How to Write About Coronavirus in a College Essay
Students can share how they navigated life during the coronavirus pandemic in a full-length essay or an optional supplement.
Writing About COVID-19 in College Essays

Getty Images
Experts say students should be honest and not limit themselves to merely their experiences with the pandemic.
The global impact of COVID-19, the disease caused by the novel coronavirus, means colleges and prospective students alike are in for an admissions cycle like no other. Both face unprecedented challenges and questions as they grapple with their respective futures amid the ongoing fallout of the pandemic.
Colleges must examine applicants without the aid of standardized test scores for many – a factor that prompted many schools to go test-optional for now . Even grades, a significant component of a college application, may be hard to interpret with some high schools adopting pass-fail classes last spring due to the pandemic. Major college admissions factors are suddenly skewed.
"I can't help but think other (admissions) factors are going to matter more," says Ethan Sawyer, founder of the College Essay Guy, a website that offers free and paid essay-writing resources.
College essays and letters of recommendation , Sawyer says, are likely to carry more weight than ever in this admissions cycle. And many essays will likely focus on how the pandemic shaped students' lives throughout an often tumultuous 2020.
But before writing a college essay focused on the coronavirus, students should explore whether it's the best topic for them.

Writing About COVID-19 for a College Application
Much of daily life has been colored by the coronavirus. Virtual learning is the norm at many colleges and high schools, many extracurriculars have vanished and social lives have stalled for students complying with measures to stop the spread of COVID-19.
"For some young people, the pandemic took away what they envisioned as their senior year," says Robert Alexander, dean of admissions, financial aid and enrollment management at the University of Rochester in New York. "Maybe that's a spot on a varsity athletic team or the lead role in the fall play. And it's OK for them to mourn what should have been and what they feel like they lost, but more important is how are they making the most of the opportunities they do have?"
That question, Alexander says, is what colleges want answered if students choose to address COVID-19 in their college essay.
But the question of whether a student should write about the coronavirus is tricky. The answer depends largely on the student.
"In general, I don't think students should write about COVID-19 in their main personal statement for their application," Robin Miller, master college admissions counselor at IvyWise, a college counseling company, wrote in an email.
"Certainly, there may be exceptions to this based on a student's individual experience, but since the personal essay is the main place in the application where the student can really allow their voice to be heard and share insight into who they are as an individual, there are likely many other topics they can choose to write about that are more distinctive and unique than COVID-19," Miller says.
Opinions among admissions experts vary on whether to write about the likely popular topic of the pandemic.
"If your essay communicates something positive, unique, and compelling about you in an interesting and eloquent way, go for it," Carolyn Pippen, principal college admissions counselor at IvyWise, wrote in an email. She adds that students shouldn't be dissuaded from writing about a topic merely because it's common, noting that "topics are bound to repeat, no matter how hard we try to avoid it."
Above all, she urges honesty.
"If your experience within the context of the pandemic has been truly unique, then write about that experience, and the standing out will take care of itself," Pippen says. "If your experience has been generally the same as most other students in your context, then trying to find a unique angle can easily cross the line into exploiting a tragedy, or at least appearing as though you have."
But focusing entirely on the pandemic can limit a student to a single story and narrow who they are in an application, Sawyer says. "There are so many wonderful possibilities for what you can say about yourself outside of your experience within the pandemic."
He notes that passions, strengths, career interests and personal identity are among the multitude of essay topic options available to applicants and encourages them to probe their values to help determine the topic that matters most to them – and write about it.
That doesn't mean the pandemic experience has to be ignored if applicants feel the need to write about it.
Writing About Coronavirus in Main and Supplemental Essays
Students can choose to write a full-length college essay on the coronavirus or summarize their experience in a shorter form.
To help students explain how the pandemic affected them, The Common App has added an optional section to address this topic. Applicants have 250 words to describe their pandemic experience and the personal and academic impact of COVID-19.
"That's not a trick question, and there's no right or wrong answer," Alexander says. Colleges want to know, he adds, how students navigated the pandemic, how they prioritized their time, what responsibilities they took on and what they learned along the way.
If students can distill all of the above information into 250 words, there's likely no need to write about it in a full-length college essay, experts say. And applicants whose lives were not heavily altered by the pandemic may even choose to skip the optional COVID-19 question.
"This space is best used to discuss hardship and/or significant challenges that the student and/or the student's family experienced as a result of COVID-19 and how they have responded to those difficulties," Miller notes. Using the section to acknowledge a lack of impact, she adds, "could be perceived as trite and lacking insight, despite the good intentions of the applicant."
To guard against this lack of awareness, Sawyer encourages students to tap someone they trust to review their writing , whether it's the 250-word Common App response or the full-length essay.
Experts tend to agree that the short-form approach to this as an essay topic works better, but there are exceptions. And if a student does have a coronavirus story that he or she feels must be told, Alexander encourages the writer to be authentic in the essay.
"My advice for an essay about COVID-19 is the same as my advice about an essay for any topic – and that is, don't write what you think we want to read or hear," Alexander says. "Write what really changed you and that story that now is yours and yours alone to tell."
Sawyer urges students to ask themselves, "What's the sentence that only I can write?" He also encourages students to remember that the pandemic is only a chapter of their lives and not the whole book.
Miller, who cautions against writing a full-length essay on the coronavirus, says that if students choose to do so they should have a conversation with their high school counselor about whether that's the right move. And if students choose to proceed with COVID-19 as a topic, she says they need to be clear, detailed and insightful about what they learned and how they adapted along the way.
"Approaching the essay in this manner will provide important balance while demonstrating personal growth and vulnerability," Miller says.
Pippen encourages students to remember that they are in an unprecedented time for college admissions.
"It is important to keep in mind with all of these (admission) factors that no colleges have ever had to consider them this way in the selection process, if at all," Pippen says. "They have had very little time to calibrate their evaluations of different application components within their offices, let alone across institutions. This means that colleges will all be handling the admissions process a little bit differently, and their approaches may even evolve over the course of the admissions cycle."
Searching for a college? Get our complete rankings of Best Colleges.
10 Ways to Discover College Essay Ideas

Tags: students , colleges , college admissions , college applications , college search , Coronavirus
2024 Best Colleges

Search for your perfect fit with the U.S. News rankings of colleges and universities.
College Admissions: Get a Step Ahead!
Sign up to receive the latest updates from U.S. News & World Report and our trusted partners and sponsors. By clicking submit, you are agreeing to our Terms and Conditions & Privacy Policy .
Ask an Alum: Making the Most Out of College
You May Also Like
Should students submit test scores.
Sarah Wood May 13, 2024

Poll: Antisemitism a Problem on Campus
Lauren Camera May 13, 2024

Federal vs. Private Parent Student Loans
Erika Giovanetti May 9, 2024

14 Colleges With Great Food Options
Sarah Wood May 8, 2024

Colleges With Religious Affiliations
Anayat Durrani May 8, 2024

Protests Threaten Campus Graduations
Aneeta Mathur-Ashton May 6, 2024

Protesting on Campus: What to Know
Sarah Wood May 6, 2024

Lawmakers Ramp Up Response to Unrest
Aneeta Mathur-Ashton May 3, 2024

University Commencements Must Go On
Eric J. Gertler May 3, 2024

Where Astronauts Went to College
Cole Claybourn May 3, 2024

Writing about COVID-19 in a college admission essay
by: Venkates Swaminathan | Updated: September 14, 2020
Print article

For students applying to college using the CommonApp, there are several different places where students and counselors can address the pandemic’s impact. The different sections have differing goals. You must understand how to use each section for its appropriate use.
The CommonApp COVID-19 question
First, the CommonApp this year has an additional question specifically about COVID-19 :
Community disruptions such as COVID-19 and natural disasters can have deep and long-lasting impacts. If you need it, this space is yours to describe those impacts. Colleges care about the effects on your health and well-being, safety, family circumstances, future plans, and education, including access to reliable technology and quiet study spaces. Please use this space to describe how these events have impacted you.
This question seeks to understand the adversity that students may have had to face due to the pandemic, the move to online education, or the shelter-in-place rules. You don’t have to answer this question if the impact on you wasn’t particularly severe. Some examples of things students should discuss include:
- The student or a family member had COVID-19 or suffered other illnesses due to confinement during the pandemic.
- The candidate had to deal with personal or family issues, such as abusive living situations or other safety concerns
- The student suffered from a lack of internet access and other online learning challenges.
- Students who dealt with problems registering for or taking standardized tests and AP exams.
Jeff Schiffman of the Tulane University admissions office has a blog about this section. He recommends students ask themselves several questions as they go about answering this section:
- Are my experiences different from others’?
- Are there noticeable changes on my transcript?
- Am I aware of my privilege?
- Am I specific? Am I explaining rather than complaining?
- Is this information being included elsewhere on my application?
If you do answer this section, be brief and to-the-point.
Counselor recommendations and school profiles
Second, counselors will, in their counselor forms and school profiles on the CommonApp, address how the school handled the pandemic and how it might have affected students, specifically as it relates to:
- Grading scales and policies
- Graduation requirements
- Instructional methods
- Schedules and course offerings
- Testing requirements
- Your academic calendar
- Other extenuating circumstances
Students don’t have to mention these matters in their application unless something unusual happened.
Writing about COVID-19 in your main essay
Write about your experiences during the pandemic in your main college essay if your experience is personal, relevant, and the most important thing to discuss in your college admission essay. That you had to stay home and study online isn’t sufficient, as millions of other students faced the same situation. But sometimes, it can be appropriate and helpful to write about something related to the pandemic in your essay. For example:
- One student developed a website for a local comic book store. The store might not have survived without the ability for people to order comic books online. The student had a long-standing relationship with the store, and it was an institution that created a community for students who otherwise felt left out.
- One student started a YouTube channel to help other students with academic subjects he was very familiar with and began tutoring others.
- Some students used their extra time that was the result of the stay-at-home orders to take online courses pursuing topics they are genuinely interested in or developing new interests, like a foreign language or music.
Experiences like this can be good topics for the CommonApp essay as long as they reflect something genuinely important about the student. For many students whose lives have been shaped by this pandemic, it can be a critical part of their college application.
Want more? Read 6 ways to improve a college essay , What the &%$! should I write about in my college essay , and Just how important is a college admissions essay? .
Homes Nearby
Homes for rent and sale near schools

How our schools are (and aren't) addressing race

The truth about homework in America

What should I write my college essay about?
What the #%@!& should I write about in my college essay?
Yes! Sign me up for updates relevant to my child's grade.
Please enter a valid email address
Thank you for signing up!
Server Issue: Please try again later. Sorry for the inconvenience
- Discussions
- Certificates
- Collab Space
- Course Details
- Announcements
An error occurred while loading the video player, or it takes a long time to initialize. You can try clearing your browser cache. Please try again later and contact the helpdesk if the problem persists.
Coronaviruses are a large family of viruses that are known to cause illness ranging from the common cold to more severe diseases such as Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS) and Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS).
A novel coronavirus (COVID-19) was identified in 2019 in Wuhan, China. This is a new coronavirus that has not been previously identified in humans.
This course provides a general introduction to COVID-19 and emerging respiratory viruses and is intended for public health professionals, incident managers and personnel working for the United Nations, international organizations and NGOs.
As the official disease name was established after material creation, any mention of nCoV refers to COVID-19, the infectious disease caused by the most recently discovered coronavirus.
Please note that the content of this course is currently being revised to reflect the most recent guidance. You can find updated information on certain COVID-19-related topics in the following courses: Vaccination: COVID-19 vaccines channel IPC measures: IPC for COVID-19 Antigen rapid diagnostic testing: 1) SARS-CoV-2 antigen rapid diagnostic testing ; 2) Key considerations for SARS-CoV-2 antigen RDT implementation
Please note: These materials were last updated on 16/12/2020.
Course contents
Emerging respiratory viruses, including covid-19: introduction:, module 1: introduction to emerging respiratory viruses, including covid-19:, module 2: detecting emerging respiratory viruses, including covid-19: surveillance:, module 3: detecting emerging respiratory viruses, including covid-19: laboratory investigations:, module 4: risk communication :, module 5 : community engagement:, module 6: preventing and responding to an emerging respiratory virus, including covid-19:, enroll me for this course, certificate requirements.
- Gain a Record of Achievement by earning at least 80% of the maximum number of points from all graded assignments.
Persuasive Essay Guide
Persuasive Essay About Covid19
How to Write a Persuasive Essay About Covid19 | Examples & Tips
11 min read

People also read
A Comprehensive Guide to Writing an Effective Persuasive Essay
200+ Persuasive Essay Topics to Help You Out
Learn How to Create a Persuasive Essay Outline
30+ Free Persuasive Essay Examples To Get You Started
Read Excellent Examples of Persuasive Essay About Gun Control
Crafting a Convincing Persuasive Essay About Abortion
Learn to Write Persuasive Essay About Business With Examples and Tips
Check Out 12 Persuasive Essay About Online Education Examples
Persuasive Essay About Smoking - Making a Powerful Argument with Examples
Are you looking to write a persuasive essay about the Covid-19 pandemic?
Writing a compelling and informative essay about this global crisis can be challenging. It requires researching the latest information, understanding the facts, and presenting your argument persuasively.
But don’t worry! with some guidance from experts, you’ll be able to write an effective and persuasive essay about Covid-19.
In this blog post, we’ll outline the basics of writing a persuasive essay . We’ll provide clear examples, helpful tips, and essential information for crafting your own persuasive piece on Covid-19.
Read on to get started on your essay.
- 1. Steps to Write a Persuasive Essay About Covid-19
- 2. Examples of Persuasive Essay About Covid19
- 3. Examples of Persuasive Essay About Covid-19 Vaccine
- 4. Examples of Persuasive Essay About Covid-19 Integration
- 5. Examples of Argumentative Essay About Covid 19
- 6. Examples of Persuasive Speeches About Covid-19
- 7. Tips to Write a Persuasive Essay About Covid-19
- 8. Common Topics for a Persuasive Essay on COVID-19
Steps to Write a Persuasive Essay About Covid-19
Here are the steps to help you write a persuasive essay on this topic, along with an example essay:
Step 1: Choose a Specific Thesis Statement
Your thesis statement should clearly state your position on a specific aspect of COVID-19. It should be debatable and clear. For example:
Step 2: Research and Gather Information
Collect reliable and up-to-date information from reputable sources to support your thesis statement. This may include statistics, expert opinions, and scientific studies. For instance:
- COVID-19 vaccination effectiveness data
- Information on vaccine mandates in different countries
- Expert statements from health organizations like the WHO or CDC
Step 3: Outline Your Essay
Create a clear and organized outline to structure your essay. A persuasive essay typically follows this structure:
- Introduction
- Background Information
- Body Paragraphs (with supporting evidence)
- Counterarguments (addressing opposing views)
Step 4: Write the Introduction
In the introduction, grab your reader's attention and present your thesis statement. For example:
Step 5: Provide Background Information
Offer context and background information to help your readers understand the issue better. For instance:
Step 6: Develop Body Paragraphs
Each body paragraph should present a single point or piece of evidence that supports your thesis statement. Use clear topic sentences, evidence, and analysis. Here's an example:
Step 7: Address Counterarguments
Acknowledge opposing viewpoints and refute them with strong counterarguments. This demonstrates that you've considered different perspectives. For example:
Step 8: Write the Conclusion
Summarize your main points and restate your thesis statement in the conclusion. End with a strong call to action or thought-provoking statement. For instance:
Step 9: Revise and Proofread
Edit your essay for clarity, coherence, grammar, and spelling errors. Ensure that your argument flows logically.
Step 10: Cite Your Sources
Include proper citations and a bibliography page to give credit to your sources.
Remember to adjust your approach and arguments based on your target audience and the specific angle you want to take in your persuasive essay about COVID-19.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job!
Examples of Persuasive Essay About Covid19
When writing a persuasive essay about the Covid-19 pandemic, it’s important to consider how you want to present your argument. To help you get started, here are some example essays for you to read:
Check out some more PDF examples below:
Persuasive Essay About Covid-19 Pandemic
Sample Of Persuasive Essay About Covid-19
Persuasive Essay About Covid-19 In The Philippines - Example
If you're in search of a compelling persuasive essay on business, don't miss out on our “ persuasive essay about business ” blog!
Examples of Persuasive Essay About Covid-19 Vaccine
Covid19 vaccines are one of the ways to prevent the spread of Covid-19, but they have been a source of controversy. Different sides argue about the benefits or dangers of the new vaccines. Whatever your point of view is, writing a persuasive essay about it is a good way of organizing your thoughts and persuading others.
A persuasive essay about the Covid-19 vaccine could consider the benefits of getting vaccinated as well as the potential side effects.
Below are some examples of persuasive essays on getting vaccinated for Covid-19.
Covid19 Vaccine Persuasive Essay
Persuasive Essay on Covid Vaccines
Interested in thought-provoking discussions on abortion? Read our persuasive essay about abortion blog to eplore arguments!
Examples of Persuasive Essay About Covid-19 Integration
Covid19 has drastically changed the way people interact in schools, markets, and workplaces. In short, it has affected all aspects of life. However, people have started to learn to live with Covid19.
Writing a persuasive essay about it shouldn't be stressful. Read the sample essay below to get idea for your own essay about Covid19 integration.
Persuasive Essay About Working From Home During Covid19
Searching for the topic of Online Education? Our persuasive essay about online education is a must-read.
Examples of Argumentative Essay About Covid 19
Covid-19 has been an ever-evolving issue, with new developments and discoveries being made on a daily basis.
Writing an argumentative essay about such an issue is both interesting and challenging. It allows you to evaluate different aspects of the pandemic, as well as consider potential solutions.
Here are some examples of argumentative essays on Covid19.
Argumentative Essay About Covid19 Sample
Argumentative Essay About Covid19 With Introduction Body and Conclusion
Looking for a persuasive take on the topic of smoking? You'll find it all related arguments in out Persuasive Essay About Smoking blog!
Examples of Persuasive Speeches About Covid-19
Do you need to prepare a speech about Covid19 and need examples? We have them for you!
Persuasive speeches about Covid-19 can provide the audience with valuable insights on how to best handle the pandemic. They can be used to advocate for specific changes in policies or simply raise awareness about the virus.
Check out some examples of persuasive speeches on Covid-19:
Persuasive Speech About Covid-19 Example
Persuasive Speech About Vaccine For Covid-19
You can also read persuasive essay examples on other topics to master your persuasive techniques!
Tips to Write a Persuasive Essay About Covid-19
Writing a persuasive essay about COVID-19 requires a thoughtful approach to present your arguments effectively.
Here are some tips to help you craft a compelling persuasive essay on this topic:
Choose a Specific Angle
Start by narrowing down your focus. COVID-19 is a broad topic, so selecting a specific aspect or issue related to it will make your essay more persuasive and manageable. For example, you could focus on vaccination, public health measures, the economic impact, or misinformation.
Provide Credible Sources
Support your arguments with credible sources such as scientific studies, government reports, and reputable news outlets. Reliable sources enhance the credibility of your essay.
Use Persuasive Language
Employ persuasive techniques, such as ethos (establishing credibility), pathos (appealing to emotions), and logos (using logic and evidence). Use vivid examples and anecdotes to make your points relatable.
Organize Your Essay
Structure your essay involves creating a persuasive essay outline and establishing a logical flow from one point to the next. Each paragraph should focus on a single point, and transitions between paragraphs should be smooth and logical.
Emphasize Benefits
Highlight the benefits of your proposed actions or viewpoints. Explain how your suggestions can improve public health, safety, or well-being. Make it clear why your audience should support your position.
Use Visuals -H3
Incorporate graphs, charts, and statistics when applicable. Visual aids can reinforce your arguments and make complex data more accessible to your readers.
Call to Action
End your essay with a strong call to action. Encourage your readers to take a specific step or consider your viewpoint. Make it clear what you want them to do or think after reading your essay.
Revise and Edit
Proofread your essay for grammar, spelling, and clarity. Make sure your arguments are well-structured and that your writing flows smoothly.
Seek Feedback
Have someone else read your essay to get feedback. They may offer valuable insights and help you identify areas where your persuasive techniques can be improved.
Tough Essay Due? Hire Tough Writers!
Common Topics for a Persuasive Essay on COVID-19
Here are some persuasive essay topics on COVID-19:
- The Importance of Vaccination Mandates for COVID-19 Control
- Balancing Public Health and Personal Freedom During a Pandemic
- The Economic Impact of Lockdowns vs. Public Health Benefits
- The Role of Misinformation in Fueling Vaccine Hesitancy
- Remote Learning vs. In-Person Education: What's Best for Students?
- The Ethics of Vaccine Distribution: Prioritizing Vulnerable Populations
- The Mental Health Crisis Amidst the COVID-19 Pandemic
- The Long-Term Effects of COVID-19 on Healthcare Systems
- Global Cooperation vs. Vaccine Nationalism in Fighting the Pandemic
- The Future of Telemedicine: Expanding Healthcare Access Post-COVID-19
In search of more inspiring topics for your next persuasive essay? Our persuasive essay topics blog has plenty of ideas!
To sum it up,
You have read good sample essays and got some helpful tips. You now have the tools you needed to write a persuasive essay about Covid-19. So don't let the doubts stop you, start writing!
If you need professional writing help, don't worry! We've got that for you as well.
MyPerfectWords.com is a professional persuasive essay writing service that can help you craft an excellent persuasive essay on Covid-19. Our experienced essay writer will create a well-structured, insightful paper in no time!
So don't hesitate and place your ' write my essay online ' request today!
Frequently Asked Questions
Are there any ethical considerations when writing a persuasive essay about covid-19.
Yes, there are ethical considerations when writing a persuasive essay about COVID-19. It's essential to ensure the information is accurate, not contribute to misinformation, and be sensitive to the pandemic's impact on individuals and communities. Additionally, respecting diverse viewpoints and emphasizing public health benefits can promote ethical communication.
What impact does COVID-19 have on society?
The impact of COVID-19 on society is far-reaching. It has led to job and economic losses, an increase in stress and mental health disorders, and changes in education systems. It has also had a negative effect on social interactions, as people have been asked to limit their contact with others.

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Caleb S. has been providing writing services for over five years and has a Masters degree from Oxford University. He is an expert in his craft and takes great pride in helping students achieve their academic goals. Caleb is a dedicated professional who always puts his clients first.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!
Keep reading


25,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today
Meet top uk universities from the comfort of your home, here’s your new year gift, one app for all your, study abroad needs, start your journey, track your progress, grow with the community and so much more.

Verification Code
An OTP has been sent to your registered mobile no. Please verify

Thanks for your comment !
Our team will review it before it's shown to our readers.

- School Education /
Essay On Covid-19: 100, 200 and 300 Words

- Updated on
- Apr 30, 2024

COVID-19, also known as the Coronavirus, is a global pandemic that has affected people all around the world. It first emerged in a lab in Wuhan, China, in late 2019 and quickly spread to countries around the world. This virus was reportedly caused by SARS-CoV-2. Since then, it has spread rapidly to many countries, causing widespread illness and impacting our lives in numerous ways. This blog talks about the details of this virus and also drafts an essay on COVID-19 in 100, 200 and 300 words for students and professionals.
Table of Contents
- 1 Essay On COVID-19 in English 100 Words
- 2 Essay On COVID-19 in 200 Words
- 3 Essay On COVID-19 in 300 Words
- 4 Short Essay on Covid-19
Essay On COVID-19 in English 100 Words
COVID-19, also known as the coronavirus, is a global pandemic. It started in late 2019 and has affected people all around the world. The virus spreads very quickly through someone’s sneeze and respiratory issues.
COVID-19 has had a significant impact on our lives, with lockdowns, travel restrictions, and changes in daily routines. To prevent the spread of COVID-19, we should wear masks, practice social distancing, and wash our hands frequently.
People should follow social distancing and other safety guidelines and also learn the tricks to be safe stay healthy and work the whole challenging time.
Also Read: National Safe Motherhood Day 2023
Essay On COVID-19 in 200 Words
COVID-19 also known as coronavirus, became a global health crisis in early 2020 and impacted mankind around the world. This virus is said to have originated in Wuhan, China in late 2019. It belongs to the coronavirus family and causes flu-like symptoms. It impacted the healthcare systems, economies and the daily lives of people all over the world.
The most crucial aspect of COVID-19 is its highly spreadable nature. It is a communicable disease that spreads through various means such as coughs from infected persons, sneezes and communication. Due to its easy transmission leading to its outbreaks, there were many measures taken by the government from all over the world such as Lockdowns, Social Distancing, and wearing masks.
There are many changes throughout the economic systems, and also in daily routines. Other measures such as schools opting for Online schooling, Remote work options available and restrictions on travel throughout the country and internationally. Subsequently, to cure and top its outbreak, the government started its vaccine campaigns, and other preventive measures.
In conclusion, COVID-19 tested the patience and resilience of the mankind. This pandemic has taught people the importance of patience, effort and humbleness.
Also Read : Essay on My Best Friend
Essay On COVID-19 in 300 Words
COVID-19, also known as the coronavirus, is a serious and contagious disease that has affected people worldwide. It was first discovered in late 2019 in Cina and then got spread in the whole world. It had a major impact on people’s life, their school, work and daily lives.
COVID-19 is primarily transmitted from person to person through respiratory droplets produced and through sneezes, and coughs of an infected person. It can spread to thousands of people because of its highly contagious nature. To cure the widespread of this virus, there are thousands of steps taken by the people and the government.
Wearing masks is one of the essential precautions to prevent the virus from spreading. Social distancing is another vital practice, which involves maintaining a safe distance from others to minimize close contact.
Very frequent handwashing is also very important to stop the spread of this virus. Proper hand hygiene can help remove any potential virus particles from our hands, reducing the risk of infection.
In conclusion, the Coronavirus has changed people’s perspective on living. It has also changed people’s way of interacting and how to live. To deal with this virus, it is very important to follow the important guidelines such as masks, social distancing and techniques to wash your hands. Getting vaccinated is also very important to go back to normal life and cure this virus completely.
Also Read: Essay on Abortion in English in 650 Words
Short Essay on Covid-19
Please find below a sample of a short essay on Covid-19 for school students:
Also Read: Essay on Women’s Day in 200 and 500 words
to write an essay on COVID-19, understand your word limit and make sure to cover all the stages and symptoms of this disease. You need to highlight all the challenges and impacts of COVID-19. Do not forget to conclude your essay with positive precautionary measures.
Writing an essay on COVID-19 in 200 words requires you to cover all the challenges, impacts and precautions of this disease. You don’t need to describe all of these factors in brief, but make sure to add as many options as your word limit allows.
The full form for COVID-19 is Corona Virus Disease of 2019.
Related Reads
Hence, we hope that this blog has assisted you in comprehending with an essay on COVID-19. For more information on such interesting topics, visit our essay writing page and follow Leverage Edu.
Simran Popli
An avid writer and a creative person. With an experience of 1.5 years content writing, Simran has worked with different areas. From medical to working in a marketing agency with different clients to Ed-tech company, the journey has been diverse. Creative, vivacious and patient are the words that describe her personality.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Contact no. *

Connect With Us

25,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today.

Resend OTP in

Need help with?
Study abroad.
UK, Canada, US & More
IELTS, GRE, GMAT & More
Scholarship, Loans & Forex
Country Preference
New Zealand
Which English test are you planning to take?
Which academic test are you planning to take.
Not Sure yet
When are you planning to take the exam?
Already booked my exam slot
Within 2 Months
Want to learn about the test
Which Degree do you wish to pursue?
When do you want to start studying abroad.
January 2024
September 2024
What is your budget to study abroad?

How would you describe this article ?
Please rate this article
We would like to hear more.
Have something on your mind?

Make your study abroad dream a reality in January 2022 with
India's Biggest Virtual University Fair

Essex Direct Admission Day
Why attend .

Don't Miss Out
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- BMJ - PMC COVID-19 Collection

Side effects of COVID-19 vaccines: a systematic review and meta-analysis protocol of randomised trials
Kleyton santos medeiros.
1 Health Sciences Postgraduate Program, Federal University of Rio Grande do Norte, Natal, Rio Grande do Norte, Brazil
2 Instituto de Ensino, Pesquisa e Inovação, Liga Contra o Câncer, Natal, Rio Grande do Norte, Brazil
Ana Paula Ferreira Costa
Ayane cristine alves sarmento, cijara leonice freitas, ana katherine gonçalves.
3 Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Norte, Natal, Brazil
Associated Data
Introduction.
SARS-CoV-2 is responsible for a large number of global COVID-19 cases. Strategies such as social isolation, personal hygiene and frequent hand washing have been implemented; however, a protective vaccine is required to achieve sufficient herd immunity to SARS-CoV-2 infection to ultimately control the COVID-19 pandemic. To meet the urgent need for a vaccine, a reduction in the development schedule has been proposed from 10–15 years to 1–2 years. For this reason, this systematic review and meta-analysis protocol aims to compare the side effects, safety and toxicity of COVID-19 vaccines available globally, including their combinations.
Methods and analysis
We will select randomised controlled trial-type studies that evaluate the side effects of the COVID-19 vaccine. PubMed, Web of Science, Embase, CINAHL, PsycINFO, LILACS, SCOPUS, ClinicalTrials.gov, International Clinical Trials Registry Platform (ICTRP), medRxiv.org, biorxiv.org, preprints.org and the Cochrane Library will be searched for eligible studies until December 2021. Three reviewers will independently screen and select studies, assess methodological quality and extract data. A meta-analysis will be performed, if possible, and the Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development and Evaluations summary of findings will be presented.
Ethics and dissemination
This study will review published data, and thus it is unnecessary to obtain ethical approval. The findings of this systematic review will be published in a peer-reviewed journal.
PROSPERO registration number
CRD42021231101.
Strengths and limitations of this study
- Four authors (KSM, APFC, ACAS, CLF) will select the articles independently using titles and abstracts.
- To the best of our knowledge, there are no existing reviews regarding the side effects of COVID-19 vaccines.
- The DerSimonian and Laird method may underestimate the true between-study variance, potentially producing overly narrow CIs for the mean effect. This fact is a limitation, so the collection of studies will be done with care and the assumptions of the analytical methods will be assessed.
SARS-CoV-2 is responsible for a large number of global COVID-19 cases. It is a highly transmissible virus among humans that has become a significant public health issue. 1 Symptoms include fever, dry cough, fatigue, shortness of breath, chills, muscle pain, headache, gastric disorders and weight loss, often leading to death. 2
Strategies such as social isolation, personal hygiene and frequent hand washing have been implemented; however, a protective vaccine is required to achieve sufficient herd immunity to SARS-CoV-2 infection to ultimately control the COVID-19 pandemic. 3 To meet the urgent need for a vaccine, a reduction in the development schedule has been proposed from 10–15 years to 1–2 years. 4
SARS-CoV-2 is an RNA virus with a high mutation rate, and that on the envelope surface has three important structural proteins that can be identified: spike protein (S), envelope protein (E) and membrane protein (M). Most innovative vaccines have focused their efforts on inducing an immune response against the S protein. Attenuated virus vaccines are based on weakened microorganisms, effective in stimulating the immune system. The inactivated ones (dead microorganisms) are more stable than the attenuated ones, but they have a short duration of immunological memory that requires the association of adjuvants. mRNA vaccines are stable—and can be easily produced in large quantities. Vaccines against COVID-19 differ in composition and mechanism of action, which may be relevant for their safety and efficacy, being essential for the success and eradication of this infection. 5 6 The viral vector (mRNA) vaccine encodes full-length S protein ectodomains of SARS-CoV-2, which contains both T and B cell epitopes that can induce cellular and humoral immune responses against viral infection. 7
Assessing the safety, efficacy and side effects of the vaccine is urgently needed, and has been heavily scrutinised by the leading medical agencies around the world, like the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the Food and Drug Administration. Developing any vaccine needs to ensure that safety risks are identified and quantified against potential benefits. Among the potential risks raised in the context of COVID-19, vaccine development is the security and effectiveness of immune responses elicited by a vaccine. Here, this systematic review protocol aims to assess the side effects, safety and toxicity of vaccines against COVID-19.
This systematic review and meta-analysis protocol aims to compare the side effects, safety and toxicity of COVID-19 vaccines available globally, including their combination.
Review question
What are the rates of adverse reactions (local and systemic) to COVID-19 vaccines?
The meta-analysis protocol follows the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Protocols guidelines. 8 9 This protocol is registered with the International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews (PROSPERO).
Eligibility criteria
The inclusion criteria involved: (1) randomised controlled trial (RCT)-type studies that evaluated the side effects of the COVID-19 vaccine; (2) experiments involving human beings; (3) studies evaluating the safety, immunogenicity and efficacy parameters of the vaccines; (4) studies that presented similar vaccination protocols; (5) studies published since January 2020 until December 2021; and (6) studies published in any language.
The exclusion criteria were as follows: (1) observational studies, and (2) case reports, meeting abstracts, review papers and commentaries.

Patients, intervention, comparison, outcome strategy and types of studies
- Patients: healthy adults aged 18 years or older who were HIV negative and previously SARS-CoV-2 infection free.
- Intervention: COVID-19 vaccine or a combination of vaccines against COVID-19.
- Comparator/control: placebo.
- Outcome: safety, tolerability and immunogenicity of the COVID-19 vaccine or the combination of vaccines against COVID-19.
- Types of studies: RCTs.
Information sources
The following databases will be searched: Medline / PubMed, Web of Science, Embase, CINAHL, PsycINFO, Latin American and Caribbean Health Sciences Literature (LILACS), SCOPUS, ClinicalTrials.gov, International Clinical Trials Registry Platform (ICTRP), medRxiv.org, biorxiv.org, preprints.org and Cochrane Central Controlled Trials Registry. Furthermore, eligible studies may also be selected from the reference lists of retrieved articles.
Patient and public involvement
The individual patient data will not be presented. A literature search will be carried out from defined databases. No patient will be involved in the study planning and application process during neither the analysis nor the dissemination of results.
Search strategy
Our keyword search will be based on Medical Subject Headings according to the following combination: (COVID-19 OR SARS-CoV-2 OR 2019-nCoV OR coronavirus) AND (vaccines OR vaccination OR COVID-19 vaccine OR SARS-CoV-2 vaccine OR BNT162 vaccine OR mRNA-1273 vaccine OR COVID-19 aAPC vaccine OR INO-4800 vaccine OR LV-SMENP-DC COVID-19 vaccine OR Ad5-nCoV vaccine OR ChAdOx1 COVID-19 vaccine OR MNA SARS-CoV-2 S1 subunit vaccines OR PittCoVacc OR Inactivated novel coronavirus 2019-CoV vaccine Vero cells OR Inactivated Vaccines OR SARS-CoV-2 inactivated vaccines OR Viral Vaccines OR Gam-COVID-Vac vaccine OR Ad26.COV2.S vaccine OR EpiVacCorona vaccine) AND (Toxicity OR Vaccine Immunogenicity OR side effects OR adverse events) AND (randomized controlled trial OR double blind method OR clinical trial) ( table 1 ). A list of vaccines available at WHO was also used.
Medline search strategy
Study records
Four researchers (KSM, APFC, ACAS, CLF) performed the selection of the studies of interest. Titles and abstracts will be read independently, and duplicate studies will be excluded. The same authors analysed the selected texts to assess the compliance with the inclusion criteria. A fifth reviewer, AKG, solves the discrepancies. The flow chart of this study is shown in figure 1 .

Flow diagram of the search for eligible studies on the side effects, safety and toxicity of the COVID-19 vaccine. CENTRAL, Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials.
Data collection process and management
A standardised data extraction form was developed and tested. Data from each included study will be extracted independently by two reviewers (ACAS and APFC), and any subsequent discrepancies will be resolved through discussion with a third reviewer (AKG). The data extracted will include information on authors, the year of publication, study location, type of study, main objectives, population, type of vaccine, follow-up of participants, rates of systemic events, gastrointestinal symptoms, injection site-related adverse effects and serious vaccine-related adverse events ( table 2 ). Furthermore, participant characteristics (eg, mean age, gender) and results for immunogenicity will be collected.
Adverse events of COVID-19 vaccines
The study authors will be contacted in case of missing data and/or to resolve any uncertainties. In addition, any additional information will be recorded. All data entries will be checked twice. If we find a set of articles with similar characteristics based on the information in the data extraction table, we will perform a meta-analysis using a random-effects model. If there are data that are not clear in some articles, the corresponding author will be contacted for possible clarification.
Risk of bias in individual studies
Three authors (KSM, ACAS, APFC) will independently assess the risk of bias in the eligible studies using the Cochrane risk-of-bias tool. 10 The Risk of Bias 2 tool 11 will be used to assess the risk of bias. Bias is assessed as a judgement (high, low or unclear) for individual elements from five domains (selection, performance, attrition, reporting and others).
Data will be entered into the Review Manager software (RevMan V.5.2.3). This software allows the user to enter protocols; complete reviews; include text, characteristics of the studies, comparison tables and study data; and perform meta-analyses. For dichotomous outcomes, we extracted or calculated the OR and 95% CI for each study. In case of heterogeneity (I 2 ≥50%), the random-effects model will be used to combine the studies to calculate the OR and 95% CI using the DerSimonian-Laird algorithm 12 .
Data synthesis and analysis
To grade the strength of evidence from the included data, we will use the Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development and Evaluation 13 approach. The summary of the assessment will be incorporated into broader measurements to ensure the judgement of the risk of bias, consistency, directness and precision. The quality of the evidence will be assessed based on the risk of bias, indirectness, inconsistency, imprecision and publication bias.
The COVID-19 pandemic represents one of the most significant global public health crises of this generation. Lockdown, quarantine, contact tracing and case isolation are suggested as effective interventions to control the epidemic; however, they may present different results in different contexts because of the specific features of the COVID-19. The lack of implementation of continued interventions or effective treatments further contributes to discovering and using effective and safe vaccines. 14 15
For all these reasons, scientists worldwide entered a race to find a vaccine candidate useful in fighting the new coronavirus pandemic. Nevertheless, it is essential to note that a vaccine’s production is not easy and quick. Before being released to the population, a vaccine must go through three phases of clinical trials that prove its safety and effectiveness. More volunteers are recruited at each stage, and the researchers analyse the test results to ensure that a vaccine can be licensed. 16–18
One hundred and seventy-three vaccines were in preclinical development and 64 in clinical trials until 20 January 2021. On 31 December 2020, the WHO listed the mRNA vaccine against COVID-19 for emergency use, making this Pfizer/BioNTech immuniser the first to receive WHO emergency validation from the beginning outbreak. Already, in January 2021, emergency approval was granted to nine vaccines by regulatory authorities in different parts of the world. 14 19
With the starting vaccination, several studies were carried out to ascertain the safety of these vaccines, since they were produced in record time. 20–22 Currently, one systematic review about the thematic showed that of 11 published clinical trials of COVID-19 vaccines included in the study, adverse reactions reported were considered mild to moderate with few severe reactions which were unrelated to the test vaccine. Common adverse events were pain at the site of injection, fever, myalgia, fatigue and headache. Serious adverse events (SAE) were reported in four trials: COVID-19 Vaccine AstraZeneca (AZD1222)—168 SAEs with only three related to the vaccine; Ad26.COV2.S—four with none related to the testing vaccine; five with Comirnaty (BNT162b1) vaccine and one with Covaxin (BBV152) vaccine. 19
One limitation about the COVID-19 vaccine safety tested until now is that clinical trials of the safety and effectiveness have had low inclusion of vulnerable groups, for example, older persons, the first population to receive the whole vaccine. That’s why pharmacovigilance postmarketing is necessary to surveillance of new drugs, as a critical aspect of evaluating medicine safety and effectiveness, particularly in risk groups.
Other prevention approaches are likely to emerge in the coming months, including antiviral agents, drugs may be to decrease disease progression, monoclonal antibodies, hyperimmune globulin and convalescent titre. If proven effective, these approaches could be used in high-risk individuals, including healthcare workers, other essential workers and older adults. 23–26 It is essential to maintain protective measures such as washing hands frequently with soap and water or gel alcohol and covering the mouth with a forearm when coughing or sneezing.
For all the reasons mentioned above, this review is necessary and essential. The latter is a well-defined protocol registered with PROSPERO, well planned to include the largest possible number of vaccines, a significant number of vaccinated patients, thus providing safe and reliable results regarding the use of vaccines.
Supplementary Material
Contributors: KSM, ACAS and APFC contributed to the design of this review. KSM and ACAS drafted the protocol manuscript. APFC and AKG revised the manuscript. KSM, AKG and APFC developed the search strategies. KSM, CLF and ACAS implemented the search strategies. KSM, CLF, ACAS and APFC tracked the potential studies, extracted the data and assessed the quality. In case of disagreement between the data extractors, AKG advised on the methodology and worked as a referee. KSM completed the data synthesis. All authors approved the final version for publication.
Funding: The authors have not declared a specific grant for this research from any funding agency in the public, commercial or not-for-profit sectors.
Competing interests: None declared.
Patient and public involvement: Patients and/or the public were not involved in the design, or conduct, or reporting, or dissemination plans of this research.
Provenance and peer review: Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
Ethics statements
Patient consent for publication.
Not applicable.
- CBSE Class 10th
- CBSE Class 12th
- UP Board 10th
- UP Board 12th
- Bihar Board 10th
- Bihar Board 12th
- Top Schools in India
- Top Schools in Delhi
- Top Schools in Mumbai
- Top Schools in Chennai
- Top Schools in Hyderabad
- Top Schools in Kolkata
- Top Schools in Pune
- Top Schools in Bangalore
Products & Resources
- JEE Main Knockout April
- Free Sample Papers
- Free Ebooks
- NCERT Notes
- NCERT Syllabus
- NCERT Books
- RD Sharma Solutions
- Navodaya Vidyalaya Admission 2024-25
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11
- NCERT solutions for Class 10
- NCERT solutions for Class 9
- NCERT solutions for Class 8
- NCERT Solutions for Class 7
- JEE Main 2024
- MHT CET 2024
- JEE Advanced 2024
- BITSAT 2024
- View All Engineering Exams
- Colleges Accepting B.Tech Applications
- Top Engineering Colleges in India
- Engineering Colleges in India
- Engineering Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- Engineering Colleges Accepting JEE Main
- Top IITs in India
- Top NITs in India
- Top IIITs in India
- JEE Main College Predictor
- JEE Main Rank Predictor
- MHT CET College Predictor
- AP EAMCET College Predictor
- GATE College Predictor
- KCET College Predictor
- JEE Advanced College Predictor
- View All College Predictors
- JEE Main Question Paper
- JEE Main Cutoff
- JEE Main Advanced Admit Card
- AP EAPCET Hall Ticket
- Download E-Books and Sample Papers
- Compare Colleges
- B.Tech College Applications
- KCET Result
- MAH MBA CET Exam
- View All Management Exams
Colleges & Courses
- MBA College Admissions
- MBA Colleges in India
- Top IIMs Colleges in India
- Top Online MBA Colleges in India
- MBA Colleges Accepting XAT Score
- BBA Colleges in India
- XAT College Predictor 2024
- SNAP College Predictor
- NMAT College Predictor
- MAT College Predictor 2024
- CMAT College Predictor 2024
- CAT Percentile Predictor 2023
- CAT 2023 College Predictor
- CMAT 2024 Admit Card
- TS ICET 2024 Hall Ticket
- CMAT Result 2024
- MAH MBA CET Cutoff 2024
- Download Helpful Ebooks
- List of Popular Branches
- QnA - Get answers to your doubts
- IIM Fees Structure
- AIIMS Nursing
- Top Medical Colleges in India
- Top Medical Colleges in India accepting NEET Score
- Medical Colleges accepting NEET
- List of Medical Colleges in India
- List of AIIMS Colleges In India
- Medical Colleges in Maharashtra
- Medical Colleges in India Accepting NEET PG
- NEET College Predictor
- NEET PG College Predictor
- NEET MDS College Predictor
- NEET Rank Predictor
- DNB PDCET College Predictor
- NEET Admit Card 2024
- NEET PG Application Form 2024
- NEET Cut off
- NEET Online Preparation
- Download Helpful E-books
- Colleges Accepting Admissions
- Top Law Colleges in India
- Law College Accepting CLAT Score
- List of Law Colleges in India
- Top Law Colleges in Delhi
- Top NLUs Colleges in India
- Top Law Colleges in Chandigarh
- Top Law Collages in Lucknow
Predictors & E-Books
- CLAT College Predictor
- MHCET Law ( 5 Year L.L.B) College Predictor
- AILET College Predictor
- Sample Papers
- Compare Law Collages
- Careers360 Youtube Channel
- CLAT Syllabus 2025
- CLAT Previous Year Question Paper
- NID DAT Exam
- Pearl Academy Exam
Predictors & Articles
- NIFT College Predictor
- UCEED College Predictor
- NID DAT College Predictor
- NID DAT Syllabus 2025
- NID DAT 2025
- Design Colleges in India
- Top NIFT Colleges in India
- Fashion Design Colleges in India
- Top Interior Design Colleges in India
- Top Graphic Designing Colleges in India
- Fashion Design Colleges in Delhi
- Fashion Design Colleges in Mumbai
- Top Interior Design Colleges in Bangalore
- NIFT Result 2024
- NIFT Fees Structure
- NIFT Syllabus 2025
- Free Design E-books
- List of Branches
- Careers360 Youtube channel
- IPU CET BJMC
- JMI Mass Communication Entrance Exam
- IIMC Entrance Exam
- Media & Journalism colleges in Delhi
- Media & Journalism colleges in Bangalore
- Media & Journalism colleges in Mumbai
- List of Media & Journalism Colleges in India
- CA Intermediate
- CA Foundation
- CS Executive
- CS Professional
- Difference between CA and CS
- Difference between CA and CMA
- CA Full form
- CMA Full form
- CS Full form
- CA Salary In India
Top Courses & Careers
- Bachelor of Commerce (B.Com)
- Master of Commerce (M.Com)
- Company Secretary
- Cost Accountant
- Charted Accountant
- Credit Manager
- Financial Advisor
- Top Commerce Colleges in India
- Top Government Commerce Colleges in India
- Top Private Commerce Colleges in India
- Top M.Com Colleges in Mumbai
- Top B.Com Colleges in India
- IT Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- IT Colleges in Uttar Pradesh
- MCA Colleges in India
- BCA Colleges in India
Quick Links
- Information Technology Courses
- Programming Courses
- Web Development Courses
- Data Analytics Courses
- Big Data Analytics Courses
- RUHS Pharmacy Admission Test
- Top Pharmacy Colleges in India
- Pharmacy Colleges in Pune
- Pharmacy Colleges in Mumbai
- Colleges Accepting GPAT Score
- Pharmacy Colleges in Lucknow
- List of Pharmacy Colleges in Nagpur
- GPAT Result
- GPAT 2024 Admit Card
- GPAT Question Papers
- NCHMCT JEE 2024
- Mah BHMCT CET
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Delhi
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Hyderabad
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Mumbai
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Maharashtra
- B.Sc Hotel Management
- Hotel Management
- Diploma in Hotel Management and Catering Technology
Diploma Colleges
- Top Diploma Colleges in Maharashtra
- UPSC IAS 2024
- SSC CGL 2024
- IBPS RRB 2024
- Previous Year Sample Papers
- Free Competition E-books
- Sarkari Result
- QnA- Get your doubts answered
- UPSC Previous Year Sample Papers
- CTET Previous Year Sample Papers
- SBI Clerk Previous Year Sample Papers
- NDA Previous Year Sample Papers
Upcoming Events
- NDA Application Form 2024
- UPSC IAS Application Form 2024
- CDS Application Form 2024
- CTET Admit card 2024
- HP TET Result 2023
- SSC GD Constable Admit Card 2024
- UPTET Notification 2024
- SBI Clerk Result 2024
Other Exams
- SSC CHSL 2024
- UP PCS 2024
- UGC NET 2024
- RRB NTPC 2024
- IBPS PO 2024
- IBPS Clerk 2024
- IBPS SO 2024
- Top University in USA
- Top University in Canada
- Top University in Ireland
- Top Universities in UK
- Top Universities in Australia
- Best MBA Colleges in Abroad
- Business Management Studies Colleges
Top Countries
- Study in USA
- Study in UK
- Study in Canada
- Study in Australia
- Study in Ireland
- Study in Germany
- Study in China
- Study in Europe
Student Visas
- Student Visa Canada
- Student Visa UK
- Student Visa USA
- Student Visa Australia
- Student Visa Germany
- Student Visa New Zealand
- Student Visa Ireland
- CUET PG 2024
- IGNOU B.Ed Admission 2024
- DU Admission 2024
- UP B.Ed JEE 2024
- LPU NEST 2024
- IIT JAM 2024
- IGNOU Online Admission 2024
- Universities in India
- Top Universities in India 2024
- Top Colleges in India
- Top Universities in Uttar Pradesh 2024
- Top Universities in Bihar
- Top Universities in Madhya Pradesh 2024
- Top Universities in Tamil Nadu 2024
- Central Universities in India
- CUET Exam City Intimation Slip 2024
- IGNOU Date Sheet
- CUET Mock Test 2024
- CUET Admit card 2024
- CUET PG Syllabus 2024
- CUET Participating Universities 2024
- CUET Previous Year Question Paper
- CUET Syllabus 2024 for Science Students
- E-Books and Sample Papers
- CUET Exam Pattern 2024
- CUET Exam Date 2024
- CUET Syllabus 2024
- IGNOU Exam Form 2024
- CUET UG Admit Card 2024 (Out) Live
- CUET 2024 Admit Card
Engineering Preparation
- Knockout JEE Main 2024
- Test Series JEE Main 2024
- JEE Main 2024 Rank Booster
Medical Preparation
- Knockout NEET 2024
- Test Series NEET 2024
- Rank Booster NEET 2024
Online Courses
- JEE Main One Month Course
- NEET One Month Course
- IBSAT Free Mock Tests
- IIT JEE Foundation Course
- Knockout BITSAT 2024
- Career Guidance Tool
Top Streams
- IT & Software Certification Courses
- Engineering and Architecture Certification Courses
- Programming And Development Certification Courses
- Business and Management Certification Courses
- Marketing Certification Courses
- Health and Fitness Certification Courses
- Design Certification Courses
Specializations
- Digital Marketing Certification Courses
- Cyber Security Certification Courses
- Artificial Intelligence Certification Courses
- Business Analytics Certification Courses
- Data Science Certification Courses
- Cloud Computing Certification Courses
- Machine Learning Certification Courses
- View All Certification Courses
- UG Degree Courses
- PG Degree Courses
- Short Term Courses
- Free Courses
- Online Degrees and Diplomas
- Compare Courses
Top Providers
- Coursera Courses
- Udemy Courses
- Edx Courses
- Swayam Courses
- upGrad Courses
- Simplilearn Courses
- Great Learning Courses
Covid 19 Essay in English
Essay on Covid -19: In a very short amount of time, coronavirus has spread globally. It has had an enormous impact on people's lives, economy, and societies all around the world, affecting every country. Governments have had to take severe measures to try and contain the pandemic. The virus has altered our way of life in many ways, including its effects on our health and our economy. Here are a few sample essays on ‘CoronaVirus’.
100 Words Essay on Covid 19
200 words essay on covid 19, 500 words essay on covid 19.

COVID-19 or Corona Virus is a novel coronavirus that was first identified in 2019. It is similar to other coronaviruses, such as SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV, but it is more contagious and has caused more severe respiratory illness in people who have been infected. The novel coronavirus became a global pandemic in a very short period of time. It has affected lives, economies and societies across the world, leaving no country untouched. The virus has caused governments to take drastic measures to try and contain it. From health implications to economic and social ramifications, COVID-19 impacted every part of our lives. It has been more than 2 years since the pandemic hit and the world is still recovering from its effects.
Since the outbreak of COVID-19, the world has been impacted in a number of ways. For one, the global economy has taken a hit as businesses have been forced to close their doors. This has led to widespread job losses and an increase in poverty levels around the world. Additionally, countries have had to impose strict travel restrictions in an attempt to contain the virus, which has resulted in a decrease in tourism and international trade. Furthermore, the pandemic has put immense pressure on healthcare systems globally, as hospitals have been overwhelmed with patients suffering from the virus. Lastly, the outbreak has led to a general feeling of anxiety and uncertainty, as people are fearful of contracting the disease.
My Experience of COVID-19
I still remember how abruptly colleges and schools shut down in March 2020. I was a college student at that time and I was under the impression that everything would go back to normal in a few weeks. I could not have been more wrong. The situation only got worse every week and the government had to impose a lockdown. There were so many restrictions in place. For example, we had to wear face masks whenever we left the house, and we could only go out for essential errands. Restaurants and shops were only allowed to operate at take-out capacity, and many businesses were shut down.
In the current scenario, coronavirus is dominating all aspects of our lives. The coronavirus pandemic has wreaked havoc upon people’s lives, altering the way we live and work in a very short amount of time. It has revolutionised how we think about health care, education, and even social interaction. This virus has had long-term implications on our society, including its impact on mental health, economic stability, and global politics. But we as individuals can help to mitigate these effects by taking personal responsibility to protect themselves and those around them from infection.
Effects of CoronaVirus on Education
The outbreak of coronavirus has had a significant impact on education systems around the world. In China, where the virus originated, all schools and universities were closed for several weeks in an effort to contain the spread of the disease. Many other countries have followed suit, either closing schools altogether or suspending classes for a period of time.
This has resulted in a major disruption to the education of millions of students. Some have been able to continue their studies online, but many have not had access to the internet or have not been able to afford the costs associated with it. This has led to a widening of the digital divide between those who can afford to continue their education online and those who cannot.
The closure of schools has also had a negative impact on the mental health of many students. With no face-to-face contact with friends and teachers, some students have felt isolated and anxious. This has been compounded by the worry and uncertainty surrounding the virus itself.
The situation with coronavirus has improved and schools have been reopened but students are still catching up with the gap of 2 years that the pandemic created. In the meantime, governments and educational institutions are working together to find ways to support students and ensure that they are able to continue their education despite these difficult circumstances.
Effects of CoronaVirus on Economy
The outbreak of the coronavirus has had a significant impact on the global economy. The virus, which originated in China, has spread to over two hundred countries, resulting in widespread panic and a decrease in global trade. As a result of the outbreak, many businesses have been forced to close their doors, leading to a rise in unemployment. In addition, the stock market has taken a severe hit.
Effects of CoronaVirus on Health
The effects that coronavirus has on one's health are still being studied and researched as the virus continues to spread throughout the world. However, some of the potential effects on health that have been observed thus far include respiratory problems, fever, and coughing. In severe cases, pneumonia, kidney failure, and death can occur. It is important for people who think they may have been exposed to the virus to seek medical attention immediately so that they can be treated properly and avoid any serious complications. There is no specific cure or treatment for coronavirus at this time, but there are ways to help ease symptoms and prevent the virus from spreading.
Applications for Admissions are open.

Aakash iACST Scholarship Test 2024
Get up to 90% scholarship on NEET, JEE & Foundation courses

ALLEN Digital Scholarship Admission Test (ADSAT)
Register FREE for ALLEN Digital Scholarship Admission Test (ADSAT)

JEE Main Important Physics formulas
As per latest 2024 syllabus. Physics formulas, equations, & laws of class 11 & 12th chapters

PW JEE Coaching
Enrol in PW Vidyapeeth center for JEE coaching

PW NEET Coaching
Enrol in PW Vidyapeeth center for NEET coaching

JEE Main Important Chemistry formulas
As per latest 2024 syllabus. Chemistry formulas, equations, & laws of class 11 & 12th chapters
Download Careers360 App's
Regular exam updates, QnA, Predictors, College Applications & E-books now on your Mobile
Certifications
We Appeared in
Essay on COVID-19 Pandemic
As a result of the COVID-19 (Coronavirus) outbreak, daily life has been negatively affected, impacting the worldwide economy. Thousands of individuals have been sickened or died as a result of the outbreak of this disease. When you have the flu or a viral infection, the most common symptoms include fever, cold, coughing up bone fragments, and difficulty breathing, which may progress to pneumonia. It’s important to take major steps like keeping a strict cleaning routine, keeping social distance, and wearing masks, among other things. This virus’s geographic spread is accelerating (Daniel Pg 93). Governments restricted public meetings during the start of the pandemic to prevent the disease from spreading and breaking the exponential distribution curve. In order to avoid the damage caused by this extremely contagious disease, several countries quarantined their citizens. However, this scenario had drastically altered with the discovery of the vaccinations. The research aims to investigate the effect of the Covid-19 epidemic and its impact on the population’s well-being.
There is growing interest in the relationship between social determinants of health and health outcomes. Still, many health care providers and academics have been hesitant to recognize racism as a contributing factor to racial health disparities. Only a few research have examined the health effects of institutional racism, with the majority focusing on interpersonal racial and ethnic prejudice Ciotti et al., Pg 370. The latter comprises historically and culturally connected institutions that are interconnected. Prejudice is being practiced in a variety of contexts as a result of the COVID-19 outbreak. In some ways, the outbreak has exposed pre-existing bias and inequity.
Thousands of businesses are in danger of failure. Around 2.3 billion of the world’s 3.3 billion employees are out of work. These workers are especially susceptible since they lack access to social security and adequate health care, and they’ve also given up ownership of productive assets, which makes them highly vulnerable. Many individuals lose their employment as a result of lockdowns, leaving them unable to support their families. People strapped for cash are often forced to reduce their caloric intake while also eating less nutritiously (Fraser et al, Pg 3). The epidemic has had an impact on the whole food chain, revealing vulnerabilities that were previously hidden. Border closures, trade restrictions, and confinement measures have limited farmer access to markets, while agricultural workers have not gathered crops. As a result, the local and global food supply chain has been disrupted, and people now have less access to healthy foods. As a consequence of the epidemic, many individuals have lost their employment, and millions more are now in danger. When breadwinners lose their jobs, become sick, or die, the food and nutrition of millions of people are endangered. Particularly severely hit are the world’s poorest small farmers and indigenous peoples.
Infectious illness outbreaks and epidemics have become worldwide threats due to globalization, urbanization, and environmental change. In developed countries like Europe and North America, surveillance and health systems monitor and manage the spread of infectious illnesses in real-time. Both low- and high-income countries need to improve their public health capacities (Omer et al., Pg 1767). These improvements should be financed using a mix of national and foreign donor money. In order to speed up research and reaction for new illnesses with pandemic potential, a global collaborative effort including governments and commercial companies has been proposed. When working on a vaccine-like COVID-19, cooperation is critical.
The epidemic has had an impact on the whole food chain, revealing vulnerabilities that were previously hidden. Border closures, trade restrictions, and confinement measures have limited farmer access to markets, while agricultural workers have been unable to gather crops. As a result, the local and global food supply chain has been disrupted, and people now have less access to healthy foods (Daniel et al.,Pg 95) . As a consequence of the epidemic, many individuals have lost their employment, and millions more are now in danger. When breadwinners lose their jobs, the food and nutrition of millions of people are endangered. Particularly severely hit are the world’s poorest small farmers and indigenous peoples.
While helping to feed the world’s population, millions of paid and unpaid agricultural laborers suffer from high levels of poverty, hunger, and bad health, as well as a lack of safety and labor safeguards, as well as other kinds of abuse at work. Poor people, who have no recourse to social assistance, must work longer and harder, sometimes in hazardous occupations, endangering their families in the process (Daniel Pg 96). When faced with a lack of income, people may turn to hazardous financial activities, including asset liquidation, predatory lending, or child labor, to make ends meet. Because of the dangers they encounter while traveling, working, and living abroad; migrant agricultural laborers are especially vulnerable. They also have a difficult time taking advantage of government assistance programs.
The pandemic also has a significant impact on education. Although many educational institutions across the globe have already made the switch to online learning, the extent to which technology is utilized to improve the quality of distance or online learning varies. This level is dependent on several variables, including the different parties engaged in the execution of this learning format and the incorporation of technology into educational institutions before the time of school closure caused by the COVID-19 pandemic. For many years, researchers from all around the globe have worked to determine what variables contribute to effective technology integration in the classroom Ciotti et al., Pg 371. The amount of technology usage and the quality of learning when moving from a classroom to a distant or online format are presumed to be influenced by the same set of variables. Findings from previous research, which sought to determine what affects educational systems ability to integrate technology into teaching, suggest understanding how teachers, students, and technology interact positively in order to achieve positive results in the integration of teaching technology (Honey et al., 2000). Teachers’ views on teaching may affect the chances of successfully incorporating technology into the classroom and making it a part of the learning process.
In conclusion, indeed, Covid 19 pandemic have affected the well being of the people in a significant manner. The economy operation across the globe have been destabilized as most of the people have been rendered jobless while the job operation has been stopped. As most of the people have been rendered jobless the living conditions of the people have also been significantly affected. Besides, the education sector has also been affected as most of the learning institutions prefer the use of online learning which is not effective as compared to the traditional method. With the invention of the vaccines, most of the developed countries have been noted to stabilize slowly, while the developing countries have not been able to vaccinate most of its citizens. However, despite the challenge caused by the pandemic, organizations have been able to adapt the new mode of online trading to be promoted.
Ciotti, Marco, et al. “The COVID-19 pandemic.” Critical reviews in clinical laboratory sciences 57.6 (2020): 365-388.
Daniel, John. “Education and the COVID-19 pandemic.” Prospects 49.1 (2020): 91-96.
Fraser, Nicholas, et al. “Preprinting the COVID-19 pandemic.” BioRxiv (2021): 2020-05.
Omer, Saad B., Preeti Malani, and Carlos Del Rio. “The COVID-19 pandemic in the US: a clinical update.” Jama 323.18 (2020): 1767-1768.
Cite this page
Similar essay samples.
- Essay on Mental Health and Homelessness in New York City
- Essay on Critically Analyse Training Methods Used in Your Sport e.g. I...
- Including Culture in Multicultural Education
- The basic theory of correlation and how to calculate it manually.
- How unequal pay (gender pay gap) is linked with deep-rooted disregard ...
- The molecular basis of neurodegenerative disorders: proposing suitable...
Financing Firms in Hibernation during the COVID-19 Pandemic: Article Review Essay
Introduction, recommendations.
The COVID-19 pandemic affected the global economy just as much as the public health domain. However, most economies were able to recover significantly due to efficient policy responses. The article Financing Firms in Hibernation during the COVID-19 Pandemic by Didier, Huneerus, Larrain and Schmukler from 2021 discusses optimal policy choices for business security during the pandemic. The authors introduce the concept of firm hibernation , which refers to minimal spending required to sustain a firm for a period of mass lockdown. This idea is proposed in hopes of saving the relationships with the firms, allowing for a quicker economic rebound once the pandemic is resolved. Along with highlighting the importance of economic relationships, the authors also talk about the government’s function as a lender and last-resort loss absorber. The text poses certain implications regarding the preferable course of policy action during periods of external systemic shock.
Firstly, the unique features of the global pandemic, as opposed to other major economic crises, are covered. Global economic disruptions began in the financial sector before the COVID-19 crisis. Conversely, the coronavirus pandemic was an external system shock that occurred outside the economy. The virus can be distinguished from other disruptive factors by a high degree of uncertainty. The recovery from the initial disturbance in the economic sphere depends entirely on the virus’s elimination. Still, even if the disease is largely eliminated, the time required for the cultural rebound is also unknown. Additionally, there have been significant changes in consumer spending and investment patterns as a result of the COVID-19 crisis. Moreover, the virus’s activity may have long-lasting negative economic effects. All of the above suggests that in order to fight the fallout of the pandemic, policymakers must account for the uncertain nature of the situation and allocate resources with caution.
A potential response to the limitations of policy inaction during the pandemic is firm hibernation. The value of hibernation lies in the fact that it allows businesses to take on as little debt as possible to stay afloat during the pandemic and when the economy recovers and accrued loans need to be serviced. Furthermore, lending monetary resources can prevent long-term economic scarring by saving industry relationships and avoiding the emergence of zombie firms, groups that are out of business with existing outstanding debts.
Business relationships with other companies and customers are invaluable assets for economic sustainability. These connections deteriorate as a result of viable businesses being forced into bankruptcy, making recovery virtually impossible. A brief shock that irreparably damages a large number of relationships can have lasting negative effects on the economy and slow its recovery. The need for the aforementioned hibernation is stark in light of the severity of economic degradation.
In conclusion, the article discusses optimal responses to the COVID-19 economic crisis. Among the topics evaluated are the difficulties of dealing with exogenous health disruptions that affect the financial domain and the appropriate approaches to resource allocation in such instances. Judging by the findings of the authors, one can argue in favor of firm hibernation, a procedure that would sustain a business during reduced operation periods and prevent viable firms from going bankrupt. The efficacy of this approach is yet to be determined; however, the preliminary assessment of the virus’s nature, creditor functions, and relationship value predicts a solid solution to the economic crisis.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2024, May 8). Financing Firms in Hibernation during the COVID-19 Pandemic: Article Review. https://ivypanda.com/essays/financing-firms-in-hibernation-during-the-covid-19-pandemic-article-review/
"Financing Firms in Hibernation during the COVID-19 Pandemic: Article Review." IvyPanda , 8 May 2024, ivypanda.com/essays/financing-firms-in-hibernation-during-the-covid-19-pandemic-article-review/.
IvyPanda . (2024) 'Financing Firms in Hibernation during the COVID-19 Pandemic: Article Review'. 8 May.
IvyPanda . 2024. "Financing Firms in Hibernation during the COVID-19 Pandemic: Article Review." May 8, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/financing-firms-in-hibernation-during-the-covid-19-pandemic-article-review/.
1. IvyPanda . "Financing Firms in Hibernation during the COVID-19 Pandemic: Article Review." May 8, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/financing-firms-in-hibernation-during-the-covid-19-pandemic-article-review/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Financing Firms in Hibernation during the COVID-19 Pandemic: Article Review." May 8, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/financing-firms-in-hibernation-during-the-covid-19-pandemic-article-review/.
- Psychological Problems: Trauma and Lessons
- The Value of In-Person Human Interaction
- Facebook Advantages over MySpace
- The Great Financial Crisis and Its Causes
- Puerto Rico's Government and Economic Challenges
- Industrialization: Regional Science and Urban Economics
- Importing Substituting Industrialization in South Korea
- The City of Los Angeles and the 2008 Crisis
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- My Account Login
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Open access
- Published: 10 May 2024
Happiness amidst the COVID-19 pandemic in Indonesia: exploring gender, residence type, and pandemic severity
- Indera Ratna Irawati Pattinasarany ORCID: orcid.org/0009-0008-1529-2751 1
Humanities and Social Sciences Communications volume 11 , Article number: 609 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
86 Accesses
Metrics details
This study delves into the dynamics shaping happiness levels in Indonesia before and during the COVID-19 pandemic, specifically emphasizing gender and residence-type disparities. Using data from the 2017 and 2021 Happiness Level Measurement Survey, it offers insights into how different population segments were affected. The analysis employs a multilevel mixed-effects ordered logistic model, considering individuals nested within provinces, and measures pandemic severity using positive COVID-19 cases per 100,000 residents. This study evaluates pandemic-related happiness shifts using nationwide cross-sectional survey data from two timeframes. It derives substantial statistical strength from data involving 137,000+ respondents gathered through comprehensive face-to-face interviews. It mitigates recall bias by capturing happiness at two distinct time points, avoiding retrospective measures. The study examines and validates four research questions. First, higher COVID-19 cases in provinces correlate with lower happiness. Second, though women were happier than men, the pandemic reduced this gender-based gap. Third, urban residents were generally happier than rural residents, but the pandemic narrowed this difference. All the estimates exhibit statistical significance at the 1 percent level. Finally, while provincial poverty showed minimal happiness impact, a negative association between unequal per capita expenditure and happiness emerged, providing partial backing for investigating the role of macroeconomic conditions. This study reveals that the COVID-19 pandemic altered happiness dynamics in Indonesia, narrowing gender and residence-based gaps. It also emphasizes the role of socioeconomic factors, particularly unequal per capita expenditure, in influencing individual happiness, highlighting implications for targeted policy interventions.
Similar content being viewed by others
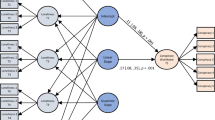
Loneliness trajectories over three decades are associated with conspiracist worldviews in midlife
Determinants of behaviour and their efficacy as targets of behavioural change interventions
Participatory action research
Introduction.
Studying factors influencing our happiness has been a persistent and important topic of investigation over the years. Happiness holds significant implications for our lives, serving not only as a personal aspiration but also as a societal objective (Petrovič et al. 2021 ; Veenhoven 2012 ). Scholars and policymakers have been paying growing attention to subjective well-being (SWB) measures in recent decades. These measures have been sought as alternative ways to gauge economic and social progress, addressing concerns with traditional welfare indicators (Ahmadiani et al. 2022 ; Deaton and Stone 2013 ; Delhey and Kroll 2013 ). Notably, Oishi and Diener’s ( 2014 ) study revealed that self-reported happiness and life satisfaction could effectively reflect objective societal and economic conditions, quantify individuals’ hardships, and evaluate the effectiveness of specific public policies.
The impact of COVID-19 on SWB presents various perspectives. Firstly, a global decline in SWB is evident across studies, including those in China (Yang and Ma, 2020 ), Germany (Bittmann, 2022a ; Möhring et al. 2021 ), and a multi-country study encompassing China, Japan, South Korea, Italy, the United Kingdom, and the United States (Nguyen 2021 ). Secondly, the World Happiness Report (WHR) 2021 indicates a non-significant increase in global life evaluation indicators from 2017–2019 to 2020 (Helliwell et al. 2021 ), similarly reflected in Rajkumar’s ( 2023 ) research across 78 countries. Thirdly, French researchers discovered improved self-reported health and well-being during lockdown compared to previous years (Recchi et al. 2020 ). These diverse outcomes underscore the complex link between the pandemic and individuals’ SWB, arising from individual and household differences, contextual factors, and varying COVID-19 severity across regions.
As the world’s fourth most populous nation, Indonesia has confronted profound repercussions from the pandemic, ranking 20th worldwide in total reported COVID-19 cases and 11th in COVID-19-related fatalities (Worldometer 2023 ). Moreover, the variability in COVID-19 exposure across provinces and the distinction between urban and rural areas within Indonesia is noteworthy. Footnote 1 In light of these circumstances, it becomes essential to undertake an exhaustive study of how the pandemic’s severity has uniquely influenced the happiness of Indonesians.
This study aims to empirically examine the factors influencing shifts in happiness levels before and during the COVID-19 pandemic in Indonesian society. Given the indications from prior research that the pandemic affects women (Dang and Nguyen 2020 ; Fortier 2020 ; Gausman and Langer 2020 ; Giurge et al. 2021 ) and urban dwellers (López-Ruiz et al. 2021 ; Shams and Kadow 2022 ) disproportionately compared to other their respected counterparts, our investigation will primarily focus on comprehending the distinct contributions of gender and residency to the observed changes in happiness levels. By exploring how being male or female and where people live affect changes in happiness during the pandemic, we can better understand the different experiences and difficulties faced by different population segments. Significantly, this study stands as a pioneering effort to investigate the changes in happiness levels stemming from the COVID-19 pandemic among the broader populace of Indonesia.
This study addresses several limitations of existing literature on changes in happiness during the COVID-19 pandemic. Many of these previous investigations have not effectively addressed the following limitations: concentration on specific population segments (e.g., healthcare workers, students), employment of single-point-in-time data collection, dependence on convenience sampling for participant recruitment, administration of online surveys, limited observation durations, and reliance on participants’ retrospective reports of pre-pandemic circumstances.
We overcome these limitations because we use national-level cross-sectional survey data for two different points in time. First, our survey data covers the period before and during the pandemic, enabling us to examine changes in self-reported happiness levels associated with the pandemic’s impact. Using survey data from over 137,000 respondents provides this study with robust statistical power, enhancing the precision of our analysis of happiness level changes over time. Second, our survey data was collected through face-to-face interviews, employing a rigorous sampling method. This approach ensures a more representative sample distribution, avoiding biases from self-selection in online surveys (Andrade 2020 ).
Third, our study evaluates happiness at multiple time points. This method acts as a temporal anchor, assisting respondents in recalling and distinguishing their experiences more accurately. Given that respondents often generalize or simplify their experiences when recalling over an extended timeframe, evaluating happiness at different times enables a comprehensive capture of fluctuations and variations in individuals’ emotional states. In this study, assessing happiness at two distinct time points, before and during the COVID-19 pandemic, guarantees a more accurate portrayal of an individual’s SWB and alleviates recall bias (Hyman 2013 ; Tadic et al. 2014 ).
This study consists of six sections. In Section 2, we offer a summary of pertinent prior studies, followed by an investigation into the research questions posed in this study. Section 3 explains the methodologies and models used and outlines the data sources. Section 4 examines and analyzes the outcomes from the estimations, while Section 5 discusses the results. Finally, Section 6 summarizes the findings and offers policy recommendations based on the results.
Literature review and research questions
Theoretical background.
The reactivity theory , embraced by social scientists, including economists and sociologists, asserts that SWB, particularly happiness, is influenced by objective external conditions at both the individual and social levels (Lee 2022 ). These objective conditions encompass various factors such as income, age, gender, marital status, occupation, family structure, geographic region, and government policies (Diener 1984 ). According to the reactivity theory, individuals’ perceptions and assessments of their happiness primarily stem from their passive responses to these objective conditions. In simpler terms, individuals tend to react to the circumstances and external factors surrounding them, significantly impacting their SWB. Within the framework of our study, positive events like economic improvements or technological advancements consistently raise happiness levels. In contrast, adverse events such as natural disasters (Calvo et al. 2015 ; Rehdanz et al. 2015 ; Sekulova and van den Bergh 2016 ) or the COVID-19 pandemic tend to decrease happiness.
The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on happiness in Indonesia
Before the pandemic, numerous studies in Indonesia explored factors influencing happiness across various scopes. These studies encompassed general population happiness levels (Aryogi and Wulansari 2016 ; Landiyanto et al. 2011 ; Sohn 2013 ; Sujarwoto et al. 2017 ) and specific demographic segments (Anna et al. 2019 on fishermen; Sollis et al. 2023 on native-immigrant). Regional studies (Firmansyah et al. 2017 ; Nandini and Afiatno 2020 ) shed light on context-specific happiness factors. Specific topics like religiosity (Kurniawati and Pierewan 2020 ), height (Sohn 2014 ), decentralization (Sujarwoto and Tampubolon 2015 ), and income inequality (Furwanti et al. 2021 ) were examined, providing valuable insights. Furthermore, Pattinasarany ( 2018 ) conducted a cross-national analysis exploring happiness and life satisfaction determinants in Indonesia, Thailand, Japan, and South Korea.
In both pre-pandemic and pandemic contexts in Indonesia, the World Happiness Report (WHR) and the Happiness Index are commonly used measures of happiness. Footnote 2 However, these two references provide contradictory information regarding the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the happiness levels of individuals in Indonesia. The WHR indicates a decrease in the happiness level of Indonesian people from 5.345 from 2018 to 2020 to 5.240 from 2019 to 2021 (Helliwell et al. 2020 ; 2021 ; 2022 ). In contrast, the Happiness Index shows an increase from 70.69 in 2017 to 71.49 in 2021 (Badan Pusat Statistik 2021a ).
Multiple studies have explored the effects of the pandemic on SWB in Indonesia. Tjahjana et al. ( 2021 ) conducted an online survey a month after the pandemic, indicating that 41% of respondents reported decreased happiness. Rahmanita et al. ( 2021 ) collected data 1–3 months post-pandemic, revealing that 59% of respondents expressed happiness in staying at home. Iskandarsyah et al. ( 2022 ) explored the effects of COVID-19 information and behaviors on anxiety and happiness a month post-outbreak, noting increased information searches linked to higher anxiety but more testing and treatment information tied to less anxiety and greater happiness. Dwidienawati et al. ( 2021 ) found ongoing pandemic adaptation challenges, with no improvement in happiness or life satisfaction reported after a year. Halimatussadiah et al. ( 2021 ) conducted two cross-sectional online surveys in 2020 and 2021, revealing a trend towards heightened happiness. In a separate study, Borualogo and Casas ( 2022 ) collected data during the same period, discovering higher SWB and positive affect among boys during the pandemic and improved satisfaction in friend interactions.
The following are overviews of studies using general population survey data to understand the pandemic’s impact on SWB in Indonesia’s neighboring countries. Tambyah et al. ( 2023 ) found a significant decrease in life satisfaction among Singaporeans, dropping from 4.51 in 2016 to 4.18 in 2022 on a scale of 1–6. The study highlighted health risks and job security as primary concerns during the COVID-19 pandemic. Phulkerd et al. ( 2023 ) reported that Thai adults had an average life satisfaction score of 22.4 during the 2021 COVID-19 epidemic, down from 25.5 before the pandemic in 2019 on a 5–35-point scale.
Research questions
This study investigates four specific research questions (RQs) to elucidate and support the study objectives within the broader context of the Indonesian population. Limited research has explored the impact of COVID-19 severity on self-reported happiness at subnational levels due to a lack of reliable data. However, some exception studies exist (Bittmann 2022a ; Le and Nguyen 2021 ). In Indonesia, the impact of the pandemic varies across provinces and districts, each of which implemented unique policies to curb the spread of the pandemic and cope with its consequences (Arifin et al. 2022 ). This study examines a connection between the severity of COVID-19 and self-reported happiness, anticipating that increased severity will correspond to decreased reported happiness.
RQ1: To what extent does the severity of COVID-19 contribute to a reduction in individuals’ happiness levels?
Global research suggests women typically report higher life evaluations than men (Blanchflower and Bryson 2022 ; Blanchflower and Oswald 2011 ; Fortin et al. 2015 ). However, women worldwide bear a disproportionate burden of socio-economic challenges during crises like natural disasters, economic downturns, and pandemics. Such inequity stems from gender roles and undervaluation of women’s work, leading to increased caregiving responsibilities and exposing women to short-term economic instability and long-term welfare declines (Dinella et al. 2023 ; Fortier 2020 ; Langer et al. 2015 ). This study investigates whether the severity of COVID-19 has narrowed the gap in self-reported happiness between women and men.
RQ2: To what extent does the severity of the COVID-19 pandemic lessen women’s happiness advantage over men?
International evidence indicates that, at low levels of economic development, substantial gaps favor urban over rural areas in income, education, and occupational structure, resulting in higher SWB for urban residents than for rural residents. Such higher life satisfaction holds despite urban challenges like pollution and congestion. However, these economic disparities diminish as development progresses, enabling rural areas to close the gap and even surpass urban life satisfaction (Burger et al. 2020 ; Easterlin et al. 2011 ). In Indonesia, Sohn ( 2013 ) identified a positive association between living in urban areas and happiness. Additionally, Sujarwoto ( 2021 ) observed that individuals residing in rural settings expressed lower life satisfaction than their urban counterparts. Given the COVID-19 pandemic’s disproportionate impact on urban areas compared to rural regions, an intriguing query arises: How did the severity of the pandemic influence the link between urban living and self-reported happiness?
RQ3: To what extent does the severity of the COVID-19 pandemic diminish the happiness advantage of urban residents compared to rural residents?
Incorporating contextual variables in measuring self-reported happiness in a multilevel framework is crucial for more accurate analyses and informed policymaking (Ballas and Tranmer 2012 ; Gómez-Balcácer et al. 2023 ). Analytically, incorporating contextual variables like macroeconomic and socio-economic conditions enhances research depth and accuracy. From a policy standpoint, this approach provides a robust foundation for informed decision-making, resulting in more effective and targeted policies. This study utilizes three provincial-level contextual variables: COVID-19 severity (as discussed in RQ1), poverty incidence, and income inequality.
RQ4: To what extent do provincial macroeconomic conditions, specifically poverty and income inequality, impact individuals’ happiness levels?
These research questions delve into diverse facets of the pandemic’s influence on happiness levels within Indonesian society. They examine consequences such as health risks, economic disruptions, and social isolation (RQ1). Furthermore, they investigate the role of societal norms, gender roles, and structural inequalities in women’s experiences during the pandemic (RQ2) and assess potential challenges in urban areas (RQ3). Finally, the study evaluates the impact of macroeconomic factors, specifically poverty and income disparities, on happiness levels during the pandemic (RQ4).
Materials and methods
Multilevel mixed-effects ordered logistic model.
In this study, we estimate a multilevel mixed-effects ordered logistic model that incorporates nesting while considering the dependent variables’ categorical nature and providing adjusted standard errors that add precision to the coefficients (Rabe-Hesketh and Skrondal 2022 ). By using multilevel models, we can control for individual and province variables, isolating the impact of pandemic severity on self-reported happiness levels (Mehmetoglu and Jakobsen 2017 ; Snijders and Bosker 2012 ). Observations in our study comprise individuals (level 1) nested within provinces (level 2). Our multilevel regressions are computed with random intercepts for each province to account for the fact that provinces are affected differently by the pandemic and that respondents in one province might be more similar than respondents in another. Finally, we used an ordered logistic model due to the ordered nature of the dependent variable.
We postulate a latent variable (y*) representing an individual’s underlying happiness. In this study, we will estimate two models: the ‘main’ (hereafter: Main Model) and the ‘with interaction terms’ (hereafter: Interaction Model) models. The Main Model’s latent variable is associated with individual traits, household attributes, and provincial-level contextual variables. Individual traits encompass gender, age along with its squared term, marital status, highest education level attained, and employment status. Household-level attributes include residence type and household income. Three contextual variables at the provincial level consist of the poverty rate, income inequality, and the count of COVID-19-infected individuals per 100,000 population, reflecting COVID-19 severity. In contrast, the Interaction Model encompasses the Main Model and incorporates additional interaction variables between gender and residence-type covariates with the severity of the pandemic measure. Footnote 3 We assume that individuals residing in provinces hardest hit by the pandemic will experience a more significant decline in happiness than those in the less affected provinces.
The Main Model is specified as follows:
while the Interaction Model is specified as follows:
where: \({y}_{{ij}}^{* }\) is the unobserved happiness for individual i who resides in province j (latent variable); \({x1}_{{ij}}\) is the individual and household characteristics for individual i living in province j; \({x2}_{j}\) is the provincial contextual variables for province j; \({{COVID}}_{j}\) is the COVID-19 pandemic severity measure for province j; \({{x3}_{{ij}}* {COVID}}_{j}\) is the interaction terms of gender and type of residence covariates with COVID-19 severity measure; this study assesses three specifications incorporating interaction terms: one specific to women, another specific to urban settings, and a third encompassing both women and urban factors; \({z}_{{ij}}\) is the covariates corresponding to the random effects; as this model follows a random-intercept model, \({z}_{{ij}}\) is simply the scalar 1; \({u}_{j}\) is the random effects; and \({\epsilon }_{{ij}}\) is the errors, distributed as logistic with mean 0 and variance π 2 /3 and are independent of \({u}_{j}\) .
This model, \({x1}_{{ij}}\) and \({x2}_{j}\) do not contain a constant term because its effect is absorbed into the cutpoints (κ).
Table 1 illustrates the estimation strategies employed in this study, encompassing three distinct approaches presented in 12 specifications. First, the Main Model uses all observations to illustrate the relationship between happiness levels and each covariate. Second, the Interaction Model examines how COVID-19 severity affects the connection between being female, living in urban areas, and happiness levels. The second approach investigates moderation effects. Lastly, the third approach delves into the factors impacting happiness across specific subgroups based on gender, residence type, and region. This granular analysis offers insights into potential differences or similarities in the determinants of happiness among these subgroups, aiming to unravel complex relationships among predictors in understanding SWB across diverse contexts.
Model estimation is performed using the meologit procedure in Stata 17.0 (StataCorp 2021 ). The meologit procedure estimates ordered logistic regression containing both fixed effects (in this study: \({x1}_{{ij}}\) and \({x2}_{j}\) along with their interaction terms) and random effects ( \({u}_{j}\) ).
The Happiness Level Measurement Survey (SPTK)
This study relies on the Happiness Level Measurement Survey (SPTK) from 2017 and 2021, administered by the Central Statistics Agency of Indonesia (Badan Pusat Statistik; BPS) (Badan Pusat Statistik 2017 ; 2021a ). Footnote 4 The 2021 wave of SPTK fieldwork took place from July 1 to August 27, 2021, during Indonesia’s peak of the COVID-19 pandemic. The data relating to COVID-19 exposure, i.e., total positive cases of COVID-19, was taken from KawalCOVID19, who collected data primarily from the Ministry of Health. The macroeconomic data on poverty levels and inequality of per capita expenditures (Gini coefficient) are all sourced from the BPS.
SPTK extends across every province and district in Indonesia, where districts consist of kabupaten (regencies) and kota (municipalities). Within each district, the BPS has established a master sampling frame comprising Census Blocks (BS) for the periodic implementation of various surveys. A BS constitutes a designated enumeration zone within a village locality consisting of 80 to 120 residential, non-residential, or household census buildings with distinct boundaries identifiable in the field. BS selection for SPTK is selected probabilistically from the master sampling frame. Household updating takes place at each selected BS, with the selection of household respondents based on updated listings that are stratified according to factors such as the household head’s education and the household’s structure.
The data collection involves conducting direct interviews with respondents utilizing structured questionnaires and computer-assisted personal interviewing applications. Footnote 5 The unit of analysis is a randomly selected household. In each sampled household, the head of the household or the spouse of the head of the household (wife/husband) is selected as the respondent to represent the household. This study focuses on 137,958 respondents aged 25–80 years who are working or spend most of their time taking care of the household. Footnote 6 Apart from the level of happiness, SPTK contributed data at the individual and household levels.
Level of happiness
The level of happiness is evaluated using the so-called Cantril ladder (Cantril 1965 ; Levin and Currie 2014 ). The SPTK employs a ladder diagram to measure happiness, prompting respondents to visualize themselves on a scale with steps numbered from zero at the bottom to ten at the top. Respondents are asked to evaluate their happiness using the question, “How happy are you with life as a whole?” The answer ranges from 0 (very unhappy) to 10 (very happy).
Figure 1 shows that the distributions of happiness are skewed to the left. Most respondents evaluate their happiness on the eighth rung (34.1 percent in 2017 and 35.6 percent in 2022). The national average was calculated at 7.78 in 2017, while for 2021, it will be slightly lower at 7.76.
Source: Calculated from SPTK.
For a comparative analysis of self-reported happiness in this study with neighboring nations, Pattinasarany ( 2018 ) investigated happiness and life satisfaction in Indonesia, Thailand, Japan, and South Korea to compare self-reported happiness with neighboring nations. The study used collected data to explore lifestyles and values related to social well-being in seven Asian countries, including the Philippines, Taiwan, and Vietnam. Results revealed similar happiness distribution, with Indonesia and Thailand displaying a left-skewed pattern, indicating majority contentment. Indonesian adults reported slightly higher average happiness (7.68) than their Thai counterparts (7.65). In Japan (6.25) and Korea (5.93), happiness levels exhibited a more normal distribution, with averages not reaching the same highs as observed in Indonesia and Thailand.
Analyzing happiness at the provincial level indicates that Gorontalo and North Maluku reported the highest average levels in 2017 (8.43) and 2021 (8.54), respectively (Fig. 2 ). In contrast, the lowest averages were recorded in East Nusa Tenggara in 2017 (7.32) and Bali in 2021 (7.26). While the national average in 2017 and 2021 remains relatively unchanged, significant differences emerge at the provincial level between the two years. Providing context, half of the 34 provinces saw an increase in their average happiness levels from 2017 to 2021, while the remaining provinces experienced a decline. Central Sulawesi notably showed the most substantial surge, with an increase of 0.347 points, while Bengkulu province witnessed the most significant decrease, dropping by 0.387 points. Recognizing the nested nature of individuals within provinces, the variance in average happiness levels between years at the provincial level becomes a crucial consideration.
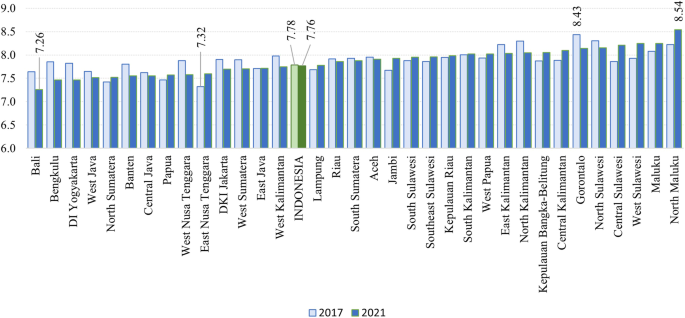
In our examination of gender and residence type on changes in SWB during the pandemic, Fig. 3 illustrates average happiness levels categorized by gender and residence type. The left panel reveals that, on average, women reported higher happiness levels than men. However, there was a slight increase in men’s average happiness during the pandemic (+0.03 points), while women experienced a decrease (−0.06 points). In the right panel, it is evident that individuals residing in urban areas typically demonstrated higher average happiness levels than those in rural settings. Interestingly, individuals in rural areas reported higher happiness levels in 2021 compared to 2017 (+0.08 points). In contrast, those living in urban areas displayed the opposite trend, experiencing a decline in happiness levels over the same period (−0.15 points).
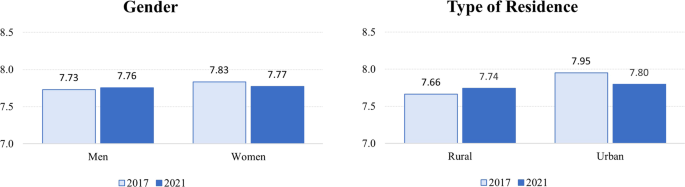
Given the limited number of respondents rating their happiness level between zero and five, these five responses were aggregated to achieve a more balanced distribution. Furthermore, data recoding follows the ordered logistic method, requiring each cell to include at least three percent of observations.
Total COVID-19 cases per 100,000 population
In this study, the evaluation of the severity of the COVID-19 pandemic relies on the total population with confirmed exposure to COVID-19. Although daily data has been available since March 2, 2020, the SPTK data lacks specific interview date information. A cut-off point, set on June 30, 2021, was established to determine COVID-19 severity for all survey respondents, conveniently aligning with the day preceding the start of SPTK face-to-face interviews. We used a normalization process to enable meaningful province-to-province comparisons, specifically normalizing the data per 100,000 population.
Figure 4 illustrates the unequal distribution of confirmed COVID-19 cases among provinces. DKI Jakarta records the highest incidence of COVID-19 cases, reaching 5210 per 100,000 population. Conversely, North Sumatera reports the lowest number of cases, only 246 per 100,000 population. These findings underscore the diverse impact and transmission rates of COVID-19 observed across different provinces.
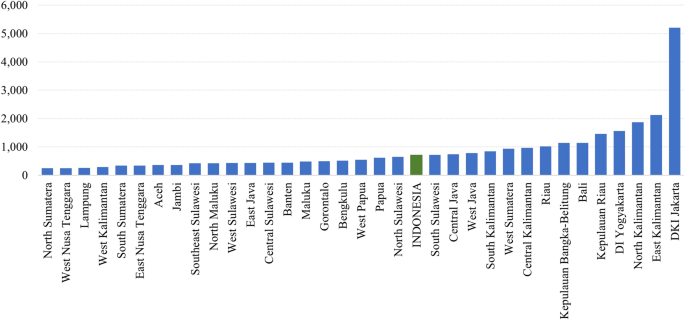
Source: Calculated from KawalCOVID-19.
Concluding the data discussion, Table 2 displays the mean and standard deviation of all variables used in this study, categorized by year.
Estimation results
Table 3 displays happiness level estimates from a multilevel mixed-effects ordered logistic analysis covering the Main and Interaction Models. The Main Model serves as the baseline, while the Interaction Model estimates examine potential changes in gender and type of residence covariates influenced by the COVID-19 pandemic.
We begin by discussing the results of the Null Model, which incorporates no predictors (Table 3 , column [1]). The Intraclass Correlation Coefficient (ICC) for the Null Model is 0.038 (second row from the bottom), indicating that approximately 3.8 percent of the variability in an underlying response is associated with differences between provinces. Footnote 7 Sommet and Morselli ( 2017 ) noted that many authors argue that an ICC below 5 percent, considered insignificant and negligible, leads them to treat the individual as a single unit of analysis, hence opting for a single-level analysis. Nevertheless, we persist with multilevel modeling, recognizing that the minimal ICC (except when zero) does not signify the absence of variation in respondents’ happiness levels between provinces. Moreover, disregarding this variation can lead to inaccurate estimates and potentially result in inappropriate policy decisions. The ICCs for the Main and Interaction Models are modest, ranging between 0.037 and 0.041.
The Likelihood Ratio (LR) test, located in the third row from the bottom, compares the multilevel mixed-effects ordered logistic model with the standard (single-level) ordered logistic model, favoring the former. A p-value of 0.000 for the LR test signifies significant variation in self-reported happiness levels between provinces. The “Variances: Province (constant)” estimates in the fourth row from the bottom indicate the variation in self-reported happiness levels attributed to differences between provinces after accounting for fixed effects and other covariates in the model. This information clarifies how the province-level factor (in our case, poverty rates, Gini coefficient of per capita expenditures, and severity of the pandemic measure) contributes to the overall variability in the outcome. A higher estimated variance suggests a more significant variation in the outcome between provinces.
The severity of the COVID-19 pandemic
The estimation results indicate that individuals in provinces with more COVID-19 cases per 100,000 population tended to assign lower ratings to their happiness (Table 3 , column [2]). Footnote 8 Our findings align with international research. A study across China, Japan, South Korea, Italy, the United Kingdom, and the United States found that individuals in areas with elevated COVID-19 rates are more likely to report lower happiness levels (Nguyen 2021 ). Similarly, a German study using panel data during the initial COVID-19 wave observed a decline in life satisfaction in regions with higher infection rates (Bittmann 2022a ).
Concerns about the robustness of conclusions drawn from estimations using the entire dataset when examining specific characteristics are typical. Table 4 provides Main Model estimates disaggregated by gender (assessing whether estimation results differ for male or female respondents), type of residence (rural versus urban), and major regions in Indonesia (Sumatera, Java-Bali, and Other regions). Table 5 facilitates a comparison of the three primary correlates: gender (women), residence type (urban), and the severity of the COVID-19 pandemic.
These findings indicate that the detrimental impact of the pandemic’s severity on happiness levels is observable for both men and women, as well as for residents in rural areas and the Java-Bali and Other regions of Indonesia. However, the absence of statistical significance for urban residents may be attributed to the predominant concentration of the COVID-19 pandemic in urban areas of Indonesia. Similarly, the lack of statistical significance for the Sumatera region is associated with the lower pandemic severity observed in that region. Despite variations across different samples, these consistent findings underscore the negative association between the severity of the COVID-19 pandemic and individuals’ happiness levels.
In Indonesia, on average, women reported higher happiness levels than men (Table 3 , column [2]). Upon analyzing a disaggregated sample by residence type, the results indicate that women exhibit higher happiness levels than men in both rural and urban areas (Table 4 , columns [8] and [9]). Moreover, women consistently report higher happiness levels than men across all three regions (Sumatera, Java, and others) (Table 4 , columns [10], [11], and [12]).
A noteworthy observation is the degree to which women in the Java-Bali region experience a smaller happiness advantage over men compared to their counterparts in Sumatera and other regions. One potential explanation is the Java-Bali region’s reputation for embracing a more egalitarian gender culture than other parts of Indonesia, suggesting that gender-based disparities in happiness might be comparatively smaller in the Java-Bali region than in other regions (Hayati et al. 2014 ; Utomo 2012 ). Moreover, the Java-Bali region’s higher level of development compared to other parts of Indonesia contributes to enhanced gender equality across various facets, including well-being and happiness.
The Interaction Model estimates reveal that in 2021, the severity of the pandemic led to a decline in women’s happiness relative to men’s (Table 3 , columns [3] and [5]). These results indicate that the pandemic’s effect diminishes the relative advantage of being female in terms of happiness levels. Our findings align with several studies (Blanchflower and Bryson 2022 ; Nguyen 2021 ), all reporting a decrease in women’s life satisfaction and happiness compared to men during the pandemic.
Type of residence
Individuals residing in urban areas generally experience higher levels of happiness than their rural counterparts (Table 3 , column [2]). Easterlin et al. ( 2011 ) provided a comprehensive explanation for such findings, highlighting that the availability of material goods like food, clothing, and shelter in urban areas contributes to higher happiness. However, they also caution that urban life comes with challenges, including traffic congestion, pollution, and feelings of alienation, which can negatively impact happiness.
The difference in happiness levels between urban and rural residents remains consistent across diverse demographics (Table 4 , columns [6], [7], [10], [11], and [12]). Particularly noteworthy is the narrower happiness gap between urban and rural residents in the Java-Bali region (Table 4 , column [11]), indicating that rural areas in Java-Bali may benefit from enhanced public services and infrastructure compared to other regions. This improved availability of resources in rural Java-Bali contributes to a more equitable distribution of opportunities and resources between urban and rural residents.
Nevertheless, as per the Interaction Model, the pandemic’s severity has weakened the traditional happiness advantage of individuals in urban areas compared to their rural counterparts (Table 2 , columns [4] and [5]). Our observation finds backing in urban Pakistan, where Shams and Kadow (2020) documented a decrease in socio-economic satisfaction amid the pandemic, particularly noticeable among unemployed individuals, married couples, men, and older demographics.
Contextual characteristics
The association between poverty levels and happiness lacked statistical significance, suggesting that the poverty rates in a respondent’s province do not influence their happiness. One possible explanation is the substantial variation in poverty rates among districts within a province. For example, in 2021, East Java Province exhibited a poverty rate of 11.4 percent, yet the rates across its 38 kabupaten / kota ranged from 4.1 to 23.8 percent (Badan Pusat Statistik 2021b ). Nevertheless, a deviation from the typical trend is evident in the Java-Bali region, exposing a negative correlation between higher poverty levels and happiness among respondents (Table 4 , column [11]). This finding aligns with the higher poverty population in the Java-Bali region compared other regions in Indonesia (Badan Pusat Statistik 2021b ).
Muthia and Isbah’s ( 2022 ) study sheds light on the lack of a correlation between poverty and happiness, particularly within the impoverished community of DI Yogyakarta Province, Indonesia. The authors argue that impoverished individuals may not find happiness in their economic situation but discover contentment. This occurrence is ascribed to the prevailing belief system and local culture, heavily influenced by the nerimo attitude, emphasizing the acceptance of one’s circumstances. By adopting this mindset, impoverished individuals improve their psychological well-being, regardless of their difficulties.
Regarding inequality, the estimation results reveal an inverse connection between per capita expenditure inequality at the provincial level and self-reported happiness levels. In another study, Furwanti et al. ( 2021 ) utilized cross-sectional data from all Indonesian provinces and a path analysis model, revealing that income inequality significantly and negatively influences happiness in Indonesia.
The findings of this study align with several international reviews exploring the relationship between inequality and happiness. For instance, a review by Ferrer-i-Carbonell and Ramos ( 2014 ) demonstrates a negative correlation between income inequality and happiness in Western countries. However, the connection in non-Western countries is diverse and less conclusive. In addition, Schroder ( 2018 ) discovered that individuals perceive their SWB as lower when inequality within their own country increases over time, but not when it is higher compared to another country.
Individual characteristics
Following is a concise discussion of individual characteristics that fall outside the scope of the four research questions outlined in this study.
Our model incorporates respondents’ age in quadratic terms, revealing a U-shaped pattern in happiness assessment (Easterlin 2004 ; Blanchflower 2021 ; Bittmann 2022b ; Toshkov 2022 ). Generally, happiness levels decline with age until reaching a certain point, after which they begin to rise. In the Main Model, this turning point is identified at 49. The U-shaped pattern corresponds to the “midlife dip” phenomenon, wherein individuals often undergo a decline in happiness during midlife before it subsequently increases later in life, as discussed by Blanchflower and Graham ( 2020 ). Factors such as heightened responsibilities, financial pressures, and changes in personal and professional circumstances can influence this midlife dip.
Individuals in a marital union tend to experience higher happiness levels than unmarried or divorced individuals. This observation is supported by Frey’s ( 2018 ) comprehensive review, affirming that married individuals generally express higher happiness levels than those living alone or in unmarried partnerships. The author highlights the role of marriage or a stable partnership in mitigating loneliness, thereby assisting in alleviating stress related to work life. Various studies (Addai et al. 2014 ; Tambyah et al. 2023 ; Wu and Zhu 2016 ) have also identified the positive influence of being in a marital relationship.
A positive correlation is evident between education and happiness. This finding indicates that higher educational attainment aligns with higher self-reported happiness levels. As noted by Frey ( 2018 ), individuals with advanced education tend to enhance their abilities and gain increased access to opportunities, resulting in heightened life satisfaction. The association between education and happiness has been thoroughly examined, including within Indonesia (Landiyanto et al. 2011 ; Sujarwoto and Tampubolon 2015 ; Rahayu 2016 ). These investigations consistently affirm a positive association between education and happiness within the Indonesian context.
In general, employed respondents report lower happiness levels, although differences exist between men and women. Among male respondents, those actively engaged in work display higher happiness levels than those who are not. This positive correlation between working and happiness among men corresponds with findings from various international studies (Clark and Oswald 1994 ; Di Tella et al. 2001 ; Winkelmann and Winkelmann 1998 ). Conversely, employed individuals report lower happiness within the female sample than those unemployed. To the extent that the SPTK dataset defines those not employed as spending most of their time taking care of the household, the negative association between employment and happiness among women can be interpreted as women who are employed facing a double burden of responsibilities at work and home (Chen et al. 2018 ).
Individuals reporting higher household earnings exhibit higher happiness levels. However, the ongoing debate on whether income contributes to increased happiness encompasses diverse viewpoints. Some studies advocate for a positive correlation between income and self-reported happiness and, therefore, in line with our findings (Diener and Biswas-Diener 2002 ; Frey and Stutzer 2002 ; Lim et al. 2020 ; Yiengprugsawan et al. 2011 ; Yu et al. 2019 ). Conversely, other studies propose that the impact of income on happiness becomes negligible once a certain income threshold is reached (Kahneman and Deaton 2010 ; Muresan et al. 2020 ).
Discussions
Our analysis reveals a significant decline in self-reported happiness among Indonesians due to the severity of the COVID-19 pandemic, addressing RQ1. The pandemic severity measure has eroded the longstanding happiness advantage for women and urban residents, addressing RQ2 and RQ3. A concerning negative correlation between income inequality and happiness is evident, addressing RQ4. These findings emphasize the urgent need for targeted interventions to mitigate these effects on the Indonesian populace’s well-being.
COVID-19 severity reduces happiness
The decrease in self-reported happiness among Indonesians amid the severity of the COVID-19 pandemic arises from various factors. First, increased vulnerability to COVID-19 elevates health apprehensions and anxiety, giving rise to concerns about the risk of infection for both oneself and loved ones. Consequently, this anxiety diminishes overall well-being (Cleofas and Oducado 2022 ; Demirbas and Kutlu 2021 ; van der Vegt and Kleinberg 2020 ). Second, provinces with higher COVID-19 cases face significant economic disruptions, including business closures, job losses, and reduced economic activity, resulting in financial stress, insecurity, and an overall happiness decline (Cheng et al. 2020 ; Greyling et al. 2021 ; Kuhn et al. 2020 ). Third, residents in heavily affected provinces may encounter challenges such as limited social support networks, reduced opportunities for social engagement, and feelings of loneliness or disconnection, significantly impacting their happiness levels (Lepinteur et al. 2022 ; Nguyen 2021 ). Lastly, the increased prevalence of anxiety, depression, or emotional distress among individuals in provinces with higher COVID-19 exposure further contributes to lower self-reported happiness levels (Iskandarsyah et al. 2022 ).
This study underscores the assessment of the COVID-19 pandemic’s impact on individuals’ happiness, specifically through a severity measure focusing on the number of affected individuals per 100,000 population. This choice differs from using time dummy variables, assigning 1 for 2021 survey data (during the pandemic) and 0 for 2017 survey data (pre-pandemic). The severity measure directly reflects the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the population, offering a tangible and quantifiable indicator of its scale within a region. This approach is especially appropriate given the considerable variation in pandemic severity across provinces in Indonesia. Nevertheless, we recognize that relying solely on the severity measure may oversimplify the complex dynamics of the pandemic’s impact. Furthermore, Bittmann, ( 2022a ) explores the functional relationship between the severity measure and self-reported happiness, considering alternatives such as linearity (as employed in this paper), quadratic, and others. This exploration opens up possibilities for future studies.
COVID-19 severity moderates gender-residence type association with happiness
The negative and statistically significant interaction terms between COVID-19 severity and gender (being female) indicate that the pandemic’s severity affects the relationship between gender and self-reported happiness. In periods of intensified pandemic severity, the conventional gender gap in happiness, where women usually report higher levels, is disturbed. The negative moderation implies that the pandemic has a more detrimental impact on women’s happiness levels than men.
Research conducted by Alon et al. ( 2020 ), Blanchflower and Bryson ( 2022 ), and Hansen et al. ( 2022 ) underscore that the decline in happiness levels among women can be attributed to heightened caregiving responsibilities, especially as primary caregivers for children. Transitioning to remote learning for children has introduced additional challenges and demands for women. Additionally, as frontline workers, women face elevated stress levels in their roles and are vulnerable to potential job layoffs and disruptions in their participation in the labor market. Conversely, a study by Choi et al. ( 2021 ) concluded that even before the onset of COVID-19, Korean women demonstrated lower levels of SWB compared to men. Therefore, the well-being disparities observed among Korean women are more likely rooted in pre-pandemic variations rather than directly caused by the effects of the pandemic.
Similarly, the adverse and statistically significant interaction terms between COVID-19 severity and residence type (urban) indicate that the severity of the pandemic influences the connection between living in urban areas and self-reported happiness. During periods of heightened pandemic severity, the typical gap in happiness based on residence type, where individuals in urban areas usually report higher levels, ceased to hold. This adverse moderation implies that the pandemic has a more harmful effect on the happiness levels of individuals in urban residences than those in rural areas.
Mayuzumi’s ( 2022 ) research provides valuable insights into the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on the happiness of urban and rural communities in Bali, Indonesia. The results indicate that individuals in subsistence farming villages, heavily dependent on agriculture, witnessed minimal changes in their livelihoods, suggesting little impact from the pandemic. In contrast, urban residents, primarily reliant on tourism, experienced significant job losses and food accessibility challenges due to government curfews and economic stagnation. On the contrary, Nguyen ( 2021 ) introduces an alternative perspective by proposing that the pandemic has a more noticeable impact on the unhappiness levels of individuals residing in rural areas than those living in urban settings.
Inequality is a catalyst for diminishing happiness
Examining contextual characteristics unveils that, excluding the Java-Bali region, provincial poverty levels have negligible effects on happiness levels. Nonetheless, there is a discernible negative correlation between inequality in per capita expenditure and happiness.
An important observation from the analysis using region-specific breakdowns is the unexpected positive association between the Gini coefficient and happiness in the Sumatera region. The uniqueness of this result in Sumatera may be ascribed to distinct factors inherent to the region, such as particular social structures, values, or expectations. These regional peculiarities in Sumatra could influence individuals’ perspectives on happiness differently than in other locales. A more thorough investigation into the specific factors contributing to these anomalies across regions is necessary to grasp the patterns observed fully.
Study limitations
The research employed a single-question methodology using a 0–10 point Likert scale to assess individual happiness. Although this approach offers a valuable metric, we acknowledged that happiness is a complex concept with multiple dimensions that a single question may need to be more comprehensive. Consequently, the study recognizes the importance of incorporating additional aspects and nuances to understand better individuals’ well-being, including factors like self-evaluated life satisfaction, positive affect, and negative affect.
Moreover, it is essential to consider two significant data constraints when interpreting the findings. First, the SPTK datasets utilized in the study lack precise location information, restricting the analysis to the provincial level and hindering a more detailed examination of the impact of COVID-19 on specific regions or communities within a province. For instance, while information on the poverty rate is accessible at the district level, the unavailability of district codes necessitates using provincial poverty rates.
Second, the datasets do not incorporate information about the interview dates for respondents, which would have facilitated a more precise correlation with the daily severity rate of COVID-19 at the provincial level. Access to interview date information could have offered valuable insights into the temporal relationship between individuals’ experiences and the evolving severity of the pandemic in their respective provinces.
The global repercussions of COVID-19 on individuals’ lives and well-being are profound. In Indonesia, there is a pressing need for more research on the correlation between happiness and pandemic severity across the population. This study addresses this gap by examining the factors influencing happiness levels before and during the pandemic, specifically focusing on gender and residence type. By posing and answering four research questions (RQs), the study provides valuable insights into the intricate dynamics of happiness during the pandemic in Indonesia.
This study employed data from the 2017 and 2021 Happiness Level Measurement Survey (SPTK) to represent pre-pandemic and during-pandemic conditions, respectively. The data analysis involved using a multilevel mixed-effects ordered logistic model, with individuals nested within provinces as the analytical framework. The severity of the pandemic was proxied using the incidence of positive COVID-19 cases per 100,000 residents.
Our analysis underscores a statistically significant decline in self-reported happiness levels among Indonesians attributable to the severity of the COVID-19 pandemic, directly addressing RQ1. Notably, this severity measure has diminished the longstanding happiness advantage previously experienced by women and urban residents, aligning with the inquiries of RQ2 and RQ3. Additionally, our study highlights a negative correlation between income inequality and happiness, illuminating the intricate interplay of socioeconomic dynamics influencing individual well-being as per RQ4. The robust support for our research questions highlights the multifaceted impact of the pandemic on happiness levels in Indonesia.
Immediate policy interventions are required to tackle these findings, encompassing targeted mental health support to aid individuals in overcoming the challenges of lockdown restrictions and the loss of loved ones; economic assistance to support families facing sudden job loss and economic downturn; reinforced public health initiatives to curb the spread of the virus and mitigate the health impact of the pandemic; educational campaigns to inform the public about necessary health protocols; and community-based social support programs to lighten the overall burden faced by communities in dealing with the pandemic. These measures aim to alleviate the negative impact of the pandemic and socioeconomic disparities on the happiness and overall welfare of the Indonesian population.
In light of the adverse effects of COVID-19 on the happiness of women and urban residents, it is important to implement proactive government programs and policies. To address women’s heightened responsibilities, especially in home-based teaching, effective communication, and support between teachers and students, such as regular home visits, are essential. Providing physical visits and care for vulnerable populations, including the elderly, chronically ill, and disabled individuals, can help alleviate some of the burdens on women. Additionally, supporting urban residents involves reinforcing community associations, particularly within neighborhood and religious networks, through collaborative efforts between the Central Government and local administrations.
The future research agenda aims to enhance the comprehensiveness of this study by incorporating field visits that include in-depth interviews and focus group discussions. Validating the findings, gaining deeper insights into individual experiences amidst the challenges posed by COVID-19, and investigating the impact of government assistance are deemed crucial. Complementing the measurement of SWB by incorporating self-evaluated life satisfaction, positive affect, and negative affect will improve our knowledge of the well-being of Indonesians. Furthermore, expanding the study by incorporating subsequent SPTK data will allow for assessing happiness before, during, and after the pandemic.
Data availability
The primary datasets analyzed in this study, the Happiness Level Measurement Survey (SPTK) 2017 and 2021, are not accessible to the public. The author is contractually prohibited from granting access to the SPTK data, as specified in the agreement with the Badan Pusat Statistik (BPS). However, the datasets are available for purchase through the BPS ( https://www.bps.go.id/ ).
The BPS defines an urban area by its primary non-agricultural activities, a functional layout that accommodates urban settlements, and the concentration and distribution of government services, social services, and economic activities. In contrast, rural areas primarily involve agricultural activities, including managing natural resources, and have a functional arrangement that supports rural settlements, government services, social services, and economic activities. In 2022, the urban areas of Indonesia were home to 56.4 percent of the population, while 43.6 percent lived in rural areas.
The WHR, an annual report comparing happiness levels across countries, relies on three well-being indicators: life evaluation, positive affect, and negative affect (Helliwell et al. 2020 ). The Happiness Index, developed by the Central Statistics Agency of Indonesia (Badan Pusat Statistik; BPS), incorporates nineteen indicators that assess dimensions such as life satisfaction, affection, and the meaning of life ( eudaimonia ) (Badan Pusat Statistik 2021a ). It is important to acknowledge that these two measures evaluate distinct aspects. Hence, direct comparison between them is inappropriate, given their representation of separate entities.
These interaction terms capture the moderating effect of the severity of the COVID-19 pandemic on the relationships of interest.
The SPTK is cross-sectional and was conducted in 2012, 2013, 2014, 2017, and 2021. The SPTK has undergone conceptual and methodological improvements (Badan Pusat Statistik 2021a ). For comparability purposes, we will use the last two batches. We need to emphasize that the 2021 SPTK does not aim to study the pandemic’s effect on the happiness level.
Amid the COVID-19 pandemic, the 2021 SPTK data collection encountered many hurdles (Badan Pusat Statistik 2021a ). Originally scheduled for July 1–31, 2021, the fieldwork encountered setbacks due to local lockdowns and the emergence of the Delta variant. Consequently, the 2021 SPTK initiatives necessitated a two-phase extension, extending field activities to two months. Field enumerators grappled with significant challenges, especially in conducting face-to-face surveys amidst stringent health protocols. Setbacks were further compounded as certain respondents refrained from participation due to concerns about infection and the extent to which the virus infected some enumerators. Additionally, due to lockdown restrictions, some survey locations had to be substituted following a month-long delay.
This study includes 67,450 participants from the SPTK 2017 dataset and 70,508 from the SPTK 2021 dataset.
The ICC (Intra-Class Correlation) scale spans from 0 to 1. An ICC value of 0 signifies complete independence of residuals, indicating that the assessment of happiness by individuals does not differ across provinces. Conversely, an ICC value of 1 indicates perfect interdependence of residuals, suggesting that variations in individual happiness levels occur exclusively between provinces.
We also conducted a comparable analysis using the overall count of COVID-19-related deaths to indicate the pandemic’s severity. The results reflected similar patterns: Individuals residing in provinces with higher COVID-19 death tolls generally reported lower levels of happiness. Nevertheless, we opted to omit these findings from our report due to the intricacies associated with attributing a death specifically to COVID-19. Determining the precise cause of death poses challenges, as some individuals might have succumbed to the disease while others had concurrent comorbidities. Consequently, this indicator may be susceptible to inaccuracies, making it a relatively less reliable measure (Bittmann 2022a ).
Addai I, Opoku-Agyeman C, Amanfu SK (2014) Exploring Predictors of Subjective Well-Being in Ghana: A Micro-Level Study. J Happiness Stud 15(4):869–90. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10902-013-9454-7
Article Google Scholar
Ahmadiani M, Ferreira S, Kessler J (2022) What Makes People Happy? Evidence from International Data. J Happiness Stud 23:2083–2111. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10902-021-00478-y
Alon TM, Doepke M, Olmstead-Rumsey J, Tertilt M (2020) The impact of COVID 19 on gender equality. National Bureau of Economic Research. https://doi.org/10.3386/w26947
Andrade C (2020) The Limitations of Online Surveys. Indian J Psychological Med 42(6):575–576. https://doi.org/10.1177/0253717620957496
Anna Z, Yusuf AA, Alisjahbana AS, Ghina AA, Rahma (2019) Are fishermen happier? Evidence from a large-scale subjective well-being survey in a lower-middle-income country. Mar Policy 106:103559. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpol.2019.103559
Arifin B, Anas T, Wicaksono E, Maududy I, Kusumaningsih N (2022) Ensuring Indonesians Are Safe from COVID-19. In: Indrawati SM, Nazara S, Anas T, Ananda CF, Verico K (eds) Keeping Indonesia Safe from the COVID-19 Pandemic: Lessons Learnt from the National Economic Recovery Programme. ISEAS Publishing and Ministry of Finance of the Republic of Indonesia, Jakarta, p 27–63
Chapter Google Scholar
Aryogi I, Wulansari D (2016) Subjective Well-being Individu dalam Rumah Tangga Di Indonesia (Subjective Well-being of Individuals in Households in Indonesia). J Ilmu Ekon Terap 1(1):1–10. https://doi.org/10.20473/jiet.v1i1.1900
Badan Pusat Statistik (2021a) Indeks Kebahagiaan 2021 (Happiness Index 2021). Badan Pusat Statistik, Jakarta
Google Scholar
Badan Pusat Statistik (2021b) Data dan Informasi Kemiskinan Kabupaten/Kota 2021 (Regency/Municipality Poverty Data and Information 2021). Badan Pusat Statistik, Jakarta
Badan Pusat Statistik (2017) Indeks Kebahagiaan 2017 (Happiness Index 2021). Badan Pusat Statistik, Jakarta
Ballas D, Tranmer M (2012) Happy people or happy places? A multilevel modeling approach to the analysis of happiness and well-being. Int Regional Sci Rev 35(1):70–102. https://doi.org/10.1177/0160017611403737
Bittmann F (2022a) Is there a dose-response relationship? Investigating the functional form between COVID-19 incidence rates and life satisfaction in a multilevel framework. J Happiness Stud 23(7):3315–3330. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10902-022-00542-1
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Bittmann F (2022b) Beyond the U‑Shape: Mapping the Functional Form Between Age and Life Satisfaction for 81 Countries Utilizing a Cluster Procedure. J Happiness Stud 22:2343–2359. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10902-020-00316-7
Blanchflower DG (2021) Is happiness U-shaped everywhere? Age and subjective well-being in 145 countries. J Popul Econ 34:575–624. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00148-020-00797-z
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Blanchflower DG, Bryson AJ (2022) The Female Happiness Paradox. National Bureau of Economic Research. https://doi.org/10.3386/w29893
Blanchflower DG, Graham C (2020) The Mid-Life Dip in Well-Being: Economists (Who Find It) Versus Psychologists (Who Don’t)! National Bureau of Economic Research. https://doi.org/10.3386/w26888
Blanchflower DG, Oswald AJ (2011) International happiness: A new view on the measure of performance. Acad Manag Perspect 25(1):6–22. http://www.jstor.org/stable/23045031
Borualogo IS, Casas F (2022) Subjective well-being of children and adolescents during the COVID-19 pandemic in Indonesia: two data collections. Curr Psychol https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-022-03346-x
Burger MJ, Morrison PS, Hendriks M, Hoogerbrugge MM (2020) Urban-Rural Happiness Differentials across the World. In: Helliwell JF, Layard R, Sachs JD, De Neve J-E (eds) World Happiness Report 2020. Sustainable Development Solutions Network, New York, p 67–93
Calvo R, Arcaya M, Baum CF, Lowe SR, Waters MC (2015) Happily ever after? Pre-and-post disaster determinants of happiness among survivors of hurricane Katrina. J Happiness Stud 16(2):427–442. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10902-014-9516-5
Cantril H (1965) Patterns of Human Concerns. Rutgers University Press, New Brunswick
Chen F, Bao L, Lin Z, Zimmer Z, Gultiano S, Borja JB (2018) Double burden for women in mid- and later life: evidence from time-use profiles in Cebu, the Philippines. Ageing Soc 38(11):2325–2355. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0144686x17000599
Cheng TC, Kim S, Koh, K (2020) The Impact of COVID-19 on Subjective Well-Being: Evidence from Singapore. IZA–Institute of Labor Economics
Choi I, Kim JH, Kim N, Choi E, Choi J, Suk HW, Na J (2021) How COVID-19 affected mental well-being: An 11-week trajectories of daily well-being of Koreans amidst COVID-19 by age, gender and region. PLOS One 16(4):e0250252. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0250252
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Clark AE, Oswald AJ (1994) Unhappiness and Unemployment. Econ J 104(424):648–659. https://doi.org/10.2307/2234639
Cleofas JV, Oducado RMF (2022) COVID-19 Death Occurrences, Pandemic Fatigue, and Well-Being. J Loss Trauma 27(7):679–682. https://doi.org/10.1080/15325024.2021.1971423
Dang H-AH, Nguyen CV (2020) Gender Inequality during the COVID-19 Pandemic: Income, Expenditure, Savings, and Job Loss. World Dev 140:105296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.worlddev.2020.105296
Deaton A, Stone AA (2013) Two Happiness Puzzles. Am Econ Rev 103(3):591–597. https://doi.org/10.1257/aer.103.3.591
Delhey J, Kroll C (2013) A “Happiness Test” for the New Measures of National Well-Being: How Much Better than GDP are They? In: Brockmann H, Delhey J (eds) Human Happiness and the Pursuit of Maximization. Happiness Studies Book Series. Springer, Dordrecht, p. 191–210. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-6609-9_14
Demirbas N, Kutlu R (2021) Effects of COVID-19 Fear on Society’s Quality of Life. Int J Ment Health Addiction 20:2813–2822. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11469-021-00550-x
Diener E (1984) Subjective Well-Being. Psychol Bull 95(3):542–575
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Diener E, Biswas-Diener R (2002) Will money increase subjective well-being? A literature review and guide to needed research. Soc Indic Res 95(2):543–575. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1014411319119
Dinella LM, Evans K, Levinson JA, Gagnon S (2023) Women disproportionately shoulder burdens imposed by the global COVID‐19 pandemic. J Soc Issues 79(3):1057–1087. https://doi.org/10.1111/josi.12591
Di Tella R, MacCulloch RJ, Oswald A (2001) Preferences over Inflation and Unemployment: Evidence from Surveys of Happiness. Am Econ Rev 91(1):335–341
Dwidienawati D, Tjahjana D, Gandasari D, Faisal M (2021) Happiness and Satisfaction after 1 year of the COVID-19 Pandemic. J Southwest Jiaotong Univ 56(2):111–123. https://doi.org/10.35741/issn.0258-2724.56.2.10
Easterlin RA (2004) The economics of happiness. Daedalus 133(2):26–32
Easterlin RA, Angelescu L, Zweig JS (2011) The Impact of Modern Economic Growth on Urban–Rural Differences in Subjective Well-Being. World Dev 39(12):2187–2198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.worlddev.2011.04.015
Ferrer-i-Carbonell A, Ramos X (2014) Inequality and Happiness. J Econ Surv 28(5):1016–1027. https://doi.org/10.1111/joes.12049
Firmansyah, Purwanti EY, Susanto H, Oktavilia S, Makhluf HM (2017) Economic of Happiness in Wonosobo Regency, Indonesia. Man India 97(5):289–298
Fortier N (2020) COVID-19, gender inequality, and the responsibility of the state. Int J Wellbeing 10(3):77–93. https://doi.org/10.5502/ijw.v10i3.1305
Frey BS (2018) Economics of Happiness. SpringerBriefs in Economics. Springer, International Publishing, Cham, 10.1007/978-3-319-75807-7
Book Google Scholar
Frey BS, Stutzer A (2002) What can economists learn from happiness research? J Econ Lit 40(2):402–435
Fortin N, Helliwell JF, Wang S (2015) How does subjective well-being vary around the world by gender and age. In: Helliwell JF, Layard R, Sachs J (eds) World Happiness Report 2015. Sustainable Development Solutions Network, New York, p 42–74
Furwanti R, Lestari DM, Muflikha M, Wibowo MG (2021) Determinant of Macro-Economics: Does Income Inequality Influence Happiness? Evidence From Indonesia. JEJAK 14(1):146–156. https://doi.org/10.15294/jejak.v14i1.28278
Gausman J, Langer A (2020) Sex and Gender Disparities in the COVID-19 Pandemic. J Womens Health 29(4):465–466. https://doi.org/10.1089/jwh.2020.8472
Giurge LM, Whillans AV, Yemiscigil A (2021) A multicountry perspective on gender differences in time use during COVID-19. Proc Natl Acad Sci 118(12). https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2018494118
Gómez-Balcácer L, Arechavala NS, Gómez-Costilla P (2023) The importance of different forms of social capital for happiness in Europe: A multilevel structural equation model (GSEM). Appl Res Qual Life 18(1):601–624. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11482-022-10097-1
Greyling T, Rossouw S, Adhikari T (2021) The good, the bad and the ugly of lockdowns during Covid-19. PLOS One 16(1):e0245546. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0245546
Halimatussadiah A, Siregar CH, Bintara H, Rezki JF, Putri LAM, Aufari MR, Sholihah NK, Fadilla RR, Al Kautsar W (2021) Buku Statistik Survei Dampak Pandemi COVID 19 (Statistical Book of Survey of the Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic). Institute for Economic and Social Research, Faculty of Economics and Business, Universitas Indonesia (LPEM-FEB UI), Jakarta, https://www.lpem.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/12/BUKU_STATISTIK_v8_opt.pdf
Hansen B, Sabia JJ, Schaller J (2022) Schools, job flexibility and married women’s labor supply: evidence from the COVID-19 pandemic. National Bureau of Economic Research. http://www.nber.org/papers/w29660
Hayati EN, Emmelin M, Eriksson M (2014) “We no longer live in the old days”: a qualitative study on the role of masculinity and religion for men’s views on violence within marriage in rural Java, Indonesia. BMC Womens Health 14(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6874-14-58
Helliwell JF, Layard R, Sachs JD, De Neve J-E, Aknin LB, Wang S (eds) (2022) World Happiness Report 2022. Sustainable Development Solutions Network, New York
Helliwell JF, Layard R, Sachs JD, De Neve J-E (eds) (2021) World Happiness Report 2021. Sustainable Development Solutions Network, New York
Helliwell JF, Layard R, Sachs JD, De Neve J-E (eds) (2020) World Happiness Report 2020. Sustainable Development Solutions Network, New York
Hyman L (2013) Happiness and Memory: Some Sociological Reflections. Sociological Res Online 19(2):1–9. https://doi.org/10.5153/sro.3268
Iskandarsyah A, Yudiana W, Shabrina A, Passchier J (2022) Perception of information about COVID-19 and protective behaviours in relation to feelings of anxiety and happiness. Int J Public Health Sci. 11(1):8–19. https://doi.org/10.11591/ijphs.v11i1.21018
Kahneman D, Deaton A (2010) High income improves evaluation of life but not emotional well-being. Proc Natl Acad Sci 107(38):16489–16493. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1011492107
Article ADS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Kuhn U, Klaas HS, Antal E, Dasoki N, Lebert F, Lipps O, Monsch G-A, Refle J-E, Ryser V-A, Tillmann R, Voorpostel M (2020) Who is most affected by the Corona crisis? An analysis of changes in stress and well-being in Switzerland. Eur Soc 23(sup1):S942–S956. https://doi.org/10.1080/14616696.2020.1839671
Kurniawati N, Pierewan AC (2020) The Determinants Of Women’s Happiness in Indonesia. Int J Sci Technol Res 9(4):3630–3635
Landiyanto EA, Ling J, Puspitasari M, Irianti SE (2011) Wealth and Happiness: Empirical Evidence from Indonesia. Chulalongkorn J Econ 23:1–17
Langer A, Meleis A, Knaul FM, Atun R, Aran M, Arreola-Ornelas H, Bhutta ZA, Binagwaho A, Bonita R, Caglia JM, Claeson M, Davies J, Donnay FA, Gausman JM, Glickman C, Kearns AD, Kendall T, Lozano R, Seboni N, Frenk J (2015) Women and Health: the key for sustainable development. Lancet 386(9999):1165–1210. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(15)60497-4
Le K, Nguyen M (2021) The psychological burden of the COVID-19 pandemic severity. Econ Hum Biol 41:100979. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ehb.2021.100979
Lee SJ (2022) Public Happiness. Springer, Cham, 10.1007/978-3-030-89643-0
Lepinteur A, Clark AE, Ferrer-i-Carbonell A, Piper A, Schröder C, D’Ambrosio C (2022) Gender, loneliness and happiness during COVID-19. J Behav Exp Econ 101:101952. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.socec.2022.101952
Levin KA, Currie C (2014) Reliability and validity of an adapted version of the Cantril ladder for use with adolescent samples. Soc Indic Res 119(2):1047–1063. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11205-013-0507-4
Lim HE, Shaw D, Liao PS, Duan H (2020) The Effects of Income on Happiness in East and South Asia: Societal Values Matter? J Happiness Stud 21(2):391–415. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10902-019-00088-9
López-Ruiz V-R, Huete-Alcocer N, Alfaro-Navarro J-L, Nevado-Peña D (2021) The relationship between happiness and quality of life: A model for Spanish society. PLOS One 16(11):e0259528. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0259528
Mayuzumi Y (2022) Survey of rural and urban happiness in Indonesia during the corona crisis. Asia Pac J Region Sci 7:29–67. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41685-022-00265-4
Mehmetoglu M, Jakobsen TG (2017) Applied Statistics Using Stata: A Guide for the Social Sciences. SAGE Publications Asia-Pacific Pte Ltd, Singapore
Möhring K, Naumann E, Reifenscheid M, Wenz A, Rettig T, Krieger U, Friedel S, Finkel M, Cornesse C, Blom AG (2021) The COVID-19 pandemic and subjective well-being: longitudinal evidence on satisfaction with work and family. Eur Soc 23(S1):S601–S617. https://doi.org/10.1080/14616696.2020.1833066
Muresan GM, Ciumas C, Achim MV (2020) Can Money Buy Happiness? Evidence for European Countries. Appl Res Qual Life 15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11482-019-09714-3
Muthia LH, Isbah MF (2022) “Poor but Happy”: Life Struggle and the Meaning of Happiness among the Poor in Yogyakarta. J Sosiol Walisongo 6(2):117–128. https://doi.org/10.21580/jsw.2022.6.2.8902
Nandini D, Afiatno BE (2020) The Determinants Of Happiness: Empirical Evidence Of Java Island. Ekonika 5(2):123. https://doi.org/10.30737/ekonika.v5i2.713
Nguyen CV (2021) Does the COVID-19 Pandemic Cause People to Be Unhappy? Evidence from a Six-Country Survey. GLO Discussion Paper No.768. Global Labor Organization (GLO), Essen, http://hdl.handle.net/10419/228738
Oishi S, Diener E (2014) Can and Should Happiness Be a Policy Goal? Policy Insights Behav Brain Sci 1(1):195–203. https://doi.org/10.1177/2372732214548427
Pattinasarany IRI (2018) Happiness and Life Satisfaction Among East and Southeast Asian Countries. Paper presented at the Fourth Conference of International Consortium for Social Well-Being Studies. Seoul National University, Seoul
Petrovič F, Murgaš F, Králik R (2021) Happiness in Czechia during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Sustainability 13(19):10826. https://doi.org/10.3390/su131910826
Article CAS Google Scholar
Phulkerd S, Thapsuwan S, Soottipong GR, Chamratrithirong A, Pattaravanich U, Ungchusak, C & Saonuam P (2023) Life Satisfaction before and during COVID-19 pandemic in Thailand. Int J Public Health 68. https://doi.org/10.3389/ijph.2023.1605483
Rabe-Hesketh S, Skrondal A (2022) Multilevel and Longitudinal Modeling Using Stata, Fourth Edition. Stata Press Publication, College Station
Rajkumar RP (2023) Cultural values and changes in happiness in 78 countries during the COVID-19 pandemic: An analysis of data from the World Happiness Reports. Front Psychol 14. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1090340
Rahayu TP (2016) The Determinants of Happiness in Indonesia. Mediterr J Soc Sci 7(2):393–404
Rahmanita M, Nurbaeti, Asmaniati F, Dewi TR, Widyastuti N (2021) COVID-19 Pandemic: Happiness Revisited through Work and Leisure during the Stay at Home Period. J Hunan Univ Nat Sci 48(4):100–107
Recchi E, Ferragina E, Helmeid E, Pauly S, Safi M, Sauger N, Schradie J (2020) The “Eye of the Hurricane” Paradox: An Unexpected and Unequal Rise of Well-Being During the Covid-19 Lockdown in France. Res Soc Stratification Mobil 68:100508. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rssm.2020.100508
Rehdanz K, Welsch H, Narita D, Okubo T (2015) Well-being effects of a major natural disaster: The case of Fukushima. J Econ Behav Organ 116:500–517. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jebo.2015.05.014
Schroder M (2018) Income Inequality and Life Satisfaction: Unrelated Between Countries, Associated Within Countries Over Time. J Happiness Stud 19:1021–1043. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10902-017-9860-3
Sekulova F, van den Bergh JCJM (2016) Floods and happiness: Empirical evidence from Bulgaria. Ecol Econ 126:51–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolecon.2016.02.014
Shams K, Kadow A (2022) COVID-19 and Subjective Well-Being in Urban Pakistan in the Beginning of the Pandemic: A Socio-Economic Analysis. Appl Res Qual Life 18:93–113. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11482-022-10114-3
Snijders TA, Bosker RJ (2012) Multilevel analysis: an introduction to basic and advanced multilevel modeling, Second Edition. Sage Publications Asia-Pacific, Singapore
Sohn K (2014) Height and Happiness in a Developing Country. J Happiness Stud 17(1):1–23. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10902-014-9566-8
Sohn K (2013) Sources of Happiness in Indonesia. Singap Econ Rev 58(02):1350014. https://doi.org/10.1142/s0217590813500148
Sollis K, Resosudarmo BP, Witoelar F, Riswandi R, Mollet JA (2023) Migrant Status and the Wellbeing Gap: The Case of an Ethnically Diverse, High-Conflict Area in Indonesia. J Happiness Stud. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10902-023-00659-x
Sommet N, Morselli D (2017) Keep Calm and Learn Multilevel Logistic Modeling: A Simplified Three-Step Procedure Using Stata, R, Mplus, and SPSS. Int Rev Soc Psychol 30(1):203–218. https://doi.org/10.5334/irsp.90
StataCorp (2021) Stata Multilevel Mixed-Effects Reference Manual Release 17. Stata Press Publication, College Station
Sujarwoto S (2021) Development as happiness: A multidimensional analysis of subjective well-being in Indonesia. Econ Sociol 14(2):274–293. https://doi.org/10.14254/2071-789x.2021/14-2/15
Sujarwoto S, Tampubolon G, Pierewan AC (2017) Individual and Contextual Factors of Happiness and Life Satisfaction in a Low Middle Income Country. Appl Res Qual Life 13(4):927–945. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11482-017-9567-y
Sujarwoto S, Tampubolon G (2015) Decentralisation and Citizen Happiness: A Multilevel Analysis of Self-rated Happiness in Indonesia. J Happiness Stud 16:455–475. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10902-014-9518-3
Tadic M, Braam H, van Vliet K, Veenhoven R (2014) Memory-Experience Gap in Early Adolescents’ Happiness Reports. Child Indic Res 7:21–40. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12187-013-9194-6
Tambyah SK, Tan SJ, Lun YW (2023) Happiness and wellbeing in Singapore: Beyond economic prosperity. Routledge, New York
Tjahjana D, Dwidienawati D, Manurung AH, Gandasari D (2021) Does People’s Well-being Get Impacted by COVID-19 Pandemic Measure in Indonesia? Stud App Econ 39(4). https://doi.org/10.25115/eea.v39i4.4873
Toshkov D (2022) The Relationship Between Age and Happiness Varies by Income. J Happiness Stud 23:1169–1188. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10902-021-00445-7
Utomo AJ (2012) Women as Secondary Earners. Asian Popul Stud 8(1):65–85. https://doi.org/10.1080/17441730.2012.646841
van der Vegt I, Kleinberg B (2020) Women Worry About Family, Men About the Economy: Gender Differences in Emotional Responses to COVID-19. Lect Notes Comput Sci 12467:397–409. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-60975-7_29
Veenhoven R (2012) Happiness: Also Known as “Life Satisfaction” and “Subjective Well-Being”. In: Land K, Michalos A, Sirgy M (eds) Handbook of Social Indicators and Quality of Life Research. Springer, Dordrecht, p 63–77. 10.1007/978-94-007-2421-1_3
Winkelmann L, Winkelmann R (1998) Why are the unemployed so unhappy? Evidence from panel data. Economica 65(257):1–15. https://doi.org/10.1111/1468-0335.00111
Worldometer (2023) Countries where Coronavirus has spread - Worldometer. https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/countries-where-coronavirus-has-spread/ . Accessed on February 23, 2023
Wu Y, Zhu J (2016) When Are People Unhappy? Corruption Experience, Environment, and Life Satisfaction in Mainland China. J Happiness Stud 17(3):1125–47. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10902-015-9635-7
Yang H, Ma J (2020) How an epidemic outbreak impacts happiness: Factors that worsen (vs. protect) emotional well-being during the coronavirus pandemic. Psychiatry Res 289:113045289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psychres.2020.113045
Yiengprugsawan V, Somboonsook B, Seubsman S, Sleigh AC (2011) Happiness, Mental Health, and Socio-Demographic Associations Among a National Cohort of Thai Adults. J Happiness Stud 13(6):1019–1029. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10902-011-9304-4
Yu GB, Lee D-J, Sirgy MJ, Bosnjak M (2019) Household Income, Satisfaction with Standard of Living, and Subjective Well-Being: The Moderating Role of Happiness Materialism. J Happiness Stud. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10902-019-00202-x
Download references
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by Grant No. NKB-1211/UN2.RST/HKP.05.00/2022 from the Publikasi Terindeks Internasional (PUTI) Q1, Directorate of Research and Development (Risbang), Universitas Indonesia. The author is grateful for the constructive inputs and discussions throughout the preparation of this study from Professor Masayuki Kanai from the School of Human Sciences, Senshu University, and Professor Iwan Gardono Sudjatmiko from the Department of Sociology, Universitas Indonesia. In addition, Peter Morley from the Australian Volunteers Indonesia assisted in shaping the report and editorial services.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Sociology, Faculty of Social and Political Sciences, Universitas Indonesia, Depok, Indonesia
Indera Ratna Irawati Pattinasarany
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Indera Ratna Irawati Pattinasarany .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The author declares no competing interests.
Ethical approval
Ethical approval was not required as the study did not involve human participants performed by the author.
Informed consent
Informed consent was not required as the study did not involve human participants performed by the author.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Pattinasarany, I.R.I. Happiness amidst the COVID-19 pandemic in Indonesia: exploring gender, residence type, and pandemic severity. Humanit Soc Sci Commun 11 , 609 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-024-03131-0
Download citation
Received : 13 July 2023
Accepted : 25 April 2024
Published : 10 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-024-03131-0
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A novel coronavirus (CoV) named '2019-nCoV' or '2019 novel coronavirus' or 'COVID-19' by the World Health Organization (WHO) is in charge of the current outbreak of pneumonia that began at the beginning of December 2019 near in Wuhan City, Hubei Province, China [1-4]. COVID-19 is a pathogenic virus. From the phylogenetic analysis ...
How to Write About Coronavirus Using the Special COVID-19 (250-Word) Section on the Common App. Option 1: The Straightforward Way. Option 2: The Slightly More Creative Way. How to Write About Coronavirus Using the (650-Word) Additional Information Section.
Start with a blank piece of paper. In the middle of the paper write the question or statement that you are trying to answer. From there, draw 5 or 6 lines out from the centre. At the end of each of these lines will be a point you want to address in your essay. From here, write down any additional ideas that you have.
Writing About COVID-19 in College Essays. Experts say students should be honest and not limit themselves to merely their experiences with the pandemic. The global impact of COVID-19, the disease ...
This essay is an opportunity to share your pandemic experience and the lessons learned. The college admissions process has experienced significant changes as a result of COVID-19, creating new challenges for high school students. Since the onset of the pandemic, admissions officers have strongly emphasized a more holistic review process.
The student or a family member had COVID-19 or suffered other illnesses due to confinement during the pandemic. The student suffered from a lack of internet access and other online learning challenges. Students who dealt with problems registering for or taking standardized tests and AP exams. Jeff Schiffman of the Tulane University admissions ...
Thinking about COVID-19 and your introduction The personal and professional context of your thesis is likely to have changed as a result of COVID-19. The changes implied are immediate and short-term, but there will also be long term implications ... (2017) History, drawing and power: essay towards reflexive methodological pluralism in sociology ...
A new virus was isolated and its genome sequenced, revealing a similarity with SARS-like coronaviruses found in bats. Although very similar to the virus causing severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) in 2003, it was different enough to be considered a new human-infecting coronavirus. Clusters of infected families, together with transmission ...
Horrific history. Looking back, the COVID-19 pandemic stands as arguably the most disruptive event of the 21st century, surpassing wars, the September 11, 2001, terrorist attacks, the effects of climate change, and the Great Recession. It has killed more than seven million people to date and reshaped the world economy, public health, education ...
1. Introduction. The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic has led to unprecedented changes in people's daily lives, with implications for mental health and well-being [1-4], both at the level of a given country's population, and when considering specific vulnerable groups [5-7].In order to mitigate the untoward impact of the pandemic (including lockdown) and support mental health ...
Introduction. Infectious disease pandemics, including SARS and COVID-19, demand intrapersonal behaviour change and present highly complex challenges for public health.1 A pandemic of an airborne infection, spread easily through social contact, assails human relationships by drastically altering the ways through which humans interact. In this essay, we draw on theories of social relationships ...
Having recognized this, the Common App added a new optional 250-word essay that will give universities a chance to understand the atypical high school experience students have had. The prompt will ...
of these disruptions. The essay concludes by providing recommendations for longer term recovery ensuring that the social relational cost of COVID-19 is adequately considered in efforts to rebuild. INTRODUCTION Infectious disease pandemics, including SARS and COVID-19, demand intrapersonal behaviour change and present highly complex challenges for
Essay Topics Related to COVID-19 Introduction The COVID-19 pandemic has had a profound impact on individuals, societies, and economies worldwide. Its multifaceted nature presents a wealth of topics suitable for academic exploration. This essay provides guidance on developing engaging and insightful essay topics related to COVID-19, offering a ...
A novel coronavirus (COVID-19) was identified in 2019 in Wuhan, China. This is a new coronavirus that has not been previously identified in humans. This course provides a general introduction to COVID-19 and emerging respiratory viruses and is intended for public health professionals, incident managers and personnel working for the United ...
The COVID-19 pandemic is far from over and could yet evolve in unanticipated ways, but one of its most important lessons is already clear: preparation and early execution are essential in ...
Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) is an infectious disease caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus. Most people infected with the virus will experience mild to moderate respiratory illness and recover without requiring special treatment. However, some will become seriously ill and require medical attention.
Joint statement by ILO, FAO, IFAD and WHO. The COVID-19 pandemic has led to a dramatic loss of human life worldwide and presents an unprecedented challenge to public health, food systems and the world of work. The economic and social disruption caused by the pandemic is devastating: tens of millions of people are at risk of falling into extreme ...
This essay serves as the introduction to TVNM's special issue on "Pandemic TV," an analysis of the ways in which the COVID-19 pandemic affected principally anglophone television and television-watching in 2020 to 2021 (including television's response to corresponding events such as the summer 2020 Black Lives Matter uprisings and the fall 2020 U.S. presidential election).
Introduction: The COVID-19 pandemic has presented an unprecedented global challenge, and in the face of this crisis, many countries have debated the implementation of vaccination mandates. ... Writing a persuasive essay about COVID-19 requires a thoughtful approach to present your arguments effectively. Here are some tips to help you craft a ...
Essay On Covid-19: 100, 200 and 300 Words. COVID-19, also known as the Coronavirus, is a global pandemic that has affected people all around the world. It first emerged in a lab in Wuhan, China, in late 2019 and quickly spread to countries around the world. This virus was reportedly caused by SARS-CoV-2. Since then, it has spread rapidly to ...
Introduction. SARS-CoV-2 is responsible for a large number of global COVID-19 cases. It is a highly transmissible virus among humans that has become a significant public health issue.1 Symptoms include fever, dry cough, fatigue, shortness of breath, chills, muscle pain, headache, gastric disorders and weight loss, often leading to death.2 Strategies such as social isolation, personal hygiene ...
During the COVID-19 pandemic, while some countries succeeded in reducing their rate of death after SARS-CoV-2 infection via vaccination by the end of 2021, some of them also faced hospital capacity strain, leading to social anxiety about delays in the diagnosis and treatment of patients with other diseases. This essay presents an allegory to explain the situation during the COVID-19 pandemic.
100 Words Essay on Covid 19. COVID-19 or Corona Virus is a novel coronavirus that was first identified in 2019. It is similar to other coronaviruses, such as SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV, but it is more contagious and has caused more severe respiratory illness in people who have been infected. The novel coronavirus became a global pandemic in a very ...
Essay on COVID-19 Pandemic. Published: 2021/11/08. Number of words: 1220. As a result of the COVID-19 (Coronavirus) outbreak, daily life has been negatively affected, impacting the worldwide economy. Thousands of individuals have been sickened or died as a result of the outbreak of this disease. When you have the flu or a viral infection, the ...
The safety and efficacy of COVID-19 vaccines in the elderly, a high-risk group for severe COVID-19 infection, have not been fully understood. ... Introduction. The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID ...
The COVID-19 pandemic and associated countermeasures had an immensely disruptive impact on people's lives. Due to the lack of systematic pre-pandemic data, however, it is still unclear how ...
Introduction. The COVID-19 pandemic affected the global economy just as much as the public health domain. However, most economies were able to recover significantly due to efficient policy responses.
This study delves into the dynamics shaping happiness levels in Indonesia before and during the COVID-19 pandemic, specifically emphasizing gender and residence-type disparities. Using data from ...