTP Application. If your application is not approved after 3 submissions, your Research Advisor cannot approve your CTP registration.
If not approved, you’ll need to take additional time for further revisions and submit a new CTP Application during the next CTP submission cycle (if your five-year degree completion date allows).
Application Eligibility Requirements. To be eligible to submit a CTP Application, you need to (1) be in good standing and (2) have completed a minimum of 32 degree-applicable credits, including the research methods/statistics and Engaging in Scholarly Conversation requirement, if required for your field.
Advising Note for Psychology Candidates View More
Students in psychology sometimes face difficulty securing necessary IRB approvals for certain projects. For this reason, Research Advisors will not approve proposals that raise significant concerns about feasibility. Such concerns include cases where projects would require the researcher to possess a level of expertise or experience exceeding documented capabilities, as well as instances where the researcher is unlikely to be able to obtain appropriate faculty supervision for a proposed topic, question, method, or procedure. You must schedule an appointment with your Research Advisor at least three months in advance of the CTP Application deadlines to discuss potential research projects to ensure adequate time for assistance in developing a viable project idea.
Advising Note for Biology and former Biotechnology and Bioengineering and Nanotechnology Candidates View More
Thesis projects in these fields are designed to support ongoing scientific research happening in Harvard University, other academic institutions, or life science industry labs and usually these are done under the direction of a principal investigator (PI). Hence, you need to have a thesis director approved by your research advisor prior to submitting CTP Application. Your CTP Application is then framed by the lab’s research. Schedule an appointment with your research advisor a few months in advance of the CTP Application deadlines in order to discuss potential research projects and thesis director assignment.
The CTP Application is sent to our central email box: [email protected] by the following firm deadlines:
- June 1 for fall CTP
- November 1 for spring CTP.
- September 1 for the three-week January session (ALM sustainability candidates only)
- International sustainability students who need a student visa to attend Harvard Summer School must be officially admitted to the degree program before February 1, must submit the CTP Application on February 1, and must register for the CTP course on March 1 in order to submit timely I-20 paperwork. See international students guidelines for more information.
3. Register and Successfully Complete Crafting the Thesis Proposal
Once your CTP Application is approved, you register for the Crafting the Thesis Proposal (CTP) tutorial or course as you would any other degree requirement.
The goal of the CTP is to produce a complete, well-written draft of a proposal containing all of the sections required by your Research Advisor. Creating an academically strong thesis proposal sets the foundation for a high-quality thesis and helps garner the attention of a well-respected thesis director.
Thesis proposals typically include approximately 15 to 20 pages of text, in addition to any required reference sections, such as bibliographies and glossary/definition of terms.
Tutorial experience. The fall and spring CTP tutorials are not courses in the traditional sense. Although there will be assignments for you to complete during the CTP, with due dates, and there will be times when you and your classmates meet as a group with your Research Advisor, there won’t be a regularly scheduled class meeting time for the CTP.
The main work for the CTP will consist of your working independently on your proposal with your Research Advisor by submitting multiple drafts and scheduling individual appointments.
Grading. You need to make self-directed progress on the proposal without special prompting from the research advisor. You receive a final grade of SAT or UNSAT (failing grade).
You are expected to incorporate all of your Research Advisor’s feedback and be fully committed to producing an academically strong proposal leading to a thesis worthy of a Harvard degree. If you are unable to take advice from your Research Advisor, follow directions, or produce an acceptable proposal, you will not pass the CTP.
The CTP for sustainability is a three-week course in the traditional sense and you receive a letter grade, and it must be B- or higher to receive degree credit for the course.
Academic Integrity. Successful CTP completion also includes a check on the proper use of sources according to our academic integrity guidelines. Violations of our academic integrity policy will be referred to the Administrative Board.
Maximum of two attempts . If you don’t pass the CTP, you’ll have — if your five-year, degree-completion date allows — just one more attempt to complete the CTP before being required to withdraw from the program. If you fail the CTP just once and have no more time to complete the degree, your candidacy will automatically expire. Please note that a WD grade counts as an attempt.
If by not passing the CTP you fall into poor academic standing, you will need to take additional degree-applicable courses to return to good standing before enrolling in the CTP for your second and final time, but only if your five-year, degree-completion date allows. If you have no more time on your five-year clock, you will be required to withdraw from the program.
Human Subjects
If your thesis, regardless of field, will involve the use of human subjects (e.g., interviews, surveys, observations), you will need to have your research vetted by the Committee on the Use of Human Subjects (CUHS) of Harvard University. Please review the IRB Lifecycle Guide located on the CUHS website. Your research advisor will help you prepare a draft copy of the project protocol form that you will then finalize with your thesis director to send to the CUHS.
Given the amount of time that can be required for IRB review, drafting of the required CUHS project protocol forms need to be started with your Research Advisor during the CTP tutorial, before a thesis director has been assigned.
4. Post-CTP Proposal Approval, Thesis Director Assignment, and Registration
Successfully completion of the CTP means you have completed a well-written full draft proposal. Ordinarily, this full draft is not a final accepted proposal. Most students reach the final accepted proposal stage by submitting additional changes and edits to their RA post-CTP.
Post-CTP Changes and Edits Deadline. We expect you to work diligently and quickly with your RA post-CTP to move from full draft to final proposal stage. Indeed, you should have an approved final proposal and be registered in the thesis soon after CTP completion, within weeks, but no later than 3 months. You cannot delay. If you take longer than 3 months after the CTP to register for the thesis, you may be required to retake the CTP.
Thesis Director Assignment. Once your RA has determined that your draft has reached the final proposal stage, you move to the thesis director assignment stage. The Research Advisor places you with a thesis director by sending out your final proposal to prospective Thesis Directors.
Do not approach faculty to ask about directing your thesis. You may suggest names of any potential Thesis Directors to your Research Advisor, but it must be the Research Advisor who makes contact with them. (If they are eligible/available to direct your thesis, after you have an approved thesis proposal.) You are not permitted to approach faculty to ask them about directing your thesis. The decision of your Research Advisor regarding the appointment of your Thesis Director is binding.
Registration. When a Thesis Director has been identified or the thesis proposal has been fully vetted by the preassigned life science Thesis Director, you will receive a letter of authorization from the Assistant Dean of Academic Programs officially approving your thesis work and providing you with instructions on how to register for the eight-credit master’s thesis. The letter will also have a tentative graduation date as well as four mandatory thesis submission dates (see Thesis Timetable below).
When registering for the thesis, you will have two weeks to pay in full. This is an eight-credit course, so be sure to have the necessary funds available when you register.
You must be good academic standing to register for the thesis. If not, you’ll need to complete additional courses to bring your GPA up to the 3.0 minimum prior to registration.
Thesis Submission Deadlines and Graduation Timetable
The thesis is a 9-to-12-month project that begins after the Crafting the Thesis Proposal (CTP); when your Research Advisor has approved your proposal and identified a Thesis Director.
The date for the appointment of your Thesis Director determines the graduation cycle that will be automatically assigned to you:
| Thesis Milestone | For May Graduation | For November Graduation | For February Graduation |
|---|---|---|---|
| March 1 – June 30 | August 15 – October 15 | November 1 – February 15 | |
| . | February 1 | July 15 | October 1 |
| . | March 1 | August 15 | November 1 |
| | April 1 | September 15 | December 1 |
| April 15 | October 1 | December 15 | |
| (see step 7 below). | May 1 | October 7 | January 3 |
As you can see above, you do not submit your thesis all at once at the end, but in four phases: (1) complete draft to TD, (2) final draft to RA for format review and academic integrity check, (3) format approved draft submitted to TD for grading, and (4) upload your 100% complete graded thesis to ETDs.
Due dates for all phases for your assigned graduation cycle cannot be missed. You must submit materials by the date indicated by 5 PM EST (even if the date falls on a weekend). If you are late, you will not be able to graduate during your assigned cycle.
If you need additional time to complete your thesis, you need to formally request an extension by emailing that petition to: [email protected] . Regardless of when you started, the maximum allotted time to complete your thesis, including any granted extensions of time is 12 months.
Advising Tip to Meet Your Five-Year Deadline: The last possible time you can register for the CTP to meet your five-year deadline date is the fall term two years prior or, if a sustainability student, in the January session one year prior. It is not, however, recommended to wait this long. Indeed, it is vigorously discouraged.
For example, if your five-year deadline is May 2026:
- Complete the CTP in fall 2024 (or in January 2025, if a sustainability student)
- Be assigned a Thesis Director (TD) in March/April 2025
- Begin the 9–12-month thesis project with TD
- Submit a complete draft of your thesis to your TD by February 1, 2026
- Follow through with all other submission deadlines (April 1, April 15 and May 1 — see table above)
- Graduate in May 2026
5. Working with Your Thesis Director
You must work diligently and independently, following the advice of your Thesis Director in a consistent, regular manner equivalent to full-time academic work to complete both the research and the writing phases of your thesis by your required timeline.
You are expected to incorporate all of your Thesis Director’s feedback and be fully committed to producing an academically strong thesis worthy of a Harvard degree. If you are unable to take advice from your Thesis Director, follow directions, or produce an acceptable scholarly thesis product, you will not receive a passing grade.
You are required to produce at least 50 pages of text (not including front matter and appendices). Chapter topics (e.g., introduction, background, methods, findings, conclusion) vary by field.
Once registered in the thesis, we will do a 3-month check-in with you and your Thesis Director to ensure progress is being made. If your Thesis Director reports little to no progress, the Dean of Academic Programs reserves the right to issue a thesis not complete (TNC) grade (see Thesis Grading below).
6. Thesis Template, Format Review, and Academic Integrity Check
All ALM thesis projects must written in Microsoft Word and follow a specific Harvard Extension School format. A properly formatted thesis is an explicit degree requirement; you cannot graduate without it.
You are required to use the Extension School ALM Thesis Template or the Extension School ALM Thesis Template for Creative Writing (specifically designed for creative writing degree candidates). The template has all the mandatory thesis formatting built in.
Besides saving you a considerable amount of time as you write your thesis, the template ensures that your submitted thesis meets the mandatory style guidelines for margins, font, title page, table of contents, and chapter headings. If you use the template, format review should go smoothly, if not, a delayed graduation is highly likely.
Your Research Advisor will complete the format review prior to submitting your thesis to your Thesis Director for final grading according to the Thesis Timetable (see above).
Academic Integrity. Format review also includes a check on the proper use of sources according to our academic integrity guidelines. Violations of our academic integrity policy will be referred to the Administrative Board.
7. Mandatory Thesis Archiving
Once your thesis is finalized, meaning that the required grade has been earned and all edits have been completed, you must upload your thesis to Harvard University’s electronic thesis and dissertation submission system (ETDs).
Uploading your thesis ETDs is an explicit degree requirement; you cannot graduate without completing this step. Furthermore, no changes to the thesis are allowed once it has been graded and archived in ETDs.
The thesis project will be sent to several downstream systems:
- Your work will be preserved using Harvard’s digital repository DASH (Digital Access to Scholarship at Harvard).
- Metadata about your work will be sent to HOLLIS (the Harvard Library catalog).
- Your work will be preserved in Harvard Library’s DRS2 (digital preservation repository).
By submitting work through ETDs @ Harvard you will be signing the Harvard Author Agreement. This license does not constrain your rights to publish your work subsequently. You retain all intellectual property rights.
For more information on Harvard’s open access initiatives, we recommend you view the Director of the Office of Scholarly Communication (OSC), Peter Suber’s brief introduction .
Thesis Grading
You need to earn a grade of B- or higher in the thesis. If you fail to complete substantial work on the thesis, you will earn a grade of TNC (thesis not complete). If you have already earned two withdrawal grades, the TNC grade will count as a zero in your cumulative GPA.
If you earn a grade below B-, you will need to petition the Administrative Board for permission to attempt the thesis for a second and final time. The petition process is only available if you are in good academic standing and your five-year, degree-completion date allows for more time. Your candidacy will automatically expire if you do not successfully complete the thesis by your required date.
If approved for a second attempt, you may be required to develop a new proposal on a different topic by re-enrolling in the CTP and being assigned a different thesis director. Tuition for the second attempt is calculated at the current year’s rate.
If by not passing the thesis you fall into poor academic standing, you’ll need to take additional degree-applicable courses to return to good standing before re-engaging with the thesis process for the second and final time. This is only an option if your five-year, degree-completion date allows for more time.
The Board only reviews cases in which extenuating circumstances prevented the successful completion of the thesis.
Harvard Division of Continuing Education
The Division of Continuing Education (DCE) at Harvard University is dedicated to bringing rigorous academics and innovative teaching capabilities to those seeking to improve their lives through education. We make Harvard education accessible to lifelong learners from high school to retirement.

- Daily Crossword
- Word Puzzle
- Word Finder
- Word of the Day
- Synonym of the Day
- Word of the Year
- Language stories
- All featured
- Gender and sexuality
- All pop culture
- Writing hub
- Grammar essentials
- Commonly confused
- All writing tips
- Pop culture
- Writing tips
Advertisement
[ thee -sis ]
He vigorously defended his thesis on the causes of war.
Synonyms: proposal , contention , theory
- a subject for a composition or essay.
- a dissertation on a particular subject in which one has done original research, as one presented by a candidate for a diploma or degree.
- Music. the downward stroke in conducting; downbeat. Compare arsis ( def 1 ) .
- a part of a metrical foot that does not bear the ictus or stress.
- (less commonly) the part of a metrical foot that bears the ictus. Compare arsis ( def 2 ) .
- Philosophy. Hegelian dialectic
/ ˈθiːsɪs /
- a dissertation resulting from original research, esp when submitted by a candidate for a degree or diploma
- a doctrine maintained or promoted in argument
- a subject for a discussion or essay
- an unproved statement, esp one put forward as a premise in an argument
- music the downbeat of a bar, as indicated in conducting
- (in classical prosody) the syllable or part of a metrical foot not receiving the ictus Compare arsis
- philosophy the first stage in the Hegelian dialectic, that is challenged by the antithesis
- The central idea in a piece of writing, sometimes contained in a topic sentence .
Word History and Origins
Origin of thesis 1
Example Sentences
“The Saudis have been proving the thesis of the film — they do in fact have an army,” said Thor Halvorssen, founder and chief executive of the nonprofit Human Rights Foundation, which funded the movie.
It’s a hypothesis that Bush pursued in her master’s thesis, and last year she began attending virtual Goth parties in a final round of field work before defending her doctoral thesis later this year.
While this partnership was planned prior to the coronavirus outbreak, co-founder Jordana Kier said the pandemic instantly proved out the expansion thesis.
They’ve had to defend that thesis for a very, very long time in front of a variety of different customers and different people.
Over the past decade, In-Q-Tel has been one of the most active investors in the commercial space sector, with a broad investment thesis that touches many aspects of the sector.
In “Back Home,” Gil also revisits the nostalgia for the South explored in his Johns Hopkins thesis, “Circle of Stone.”
At least father and son were in alignment on this central thesis: acting “gay”—bad; being thought of as gay—bad.
Her doctoral thesis, says Ramin Takloo at the University of Illinois, was simply outstanding.
Marshall McLuhan long ago argued the now accepted thesis that different mediums have different influences on thinking.
He wrote his Master's thesis on the underrepresentation of young people in Congress.
And indeed for most young men a college thesis is but an exercise for sharpening the wits, rarely dangerous in its later effects.
It will be for the reader to determine whether the main thesis of the book has gained or lost by the new evidence.
But the word thesis, when applied to Systems, does not mean the 'position' of single notes, but of groups of notes.
This conclusion, it need hardly be said, is in entire agreement with the main thesis of the preceding pages.
Sundry outlying Indians, with ammunition to waste, took belly and knee rests and strengthened the thesis to the contrary.
Related Words
- proposition
- supposition
What Is The Plural Of Thesis?
Plural word for thesis.
The plural form of thesis is theses , pronounced [ thee -seez ]. The plurals of several other singular words that end in -is are also formed in this way, including hypothesis / hypotheses , crisis / crises , and axis / axes . A similar change is made when pluralizing appendix as appendices .
Irregular plurals that are formed like theses derive directly from their original pluralization in Latin and Greek.
Words and phrases
Personal account.
- Access or purchase personal subscriptions
- Get our newsletter
- Save searches
- Set display preferences
Institutional access
Sign in with library card
Sign in with username / password
Recommend to your librarian
Institutional account management
Sign in as administrator on Oxford Academic
thesis noun
- Hide all quotations
What does the noun thesis mean?
There are seven meanings listed in OED's entry for the noun thesis . See ‘Meaning & use’ for definitions, usage, and quotation evidence.
thesis has developed meanings and uses in subjects including
Entry status
OED is undergoing a continuous programme of revision to modernize and improve definitions. This entry has not yet been fully revised.
How common is the noun thesis ?
| 1750 | 1.6 |
| 1760 | 1.8 |
| 1770 | 2.6 |
| 1780 | 1.9 |
| 1790 | 1.7 |
| 1800 | 1.9 |
| 1810 | 1.4 |
| 1820 | 1.3 |
| 1830 | 1.3 |
| 1840 | 1.8 |
| 1850 | 2.0 |
| 1860 | 1.8 |
| 1870 | 2.6 |
| 1880 | 2.9 |
| 1890 | 3.7 |
| 1900 | 4.2 |
| 1910 | 5.7 |
| 1920 | 8.2 |
| 1930 | 13 |
| 1940 | 15 |
| 1950 | 19 |
| 1960 | 24 |
| 1970 | 27 |
| 1980 | 27 |
| 1990 | 25 |
| 2000 | 23 |
| 2010 | 23 |
How is the noun thesis pronounced?
British english, u.s. english, where does the noun thesis come from.
Earliest known use
Middle English
The earliest known use of the noun thesis is in the Middle English period (1150—1500).
OED's earliest evidence for thesis is from before 1398, in a translation by John Trevisa, translator.
thesis is a borrowing from Greek .
Etymons: Greek θέσις .
Nearby entries
- thesaurus, n. 1823–
- thesaury, n. a1639–1708
- these, n. a1600–48
- these, pron. & adj. Old English–
- Thesean, adj. 1815–
- Theseid, n. 1725–
- Theseium, n. 1819–
- these-like, adj. 1644–
- thesial, adj. 1654
- thesicle, n. 1863–
- thesis, n. a1398–
- thesis-novel, n. 1934–
- thesis-play, n. 1902–
- thesmophilist, n. 1644–
- Thesmophorian, adj. 1891–
- Thesmophoric, adj. 1788–
- thesmothete, n. 1603–
- thesocyte, n. 1887–
- thesp, n. 1962–
- Thespian, adj. & n. 1675–
- Thespianism, n. 1914–
Thank you for visiting Oxford English Dictionary
To continue reading, please sign in below or purchase a subscription. After purchasing, please sign in below to access the content.
Meaning & use
Pronunciation, compounds & derived words, entry history for thesis, n..
thesis, n. was first published in 1912; not yet revised.
thesis, n. was last modified in June 2024.
Revision of the OED is a long-term project. Entries in oed.com which have not been revised may include:
- corrections and revisions to definitions, pronunciation, etymology, headwords, variant spellings, quotations, and dates;
- new senses, phrases, and quotations which have been added in subsequent print and online updates.
Revisions and additions of this kind were last incorporated into thesis, n. in June 2024.
Earlier versions of this entry were published in:
OED First Edition (1912)
- Find out more
OED Second Edition (1989)
- View thesis in OED Second Edition
Please submit your feedback for thesis, n.
Please include your email address if you are happy to be contacted about your feedback. OUP will not use this email address for any other purpose.
Citation details
Factsheet for thesis, n., browse entry.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
- What Is a Thesis? | Ultimate Guide & Examples
What Is a Thesis? | Ultimate Guide & Examples
Published on 15 September 2022 by Tegan George . Revised on 25 September 2024.
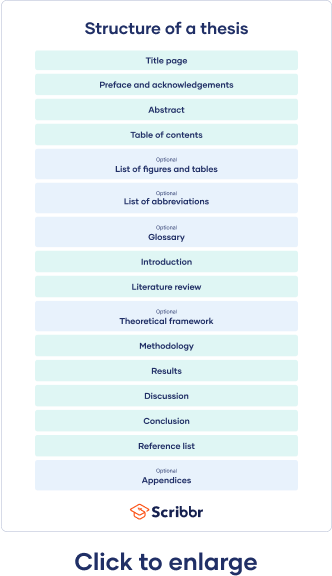
A thesis is a type of research paper based on your original research. It is usually submitted as the final step of a PhD program in the UK.
Writing a thesis can be a daunting experience. Indeed, alongside a dissertation , it is the longest piece of writing students typically complete. It relies on your ability to conduct research from start to finish: designing your research , collecting data , developing a robust analysis, drawing strong conclusions , and writing concisely .
Thesis template
You can also download our full thesis template in the format of your choice below. Our template includes a ready-made table of contents , as well as guidance for what each chapter should include. It’s easy to make it your own, and can help you get started.
Download Word template Download Google Docs template
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
Thesis vs. thesis statement, how to structure a thesis, acknowledgements or preface, list of figures and tables, list of abbreviations, introduction, literature review, methodology, reference list, proofreading and editing, defending your thesis, frequently asked questions about theses.
You may have heard the word thesis as a standalone term or as a component of academic writing called a thesis statement . Keep in mind that these are two very different things.
- A thesis statement is a very common component of an essay, particularly in the humanities. It usually comprises 1 or 2 sentences in the introduction of your essay , and should clearly and concisely summarise the central points of your academic essay .
- A thesis is a long-form piece of academic writing, often taking more than a full semester to complete. It is generally a degree requirement to complete a PhD program.
- In many countries, particularly the UK, a dissertation is generally written at the bachelor’s or master’s level.
- In the US, a dissertation is generally written as a final step toward obtaining a PhD.
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
The final structure of your thesis depends on a variety of components, such as:
- Your discipline
- Your theoretical approach
Humanities theses are often structured more like a longer-form essay . Just like in an essay, you build an argument to support a central thesis.
In both hard and social sciences, theses typically include an introduction , literature review , methodology section , results section , discussion section , and conclusion section . These are each presented in their own dedicated section or chapter. In some cases, you might want to add an appendix .
Thesis examples
We’ve compiled a short list of thesis examples to help you get started.
- Example thesis #1: ‘Abolition, Africans, and Abstraction: the Influence of the “Noble Savage” on British and French Antislavery Thought, 1787-1807’ by Suchait Kahlon.
- Example thesis #2: ‘A Fistful of Genomes: Adventures in Comparative Genomics of Seed-Free Plants’ by David Wickell.
The very first page of your thesis contains all necessary identifying information, including:
- Your full title
- Your full name
- Your department
- Your institution and degree program
- Your submission date.
Sometimes the title page also includes your student ID, the name of your supervisor, or the university’s logo. Check out your university’s guidelines if you’re not sure.
Read more about title pages
The acknowledgements section is usually optional. Its main point is to allow you to thank everyone who helped you in your thesis journey, such as supervisors, friends, or family. You can also choose to write a preface , but it’s typically one or the other, not both.
Read more about acknowledgements Read more about prefaces
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
An abstract is a short summary of your thesis. Usually a maximum of 300 words long, it’s should include brief descriptions of your research objectives , methods, results, and conclusions. Though it may seem short, it introduces your work to your audience, serving as a first impression of your thesis.
Read more about abstracts
A table of contents lists all of your sections, plus their corresponding page numbers and subheadings if you have them. This helps your reader seamlessly navigate your document.
Your table of contents should include all the major parts of your thesis. In particular, don’t forget the the appendices. If you used heading styles, it’s easy to generate an automatic table Microsoft Word.
Read more about tables of contents
While not mandatory, if you used a lot of tables and/or figures, it’s nice to include a list of them to help guide your reader. It’s also easy to generate one of these in Word: just use the ‘Insert Caption’ feature.
Read more about lists of figures and tables
If you have used a lot of industry- or field-specific abbreviations in your thesis, you should include them in an alphabetised list of abbreviations . This way, your readers can easily look up any meanings they aren’t familiar with.
Read more about lists of abbreviations
Relatedly, if you find yourself using a lot of very specialised or field-specific terms that may not be familiar to your reader, consider including a glossary . Alphabetise the terms you want to include with a brief definition.
Read more about glossaries
An introduction sets up the topic, purpose, and relevance of your thesis, as well as expectations for your reader. This should:
- Ground your research topic , sharing any background information your reader may need
- Define the scope of your work
- Introduce any existing research on your topic, situating your work within a broader problem or debate
- State your research question(s)
- Outline (briefly) how the remainder of your work will proceed
In other words, your introduction should clearly and concisely show your reader the “what, why, and how” of your research.
Read more about introductions
A literature review helps you gain a robust understanding of any extant academic work on your topic, encompassing:
- Selecting relevant sources
- Determining the credibility of your sources
- Critically evaluating each of your sources
- Drawing connections between sources, including any themes, patterns, conflicts, or gaps
A literature review is not merely a summary of existing work. Rather, your literature review should ultimately lead to a clear justification for your own research, perhaps via:
- Addressing a gap in the literature
- Building on existing knowledge to draw new conclusions
- Exploring a new theoretical or methodological approach
- Introducing a new solution to an unresolved problem
- Definitively advocating for one side of a theoretical debate
Read more about literature reviews
Theoretical framework
Your literature review can often form the basis for your theoretical framework, but these are not the same thing. A theoretical framework defines and analyses the concepts and theories that your research hinges on.
Read more about theoretical frameworks
Your methodology chapter shows your reader how you conducted your research. It should be written clearly and methodically, easily allowing your reader to critically assess the credibility of your argument. Furthermore, your methods section should convince your reader that your method was the best way to answer your research question.
A methodology section should generally include:
- Your overall approach ( quantitative vs. qualitative )
- Your research methods (e.g., a longitudinal study )
- Your data collection methods (e.g., interviews or a controlled experiment
- Any tools or materials you used (e.g., computer software)
- The data analysis methods you chose (e.g., statistical analysis , discourse analysis )
- A strong, but not defensive justification of your methods
Read more about methodology sections
Your results section should highlight what your methodology discovered. These two sections work in tandem, but shouldn’t repeat each other. While your results section can include hypotheses or themes, don’t include any speculation or new arguments here.
Your results section should:
- State each (relevant) result with any (relevant) descriptive statistics (e.g., mean , standard deviation ) and inferential statistics (e.g., test statistics , p values )
- Explain how each result relates to the research question
- Determine whether the hypothesis was supported
Additional data (like raw numbers or interview transcripts ) can be included as an appendix . You can include tables and figures, but only if they help the reader better understand your results.
Read more about results sections
Your discussion section is where you can interpret your results in detail. Did they meet your expectations? How well do they fit within the framework that you built? You can refer back to any relevant source material to situate your results within your field, but leave most of that analysis in your literature review.
For any unexpected results, offer explanations or alternative interpretations of your data.
Read more about discussion sections
Your thesis conclusion should concisely answer your main research question. It should leave your reader with an ultra-clear understanding of your central argument, and emphasise what your research specifically has contributed to your field.
Why does your research matter? What recommendations for future research do you have? Lastly, wrap up your work with any concluding remarks.
Read more about conclusions
In order to avoid plagiarism , don’t forget to include a full reference list at the end of your thesis, citing the sources that you used. Choose one citation style and follow it consistently throughout your thesis, taking note of the formatting requirements of each style.
Which style you choose is often set by your department or your field, but common styles include MLA , Chicago , and APA.
Create APA citations Create MLA citations
In order to stay clear and concise, your thesis should include the most essential information needed to answer your research question. However, chances are you have many contributing documents, like interview transcripts or survey questions . These can be added as appendices , to save space in the main body.
Read more about appendices
Once you’re done writing, the next part of your editing process begins. Leave plenty of time for proofreading and editing prior to submission. Nothing looks worse than grammar mistakes or sloppy spelling errors!
Consider using a professional thesis editing service to make sure your final project is perfect.
Once you’ve submitted your final product, it’s common practice to have a thesis defense, an oral component of your finished work. This is scheduled by your advisor or committee, and usually entails a presentation and Q&A session.
After your defense, your committee will meet to determine if you deserve any departmental honors or accolades. However, keep in mind that defenses are usually just a formality. If there are any serious issues with your work, these should be resolved with your advisor way before a defense.
The conclusion of your thesis or dissertation shouldn’t take up more than 5-7% of your overall word count.
When you mention different chapters within your text, it’s considered best to use Roman numerals for most citation styles. However, the most important thing here is to remain consistent whenever using numbers in your dissertation .
If you only used a few abbreviations in your thesis or dissertation, you don’t necessarily need to include a list of abbreviations .
If your abbreviations are numerous, or if you think they won’t be known to your audience, it’s never a bad idea to add one. They can also improve readability, minimising confusion about abbreviations unfamiliar to your reader.
A thesis or dissertation outline is one of the most critical first steps in your writing process. It helps you to lay out and organise your ideas and can provide you with a roadmap for deciding what kind of research you’d like to undertake.
Generally, an outline contains information on the different sections included in your thesis or dissertation, such as:
- Your anticipated title
- Your abstract
- Your chapters (sometimes subdivided into further topics like literature review, research methods, avenues for future research, etc.)
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
George, T. (2024, September 25). What Is a Thesis? | Ultimate Guide & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 14 October 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/thesis-dissertation/thesis-ultimate-guide/
Is this article helpful?
Tegan George
Other students also liked, dissertation & thesis outline | example & free templates, how to write a thesis or dissertation conclusion, how to write a thesis or dissertation introduction.
How do I define the state of research for my dissertation?
The state of research is very important in a dissertation. You can only find the research gap if you already know what you want to know. Without this gap, you will not receive a doctorate. But how do I find out what we already know? With a proven scheme.
What is the state of research, anyway?
This is a systematic overview of previous findings on a specific topic, question or object of investigation. The overview is either a table, a full text or both.
Why input do I need for the research status?
You will need the information from the state of research for these phases of the thesis:
- for the introduction (short study overview),
- to deduce the research gap,
- for consultation on the subject and the procedure,
- in the colloquium, to describe the research gap,
- for defending your findings at the end of the thesis.
- to define your own research design with methods, samples and procedures.
What exactly should I look for when I determine the state of research?
You are looking for scientific studies (papers) on your topic. The aim is to provide an overview of the following contents in these studies:
- they examine models and factors,
- the data basis (the so-called sample),
- the respective methodology of the investigation,
- the results of the analyses and their interpretation,
- the outstanding issues.
When, where and how do I start compiling the state of research?
You start with it on your first day of work! You need related studies quickly.
- Define your most important keywords. Look at the terms of the first studies.
- Familiarize yourself with the criteria for evaluating scientific sources.
- Search for the best articles and papers in the best catalogs for scientific studies.
- Limit the time you give yourself to search to 2 hours at a time, otherwise you will lose days
- Find the studies that best match your search terms.
- Don't read into the articles, just read the abstracts first.
- You need a list of relevant articles as soon as possible.
- Be selective and evaluate fewer studies at the beginning. That sounds paradoxical but when you include studies on less relevant issues, you carry these less important questions around with you for far too long. They only end up taking up your time.
How can I recognize that my research status is "complete"?
Complete means that you will not find any other scientific sources on a specific topic. You can see this from the fact that well-known papers are repeatedly quoted in later studies.
By the way, you will also notice it very quickly based on the source list of the article that is closest to your topic and most current (because such an article will list all the important sources).
How do I present the state of research in the text and at what point?
This is a separate longer main chapter in the monograph. This chapter follows a certain structure.
A table is also welcome. This will make previous research on the topic transparent. This so-called Review Matrix follows a certain structure and can be downloaded in the Dissertation Guide.
In the case of article-based dissertations, the state of research is presented only very briefly. Actually only the authors and their questions are listed. The interested reader must then find the details himself.
How do I work with the research status?
- I define and operationalize the research gap in my own thesis.
- With the state of research I classify my own project into the research area and make my supervisors happy.
- I use the same terms as the authors of the studies and build on the appropriate models of the evaluated studies.
- The methods and data samples of the studies give me orientation for my own choice of methods and samples.
- In the end, I classify my own findings into the state of research chapter. Discussion and Conclusion.
How long will it take to determine the state of research?
At the beginning of the dissertation, this will take about 3-4 weeks but then you have the most important 20-30 studies on the topic. After that you will always find new studies to add to the chapter with the state of research.
Compile the state of research according to the plan using the instructions and templates in the PhD-Guide. A thorough survey of previous findings will make the path to the finished dissertation much easier. You will finish faster and receive a better grade.
We wish you success with your dissertation! Silvio and the Aristolo Team PS: Check out the PhD Guide for writing a PhD in 200 days .

Social and scientific relevance of your thesis
Explanations & examples, starting your thesis.
- Start writing your thesis
View our services

Language check
Have your thesis or report reviewed for language, structure, coherence, and layout.

Plagiarism check
Check if your document contains plagiarism.

APA-generator
Create your reference list in APA style effortlessly. Completely free of charge.
What does the relevance of your thesis mean?
Social relevance thesis, scientific relevance thesis, practical relevance thesis, sample relevance thesis, we are happy to review your thesis.
It is important that your thesis topic is relevant. That means it is useful for society, for science and/or for practice. Therefore, when choosing a thesis topic, also look at the relevance of your subject. Also, dedicate a paragraph in your introduction to the relevance of your thesis. Read below what to look out for.
The outcomes of your thesis should be interesting and useful to others in one or more ways. People should be able to do something with it: in practice, in science and/or in society.
You explain the relevance of your thesis in the introduction and address this in your plan of action.
A thesis topic can be relevant in several ways. For instance, your chosen topic should be relevant to your study field and your possible client. In addition, there are three types of relevance:
- social relevance of your thesis;
- scientific relevance of your thesis;
- practical relevance of your thesis.
For practical theses, practical and social relevance are usually the most important. For university theses, scientific relevance can also be very important and practical relevance is not always as important. Your thesis supervisor can tell you what to pay more attention to in your thesis.
Besides choosing a relevant topic, your thesis topic must meet certain requirements . Furthermore, make sure you demarcate the topic properly.
A socially relevant thesis topic is useful to society. You help find a solution to a social problem or provide insight into a current issue with your thesis research.
For example, we speak of social relevance when...
- ... your research leads to recommendations for a problem solution.
- ... when your research explores a current social issue.
- ... if your research shows whether or not a particular method contributes to an important social solution.
- ... when you figure out what underlies a particular problem.
- ... when you gauge people's opinions on a topic to learn more about it.
In addition, your thesis may be academically relevant. This applies especially to theses written for a university course. The scientific relevance of your thesis means that your research complements existing scientific literature. You supplement the literature with new knowledge on a particular topic.
To choose a scientifically relevant topic, first, delve into available literature. What has already been researched? What are possible gaps in the literature?
We may speak of the scientific relevance of your thesis if e.g.
- ... you highlight a specific aspect of a topic that has not yet been researched.
- ... if you build on the suggestions for follow-up research in previous studies.
- ... if you use a new research method to investigate a particular topic.
Are you writing your thesis for a client? In that case, the practical relevance of your thesis is important. Even if you are writing your thesis for your study programme, practical relevance is sometimes important.
There is practical relevance if your thesis leads to recommendations or insights that are useful to practitioners (a profession, industry, organisation, etc.).
Suppose you are writing a thesis for a GP practice on more effective education on diabetes for overweight patients. In this case, the results of your research will be relevant for the staff of this GP practice. Other GP practices may also benefit.
In the introduction of your thesis, you briefly note what makes your thesis topic relevant. This example shows how to describe the relevance of your thesis.
This study is practically relevant because the results will help GP practice Jansen to improve their education on diabetes. This will make it more appealing for the target group to attend this information evening and allow the practice to motivate more patients to start losing weight and thus prevent diabetes.
The recommendations arising from the study are also relevant for other GPs in the Netherlands and diabetes prevention in general. Obesity is a major contributor to type 2 diabetes, a disease currently affecting over X Dutch people. The more people are aware of the link between obesity and type 2 diabetes, the more we can prevent it from reaching that point in obese people.
Furthermore, this study is scientifically relevant because little research has been done on diabetes education in the form of presentations by GPs. Previously, leaflets and brochures on this disease have been studied, but little is known about presentations. This study contributes to the knowledge on this topic, providing a more complete picture of effective education about type 2 diabetes.
The relevance of your thesis is one of the many things you need to formulate correctly in your thesis. Do you doubt whether your thesis is well put together in terms of structure, argumentation, language and spelling? Have our experienced editors review your thesis and give you personal feedback.
Graduate School
- Resources to Prepare for Graduate School
- Adonara Mucek, Ph.D. Geology '17
- Adriana Mendoza, Ph.D. Mathematics '14
- Andrew Olsen
- Becca Maher ('21, Ph.D.)
- Bryan Lynn, Ph.D. Integrative Biology
- Celeste Frazier Barthel, Ph.D. Education '21
- Diane Brandt
- Francesca Germano, Toxicology, M.S.
- Garrett Rogers
- Jafra Thomas
- Jen Hayes, Horticulture, PhD
- Jordan Jimmie
- Jordan Spradlin, Public Health, MPH
- Kalina Fahey, Psychology, Ph.D.
- Katie Stelling, Earth, Ocean and Atmospheric Sciences, Ph.D.
- Kelsey Contreras
- Layla Ghazi
- Marie Tosa, Ph.D. Wildlife Sciences
- Sara Letton
- Tiara Walz, Ph.D. Public Health
- Apply to Graduate School
- Glossary of Terms
- Master's Students
- Doctoral Students
- Certificate Students
- Graduate School Orientation 2024
- Graduate Teaching Orientation 2024
- Do I Qualify to Attend Graduate Summer Step?
- Orientation for Winter, Spring and Summer Terms
- Co-sponsorships
- Your Graduate Committee
- Student Resources
- Grad Research Photo Competition
- Tips for Scheduling Committee Meetings
- Program of Study
- Formatting a Thesis or Dissertation
- Pretext Pages Templates
- Commencement
- Grad Inspire
- Grievance Procedures
- Request a Workshop
- Earning Concurrent Degrees or Pursuing a Dual Major
- Career Preparation
- Grad Writing Group Challenge
- Graduate Writing Center Online
- Changing or Adding a Degree, Major or Certificate
- GRAD 420 - Graduate School Preparation
- GRAD 512 - Current Issues in Higher Education
- GRAD 513 - Professional Development in College and University Teaching
- GRAD 516 - Graduate Teaching Seminar
- GRAD 520 - Responsible Conduct of Research
- GRAD 521 - Research Data Management
- GRAD 542 - The Inclusive College Classroom
- GRAD 543 - Dialogue Facilitation in Professional Contexts: Skills and Practice for Graduate Students
- GRAD 550 - Introduction to Online Course Development and Facilitation
- GRAD 560 - Theories of Teaching and Learning
- GRAD 561 - Course Design and Methods
- GRAD 599 - Creating Happiness
- GRAD 599 - Cultivating Productive and Positive Academic Relationships for Graduate Success
- WR 599 - Graduate Writing for English Language Learners
- WR 599 - Scientific and Technical Research Writing
- WR 599 - Writing Workshop for Thesis and Dissertation Writers
- OSU Grad Advantage
Three-Minute Thesis
- Graduate Faculty Membership
- Graduate Council Representatives
- Policy updates
- Holistic Admissions
- Defining the Graduate Mentor
- The Importance of Mentors
- Apprenticeship and Mentoring
- Mentor and Mentee Pairing
- Maintaining and Evaluating Mentoring
- Suggestions for Mentoring Programs
- Handbooks, Manuals, and Guides
- Mentoring Bibliography
- Academy for Graduate Curriculum Renovation and Graduate School Faculty Fellows
- Communication Items
- Detailed Considerations for a Joint Degree Program
- MOU Outline for Creating a Joint Program
- College and Program Recruitment Representatives
- Graduate Recruitment Tips
- Helpful Recruitment Links
- Shared Graduate Recruitment Schedule
- Leave of Absence and Family Medical Leave Eligibility
- Mentor Training for Faculty
- Student Funding
- Student Progress
- Student Progress Information for Programs
- Student Registration Information
- August 2023 Newsletter
- Sept 2023 Newsletter
- October 2023 Newsletter
- November 2023 Newsletter
- April 2024 Newsletter
- Dec 2023 Newsletter
- Feb 2024 Newsletter
- Jan 2024 Newsletter
- June 2024 Newsletter
- March 2024 Newsletter
- May 2024 Newsletter
- Strategic Plan
- Request Info
- Current Students
- Faculty Resources
You are here
The Graduate School and University of Queensland Present
Info Session: October 16, 2024 3:30 to 2 p.m.  Paddle Tail (6420 Valley Library) or live stream
An 80,000-word PhD thesis would take 9 hours to present. Your time limit... 3 minutes.
The Three Minute Thesis (3MT®) competition challenges graduate students to present their topic of research in just three minutes, using one static slide to a non-technical audience. The Three Minute Thesis (3MT®) is an academic research communication competition developed by The University of Queensland (UQ), Australia.
The winner of the Oregon State University Graduate School 3MT competition will be eligible to compete in Denver at the Western Association of Graduate Schools (WAGS) Regional Competition .
Eligibility
Active Ph.D. and professional doctorate research (program composed of at least two-thirds research and eligible for RTP) candidates who have successfully passed their confirmation milestone/progress review (including candidates whose thesis is under submission) by the date of their first presentation are elible to participate in 3MT competitions at all levels. Graduates are not eligible.
- A single, static PowerPoint slide is shown fromt he beginning of the presentation through the completion. Slide transitions, animations or "movement" of any kind is not allowed in the graphic.
- No additional electronic media (e.g. sound and video files) are permitted.
- No additional props (e.g. cosutmes, musical instruments, laboratory equipment) are permitted.
- Presentations are limited to three minutes maximum. Competitors exceeding three minutes are disqualified.
- Presentationsare to be spoken word (e.g. no poems, raps or songs).
- Presentations are to commence from the stage, and time will start when a presenter advances from the title slide to the presntation slide.
- The decision of the adjudicating panel is final.
- This is an in-person event. Participants must be able to present in person during the preliminary comopetition January 22 and, if selected, the final competition on February 5, both at the Corvallis campus.
Registration
Applications will be accepted via Qualitrics Thursday, October 17, through Monday, November 19. To apply, you will need to include the title of your presentation and a 200-word abstract.
Contact Info
Graduate School Heckart Lodge 2900 SW Jefferson Way Oregon State University Corvallis, OR 97331-1102
Phone: 541-737-4881 Fax: 541-737-3313
- Programs - Majors, minors and certificates
- Academic Progress
- Student Success
- Faculty Support
- Staff Directory
- Graduate Catalog
Have a language expert improve your writing
Check your paper for plagiarism in 10 minutes, generate your apa citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Plural of Thesis | Definition & Examples
Plural of Thesis | Definition & Examples
Published on October 8, 2024 by Ryan Cove .
The plural of thesis is theses , pronounced [ thee -seez]. It’s a Greek-derived irregular plural noun that doesn’t follow regular pluralization rules, which add “ -s ” or “ -es ” to the end of the singular to form the plural.
Table of contents
What is the plural of thesis, what is an irregular plural, frequently asked questions about the plural of thesis.
The plural of thesis is theses . Some people think that “thesises” or “thesi” are the plural of “thesis,” but those are incorrect.
- The panel of experts discussed the merits of the competing theses during the debate.
- The university encourages students to publish their theses in academic journals.
- Several of the thesises addressed ethical considerations in modern technology.
- Networking at the conference allowed her to connect with other authors of similar thesi .
Theses is considered an irregular plural noun . Unlike regular plural nouns (e.g., pizza/pizzas and class/classes ), you don’t simply add an “ -s ” or “ -es ” to the singular form of an irregular plural noun. This is why the plural of “thesis” is not “thesises,” even though this is a common misspelling.
Thesis is a Greek-derived word and follows Greek pluralization rules, meaning you change the “ -is ” at the end of the singular form to “ -es ” to create the plural (e.g., analysis/analyses and axis/axes ).
Not all irregular plurals come from Greek origins. Some irregular plurals are Latin-derived words, and others come from other linguistic origins like Old English or Dutch.
| Singular | Plural |
|---|---|
| goose | geese |
| person | people |
| oasis | oases |
| hoof | hooves |
A zero plural is another type of plural noun, which is a noun that remains the same in both the singular and plural forms.
| Singular | Plural |
|---|---|
| shrimp | shrimp |
| deer | deer |
| police | police |
| spacecraft | spacecraft |
Thesis is singular, and the plural of thesis is theses .
Thesis is an irregular plural noun that doesn’t follow the regular pluralization rules of adding “ -s ” or “ -es ” to the singular to form the plural.
Use Scribbr’s free Grammar Checker to ensure you use the correct noun forms in your online documents.
The plural of thesis is not thesises because thesis is an irregular plural noun and doesn’t follow the regular pluralization rules, which add “ -s ” or “ -es ” to the end of the singular to form the plural.
Thesis is a Greek-derived irregular plural that follows Greek pluralization rules, which change the “ -is ” at the end of the singular form to “ -es ” in the plural. So, the plural of thesis is theses .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Cove, R. (2024, October 08). Plural of Thesis | Definition & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved October 14, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/plurals/plural-of-thesis/
Is this article helpful?

Other students also liked
Appositive | examples, definition & punctuation, apostrophes | definition, guide, rules & examples, pronoun-antecedent agreement | examples & tips.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A thesis is an in-depth research study that identifies a particular topic of inquiry and presents a clear argument or perspective about that topic using evidence and logic. Writing a thesis showcases your ability of critical thinking, gathering evidence, and making a compelling argument. Integral to these competencies is thorough research ...
Revised on April 16, 2024. A thesis is a type of research paper based on your original research. It is usually submitted as the final step of a master's program or a capstone to a bachelor's degree. Writing a thesis can be a daunting experience. Other than a dissertation, it is one of the longest pieces of writing students typically complete.
Step 2: Write your initial answer. After some initial research, you can formulate a tentative answer to this question. At this stage it can be simple, and it should guide the research process and writing process. The internet has had more of a positive than a negative effect on education.
The meaning of THESIS is a dissertation embodying results of original research and especially substantiating a specific view; especially : one written by a candidate for an academic degree. ... These examples are programmatically compiled from various online sources to illustrate current usage of the word 'thesis.' Any opinions expressed in the ...
Thesis. Your thesis is the central claim in your essay—your main insight or idea about your source or topic. Your thesis should appear early in an academic essay, followed by a logically constructed argument that supports this central claim. A strong thesis is arguable, which means a thoughtful reader could disagree with it and therefore ...
Dissertations and theses (the plural of thesis) are often confused because they're both lengthy research papers written for higher education. In American English, a dissertation is written to earn a doctorate whereas a thesis is written to earn a master's (or sometimes a bachelor's). In many informal situations, however, the terms ...
THESIS definition: 1. a long piece of writing on a particular subject, especially one that is done for a higher…. Learn more.
Grammarly helps you communicate confidently. Write with Grammarly. In a student's final year, the thesis can be seen as the final component of one's candidacy for a degree; in other words, it is the last opportunity a student has to show off what they've learned and internalized. Generally speaking, a thesis should challenge an ...
THESIS meaning: 1. a long piece of writing on a particular subject, especially one that is done for a higher…. Learn more.
Craft a convincing dissertation or thesis research proposal. Write a clear, compelling introduction chapter. Undertake a thorough review of the existing research and write up a literature review. Undertake your own research. Present and interpret your findings. Draw a conclusion and discuss the implications.
The term thesis comes from the Greek word θέσις, meaning "something put forth", and refers to an intellectual proposition. Dissertation comes from the Latin dissertātiō, meaning "discussion". Aristotle was the first philosopher to define the term thesis.. A 'thesis' is a supposition of some eminent philosopher that conflicts with the general opinion...for to take notice when any ...
A thesis statement makes a promise to the reader about the scope, purpose, and direction of the paper. It summarizes the conclusions that the writer has reached about the topic. A thesis statement is generally located near the end of the introduction. Sometimes in a long paper, the thesis will be expressed in several sentences or an entire ...
Thesis. Definition: Thesis is a scholarly document that presents a student's original research and findings on a particular topic or question. It is usually written as a requirement for a graduate degree program and is intended to demonstrate the student's mastery of the subject matter and their ability to conduct independent research.
thesis (that…) a statement or an opinion that is discussed in a logical way and presented with evidence in order to prove that it is true. The basic thesis of the book is fairly simple. These latest findings support the thesis that sexuality is determined by nature rather than choice.
The definition of thesis (ˈθi sɪs, ˈθiːsɪs, the-sis, plural theses) in American English is the main idea presented in an essay. In other words, the central message of the piece. Behind every literary device and rhetorical strategy stands a thesis. Thesis statements don't just appear at the beginning of your paper; they should be woven ...
Creating an academically strong thesis proposal sets the foundation for a high-quality thesis and helps garner the attention of a well-respected thesis director. Thesis proposals typically include approximately 15 to 20 pages of text, in addition to any required reference sections, such as bibliographies and glossary/definition of terms.
Example 1: Passive construction. The passive voice is a common choice for outlines and overviews because the context makes it clear who is carrying out the action (e.g., you are conducting the research). However, overuse of the passive voice can make your text vague and imprecise. Example: Passive construction.
Thesis definition: a proposition stated or put forward for consideration, especially one to be discussed and proved or to be maintained against objections. See examples of THESIS used in a sentence.
There are seven meanings listed in OED's entry for the noun thesis. See 'Meaning & use' for definitions, usage, and quotation evidence. thesis has developed meanings and uses in subjects including. prosody (Middle English) music (Middle English) rhetoric (late 1500s) logic (late 1500s) education (late 1700s) philosophy (1830s)
A thesis is a type of research paper based on your original research. It is usually submitted as the final step of a PhD program in the UK. Writing a thesis can be a daunting experience. Indeed, alongside a dissertation, it is the longest piece of writing students typically complete.It relies on your ability to conduct research from start to finish: designing your research, collecting data ...
At the beginning of the dissertation, this will take about 3-4 weeks but then you have the most important 20-30 studies on the topic. After that you will always find new studies to add to the chapter with the state of research. Compile the state of research according to the plan using the instructions and templates in the PhD-Guide.
A thesis topic can be relevant in several ways. For instance, your chosen topic should be relevant to your study field and your possible client. In addition, there are three types of relevance: social relevance of your thesis; scientific relevance of your thesis; practical relevance of your thesis. For practical theses, practical and social ...
Overview of the structure. To help guide your reader, end your introduction with an outline of the structure of the thesis or dissertation to follow. Share a brief summary of each chapter, clearly showing how each contributes to your central aims. However, be careful to keep this overview concise: 1-2 sentences should be enough.
The Three Minute Thesis (3MT®) competition challenges graduate students to present their topic of research in just three minutes, using one static slide to a non-technical audience. The Three Minute Thesis (3MT®) is an academic research communication competition developed by The University of Queensland (UQ), Australia.
Plural of Thesis | Definition & Examples. Published on October 8, 2024 by Ryan Cove. The plural of thesis is theses, pronounced [thee-seez].It's a Greek-derived irregular plural noun that doesn't follow regular pluralization rules, which add "-s" or "-es" to the end of the singular to form the plural.. Theses in a sentence examples The library has a comprehensive collection of past ...